Page 1
LN-25™ PRO
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
IM2071
10/2017
REV01
ENGLISH
22801 St. Clair Ave., Cleveland Ohio 44117-1199 USA
THE LINCOLN ELECTRIC COMPANY
www.lincolnelectric.eu
Page 2

THE LINCOLN ELECTRIC COMPANY
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer and technical documentation
holder:
Address:
EC Company:
Address:
Hereby declare that welding equipment:
Product Numbers:
Is in conformity with Council Directives and
amendments:
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
Standards: EN 60974-5: 2013, Arc Welding Equipment – Part 5: Wire Feeders,
CE marking affixed in 08
Samir Farah, Manufacturer Dario Gatti, European Community Representative
Compliance Engineering Manager European Engineering Director Machines
17 May 2016 19 May 2016
MCD143e
The Lincoln Electric Company
22801 St. Clair Ave.
Cleveland Ohio 44117-1199 USA
Lincoln Electric Europe S.L.
c/o Balmes, 89 - 80 2a
08008 Barcelona
SPAIN
LN-25 PRO & LN-25 PRO Dual, Wire Feeders
K2613 & K2614
(Product numbers may also contain prefixes and suffixes)
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU
EN 60974-10: 2007 Arc Welding Equipment – Part 10:
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements;
English English
I
Page 3

THANKS! For having chosen the QUALITY of the Lincoln Electric products.
Please Examine Package and Equipment for Damage. Claims for material damaged in shipment must be notified
immediately to the dealer.
For future reference record in the table below your equipment identification information. Model Name, Code &
Serial Number can be found on the machine rating plate.
Model Name:
………………...…………………………….…………………………………………………………………………………………..
Code & Serial number:
………………….……………………………………………….. …………………………………………………….……………..
Date & Where Purchased:
…………………………………………………………………... ……………………….…………………………………………..
ENGLISH INDEX
Technical specifications ...................................................................................................................................................... 1
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ................................................................................................................................. 2
Safety .................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
Installation and Operator Instructions ................................................................................................................................. 4
WEEE ................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
Spare Parts ....................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Authorized Service Shops Location .................................................................................................................................. 18
Electrical Schematic .......................................................................................................................................................... 19
Suggested Accessories ..................................................................................................................................................... 20
12/05
English English
II
Page 4
Technical specifications
LN-25™ PRO (K2613-5, K2613-7) (CODE NUMBER: 11746, 11747).
INPUT VOLTAGE AND CURRENT
INPUT VOLTAGE ± 10% INPUT AMPERES
DUTY CYCLE INPUT AMPERES
60% RATING 450
GEARING - WIRE FEED SPEED RANGE-WIRE SIZE
GEARING
EXTRA TORQUE K2613-7
STANDARD SPEED
K2613-5
HEIGHT WIDTH DEPTH WEIGHT
14.8 INCHES
(376 MM)
HANDLE FOLDED DOWN
15-110 VDC
4A
RATED OUTPUT @ 104°F (40°C)
GMAW FCAW
WFS RANGE WIRE SIZES WFS RANGE WIRE SIZES
50 – 400 IPM
(1.3 – 10.1M/MIN)
50 – 700 IPM
(1.3 – 17.7M/MIN)
.023 – 1/16"
(0.6 – 1.6MM)
.023 – 1/16"
(0.6 – 1.6MM)
50 – 400 IPM
(1.3 – 10.1M/MIN)
50 – 700 IPM
(1.3 – 17.7M/MIN)
.030 - 3/32”
(0.8 – 2.4MM)
.030 - 5/64
(0.8 - 2.0MM)
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
8.7 INCHES
( 221 MM)
23.2 INCHES
(589 MM)
38 LBS
(17 KG)
TEMPERATURE RANGE
OPERATION: STORAGE:
Thermal tests have been performed at ambient temperature. The duty cycle (duty factor) at 40°C has been
determined by simulation.
Duty cycle is based upon the amount of welding performed in a 10 minute period.
-40°F TO 104°F (-40°C TO 40°C)
-40°F TO 122°F (-40°C TO 50°C)
IP23
IEC 60974-5
English English
1
Page 5

Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This machine has been designed in accordance with all relevant directives and standards. However, it may still generate
electromagnetic disturbances that can affect other systems like telecommunications (telephone, radio, and television) or
other safety systems. These disturbances can cause safety problems in the affected systems. Read and understand
this section to eliminate or reduce the amount of electromagnetic disturbance generated by this machine.
with, if necessary, assistance from Lincoln Electric.
Before installing the machine, the operator must check the work area for any devices that may malfunction because of
electromagnetic disturbances. Consider the following.
Input and output cables, control cables, and telephone cables that are in or adjacent to the work area and the
machine.
Radio and/or television transmitters and receivers. Computers or computer controlled equipment.
Safety and control equipment for industrial processes. Equipment for calibration and measurement.
Personal medical devices like pacemakers and hearing aids.
Check the electromagnetic immunity for equipment operating in or near the work area. The operator must be sure
that all equipment in the area is compatible. This may require additional protection measures.
The dimensions of the work area to consider will depend on the construction of the area and other activities that are
taking place.
Consider the following guidelines to reduce electromagnetic emissions from the machine.
Connect the machine to the input supply according to this manual. If disturbances occur if may be necessary to take
additional precautions such as filtering the input supply.
The output cables should be kept as short as possible and should be positioned together. If possible connect the
work piece to ground in order to reduce the electromagnetic emissions. The operator must check that connecting
the work piece to ground does not cause problems or unsafe operating conditions for personnel and equipment.
Shielding of cables in the work area can reduce electromagnetic emissions. This may be necessary for special
applications.
EMC classification of this product is class A in accordance with electromagnetic compatibility standard EN 60974-10 and
therefore the product is designed to be used in an industrial environment only.
The Class A equipment is not intended for use in residential locations where the electrical power is provided by the public
low-voltage supply system. There can be potential difficulties in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility in those locations,
due to conducted as well as radio-frequency disturbances.
This machine has been designed to operate in an industrial area. To operate in a domestic area it is
necessary to observe particular precautions to eliminate possible electromagnetic disturbances. The
operator must install and operate this equipment as described in this manual. If any electromagnetic
disturbances are detected the operator must put in place corrective actions to eliminate these disturbances
WARNING
WARNING
01/11
English English
2
Page 6
Safety
11/04
WARNING
This equipment must be used by qualified personnel. Be sure that all installation, operation, maintenance and repair
procedures are performed only by qualified person. Read and understand this manual before operating this equipment.
Failure to follow the instructions in this manual could cause serious personal injury, loss of life, or damage to this
equipment. Read and understand the following explanations of the warning symbols. Lincoln Electric is not responsible
for damages caused by improper installation, improper care or abnormal operation.
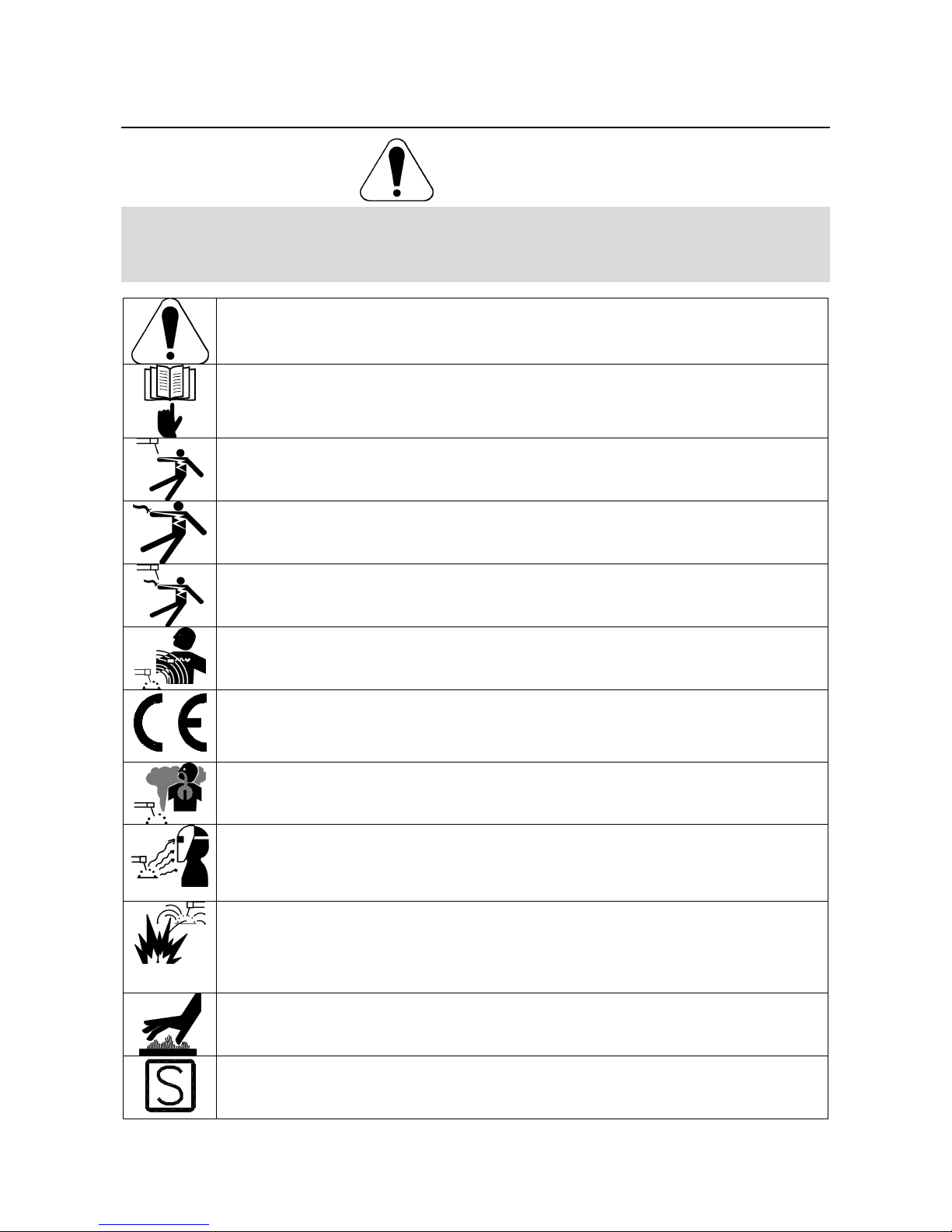
WARNING: This symbol indicates that instructions must be followed to avoid serious personal injury,
loss of life, or damage to this equipment. Protect yourself and others from possible serious injury or
death.
READ AND UNDERSTAND INSTRUCTIONS: Read and understand this manual before operating this
equipment. Arc welding can be hazardous. Failure to follow the instructions in this manual could cause
serious personal injury, loss of life, or damage to this equipment.
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL: Welding equipment generates high voltages. Do not touch the
electrode, work clamp, or connected work pieces when this equipment is on. Insulate yourself from the
electrode, work clamp, and connected work pieces.
ELECTRICALLY POWERED EQUIPMENT: Turn off input power using the disconnect switch at the
fuse box before working on this equipment. Ground this equipment in accordance with local electrical
regulations.
ELECTRICALLY POWERED EQUIPMENT: Regularly inspect the input, electrode, and work clamp
cables. If any insulation damage exists replace the cable immediately. Do not place the electrode
holder directly on the welding table or any other surface in contact with the work clamp to avoid the
risk of accidental arc ignition.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS MAY BE DANGEROUS: Electric current flowing through any
conductor creates electric and magnetic fields (EMF). EMF fields may interfere with some
pacemakers, and welders having a pacemaker shall consult their physician before operating this
equipment.
CE COMPLIANCE: This equipment complies with the European Community Directives.
FUMES AND GASES CAN BE DANGEROUS: Welding may produce fumes and gases hazardous to
health. Avoid breathing these fumes and gases. To avoid these dangers the operator must use
enough ventilation or exhaust to keep fumes and gases away from the breathing zone.
ARC RAYS CAN BURN: Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your eyes from
sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or observing. Use suitable clothing made from durable
flame-resistant material to protect you skin and that of your helpers. Protect other nearby personnel
with suitable, non-flammable screening and warn them not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to
the arc.
WELDING SPARKS CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION: Remove fire hazards from the welding area
and have a fire extinguisher readily available. Welding sparks and hot materials from the welding
process can easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Do not weld on any
tanks, drums, containers, or material until the proper steps have been taken to insure that no
flammable or toxic vapors will be present. Never operate this equipment when flammable gases,
vapors or liquid combustibles are present.
WELDED MATERIALS CAN BURN: Welding generates a large amount of heat. Hot surfaces and
materials in work area can cause serious burns. Use gloves and pliers when touching or moving
materials in the work area.
SAFETY MARK: This equipment is suitable for supplying power for welding operations carried out in
an environment with increased hazard of electric shock.
English English
3
Page 7
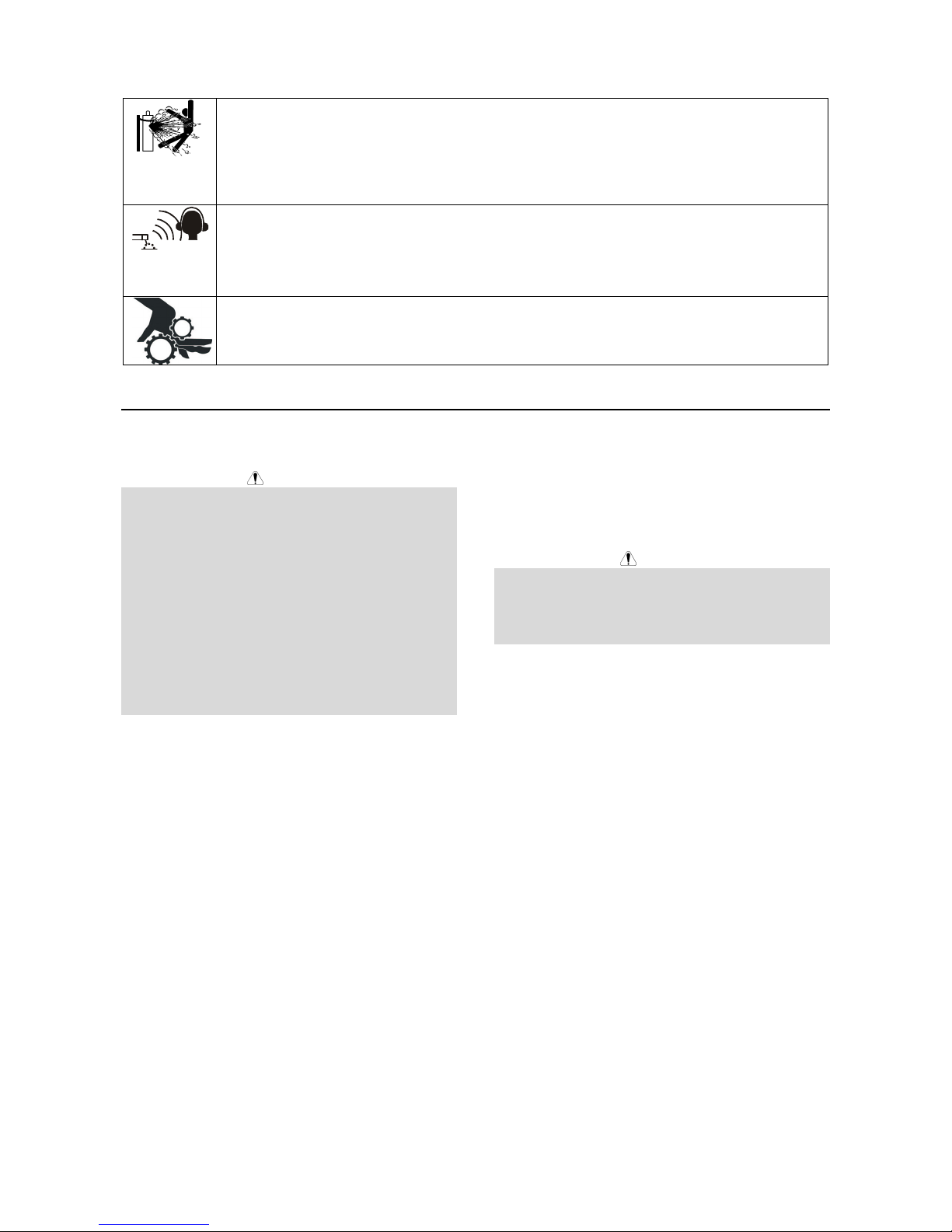
CYLINDER MAY EXPLODE IF DAMAGED: Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct
shielding gas for the process used and properly operating regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to a fixed support. Do
not move or transport gas cylinders with the protection cap removed. Do not allow the electrode,
electrode holder, work clamp or any other electrically live part to touch a gas cylinder. Gas cylinders
must be located away from areas where they may be subjected to physical damage or the welding
process including sparks and heat sources.
NOISE APPEARES DURING WELDING CAN BE HARMFUL: Welding arc can cause noise with high
level of 85dB for 8-hour week day. Welders operating welding machines are obligated to wear the
proper ear protectors /appendix No. 2 for the Decree of the Secretary of Labor and Social Policy from
17.06 1998 – Dz.U. No. 79 pos. 513/. According to the Decree the Secretary of Health and Social
Welfare from 09.07.1996 /Dz.U. No. 68 pos. 194/, employers are obligated to carry examinations and
measurements of health harmful factors.
MOVING PARTS ARE DANGEROUS: There are moving mechanical parts in this machine, which can
cause serious injury. Keep your hands, body and clothing away from those parts during machine
starting, operating and servicing.
Installation and Operator Instructions
Read this entire section before installation or operation
of the machine.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the disconnect switch or
fuse box before attempting to connect or disconnect
input power lines, output cables or control cables.
• Only qualified personnel should perform this
installation.
• Do not touch metal portions of the LN-25™ PRO
work clip when the welding power source is on.
• Do not attach the work clip to the wire feeder.
• Connect the work clip directly to the work, as close
as possible to the welding arc.
• Turn power off at the welding power source before
disconnecting the work clip from the work.
• Only use on power sources with open circuit voltages
less than 110 VDC.
Location
For best wire feeding performance, place the LN- 25™
Pro on a stable and dry surface. Keep the wire feeder in
a vertical position. Do not operate the wire feeder on an
angled surface of more than 15 degrees.
Do not submerge the LN-25™ Pro.
The LN-25™ Pro is rated IP23 and is suitable for
outdoor use.
The handle of the LN-25™ Pro is intended for moving
the wire feeder about the work place only.
When suspending a wire feeder, insulate the hanging
device from the wire feeder enclosure.
High Frequency Protection
Locate the LN-25™ PRO away from radio controlled
machinery. The normal operation of the LN-25™ PRO
may adversely affect the operation of RF controlled
equipment, which may result in bodily injury or damage
to the equipment.
Weld cable size
Table 1 located below are copper cable sizes
recommended for different currents and duty cycles.
Lengths stipulated are the distance from the welder to
work and back to the welder again. Cable sizes are
increased for greater lengths primarily for the purpose of
minimizing cable drop.
Electrode lead
The electrode lead is a 4/0 cable.
WARNING
English English
4
Page 8
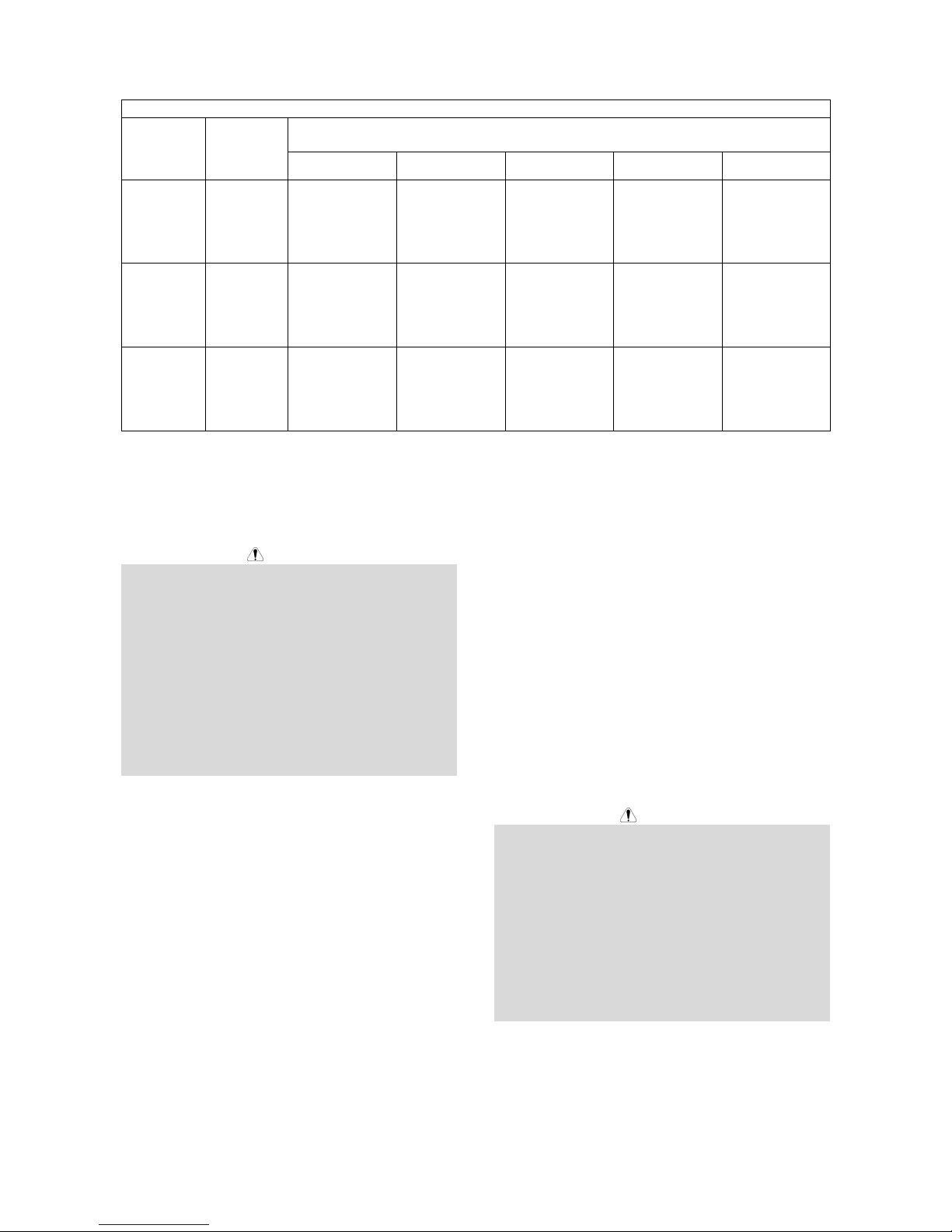
RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZES (RUBBER COVERED COPPER - RATED 167°F OR 75°C)**
CABLE SIZES FOR COMBINED LENGTHS OF ELECTRODE AND WORK
CABLES
0 to 50 Ft.
(0 to15m)
2
2
4 or 5
3
3
50 to 100 Ft.
(15 to 30m)
2
2
3
3
3
100 to 150 Ft.
(30 to 46m)
2
2
2
2
2
150 to 200 Ft.
(46 to 61m)
1
1
1
1
1
AMPERES
200
200
225
225
250
PERCENT
DUTY
CYCLE
60
100
20
40 & 30
30
200 to 250 Ft.
(61 to 76m)
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
250
250
250
300
325
350
400
400
500
** Tabled values are for operation at ambient temperatures of 104°F(40°C) and below. Applications above 104°F(40°C) may require
cables larger than recommended, or cables rated higher than 167°F(75°C).
40
60
100
60
100
60
60
100
60
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
1
1
1
1
2/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
1
1
1
1/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
3/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
4/0
4/0
4/0
Table 1
Shielding gas connection
WARNING
CYLINDER MAY EXPLODE IF DAMAGED.
• Keep cylinder upright and chained to support.
• Keep cylinder away from areas where it may be
damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached.
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from welding or other live
electrical circuits.
• BUILD UP OF SHIELDING GAS MAY HARM
HEALTH OR KILL.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
• See American National Standard z-49.1, "Safety in
Welding and Cutting” Published by the American
Welding Society.
Maximum inlet pressure is 100 psi. (6.9 bar.)
Install the shielding gas supply as follows:
1. Secure the cylinder to prevent it from falling.
2. Remove the cylinder cap. Inspect the cylinder valves
and regulator for damaged threads, dirt, dust, oil or
grease. Remove dust and dirt with a clean cloth. DO
NOT ATTACH THE REGULATOR IF OIL, GREASE
OR DAMAGE IS PRESENT! Inform your gas
supplier of this condition. Oil or grease in the
presence of high pressure oxygen is explosive.
3. Stand to one side away from the outlet and open the
cylinder valve for an instant. This blows away any
dust or dirt which may have accumulated in the valve
outlet.
4. Attach the flow regulator to the cylinder valve and
tighten the union nut(s) securely with a wrench. Note:
if connecting to 100% CO2 cylinder, insert regulator
adapter between regulator and cylinder valve. If
adapter is equipped with a plastic washer, be sure it
is seated for connection to the CO2 cylinder.
5. Attach one end of the inlet hose to the outlet fitting of
the flow regulator. Attach the other end to the
welding system shielding gas inlet. Tighten the union
nuts with a wrench.
6. Before opening the cylinder valve, turn the regulator
adjusting knob counterclockwise until the adjusting
spring pressure is released.
7. Standing to one side, open the cylinder valve slowly
a fraction of a turn. When the cylinder pressure gage
stops moving, open the valve fully.
8. The flow regulator is adjustable. Adjust it to the flow
rate recommended for the procedure and process
being used before making a weld.
Wire drive configuration
(See Figure 1)
Gun bushing, thumb screw and socket head
cap screw
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several seconds after the
gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform
maintenance work.
English English
5
Page 9

A
A
Tools required:
• 1/4" hex key wrench.
Note: Some gun bushings do not require the use of
the thumb screw.
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
2. Remove the welding wire from the wire drive.
3. Remove the thumb screw from the wire drive.
4. Remove the welding gun from the wire drive.
5. Loosen the socket head cap screw that holds the
connector bar against the gun bushing. Important:
Do not attempt to completely remove the socket
head cap screw.
6. Remove the outer wire guide, and push the gun
bushing out of the wire drive. Because of the
precision fit, light tapping may be required to remove
the gun bushing.
7. Disconnect the shielding gas hose from the gun
bushing, if required.
8. Connect the shielding gas hose to the new gun
bushing, if required.
9. Rotate the gun bushing until the thumb screw hole
aligns with the thumb screw hole in the feed plate.
Slide the gun receiver bushing into the wire drive and
verify the thumb screw holes are aligned.
10. Tighten the socket head cap screw 10 to 14 ft-lbs
(13.5 to 19.0 Nm).
11. Insert the welding gun into the gun bushing and
tighten the thumb screw.
Procedure to install drive rolls and wire
guides
WARNING
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several seconds after the
gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform
maintenance work.
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
2. Release the idle roll pressure arm.
3. Remove the outer wire guide by turning the knurled
thumbscrews counter-clockwise to unscrew them
from the feed plate.
4. Rotate the triangular lock and remove the drive rolls.
B
C
D
A. THUMB SCREW
B. GUN RECEIVER BUSHING
C. CONNECTOR BLOCK
D. SOCKET HEAD CAP SCREW
E. OUTER WIRE GUIDE
F. LOOSEN
G. TIGHTEN
Figure 1
A. UNLOCKED POSITION
B. LOCKED POSITION
5. Remove the inner wire guide.
E
F
G
6. Insert the new inner wire guide, groove side out, over
the two locating pins in the feed plate.
7. Install a drive roll on each hub assembly secure with
the triangular lock.
8. Install the outer wire guide by aligning it with the pins
and tightening the knurled thumbscrews.
9. Close the idle arm and engage the idle roll pressure
arm. Adjust the pressure appropriately.
LOADING SPOOLS OF WIRE
• Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from
rotating equipment.
• Do not wear gloves when threading wire or changing
wire spool.
• Only qualified personnel should install, use or service
this equipment.
Loading 10 to 15 lb. (4.5 – 6.8kg) Spools.
A K468 spindle adapter is required for loading 2"
(51mm) wide spools on 2" (51mm) spindles. Use a K468
spindle adapter for loading 2-1/2" (64mm) wide spools.
1. Squeeze the release bar on the retaining collar and
remove it from the spindle.
2. Place the spindle adapter on the spindle, aligning the
spindle brake pin with the hole in the adapter.
WARNING
B
English English
6
Page 10

A
A
3. Place the spool on the spindle and align the adapter
brake tab with one of the holes in the back side of
the spool. An indicator mark on the end of the
spindle shows the orientation of the brake tab. Be
certain the wire feeds off of the spool in the proper
direction.
4. Re-install the retaining collar. Make sure that the
release bar snaps out and that the retaining collar
fully engages the groove on the spindle.
Pressure arm and adjustment
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several seconds after the
gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform
maintenance work.
The pressure arm controls the amount of force the drive
rolls exert on the wire. Proper adjustment of the pressure
arm gives the best welding performance. Many welding
problems can be attributed to setting the pressure arm
too high and causing wire deformation. Set the pressure
arm to minimum amount that provides reliable feeding.
Set the pressure arm as follows: (See Figure 2)
Aluminum wires between 1 and 2
Cored wires between 1 and 3
Steel, Stainless wires between 3 and 5
Gun connection
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several seconds after the
gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform
maintenance work.
The LN-25™ PRO comes with a K1500-2 gun adapter
installed. (See Figure 3)
To install a gun,
1. Turn power OFF.
2. Remove the thumb screw.
3. Push the gun the completely into the gun bushing.
4. Secure the gun in place with the thumb screw.
5. Connect the trigger cable from the gun to the trigger
connector on the front of the feeder.
Note: Not all gun bushings require the use of the thumb
screw.
B
A. THUMB SCREW
B. GUN
B
C
A. AL - ALUMINUM WIRES
B. FCAW - CORED WIRES
C. GMAW - STEEL, STAINLESS WIRES
English English
Figure 2
7
Figure 3
Page 11

k
k
Power source to LN-25™ PRO cable
connection diagrams
Across the arc set-ups
CC power sources with output terminals
always hot (see figure 4)
CC Power Source
Classics
Big Red’s
Eagle 10,000 Plus
Pipeliner 200D Without Wire Feed module
SAE’s Without CV Adapter
SAE 400 with CV adapter
Engine Driven welder with
Wire Feed Module
If the power source has a Remote/Local switch, place
the switch in the Local position.
Place the CV/CC switch in the feeder in the "CC"
position.
CV power sources with stud connectors and
remote/local switch (see figure 5)
Electrode
Figure 4
LN-25™ PRO
(Across the Arc)
Wor
Work clip
K# Description
K2613-5 LN-25™ PRO Wire Feeder
K2613-7 LN-25™ PRO Extra Torque
KP1695-xx
KP1696-xx
Drive Roll Kit
KP1697-xx
See Magnum Literature Welding Gun
CC power source
K1803-xx Welding Cables
CV-400
CV-655
DC-400
DC-600
DC-655
V450-Pro
SAE 400 with CV adapter
Engine Driven welder with
Wire Feed Module Ranger
250 GXT
Electrode
Wor
Place the power source Remote/Local switch in the
Local position.
Place CV/CC switch in the feeder in the "CV" position.
Figure 5
LN-25™ PRO
(Across the Arc)
Work clip
K# Description
K2613-5 LN-25™ PRO
K2613-7 LN-25™ PRO Extra Torque
KP1695-XX
KP1696-XX
Drive Roll Kit
KP1697-XX
See magnum Literature Welding Gun
CV power Source
K1803-XX Welding Cables
K484 Jumper Plug Kit
English English
8
Page 12

A
k
k
CV power sources with stud connectors and no
remote/local switch. (see figure 6)
Ranger 250, 250 LPG
Ranger 305G, 305D
Ranger 10,000
Ranger 3 Phase
Ranger 225, 225GXT
Commander 300
Vantage 300, 400, 500
ir Vantage 500
Electrode
Wor
Place CV/CC switch in the feeder in the "CV" position.
CV power source with twist-mate connectors
and remote/local switch. (see figure 7)
Figure 6
LN-25™ PRO
(Across the Arc)
Work clip
K# Description
K2613-5 LN-25™ PRO
K2613-7 LN-25™ PRO Extra Torque
KP1695-XX
KP1696-XX
KP1697-XX
See Magnum Literature Welding Gun
CC power Source
K1803-XX Welding Cables
Drive Roll Kit
V350-Pro
CV 305
Electrode
Wor
Place the power source Remote/Local switch in the
Local position.
Place CV/CC switch in the feeder in the “CV” position.
CV Power Source with Twist-Mate Connectors and no
Remote/Local Switch. (See Figure 8)
Figure 7
LN-25™ PRO
(Across the Arc)
Work clip
K# Description
K2613-5 LN-25™ PRO
K2613-7 LN-25™ PRO Extra Torque
KP1695-XX
KP1696-XX
Drive Roll Kit
KP1697-XX
See Magnum Literature Welding Gun
CV power Source
K1841-XX Welding Cables
K852-95 Twist-Mate Cable Plug
English English
9
Page 13

k
CV power source with twist-mate connectors
and no remote/local switch. (see figure 8)
Jumper
CV-250
CV-300
Place CV/CC switch in the feeder in the "CV" position.
Electrode
Wor
Figure 8
LN-25™ PRO
(Across the Arc)
Work clip
K# Description
K2613-5 LN-25™ PRO
K2613-7 LN-25™ PRO Extra Torque
KP1695-XX
KP1696-XX
Drive Roll Kit
KP1697-XX
See Magnum Literature Welding Gun
CV power Source
K1841-XX Welding Cables
K852-95 Twist-Mate Cable Plug
K484 Jumper Plug kit
English English
10
Page 14

Graphic symbols that appear on this
machine or in this manual
INPUT POWER
ON
OFF
WIRE FEEDER
POSITIVE OUTPUT
NEGATIVE OUTPUT
INPUT POWER
DIRECT CURRENT
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
INPUT VOLTAGE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
INPUT CURRENT
OUTPUT CURRENT
PROTECTIVE GROUND
Definition of welding terms
WFS
• Wire Feed Speed
CC
• Constant Current
CV
• Constant Voltage
GMAW
• Gas Metal Arc welding
SMAW
• Shielded Metal Arc welding
FCAW
• Flux Core Arc Welding
General description
General physical description
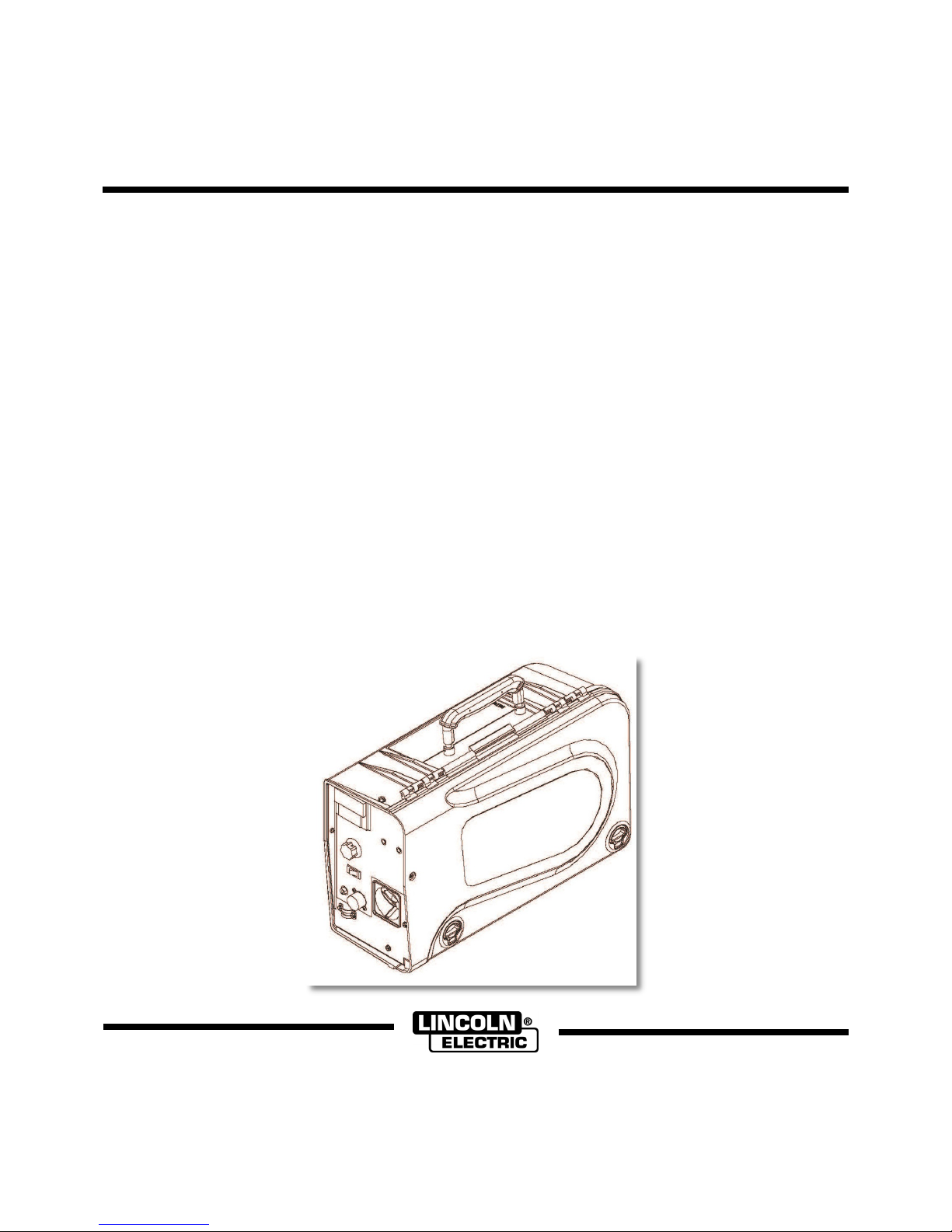
The LN-25™ PRO is specially engineered to be the most
rugged portable wire feeder available.
Several models of the LN-25™ PRO are offered to best
meet individual welder needs. The Extra Torque model
features additional torque gearing for reliable feeding of
large diameter FCAW wires. The Standard and Dual
Power models feature wire drive gearing for great
performance for both FCAW and GMAW wires of
common sizes. All of the models include a gas solenoid
for the flexibility to run most wire processes.
The plastic case is molded from a high impact, flame
retardant plastic for durability and low weight.
The heart of the LN-25™ PRO is the 2 roll MAX-TRAC™
drive. The patented features on the wire drive offer toolless changing of the drive rolls and wire guides for quick
spool changes. A tachometer controlled motor powers
the patented drive rolls for smooth, steady feeding
without slippage.
With a 450 amp, 60% duty cycle rating, these feeders
are ready for heavy duty welding.
General functional description
All LN-25™ PRO’s have adjustable WFS range for
improving the knob sensitivity. The low range is great for
critical welds with Innershield wires, and the upper range
is suitable for general purpose welding. Selection of the
WFS range is by a rocker switch or through the set-up
menu on meters with digital displays.
Recommended processes
• GMAW
• FCAW
WARNING OR CAUTION
English English
11
Page 15

A
Process limitations
• GMAW-P procedures must be qualified by the customer.
• Across-the-Arc models are not recommended for
stitch or spot welding.
(See Customer Assistance Policy in the front of this
Instruction Manual)
Case front controls
(See Figure 9)
Equipment limitations
• The duty cycle of the wire feeder is 450A, 60%. Duty
cycle is based upon the amount of welding
performed in a 10 minute period.
• The maximum spool size is 45 lb. (24 Kg), 12”
(305mm) diameter.
• Maximum FCAW gun length is 15 ft.
• Maximum GMAW gun length is 25 ft.
• K2330-1 Timer Kits do not work with the feeder. Use
K2330-2 kits.
• Push-pull guns do not work with the LN-25™ PRO.
• Not compatible with K489-7 Euro connector (except
K2614-7,-8)
B
C
Recommended power sources
• CV-305 • Ranger 3 Phase
• CV-400 • Ranger 225
• CV-655 • Ranger 225 GXT
• DC-400 • Ranger 250
• DC-600 • Ranger 305
• DC-655 • SAE-400
• Invertec V-350 • Pipeliner 200G
• FlexTec 450 • Classic 300
• Multi-Weld 350 • Vantage 300
• Ranger 10,000 • Vantage 400
• Vantage 500
D
E
A. ANALOG VOLTMETER
B. WIRE FEED SPEED KNOB
C. WIRE FEED SPEED RANGE SWITCH
D. 5-PIN GUN TRIGGER CONNECTOR
E. WORK SENSE LEAD
F. THERMAL LED, MOTOR OVERLOAD
G. POLARITY LED
Analog voltmeter
Reads 0 – 40 VDC and is polarity insensitive. Shows
OCV when not welding and arc voltage when
welding.
The serviceability of a product or structure utilizing the
LN-25™ PRO wire feeder is and must be the sole
responsibility of the builder/user. Many variables beyond
the control of The Lincoln Electric Company affect the
results obtained in using the LN-25™ PRO wire feeder.
These variables include, but are not limited to, welding
procedure, plate chemistry and temperature, weldment
design, fabrication methods and service requirements.
The available range of the LN-25™ PRO wire feeder
may not be suitable for all applications, and the
builder/user is and must be solely responsible for
welding settings.
F
G
Figure 9
English English
12
Page 16

CV OPERATION
Minimum Arc
Volts
Maximum WFS
(Standard
Torque)
Maximum WFS
(Extra Torque )
15 V 400 220
17 V 450 250
21 V 570 300
24 V 650 350
27 V 700 400
Wire Feed Speed, CC Operation
When Across the Arc models are operated with CC
power sources, the wire feed speed changes as the arc
voltage changes. When the arc voltage increases, the
wire feed speed will increase; and when the arc voltage
decreases, the wire feed speed will decrease.
To preset the wire feed speed on CC power sources:
1. Set the Wire Feed Mode switch inside the LN-25™
Pro to "CC".
2. Refer to the Figure 10 graph for the setting for the
wire feed speed knob setting. Select the horizontal
line representing the Desired Wire Feed Speed. (See
Figure 10 arrow for 375 in/min.)
3. Select the diagonal line representing the Arc Volts.
(See Figure 10 for 29 volts.)
4. Determine the vertical line representing the CC
representing the CC Wire Feed Speed setting where
the above two lines cross. (See Figure 10 arrow line
for 450.) Set the LN-25™ Pro wire feed speed knob
to this value.
CC WFS dial setting = desiredWFSx35
Arc Volts
Example:
= 375in/min.(HorizontalLine)x35
29 Arc Volts (Diagonal Line)
= 452.5 (Vertical Line) Use 450 setting
(See Figure 10)
A constant voltage (CV) power
source is recommended for
fluxcored arc welding. (FCAW) and
gas metal arc welding (GMAW) to
obtain code qual i ty resul ts.
However, this wire feeder may also
be used with a constant current (CC)
power source to obtain passable
results for noncritical quality
applications.
Figure 10
English English
13
Page 17

Constant current wire welding
(See Figure 11)
Most semiautomatic welding processes perform better
using constant voltage power sources.
Welding codes usually do not address the power source
selection or specifically, whether the welding process is
to be operated in the constant voltage or constant
current mode. Instead, codes typically specify limitations
on the current, voltage, heat input and preheat
temperature based on the material to be welded. The
intention is to assure that proper weld material properties
will develop.
Welding is sometimes performed using constant current
power sources. The operation can be more convenient
because it may allow the use of an existing stick
(SMAW) power source and the power source can be
placed at a distant location without any provision for
adjusting the output settings.
For constant current operation, the power source is set
to deliver the specified current. The power source
regulates this current regardless of changes in the
welding circuit, including cable length, electrode
diameter, wire feed speed, contact tip to work distance,
etc.
Changes in the wire feed speed (WFS) or contact tip to
work distance (CTWD) affect the arc voltage when
constant current power sources are used. Lowering the
wire feed speed raises the voltage, raising the wire feed
speed lowers the voltage. Lengthening the contact tip to
work distance raises the voltage, shortening the contact
tip to work distance lowers the voltage.
Current
Constant Current
Power Source
If the contact tip to work distance is properly maintained,
a satisfactory operating voltage range may be achieved,
and a sound weld may result. However, when a welder
uses a longer contact tip to work distance, an arcsensing wire feeder compensates by increasing the wire
feed speed to regulate the voltage. Even if the voltage
and current remain unchanged, the increased wire feed
speed may result in a deposition rate well beyond the
specified range of the electrode. Under these conditions,
the specified weld metal properties may not be achieved.
Constant voltage power sources deliver large current
surges to stabilize the arc when the electrode is shorted
or the arc length is very short. However, a constant
current power source does not provide such a response
to stabilize the arc. It may be difficult to achieve required
weld metal properties, or to achieve the required quality
of welds needed to pass nondestructive tests, when
such welds are made under constant current operation.
For these reasons, Lincoln Electric does NOT
recommend constant current semiautomatic welding for
applications which need to meet specified weld metal
chemical or mechanical property requirements or weld
quality requirements.
Wire
Feeder
CTWD
WFS
2. Wire feed speed knob
Use the Wire Feed Speed Knob to adjust the rate of wire
feed speed.
WFS range for standard torque:
High = 50 to 700 ipm
Low = 50 to 200 ipm
WFS range for extra torque:
High = 50 to 400 ipm
Low = 50 to 200 ipm
English English
Current
Figure 11
Because the wire feeder is powered by the arc voltage,
the full range of wire feed speed may not be available at
low voltages.
3. Wire feed speed range switch
Use to select either the low range or high range for the
wire feed speed knob. Note – selecting the low range
does not increase the torque of the wire drive.
14
Page 18

4. 5-Pin gun trigger connector
There is one circular connector for the gun trigger on the
front of the LN-25™ PRO. Note – if the gun trigger is
already depressed when the feeder is powered up, the
feeder will not activate. Release and then press the gun
trigger to begin welding.
Function Pin Wiring
5-pin trigger
connector for
push-guns
only.
5. Work sense lead
Always turn power off at the welding power source
before moving the work sense lead.
The work sense lead attaches to the item being welded.
6. Thermal led, motor overload
The thermal light illuminates when the wire
drive motor draws too much current. If the
thermal light illuminates, the wire drive will
automatically shutdown for up to 30
seconds to allow the motor to cool. To start
welding again, release the gun trigger,
inspect the gun cable, liner (and conduit). Clean and
make repairs as necessary. Start welding again when
the problem has been safely resolved.
For best results, keep the gun cable and conduit as
straight as possible. Perform regular maintenance and
cleaning on the gun liner, conduit and gun. Always use
quality electrode, such as L-50 or L-56 from Lincoln
Electric.
7. Polarity LED
The Polari ty LED lights when the wire feeder is
connected for positive polarity. Use the polari ty LED to
verify if the wire feeder is connected for the proper
polarity.
+ POLARITY
POLARDAD
- POLARITÉ
A 5 volt supply
B Not used
C Trigger
D Not used
E Not used
Internal controls
D
C
B
A
G
I
H
A. 2 STEP TRIGGER INTERLOCK SWITCH
B. CV / CC SWITCH
C. PRESSURE ADJUSTMENT ARM
D. OPTIONAL TIMER KIT
E. SPOOL RETAINER
F. SPINDLE BRAKE
G. GUN BUSHING, THUMB SCREW AND SOCKET
HEAD CAP SCREW
H. DRIVE HUBS
I. COLD FEED PUSHBUTTON
Figure 12
Internal controls description
(See Figure 12)
1. 2 Step - Trigger interlock switch
The 2 Step - Trigger Interlock switch
changes the function of the gun trigger.
2 Step trigger operation turns welding
on and off in direct response to the
trigger. Trigger Interlock operation
allows welding to continue when the
trigger is released for comfort on long
welds.
Place the toggle switch in the DOWN
position for 2 Step operation or in the
UP position for Trigger Interlock operation.
2 Step Trigger
2 Step trigger operation is the most common. When the
gun trigger is pulled, the welding power source
energizes the electrode output and the wire feeder feeds
wire for welding. The power source and wire feeder
continue welding until the trigger is released.
Trigger Interlock
Trigger Interlock operation provides for operator comfort
when making long welds. When the gun trigger is first
pulled, the welding power source energizes the output
and the wire feeder feeds wire for welding. The gun
trigger is then released while the weld is made. To stop
welding, the gun trigger is pulled again, and when it is
released the welding power source output turns off and
the wire feeder stops feeding wire.
E
F
English English
15
Page 19

A
If the arc goes out while welding with trigger interlock
WARNING
operation, the electrode output from the welding power
source remains energized and the wire feeder will
continue to feed wire until the gun trigger is again pulled
and then released.
2. CV/CC switch
The CV/CC switch sets the wire feed
speed control method for the wire
feeder.
In the CV position, the wire feed speed
remains constant during welding. A
steady arc voltage is regulated by the
power source by adjusting the arc
current.
In the CC position, the wire feed speed varies during
welding. The arc length is maintained by changing the
wire feed speed.
3. Pressure arm and adjustment
(See installation section)
4. Optional timer kit
The optional Timer Kit provides control of preflow time,
burnback, and postflow time.
5. Spool retainer
To release the spool retainer, squeeze the metal bar
inwards. When securing the spool, verify the spool
retainer is fully seated in place in one of the three
grooves of the spindle.
6. Spool brake
Adjust the spool brake to provide enough friction to stop
wire overrun. Excessive brake force may cause motor
thermal overloads or welding problems.
7. Gun bushing, thumb screw and socket head cap
screw
(SEE INSTALLATION SECTION)
8. Drive rolls and wire guides
(See installation section)
9. Cold feed pushbutton
When cold feeding, the wire drive will feed electrode but
neither the power source nor the gas solenoid will be
energized. Adjust the speed of cold feeding by rotating
the WFS knob. Cold feeding, or "cold inching" the
electrode is useful for threading the electrode through
the gun.
Rear controls:
(See Figure 13)
1. Gas purge pushbutton
The gas solenoid valve will energize but neither the
power source output nor the drive motor will be turned
on. The Gas Purge switch is useful for setting the proper
flow rate of shielding gas. Flow meters should always be
adjusted while the shielding gas is flowing.
B
C
A. GAS PURGE PUSHBUTTON
B. SHIELDING GAS INLET
C. ELECTRODE LEAD
Figure 13
English English
16
Page 20

A
A
Maintenance
Safety precautions
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several seconds after the
gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform mainte
nance work.
Routine maintenance
• Check weld cables, control cables and gas hoses for
cuts.
• Clean and tighten all weld terminals.
Periodic maintenance
• Clean drive rolls and inner wire guide and replace if
worn.
• Blow out or vacuum the inside of the feeder.
• Inspect the motor brushes every 6 months. Replace
if shorter than 0.5” (12.7mm).
Calibration specification
Voltmeter validation
(See Figure 14)
To verify the analog voltmeter accuracy:
1. Turn power OFF.
2. Connect the LN-25™ PRO to the constant voltage
DC power supply capable of supply at least 4 amps.
Connect the electrode to the “+” positive terminal and
the work clip to the “-“ negative terminal.
3. Connect a reference voltmeter between the brass
block of the LN-25™ PRO and the work lead.
4. Turn power ON.
5. Energize the power supply. Adjust the power source
output to 20.0 VDC as measured on the reference
meter.
6. Verify that LN-25™ PRO voltmeter reads 20 volts.
Adjust the voltmeter as necessary by turning the
screw on the voltmeter.
Wire feed speed validation
Calibration of the LN-25™ PRO may be required when
the P.C. board, wire feed speed potentiometer or motor
is replaced or serviced. Calibration matches the scale on
the name plate to the actual wire feed speed.
To calibrate the LN-25™ PRO:
1. Turn power OFF at the welding source.
2. Remove the spool of wire and the cover from the
feeder. Remove the gun from the feeder plate,
leaving the gun trigger attached to the feeder.
Remove the plastic cover on the feed plate to reveal
the motor gear.
3. Place the WFS range switch in the “high” setting. Set
the WFS knob to
• 50 ipm for K2613-5
• 25 ipm for K2613-7
4. Trigger the LN-25™ PRO and measure the rpm of
the motor gear. Adjust the WFS knob as required
until the rpm measures 8.9 to 9.2 rpm.
5. Insert the shorting plug into the control board for 1
second and then remove the shorting plug. The
shorting plug shorts pins 4 and 7 of J3.
6. Set the WFS knob to
• 800 ipm for K2613-5
• 400 ipm for K2613-7
7. Trigger the LN-25™ PRO and measure the rpm of
the motor gear. Adjust the WFS knob as required
until the rpm measure 128.0 to 130.0 rpm.
8. Insert the shorting plug into the control board for 1
second and then remove the shorting plug. The
shorting plug shorts pins 4 and 7 of J3.
9. Turn power OFF and reassemble.
B
A. COVER
B. PC BOARD
Figure 15
A. CALIBRATION SCREW
English English
Figure 14
17
Page 21

WEEE
Do not dispose of electrical equipment together with normal waste!
In observance of European Directive 2012/19/EC on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
and its implementation in accordance with national law, electrical equipment that has reached the end of its
life must be collected separately and returned to an environmentally compatible recycling facility. As the
English
owner of the equipment, you should get information on approved collection systems from our local
representative.
By applying this European Directive you will protect the environment and human health!
Spare Parts
For Spare Parts references visit the Web page: https://www.lincolnelectric.com/LEExtranet/EPC/
Authorized Service Shops Location
The purchaser must contact a Lincoln Authorized Service Facility (LASF) about any defect claimed under Lincoln's
warranty period.
Contact your local Lincoln Sales Representative for assistance in locating a LASF or go to
www.lincolnelectric.com/en-gb/Support/Locator.
07/06
12/05
09/16
English English
18
Page 22

Electrical Schematic
NOTE: this diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific
diagram for a partiuclar code is pasted inside the machine on one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is ellegible,
write to the Service Department for a raplacement. Give the equipment code number.
English English
19
Page 23

A
Suggested Accessories
Factory installed equipment
• K1500-2 Gun Receiver Bushing.
WIRE TYPE ELECTRODE SIZE KP KIT
Steel Wires: .023-.030 (0.6-0.8mm)
.035 (0.9mm)
.045 (1.2mm)
.052 (1.4mm)
1/16 (1.6mm)
.035,.045 (0.9, 1.2mm)
.040 (1.0mm)
KP1696-030S
KP1696-035S
KP1696-045S
KP1696-052S
KP1696-1/16S
KP1696-1
KP1696-2
Includes: 2 V groove
drive rolls and inner wire
guide.
Cored Wires: .030-.035" (0.8-0.9mm)
(Extra Torque Models
only)
luminum Wires: .035" (0.9 mm)
K2330-2 Timer Kit Includes: Panel and harness for adjusting
K2596-2 Plastic Case Includes: a complete engineered plastic
K1796-xx AWG 1/0 Co-Axial Power
K2593-xx AWG #1 Coaxial Power
.040-.045" (1.0-1.2mm)
.052" (1.4mm)
1/16" (1.6mm)
.068-.072" (1.7-1.8mm)
5/64" (2.0mm)
3/32” (2.4mm)
.040" (1.0mm)
3/64" (1.2mm)
1/16" (1.6mm)
Cable
Cable
KP1697-035C
KP1697-045C
KP1697-052C
KP1697-1/16C
KP1697-068
KP1697-5/64
KP1697-3/32
KP1695-035A
KP1695-040A
KP1695-3/64A
KP1695-1/16A
preflow, burnback and postflow times.
Includes: 1/0 Coaxial weld cable of length
"xx". Ends of the weld cable have lug con-
nections. Use for Pulse welding.
Includes: AWG #1 Coaxial weld cable of
length "xx". Ends of the weld cable have
lug connections. Use for Pulse or STT™
Includes: 2 Knurled drive
rolls and inner wire
Includes: 2 polished U
groove drive rolls, outer
wire guide and inner
wire guide.
case.
welding.
guide.
K1803-1 Work and Feeder Cables
K1840-xx Weld Power Cable, Twist-
K1842-xx Weld Power Cable, Lug to
K484 Jumper Plug Kit Includes: 14 pin circular connector with
English English
Package
Mate to Lug
Lug
Includes: Twist-Mate to Lug 2/0 cable 14'
(1.2m) long with Ground Clamp, and
Twist- Mate to Lug 2/0 Cable 9' (2.7m)
long.
Includes: Twist-Mate to Lug, 1/0 cable of
length "xx".
Includes: Lug to Lug, 3/0 Cable of length
"xx" for lengths up to 60' (18.3m). Lug to
Lug, 4/0 Cable of length "xx" for lengths
greater than 60' (18.3m).
jumper for leads 2-4. For use in power
sources for turning the weld terminals "ON"
at all times.
20
Page 24

K910-1 Ground Clamp Includes: One 300 Amp
Ground Clamp.
K910-2 Ground Clamp Includes: One 500 Amp
Ground Clamp.
K1500-1 Gun Receiver Bushing (for
guns with K466-1 Lincoln
Includes: Gun receiver bushing, set screw
and hex key wrench.
gun connectors; Innershield
and Subarc guns)
K1500-2 Gun Receiver Bushing (for
guns with K466-2, K466-10
Includes: Gun receiver bushing with hose
nipple, set screw and hex key wrench.
Lincoln gun connectors;
Magnum 200/300/400 guns
and compatible with
Tweco® #2-#4)
K1500-3 Gun Receiver Bushing (for
guns with K613-7 Lincoln
Includes: Gun receiver bushing with hose
nipple, set screw and hex key wrench.
gun connectors; Magnum
550 guns and compatible
with Tweco® #5)
K1500-4 Gun Receiver Bushing (for
gun with K466-3 Lincoln
Includes: Gun receiver bushing with hose
nipple, set screw and hex key wrench.
gun connectors; compatible
with Miller® guns.)
K1500-5 Gun Receiver Bushing
(compatible with Oxo®
Includes: Gun receiver bushing with hose
nipple, 4 guide tubes, set screw and hex
guns.)
K435 Spindle Adapter, for
mounting 14 lb. (6.4 kg)
Includes: Spindle Adapter made from 2
coil retainers. (Electrode not included.)
Innershield Coils on 2 in
(51 mm) spindles.
K468 Spindle Adapter, for
mounting 8in (203mm)
Includes: 2 Spindle Adapters, one for 2"
wide spools and the other for 3" wide
diameter spools on 2 in (51
mm) spindles.
K590-6 Water Connection Kit (for
Includes: 2 hoses with female quick
European and Control
cable models only)
connectors for 3/16" ID hose, 2 male
connectors for _" ID hose, and mounting
K586-1 Deluxe Adjustable Gas
Regulator
Includes: Deluxe Gas Regulator for Mixed
Gases, Adapter for CO2 and 10' (3.0m)
key wrench.
spools.
connectors at each end, 2 male
hardware.
Hose.
K283 Wire Feed Speed Meter Includes: A wire feed speed meter with
English English
digital display.
21
 Loading...
Loading...