Page 1
Description
+
–
DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
LTC4121EUD/LTC4121EUD-4.2
400mA Synchronous Buck
Battery Charger
DC1977A-A LTC4120EUD-4.2 (Fixed Output)
DC1977A-B LTC4121EUD (Adjustable Output)
The LTC4121 and LTC4121-4.2 feature constant-current–
constant-voltage charging capability suitable for lithiumion or lead-acid cells. The LTC4121-4.2 supports charging
Demonstration Board DC1977A showcases the
LTC4121-4.2 and LTC4121 40V, 400mA synchronous-
buck battery charger integrated circuit. The DC1977A
a single lithium-ion cell with a cell voltage of 4.2V. The
LTC4121 may be programmed to charge battery voltages
up to 18V with a resistive divider.
supports the maximum-power-point tracking (MPPT)
feature of the LTC4121EUD to optimize power delivery
from photovotalic cells or highly resistive sources.
performance summary
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
IN DC1977A Input Voltage I(IN) < 800mA 4.4 40 V
PV
IN
DC1977A PV Cell Input I(IN) < 800mA 5 40.5 V
V(BAT) DC1977A BAT Pin Voltage R11 = 1.40MΩ, R12 = 1.05MΩ 2.5 4.25 V
I(BAT) DC1977A BAT Pin Current V(BAT) = 3.7V; DC1977A; (R7) = 3.01kΩ; JP1 (“MPPT”) = ‘OFF’ 383 402 421 mA
Note: Reference designators refer to Schematic on p. 7.
Specifications are at TA = 25°C
Design files for this circuit board are available at
http://www.linear.com/demo/DC1977
L, LT, LTC, LTM, Linear Technology and the Linear logo are registered trademarks of Analog
Devices, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
MIN TYP MAX
UNITS
Demo BoarD application
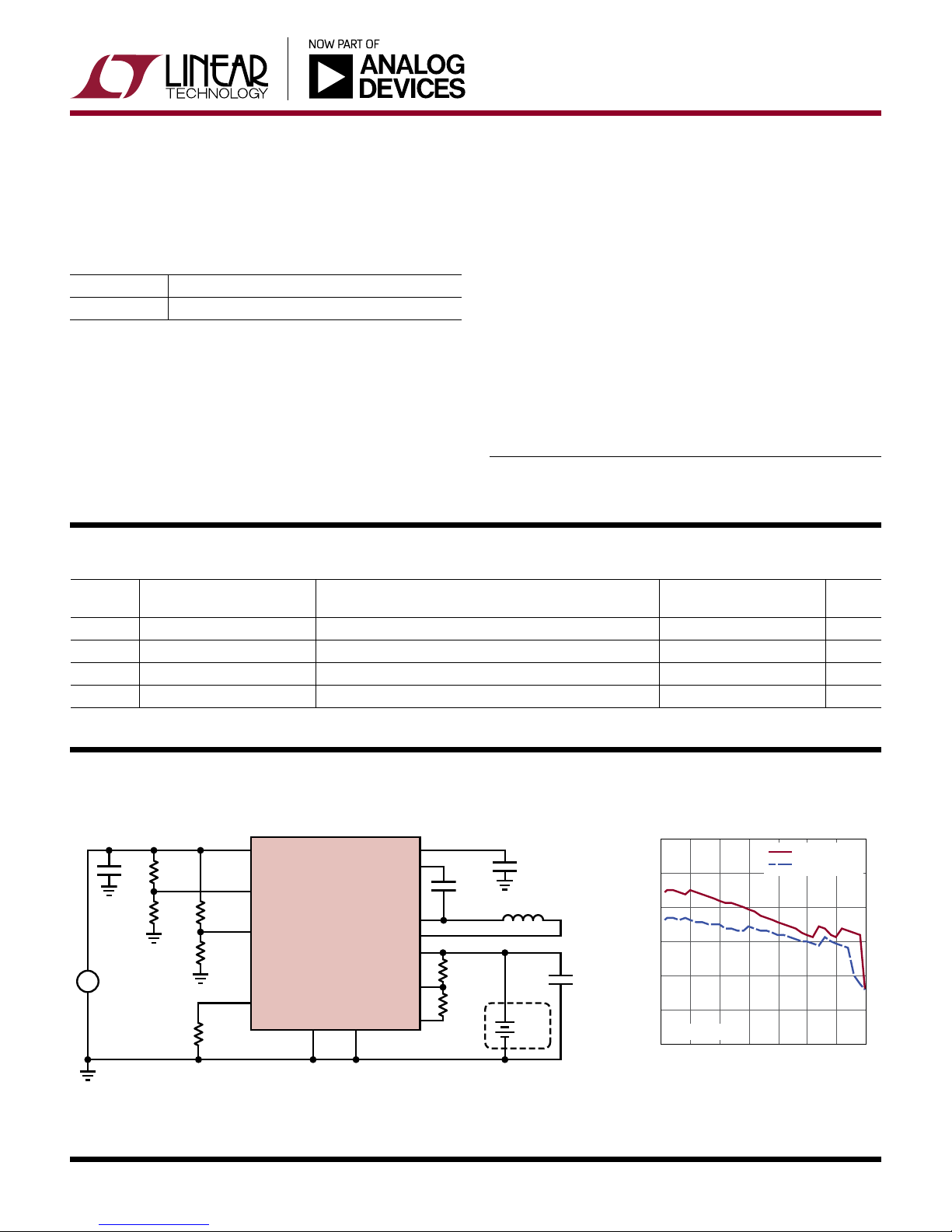
High Efficiency, Wide Input Voltage Range Charging with LTC4121
MPPT1
MPPT2
PROG
IN
RUN
LTC4121
MPPT
PROG
FREQ
C
IN
R
RUN1
10µF
261k
R
R
RUN2
787k
324k
R
V
IN
V
+ 200mV
BAT
TO 40V
121k
R
3.01k
GND
INTV
BOOST
SW
CHGSNS
BAT
FBG
LTC4121 Efficiency vs V
CC
C
BOOST
22nF
R
FB1
1.05M
FB
R
FB2
1.40M
C
INTVCC
2.2µF
LPS4018-333ML
+
Li-Ion
dc1977a F01
C
BAT
47µF
100
95
90
85
EFFICIENCY (%)
80
75
V
BAT
70
5
= 4.1V
10 15 20 25 30 35 40
VIN (V)
R
R
PROG
PROG
IN
= 6.04k
= 3.01k
DC1977A F02
dc1977afb
1
Page 2
DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
assemBly test proceDure
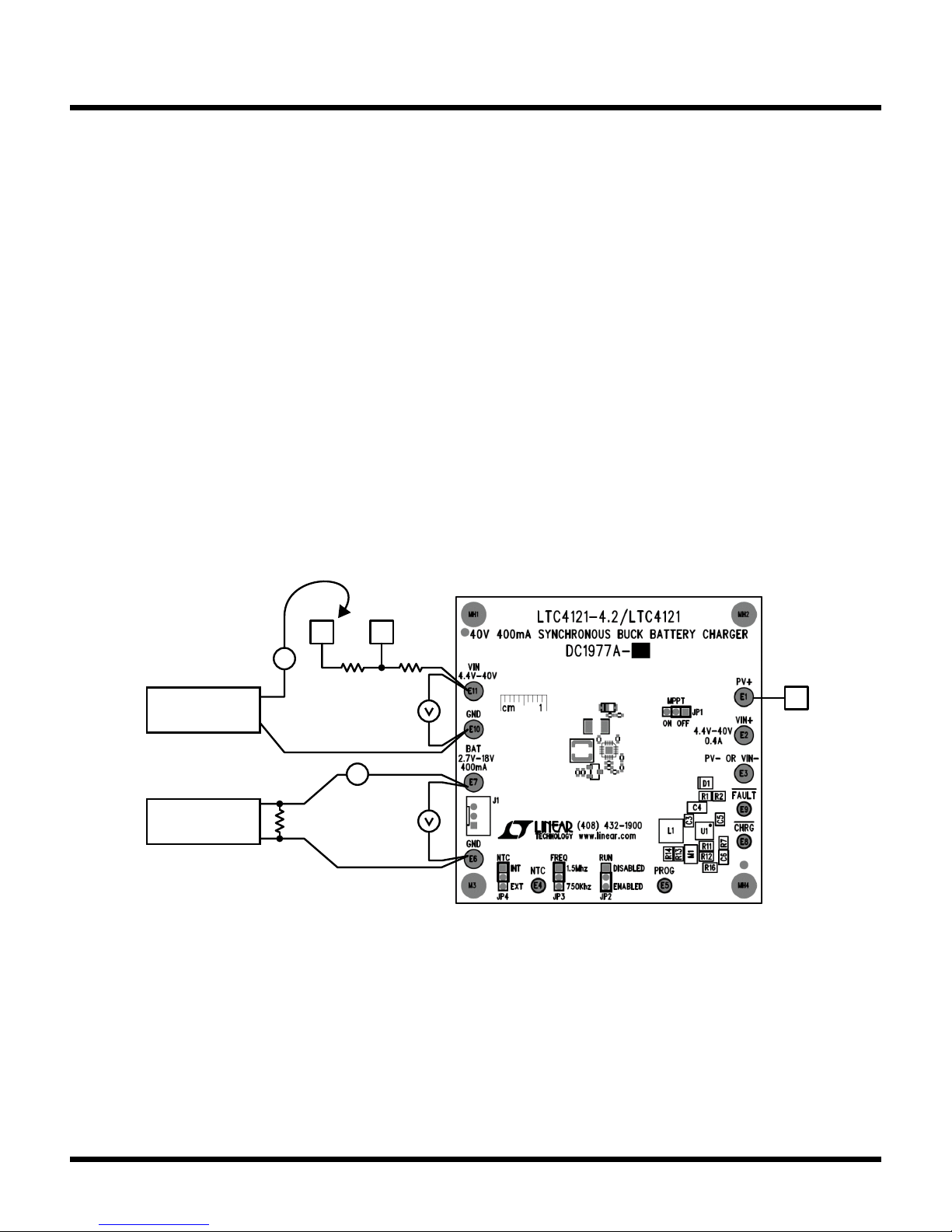
Refer to Figure 1 for the proper measurement equipment
setup and jumper settings and follow the procedure below.
1. Set JP1 (“MPPT”) to ‘ON’, set PS1 to 3.6V and turn
on.
2. Connect PS2 to point A, set to 15V and turn on.
3. Verify that VM1 indicates 3.3V to 3.9V, and then verify
that AM1 indicates 387mA to 417mA. Verify that VM2
shows 14.5V to 15.1V. There is only a series diode
between PV+ and the VIN pin of the LTC4121. The
purpose of this diode is prevent backfeeding a PV
cell, if connected. A single diode Vf is insufficient to
activate the MPPT feature, and the LTC4121 delivers
full charge current to the battery.
4. Turn PS2 off, move connection to point B, and turn
PS2 on.
5. Verify that VM1 indicates 3.3V to 3.9V, and then verify
that AM1 indicates 387mA to 417mA. Verify that VM2
shows 12.6V to 13.2. The source impedance of the
power supply is now ≈ 16Ω. But this impedance still
allows delivering full charge current without engaging
the MPPT feature.
6. Turn PS2 off, move connection to Point C, and turn
PS2 on.
7. Verify that VM1 indicates 3.3V to 3.9V, and then Verify
that AM1 indicates 105mA to 115mA. Verify that VM2
shows 10.6V to 11.3V. The source impedance of the
power supply is now 98Ω. The MPPT feature has
engaged and the charge delivered to the battery has
been reduced to allow V
to stay at the programmed
IN
MPPT point.
8. Set JP1 (“MPPT”) to ‘OFF’, test is finished.
PS2
15V POWER SUPPLY
0.25A
PS1
3.6V BIPOLAR SUPPLY
1A
AM2
+
–
+
–
– +
–
3.6Ω
BC
82.4Ω
2W
AM1
15.8Ω
2W
+
VM2
–
+–
–
+
VM1
–
Figure1. DC1977A Equipment Setup
Note: All connections from equipment should be kelvin-connected directly to the board pins
which they are connected on this diagram. All input or output leads should be twisted pair.
A
DC1977a F03
2
dc1977afb
Page 3

theory of operation
V
1.227V
DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
The LTC4121EUD-4.2/LTC4121EUD is a 4.4V ~ 40V input
buck topology battery charger with maximum power point
tracking (MPPT) for use with PV cells or highly resistive
power supplies. The buck-topology charger uses current
mode control for stable operation.
LTC4121EUD ENABLE
The LTC4121 can be enabled or disabled via the RUN pin,
and this functionality can be accessed via JP2, the RUN
jumper. When JP2 is in the “ENABLE” position, R3 and
R4 ensure that the LTC4121 is not enabled until Vin is
greater than 4.4V.
Note: Do not float the LTC4121 RUN pin. Operate
the demo board with JP2 in either the DISABLED or
ENABLED position.
Buck Charger
The heart of the LTC4121EUD is the buck-topology bat
tery charger. The buck-topology charger is a synchronous,
current-mode-control regulator with N-channel FETs. The
use of N-channel FETs minimizes conduction losses, and
requires only a single external 0.022µF capacitor to generate the high-side gate drive.
The LTC4121EUD can charge up to four Li-Ion cells in
series, and supports a maximum battery voltage of 18V.
The LTC4121EUD-4.2 is optimized for charging a single
Li-Ion cell to a fixed cell voltage of 4.2V.
The current in the buck inductor passes through a small
on-die resistor for current measurement, and then goes
back out to the BAT pin. The battery is connected to the
BAT pin; this allows the LTC4121EUD to measure not only
the cycle-by-cycle current, but also the average current.
The cycle-by-cycle current is used by the current-mode
buck regulator, and the average current is the battery
charge current as programmed by R
= 3.01kΩ, so I(BAT) = 402mA provided that the
R
PROG
MPPT function does not reduce the current.
. On DC1977A,
PROG
-
The buck regulator acts as a current source when the
battery is in the constant-current charging region and as
a classic voltage output buck regulator when the battery
is in the constant-voltage charging region.
The battery charge current is programmed by
R
=3.01kΩ. The equation for R
PROG
R
The LTC4121EUD provides a switching frequency select
pin, FREQ, to select between 750kHz and 1.5MHz; this
function is accessed by JP4, the “FREQ” jumper.
Note: Do not float the LTC4121 FREQ pin. Operate the
demo board with JP3 in either the 750kHz or 1.5MHz
position.
Figure2 shows various nodes of interest with V
and the switching frequency at 750kHz (T = 1.333µs), The
duty cycle is 86% for V(BAT) = 3.6V, not the 72% duty
expected from a buck regulator. When the battery voltage
is 3.6V, the charger is in constant-current mode, so the
control loop is forcing the output of the buck regulator
to the voltage necessary to push 400mA into the battery.
This “effective” voltage, 5 • 0.86 = 4.3V, is the voltage
necessary to ensure that a 400mA average current is flowing through the on-die sense resistor.
Figure3 shows the same nodes as Figure2, but with
VIN = 40V. The switching frequency is still 750kHz. The
duty cycle is ≈ 200ns/1.333µs, or 15%, but the period is
2.7µs. This is because the LTC4121 minimum on time was
greater than that needed to achieve 4.3V, and the LTC4121
starts to pulse skip to get the necessary average duty
cycle. The average duty cycle is 300ns/2.667µs=11%.
This produces an output voltage of 4.3V, so the battery
still charges at 400mA.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
The LTC4121EUD provides a maximum-power-point
tracking (MPPT) function for use with PV cells or highly
PROG
= h
PROG
•
PROG
I
CHG
= 986 •
PROG
0.4
is:
= 3.01kΩ
= 5V,
IN
dc1977afb
3
Page 4

DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
theory of operation
Figure2. Normal Operation, Zoom, VIN = 5.1V, DK. Blue = VIN,
Grn = I
, LT. Blue = VSW, Pk. = INTVCC, 750kHz
CHARGE
resistive power supplies. The MPPT pin allows programming of the MPPT point as a percentage of the opencircuit VIN (VOC). To access this functionality the demo
board provides JP1, the “MPPT” jumper, and R1 and R2.
It is important to note that the disabled position for MPPT
is the MPPT pin at VIN. To enable MPPT, set the MPPT
point as a fraction of VOC. See the discussion in Maximum
Power Point Tracking section of the LTC4121 data sheet.
When MPPT is enabled (not equal to VIN), the LTC4121EUD
periodically disconnects the load from the power source,
and measures V
the load on V
with no load = VOC. It then increases
IN
to meet charger demand until the V
IN
MPPT
threshold is reached, after which it no longer increases
the load. This allows the MPPT voltage divider to set the
desired MPPT point as a percentage of V
with no load.
IN
Figure4 shows the LTC4121EUD operating from a source
impedance of 98Ω. The MPPT pin of the LTC4121EUD
sets the MPPT point to 0.75 of the open-circuit voltage.
First, V
V
IN
until the voltage at V
is determined by removing all load and letting
OC
rise to VOC. The power drawn from VIN is increased
falls to the MPPT point, 0.75 • VOC
IN
= 0.75•15V = 11.25V. The resolution of the MPPT DAC
is 330mV, thus this example has the MPPT point at
11V. The LTC4121 stops drawing power at this point, and
the charge current (green) never exceeds 200mA, even
though the Rprog value was chosen for 400mA.
Figure3. Normal Operation, Zoom, VIN = 40V, DK. Blue = VIN,
Grn = I
, LT. Blue = VSW, Pk. = V
CHARGE
BOOST
4
, 750kHz
Figure5 shows the same system, but the source imped
ance was lowered to 16Ω. Consequently, the full power
needed to meet the requirements of the programmed
charge current is available before VIN falls to the MPPT
voltage.
dc1977afb
Page 5

theory of operation
Battery capacitors C1 and C2
The maximum battery voltage for the LTC4121EUD is
18V, and for the LTC4121EUD-4.2, it is 4.2V. Analog
Devices recommends 47µF of capacitance on the BAT
pin, if the battery is not present. For the LTC4121EUD
the voltage rating of the capacitor will need to be 25V, so
two 22µF, 25V, MLCC capacitors are used. In the case of
the LTC4121EUD-4.2, a 6.3V capacitor will suffice, and
a single 47µF, 6.3V, MLCC capacitor is used for C1, with
C2 not placed.
Reverse-Blocking Circuit
Components Q1, R16 and C6 comprise a reverse-blocking
circuit. The circuit performs two functions. First, the circuit prevents the battery from back-charging the power
source when the power sour
cell in the absence of illumination). Note that this func
tionality can also be provided through D1. Second, when a
charged battery is connected to the circuit in the absence
of input voltage, current will flow from the battery into the
BAT pin and out the IN pin, charging C4. With battery voltages in excess of ~10V, this current surge can destroy the
device. Note that this is not a problem when only one or
two series Li-Ion cells are employed. Thus, this reverseblocking circuit may not be necessary depending on the
application. If reverse-blocking is not required, C6 and
R16 also become unnecessary. These two components
provide a path to the BAT pin from which the LTC4121
derives bias for internal circuits which would be provided
by the battery directly in the absence of Q1. See, for example, the application on the first page of this manual.
ce is dormant (e.g., a solar
-
DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
Figure4. MPPT Test, DK. Blue = VIN (Through 98Ω), Green = IL,
LT. Blue = V(SW), k = 0.15, V
Figure5. MPPT Test, DK. Blue = VIN (Through 16Ω), Green = IL,
LT. Blue = V(SW), k = 0.15, V
MPPT/VOC
MPPT/VOC
= 0.75
= 0.75
dc1977afb
5
Page 6

DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
parts list
ITEM QTY REFERENCE PART DESCRIPTION MANUFACTURER/PART NUMBER
DC1977A General Bill of Materials
Required Circuit Components
1 1 C3 CAP, CHIP, X7R, 0.022µF, ±10%, 50V, 0402 TDK, C1005X7R1E223K
2 1 C4 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 10µF, ±10%, 50V, 1210 TAIYO-YUDEN, UMK325BJ106KM-T
3 1 C5 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 2.2µF, ±20%, 6.3V, 0402 MURATA, GRM155R60J225ME15D
4 1 L1 IND, SMT, 33µH, 420mΩ, ±20%, 0.80A, 4mm × 4mm COILCRAFT, LPS4018-333ML
5 1 R1 RES, CHIP, 787kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW0402787KFKED
6 1 R2 RES, CHIP, 121kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW0402121KFKED
7 1 R3 RES, CHIP, 261kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW0402261KFKED
8 1 R4 RES, CHIP, 324kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW0402324KFKED
9 1 R7 RES, CHIP, 3.01kΩ, ±1, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04023K01FKED
Additional Demo Board Circuit Components
1 1 C6 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 4.7µF, ±20%, 6.3V, 0603 MURATA, GRM188R60J475KE19D
2 1 D1 DIODE, SCHOTTKY, 40V, 2A, PowerDI123 DIODES, DFLS240L
3 1 M1 MOSFET, P-Channel, –30V, –5.9A, 45mΩ, SOT-23 VISHAY, Si2343CDS
4 2 R5, R9 RES, CHIP, 10kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW040210K0FKED
5 1 R6 RES, CHIP, 2kΩ, ±5%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04022K00JNED
6 2 R8, R10 RES, CHIP, 0Ω jumper, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04020000Z0ED
7 1 R13 RES, CHIP, 47kΩ, ±5%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW040247K0JNED
8 1 R14 RES, CHIP, 5.1kΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04025K10JNED
9 1 R15 RES, CHIP, 100kΩ, ±5%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW0402100KJNED
10 1 R16 RES, CHIP, 464kΩ, ±1%, 1/10W, 0603 YAGEO, RC0603FR-07464KL
Hardware: For Demo Board Only
1 7 E1, E2, E3, E6, E7, E10, E11 TURRET, 0.09 DIA MILL-MAX, 2501-2-00-80-00-00-07-0
2 4 E4, E5, E8, E9 TURRET, 0.061" MILL-MAX, 2308-2-00-80-00-00-07-0
3 0 J1-OPT CONN, 3 Pin Polarized HIROSE, DF3-3P-2DSA
4 4 JP1-JP4 HEADER, 3 Pin, SMT, 2mm SULLIN, NRPN031PAEN-RC
5 4 JP1-JP4 SHUNT, 2mm SAMTEC, 2SN-BK-G
ITEM QTY REFERENCE PART DESCRIPTION MANUFACTURER/PART NUMBER
DC1977A-A Bill of Materials
Required Circuit Components
1 0 R11 DO NOT INSTALL
2 1 R12 RES, CHIP, 0Ω jumper, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04020000Z0E
3 1 U1 40V 400mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN BATTERY
1 1 C1 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 47µF, ±10%, 16V, 1210 MURATA, GRM32ER61C476KE15L
2 0 C2 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 47µF, ±10%, 16V, 1210 MURATA, GRM32ER61C476KE15L
ITEM QTY REFERENCE PART DESCRIPTION MANUFACTURER/PART NUMBER
DC1977A-B Bill of Materials
Required Circuit Components
1 1 R11 RES, CHIP, 1.40MΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04021M40FKE
2 1 R12 RES, CHIP, 1.05MΩ, ±1%, 1/16W, 0402 VISHAY, CRCW04021M05FKED
3 1 U1 40V, 400mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN BATTERY
1 2 C1, C2 CAP, CHIP, X5R, 47µF, ±10%, 16V, 1210 MURATA, GRM32ER61C476KE15L
6
CHARGER, 3mm × 3mmQFN16
LINEAR TECH., LTC4121EUD-4.2#PBF
LINEAR TECH., LTC4121EUD#PB
CHARGER, 3mm × 3mmQFN16
dc1977afb
Page 7

schematic Diagram
1
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION DATEAPPROVEDECO REV
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION DATEAPPROVEDECO REV
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION DATEAPPROVEDECO REV
-
-
-
2
VIN
4.4V - 40V
E11
C4
10uF
GND
E10
E9
5%
R15
100k
50V
1210
U1
LTC4121EUD-4.2 / LTC4121EUD
3
FAULT
IN
JP2
DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
1
1
1
1
1
1
CHRG
E8
R14
5.1k
5%
6.3V
20%
C5
2.2uF
INTVCC
C3
0.022µF
25V
1
2
INTVcc
BOOST
4
sw
FREQ
7
14
15
CHRG
FAULT
RUN
16
BAT
2.7V - 18V
E7
R12 TO BE CONNECTED TO C2 & C3
R13
47k
5%
Q1
Si2343DS
L1
33.0uH
8
9
BAT
CHGSNS
MPPT
6
JP3
R16
12
400mA
E6
464k
C6
NTC
6.3V
GND
0603
*
*
C2
C1
4.7uF
0603
BATSNS/FB
10
OPT
J1
DF3-3P-2DSA
BAT1GND2ENTC
3
www.linear.com
www.linear.com
0 Ohm
JUMPER
R10
www.linear.com
1
1
1
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
OPEN47µF/16V
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
C1 C2
22µF/25V 22µF/25V
R12
0 OhmOPEN
R11
1.40M 1.05M
*
R12
*
R11
11
NC/FBG
17
EPAD
5
GND
PROG
13
R7
3.01k
U1
LTC4121EUD
LTC4121EUD - 4.2
-B
-A
ASSY
*
UNLESS NOTED:
RESISTORS: OHMS, 0402, 1%, 1/16W
CAPACITORS: uF, 0402, 10%, 50V
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
BATTERY CHARGER
40V 400mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN
40V 400mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN
40V 400mA SYNCHRONOUS STEP-DOWN
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC
TITLE:
TITLE:
TITLE:
NC
WAT
NC
WAT
NC
WAT
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
1
DEMO CIRCUIT 1977A - A / B
DEMO CIRCUIT 1977A - A / B
DEMO CIRCUIT 1977A - A / B
LTC4121EUD - 4.2 / LTC4121EUD
LTC4121EUD - 4.2 / LTC4121EUD
LTC4121EUD - 4.2 / LTC4121EUD
2017-02-22
2017-02-22
2017-02-22
IC NO. REV.
IC NO. REV.
IC NO. REV.
N/A
N/A
N/A
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
DATE:
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
2
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
3
R3
261k
R1
787k
D1
DFLS240L
4
E1
E2
PV+
VIN +
4.4V - 40V
4 4
0.4A
RUN
E3
PV- or Vin-
Information furnished by Linear Technology Corporation is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed for its use. Linear Technology Corporation makes no representation that the interconnection of its circuits as described herein will not infringe on existing patent rights.
ENABLED
DISABLED
R4
324k
R2
121k
INTVCC
JP1
MPPT
FREQ
750 kHz
1.5 MHz
R5
10.0k
ON
OFF
5%
R6
2.0k
E4
3 3
NTC
E5
PROG
2 2
JP4
NTC
EXT
INT
R8
0 Ohm
JUMPER
R9
10.0k
1 1
3
4
dc1977afb
7
Page 8

DEMO MANUAL
DC1977A-A/DC1977A-B
DEMONSTRATION BOARD IMPORTANT NOTICE
Linear Technology Corporation (LTC) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following AS IS conditions:
This demonstration board (DEMO BOARD) kit being sold or provided by Linear Technology is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT
OR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY and is not provided by LTC for commercial use. As such, the DEMO BOARD herein may not be complete
in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective considerations, including but not limited to product safety
measures typically found in finished commercial goods. As a prototype, this product does not fall within the scope of the European Union
directive on electromagnetic compatibility and therefore may or may not meet the technical requirements of the directive, or other regulations.
If this evaluation kit does not meet the specifications recited in the DEMO BOARD manual the kit may be returned within 30 days from the date
of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY THE SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THIS INDEMNITY, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER FOR
ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user releases LTC from all claims
arising from the handling or use of the goods. Due to the open construction of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to take any and all
appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic discharge. Also be aware that the products herein may not be regulatory compliant or
agency certified (FCC, UL, CE, etc.).
No License is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property whatsoever. LTC assumes no liability for applications assistance,
customer product design, software performance, or infringement of patents or any other intellectual property rights of any kind.
LTC currently services a variety of customers for products around the world, and therefore this transaction is not exclusive.
Please read the DEMO BOARD manual prior to handling the product. Persons handling this product must have electronics training and
observe good laboratory practice standards. Common sense is encouraged.
This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and voltages. For further safety concerns, please contact a LTC application
engineer.
Mailing Address:
Linear Technology
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
Milpitas, CA 95035
Copyright © 2004, Linear Technology Corporation
8
dc1977afb
LT 0817 REV B • PRINTED IN USA
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 2014
 Loading...
Loading...