Page 1

A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
®
Model No.
Notebook Adapter
Wireless-G
WPC54G (EU/LA)
User Guide
WIRELESS
GHz
2.4
802.11g
Page 2

Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All
rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
How to Use this User Guide
This user guide has been designed to make understanding networking with the Notebook Adapter easier than
ever. Look for the following items when reading this User Guide:
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like
this:
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the "List of Figures" section.
This exclamation point means there is a caution or warning and is
something that could damage your property or the Notebook Adapter.
word: definition.
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and is something you
should pay special attention to while using the Notebook Adapter.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about something
you might need to do while using the Notebook Adapter.
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description
wpc54g v7-UG-51121 TE
Page 3

Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this User Guide? 2
Chapter 2: Planning your Wireless Network 4
Network Topology 4
Roaming 4
Network Layout 5
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter 6
The LED Indicators 6
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter 7
Starting the Setup 7
Connecting the Adapter 8
Setting up the Adapter 8
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor 19
Accessing the Wireless Network Monitor 19
Using the Wireless Network Monitor 19
Link Information 19
Site Survey 22
Profiles 23
Creating a New Profile 24
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 34
Common Problems and Solutions 34
Frequently Asked Questions 35
Appendix B: Wireless Security 37
Security Precautions 37
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks 37
Appendix C: Windows Help 40
Appendix D: Glossary 41
Appendix E: Specifications 46
Appendix F: Warranty Information 47
Appendix G: Regulatory Information 48
Page 4

Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix H: Contact Information 49
Page 5

Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
List of Figures
Figure 3-1: Front Panel 6
Figure 4-1: Setup Wizard’s Welcome Screen 7
Figure 4-2: Setup Wizard’s License Agreement 7
Figure 4-3: Connecting the Adapter 8
Figure 4-4: Available Wireless Network 8
Figure 4-5: Available Wireless Network 9
Figure 4-6: WEP Key Needed for Connection 9
Figure 4-7: WPA - Personal Needed for Connection 10
Figure 4-8: Congratulations 10
Figure 4-9: Available Wireless Network 11
Figure 4-10: Network Settings 11
Figure 4-11: Wireless Mode 12
Figure 4-12: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings 12
Figure 4-13: Wireless Security - WEP 13
Figure 4-14: Wireless Security - WPA Personal 14
Figure 4-15: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise - EAP-TLS 15
Figure 4-16: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise - PEAP 15
Figure 4-17: Wireless Security - RADIUS - EAP-TLS 16
Figure 4-18: Wireless Security - RADIUS - PEAP 16
Figure 4-19: Wireless Security - LEAP 17
Figure 4-20: Confirm New Settings 17
Figure 4-21: Congratulations 18
Figure 5-1: Wireless Network Monitor Icon 19
Figure 5-2: Link Information 19
Figure 5-3: More Information - Wireless Network Status 20
Figure 5-4: More Information-Network Statistics 21
Figure 5-5: Site Survey 22
Figure 5-6: WEP Key Needed for Connection 22
Figure 5-7: WPA-Personal Needed for Connection 22
Figure 5-8: Profiles 23
Page 6

Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Figure 5-9: Import a Profile 23
Figure 5-10: Export a Profile 23
Figure 5-11: Create a New Profile 24
Figure 5-12: Available Wireless Network 24
Figure 5-13: Available Wireless Network 25
Figure 5-14: WEP Key Needed for Connection 25
Figure 5-15: WPA Personal Needed for Connection 26
Figure 5-16: Congratulations 26
Figure 5-17: Network Settings for New Profile 27
Figure 5-18: Wireless Mode for New Profile 27
Figure 5-19: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings for New Profile 28
Figure 5-20: Wireless Security - WEP for New Profile 28
Figure 5-21: Wireless Security - WPA Personal for New Profile 29
Figure 5-22: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise Using EAP-TLS for New Profile 30
Figure 5-23: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise Using PEAP for New Profile 30
Figure 5-24: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using EAP-TLS for New Profile 31
Figure 5-25: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using PEAP for New Profile 31
Figure 5-26: Wireless Security - LEAP for New Profile 32
Figure 5-27: Confirm New Settings for New Profile 32
Figure 5-28: Congratulations for New Profile 33
Page 7

1
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter. Like all wireless products, the Adapter allows for
greater range and mobility within your wireless network. This adapter communicates over the 54Mbps 802.11g
wireless standard, which is almost five times faster than 802.11b. But since they share the same 2.4GHz radio
band, the Adapter can also communicate with the widely used 11Mbps 802.11b standard.
PCs equipped with wireless cards and adapters can communicate without cumbersome cables. By sharing the
same wireless settings, within their transmission radius, they form a wireless network.
The included Setup Wizard will walk you through configuring the adapter to your network's settings, step by step.
Then just slide it into your notebook's PC Card slot and enjoy network access with your notebook computer, while
retaining true mobility.
Once you're connected, you can keep in touch with your e-mail, access the Internet, and share files and other
resources such as printers and network storage with other computers on the network. At home, you can surf the
web or use instant messaging to chat with friends while sitting out on the patio. Your wireless connection is
protected by up to 128-bit encryption.
You'll also be able to connect with any of the growing number of public wireless hotspots springing up in coffee
shops, airport lounges, hotels and convention centers. And as those hotspots upgrade to the new high-speed
Wireless-G standard, you'll be ready to take advantage of the increased speeds.
Get connected to current-standard 802.11b networks today, and be prepared for the future with the Wireless-G
Notebook Adapter from Linksys.
802.11b: a wireless networking standard that
specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps
and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
adapter: a device that adds network functionality
to your PC.
network: a series of computers or devices
connected for the purpose of data sharing,
storage, and/or transmission between users.
802.11g a wireless networking standard that
specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 54Mbps
and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
bit: a binary digit.
encryption: encoding data transmitted in a network
Page 8

2
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this User Guide?
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
What’s in this User Guide?
This user guide covers the steps for setting up and using the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter.
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Adapter’s applications and this User Guide.
• Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
This chapter discusses a few of the basics about wireless networking.
• Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
This chapter describes the physical features of the Adapter.
• Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
This chapter instructs you on how to install and configure the Adapter.
• Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
This chapter show you how to use the Adapter’s Wireless Network Monitor.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions, regarding
installation and use of the Adapter.
• Appendix B: Wireless Security
This appendix discusses security issues regarding wireless networking and measures you can take to help
protect your wireless network.
• Appendix C: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as installing
the TCP/IP protocol.
• Appendix D: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
• Appendix E: Specifications
This appendix provides the Adapter’s technical specifications.
• Appendix F: Warranty Information
This appendix supplies the Adapter’s warranty information.
• Appendix G: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the Adapter’s regulatory information.
Page 9

3
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this User Guide?
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
• Appendix H: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
Page 10

4
Chapter 2: Planning your Wireless Network
Network Topology
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Chapter 2: Planning your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless network is a group of computers, each equipped with one wireless adapter. Computers in a wireless
network must be configured to share the same radio channel. Several PCs equipped with wireless cards or
adapters can communicate with one another to form an ad-hoc network.
Linksys wireless adapters also provide users access to a wired network when using an access point or wireless
router. An integrated wireless and wired network is called an infrastructure network. Each wireless PC in an
infrastructure network can talk to any computer in a wired network infrastructure via the access point or wireless
router.
An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a wireless PC to a wired network, and can double the
effective wireless transmission range for two wireless adapter PCs. Since an access point is able to forward data
within a network, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure network can be doubled.
Roaming
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. Roaming means that you can move your
wireless PC within your network and the access points will pick up the wireless PC's signal, providing that they
both share the same channel and SSID.
Before enabling you consider roaming, choose a feasible radio channel and optimum access point position.
Proper access point positioning combined with a clear radio signal will greatly enhance performance.
infrastructure: a wireless network that is
bridged to a wired network via an access point.
ad-hoc: a group of wireless devices
communicating directly with each other (peerto-peer) without the use of an access point.
roaming: the ability to take a wireless device
from one access point's range to another without
losing the connection.
ssid: your wireless network's name.
topology: the physical layout of a network.
access point: a device that allows wireless-
equipped computers and other devices to
communicate with a wired network
Page 11

5
Chapter 2: Planning your Wireless Network
Network Layout
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Network Layout
Linksys wireless access points and wireless routers have been designed for use with 802.11a, 802.11b, and
802.11g products. With 802.11g products communicating with the 802.11b standard and some products
incorporating both “a” and “g”, products using these standards can communicate with each other.
Access points and wireless routers are compatible with 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g adapters, such at the PC
Cards for your laptop computers, PCI Card for your desktop PC, and USB Adapters for when you want to enjoy USB
connectivity. Wireless products will also communicate with the wireless PrintServer.
When you wish to connect your wired network with your wireless network, network ports on access points and
wireless routers can be connected to any of Linksys's switches or routers.
With these, and many other, Linksys products, your networking options are limitless. Go to the Linksys website at
www.linksys.com for more information about wireless products.
Page 12

6
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
The LED Indicators
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Notebook
Adapter
The LED Indicators
The Network Adapter's LEDs display information about network activity.
Power Green. The Power LED lights up when the Adapter is powered on.
Link Green. The Link LED lights up when the Adapter has an active connection.
Figure 3-1: Front Panel
Page 13

7
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Starting the Setup
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G
Notebook Adapter
Starting the Setup
The Wireless-G Notebook Adapter Setup Wizard will guide you through the installation procedure. The Setup
Wizard will install the driver and Wireless Network Monitor, as well as connect and configure the Adapter.
Insert the Setup Wizard CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive. The Setup Wizard should run automatically, and the
Welcome screen should appear. If it does not, click the Start button and choose Run. In the field that appears,
enter D:\setup.exe (if “D” is the letter of your CD-ROM drive).
On the Welcome screen, you have the following choices:
Click Here to Start- Click the Click Here to Start button to begin the software installation process.
User Guide - Click the User Guide button to open the PDF file of this User Guide.
Exit - Click the Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
1. To install the Adapter, click the Click Here to Start button on the Welcome screen.
2. After reading the License Agreement, click the Next button if you agree and want to continue the installation,
or click the Cancel button to end the installation.
3. Windows will begin copying the files onto your PC.
Figure 4-1: Setup Wizard’s Welcome Screen
Figure 4-2: Setup Wizard’s License Agreement
IMPORTANT: Do not connect the Adapter until you are instructed to
do so or the setup will not work.
Page 14

8
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Connecting the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Connecting the Adapter
1. Locate an available CardBus slot on your notebook PC.
2. With the connector pin end facing the CardBus slot and the label facing up, slide the Adapter into the CardBus
slot until it locks in place.
3. Windows 98 and Windows Me users may need to restart their PCs again when prompted to do so. The Power
LED should light up when the Adapter is installed correctly.
4. Windows will begin copying the driver files to your computer. If Windows asks you for the original Windows
CD-ROM, insert the CD-ROM, and direct Windows to its correct location (e.g., D:\).
5. Then, click Next.
Setting up the Adapter
The next screen to appear will be the Available Wireless Network screen.
This screen provides two options for setting up the Adapter.
• Available Wireless Network. The networks available to this Adapter will be listed on this screen. You can
choose one of these networks and click the Connect button to connect to it. Click the Refresh button to
update the Available Wireless Network list.
• Manual Setup. If your network is not listed on this screen, select Manual Setup to set up the adapter
manually. This method of setting up the Adapter is intended for Advanced Users only.
The setup for each option is described, step by step, under the appropriate heading on the following pages.
Click Exit to close the Setup Wizard, if you wish to set up the Adapter later.
Figure 4-3: Connecting the Adapter
Figure 4-4: Available Wireless Network
Page 15

9
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Available Wireless Network
The available networks are listed in the table on the center of the screen by SSID. Select the wireless network you
wish to connect to and click the Connect button. (If you do not see your network listed, you can click the Refresh
button to bring the list up again.) If the network utilizes wireless security, you will need to configure security on
the Adapter. If not, you will be taken directly to the Congratulations screen.
1. If you have wireless security enabled on your network, continue to step 2. If you don’t have wireless security
enabled, continue to step 3.
2. If your network has the wireless security WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) enabled, this screen will appear.
Select 64-bit or 128-bit.
Then enter a passphrase or WEP key.
Passphrase - Enter a passphrase in the Passphrase field, so a WEP key is automatically generated. The
passphrase is case-sensitive and should not be longer than 31 alphanumeric characters. It must match the
passphrase of your other wireless network devices and is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. (If
you have any non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key manually on those products.)
WEP Key - The WEP key you enter must match the WEP key of your wireless network. For 64-bit encryption,
enter exactly 10 hexadecimal characters. For 128-bit encryption, enter exactly 26 hexadecimal characters.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”.
Then click Connect and proceed to Step 3.
Figure 4-5: Available Wireless Network
Figure 4-6: WEP Key Needed for Connection
Page 16
10
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
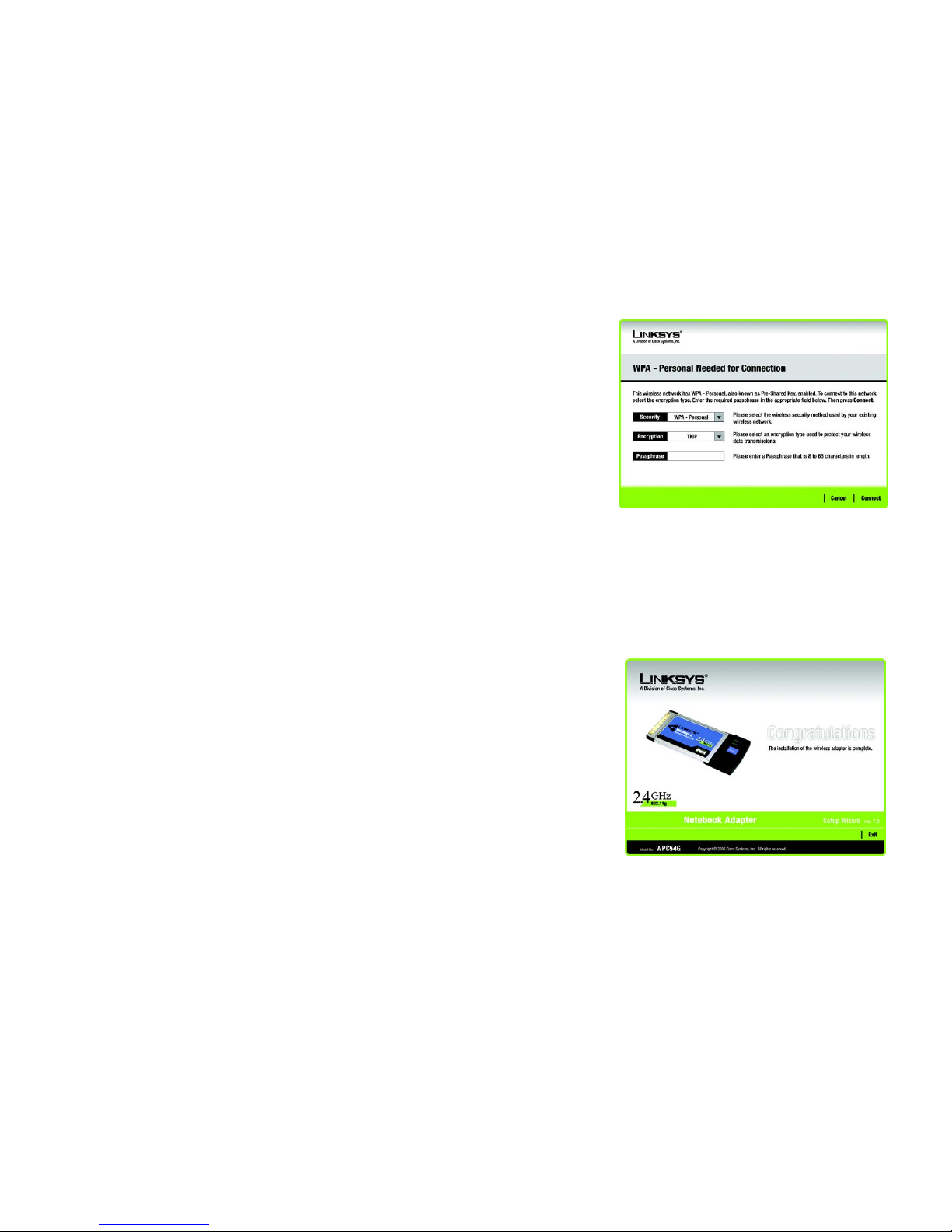
If your network has the wireless security WPA Personal (Wi-Fi Protected Access) enabled, this screen will
appear.
Encryption - Select the type of algorithm you want to use, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down
menu.
Passphrase - Enter a Passphrase, also called a pre-shared key, of 8-63 characters in the Passphrase field.
The longer and more complex your Passphrase is, the more secure your network will be.
Then click Connect and proceed to Step 3.
3. After the software has been successfully installed, the Congratulations screen will appear. Click Connect to
Network to connect to your network. For more information about the Wireless Network Monitor, refer to
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor.
Congratulations! The Automatic Setup’s installation of the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter is complete.
To check the link information, search for available wireless networks, or make additional configuration
changes, proceed to Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor.
Figure 4-7: WPA - Personal Needed for Connection
encryption: encoding data transmitted in a network.
wpa (wi-fi protected access: a wireless security protocol
using TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) encryption,
which can be used in conjunction with a RADIUS server.
wep (wired equivalent privacy): a method of encrypting network
data transmitted on a wireless network for greater security.
Figure 4-8: Congratulations
Page 17

11
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Manual Setup
If you are not taking advantage of SecureEasySetup and your network is not listed with the available networks,
you can use Manual Setup.
1. Click Manual Setup on the Available Wireless Network screen to set up the adapter manually.
2. The Network Settings screen from the Wireless Network Monitor will appear. If your network has a router or
other DHCP server, click the radio button next to Obtain network settings automatically (DHCP).
If your network does not have a DHCP server, click the radio button next to Specify network settings. Enter
an IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS addresses appropriate for your network. You must
specify the IP Address and Subnet Mask on this screen. If you are unsure about the Default Gateway and DNS
addresses, leave these fields empty.
IP Address - This IP Address must be unique to your network.
Subnet Mask - The Adapter’s Subnet Mask must be the same as your wired network’s Subnet Mask.
Default Gateway - Enter the IP address of your network’s Gateway here.
DNS 1 and DNS 2 - Enter the DNS address of your wired Ethernet network here.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-9: Available Wireless Network
Figure 4-10: Network Settings
Page 18
12
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
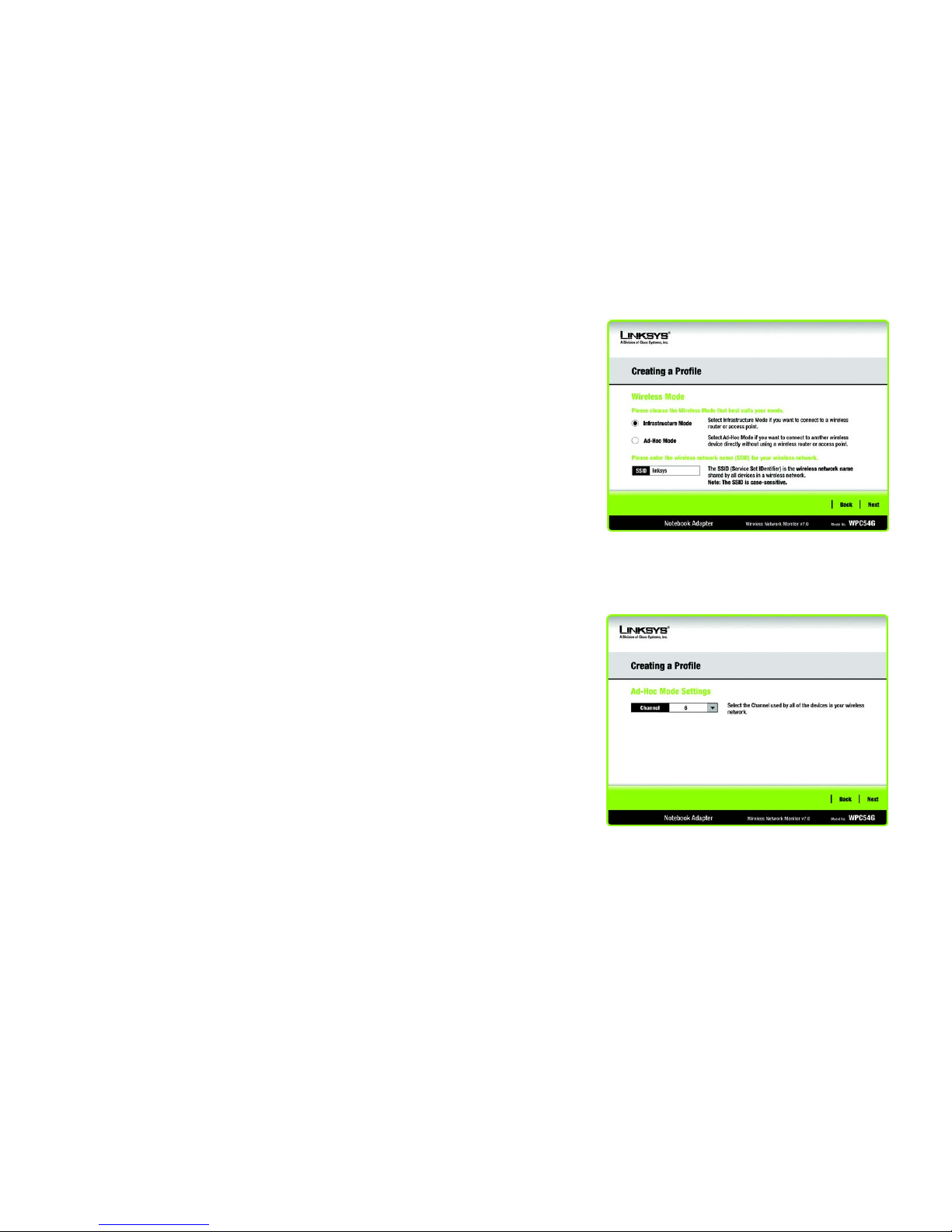
3. The Wireless Mode screen shows a choice of two wireless modes. Click the Infrastructure Mode radio
button if you want to connect to a wireless router or access point. Click the Ad-Hoc Mode radio button if you
want to connect to another wireless device directly without using a wireless router or access point. Enter the
SSID for your network.
Infrastructure Mode - Use this mode if you want to connect to a wireless router or access point.
Ad-Hoc Mode - Use this mode if you want to connect to another wireless device directly without using a
wireless router or access point.
SSID - This is the wireless network name that must be used for all the devices in your wireless network. It is
case- sensitive and should be a unique name to help prevent others from entering your network.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
4. If you chose Infrastructure Mode, go to Step 5 now. If you chose Ad-Hoc Mode, the Ad-Hoc Mode Settings
screen will appear.
Select the correct operating channel for your wireless network. The channel you choose should match the
channel set on the other devices in your wireless network. If you are unsure about which channel to use, keep
the default setting.
Click the Next button. Click the Back button to change any settings.
Figure 4-11: Wireless Mode
Figure 4-12: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings
Page 19

13
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
5. If your wireless network doesn’t have wireless security, select Disabled and then click the Next button to
continue. Proceed to Step 6.
If your wireless network has wireless security, select the method of security used: WEP, WPA-Personal,
WPA-Enterprise, RADIUS, or LEAP. WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy, and WPA stands for Wi-Fi
Protected Access. WPA is a stronger security method than WEP. RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication
Dial-In User Service, and LEAP stands for Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol. Click the Next
button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Proceed to the appropriate section for your security method: WEP, WPA-Personal, WPA-Enterprise, RADIUS, or
LEAP.
WEP
WEP - Select 64-bit or 128-bit encryption
Passphrase - Enter a passphrase in the Passphrase field, so a WEP key is automatically generated. It is case-
sensitive and should not be longer than 31 alphanumeric characters. This passphrase must match the
passphrase of your other wireless network devices and is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. (If
you have any non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key manually on those products.)
WEP Key - The WEP key you enter must match the WEP key of your wireless network. For 64-bit encryption,
enter exactly 10 hexadecimal characters. For 128-bit encryption, enter exactly 26 hexadecimal characters.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”.
Advanced Users
TX Key - The default transmit key number is 1. If your network’s access point or wireless router uses transmit
key number 2, 3, or 4, select the appropriate number from the TX Key drop-down box.
Authentication -The default is set to Auto, so it will auto-detect for Shared Key or Open System
authentication. For Shared Key authentication, both the sender and the recipient share a WEP key for
authentication. For Open System authentication, the sender and the recipient do not share a WEP key for
authentication. If you are not sure which authentication method to select, keep the default, Auto.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-13: Wireless Security - WEP
Page 20
14
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
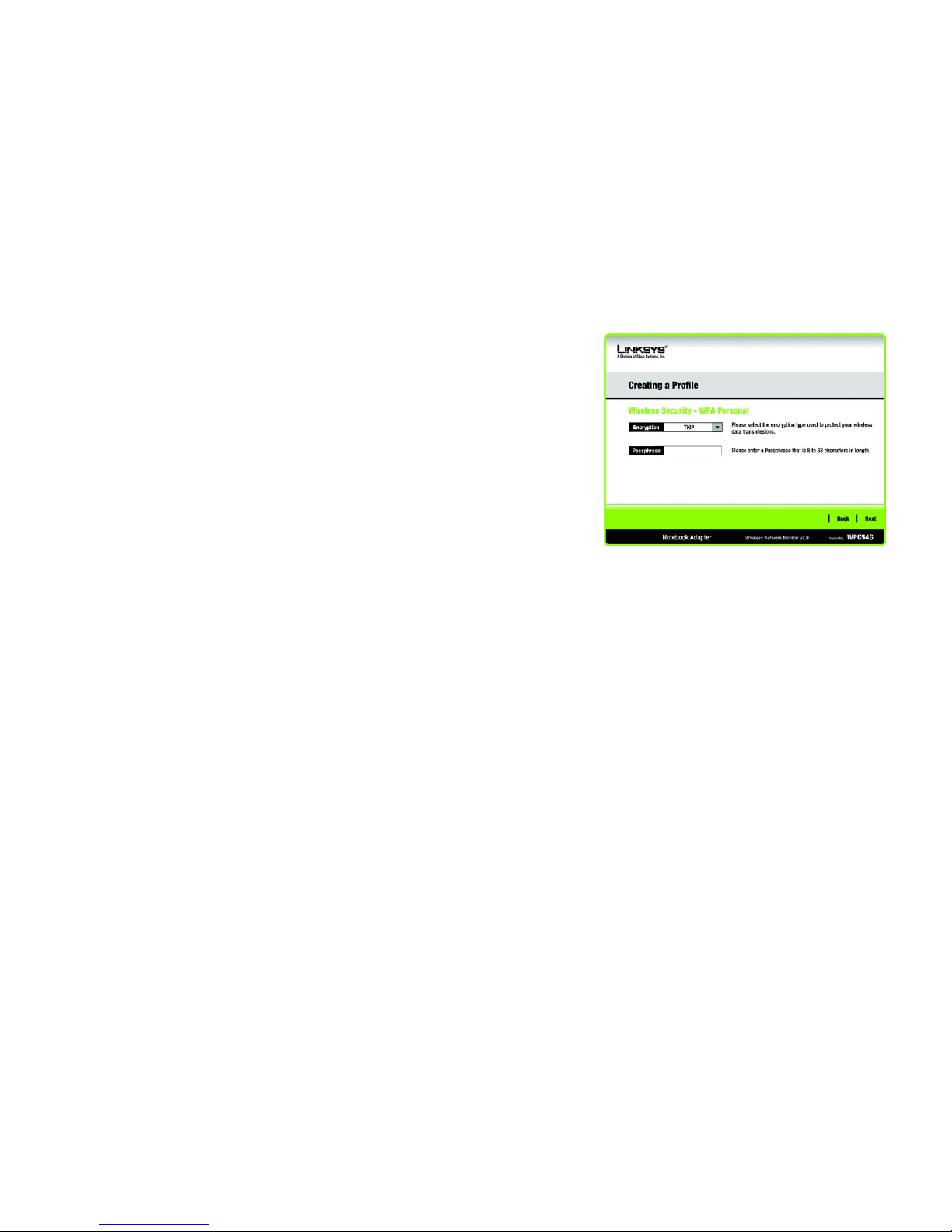
WPA Personal
WPA Personal offers two encryption methods, TKIP and AES, with dynamic encryption keys. Select TKIP or
AES for encryption. Then enter a Passphrase that is 8-63 characters in length.
Encryption - Select the type of algorithm you want to use, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down
menu.
Passphrase - Enter a Passphrase, also called a pre-shared key, of 8-63 characters in the Passphrase field.
The longer and more complex your Passphrase is, the more secure your network will be.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-14: Wireless Security - WPA Personal
Page 21

15
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
WPA Enterprise
WPA Enterprise features WPA security used in coordination with a RADIUS server. (This should only be used
when a RADIUS server is connected to the Router.) WPA Enterprise offers two authentication methods, EAPTLS and PEAP, as well as two encryption methods, TKIP and AES, with dynamic encryption keys.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down
menu, select the certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network. Select the type
of encryption, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have
installed to authenticate you on your wireless network; if you want to use any certificate, keep the default
setting, Trust Any. Then select the authentication method used inside the PEAP tunnel. Select the type of
encryption, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-16: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise - PEAP
Figure 4-15: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise - EAP-TLS
Page 22

16
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
RADIUS
RADIUS features use of a RADIUS server. (This should only be used when a RADIUS server is connected to the
Router.) RADIUS offers two authentication types: EAP-TLS and PEAP.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down
menu, select the certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have
installed to authenticate you on your wireless network; if you want to use any certificate, keep the default
setting, Trust Any. Then select the authentication method used inside the PEAP tunnel.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 4-17: Wireless Security - RADIUS - EAP-TLS
Figure 4-18: Wireless Security - RADIUS - PEAP
Page 23

17
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
LEAP
If you selected LEAP, then enter the Username and Password that will authenticate you on your wireless
network.
Username - Enter the username used for authentication.
Password - Enter the password used for authentication.
Confirm - Enter the password again.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
6. The Confirm New Settings screen will appear next and show the new settings. To save the new settings, click
the Save button. To edit the new settings, click the Back button. To exit the Manual Setup through the
Wireless Network Monitor, click Exit.
Figure 4-19: Wireless Security - LEAP
Figure 4-20: Confirm New Settings
Page 24

18
Chapter 4: Setting up and Connecting the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Setting up the Adapter
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
7. The Congratulations screen will appear next. Click Connect to Network to implement the new settings
immediately and return to the Link Information screen. Click Return to Profiles Screen to keep the current
settings active and return to the Profiles screen.
Congratulations! Your manual setup through the Wireless Network Monitor is complete.
To check the link information, search for available wireless networks, or make additional configuration
changes, proceed to Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor.
Figure 4-21: Congratulations
Page 25

19
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Accessing the Wireless Network Monitor
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Use the Wireless Network Monitor to check the link information, search for available wireless networks, or create
profiles that hold different configuration settings.
Accessing the Wireless Network Monitor
After installing the Adapter, the Wireless Network Monitor icon will appear in the system tray of your computer. If
the Wireless Network Monitor is enabled, then the icon will be green. If the Wireless Network Monitor is disabled
or the Adapter is not connected, then the icon will be gray.
Using the Wireless Network Monitor
The opening screen of the Wireless Network Monitor is the Link Information screen. From this screen, you can
find out how strong the current wireless signal is and how good the connection’s quality is. You can also click the
More Information button to view additional status information about the current wireless connection. To search
for available wireless networks, click the Site Survey tab. To perform configuration changes or create connection
profiles, click the Profiles tab.
Link Information
The Link Information screen displays network mode, signal strength, and link quality information about the
current connection. It also provides a button to click for additional status information.
Ad-Hoc Mode or Infrastructure Mode - The screen indicates whether the Adapter is currently working in adhoc or infrastructure mode.
Signal Strength - The Signal Strength bar indicates signal strength.
Link Quality - The Link Quality bar indicates the quality of the wireless network connection.
Click the More Information button to view additional information about the wireless network connection on the
Wireless Network Status screen.
Figure 5-1: Wireless Network Monitor Icon
Figure 5-2: Link Information
Page 26

20
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Link Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Wireless Network Status
The Wireless Network Status screen provides information on your current network settings.
Status - This shows the status of the wireless network connection.
SSID - This is the unique name of the wireless network.
Wireless Mode - The mode of the wireless network currently in use is displayed here.
Transfer Rate - The data transfer rate of the current connection is shown here.
Channel - This is the channel to which the wireless network devices are set.
Security - The status of the wireless security feature is displayed here.
Authentication - This is your wireless network’s authentication method.
IP Address - The IP Address of the Adapter is displayed here.
Subnet Mask - The Subnet Mask of the Adapter is shown here.
Default Gateway - The Default Gateway address of the Adapter is displayed here.
DNS - This is the DNS address of the Adapter.
DHCP Client - This displays the Adapter’s status as a DHCP client.
MAC Address- The MAC address of the wireless network’s access point or wireless router is shown here.
Signal Strength - The Signal Strength bar indicates the signal strength.
Link Quality - The Link Quality bar indicates the quality of the wireless network connection.
Click the Statistics button to go to the Wireless Network Statistics screen. Click the Back button to return to the
initial Link Information screen. Click the Save to Profile button to save the currently active connection settings to
a profile.
Figure 5-3: More Information - Wireless Network Status
Page 27

21
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Link Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Wireless Network Statistics
The Wireless Networks Statistics screen provides statistics on your current network settings.
Transmit Rate - This is the data transfer rate of the current connection. (In Auto mode, the Adapter dynamically
shifts to the fastest data transfer rate possible at any given time.)
Receive Rate - This is the rate at which data is received.
Packets Received - This shows the packets received by the Adapter, in real time, since connecting to the
wireless network or since the Refresh Statistics button was last pressed.
Packets Transmitted - This shows the packets transmitted from the Adapter, in real time, since connecting to
the wireless network or since the Refresh Statistics button was last pressed.
Bytes Received - This shows the number of bytes received by the Adapter, in real time, since connecting to the
wireless network or since the Refresh Statistics button was last pressed.
Bytes Transmitted - This shows the number of bytes transmitted from the Adapter, in real time, since connecting
to the wireless network or since the Refresh Statistics button was last pressed.
Driver Version - This shows the version of the Adapter’s driver.
Noise Level - This shows the level of background noise affecting the wireless signal. A lower reading translates
into a higher quality signal.
Signal Strength - This is the intensity of the wireless signal received by the Adapter.
Transmit Power - This is the power output at which the Adapter is transmitting.
Up Time - This indicates the length of the most recent connection to a wireless network.
Tot a l Up Tim e - This indicates the cumulative total of the Adapter’s connection time.
Signal Strength - The Signal Strength bar indicates the signal strength.
Link Quality - The Link Quality bar indicates the quality of the wireless network connection.
Click the Back button to return to the initial Link Information screen. Click the Status button to go to the Wireless
Network Status screen. Click the Save to Profile button to save the currently active connection settings to a
profile. Click the Refresh button to reset the statistics.
Figure 5-4: More Information-Network Statistics
Page 28

22
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Site Survey
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Site Survey
The Site Survey screen displays a list of available networks in the table on the left. The table shows each
network’s SSID, Channel, and the quality of the wireless signal the Adapter is receiving. You may click SSID, CH
(Channel), or Signal, to sort by that field.
SSID - The SSID or unique name of the wireless network is displayed here.
CH - This is the channel that the network uses.
Signal - This is the percentage of signal strength, from 0 to 100%.
Site Information
For each network selected, the following settings are listed:
SSID - This the SSID or unique name of the wireless network.
Wireless Mode - This is the mode of the wireless network currently in use.
Channel - This is the channel to which the wireless network devices are set.
Security - The status of the wireless security feature is displayed here.
MAC Address- The MAC address of the wireless network’s access point is displayed here.
Refresh - Click the Refresh button to perform a new search for wireless devices.
Connect - To connect to one of the networks on the list, select the wireless network, and click the Connect
button. If the network has encryption enabled, then you will see a new screen appear.
If the network has the wireless security WEP encryption enabled, then you will see the WEP Key Needed for
Connection screen. Select the appropriate level of WEP encryption, 64-bit or 128-bit). Then enter the network’s
Passphrase or WEP Key. Click the Connect button. To cancel the connection, click the Cancel button.
If the network has the wireless security WPA-Personal security enabled, then you will see the WPA-Personal
Needed for Connection screen. Select the appropriate encryption type, TKIP or AES. Enter the network’s
Passphrase or pre-shared key in the Passphrase field. Then click the Connect button. To cancel the connection,
click the Cancel button.
Figure 5-5: Site Survey
Figure 5-6: WEP Key Needed for Connection
Figure 5-7: WPA-Personal Needed for Connection
Page 29

23
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Profiles
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Profiles
The Profiles screen lets you save different configuration profiles for different network setups. The table on the left
displays a list of available profiles with their profile names and SSIDs.
Profile - The name of the profile is displayed here.
SSID - The SSID or unique name of the wireless network is displayed here.
Profile Information
For each profile selected, the following are listed:
Wireless Mode - This is the mode of the wireless network currently in use.
Transfer Rate - The data transfer rate of the current connection is shown here.
Channel - This is the channel to which the wireless network devices are set.
Security - The status of the wireless security feature is displayed here.
Authentication - The authentication setting for the network is shown here.
Connect - To connect to a wireless network using a specific profile, select the profile, and click the Connect
button.
New - Click the New button to create a new profile. See the next section, “Creating a New Profile,” for detailed
instructions.
Edit - Select the profile you want to change, and then click the Edit button.
Import - Click the Import button to import a profile that has been saved in another location. Select the
appropriate file, and click the Open button.
Export - Select the profile you want to save in a different location, and click the Export button. Direct Windows to
the appropriate folder, and click the Save button.
Delete - Select the profile you want to delete, and then click the Delete button.
Figure 5-8: Profiles
Figure 5-9: Import a Profile
Figure 5-10: Export a Profile
NOTE: If you want to export more than one profile, you have to export them one at a time.
Page 30

24
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Creating a New Profile
On the Profiles screen, click the New button to create a new profile. Enter a name for the new profile, and click
the OK button. Click the Cancel button to return to the Profiles screen without entering a name.
The Available Wireless Network screen will appear. This screen provides two options for setting up the Adapter.
• Available Networks. Use this option if you already have a network set up. The networks available to this
Adapter will be listed on this screen. You can choose one of these networks and click the Connect button to
connect to it. Click the Refresh button to update the Available Wireless Network list.
• Manual Setup. If your network is not listed on this screen, select Manual Setup to set up the adapter
manually. This method of setting up the Adapter is intended for Advanced Users onl
The setup for each option is described, step by step, under the appropriate heading on the following pages.
Click Exit to close the Setup Wizard.
Figure 5-11: Create a New Profile
Figure 5-12: Available Wireless Network
Page 31

25
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Available Networks
Another method for setting up the Adapter is with the available networks listed on the Available Wireless Network
screen. The available networks are listed in the table on the center of the screen by SSID. Select the wireless
network you wish to connect to and click the Connect button. (If you do not see your network listed, you can click
the Refresh button to bring the list up again.) If the network utilizes wireless security, you will need to configure
security on the Adapter. If not, you will be taken directly to the Congratulations screen.
1. If you have wireless security enabled on your network, continue to step 2. If you don’t have wireless security
enabled, continue to step 3.
2. If your network has the wireless security WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) enabled, this screen will appear.
Select 64-bit or 128-bit.
Then enter a passphrase or WEP key.
Passphrase - Enter a passphrase in the Passphrase field, so a WEP key is automatically generated. The
passphrase is case-sensitive and should not be longer than 31 alphanumeric characters. It must match the
passphrase of your other wireless network devices and is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. (If
you have any non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key manually on those products.)
WEP Key - The WEP key you enter must match the WEP key of your wireless network. For 64-bit encryption,
enter exactly 10 hexadecimal characters. For 128-bit encryption, enter exactly 26 hexadecimal characters.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”.
Then click Connect.
Figure 5-13: Available Wireless Network
Figure 5-14: WEP Key Needed for Connection
encryption: encoding data transmitted in a network.
wpa (wi-fi protected access: a wireless security protocol
using TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) encryption,
which can be used in conjunction with a RADIUS server.
wep (wired equivalent privacy): a method of encrypting network
data transmitted on a wireless network for greater security.
Page 32

26
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
If your network has the wireless security WPA Personal (Wi-Fi Protected Access) enabled, this screen will
appear.
Encryption - Select the type of algorithm you want to use, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down
menu.
Passphrase - Enter a Passphrase, also called a pre-shared key, of 8-63 characters in the Passphrase field.
The longer and more complex your Passphrase is, the more secure your network will be.
Then click Connect.
3. After the software has been successfully installed, the Congratulations screen will appear. Click Connect to
Network to connect to your network.
Congratulations! The setup is complete.
Figure 5-15: WPA Personal Needed for Connection
Figure 5-16: Congratulations
Page 33

27
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Manual Setup
1. The Network Settings screen will appear. If your network has a router or other DHCP server, click the radio
button next to Obtain network settings automatically (DHCP).
If your network does not have a DHCP server, click the radio button next to Specify network settings. Enter
an IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS addresses appropriate for your network. You must
specify the IP Address and Subnet Mask on this screen. If you are unsure about the Default Gateway and DNS
addresses, leave these fields empty.
IP Address - This IP Address must be unique to your network.
Subnet Mask - The Adapter’s Subnet Mask must be the same as your wired network’s Subnet Mask.
Default Gateway - Enter the IP address of your network’s Gateway here.
DNS 1 and DNS 2 - Enter the DNS address of your wired Ethernet network here.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
2. The Wireless Mode screen shows a choice of two wireless modes. Click the Infrastructure Mode radio
button if you want to connect to a wireless router or access point. Click the Ad-Hoc Mode radio button if you
want to connect to another wireless device directly without using a wireless router or access point. Enter the
SSID for your network.
Infrastructure Mode - Use this mode if you want to connect to a wireless router or access point.
Ad-Hoc Mode - Use this mode if you want to connect to another wireless device directly without using a
wireless router or access point.
SSID - This is the wireless network name that must be used for all the devices in your wireless network. It is
case- sensitive and should be a unique name to help prevent others from entering your network.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 5-17: Network Settings for New Profile
Figure 5-18: Wireless Mode for New Profile
Page 34

28
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
3. If you chose Infrastructure Mode, go to Step 4 now. If you chose Ad-Hoc Mode, the Ad-Hoc Mode Settings
screen will appear.
Select the correct operating channel for your wireless network. The channel you choose should match the
channel set on the other devices in your wireless network. If you are unsure about which channel to use, keep
the default setting.
Click the Next button. Click the Back button to change any settings.
4. If your wireless network doesn’t have wireless security, select Disabled and then click the Next button to
continue. Proceed to Step 5.
If your wireless network has wireless security, select the method of security used: WEP, WPA-Personal,
WPA-Enterprise, RADIUS, or LEAP. WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy, and WPA stands for Wi-Fi
Protected Access. WPA is a stronger security method than WEP. RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication
Dial-In User Service, and LEAP stands for Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol. Click the Next
button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Proceed to the appropriate section for your security method: WEP, WPA-Personal, WPA-Enterprise, RADIUS, or
LEAP.
WEP
WEP - Select 64-bit or 128-bit encryption
Passphrase - Enter a passphrase in the Passphrase field, so a WEP key is automatically generated. It is case-
sensitive and should not be longer than 31 alphanumeric characters. This passphrase must match the
passphrase of your other wireless network devices and is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. (If
you have any non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key manually on those products.)
WEP Key - The WEP key you enter must match the WEP key of your wireless network. For 64-bit encryption,
enter exactly 10 hexadecimal characters. For 128-bit encryption, enter exactly 26 hexadecimal characters.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”.
Figure 5-19: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings for New Profile
Figure 5-20: Wireless Security - WEP for New Profile
Page 35

29
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Advanced Users
TX Key - The default transmit key number is 1. If your network’s access point or wireless router uses transmit
key number 2, 3, or 4, select the appropriate number from the TX Key drop-down box.
Authentication -The default is set to Auto, so it will auto-detect for Shared Key or Open System
authentication. For Shared Key authentication, both the sender and the recipient share a WEP key for
authentication. For Open System authentication, the sender and the recipient do not share a WEP key for
authentication. If you are not sure which authentication method to select, keep the default, Auto.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
WPA Personal
WPA Personal offers two encryption methods, TKIP and AES, with dynamic encryption keys. Select TKIP or
AES for encryption. Then enter a Passphrase that is 8-63 characters in length.
Encryption - Select the type of algorithm you want to use, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down
menu.
Passphrase - Enter a Passphrase, also called a pre-shared key, of 8-63 characters in the Passphrase field.
The longer and more complex your Passphrase is, the more secure your network will be.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 5-21: Wireless Security - WPA Personal for
New Profile
Page 36

30
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
WPA Enterprise
WPA Enterprise features WPA security used in coordination with a RADIUS server. (This should only be used
when a RADIUS server is connected to the Router.) WPA Enterprise offers two authentication methods, EAPTLS and PEAP, as well as two encryption methods, TKIP and AES, with dynamic encryption keys.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down
menu, select the certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network. Select the type
of encryption, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have
installed to authenticate you on your wireless network; if you want to use any certificate, keep the default
setting, Trust Any. Then select the authentication method used inside the PEAP tunnel. Select the type of
encryption, TKIP or AES, from the Encryption drop-down menu.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 5-23: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise Using
PEAP for New Profile
Figure 5-22: Wireless Security - WPA Enterprise Using
EAP-TLS for New Profile
Page 37

31
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
RADIUS
RADIUS features use of a RADIUS server. (This should only be used when a RADIUS server is connected to the
Router.) RADIUS offers two authentication types: EAP-TLS and PEAP.
Authentication - Select the authentication method your network is using, EAP-TLS or PEAP.
EAP-TLS
If you selected EAP-TLS, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
name of the authentication server in the Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down
menu, select the certificate you have installed to authenticate you on your wireless network.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
PEAP
If you selected PEAP, enter the login name of your wireless network in the Login Name field. Enter the
password of your wireless network in the Password field. Enter the name of the authentication server in the
Server Name field (this is optional). From the Certificate drop-down menu, select the certificate you have
installed to authenticate you on your wireless network; if you want to use any certificate, keep the default
setting, Trust Any. Then select the authentication method used inside the PEAP tunnel.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
Figure 5-24: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using EAP-TLS
for New Profile
Figure 5-25: Wireless Security - RADIUS Using PEAP for
New Profile
Page 38

32
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
LEAP
If you selected LEAP, then enter the Username and Password that will authenticate you on your wireless
network.
Username - Enter the username used for authentication.
Password - Enter the password used for authentication.
Confirm - Enter the password again.
Click the Next button to continue, or click the Back button to return to the previous screen.
4. The Confirm New Settings screen will appear next and show the new settings. To save the new settings, click
the Save button. To edit the new settings, click the Back button. To exit the Wireless Network Monitor, click
Exit.
Figure 5-26: Wireless Security - LEAP for New Profile
Figure 5-27: Confirm New Settings for New Profile
Page 39

33
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
5. The Congratulations screen will appear next. Click Connect to Network to implement the new settings
immediately and return to the Link Information screen. Click Return to Profiles Screen to keep the current
settings active and return to the Profiles screen.
You have successfully created a connection profile.
Figure 5-28: Congratulations for New Profile
Page 40

34
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix consists of two parts: “Common Problems and Solutions” and “Frequently Asked Questions.” This
appendix provides solutions to problems that may occur during the installation and operation of the Wireless-G
Notebook Adapter. Read the description below to solve your problems. If you can't find an answer here, check the
Linksys website at www.linksys.com.
Common Problems and Solutions
1. My computer does not recognize the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter.
Make sure that the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter is properly inserted into the PC Card slot.
2. The Wireless-G Notebook Adapter does not work properly.
Reinsert the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter into the notebook or desktop’s USB port.
For Windows 98SE or Me, right-click on My Computer, and select Properties. Select the Device Manager
tab, and click on the Network Adapter. You will find the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter if it is installed
successfully. If you see a yellow exclamation mark, the resources may be conflicting and you must follow the
steps below:
• Uninstall the driver software from your PC.
• Restart your PC and repeat the hardware and software installation as specified in this User Guide.
3. I cannot communicate with the other computers linked via Ethernet in the Infrastructure
configuration.
Make sure that the notebook or desktop is powered on.
Make sure that the Wireless-G Notebook Adapter is configured with the same SSID and WEP settings as the
other computers in the Infrastructure configuration.
Page 41

35
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network?
This will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a network. Consult the
application’s user guide to determine if it supports operation over a network.
Can I play computer games with other members of the wireless network?
Yes, as long as the game supports multiple players over a LAN (local area network). Refer to the game’s user
guide for more information.
What is the 802.11b standard?
It is one of the standards for wireless networks. The 802.11b standard allows wireless networking hardware from
different manufacturers to communicate, provided that the hardware complies with the 802.11b standard. The
802.11b standard states a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
What 802.11b features are supported?
The product supports the following 802.11b functions:
• CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge protocol
• Multi-Channel Roaming
• Automatic Rate Selection
• RTS/CTS feature
• Fragmentation
• Power Management
What is ad-hoc mode?
When a wireless network is set to ad-hoc mode, the wireless-equipped computers are configured to
communicate directly with each other. This type of network will not communicate with any wired network.
What is infrastructure mode?
When a wireless network is set to infrastructure mode, the wireless network is configured to communicate with a
wired network through a wireless access point.
What is roaming?
Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while moving freely throughout
an area greater than that covered by a single access point. Before using the roaming function, the workstation
must make sure that it is the same channel number with the access point of dedicated coverage area.
To achieve true seamless connectivity, the wireless LAN must incorporate a number of different functions. Each
node and access point, for example, must always acknowledge receipt of each message. Each node must
maintain contact with the wireless network even when not actually transmitting data. Achieving these functions
Page 42

36
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
simultaneously requires a dynamic RF networking technology that links access points and nodes. In such a
system, the user’s end node undertakes a search for the best possible access to the system. First, it evaluates
such factors as signal strength and quality, as well as the message load currently being carried by each access
point and the distance of each access point to the wired backbone. Based on that information, the node next
selects the right access point and registers its address. Communications between end node and host computer
can then be transmitted up and down the backbone.
As the user moves on, the end node’s RF transmitter regularly checks the system to determine whether it is in
touch with the original access point or whether it should seek a new one. When a node no longer receives
acknowledgment from its original access point, it undertakes a new search. Upon finding a new access point, it
then re-registers, and the communication process continues.
What is ISM band?
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth for unlicensed use in the ISM
(Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available
worldwide. This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed wireless capabilities in
the hands of users around the globe.
What is Spread Spectrum?
Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the military for use in
reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth efficiency for
reliability, integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of narrowband
transmission, but the trade-off produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that
the receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a receiver is not tuned to
the right frequency, a spread-spectrum signal looks like background noise. There are two main alternatives,
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).
What is DSSS? What is FHSS? And what are their differences?
Frequency-Hopping Spread-Spectrum (FHSS) uses a narrowband carrier that changes frequency in a pattern that
is known to both transmitter and receiver. Properly synchronized, the net effect is to maintain a single logical
channel. To an unintended receiver, FHSS appears to be short-duration impulse noise. Direct-Sequence SpreadSpectrum (DSSS) generates a redundant bit pattern for each bit to be transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip
(or chipping code). The longer the chip, the greater the probability that the original data can be recovered. Even if
one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission, statistical techniques embedded in the radio can
recover the original data without the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears as low
power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband receivers.
What is WEP?
WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a shared key algorithm, as described in the
802.11 standard.
Page 43

37
Appendix B: Wireless Security
Security Precautions
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix B: Wireless Security
Linksys wants to make wireless networking as safe and easy for you as possible. The current generation of
Linksys products provide several network security features, but they require specific action on your part for
implementation. So, keep the following in mind whenever you are setting up or using your wireless network.
Security Precautions
The following is a complete list of security precautions to take (at least steps 1 through 5 should be followed):
1. Change the default SSID.
2. Disable SSID Broadcast.
3. Change the default password for the Administrator account.
4. Enable MAC Address Filtering.
5. Change the SSID periodically.
6. Use the highest encryption algorithm possible. Use WPA if it is available. Please note that this may reduce
your network performance.
7. Change the WEP encryption keys periodically.
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are easy to find. Hackers know that in order to join a wireless network, wireless networking
products first listen for “beacon messages”. These messages can be easily decrypted and contain much of the
network’s information, such as the network’s SSID (Service Set Identifier). Here are the steps you can take:
Change the administrator’s password regularly. With every wireless networking device you use, keep in mind
that network settings (SSID, WEP keys, etc.) are stored in its firmware. Your network administrator is the only
person who can change network settings. If a hacker gets a hold of the administrator’s password, he, too, can
change those settings. So, make it harder for a hacker to get that information. Change the administrator’s
password regularly.
SSID. There are several things to keep in mind about the SSID:
Note: Some of these security features are
available only through the network router or
access point. Refer to the router or access
point’s documentation for more information.
Page 44

38
Appendix B: Wireless Security
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
1. Disable Broadcast
2. Make it unique
3. Change it often
Most wireless networking devices will give you the option of broadcasting the SSID. While this option may be
more convenient, it allows anyone to log into your wireless network. This includes hackers. So, don’t broadcast
the SSID.
Wireless networking products come with a default SSID set by the factory. (The Linksys default SSID is “linksys”.)
Hackers know these defaults and can check these against your network. Change your SSID to something unique
and not something related to your company or the networking products you use.
Change your SSID regularly so that any hackers who have gained access to your wireless network will have to
start from the beginning in trying to break in.
MAC Addresses. Enable MAC Address filtering. MAC Address filtering will allow you to provide access to only
those wireless nodes with certain MAC Addresses. This makes it harder for a hacker to access your network with
a random MAC Address.
WEP Encryption. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is often looked upon as a cure-all for wireless security
concerns. This is overstating WEP’s ability. Again, this can only provide enough security to make a hacker’s job
more difficult.
There are several ways that WEP can be maximized:
1. Use the highest level of encryption possible
2. Use “Shared Key” authentication
3. Change your WEP key regularly
WPA. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is the newest and best available standard in Wi-Fi security. Three modes are
available: WPA-Personal, WPA Enterprise, and Radius. WPA-Personal gives you a choice of two encryption
methods: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), which utilizes a stronger encryption method and incorporates
Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers, and AES (Advanced Encryption System),
which utilizes a symmetric 128-Bit block data encryption. WPA Enterprise offers two encryption methods, TKIP
and AES, with dynamic encryption keys. RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) utilizes a RADIUS
server for authentication.
Important: Always remember that each
device in your wireless network MUST use
the same encryption method and encryption
key or your wireless network will not function
properly.
Page 45

39
Appendix B: Wireless Security
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
WPA-Personal. If you do not have a RADIUS server, Select the type of algorithm, TKIP or AES, and enter a
password in the Passphrase field of 8-63 characters.
WPA Enterprise. WPA used in coordination with a RADIUS server. (This should only be used when a RADIUS
server is connected to the Router or other device.) WPA Enterprise offers two encryption methods, TKIP and
AES, with dynamic encryption keys.
RADIUS. WEP used in coordination with a RADIUS server. (This should only be used when a RADIUS server is
connected to the Router or other device.)
Implementing encryption may have a negative impact on your network’s performance, but if you are transmitting
sensitive data over your network, encryption should be used.
These security recommendations should help keep your mind at ease while you are enjoying the most flexible
and convenient technology Linksys has to offer.
Page 46

40
Appendix C: Windows Help
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix C: Windows Help
All wireless products require Microsoft Windows. Windows is the most used operating system in the world and
comes with many features that help make networking easier. These features can be accessed through Windows
Help and are described in this appendix.
TCP/IP
Before a computer can communicate with an access point or wireless router, TCP/IP must be enabled. TCP/IP is a
set of instructions, or protocol, all PCs follow to communicate over a network. This is true for wireless networks
as well. Your PCs will not be able to utilize wireless networking without having TCP/IP enabled. Windows Help
provides complete instructions on enabling TCP/IP.
Shared Resources
If you wish to share printers, folder, or files over your network, Windows Help provides complete instructions on
utilizing shared resources.
Network Neighborhood/My Network Places
Other PCs on your network will appear under Network Neighborhood or My Network Places (depending upon the
version of Windows you're running). Windows Help provides complete instructions on adding PCs to your
network.
Page 47

41
Appendix D: Glossary
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix D: Glossary
This glossary contains some basic networking terms you may come across when using this product. For more
advanced terms, see the complete Linksys glossary at http://www.linksys.com/glossary.
Access Point - A device that allows wireless-equipped computers and other devices to communicate with a
wired network. Also used to expand the range of a wireless network.
Ad-hoc - A group of wireless devices communicating directly with each other (peer-to-peer) without the use of
an access point.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) - A security method that uses symmetric 128-bit block data encryption.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given device or network.
Bit - A binary digit.
Boot - To start a device and cause it to start executing instructions.
Broadband - An always-on, fast Internet connection.
Browser - An application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the information on the
World Wide Web.
Byte - A unit of data that is usually eight bits long
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in turn connects to the
Internet.
Daisy Chain - A method used to connect devices in a series, one after the other.
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) - Allows the hosting of a website, FTP server, or e-mail server with a
fixed domain name (e.g., www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP address.
Default Gateway - A device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A networking protocol that allows administrators to assign
temporary IP addresses to network computers by "leasing" an IP address to a user for a limited amount of time,
instead of assigning permanent IP addresses.
Page 48

42
Appendix D: Glossary
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Removes the Router's firewall protection from one PC, allowing it to be "seen" from
the Internet.
DNS (Domain Name Server) - The IP address of your ISP's server, which translates the names of websites into IP
addresses.
Domain - A specific name for a network of computers.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - An always-on broadband connection over traditional phone lines.
Dynamic IP Address - A temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) - A general authentication protocol used to control network access.
Many specific authentication methods work within this framework.
Encryption - Encoding data transmitted in a network.
Ethernet - IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common
transmission medium.
Firewall - A set of related programs located at a network gateway server that protects the resources of a
network from users from other networks.
Firmware - The programming code that runs a networking device.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network.
Full Duplex - The ability of a networking device to receive and transmit data simultaneously.
Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible communications protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single line, but only one direction at a
time.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used to connect to servers on the World
Wide Web.
Infrastructure - A wireless network that is bridged to a wired network via an access point.
IP (Internet Protocol) - A protocol used to send data over a network.
Page 49

43
Appendix D: Glossary
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
IP Address - The address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
IPCONFIG - A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays the IP address for a particular networking device.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A VPN protocol used to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet.
LAN - The computers and networking products that make up your local network.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address that a manufacturer assigns to each networking
device.
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) - One million bits per second; a unit of measurement for data transmission.
NAT (Network Address Translation) - NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a different
IP address for the Internet.
Network - A series of computers or devices connected for the purpose of data sharing, storage, and/or
transmission between users.
Packet - A unit of data sent over a network.
Passphrase - Used much like a password, a passphrase simplifies the WEP encryption process by automatically
generating the WEP encryption keys for Linksys products.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether a particular IP address is online.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) - A standard mail server commonly used on the Internet.
Port - The connection point on a computer or networking device used for plugging in cables or adapters.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) - A technology enabling an Ethernet network cable to deliver both data and power.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - A type of broadband connection that provides authentication
(username and password) in addition to data transport.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - A VPN protocol that allows the Point to Point Protocol (PPP) to be
tunneled through an IP network. This protocol is also used as a type of broadband connection in Europe.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) - A protocol that uses an authentication server to control
network access.
Page 50

44
Appendix D: Glossary
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - An Ethernet connector that holds up to eight wires.
Roaming - The ability to take a wireless device from one access point's range to another without losing the
connection.
Router - A networking device that connects multiple networks together.
Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access to files, printing, communications,
and other services.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The standard e-mail protocol on the Internet.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - A widely used network monitoring and control protocol.
SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) Firewall - A technology that inspects incoming packets of information before
allowing them to enter the network.
SSID (Service Set IDentifier) - Your wireless network's name.
Static IP Address - A fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a network.
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path.
Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network.
Switch - 1. A data switch that connects computing devices to host computers, allowing a large number of
devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an
electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that requires acknowledgement
from the recipient of data sent.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - A set of instructions PCs use to communicate over a
network.
Tel ne t - A user command and TCP/IP protocol used for accessing remote PCs.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no directory or password
capability.
Throughput - The amount of data moved successfully from one node to another in a given time period.
Page 51

45
Appendix D: Glossary
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) - a wireless encryption protocol that provides dynamic encryption keys for
each packet transmitted.
Topology - The physical layout of a network.
TX Rate - Transmission Rate.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file over a network.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address of a file located on the Internet.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - A security measure to protect data as it leaves one network and goes to another
over the Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network)- The Internet.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A method of encrypting network data transmitted on a wireless network for
greater security.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associated devices that communicate with
each other wirelessly.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) - a wireless security protocol using TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
encryption, which can be used in conjunction with a RADIUS server.
Page 52

46
Appendix E: Specifications
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix E: Specifications
Standards IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11b, CardBus
Channels 11 Channels (Most of North, Central, and South America)
13 Channels (Most of Europe and Asia)
LEDs Power, Link
Transmit Power 18 dBm
802.11b,
15 dBm
802.11g
Protocols 802.11b: CCK (11 Mbps), DQPSK (2 Mbps), DBPSK (1 Mbps); 802.11g: OFDM
Security Features WEP, AES, TKIP, 802.1x
WEP Key Bits 64, 128 Bit
Dimensions 115 mm x 54 mm x 7.5 mm
Unit Weight 0.04 kg.
Certifications FCC, IC-03, CE
Operating Temp. 0ºC to 40ºC
Storage Temp. -20ºC to 60ºC
Operating Humidity 10% to 85%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 5% to 90%, Non-Condensing
Page 53

47
Appendix F: Warranty Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix F: Warranty Information
Linksys warrants to You that, for a period of three years (the “Warranty Period”), your Linksys Product will be substantially
free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal use. Your exclusive remedy and Linksys' entire liability under
this warranty will be for Linksys at its option to repair or replace the Product or refund Your purchase price less any rebates.
This limited warranty extends only to the original purchaser.
If the Product proves defective during the Warranty Period call Linksys Technical Support in order to obtain a Return
Authorization Number, if applicable. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING. If You are
requested to return the Product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package and include a
copy of your original proof of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. You
are responsible for shipping defective Products to Linksys. Linksys pays for UPS Ground shipping from Linksys back to You
only. Customers located outside of the United States of America and Canada are responsible for all shipping and handling
charges.
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE LIMITED
TO THE DURATION OF THE WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED. Some jurisdictions do not
allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to You. This warranty gives
You specific legal rights, and You may also have other rights which vary by jurisdiction.
This warranty does not apply if the Product (a) has been altered, except by Linksys, (b) has not been installed, operated,
repaired, or maintained in accordance with instructions supplied by Linksys, or (c) has been subjected to abnormal physical
or electrical stress, misuse, negligence, or accident. In addition, due to the continual development of new techniques for
intruding upon and attacking networks, Linksys does not warrant that the Product will be free of vulnerability to intrusion or
attack.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE OR PROFIT,
OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF
LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT
(INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN IF LINKSYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
WILL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT. The foregoing limitations will apply even if
any warranty or remedy provided under this Agreement fails of its essential purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to You.
This Warranty is valid and may be processed only in the country of purchase.
Please direct all inquiries to: Linksys, P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623 USA.
Page 54

48
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
FCC Statement
This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver's
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator and your body.
Safety Notices
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire, use only No.26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
Industry Canada (Canada)
This device complies with Canadian ICES-003 and RSS210 rules.
Cet appareil est conforme aux normes NMB-003 et RSS210 d'Industry Canada.
Page 55

49
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Compliance Information for 2.4-GHz Wireless Products
Relevant to the EU and Other Countries Following the EU
Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the EU Directive
1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
Page 56

50
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
The following standards were applied during the assessment of the product against the requirements of the Directive
1999/5/EC:
• Radio: EN 300 328
• EMC: EN 301 489-1, EN 301 489-17
• Safety: EN 60950 and either EN 50385 or EN 50371
CE Marking
For the Linksys Wireless-B and Wireless-G products, the following CE mark, notified body number (where applicable), and
class 2 identifier are added to the equipment.
Check the CE label on the product to find out which notified body was involved during the assessment.
National Restrictions
This product may be used in all EU countries (and other countries following the EU directive 1999/5/EC) without any
limitation except for the countries mentioned below:
Ce produit peut être utilisé dans tous les pays de l’UE (et dans tous les pays ayant transposés la directive 1999/5/CE) sans
aucune limitation, excepté pour les pays mentionnés ci-dessous:
Questo prodotto è utilizzabile in tutte i paesi EU (ed in tutti gli altri paesi che seguono le direttive EU 1999/5/EC) senza
nessuna limitazione, eccetto per i paesii menzionati di seguito:
Das Produkt kann in allen EU Staaten ohne Einschränkungen eingesetzt werden (sowie in anderen Staaten die der EU
Direktive 1999/5/CE folgen) mit Außnahme der folgenden aufgeführten Staaten:
NOTE: For all products, the Declaration of Conformity is available through one or more of these options:
• A pdf file is included on the product's CD.
• A print copy is included with the product.
• A pdf file is available on the product's webpage. Visit www.linksys.com/international and select your country or
region. Then select your product.
If you need any other technical documentation, see the “Technical Documents on www.linksys.com/international”
section, as shown later in this appendix.
or or
Page 57

51
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Belgium
The Belgian Institute for Postal Services and Telecommunications (BIPT) must be notified of any outdoor wireless link
having a range exceeding 300 meters. Please check http://www.bipt.be for more details.
Draadloze verbindingen voor buitengebruik en met een reikwijdte van meer dan 300 meter dienen aangemeld te worden
bij het Belgisch Instituut voor postdiensten en telecommunicatie (BIPT). Zie http://www.bipt.be voor meer gegevens.
Les liaisons sans fil pour une utilisation en extérieur d’une distance supérieure à 300 mètres doivent être notifiées à
l’Institut Belge des services Postaux et des Télécommunications (IBPT). Visitez
http://www.ibpt.be pour de plus amples détails.
France
In case the product is used outdoors, the output power is restricted in some parts of the band. See Table 1 or check
http://www.arcep.fr/ for more details.
Dans la cas d’une utilisation en extérieur, la puissance de sortie est limitée pour certaines parties de la bande. Reportezvous à la table 1 ou visitez http://www.arcep.fr/ pour de plus amples détails.
Italy
This product meets the National Radio Interface and the requirements specified in the National Frequency Allocation Table
for Italy. Unless operating within the boundaries of the owner’s property, the use of this 2.4 GHz Wireless LAN product
requires a ‘general authorization’. Please check with http://www.comunicazioni.it/it/ for more details.
Questo prodotto è conforme alla specifiche di Interfaccia Radio Nazionali e rispetta il Piano Nazionale di ripartizione delle
frequenze in Italia. Se non viene installato all’interno del proprio fondo, l’utilizzo di prodotti Wireless LAN a 2.4 GHz richiede
una “Autorizzazione Generale”. Consultare http://www.comunicazioni.it/it/ per maggiori dettagli.
Table 1: Applicable Power Levels in France
Location Frequency Range (MHz) Power (EIRP)
Indoor (No restrictions) 2400-2483.5 100 mW (20 dBm)
Outdoor 2400-2454
2454-2483.5
100 mW (20 dBm)
10 mW (10 dBm)
Page 58

52
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Product Usage Restrictions
This product is designed for indoor usage only. Outdoor usage is not recommended.
This product is designed for use with the standard, integral or dedicated (external) antenna(s) that is/are shipped together
with the equipment. However, some applications may require the antenna(s), if removable, to be separated from the
product and installed remotely from the device by using extension cables. For these applications, Linksys offers an R-SMA
extension cable (AC9SMA) and an R-TNC extension cable (AC9TNC). Both of these cables are 9 meters long and have a
cable loss (attenuation) of 5 dB. To compensate for the attenuation, Linksys also offers higher gain antennas, the HGA7S
(with R-SMA connector) and HGA7T (with R-TNC connector). These antennas have a gain of 7 dBi and may only be used
with either the R-SMA or R-TNC extension cable.
Combinations of extension cables and antennas resulting in a radiated power level exceeding 100 mW EIRP are illegal.
Power Output of Your Device
To comply with your country’s regulations, you may have to change the power output of your wireless device. Proceed to
the appropriate section for your device.
Wireless Adapters
Wireless adapters have the power output set to 100% by default. Maximum power output on each adapter does not exceed
20 dBm (100 mW); it is generally 18 dBm (64 mW) or below. If you need to alter your wireless adapter’s power output,
follow the appropriate instructions for your computer’s Windows operating system:
Windows XP
1. Double-click the Wireless icon in your desktop’s system tray.
2. Open the Wireless Network Connection window.
3. Click the Properties button.
4. Select the General tab, and click the Configure button.
5. In the Properties window, click the Advanced tab.
6. Select Power Output.
7. From the pull-down menu on the right, select the wireless adapter’s power output percentage.
NOTE: The power output setting may not be available on all wireless products. For more information, refer to
the documentation on your product’s CD or http://www.linksys.com/international.
Page 59

53
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Windows 2000
1. Open the Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network and Dial-Up Connections.
3. Select your current wireless connection, and select Properties.
4. From the Properties screen, click the Configure button.
5. Click the Advanced tab, and select Power Output.
6. From the pull-down menu on the right, select the wireless adapter’s power setting.
If your computer is running Windows Millennium or 98, then refer to Windows Help for instructions on how to access the
advanced settings of a network adapter.
Wireless Access Points, Routers, or Other Wireless Products
If you have a wireless access point, router or other wireless product, use its Web-based Utility to configure its power
output setting (refer to the product’s documentation for more information).
Technical Documents on www.linksys.com/international
Follow these steps to access technical documents:
1. Browse to http://www.linksys.com/international.
2. Click the region in which you reside.
3. Click the name of the country in which you reside.
4. Click Products.
5. Click the appropriate product category.
6. Select a product.
7. Click the type of documentation you want. The document will automatically open in PDF format.
NOTE: If you have questions regarding the compliance of these products or you cannot find the information
you need, please contact your local sales office or visit http://www.linksys.com/international for more details.
Page 60

54
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
User Information for Consumer Products Covered by EU Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste Electric and Electronic
Equipment (WEEE)
This document contains important information for users with regards to the proper disposal and recycling of Linksys
products. Consumers are required to comply with this notice for all electronic products bearing the following symbol:
Page 61

55
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Page 62

56
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Page 63

57
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Page 64

58
Appendix G: Regulatory Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
For more information, visit www.linksys.com/international.
Page 65

59
Appendix H: Contact Information
Wireless-G Notebook Adapter
Appendix H: Contact Information
Need to contact Linksys?
Visit us online for information on the latest products and updates to your existing products at:
http://www.linksys.com/international
If you experience problems with any Linksys product, you can e-mail us at:
In Europe E-mail Address
Austria support.at@linksys.com
Belgium support.be@linksys.com
Denmark support.dk@linksys.com
France support.fr@linksys.com
Germany support.de@linksys.com
Italy support.it@linksys.com
Netherlands support.nl@linksys.com
Norway support.no@linksys.com
Portugal support.pt@linksys.com
Spain support.es@linksys.com
Sweden support.se@linksys.com
Switzerland support.ch@linksys.com
United Kingdom & Ireland support.uk@linksys.com
Outside of Europe E-mail Address
Asia Pacific asiasupport@linksys.com (English only)
Latin America support.portuguese@linksys.com or support.spanish@linksys.com
Middle East & Africa support.mea@linksys.com (English only)
U.S. and Canada support@linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...