Page 1

PTReportGen
User Manual
Version 2.9
2009-08
Copyright© 2006-2009 LJZsoft Corporation
All rights reserved
Page 2

Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................1
1.1 OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................................1
1.2 FEATURES.......................................................................................................................................1
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION AND STARTUP...............................................................................5
2.1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS............................................................................................................5
2.2 INSTALLING PTREPORTGEN...........................................................................................................5
2.3 UNINSTALLING PTREPORTGEN......................................................................................................5
2.4 COMMAND LINE .............................................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 3 QUICK START...............................................................................................................8
3.1 LEARNING HOW TO USE PTREPORTGEN .........................................................................................8
3.2 SAMPLE DATABASE ........................................................................................................................8
3.3 STEPS OF REPORTING......................................................................................................................9
3.4 MY FIRST REPORT ........................................................................................................................10
3.4.1 Creating a report template...................................................................................................10
3.4.2 Creating a PTR file..............................................................................................................11
3.4.3 Configuring the report.........................................................................................................11
3.4.4 Inputting a function..............................................................................................................12
3.4.5 Understanding the function..................................................................................................12
3.4.6 Running a PTR file...............................................................................................................13
3.4.7 Opening a report..................................................................................................................13
3.4.8 Modifying the report template..............................................................................................13
3.4.9 Modifying the function.........................................................................................................14
3.4.10 Generating the report again...............................................................................................15
3.5 SAMPLES.......................................................................................................................................15
CHAPTER 4 REPORT TEMPLATES ..............................................................................................17
- I -
Page 3

4.1 ABOUT REPORTS ..........................................................................................................................17
4.2 ABOUT REPORT TEMPLATES.........................................................................................................17
4.3 POWERPOINT BASIC CONCEPTS....................................................................................................17
4.3.1 Presentations........................................................................................................................17
4.3.2 Slides....................................................................................................................................18
4.3.3 Layout..................................................................................................................................18
4.3.4 Headers and Footers............................................................................................................18
4.3.5 Formatting...........................................................................................................................18
4.3.6 Shapes..................................................................................................................................19
4.3.7 Pictures................................................................................................................................19
4.3.8 Tables...................................................................................................................................20
4.3.9 Charts...................................................................................................................................20
4.3.10 Sound, Music, Video, and Voice.........................................................................................20
4.4 TABLE REPORTS ...........................................................................................................................21
4.4.1 About Table Reports.............................................................................................................21
4.4.2 Creating a Table for a Fixed Table Report..........................................................................22
4.4.3 Creating a Table for a Variable Table Report.....................................................................22
4.4.4 Formatting Cells..................................................................................................................23
4.4.5 Irregular Tables...................................................................................................................25
4.4.6 Referencing Cells.................................................................................................................26
4.4.7 Referencing Tables...............................................................................................................26
4.4.8 Formatting Cells for Pictures..............................................................................................27
4.5 FORM REPORTS.............................................................................................................................28
4.5.1 About Form Reports.............................................................................................................28
4.5.2 Creating a Slide ...................................................................................................................28
4.5.3 Naming Objects....................................................................................................................29
4.5.4 Formatting text in an Object................................................................................................31
4.5.5 Formatting Pictures.............................................................................................................32
- II -
Page 4

4.6 CHARTS ........................................................................................................................................32
4.6.1 About Charts........................................................................................................................32
4.6.2 Creating a Blank Chart using Microsoft Graph..................................................................33
4.6.3 Creating a Blank Chart using Microsoft Excel....................................................................34
4.6.4 Referencing Charts ..............................................................................................................35
CHAPTER 5 REPORTING WITH PTREPORTGEN.....................................................................36
5.1 CREATING AND OPENING PTR FILES............................................................................................36
5.1.1 About PTR files....................................................................................................................36
5.1.2 Create a new PTR file..........................................................................................................36
5.1.3 Open a PTR file....................................................................................................................36
5.1.4 Save a PTR file.....................................................................................................................36
5.2 CONFIGURING FILES.....................................................................................................................37
5.2.1 About files.............................................................................................................. ..............37
5.2.2 Configuring file information................................................................................................37
5.2.3 Converting files....................................................................................................................38
5.3 CONFIGURING DATA SOURCES.....................................................................................................39
5.3.1 About data sources...............................................................................................................40
5.3.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a data source.....................................................................40
5.4 CONFIGURING PARAMETERS.........................................................................................................42
5.4.1 About parameters.................................................................................................................42
5.4.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a parameter.......................................................................42
5.5 INPUTTING FUNCTIONS.................................................................................................................43
5.6 RUNNING PTR FILES....................................................................................................................44
5.6.1 Windows mode.....................................................................................................................44
5.6.2 Command line mode.............................................................................................................44
5.7 SORTING, GROUPING AND TOTALING...........................................................................................45
5.7.1 Sorting data..........................................................................................................................45
5.7.2 Totaling................................................................................................................................45
- III -
Page 5

5.7.3 Grouping data and subreports.............................................................................................46
5.7.4 Subtotaling...........................................................................................................................46
5.8 PICTURES......................................................................................................................................47
5.8.1 Inserting pictures into a report template..............................................................................47
5.8.2 Inserting pictures into a report............................................................................................47
5.9 USING PARAMETERS.....................................................................................................................49
5.10 PROGRAMMING...........................................................................................................................52
5.10.1 Using add-ins, macros.......................................................................................................52
5.10.2 Making PTR files programmatically..................................................................................52
CHAPTER 6 FUNCTION REFERENCE..........................................................................................54
6.1 REPORT FUNCTION.......................................................................................................................54
6.1.1 Report Function...................................................................................................................54
6.1.2 Fixed Table Report Function...............................................................................................54
6.1.3 Non-group Variable Table Report Function........................................................................58
6.1.4 Group Variable Table Report Function...............................................................................63
6.1.5 Form Report Function .........................................................................................................70
6.2 CHART FUNCTION.........................................................................................................................75
6.2.1 MSGraph Chart Function....................................................................................................75
6.2.2 Excel Chart Function...........................................................................................................79
6.3 EXECSQL FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................83
CHAPTER 7 MENUS, TOOLBAR AND SHORTCUT KEYS........................................................85
7.1 FILE MENU ...................................................................................................................................85
7.2 EDIT MENU...................................................................................................................................85
7.3 REPORT MENU..............................................................................................................................85
7.4 TOOLS MENU................................................................................................................................86
7.5 HELP MENU..................................................................................................................................86
7.6 TOOLBAR......................................................................................................................................86
- IV -
Page 6

7.7 SHORTCUT KEYS ..........................................................................................................................87
CHAPTER 8 HINTS AND TIPS.........................................................................................................89
CHAPTER 9 PTR FILE REFERENCE.............................................................................................95
9.1 PTR FILE FORMAT .......................................................................................................................95
9.2 [DATA SOURCE] SECTION.............................................................................................................96
9.3 [FILE] SECTION ...........................................................................................................................98
9.4 [PARAMETER] SECTION............................................................................................................99
CHAPTER 10 FORMAT EXPRESSIONS......................................................................................101
A.1 FORMATS FOR NUMERIC VALUES..............................................................................................101
A.2 FORMATS FOR STRING VALUES .................................................................................................105
A.3 FORMATS FOR DATE/TIME VALUES...........................................................................................106
CHAPTER 11 LICENSE AND SUPPORT......................................................................................110
11.1 LICENSE....................................................................................................................................110
11.2 TECHNICAL SUPPORT................................................................................................................111
- V -
Page 7
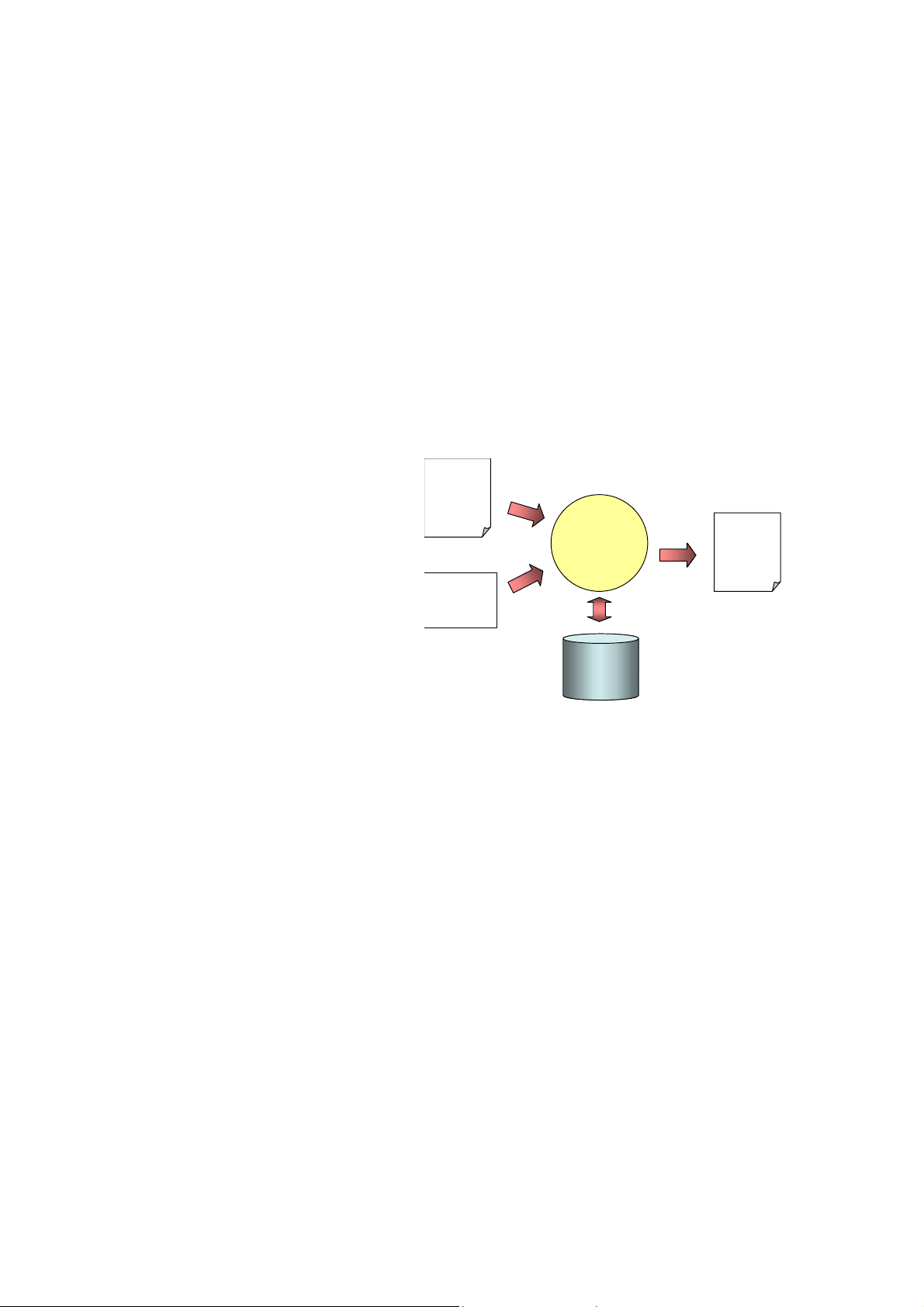
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
PTReportGen is a report generator for Microsoft PowerPoint that outputs
reports in Microsoft PowerPoint format. If you know how to use Microsoft
PowerPoint and write SQL statements, you can use PTReportGen to create all
kinds of reports as you need.
To create a report, PTReportGen
need to read a report template
Report
Template
file and a PTR file. The report
PTReportGen
Report
template file is a Microsoft
PowerPoint presentation that
SQL
defines the layouts and formats
of a report. The PTR file contains
Database
SQL statements and some
information, and tells PTReportGen how to get data from database and how to
put data into a report. First PTReportGen creates a blank report using the
report template file, and then executes SQL statements in the PTR file to get
data from database, and fills data into the report to generate the desired report
in Microsoft PowerPoint format.
1.2 Features
PTReportGen includes the following features:
Using Microsoft PowerPoint as your reporting tool
Just use Microsoft PowerPoint as your reporting tool. You design reports like
layouts, formats and styles directly using Microsoft PowerPoint. And you will
get reports in Microsoft PowerPoint presentation format as a result.
- 1 -
Page 8

Making report template directly using Microsoft PowerPoint
The main advantage of using PTReportGen is based on the fact that all
formatting is done directly in Microsoft PowerPoint. You can take full
advantage of Microsoft PowerPoint including text formatting, tables, charts,
pictures and graphics, drawing, headers and footers, preview and printing,
VBA, macros, and more.
Accessing to databases using SQL
PTReportGen executes SQL statements to extract data from database.
Supports all type SQL: DML, DDL and DCL. Multiple SQL statements can be
executed in one report building process. You can perform queries on
databases, insert data into databases, and create database objects like tables.
The power of SQL can be harnessed for maximum efficiency in reporting.
Creating reports without programming experience
You know how to use Microsoft PowerPoint and how to write SQL, it is enough.
It does not require programming to create reports.
Connection to all databases using ODBC
PTReportGen connects to databases using ODBC. Access to all databases
which support ODBC such as Oracle, DB2, Sybase, Informix, Microsoft SQL
Server, Teradata, MySQL, Microsoft Access, dBase.
Supporting multi-databases in one report
PTReportGen supports multi-databases in one report. You can get data from
some different databases such as Oracle, DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server, and
put these data into one report.
Generating reports with parameters
PTReportGen gives you an opportunity to create reports with parameters. You
may use parameters in SQL statements. You will be asked to input the values
of parameters while generating reports.
Supporting Windows mode and command line mode
- 2 -
Page 9

PTReportGen supports command line mode. So it is possible to call
PTReportGen from other program. For developers, you can integrate
PTReportGen into your application.
Creating complex reports
You can create complex reports. The complexity might come from report
formatting as well as report content.
Creating reports with charts
PTReportGen enables you to include sophisticated, colorful charts in your
reports. You can use charts any time you want to improve the usefulness of a
report.
Creating reports with pictures
PTReportGen can insert pictures from the graphics files, and set the inserted
way, text wrapping style and size of the pictures according to your instruction.
Many reports in one Microsoft PowerPoint presentation
One Microsoft PowerPoint presentation may contain many reports. One report
may be one or more slides. You can generate a presentation in one generating
process.
Conversion of file formats
PTReportGen is a converter too. You can convert PowerPoint presentation to
and from other formats, such as HTML, RTF, GIF, JPG and BMP. You also
can convert data from database to other file format.
Generating reports automatically
The process of report generation can be fully automated, periodically or on
events. PTReportGen can be scheduled with Windows Scheduled Tasks or
other tools.
One time configuration
With on time configuration, you can repeatedly generate reports especially
periodic reports such as daily, weekly, monthly and annual reports.
- 3 -
Page 10

Flexible deployment
PTReportGen can be run on your desktop or server.
- 4 -
Page 11

Chapter 2 Installation and Startup
2.1 Software Requirements
Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows
XP, Windows 2003, Windows Vista or later.
Microsoft Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 or later.
2.2 Installing PTReportGen
Run installation program, and follow the instructions to complete PTReportGen
installation. For Windows Vista, the data folder should be different from the
application folder.
If you don’t have Microsoft Office installed, please install it first.
If your environment is Windows 95/98 and Office 2000, and you don’t have
VB6.0 run-time files installed, please install it. For Windows 2000, Windows XP,
Windows 2003 and Office 2000 or later, you do not need to install VB6.0
run-time files because they are included in OS and Office. To install VB6.0
run-time files, just run vbrun60sp5.exe, and follow the instructions.
If you don’t have ODBC Driver for the database you want to access installed,
please install it.
If your OS is Windows 95/98 and you don’t have Microsoft Data Access
Components 2.0 (MDAC_TYP) or later installed, please install it. For Windows
2000, Windows XP and Windows 2003, you do not need to install MDAC_TYP
because it is preinstalled in OS. To install MDAC_TYP, just run mdac_typ.exe,
and follow the instructions.
2.3 Uninstalling PTReportGen
1. Quit PTReportGen.
- 5 -
Page 12

2. Double-click the Add/Remove Programs icon in the Windows Control
Panel.
3. Do one of the following:
For Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows 2003 Edition:
Click PTReportGen in the Currently installed programs box, and then click
the Change/Remove button.
For Windows 98 and Windows NT 4.0:
Click PTReportGen on the Install/Uninstall tab, and then click the
Add/Remove button.
4. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete uninstalling the program.
2.4 Command Line
PTReportGen can be run in Windows mode or command line mode. The
Syntax of command is:
pptreport <ptr file name> [-C] [-D] [-I interval] [-U1 user1] [-P1 pwd1] …
[-U10 user10] [-P10 pwd10] [pa1 pa2 … pa10]
ptr file name Specifying a PTR (.ptr) file that tells PTReportGen how to get
data from data sources and how to put data into a report.
-C Running in command line mode.
-D Display the generated report with Microsoft PowerPoint.
-I interval Log the processing records message. If interval is greater than
1, it is the interval of records. If interval is less than 1, it is the
percent of interval.
-U1 user1 …
Specify the user names. user1 is the user name of the first
-U10 user10
-P1 pwd1 ... Specify the passwords. pwd1 is the password of the first data
data source. user2 is the user name of the second data
source……
- 6 -
Page 13

-P10 pwd10 source. pwd2 is the password of the second data source……
pa1 … pa10 The values of the parameters defined in the PTR file. You can
use parameters in SQL statements. PTReportGen will replace
the names of parameters in a SQL statement with the actual
values before it executes a SQL statement. You can use no
more than 10 parameters in one report.
For example, you have defined two parameters in your PTR file. The first
parameter is sales date, and the second is the category of the products. You
can run PTReportGen in command line mode as follows:
pptreport c:\PPTReport\myreport.ptr -c 1996-05-01 “Dairy Products”
- 7 -
Page 14

Chapter 3 Quick Start
3.1 Learning how to use PTReportGen
You can teach yourself how to use PTReportGen by choosing from the
methods available in this section:
You can study the sample reports and sample database included with
PTReportGen.
You can use the detailed descriptions and instructions in the “My First
Report”.
3.2 Sample Database
PTReportGen comes with Sample.mdb, a sample database you can use when
learning the program. Sample.mdb is a Microsoft Access database. Virtually all
of the examples in this manual are based on Sample.mdb data.
The sample reports access the sample database through the ODBC data
source name “Report Sample”. When you install PTReportGen, you can
choose to add the ODBC data source name. And you also can add the ODBC
data source name manually.
To create the System DSN “Report Sample”, do as follows:
1. Click the Windows Start button, choose Settings, and then click Control
Panel.
2. On computers running Microsoft Windows 2000 or later, double-click
Administrative Tools, and then double-click Data Sources (ODBC). The
ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box appears. On computers
running previous versions of Microsoft Windows, double-click 32-bit ODBC or
ODBC.
3. Select the System DSN tab, and then press Add button.
- 8 -
Page 15

4. Choose Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb), then press Finish button.
5. In the ODBC Microsoft Access Setup dialog box, type Report Sample in
the Data Source Name box.
6. Press the Select button, and browse to select Sample.mdb.
7. Press OK button to close the ODBC Microsoft Access Setup dialog box.
8. Press OK button to close the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog
box.
3.3 Steps of Reporting
To create a report with PTReportGen, you should do as follows:
1. Prepare works
Before you create a report, you should determine the layout of the report, and
know where and how to get the data.
You must know how to access the databases you are reporting from. So you
need the data source name, user name and password. If you don’t have added
data sources, please add data sources first. Run ODBC Administrator, you can
add a new data source. For detailed information about configuring ODBC, refer
to ODBC Administrator Help.
2. Make a report template file
Create a report template file using Microsoft PowerPoint. The report template
file is a Microsoft PowerPoint presentation. For detailed information about
report template, refer to “Report Templates” in this document.
3. Create a PTR file
Create a PTR file with a .ptr extension using PTReportGen. There are tow
steps to create a PTR file.
(1) Configure the report
Define the names of data sources, the name of the report template file, the
name of the report file and the name of the log file. If you want to use
- 9 -
Page 16

parameters in SQL statements, define these parameters.
(2) Write functions
Write functions and SQL statements that specify how to get data from data
sources and how to put data into the report.
For detailed information, refer to “Reporting with PTReportGen” in this
document.
4. Run the PTR file
Run the PTR file to generate a report in Microsoft PowerPoint presentation.
For detailed information about running report, refer to “Running a PTR File” in
this document.
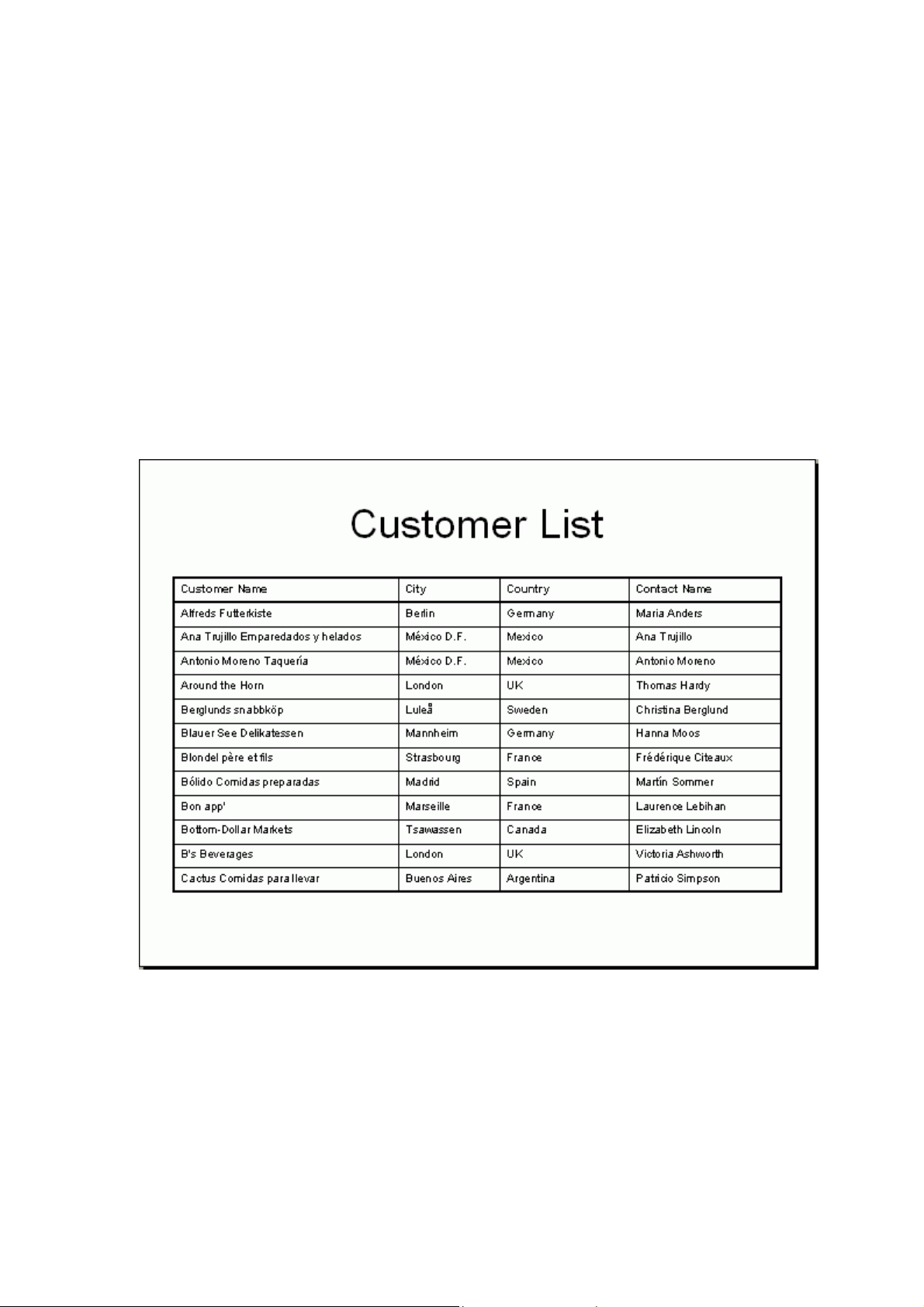
3.4 My First Report
The following tutorial has been designed to guide you to create your first report.
In this tutorial, you will get an introduction to the program as you create a
Customer List report. The Customer List is one of the most basic business
reports and typically has information such as Customer Name, City, Country,
and Contact Name.
3.4.1 Creating a report template
1. Run Microsoft PowerPoint, create a new presentation with a blank slide.
2. On the Insert menu, click Table. Select the number of columns and rows.
Press OK button.
3. Click the cell A1, type “Customer Name”. In the same way, you input “City”,
“Country” and “Contact Name” into the cells B1, C1 and D1.
4. Format the text of A1, B1, C1 and D1 as you like, including font, font size,
font colour, bold, background, alignment and border.
5. You can change the width of these columns. The report template you have
made is as follows:
- 10 -
Page 17

6. Click Save on the File menu, chose a directory such as “C:\Report”, type
custlist.ppt in the File name box and press Save button.
7. Click Close on the File menu.
3.4.2 Creating a PTR file
1. Run PTReportGen.
2. Click New on the File menu.
3. Click Save on the File menu, chose the directory to which you have saved
the report template, type custlist.ptr in the File name box and press Save
button.
3.4.3 Configuring the report
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the File tab.
In the Template File box, type custlist.ppt; In the Report File box, type
Report\custlist.ppt; In the Log File box, type Log\custlist.log.
3. Click the Data Source tab.
Press New button, the New Data Source dialog box appears. In the Name
box, type Report Sample, press OK button.
4. On the Configuration dialog box, press OK button.
- 11 -
Page 18

3.4.4 Inputting a function
In the editor windows, input a function as follows:
@F1=Report(slide=1 cell=A2)
SELECT CompanyName
,CityName
,CountryName
,ContactName
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
AND CountryName = 'USA'
ORDER BY CompanyName,CityName,CountryName
;
Please note the WHERE clause. It passes only records of customers in USA.
You can test the SQL statement in a query tool such as Microsoft Access or
Microsoft Query.
3.4.5 Understanding the function
Before going any further, let us understand this function.
1. The Report function will execute the SQL statement, get data from data
source, and put data into the report.
2. The slide argument identifies a slide, and the value 1 is the index number of
the slide. So it is the first slide. You do not identify a table. So PTReportGen
will put data into the first table in the slide.
3. The cell argument specifies the cells that the first record will be filled into.
The value is A2. So PTReportGen will fetch the first record, put the value of
- 12 -
Page 19

CompanyName field into A2, the value of CityName field into B2, the value of
CountryName field into C2, and the value of ContactName field into D2. An
then it fetch the next record, put them into A3,B3,C3 and D3……
3.4.6 Running a PTR file
1. On the Report menu, click Run, the Run Report dialog box appears.
2. Press Start button to run the PTR file.
3. PTReportGen will generate a report.
4. After the status is Done, click Close button.
3.4.7 Opening a report
1. On the File menu, click Open Report File to open the report you have
generated.
You can view and check the report.
2. On the File menu, click Open Log File to open the log file that recorded the
log information in the report generating..
You can check the log.
3. Close the report file and the log file.
3.4.8 Modifying the report template
1. On the File menu, click Open Template File to open the report template.
2. Change the width of columns. It is very useful to copy some sample data
from the report file into the report template for formatting.
3. Select the second row, and insert a row to the table.
4. Change the border width of the first row. Select the first row, click Table on
the Format menu, and then click the Borders tab. Change the border width,
and press OK button. The border of the first row is different from the border of
the other rows. The report template you have made is as follows:
- 13 -
Page 20

5. Save and close the template file.
3.4.9 Modifying the function
Now you want a full customer list. In the editor windows, modify the function as
follows:
@F1=Report(slide=1 cell=A2 pagebreak=12 reserve=2)
SELECT CompanyName
,CityName
,CountryName
,ContactName
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName,CityName,CountryName
;
1. The reserve argument specifies the number of records for that you reserve
some rows. You have reserve two blank rows in the report template so that the
format of the last row/column border may be different from the others.
2. The pagebreak argument specifies the number of records in one slide. You
want a full customer list, and remove the specified condition in the WHERE
clause. But a full customer list is too long in one slide. So you can put records
- 14 -
Page 21
into more slides using pagebreak argument. In this case, one slide contains 12
records.
3.4.10 Generating the report again
1. Save the PTR file.
2. Run the PTR file to generate the report.
3. Open the report, view and check the report.
The report should now look similar to the following:
Now you have created a report.
3.5 Samples
After PTReportGen is installed, some sample reports are installed too. Use
these reports to learn PTReportGen. The sample reports can be changed to
- 15 -
Page 22
adapt to your own needs.
The sample reports include a sample database, some report template files
(.ppt) and PTR files (.ptr). They are located in the Application Data\LJZsoft
under All Users or your profile folder. PTReportGen was tested with Microsoft
Office 2007. Please download the sample reports for Microsoft Office 2007
from our website.
Directory Description
{data}\Common\SampleDatabase Contains the sample database
“Sample.mdb”.
{data}\PTReportGen\Samples Contains the report template files
(.ppt) and the PTR files (.ptr).
{data}\PTReportGen\Samples\Report Contains the report files (.ppt)
generated by PTReportGen.
{data}\PTReportGen\Samples\Log Contains the log files created by
PTReportGen during generating
report files.
{data} is the path of the data folder. You can select the data folder when you
install PTReportGen. By default, the data folder is the Application Data\LJZsoft
folder under All Users. If you install PTReportGen without administrative
privileges, the data folder is the Application Data\LJZsoft folder under the
current user. The data folder is usually at:
Windows 95/98: C:\windows\All Users\Application Data\LJZsoft
Windows NT: C:\WinNT\Profiles\All Users\Application Data\LJZsoft
Windows 2000/XP: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application
Data\LJZsoft
Windows Vista: C:\ProgramData\LJZsoft
- 16 -
Page 23

Chapter 4 Report Templates
4.1 About Reports
The report generated by PTReportGen is a Microsoft PowerPoint presentation.
The layouts, formats and styles of the report are defined by a report template,
and the data of the report are got from databases such as Oracle, DB2.
4.2 About Report Templates
To make a report using PTReportGen, you should create a report template first.
The report template is a Microsoft PowerPoint presentation that defines the
layouts, formats and styles of the report. In the Microsoft PowerPoint report
template, you can input static content such as titles, descriptions, comments, a
cover, a company logo, format the static content, and define the format of the
data you will get from databases.
When generating a report, PTReportGen will copy the report template file to a
blank report file, and then put data into the report. So the layouts, formats and
styles defined in the report template file will be brought to the final report file.
4.3 PowerPoint Basic Concepts
If you have known these concepts of Microsoft PowerPoint, please skip this
section. For more detail information about Microsoft PowerPoint, refer to
Microsoft PowerPoint Help.
4.3.1 Presentations
A presentation is a Microsoft PowerPoint file with extension .ppt. You can open
- 17 -
Page 24

and save it using Microsoft PowerPoint. The presentation is made up of a
series of slides.
4.3.2 Slides
A slide is a frame in a presentation. A presentation contains one or more slides.
Slide is the primary component that contains content.
4.3.3 Layout
Layout refers to the way things are arranged on a slide. A layout contains
placeholders, which in turn hold text such as titles and bulleted lists and slide
content such as tables, charts, pictures, shapes, and clip art. Each time you
add a new slide, you can choose a layout for it. You can also choose a blank
layout.
4.3.4 Headers and Footers
Headers and footers consist of the header and footer text, slide or page
number, and date you want at the top or bottom of your slides or notes and
handouts.
You can use headers and footers on single slides or all slides. For notes and
handouts, when you apply a header or footer, it applies to all notes and
handouts. Headers and footers that you create for handouts also apply to
printed outlines.
4.3.5 Formatting
You can use these formatting features of Microsoft PowerPoint to effectively
display your data.
Characters formatting
To make text stand out, you can format the text in selected characters. You
- 18 -
Page 25

can change the font, color, size of text, bold and italic formats.
Paragraphs formatting
You can align, center or justify a paragraph, change indent and tab settings,
and change the line spacing of a paragraph.
Bulleted and numbered lists
Bulleted and numbered lists in Microsoft PowerPoint are easy to create. You
can quickly add bullets or numbers to existing lines of text, or Microsoft
PowerPoint can automatically create lists as you type.
Automatic formatting
Microsoft PowerPoint, by default, automatically formats certain types of text as
you type. Automatic paragraph formatting includes automatic bulleted and
numbered lists and resizing of text in text placeholders if the text doesn't fit at
its current font size.
4.3.6 Shapes
Shapes can be resized, rotated, flipped, colored, and combined to make more
complex shapes. Many have an adjustment handle that you can use to change
the most prominent feature of a shape — for example, you can change the size
of the point on an arrow. The AutoShapes include several categories of shapes:
lines, connectors, basic shapes, flowchart elements, stars and banners, and
callouts. You can add text to shapes (except lines, connectors, and freeforms).
The text you add becomes part of the shape.
Text boxes can be treated as shapes. They are formatted in many of the same
ways shapes are formatted, including adding colors, fills, and borders.
4.3.7 Pictures
There are two types of pictures: bitmaps or drawn pictures.
Bitmap pictures are made from a series of small dots, much like a piece of
- 19 -
Page 26

graph paper with specific squares filled in to form an image. Bitmaps are
created with and edited in paint programs, such as Microsoft Paint. All scanned
graphics and photographs are bitmaps. Bitmap pictures are often saved with
a .bmp, .png, .jpg, or .gif extension.
Drawn pictures are created from lines, curves, rectangles, and other objects.
The individual lines can be edited, moved, and rearranged. When a drawn
picture is resized, the computer redraws the lines and shapes so that they
retain their original definition and perspective. AutoShapes are drawn pictures.
Drawn pictures are saved in the format of the application that created them.
For example, Microsoft Windows Metafiles are saved with a .wmf extension.
4.3.8 Tables
A table is made up of rows and columns of cells that you can fill with text and
graphics. Tables are often used to organize and present information. You can
create tables in PowerPoint, or you can add a table from another program.
When you use PowerPoint, you can create a simple table with little formatting,
or one with more complex formatting. You can include fills and border colors
from the presentation's color scheme.
4.3.9 Charts
Charts are visually appealing and make it easy for users to see comparisons,
patterns, and trends in data. You can create a chart in a slide using Microsoft
Graph or Microsoft Excel. When you create a new chart in PowerPoint,
Microsoft Graph or Microsoft Excel opens and a chart is displayed with its
associated data in a data sheet or worksheet.
4.3.10 Sound, Music, Video, and Voice
You can add music and sounds from files on your computer, a network, the
- 20 -
Page 27

Internet, or Microsoft Clip Organizer. You can also record your own sounds to
add to a presentation, or use music from a CD.
You can add movies and animated GIFs to slides from files on your computer,
the Microsoft Clip Organizer, a network or intranet, or the Internet. "Movies"
are desktop video files with formats such as AVI, QuickTime, and MPEG, and
file extensions such as .avi, .mov, .qt, .mpg, and .mpeg. An animated GIF file
includes motion and has a .gif file extension. Though not technically movies,
animated GIFs contain multiple images which stream to create an animation
effect.
4.4 Table Reports
4.4.1 About Table Reports
A table is made up of rows and columns of cells that you can fill with text and
graphics. Tables are often used to make reports, and organize and present
information.
PTReportGen supports two types of table reports: fixed table report, variable
table report.
Fixed table report: The number of rows and columns in the table is fixed. When
PTReportGen executes a SQL statement, directly puts the result data into cells
in the table.
Variable table report: The number of rows or columns in the table is unfixed,
and it is variable as the number of result records. When PTReportGen
executes a SQL statement, it repeats the table rows or columns for each
record or group, and then puts data into cells of the table.
- 21 -
Page 28
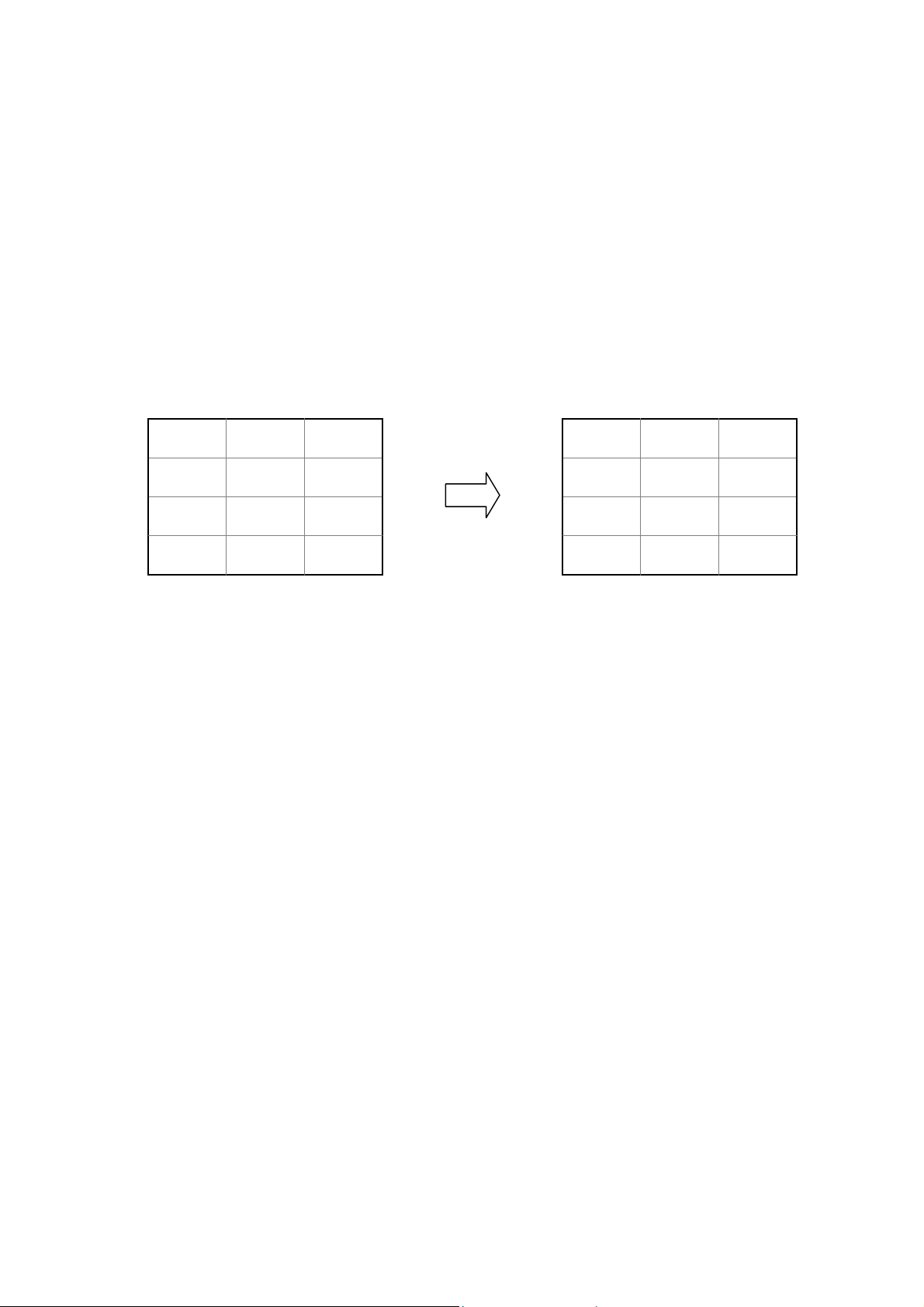
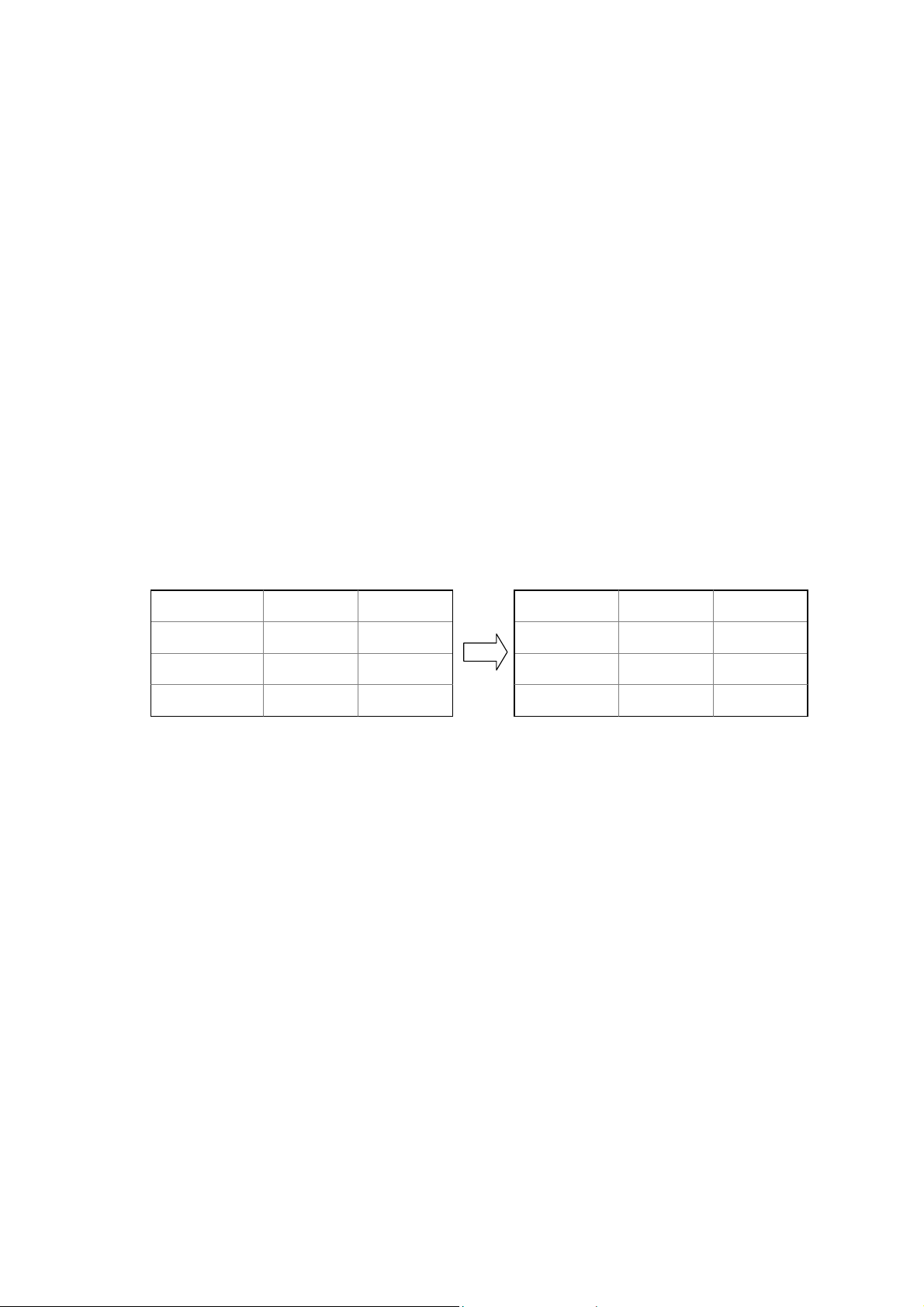
4.4.2 Creating a Table for a Fixed Table Report
For a fixed table report, you need to create a table in the report template file
according to the report. The format of the table is the same as the format in the
report, but cells that should be filled data into are blank. When PTReportGen
executes a SQL statement, the data values from data source will be filled into
these cells.
BA
BA
1
1
2
2
3
3
BA
BA
3.4141
3.4141
5.2202
5.2202
2.783
2.783
The fixed table defined
in the report template file
The fixed table filled data
by rows in the re port file
4.4.3 Creating a Table for a Variable Table Report
For a variable table report, you also need to create a table in the report
template file according to the report. But you just need to reserve some
rows/columns in the table for one or two records. PTReportGen will add some
rows/columns according to the records from data source.
- 22 -
Page 29
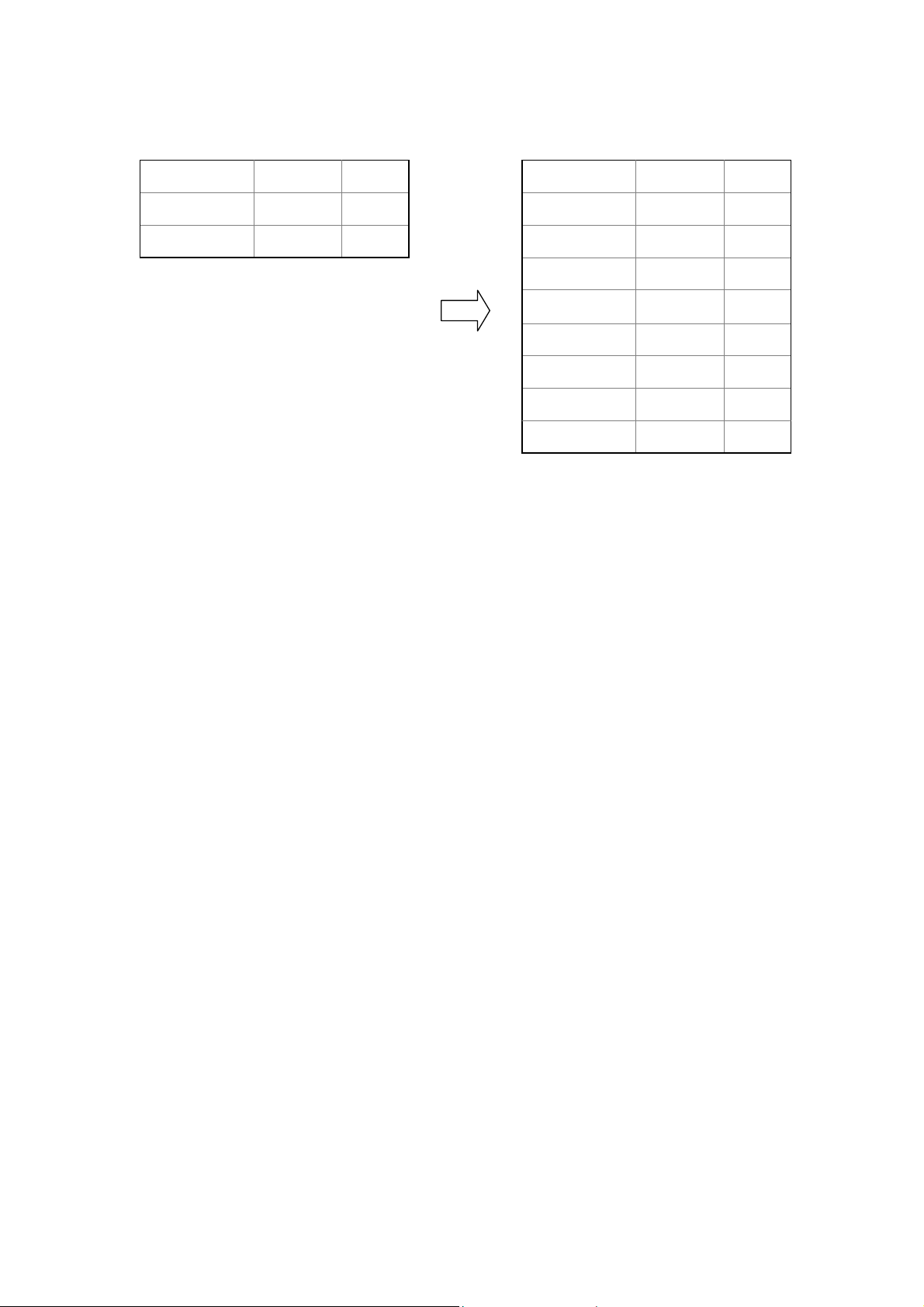
SalesItem IdDate
SalesItem IdDate SalesItem IdDate
SalesItem IdDate
1503 1998-01-01
1503 1998-01-01
2003 1998-01-02
2003 1998-01-02
2503 1998-01-03
2503 1998-01-03
3503 1998-01-05
3503 1998-01-05
5503 1998-01-10
5503 1998-01-10
1503 1998-01-21
1503 1998-01-21
2003 1998-01-25
2003 1998-01-25
1003 1998-01-31
1003 1998-01-31
The variable-rows tab le defined
in the report template file
The format of the last row/column border can be different from the others. For
example, the outside borders used double lines, and the inside borders used
single lines. To do this, you should reserve the blank rows/columns for 2
records. When PTReportGen inserts some blank rows/columns, the new
rows/columns will inherit the format of the first row/column in the reserved
rows/columns.
One record from data source can be put into two or more rows/columns. To do
this, you need to reserve the blank rows/columns for all records that you want
to put them into one slide. For example, there are 91 records returned from a
database, and you want to put 5 records per slide and 3 rows per record. You
must prepare one slide that contain one table and reserve 15 blank rows in the
The variable-rows table filled data
by rows in the report file
table. If 1 rows per record, you just need to reserve 1 or 2 blank rows in the
table. PTReportGen can insert rows, delete rows, copy slides with tables, but
can not copy rows in one slide.
4.4.4 Formatting Cells
To format cells that contain static contents, use “Format” menu in Microsoft
- 23 -
Page 30
PowerPoint. For more detail information, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help.
For cells in which data are got from database, you can set font, color,
alignment using Microsoft PowerPoint. But to display values in formatting
string, you should use other way.
You should write formatting expressions into data cells in the report template
file. PTReportGen will get the text of the cell as a format expression before it
puts a value into a cell, and output the value using the format expression. In
fact, PTReportGen calls the format function in Visual Basic. The text got from a
cell is used as the format expression in format function. For a variable table
report, PTReportGen will use the format expressions in the reserved
rows/columns. For more information about format expression, refer to “Format
Expressions”.
AmountQuantityDate
AmountQuantityDate
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
#,##0.00#,##0yyyy-mm-dd
The table defined in the report template file The table generated in the report file
AmountQuantityDate
AmountQuantityDate
827.795601999-02-18
827.795601999-02-18
1,113.058901999-06-14
1,113.058901999-06-14
1,552.251,2402000-01-21
1,552.251,2402000-01-21
A format expression for numbers can have from one to four sections separated
by semicolons. You can define the different formats and colors for positive
values, negative values and zeros.
For example, the format "$#,##0;($#,##0)" has two sections: the first defines
the format and color (black) for positive values and zeros; the second section
defines the format and color (red) for negative values. It displays “2345.12” as
“$2,345”, displays “-5432” as “($5,432)”.
The format “#,##0.00;;” has three sections: the first defines the format and
color (black) for positive values, the second defines the format and color (red)
for negative values, the third section defines the format and color (blue) for
zeros. Note, the first semicolon “;” is red, the second semicolon “;” is blue. The
- 24 -
Page 31

negative values and zeros are printed using the format of the positive value.
But the color for negative values is red, the color for zeros is blue. It displays
“8.9” as “8.90”, displays “-123” as “-123.00”, and displays “0” as “0.00”.
4.4.5 Irregular Tables
Tables don't have to consist of simple grids. Not every row has to have the
same number of columns. You can merge and split cells to create irregular
tables. An irregular table is the table that contains split cells or merge cells, and
it does not have the same number of cells for each row or column. While an
irregular table provides for an attractive way to display data, but it is harder to
be processed. You have some difficulty to reference a cell in an irregular table.
For example in the following table, for most Office version, cell1 is in column 3
and row 2, cell2 is in column 3 and row 3. But for some lower Office version,
cell2 is not in column 3 and row 3. Moreover, an error may occur when you try
to work with some rows or columns in an irregular table.
CBA
CBA
Cell1
Cell1
Cell2
Cell2
Irregular table
To simplify your work and ensure that report function can be executed correctly,
you should regularize the irregular tables. Split the merge cells, and remove
the border in these cells. For example, the following table is a regularized table,
cell1 is in column 3 and row 2, and cell2 is in column 3 and row 3.
CBA
CBA
Cell1
Cell1
Cell2
Cell2
Regularized table
- 25 -
Page 32

4.4.6 Referencing Cells
You can reference table cells as A1, A2, B1, B2, and so on, with the letter
representing a column and the number representing a row. Cell references in
Microsoft PowerPoint are always absolute references and are not shown with
dollar signs. You can reference an entire row or column in a calculation in the
following ways:
Use a range that includes only the letter or number that represents it - for
example, 1:1 to reference the first row in the table. This designation allows
the calculation to automatically include all the cells in the row if you decide
to add other cells later.
Use a range that includes the specific cells - for example, a1:a3 to
reference a column with three rows. This designation allows the calculation
to include only those particular cells. If you add other cells later and you
want the calculation to include them, you need to edit the calculation.
4.4.7 Referencing Tables
If you want to reference a table, you should reference a slide first. You can
reference a slide by an index number. The index number represents the
position of the slide in a presentation. The index number starts at 1. If the index
number is less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation.
So slide 1 is the first slide in a presentation, slide 2 is the second slide in a
presentation, slide -1 is the last slide in a presentation. You can reference a
slide dynamically. “N” means the next slide.
You can reference a table in the slide by an index number. The index number
represents the position of the table in the slide. The index number starts at 1.
So table 1 is the first table in a slide, table 2 is the second table, and so on.
- 26 -
Page 33

4.4.8 Formatting Cells for Pictures
To enhance the visual impact of your report, you can insert pictures into your
report. PTReportGen supports many popular graphics file formats: bitmap,
JPG, GIF, PNG, TIFF and so on. For the graphics file formats PTReportGen
supports, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help.
You should store the path and name of the graphics files in the database, and
identify the image fields in the report function. PTReportGen will read the
graphics files, and insert them into the cells in the report file.
To specify the size, you should write a formatting expression into the cell in the
report template file. PTReportGen will get the text of the cell, and insert a
picture into the cell according to the instruction in the format expression. The
format expression for pictures as follows:
[size]
The size specifies the size of a picture. Possible values are STRETCH, Wnnn
or / and Hnnn. "STRETCH" means that the picture is resized to fit within the
cell. “W100” means that the width of the picture is set to 100 points. “H50”
means that the height of the picture is set to 50 points. The default means the
original size. If you just specify the width or height of the picture, not both,
PTReportGen will retain the original proportions of the picture when
PTReportGen resize it.
Example
w120 h90
Remarks
PTReportGen will insert a picture, and set the width of the picture to 120 points,
the height to 90 points.
- 27 -
Page 34

4.5 Form Reports
4.5.1 About Form Reports
Beside table reports, PTReportGen supports form reports too. For a form
report, you can get data from data sources, and put data into shapes or text
boxes. So you can make a form report as follows:
4.5.2 Creating a Slide
For a form report, you must create a slide including some shapes or text boxes
in the report template file according to the report. When PTReportGen
executes a SQL statement, the data values from data source will be put into
these shapes or text boxes. PTReportGen will add some slides according to
results returned. One record makes one slide.
- 28 -
Page 35

You can add some shapes as your needs, such as reshaping shapes, resizing
shapes, changing colors, changing the font. For more detail information about
shapes, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help.
To generate the previous PowerPoint report, you should make the following
slide in the report template file.
4.5.3 Naming Objects
How to reference an object in a slide? PTReportGen can reference an object
using its name. The name is not case-sensitive, and uniquely identifies an
object in a slide. But Microsoft PowerPoint can not give a way to know the
name of an object.
We developed a PowerPoint add-in “name.ppa” that can name an object in a
slide. The add-in file is located in the PTReportGen's working directory. To
- 29 -
Page 36

load the add-in:
1. Launch Microsoft PowerPoint.
2. Click Add-Ins under Tools menu. The Add-Ins dialog box appears.
3. Press Add New button, and browse to “name.ppa” file, and Press OK
button.
4. If prompted to enable macros, press Enable Macros button. The add-in will
be listed in the Add-Ins dialog box. Press Close button to close the dialog box.
If however you do not find the add-in listed in the Add-Ins dialog box, then
check the macro settings. If this is not set to at least Medium, the add-in won't
load. To resolve this:
1. Click Macros under Tools menu, and click Security. The Security dialog
box appears.
2. Click the Security Level tab, and click Medium.
3. Press OK button.
4. Now load the add-in.
5. Once the add-in has been loaded you can set the security level back to
High.
When you open Microsoft PowerPoint after “name.ppa” have been loaded, a
Name menu item will appear under Tools menu. You can show the name of
an object, and rename the object. To name an object:
1. Select an object in a slide.
2. On the Tools menu, click Name. The Object Name dialog box appears.
3. You will see the name of the object you have selected.
4. If you want to rename the object, input a new name in the New Name box,
and press Rename button. If you get an error message “Permission denied”, it
probably means that the name already exists.
5. Press Close button to close the Object Name dialog box.
Remember to save all your works. To ensure to save your change to object
- 30 -
Page 37

names, you should save a complete file.
1. On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Save tab.
2. Clear the Allow fast saves check box when you finish working on the file,
and then save it one last time. A full save occurs when this check box is clear.
4.5.4 Formatting text in an Object
You can use Microsoft PowerPoint to change an object and the attached text.
You can change the font, color, fill, shadow and so on. For more detail
information, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help. But to display values in
formatting string, you should use the way similar to cell formatting.
You should write formatting expressions into a shape or text box in the report
template file. PTReportGen will get the text as a format expression before it
puts a value into the object, and output the value using the format expression.
In fact, PTReportGen calls the format function in Visual Basic. The text got
from an object is used as the format expression in format function. For more
information about format expression, refer to “Format Expressions”.
For example, you add a text box with a text “YYYY-MM-DD” in the report
template file. In the report file, you will get a formatted date string. For example,
“1996-04-01”.
A format expression for numbers can have from one to four sections separated
by semicolons. You can define the different formats and colors for positive
values, negative values and zeros.
For example, the format "$#,##0;($#,##0)" has two sections: the first defines
the format and color (black) for positive values and zeros; the second section
defines the format and color (red) for negative values. It displays “2345.12” as
“$2,345”, displays “-5432” as “($5,432)”.
The format “#,##0.00;;” has three sections: the first defines the format and
color (black) for positive values, the second defines the format and color (red)
- 31 -
Page 38

for negative values, the third section defines the format and color (blue) for
zeros. Note, the first semicolon “;” is red, the second semicolon “;” is blue. The
negative values and zeros are printed using the format of the positive value.
But the color for negative values is red, the color for zeros is blue. It displays
“8.9” as “8.90”, displays “-123” as “-123.00”, and displays “0” as “0.00”.
4.5.5 Formatting Pictures
As same as the table report, you can insert pictures into your form report too.
You should store the path and name of the graphics files in the database, and
identify the image fields in the report function. PTReportGen will read the
graphics files, and put them at the position of the objects in the report file.
To specify the size, you should write a formatting expression into the shape or
text box in the report template file. The format expression for pictures in form
report is the same as the format expression in table report.
[size]
The size specifies the size of a picture. Possible values are STRETCH, Wnnn
or / and Hnnn. "STRETCH" means that the picture is resized to fit within the
object. “W100” means that the width of the picture is set to 100 points. “H50”
means that the height of the picture is set to 50 points. The default means the
original size. If you just specify the width or height of the picture, not both,
PTReportGen will retain the original proportions of the picture when
PTReportGen resize it.
4.6 Charts
4.6.1 About Charts
You can create many different types of charts in Microsoft PowerPoint. The
chart software may be Microsoft Graph or Microsoft Excel. It is depended on
- 32 -
Page 39

the version of your Microsoft PowerPoint. For Microsoft PowerPoint 2003 or
earlier, the default chart software is Microsoft Graph. For Microsoft PowerPoint
2007 or later, the default chart software is Microsoft Excel.
PTReportGen supports two kinds of charts created by Microsoft Graph or
Excel. It executes a SQL statement, and puts the result data into the datasheet
or worksheet of the chart. To work with charts created in Graph or Excel, you
must have Graph or Excel installed.
4.6.2 Creating a Blank Chart using Microsoft Graph
To create a Graph chart in the report using PTReportGen, you need to add a
Graph chart in the report template file first. The chart will be brought into the
report file with the same chart type, display option, data format, label format
and other chart item
If your Microsoft Office is earlier than Office 2007, or Microsoft Excel 2007 is
not installed, when you create a new chart in Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft
Graph opens.
To add a Graph chart in the template file:
1. Open the report template file using Microsoft PowerePoint.
2. On the Insert menu, click Chart.
3. Change the sample data on the datasheet as you need.
4. Modify the chart. For example, you want to change the chart type, make the
text larger, or change colors, patterns, lines, fills, and borders in charts.
5. After you have finished the modification, delete data from the chart. You
should keep a blank chart in the report template file. PTReportGen will put data
into the datasheet of the chart.
For more detail information, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help and Microsoft
Graph Help.
- 33 -
Page 40

4.6.3 Creating a Blank Chart using Microsoft Excel
To create an Excel chart in the report using PTReportGen, you need to add an
Excel chart in the report template file first. The chart will be brought into the
report file with the same chart type, display option, data format, label format
and other chart item.
To add an Excel chart in the template file:
1. Open the report template file using Microsoft PowerPoint.
2. Insert a chart with a chart sheet and a worksheet. For more information to
insert an Excel chart object in Microsoft PowerPoint, please refer to the
following part.
3. Change the sample data on the worksheet as you need.
4. Modify the chart. For example, you want to change the chart type, make the
text larger, or change colors, patterns, lines, fills, and borders in charts.
If the report type is fix, the data range of the chart should be all
rows/columns for the returned records.
If the report type is var, the data range of the chart should be 2
rows/columns.
5. After you have finished the modification, delete data from the chart. You
should keep a blank chart in the report template file, and make the chart sheet
active. PTReportGen will put data into the worksheet of the chart.
By default, Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 uses Microsoft Excel to create charts,
but doesn't expose the chart as a normal Excel object. To insert an Excel chart
object, you can insert an Excel worksheet first, and then create a chart in the
Excel worksheet object. Another way is to copy an Excel chart object from
earlier PowerPoint presentation.
For Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 or later, to insert an Excel chart object:
1. In Microsoft PowerPoint, on the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click Table,
- 34 -
Page 41

and then click Excel Spreadsheet. You will see an Excel worksheet object.
2. Right-click the object, point to Worksheet Object on the shortcut menu, and
choose Open from the submenu. Microsoft Excel will appear.
3. Create a chart in Microsoft Excel, and move the chart to a new worksheet.
4. When you've finished, choose Close & Return from the File menu.
For Microsoft PowerPoint 2003 or earlier, to insert an Excel chart object:
1. In Microsoft PowerPoint, click Object on the Insert menu, and then select
the Microsoft Excel Chart.
2. You can work the Excel chart object by right-clicking the object, and pointing
to Chart Object on the shortcut menu, and choosing Open from the submenu.
3. When you've finished, choose Close & Return from the File menu.
For more detail information, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help and Microsoft
Excel Help.
4.6.4 Referencing Charts
If you want to reference a chart, you should reference a slide first. You can
reference a slide by an index number. The index number represents the
position of the slide in a presentation. The index number starts at 1. If the index
number is less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation.
So slide 1 is the first slide in a presentation, slide 2 is the second slide in a
presentation, slide -1 is the last slide in a presentation. You can reference a
slide dynamically. “N” means the next slide.
You can reference a chart in the slide by an index number. The index number
represents the position of the chart in the slide. The index number starts at 1.
So chart 1 is the first chart in a slide, chart 2 is the second chart, and so on.
- 35 -
Page 42

Chapter 5 Reporting with PTReportGen
5.1 Creating and Opening PTR Files
5.1.1 About PTR files
To generate a report with PTReportGen, you must create a PTR file with a .ptr
extension. The PTR file contains information such as the name of the report
template file, the name of the report file, the log file name, data sources,
parameters and functions. The PTR file tells PTReportGen how to get data
from data sources and how to put data into a report.
5.1.2 Create a new PTR file
On the File menu, click New.
5.1.3 Open a PTR file
1. On the File menu, click Open.
2. In the Look in list, click the drive, folder, or Internet location that contains
the file you want to open.
3. In the folder list, locate and open the folder that contains the file.
4. Click the file, and then press Open button.
5.1.4 Save a PTR file
On the File menu, click Save. If you're saving the file for the first time, you'll be
asked to give it a name.
If you want save a file to another name, do as follows:
1. On the File menu, click Save As.
2. In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
- 36 -
Page 43

3. Press Save button.
5.2 Configuring Files
5.2.1 About files
You should specify the report template file, report file, report file type and log
file. The report template file defines layouts, formats and styles of the report.
The report file is the report you want to generate. The type of the report file can
be different from the template file. The log file records the log information in the
report generating.
The file path can be a relative path or an absolute path. If it is a relative path,
the base path is the path of the PTR file. In the paths and names of report file,
template file and log file, you can use parameters. For detailed information
about parameters, refer to “Configuring Parameters” in this document.
5.2.2 Configuring file information
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the File tab.
3. Input the path and name of the template file, the report file and the log file
into their text box.
4. In the File Type box, click the file type you want. If the file type of the report
is same as the template file, click the (Default) in the File Type box.
5. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
changes.
- 37 -
Page 44

5.2.3 Converting files
You can convert a file from Microsoft PowerPoint presentation to and from
another file format. For example, the template file is a presentation file with
a .ppt extension, and the report file is a PowerPoint show file with a .pps
extension.
The file formats PTReportGen supports can be one of these. What file format
PTReportGen supports is dependent on your Microsoft PowerPoint. For
example, Microsoft PowerPoint 2003 supports Web archive (.mht), but
Microsoft PowerPoint 2000 does not support it. For more information about
converting files, please refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help. The file “pconv.cfg”
located in the PTReportGen directory contains the information of file formats.
You can expand it if your Microsoft PowerPoint supports more file formats.
File Format Name Value Description Extension Converter
ppSaveAsPresentation 1 Presentation ppt Office2000
ppSaveAsPowerPoint7 2 PowerPoint 95
Presentation
ppSaveAsPowerPoint4 3 PowerPoint 4 Presentation ppt Office2000
ppSaveAsPowerPoint3 4 PowerPoint 3 Presentation ppt Office2000
ppSaveAsTemplate 5 Design Template pot Office2000
ppSaveAsRTF 6 Outline/RTF rtf Office2000
ppSaveAsShow 7 PowerPoint Show pps Office2000
ppSaveAsAddIn 8 PowerPoint Add-In ppa Office2000
ppSaveAsPowerPoint4FarEast
ppSaveAsHTML 12 Web Page htm html Office2000
ppSaveAsHTMLv3 13 Web Page v3 htm html Office2000
ppSaveAsHTMLDual 14 Web Page Dual htm html Office2000
ppSaveAsMetaFile 15 Windows Metafile wmf Office2000
ppSaveAsGIF 16 GIF (Graphics Interchange
ppSaveAsJPG 17 JPEG (File Interchange
ppSaveAsPNG 18 PNG (Portable Network
ppSaveAsBMP 19 Device Independent bmp Office2000
10 PowerPoint 4 Far East ppt Office2000
Format)
Format)
Graphics Format)
ppt Office2000
gif Office2000
jpg Office2000
png Office2000
- 38 -
Page 45

Bitmap
ppSaveAsWebArchive 20 Single File Web Page mht
Office2002
mhtml
ppSaveAsTIF 21 TIFF (Tag Image Format
tif Office2002
File)
ppSaveAsPresForReview 22 Presentation for Review ppt Office2003
ppSaveAsEMF 23 Enhanced Windows
emf Office2003
Metafile
For Microsoft PowerPoint 2007, please copy “pconv2007.cfg” to “pconv.cfg”.
This file contains the information of file formats for Microsoft PowerPoint 2007.
File Format Name Value Description Extension
ppSaveAsOpenXMLPresentation 24 PowerPoint
Presentation
ppSaveAsOpenXMLPresentationMacroEnabled
25 PowerPoint
Macro-enabled
Presentation
ppSaveAsPresentation 1 PowerPoint 97-2003
Presentation
ppSaveAsPDF 32 PDF pdf
ppSaveAsXPS 33 XPS Document
Format
ppSaveAsOpenXMLTemplate 26 PowerPoint Template potx
ppSaveAsOpenXMLTemplateMacroEnabled
27 PowerPoint
Macro-enabled
Presentation Template
ppSaveAsTemplate 5 PowerPoint 97-2003
Template
ppSaveAsOpenXMLTheme 31 Office Theme thmx
ppSaveAsOpenXMLShow 28 PowerPoint Slide
Show
ppSaveAsOpenXMLShowMacroEnabled
29 PowerPoint
Macro-enabled Slide
Show
ppSaveAsShow 7 PowerPoint 97-2003
Show
ppSaveAsOpenXMLAddin 30 PowerPoint Add-in ppam
ppSaveAsAddIn 8 PowerPoint 97-2003
Add-In
ppSaveAsXMLPresentation 34 PowerPoint XML
Presentation
pptx
pptm
ppt
xps
potm
pot
ppsx
ppsx
pps
ppa
xml
- 39 -
Page 46

ppSaveAsWebArchive 20 Single File Web Page mht
mhtml
ppSaveAsHTML 12 Web Page htm html
ppSaveAsHTMLv3 13 Web Page v3 htm html
ppSaveAsHTMLDual 14 Web Page Dual htm html
ppSaveAsGIF 16 GIF (Graphics
Interchange Format)
ppSaveAsJPG 17 JPEG (File
Interchange Format)
ppSaveAsPNG 18 PNG (Portable
Network Graphics
Format)
ppSaveAsTIF 21 TIFF (Tag Image
Format File)
ppSaveAsBMP 19 Device Independent
Bitmap
ppSaveAsMetaFile 15 Windows Metafile wmf
ppSaveAsEMF 23 Enhanced Windows
Metafile
ppSaveAsRTF 6 Outline/RTF rtf
gif
jpg
png
tif
bmp
emf
5.3 Configuring Data Sources
5.3.1 About data sources
A data source identifies a database computer you want to access. Because of
accessing data through ODBC, PTReportGen can access a wide range of data
sources, such as Oracle, DB2, Sybase, Informix, Microsoft SQL Server,
Teradata, MySQL, Microsoft Access, dBase. PTReportGen supports more
than one data sources in one report. You can get data from some different
databases such as Oracle, DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server, and put them into
one report.
5.3.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a data source
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
- 40 -
Page 47

appears.
2. Click the Data Source tab.
3. If you want to add a data source, press New button, the New Data Source
dialog box appears.
To define a connection using an ODBC data source name, click Using
ODBC data source name option, input data source name, user name and
password, press OK button.
To define a connection using a connection string, click Using connection
string option, input data source name, and connection string, press OK
button.
4. If you want to modify a data source, click the data source name in the Data
Source list box, and press Edit button, the Edit Data Source dialog box
appears.
To define a connection using an ODBC data source name, click Using
ODBC data source name option, change data source name, user name
and password, press OK button.
To define a connection using a connection string, click Using connection
string option, change data source name, and connection string, press OK
button.
5. If you want to delete a data source, click the data source name in the Data
Source list box, and press Delete button, the confirmation dialog box appears.
Press Yes button to delete the data source.
6. You can test a data source. Click the data source name in the Data Source
list box, and Press Test button to display the information of connection to the
data source.
7. Select or clear the Encrypt Password check box. If the check box is
selected, passwords will be saved in an encrypted format. Or passwords will
be saved in plain text.
- 41 -
Page 48

8. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
changes.
5.4 Configuring Parameters
5.4.1 About parameters
You can use parameters in SQL statements. These values need to be
provided to PTReportGen before it executes these SQL statements. To use a
parameter, you must declare it first. When PTReportGen generate a report, it
will prompt you to input the value of the parameter. PTReportGen will replace
the parameter name in the SQL statements with the actual value before it
submits the SQL statements to data sources.
A parameter has a name, a title and a default value. The name of a parameter
identifies the parameter. You can use the names in SQL statements. The titles
will be displayed in the prompt dialog box when PTReportGen is run.
Note: PTReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of
the parameters. You should be careful to define a unique name for each
parameter. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character. For
example, you give the name “$ReportDate” for a parameter. Parameters are
case-sensitive.
5.4.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a parameter
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the Parameter tab.
3. If you want to add a parameter, press New button, the New Parameter
dialog box appears. Input parameter name, parameter title and default value,
press OK button.
- 42 -
Page 49

4. If you want to modify a parameter, click the parameter name in the
Parameter list box, and press Edit button, the Edit Parameter dialog box
appears. Change the name, title and default value of the parameter, press OK
button.
5. If you want to delete a parameter, click the parameter name in the
Parameter list box, and press Delete button, the confirmation dialog box
appears. Press Yes button to delete the parameter.
6. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
changes.
5.5 Inputting Functions
You should input functions in the editor window. A function includes a SQL
statement and some arguments. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement,
and determines whether or how to add data into the report. PTReportGen
sequentially executes functions.
Each function is begin with the ”@” character. Syntax:
@functionno=functionname(arguments)
sqlstatement
The functionno is a label of the report function.
The functionname represents a report function.
The arguments for a function define various properties for the function. For
example, the “slide” argument identifies a slide in the Microsoft PowerPoint
presentation. An argument takes the form Name="Value". The argument value
can be delimited by single or double quotes.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement.
For more detailed information about functions, see “Function Reference” in this
document.
- 43 -
Page 50

You can use comments in text. A comment is the “/*” characters, followed by
any sequence of characters (including new lines), followed by the “*/”
characters. You cannot nest comments.
5.6 Running PTR Files
You can run a PTR file to generate a report in Microsoft PowerPoint format.
PTReportGen supports Windows mode and command line mode.
5.6.1 Windows mode
1. On the Report menu, click Run, the Run Report dialog box appears.
2. If you want to display the generated report, select the Display Report with
Microsoft PowerPoint check box.
3. Press Start button to run the PTR file.
4. If parameters are defined in the PTR file, PTReportGen will pop up a prompt
dialog box. Input the values of the parameters, and press OK button.
5. While PTReportGen is being run, it will display some information such as
status, SQL count, error count, function No., records count and log information.
6. You can interrupt the running. Click End button to interrupt it. PTReportGen
will immediately save and close the report.
7. Click Close button after completion.
8. If you want to open the report, click Open Report File on the File menu.
9. If you want to check the log, click Open Log File on the File menu.
5.6.2 Command line mode
You can run a PTR file in command line. You have defined two parameters in
the PTR file “myreport.ptr”. The first parameter is sales date “$SalesDate”, and
the second is the category of the products “$Category”. You can run
- 44 -
Page 51

PTReportGen in command line mode as follows:
pptreport c:\PPTReport\myreport.ptr -c 1996-05-01 “Dairy Products”
PTReportGen will replace “$SalesDate” in SQL statements with “1996-05-01”,
replace “$Category” with “Dairy Products”, and then submit SQL statements to
data sources.
5.7 Sorting, Grouping and Totaling
5.7.1 Sorting data
Sorting means placing data in some kind of order to help you find and evaluate
it. For example, you may want to have a customer list sorted alphabetically by
name or by country.
To sort your data, you can use SQL. Use the ORDER BY clause to have your
results displayed in a sorted order.
SELECT EmployeeID
,LastName
,FirstName
,HireDate
FROM Employees
ORDER BY HireDate; /* ascending sort */
In the example above, results will come back in ascending order by hire date.
To explicitly specify ascending or descending order, add ASC or DESC, to the
end of your ORDER BY clause. The following is an example of a descending
order sort.
ORDER BY HireDate DESC; /* descending sort */
5.7.2 Totaling
You can sum the values, count all the values or only those values that are
- 45 -
Page 52

distinct from one another, and determine the maximum, minimum, average. To
add totals, you can use aggregate functions in SQL statement, such as
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MAX, MIN.
1. In the fixed table report, you can add total directly using a separate SQL.
2. In the variable table report, you must add total first using a Fixed Table
report function before you use the Variable Table report function. Because the
cell address of the total field will change after you use Variable Table report
function.
5.7.3 Grouping data and subreports
Grouped data is data that is sorted and broken up into meaningful groups. In a
customer list, for example, a group might consist of all those customers living
in the same Region.
To group data in a report, you should use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE
REPORT function. For more detail information, refer to “Group Variable Table
Report” in this document.
Using GROUP REPORT function, you can make subreports within a report. A
subreport would typically be used to perform one-to-many lookups such as
Customer / Order / OrderDetails.
To make sub reports within the main report,
1. Write a JOIN SQL statement to access data from two or more tables. For
example, you can join Customers, Orders and OrderDetails tables.
2. Use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE REPORT function.
For more detail information, refer to the samples customer_profile.ptr,
product_catalog.ptr and sales_detail.ptr within PTReportGen.
5.7.4 Subtotaling
A subtotal is a summary that totals or sums numeric values in a group. You
- 46 -
Page 53

can sum the values in each group, count all the values in each group, and
determine the maximum, minimum, average in each group. For example,
determine the total sales per sales representative in a sales report.
To add subtotals, you can use aggregate function in SQL statement.
1. Use aggregate function and GROUP BY clause, get summary data for each
group, and insert results into a temporary table.
2. If you have different kinds of summaries, repeat the step 1, and insert results
into another temporary table.
3. Use group report function, and join the detail data and the summary data
using JOIN. The summary fields must be included in the group list.
4. Except for sub-totals, you can add total too using aggregate function in SQL
statement. You must add total first using a Fixed Table report function before
you use the Variable Table report function. Because the cell address of the
total field will change after you use Variable Table report function.
For more information, refer to the samples sales_detail.ptr within
PTReportGen.
5.8 Pictures
5.8.1 Inserting pictures into a report template
To make eye-catching reports, you can add pictures to your reports. You can
insert pictures into the report template directly in Microsoft PowerPoint. For
example, you want to display a logo in your report. You can insert the logo
graphics file into the report template. For more information about adding
pictures to a presentation, refer to Microsoft PowerPoint Help.
5.8.2 Inserting pictures into a report
Except for inserting the static pictures during report design, you want to insert
- 47 -
Page 54

pictures during report building process. You hope a reporting tool to pull
pictures from database into PowerPoint report. PTReportGen can insert
pictures from the graphics files, and support all graphics file format that
Microsoft PowerPoint support.
To insert pictures into a report using PTReportGen, you should do as follows:
1. Store the path and name of the graphics files in the database
You stored the path and file name of the pictures in database, did not store the
pictures. The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. For
example, you store "images\emp1.jpg" in Photo field.
2. Identify the image fields in the report function
Write a report function in the PTR file, and identify the image fields using
IMAGE argument. For example,
@F1=Report(slide=1 ... image=photo)
3. Specify the size in the report template
To specify the size, you should write a formatting expression in the report
template file. For a table report, you write a formatting expression in the cell.
PTReportGen will get the formatting expression, and insert a picture into the
report according to the instruction in the format expression.
4. Run PTReportGen to generate report with pictures
During report generating process, PTReportGen will read the graphics files,
and insert them into the report according to your instruction. If the path and file
name of the picture is “”, PTReportGen will return “”. PTReportGen will return
“#Error” if it does not find the file of the picture.
For more detail information about pictures, refer to the samples
employee_profile.ptr, product_catalog.ptr within PTReportGen.
- 48 -
Page 55

5.9 Using Parameters
To use a parameter, you must define it first. If you have defined a parameter
name, you can use it in SQL statements. When PTReportGen is run, it will
replace the parameter name in the SQL statements with the actual value
before it submits the SQL statements to data sources. Besides in SQL
statements, you can use parameters in the paths and names of report file and
log file.
In fact, PTReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of
the parameters. You should be careful to define a unique name for each
parameter. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character.
Example
Input an order id to get the order information. The field OrderID is numeric
type.
1. Defining a parameter
Define a parameter as follows:
Name: $OrderID
Title: Order ID (>=10248)
Default: 10360
2. Using a parameter
You can use the parameter “$OrderID” in SQL statements. For example:
SELECT o.OrderID
,o.OrderDate
,SUM(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount)) AS Amount
FROM Orders o, OrderDetails d
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND o.OrderID = $OrderID
GROUP BY o.OrderID, o.OrderDate
- 49 -
Page 56

;
Example
Define two parameters. The first parameter is sales date, and the second is the
category of the products. The field OrderDate is date type, and CategoryName
is char type.
1. Defining parameters
Define parameters as follows:
Name1: $SalesDate
Title1: Sales Date
Default1: 1996-05-01
Name2: $Category
Title2: Category of Products
Default2:
2. Using parameters
You can use the parameters “$SalesDate”, “$Category” in SQL statements.
For example:
SELECT ……
FROM Orders, OrderDetails, Products, Categories
WHERE ……
AND OrderDate = ‘$SalesDate’
AND CategoryName LIKE '$Category%'
;
/* For Microsoft Jet SQL, LIKE '$Category*' */
Example
Get the information from the database, table and column that you identify when
the report is generated.
1. Defining parameters
Define parameters as follows:
- 50 -
Page 57

Name1: $Database
Title1: Database Name
Default1:
Name2: $Table
Title2: Table Name
Default2:
Name3: $Column
Title3: Column Name
Default3:
2. Using parameters
You can use the parameters “$Database”, ”$Table” and “$Column” in SQL
statements. For example:
USE $Database;
or
DATABASE $Database;
SELECT $Column
FROM $Table
;
Example
Use parameters in the path and name of the report file and log file.
1. Defining a parameter
Define a parameter as follows:
Name: $CustomerID
Title: Customer ID
Default: C000001
2. Using a parameter
ReportFileName=report\report_$CustomerID.ppt
LogFileName=log\report_$CustomerID.log
- 51 -
Page 58

or
ReportFileName=report\$CustomerID\report.ppt
LogFileName=log\$CustomerID\report.log
5.10 Programming
5.10.1 Using add-ins, macros
In Microsoft PowerPoint, you can automate a task with a macro. A macro is a
series of commands and functions that are stored in a Microsoft Visual Basic
module and can be run whenever you need to perform the task.
You can write macros in the report template file, and can use automatic
macros, such as Auto_Open, Auto_Close to automate a task. For examples,
you can use Auto_Open macro to make the template, or use Auto_Close to
change the report after PTReportGen puts data into the report.
5.10.2 Making PTR files programmatically
Sometimes you want to make a PTR file programmatically. You can do this
because the PTR file is a text file. You can write a program to make a PTR file
using C, Perl or DOS shell, and then run PTReportGen to generate report. The
two steps can be written into a batch file.
1. Write a program to make the PTR file as you need.
2. Write a batch file to call the program and PTReportGen in command line
mode.
For example, you write a batch file runrpt.bat as follows. changeptr is an
executable file that reads template.txt and output template.ptr. First runrpt.bat
call changeptr to make the PTR file, and then call PTReportGen to generate
the report.
@echo off
- 52 -
Page 59

if "%1"=="" goto usage
goto process
:usage
echo Usage: runrpt ReportDate
echo ReportDate Date format 'YYYY-MM-DD'
goto :EOF
:process
changeptr %1 <"template.txt" >"template.ptr"
PPTReport "template.ptr" –C %1
- 53 -
Page 60

Chapter 6 Function Reference
6.1 Report Function
6.1.1 Report Function
The REPORT function can execute a SQL statement to get data from data
source, and put data into the slides in the report file. The REPORT function
can make four types of reports:
Fixed table report
Non-group variable table report
Group variable table report
Form report
6.1.2 Fixed Table Report Function
In a fixed table report, the number of rows and columns is fixed. PTReportGen
executes a SQL statement to get data from data source, and directly fills data
into the cells of a table.
Syntax
Report (…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “fix”
SLIDE = slide
TABLE = table
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
- 54 -
Page 61

IMAGE = fieldlist
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "fix" means a fixed table report.
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The TABLE argument identifies a table in a slide for a table report. The table is
the index number of the table in a slide. The index number starts at 1. For
examples, table 1 is the first table in a slide, table 2 is the second table. Default
is 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which PTReportGen fill data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells separated by the “,” character. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
PTReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE argument specifies the range in the table to be used for the
records. PTReportGen will skip the range for each record. You can reference a
range of cells like “2:4” or “B:D”. The default range is the area that includes all
cells for the records.
- 55 -
Page 62

The IMAGE argument specifies the data source fields are picture files. The
fieldlist is the list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can
identify a field using the name of field or the index number of field, but not
simultaneously. In data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture,
not the picture. The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL.
If it is a relative path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function makes the report: Top 5 Employees for Sales.
@F1=REPORT(slide=5 type=fix cell=B2)
SELECT TOP 5 e.FirstName + ' ' + e.LastName
, SUM(d.Quantity)
, Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount)) AS SalesAmount
, SalesAmount / (SELECT amount FROM tmp_amount)
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Employees e
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND o.EmployeeID = e.EmployeeID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = 1996
- 56 -
Page 63

AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = 04
GROUP BY e.FirstName, e.LastName
ORDER BY 3 DESC
;
Result
The fixed table report defined in the report template:
The fixed table report generated in the report:
Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of top 5 employees for sales,
including employee name, quantity of products, sales amount, and percent of
Total.
- 57 -
Page 64

2. type=”fix”. It is a fixed table report.
3. slide = 5. It means the fifth slide.
4. The default table is 1. PTReportGen will put data into the first table in the
sixth slide in the report file.
5. cell=B2. The cells corresponding to the first record are “B2,C2,D2,E2”.
6. The default range is “B2:E2”.
7. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it fetches the first record, puts the value of the first field into cell B2, the
value of the second field into cell C2, the value of the third field into D2, and the
value of the fourth field into E2. And then it fetches the next record, skips one
row, and puts data into cells B3, C3, D3 and E3……
6.1.3 Non-group Variable Table Report Function
In a variable table report, the number of rows or columns in the table is unfixed,
and it is variable as the number of the result records. PTReportGen executes a
SQL statement to get data from data source, inserts some blank rows/columns
or insert new slide for some records, then fills data into the cells of a table.
Syntax
Report (…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “var”
SLIDE = slide
TABLE = table
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
IMAGE = fieldlist
- 58 -
Page 65

RESERVE = reserverecords
PAGEBREAK = pagelength
NODATA = nodataoption
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "var" means a variable table
report. Default is var.
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The TABLE argument identifies a table in a slide for a table report. The table is
the index number of the table in a slide. The index number starts at 1. For
examples, table 1 is the first table in a slide, table 2 is the second table. Default
is 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which PTReportGen fill data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells separated by the “,” character. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
PTReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE argument specifies the range in the table to be used for the
- 59 -
Page 66

records. A range is composed of some rows or columns. You can reference a
range of cells like “2:4” or “B:D”. PTReportGen will insert some rows/columns
for each record, or copy slides for some records. If the length of the range is 1
row/column, you need to reserve 1 or 2 rows/columns in one slide. Otherwise
you must reserve all blank rows/columns for records in one slide. The default
range is the area that includes all cells for the records.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The RESERVE argument specifies the number of the records for which you
reserved some rows/columns in the report template for the report. The
reserverecords represents the number of the records you reserved in the
report template. One means you reserved some rows/columns for one record,
and two means some rows/columns for two records. Default is 1. If the length
of the range is 1 row/column, you need to reserve 1 or 2 rows/columns in one
slide. Otherwise the value of RESERVE must be equal to the value of
PAGEBREAK.
The PAGEBREAK argument specifies the page breaks, and tells
PTReportGen to insert new pages in the report. One page is one slide. The
unit of page length is r that means record. For example, “6r” or “6” means that
PTReportGen will put 6 records per slide. Default is no page break. If the
length of the range is more than 1, the value of PAGEBREAK must be equal to
the value of RESERVE.
The NODATA argument specifies an option when no data are returned from
data source. If the value is "delrange", PTReportGen will delete the range
- 60 -
Page 67

when no data are returned. "deltable" means to delete the table. "delslide"
means to delete the slide. Default is to do nothing.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function will makes the report: Customer List.
@F1=Report(slide=2 type=var cell=A2 pagebreak=19 reserve=2)
SELECT CompanyName
,CityName
,CountryName
,ContactName
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName,CityName,CountryName
Result
The non-group variable table report defined in the report template:
- 61 -
Page 68

The non-group variable table report generated in the report:
Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of customers including customer
name, city name, country name, and contact name.
2. type=”var”. It is a variable table report. And there is no GROUP argument,
so it is a non-group variable table report.
3. slide=2. It is the second slide.
- 62 -
Page 69

4. The default table is 1. PTReportGen will put data into the first table in the
second slide in the report file.
5. cell=A2. The cells corresponding to the first record are “A2,B2,C2,D2”.
6. The default range is “A2:D2”.
7. pagebreak = 19. PTReportGen will add a new slide per 19 records. One
slide contains 19 records.
8. reserve = 2. You have reserved 2 rows for 2 records in the table in the report
template file.
9. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it fetches the first record, and fill data. And then it fetches the next
record…… PTReportGen will add some rows after the number of records
exceeds the number of rows you have reserved, and add a new slide per 19
records. One slide contains 19 records.
6.1.4 Group Variable Table Report Function
The Group Variable Table Report function generates a variable table report
and group data. In a variable table report, the number of rows or columns in
the table is unfixed, and it is variable as the number of the result records.
PTReportGen executes a SQL statement to get data from data source, copy
the group range for each group, copy the detail range for each record, then fills
data into the table.
Syntax
Report (…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “var”
SLIDE = slide
TABLE = table
- 63 -
Page 70

FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
GROUP= grouplist
GROUPRANGE = grouprange
IMAGE = fieldlist
RESERVE = reserverecords
PAGEBREAK = pagelength
NODATA = nodataoption
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "var" means a variable table
report. Default is var.
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The TABLE argument identifies a table in a slide for a table report. The table is
the index number of the table in a slide. The index number starts at 1. For
examples, table 1 is the first table in a slide, table 2 is the second table. Default
is 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which PTReportGen fill data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells separated by the “,” character. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
- 64 -
Page 71

source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
PTReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE argument specifies the range in the table to be used for the
details. A range is composed of some rows or columns. You can reference a
range of cells like “2:4” or “B:D”. PTReportGen will insert some rows/columns
for each record, or copy slides for some records. If the length of the range is 1
row/column, you need to reserve 1 or 2 rows/columns in one slide. Otherwise
you must reserve all blank rows/columns for records in one slide. The default
range is the area that includes all cells for the records.
The GROUP argument specifies the group of the report. The grouplist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name or index number of the field, but not simultaneously. In one
report, there may be up to 10 groups. Notes: the order of the groups should be
in accordance with the order of the ORDER BY clause in the SQL statement.
The GROUPRANGE argument follows the GROUP argument, and specifies
the range of the group in the table. For example, the grouprange of level 1
must follow the group of level 1, and the grouprange of level 2 must follow the
group of level 2. PTReportGen will repeat the group range for each group. The
range of the group should contain the range of the details and the area that
includes all cells for this group. You reference a group range like “2:4” or “B:D”.
For example, there are two groups, the range of the group one contains all
cells for the group one and the range of the group two, and the range of the
group two contains all cells for the group two and the range of the details. The
default range is the area that includes all cells for this group and the range or
group range for the lower level group. If the grouprange is not same as the
- 65 -
Page 72

range of the detail, you must add a pagebreak by group, and the length of the
range can not be more then 1 row/column.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The RESERVE argument specifies the number of the records for which you
reserved some rows/columns in the report template for the report. The
reserverecords represents the number of the records you reserved in the
report template. One means you reserved some rows/columns for one record,
and two means some rows/columns for two records. Default is 1. If the length
of the range is 1 row/column, you need to reserve 1 or 2 rows/columns in one
slide. Otherwise the value of RESERVE must be equal to the value of
PAGEBREAK.
The PAGEBREAK argument specifies the page breaks, and tells
PTReportGen to insert new pages in the report. One page is one slide. The
unit of page length is r or g. "r" means record, "g1" means group one, "g2"
means group two...... For example, “6r” or “6” means that PTReportGen will put
6 records per slide, “1g” means one group per slide, and “1g,6r” means one
group or 6 records per slide. Default PTReportGen will not show the group
name in the new page. You can add “s” to show them. For example, “1gs,6rs”.
If the grouprange is not same as the range of the detail, you must add a
pagebreak by group, and the length of the range can not be more then 1
row/column. If the grouprange is same as the range of the detail, and the
length of the range is more than 1, you should add a pagebreak by record, and
the value of PAGEBREAK must be equal to the value of RESERVE.
- 66 -
Page 73

The NODATA argument specifies an option when no data are returned from
data source. If the value is "delrange", PTReportGen will delete the range
when no data are returned. "deltable" means to delete the table. "delslide"
means to delete the slide. Default is to do nothing.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function will makes the report: Customer Profile.
@F1=Report(slide=2 cell=A2,B3,C3,D3,D4,E3,E4,E5
range=2:5 group=1 pagebreak=5 reserve=5)
SELECT LEFT(CompanyName,1)
,CompanyName
,ContactName
,'Phone: ' & Phone
,'Fax: ' & Fax
,Address
,CityName & ', ' & CountryName
,PostalCode
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName
- 67 -
Page 74

Result
The group varibale table report defined in the report template:
The group variable table report generated in the report:
- 68 -
Page 75

Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of customers including company
name, contact name, phone, fax, address, city name, country name, and
postal code.
2. There is GROUP argument, so it is a group variable table report.
3. slide=2. It is the second slide.
4. The default table is 1. PTReportGen will put data into the first table in the
second slide in the report file.
5. group=1. PTReportGen will group data by the first letter of the company
name.
6. cell= A2,B3,C3,D3,D4,E3,E4,E5. These cells correspond to the first record.
7. range=2:5. Because the default range is “B3:E5”, you must specify a range
explicitly.
- 69 -
Page 76

8. There is no grouprange. PTReportGen will give a default. The default
grouprange is “2:5”.
9. pagebreak = 5. PTReportGen will add a new slide per 5 records.
10. reserve = 5. Because the grouprange is same as the range of the detail,
and the length of the range is more than 1, you must reserve some rows for 5
records.
11. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, gets data from data source,
and puts data into the table in the report file. PTReportGen will add a new slide
per 5 records. One slide contains the information of 5 records.
6.1.5 Form Report Function
For a form report, you can put data from data source into shapes or text boxes
in the report file. PTReportGen executes a SQL statement to get data from
data source, and copy the slide for each record, then fills data into the slides.
Syntax
Report (…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “form”
SLIDE = slide
CELL= celllist
GROUP= grouplist
IMAGE = fieldlist
NODATA = nodataoption
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "form" means a form report.
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
- 70 -
Page 77

less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of shapes or text boxes separated by the “,” character. For
example, “ProductName,ProductID,QuantityPerUnit,UnitPrice”. The shapes or
text boxes in the celllist should correspond to the data source fields in the SQL
statement. The value of the first data source field is put into the first object as a
text, and the value of the second data source field is put into the second
object……You can get the name of the shape or text box using the add-in
“name.ppa”.
The GROUP argument specifies the group of the report. The grouplist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
one report, there may be up to 10 groups. The first GROUP is group one, the
second is group two...... Notes: the order of groups should be in accordance
with the order of ORDER BY clause in the SQL statement.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The NODATA argument specifies an option when no data are returned from
data source. If the value is "delrange" or “delslide”, PTReportGen will delete
the slide when no data are returned. Default is to do nothing.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
- 71 -
Page 78

CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Remarks
In FormReport method, there is no Range and PageBreak. It will put only one
record per slide.
Example
The following function will makes the report: Supplier Profile.
@F1=Report(slide=2 type=form cell=SlideTitle,Company,ContactName
,ContactTitle,Address,City,Country,PostCode,Phone,Fax,HomePage)
SELECT CompanyName
,CompanyName
,ContactName
,ContactTitle
,Address
,CityName
,CountryName
,PostalCode
,Phone
,Fax
,HomePage
FROM Suppliers, Countries, Cities
WHERE Suppliers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Suppliers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Suppliers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
- 72 -
Page 79

ORDER BY CompanyName
Result
The form report defined in the report template:
The form report generated in the report:
- 73 -
Page 80

Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of suppliers including company
name, contact name, contact title, address, city, country, postal code, phone,
fax, home page.
2. type=”form”. It is a form report.
3. slide=2. It is the second slide.
4. cell=SlideTitle, Company, ContactName, ContactTitle, Address, City,
Country, PostCode, Phone, Fax, HomePage. These shapes or text boxes are
in the second slide, and correspond to data source fields in the SQL statement.
5. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
It fetches records, copy the slide for each record, and inserts data into the
shapes or text boxes.
- 74 -
Page 81

6.2 Chart Function
The CHART function executes a SELECT statement to get data from data
source, and put data into the datasheet of a chart in the report file. The CHART
function supports two types of charts:
MSGraph chart
Excel chart
6.2.1 MSGraph Chart Function
If you use Microsoft Graph to create a chart, you can use MSGraph Chart
function.
Syntax
Chart(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
SLIDE = slide
CHART = chart
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
CONNECT = datasource
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The CHART argument identifies a chart in the report template. The chart is the
- 75 -
Page 82

index number of the chart in the slide. The index number starts at 1. For
examples, chart 2 is the second chart in the slide.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which PTReportGen fill data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is col.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells separated by the “,” character. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
PTReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell. Note: On the datasheet, the leftmost column and the top
row, which are commonly used for legend text or axis labels, are referred to as
column 0 (zero) and row 0 (zero).
The RANGE argument specifies the range in the datasheet of the chart to be
used for the records. PTReportGen will skip the rows/columns of the range for
each record. A range is composed of some rows or columns. You can
reference a range of cells like “2:4” or “B:D”. The default range is the area that
includes all cells for the records.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function makes the chart: Sales by Categories.
- 76 -
Page 83

@F3_3=CHART(slide=3 cell=A0)
SELECT c.CategoryName
, Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount))
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Categories c
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND p.CategoryID = c.CategoryID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = 1996
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = 04
GROUP BY c.CategoryName
ORDER BY c.CategoryName
Result
The datasheet of the chart defined in the report template:
The chart defined in the report template is a blank chart.
The datasheet of the chart generated in the report:
The chart generated in the report:
- 77 -
Page 84

Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of sales by categories, including
category name, and sales amount.
2. slide = 3. It means the third slide.
3. The default chart is 1. PTReportGen will put data into the first chart in the
third slide in the report file.
4. The default fillorder is col. PTReportGen will fill data by columns.
5. cell=A0. The cells corresponding to the first record are “A0,A1”.
6. The default range is “A:A”.
7. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it fetches the first record, puts the value of the first field into cell A0, the
value of the second field into cell A1. And then it fetches the next record, skips
one cplumn, and puts data into cells B0, B1……
- 78 -
Page 85

6.2.2 Excel Chart Function
If you use Microsoft Excel to create a chart, you can use Excel Chart function.
Syntax
Chart(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
SLIDE = slide
CHART = chart
TYPE = type
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
CONNECT = datasource
The SLIDE argument identifies a slide in the report template. The slide is the
index number of the slide. The index number starts at 1. If the index number is
less than 0, it represents the position from the end of presentation. For
examples, slide 2 is the second slide in a presentation, slide -1 is the last slide
in a presentation. You can also reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the
next slide. “N-1” means the last slide that the previous function processed.
The CHART argument identifies a chart in the report template. The chart is the
index number of the chart in the slide. The index number starts at 1. For
examples, chart 2 is the second chart in the slide.
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. Possible values are fix or var.
"fix" means that PTReportGen will directly fill data vales into the worksheet of
the chart. "var" means that PTReportGen will add some blank rows/columns
before filling data values into the worksheet of the chart. Default is var. When
the report type is “var”, you should reserve two rows/columns in the worksheet
- 79 -
Page 86

in the report template, and set the data range of the chart to 2 rows/columns.
The RESERVE must be 2.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which PTReportGen fill data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells or fields separated by the “,” character. The celllist
identifies the cells in a worksheet. For example, “A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in
the celllist should correspond to the data source fields in the SQL statement.
The value of the first field is put into the first cell, and the value of the second
field is put into the second cell …… PTReportGen will use the next cell if you
omit a cell except the first cell. If FILLORDER=”row”, the next cell is the right
cell. If FILLORDER=”col”, the next cell is the below cell.
The RANGE argument specifies the range in the worksheet of the chart to be
used for the records. PTReportGen will skip the rows/columns of the range for
each record. A range is composed of some rows or columns. You can
reference a range of cells like “2:4” or “B:D”. The default range is the area that
includes all cells for the records. For a variable table report, PTReportGen will
insert the blank rows/columns of the range for each record.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function makes the chart: Sales by Categories.
@F3_3=CHART(slide=3 cell=A2)
- 80 -
Page 87

SELECT c.CategoryName
, Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount))
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Categories c
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND p.CategoryID = c.CategoryID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = 1996
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = 04
GROUP BY c.CategoryName
ORDER BY c.CategoryName
Result
The worksheet of the chart defined in the report template:
The chart defined in the report template is a blank chart.
The worksheet of the chart generated in the report:
The chart generated in the report:
- 81 -
Page 88

Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of sales by categories, including
category name, and sales amount.
2. slide = 3. It means the third slide.
3. The default chart is 1. PTReportGen will put data into the first chart in the
third slide in the report file.
4. The default type is var. You should reserve 2 blank rows in the worksheet,
and select the 2 rows as the data range of the chart.
5. The default fillorder is row. PTReportGen will fill data by rows.
6. cell=A2. The cells corresponding to the first record are “A2,B2”.
7. The default range is “2:2”.
8. PTReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it will add some blank rows in the worksheet according to the number of
the records. And then it will put data into the worksheet.
- 82 -
Page 89

6.3 ExecSQL Function
The EXECSQL function executes a SQL statement, but does not return result
to report.
Syntax
ExecSQL(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
CONNECT= datasource
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the PTR file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement that can be DDL (Data Definition
Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language) and even DCL (Data Control
Language).
Using EXECSQL function, you can open a database, create a temporary table,
insert data into a temporary table, update data, execute a stored procedure,
and drop a table. It is very useful to create a temporary table, and prepare data
for REPORT function.
Example
The following functions will create a table tmp0, and add some records into
table. No result is returned to the report file.
@F1=EXECSQL()
CREATE TABLE tmp0 (
min_date DATE,
max_date DATE)
- 83 -
Page 90

;
@F2=EXECSQL()
INSERT INTO tmp0
SELECT …
;
- 84 -
Page 91

Chapter 7 Menus, Toolbar and Shortcut Keys
7.1 File Menu
The File menu offers the following commands:
New Creates a new PTR file.
Open Opens an existing PTR file.
Close Closes an opened PTR file.
Save Saves an opened PTR file using the same filename.
Save As Saves an opened PTR file to a specified file name.
Open Report
Template
Open Report File Opens an existing report file.
Open Log File Opens an existing log file.
Recent Files Opens last PTR files you closed.
Exit Exits PTReportGen.
Opens an existing report template file.
7.2 Edit Menu
The Edit menu offers the following commands:
Undo Reverse previous editing operation.
Cut
Copy Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Paste Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Delete Deletes the selection.
Select All Selects the entire text.
Find Finds the specified text.
Find Next Finds the next matching text.
Replace Replaces specific text with different text.
Go to Goes to specified line or function in the document.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
7.3 Report Menu
The Report menu offers the following commands:
Configuration
Configures the file names, data sources and
parameters.
- 85 -
Page 92

Run Runs the PTR file to generate a report.
7.4 Tools Menu
The Tools menu offers the following commands:
Option Sets options.
7.5 Help Menu
The Help menu offers the following commands:
Help Context Starts the online help system.
Tutorial Starts a brief step-by-step tutorial.
Tip of the Day
Hints and Tips
Shortcut Keys Shows the keyboard map.
Home Page
Support
Buy Now Buy PTReportGen immediately.
About Displays the version number of PTReportGen.
Displays a dialog containing a useful tip about
PTReportGen.
Displays miscellaneous hints and tips on how to use
PTReportGen productively.
Takes you to the home page of PTReportGen web
site.
Takes you to the support page of PTReportGen web
site.
7.6 Toolbar
The toolbar provides quick access to many features. The buttons on the
toolbar perform the following commands:
Buttons Commands
Creates a new PTR file.
Opens an existing PTR file.
Saves an opened PTR file using the same filename.
Open the report template file.
- 86 -
Page 93

Open the report file.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Reverse previous editing operation.
Finds the specified text.
Goes to specified line or function in the document.
Runs the PTR file to generate a report.
Starts the online help system.
Buy PTReportGen immediately.
7.7 Shortcut Keys
Shortcut Keys Commands
Ctrl+N Creates a new PTR file.
Ctrl+O Opens an existing PTR file.
Ctrl+S Saves an opened PTR file using the same filename.
Ctrl+U Reverse previous editing operation.
Ctrl+X
Ctrl+C Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
Ctrl+V Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Delete Deletes the selection.
Ctrl+A Selects the entire text.
Ctrl+F Finds the specified text.
- 87 -
Page 94

F3 Finds the next matching text.
Ctrl+H Replaces specific text with different text.
Ctrl+G Goes to specified line or function in the document.
F2 Configures the file names, data sources and parameters.
F5 Runs the PTR file to generate a report.
F1 Starts the online help system.
- 88 -
Page 95

Chapter 8 Hints and Tips
You can run PTReportGen from the command line. The format is:
pptreport <ptr file name> [-c] [-d] [-u1 user1] [-p1 pwd1] … [pa1 pa2 …]
For example:
pptreport c:\pptreport\monthlysales.ptr -c 199605
PTReportGen can be scheduled with Windows Scheduled Tasks or other tools.
The process of generating reports can be fully automated, periodically or on
events.
PTReportGen comes with a sample database Sample.mdb and some sample
reports. You can use them when learning the program. To use the sample
reports, you must add a data source named “Report Sample” to specify the
sample database.
You can test SQL statements using Microsoft Query that is a component of
Microsoft Office. You can find it under the installation directory of Microsoft
Office.
To make a report template, you can use some sample data. It is very useful
especially for formatting. After you have made the report template, you delete
the sample data.
For a table report, you can format the value from data sources with a format
expression. You should write a format expression into a data cell in the report
template file first. PTReportGen will get the text of the cell as a format
expression before it puts a value into a cell, and output the value using the
- 89 -
Page 96

format expression.
An irregular table does not have the same number of cells for each row or
column. It does make it harder to process the document. In an irregular table,
you have some difficulty to reference a cell, and an error may occur when you
try to work with some rows or columns.
For a form report, you can reference a shape or text box by its name. You can
find a PowerPoint add-in “name.ppa” under the PTReportGen's working
directory that can name an object in a slide.
For a form report, you can format the value from data sources with a format
expression too. PTReportGen will get the text of the object as a format
expression, and output the value using the format expression.
You can define the different formats and colors for positive values, negative
values and zeros.
To create a chart in the report template file, you can use some sample data.
Using sample data, you can set the various chart options. After you have made
the report template, you delete the sample data.
For MSGraph chart, on the datasheet, the leftmost column and the top row,
which are commonly used for legend text or axis labels, are referred to as
column 0 (zero) and row 0 (zero).
By default, Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 uses Microsoft Excel to create charts,
but doesn't expose the chart as a normal Excel object. PTReportGen can not
- 90 -
Page 97

access the charts. You must insert an Excel chart object that PTReportGen
can access.
PTReportGen is a converter too. Besides Microsoft PowerPoint document, you
can generate a report in other file format such as HTML, RTF, GIF, JPG and
BMP. You also can convert data from database to other file format.
You can edit a PTR file (.ptr) with a text editor such as Notepad.
If you associate PTReportGen with the file extension “.ptr”, a PTR file with the
extension “.ptr” will open in PTReportGen when you double-click the file. The
information:
File Extension: .ptr
Action: open
Application: "C:\Program Files\LJZsoft\pptreport.exe" “%1”
For the report template file, report file and log file, it is possible to give a
relative path. If it is a relative path, the base path is the path of the PTR file.
In the SQL statements, you can use parameters. To use parameters, you must
define them first.
In the paths and names of the report file, template file and log file, you can use
parameters. To use parameters, you must define them first.
The default log file is pptreport.log under the PTReportGen program directory.
If you do not define the log file name, or can not create the log file defined, you
can find log information in the pptreport.log under the PTReportGen program
- 91 -
Page 98

directory.
You should be careful to define a unique name for each parameter, because
PTReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of the
parameters. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character such as
“$ReportDate”.
In the text editor window, you can use comments. A comment is the “/*”
characters, followed by any sequence of characters (including new lines),
followed by the “*/” characters. You cannot nest comments.
You can reference a slide dynamically. “N” means the next slide. “N-1” means
the last slide that the previous function processed.
To add totals or subtotals, you can use the aggregate functions in SQL
statement.
To group data in a report, you should use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE
REPORT function.
In REPORT function, the order of groups should be in accordance with the
order of ORDER BY clause in the SQL statement.
For a non-group variable table report, if the length of the range is 1 row/column,
you need to reserve 1 or 2 rows/columns. PTReportGen will insert some
rows/columns for each record. If the length of the range is more than 1
row/column, you should add PAGEBREAK argument, and the value of
PAGEBREAK must be equal to the value of RESERVE. PTReportGen will
- 92 -
Page 99

copy some slides.
For a group variable table report, if the grouprange is not same as the range of
the detail, you must add a pagebreak by group, and the length of the range can
not be more then 1 row/column. If the grouprange is same as the range of the
detail, and the length of the range is more than 1, you should add a pagebreak
by record, and the value of PAGEBREAK must be equal to the value of
RESERVE.
You can create reports with pictures unsing PTReportGen. You should store
the path and name of the graphics file in the database, identify the image fields
in the report function, and specify the size in the report template file.
To convert from pixels to points, it is depend on the screen resolution (DPI). If
you have a 96 dpi screen (Windows PC), 4 pixels are equal to 3 points.
It is very useful to create a temporary table. You can prepare data using
INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/INSERT SELECT, and then make a report using
REPORT function.
You can write a program to make a PTR file using C, perl or DOS shell, and
then run PTReportGen to generate report. The two steps can be written into a
batch file.
If you do not save a password in the PTR file, a login dialog box will appear
when you run the PTR file in PTReportGen. You can input password
interactively to log on to the data source.
- 93 -
Page 100

PTReportGen supports Microsoft PowerPoint 2007. You can use pptx file as
report file and template file. Please copy “pconv2007.cfg” to “pconv.cfg”.
- 94 -
 Loading...
Loading...