Page 1
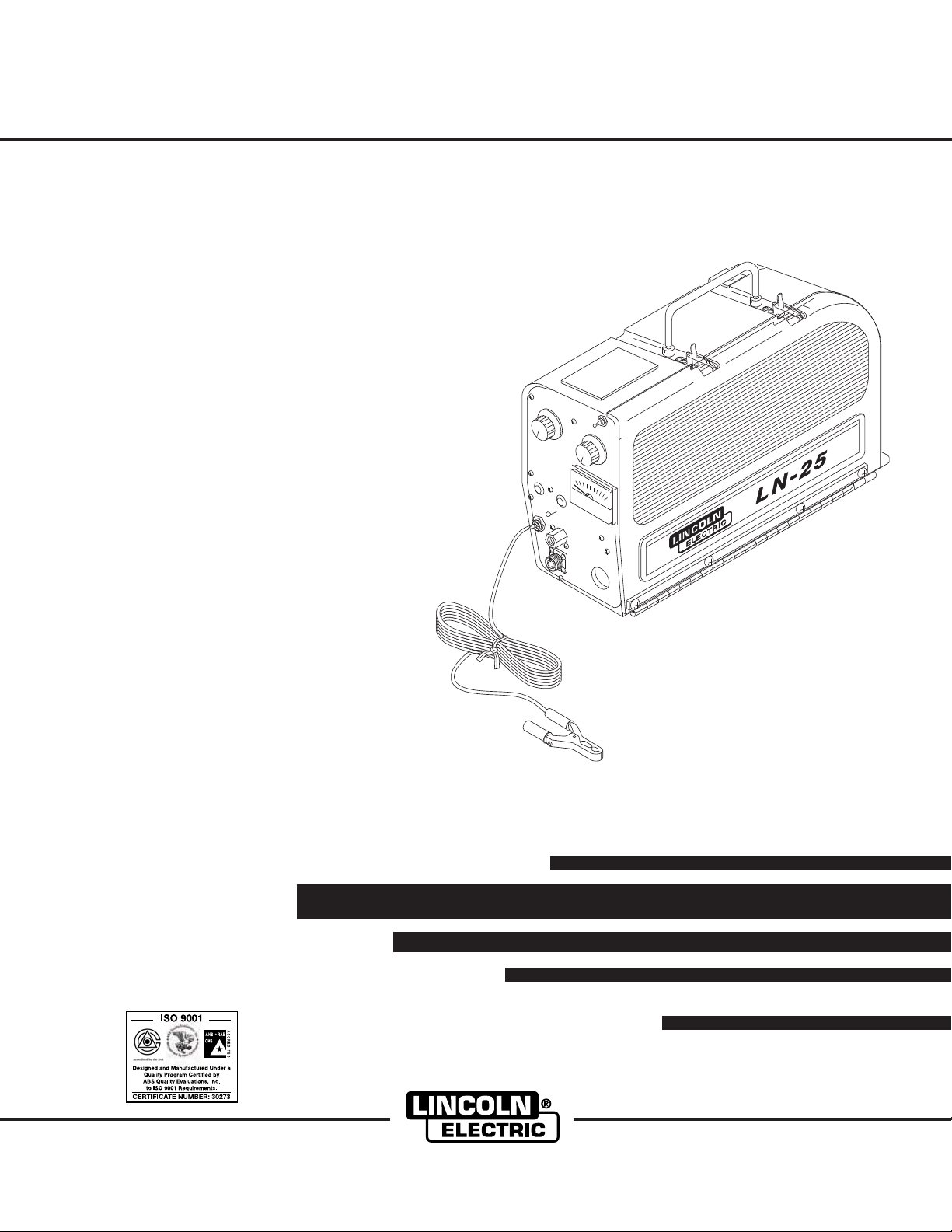
LN-25 PORTABLE CV/CC
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
SEMIAUTOMATIC WIRE FEEDER
For use with machines having Code Number 10556 11144
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding and cutting
equipment is designed and built with
safety in mind. However, your overall
safety can be increased by proper
installation ... and thoughtful operation on your part. DO NOT
INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR
THIS EQUIPMENT WITHOUT
READING THIS MANUAL AND
THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And,
most importantly, think before you
act and be careful.
IM620-B
November, 2006
10557 11145
10558 11282
11283
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
OPERATING MANUAL
Copyright © 2006 Lincoln Global Inc.
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Page 2
i
SAFETY
i
WARNING
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents
are known to the State of California to cause cancer,
birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
The Above For Diesel Engines
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP
CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a copy of “Safety in
Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A
Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE PERFORMED ONLY BY
QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer,
birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
The Above For Gasoline Engines
FOR ENGINE
powered equipment.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance
work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running.
____________________________________________________
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes
outdoors.
____________________________________________________
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame welding
arc or when the engine is running. Stop the engine
and allow it to cool before refueling to prevent
spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot
engine parts and igniting. Do not spill fuel when
filling tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not
start engine until fumes have been eliminated.
____________________________________________________
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in position
and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from Vbelts, gears, fans and all other moving parts when starting, operating
or repairing equipment.
____________________________________________________
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety
guards to perform required maintenance. Remove
guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete.
Always use the greatest care when working near moving
parts.
___________________________________________________
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not
attempt to override the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control rods while the engine is
running.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the
radiator pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and
welding machines
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and
welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician
before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health
effects which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and
work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right
side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
___________________________________________________
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while
turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance
work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magneto wire as appropriate.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
Mar ‘95
Page 3
ii
SAFETY
ii
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits
are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare
skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-freegloves
to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full
area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding
must be performed under electrically hazardous
conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet
clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or
scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use
the following equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic
welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection
should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition.
Replace damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of
electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage
between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of
both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8.
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover
plates to protect your eyes from sparks and
the rays of the arc when welding or observing
open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens
should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
can be dangerous.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep
your head out of the fume. Use enough
ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When
welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see
instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or
cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as
low as possible and below Threshold Limit Values (TLV)
using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In
confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a
respirator may be required. Additional precautions are
also required when welding on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected
by various factors including proper use and positioning of
the equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific welding procedure and application involved. Worker
exposure level should be checked upon installation and
periodically thereafter to be certain it is within applicable
OSHA PEL and ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations.
The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
vapors
to
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation,
especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your
employer’s safety practices. MSDS forms are available from
your welding distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
AUG 06
Page 4
iii
SAFETY
iii
WELDING SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
6.a. Remove fire hazards from the welding area.
If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
the welding sparks from starting a fire.
Remember that welding sparks and hot
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI
Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the
equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can
cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures
will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even though they have
been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended
Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous
Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society
(see address above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil
free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt,
cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear
ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places.
Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding
area as practical. Work cables connected to the building
framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing through
lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can
create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they
fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
CYLINDER may explode
if damaged.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders
containing the correct shielding gas for the
process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for
the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and
any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas
cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l,
“Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
powered equipment.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on
the equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Mar ‘95
Page 5
iv
SAFETY
iv
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ
Pour votre propre protection lire et observer toutes les instructions et
les précautions de sûreté specifiques qui parraissent dans ce manuel
aussi bien que les précautions de sûreté générales suivantes:
Sûreté Pour Soudage A L’Arc
1. Protegez-vous contre la secousse électrique:
a. Les circuits à l’électrode et à la piéce sont sous tension
quand la machine à souder est en marche. Eviter toujours
tout contact entre les parties sous tension et la peau nue ou
les vétements mouillés. Porter des gants secs et sans trous
pour isoler les mains.
b. Faire trés attention de bien s’isoler de la masse quand on
soude dans des endroits humides, ou sur un plancher metallique ou des grilles metalliques, principalement dans l e s
positions assis ou couché pour lesquelles une grande partie
du corps peut être en contact avec la masse.
c. Maintenir le porte-électrode, la pince de masse, le câble de
soudage et la machine à souder en bon et sûr état defonctionnement.
d.Ne jamais plonger le porte-électrode dans l’eau pour le
refroidir.
e. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les parties sous tension des
porte-électrodes connectés à deux machines à souder parce
que la tension entre les deux pinces peut être le total de la
tension à vide des deux machines.
f. Si on utilise la machine à souder comme une source de
courant pour soudage semi-automatique, ces precautions
pour le porte-électrode s’applicuent aussi au pistolet de
soudage.
7. Quand on ne soude pas, poser la pince à une endroit isolé de la
masse. Un court-circuit accidental peut provoquer un échauffement et un risque d’incendie.
8. S’assurer que la masse est connectée le plus prés possible de la
zone de travail qu’il est pratique de le faire. Si on place la masse
sur la charpente de la construction ou d’autres endroits éloignés
de la zone de travail, on augmente le risque de voir passer le
courant de soudage par les chaines de levage, câbles de grue,
ou autres circuits. Cela peut provoquer des risques d’incendie ou
d’echauffement des chaines et des câbles jusqu’à ce qu’ils se
rompent.
9. Assurer une ventilation suffisante dans la zone de soudage. Ceci
est particuliérement important pour le soudage de tôles galvanisées plombées, ou cadmiées ou tout autre métal qui produit
des fumeés toxiques.
10. Ne pas souder en présence de vapeurs de chlore provenant
d’opérations de dégraissage, nettoyage ou pistolage. La chaleur
ou les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs du solvant
pour produire du phosgéne (gas fortement toxique) ou autres produits irritants.
11. Pour obtenir de plus amples renseignements sur la sûreté, voir le
code “Code for safety in welding and cutting” CSA Standard W
117.2-1974.
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ POUR
2. Dans le cas de travail au dessus du niveau du sol, se protéger
contre les chutes dans le cas ou on recoit un choc. Ne jamais
enrouler le câble-électrode autour de n’importe quelle partie du
corps.
3. Un coup d’arc peut être plus sévère qu’un coup de soliel, donc:
a. Utiliser un bon masque avec un verre filtrant approprié ainsi
qu’un verre blanc afin de se protéger les yeux du rayonnement de l’arc et des projections quand on soude ou quand
on regarde l’arc.
b. Porter des vêtements convenables afin de protéger la peau
de soudeur et des aides contre le rayonnement de l‘arc.
c. Protéger l’autre personnel travaillant à proximité au soudage
à l’aide d’écrans appropriés et non-inflammables.
4. Des gouttes de laitier en fusion sont émises de l’arc de soudage.
Se protéger avec des vêtements de protection libres de l’huile,
tels que les gants en cuir, chemise épaisse, pantalons sans
revers, et chaussures montantes.
5. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité dans la zone de
soudage. Utiliser des lunettes avec écrans lateraux dans les
zones où l’on pique le laitier.
6. Eloigner les matériaux inflammables ou les recouvrir afin de
prévenir tout risque d’incendie dû aux étincelles.
LES MACHINES À SOUDER À
TRANSFORMATEUR ET À
REDRESSEUR
1. Relier à la terre le chassis du poste conformement au code de
l’électricité et aux recommendations du fabricant. Le dispositif de
montage ou la piece à souder doit être branché à une bonne
mise à la terre.
2. Autant que possible, I’installation et l’entretien du poste seront
effectués par un électricien qualifié.
3. Avant de faires des travaux à l’interieur de poste, la debrancher à
l’interrupteur à la boite de fusibles.
4. Garder tous les couvercles et dispositifs de sûreté à leur place.
Mar. ‘93
Page 6

v
for selecting a QUALITY product by Lincoln Electric. We want you
Thank You
to take pride in operating this Lincoln Electric Company product
••• as much pride as we have in bringing this product to you!
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims
for material damaged in shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation company at the
time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This information can be
found on your machine nameplate.
Product _________________________________________________________________________________
Model Number ___________________________________________________________________________
Code Number or Date Code_________________________________________________________________
Serial Number____________________________________________________________________________
Date Purchased___________________________________________________________________________
v
Where Purchased_________________________________________________________________________
Whenever you request replacement parts or information on this equipment, always supply the information you
have recorded above. The code number is especially important when identifying the correct replacement parts.
On-Line
- Register your machine with Lincoln Electric either via fax or over the Internet.
• For faxing: Complete the form on the back of the warranty statement included in the literature packet
accompanying this machine and fax the form per the instructions printed on it.
• For On-Line Registration: Go to our
“Product Registration”. Please complete the form and submit your registration.
Read this Operators Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual and keep it
handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection.
The level of seriousness to be applied to each is explained below:
WEB SITE at www.lincolnelectric.com. Choose “Quick Links” and then
Product Registration
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed exactly to avoid serious personal injury or
loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to avoid minor personal injury or damage to
this equipment.
Page 7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY ..............................................................................................................................................................i-iv
INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................................SECTION A
Technical Specifications .................................................................................................................................A-1
Safety Precautions ..........................................................................................................................................A-2
Power Source Connections............................................................................................................................A-2
Gun Cable Connection to Feeder .................................................................................................................A-3
Weld Cable Connection ..................................................................................................................................A-4
Electrode Cable Connection......................................................................................................................A-4
Work Cable Connection .............................................................................................................................A-4
Wire Feed Drive Roll and Guide Tube Kits .................................................................................................A-4
OPERATION..........................................................................................................................................SECTION B
Safety Precautions ..........................................................................................................................................B-1
General Description.........................................................................................................................................B-1
Recommended Processes and Equipment..................................................................................................B-1
Welding Capability...........................................................................................................................................B-1
Controls and Settings......................................................................................................................................B-2
Sequence of Operation...................................................................................................................................B-4
Loading Electrode .......................................................................................................................................B-4
Loading Wire Drive .....................................................................................................................................B-5
Idle Roll Pressure Setting ..........................................................................................................................B-5
Presetting Wire Feed Speed .....................................................................................................................B-6
Making a Weld.............................................................................................................................................B-7
Procedure at End of Coil ................................................................................................................................B-8
Automatic Protection Shutdown.....................................................................................................................B-8
ACCESSORIES ....................................................................................................................................SECTION C
LN-25 Option Chart .........................................................................................................................................C-1
Options and Accessories................................................................................................................................C-2
K430-2 Gas Solenoid Kit ...........................................................................................................................C-2
K434-1 Gas Flow Timer Kit .......................................................................................................................C-2
K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit..............................................................................................................C-3
K461 Pulse Power Control Cable Assembly...........................................................................................C-3
K443-2, K443-3 LN-25 Contactor Kits....................................................................................................C-3
Remote Output Control Options and Control Cable Assemblies..............................................................C-3
K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit ..........................................................................................................C-3
K433 Power Source Remote Box.............................................................................................................C-4
K432 Remote Control Cable Assembly ...................................................................................................C-4
K439 Remote Extension Cable Assembly...............................................................................................C-4
K624-1 42V Remote Output Control Module ..........................................................................................C-4
K625, K626, K626 Remote Control Cable Assembly ............................................................................C-4
K444, K444-1 or K444-2 Remote Voltage Control Kit...........................................................................C-5
K557-1 Rear Handle Kit.............................................................................................................................C-5
MAINTENANCE....................................................................................................................................SECTION D
Safety Precautions ..........................................................................................................................................D-1
Routine Maintenance ......................................................................................................................................D-1
Circuit Protection and Automatic Shutdown ................................................................................................D-1
Adjusting Speed Sensor Module...................................................................................................................D-1
Calibration of the LN-25 Wire Speed Dial ...................................................................................................D-2
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE............................................................................................................SECTION E
How to Use the Troubleshooting Guide .......................................................................................................E-1
Troubleshooting Guide....................................................................................................................................E-2
WIRING DIAGRAM...............................................................................................................................SECTION F
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS....................................................................................................................SECTION F
PARTS MANUAL ..............................................................................................................................P333 SERIES
Page 8
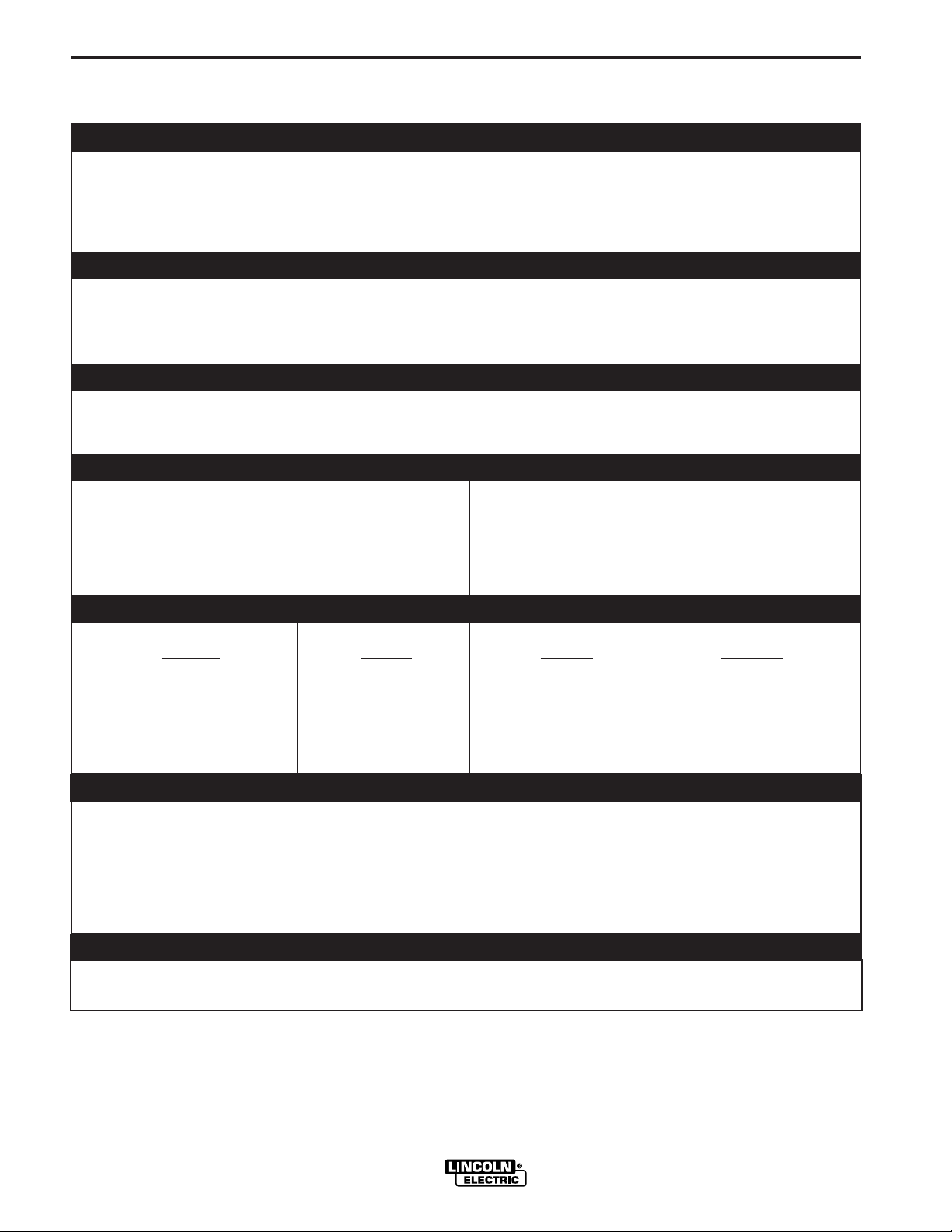
A-1
RATED CCURRENT
WIRE FFEED SSPEED
PHYSICAL DDIMENSIONS
ENVIRONMENTAL RRATING
WIRE DDIAMETERS
VOLTAGE
INSTALLATION
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – LN-25
A-1
OPERATING ARC VOLTAGE
Constant Voltage (CV)
or 15-40 VDC (110VDC Maximum OCV)
Constant Current (CC)
Rated current without contactor 500 Amps 60% Duty Cycle
Rated current with contactor 300 Amps 60% Duty Cycle
50 – 700 Inches Per Minute (IPM)
RECOMMENDED ELECTRODE WIRE SIZES
.023” to
.045” to
1
16” SOLID STEEL WIRE
5
64” CORED WIRE
RATED CURRENT
WIRE SPEED RANGE
.035” to 116” ALUMINUM WIRE
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
HEIGHT WIDTH DEPTH WEIGHT
(Handle Down) w/o Options
14 Inches 7.4 Inches 21 Inches 28 lbs
(354 mm) (187 mm) (531 mm) (13 kg)
TEMPERATURE RANGE
OPERATION: - 40oC to +40oC (- 40oF to +104oF)
o
STORAGE: - 40
C to +85oC (- 40oF to +185oF)
IP23
LN-25
Page 9

A-2
INSTALLATION
A-2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
Unless an optional output control or contactor is used
with the LN-25, the electrode circuit (including welding
wire, wire drive and welding gun) is electrically hot
when the welding power source is on. The gun trigger
controls wire feed only.
Disconnect or shut off welding power source before
making connections or installations to the LN-25.
Welding gun should be stored in the insulated
gun holder, located near the rear on the top of the
LN-25 case, to avoid accidental arcing.
The LN-25 should be positioned upright on a
horizontal surface.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch metal portions
of the LN-25 lead clip when
welding power source is on.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not operate with covers
removed.
• Turn off power source before
installing or servicing.
• Do not touch electrically
hot parts.
• Turn the input power to the
welding power source off at the
fuse box before working in the
terminal strip.
• Only qualified personnel should
install, use or service this
equipment.
DC-250
a. Connect a jumper from 2 to 4 on the power source
terminal strip so the output will be energized when
the DC-250 is turned on.
POWER SOURCE CONNECTION
The LN-25 can be used with most DC welding power
source. A constant voltage power source is
recommended; however, the LN-25 can also be used
with a constant current power source as long as the
open circuit voltage is less than 110V DC.
CAUTION
Do not use LN-25 models below Code 9200 with any
TIG or Square Wave welding power sources. Do not
use LN-25 models equipped with internal contactors
with non- Lincoln TIG or Square Wave welding power
sources. Damage to the LN-25 circuit can occur as a
result of the high output inductance typically
associated with these power sources. TIG high
frequency power should never be applied to the LN-25.
If not using an LN-25 Remote Output Control option
(See Remote Output Control Options and Cable
Assemblies Section), the power source output must
be electrically “hot” at all times when the power
source is turned on.
b. Connect electrode cable to the “Innershield/
GMAW” output terminal of polarity required by
electrode. Connect work lead to other
“Innershield/GMAW” output terminal.
c. Place “Set to CV Electrode Cable Polarity” switch
at appropriate position.
d. Place power source toggle switch in “Output
Control at DC-250” position, unless a Remote
Control is connected to 75, 76 and 77 on the DC250 terminal strip.
e. Place mode switch in “Innershield GMAW (CV)”
position. Set CV arc control to “2” (or “NORMAL”
on some machines). Initially set the output
control on “7”.
DC-400 AND CV-400
a. Connect a jumper from 2 to 4 on the power
source terminal strip so the output will be
energized when the power source is turned on.
NOTE: DC-400 machines above Code 9200 have
an output toggle switch to perform this function.
See the power source instruction manual for proper
power source connections and setting required.
LN-25
b. Connect the electrode cable to the output
terminal of polarity required by electrode.
Connect work lead to other output terminal.
Page 10

A-3
INSTALLATION
A-3
c. Place “Set to Same Polarity As Electrode Cable
Connection” switch at appropriate position.
d. Place power source toggle switch in “Output
Control at DC(CV) -400” position, unless a
remote control is connected to 75, 76 and 77 on
the power source terminal strip.
e. If power source has a mode switch, set switch to
Constant Voltage Innershield. Initially set the
output control on “6”.
DC-600
a. Connect a jumper from 2 to 4 on the power
source terminal strip so the output will be
energized when the DC-600 is turned on. (For
DC-600 below Code 8200, also jumper N to S.)
b. Connect the electrode cable to the output
terminal of polarity required by electrode.
Connect work lead to other output terminal.
c. Place “Set to Same Polarity As Electrode Cable
Connection” switch at appropriate position.
d. Place power source toggle switch in “Output
Control at DC-600” position, unless a remote
control is connected to 75, 76 and 77 on the DC600 terminal strip.
e. Set mode switch to Constant Voltage Innershield.
Initially set output control on “4”.
R3S-325
a. Connect a jumper from 4 to 32 on the power
source terminal strip so that the output will be
energized when the R3S-325 is turned on.
c. Set ELECTRODE POLARITY switch to constant
voltage polarity required by electrode.
d. Set toggle switch to “Constant Voltage” and set
the Constant Voltage Control on welder and the
portable field control on #5 for initial start.
SA-200, —250 OR SAE-300, —400 (WITH
CV ADAPTER)
a. For electrode negative welding, connect the
electrode lead from the LN-25 to the output
terminal on the CV Adapter, and the work lead to
the power source output terminal labeled
“POSITIVE”. For electrode positive welding,
interchange the above lead connections so the
LN-25 electrode lead is then connected to the
positive power source terminal.
b. Place both switches on the CV Adapter to the CV
INNERSHIELD position and make appropriate
power source settings per the CV Adapter instructions provided for the power source being used.
c. The output voltage is set with the voltage control
on the CV Adapter.
NOTE: Refer to the Instruction Manual provided with
the machine for details on connection and operation
of the LN-25 with the power source.
INVERTEC, CV300 AND OTHER NEWER
LINCOLN POWER SOURCES
Refer to the instruction manual provided with the
power source for details on connection and operation
of the LN-25 with these newer machines.
b. Connect the electrode cable to the output
terminal of polarity required by electrode.
Connect work lead to other output terminal.
c. Set power source per its instruction manual.
NOTE: Use of the optional Line Voltage
Compensator available for the R3S-325 is
recommended if input line voltage variation
exceeds ±3%.
SAM-400, —650
a. Connect a jumper from 2 to C4 on the power
source terminal strip so the output will be
energized when the SAM power source is on.
b. Connect work lead to WORK stud. Connect
electrode to AUTO EQUIPMENT stud. Connect
SAM-650 “Tap” lead to the Innershield stud
desired.
LN-25
GUN CABLE CONNECTION
TO FEEDER
Lay the cable out straight. Insert the connector on the
welding conductor cable into the brass conductor
block on the front of the wire drive unit. Make sure it is
all the way in and tighten the hand wheel clamp. Keep
this connection clean and bright. Connect the control
cable polarized amphenol plug into the mating 5-cavity
receptacle on the front panel of the wire feeder case.
FOR GMA GUN AND CABLES:
Requires installation of K430-1 Gas Solenoid Kit
(factory installed on K446 and K449 models).
See K430-1 Gas Solenoid Kit Section (in Accessories
Section) for gas solenoid operation and gas supply
connection.
Page 11
A-4
INSTALLATION
A-4
Install the barbed fitting and union nut to the 58-18
female inert gas fitting on the front panel of the
LN-25 case. Connect the 316” I.D. gas hose from the
gun cable to the barbed fitting.
When the gun is to be removed, this fitting can be
easily detached by loosening the union nut.
WELD CABLE CONNECTION
The size of the electrode cable and work cable must
be sufficient for the maximum weld current and total
cable length to be used. Refer to table A.1.
TABLE A.1
Weld Current
60% Duty Cycle 50’-100’ 100’-150’ 150’-200’ 200’-250’
200Amps 2 AWG 2 AWG 1 AWG 1/0
300Amps 1 AWG 1 AWG 1/0 2/0
400Amps 2/0 2/0 3/0 3/0
500Amps 2/0 3/0 3/0 4/0
ELECTRODE CABLE CONNECTION
Route the electrode cable through the oval hole in
the lower portion of the LN-25 rear panel. Connect
the electrode cable to the LN-25 input stud using the
1
2” nut provided.
Secure the cable with the strain relief clamp provided.
All units are supplied with an optional pigtail for
customers that prefer to make a taped and bolted
connection externally.
Total Cable Length
WIRE FEED DRIVE ROLL AND
GUIDE TUBE KITS
WARNING
Turn off power source before installing or changing
drive roll and/or guide tubes.
NOTE: The maximum wire sizes the LN-25 will
satisfactorily feed are
electrodes.
The electrode sizes that can be fed with each roll and
guide tube are stencilled
for proper components. See the instructions, included
with the drive roll kit, to install these parts on new
machines or replace them on used machines. Refer
to table A.2.
Steel Wire Sizes:
.068-564 Cored KP653-332 L9932
1
16 (.062) Cored or Solid -116
Steel
(Can also be used for .052)
.045 and .052 Solid Steel -.052
.045 and .052 Cored -.052C
.035 Solid Steel -.035S
.035 Cored -.035C
.030 Solid Steel -.030S
.025 Solid Steel -.025S
5
64” cored and 116” solid
(1)
on each part. Check the kit
TABLE A.2
Kit Instructions
WORK CABLE CONNECTION
Connect a work lead of sufficient size between
the proper output stud on the power source and
the work. Be sure the connection to the work
makes tight metal-to-metal electrical contact.
Poor work lead connections can result in poor
welding performance.
LN-25
Aluminum Wire Sizes:
1
16 KP654-
3
64 -364A
.035 -.035A
(1)
Drive rolls for only cored electrode sizes are stencilled with a
“C” suffix to the wire sizes.
Drive rolls for only solid electrode sizes are stencilled with an
“S” suffix to the wire sizes.
Drive rolls for aluminum wire sizes are stencilled with an “A” suffix
to the wire sizes.
1
16A L9932
Page 12

B-1
OPERATION
B-1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
READ AND UNDERSTAND ENTIRE SECTION
BEFORE OPERATING MACHINE
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live
part or electrode with skin or
wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work
and ground.
• Always wear dry insulating
gloves.
FUMES AND GASSES can be
dangerous.
• Keep your head out of fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing
zone.
WELDING SPARKS can cause
fire or explosion.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The LN-25 is a lightweight portable semiautomatic
wire feeder designed for “across-the-arc” operation
without a control cable on most any DC welding
power source. Simply connect the LN-25 to the
electrode cable, clip it to Work and it is ready to weld,
using up to 30 lb. coils or spools.
The wire drive, controls and wire reel are fully
enclosed in a rugged molded plastic case providing
a compact and versatile welding package ideally
suited to “on-the-go” field welding applications in
virtually any environment.
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES
AND EQUIPMENT
When combined with the quality drive roll kits and
accessories available for use with the LN-25, a
versatile portable welding system can be provided to
meet the specific needs of Innershield, submerged
arc or gas metal arc welding applications within the
wire feed capabilities of the LN-25.
The LN-25 provides constant wire feed speed for use
with constant voltage (CV) power sources, and arcsensing wire feed speed for use with constant current
(CC) (formerly variable voltage) power sources. Wire
speed is presettable on a dual-range calibrated dial.
• Keep flammable material away.
ARC RAYS can burn.
• Wear eye, ear and body protection.
The power sources recommended for use with the
LN-25 include the DC-250, -400, -600, CV-400 and
R3S type transformer machines, and the SAM-400,
-650 engine welders, as well as the SA-200, -250 or
SAE-300, -400 with CV Adapter and Pulse Power
500 with K460-1 LN-25 Kit.
WELDING CAPABILITY
The LN-25 will handle up to 500 Amp 60% duty cycle
welding currents. However, when equipped with a
K443-2 Contactor, the LN-25 will handle up to 300
Amp 60% duty cycle.
LN-25
Page 13

B-2
REMOTE
ARC VOLTAGE
CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
WIRE SPEED
DIAL RANGE
SWITCH
WIRE
SPEED
DIAL
VOLT
METER
WORK CLIP
LEAD
GUN
CONNECTION
BLOCK
GUN
TRIGGER
AMPHENOL
CONNECTOR
GAS
FITTING
(OPTIONAL)
ELECTRODE
POLARITY
SWITCH
GAS POST/
PRE FLOW
TIMERS
(OPTIONAL)
ELECTRODE
CABLE
OPTIONAL
GAS INPUT
FITTING
GAS PURGE
BUTTON
OPERATION
B-2
LN-25 INSTRUMENTS AND
CONTROLS
Refer to Figure B.1 for control locations.
NOTE:
1. The Voltmeter will read zero if the LN-25 work
clip lead is not connected to work, even if the
electrode is electrically “hot” to work.
2. The Voltmeter will read below zero if the LN-25
polarity switch is not set to the same polarity as
the electrode.
3. The Voltmeter will read power source open
circuit voltage when the gun trigger is open, even
if the LN-25 is equipped with the internal
contactor.
“ELECTRODE POLARITY” SWITCH
The polarity switch is located on the front panel of
the LN-25 case.
Set the switch to the same polarity as the electrode
lead connection to the power source. If the switch is
not set for the correct polarity, the wire feeder will not
operate.
WIRE FEED MODE SWITCH
VOLTMETER
(Factory installed on model Codes above 9218)
The 40V DC analog voltmeter is mounted to the front
control panel of the LN-25 and is connected to read
the arc voltage between the LN-25 electrode cable
connection and the work clip lead.
FIGURE B.1 CONTROL LOCATIONS
The CV-VV (CC) Wire Feed Mode switch is located
inside the LN-25 case. The toggle switch extends
from beneath the control box just above the wire
drive.
The forward “CV” position provides constant wire
feed speed mode for use with constant voltage (CV)
welding power sources.
The backward “VV (CC)” position provides arc-sensing
wire feed speed mode for use with constant current
(formerly variable voltage) welding power sources.
WIRE SPEED DIAL AND RANGE SWITCH
The Wire Speed control dial on the front panel of the
LN-25 has two calibrated dial ranges selected by the
HI-LO Dial Range switch.
When switched to the LO range position, the constant
wire feed speed (CV Wire Feed Mode) is set on the
inside (white) or (red) dial range calibrated for 50 to
350 in/min.
When switched to the HI range position, the constant
wire feed speed (CV Wire Feed Mode) is set on the
outside (black) or (blue) dial range calibrated
for 50 to 700 in/min.
LN-25
Page 14

B-3
OPERATION
B-3
The volts marks around the HI range calibrated dial
indicate the minimum arc volts required to obtain the
indicated HI range wire feed speeds. For example;
if wire speed is set to 400 in/min., a welding
procedure arc voltage of at least 17V would be
required to obtain the 400 in/min. wire feed speed.
WORK CLIP LEAD
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch metal portions
of the LN-25 lead clip when
welding power source is on.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
WARNING
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: To avoid possible
electrical shock, do not touch the metal portions of
the LN-25 work lead clip if the power source output
is on. The clip will be electrically “HOT” to work if the
input electrode cable to the LN-25 is electrically
“HOT” even if the gun trigger is off and even if an
internal contactor is used. Care should be taken to
only handle the LN-25 work clip by its non-metal
insulated portions and/or the welding power source
should be turned off before handling the work clip.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
The 15 ft. (4.6m) work clip lead attached to the front
panel of the LN-25 case must be connected directly
to the work using the spring clip on the end of the
lead.
When used with a K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit,
the LN-25 does not need a clip lead.
NOTE: The clip lead also serves as a work sensing
lead for the LN-25 Voltmeter (if installed). If the clip
lead is extended by the user beyond the standard
15 ft. (4.6m) length, the voltmeter reading will be
lower than the actual arc volts due to the LN-25
motor control current flowing through the resistance
of the extended lead. To minimize this voltmeter
error, the following minimum lead size is
recommended for the maximum extended lengths
shown:
AWG Maximum Length
#14 25 Ft(7.6m)
#12 50 Ft(15.2m)
#10 100 Ft(30.5m)
#6 200 Ft(61m)
REMOTE ARC VOLTAGE CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
This rheostat control allows you to control the power
source output arc voltage level. Refer to K444, K4441 and K444-2 Remote Voltage Kits in the
Accessories section.
GAS FITTING (OPTIONAL)
Provides gas output connection to the welding gun
for the GMAW process. Refer to K430-2 Gas
Solenoid Kit in the Accessories Section.
GAS POST PRE-FLOW TIMERS (OPTIONAL)
Allows for variable adjustment of gas pre-flow &
post-flow at the start and end of the weld. Refer to
K434-1 Gas Flow Timer Kit in Accessories Section.
If not connected, the LN-25 will not operate even if
a K431-1 or K624-1 (42V) Remote Output Control
option (refer to Accessories Section) is used.
However, the electrode will still be electrically “HOT”
when the clip lead is disconnected, if K431-1 or
K624-1 (42V) Remote Output Control Option, or
Internal Contactor (K443-2), is not used.
LN-25
Page 15

B-4
OPERATION
B-4
SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
LOADING ELECTRODE
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Unless an optional output
control or internal contactor
is used with the LN-25, the
electrode circuit is electrically
“Hot” when the power source
is on.
• Turn off the power source
while mounting electrode
coils.
MOUNTING 22 TO 30 LB READI-REEL®COILS
The LN-25 will require an optional K363-P ReadiReel®Adapter which is required to load Lincoln 22 to
30 lb Readi-Reel coils.
a. Make certain that the threaded locking collar is
tight and securely locks the adapter on the
spindle (see figure B.2).
b. Rotate the spindle and adapter so the retaining
spring is at the 12 o’clock position.
c. Position the Readi-Reel so that it will rotate in a
clockwise direction when feeding (wire is to be
dereeled from bottom of the coil).
d. Set one of the Readi-Reel inside cage wires on
the slot in the retaining spring tab.
e. Lower the Readi-Reel to depress the retaining
spring and align the other inside cage wires with
the grooves in the molded adapter.
f. Slide cage all the way onto the adapter until the
retaining spring “pops up” fully.
g. To remove Readi-Reel from Adapter, depress re-
taining spring tab with thumb while pulling the
Readi-Reel cage from the molded adapter with
both hands. It is not necessary to remove
adapter from spindle.
h. Load wire into wire drive per Loading Wire Drive
Section.
MOUNTING 10 TO 30 LB SPOOLS
For 12” Diameter Spools:
a. Remove the locking collar and the Readi-Reel
adapter (if so equipped) on the 2” diameter
spindle (adapter is not required).
b. Place the spool on the spindle so the brake
holding pin enters one of the holes in the back
side of the spool. Be sure the wire comes off the
spool in a clockwise direction when dereeled
from the bottom of the coil.
c. Replace and tighten the locking collar.
d. See Loading Wire Drive section for loading
instructions.
For 8” Diameter Spools (Requires optional K468
Spindle Adapter for 8” Spools):
a. Remove the locking collar and the Readi-Reel
adapter (if so equipped) on the 2” diameter
spindle (adapter is not required).
b. Slide S18221 Spindle Adapter onto the 2”
spindle so the brake holding pin enters the
adapter pin hole.
c. Place the spool on the spindle so the adapter tab
enters one of the holes in the back side of the
spool. Be sure the wire comes off the spool in a
clockwise direction when dereeled from the
bottom of the coil.
d. Replace and tighten the Locking Collar.
WARNING
Check to be sure the retaining spring has fully
returned to the locking position and has securely
locked the Readi-Reel cage in place. Retaining
spring must rest on the cage, not the welding
electrode.
LN-25
e. Load wire into wire drive per Loading Wire Drive
Section.
MOUNTING 13 OR 14 LB INNERSHIELD COILS
(Requires Optional K435 Spindle Adapter for 14 lb
Coils.)
a. Remove the locking collar and the Readi-Reel
adapter (if so equipped) on the 2” diameter
spindle (adapter is not required).
b. Mount K435 Spindle Adapter and Innershield coil
per the Instructions (S18256) included with the
K435.
Page 16

B-5
2" O.D. SPINDLE
MOLDED ADAPTER
RETAINING SPRING
INSIDE CAGE WIRES
READI-REEL
GROOVES
BRAKE HOLDING PIN
(MUST ENGAGE HOLE IN
ADAPTER RIB)
THREAD LOCKING COLLAR
OPERATION
FIGURE B.2 READI-REEL INSTALLATION
B-5
LOADING WIRE DRIVE
a. Turn the reel or spool until the free end of the
electrode is accessible.
b. While tightly holding the electrode, cut off the
bent end and straighten the first six inches. Cut
off the first inch. (If the electrode is not properly
straightened, it may not feed or may not go into
the outgoing guide tube causing a “bird nest”.)
c. Insert the free end through the incoming guide
tube to the drive roll.
d. Turn on the welding power source.
Unless an optional output control or internal
contactor is used with the LN-25, the electrode circuit
is electrically “hot” when the power source is on.
e. Press the gun trigger and push the electrode
until it just enters the drive roll.
When inching with gun trigger, the electrode and
drive mechanism are always “hot” to work and
ground. Use the “cold” inch switch on models with
internal contactor.
WARNING
WARNING
f. Inch the electrode through the gun.
g. Adjust the brake tension with the thumbscrew on
the spindle hub until the reel turns freely, but
with little or no overrun when wire feeding is
stopped. Do not over tighten.
CAUTION
Keep gun in LN-25 gun holder when not feeding wire
to prevent accidental arcing.
IDLE ROLL PRESSURE SETTING
The idle roll pressure is set at the factory backed out
two turns from full pressure. This is an approximate
setting. For small wire sizes and aluminum wire, the
optimum idle roll pressure varies with type of wire,
surface condition, lubrication and hardness. The optimum idle roll setting can be determined as follows:
1. Press end of gun against a solid object that is
electrically isolated from the welder output.
Press the gun trigger for several seconds.
2. If the wire “bird nests,” jams or breaks at the
drive roll, the idle roll pressure is too great. Back
the pressure setting out
through gun, and repeat above steps.
LN-25
1
2 turn, run new wire
Page 17

B-6
3. If the only result is drive roll slippage, shut off
the power source, then loosen the gun cable
clamping screw in the gearbox conductor block
and pull the gun cable forward about six inches.
There should be a slight waviness in the
exposed wire. If there is no waviness, the
pressure is too low. Increase the pressure
setting
repeat the above steps.
1
4 turn, lock the gun cable in place and
PRESETTING WIRE FEED SPEED
The LN-25 permits accurate presetting of the desired
wire feed speed, before welding, in both CV and CC
wire feed modes.
SETTING CONSTANT WIRE FEED SPEED (CV
MODE)
a. Set Wire Feed Mode switch to CV position.
b. Set Dial Range switch to LO position for wire
feed speeds up to 350 in/min., or HI position for
wire feed speeds over 350 in/min.
c. Set Wire Feed dial to the desired wire feed
speed on the selected calibrated dial range.
OPERATION
FIGURE B.3 CC WIRE SPEED SETTING
B-6
(Hl or LO Range)
The wire speed will remain constant at the value set,
independent of arc voltage changes, as long as the
arc voltage does not drop below the value per the
chart below for the max. wire feed speed shown:
Maximum Speed Minimum Arc Volts
350 IPM 15V
400 IPM 17V
500 IPM 21V
600 IPM 24V
700 IPM 27V
SETTING ARC SENSING WIRE FEED SPEED
(VV [CC] MODE)
When using a constant current (formerly variable
voltage) power source, welding performance is improved using arc sensing wire feed speed (VV [CC]
mode). In this wire feed mode the wire speed
increases if arc voltage increases, and decreases if
arc voltage decreases, but remains constant at any
specific voltage level.
The LN-25 permits accurate VV (CC) mode
presetting of the desired wire feed speed, for the
desired arc voltage to be used, by setting the Wire
Speed dial in the following manner before welding:
b. Referring to the graph located above the Mode
switch (also shown in Figure B.3):
1. Select the horizontal line representing the DESIRED IN/MIN. for the welding procedure. (See
example arrow line for 375 in/min.)
2. Select the diagonal line representing the ARC
VOLTS to be used for the welding procedure.
(See example arrow line for 29 volts.)
3. Determine the vertical line representing the CC
WIRE SPEED SETTING where the above two
lines cross. (See example arrow line for 450.)
c. Set the Wire Speed dial to the value determined
in Step (3) above (450 for example used). Use
HI Dial Range if value to be set is over 350.
The wire will feed at the DESIRED IN/MIN speed
when the welding power source is set to the arc
voltage to be used for the weld procedure (375
in/min. at 29V for example used).
A chart representation of the VV (CC) wire speed
setting graph is shown in Figure B.4, giving the Wire
Speed dial setting required for the DESIRED IN/MIN
and ARC VOLTS used for the welding procedures:
a. Set Wire Feed Mode switch to VV (CC) position.
LN-25
Page 18

B-7
Desired
In/Min 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34
50 109 97 88 80 73 67 63 58 55 51
60 131 117 105 95 88 81 75 70 66 62
70 153 136 123 111 102 94 88 82 77 72
80 175 156 140 127 117 108 100 93 88 82
90 197 175 158 143 131 121 113 105 98 93
100 219 194 175 159 146 135 125 117 109 103
110 241 214 193 175 160 148 138 128 120 113
120 263 233 210 191 175 162 150 140 131 124
130 284 253 228 207 190 175 163 152 142 134
140 306 272 245 223 204 188 175 163 153 144
150 328 292 263 239 219 202 188 175 164 154
160 350 311 280 255 233 215 200 187 175 165
170 372 331 298 270 248 229 213 198 186 175
180 394 350 315 286 263 242 225 210 197 185
190 416 369 333 302 277 256 238 222 208 196
200 438 389 350 318 292 269 250 233 219 206
210 459 408 368 334 306 283 263 245 230 216
220 481 428 385 350 321 296 275 257 241 226
230 503 447 403 366 335 310 288 268 252 237
240 525 467 420 382 350 323 300 280 263 247
250 547 486 438 398 365 337 313 292 273 257
260 569 506 455 414 379 350 325 303 284 268
270 591 525 473 430 394 365 338 315 295 278
280 613 544 490 445 408 377 350 327 306 288
290 634 564 508 461 423 390 363 338 317 299
300 656 583 525 477 438 404 375 350 328 309
310 678 603 543 493 452 417 388 362 339 319
320 700 622 560 509 467 431 400 373 350 329
330 642 578 525 481 444 413 385 361 340
340 661 595 541 496 458 425 397 372 350
350 681 613 557 510 471 438 408 383 360
360 700 630 572 526 484 450 420 394 370
380 666 604 554 512 472 444 416 392
400 700 636 584 538 500 466 438 412
420 668 612 566 526 490 460 432
440 700 642 592 550 514 482 452
460 670 620 576 536 504 472
480 700 646 600 560 526 494
500 674 626 584 546 514
520 700 650 606 568 536
540 676 630 590 556
560 700 654 612 576
580 676 634 598
600 700 656 618
620 678 638
640 700 658
660 680
680 700
700
VV (CC) Speed Setting =
Arc Volts Used
Desired IPM
OPERATION
X 35
( Arc Volts)
B-7
MAKING A WELD
The serviceability of a product or structure utilizing
the LN-25 wire feeder is and must be the sole
responsibility of the builder/user. Many variables
beyond the control of The Lincoln Electric Company
affect the results obtained in using the LN-25 wire
feeder. These variables include, but are not limited to,
welding procedure, plate chemistry and temperature,
weldment design, fabrication methods and service
requirements. The available range of the LN-25 wire
feeder may not be suitable for all applications, and
the builder/user is and must be solely responsible for
welding settings.
SETUP
a. Connect work cable to metal to be welded. Work
cable must make good electrical contact to the
work. The work must also be grounded as stated
in “Arc Welding Safety Precautions.”
b. Check that the LN-25 is properly connected to
the power source for the polarity and process to
be used, and appropriate power source settings
are made for the procedure to be used. (Refer to
power source operating and connection
instructions.)
NOTE: If the K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit or
K624-1 42V Remote Control Module is installed but
the LN-25 is to be used without the K432 Remote
Control Cable Assembly, then the Remote Board
harness plug must be removed from the 16-pin
receptacle on the Control Board and the jumper plug
(T13498-21) reinstalled.
NOTE: If the K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit is
installed but the LN-25 is to be used without the K461
Pulse Power Control Cable Assembly, then the
instructions for returning the unit to across the arc
operation included with the Installation Instructions
(L9636) must be followed.
c. Place the LN-25 conveniently near the work area
in a location to minimize exposure to weld spatter
and to avoid sharp bends in the gun cable.
d. Connect the LN-25 Clip Lead to work and set Po-
larity Switch to same polarity as electrode.
e. Set WIRE FEED MODE switch to CV or CC, as
appropriate for the power source, then set the
proper DIAL RANGE and WIRE SPEED dial setting for the proper wire feed speed per the
welding procedure:
FIGURE B.4 VV(CC) WIRE SPEED SETTING
LN-25
Page 19

B-8
OPERATION
B-8
For CV: Set dial to the calibrated IN/MIN
desired. (Refer to Setting Constant Wire Feed
Speed Section.)
For CC: Set dial to value determined from the
CC Wire Speed Graph for the DESIRED IN/
MIN and ARC VOLTS to be used. (Refer to
Setting Arc Sensing Wire Feed Speed
Section.)
NOTE: If procedure permits a range of acceptable
arc voltage, use the middle of the range to
determine proper WIRE SPEED setting.
f. If using the optional Gas Flow Timer, set the de-
sired PREFLOW TIME and POSTFLOW TIME.
g. Be sure the proper contact tip for the wire size
being used is in the gun, and the gun is safe
from work contact. (Use the LN-25 insulated
gun holder.)
h. Turn on the welding power source, as well as the
shielding gas supply (if used).
WARNING
Unless an optional output control or internal contactor
is used, the electrode is electrically “hot” when the
power source is on. The gun trigger controls wire
feed and gas supplied to the nozzle area (if used).
-----------------------------------------------------------------
a. Cut the electrode within approximately 3
end of the contact tip for solid wire and within
approximately
wire.
b. Position electrode over joint. End of electrode
should be slightly off the work.
c. Lower welding helmet, close gun trigger, and
begin welding. Hold the gun so the contact tip to
work distance gives the correct electrical stickout
as required for the procedure being used.
NOTE: If the arc voltage is not within the proper
procedure range adjust the power source output
control. (The CC mode WIRE SPEED setting should
not be changed from the preset procedure value for
the proper arc voltage.)
d. To stop welding, release the gun trigger and
then pull the gun away from the work. Store the
gun in the LN-25 insulated gun holder when
not welding.
34
” of the extension guide for cored
8” of the
PROCEDURE AT END OF COIL
When the wire on the reel is used up, the following
procedure is to be followed for removing the old wire
from the gun cable and loading a new reel.
a. Shut off power source if a Remote Output
Control Option or internal contactor is not used.
WARNING
CYLINDER may explode if
damaged.
• Keep cylinder upright and
chained to support.
• Keep cylinder away from
areas where it may be damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from
welding or other live electrical circuits.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
WELDING
WARNING
ARC RAYS can burn.
• Do not touch metal portions of the LN-25 lead Clip
when welding power
source is on.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
b. Cut the end of the electrode off at the gun end.
Do not break it off by hand since this puts a slight
bend in the wire and makes it difficult or
impossible to pull it back through the nozzle.
c. Uncouple the gun conductor cable from
the LN-25.
d. Lay the cable out straight.
e. Using pliers to grip the wire, pull it out of the
cable from the connector end. Do not pull it from
the gun end.
f. Put the conductor cable back on wire drive unit
after the electrode has been removed.
g. Load a new coil of wire and feed it through the
cable as described in Loading Electrode Section.
OPEN ARC WELDING WITH A
CONSTANT CURRENT (formerly
variable voltage) POWER SOURCE
WARNING
The LN-25 should be used with a constant current
machine only upon non-critical weldments and after
testing is done to assure quality is adequate for the
application.
------------------------------------------------------------------
LN-25
Page 20

B-9
OPERATION
B-9
CAUTION
Do not use LN-25 models below Code 9200 with
any TIG or Square Wave welding power sources.
Do not use LN-25 models equipped with internal
contactors with non-Lincoln TIG or Square Wave
welding power sources. Damage to the LN-25 circuit
can occur as a result of the high output inductance
typically associated with these power sources. TIG
high frequency power should never be applied to
the LN-25.
While welding with a continuously fed electrode,
weld current variations are continuously taking place.
There are many causes for these variations, but
predominantly they occur due to changes in
electrical stick out (operator hand movements,
nozzle tip contact variations, etc.) and the dynamic
metal transfer characteristics of the process or
procedure being used (short arc, globular transfer,
etc.).
When using a CV power source, these current
variations have essentially no effect on the welding
arc stability since CV power sources can provide a
wide range of weld current levels with virtually no
change in average arc voltage. These “flat slope” CV
power sources, therefore, provide the arc power
required to produce the best welding characteristics
and ease of operation for most open arc, constant
wire feed speed, welding processes.
CC (formerly VV) power sources, on the other hand,
permit the arc voltage to decrease with increases in
welding current. The output characteristics of these
power sources can range from a “drooping slope,”
which provide minor arc voltage changes with weld
current variations, to “steep slope” which provide
broad voltage changes with only minor current
variations. The steeper the slope the more difficult it
becomes to maintain arc voltage stability with a
constant wire speed open arc process.
To aid in stabilizing the arc voltage when welding on
CC power sources the LN-25 is provided with a VV
(CC) wire feed mode. This arc voltage sensing feed
mode decreases (or increases) the wire speed when
the arc voltage decreases (or increases). However,
if the electrode shorts to the work, the arc voltage
will essentially drop to zero and the short circuit
current supplied by the CC power source may not
provide enough power to re-establish the arc
(especially with steeper slope machines). Under this
condition the LN-25 feeder will stop, as if the trigger
was released, and not restart until the short has
been opened.
Arc shorting is more difficult to avoid when using
a CC power source, and requires a more refined
operator technique than when using a CV power
source. Improved performance can be obtained
on CC power source applications within the
following guidelines:
1. Flatter slope power sources with higher arc
force (short circuit current) will improve
performance over steep slope machines. The
steeper the slope, the more critical it is to hold
proper electrode stick out to maintain arc
stability. Welding techniques, such as weaving,
will be more difficult to control. Use the highest
output current tap or setting capable of providing
the voltage adjustment required for the
procedure.
2. Use spray or non-shorting small ball type
transfer processes at higher procedure voltage
levels. Generally, open arc processes with
procedure voltage levels over 22 volts perform
satisfactorily. Arc stability at procedure voltage
levels below 22 volts may be more difficult to
control, with the general exception of fine (.023—
.035) solid steel electrodes with Argon-rich
AUTOMATIC PROTECTION
SHUTDOWN
The LN-25 control provides automatic electronic
protection circuits which shut down the LN-25 for
excessively high power source open circuit voltage
or excessive motor overload.
OVERVOLTAGE SHUTDOWN
If the power source open circuit voltage exceeds
about 110-120 volts, the LN-25 will not operate until
the power source voltage drops below about 102110 volts.
MOTOR OVERLOAD SHUTDOWN
If excessive motor overload occurs (due to prolonged
excessive feeding force, jammed drive rolls or
shorted motor leads), the LN-25 will shut down within
a few seconds after the overload occurs.
The shutdown will reset automatically when the gun
trigger is released, but will reoccur if the overload
situation is not remedied.
LN-25
Page 21

C-1
ACCESSORIES
How to use Table C.1.
Determine which Kit No. is to be used. Locate that Kit No. in the left hand vertical column.
Scan horizontally to determine which LN-25 model is required and what additional kits may be required.
TABLE C.1
LN-25 OPTION CHART
O=CANNOT BE USED WITH X = REQUIRED ➀ = REQUIRES ONE OF THESE + = INCLUDED WITH
SEE TEXT
LN-25 MODELS LN-25 KITS
C-1
KIT NO.
K430-2
K431-1
K432
K433
K434-1
K439
K443-2
K443-3 Contactor Kit
K444
K444-1
K444-2
K-624-1
K625
K626
K627
K460-1
K461
Source w/Terminal Strip
Source w/6 Pin Amphenol
Source w/14 Pin Amphenol
500 Amp Cable /w Stud-
350 Amp Cable /w Stud-
400 Amp Cable /w Twist-
Solenoid
Kit
Remote Output
Control Module
Remote
Control Cable
115VAC
Power Source
Remote Box
Gas Flow
Timer Kit
50 Ft.
Ext. Cable
Contactor Kit
Codes 10500,10558
Codes 11144 & Above
Remote for Power
Remote for Power
Remote for Power
42VAC Remote
Output Control Module
Type Output Terminals
Type Output Terminals
Mate Type Terminals
Pulse Power
Adapter Kit
Pulse Power
Control Cable
K428
LN-25
K446
LN-25
K449
LN-25
K431-1
K432
K433
K443-1
K444
K444-1
K444-2
K460-1
K461
K624-1
K625
K626
K627
++
X
➀➀ OXXOOOOOO
XX
XX
➀➀ ➀ ➀ ➀
X
+ OOO
+ OOO
➀➀ ➀ OOO
➀➀ ➀ OOO
➀➀ ➀ OOO
➀➀ OO OOOOO ➀➀➀
X
X
X
➀➀ OO OOOO X O
X
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: This wire feeder provides “COLD” electrode when gun trigger is released if equipped with K431-1, K432 or
K433 remote output control system, or K443-2 internal contactor kit. This feature and the use of a DC Constant Voltage welder provide an
added margin of safety when welding must be performed under electrically hazardous conditions such as:
• Damp locations • While wearing wet clothing • On metal structures, or, • In cramped positions (sitting, kneeling or lying) if there is a high risk
of unavoidable or accidental contact with the workpiece or ground.
LN-25
Page 22

C-2
ACCESSORIES
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
C-2
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not operate with covers
removed.
• Turn off power source before
installing or servicing.
• Do not touch electrically hot
parts.
• Turn the input power to the
welding power source off at
the fuse box before working
in the terminal strip.
•Only qualified personnel
should install, use or service
this equipment.
K430-2 GAS SOLENOID KIT
(For Codes above 10500 only)
(Factory Installed on K446 and K449 Models)
WARNING
CYLINDER may explode if
damaged.
• Keep cylinder upright and
chained to support.
• Keep cylinder away from areas where it may be
damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached.
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from welding or other live electrical circuits.
• See American National Standard Z-49.1, “Safety in Welding and
Cutting” published by the American Welding Society.
See GMA Gun Cable Gas Connection.
Installation instructions (M19154) are included with
the kit.
The kit permits the LN-25 to be used for Gas
Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) processes with a
GMA gun cable.
The kit can be used with or without a Remote Output
Control option installed in the LN-25 and provides
flow of shielding gas:
1. With wire feed, when the gun trigger is closed.
2. Without wire feed, when the kit’s Purge button
(located beneath the gas inlet fitting) is pressed.
NOTE: Always shut off the valve at the gas cylinder
before making any gas connections to the LN-25.
User must provide a supply of shielding gas, a pressure regulator, a flow control valve and a hose from
the flow valve to the gas inlet fitting of the LN-25.
Install by connecting a supply hose from the gas flow
valve outlet to the
back panel of the LN-25 case.
The LN-25 can be used with any shielding gas
recommended in the electrode’s product literature at
a maximum pressure of 60 psi (4.1 bar). This may
include gases such as Argon, Helium, Nitrogen and
blended gasses such as Ar-He, Ar-N2, Ar-O2, ArCO2, CO2, Ar-CO2-O2.
5
8-18 female inert gas fitting on the
K434-1 GAS FLOW TIMER KIT
(Requires either a K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit,
K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit, K624-1 42V
Remote Output Control Kit, or internal contactor
K443-1 installed in LN-25).
The K434-1 Gas Flow Timer Kit is used with the
LN-25 Gas Solenoid when the LN-25 is equipped
with any of the Remote Output Control Options or
internal contactor.
This kit provides the following gas flow timer functions:
1. Preflow Control - Provides flow of shielding
gas to the work before the arc is established.
The solenoid valve is energized immediately
when the gun trigger is closed, but the time
delay before the wire feeder and welding output
are energized is adjustable between at least
0 to 1 second.
2. Postflow Control - Provides flow of shielding
gas to the work after welding is stopped. Delay
of the shut off of the solenoid valve after the gun
trigger is released is adjustable between at least
0.5 to 5 seconds.
Installation instructions (M17590) are included with
LN-25
this kit.
Page 23

C-3
ACCESSORIES
C-3
K460-1 PULSE POWER ADAPTER KIT (For use with
K461 Pulse Power Control Cable.)(No Longer Available)
This kit enables the LN-25 to pulse weld with a Pulse
Power 500 power source above Code 9300 (or lower
Codes updated with Kit).
The kit includes a Remote PC board with output voltage control, and control cable receptacle which mount
and connect inside the LN-25 control box per the
Installation Instructions (L9636) included with the kit.
NOTE: If the K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit is in-
stalled but the LN-25 is to be used without the K461
Pulse Power Control Cable Assembly, then the instructions for returning the unit to across the arc operation included with the Installation Instructions
(L9636) must be followed.
K461 PULSE POWER CONTROL CABLE
ASSEMBLY (No Longer Available)
(Requires K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter Kit installed in
LN-25.)
CAUTION
This kit can only be used with LN-25’s Code 10500-
10558. To prevent possible damage to the LN-25 with
internal contactor, do not connect to non-Lincoln TIG
or Square Wave power sources. TIG high frequency
power should never be applied to the LN-25.
K443-3 LN-25 CONTACTOR KIT
(For Codes above 11100 only)
(Factory installed in K449 Model.)
The internal contactor provides “cold” electrode until
the gun trigger is pressed, and a fixed burnback time
delay to prevent electrode from sticking in the weld
crater when the trigger is released. The contactor is
rated for use up to 300 amps. A cold inch switch
allows the wire to be loaded into the system without
being electrically “hot”.
Installation Instructions (L12319) are included with
the kit.
The K461 control cable assemblies include an electrode cable, rated for up to 500 amps 60% duty cycle,
and a 9-conductor control cable. The control cable pin
connector connects to the LN-25 and the lugged leads
connect to the Pulse Power. Available in 25, 50, 75 and
100 ft. lengths.
K443-2 LN-25 CONTACTOR KIT
(For Codes 10500 - 10558 only)
(Factory installed in K449 Model.)
The internal contactor provides “cold” electrode until
the gun trigger is pressed, and a fixed burnback time
delay to prevent electrode from sticking in the weld
crater when the trigger is released. The contactor is
rated for use up to 300 amps. A cold inch switch allows
the wire to be loaded into the system without being
electrically “hot”.
Installation Instructions (L10923) are included with
the kit.
NOTE: The K443-2 cannot be used with K431-1 or
K624-1 Remote Output Control Kit or K460-1 Pulse
Power Adapter Kit. If remote voltage control is desired
along with the internal contactor, obtain a K444, K4441 or K444-2 Remote Voltage Control Kit.
NOTE: The K443-3 cannot be used with K431-1 or
K624-1 Remote Output Control Kit or K460-1 Pulse
Power Adapter Kit. If remote voltage control is desired
along with the internal contactor, obtain a K444, K4441 or K444-2 Remote Voltage Control Kit.
CAUTION
This kit can only be used with LN-25’s above Code
11100. To prevent possible damage to the LN-25 with
internal contactor, do not connect to non-Lincoln TIG
or Square Wave power sources. TIG high frequency
power should never be applied to the LN-25.
REMOTE OUTPUT CONTROL OPTIONS
AND CONTROL CABLE ASSEMBLIES
Remote Output Control Options are available to provide the LN-25 with the following additional features:
1. “Cold” electrode until the gun trigger is pressed,
and a fixed burnback time delay to prevent electrode from sticking in the weld crater when the
gun trigger is released.
2. Remote (10K ohm rheostat) control of power
source output arc voltage level.
K431-1 REMOTE OUTPUT CONTROL KIT
LN-25
(For use with K432 Remote Control Cable and K433
Power Source Remote Box.)
Page 24

C-4
ACCESSORIES
C-4
The Kit includes a Remote PC board and control
cable receptacle which mount and connect inside the
LN-25 control box per the Installation Instructions
(M17584) included with the kit.
NOTE: If the K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit is
installed but the LN-25 is to be used without the
K432 Remote Control Cable Assembly, then the Remote Board harness plug must be removed from the
16-pin receptacle on the Control Board and the
jumper plug (T13498-21) reinstalled.
K433 POWER SOURCE REMOTE BOX
(Requires K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit installed
in LN-25 using K432 Remote Control Cable.)
The Remote Box is designed to mount and connect
to Lincoln Idealarc
the Installation Instructions (M15324) and power
source connection diagrams included with the kit.
The Remote Box provides the proper welding power
source control interface and isolated 24V AC input
supply for the LN-25 equipped with the K431-1
Remote Output Control Kit.
Remote Box requires 115V AC, 50/60 Hz input and
a welding power source using a contact closure
output pilot circuit, as available on appropriate
Lincoln welding power sources.
K432 REMOTE CONTROL CABLE ASSEMBLY
(Requires K431-1 Remote Output Control Kit
installed in LN-25 and K433 Remote Box mounted to
power source with 115V AC auxiliary power.)
The K432 control cable assemblies include an
electrode cable, rated for up to 500 amps 60% duty
cycle, and a 6-conductor control cable with pin
connectors on both ends. Available in 25, 50, 75 and
100 ft. lengths.
The cable assembly end with the socket pin
connector connects to the LN-25 per the Instructions
(M17584) included with the K431-1 kit.
The cable assembly end with the male pin connector
connects to the K433 and power source per the Instructions included with the K433 kit.
®
semiautomatic power sources per
Multiple K439 Extensions may be used, however, to
prevent excessive weld cable voltage drops, the 500
amp max. rating of the K432 should be reduced by
at least 50 amps for each K439 Extension used. For
example, if three K439 Extensions are used (150 ft
total extension), the maximum welding current used
should be less than 350 amps.
The K439 Extension cable end with the male pin
connector connects to the K433 Remote Box and
power source per the Instructions included with the
K433 kit.
The K439 Extension cable end with the socket pin
connector connects to the mating K432 cable end (or
next K439 Extension cable end). The electrode
cables are connected using the bolt and nut provided
with the K439 Extension. Properly insulate the bolted
connection with electrical tape.
K624-1 42V REMOTE OUTPUT CONTROL
MODULE
(For use with K625, K626, K627 Remote
Control Cable)
The Module includes a 42V Remote PC board and
control cable receptacle which mount and connect
inside the LN-25 control box per the Installation
Instructions (M17253) included with the kit.
NOTE: If the K624-1 42V Remote Output Control
Module is installed but the LN-25 is to be used
without the K625, K626 or K627 Remote Control
Cable Assembly, then the Remote Board harness
plug must be removed from the 16-pin receptacle on
the Control Board and the jumper plug (T13498-21)
reinstalled.
K625, K626, K627 REMOTE CONTROL CABLE
ASSEMBLY
(Requires K624-1 Remote Output Control Module
installed in LN-25.)
The K625, K626, K627 control cable assemblies include an electrode cable and a 8-conductor
control cable:
K439 REMOTE EXTENSION CABLE ASSEMBLY
The 50 ft. Extension cable assemblies are used to
extend the K432 Remote Control Cable Assembly
when longer cable lengths are required.
LN-25
Page 25

C-5
ACCESSORIES
C-5
The cable assembly end with the socket pin
connector connects to the LN-25 per the Instructions
(M17253) included with the K624-1 Kit.
CABLE 60% DUTY POWER SOURCE
TYPE RATING ELECTRODE
CONNECTION
K625 500 Amps Stud Terminal
K626 350 Amps Stud Terminal
K627 400 Amps Twist-Mate™
The cable assembly end with the male pin connector
connects to the power source per the Instructions
(M17253) included with the K624-1 kit.
K444, K444-1 OR K444-2 REMOTE VOLTAGE
CONTROL KIT
(Not required if using K431-1 or K624-1 Remote
Output Control Kit or K460-1 Pulse Power Adapter
Kit.)
The Remote Voltage Control Kit provides remote
(10K ohm rheostat) control of power source output
arc voltage level.
K577-1 REAR HANDLE KIT
(For LN-25 model codes above 9383)
The fold-down handle mounts to the rear of the LN25 case per the Installation Instructions (M16567)
shipped with the kit.
This handle provides a means to also carry the LN25 in the vertical position, especially convenient for
passing the unit through a manhole.
K363P READI-REEL ADAPTER KIT
Adapts Lincoln Redi-Reel coils of electrode 30 lb.
(14 kg) and 22 lb. (10 kg) to a 2” (51mm) spindle.
Durable molded plastic one piece construction.
Designed for easy loading; adapter remains on
spindle for quick changeover.
K444 connects to power sources with control
terminal strip connections for lead numbers 75, 76
and 77.
K444-1 connects to power sources with a 6-pin
control receptacle.
NOTE: To use a K444-1 with power sources with
only a 14-pin control receptacle, a K864 Adapter is
required to connect to K444-1 and if using a power
source without an output control switch, a K484
Jumper Plug will also be required to jumper the
output pilot circuit (2-4).
K444-2 connects to power sources with a 14-pin
control receptacle and provides a 2-4 jumper to
activate power source output.
Installation Instructions are included with the kit.
LN-25
Page 26

C-6
ACCESSORIES
The following Figures C.1 and C.2 should serve as a guide to determine if a particular gun or switch
can be connected to the LN-25.
GUN CABLE CONNECTOR REQUIREMENTS
TO PERMIT PROPER CONNECTION TO
LINCOLN LN-25 WIRE FEEDER.
C-6
LN-25 Cable Connector for .023 through .052 Wire
(For all other dimensions, see above)
NOTE: Connector part with .749/.747 diameter
should be made from brass if it is to be part of the
welding current carrying circuit.
Wire Size Dia. Within .008 F.I.M.
To be Concentric to .749/.747
.068 thru
5
64 .125 (18 Drill)
1
16 (.062) .078 (564 Drill)
.045 & .052 .062 (
.023 thru .035 .055 (#54 Drill)
Drive Roll & Guide Tube Wire Sizes Used
Kit No.
T-13355-
T-13355-
3
32
(1)
1
16
T-13355-.052C .045, .052 Cored
T-13355-.052 .045, .052 Solid
T-15010.-.035S .023 thru .035 Solid
(1)
Can also be used for .052” wire
“A Dia. Hole”
1
16 Drill)
5
64, .072 & .068
1
16, .062
FIGURE C.1
SWITCH REQUIREMENTS
1
2 Amp AC 24 Volts – Inductive
1
2 Amp DC 24 Volts – Inductive
S12024-1 (L.E. Part No.)
Amphenol AN3057-10 (or equiv.)
S12020-6 (L.E. Part No.)
Amphenol MS-3106A-18-11P (or equiv.)
FIGURE C.2 SWITCH REQUIREMENTS
LN-25
Page 27

D-1
MAINTENANCE
D-1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not operate with covers
removed.
• Turn off power source before
installing or servicing.
• Do not touch electrically hot
parts.
• Turn the input power to the
welding power source off at
the fuse box before working
in the terminal strip.
•Only qualified personnel
should install, use or service
this equipment.
CONTROL BOX
Every six months open and inspect the control section. The accumulated dirt should be gently blown off
all of the electrical components. Be sure the air that
is being used is dry. Check that lead plugs are secure
in their receptacles.
WIRE DRIVE MOTOR AND GEAR BOX
Every year examine the gear box. Paint the gear
teeth with molydisulfide filled grease. Lincoln
specification E2322. Do not use a graphite grease.
Check the motor brushes. Replace if they are worn
down to 14’’ or less. When ordering feed motor
brushes, give all information from the motor
nameplate.
GUN AND CABLE MAINTENANCE
See IM manual provided with the gun and cable
assembly.
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
DRIVE ROLLS AND GUIDE TUBES
After feeding every coil of wire, inspect the drive roll
section. Clean it as necessary. Do not use a solvent
for cleaning the idle roll because it may wash the
lubricant out of the bearing. The drive roll, idle roll
and guide tubes are stamped with the wire sizes they
will feed. If a wire size other than that stamped on
the rolls is to be used, the rolls and guide tubes must
be changed.
The drive rolls for .035 through .052 cored electrode
1
and
16 through564 electrode have a double set of
teeth so they can be reversed for additional life.
Drive rolls for .023 through .052 solid electrode and
aluminum sizes have no teeth but use two grooves
so they also can be reversed for additional life.
See Wire Feed Drive Roll and Guide Tube Kits Section for roll changing instructions.
WIRE REEL SPINDLE
No routine maintenance required. Do not lubricate spindle.
CIRCUIT PROTECTION AND
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN
CONTROL PC BOARD
The Control P.C. Board has electronic protection for
trigger circuit faults to the electrode circuit.
AUTOMATIC PROTECTION SHUTDOWN
(See Automatic Protection Shutdown Section.)
ADJUSTING SPEED
SENSOR MODULE
The LN-25 Speed Sensor Module is a three lead Hall
Effect switch device encased in an externally
threaded housing which is screwed into a mounting
plate on the motor side of the wire drive gearbox.
Proper positioning of this module is critical to proper
operation of the LN-25 wire feed speed control. If the
device is not screwed in far enough, the LN-25 motor
speed could be unstable or run at full speed with no
control. If screwed in too far, it will rub a moving part
inside the gearbox.
LN-25
The module is properly mounted to the gearbox
as shipped from the factory. If the device is ever
removed or replaced, proper mounting technique is
as follows:
Page 28

D-2
MAINTENANCE
D-2
1. Be sure all power to the LN-25 is shut off at the
power source.
2. Check that the module mounting plate is screwed
securely to the side of the gearbox.
3. Gently screw the module into the mounting plate
until it just touches and stops against the
rotating part inside the gearbox.
1
4. Back the module out
module lock nut without rotating the module
position. Do not over tighten lock nut.
2 turn, then snug the
CALIBRATION OF LN-25 WIRE
SPEED DIAL
Calibration of the LN-25 Wire Speed dial is achieved
by proper mounting of the dial knob to the speed
potentiometer shaft. Whenever the knob is removed,
the dial is recalibrated as follows:
NOTE: Knob set screw does not seat on shaft flat.
1. Be sure the Wire Speed potentiometer mounting
nut is securely tightened, then rotate the
potentiometer shaft so its flat faces about to the
100 mark on the LO range calibrated dial.
WARNING
Electrode will be electrically “hot”. Do not allow fed
wire to contact any metal common with welding work.
An alternate means to measure wire feed speed
is as follows:
a. Cut wire off at the end of the gun tip.
b. Press trigger to feed wire for exactly 30 seconds.
c. Cut fed wire off at the end of the gun tip and
accurately measure its length.
d. Multiply the measured length by 2 to obtain
the wire speed (IN/MIN).
e.Repeat above steps to assure repeatable
accuracy.
4. Carefully slip speed knob onto potentiometer
shaft so it points precisely to the wire speed
measured in step 3, then secure the knob set
screw without disturbing the position. Recheck by
repeating step 3.
2. Set DIAL RANGE switch to LO and WIRE FEED
MODE switch to CV position.
3. Press gun trigger to feed wire and measure
the wire feed speed (IN/MIN) using a Portable
Digital Wire Feed Speed Meter (Lincoln K283).
Take at least two readings to assure repeatable accuracy.
Feed Speed Meter (Lincoln K283). Take at least
two readings to assure repeatable accuracy.
LN-25
Page 29

E-1
TROUBLESHOOTING
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
WARNING
Service and Repair should only be performed by Lincoln Electric Factory Trained Personnel.
Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician and
machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid Electrical
Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual.
__________________________________________________________________________
E-1
This Troubleshooting Guide is provided to help you
locate and repair possible machine malfunctions.
Simply follow the three-step procedure listed below.
Step 1. LOCATE PROBLEM (SYMPTOM).
Look under the column labeled “PROBLEM (SYMPTOMS)”. This column describes possible symptoms
that the machine may exhibit. Find the listing that
best describes the symptom that the machine is
exhibiting.
Step 2. POSSIBLE CAUSE.
The second column labeled “POSSIBLE CAUSE” lists
the obvious external possibilities that may contribute
to the machine symptom.
Step 3. RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION
This column provides a course of action for the
Possible Cause, generally it states to contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
If you do not understand or are unable to perform the
Recommended Course of Action safely, contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
LN-25
Page 30

E-2
TROUBLESHOOTING
E-2
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
No wire feed when gun trigger is
pulled
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
FEEDING PROBLEMS
1. Power source must be on
and open circuit voltage
(OCV) present at weld
terminals.
2. LN-25 work clip may not be
connected.
3. LN-25 polarity switch must
match electrode polarity.
4. Jumper plug on control or
option board may be loose
or missing.
5. The power source O.C.V.
must be above 15 VDC. But
not more than 110 VDC.
6. The gun trigger may be
faulty.- Replace gun.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
Contact your local
Lincoln Authorized
Wire feeds for a short time but
stops feeding. When gun trigger
is released and retriggered wire
feeding starts but stops again.
Wire feeds OK, but stubs or
stops while welding.
Field Service Facility
1. The drive motor may be
overloaded. Check the wire
feeding system. EX. Drive
roll tension, reel brake and
gun cable liner.
1. If the power source is a
constant current type
supply the arc voltage may
be “dipping” below 15 VDC
causing the LN-25 to stop
or hesitate.
2. Connect a constant voltage
type power supply to the
LN-25.
3. Make sure wire-feed mode
switch (S3) is in the proper
position.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your local authorized field service facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
LN-25
Page 31

E-3
TROUBLESHOOTING
E-3
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Rough wire feeding or wire not
feeding but drive rolls turning.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
FEEDING PROBLEMS
1. Gun cable kinked and/or
twisted.
2. Wire jammed in gun and cable.
3. Incorrect size or installation
of drive roll and guide tubes.
4. Drive roll loose.
5. Gun cable dirty.
6. Worn drive roll.
7. Electrode rusty and/or dirty.
8. Worn nozzle or cable liner.
9. Partially flashed or melted
contact tip.
10. Incorrect idle roll pressure.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
Contact your local
Lincoln Authorized
Field Service Facility
11. Wire reel brake tension set
too high.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your local authorized field service facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
LN-25
Page 32

E-4
TROUBLESHOOTING
E-4
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Solenoid does not close when
trigger is pulled or purge button
is pressed. Wire feeds properly.
Variable or “hunting” arc.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
OUTPUT PROBLEMS
1. Make certain that plugs J2
and J3 are connected to the
control board securely.
WELD PROBLEMS
1. Worn and/or melted contact
tip -Replace.
2. Worn work cable or poor
work connection.
3. Loose electrode connections. -Check for loose or
faulty connections.
4. Wrong electrode polarity for
process being used.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
Contact your local
Lincoln Authorized
Field Service Facility
Weld porosity, narrow and ropey
bead, or electrode stubbing into
plate when welding.
Motor feeds but there is no wire
feed speed control.
1. Contaminated weld joint or
improper procedures. Clean joint and check
procedure (wire speed and
all voltage).
1. Make sure all molex plugs
and leads are securely
connected to the control
board.
2. Check speed sensor - see
maintenance section.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your local authorized field service facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
LN-25
Page 33

F-1
WIRING DIAGRAM
F-1
WIRING DIAGRAM LN-25 FOR CODES 10556, 10557 AND 10558
LN-25
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside the machine on
one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number.
Page 34

F-2
WIRING DIAGRAM
F-2
LN-25
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside the machine on
one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number.
Page 35

F-3
16.60
14.00
21.00
7.40
.25
DIMENSIONS
LN-25 PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
F-3
LN-25
Page 36

NOTES
LN-25
Page 37

NOTES
LN-25
Page 38

WARNING
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
● Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
● Insulate yourself from work and
ground.
● No toque las partes o los electrodos
bajo carga con la piel o ropa mojada.
● Aislese del trabajo y de la tierra.
● Keep flammable materials away.
● Mantenga el material combustible
fuera del área de trabajo.
● Wear eye, ear and body protection.
● Protéjase los ojos, los oídos y el
cuerpo.
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
● Ne laissez ni la peau ni des vête-
ments mouillés entrer en contact
avec des pièces sous tension.
● Isolez-vous du travail et de la terre.
● Berühren Sie keine stromführenden
Teile oder Elektroden mit Ihrem
Körper oder feuchter Kleidung!
● Isolieren Sie sich von den
Elektroden und dem Erdboden!
● Não toque partes elétricas e elec-
trodos com a pele ou roupa molhada.
● Isole-se da peça e terra.
● Gardez à l’écart de tout matériel
inflammable.
● Entfernen Sie brennbarres Material!
● Mantenha inflamáveis bem guarda-
dos.
● Protégez vos yeux, vos oreilles et
votre corps.
● Tragen Sie Augen-, Ohren- und Kör-
perschutz!
● Use proteção para a vista, ouvido e
corpo.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE MANUFACTURER’S INSTRUCTION FOR THIS EQUIPMENT AND THE CONSUMABLES TO BE
USED AND FOLLOW YOUR EMPLOYER’S SAFETY PRACTICES.
SE RECOMIENDA LEER Y ENTENDER LAS INSTRUCCIONES DEL FABRICANTE PARA EL USO DE ESTE EQUIPO Y LOS
CONSUMIBLES QUE VA A UTILIZAR, SIGA LAS MEDIDAS DE SEGURIDAD DE SU SUPERVISOR.
LISEZ ET COMPRENEZ LES INSTRUCTIONS DU FABRICANT EN CE QUI REGARDE CET EQUIPMENT ET LES PRODUITS A
ETRE EMPLOYES ET SUIVEZ LES PROCEDURES DE SECURITE DE VOTRE EMPLOYEUR.
LESEN SIE UND BEFOLGEN SIE DIE BETRIEBSANLEITUNG DER ANLAGE UND DEN ELEKTRODENEINSATZ DES HERSTELLERS. DIE UNFALLVERHÜTUNGSVORSCHRIFTEN DES ARBEITGEBERS SIND EBENFALLS ZU BEACHTEN.
Page 39

● Keep your head out of fumes.
● Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing zone.
● Turn power off before servicing.
● Do not operate with panel open or
guards off.
WARNING
● Los humos fuera de la zona de res-
piración.
● Mantenga la cabeza fuera de los
humos. Utilice ventilación o
aspiración para gases.
● Gardez la tête à l’écart des fumées.
● Utilisez un ventilateur ou un aspira-
teur pour ôter les fumées des zones
de travail.
● Vermeiden Sie das Einatmen von
Schweibrauch!
● Sorgen Sie für gute Be- und
Entlüftung des Arbeitsplatzes!
● Mantenha seu rosto da fumaça.
● Use ventilação e exhaustão para
remover fumo da zona respiratória.
● Desconectar el cable de ali-
mentación de poder de la máquina
antes de iniciar cualquier servicio.
● Débranchez le courant avant l’entre-
tien.
● Strom vor Wartungsarbeiten
abschalten! (Netzstrom völlig öffnen; Maschine anhalten!)
● Não opere com as tampas removidas.
● Desligue a corrente antes de fazer
serviço.
● Não toque as partes elétricas nuas.
● No operar con panel abierto o
guardas quitadas.
● N’opérez pas avec les panneaux
ouverts ou avec les dispositifs de
protection enlevés.
● Anlage nie ohne Schutzgehäuse
oder Innenschutzverkleidung in
Betrieb setzen!
● Mantenha-se afastado das partes
moventes.
● Não opere com os paineis abertos
ou guardas removidas.
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
LEIA E COMPREENDA AS INSTRUÇÕES DO FABRICANTE PARA ESTE EQUIPAMENTO E AS PARTES DE USO, E SIGA AS
PRÁTICAS DE SEGURANÇA DO EMPREGADOR.
Page 40

• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
 Loading...
Loading...