Page 1
(
)
)
RS-422/485 PCI Card
User Manual English
No. 51202 (4 Port
No. 51200
2 Port)
No. 51204 (8 Port
www.lindy.com
© LINDY ELECTRONICS LIMITED & LINDY-ELEKTRONIK GMBH - SECOND EDITION (Nov 2005)
Page 2

Page 3

1.0 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the LINDY RS-422/485 Controller. This PCI serial
card enables your computer to support serial RS-422/485 ports with 128Kbyte
FIFO, Auto Identify and Switch RS-422/485 and ARSC™ technology.
2.0 Packing List
Please check if the following items are present and in good condition upon
opening the packaging. Contact your vendor if any items are damaged or
missing.
1. Hardware:
Serial Communication Board: LINDY PCI Host Controller × 1
Cables:
4 Port, No.51202 : DB37 Male to 4 Port DB9 × 1
8 Port, No.51204 : DB78 Male to 8 Port DB9 × 1
2. Driver CD
3. This User Manual
- 1 -
Page 4

3.0 Features
1. Fully compliant with PCI Specification Version 2.2
2. Supports both 64 Bit & 32 Bit PCI Bus and 3.3V & 5V connector keys.
3. High speed serial ports support baud rates of up to 921.6Kbps.
4. Provides a FIFO maximize size of 128Kbytes. The 128K FIFO can reduce
CPU loading, improving system performance dramatically.
5. The unique Auto Switch RS-422/485 technology makes it easy and
convenient to manage the device without the need for jumper or switch
settings.
6. ARSC™ (Auto RTS Signal Control) technology can identify the status of
the data transceiver or receiver and send the RTS signal automatically,
instead of using software to control the transmitter.
7. High speed 16C650 compatible communication controller with SUN1889
single chip hardware flow control to guarantee no data loss
8. LINDY industrial host controller series are certified by WHQL, CE, and
FCC approval.
9. Ready for the Intel® Itanium® and AMD® Athlon 64® 64-bit CPU on
Microsoft Windows® XP 64-bit Edition Version 2003 and Windows®
Server 2003 for 64-bit Itanium-based or Extended Systems.
- 2 -
Page 5
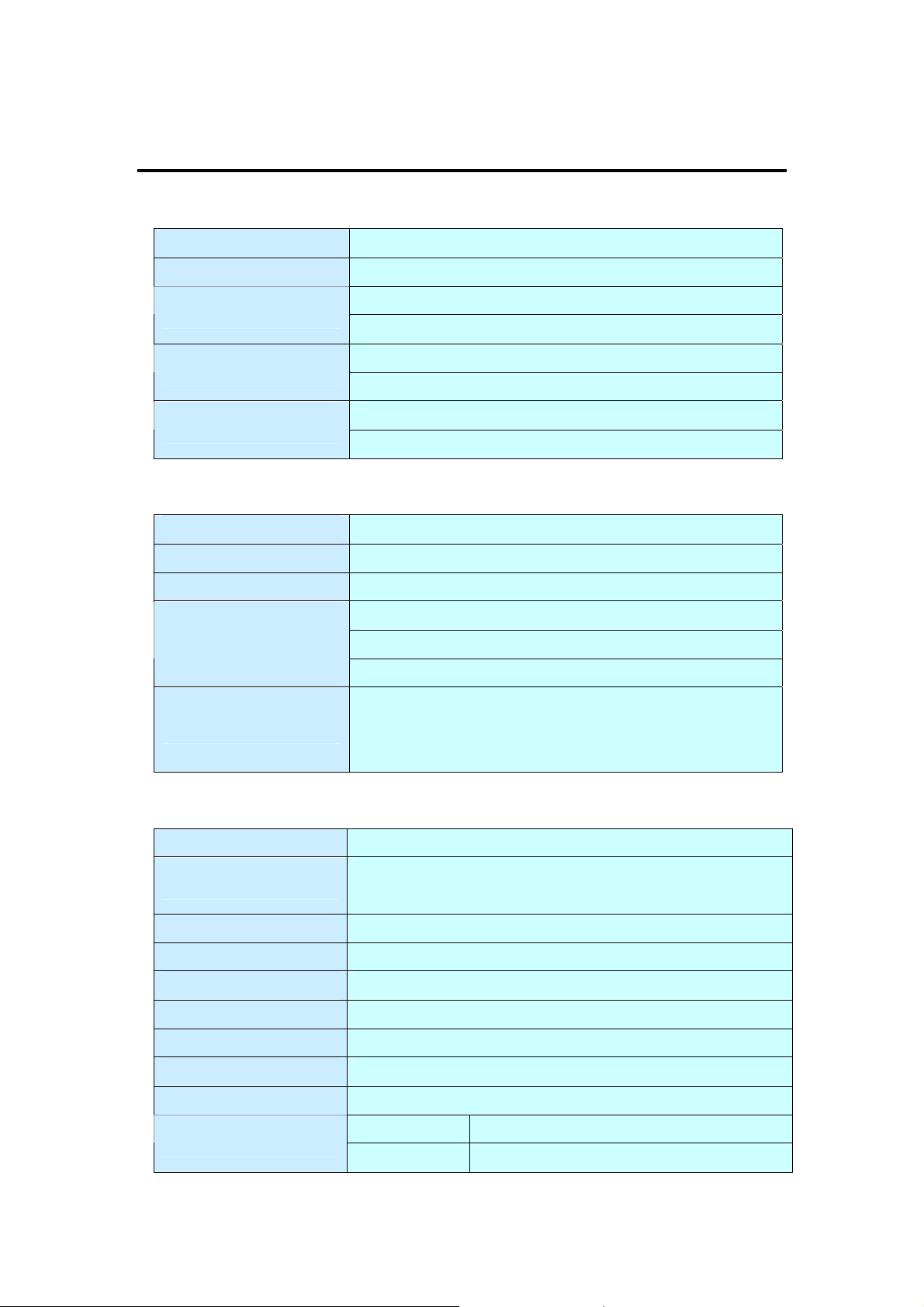
4.0 Specifications
4.1 Function
Type LINDY Industrial Host Controller
Mode of Operation Differential
Bus Trans ceivers
Drivers per Line
Receivers per Line
RS-422 Full-Duplex
RS-485 Half-Duplex
RS-422 1 Driver
RS-485 10 Drivers
RS-422 10 Receivers
RS-485 32 Receivers
4.2 Hardware
IC SUN1889
Controller UART (16C650 compatible)
Bus Interface 64 Bit & 32 Bit PCI Bus, 3.3V & 5V connector keys
51200: 2 ports
Number of Ports
Connector
51202: 4 ports
51204: 8 ports
51200: 2 x DB9 Male
51202: 1 x DB37 Female to 4 x DB9/Male
51204: 1 x DB78 Female to 8 x DB9/Male
4.3 Communication
IRQ & I/O address BIOS assigned
FIFO
RS-485 Signal Control ARSC™ technology
Select RS-422/485 Auto Switch RS-422/485 technology
Baud rate 75bps ~ 921.6 Kbps
Data bit 4,5,6,7,8
Stop bit 1,1.5,2
Parity even, odd, none, mark, space
Flow Control None, Xon/Xoff, Hardware
Data Signal
32 byte hardware FIFO
128Kbyte software FIFO
RS-422 TxD+/-, RxD+/-, RTS+/-, CTS+/-, GND
RS-485 Data+/-, RTS+/-, CTS+/-, GND
- 3 -
Page 6
4.4 Driver support
Driver Support
Windows3.x/95/98SE/ME/NT/2000/XP/2003
DOS, OS/2 , Linux 2.0.x / 2.2.x / 2.4.18 / 2.4.20
4.5 Dimensions
Dimensions (W × D)
(Std.Bracket:121mm)
51200 120 × 80mm
51202 160 × 104mm
51204 180 × 108mm
4.6 Regulatory Approvals
Regulatory Approvals
Hardware CE, FCC
Software WHQL
4.8 System Requirements
1. Pentium or equivalent computer with an available PCI slot.
2. CD-ROM / DVD-ROM required for software installation.
3. Windows 3.x/ 95/98SE/Me/NT/2000/XP/2003, DOS, Linux OS system
5.0 Operating Environment
1. Operating temperature: 0° ~ 57°
2. Operating humidity: 5 to 95%
3. Storage temperature:-20° ~ 85°
- 4 -
Page 7
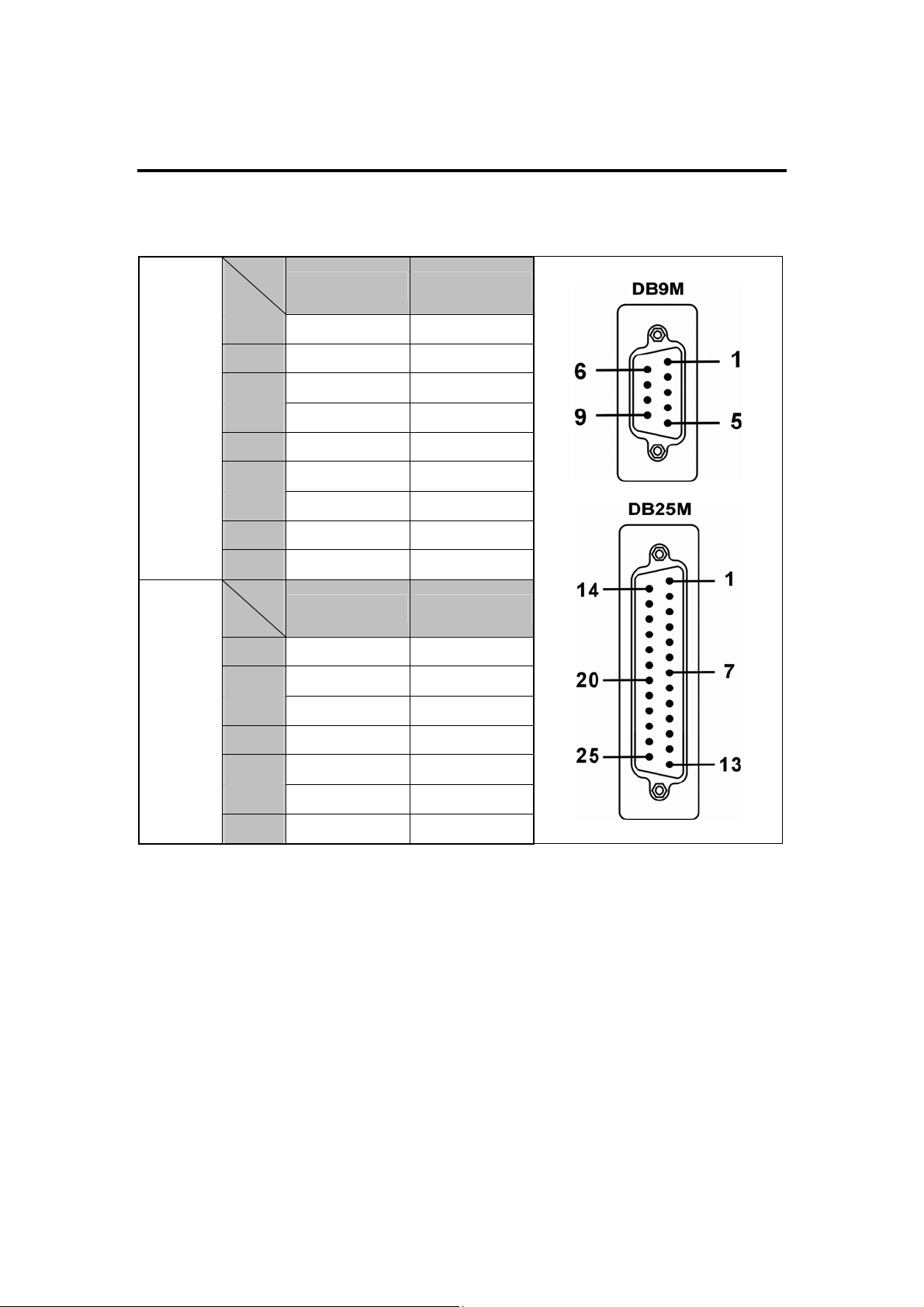
6.0 Pin Assignments & Cable Wiring
The pin assignments of the DB9 and DB25 Male port are stated as below:
Type
Signal
DB9M DB25M
RS-422
RS-485
TxDTxD+
RxD+
RxD-
RTSRTS+
CTS+
CTS-
GND
Signal
Data+
Data-
RTSRTS+
CTS+
Type
1 8
2 3
3 2
4 20
6 6
7 4
8 5
9 22
5 7
DB9M DB25M
2 3
1 8
6 6
7 4
8 5
CTS-
GND
9 22
5 7
- 5 -
Page 8

LINDY Serial Communication Boards have one DB37 female port for the 4 port
version and one DB78 female port for the 8 port version. The pin assignments
of the DB37 female port and the DB78 female port are shown below and on the
following page.
LINDY DB37 female 4 Port Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
Signal
1 2 3 4
RS-422
RS-485
TxDTxD+
RxD+
RxDRTS-
RTS+
CTS+
CTS-
GND
Signal
Data+
Data-
RTS-
RTS+
CTS+
Port
34 11 25 2
37 14 28 5
19 33 10 24
16 30 7 21
17 31 8 22
18 32 9 23
36 13 27 4
15 29 6 20
35 12 26 3
1 2 3 4
37 14 28 5
34 11 25 2
17 31 8 22
18 32 9 23
36 13 27 4
CTS-
GND
15 29 6 20
35 12 26 3
- 6 -
Page 9

LINDY DB78 female 8 Port Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
Signal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
RS-422
RS-485
TxD-
TxD+
RxD+
RxDRTS-
RTS+
CTS+
CTSGND
Port
Signal
Data+
Data-
RTS-
RTS+
CTS+
21 6 30 15 60 45 69 54
1 25 10 34 40 64 49 73
2 26 11 35 41 65 50 74
22 7 31 16 61 46 70 55
3 27 12 36 42 66 51 75
24 9 33 18 63 48 72 57
4 28 13 37 43 67 52 76
5 29 14 38 44 68 53 77
23 8 32 17 62 47 71 56
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 25 10 34 40 64 49 73
21 6 30 15 60 45 69 54
3 27 12 36 42 66 51 75
24 9 33 18 63 48 72 57
4 28 13 37 43 67 52 76
CTSGND
5 29 14 38 44 68 53 77
23 8 32 17 62 47 71 56
- 7 -
Page 10

LINDY Serial Communication Boards feature a 1 x DB37 Male to 4 DB9 Male
cable for the 4 port version, and a 1 x DB78 Male port to 8 x DB9 Male ports
cable, for 8 port version.
DB37 Male to 4 x DB9 or DB25 Male Cable
DB78 Male to 8 x DB9 or DB25 Male Cable
- 8 -
Page 11

6.1 Jumper Settings
These cards feature built-in termination resistors for each serial port. You can
modify the jumper settings (short the pins) to avoid impedance mismatch
problems when operating under multi-drop transmission.
When an electrical signal travels through two resistance junctions in a
transmission line, the impedance mismatch will sometimes cause signal
reflection. Signal reflection causes signal distortion, which in turn contributes to
communication errors. The solution to this problem is to establish the same
impedance at the line ends as in the line itself by terminating them with
resistors. It is normally sufficient when the value of the termination resistors
equals the characteristic impedance of the transmission line. LINDY
RS-422/485 serial boards feature built-in termination resistors to prevent these
problems.
- 9 -
Page 12

7.0 Driver Installation
7.1 Windows 2000 / XP / 2003:
On booting up, the system will detect the presence of the PCI Serial card and
prompt for the driver installation wizard. Please ignore this for known and
insert the driver CD in your CD/DVD ROM drive. Run the setup file:
: \PCI IO\win2k and xp\setup.exe
(1) Please click “Next” to continue.
- 10 -
Page 13

(2) You can select the folder location in which the driver is installed. Click Next”
to continue.
(3)The Software Installation Notice will appear, please click “Continue
Anyway”, and the system will install the driver automatically.
(4) Please click “Finish” and eject the driver CD.
- 11 -
Page 14

(5) Please go back to the “Found New Hardware Wizard” window. Select
“Install the software automatically (Recommend)” and click “Next”.
(6) The system will search and install the appropriate I/O driver automatically.
(7) The “Hardware Installation Notice” will appear, please click “Continue
Anyway” and the system will install the driver automatically.
(8) Please click “Finish” to complete this installation step.
Note:
The “Found New Hardware Wizard” windows will show up and re-install the
driver several times until you finish setting up each serial port.
- 12 -
Page 15

(9) To uninstall the driver:
Please click Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove
Programs
Click “Change/Remove” to uninstall the I/O driver.
7.2 Windows 2000 / XP / 2003 on a 64-bit system:
On booting up, Windows 2000 / XP / 2003 will detect the presence of the PCI
Serial card and will prompt for driver installation. Insert the driver CD in your
CD/DVD ROM drive and point to the directory:
: \PCI IO\win2k and xp_64bit\
(Now follow the Windows 2000 / XP / 2003 installation procedure. Section 7.1)
7.3 Windows NT4.0:
On booting up, Windows NT4.0 will detect the presence of the PCI Serial card
and will prompt for driver installation. Insert the driver CD in your CD/DVD
ROM drive and run the setup file:
: \PCI IO\winNT\setup.exe
(Now follow the Windows 2000 / XP / 2003 installation procedure. Section 7.1)
7.4 Linux:
Please read the detailed files about the Linux OS RedHat system installation
procedure on the CD ROM :
Kernal: 2.2.x :\PCI IO\Linux\RedHat V6.0.pdf
Kernal: 2.4.18 :\PCI IO\Linux\RedHat V8.0.pdf
Kernal: 2.4.20 :\PCI IO\Linux\RedHat V9.0.pdf
- 13 -
Page 16

7.5 Dos:
Please install the driver from the CD ROM: \PCI IO\DOS\install.exe,
and follow the installation steps from the CD ROM: \PCI IO\serial.pdf
7.6 Windows 95 / 98SE / ME:
On booting up, Windows 95 / 98SE / ME will detect the presence of the PCI
Serial card and will prompt for driver installation. Insert the driver CD in your
CD/DVD ROM drive and point to the directory:
: \PCI IO\win9x\
(1) The system will detect the new hardware device “ PCI Serial Controller”
and the “Found New Hardware Wizard” windows will display. Please click
“Next” to continue.
- 14 -
Page 17

(2) Select “Search for the best driver for your device (Recommended)” and
click “Next” to continue.
(3) Please select “Specify a location” and point to the CD Driver directory to
install the driver.
: \PCI IO\win9x\
- 15 -
Page 18

(4) The system will search and install the appropriate IO driver automatically.
Please click “Next” to continue.
(5) Please click “Finish” to complete this installation step.
Note:
The “Add New Hardware Wizard” windows will display and install drivers
several times until you finish setting up each serial port.
7.7 Verifying Serial PCI card installation:
- 16 -
Page 19

When Windows has finished installing the driver you must check:
Control Panel > System > Hardware > Device Manager >Ports[COM&LPT]
It will show the additional ports:
Note:
1. If you have installed PCI Serial ports in your system, you will be requested
to restart your computer , when you have finished setting up each serial port.
Click “Yes” if all serial ports have been installed, otherwise click “No”.
2. The item number you see during the installation may be different from the
item you have installed.
- 17 -
Page 20

8.0 Configure COM port
(1) Select the PCI Serial Port which you want to configure, for example COM3.
Right click the mouse, and select “Properties”.
(2) Click “Port Settings”.
Configure the Bits per second, Data bits, Parity, Stop bits and Flow control if
you want to change them.
There are three kinds of flow control: Xon/Xoff, Hardware and None.
Xon/Xoff is using software protocol. Hardware means the flow control is using
RTS/CTS, but the RTS/CTS is controlled by software. None means there is no
flow control.
- 18 -
Page 21

Click the “Advanced” button to set more advanced features.
(3) Configure the “Enable Auto CTS/RTS Flow Control ”,“ 16/32 bytes FIFO
length and Receive/Transmit Buffer trigger level if you want to change these
settings
(The 128K software FIFO adjustment only supports Microsoft Windows 2000
/ XP / 2003 OS. You can change the FIFO size and COM port Number as
you need.)
The window below would be shown under Windows 2000/XP/2003.
The window to the right would be
shown under Windows 95/98SE/ME.
*Enable Auto CTS/RTS Flow Control
means the CTS/RTS flow control is
controlled by hardware automatically.
The system will be more stable if the
function is enabled.
*Setting the Receive/Transmit Buffer to a higher value will get faster
performance because the CPU interrupts will be reduced, but the time for
interrupt service routine will become shorter. If the system is not stable, reset
the lower value to solve problem.
- 19 -
Page 22

- 20 -
Page 23

This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause
undesired operations.
- 21 -
 Loading...
Loading...