Page 1
Operator’s Manual
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
For use with machines having Code Numbers:
10420, 10421, 10422,
10423, 10424, 11074,
11602, 11603, 11604,
11674, 11675
Save for future reference
Date Purchased
Code: (ex: 10859)
Serial: (ex: U1060512345)
IMT237-P | Issue D ate Nov-13
© Lincoln Global, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Register your machine:
www.lincolnelectric.com/register
Authorized Service and Distributor Locator:
www.lincolnelectric.com/locator
Page 2

THANK YOU FOR SELECTING
A QUALITY PRODUCT BY
LINCOLN ELEC TRIC.
PLEASE EXAMINE CARTON AND EQUIPMENT FOR
DAMAGE IMMEDIATELY
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon
receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims for material damaged in
shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation
company at the time the shipment is received.
SAFETY DEPENDS ON YOU
Lincoln arc welding and cutting equipment is designed and built with
safety in mind. However, your overall safety can be increased by
proper installation ... and thoughtful operation on your part.
DO NOT INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS EQUIPMENT
WITHOUT READING THIS MANUAL AND THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And, most importantly, think before you
act and be careful.
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed
exactly to avoid serious personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to
avoid minor personal injury or damage to this equipment.
KEEP YOUR HEAD OUT OF THE FUMES.
DON’T get too close to the arc. Use
corrective lenses if necessary to
stay a reasonable distance away
from the arc.
READ and obey the Material Safety
Data Sheet (MSDS) and the warning
label that appears on all containers
of welding materials.
USE ENOUGH VENTILATION or
exhaust at the arc, or both, to keep
the fumes and gases from your breathing zone and the general area.
IN A LARGE ROOM OR OUTDOORS, natural ventilation may be
adequate if you keep your head out of the fumes (See below).
USE NATURAL DRAFTS or fans to keep the fumes away from your
face.
If you de velop unusual symptoms, see your supervisor. Perhaps the
welding atmosphere and ventilation system should be checked.
WEAR CORRECT EYE, EAR & BODY PROTECTION
PROTECT your eyes and face with welding helmet
properly fitted and with proper grade of filter plate
(See ANSI Z49.1).
PROTECT your body from welding spatter and arc
flash with protective clothing including woolen
clothing, flame-proof apron and gloves, leather
leggings, and high boots.
PROTECT others from splatter, flash, and glare with
protective screens or barriers.
IN SOME AREAS, protection from noise may be
appropriate.
BE SURE protective equipment is in good condition.
Also, wear safety glasses in work area AT ALL
TIMES.
SPECIAL SITUATIONS
DO NOT WELD OR CUT containers or materials which previously had
been in contact with hazardous substances unless they are properly
cleaned. This is extremely dangerous.
DO NOT WELD OR CUT painted or plated parts unless special
precautions with ventilation have been taken. They can release highly
toxic fumes or gases.
Additional precautionary measures
PROTECT compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical
shocks, and arcs; fasten cylinders so they cannot fall.
BE SURE cylinders are never grounded or part of an electrical circuit.
REMOVE all potential fire hazards from welding area.
ALWAYS HAVE FIRE FIGHTING EQUIPMENT READY FOR
IMMEDIATE USE AND KNOW HOW TO USE IT.
Page 3

SECTION A:
WARNINGS
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel Engines
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other
reproductive harm.
Gasoline Engines
The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm.
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT
YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS
INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR
DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional
safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a
copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the
American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or
CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety”
booklet E205 is available from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801
St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
SAFETY
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and
devices in position and in good repair.Keep
hands, hair, clothing and tools away from
V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts
when starting, operating or repairing
equipment.
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety guards to
perform required maintenance. Remove guards only when
necessary and replace them when the maintenance requiring
their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when
working near moving parts.
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to
override the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control
rods while the engine is running.
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while turning
the engine or welding generator during maintenance work,
disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or magneto wire
as appropriate.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the radiator
pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS MAY
BE DANGEROUS
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor
causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and welding
machines
FOR ENGINE POWERED
EQUIPMENT.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting
and maintenance work unless the
maintenance work requires it to be running.
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes outdoors.
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from
vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts
and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling
tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start engine until
fumes have been eliminated.
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and welders
having a pacemaker should consult their physician before
welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health effects
which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and work
cables. If the electrode cable is on your right side, the
work cable should also be on your right side.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
3
Page 4
SAFETY
ELECTRIC SHOCK
CAN KILL.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are
electrically “hot” when the welder is on. Do
not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin
or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full area
of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if
welding must be performed under electrically
hazardous conditions (in damp locations or while
wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such as
floors, gratings or scaffolds; when in cramped
positions such as sitting, kneeling or lying, if there
is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact
with the workpiece or ground) use the following
equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding
gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection should
be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical (earth)
ground.
3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode
holders connected to two welders because voltage
two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of both
welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
between the
ARC RAYS CAN BURN.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your
eyes from sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or
observing open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens should
conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material
to protect your skin and that of your helpers from the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
CAN BE DANGEROUS.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep your head out of the fume.
Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep fumes
and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding
with electrodes which require special ventilation
such as stainless or hard facing (see instructions
on container or MSDS) or on lead or cadmium
plated steel and other metals or coatings which
produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low
as possible and within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits using local exhaust or
mechanical ventilation. In confined spaces or in
some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may
be required. Additional precautions are also
required when welding on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected by
various factors including proper use and positioning of the
equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific
welding procedure and application involved. Worker exposure
level should be checked upon installation and periodically
thereafter to be certain it is within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c. Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The
heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors to form
phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
3.j. Also see It ems 6.c. and 8.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
injury or death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in
confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your employer’s
safety practices. MSDS forms are available from your welding
distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
4
cause
Page 5

SAFETY
WELDING AND CUTTING
SPARKS CAN CAUSE
FIRE OR EXPLOSION.
6.a. Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If
this is not possible, cover them to prevent the
welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that welding
sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through
small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special
precautions should be used to prevent hazardous situations.
Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI Standard Z49.1)
and the operating information for the equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is
touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause
overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures will
not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances inside.
They can cause an explosion even though they have been
“cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended Safe
Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”,
AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society (see address
above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free
protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless
trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs
when welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear
safety glasses with side shields when in a welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area
as practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or
other locations away from the welding area increase the
possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains,
crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire
hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
CYLINDER MAY EXPLODE IF
DAMAGED.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders containing
the correct shielding gas for the process used
and properly operating regulators designed for
the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings,
etc. should be suitable for the application and
maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to
an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected
to physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations
and any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight
except when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l, “Precautions for
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available
from the Compressed Gas Association 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
POWERED EQUIPMENT.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on the
equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National Electrical
Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.I. Read and follow NFPA 51B “ Standard for Fire Prevention During
Welding, Cutting and Other Hot Work”, available from NFPA, 1
Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
6.j. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Refer to
http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety
for additional safety information.
Welding Safety
Interactive Web Guide
for mobile devices
5
Page 6

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Installation.......................................................................................................Section A
Operating Instructions .................................................................................................................A-1
Input Power and Grounding Connections ............................................................................A-1
Attach Electrode Cable to Holder.........................................................................................A-1
Type A Holder with Octagon Shape.....................................................................................A-1
Type B Holder with Round Ribbed Handle...........................................................................A-2
Electrode and Work Replacement........................................................................................A-2
Operation.........................................................................................................Section B
Welding Polarity Selection....................................................................................................B-1
Duty Cycle............................................................................................................................B-1
Circuit Breakers....................................................................................................................B-1
How to Learn Stick Welding .................................................................................................B-1
Electrode Selection Guide....................................................................................................B-1
Electrode Guide....................................................................................................................B-2
Stick Welding Motions A thru G............................................................................................B-2
Cutting and Piercing Holes ..................................................................................................B-3
Maintenance ....................................................................................................Section C
Routine preventative maintenance
Parts Pages.......................................................................................P-65, P-140 Series
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
...........................................................................................C-1
6
Page 7
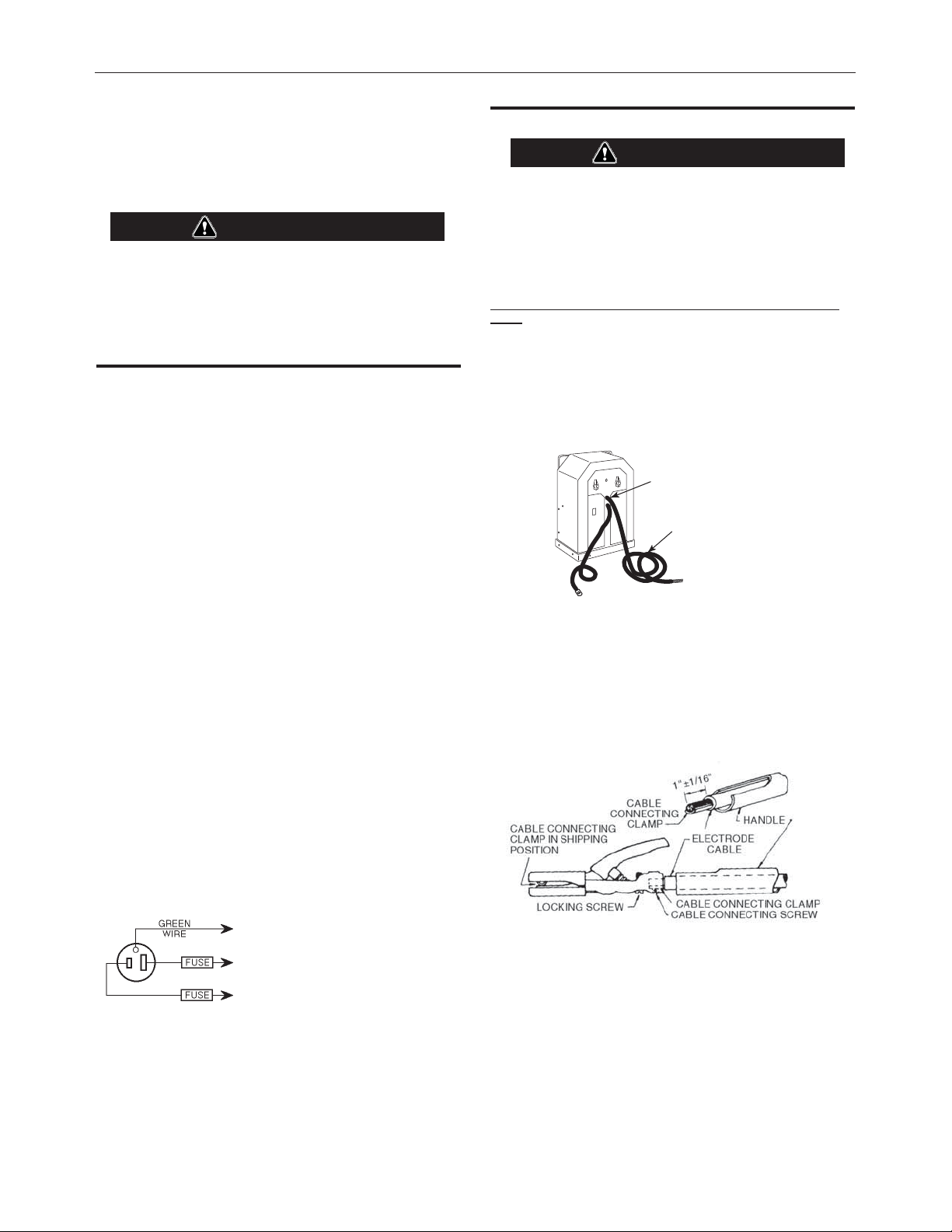
INSTALLATIONAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
• Have an electrician ins ta ll and service this equipment.
• Turn the input power off at the fuse box before working on equipment.
• Do not touch electrically hot parts.
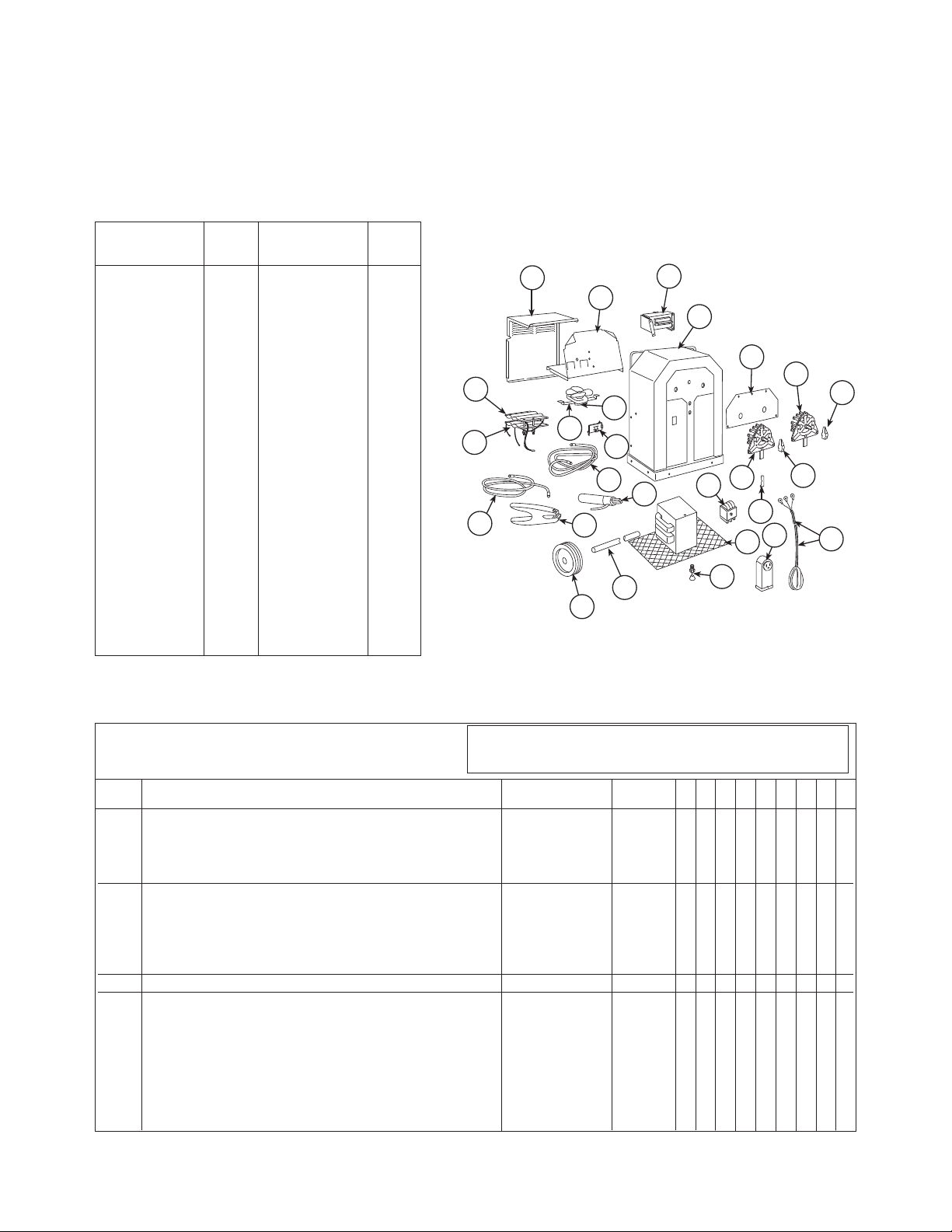
Identify the holder type before installing.
FIGURE 1A
OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING
Input Power and Grounding Connections
Before starting the installation, check with the power company to be
sure your power supply is adequate for the voltage, amperes, phase
and frequency specified on the welder nameplate. Also, be sure the
planned installation will meet the United States National Electrical
Code and local code requirements. This welder may be operated
from a single phase line or from one phase of a two or three phase
line.
All models designed to operate on less than 250 volt input lines are
shipped with the input cable connected to the welder.
Place the welder so there is free circulation of air in through the
louvers in the back and sides of the case and out of the bottom on
all four sides. Mount a NEMA Type 6-50R receptacle in a suitable
location. Be sure it can be reached by the plug on the input cable
attached to the welder.
Using the following instructions, have a qualified electrician connect
this receptacle (NEMA 6-50R Type) to the power lines at the fuse
box. Three #10 or larger copper wires are required if conduit is
used. For long cable runs over 100'(31m), #8 or larger wire in
conduit will be needed to prevent excessive voltage drops. Fuse the
two hot lines with 50 ampere super lag type fuses as shown in the
following diagram. The center contact in the receptacle is for the
grounding connection. A green wire in the input cable connects this
contact to the frame of the welder. This insures proper grounding of
the welder frame when the welder plug is inserted into the
receptacle. If a separate disconnect switch is used, it should have
two poles for the two hot lines and both should be fused for 50
amperes.
Attaching Electrode Cable to Holder
WARNING
Before attaching the electrode cable to the electrode holder
or the work cable to clamp, be certain the welder is turned
off or the input power is disconnected.
Type A - Holder with Octagon shaped handle and Clamp in
Jaws
1. Loosen locking screw and slide handle off holder. Place handle over electrode cable. The longer cable is used for the
Electrode Cable and is located in the front of machine upper
hole as shown in
2. Remove insulation from electrode cable 1” ± 1/16” (25.4mm
± 1.6mm) from end.
3. Back out cable connecting screw until end is flush with inside
surface of jaw body.
4. Remove cable connecting clamp from holder jaws. Place
clamp over bare end of electrode cable and insert into holder
with clamp centered against connecting screw.
.
FIGURE 1A
Upper Hole
with Longer Cable
Electrode Cable
CONNECT TO A SYSTEM
GROUNDING WIRE. SEE THE UNITED STATES NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE AND/OR LOCAL CODES
FOR OTHER DETAILS AND MEANS
FOR PROPER GROUNDING.
CONNECT TO HOT WIRES
OF A THREE-WIRE, SINGLE
PHASE SYSTEM OR TO
}
ONE PHASE OF A TWO OR
THREE PHASE SYSTEM.
5. Tighten cable connecting screw securely against clamp.
A-1
Page 8
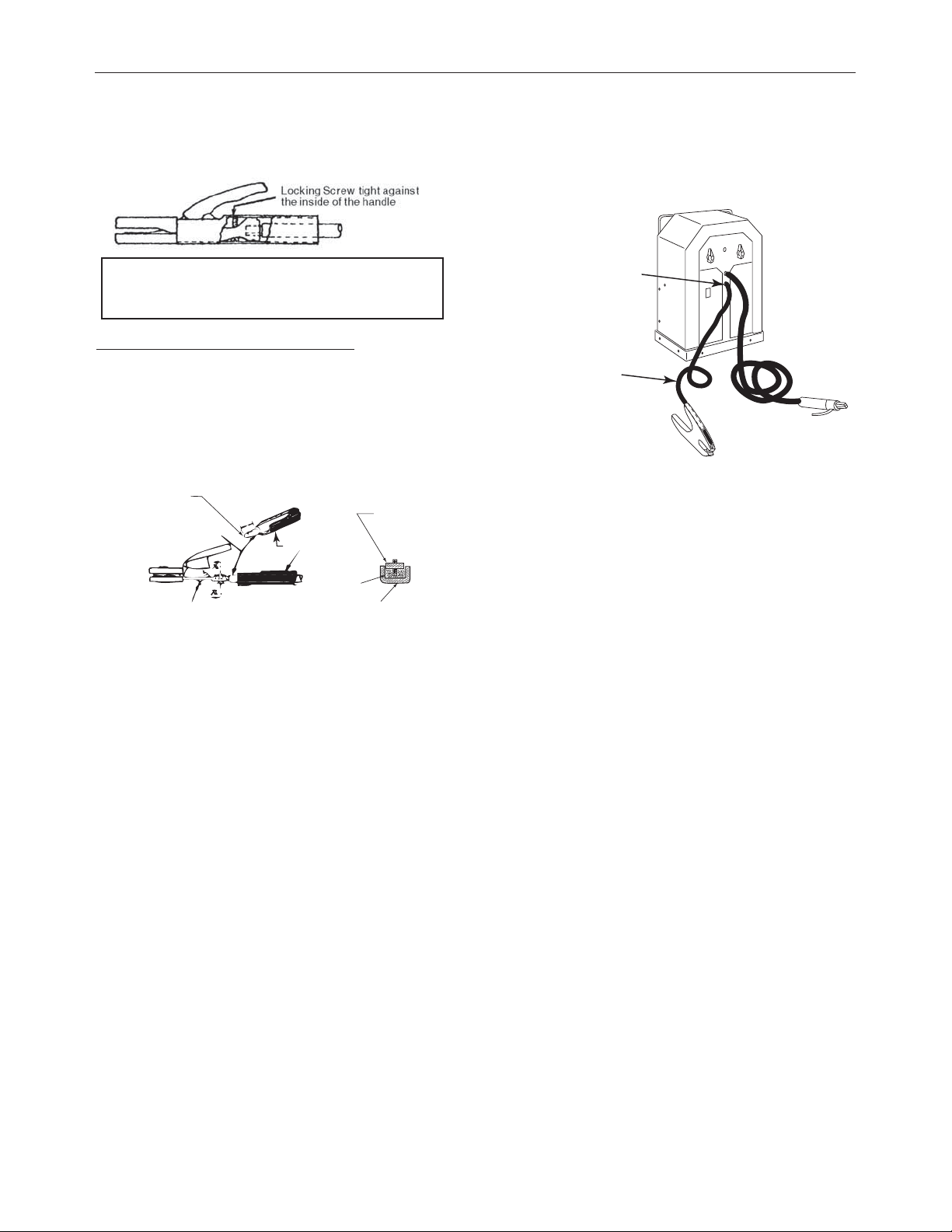
INSTALLATIONAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Attaching Work Cable to Clamp
Electrode and Work Cable Replacement
6. Slide handle into position and secure by turning the locking
screw in until it is tight. The threaded end of the screw will
then pass against the inside of the handle and the head of the
screw will be completely inside the handle.
Important Safety Note: Make sure insulation is secure and that
screws are tight and cannot be touched. If screw can be touched,
DO NOT USE HOLDER, contact your distributor.
Type B - Holder with Round, Ribbed Handle
1. Remove handle mounting screw and slide handle off
holder. Place handle over electrode cable.The longer cable
is used for the Electrode Cable and is located in the front of
machine upper hole as shown in Figure 1A.
2. If electrode cable does not have a terminal on it, remove
insulation from electrode cable 1” ± 1/16” (25.4mm ±
Terminal or
bare strands
Electrode
cable
Handle mounting screw
1" ± 1/16"
Handle
Clamp connecting screw
Cable
connecting
clamp
Cable
1.6mm) from end.
3. Back out clamp connecting screw and remove cable
connecting clamp.
4. If electrode cable has a terminal attached (#10 clearance
hole), place terminal over cable connecting screw.
Otherwise, place bare end of electrode cable into holder
with cable strands divided equally on both sides of clamp
connecting screw.
5. Tighten cable connecting screw securely into clamp so clamp holds
cable in place.
6. Slide handle into position and secure with handle mounting screw.
Insert work cable (with 5/16” clearance hole terminal) through strain
relief hole in work clamp and fasten securely with bolt and nut
provided. The shorter cable is used for the Work Cable and is located
in the front of the machine lower hole as shown below.
Lower Hole
with Shorter
Cable
Work
Cable
Substitution of cables with larger sizes requiring connections to be
made internally is not recommended. Connections for additional
lengths or larger sizes should be properly made externally. Lincoln
Electric QD (Quick Disconnect) connectors are available for this
purpose.
If either cable requires replacement for other reasons, they should be
replaced with the appropriate Lincoln parts— and only by qualified
personnel.
A-2
Page 9

Welding Current Selection
Welding Polarity Selection
Duty Cycle
Circuit Breakers
How to Learn Stick Welding
Electrode Selection Guide
Selecting Electrodes
Out-of-Position Group (E6011)
High-Deposit Group (E6027, E7024)
High-Speed Group (E6012, E6013, E7014)
Low Hydrogen Group (E7018, E7028)
AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
OPERATION
Each position on the current selector switch is marked with the
output amperes for that setting. Turn the switch to the current
required for each application.
There is a slight amount of play in each switch position. It is good
practice to move the switch back and forth once within this play
after switching to a new position. This wiping action keeps the
contacts free from dirt and oxides.
CAUTION
Do not turn the selector switch while welding as this will
damage the contacts.
To get the best results with today’s arc welding electrodes, it is
important to use the proper polarity. The AC/DC Arc Welder permits
the choice of AC, DC(+) or DC(-), giving additional versatility.
Lincoln Electrodes are listed in the chart at the end of this manual.
Each electrode is designed to work best on either DC(+), DC(-) or AC.
In this electrode chart the preferred polarity is listed first. This is the
polarity which should be used - when available - for best results.
(For Codes 11604 and below). The 60 Hz welders are rated 20% duty
cycle and the 50 Hz welders are rated 15% duty cycle for the welding
current shown on each switch position.
(For Codes 11674 and above). The 60 Hz welders are rated 20% duty
cycle and the 50 Hz welders are rated 13% duty cycle for the welding
current shown on each switch position.
See the following Electrode Selection Guide and additional electrode
selection information. Also refer (C2.10) for Stick Electrode Welding
Guide and electrode sizes: www.lincolnelectric.com.
Which electrode is best for the particular job . . . how do you use it?
These are important questions because the cost, quality, and
appearance of your work depends on proper electrode selection and
application. MILD STEEL ELECTRODES may be classified into the
following groups:
This group includes electrodes which have a snappy, deep
penetrating arc and fast freezing deposits.
These electrodes are used for general purpose all-position fabrication
and repair welding; also the best choice for pipe welding and sheet
metal butt, corner and edge welds. They can be used for repair work
when dirt, grease, plating or paint cannot be completely cleaned from
the steel. Typically used with motions “A’’ and “B’’ (below) for the
first pass on vertical-up welds.
This group includes the heavy coated, iron powder electrodes with
their soft arc and fast deposit rates. These electrodes have a heavy
slag and produce exceptionally smooth beads. They are generally
used for production welding where all work can be positioned for
downhand welding. Stringer beads, with drag technique, are always
preferred over weave passes with these electrodes.
Duty cycle is based on a ten minute period. This means that the arc
can be drawn for 2 minutes out of each ten minute period (with a
20% duty cycle unit) without any danger of overheating. If the welder
is used for more than 2 minutes during several successive ten minute
periods, it may overheat. Be sure to leave the unit “on” during each
10 minute period to let the fan motor run for adequate cooling.
Overheating reduces welder life.
AC/DC models above Code 8800 have an internal circuit breaker to
prevent overheating when welding on DC. The breaker will trip and
shut off the DC welding output if the duty cycle is exceeded or if the
cooling air flow is blocked. The cooling fan will continue to run and
the DC welding output will automatically come on when the breaker
has cooled and resets.
Refer to “Learning to Stick Weld” (LTW2) in the operator manual
section of www.lincolnelectric.com
This group includes electrodes which have a moderately forceful arc
and deposit rates between those of the out-off position and highdeposit electrodes. They are primarily general purpose production
electrodes especially for downhill fillets and laps or short and irregular
welds that change direction or position. Also widely used in
maintenance and recommended for sheet metal fillet and lap welds.
Motion “D’’ (below) is generally used for vertical-up welding, but
motions “A” and “B” are also suitable.
These electrodes are generally called “low hydrogen.” The name
comes from the fact that their coating contains little hydrogen in
either moisture or chemical form. Low hydrogen electrodes offer
these benefits: outstanding crack resistance, lowest porosity on
sulphur bearing steels, and capable of X-ray quality deposits. Thus,
they are the first choice when welding “problem” steels. E7018 can
be used in all positions, with Motion “C” recommended for the first
pass on vertical-up welds. NEVER use a whipping technique or a long
arc with these electrodes. ALWAYS fill craters by drawing electrodes
away slowly. ALWAYS keep these electrodes dry. Electrodes not used
within a few hours after a container is opened must be stored in heat
cabinets. LH-73 is recommended with the AC-225. Normally, DC(+) is
preferred for these electrodes.
B-1
Page 10
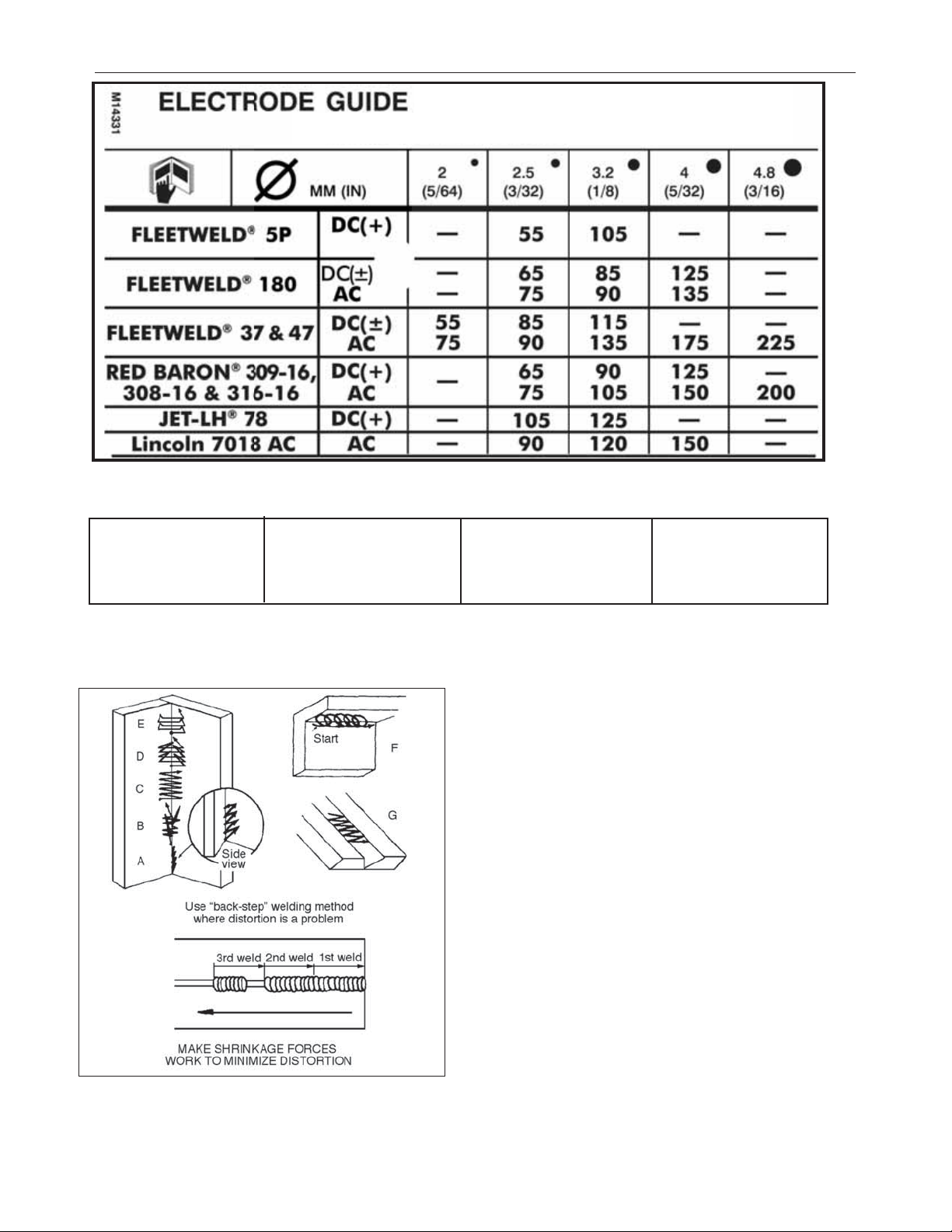
Stick Welding Motions
Manipulation
AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
In Addition to the Electrodes Listed Above the ones listed below may also be used. To determine the correct electrode
diameter and current settings to use please consult the Lincoln Weldirectory (Bulletin #C2.10)
OPERATION
• Fleetweld® 35
• Jetweld® 1
• Blue Max® 2100
• Red Baron® 309/309L MR
• Red Baron® 308L MR
• Wearshield® ME
• Wearshield® MI
• Wearshield® BU
• Wearshield® Mangjet®
• Wearshield® ABR
• Ferroweld®
• Softweld® 99 Ni
shown below
depends on the joint. Some of the common motions are
.
Motion “A” is a straight whipping motion used with fastfreeze
electrodes to make stringer beads in all positions and on all types of
joints. It keeps the molten pool small and lets it freeze quickly so the
weld metal doesn’t spill down or through the joint. Keep arc short
when in the crater and longer during whip out from the crater.
Motion “B” is a whipping motion combined with a slight weave in the
crater. It is used with fast-freeze electrodes as the first pass on
vertical fillets and V-butts.
Motion “C” is a simple side-to-side weave used with all types of
electrodes to make fill passes on vertical fillets and V-butts. Also
sometimes used with fill-freeze and low hydrogen electrodes to make
the first pass on these joints.
Motion “D” is a triangular weave used with fill-freeze and low
hydrogen electrodes to make one pass vertical fillets and V-butts. It
results in a larger weld than Motion “C’’.
Motion “E” is a box weave used with all types of electrodes to make
fill passes on vertical fillets and V-butts. It is similar to Motion “C,’’
but with a distinct pause and slight upward motion at each edge of
the weld to assure complete crater filling and elimination of undercut.
Motion “F” is a circular motion used with all types of electrodes to
make overhead welds. Sometimes accompanied by a slight whip after
each oscillation in the crater. Always use a series of stringer beads
overhead; do not weave.
Motion “G” is a simple side-to-side weave used with all electrodes on
wide fillets or butts in the flat position.
B-2
Page 11

Cutting (Do not exceed the Duty Cycle — At the beginnig of this
Operation Section)
Piercing Holes
NOTE:
AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
The arc welder and the electrode can be used for cutting steel and cast
iron. Follow this procedure:
1. Use 1/8” (3.2mm) or 5/32" (4.0mm) Fleetweld 180 electrode.
2. Set welder on maximum (225 amps).
3. Hold long arc on edge of metal, melting it.
4. Push the arc through the molten metal, forcing it to fall away.
5. Raise the electrode, and start over again.
The important thing is to continue this up-and-down, sawing motion,
melting the metal and pushing it away.
1. Welder setting: Maximum (225
amps).
2. Electrode: 1/8” (3.2mm) or 5/32"
(4.0mm) Fleetweld 180.
3. Hold the electrode with a long arc
perpendicular over the spot
where the hole is to be made.
4. When the metal is molten, push
the electrode through the molten
puddle.
5. Give the molten metal a chance
to fall through the hole.
6. Circle with a long arc around the
edge of the hole until the desired
diameter hole has been made.
OPERATION
If the electrode is pushed through too soon it will stick in the puddle. Be
sure the metal is molten before pushing through .
On heavy metal (5/16" (7.9mm) or thicker), position the plate to be
pierced vertically, and the electrode horizontally. This allows the molten
metal to drip away freely as you are boring through.
B-3
Page 12

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
MAINTENANCE
Routine preventative maintenance is not required. See your
local Lincoln Electric Authorized Field Service Shop for necessary repairs.
MAINTENANCE
D-1
Page 13

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
NOTES
Page 14

15A
2
2A
15
14A
14B
13
3
2
5
6
7
8
9A
10
11
9
16A
16
17
18
20
21
23
12
28
29
22B
22A
1
15B
15A
AC-225-S
Model Index
15B
P-65-A.aP-65-A.a
BELOW CODE 6300 ONLY
and Codes 6342, 6343 and 6453
2A
13
14A
14B
15
18
20
16
17
22B
21
16A
22A
23
12
28
10
11
9A
29
04-19-2010
Page 15

P-65-A.bP-65-A.b
PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./
CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO.
4665 A.1.a 1 7093 A.1a 7 9424 A.1a 12
4763 A.1a 2 7094 A.1a 7 9425 A.1a 12
4798 A.1a 2 7098 A.1a 7 9426 A.1a 12
4852 A.1a 2 7099 A.1a 7 9427 A.1a 12
4953 A.1a 2 7100 A.1a 7 9428 A.1a 12
5130 A.1a 2 7101 A.1a 7 10420 A.1a 13
5167 A.1a 3 7102 A.1a 7 10421 A.1a 13
5169 A.1a 3 7103 A.1a 7 10422 A.1a 13
5227 A.1a 3 7234 A.1a 7 10423 A.1a 13
5341 A.1a 4 7330 A.1a 8 10424 A.1a 12
5348 A.1a 4 7333 A.1a 7 11074 A.1a 14
5381 A.1a 3 7351 A.1a 8
5438 A.1a 4 7352 A.1a 8
5440 A.1a 4 7523 A.1a 7
5449 A.1a 4 7533 A.1a 9 11602 B.1.a 1
5451 A.1a 4 7731 A.1a 9 11603 B.1.a 2
5465 A.1a 4 7743 A.1a 9 11604 B.1.a 3
5470 A.1a 4 7744 A.1a 9 11674 B.1.a 4
5678 A.1a 4 7745 A.1a 9
5683 A.1a 4 7746 A.1a 9
5880 A.1a 5 7755 A.1a 9
5896 A.1a 4 7805 A.1a 9
5897 A.1a 4 7813 A.1a 9
5903 A.1a 4 8226 A.1a 9
6140 A.1a 5 8370 A.1a 10
6184 A.1a 5 7382 A.1a 10
6295 A.1a 5 8383 A.1a 10
6304 A.1a 6 8384 A.1a 10
6342 A.1a 5 8385 A.1a 10
6343 A.1a 5 8386 A.1a 10
6453 A.1a 5 8459 A.1a 10
6518 A.1a 5 8511 A.1a 10
6592 A.1a 6 8712 A.1a 10
6600 A.1a 6 8780 A.1a 10
6601 A.1a 6 8894 A.1a 10
6616 A.1a 6 8897 A.1a 10
6661 A.1a 6 8898 A.1a 10
6734 A.1a 6 8900 A.1a 10
6898 A.1a 6 8918 A.1a 10
6967 A.1a 6 8959 A.1a 10
6991 A.1a 6 8983 A.1a 10
7009 A.1a 6 9039 A.1a 10
7010 A.1a 6 9291 A.1a 11
7011 A.1a 6 9292 A.1a 11
7012 A.1a 6 9293 A.1a 11
7013 A.1a 6 9294 A.1a 11
7030 A.1a 6 9295 A.1a 11
7050 A.1a 7 9296 A.1a 11
7068 A.1a 6 9422 A.1a 12
7072 A.1a 6 9423 A.1a 12
04-19-2010
Page 16
# Indicates a Change This Printing
P-65-A.1.aP-65-A.1.a
Use only the parts marked “X” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY
This Page for Codes Below 11600
1 Upper Back Panel M9873
1
Upper Back Panel (Code 5600 to 6600 except 6304)
2 Fan Motor & Blade (60 Hz), Includes; M13539-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
2A Fan M13525 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
2 Fan Motor & Blade (50 Hz), Includes: M13539-2 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
2A Fan M13525-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
3 Fan Mounting Bracket M9874 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
3 Fan Mounting Bracket M10396
5 Case L3786-6 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Case L3786-7 1 • X X X • • • • • • • • • •
5 Case L3786-12 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Case L3786-13
5 Case L3786-19 1 • • • • • • • • • X X X • •
5 Case L3786-14 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts M9803
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts M13029 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts M14008 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts M15411 1 • • • • • • • • • • X • • •
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 208 Volts M15411-2 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
6
Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Above 250 Volts
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 & 60 Hz, Other Voltages
6
6
Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Above 250 Volts
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 208V Only M15725-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 & 60 Hz, Other Voltages
6
6
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 & 60 Hz, Other Voltages
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230V Only M15725 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X X
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 Hz, 15% Duty Cycle Only
6
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Duty Cycle 220V OnlyM14009 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
6
6
Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 Hz, 15% Duty Cycle Other Volt.
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 50 Hz M15727 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
6 Nameplate, Montgomery Ward M9934
6 Nameplate, Lincoln, 60 Hz M22165 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Fastener Button (White) T14659
Fastener Button (Black) T14659-1
7 Selector Switch (50 Hz Only), Includes: M10830-8 1 • • • • • • X X • • • • • •
7 Selector Switch, Includes: M10830-3 1 X X X X X X X X • • • • • •
7 Selector Switch, Includes: M10830-9 1 • • • • • • • • X X X X X X
Switch Shaft S13206 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
8 Switch Handle (Black) T13990-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
9 Output Lead Grommets T9274-4 2 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
9A Output Lead Clamp S15761 1 • • • X X X X X X X X X X X
10 Line Switch Nameplate S12070
11 Line Switch S7670 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X • •
11 Line Switch S18815 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
12 Transformer & Base
13 Cover Panel, Terminal Block L3936-1 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
14A Input Terminal Block T11813
14B Input Panel, 60 Hertz T11881 1 • X X • • • • • • • • • • •
ø
This part is obsolete and no longer available.
M10894 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
M15411-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M9803-1 1 • X X X X X X • • • • • • •
M15726 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
M13029-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
M14008-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M13880 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
M14009-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • X • • •
Not Available
ø
ø
ø
ø
ø
(As Req)
(As Req)
ø
ø
1234567891011121314
1 XXXX••••••••••
1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
1•• •••XXXX•••••
1 XXXXXXXXX • • • ••
1 •XXX••••••••••
XXXXXXXXXXXX ••
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
1 X•••••••••••••
1 X•••••••••••••
04-19-2010
Page 17
# Indicates a Change This Printing
P-65-A.1.bP-65-A.1.b
Use only the parts marked “X” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY.
15 Back Cover L3936 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Back Cover L4143 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Back Cover L4143-1
15A Lower Back Panel L4595 1 • • • • • X X • • • • • • •
15A Lower Back Panel L4595-2 • • • • • • X X X X X X X X
15B Upper Back Panel G1239 1 • • • • • X X X • X X X • •
15B Upper Back Panel G1395 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X
16A Cover Panel L3935-A 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
16 Electrode Cable S11609-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
17 Electrode Holder K909-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
18 Ground Cable S11609-3 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
19 Headshield M9673-6 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
20 Ground Clamp M12033 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
28 Receptacle (230 Volts Only) S7733
28 Receptacle (230 Volts Only) S13700 1 • • • • X X X X X X X X X •
29 Input Cord (230 Volts Only)
29 Input Cord (230 Volts Only) S13699-2 1 • • • • X X X • • • • • • •
29
Input Cord (230 Volts or Less Only) (60 Hz)
Input Cord 230V 50 Hz (Codes 8894, 9428 &
29
10424 Only)
Undercarriage Kit
(Includes Items 21, 22A, 22B & 23)
S13699-2 & S13700
S15599-1 1 • • • • • • • X X X X X X X
S18021 1 • • • • • • • • • X • X X •
Order K761 1 • • • • X X X X X X X X X X
ø
ø
1234567891011121314
1 ••••X•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
Parts Not Illustrated
Warning Decal (Mounts to Case Upper Corner)
Electrode Selection Decal M14331 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
Earth Ground Decal T13260-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X •
M14330 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
ø
This part is obsolete and no longer available.
04-19-2010
Page 18
# Indicates a Change This Printing
P-65-B.1.aP-65-B.1.a
Use only the parts marked “X” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY.
This Page for Codes Above 11600:
2 Fan Motor & Blade, Includes: M13539-1 1 X • X •
Fan M13525 1 X • X •
2 Fan Motor & Blade, Includes: M13539-2 1 • X • X
Fan M13525-1 1 • X • X
5 Case L3786-14 1 X X X X
6 Nameplate (Codes 11602 & 11604) M22165 1 X • X •
6 Nameplate (Code 11603) M15727 1 • X • •
6 Nameplate (Code 11674) M22167 1 • • • X
Fastener Button (Black) T14659-1 1 X X X X
8 Handle Assembly T13990-1 1 X X X X
9A Lead Clamp S15761 1 X X X X
11 Line Switch S18815 1 X X X X
12 Transformer & Base NSS 1XXXX
15A Lower Case Back L4595-2 1 X X X X
15B Upper Case Back G1395 1 X X X X
16 Electrode Cable S11609-4 1 X X X X
17 Electrode Holder K909-1 1 X X X X
18 Ground Cable S11609-3 1 X X X X
20 Ground Clamp M12033 1 X X X X
Undercarriage Kit, Includes: K761
21 Wheel S11662-3 2 • • X •
22 Mounting Kit, Includes: T14160 1 • • X •
22A Plain Washer S9262-1 2 • • X •
22B Push Nut T12570 2 • • X •
22C 3/8-16 x 2.00 HHCS CF000071 1 • • X •
23 Axle M8809-61 1 • • X •
29 Power Input Cable
29 Power Input Cable (Code 11603 & 11674) S18021 1 • X • X
30 Warning Decal (Not Shown) M14330-3 1 X X X X
31 Electrode Selection Decal (Not Shown) M14331 1 X X X X
32
32
32
33 Warranty Decal (Not Shown) S22127-1 1 • X • •
Wiring Diagram (Not Shown) (Codes 11602 & 11604)
Wiring Diagram (Not Shown) (Code 11603)
Wiring Diagram (Not Shown) (Code 11674)
(Codes 11602 & 11604
) S15599-1 1 X • X •
* ••X•
S15621 1 X • X •
S16671 1 • X • •
S28364 1 • • • X
1234567891011121314
* Undercarriage Kit Optional on all Codes - Standard where indicated.
NSS - Not Sold Separately
04-19-2010
Page 19

NOTES
Page 20
AC/DC 225/125
COL. COL.
CODE NO. CODE NO.
8566 1 9025 2
8581 1 9186 2
8650 1 9221 3
8663 1 9222 3
8666 1 9223 3
8700 1 9224 3
8737 1 9225 3
8742 1 9226 3
8777 1 9365 3
8788 1 10426 3
8811 2 10427 3
8815 2 10428 3
8817 1 10429 3
8893 2 11675 4
8901 2
8903 2
8910 2
8955 2
8986 2
9005 2
9015 2
Model Index
6A
1B
1A
10
4
20
31B
6B
P-140-AP-140-A
3
5
15
7
2
13
8
17
31A
14
11
9A
28
12
25
7A
14A
29
Use only the parts marked “X” in the column under the
# Indicates a Change This Printing
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY.
heading number called for in the model index page.
123456789
1 Rectifier Assembly, Includes: L7029 ø 1X•••
1A (–) Rectifier Half (Bottom) S12837-7A ø 1X•••
1B (+) Rectifier Half (Top) S12837-7B ø 1X•••
1 Rectifier Assembly, Includes: L6974 ø 1•X••
1 Rectifier Assembly (Below Code 10000), Includes: L7491 1 • X X •
1 A (–) Diode M9661-39R 2 • X X •
1 B (+) Diode M9661-39 2 • X X •
Suppressor Assembly M14705 1 • X X •
1 Rectifier Assembly, (Above Code 10000) G3648 1 • • X X
2 Fan Motor & Blade (60 Hz), Includes: M13539-1 1 X X X •
Fan M13525 1 X X X •
2 Fan Motor & Blade (50 Hz), Includes: M13539-2 1 X X X X
Fan M13525-1 1 X X X X
ø
This part is obsolete and no longer available
03-10-2010
Page 21
# Indicates a Change This Printing
P-140-A.1P-140-A.1
Use only the parts marked “X” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY.
3 Choke S18336 1 X X • •
3 Choke M15371 1 • • X X
4 Fan Motor Bracket S17194 1 X • • •
5 Case (Below Code 10400) L3786-19 1 X X X •
5 Case (Above Code 10400) L3786-14 1 • • X X
6A Lower Back Panel L6650 1 X X X X
6B Upper Back Panel L6651 ø 1X•••
6B Upper Back Panel G1395-1 1 • X X X
7 Range Selector Switch Includes: M10830-9 1 X X X X
Switch Shaft S13206 1 X X X X
7A Handle M13989-1 1 X X X X
8 Electrode Cable S11609-9 1 X X X X
9A Output Lead Clamp S15761 1 X X X X
10 Work Cable S11609-10 1 X X X X
11 Line Switch (Below Code 10400) S7670 1 X X X •
11 Line Switch (Above Code 10400) S18815 1 • • X X
12 Transformer and Base Not Available 1 X X X X
13 Suppressor S17203 1 X • • •
14 Polarity Switch, Includes: M14063 1 X X X X
Switch Shaft M14337 1 X X X X
14A Handle M13989-1 1 X X X X
15 Nameplate (60 Hz. 230 Volt Only) M15784 1 X X X •
15 Nameplate (60 Hz. All Voltages except 208 & 230 Volt) M15784-1 1 X X X •
15 Nameplate (60 Hz. 208 Volt Only) M15784-2 1 X X X •
15 Nameplate (50 Hz. All Voltages) M15785 1 X X X •
15 Nameplate (50 Hz) (Code 11675) M22168 1 • • • X
15A Warning Plate (Not Shown) M14330 1 X X X •
15A Warning Decal M14330-3 1 • • • X
15B Electrode Selector Plate (60 Hz) (Not Shown) M14331 1 X X X •
15B Electrode Selector Plate (50 Hz) (Not Shown) M14335 1 X X X •
16 Nameplate Fastener Button T14659-1 4 X X X X
17 Electrode Holder K909-1 1 X X X X
20 Work Clamp M12033 1 X X X X
28 Receptacle (60 Hz., 250 Volts or Less Only) S13700 1 X X X •
29 Input Cable (60 Hz., 250 Volts or Less Only) S15599-1 1 X X X X
29 Input Cable (50 Hz., 250 Volts or Less Only) S18021 1 • X X X
Circuit Breaker - Not Illustrated S10657-3 1 • X X X
Earth Ground Decal (Not Shown) T13260-4 1 X X X X
Optional Items:
30 Head Shield (Not Shown) Customerʼs1XXX•
Choice
31 Undercarriage Kit, Includes: K761 1 X X X X
31A Axle M8809-61 1 X X X X
31B Wheel S11662-3 2 X X X X
31C Mounting Kit T14160 1 X X X X
123456789
NSS - Not Sold Separately
ø
This part is obsolete and no longer available.
03-10-2010
Page 22

NOTES
Page 23

Manual del Operador
AC-225-S y AC/DC 225/125
Para usarse con máquinas con números de código:
10420, 10421, 10422,
10423, 10424, 11074,
11602, 11603, 11604,
11674, 11675
Registre su máquina:
www.lincolnelectric.com/register
Servicio Autorizado y Localizador de Distribuidores:
www.lincolnelectric.com/locator
Guarde para consulta futura
Fecha de Compra
Código: (ejemplo: 10859)
Número de serie: (ejemplo: U1060512345)
IMS237-P
© Lincoln Global, Inc. Todos los derechos reservados.
Page 24

GRACIAS POR SELECCIONAR UN
MANTENGA SU CABEZA ALEJADA DE LOS HUMOS.
PRODUCTO DE CALIDAD DE LINCOLN ELECTRIC.
SÍRVASE EXAMINAR INMEDIATAMENTE SI LA CAJA
Y EL EQUIPO ESTÁN DAÑADOS
Cuando este equipo se envía, los derechos pasan al comprador en
cuanto lo recibe del transportista. En consecuencia, el comprador es
el que debe hacer los reclamos por daños en el material durante el
envío ante la compañía de transporte al momento en que lo recibe.
LA SEGURIDAD DEPENDE DE USTED
El equipo de soldadura y corte de Lincoln está diseñado y construido
con la seguridad en mente. Sin embargo, su seguridad general puede
mejorar a través de una instalación adecuada...y una operación
cuidadosa por su parte.
NO INSTALE, OPERE O REPARE ESTE EQUIPO SIN LEER ESTE MANUAL
Y LAS PRECAUCIONES DE SEGURIDAD QUE CONTIENE. Y, lo más
importante, piense antes de actuar y tenga cuidado.
ADVERTENCIA
Esta palabra aparece donde la información debe seguirse
exactamente para evitar lesiones personales serias o pérdida de la
vida.
PRECAUCIÓN
Esta palabra aparece donde la información debe seguirse para evitar
lesiones personales menores o daño a este equipo.
NO se acerque mucho al arco. Use
lentes correctivos si es necesario para
permanecer a una distancia razonable
del arco.
LEA y obedezca la Ficha Técnica de
Seguridad del Material (MSDS) y la
etiqueta de advertencia que aparece en
todos los contenedores de los
materiales de soldadura.
UTILICE SUFICIENTE VENTILACIÓN o
escape en el arco, o ambos, para
mantener los humos y gases alejados de su zona de respiración y del área en
general.
EN UN ESPACIO GRANDE O EN EXTERIORES, la ventilación natural es
adecuada si mantiene su cabeza fuera de los humos (Vea a continuación).
UTILICE LAS CORRIENTES NATURALES o ventiladores para mantener los
humos alejados de su cara.
Si desarrolla síntomas inusuales, vea a su supervisor. Tal vez se necesario
revisar la atmósfera de soldadura y sistema de ventilación.
UTILICE PROTECCIÓN ADECUADA PARA LOS OJOS, OÍDOS Y CUERPO
PROTEJA sus ojos y cara con la careta de soldadura bien
colocada y con el grado adecuado de placa de filtro (Vea
ANSi Z49.1).
PROTEJA su cuerpo contras las salpicaduras de soldadura
y las chispas del arco con ropa protectora incluyendo
vestimenta de lana, mandil y guantes a prueba de fuego,
pantalones de cuero y botas altas.
PROTEJA a otros de la salpicadura, chispas y
destellos con pantallas o barreras protectoras.
EN ALGUNAS ÁREAS, puede resultar útil la
protección contra el ruido.
ASEGÚRESE de utilizar equipo protector en buen estado.
Asimismo, use lentes de seguridad en el área de tra-
bajo EN TODO MOMENTO.
SITUACIONES ESPECIALES
NO SUELDE O CORTE contenedores o materiales que habían estado
previamente en contacto con sustancias peligrosas a menos que
se hayan limpiado adecuadamente. Esto es extremadamente
peligroso.
NO SUELDE O CORTE partes pintadas o enchapadas a menos que
tome precauciones especiales con la ventilación. Pueden liberar
humos o gases altamente tóxicos.
Medidas de precaución adicionales.
PROTEJA a los cilindros de gas comprimido del calor excesivo,
descargas mecánicas y arcos; sujete a los cilindros para que no
se caigan.
ASEGÚRESE de que los cilindros nunca estén aterrizados o sean
parte de un circuito eléctrico.
REMUEVA todos los riesgos potenciales de incendio del área de
soldadura.
SIEMPRE TENGA A LA MANO EQUIPO CONTRA INCENDIOS LISTO PARA SU
USO INMEDIATO Y SEPA CÓMO USARLO.
Page 25

1.d. Mantener todos los protectores, cubiertas y
SECCIÓN A:
ADVERTENCIAS
ADVERTENCIA DE LA LEY 65 DE CALIFORNIA
Motores Diesel
En el estado de California, se considera a las emisiones del motor de
diesel y algunos de sus componentes como dañinas para la salud, ya que
provocan cáncer, defectos de nacimiento y otros daños reproductivos.
Motores de Gasolina
Las emi sio nes de este tipo de pro duc tos con tie nen químicos que, para el
es ta do de Ca li for nia, pro vo can cáncer, de fec tos de na ci mien to y otros
daños reproduc tivos.
LA SOLDADURALA SOLDADURA AL ARCO PUEDE SER
PELIGROSA. PROTEJASE USTED Y A LOS DEMAS CONTRA POSIBLES LESIONES DE DIFERENTE GRAVEDAD,
INCLUSO MORTALES. NO PERMITA QUE LOS NIÑOS SE
ACERQUEN AL EQUIPO. LAS PERSONAS CON MARCAPASOS DEBEN CONSULTAR A SU MEDICO ANTES DE
USAR ESTE EQUIPO.
1.e. En algunos casos puede ser necesario quitar los protectores para hacer
1.f. No poner las manos cerca del ventilador del motor. No tratar de
1.g. Para impedir el arranque accidental de los motores de gasolina mientras
1.h. Para evitar quemarse con agua caliente, no quitar la
SEGURIDAD
dispositivos de seguridad del equipo en su lugar y en
buenas condiciones. No acercar las manos, cabello,
ropa y herramientas a las correas en V, engranajes,
ventiladores y todas las demás piezas móviles
durante el arranque, funcionamiento o reparación del
equipo.
algún trabajo de mantenimiento requerido. Quitarlos solamente cuando
sea necesario y volver a colocarlos después de terminado el trabajo de
mantenimiento. Tener siempre el máximo cuidado cuando se trabaje cerca
de piezas en movimiento.
sobrecontrolar el regulador de velocidad en vacío empujando las varillas
de control del acelerador mientras el motor está funcionando.
se hace girar el motor o generador de la soldadura durante el trabajo de
mantenimiento, desconectar los cables de las bujías, tapa del distribuidor
o cable del magneto, según corresponda.
tapa a presión del radiador mientras el motor está
caliente.
Lea y entienda los siguientes mensajes de seguridad. Para más información
acerca de la seguridad, se recomienda comprar un ejemplar de "Safety in
Welding & Cutting - ANIS Standard Z49.1" de la Sociedad Norteamericana
de Soldadura, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 ó CSA Norma
W117.2-1974. Un ejemplar gratis del folleto "Arc Welding Safety"
(Seguridad de la soldadura al arco) E205 está disponible de Lincoln Electric
Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
ASEGURESE QUE TODOS LOS TRABAJOS DE
INSTALACION, FUNCIONAMIENTO, MANTENIMIENTO Y
REPARACION SEAN HECHOS POR PERSONAS
CAPACITADAS PARA ELLO.
PARA EQUIPOS ACCIONADOS POR
2.a. La corriente eléctrica que circula a través de un
2.b. Los campos EMF pueden interferir con los marcapasos y en otros
2.c. La exposición a los campos EMF en soldadura puede tener otros efectos
MOTOR.
1.a. Apagar el motor antes de hacer trabajos de localización
de averías y de mantenimiento, salvo en el caso que el
trabajo de mantenimiento requiera que el motor esté
funcionando.
1.b. Los motores deben funcionar en lugares abiertos bien
ventilados, o expulsar los gases de escape del motor al exterior.
1.c. No cargar combustible cerca de un arco de soldadura
cuando el motor esté funcionando. Apagar el motor y
dejar que se enfríe antes de rellenar de combustible
para impedir que el combustible derramado se vaporice
al quedar en contacto con las piezas del motor caliente.
No derramar combustible al llenar el tanque. Si se derrama, limpiarlo con un trapo
y no arrancar el motor hasta que los vapores se hayan eliminado.
2.d. Todo soldador debe emplear los procedimientos siguientes para reducir
LOS CAMPOS ELÉTRICOS
Y MAGNÉTICOS PUEDEN
SER PELIGROSOS.
conductor origina campos eléctricos y magnéticos (EMF) localizados. La
corriente de soldadura crea campos EMF alrededor de los cables y los
equipos de soldadura.
equipos médicos individuales, de manera que los operarios que utilicen
estos aparatos deben consultar a su médico antes de trabajar con una
máquina de soldar.
sobre la salud que se desconocen.
al mínimo la exposición a los campos EMF del circuito de soldadura:
2.d.1. Pasar los cables de pinza y de trabajo juntos - Encintarlos juntos
siempre que sea posible.
2.d.2. Nunca enrollarse el cable de electrodo alrededor del cuerpo.
2.d.3. No colocar el cuerpo entre los cables de electrodo y trabajo. Si
el cable del electrodo está en el lado derecho, el cable de trabajotambién debe estar en el lado derecho.
2.d.4. Conectar el cable de trabajo a la pieza de trabajo lo más cerca
posible del área que se va a solda.
2.d.5. No trabajar al lado de la fuente de corriente.
3
Page 26

Además de las medidas de seguridad normales, si es necesario
soldar en condiciones eléctricamente peligrosas (en lugares
húmedos o mientras se está usando ropa mojada; en las
estructuras metálicas tales como suelos, emparrillados o
andamios; estando en posiciones apretujadas tales como sentado,
arrodillado o acostado, si existe un gran riesgo de que ocurra
contacto inevitable o accidental con la pieza
de trabajo o con tierra,
usar el equipo siguiente:
Cuando se suelda con
electrodos de acero inoxidable o recubrimiento duro que requieren
ventilación especial (Ver instrucciones en el contenedor o la MSDS)
o cuando se suelda chapa galvanizada, chapa recubierta de Plomo
y Cadmio, u otros metales que producen humos tóxicos, se deben
tomar precauciones suplementarias. Mantenga la exposición lo más
baja posible, por debajo de los valores límites umbrales
(TLV) ,
utilizando un sistema de extracción local o una ventilación
mecánica. En espacios confinados o en algunas situaciones, a la
intemperie, puede ser necesario el uso de respiración asistida.
SEGURIDAD
LA DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA
PUEDE CAUSAR LA MUERTE.
3.a. Los circuitos del electrodo y de trabajo están
eléctricamente con tensión cuando el equipo de
soldadura está encendido. No tocar esas piezas con
tensión con la piel desnuda o con ropa mojada. Usar guantes secos sin
agujeros para aislar las manos.
3.b. Aislarse del circuito de trabajo y de tierra con la ayuda de material
aislante seco. Asegurarse de que el aislante es suficiente para
protegerle completamente de todo contacto físico con el circuito de
trabajo y tierra.
A
• Equipo de soldadura semiautomática de C.C. a tensión constante.
• Equipo de soldadura manual C.C.
• Equipo de soldadura de C.A. con control de voltaje reducido.
3.c. En la soldadura semiautomática o automática con alambre continuo, el
electrodo, carrete de alambre, cabezal de soldadura, boquilla o pistola
para soldar semiautomática también están eléctricamente con tensión.
3.d. Asegurar siempre que el cable de trabajo tenga una buena conexión
eléctrica con el metal que se está soldando. La conexión debe ser lo más
cercana posible al área donde se va a soldar.
3.e. Conectar el trabajo o metal que se va a soldar a una buena toma de
tierra eléctrica.
3.f. Mantener el portaelectrodo, pinza de trabajo, cable de soldadura y
equipo de soldadura en unas condiciones de trabajo buenas y seguras.
Cambiar el aislante si está dañado.
LOS RAYOS DEL ARCO
PUEDEN QUEMAR.
4.a. Colocarse una pantalla de protección con el filtro adecuado para
protegerse los ojos de las chispas y rayos del arco cuando se suelde o se
observe un soldadura por arco abierto. Cristal y pantalla han de
satisfacer las normas ANSI Z87.I.
4.b. Usar ropa adecuada hecha de material resistente a la flama durable para
protegerse la piel propia y la de los ayudantes de los rayos del arco.
4.c. Proteger a otras personas que se encuentren cerca del arco, y/o
advertirles que no miren directamente al arco ni se expongan a los rayos
del arco o a las salpicaduras.
LOS HUMOS Y GASES
PUEDEN SER
PELIGROS.
5.a. La soldadura puede producir humos y gases
peligrosos para la salud. Evite respirarlos. Durantela soldadura,
mantener la cabeza alejada de los humos. Utilice ventilación y/o
extracción de humos junto al arco para mantener los humos y
gasesalejados de la zona de respiración.
5. b. La operación de equipo de control de humos de soldadura se ve afectada
por diversos factores incluyendo el uso adecuado y el posicionamiento
del equipo así como el procedimiento de soldadura específico y la
aplicación utilizada. El nivel de exposición del trabajador deberá ser
verificado durante la instalación y después periodicamente a fin de
asegurar que está dentro de los límites OSHA PEL y ACGIH TLV
permisibles.
3.g. Nunca sumergir el electrodo en agua para enfriarlo.
3.h. Nunca tocar simultáneamente la piezas con tensión de los
portaelectrodos conectados a dos equipos de soldadura porque el voltaje
entre los dos puede ser el total de la tensión en vacío de ambos
equipos..
3.i. Cuando se trabaje en alturas, usar un cinturón de seguridad para
protegerse de una caída si hubiera descarga eléctrica.
3.j. Ver también 6.c. y 8.
5.c. No soldar en lugares cerca de una fuente de vapores de hidrocarburos
clorados provenientes de las operaciones de desengrase, limpieza o
pulverización. El calor y los rayos del arco puede reaccionar con los
vapores de solventes para formar fosgeno, un gas altamente tóxico, y
otros productos irritantes.
5.d. Los gases protectores usados para la soldadura por arco pueden
desplazar el aire y causar lesiones graves, incluso la muerte. Tenga
siempre suficiente ventilación, especialmente en las áreas confinadas,
para tener la seguridad de que se respira aire fresco.
5.e. Lea atentamente las instrucciones del fabricante de este equipo y el
material consumible que se va a usar, incluyendo la hoja de datos de
seguridad del material (MSDS) y siga las reglas de seguridad del
empleado, distribuidor de material de soldadura o del fabricante.
5.f. Ver también 1.b.
4
Page 27

SEGURIDAD
LAS CHISAS DE
SOLDADURA PUEDEN
PROVOCAR UN INCENDIO
O UNA EXPLOSIÓN.
6.a. Quitar todas las cosas que presenten riesgo de
incendio del lugar de soldadura. Si esto no es posible, taparlas para
impedir que las chispas de la soldadura inicien un incendio. Recordar
que las chispas y los materiales calientes de la soldadura puede pasar
fácilmente por las grietas pequeñas y aberturas adyacentes al área. No
soldar cerca de tuberías hidráulicas. Tener un extintor de incendios a
mano.
6.b. En los lugares donde se van a usar gases comprimidos, se deben tomar
precauciones especiales para prevenir situaciones de riesgo. Consultar
“Seguridad en Soldadura y Corte“ (ANSI Estándar Z49.1) y la información
de operación para el equipo que se esté utilizando.
6.c. Cuando no esté soldando, asegúrese de que ninguna parte del circuito
del electrodo haga contacto con el trabajo o tierra. El contacto accidental
podría ocasionar sobrecalentamiento de la máquina y riesgo de incendio.
6.d. No calentar, cortar o soldar tanques, tambores o contenedores hasta
haber tomado los pasos necesarios para asegurar que tales
procedimientos no van a causar vapores inflamables o tóxicos de las
sustancias en su interior. Pueden causar una explosión incluso después
de haberse “limpiado”. Para más información, consultar “Recommended
Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers
and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”, AWS F4.1 de la
American Welding Society.
6.e. Ventilar las piezas fundidas huecas o contenedores antes de calentar,
cortar o soldar. Pueden explotar.
6.f. Las chispas y salpicaduras son lanzadas por el arco de soldadura. Usar
ropa adecuada que proteja, libre de aceites, como guantes de cuero,
camisa gruesa, pantalones sin bastillas, zapatos de caña alta y una
gorra. Ponerse tapones en los oídos cuando se suelde fuera de posición
o en lugares confinados. Siempre usar gafas protectoras con
protecciones laterales cuando se esté en un área de soldadura.
6.g. Conectar el cable de trabajo a la pieza tan cerca del área de soldadura
como sea posible. Los cables de la pieza de trabajo conectados a la
estructura del edificio o a otros lugares alejados del área de soldadura
aumentan la posibilidad de que la corriente para soldar traspase a otros
circuitos alternativos como cadenas y cables de elevación. Esto puede
crear riesgos de incendio o sobrecalentar estas cadenas o cables de izar
hasta hacer que fallen.
6.h. Ver también 1.c.
6.I. Lea y siga el NFPA 51B “ Estándar para Prevención de Incendios Durante
la Soldadura, Corte y otros Trabajos Calientes”, disponible de NFPA, 1
Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
6.j. No utilice una fuente de poder de soldadura para descongelación de
tuberías.
LA BOTELLA DE GAS
PUEDE EXPLOTAR SI ESTÁ
DAÑADA.
7.a. Emplear únicamente botellas que contengan el gas
de protección adecuado para el proceso utilizado, y
reguladores en buenas condiciones de funcionamiento diseñados para el
tipo de gas y la presión utilizados. Todas las mangueras, rácores, etc.
deben ser adecuados para la aplicación y estar en buenas condiciones.
7.b. Mantener siempre las botellas en posición vertical sujetas firmemente
con una cadena a la parte inferior del carro o a un soporte fijo.
7.c. Las botellas de gas deben estar ubicadas:
• Lejos de las áreas donde puedan ser golpeados o estén sujetos
a daño físico.
• A una distancia segura de las operaciones de corte o soldadura
por arco y de cualquier fuente de calor, chispas o llamas.
7.d. Nunca permitir que el electrodo, portaelectrodo o cualquier otra pieza
con tensión toque la botella de gas.
7.e. Mantener la cabeza y la cara lejos de la salida de la válvula de la botella
de gas cuando se abra.
7.f. Los capuchones de protección de la válvula siempre deben estar
colocados y apretados a mano, excepto cuando la botella está en uso o
conectada para uso.
7.g. Leer y seguir las instrucciones de manipulación en las botellas de gas y
el equipamiento asociado, y la publicación P-I de CGA, “Precauciones
para un Manejo Seguro de los Gases Comprimidos en los Cilindros“,
publicado por Compressed Gas Association 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
PARA EQUIPOS ELÉCTRICOS.
8.a. Cortar la electricidad entrante usando el interruptor de
desconexión en la caja de fusibles antes de trabajar en
el equipo.
8.b. Conectar el equipo a la red de acuerdo con U.S. National Electrical Code,
todos los códigos y las recomendaciones del fabricante.
8.c. Conectar el equipo a tierra de acuerdo con U.S. National Electrical Code,
todos los códigos y las recomendaciones del fabricante.
Vaya a
http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety para
información adicional de seguridad.
Guía Web Interactiva de
Seguridad de Soldadura
para los dispositivos
móviles.
Page 28

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Instalación.......................................................................................................Sección A
Instrucciones de operación..........................................................................................................A-1
Alimentación y Conexiones a Tierra.....................................................................................A-1
Conexión del cable del electrodo al portaelectrodo .............................................................A-1
Portaelectrodo Tipo A con Forma Octagonal .......................................................................A-1
Portaelectrodo Tipo B con Forma Circular Estriado.............................................................A-2
Reemplazo del electrodo y trabajo.......................................................................................A-2
Operación........................................................................................................Sección B
Selección de la polaridad de soldadura ...............................................................................B-1
Ciclo de Trabajo .................................................................................................................B-1
Interruptores Automáticos ...................................................................................................B-1
Cómo Aprender a Soldar con Electrodo Revestido .............................................................B-1
Guía de Selección de Electrodos ........................................................................................B-1
Guía de Electrodos ..............................................................................................................B-2
Movimientos A a G de la Soldadura con Electrodo Revestido.............................................B-2
Corte y Perforación ............................................................................................................B-3
Mantenimiento................................................................................................Sección C
Mantenimiento Preventivo de Rutina ..................................................................................C-1
Páginas de Partes ............................................................................. Serie P-65, P-140
TABLA DE CONTENIDO
Página
6
Page 29

INSTRUCCIONES DE
INSTALACIÓNAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
OPERACIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
• Haga que un electricista instale y dé servicio a este equipo.
• Apague la alimentación en la caja de fusibles antes de trabajar en este equipo.
• No toque las partes eléctricamente calientes.
Alimentación y Conexiones a Tierra
Antes de empezar la instalación, consulte con la
compañía de electricidad para saber si su fuente de
energía es adecuada para el voltaje, amperios, fase y
frecuencia especificados en la placa de identificación de
la soldadora. Asimismo, asegúrese de que la instalación
planeada cumplirá con el Código Eléctrico Nacional de
los Estados Unidos y los requerimientos del código local.
Esta soldadora se puede operar desde una línea
monofásica, o desde una fase de una línea bifásica o
trifásica.
Todos los modelos que están diseñados para operar con
líneas de entrada de menos de 250 voltios se envían con
el cable de alimentación conectado a la soldadora.
Coloque la soldadora donde el aire pueda circular
libremente a través de la rejillas posteriores y a los lados
del gabinete y hacia fuera por la parte inferior de todos
los cuatro lados. Monte un receptáculo NEMA Tipo 650R en un lugar adecuado. Asegúrese de que el enchufe
del cable de alimentación conectado a la soldadora
pueda alcanzarlo.
Basándose en las siguientes instrucciones, haga que un
electricista calificado conecte este receptáculo (Tipo
NEMA 6-50R) a las líneas de alimentación de la caja de
fusibles. Se requieren tres cables de cobre #10 o
mayores si se utiliza un conducto. Para cables largos de
más de 31m (100'), se necesitará un cable #8 o mayor
en el conducto para evitar caídas excesivas de voltaje.
Instale en las dos líneas calientes fusibles tipo quemado
lento de 50 amperios como se muestra en el siguiente
diagrama. El contacto central en el receptáculo es para
la conexión a tierra. Un alambre verde en el cable de
entrada conecta este contacto al armazón de la
soldadora.
Esto asegura un aterrizamiento adecuado al armazón de
la soldadora cuando el enchufe de la misma se inserta
en el receptáculo. Si se utiliza un interruptor de
desconexión separado, deberá tener dos polos para dos
líneas calientes y ambos deberán tener fusibles para 50
amperios.
CONECTE A UN CABLE DE ATERRIZAMIENTO DEL SISTEMA. CONSULTE EL CÓDIGO
ELÉCTRICO NACIONAL DE LOS ESTADOS
UNIDOS Y/O CÓDIGOS LOCALES PARA
OBTENER OTROAS DETALLES Y MEDIOS
PARA UN ATERRIZAMIENTO ADECUADO.
CONECTE A CABLES CALIENTES
DE UN SISTEMA MONOFÁSICO DE
TRES ALAMBRES O A UNA FASE
}
DE UN SISTEMA BIFÁSICO O
TRIFÁSICO.
ADVERTENCIA
Orificio Superior con
Cable Más Largo
Cable del Electrodo
FIGURA 1A
Conexión del Cable del Electrodo al Portaelectrodo
Antes de conectar el cable del electrodo al portaelectrodo o
el cable de trabajo a la pinza, asegúrese de que la soldadora esté apagada o la alimentación desconectada.
Identifique el tipo de portaelectrodo antes de instalarlo
Tipo A – Portaelectrodo con Manija Octagonal y Pinza
con Mordazas
1. Afloje el tornillo de fijación y deslice la manija fuera
del portaelectrodo. Coloque la manija sobre el
cable del electrodo. El cable más largo se utiliza
para el cable del electrodo y se localiza enfrente de
los orificios superiores de la máquina como se
muestra en la siguiente figura.
PINZA DE
PINZA DE CONEXIÓN
DE CABLE EN
POSICIÓN DE ENVÍO
TORNILLO DE FIJACIÓN
CONEXIÓN
DE CABLE
CABLE DEL
ELECTRODO
PINZA DE CONEXIÓN DE CABLE
TORNILLO DE CONEXIÓN DE CABLE
MANIJA
FIGURA 1A
2. Remueva 25.4mm ± 1.6mm (1” ± 1/16”) del ais-
lamiento de la punta del cable del electrodo.
3. Mueva hacia atrás el tornillo de conexión del cable
hasta que esté nivelado con la superficie interna
del cuerpo de la mordaza.
4. Remueva la pinza de conexión del cable de las
mordazas del portaelectrodo. Coloque la pinza
sobre la punta desnuda del cable del electrodo e
inserte en el portaelectrodo con la pinza centrada
contra el tornillo de conexión.
5. Apriete bien el tornillo de conexión del cable contra
la pinza.
.
A-1
Page 30

INSTALACIÓNAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
6. Deslice la manija en posición y asegure girando el
tornillo de fijación hasta que esté apretado. El lado
roscado del tornillo pasará entonces al interior de la
manija y su cabeza estará completamente dentro de
la misma.
El tornillo de fijación se aprieta
contra el interior de la manija
Nota importante de seguridad: asegúrese de que el aislamien-
Conexión del Cable de Trabajo a la Pinza
Inserte el cable de trabajo (con terminal de orificio de
paso de 5/16”) a través del orificio de anclaje en la pinza
de trabajo, y sujete bien con el perno y tuerca
proporcionados. El cable más corto se utiliza para el
Cable de Trabajo y se localiza al frente del orificio inferior
de la máquina como se muestra a continuación.
Orificio Inferior
to esté seguro y de que los tornillos estén apretados y no se
puedan tocar. Si puede tocar un tornillo, NO UTILICE EL
PORTAELECTRODO, contacte a su distribuidor.
Tipo B – Portaelectrodo con Manija Redonda Estriada
1.
Remueva el tornillo de montaje de la manija y
deslice la misma fuera del portaelectrodo. Coloque
la manija sobre el cable del electrodo. El cable más
largo se utiliza para el cable del electrodo y se
localiza enfrente del orificio superior de la máquina
como se muestra en la Figura 1A.
Terminal o alambres
desnudos
Cable
del electrodo
1" ± 1/16"
Manija
Pinza de conexión
del cable
Reemplazo del Electrodo y Pinza de Trabajo
No se recomienda sustituir cables de tamaños más
grandes que requieren conexiones internas. Las
conexiones de longitudes adicionales o tamaño más
grandes deberán hacerse externamente de manera
adecuada. Los conectores QD (Desconexión Rápida) de
Lincoln se encuentran disponibles para este fin.
Tornillo de montaje de la manija
Cable
Tornillo de conexión de la pinza del cable
2. Si el cable del electrodo no tiene una terminal,
remueva 25.4mm ± 1.6mm (1” ± 1/16”) del
aislamiento de la punta.
3. Mueva hacia atrás el tornillo de conexión de la
Si se requiere reemplazar alguno de los cables por otras
razones, deberán reemplazarse con partes apropiadas de
Lincoln— y sólo por personal calificado.
pinza y remueva la pinza de conexión del cable.
4. Si el cable del electrodo tiene una terminal
conectada (orificio de paso #10), coloque la
terminal sobre el tornillo de conexión de cable.
De lo contrario, coloque la punta desnuda del
cable del electrodo en el portaelectrodo con las
hebras de los cables divididas a ambos lados del
tornillo de conexión de la pinza.
5. Apriete bien el tornillo de conexión del cable en
la pinza, de tal manera que ésta mantenga al
cable en su lugar.
6. Deslice la manija en posición y asegure con el
tornillo de montaje de la manija.
Selección de la Corriente de Soldadura
Cada posición del interruptor de selección de corriente
está marcada con los amperios de salida para ese
parámetro. Gire el interruptor a la corriente requerida
para cada aplicación.
Hay una pequeña cantidad de holgura en cada posición del interruptor. Es una buena práctica mover el
interruptor hacia atrás y adelante una vez dentro de
esta holgura después de cambiar a una nueva posición. Esta acción mantiene a los contactos libres de
suciedad y óxidos.
con Cable
Más Corto
Cable de
Trabajo
A-2
Page 31

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
OPERACIÓN
Selección de la Polaridad de Soldadura
Selección de Electrodos
A fin de obtener los mejores resultados con los electrodos de
soldadura de arco de hoy en día, es importantes utilizar la polaridad
adecuada. La Soldadora de Arco de CA/CD permite elegir entre CA,
CD(+) ó CD(-), brindando versatilidad adicional.
Los electrodos de Lincoln están enumerados en la tabla al final de
este manual. Cada electrodo está diseñado para trabajar mejor con
CD(+), CC(-) ó CA. En esta tabla de electrodos, la polaridad preferida
se enumera primero. Esta es la polaridad que deberá utilizarse
–cuando está disponible- para mejores resultados.
PRECAUCIÓN
No gire el interruptor de selección mientras está soldando
ya que esto dañaría los contactos.
Ciclo de Trabajo
(Para códigos 11604 y menores). Las soldadoras de 60
Hz están clasificadas a un ciclo de trabajo del 20%, y las
de 50 Hz a un ciclo de trabajo del 15% para la corriente
de soldadura que se muestra en cada posición del
interruptor.
(Para códigos 11674 y superiores). Las soldadoras de 60
Hz están clasificadas a un ciclo de trabajo del 20%, y las
de 50 Hz a un ciclo de trabajo del 13% para la corriente
de soldadura que se muestra en cada posición del
interruptor.
El ciclo de trabajo se basa en un periodo de diez minutos.
Esto significa que el arco se puede generar 2 minutos de
cada periodo de 10 (con una unidad de ciclo de trabajo
del 20%) sin ningún peligro de sobrecalentamiento. Si la
soldadora se utiliza por más de 2 minutos durante varios
periodos sucesivos de 10, se puede sobrecalentar.
Asegúrese de dejar la unidad “encendida” durante cada
periodo de 10 minutos para permitir que el motor del
ventilador funcione y lograr un enfriamiento adecuado; el
sobrecalentamiento reduce la vida de la soldadora.
Interruptores Automáticos
Los modelos de CA/CD arriba del código 8800 tienen un
interruptor automático de circuito interno para evitar
sobrecalentamiento al soldar con CD. El interruptor se
abrirá y cerrará la salida de soldadura de CD si se excede
el ciclo de trabajo o si se bloquea el flujo de aire de
enfriamiento. El ventilador de enfriamiento continuará
funcionando y la salida de soldadura de CD se encenderá
automáticamente cuando el interruptor se haya enfriado y
restablecido.
Cómo Aprender a Soldar con Electrodo Revestido
Consulte “Aprendiendo a Soldar con Electrodo Revestido”
(lTW2) en la sección del manual del operador de
www.lincolnelectric.com.
Guía de Selección de Electrodos
Vea la siguiente Guía de Selección de Electrodos e
información adicional de selección de electrodos.
También consulte (C2.10) para la Guía de Soldadura con
Electrodo Revestido y tamaños de electrodos:
www.lincolnelectric.com.
¿Cuál electrodo es el mejor para un trabajo en particular?. .
.¿cómo utilizarlo? Estas son preguntas importantes porque el
costo, calidad y apariencia de su trabajo dependen de la
selección y aplicación adecuadas del electrodo. Los
electrodos de acero suave se pueden clasificar en los
siguientes grupos:
Grupo Fuera de Posición (e6011)
E
ste grupo incluye electrodos que tiene un arco penetrante
profundo y vigoroso y depósitos de congelamiento rápido.
Estos electrodos se utilizan para fabricación en todas las
posiciones de fines generales y soldadura de reparación;
asimismo, son la mejor opción para soldadura de tuberías y
soldadura a tope, de esquinas y bordes de hojas metálicas.
Se pueden utilizar para trabajo de reparación cuando no es
posible limpiar totalmente del acero la suciedad, grasa,
enchapado o pintura. Se utilizan normalmente con los
movimiento “Aʼʼ y “Bʼʼ (a continuación) para el primer pase en
las soldaduras verticales hacia arriba.
Grupo de Alto Depósito (E6027, E7024)
Este grupo incluye a los electrodos de polvo de fierro
altamente revestidos con su arco suave y velocidades
rápidas de depósito. Estos electrodos tienen una escoria
pesada y producen cordones excepcionalmente suaves. Se
utilizan generalmente para soldadura de producción donde
todo el trabajo se puede posicionar para soldadura en
posición plana. Con estos electrodos, siempre se prefieren
más los cordones extendidos, con la técnica de arrastre, que
los pases ondulados.
Grupo de alta velocidad (E6012, E6013, EE7014)
Este grupo incluye a los electrodos que tienen un arco
moderadamente vigoroso y velocidades de depósito entre las
de los electrodos de fuera de posición y de alto depósito. Son
principalmente electrodos de producción de fines generales
especiales para filetes pendiente abajo y traslapes, o
soldaduras cortas e irregulares que cambian de dirección o
posición. También se utilizan ampliamente en mantenimiento
y recomendados para soldadura de filete y traslape en hojas
metálicas. El movimiento “Dʼʼ (a continuación) se utiliza
generalmente para soldadura vertical hacia arriba, pero los
movimientos “A” y “B” son también adecuados.
Grupo de Bajo Hidrógeno (E7018, E7028)
Estos electrodos se llaman generalmente de “bajo
hidrógeno.” El nombre proviene del hecho de que su
recubrimiento contiene poco hidrógeno ya sea en humedad o
forma química. Los electrodos de bajo hidrógeno ofrecen
estos beneficios: resistencia sobresaliente a fisuras, la
porosidad más baja en los aceros portadores de azufre, y
son capaces de depósitos de calidad de rayos x. Entonces,
son la primera opción al soldar aceros “problema”. e7018 se
puede utilizar en todas las posiciones, con el Movimiento “C”
recomendado para el primer pase en las soldadura verticales
hacia arriba. Nunca utilice una técnica de latigueo o un arco
largo con estos electrodos. Siempre llene los cráteres
retirando los electrodos lentamente. SIEMPRE mantenga los
electrodos secos. Los electrodos que no se utilicen dentro de
unas cuantas horas después de que se abre un contenedor,
deben almacenarse en gabinetes con calentamiento. Se
recomienda LH-73 con AC-225. Normalmente, se prefiere la
CD(+) para estos electrodos.
B-1
Page 32

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
OPERACIÓN
GUÍA DE ELECTRODOS
Además de los electrodos antes mencionados, también es posible utilizar los que se enumeran a continuación. A fin de determinar el
diámetro correcto de un electrodo y los parámetros de corriente a utilizar, consulte el Lincoln Weldirectory (Boletín #C2.10)
• Fleetweld® 35
• Jetweld® 1
Movimientos de la Soldadura con Electrodo Revestido
• Blue Max® 2100
• Red Baron® 309/309L
MR
• Red Baron® 308L MR
• Wearshield® ME
• Wearshield® MI
• Wearshield® BU
• Wearshield® •
Minimiza el charco derretido y lo deja congelar rápidamente para que
el metal de soldadura no se derrame ni atraviese la junta. Mantenga
el arco corto cuando esté en el cráter y largo cuando salga del
mismo.
Inicio
El movimiento “B” es un movimiento de latigueo combinado con una
ligera onda en el cráter. Se utiliza con los electrodos de
congelamiento rápido como el primer pase en los filetes verticales y
juntas a topo en V.
El movimiento “C” es una oscilación simple de lado a lado utilizado
con todo tipo de electrodos para realizar pases de llenado sobre los
filetes verticales y juntas a tope en V. Asimismo, a veces se utiliza
Vista
lateral
con electrodos de llenado-congelamiento y bajo hidrógeno para
hacer el primer pase en estas juntas.
El movimiento “D” es una oscilación triangular que se utiliza con los
electrodos de llenado-congelamiento y bajo hidrógeno para hacer
Utilice el método de soldadura de “paso atrás”
donde la distorsión es un problema
3ra soldadura
2da soldadura
1ra soldadura
filetes verticales de un pase y juntas a tope en V. da como resultado
una soldadura más grandes que el Movimiento “Cʼʼ.
El movimiento “E” es una oscilación cuadrada que se utiliza con
todos los tipos de electrodos para hacer pases de llenado en filetes
verticales y juntas a tope en V. Es similar al movimiento “Cʼʼ pero con
una pausa distintiva y un movimiento ligero hacia arriba en cada
borde de la soldadura para asegurar un llenado completo del cráter y
eliminar la socavación.
HAGA QUE LAS FUERZAS DE REDUCCIÓN
FUNCIONEN PARA MINIMIZAR LA DISTORSIÓN
El movimiento “F” es un movimiento circular que se utiliza con todo
tipo de electrodos para hacer soldaduras sobre la cabeza. Algunas
veces se acompaña de un ligero latigueo después de cada oscilación
en el cráter. Siempre utilice una serie de cordones extendidos sobre
La manipulación depende de la junta. A continuación, se muestran
algunos de los movimientos comunes.
la cabeza; no oscile.
El movimiento “G” es una oscilación simple de lado a lado utilizado
con todos los electrodos en filetes amplios o juntas a tope en la
El movimiento “A” es un movimiento recto de latigueo que se utiliza
posición plana.
con los electrodos de congelamiento rápido para hacer cordones
extendidos en todas las posiciones y en todos los tipos de juntas.
• Mangjet®
• Wearshield® ABR
• Ferroweld®
• Softweld® 99 Ni
B-2
Page 33

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Corte (no exceda el ciclo de trabajo — al inicio de esta
sección de operación)
La soldadora de arco y electrodo se pueden utilizar para
cortar acero y hierro fundido. Siga este procedimiento:
1 Utilice un electrodo Fleetweld 180 de 3.2mm (1/8”) ó
4.0mm (5/32").
2. Establezca la soldadora al máximo (225 amps).
3. Mantenga un arco largo sobre el borde del metal, derritiéndolo.
4. Empuje el arco a través del metal derretido, forzándolo
a caer.
5. Levante el electrodo, y empiece de nuevo.
Electrodo
Parte inferior de la placa
Corte de la placa con un electrodo
Lo importante es continuar este movimiento en zigzag
hacia arriba y abajo, derritiendo el metal y alejándolo.
OPERACIÓN
Perforación
1. Configuración de la sol-
dadora: Máximo (225
amps).
lectrodo de 4.0 mm (5/32”)
ó 3.2 mm (1/8”)
Utilice 225
amperios
2. Electrodo: Fleetweld 180
3.2mm (1/8”) ó 4.0mm
(5/32").
Tabla
Placa de ¼”
(6 mm)
3. Mantenga el electrodo
con un arco largo perpendicular sobre el punto
donde se va a hacer el
orificio.
Haciendo orificios con un electrodo
Contenedor para
capturar el
metal caliente
4. Cuando el metal esté derretido, empuje el electrodo a
través del charco derretido.
5. Permita que el metal derretido caiga por el orificio.
6. Mueva en círculo con un arco largo alrededor del borde
del orificio hasta lograr el orificio del diámetro deseado.
Si el electrodo se empuja y atraviesa muy rápido, se
adherirá al charco de soldadura. Asegúrese de que el
metal esté derretido antes de atravesar.
NOTA: en metal pesado (7.9mm (5/16") o más grueso),
posicione la placa a perforar verticalmente, y el electrodo
horizontalmente. Esto permite que el metal derretido
gotee libremente a medida que perfora.
B-3
Page 34

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
MANTENIMIENTO
No es necesario un mantenimiento preventivo de rutina.
Acuda a su Taller de Servicio Autorizado de Campo de Lincoln
Electric local para las reparaciones necesarias.
MANTENIMIENTO
D-1
Page 35

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
NOTAS
Page 36

15A
2
2A
15
14A
14B
13
3
2
5
6
7
8
9A
10
11
9
16A
16
17
18
20
21
23
12
28
29
22B
22A
1
15B
15A
AC-225-S
Índice del Modelo
15B
P-65-A.a (S)P-65-A.a (S)
ÚNICAMENTE DEBAJO DEL CÓDIGO 6300
y los Códigos 6342, 6343 y 6453
2A
13
14A
14B
15
18
20
16
17
22B
21
16A
22A
23
12
28
10
11
9A
29
04-19-2010
Page 37

P-65-A.b (S)P-65-A.b (S)
PÁGINA NÚM./ PÁGINA NÚM./ PÁGINA NÚM./ PÁGINA NÚM./
CÓDIGO COL. NÚM. CÓDIGO COL. NÚM. CÓDIGO COL. NÚM. CÓDIGO COL. NÚM.
4665 A.1.a 1 7093 A.1a 7 9424 A.1a 12
4763 A.1a 2 7094 A.1a 7 9425 A.1a 12
4798 A.1a 2 7098 A.1a 7 9426 A.1a 12
4852 A.1a 2 7099 A.1a 7 9427 A.1a 12
4953 A.1a 2 7100 A.1a 7 9428 A.1a 12
5130 A.1a 2 7101 A.1a 7 10420 A.1a 13
5167 A.1a 3 7102 A.1a 7 10421 A.1a 13
5169 A.1a 3 7103 A.1a 7 10422 A.1a 13
5227 A.1a 3 7234 A.1a 7 10423 A.1a 13
5341 A.1a 4 7330 A.1a 8 10424 A.1a 12
5348 A.1a 4 7333 A.1a 7 11074 A.1a 14
5381 A.1a 3 7351 A.1a 8
5438 A.1a 4 7352 A.1a 8
5440 A.1a 4 7523 A.1a 7
5449 A.1a 4 7533 A.1a 9 11602 B.1.a 1
5451 A.1a 4 7731 A.1a 9 11603 B.1.a 2
5465 A.1a 4 7743 A.1a 9 11604 B.1.a 3
5470 A.1a 4 7744 A.1a 9 11674 B.1.a 4
5678 A.1a 4 7745 A.1a 9
5683 A.1a 4 7746 A.1a 9
5880 A.1a 5 7755 A.1a 9
5896 A.1a 4 7805 A.1a 9
5897 A.1a 4 7813 A.1a 9
5903 A.1a 4 8226 A.1a 9
6140 A.1a 5 8370 A.1a 10
6184 A.1a 5 7382 A.1a 10
6295 A.1a 5 8383 A.1a 10
6304 A.1a 6 8384 A.1a 10
6342 A.1a 5 8385 A.1a 10
6343 A.1a 5 8386 A.1a 10
6453 A.1a 5 8459 A.1a 10
6518 A.1a 5 8511 A.1a 10
6592 A.1a 6 8712 A.1a 10
6600 A.1a 6 8780 A.1a 10
6601 A.1a 6 8894 A.1a 10
6616 A.1a 6 8897 A.1a 10
6661 A.1a 6 8898 A.1a 10
6734 A.1a 6 8900 A.1a 10
6898 A.1a 6 8918 A.1a 10
6967 A.1a 6 8959 A.1a 10
6991 A.1a 6 8983 A.1a 10
7009 A.1a 6 9039 A.1a 10
7010 A.1a 6 9291 A.1a 11
7011 A.1a 6 9292 A.1a 11
7012 A.1a 6 9293 A.1a 11
7013 A.1a 6 9294 A.1a 11
7030 A.1a 6 9295 A.1a 11
7050 A.1a 7 9296 A.1a 11
7068 A.1a 6 9422 A.1a 12
7072 A.1a 6 9423 A.1a 12
/
04-19-2010
Page 38

# Indica un cambio en esta impresión.
P-65-A.1.a (S)P-65-A.1.a (S)
Utilice únicamente partes marcadas con una “x” en la columna debajo del
número del encabezado nombrado en la página del índice del modelo.
ART. DESCRIPCIÓN PARTE NO. CANT.
Esta página es para Códigos Debajo del 11600
1 Panel Posterior Superior M9873
1
Panel Posterior Superior (Código 5600 a 6600 excepto 6304)
El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa (60 Hz) Incluye;
2
2A Ventilador M13525 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa (50 Hz), Incluye:
2
2A Ventilador M13525-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
3 Soporte del Montaje del Ventilador M9874 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
3 Soporte del Montaje del Ventilador M10396
5 Gabinete L3786-6 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Gabinete L3786-7 1 • X X X • • • • • • • • • •
5 Gabinete L3786-12 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Gabinete L3786-13
5 Gabinete L3786-19 1 • • • • • • • • • X X X • •
5 Gabinete L3786-14 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Voltios
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Voltios
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Voltios
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Voltios
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 208 Voltios
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Arriba de 250 Voltios
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 y 60 Hz, Otros Voltajes
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Arriba de 250 Voltios
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Sólo 208V
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 & 60 Hz, Otros Voltajes
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 & 60 Hz, Otros Voltajes
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Sólo 230V
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Sólo Ciclo de Trabajo del 15%
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Sólo Ciclo de Trabajo de 220V
6
6
Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Ciclo de Trabajo del 15% Otro Voltaje.
6 Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 50 Hz M15727 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
6 Placa de Identificación, Montgomery Ward M9934
6 Placa de Identificación, Lincoln, 60 Hz M22165 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Botón del Sujetador (Blanco) T14659
Botón del Sujetador (Negro) T14659-1
El Interruptor del Selector (Sólo 50 Hz) Incluye:
7
7 El Interruptor del Selector Incluye: M10830-3 1 X X X X X X X X • • • • • •
7 El Interruptor del Selector Incluye: M10830-9 1 • • • • • • • • X X X X X X
Eje del Interruptor S13206 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
8 Manija del Interruptor (Negra) T13990-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
9 Roldanas Aislantes del Cable de Salida T9274-4 2 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
9A Pinza del Cable de Salida S15761 1 • • • X X X X X X X X X X X
10
Placa de Identificación del Interruptor de Línea
11 Interruptor de Línea S7670 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X • •
11 Interruptor de Línea S18815 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
12 Transformador y Base
13 Panel de Cubierta, Bloque de la Terminal L3936-1 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
14A Bloque de la Terminal de Entrada T11813
14B Panel de Entrada, 60 Hertz T11881 1 • X X • • • • • • • • • • •
ø
Esta parte es obsoleta y ya no está disponible.
M10894 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
M13539-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
M13539-2 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
M9803
M13029 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
M14008 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15411 1 ••••••••••X•••
M15411-2 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15411-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M9803-1 1 • X X X X X X • • • • • • •
M15726 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
M15725-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
M13029-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
M14008-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15725 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X X
M13880 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
M14009 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M14009-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • X • • •
M10830-8 1 • • • • • • X X • • • • • •
S12070
No Disponible
ø
ø
ø
ø
ø
(Según se requiera)
(Según se requiera)
ø
ø
1234567891011121314
1 XXXX••••••••••
1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
1•• •••XXXX•••••
1 XXXXXXXXX • • • ••
1 •XXX••••••••••
XXXXXXXXXXXX ••
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
1 X•••••••••••••
1 X•••••••••••••
04-19-2010
Page 39

# Indica un cambio en esta impresión.
P-65-A.1.b (S)P-65-A.1.b (S)
Utilice únicamente partes marcadas con una “x” en la columna debajo del
número del encabezado nombrado en la página del índice del modelo.
ART. DESCRIPCIÓN PARTE NO. CANT.
15 Cubierta Posterior L3936 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Cubierta Posterior L4143 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Cubierta Posterior L4143-1
15A Panel Posterior Inferior L4595 1 • • • • • X X • • • • • • •
15A Panel Posterior Inferior L4595-2 • • • • • • X X X X X X X X
15B Panel Posterior Superior G1239 1 • • • • • X X X • X X X • •
15B Panel Posterior Superior G1395 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X
16A Panel de la Cubierta L3935-A 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
16 Cable del Electrodo S11609-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
17 Portaelectrodo K909-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
18 Cable de Aterrizamiento S11609-3 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
19 Careta M9673-6 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
20 Pinza de Aterrizamiento M12033 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
28 Receptáculo (Sólo 230 Voltios) S7733
28 Receptáculo (Sólo 230 Voltios) S13700 1 • • • • X X X X X X X X X •
29 Cable de Alimentación (Sólo 230 Voltios)
29 Cable de Alimentación (Sólo 230 Voltios) S13699-2 1 • • • • X X X • • • • • • •
29
Cable de Alimentación (Sólo 230 Voltios o Menos) (60 Hz)
Cable de Alimentación 230V 50 Hz (Sólo Códigos 8894,
29
9428 y 10424)
Kit de Carro de Transporte
(Incluye los Elementos 21, 22A, 22B y 23)
S13699-2 y S13700
S15599-1 1 • • • • • • • X X X X X X X
S18021 1 • • • • • • • • • X • X X •
Ordene K761
ø
ø
1234567891011121314
1 ••••X•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
1 • • • •XXXXXXXXXX
Partes No Ilustradas
Etiqueta de Advertencia (Se Monta en la Esquina Superior del Gabinete)
Etiqueta de Selección de Electrodo M14331 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
Etiqueta de Tierra Física T13260-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X •
M14330 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
ø
Esta parte es obsoleta y ya no está disponible.
04-19-2010
Page 40

# Indica un cambio en esta impresión.
P-65-B.1.a (S)P-65-B.1.a (S)
Utilice únicamente partes marcadas con una “x” en la columna debajo del
número del encabezado nombrado en la página del índice del modelo.
ART. DESCRIPCIÓN PARTE NO. CANT.
Esta Página para Códigos Arriba de 11600:
2 El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa Incluye: M13539-1 1 X • X •
Ventilador M13525 1 X • X •
2 El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa Incluye: M13539-2 1 • X • X
Ventilador M13525-1 1 • X • X
5 Gabinete L3786-14 1 X X X X
6
6 Placa de Identificación (Código 11603) M15727 1 • X • •
6 Placa de Identificación (Código 11674) M22167 1 • • • X
8 Ensamble de la Manija T13990-1 1 X X X X
9A Pinza del Cable S15761 1 X X X X
11 Interruptor de Línea S18815 1 X X X X
12 Transformador y Base NSS 1XXXX
15A Parte Posterior Inferior del Gabinete L4595-2 1 X X X X
15B Parte Posterior Superior del Gabinete G1395 1 X X X X
16 Cable del Electrodo S11609-4 1 X X X X
17 Portaelectrodo K909-1 1 X X X X
18 Cable de Aterrizamiento S11609-3 1 X X X X
20 Pinza de Aterrizamiento M12033 1 X X X X
21 Rueda S11662-3 2 • • X •
22 El Kit De Montaje Incluye: T14160 1 • • X •
22A Roldana Plana S9262-1 2 • • X •
22B Tuerca de Empuje T12570 2 • • X •
22C HHCS de 3/8-16 x 2.00 CF000071 1 • • X •
23 Eje M8809-61 1 • • X •
29
29
30 Etiqueta de Advertencia (No Se Muestra) M14330-3 1 X X X X
31
32
32
32
33 Etiqueta de Advertencia (No Se Muestra) S22127-1 1 • X • •
Placa de Identificación (Códigos 11602 y 11604)
Botón del Sujetador (negro) T14659-1 1 X X X X
El Kit de Carro de Transporte Incluye: K761
Cable de Alimentación (Códigos 11602 y 11604)
Cable de Alimentación (Códigos 11603 y 11674)
Etiqueta de Selección del Electrodo (No Se Muestra)
Diagrama de Cableado (No Se Muestra) (Códigos 11602 & 11604)
Diagrama de Cableado (No Se Muestra) (Código 11603)
Diagrama de Cableado (No Se Muestra) (Código 11674)
M22165 1 X • X •
* ••X•
S15599-1 1 X • X •
S18021 1 • X • X
M14331 1 X X X X
S15621 1 X • X •
S16671 1 • X • •
S28364 1 • • • X
1234567891011121314
* Kit de Carro de Transporte en todos los Códigos – Estándar donde se indica.
NSS -
No se vende por separado.
04-19-2010
Page 41

NOTAS
Page 42

AC/DC 225/125
Índice del Modelo
COL. COL.
CÓDIGO NÚM. CÓDIGO NÚM.
8566 1 9025 2
8581 1 9186 2
8650 1 9221 3
8663 1 9222 3
8666 1 9223 3
8700 1 9224 3
8737 1 9225 3
8742 1 9226 3
8777 1 9365 3
8788 1 10426 3
8811 2 10427 3
8815 2 10428 3
8817 1 10429 3
8893 2 11675 4
8901 2
8903 2
8910 2
8955 2
8986 2
9005 2
9015 2
1B
1A
10
6A
4
20
31B
6B
P-140-A (S)P-140-A (S)
3
5
15
7
2
13
8
17
31A
14
11
9A
28
12
25
7A
14A
29
Utilice únicamente partes marcadas con una “x” en la columna debajo del número del encabezado nombrado en la página del índice del
# Indica un cambio en esta impresión.
ART.
DESCRIPCIÓN
modelo.
PARTE NO. CANT.
123456789
1 El Ensamble del Rectificador Incluye: L7029 ø 1X•••
1A (–) Mitad del Rectificador (Inferior) S12837-7A ø 1X•••
1B (+)Mitad del Rectificador (Superior) S12837-7B ø 1X•••
1 El Ensamble del Rectificador Incluye: L6974 ø 1•X••
1
El Ensamble del Rectificador (Debajo del Código 10000) Incluye:
L7491 1 • X X •
1 A (–) Diodo M9661-39R 2 • X X •
1 B (+) Diodo M9661-39 2 • X X •
Ensamble del Supresor M14705 1 • X X •
1 Ensamble del Rectificador, (Arriba del Código 10000) G3648 1 • • X X
2 El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa (60 Hz) Incluye: M13539-1 1 X X X •
Ventilador M13525 1 X X X •
2 El Motor del Ventilador y Aspa (50 Hz) Incluye: M13539-2 1 X X X X
Ventilador M13525-1 1 X X X X
ø
Esta parte es obsoleta y ya no está disponible.
03-10-2010
Page 43

# Indica un cambio en esta impresión.
P-140-A.1 (S)P-140-A.1 (S)
Utilice únicamente partes marcadas con una “x” en la columna debajo del número del encabezado nombrado en la página del índice del
modelo.
ART.
DESCRIPCIÓN
PARTE NO. CANT.
123456789
3 Ahogador S18336 1 X X • •
3 Ahogador M15371 1 • • X X
4 Soporte del Motor del Ventilador S17194 1 X • • •
5 Gabinete (Debajo del Código 10000) L3786-19 1 X X X •
5 Gabinete (Arriba del Código 10000) L3786-14 1 • • X X
6A Panel Posterior Inferior L6650 1 X X X X
6B Panel Posterior Superior L6651 ø 1X•••
6B Panel Posterior Superior G1395-1 1 • X X X
7 El Interruptor del Selector de Rango Incluye: M10830-9 1 X X X X
Eje del Interruptor S13206 1 X X X X
7A Manija M13989-1 1 X X X X
8 Cable del electrodo S11609-9 1 X X X X
9A Output Lead Clamp S15761 1 X X X X
10 Work Cable S11609-10 1 X X X X
11 Interruptor de Línea (Debajo del Código 10400) S7670 1 X X X •
11 Interruptor de Línea (Arriba del Código 10400) S18815 1 • • X X
12 Transformador y Base
No Está Disponible
1XXXX
13 Supresor S17203 1 X • • •
14 El Interruptor de Polaridad Incluye: M14063 1 X X X X
Eje del Interruptor M14337 1 X X X X
14A Manija M13989-1 1 X X X X
15 Placa de Identificación (60 Hz. Sólo 230 Voltios) M15784 1 X X X •
Placa de Identificación (60 Hz. Todos los voltajes excepto 208 y 230 Voltios)
15
M15784-1 1 X X X •
15 Placa de Identificación (60 Hz. Sólo 208 Voltios) M15784-2 1 X X X •
15 Placa de Identificación (50 Hz. Todos los Voltajes) M15785 1 X X X •
15 Placa de Identificación (50 Hz.) (Código 11675) M22168 1 • • • X
15A Placa de Advertencia (No Se Muestra) M14330 1 X X X •
15A Etiqueta de Advertencia M14330-3 1 • • • X
15B
15B
Placa de Selector de Electrodo (60 Hz) (No Se Muestra)
Placa de Selector de Electrodo (50 Hz) (No Se Muestra)
M14331 1 X X X •
M14335 1 X X X •
16 Botón del Sujetador de la Placa de Identificación T14659-1 4 X X X X
17 Portaelectrodo K909-1 1 X X X X
20 Pinza de Trabajo M12033 1 X X X X
28 Receptáculo (60 Hz. Sólo 250 Voltios o Menos) S13700 1 X X X •
29
Cable de Alimentación (60 Hz. Sólo 250 Voltios o Menos)
Cable de Alimentación (50 Hz. Sólo 250 Voltios o Menos)
29
S15599-1 1 X X X X
S18021 1 • X X X
Interruptor Automático – No se Ilustra S10657-3 1 • X X X
Etiqueta de Conexión a Tierra (No Se Muestra) T13260-4 1 X X X X
Elementos Opcionales:
30 Careta (No Se Muestra) Elección 1 X X X •
del Cliente
31 Kit de Carro de Transporte, Incluye: K761 1 X X X X
31A Eje M8809-61 1 X X X X
31B Rueda S11662-3 2 X X X X
31C Kit de Montaje T14160 1 X X X X
NSS -
No se vende por separado
ø
Esta parte es obsoleta y ya no está disponible.
03-10-2010
Page 44

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
NOTAS
Page 45

Manuel de l’Opérateur
AC-225-S et AC/DC 225/125
Pour utilisation avec les machines ayant les Numéros de Code:
10420, 10421, 10422,
10423, 10424, 11074,
11602, 11603, 11604,
11674, 11675
Pour enregistrer la machine :
www.lincolnelectric.com/register
Recherche d’Atelier de Service et Distributeur Agréés:
www.lincolnelectric.com/locator
Conserver comme référence future
Date d’Achat
Code: (ex: 10859)
Série: (ex: U1060512345)
IMF237-P
© Lincoln Global, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

MERCI D'AVOIR SÉLECTIONNÉ UN
PRODUIT DE QUALITÉ PAR LINCOLN
ELECTRIC.
S'IL VOUS PLAÎT EXAMINER CARTON ET LE
MATÉRIEL POUR LES DOMMAGES IMMÉDIATEMENT
Quand ce matériel est expédié, son titre passe à
l'acheteur dès la réception par le transporteur. Par
conséquent, les réclamations pour matériel endommagé
au cours du transport doivent être faites par l'acheteur
contre la société de transport au moment où l'envoi a été
reçu.
LA SÉCURITÉ DEPEND DE VOUS
Lincoln arc welding and cutting equipment is designed
and built with safety in mind. However, your overall
safety can be increased by proper installation ... and
thoughtful operation on your part
NE PAS INSTALLER, UTILISER OU RÉPARER CE MATÉRIEL SANS
AVOIR LU CE MANUEL ET LES MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ QU'IL
CONTIENT
Et, par dessus tout, réfléchir avant d'agir et exercer la
plus grande prudence
.
.
AVERTISSEMENT
Cette déclaration apparaît lorsque les indications doivent
être suivies avec exactitude afin d’éviter des blessures
graves ou un décès.
ATTENTION
Cette déclaration apparaît lorsque les indications doivent
être suivies avec exactitude afin d’éviter des blessures
légères ou des dommages à l’appareil.
.
TENIR SA TÊTE HORS DES VAPEURS DE SOUDAGE.
NE PAS s’approcher trop près de
l’arc. Utiliser des verres de correction
si besoin est pour rester à une
distance raisonnable de l’arc.
LIRE et respecter la Fiche Technique
Santé - Sécurité (MSDS) et l’étiquette
d’avertissement qui figure sur tous les
conteneurs de matériel de soudage.
UTILISER SUFFISAMMENT DE
VENTILATION ou d’échappement au
niveau de l’arc, ou les deux, pour
maintenir les vapeurs et les gaz hors
de la zone de respiration et de la zone générale de travail.
IDANS UNE GRANDE PIÈCE OU EN EXTÉRIEUR, la ventilation naturelle
peut s’avérer appropriée si on maintient sa tête en dehors des vapeurs
(voir ci-dessous).
UTILISER DES APPELS D’AIR NATURELS ou des ventilateurs pour
éloigner les vapeurs du visage.
Si des symptômes inhabituels apparaissent, prévenir le superviseur.
L’atmosphère de soudage et le système de ventilation ont peut-être
besoin d’une révision.
PORTER DES VERRES DE CORRECTION AINSI QUE DES PROTECTIONS AUDITIVES ET CORPORELLES
SE PROTÉGER les yeux et le visage avec un casque de
soudage adapté comportant une plaque filtre d’un degré
approprié (Voir ANSI Z49.1).
SE PROTÉGER le corps contre les projections de
soudure et les coups d’arc au moyen de vêtements de
protection comprenant des vêtements en laine, un tablier
et des gants ignifuges, des leggings en cuir et des bottes
montantes.
PROTÉGER les autres contre les projections, les coups
d’arc et l’éblouissement à l’aide d’écrans ou de barrières
de protection.
DANS CERTAINS ENDROITS, une protection sonore
peut s’avérer appropriée.
VÉRIFIER que l’équipement de protection soit en bon état.
Porter également EN PERMANENCE des lunettes de
sécurité dans la zone de travail.
SITUATIONS PARTICULIÈRES
NE PAS SOUDER NI COUPER des conteneurs ou des matériaux ayant
préalablement été en contact avec des substances dangereuses à moins
qu’ils n’aient été parfaitement nettoyés. Ceci est extrêmement dangereux..
NE PAS SOUDER NI COUPER des pièces peintes ou plaquées à moins
de prendre des précautions spéciales en matière de ventilation. Elles
peuvent émettre des vapeurs ou des gaz fortement toxiques.
Mesures de sécurité supplémentaires
PROTÉGER les bouteilles de gaz comprimé de la chaleur excessive, des
chocs mécaniques et des arcs ; attacher les bouteilles afin qu’elles ne
puissent pas tomber.
VÉRIFIER que les bouteilles ne soient jamais mises à la terre et qu’elles
ne fassent pas partie d’un circuit électrique.
ÉLIMINER tous les risques d’incendie potentiels de la zone de soudage.
L’ÉQUIPEMENT DE LUTTE CONTRE LES INCENDIES DOIT
TOUJOURS ÊTRE PRÊT POUR UN USAGE IMMÉDIAT ET LES
USAGERS DOIVENT SAVOIR COMMENT S’EN SERVIR.
Page 47

SECTION A:
1.d.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT DE LA PROPOSITION DE CALIFORNIE 65
Moteurs Diesel
Les gaz d’échappement du moteur diesel et certains de leurs constituants sont connus par l’État de Californie pour provoquer le cancer,
des malformations ou autres dangers pour la reproduction.
Moteurs à essence
Les gaz d’échappement de ce produit contiennent des produits chimiques connus par l’État de Californie pour provoquer le cancer, des
malformations et des dangers pour la reproduction
LE SOUDAGE À L’ARC PEUT ÊTRE DANGEREUX. SE PROTÉGER ET
PROTÉGER LES AUTRES CONTRE LES BLESSURES GRAVES VOIRE
MORTELLES. ÉLOIGNER LES ENFANTS. LES PERSONNES QUI PORTENT UN STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE DEVRAIENT CONSULTER LEUR
MÉDECIN AVANT D’UTILISER L’APPAREIL.
Prendre connaissance des caractéristiques de sécurité suivantes. Pour
obtenir des renseignements supplémentaires sur la sécurité, on recommande vivement d’acheter un exemplaire de la norme Z49.1, de l’ANSI
auprès de l’American Welding Society, P.O. Box 350140, Miami, Floride
33135 ou la norme CSA W117.2-1974. On peut se procurer un exemplaire gratuit du livret «Arc Welding Safety» E205 auprès de la société
Lincoln Electric, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
.
1.e.
1.f.
1.g.
1.h. Pour éviter de s’ébouillanter, ne pas
SÉCURITÉ
Les protecteurs, bouchons, panneaux et
dispositifs de sécurité doivent être toujours
en place et en bon état. Tenir les mains, les
cheveux, les vêtements et les outils éloignés
des courroies trapézoïdales, des engrenages,
des ventilateurs et d’autres pièces en
mouvement quand on met en marche, utilise
ou répare le matériel
Dans certains cas, il peut être nécessaire de déposer les
protecteurs de sécurité pour effectuer l’entretien prescrit.
Ne déposer les protecteurs que quand c’est nécessaire et
les remettre en place quand l’entretien prescrit est terminé.
Toujours agir avec la plus grande prudence quand on
travaille près de pièces en mouvement
Ne pas mettre les mains près du ventilateur du moteur. Ne
pas appuyer sur la tige de commande des gaz pendant que
le moteur tourne
Pour ne pas faire démarrer accidentellement les moteurs à
essence en effectuant un réglage du moteur ou en
entretenant le groupe électrogène de soudage, de
connecter les fils des bougies, le chapeau de distributeur ou
la magnéto
enlever le bouchon sous pression du
radiateur quand le moteur est chaud.
.
.
.
.
S’ASSURER QUE LES ÉTAPES D’INSTALLATION, D’UTILISATION, D’ENTRETIEN ET DE RÉPARATION NE SONT CONFIÉES QU’À DES PERSONNES QUALIFIÉES.
2.a. Le courant électrique qui circule dans les conducteurs crée
POUR LES GROUPES
ÉLECTROGÈNES.
1.a. Arrêter le moteur avant de dépanner et
d’entretenir à moins qu’il ne soit nécessaire que le
moteur tourne pour effectuer l’entretien.
1.b. Ne faire fonctionner les moteurs qu’à l’extérieur ou
dans des endroits bien aérés ou encore évacuer
les gaz d’échappement du moteur à l’extérieur.
1.c. Ne pas faire le plein de carburant près d’une
flamme nue, d’un arc de soudage ou si le moteur
tourne. Arrêter le moteur et le laisser refroidir
avant de faire le plein pour empêcher que du
carburant renversé ne se vaporise au contact de
pièces du moteur chaudes et ne s’enflamme. Ne
pas renverser du carburant quand on fait le plein.
Si du carburant s’est renversé, l’essuyer et ne pas remettre le moteur en
marche tant que les vapeurs n’ont pas été éliminées.
2.b. Les champs électromagnétiques peuvent créer des
2.c. L’exposition aux champs électromagnétiques lors du
2.d. Les soudeurs devraient suivre les consignes suivantes afin
LES CHAMPS
ÉLECTROMAGNÉTIQUES
DANGEROUS
des champs électromagnétiques locaux. Le courant de
soudage crée des champs magnétiques autour des câbles
et des machines de soudage.
interférences pour les stimulateurs cardiaques, et les
soudeurs qui portent un stimulateur cardiaque devraient
consulter leur médecin avant d’entreprendre le soudage.
soudage peut avoir d’autres effets sur la santé que l’on ne
connaît pas encore.
de réduire au minimum l’exposition aux champs
électromagnétiques du circuit de soudage:
2.d.1. Regrouper les câbles d’électrode et de retour. Les
fixer si possible avec du ruban adhésif.
2.d.2. Ne jamais entourer le câble électrode autour du
corps.
2.d.3. Ne pas se tenir entre les câbles d’électrode et de
retour. Si le câble d’électrode se trouve à droite, le
câble de retour doit également se trouver à droite.
2.d.4. Connecter le câble de retour à la pièce le plus près
possible de la zone de soudage.
2.d.5. Ne pas travailler juste à côté de la source de courant
de soudage.
3
Page 48

SÉCURITÉ
LES CHOCS
ÉLECTIQUES PEUVENT
ÊTRE MORTELS.
3.a. Les circuits de l’électrode et de retour
(ou masse) sont sous tension quand la source de
courant est en marche. Ne pas toucher ces pièces
sous tension les mains nues ou si l’on porte des
vêtements mouillés. Porter des gants isolants secs et
ne comportant pas de trous.
3.b. S'isoler de la pièce et de la terre en utilisant un moyen
d'isolation sec. S'assurer que l'isolation est de
dimensions suffisantes pour couvrir entièrement la
zone de contact physique avec la pièce et la terre.
En plus des consignes de sécurité normales, si l'on
doit effectuer le soudage dans des conditions
dangereuses au point de vue électrique (dans les
endroits humides ou si l'on porte des vêtements
mouillés; sur les constructions métalliques comme
les sols, les grilles ou les échafaudages; dans une
mauvaise position par exemple assis, à genoux ou
couché, s’il y a un risque élevé de contact
inévitable ou accidentel avec la pièce ou la terre)
utiliser le matériel suivant:
• Source de courant (fil) à tension constante c.c.
semi-automatique
• Source de courant (électrode enrobée) manuelle c.c.
• Source de courant c.a. à tension réduite.
3.c. En soudage semi-automatique ou automatique, le fil,
le dévidoir, la tête de soudage, la buse ou le pistolet
de soudage semi-automatique sont également sous
tension.
3.d. Toujours s'assurer que le câble de retour est bien
connecté au métal soudé. Le point de connexion
devrait être le plus près possible de la zone soudée.
3.e. Raccorder la pièce ou le métal à souder à une bonne
prise de terre.
3.f.
Tenir le porte-électrode, le connecteur de pièce, le
câble de soudage et l'appareil de soudage dans un bon
état de fonctionnement. Remplacer l'isolation
endommagée.
3.g. Ne jamais tremper l'électrode dans l'eau pour la
refroidir.
3.h. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les pièces sous
tension des porte-électrodes connectés à deux
sources de courant de soudage parce que la tension
entre les deux peut correspondre à la tension à vide
totale des deux appareils
3.i. Quand on travaille au-dessus du niveau du sol, utiliser
une ceinture de sécurité pour se protéger contre les
chutes en cas de choc.
3.j. Voir également les points 6.c. et 8.
.
LE RAYONNEMENT DE
L’ARC PEUT BRÛLER.
4.a. Utiliser un masque à serre-tête avec oculaire filtrant adéquat
et protège-oculaire pour se protéger les yeux contre les
étincelles et le rayonnement de l'arc quand on soude ou
quand on observe l'arc de soudage. Le masque à serre-tête
et les oculaires filtrants doivent être conformes aux normes
ANSI Z87.1.
4.b. Utiliser des vêtements adéquats en tissu ignifugé pour se
protéger et protéger les aides contre le rayonnement de l'arc.
4.c. Protéger les autres employés à proximité en utilisant des
paravents ininflammables convenables ou les avertir de ne
pas regarder l'arc ou de ne pas s'exposer au rayonnement
de l'arc ou aux projections ou au métal chaud
.
LES FUMÉES ET LES
GAZ PEUVENT ÊTRE
DANGEREUX.
5.a. Le soudage peut produire des fumées et des gaz
dangereux pour la santé. Éviter d'inhaler ces fumées et ces gaz.
Quand on soude, tenir la tête à l'extérieur des fumées. Utiliser un
système de ventilation ou d'évacuation suffisant au niveau de l'arc
pour évacuer les fumées et les gaz de la zone de travail. Quand on
soude avec des électrodes qui nécessitent une ventilation
spéciale comme les électrodes en acier inoxydable ou pour
revêtement dur (voir les directives sur le contenant ou la fiche
signalétique) ou quand on soude de l'acier au plomb ou cadmié
ainsi que d'autres métaux ou revêtements qui produisent des
fumées très toxiques, limiter le plus possible l'exposition et audessous des valeurs limites d'exposition (TLV) en utilisant une
ventilation mécanique ou par aspiration à la source. Dans les
espaces clos ou dans certains cas à l'extérieur, un appareil
respiratoire peut être nécessaire. Des précautions
supplémentaires sont également nécessaires quand on soude
sur l'acier galvanisé..
5. b. Le fonctionnement de lʼappareil de contrôle des vapeurs de soudage
est affecté par plusieurs facteurs y compris lʼutilisation et le
positionnement corrects de lʼappareil, son entretien ainsi que la
procédure de soudage et lʼapplication concernées. Le niveau
dʼexposition aux limites décrites par OSHA PEL et ACGIH TLV pour
les ouvriers doit être vérifié au moment de lʼinstallation et de façon
périodique par la suite afin dʼavoir la certitude quʼil se trouve dans
lʼintervalle en vigueur.
5.c. Ne pas souder dans les endroits à proximité des vapeurs
d'hydrocarbures chlorés provenant des opérations de dégraissage,
de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et le rayonnement de
l'arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs de solvant pour former du
phosgène, gaz très toxique, et d'autres produits irritants.
5.d. Les gaz de protection utilisés pour le soudage à l'arc peuvent
chasser l'air et provoquer des blessures graves voire mortelles.
Toujours utiliser une ventilation suffisante, spécialement dans les
espaces clos pour s'assurer que l'air inhalé ne présente pas de
danger.
5.e. Lire et comprendre les instructions du fabricant pour cet appareil et
le matériel de réserve à utiliser, y compris la fiche de données de
sécurité des matériaux (MSDS) et suivre les pratiques de sécurité de
lʼemployeur. Les fiches MSDS sont disponibles auprès du
distributeur de matériel de soudage ou auprès du fabricant.
5.f.
Voir également le point 1.b
4
.
Page 49

SÉCURITÉ
LES ÉTINCELLES DE
SOUDAGE PEUVENT
PROVOQUER UN INCENDIE
OU UNE EXPLOSION.
6.a. Enlever les matières inflammables de la zone de
soudage. Si ce n'est pas possible, les recouvrir pour empêcher que
les étincelles de soudage ne les atteignent. Les étincelles et
projections de soudage peuvent facilement s'infiltrer dans les
petites fissures ou ouvertures des zones environnantes. Éviter de
souder près des conduites hydrauliques. On doit toujours avoir un
extincteur à portée de la main.
6.b. Quand on doit utiliser des gaz comprimés sur les lieux de travail, on
doit prendre des précautions spéciales pour éviter les dangers. Se
référer à la “Sécurité pour le Soudage et le Coupage” (ANSI Z49.1)
et les consignes d'utilisation relatives au matériel.
6.c. Quand on ne soude pas, s'assurer qu'aucune partie du circuit de
l'électrode ne touche la pièce ou la terre. Un contact accidentel
peut produire une surchauffe et créer un risque d'incendie.
6.d. Ne pas chauffer, couper ou souder des réservoirs, des fûts ou des
contenants sans avoir pris les mesures qui s'imposent pour
s'assurer que ces opérations ne produiront pas des vapeurs
inflammables ou toxiques provenant des substances à l'intérieur.
Elles peuvent provoquer une explosion même si elles ont été
«nettoyées». For information, purchase “Recommended Safe
Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers
and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”, AWS F4.1 from
the American Welding Society (see address above).
6.e. Mettre à l'air libre les pièces moulées creuses ou les contenants
avant de souder, de couper ou de chauffer. Elles peuvent exploser.
6.f. Les étincelles et les projections sont expulsées de l'arc de soudage.
Porter des vêtements de protection exempts d'huile comme des
gants en cuir, une chemise épaisse, un pantalon sans revers, des
chaussures montantes et un casque ou autre pour se protéger les
cheveux. Utiliser des bouche-oreilles quand on soude hors position
ou dans des espaces clos. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité
avec écrans latéraux quand on se trouve dans la zone de soudage.
LES BOUTEILLES PEUVENT
EXPLOSER SI ELLES SONT
ENDOMMAGÉES.
7.a. N'utiliser que des bouteilles de gaz comprimé
contenant le gaz de protection convenant
pour le procédé utilisé ainsi que des
détendeurs en bon état conçus pour les gaz
et la pression utilisés. Choisir les tuyaux
souples, raccords, etc. en fonction de
l'application et les tenir en bon état.
7.b. Toujours tenir les bouteilles droites, bien fixées par une chaîne à
un chariot ou à support fixe.
7.c. On doit placer les bouteilles:
• Loin des endroits où elles peuvent être frappées ou
• À une distance de sécurité des opérations de soudage à
7.d. Ne jamais laisser l'électrode, le porte-électrode ou toute autre
pièce sous tension toucher une bouteille.
7.e. Éloigner la tête et le visage de la sortie du robinet de la bouteille
quand on l'ouvre.
7.f. Les bouchons de protection des robinets doivent toujours être
en place et serrés à la main sauf quand la bouteille est utilisée
ou raccordée en vue de son utilisation.
7.g. Lire et suivre les instructions sur les bouteilles de gaz
comprimé, et le matériel associé, ainsi que la publication P-1 de
la CGA “Précautions pour le Maniement en toute Sécurité de
Gaz Comprimés dans des Cylindres », que l'on peut se procurer
auprès de la Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson
Davis Highway, Arlington, VA22202.
endommagées.
l'arc ou de coupage et de toute autre source de chaleur,
d'étincelles ou de flammes.
6.g. Connecter le câble de retour à la pièce le plus près possible de la
zone de soudage. Si les câbles de retour sont connectés à la
charpente du bâtiment ou à d'autres endroits éloignés de la zone de
soudage cela augmente le risque que le courant de soudage passe
dans les chaînes de levage, les câbles de grue ou autres circuits
auxiliaires. Cela peut créer un risque d'incendie ou surchauffer les
chaînes de levage ou les câbles et entraîner leur défaillance.
6.h. Voir également le point 1.c.
6.I. Lire et appliquer la Norme NFPA 51B “pour la Prévention des
Incendies Pendant le Soudage, le Coupage et d’Autres Travaux
Impliquant de la Chaleur”, disponible auprès de NFPA, 1
Batterymarch Park,PO Box 9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
6.j. Ne pas utiliser de source de puissance de soudage pour le dégel
des tuyauteries.
8.a.
8.b. Installer le matériel conformément au Code Électrique National
8.c. Mettre à la terre le matériel conformément au Code Électrique
5
POUR DES APPAREILS À
PUISSANCE ÉLECTIQUE.
Couper l'alimentation d'entrée en utilisant le
disjoncteur à la boîte de fusibles avant de
travailler sur le matériel
des États Unis, à tous les codes locaux et aux recommandations
du fabricant.
National des États Unis et aux recommandations du fabricant.
http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety
pour plus dʼinformations en matière de sécurité.
Obtenez l’application gratuite sur
http://gettag.mobi
.
Visitez le site
Guide Interactif sur
Internet pour la Sûreté
du Soudage pour les
dispositifs mobiles
Page 50

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Installation .......................................................................................................Section A
Instructions De Fonctionnement..................................................................................................A-1
Branchements de lʼAlimentation dʼEntrée et de la Masse ....................................................A-1
Raccordement du Câble dʼÉlectrode sur le Support ............................................................A-1
Type A – Support avec Poignée Octogonale et Pince à Mâchoires.....................................A-1
Type B – Support avec Poignée Ronde Cannelée...............................................................A-2
Changement du Câble dʼÉlectrode et du Câble de Travail ..................................................A-2
Fonctionnement ..............................................................................................Section B
Choix de la Polarité de Soudage..........................................................................................B-1
Facteur de Marche ...............................................................................................................B-1
Disjoncteurs..........................................................................................................................B-1
Comment Apprendre à Souder à la Baguette ......................................................................B-1
Guide de Sélection dʼÉlectrodes ..........................................................................................B-1
Guide Des Électrodes ..........................................................................................................B-2
Mouvements de Soudage à la Baguette
Coupage et Perforation dʼOrifices .......................................................................................B-3
Entretien...........................................................................................................Section C
Routine preventative maintenance
Liste de Pièces..................................................................................P-65, P-140 Series
TABLE DES MATIÈRES
Page
A thru G ......................................................................B-2
.................................................................................C-1
6
Page 51

INSTRUCTIONS DE
INSTALLATIONAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
AVERTISSEMENT
FONCTIONNEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
• Faire réaliser lʼinstallation et lʼentretien de cet appareil par
un électricien.
• Éteindre lʼalimentation dʼentrée au niveau de la boîte à
fusibles avant de travailler sur lʼappareil.
• Ne pas toucher les pièces électriques sous tension.
Branchements de lʼAlimentation dʼEntrée et de la Masse
Avant de commencer lʼinstallation, vérifier auprès de la compagnie
dʼélectricité que lʼalimentation soit appropriée pour la tension,
lʼ ampérage, la phase et la fréquence spécifiés sur la plaque
nominative de la soudeuse. Sʼassurer également que lʼinstallation
prévue sera conforme aux exigences du Code Électrique National
Américain et des codes locaux. Cette soudeuse peut fonctionner à
partir dʼune ligne monophasique ou à partir dʼune phase dʼune ligne
biphasique ou triphasique.
Tous les modèles conçus pour fonctionner sur des lignes dʼentrée
de moins de 250 volts sont livrés avec le câble dʼentrée branché sur
la soudeuse.
Placer la soudeuse de sorte que lʼair circule librement vers
lʼintérieur à travers les claires-voies se trouvant sur lʼarrière et les
côtés de la console, et vers lʼextérieur par le bas sur les quatre
côtés. Monter un réceptacle 6-50R de type NEMA dans un endroit
adapté. Vérifier que la prise se trouvant sur le câble dʼentrée
raccordé à la soudeuse puisse lʼatteindre.
En respectant les instructions suivantes, faire brancher par un
électricien qualifié ce réceptacle (6-50R de Type NEMA) sur les
lignes dʼalimentation au niveau de la boîte à fusibles. Trois fils en
cuivre du No.10 ou supérieurs sont nécessaires si le conduit est
utilisé. Pour des longueurs de câble supérieures à 100ʼ (31 m), un
fil du No.8 ou supérieur sera nécessaire dans le conduit afin
dʼempêcher les chutes de tension excessives. Placer des fusibles
de 50 ampères de type « Super lag » sur les deux lignes sous
tension comme le montre le schéma suivant. Le contact central du
réceptacle sert au branchement de la masse. Un fil vert dans le
câble dʼentrée raccorde ce contact sur le châssis de la soudeuse.
Raccordement du Câble dʼÉlectrode sur le Support
Avant de raccorder le câble dʼélectrode sur le support
dʼélectrode ou le câble de travail sur la pince, vérifier
que la soudeuse soit éteinte ou que la puissance
dʼentrée soit débranchée.
Identifier le type de support avant lʼinstallation.
Type A - Support avec Poignée Octogonale et Pince à
Mâchoires
1. Desserrer les vis de blocage et faire glisser la
poignée pour la retirer du support. Placer la poignée
sur le câble dʼélectrode. Le câble plus long est utilisé
pour le Câble dʼÉlectrode et il se trouve devant lʼorifice supérieur de la machine, tel quʼillustré
PINCE DE RACCORDEMENT
DU CÂBLE EN POSITION
DE LIVRAISON
Orifice Supérieur avec
Câble plus Long
FIGURE 1A
PINCE DE
RACCORDEMENT
DU CÂBLE
VIS DE BLOCAGE
FIGURE 1A.
Câble d'électrode
POIGNÉE
CÂBLE
D’ÉLECTRODE
PINCE RACCORDEMENT DU CÂBLE
VIS DE RACCORDEMENT DU CÂBLE
BRANCHER SUR UN FIL DE MASSE DE
SYSTÈME. VOIR LE CODE ÉLECTRIQUE
NATIONAL AMÉRICAIN ET/OU LES
FIL
VERT
FUSIBLE
FUSIBLE
Ceci garantit une mise à la
CODES LOCAUX POUR DʼAUTRES
DÉTAILS ET MOYENS APPROPRIÉS DE
MISE À LA TERRE.
BRANCHER SUR LES FILS SOUS
TENSION DʼUN SYSTÈME
MONOPHASIQUE À TROIS FILS
}
OU SUR UNE PHASE DʼUN
SYSTÈME BIPHASIQUE OU
TRIPHASIQUE.
terre correcte du châssis de la soudeuse lorsque la prise de la
machine est insérée dans le réceptacle. Si un interrupteur de
2. Retirer lʼisolation du câble dʼélectrode à 1" ± 1/16"
(25,4 mm ± 1,6 mm) de lʼextrémité.
3. Faire sortir la vis de raccordement du câble jusquʼà
ce que son extrémité soit au niveau de la surface
intérieure du corps de la mâchoire.
4. Retirer la pince de raccordement du câble des
mâchoires du support. Placer la pince sur lʼextrémité dénudée du câble dʼélectrode et lʼinsérer
dans le support avec la pince centrée contre la vis
de raccordement.
5. Bien serrer la vis de raccordement du câble contre
la pince.
déconnexion séparé est utilisé, il doit être bipolaire pour les deux
lignes sous tension et les deux doivent comporter des fusibles pour
50 ampères.
A-1
Page 52

6.
Faire glisser la poignée à sa place et la fixer en faisant
tourner la vis de blocage vers lʼintérieur jusquʼà ce quʼelle
soit serrée. Lʼextrémité filetée de la vis passe alors contre
lʼintérieur de la poignée et la tête de la vis se retrouve complètement à lʼintérieur de la poignée.
Vis de blocage serrée contre
l’intérieur de la poignée
INSTALLATIONAC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Fixation du Câble de Travail sur la Pince
Insérer le câble de travail (avec une terminale à orifice de
passage de 5/16") au travers de lʼorifice de décharge de
tension de la pince à souder et le fixer au moyen du
boulon et de lʼécrou fournis. Le câble plus court est utilisé
pour le Câble de Travail et se trouve devant lʼorifice
supérieur de la machine, tel quʼillustré ci-dessous.
Note Importante concernant la Sécurité: vérifier que lʼinstalla-
Orifice Inférieur
tion soit sûre et que les vis soient serrées et ne puissent pas
être touchées. Si les vis peuvent être touchées, NE PAS
UTILISER LE SUPPORT et contacter le distributeur.
Type B - Support avec Poignée Ronde Cannelée
1. Retirer la vis de montage de la poignée et faire glisser la
poignée hors du support. Placer la poignée sur le câble
dʼélectrode. Le câble plus long est utilisé pour le Câble
dʼÉlectrode et il se trouve devant lʼorifice supérieur de la
machine, tel que le montre la Figure 1A.
Changement du Câble dʼÉlectrode et du Câble de
Terminale ou
conducteurs nus
d’électrode
Câble
1" ± 1/16"
Poignée
Pince de
raccordement
du câble
Travail
La substitution de câbles par dʼautres de plus grande taille
demandant des branchements internes nʼest pas
recommandée. Les branchements pour des longueurs
supplémentaires ou des tailles supérieures doivent être
Vis de montage de la poignée
Câble
Vis de raccordement de la pince
effectués de façon externe. Des connecteurs Lincoln
Electric QD (Déconnexion Rapide) sont disponibles à cet
effet.
2. Si le câble dʼélectrode nʼest pas équipé dʼune terminale,
retirer lʼisolation du câble dʼélectrode à 1" ± 1/16" (25,4
mm ± 1,6 mm) de lʼextrémité.
3. Faire sortir la vis de raccordement de la pince et retirer
Si lʼun des câbles doit être changé pour une autre raison,
il doivent être remplacé par la pièce Lincoln appropriée –
et uniquement par le personnel qualifié
la pince de raccordement du câble.
4. Si le câble dʼélectrode est équipé dʼune terminale (orifice
de passage No.10), placer la terminale sur la vis de
raccordement du câble. Autrement, placer lʼextrémité
dénudée du câble dʼélectrode dans le support avec les
conducteurs du câble divisés pareillement des deux
côtés de la vis de raccordement de la pince
.
5. Bien serrer la vis de raccordement du câble dans la
pince de sorte que la pince maintienne le câble en
place.
6. Faire glisser la poignée à sa place et la fixer avec la
Sélection du Courant de Soudage
Chaque position de lʼinterrupteur sélecteur de courant
porte lʼindication de lʼampérage de sortie pour ce
réglage. Tourner lʼinterrupteur sur le courant nécessaire pour chaque application.
Il y a un léger jeu sur chaque position de lʼinterrupteur.
Il est bon de faire bouger une fois lʼinterrupteur vers lʼavant et vers lʼarrière dans ce jeu après être passé à
une nouvelle position. Ce mouvement de balayage permet de conserver les contacts sans saleté ni oxydes.
vis de montage de la poignée.
Avec Câble
Plus Court
Câble de
Travail
A-2
Page 53

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
FONCTIONNEMENT
Choix de la Polarité de Soudage
Pour obtenir les meilleurs résultats avec les électrodes de
soudage à lʼarc actuelles, il est important dʼutiliser la
polarité correcte. La Soudeuse à lʼArc AC/DC permet de
choisir entre AC, DC(+) ou DC(-), pour plus de versatilité.
Les électrodes de Lincoln figurent sur la liste du tableau à
la fin de ce manuel. Chaque électrode est conçue pour
mieux fonctionner en DC(+), DC(-) ou AC. Dans ce tableau
dʼélectrodes, la polarité préférée figure en premier. Cʼest la
polarité qui doit être utilisée – si elle est disponible – pour
obtenir de meilleurs résultats.
ATTENTION
Ne pas tourner l’interrupteur de sélection pendant le
soudage car cela pourrait endommager les contacts.
Facteur de Marche
(Pour les Codes 11604 et inférieurs). Les soudeuses de 60
Hz ont un facteur de marche nominal de 20% et les
soudeuses de 50 Hz ont un facteur de marche nominal de
15% pour le courant de soudage indiqué sur chaque position
de lʼinterrupteur.
(For Codes 11674 and above). The 60 Hz welders are rated
20% duty cycle and the 50 Hz welders are rated 13% duty
cycle for the welding current shown on each switch position.
Duty cycle is based on a ten minute period. This means that
the arc can be drawn for 2 minutes out of each ten minute
period (with a 20% duty cycle unit) without any danger of
overheating. If the welder is used for more than 2 minutes
during several successive ten minute periods, it may overheat.
Be sure to leave the unit “on” during each 10 minute period to
let the fan motor run for adequate cooling. Overheating
reduces welder life.
Disjoncteurs
Les modèles AC/DC avec un Code supérieur à 8800
possèdent un disjoncteur interne afin dʼéviter la surchauffe en
soudage DC. Le disjoncteur saute et coupe la sortie de
soudage DC si le facteur de marche est dépassé ou si la
circulation dʼair refroidissant est bloquée. Le ventilateur de
refroidissement continue à fonctionner et la sortie de soudage
DC sʼallumera automatiquement lorsque le disjoncteur aura
refroidi et se sera refroidi.
Comment Apprendre à Souder à la Baguette
Se reporter à « Apprendre à Souder à la Baguette » (LTW2)
dans la section du manuel de lʼopérateur du site
www.lincolnelectric.com
Guide de Sélection dʼÉlectrodes
Voir le Guide de Sélection dʼÉlectrodes ci-après et les
informations complémentaires concernant le choix des
électrodes. Se reporter également à (C2.10) pour le Guide de
Soudage à La Baguette Électrode et les tailles dʼélectrodes :
www.lincolnelectric.com
.
Choix des Électrodes
Quelle électrode est la meilleure pour un travail particulier...
comment lʼutiliser ? Ce sont là des questions importantes car le
coût, la qualité et lʼapparence du travail dépendent dʼun choix
dʼélectrode approprié et de lʼapplication. LES ÉLECTRODES EN
ACIER DOUX peuvent être classées dans les groupes suivants :
Groupe Hors-Position (E6011)
Ce groupe comprend des électrodes ayant un arc profond,
claquant et pénétrant ainsi que des dépôts qui refroidissent vite.
Ces électrodes sont utilisées pour le soudage de fabrication et de
réparation à usage général dans toutes les positions ; cʼest
également le meilleur choix pour le soudage de tuyauteries, de
joints en tôle et les soudures en coin et en bordure. Elles peuvent
être utilisées pour le travail de réparation lorsque la saleté, la
graisse, le plaqué ou la peinture ne peuvent pas être
complètement éliminés de lʼacier. Typiquement utilisées avec les
mouvements « A » et « B » (ci-dessous) pour la première passe
sur des soudures verticales montantes.
Groupe à Dépôt Élevé (E6027, E7024)
Ce groupe comprend les électrodes en poudre de fer à gros
recouvrement qui donnent un arc souple avec des taux de
dépôts rapides. Ces électrodes ont un lourd laitier et produisent
des cordons de soudure exceptionnellement lisses. Elles sont
généralement utilisées pour le soudage de production où tout le
travail peut être positionné pour le soudage horizontal. Les
premières passes de soudure, avec une technique de traînée,
sont toujours préférées aux passes transversales avec ces
électrodes.
Groupe à Grande Vitesse (E6012, E6013, E7014)
Ce groupe comprend les électrodes ayant un arc à puissance
modérée et des taux de dépôts entre ceux des électrodes horsposition et à dépôt élevé. Il sʼagit essentiellement dʼélectrodes de
production à usage général, en particulier pour les joints
descendants en filets et à recouvrement ou pour des soudures
courtes et irrégulières changeant de direction ou de position.
Également très utilisées pour lʼentretien et recommandées pour
souder de la tôle avec des joints en filet et à recouvrement. Le
mouvement « D » (ci-dessous) est généralement utilisé pour le
soudage vertical montant, mais les mouvements « A » et « B »
sont aussi appropriés.
Groupe à Faible Teneur en Hydrogène (E7018, E7028)
Ces électrodes sont généralement appelées « à faible teneur en
hydrogène ». Ce nom vient du fait que leur revêtement contient
peu dʼhydrogène sous forme soit humide soit chimique. Les
électrodes à faible teneur en hydrogène offrent les bénéfices
suivants : résistance remarquable aux craquelures, la plus faible
porosité sur lʼacier à roulements de soufre, et capacité de dépôts
de qualité rayons X. Cʼest pour cela quʼelles représentent le
premier choix lorsquʼil sʼagit de souder de lʼacier « à problème ».
La E7018 peut être utilisée dans toutes les positions, avec une
recommandation de Mouvement « C » pour la première passe
sur des soudures verticales ascendantes. NE JAMAIS utiliser
une technique de fouet ni un arc long avec ces électrodes.
TOUJOURS remplir les cratères en éloignant lentement les
électrodes. Ces électrodes doivent TOUJOURS rester sèches.
Les électrodes nʼayant pas été utilisées dans les heures suivant
lʼouverture dʼune boîte doivent être rangées dans des cabinés
chauffés. LH-73 est recommandé avec la AC-225. Normalement,
DC(+) est préféré pour ces électrodes.
B-1
Page 54

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Outre les électrodes mentionnées ci-dessus, celles qui figurent dans la liste suivante peuvent également être utilisées. Pour déterminer
le diamètre correct de l’électrode et les réglages de courant à utiliser, consulter le Répertoire de Soudage de Lincoln (Bulletin No. C2.10).
FONCTIONNEMENT
GUIDE DES ÉLECTRODES
• Fleetweld® 35
• Jetweld® 1
• Blue Max® 2100
• Red Baron® 309/309L
MR
• Red Baron® 308L MR
• Wearshield® ME
• Wearshield® MI
• Wearshield® BU
• Wearshield®
Mangjet®
• Wearshield® ABR
• Ferroweld®
• Softweld® 99 Ni
Mouvements de Soudage à la Baguette
le métal de soudure ne se déverse pas le long ou au travers du joint. Maintenir
un arc court dans le cratère et plus long durant le fouettage hors du cratère.
La Manipulation dépend du joint. Certains des mouvements
courants sont illustrés ci-dessous
.
Le Mouvement « B » est un mouvement de fouet combiné avec une légère
passe transversale dans le cratère. Il est utilisé avec les électrodes à
refroidissement rapide comme première passe sur des soudures en filets
verticales et des joints bout-à-bout en V.
Démarrage
Le Mouvement « C » est une simple passe transversale côte-à-côte utilisée
avec tous les types dʼélectrodes pour effectuer des passes de remplissage sur
des soudures en filets verticales et des joints bout-à-bout en V. Également
parfois utilisé avec des électrodes refroidissant au remplissage et à faible
teneur en hydrogène pour effectuer les premières passes sur ces joints.
Vue
Latérale
Le Mouvement « D » est une passe transversale triangulaire utilisée avec des
électrodes refroidissant au remplissage et à faible teneur en hydrogène pour
effectuer des soudures en filets verticales et des joints bout-à-bout en V en une
seule passe. Il donne une soudure plus grande quʼavec le mouvement « C ».
Utiliser la méthode de soudage « à pas de pèlerin »
lorsque la déformation représente un problème.
Le Mouvement « E » est une passe transversale de boîte utilisée avec tous les
types dʼélectrodes pour effectuer des passes de remplissage sur des soudures
en filets verticales et des joints bout-à-bout en V. Il ressemble au Mouvement «
3ème soudure 2ème soudure
èr soudure
C », mais avec une pause différente et un léger mouvement ascendant sur
1
chaque bord de la soudure pour garantir un remplissage de cratère complet et
lʼélimination des caniveaux.
Le Mouvement « F » est un mouvement circulaire utilisé avec tous les types
FAIRE TRAVAILLER LES FORCES RÉTRÉCISSANTES
POUR MINIMISER LES DÉFORMATIONS
dʼélectrodes pour effectuer des soudures au plafond. Parfois accompagné dʼun
léger fouettage après chaque oscillation dans le cratère. Toujours utiliser une
série de premières passes au plafond ; ne pas effectuer de passes
transversales.
Le Mouvement « A » est un mouvement de fouet droit utilisé avec les
électrodes qui refroidissent rapidement afin dʼeffectuer des soudures de
première passe dans toutes les positions et sur tous les types de joints. Il
Le Mouvement « G » est une simple passe transversale côte-à-côte utilisée
avec toutes les électrodes sur de larges soudures en filets ou en joint bout-àbout en position à plat.
maintient un petit bain de soudure et lui permet de refroidir rapidement afin que
B-2
Page 55

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
Coupage (Ne pas dépasser le Facteur de Marche – Au
début de cette Section de Fonctionnement)
La soudeuse à lʼarc et lʼélectrode peuvent être utilisées pour
couper lʼacier et la fonte. Suivre cette procédure :
1. Utiliser une électrode Fleetweld 180 de 1/8" (3,2 mm) ou
de 5/32" (4,0 mm).
2. Régler la soudeuse sur le maximum (225 amp).
3. Maintenir un arc long sur le bord du métal tout en le faisant
fondre.
4. Pousser lʼarc à travers le métal fondu, en le forçant à se
désaxer.
5. Soulever lʼélectrode et recommencer.
Il est important de continuer ce mouvement ascendant et
descendant, comme celui dʼune scie, en faisant fondre le
métal et en le repoussant.
Électrode
Bas de la plaque
Coupage de la plaque avec une électrode
Perforation dʼOrifices
FONCTIONNEMENT
1. Réglage de la soudeuse:
Maximum (225 amps).
2. Électrode : Fleetweld
5/32” (4,0 mm) ou
1/8” (3,2 mm) électrode
Utiliser 225
ampères
180 de 1/8" (3,2 mm) ou
de 5/32" (4,0 mm).
3. Tenir lʼélectrode avec un
Tableau
1/4” Plaque
(6 mm)
arc long perpendiculaire
sur lʼemplacement où
lʼorifice doit être percé.
4. Lorsque le métal a
fondu, pousser lʼélec-
Fabrication de trous avec une électrode
Récipient pour
récupérer le
métal chaud
trode à travers le bain de
fusion.
5. Permettre au métal fondu de tomber à travers lʼori-
fice.
6. Tourner en cercle avec un arc long autour du bord de
lʼorifice jusquʼà avoir formé le diamètre dʼorifice
souhaité.
Si on pousse lʼélectrode à travers le bain de fusion trop
tôt, elle sʼy colle. Vérifier que le métal soit fondu avant
de pousser pour le traverser.
NOTE: Sur du métal lourd (5/16" (7,9 mm) ou plus
épais), placer la plaque à perforer en position verticale
et lʼélectrode horizontalement. Ceci permet au métal
fondu de sʼécouler librement pendant la perforation.
B-3
Page 56

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
ENTRETIEN
Aucun entretien préventif de routine n’est requis. Contacter
l’Atelier de Service sur le Terrain Agréé par Lincoln le plus
proche pour les réparations nécessaires.
ENTRETIEN
D-1
Page 57

AC-225-S & AC/DC 225/125
NOTES
Page 58

15A
2
2A
15
14A
14B
13
3
2
5
6
7
8
9A
10
11
9
16A
16
17
18
20
21
23
12
28
29
22B
22A
1
15B
15A
AC-225-S
Indice du Modèle
15B
P-65-A.a (F)P-65-A.a (F)
INFÉRIEUR AU CODE 6300 UNIQUEMENT
plus Codes 6342, 6343 et 6453
13
14A
14B
2A
15
18
20
16
17
22B
21
16A
22A
23
12
28
10
11
9A
29
04-19-2010
Page 59

P-65-A.b (F)P-65-A.b (F)
PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./ PAGE NO./
CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO. CODE COL. NO.
4665 A.1.a 1 7093 A.1a 7 9424 A.1a 12
4763 A.1a 2 7094 A.1a 7 9425 A.1a 12
4798 A.1a 2 7098 A.1a 7 9426 A.1a 12
4852 A.1a 2 7099 A.1a 7 9427 A.1a 12
4953 A.1a 2 7100 A.1a 7 9428 A.1a 12
5130 A.1a 2 7101 A.1a 7 10420 A.1a 13
5167 A.1a 3 7102 A.1a 7 10421 A.1a 13
5169 A.1a 3 7103 A.1a 7 10422 A.1a 13
5227 A.1a 3 7234 A.1a 7 10423 A.1a 13
5341 A.1a 4 7330 A.1a 8 10424 A.1a 12
5348 A.1a 4 7333 A.1a 7 11074 A.1a 14
5381 A.1a 3 7351 A.1a 8
5438 A.1a 4 7352 A.1a 8
5440 A.1a 4 7523 A.1a 7
5449 A.1a 4 7533 A.1a 9 11602 B.1.a 1
5451 A.1a 4 7731 A.1a 9 11603 B.1.a 2
5465 A.1a 4 7743 A.1a 9 11604 B.1.a 3
5470 A.1a 4 7744 A.1a 9 11674 B.1.a 4
5678 A.1a 4 7745 A.1a 9
5683 A.1a 4 7746 A.1a 9
5880 A.1a 5 7755 A.1a 9
5896 A.1a 4 7805 A.1a 9
5897 A.1a 4 7813 A.1a 9
5903 A.1a 4 8226 A.1a 9
6140 A.1a 5 8370 A.1a 10
6184 A.1a 5 7382 A.1a 10
6295 A.1a 5 8383 A.1a 10
6304 A.1a 6 8384 A.1a 10
6342 A.1a 5 8385 A.1a 10
6343 A.1a 5 8386 A.1a 10
6453 A.1a 5 8459 A.1a 10
6518 A.1a 5 8511 A.1a 10
6592 A.1a 6 8712 A.1a 10
6600 A.1a 6 8780 A.1a 10
6601 A.1a 6 8894 A.1a 10
6616 A.1a 6 8897 A.1a 10
6661 A.1a 6 8898 A.1a 10
6734 A.1a 6 8900 A.1a 10
6898 A.1a 6 8918 A.1a 10
6967 A.1a 6 8959 A.1a 10
6991 A.1a 6 8983 A.1a 10
7009 A.1a 6 9039 A.1a 10
7010 A.1a 6 9291 A.1a 11
7011 A.1a 6 9292 A.1a 11
7012 A.1a 6 9293 A.1a 11
7013 A.1a 6 9294 A.1a 11
7030 A.1a 6 9295 A.1a 11
7050 A.1a 7 9296 A.1a 11
7068 A.1a 6 9422 A.1a 12
7072 A.1a 6 9423 A.1a 12
04-19-2010
Page 60

# Indique un changement dans cette impression.
P-65-A.1.a (F)P-65-A.1.a (F)
Nʼutiliser que les pièces marquées dʼun “x” dans la colonne portant
le numéro qui apparaît sur la page de lʼindice du modèle.
ARTICLE
Cette Page pour les Codes Inférieurs à 11600
1 Panneau Arrière Supérieur M9873
1
Panneau Arrière Supérieur (Codes 5600 à 6600, sauf 6304)
Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale (60 Hz), Comprend ;
2
2A Ventilateur M13525 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale (50 Hz), Comprend :
2
2A Ventilateur M13525-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
3 Plaque de Fixation du Ventilateur M9874 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
3 Plaque de Fixation du Ventilateur M10396
5 Console L3786-6 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Console L3786-7 1 • X X X • • • • • • • • • •
5 Console L3786-12 1 X • • • • • • • • • • • •
5 Console L3786-13
5 Console L3786-19 1 • • • • • • • • • X X X • •
5 Console L3786-14 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 208 Volts
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, Plus de 250 Volts
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 et 60 Hz, Autres Tensions
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Plus de 250 Volts
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 208 Volts Uniquement
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 et 60 Hz, Autres Tensions
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 et 60 Hz, Autres Tensions
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz, 230 Volts Uniquement
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 Hz, 15% Facteur de Marche Uniquement
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 Hz, Facteur de Marche 220V Uniquement
6
6
Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 Hz, 15% Facteur de Marche Autres Tensions
6 Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 50 Hz M15727 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
6 Plaque Nominative, Montgomery Ward M9934
6 Plaque Nominative, Lincoln, 60 Hz M22165 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Bouton dʼAttache (Blanc) T14659
Bouton dʼAttache (Noir) T14659-1
Interrupteur de Sélection (50 Hz Uniquement), Comprend :
7
7 Interrupteur de Sélection, Comprend : M10830-3 1 X X X X X X X X • • • • • •
7 Interrupteur de Sélection, Comprend : M10830-9 1 • • • • • • • • X X X X X X
Axe de lʼInterrupteur S13206 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
8 Poignée de lʼInterrupteur (Noire) T13990-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
9 Passe-fils du Fil de Sortie T9274-4 2 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
9A Collier de Serrage du Fil de Sortie S15761 1 • • • X X X X X X X X X X X
10
Plaque Nominative de lʼInterrupteur de Ligne
11 Interrupteur de Ligne S7670 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X • •
11 Interrupteur de Ligne S18815 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X X
12 Transformateur et Base
13 Panneau Couvercle, Plaque à Bornes L3936-1 1 X X X • • • • • • • • • • •
14A Plaque à Bornes dʼEntrée T11813
14B Panneau dʼEntrée, 60 Hertz T11881 1 • X X • • • • • • • • • • •
ø
Cette pièce est obsolète et nʼest plus disponible.
DESCRIPTION PIÈCE No. QTÉ
ø
M10894 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
M13539-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
M13539-2 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
ø
ø
M9803
M13029 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
M14008 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15411 1 ••••••••••X•••
M15411-2 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15411-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M9803-1 1 • X X X X X X • • • • • • •
M15726 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
M15725-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X •
M13029-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
M14008-1 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M15725 1 • • • • • • • • • • • X X X
M13880 1 • • • • • • • • X • • • • •
M14009 1 • • • • • • • • • X • • • •
M14009-1 1 • • • • • • • • • • X • • •
M10830-8 1 • • • • • • X X • • • • • •
S12070
Non Disponible
ø
ø
(Tel que Requis)
(Tel que Requis)
ø
ø
1234567891011121314
1 XXXX••••••••••
1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
1•• •••XXXX•••••
1 XXXXXXXXX • • • ••
1 •XXX••••••••••
XXXXXXXXXXXX ••
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
1 X•••••••••••••
1 X•••••••••••••
04-19-2010
Page 61

# Indique un changement dans cette impression.
P-65-A.1.b (F)P-65-A.1.b (F)
Nʼutiliser que les pièces marquées dʼun “x” dans la colonne portant
le numéro qui apparaît sur la page de lʼindice du modèle.
ARTICLE
15 Couvercle Arrière L3936 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Couvercle Arrière L4143 1 • • • X • • • • • • • • • •
15 Couvercle Arrière L4143-1
15A Panneau Arrière Inférieur L4595 1 • • • • • X X • • • • • • •
15A Panneau Arrière Inférieur L4595-2 • • • • • • X X X X X X X X
15B Panneau Arrière Supérieur G1239 1 • • • • • X X X • X X X • •
15B Panneau Arrière Supérieur G1395 1 • • • • • • • • • • • • X
16A Panneau Couvercle L3935-A 1 • • • X X • • • • • • • • •
16 Câble dʼÉlectrode S11609-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
17 Support dʼÉlectrode K909-1 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
18 Câble de Masse S11609-3 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
19 Casque M9673-6 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
20 Prise de Masse M12033 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
28 Réceptacle (230 Volts Uniquement) S7733
28 Réceptacle (230 Volts Uniquement) S13700 1 • • • • X X X X X X X X X •
29 Cordon dʼEntrée (230 Volts Uniquement)
29 Cordon dʼEntrée (230 Volts Uniquement) S13699-2 1 • • • • X X X • • • • • • •
29
Cordon dʼEntrée (230 Volts ou Moins Uniquement) (60 Hz)
Cordon dʼEntrée 230V 50 Hz (Codes 8894, 9428
29
et 10424 Uniquement)
Kit de Chariot
(Comprend les Articles 21, 22A, 22B et 23)
DESCRIPTION PIÈCE No. QTÉ
ø
ø
S13699-2 & S13700
S15599-1 1 • • • • • • • X X X X X X X
S18021 1 • • • • • • • • • X • X X •
Commander K761
1234567891011121314
1 ••••X•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
1 XXXXX•••••••••
1 • • • • XXXXXXXXXX
Pièces Non Illustrées
Etiquette Autocollante dʼAvertissement (Sʼappose sur le Coin Supérieur de la Console)
Etiquette Autocollante de Sélection dʼÉlectrode
Etiquette Autocollante de Massel T13260-4 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X •
M14330 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
M14331 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
ø
Cette pièce est obsolète et nʼest plus disponible
.
04-19-2010
Page 62

# Indique un changement dans cette impression.
P-65-B.1.a (F)P-65-B.1.a (F)
Nʼutiliser que les pièces marquées dʼun “x” dans la colonne portant
le numéro qui apparaît sur la page de lʼindice du modèle.
ARTICLE
Cette Page pour les Codes Supérieurs à 11600:
2
2
5 Console L3786-14 1 X X X X
6
6 Plaque Nominative (Code 11603) M15727 1 • X • •
6 Plaque Nominative (Code 11674) M22167 1 • • • X
8 Poignée de lʼInterrupteur T13990-1 1 X X X X
9A Collier de Serrage pour Fil S15761 1 X X X X
11 Interrupteur de Ligne S18815 1 X X X X
12 Transformateur et Base NSS 1XXXX
15A Arrière Bas de la Console L4595-2 1 X X X X
15B Arrière Haut de la Console G1395 1 X X X X
16 Câble dʼÉlectrode S11609-4 1 X X X X
17 Support dʼÉlectrode K909-1 1 X X X X
18 Câble de Masse S11609-3 1 X X X X
20 Prise de Masse M12033 1 X X X X
21 Roue S11662-3 2 • • X •
22 Kit de Montage, Comprend : T14160 1 • • X •
22A Rondelle Plate S9262-1 2 • • X •
22B Cheville dʼAssemblage T12570 2 • • X •
22C
23 Essieu M8809-61 1 • • X •
29
29
30
31
32
32
32
33
Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale, Comprend :
Ventilateur M13525 1 X • X •
Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale, Comprend :
Ventilateur M13525-1 1 • X • X
Plaque Nominative (Codes 11602 et 11604)
Bouton dʼAttache (Noir) T14659-1 1 X X X X
Kit de Chariot, Comprend : K761
Vis Borgne à Tête Hexagonale 3/8-16 x 2,00
Câble dʼAlimentation dʼEntrée (Codes 11602 et 11604)
Câble dʼAlimentation dʼEntrée (Codes 11603 et 11674)
Etiquette Autocollante dʼAvertissement (Non Illustrée)
Etiquette Autocollante de Sélection dʼÉlectrode (Non Illustrée)
Diagramme de Câblage (Non Illustré) (Codes 11602 et 11604)
Diagramme de Câblage (Non Illustré) (Code 11603)
Diagramme de Câblage (Non Illustré) (Codes 11674)
Etiquette Autocollante de Garantie (Non Illustrée)
DESCRIPTION PIÈCE No. QTÉ
M13539-1 1 X • X •
M13539-2 1 • X • X
M22165 1 X • X •
* ••X•
CF000071 1 • • X •
S15599-1 1 X • X •
S18021 1 • X • X
M14330-3 1 X X X X
M14331 1 X X X X
S15621 1 X • X •
S16671 1 • X • •
S28364 1 • • • X
S22127-1 1 • X • •
1234567891011121314
* Kit de Chariot en Option pour tous les Codes – Standard lorsquʼindiqué.
NSS - Nʼest Pas Vendu Séparément
04-19-2010
Page 63

NOTES
Page 64

AC/DC 225/125
Indice du Modèle
COL. COL.
CODE NO. CODE NO.
8566 1 9025 2
8581 1 9186 2
8650 1 9221 3
8663 1 9222 3
8666 1 9223 3
8700 1 9224 3
8737 1 9225 3
8742 1 9226 3
8777 1 9365 3
8788 1 10426 3
8811 2 10427 3
8815 2 10428 3
8817 1 10429 3
8893 2 11675 4
8901 2
8903 2
8910 2
8955 2
8986 2
9005 2
9015 2
1B
1A
10
6A
4
20
31B
6B
P-140-A (F)P-140-A (F)
3
5
15
7
2
13
8
17
31A
14
11
9A
28
12
25
7A
14A
29
Nʼutiliser que les pièces marquées dʼun “x” dans la colonne portant le
# Indique un changement dans cette impression.
ARTICLE
DESCRIPTION PIÈCE No. QTÉ
numéro qui apparaît sur la page de lʼindice du modèle.
123456789
1 Ensemble du Redresseur, Comprend : L7029 ø 1X•••
1A (–) Moitié du Redresseur (Inférieure) S12837-7A ø 1X•••
1B (+) Moitié du Redresseur (Supérieure) S12837-7B ø 1X•••
1 Ensemble du Redresseur, Comprend: L6974 ø 1•X••
1
Ensemble du Redresseur (Code Inférieur à 10000), Comprend :
L7491 1 • X X •
1 A (–) Diode M9661-39R 2 • X X •
1 B (+) Diode M9661-39 2 • X X •
Ensemble de lʼÉliminateur M14705 1 • X X •
1 Ensemble du Redresseur (Code Supérieur à 10000) G3648 1 • • X X
2 Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale (60 Hz), Comprend : M13539-1 1 X X X •
Ventilateur M13525 1 X X X •
2 Moteur du Ventilateur et Pale (50 Hz), Comprend : M13539-2 1 X X X X
Ventilateur M13525-1 1 X X X X
ø
Cette pièce est obsolète et nʼest plus disponible
03-10-2010
Page 65

# Indique un changement dans cette impression.
P-140-A.1 (F)P-140-A.1 (F)
Nʼutiliser que les pièces marquées dʼun “x” dans la colonne por-
tant le numéro qui apparaît sur la page de lʼindice du modèle.
ARTICLE
3 Étrangleur S18336 1 X X • •
3 Étrangleur M15371 1 • • X X
4 Plaque de Fixation du Moteur du Ventilateur S17194 1 X • • •
5 Console (Code Inférieur à 10400) L3786-19 1 X X X •
5 Console (Code Supérieur à 10400) L3786-14 1 • • X X
6A Panneau Arrière Inférieur L6650 1 X X X X
6B Panneau Arrière Supérieur L6651 ø 1X•••
6B Panneau Arrière Supérieur G1395-1 1 • X X X
7 Interrupteur de Sélection dʼIntervalle, Comprend : M10830-9 1 X X X X
Axe de lʼInterrupteur S13206 1 X X X X
7A Poignée M13989-1 1 X X X X
8 Câble dʼÉlectrode S11609-9 1 X X X X
9A Collier de Serrage du Fil de Sortie S15761 1 X X X X
10 Câble de Travail S11609-10 1 X X X X
11 Interrupteur de Ligne (Code Inférieur à 10400) S7670 1 X X X •
11 Interrupteur de Ligne (Code Supérieur à 10400) S18815 1 • • X X
12 Transformateur et Base Pas Disponible 1 X X X X
13 Éliminateur S17203 1 X • • •
14 Interrupteur de Polarité, Comprend : M14063 1 X X X X
Axe de lʼInterrupteur M14337 1 X X X X
14A Poignée M13989-1 1 X X X X
15 Plaque Nominative (60 Hz. 230 Volts Uniquement) M15784 1 X X X •
Plaque Nominative (60 Hz. Toutes les Tensions sauf 208 et 230 Volts)
15
15 Plaque Nominative (60 Hz. 208 Volts Uniquement) M15784-2 1 X X X •
15 Plaque Nominative (50 Hz. Toutes les Tensions) M15785 1 X X X •
15 Plaque Nominative (50 Hz) (Code 11675) M22168 1 • • • X
15A Plaque dʼAvertissement (Non Illustrée) M14330 1 X X X •
15A Etiquette Autocollante dʼAvertissement M14330-3 1 • • • X
15B Plaque de Sélection dʼÉlectrode (60 Hz) (Non Illustrée)
15B
Plaque de Sélection dʼÉlectrode (50 Hz) (Non Illustrée)
16 Bouton dʼAttache de la Plaque Nominative T14659-1 4 X X X X
17 Support dʼÉlectrode K909-1 1 X X X X
20 Pince de Soudage M12033 1 X X X X
28 Réceptacle (60 Hz., 250 Volts ou Moins Uniquement) S13700 1 X X X •
29
Câble dʼEntrée (60 Hz., 250 Volts ou Moins Uniquement)
Câble dʼEntrée (50 Hz., 250 Volts ou Moins Uniquement)
29
Disjoncteur - Non Illustré S10657-3 1 • X X X
Etiquette Autocollante de Prise de Terre (Non Illustrée)
Articles en Option :
30 Casque (Non Illustré) Le choix 1 X X X •
31 Kit de Chariot, Comprend : K761 1 X X X X
31A Essieu M8809-61 1 X X X X
31B Roue S11662-3 2 X X X X
31C Kit de Montage T14160 1 X X X X
DESCRIPTION PIÈCE No. QTÉ
M15784-1 1 X X X •
M14331 1 X X X •
M14335 1 X X X •
S15599-1 1 X X X X
S18021 1 • X X X
T13260-4 1 X X X X
du Client
123456789
NSS - Nʼest pas Vendu Séparément
ø
Cette pièce est obsolète et nʼest plus disponible.
03-10-2010
Page 66

(NOTAS) NOTES
Page 67

(NOTAS) NOTES
Page 68

CUSTOMER ASSISTANCE POLICY
The business of The Lincoln Electric Company is manufacturing and selling
high quality welding equipment, consumables, and cutting equipment. Our
challenge is to meet the needs of our customers and to exceed their expectations. On occasion, purchasers may ask Lincoln Electric for advice or
information about their use of our products. We respond to our customers
based on the best information in our possession at that time. Lincoln Electric
is not in a position to warrant or guarantee such advice, and assumes no
liability, with respect to such information or advice. We expressly disclaim
any warranty of any kind, including any warranty of fitness for any customer’s
particular purpose, with respect to such information or advice. As a matter of
practical consideration, we also cannot assume any responsibility for
updating or correcting any such information or advice once it has been given,
nor does the provision of information or advice create, expand or alter any
warranty with respect to the sale of our products.
Lincoln Electric is a responsive manufacturer, but the selection and use of
specific products sold by Lincoln Electric is solely within the control of, and
remains the sole responsibility of the customer. Many variables beyond the
control of Lincoln Electric affect the results obtained in applying these types
of fabrication methods and service requirements.
Subject to Change – This information is accurate to the best of our knowledge
at the time of printing. Please refer to
www.lincolnelectric.com for any updated information.
POLÍTICA DE ASISTENCIA AL CLIENTE
El negocio de The Lincoln Electric Company es la fabricación y venta de
equipo de soldadura, consumibles y equipo de corte de alta calidad. Nuestro
reto es satisfacer las necesidades de nuestros clientes y exceder sus expectativas. A veces, los compradores pueden solicitar consejo o información a
Lincoln Electric sobre el uso de nuestros productos. Respondemos a nuestros
clientes con base en la mejor información que tengamos en ese momento.
Lincoln Electric no está en posición de garantizar o asegurar dicha asesoría, y
no asume ninguna responsabilidad con respecto a dicha información o
consejos. Desconocemos expresamente cualquier garantía de cualquier tipo,
incluyendo cualquiera sobre la aptitud para algún fin en especial de algún
cliente con respecto a dicha información o consejos. Como un asunto de
consideración práctica, tampoco podemos asumir ninguna responsabilidad
por actualizar o corregir dicha información o asesoría una vez que se ha
dado, así como tampoco proporcionar la información o consejos crea, amplía
o altera alguna garantía con respecto a la venta de nuestros productos.
Lincoln Electric es un fabricante receptivo pero la selección y uso de los
productos específicos vendidos por Lincoln Electric está únicamente dentro
del control de, y permanece la única responsabilidad, del cliente. Numerosas
variables más allá del control de Lincoln Electric afectan los resultados
obtenidos en aplicar estos tipos de métodos de fabricación y requerimientos
de servicio.
Sujeto a cambio — Esta información era exacta, según nuestro mejor saber y
entender, al momento de la impresión. Sírvase consultar
www.lincolnelectric.com para cualquier información actualizada.
POLITIQUE D’ASSISTANCE AU CLIENT
Les activités de The Lincoln Electric Company sont la fabrication et la vente
d’appareils à souder, de matériel consommable et de machines à couper de
grande qualité. Notre défi est de satisfaire les besoins de nos clients et de
dépasser leurs attentes. Les acheteurs peuvent parfois demander à Lincoln
Electric des conseils ou des informations sur l’usage qu’ils font de nos
produits. Nous répondons à nos clients sur la base des meilleures informations en notre possession à ce moment précis. Lincoln Electric n’est pas
en mesure de garantir ni d’avaliser de tels conseils et n’assume aucune
responsabilité quant à ces informations ou conseils. Nous nions
expressément toute garantie de toute sorte, y compris toute garantie
d’aptitude à satisfaire les besoins particuliers d’un client, en ce qui concerne
ces informations ou conseils. Pour des raisons pratiques, nous ne pouvons
pas non plus assumer de responsabilité en matière de mise à jour ou de
correction de ces informations ou conseils une fois qu’ils ont été donnés ; et
le fait de donner des informations ou des conseils ne crée, n’étend et ne
modifie en aucune manière les garanties liées à la vente de nos produits.
Lincoln Electric est un fabricant responsable, mais le choix et l’utilisation de
produits spécifiques vendus par Lincoln Electric relèvent uniquement du
contrôle et de la responsabilité du client. De nombreuses variables échappant
au contrôle de Lincoln Electric affectent les résultats obtenus en appliquant
ces types de méthodes de fabrication et d’exigences de services.
Sujet à Modification - Ces informations sont exactes à notre connaissance
au moment de l’impression. Se reporter à www.lincolnelectric.com pour des
informations mises à jour.
 Loading...
Loading...