Page 1
Description
DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
LTC7860
High Voltage Switching
Surge Stopper
Demonstration circuit 2392A is a high efficiency switching
®
surge stopper featuring the LT C
7860. The board operates
from an input range of 7V to 100V, and provides a 7V to
34V output at 0A to 10A. Its output is current limited. A
soft-start feature controls output voltage slew rate at startup, reducing current surge and voltage overshoot. The
demonstration board includes an optional reverse polarity
protection MOSFET and has options for an input filter and
diode to attenuate spikes. For a lower output voltage limit
of less than 12V, there is an optional feedback circuit.
The LTC7860 high efficiency surge stopper protects loads
from high voltage transients. High efficiency compared to
linear circuits permits higher currents and smaller solution
sizes. During an input overvoltage event, such as a load
dump in vehicles, the LTC7860 controls the gate of an
external MOSFET to act as a switching DC/DC regulator
(PROTECTIVE PWM mode). This operation regulates the
output voltage to a safe level, allowing the loads to oper
ate through the input overvoltage event. During normal
operation (SWITCHON mode), the
LTC7860
turns on the
external MOSFET continuously, passing the input voltage
through to the output. An internal comparator limits the
voltage across the current sense resistor and regulates the
maximum output current to protect against overcurrent
faults. An adjustable timer limits the time that the LTC7860
can spend in overvoltage or overcurrent regulation. When
the timer expires, the external MOSFET is turned off until
the LTC7860 restarts after a cool down period. By strictly
limiting the time in PROTECTIVE PWM mode when the
power loss is higher, the components and thermal design
can be optimized for normal operation and safely oper
ate through high voltage input surges and/or overcurrent
faults. This demo board takes advantage of the LTC7860’s
-centric PMOS architecture to float the control ground
V
IN
allowing operation beyond the controller’s 60V rating.
This board is suitable for a wide range of automotive,
military, telecom, industrial, and other applications. The
LTC7860 is available in a small 12-pin thermally enhanced
MSOP package. For other output requirements, see the
LTC7860 data sheet or contact the LTC factory.
Design files for this circuit board are available at
http://www.linear.com/demo/DC2392A
L, LT, LTC, LTM, Linear Technology and the Linear logo are registered trademarks of Linear
Technology Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
performance summary
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
V
IN
V
OUT
I
OUT
I
LIMIT
I
LIMIT
V
IN-VOUT
F
SW
T
PWM
V
OUT P-P
Input Supply Range Normal Operation 7 32 V
Output Voltage 7 28 35 V
Output Current Range, continuous Free Air 0 10 A
Current Limit VIN = 28V 13 A
Current Limit VIN = 40V 10.5 A
Insertion Loss VIN = 28V, I
Switching (Clock) Frequency 350 kHz
PROTECTIVE PWM Mode Time Limit VIN > 35V 0.85 1.06 1.24 s
Output Ripple VIN = 40V, V
Approximate Size Component Area x Top Component Height 35 × 42 × 10 mm
Specifications are at TA = 25°C
500ms Ride-Through 7 100 V
DC Survival 0 100 V
= 10A 400 mV
OUT
= 17.2V, I
OUT
= 5A (20MHz BW) 100 mV
OUT
P–P
dc2392af
1
Page 2

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
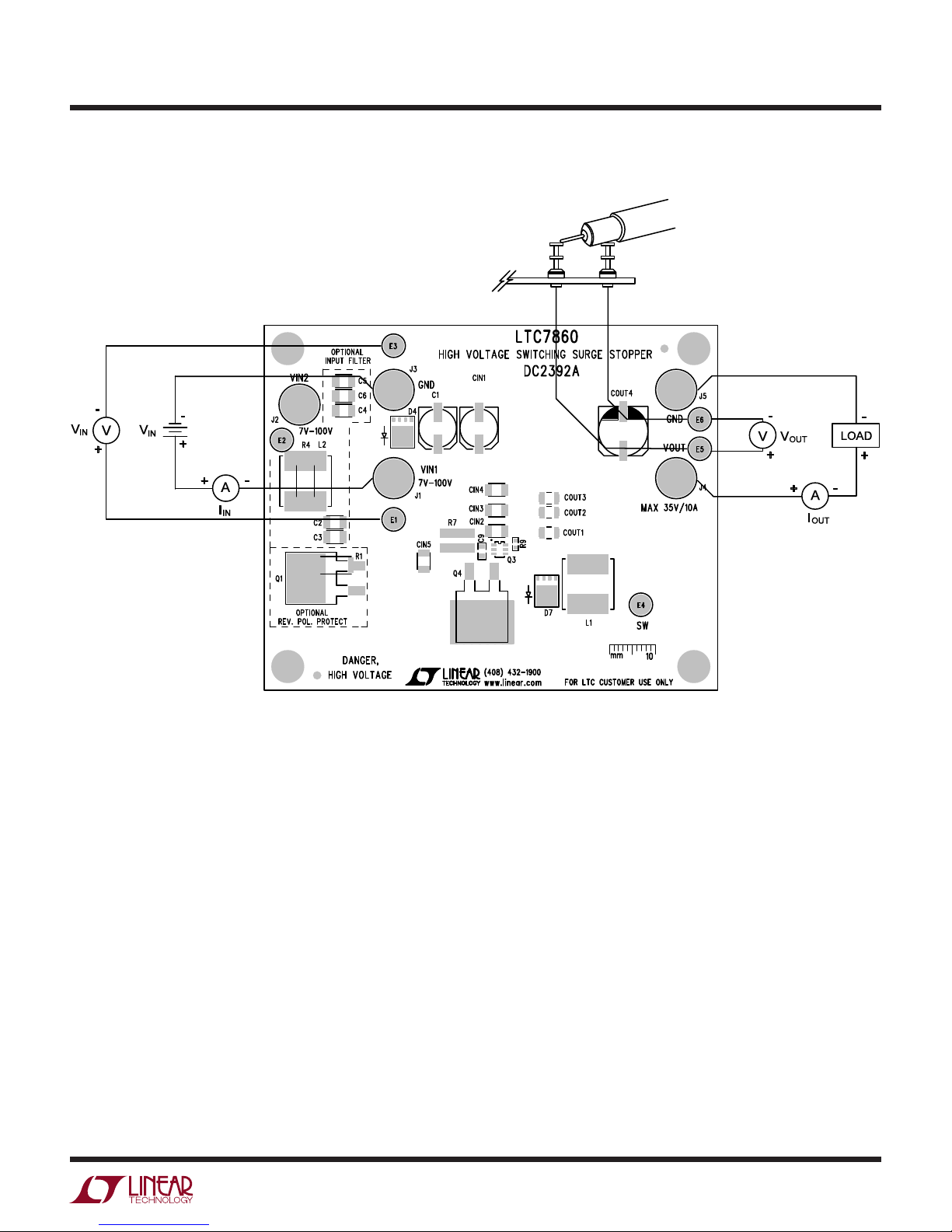
Quick start proceDure
Demonstration circuit 2392 is easy to set up to evaluate
the performance of the LTC7860. Refer to Figure 1 for
proper measurement equipment setup and follow the
procedure below:
NOTE: When measuring the output voltage ripple, care must
be taken to avoid a long ground lead on the oscilloscope
probe. Measure the output voltage ripple by touching the
probe tip and ground ring directly across the last output
capacitor as shown in Figure 1.
1. Set an input power supply that is capable of 7V to
100V to 10V. Then turn off the supply.
2. With power off, connect the supply to the input termi
nals +VIN and –VIN.
a. Input Voltages lower than 7V can keep the converter
from turning on due to the undervoltage lockout feature
of the LTC7860.
b. A voltmeter with a capability of measuring at least 100V
can be placed across the input terminals in order to
get an accurate input voltage measurement.
3. Turn on the power at the input.
-
5. Once the proper output voltage is established, connect
a variable load capable of sinking 10A at 34V to the
output terminals +V
0A.
a. A Voltmeter with a capability of measuring at least 36V
can be placed across the output terminals in order to
get an accurate output voltage measurement.
6. Turn on the power at the input.
NOTE: If there is no output, temporarily disconnect the
load to make sure that the load is not set too high.
7. Once the proper output voltage is again established,
adjust the load and/or input within the operating range
up to 33V
desired parameters.
8. Now apply an input between 35V and 100V and observe the output voltage and fault timer operation.
9. If desired, you may apply input transient profiles in
the range of 0V
to illustrate operation of the circuit to prevent input
surges from reaching the output.
and observe the output voltage and other
IN
IN
and –V
OUT
to 100VIN and observe the output
. Set the current for
OUT
NOTE: Make sure that the input voltage never exceeds
100V.
4. Check for the proper output voltage of 10V. Turn off
the power at the input.
10. The output limit voltage can be set in accordance
with the feedback notes on the schematic. The first
line shows the complete formula. The second line is
simplified for the use of a 2:1 divider as shown on the
schematic.
2
dc2392af
Page 3
Quick start proceDure
DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
Figure 1. Proper Measurement Equipment Setup
dc2392af
3
Page 4

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
DC2392A F03
Quick start proceDure
V
100V
IN
V
OUT
0V
TIME
DC2392A F02
Figure 2. Output Response Waveform with 28V to 100V
to 28V Input Surge, (10A
100
98
96
94
92
5A
90
EFFICIENCY (%)
88
86
84
6
OUT
10A
OUT
10A
OUT-PD
10 100
) (20V, 20V, 10ms/DIV)
OUT
V
IN
40
35
POWER DISSIPATION (W)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Figure 3. Efficiency and Power Dissipation
4
dc2392af
Page 5

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
parts List
ITEM QTY REFERENCE PART DESCRIPTION MANUFACTURER/PART NUMBER
Required Circuit Components
1 1 CIN1 CAP., ALUM, 15µF, 100V 8X12 PANASONIC, 100SXV15M
2 4 CIN2, CIN3, CIN4, CIN5 CAP., X7R, 2.2µF, 100V, 10%, 1210 MURATA, GCJ32DR72A225KA01L
3 3 COUT1, COUT2, COUT3 CAP., X7S, 10µF, 50V, 10%, 1210 MURATA, GCM32EC71H106KA01L
4 1 COUT4 CAP., ALUM 150µF 50V 10x10 SUN ELECTRONIC INDUSTRIES CORP., 50CE150AX
5 1 C9 CAP., X7R, 1µF, 50V, 10%, 0805 MURATA, GCM21BR71H105KA01L
6 1 C10 CAP., X7R, 22µF, 10V, 10%, 1206 MURATA, GCM31CR71A226KE01L
7 1 C11 CAP., NPO, 100pF, 50V, 10%, 0603 AVX, 06035A101KAT2A
8 1 C12 CAP., X7R, 0.1µF, 50V, 10%, 0603 MURATA, GCM188R71H104KA57D
9 1 C13 CAP., X7R, 0.47µF, 16V, 10%, 0603 MURATA, GCM188R71C474KA55L
10 1 C14 CAP., X7R, 0.1µF, 50V, 10%, 0805 MURATA, GCM21BR71H104KA37L
11 1 C15 CAP., COG, 47pF, 50V, 5%, 0603 MURATA, GCM1885C1H470JA16D
12 1 C17 CAP., COG, 3300pF, 50V, 5%, 0603 MURATA, GCM1885C1H332JA16D
13 1 C18 CAP, 1.5nF, X7R, 50V,10%,0603 AVX, 06035C152KAT2A
14 1 D1 ZENER DIODE, 500mW, SOD123 ON SEMI, SZMMSZ5242BT1G/T3G
15 1 D7 SCHOTTKY DIODE, 100V, 10A, DFN5-SO-8FL ON SEMI, NRVTS10100MFST1G
16 1 D8 SWITCH DIODE, SOD323 ON SEMI., SMMDL914T1G
17 1 L1 INDUCTOR, 10µH COILCRAFT, XAL1010-103ME
18 2 Q1, Q4 FET, P-CHAN.,100V, TO-263 VISHAY, SUM90P10-19L-E3
19 1 Q2 FET, P-CHAN., POWER, TO-252 ON SEMI, SFT1345-TL-H
20 1 Q3 DIODE, IGBT MOSFET 10A, SOT23-6 DIODES INC., ZXGD3005E6TA
21 1 Q6 FET, NPN, SOT23 ON SEMI, SMMBTA42LT1G
22 2 R3, R13 RES., 100k, 1/8W, 1%, 0805 VISHAY, CRCW0805100KFKEA
23 1 R5 RES., 35.7k, 1/10W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW060335K7FKEA
24 2 R6, R8 RES., 100Ω, 1/10W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW0603100RFKEA
25 1 R7 RES., 6m, 3W, 1%, 1225 SUSUMU, KRL6432E-M-R006-F-T1
26 1 R9 RES., 1.0k, 1/10W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW06031K00FKEA
27 1 R16 RES., 10Ω, 1/10W, 5%, 0805 VISHAY, CRCW080510R0JNEA
28 2 R17, R19 RES., 10k, 1/16W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW060310K0FKEA
29 2 R24, R26 RES., 31.6k, 1/10W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW060331K6FKEA
30 1 R25 RES., 205k, 1/16W, 1%, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW0603205KFKEA
31 1 U1 IC, LTC7860EMSE MSE12 LINEAR TECH.CORP. LTC7860EMSE#PBF
Additional Demo Board Circuit Components
1 0 C1 CAP., OPT 8×12 OPT
2 0 C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C8 CAP., OPT 1210 OPT
3 0 C7, C16 CAP., OPT 0603 OPT
4 0 D2, D3, D5 ZENER DIODE, OPT SOD123 OPT
5 0 D4
6
7 0 L2 INDUCTOR, 1µH OPT
8 0 L3 INDUCTOR, 0.6µH OPT
0 D6 ZENER DIODE, OPT, SOD323 OPT
DIODE, OPT, DFN5-SO-8FL OPT
dc2392af
5
Page 6

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
parts List
ITEM QTY REFERENCE PART DESCRIPTION MANUFACTURER/PART NUMBER
9 0 Q4 HEATSINK, OPT, 573100D00010G OPT
10 0 Q5 OPT, SOT363 OPT
11 0 R1, R2, R29 RES., OPT, 2512 OPT
12 3 R11, R14, R21 RES., 0Ω, 1/16W, 0603 VISHAY, CRCW06030000Z0EA
13 1 R4 RES., 1mΩ, 1%, 1W, 2512 PANASONIC, ERJ-M1WTF1M0U
14 0 R12 RES., OPT, 0805 OPT
15 0 R10, R15, R18, R20,
R22, R23, R27, R28
Hardware: For Demo Board Only
1 6 E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6 TESTPOINT, TURRET, .094" MILL MAX, 2501-2-00-80-00-00-07-0
2 5 J1, J2, J3, J4, J5 CONN, BANANA JACK, KEYSTONE 575-4
3 4 MTGS AT 4 CORNERS STAND-OFF, SNAP ON NYLON 0.50" TALL KEYSTONE, 8833(SNAP ON)
RES., OPT, 0603 O PT
6
dc2392af
Page 7

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
5
4
3
2
1
12
12
12
schematic Diagram
2
2
DATE
DATE
DATE
DBPRODUCTION2 09-29-15
DBPRODUCTION2 09-29-15
DBPRODUCTION2 09-29-15
APPROVED
APPROVED
APPROVED
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
REV
REV
REV
__
__
__
ECO
ECO
ECO
3W
R76m1225
R8
100
R9
C9
Q3
1K
SW
E4
Q4
SUM90P10-19L
1uF
0805
50V
4
2
ZXGD3005E6TA
VOUT
VOUT
J4
E5
VOUT
L1
10uH
316
5
COUT3
COUT2
XAL1010-103
10Aout,
COUT4
+
COUT1
D7
R15
Limited at 34V
150uF
GND
E6
J5
10X10
50V
50CE150AX
1210
10uF
50V
100V
10A
NRVTS10100MFST
R16100805
VIN-10V
OPT
GND
CAP
28V
100V
7.0V-32.0V
100V, 500ms
NOMINAL INPUT
INPUT DC SURVIVAL
SURGE RIDE-THROUGH
OUTPUT VOLTAGE LIMIT 34.0V
INPUT OPERATING RANGE
www.linear.com
www.linear.com
www.linear.com
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
LT
LT
LT
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
2
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
1
DC2392A
LTC7860EMSE
LTC7860EMSE
LTC7860EMSE
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
IC NO. REV.
IC NO. REV.
IC NO. REV.
SCHEMATIC
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
SCHEMATIC
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
SCHEMATIC
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
N/A
N/A
N/A
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
TITLE:
TITLE:
TITLE:
DB
DB
DB
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
DATE:
2
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
R6
100
R28
OPT
C11
12
U1
LTC7860EMSE
1
R10 OPT
C10 22uF
VIN-10V
Q2
C C
11
GATE
FREQ
1206
D5
R12
SFT1345
100pF
VIN
FREQ2TMR
OPT
OPT
R13
R11 0
0805
100K
10
3
0805
CAP
9
SENSE
C12 0.1uF
CAP
C14
C13
8
RUN
VFB5SS4SGND
VIN-10V
D6
0.1uF
50V
0.47uF
7
6
OPT
R14
0805
16V
VFBN
ITH
0
PGND
VIN-10V
13
R17
10K
VIN
C16
C15
VIN-10V
OPT
C17
47pF
R19
10K
R18
3.3nF
OPT
VFB
VIN-10V
R20
FREQ
SMMDL914
OPT
D8
VIN-10V
R21
0
B B
Q6C
C18
1.5nF
R24
31.6K
Q6
SMMBTA42L
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
CAUTION, SHOCK HAZARD: CONTACT WITH HIGH VOLTAGE
CAN RESULT IN A DANGEROUS ELECTRIC SHOCK.
R26
31.6K
R25
205K
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
Feedback Notes
V-limit = ( R24 + R26 ) / R26 * ( 0.8V / R19 * R25 + Q6Vbe )
= 2 * ( 0.8 / 10K * 205K + 0.6 ) = 34.0Vnominal
NOTE: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED:
ALL RESISTORS ARE 0603.
ALL CAPACITORS ARE 0603 50V.
150uF 50V Suncon 50CE150AX (10x10mm)
15uF 100V Panasonic 100SXV15M (8x12mm)
2.2uF 100V Murata GCJ32DR72A225KA01L
A A
10uF 50V Murata GCM32EC71H106KA01L
22uF 10V Murata GCM31CR71A226KE01L
10uH Coilcraft XAL1010-103ME
0.006 Susumu KRL6432E-M-R006-F-T1
3
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
4
5
D3
OPT
D2
OPT
C7
R3
CIN4
2.2uF
CIN5
2.2uF
CIN3
2.2uF
CIN2
2.2uF
C1
OPT
+
CIN1
15uF
+
7V - 100V
100K
100V
0805
100V
100V
8X12
8x12
J3
R5
1210
1210
1210
1210
100SXV15M
GND
OPT
35.7K
E3
GND
VIN-10V
C8
OPT
1210
D1
SZMMSZ5242B
VIN
J1
E1
VIN1
VIN1
D D
dc2392af
7
Page 8

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
5
4
3
2
1
22
22
22
schematic Diagram
2
2
2
C4
OPT
C2
7V - 100V
C6
C5
OPT
C3
OPT
D4
VIN2
E2
OPT
1210
100V
OPT
1210
100V
OPT
1210
100V
R41m2512
1210
1210
100V
CAP
OPT
www.linear.com
www.linear.com
www.linear.com
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
LT
LT
LT
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
PCB DES.
1
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
SHEET OF
DC2392A
DC2392A
DC2392A
LTC7860EMSE
LTC7860EMSE
LTC7860EMSE
2
Monday, November 16, 2015
Monday, November 16, 2015
Monday, November 16, 2015
IC NO. REV.
IC NO. REV.
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC
TITLE:
TITLE:
TITLE:
DB
DB
DB
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
APP ENG.
IC NO. REV.
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
N/A
N/A
N/A
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
DATE:
SIZE
DATE:
3
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
SCALE = NONE
VIN2
J2
PROTECTED )
( REVERSE POLARITY
R29
OPT
2512
R2
OPT
2512
OPT
0.6uH
OPT
2512
L2
1uH
Q1
SUM90P10-19L
L3
OPTIONAL INPUT FILTER
R1
OPTIONAL
VIN
REV. POL. PROTECT
OPTIONAL
INPUT FILTER
R23
OPT
4
VIN
D D
R22
Q5
OPT
BC857BS
16
8
4
R27
OPT
3
5
2
VIN-10V
FOR VOUT < 12V
OPTIONAL FEEDBACK CIRCUIT
VFB
Q6C
C C
B B
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
A A
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
5
dc2392af
Page 9

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
GND
CAUTION, SHOCK HAZARD: CONTACT WITH HIGH VOLTAGE
OPTIONAL REVERSE POLARITY PROTECTION
0805
3W
CAN RESULT IN A DANGEROUS ELECTRIC SHOCK.
DC2392 - Simplified
7V - 100Vin
VIN1
16V
100V
100SXV15M
7V - 100V
GND
10Aout
Limited at 34V
100V
VIN2
100V
50V
50V
10A
VOUT
8x12
50V
50V
0805
12V
0805
FLOATING
GROUND
(INPUT DC SURVIVAL = -100V to +100V)
7.0V-32.0V
100V
100V, 500ms
NOMINAL INPUT
INPUT DC SURVIVAL
INPUT OPERATING RANGE
28V
SURGE RIDE-THROUGH
OUTPUT VOLTAGE LIMIT
34.0V
Feedback Notes
V-limit = ( R24 + R26 ) / R26 * ( 0.8V / R19 * R25 + Q6Vbe )
= 2 * ( 0.8 / 10K * 205K + 0.6 ) = 34.0Vnominal
NOTE: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED:
ALL RESISTORS ARE 0603.
ALL CAPACITORS ARE 0603 50V.
150uF 50V Suncon 50CE150AX (10x10mm)
15uF 100V Panasonic 100SXV15M (8x12mm)
2.2uF 100V Murata GCJ32DR72A225KA01L
10uF 50V Murata GCM32EC71H106KA01L
22uF 10V Murata GCM31CR71A226KE01L
10uH Coilcraft XAL1010-103ME
0.006 Susumu KRL6432E-M-R006-F-T1
+VIN
+VIN
CAP
CAP
+VOUT
+VOUT
VIN-10V
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
DATE
APPROVED
ECO
REV
DAVID B.PROTOTYPE2 09-29-15
__
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
DATE
APPROVED
ECO
REV
DAVID B.PROTOTYPE2 09-29-15
__
REVISION HISTORY
DESCRIPTION
DATE
APPROVED
ECO
REV
DAVID B.PROTOTYPE2 09-29-15
__
SIZE
DATE:
IC NO. REV.
SHEET OF
TITLE:
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
APP ENG.
TECHNOLOGY
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SCHEMATIC
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
SCALE = NONE
www.linear.com
2
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
11
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
LT
DAVID B.
N/A
LTC7860EMSE
SIZE
DATE:
IC NO. REV.
SHEET OF
TITLE:
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
APP ENG.
TECHNOLOGY
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SCHEMATIC
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
SCALE = NONE
www.linear.com
2
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
11
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
LT
DAVID B.
N/A
LTC7860EMSE
SIZE
DATE:
IC NO. REV.
SHEET OF
TITLE:
APPROVALS
PCB DES.
APP ENG.
TECHNOLOGY
Fax: (408)434-0507
Milpitas, CA 95035
Phone: (408)432-1900
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
LTC Confidential-For Customer Use Only
CUSTOMER NOTICE
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY HAS MADE A BEST EFFORT TO DESIGN A
CIRCUIT THAT MEETS CUSTOMER-SUPPLIED SPECIFICATIONS;
HOWEVER, IT REMAINS THE CUSTOMER'S RESPONSIBILITY TO
VERIFY PROPER AND RELIABLE OPERATION IN THE ACTUAL
APPLICATION. COMPONENT SUBSTITUTION AND PRINTED
CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT MAY SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECT CIRCUIT
PERFORMANCE OR RELIABILITY. CONTACT LINEAR
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS ENGINEERING FOR ASSISTANCE.
THIS CIRCUIT IS PROPRIETARY TO LINEAR TECHNOLOGY AND
SCHEMATIC
SUPPLIED FOR USE WITH LINEAR TECHNOLOGY PARTS.
SCALE = NONE
www.linear.com
2
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
11
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING SURGE STOPPER
LT
DAVID B.
N/A
LTC7860EMSE
Q3
ZXGD3005E6TA
+
CIN1
15uF
R3
100K
R26
31.6K
D8
SMMDL914
C13
0.47uF
CIN2,3,4,5
4x2.2uF
1210
C17
3.3nF
R24
31.6K
C18 1.5nF
Q4
SUM90P10-19L
D7
NRVTS10100MFST
C9
1uF
0805
R16
10
U1
LTC7860EMSE
VFB
5SS4
SGND
3
FREQ
2
TMR
1
PGND
13
SENSE
10
CAP
9
RUN
8
VFBN
7
ITH
6
VIN
11
GATE
12
R9
1K
R8
100
R13
100K
R6
100
Q6
SMMBTA42L
C15
47pF
C12 0.1uF
R25
205K
COUT1,2,3
3x10uF
1210
R17
10K
C14
0.1uF
0805
+
COUT4
150uF
Q1
SUM90P10-19L
R19
10K
L1
10uH
R7
0.006
1225
J4
Q2
SFT1345
R5
35.7K
D1
SZMMSZ5242B
C11
100pF
C10 22uF
10V
schematic Diagram
Information furnished by Linear Technology Corporation is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed for its use. Linear Technology Corporation makes no representation that the interconnection of its circuits as described herein will not infringe on existing patent rights.
dc2392af
9
Page 10

DEMO MANUAL DC2392A
DEMONSTRATION BOARD IMPORTANT NOTICE
Linear Technology Corporation (LTC) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following AS IS conditions:
This demonstration board (DEMO BOARD) kit being sold or provided by Linear Technology is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT
OR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY and is not provided by LTC for commercial use. As such, the DEMO BOARD herein may not be complete
in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective considerations, including but not limited to product safety
measures typically found in finished commercial goods. As a prototype, this product does not fall within the scope of the European Union
directive on electromagnetic compatibility and therefore may or may not meet the technical requirements of the directive, or other regulations.
If this evaluation kit does not meet the specifications recited in the DEMO BOARD manual the kit may be returned within 30 days from the date
of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY THE SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THIS INDEMNITY, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER FOR
ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user releases LTC from all claims
arising from the handling or use of the goods. Due to the open construction of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to take any and all
appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic discharge. Also be aware that the products herein may not be regulatory compliant or
agency certified (FCC, UL, CE, etc.).
No License is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property whatsoever. LTC assumes no liability for applications assistance,
customer product design, software performance, or infringement of patents or any other intellectual property rights of any kind.
LTC currently services a variety of customers for products around the world, and therefore this transaction is not exclusive.
Please read the DEMO BOARD manual prior to handling the product. Persons handling this product must have electronics training and
observe good laboratory practice standards. Common sense is encouraged.
This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and voltages. For further safety concerns, please contact a LTC application
engineer.
Mailing Address:
Linear Technology
1630 McCarthy Blvd.
Milpitas, CA 95035
Copyright © 2004, Linear Technology Corporation
Linear Technology Corporation
10
1630 McCarthy Blvd., Milpitas, CA 95035-7417
(408) 432-1900 ● FAX: (408) 434-0507 ● www.linear.com
dc2392af
LT 1215 • PRINTED IN USA
© LINEAR TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 2015
 Loading...
Loading...