Lincoln Electric Welding Inverter and Chopper User Manual

TECHNOLOGY
POWER ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
Inverters and Choppers
Technology creates change.
The ability to evolve along
with change is what
distinguishes a successful
product from the rest.
Power source design is
almost entirely devoted
to reliability. Fast power
conversion is important to
obtaining a smooth
welding output, but we
also know that speed is
inconsequential without
reliability. No matter how
fast your machine operates,
if it is not durable, then it is
not usable for welding. And
if it is not welding, you are
not meeting your
production goals and
making a living.
The Chopper
Technology
Ranger
the same control over
the welding arc as an
inverter machine
The inverter technology in
the Invertec
gives it equivalent power
®
in the
®
305D offers
®
V350-PRO
capabilities as a
conventional
transformer/rectifier
such as the Lincoln
CV-305, but in
a much smaller and
portable machine.
QUICKER RESPONSE
High-speed power conversion allows for quick response to changing
arc conditions.
SMALLER FOOTPRINT
Power electronic components are compact, making equipment size smaller and
therefore more portable.
UNIVERSAL INPUT VOLTAGE
Capable of operating from 208 to 575 volts on virtually any power supply for
versatile, consistent performance.
HIGHLY EFFICIENT
Smaller transformer coils, higher thermal conductivity, and higher operating
frequencies means more efficient output power, and more economical use
of power. This translates to decreased utility costs and increased power
source efficiency.
WAVEFORM CONTROL TECHNOLOGY®COMPATIBLE
Waveform Control Technology®gives the operator improved control over the
characteristics of the welding arc.
The future of welding is here.
NX-1.30 6/06
®
POWER ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
Inverter Technology
What is
Inverter Technology?
Inverter-based welding power
sources operate at frequencies
above 20 kHz, whereas
traditional power sources
operate at a line frequency
of 50 or 60 Hz. Some of the
advantages an inverter has
are smaller magnetic
components (chokes and
transformers), higher
efficiency, and a fast
response to the welding arc.
Inverter power sources were
first introduced into the
welding industry in the early
1980s. The initial attraction of
the inverter was its small size
and easy portability. For
example, a rectifier-based
machine, like the Lincoln CV305,
weighs four times more than the
Invertec V350-PRO. Less space
is needed and the inverter unit is
easily moved around the job site.
As the popularity and reliability of
Inverter Technology
The Invertec®V350-PRO
The Power Wave
the inverter increased, the capabilities
were expanded. Inverters are now
designed for many different
processes: SMAW, GTAW, FCAW,
SAW, and are capable of operating in
®
355M
Inverter Technology is
showcased in Lincoln’s
®
Invertec
Power Wave
V350-PRO, and
®
welding systems
2/8
The Power Wave®455M/STT
The Power Wave
extreme environments. Over the last
decade, Lincoln Electric has invested
heavily in developing inverter
technology, producing highly reliable
inverter machines.
®
AC/DC 1000™
How
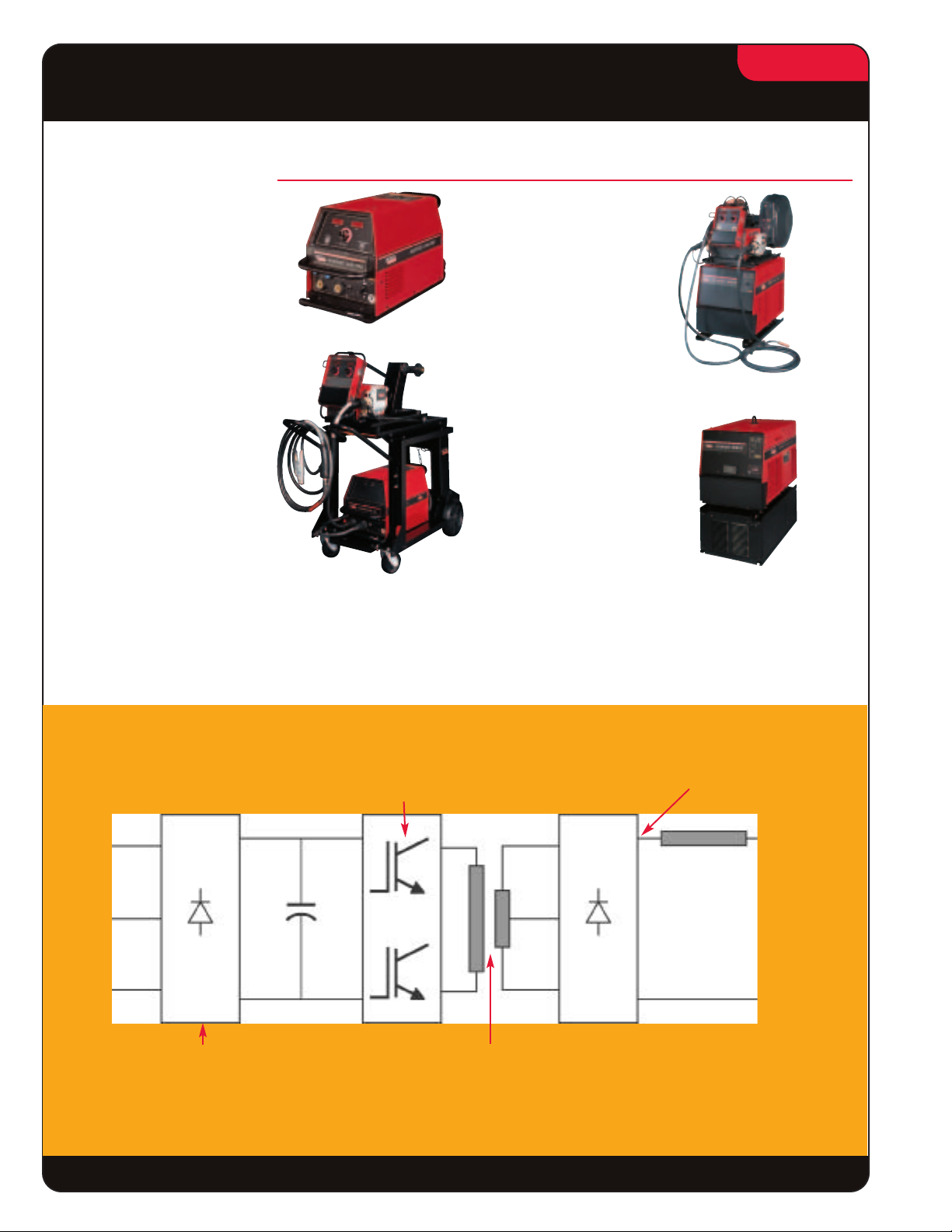
Inverter Works
Incoming 50 to 60 Hz alternating
current (AC) is converted
to direct current (DC) by a full
wave rectifier.
The future of welding is here.
The DC power is inverted into high-frequency AC power,
using semiconductor switches above 20 kHz. High-speed
switching improves welding. Switching above 20 kHz
improves efficiency, reduces weight, and is above the
maximum frequency people can hear. Digital controls
dictate the switching rate of the transistors.
The high-frequency AC voltage
requires a step-down
transformer. The transformer
takes high voltage, high
frequency AC and converts it to
low voltage, high frequency AC.
The current is “smoothed”
by a rectifying and
filtering circuit to make it
suitable for welding.
®

POWER ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
Inverter Technology
Using
Inverter Technology
For Multi-Process Welding
Inverters are capable of multiple process welding, providing
optimum arc characteristics for each process.
For Reduced Electrical Power Consumption
Copper conductors, compact transformers, and smaller coils
translate to energy savings.
For Waveform Control Technology*
Inverter machines are software programmable, which means
that they are equipped to use Waveform Control Technology
to manipulate output weld characteristics.
For Networking Capability*
Multiple inverter machines can be networked together over a
Local Area Network (LAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN) with
an Ethernet/DeviceNet Gateway board.
Advantages
Of Inverter Technology
Reliable
Every inverter undergoes rigorous testing to ensure
product reliability.
Compact and Portable
Smaller chokes, transformers, and rectifiers, give the inverter
equivalent power to older SCR machines, without the added
size and weight.
Fast Response to Welding Arc
®
Digital controls regulate the output very accurately so the
welding performance is consistent from machine to machine.
Universal Input Voltage**
The inverter can run on any power supply that supplies
between 208 to 575 volts.
Efficient
The smaller chokes and transformers of the inverter yield an
efficiency rating of 87% to 90%, which means the inverter
consumes less energy to convert the same amount of energy
as SCR-based machines.
3/8
The Power Wave
technology to produce consistent
welds with a variety of weld processes.
* Applies only to Power Wave Welding Systems F355i, 355M, 455M, 455M/STT, 655
Robotic, and Power Wave AC/DC 1000.
**Power Wave 655 Robotic and Power Wave AC/DC 1000 operate from 460 to 575 volts.
The future of welding is here.
®
455M uses Inverter
®
 Loading...
Loading...