Page 1
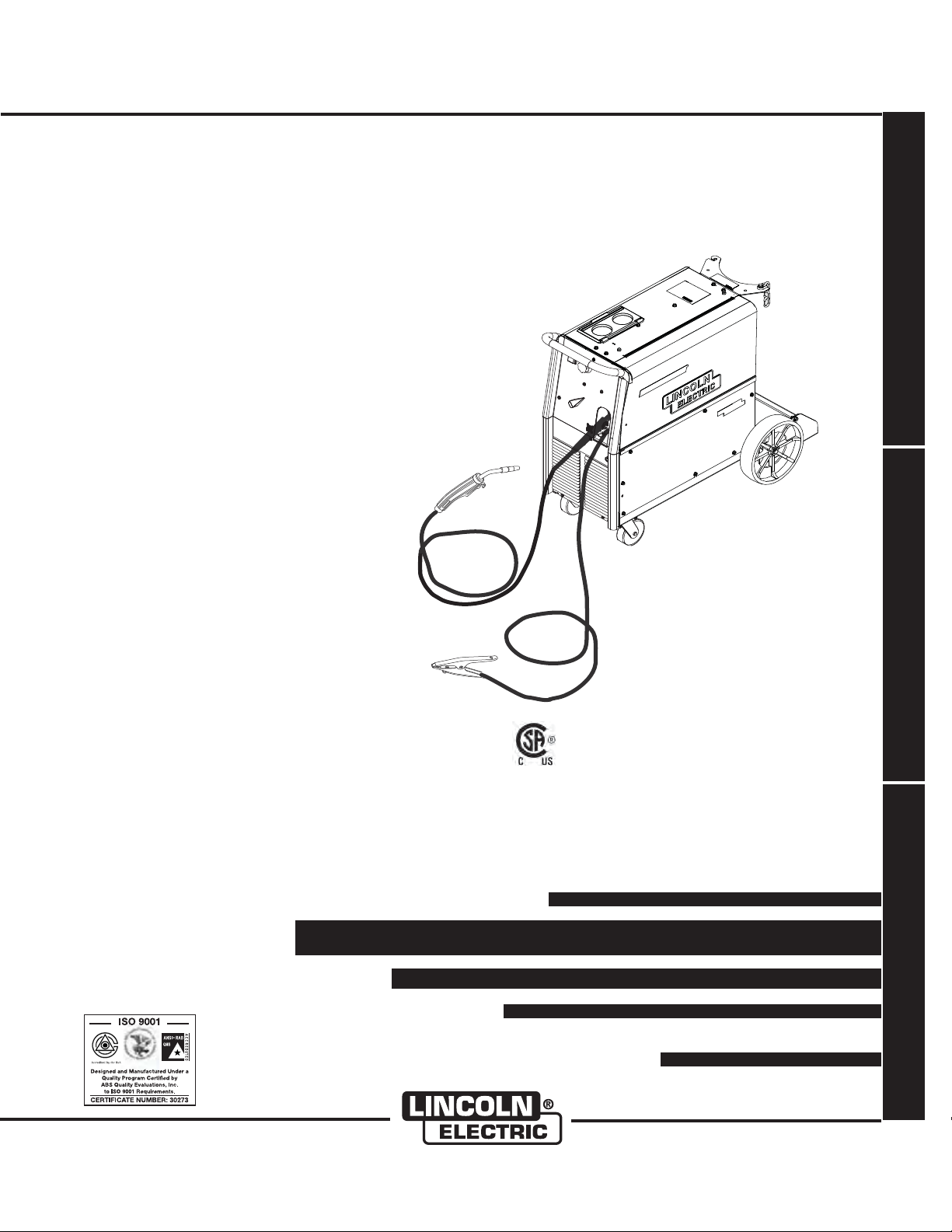
IMT10097
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding and cutting
equipment is designed and built
with safety in mind. However,
your overall safety can be
increased by proper installation
... and thoughtful operation on
your part. DO NOT INSTALL,
OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS
EQUIPMENT WITHOUT READING THIS MANUAL AND THE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And,
most importantly, think before
you act and be careful.
POWER MIG®216
For use with machine Code Numbers
For use with machine Code Numbers
11817
May, 2011
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
Copyright © Lincoln Global Inc.
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 2
i
SAFETY
i
WARNING
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents
are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
The Above For Diesel Engines
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040,
Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available from the
Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
The engine exhaust from this product contains
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
The Above For Gasoline Engines
FOR ENGINE
powered equipment.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance
work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running.
____________________________________________________
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes
outdoors.
____________________________________________________
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts and
igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If
fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start
engine until fumes have been eliminated.
____________________________________________________
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in
position and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and
tools away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving
parts when starting, operating or repairing equipment.
____________________________________________________
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety
guards to perform required maintenance. Remove
guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete.
Always use the greatest care when working near moving
parts.
___________________________________________________
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan.
Do not attempt to override the governor or
idler by pushing on the throttle control rods
while the engine is running.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the
radiator pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and
welding machines
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and
welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician
before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health
effects which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1.
Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and
work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right
side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
___________________________________________________
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while
turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance
work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magneto wire as appropriate.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
Page 3
ii
SAFETY
ii
ELECTRIC SHOCK can
kill.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits
are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare
skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full
area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding
must be performed under electrically hazardous
conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet
clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or
scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use
the following equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic
welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection
should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
3.f.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of
electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage
between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage
of both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8.
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover
plates to protect your eyes from sparks and
the rays of the arc when welding or observing
open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens
should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
can be dangerous.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep
your head out of the fume. Use enough
ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When
welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see
instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or
cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as
low as possible and within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits using local exhaust or mechanical
ventilation. In confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be required.
Additional precautions are also required when welding
on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected
by various factors including proper use and positioning of
the equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific welding procedure and application involved. Worker
exposure level should be checked upon installation and
periodically thereafter to be certain it is within applicable
OSHA PEL and ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations.
The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation,
especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
vapors
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
to
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturerʼs instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your
employerʼs safety practices. MSDS forms are available from
your welding distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
Page 4
iii
SAFETY
iii
WELDING and CUTTING
SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
6.a.
Remove fire hazards from the welding area.
If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
Remember that welding sparks and hot
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI
Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the
equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact
can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures
will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even
been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended
Safe Practices for the
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous
Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society
(see address above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil
6.f.
free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt,
cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear
ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places.
Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding
area as practical. Work cables connected to the building
framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing
through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains
or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
the welding sparks from starting a fire.
though
they have
Preparation
for Welding and Cutting of
CYLINDER may explode
if damaged.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders
containing the correct shielding gas for the
process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for
the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and
any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas
cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l,
“Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
powered equipment.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on
the equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturerʼs
recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturerʼs recommendations.
6.I. Read and follow NFPA 51B “ Standard for Fire Prevention
During Welding, Cutting and Other Hot Work”, available
from NFPA, 1 Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma
022690-9101.
6.j. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
Refer to http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety for additional safety information.
Page 5

NOTES
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
Page 6
Thank You
vv
for selecting a QUALITY product by Lincoln Electric. We want you
to take pride in operating this Lincoln Electric Company product
••• as much pride as we have in bringing this product to you!
The business of The Lincoln Electric Company is manufacturing and selling high quality welding equipment, consumables, and cutting equipment. Our challenge is to meet the needs of our customers and to exceed their expectations. On occasion, purchasers may ask Lincoln
Electric for advice or information about their use of our products. We respond to our customers based on the best information in our possession at that time. Lincoln Electric is not in a position to warrant or guarantee such advice, and assumes no liability, with respect to such information or advice. We expressly disclaim any warranty of any kind, including any warranty of fitness for any customerʼs particular purpose,
with respect to such information or advice. As a matter of practical consideration, we also cannot assume any responsibility for updating or
correcting any such information or advice once it has been given, nor does the provision of information or advice create, expand or alter any
warranty with respect to the sale of our products.
Lincoln Electric is a responsive manufacturer, but the selection and use of specific products sold by Lincoln Electric is solely within the control
of, and remains the sole responsibility of the customer. Many variables beyond the control of Lincoln Electric affect the results obtained in
applying these types of fabrication methods and service requirements.
Subject to Change – This information is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of printing. Please refer to www.lincolnelectric.com
for any updated information.
CUSTOMER ASSISTANCE POLICY
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims
for material damaged in shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation company at the
time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This information can be
found on your machine nameplate.
Product _________________________________________________________________________________
Model Number ___________________________________________________________________________
Code Number or Date Code_________________________________________________________________
Serial Number____________________________________________________________________________
Date Purchased___________________________________________________________________________
Where Purchased_________________________________________________________________________
Whenever you request replacement parts or information on this equipment, always supply the information you
have recorded above. The code number is especially important when identifying the correct replacement parts.
On-Line Product Registration
- Register your machine with Lincoln Electric either via fax or over the Internet.
• For faxing: Complete the form on the back of the warranty statement included in the literature packet
accompanying this machine and fax the form per the instructions printed on it.
• For On-Line Registration: Go to our
“Product Registration”. Please complete the form and submit your registration.
Read this Operators Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual and keep it
handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection.
The level of seriousness to be applied to each is explained below:
WEB SITE at www.lincolnelectric.com. Choose “Quick Links” and then
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed exactly to avoid serious personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to avoid minor personal injury or damage to this equipment.
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENT
Page
________________________________________________________________________
Installation .......................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications ........................................................................................A-1
Safety Precautions.................................................................................................A-2
Uncrating the POWER MIG® 216 .........................................................................A-2
Location .................................................................................................................A-2
Input Power, Grounding and Connection Diagram ........................................A-2, A-3
Output Polarity Connections..................................................................................A-3
Gun and Cable Installation ....................................................................................A-4
Shielding Gas ........................................................................................................A-4
Coil Claw™ Installation..........................................................................................A-5
________________________________________________________________________
vi vi
Operation .........................................................................................................Section B
Safety Precautions.................................................................................................B-1
Product Description ...............................................................................................B-2
Recommended Processes and Equipment ...........................................................B-2
Welding Capability.................................................................................................B-2
Limitations..............................................................................................................B-2
Description of Controls ..........................................................................................B-2
Wire Drive Roll.......................................................................................................B-3
Wire Size Conversion parts ...................................................................................B-3
Procedure for Changing Drive Roll........................................................................B-3
Wire Reel Loading .................................................................................................B-3
Mounting of 10 to 44 lbs. Spools ...........................................................................B-3
To Start the Welder................................................................................................B-4
Feeding Electrode..................................................................................................B-4
Idle Roll Pressure Setting ......................................................................................B-4
Wire Drive Configuration................................................................................B-4, B-5
Making a Weld.......................................................................................................B-5
Avoiding Wire Feeding Problems ..........................................................................B-6
Fan Control............................................................................................................B-6
Input Line Voltage Protection.................................................................................B-6
Wire Feed overload Protection ..............................................................................B-6
Welding Thermal Overload Protection...................................................................B-6
Welding Procedure Information .............................................................................B-6
Learning To Weld ..................................................................................................B-6
________________________________________________________________________
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
Accessories.....................................................................................................Section C
Drive Roll Kits........................................................................................................C-1
Dual Cylinder Mounting Kit ...................................................................................C-1
Small Spool Spindle Adapter.................................................................................C-1
Alternative Magnum GMAW Gun and Cable Assemblies .....................................C-1
Magnum Gun Connection Kit ...............................................................................C-1
Optional Spool Guns and Adapters.......................................................................C-1
Making a Weld with the Spool Gun Adapter Kit and Spool Gun Installed .............C-2
________________________________________________________________________
Page 8

vii vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Maintenance ....................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions ................................................................................................D-1
General Maintenance ............................................................................................D-1
Drive Rolls and guide Tubes .................................................................................D-1
Contact Tip and Gas Nozzle Installation ...............................................................D-1
Gun Tubes and Nozzles........................................................................................D-1
Gun Cable Cleaning ..............................................................................................D-1
Liner Removal and Replacement ..........................................................................D-2
Gun Handle Disassembly......................................................................................D-3
Troubleshooting..............................................................................................Section E
How to Use Troubleshooting Guide.......................................................................E-1
Troubleshooting Guide ............................................................................E-2 thru E-4
Application Chart, Wiring Diagram and Dimension Print............................Section F
Parts Manual....................................................................................................Appendix
POWER MIG® 216 ..................................................................................................P-611
Magnum Pro 250L Gun ..............................................................................P-202-H.2
Page 9
A-1
INSTALLATION
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – POWER MIG® 216
INPUT – SINGLE PHASE ONLY
Standard Voltage/Phase/Frequency
208/230/1/60 Hz 33/29 Amps 40/36 Amps
220/1/50 Hz 30 Amps 37 Amps
Duty Cycle Amps Volts at Rated Amperes
30% 216 Amps 22 Volts
40% 190 Amps 23 Volts
60% 170 Amps 24
Welding Current Range Maximum Open Circuit Voltage Welding Voltage Range
30 – 250Amps 36 Volts 13-24 Volts
RECOMMENDED INPUT WIRE AND FUSE SIZES
Input Voltage/ Fuse or Breaker Rating On
Frequency (Hz) Size (Super Lag) Nameplate
Input Current @ 170 Amp Rated Output Input Current @ 216 Amp Rated Output
RATED OUTPUT
OUTPUT
Input Ampere Power Cord
(30% Duty Cycle)
A-1
* Volts
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
208/60 50 40A 50 Amp, 250V
230/60 50 36A Three Prong Plug
220/50 50 37A (NEMA) Type 6-50P)
WIRE SPEED RANGE
Wire Speed 50 – 700 IPM (1.27 – 17.8 m/minute)
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
Height Width Depth Weight
With Coil Claw™ Without Coil Claw™
32.56 in. 20.12 in. 19.15 in. 39.92 in. 215.5 Ibs. 206.5 lbs.
827 mm 512 mm 487 mm 1014 mm 97.8 kg. 93.7 kg.
With Gun and Cable Without Gun and Cable
and Work Cable and Work Cable
TEMPERATURE RANGES
OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE
-4°F to 104°F(-20°C to +40°C)
STORAGE TEMPERATURE RANGE
-40°F to 185°F(-40°C to +40°C)
* 23 Volts at 50 Hz.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 10
A-2
INSTALLATION
A-2
Read entire installation section before starting
installation.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Only qualified personnel should
perform this installation.
• Only personnel that have read
and understood the POWER
MIG® 216 Operatorʼs Manual
should install and operate this
equipment.
• Machine must be grounded per
any national, local or other applicable electrical codes.
• The POWER MIG® 216 power
switch is to be in the OFF position when installing work cable
and gun and when connecting
other equipment.
UNCRATING THE POWER MIG® 216
Cut banding and lift off cardboard carton. Cut banding
holding the machine to the skid. Remove foam and
corrugated packing material. Untape accessories from
Gas Bottle Platform. Unscrew the two wood screws
(at the Gas Bottle Platform) holding the machine to
the skid. Roll the machine off the skid assembly.
LOCATION
Locate the welder in a dry location where there is free
circulation of clean air into the brickwork in the back
and the louvers out the front. A location that minimizes
the amount of smoke and dirt drawn into the rear
brickwork reduces the chance of dirt accumulation
that can block air passages and cause overheating.
INPUT POWER, GROUNDING AND
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts such as
output terminals or internal wiring.
• All input power must be electrically disconnected before proceeding.
1. Before starting the installation, check with the local
power company if there is any question about
whether your power supply is adequate for the voltage, amperes, phase, and frequency specified on
the welder rating plate. Also be sure the planned
installation will meet the U.S. National Electrical
Code and local code requirements. This welder
may be operated from a single phase line or from
one phase of a two or three phase line.
2. Models that have multiple input voltages specified
on the rating plate (e.g. 208/230) are shipped connected for the highest voltage. If the welder is to be
operated on lower voltage, it must be reconnected
according to the instructions in Figure A.1 for dual
voltage machines.
WARNING
Make certain that the input power is electrically
disconnected before removing the screw on the
reconnect panel access cover.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 11

INSTALLATION
FIGURE A.1 — Dual Voltage Machine Input Connections
WARNING ADVERTISSEMENT ADVERTENCIA
Disconnect input power before inspecting
or servicing machine.
Do not operate with covers removed.
Do not touch electrically live parts.
Use CU wire only .
Install and Ground machine per National Electrical Code and local codes. Use Grounding Stud or Lug inside.
Only qualified persons should install, use, or service this equipment.
Consult instruction manual before installing or operating.
Débrancher l’alimentation d’entrée avant de réaliser l’inspection ou l’entretien de la machine.
Ne pas faire fonctionner sans les couvercles.
Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique.
Utiliser uniquement du fil CU.
Installer et mettre la machine à la terre conformément au Code Électrique National et aux réglementations locales.
Utiliser une Borne ou un Ergot de Terre à l’intérieur.
Seules des personnes qualifiées peuvent installer
Consulter le Manuel d’Instructions avant d’installer ou de faire fonctionner la machine.
Desconecte elcable de alimentación antes de iniciar caulquier inspeccion ó servicio.
No opere la máquina con las cubiertas removidas.
No toque las partes elécticas vivas.
Use solo cable con alambre de cobre.
Instale y aterrice la máquina de acuerdo a las normas eléctricas locales y nacionales. Use el Tornillo de
Tierra de la máquina.
Únicamente personal calificado debe instalar
Antes de instaler u poerar éste equipo consulte el Manual de Intruccion.
INPUT SUPPLY CONNECTION DIAGRAM
DIAGRAMME DE CONNEXION DE L’ALIMENTATION D’ENTRÉE
DIAGRAMA DE CONEXION DE LA FUENTE DE ENTRADA
Connect leads for
desired voltage range
Connecter les câbles
pour obtenir la tension
désirée.
Conecte cable selector
para el voltage de
alimentacion deseado.
, utilizar ó dar servicio a éste equipo.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels
DESCARGAS ELECTRICAS pueden matar
, utiliser ou réaliser l’entretien de cet appareil.
SINGLE PHASE
MONOPHASE
MONOFASICO
A-3 A-3
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
RECONNECT
RECONEXION
REBRANCHER
ALIMENTACION
INPUT
ENTRÉE
3. The 208/230 volts 50/60 Hz model POWER MIG is
shipped with a 10ft.(3.0m) input cable and plug
connected to the welder.
4. Have a qualified electrician connect a receptacle
(Customer Supplied) or cable to the input power
lines and the system ground per the U.S. National
Electrical Code and any applicable local codes.
OUTPUT POLARITY CONNECTIONS
The welder, as shipped from the factory, is connected
for electrode positive (+) polarity. This is the normal
polarity for GMAW.
If negative (–) polarity is required, interchange the
connection of the two cables located in the wire drive
compartment near the front panel. The electrode
cable, which is attached to the wire drive, is to be connected to the negative (–) labeled terminal and the
work lead, which is attached to the work clamp, is to
be connected to the positive (+) labeled terminal.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 12
A-4
INSTALLATION
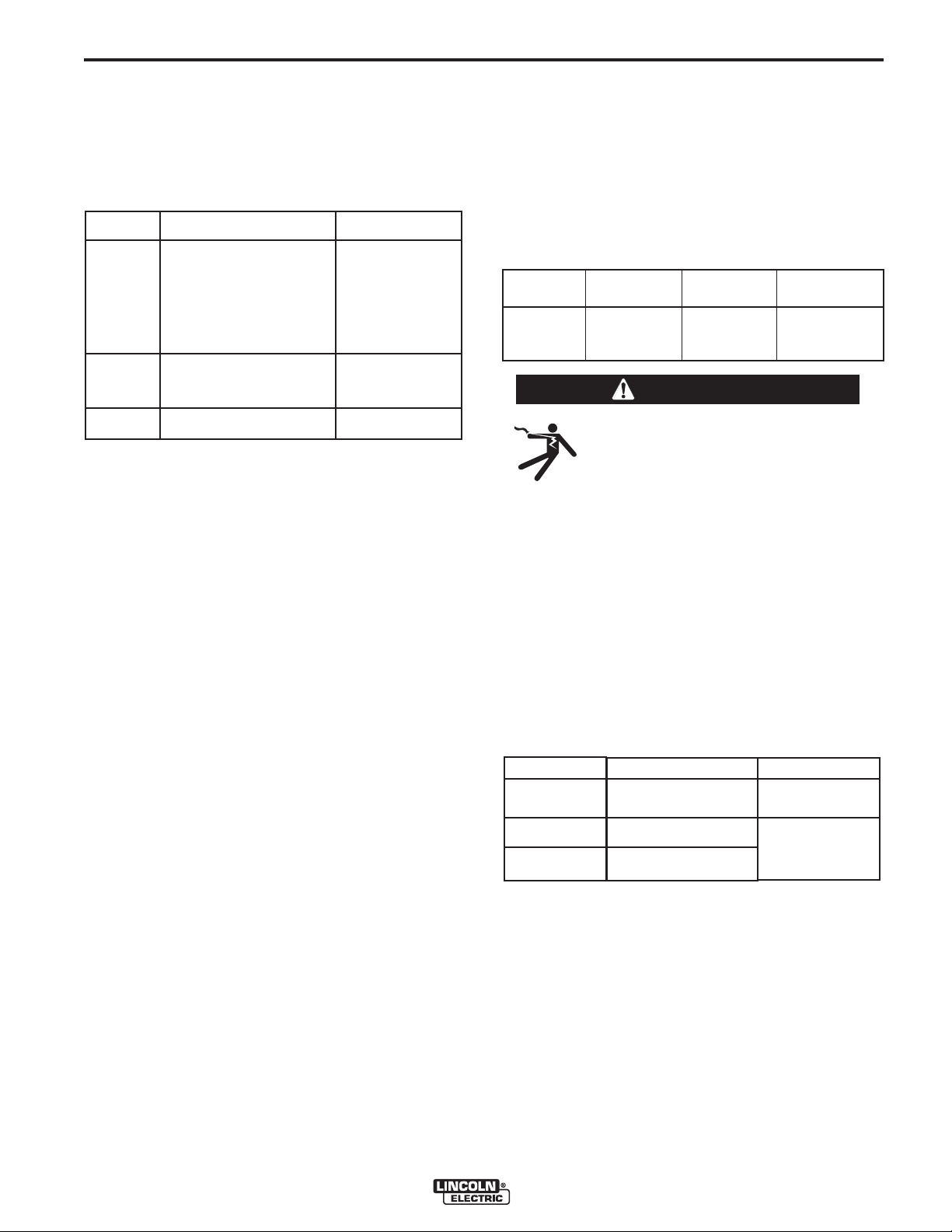
GUN AND CABLE INSTALLATION
The Magnum Pro 250L gun and cable provided with the
POWER MIG® 216 is factory installed with a liner for .035.045" (0.9-1.1 mm) electrode and an .035" (0.9 mm) contact
tip. Be sure that the contact tip, liner, and drive rolls all
match the size of the wire being used.
WARNING
Turn the welder power switch off before installing gun
and cable.
1. Lay the cable out straight.
2. Unscrew the Hand Screw on the drive unit front end
(inside wire feed compartment) until tip of screw no
longer protrudes into Gun Adapter opening as seen
from front of machine. (See Figure A.2)
3. Insert the male end of gun cable into the Gun Adapter
through the opening in front panel. Make sure connector
is fully inserted and tighten Hand Screw.
4. Connect the Gun Trigger Connector from the gun and
cable to the mating Receptacle outside the compartment
located left of the opening on the Front Panel. Make sure
that the keyways are aligned, insert and tighten retaining
ring.
SHIELDING GAS
[For Gas Metal Arc Welding(GMAW) Processes]
Customer must provide cylinder of appropriate type shielding gas for the process being used.
A gas flow regulator, for Argon blend gas, and an inlet gas
hose are factory provided with the POWER MIG® 216.
When using 100% CO2an additional adapter will be
required to connect the regulator to the gas bottle.
A-4
INSTALL SHIELDING GAS SUPPLY AS FOLLOWS:
1. Set gas cylinder on rear platform of POWER MIG® 216.
Hook chain in place to secure cylinder to rear of welder.
2. Remove the cylinder cap. Inspect the cylinder valves and
regulator for damaged threads, dirt, dust, oil or grease.
Remove dust and dirt with a clean cloth.
DO NOT ATTACH THE REGULATOR IF OIL, GREASE
OR DAMAGE IS PRESENT! Inform your gas supplier of
this condition. Oil or grease in the presence of high pressure oxygen is explosive.
3. Stand to one side away from the outlet and open the
cylinder valve for an instant. This blows away any dust or
dirt which may have accumulated in the valve outlet.
WARNING
Be sure to keep your face away from the valve outlet
when “cracking” the valve.
4. Attach the flow regulator to the cylinder valve and tighten
the union nut(s) securely with a wrench.
NOTE: If connecting to 100% CO
regulator adapter must be installed between the regulator and cylinder valve. If adapter is equipped with a plastic washer, be sure it is seated for connection to the CO
cylinder.
5. Attach one end of the inlet gas hose to the outlet fitting of
the flow regulator, the other end to the POWER MIG®
216 rear fitting, and tighten the union nuts securely with
a wrench.
6. Before opening the cylinder valve, turn the regulator
adjusting knob counterclockwise until the adjusting
spring pressure is released.
7. Standing to one side, open the cylinder valve slowly a
fraction of a turn. When the cylinder pressure gauge
pointer stops moving, open the valve fully.
cylinder, an additional
2
2
WARNING
WARNING
CYLINDER may explode if
damaged.
• Gas under pressure is explosive.
Always keep gas cylinders in an
upright position and always keep
chained to undercarriage or stationary
support.
See American National Standard Z-49.1, “Safety in
Welding and Cutting” published by the American
Welding Society.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Never stand directly in front of or behind the flow regulator when opening the cylinder valve. Always stand to
one side.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8. The flow regulator is adjustable. Adjust it to the flow rate
recommended for the procedure and process being used
before making the weld.
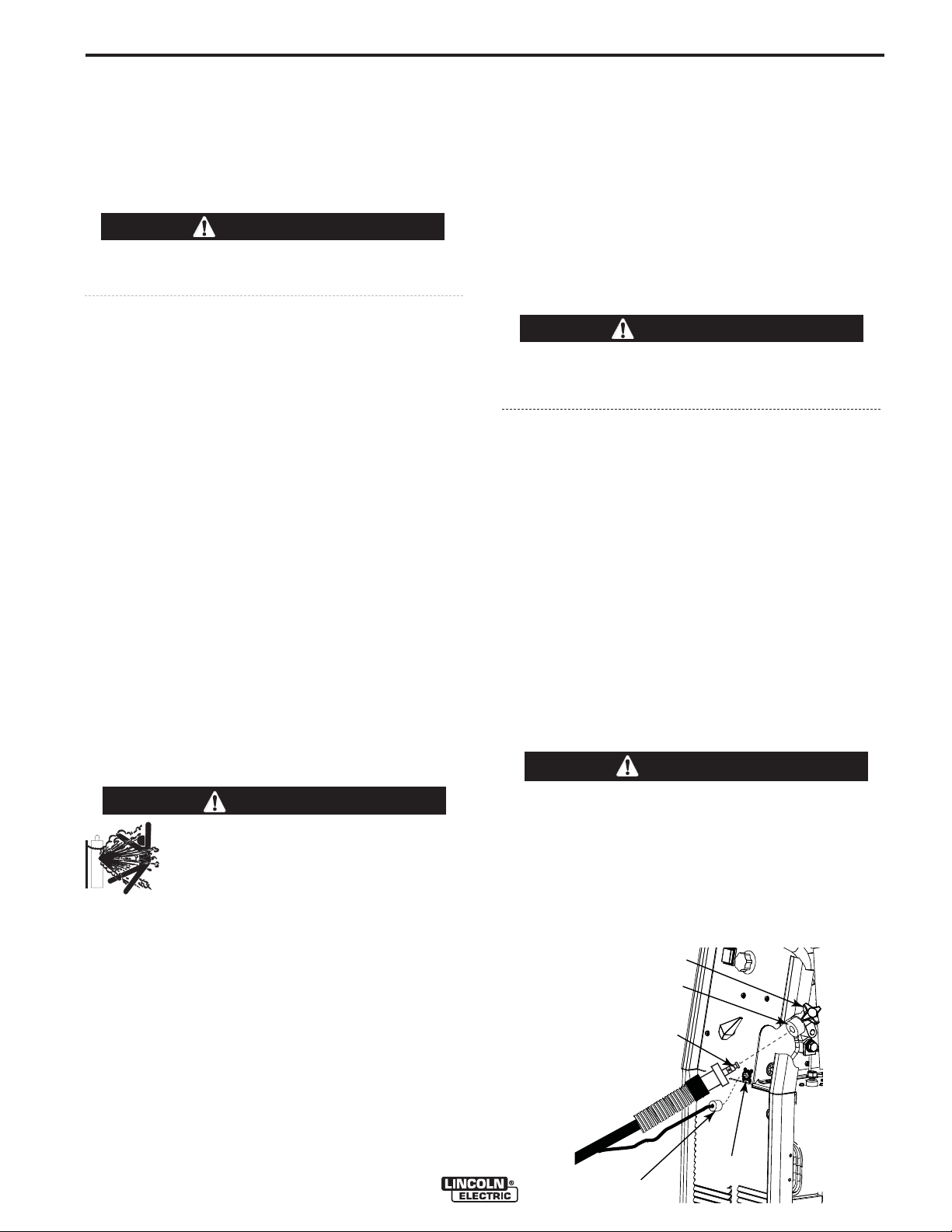
FIGURE A.2
Hand Screw
Gun Adapter
Male End
Gun and Cable
Receptacle
Gun Trigger
Connector
Page 13
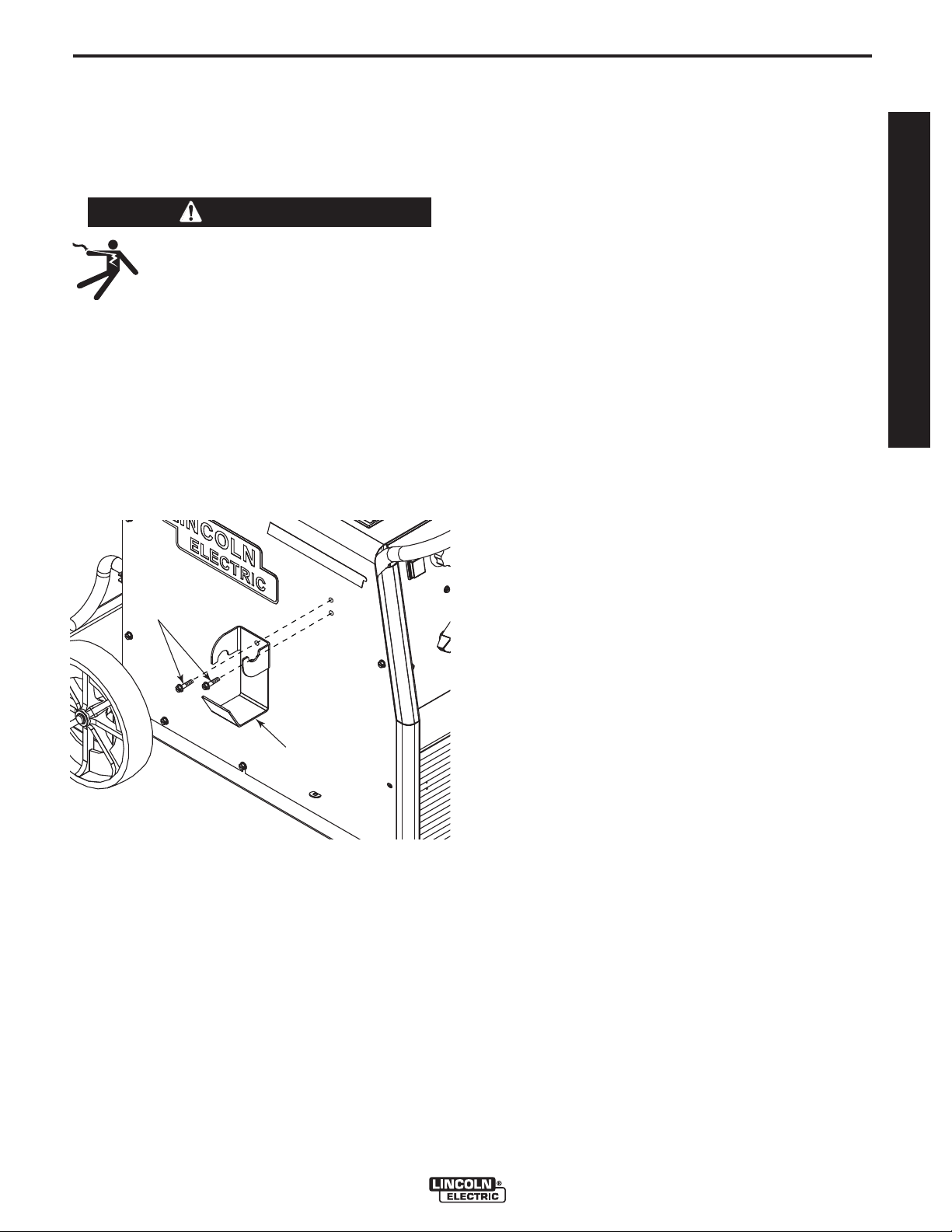
A-5
INSTALLATION
COIL CLAW™ INSTALLATION
The Coil Claw™ and mounting screws are provided
as an optional accessory for the POWER MIG® 216.
This user-install accessory provides cable management for the machine.
WARNING
Turn the welder power switch OFF
before installing Coil Claw™.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Unwrap Coil Claw™ from its protective paper and
remove the bag of mounting screws from the back
of the Coil Claw™.
2. Mount
ing screws to the left side of the machine, when
viewed from the front. Make sure the Coil Claw™ is
firmly mounted. (See Figure A.3)
the Coil Claw™ using the provided mount-
A-5
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
MOUNTING
SCREWS
FIGURE A.3
COIL CLAW™
POWER MIG® 216
Page 14

B-1
OPERATION
Read entire Operation section before
operating the POWER MIG® 216.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live
parts or electrode with skin or
wet clothing. Insulate yourself
from work and ground.
• Always wear dry insulating
gloves.
FUMES AND GASES can be
dangerous.
• Keep your head out of fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing
zone.
B-1
WELDING SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
• Keep flammable material away.
• Do not weld on closed containers.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes
and skin.
• Wear eye, ear and body protection.
Observe all safety information throughout
this manual.
------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 15
B-2 B-2
3
2
1
4
5
OPERATION
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The POWER MIG® 216 is a complete semiautomatic
DC voltage arc welding machine built to meet NEMA
specifications. It combines a tapped transformer voltage power source with a constant speed wire feeder
to form a reliable and robust performance welding
system. A simple control scheme, consisting of continuous full range wire feed speed control, and 7 output
voltage tap selections provides versatility with ease of
use and accuracy. An enhanced feature to the
POWER MIG® 216, is that it is Magnum 100SG Spool
Gun ready.
Other features include a 2" (51 mm) O.D. wire reel
spindle with adjustable brake, an integral gas cylinder
mounting undercarriage, an adjustable Argon blend
flow regulator with cylinder pressure gauge and inlet
hose, a 15 ft. (3.6 m) Magnum Pro 250L GMAW gun
and cable with fixed (flush) nozzle, a 10 ft. (3.0 m)
power cable with plug, and a 10 ft. (3.0 m) work cable
with clamp.
Optional Magnum Spool Gun, Adapter kits and Dual
Cylinder Mounting kit for push feeding with standard
built in feeder are also available.
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES AND
EQUIPMENT
LIMITATIONS
The output voltage/current of the POWER MIG® 216
is subject to vary if the input power to the machine
varies, due to its tapped transformer power topology.
In some cases an adjustment of WFS preset and/or
voltage tap selection may be required to accommodate a significant drift in input power.
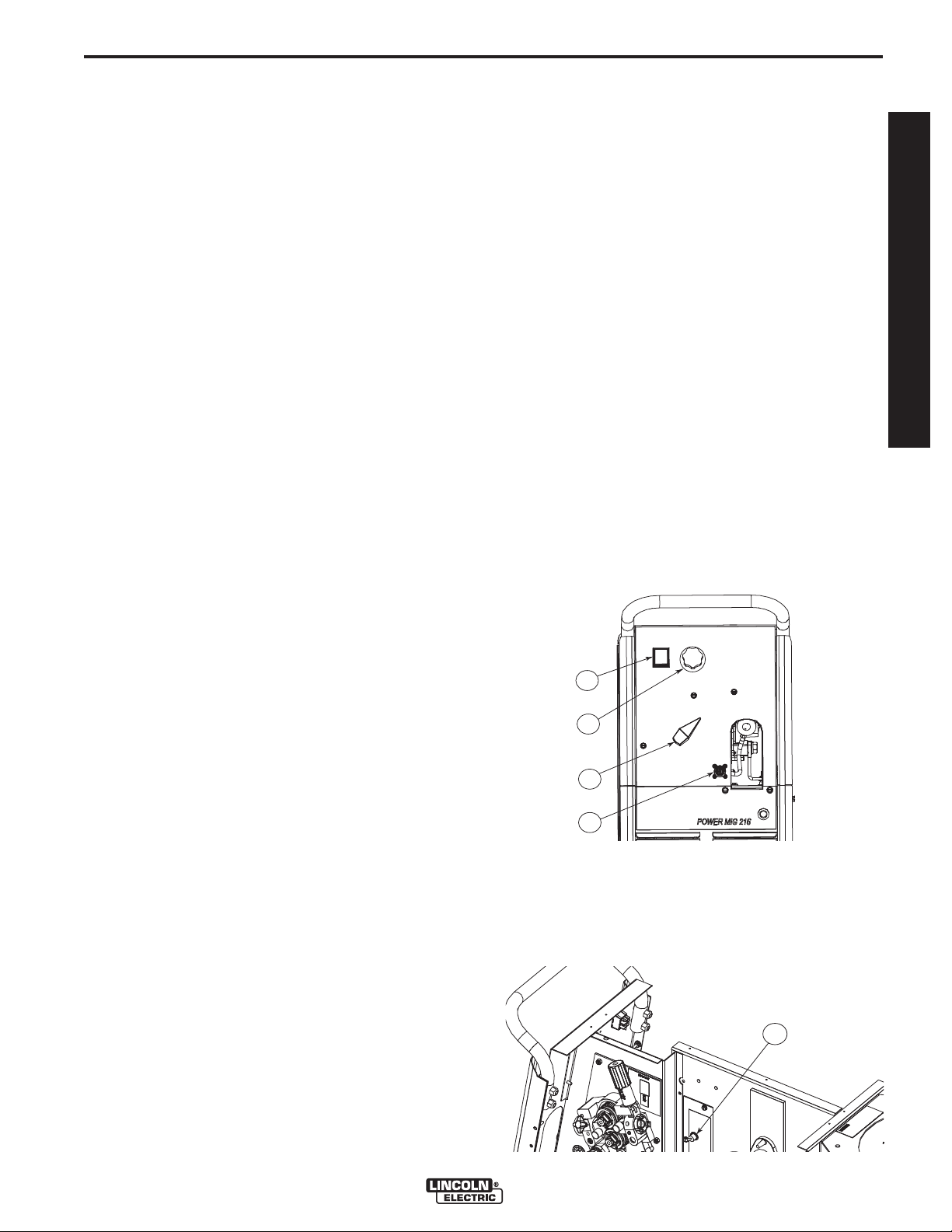
DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS
See Figure B.1
1. Power ON/OFF Switch - Press the switch to "ON"
position to energize the POWER MIG® 216.
2. Voltage Control - Seven voltage tap selections are
provided labeled "A" (minimum voltage) through "G"
(maximum voltage). It should only be adjusted
when NOT welding. The control selection can be
preset to the setting specified on the Application
Chart / Procedure Decal on the inside of the wire
compartment door or Section F of this Instruction
Manual.
3. Wire Speed Control - This controls the wire feed
speed from 50 – 700 inches per minute (1.2 – 17.8
m/min). Wire speed is not affected when changes
are made in the voltage control.
4. 4-Pin Connector - For Push Gun and Spool Gun
Operations.
FIGURE B.1
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
The POWER MIG® 216 is recommended for GMAW
processes using 10 to 44 lb (4.5 to 20 kg) 2" (51 mm)
I.D. spools of .025" through .045" (0.6 – 1.1 mm) solid
wire, .035" (0.9 mm) stainless, 3/64" (1.2 mm) aluminum, .035” (0.9 mm), .045" (1.1 mm) Outershield
and .045”(1.1mm) Ultracore® as well as .035" (0.9
mm) and .045" (1.1 mm) Innershield®self-shielding
electrodes.
The POWER MIG® 216 is factory equipped to feed
.035" (0.9 mm) electrodes. It also includes a 200A,
60% duty cycle (or 250A, 40% duty cycle) rated, 15 ft.
(3.6 m) GMAW gun and cable assembly equipped for
these wire sizes. Use of GMAW processes requires a
supply of shielding gas.
®
5. Magnum Push Gun and Spool Gun toggle
switch - Toggle the switch (Item 5 see Figure B.2)
to select between push gun and spool gun. When
either operation is selected, insert the cable to 4-pin
Connector. (Item 4, See Figure B.1)
FIGURE B.2
WELDING CAPABILITY
The POWER MIG® 216 is rated at 216 amps @ 22
volts, at a 30% duty cycle based on a ten minute cycle
time. It is capable of higher duty cycles at lower output
currents. The tapped transformer design makes it
well suited for use with most portable or in-plant generating systems.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 16
OPERATION
B-3 B-3
WIRE DRIVE ROLL
The drive rolls installed with the POWER MIG® 216
have two grooves, one for .035”(0.9mm) wire and the
other for .045”(1.1mm) wire. Drive roll size is indicated
by the stenciling on the exposed side of the drive roll.
WIRE SIZE CONVERSION PARTS
The POWER MIG® 216 is rated to feed .025” through
.045" (0.6-1.1mm) solid or cored electrode sizes.
The drive roll kits and Magnum Pro 250L gun and
cable parts are available to feed different sizes and
types of electrodes. See Accessories and
Maintenance sections of this Instruction Manual.
PROCEDURE FOR CHANGING
DRIVE AND IDLE ROLL SETS
1. Turn OFF the power source.
2. Release the pressure on the idle roll by swinging
the adjustable pressure arm down toward the back
of the machine. Lift the cast idle roll assembly and
allow it to sit in an upright position.
3. Remove the outside wire guide retaining plate by
loosening the two large knurled screws.
4. Twist the drive roll retaining mechanism to the
unlocked position as shown below and remove the
drive rolls.
FIGURE B.3
WIRE REEL LOADING - SPOOLS
OR COILS
To Mount 10 to 44 Lb. (4.5-20 kg) Spools
(12"/300 mm Diameter) or 14Lb.(6 Kg)
Innershield Coils:
(For 13-14 lb. (6 Kg) Innershield coils, a K435 Coil
Adapter must be used).
1. Open the Wire Drive Compartment Door
2. Depress the Release Bar on the Retaining Collar
and remove it from the spindle.
3. Place the spool on the spindle making certain the
spindle brake pin enters one of the holes in the
back side of the spool
Note: The arrow marked on the spindle lines up
with the brake holding pin to assist in lining
up a hole. Be certain the wire comes off the
reel in a direction so as to de-reel from the
top of the coil.
4. Re-install the Retaining Collar. Make sure that the
Release Bar “pops up” and that the collar retainers
fully engage the retaining ring groove on the spindle.
UNLOCKED POSITION
(See Figure B.3)
5. Remove the inside wire guide plate.
6. Replace the drive rolls and inside wire guide with a
set marked for the new wire size.
NOTE: Be sure that the gun liner and contact tip
are also sized to match the selected wire
size.
7. Manually feed the wire from the wire reel, over the
drive roll groove and through the wire guide and
then into the brass bushing of the gun and cable
assembly.
8. Replace the outside wire guide retaining plate by
tightening the two large knurled screws. Reposition
the adjustable pressure arm to its original position
to apply pressure. Adjust pressure as necessary.
LOCKED POSITION
POWER MIG® 216
Page 17

B-4
OPERATION
B-4
TO START THE WELDER
Turn the “Power Switch” switch to “ON”. With the desired voltage
and wire speed selected, operate the gun trigger for welder output
and to energize the wire feed motor.
The pressure arm controls the amount of force the drive
rolls exert on the wire. Proper adjustment of pressure
arm gives the best welding performance. For best
results, set pressure arm to the suggested value.
FEEDING WIRE ELECTRODE
Set the pressure arm as follows (See Figure B.4):
WARNING
When triggering, the electrode and
drive mechanism are electrically
“hot” relative to work and ground and
remain “hot” for several seconds
after the gun trigger is released.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: Check that drive rolls, guide plates and gun
parts are proper for the wire size and type being used.
Refer to Table C.1 in Accessories section.
1. Turn the spool until the free end of the electrode is
accessible.
2. While securely holding the electrode, cut off the
bent end and straighten the first six inches. If the
electrode is not properly straightened, it may not
feed properly through the wire drive system.
WIRE DRIVE CONFIGURATION
See Figure B.5
Aluminum wires between 1 and 3
Cored wires between 3 and 4
Steel, Stainless wires between 4 and 6
FIGURE B.4
CORED WIRES
OU TE R S HI E L D
METAL SHIELD
INNERSHIELD
1
3
5
SOLID WIRES
2
4
6
ALUMINUM
STEEL
STAINLESS
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
3. Release the pressure on the idle roll by swinging
the adjustable pressure arm down toward the back
of the machine. Lift the cast idle roll assembly and
allow it to sit in an upright position. Leave the outer
wire guide plate installed. Manually feed the wire
through the incoming guide bushing and through
the guide plates (over the drive roll groove). Push a
sufficient wire length to assure that the wire has fed
into the gun and cable assembly without restriction.
Reposition the adjustable pressure arm to its original position to apply pressure to the wire.
4. Press gun trigger to feed the electrode wire through
the gun.
IDLE ROLL PRESSURE SETTING
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power source before installation or
changing drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode
and drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
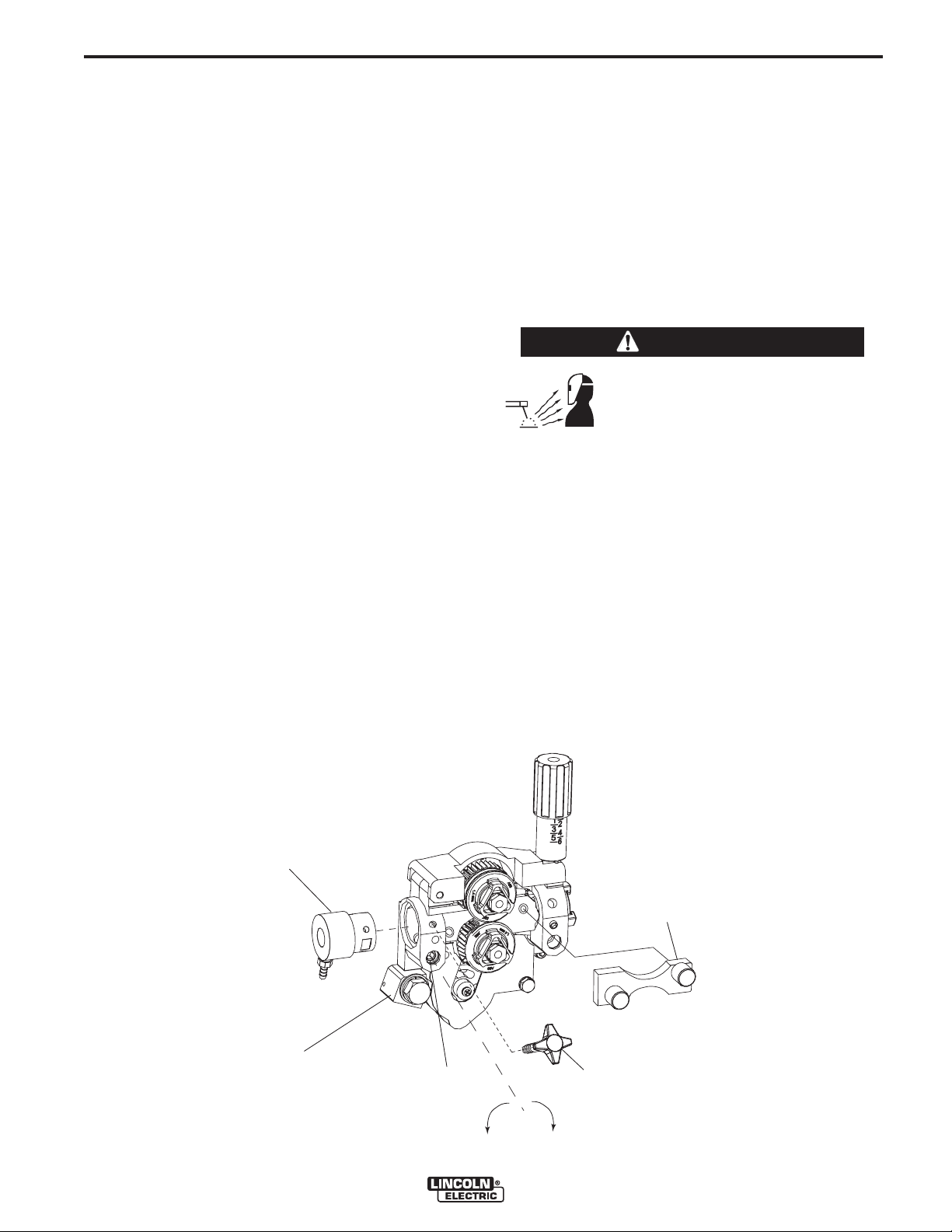
Changing the Gun Adapter
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power source before installation or
changing drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode
and drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Tools required:
• 1/4" hex key wrench.
NOTE: Some gun adapters do not require the use of
the hand screw.
1. Turn power OFF at the welding power source.
2. Remove the welding wire from the wire drive.
3. Remove the hand screw from the wire drive.
4. Remove the welding gun from the wire drive.
Page 18
B-5 B-5
5. Loosen the socket head cap screw that holds the
connector bar against the gun adapter.
Important: Do not attempt to completely
remove the socket head cap screw.
OPERATION
3. Press the trigger to feed the wire electrode through
the gun and cable. For solid wire cut the electrode
within approximately 3/8" (10 mm) of the end of the
contact tip [3/4" (20 mm) for Outershield®].
6. Remove the outer wire guide, and push the gun
adapter out of the wire drive. Because of the precision fit, light tapping may be required to remove
the gun adapter.
4. When welding with gas, turn on the gas supply and
set the required flow rate (typically 30-40 CFH; 1419 liters/min).
7. Disconnect the shielding gas hose from the gun
adapter, if required.
8. Connect the shielding gas hose to the new gun
adapter, if required.
9. Rotate the gun adapter until the hand screw hole
5. Connect work cable to metal to be welded. Work
clamp must make good electrical contact to the
work. The work must also be grounded as stated in
“Arc Welding Safety Precautions”.
aligns with the hand screw hole in the feed plate.
Slide the gun adapter into the wire drive and verify
the hand screw holes are aligned.
10. Tighten the socket head cap screw.
11. Insert the welding gun into the gun adapter and
tighten the hand screw.
• When using an open arc process, it
is necessary to use correct eye,
head, and body protection.
WARNING
MAKING A WELD
1. Check that the electrode polarity is correct for the
process being used, then turn the power switch ON.
2. Set desired arc voltage tap and wire speed for the
particular electrode wire, material type and thickness, and gas (for MIG and Outershield
used. Use the Application Chart on the door inside
the wire compartment as a quick reference for
some common welding procedures.
NOTE: Application Chart can also be found in
Section F of this Instruction Manual.
GUN ADAPTER
®
) being
Figure B.5
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
6. Position electrode over joint. End of electrode may
be lightly touching the work.
7. Lower welding helmet, close gun trigger, and
begin welding. Hold the gun so that the contact tip
to work distance is about 3/8" (10 mm) [3/4" (20
mm) for Outershield®].
8. To stop welding, release the gun trigger and then
pull the gun away from the work after the arc goes
out.
CONNECTOR BLOCK
SOCKET HEAD
CAP SCREW
LOOSEN TIGHTEN
POWER MIG® 216
OUTER WIRE GUIDE
HAND SCREW
Page 19

OPERATION
9. When no more welding is to be done, close valve
on gas cylinder (if used), momentarily operate gun
trigger to release gas pressure, and turn OFF
POWER MIG® 216.
NOTE: When using Innershield electrode, the gas
nozzle may be removed from the insulation
on the end of the gun and replaced with the
gasless nozzle. This will give improved visibility and eliminate the possibility of the gas nozzle overheating.
AVOIDING WIRE FEEDING
PROBLEMS
Wire feeding problems can be avoided by observing
the following gun handling procedures:
1. Do not kink or pull cable around sharp corners.
2. Keep the gun cable as straight as possible when
welding or loading electrode through cable.
3. Do not allow dolly wheels or trucks to run over
cables.
4. Keep cable clean by following maintenance instruc-
tions.
5. Use only clean, rust-free electrode. The Lincoln
electrodes have proper surface lubrication.
6. Replace contact tip when the arc starts to become
unstable or the contact tip end is fused or
deformed.
7. Keep wire reel spindle brake tension to minimum
required to prevent excess reel over-travel which
may cause wire “loop-offs” from coil.
8. Use proper drive rolls and wire drive idle roll pres-
sure for wire size and type being used.
B-6 B-6
WIRE FEED OVERLOAD
PROTECTION
The POWER MIG® 216 has solid state overload protection of the wire drive motor. If the motor becomes
overloaded, the protection circuitry turns off the wire
drive motor and gas solenoid. Check for proper size
tip, liner, and drive rolls, for any obstructions or bends
in the gun cable, and any other factors that would
impede the wire feeding. To resume welding, simply
pull the trigger. There is no circuit breaker to reset, as
the protection is done with reliable solid state electronics.
WELDING THERMAL OVERLOAD
PROTECTION
The POWER MIG® 216 has built-in protective thermostats that respond to excessive temperature. They
open the wire feed and welder output circuits if the
machine exceeds the maximum safe operating temperature because of a frequent overload, or high
ambient temperature plus overload. The thermostats
automatically reset when the temperature reaches a
safe operating level and welding and feeding are
allowed again, when gun is retriggered.
WELDING PROCEDURE
INFORMATION
NOTE: See inside cover of machine or Section F of this
Instruction Manual for additional, commonly used welding
procedure.
LEARNING TO WELD
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
FAN CONTROL
The fan is designed to come on when input power is
applied to the POWER MIG® 216 and go off when
power is removed.
INPUT LINE VOLTAGE VARIATIONS
High Line Voltage — Higher than rated input voltage
will result in output voltages higher than normal for a
given tap setting. If your input line is high, you may
want to select a lower voltage tap than given on the
recommended procedure chart.
Low Line Voltage — You may not be able to get
maximum output from the machine if the line voltage
is less than rated input. The unit will continue to weld,
but the output may be less than normal for a given tap
setting. If your input line is low, you may want to select
a higher voltage tap than given on the recommended
procedure chart.
POWER MIG® 216
Welding is a skill that can only be learned by practicing. No one can become an accomplished welder
simply by reading about it. The following link
“Learning to Weld” document will help the inexperienced operator to understand the basics about wire
welding and provide guidance to help develop this
skill.
“Learning to Weld” link:
http://content.lincolnelectric.com/pdfs/products/
navigator/im/LTW1tri.pdf
Page 20
C-1 C-1
ACCESSORIES
DRIVE ROLL KITS
Refer to Table C.1 for various drive roll kits that are
available for the POWER MIG® 216.The item in Bold
is supplied standard with the POWER MIG® 216.
TABLE C.1
Wire Size Drive Roll Kit
Solid
Steel
Cored
Aluminum
.023”-.030” (0.6-0.8 mm)
.035” (0.9 mm) KP1696-035S
.045” (1.1 mm) KP1696-045S
.035”-.045” (0.9-1.1mm) KP1696-1
.040” (1.0mm) KP1696-2
.035” (0.9 mm) KP1697-035C
.045” (1.1 mm) KP1697-045C
3/64” (1.2 mm) KP1695-3/64A
KP1696-030S
DUAL CYLINDER MOUNTING KIT
(K1702-1)
Permits stable side-by-side mounting of two full size
228.6mm dia x 1.524m high(9" dia. x 5' high) gas
cylinders with “no lift” loading. Simple installation and
easy instructions provided. Includes upper and lower
cylinder supports, wheel axles and mounting hardware.
SMALL SPOOL SPINDLE ADAPTER
(K468)
ALTERNATIVE MAGNUM GMAW
GUN AND CABLE ASSEMBLIES
The following Magnum Pro 250L gun and cable
assemblies are separately available for use with the
POWER MIG® 216. Each is rated at 250 amps 40%
duty cycle and is equipped with the integrated connector, twist-lock trigger connector, fixed nozzle and insulator, and includes a liner, diffuser, and contact tips for
the wire sizes specified:
English Wire Metric Wire
Length Part No. Size Size
10' (3.0 m)
12' (3.6 m) KP42-4045-15 .035” – .045" 0.9 – 1.1 mm
15' (4.5 m)
WARNING
• Unplug or Disconnect all input power
from the POWER MIG® 216 before
installing the Spool Gun and Kit.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAGNUM GUN CONNECTION KIT
(K466-6)
Using the optional K466-6 Magnum Connection kit for
the POWER MIG® 216 permits use of standard
Magnum 200, 300 or 400 gun and cable assemblies.
OPTIONAL SPOOL GUNS AND
ADAPTERS
The K468 spindle adapter allows the use of 8" diameter small spools.
SPINDLE ADAPTER FOR 14 LBS.
COILS (K435)
The K435 spindle adapter allows 14lbs. (6kg.)
Innershield Coils to be mounted on 2” (51mm) O.D.
spindle.
POWER MIG® 216
The
POWER MIG® 216
following optional spool guns:
SPOOL GUN
Magnum 100SG
(K2532-1)
Magnum SG
(K487-25)
Magnum 250LX
(K2490-1)
Spool gun Adapter (K2703-1)
This kit is designed to allow the Magnum SG or Magnum
250LX spool gun to operate with the
The kit includes the gas solenoid, gas lines, wiring harness
and gun connection panel. The gun connection panel features a 6 pin ms-type connector for the Magnum SG spool
gun and a 7 pin ms-type connector for the Magnum 250LX
spool gun and a selector switch to choose which gun you
are using.
NOTE: The K2703-1 spool gun adapter disables the
Magnum 100SG capability.
130amp 30% Duty Cycle
250Amp 60% Duty Cycle
300 Amp 60% Duty Cycle
is capable of operating with the
RATING
Light Duty
Medium Duty
Heavy Duty
POWER MIG® 216
ADAPTER
Factory Ready
No Adapter Required
Spool Gun Adapter
K2703-1
.
Page 21

C-2
ACCESSORIES
MAKING A WELD WITH THE SPOOL GUN
ADAPTER KIT AND SPOOL GUN
INSTALLED
CAUTION
In either toggle switch position, closing either gun
trigger will cause the electrode of both guns to be
electrically “HOT”. Be sure unused gun is positioned so electrode or tip will not contact metal
case or other metal common to work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Setting the toggle switch to “Push Gun” position
disables the spool gun operation and spool gun
gas solenoid valve. Closing the gun trigger enables
the push gun welding and both electrodes will be
electrically “HOT”.
2. Setting the toggle switch to the “Spool Gun” position disables the built-in push gun operation and
feeder gas solenoid valve. It will also enables the
spool gun operation and spool gun gas solenoid
valve. Closing the spool gun trigger enables spool
gun welding and both electrodes will be electrically
“HOT”.
C-2
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
3. Operation with POWER MIG® 216:
• Turn the POWER MIG® 216 input power ON.
• Adjusting the voltage tap control will increase or
decrease your welding voltage.
• Adjusting the wire speed control on the spool
gun will increase or decrease the spool gun
wire feed speed.
NOTE: Adjusting the wire feed speed control on the
Machineʼs Front Panel has no affect on the spool
gunʼs wire feed speed.
4. Refer to the welding procedure on the machine or
Section F of this Instruction Manual for initial aluminum settings. Make a test weld to determine the
final settings.
5. Set the spool gun selector switch to “Push Gun”
position to return to push gun operation.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 22

D-1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
MAINTENANCE
• Be sure the nozzle insulator is fully screwed
onto the gun tube and does not block the gas
holes in the diffuser.
D-1
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Have an electrician install and
service this equipment.
• Turn the input power OFF at the
fuse box before working on
equipment
• Do not touch electrically hot
parts.
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
In extremely dusty locations, dirt may clog the air passages causing the welder to run hot. Blow dirt out of
the welder with low-pressure air at regular intervals to
eliminate excessive dirt and dust build-up on internal
parts.
The fan motors have sealed ball bearings which
require no service.
DRIVE ROLLS AND GUIDE PLATES
After every coil of wire, inspect the wire drive mechanism. Clean it as necessary by blowing with low pressure compressed air. Do not use solvents for cleaning
the idle roll because it may wash the lubricant out of
the bearing. All drive rolls are stamped with the wire
sizes they will feed. If a wire size other than that
stamped on the roll is used, the drive roll must be
changed.
• Slip the appropriate gas nozzle onto the nozzle
insulator. Either a standard .50" (12.7 mm) or
optional .62" (15.9 mm) I.D. slip-on gas nozzle
may be used and should be selected based on
the welding application.
• Adjust the gas nozzle as appropriate for the
GMAW process to be used. Typically, the contact tip end should be flush to .12" (3.2 mm)
extended for the short-circuiting transfer
process and .12" (3.2 mm) recessed for spray
transfer.
GUN TUBES AND NOZZLES
1. Replace worn contact tips as required.
2. Remove spatter from inside of gas nozzle and from
tip after each 10 minutes of arc time or as required.
GUN CABLE CLEANING
To help prevent feeding problems, clean cable liner
after using approximately 300 pounds (136 kg) of
electrode. Remove the cable from the wire feeder and
lay it out straight on the floor. Remove the contact tip
from the gun. Using an air hose and only partial pressure, gently blow out the cable liner from the gas diffuser end.
CAUTION
For instructions on replacing or changing drive roll,
see “Wire Drive Rolls” in Operation section.
CONTACT TIP AND GAS NOZZLE
INSTALLATION
1. Choose the correct size contact tip for the electrode being used (wire size is stenciled on the side
of the contact tip) and screw it snugly into the gas
diffuser.
2. Screw the appropriate fixed gas nozzle fully onto
the diffuser. Either the standard .50" (12.7 mm)
flush nozzle or other optional flush or recessed
(spray arc) nozzle sizes may be used. (See Table
D.2 in this section.)
3. If using optional adjustable slip-on nozzles, see
Table D.2 in this section.
POWER MIG® 216
Excessive pressure at the beginning of the cleaning procedure may cause the dirt to form a plug.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Flex the cable over its entire length and again blow
out the cable. Repeat this procedure until no further
dirt comes out. If this has been done and feed problems are experienced, try liner replacement, and refer
to trouble shooting section on rough wire feeding.
Page 23
D-2
MAINTENANCE
LINER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT
NOTE: Changing the liner for a different wire size
requires replacement of the gas diffuser per Table D.1
to properly secure the different liner.
TABLE D.1
Fixed
Diameter of Liner Part on End of Part No.
Replacement Size Stencilled Gas Diffuser
Electrodes Used Number Liner Bushing (and Stencil)
.025”-.030" Steel KP42-25-15 .030” (0.8 mm)
(0.6-0.8 mm)
.035”-.045" Steel KP42-4045-15 .045” (1.1 mm) KP2746-1
(0.9-1.1 mm)
3/64" Aluminum KP42-4045-15 3/64" (1.2 mm)
(1.2 mm)
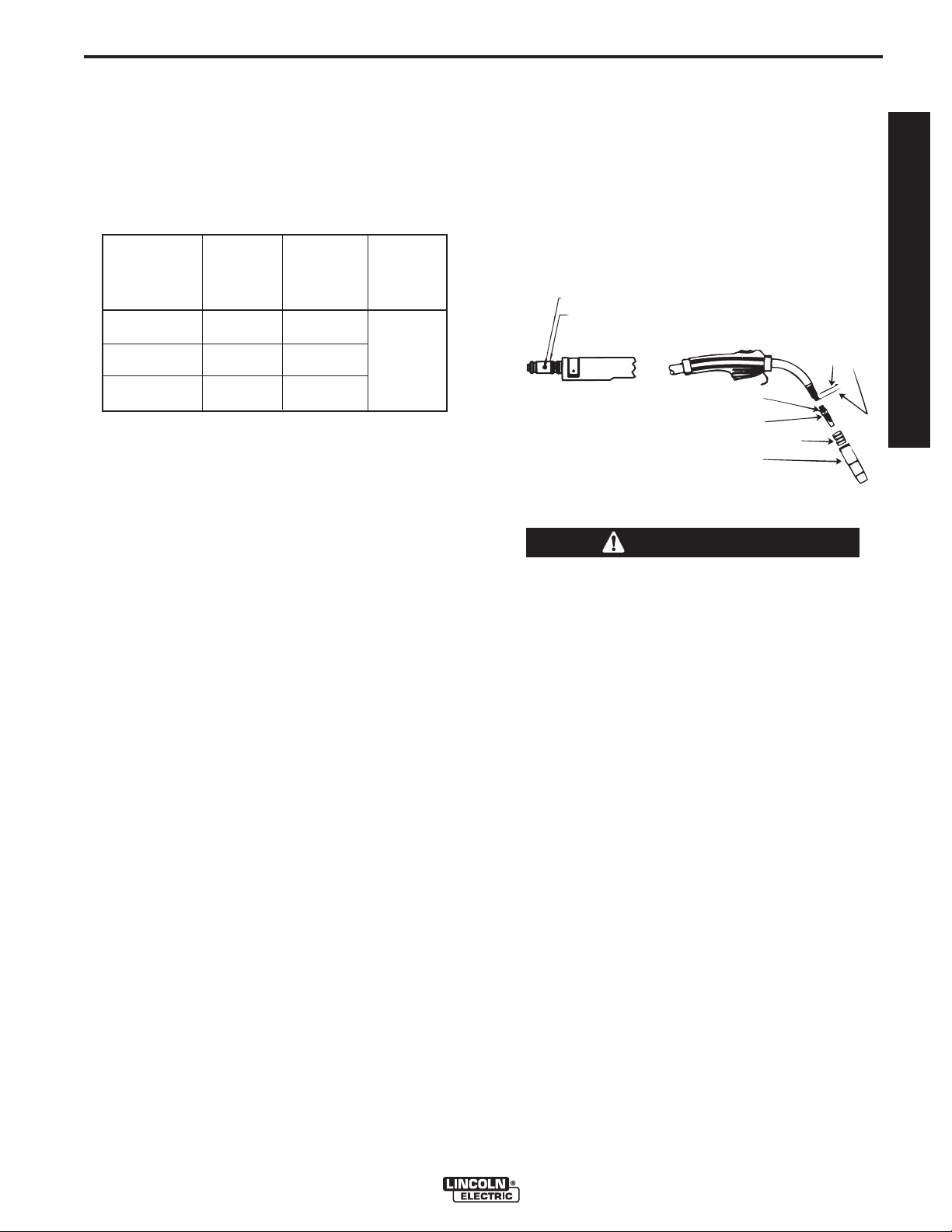
LINER REMOVAL, INSTALLATION AND TRIMMING
INSTRUCTIONS FOR MAGNUM PRO 250L
Nozzle
D-2
7. Screw the gas diffuser onto the end of the gun tube
and securely tighten. Be sure the gas diffuser is
correct for the liner being used. (See table and diffuser stencil.)
8. Tighten the set screw in the side of the gas diffuser
against the cable liner using a 5/64" (2.0 mm) Allen
wrench.
FIGURE D.1
SET SCREW
BRASS CABLE CONNECTOR
SET SCREW
GAS DIFFUSER
NOZZLE INSULATOR (IF USED)
GAS NOZZLE
1-1/4"
(31.8mm)
LINER
TRIM
LENGTH
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
NOTE: The variation in cable lengths prevents the
interchangeability of liners between guns. Once a liner
has been cut for a particular gun, it should not be
installed in another gun unless it can meet the liner
cutoff length requirement. Liners are shipped with the
jacket of the liner extended the proper amount.
1. Remove the gas nozzle and nozzle insulator, if
used, to locate the set screw in the gas diffuser
which is used to hold the old liner in place. Loosen
the set screw with a 5/64" (2.0 mm) Allen wrench.
2. Remove the gas diffuser from the gun tube.
3. Lay the gun and cable out straight on a flat surface.
Loosen the set screw located in the brass connector at the feeder end of the cable and pull the liner
out of the cable.
4. Insert a new untrimmed liner into the connector
end of the cable. Be sure the liner bushing is stencilled appropriately for the wire size being used.
5. Fully seat the liner bushing into the connector.
tighten the set screw on the brass cable connector.
The gas diffuser, at this time, should not be
installed onto the end of the gun tube.
CAUTION
This screw should only be gently tightened.
Overtightening will split or collapse the liner and
cause poor wire feeding.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. With the gas diffuser still removed from the gun
tube, be sure the cable is straight, and then trim
the liner to the length shown in Figure D.1.
Remove any burrs from the end of the liner.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 24
D-3
MAINTENANCE
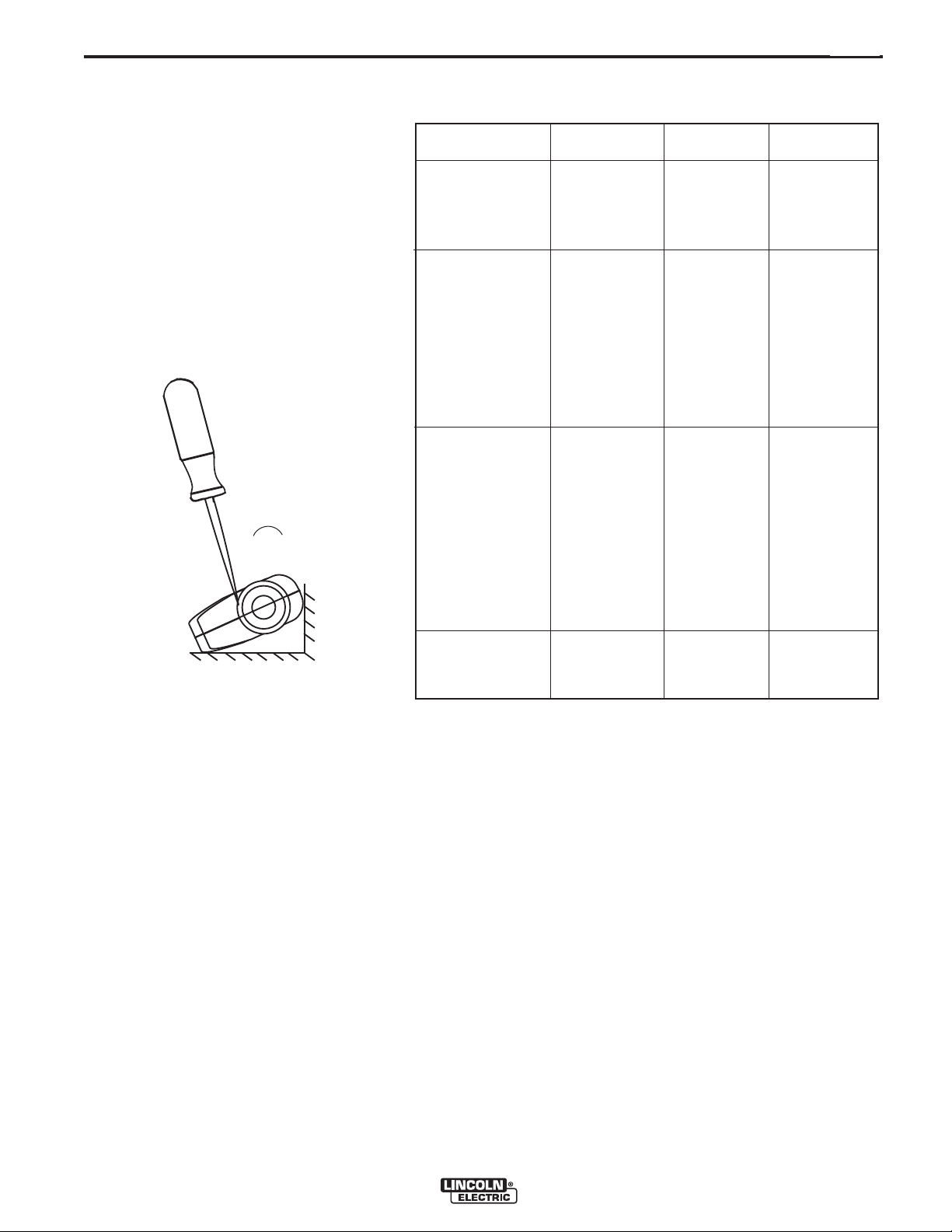
GUN HANDLE DISASSEMBLY
The internal parts of the gun handle may be
inspected or serviced if necessary.
The gun handle consists of two halves that are
held together with a collar on each end. To
open up the handle, turn the collars approximately 60 degrees counterclockwise (the same
direction as removing a right hand thread) until
the collar reaches a stop. Then pull the collar
off the gun handle. If the collars are difficult to
turn, position the gun handle against a corner,
place a screwdriver against the tab on the collar and give the screwdriver a sharp blow to
turn the collar past an internal locking rib.
Counterclockwise
„
D-3
TABLE D.2
ACCESSORIES AND EXPENDABLE REPLACEMENT PARTS
FOR MAGNUM PRO 250L GUN AND CABLE ASSEMBLIES
Description Part No. Size Size
CABLE LINER
For 15' (4.5 m) or KP42-25-15 .025" – .030" 0.6 – 0.8 mm
shorter Cable KP42-4045-15 .035" – .045" 0.9 – 1.1 mm
KP42-4045-15 3/64" 1.2 mm
CONTACT TIPS
Standard Duty KP2744-025 .025" 0.6 mm
KP2744-030 .030" 0.8 mm
KP2744-035 .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045 .045" 1.1 mm
Tapered KP2744-030T .030" 0.8 mm
KP2744-035T .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045T .045" 1.1 mm
Tab (For Aluminum) KP2744-364A 3/64" 1.2 mm
GAS NOZZLES
Fixed (Flush) KP2742-1-38F 3/8" 9.5 mm
KP2742-1-50F* 1/2" 12.7 mm
KP2742-1-62F 5/8" 15.9 mm
Fixed (Recessed) KP2742-1-38R 3/8" 9.5 mm
KP2742-1-50R
KP2742-1-62R 5/8" 15.9 mm
Requires: Gas
Diffuser As'bly KP2746 * .025" – .045" 0.6 – 1.1 mm
English Metric
(Alum. wire) (Alum. wire)
(Alum. Wire) (Alum. Wire)
1/2" 12.7 mm
Insulator KP2773-2 *
GUN TUBE ASSEMBLIES
Standard (60°) KP3078-60 *
45° KP3078-45 *
* Included with POWER MIG® 216
** Tapered tips are required with 3/8” I.D. and 1/2” I.D. Nozzles.
See www.lincolnelectric.com for complete offering of Magnum Pro consumables.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 25

TROUBLESHOOTING
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
WARNING
Service and Repair should only be performed by Lincoln Electric Factory Trained Personnel.
Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician and
machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid Electrical
Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual.
__________________________________________________________________________
E-1 E-1
This Troubleshooting Guide is provided to help you
locate and repair possible machine malfunctions.
Simply follow the three-step procedure listed below.
Step 1. LOCATE PROBLEM (SYMPTOM).
Look under the column labeled “PROBLEM (SYMPTOMS)”. This column describes possible symptoms
that the machine may exhibit. Find the listing that
best describes the symptom that the machine is
exhibiting.
Step 2. POSSIBLE CAUSE.
The second column labeled “POSSIBLE CAUSE” lists
the obvious external possibilities that may contribute
to the machine symptom.
Step 3. RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION
This column provides a course of action for the
Possible Cause, generally it states to contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
If you do not understand or are unable to perform the
Recommended Course of Action safely, contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 26
TROUBLESHOOTING
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
E-2 E-2
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Major Physical or Electrical
Damage is Evident
There is no wire feed or open circuit voltage when the gun trigger is
pulled. Input power is applied to
POWER MIG® 216.
Output voltage and wire feed is present when gun trigger is not pulled
(not activated).
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
OUTPUT PROBLEMS
1. Contact your Local Lincoln
Authorized Field Service Facility.
1 The gun trigger or cable may be
faulty. Check or replace gun
assembly.
2. The thermal protection circuit
may be activated. If this is the
case, allowing the machine to
cool will clear the error condition.
3. Make sure input voltage is correct and matches nameplate rating and reconnect panel configuration.
4. If spool gun option kit is in-
stalled, check to see that it is set
to “Push Gun” if pulling the gun
trigger associated with built in
feeder, and “Spool Gun” if pulling
spool gun trigger.
1. Remove gun assembly from
machine. If problem is solved,
gun assembly is faulty. Repair or
replace.
2. If problem persists when gun
assembly is removed from
machine, then the problem is
within the POWER MIG® 216.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
If all recommended possible areas
of misadjustment have been
checked and the problem persists,
Contact your local Lincoln
Authorized Field Service Facility.
Machine output is low. Welds are
“cold”, weld bead is rounded or
bumped up demonstrating poor
wetting into plate.
1. Check input voltage. Make sure
input voltage matches nameplate rating and reconnect panel
configuration.
2. Make sure settings for wire feed
speed and voltage are correct
for process being used.
3. Make sure output polarity is correct for process being used.
4. Check welding cables and gun
assembly for loose or faulty connections.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
LOCAL AUTHORIZED LINCOLN ELECTRIC FIELD SERVICE FACILITY for assistance before you proceed.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 27
TROUBLESHOOTING
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
E-3 E-3
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Poor arc striking with electrode
sticking or blasting off.
Rough wire feeding or wire will not
feed but drive rolls are turning.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
OUTPUT PROBLEMS
1. Make sure settings for wire feed
speed and voltage are correct
for process being used.
2. The gas shielding may be
improper for process being used.
3. Check input line voltage to be
within machineʼs recommended
rating range.
4. Check that the machine recon-
nect panel is configured properly
for the applied voltage.
FEEDING PROBLEMS
1.
The gun cable may be kinked or twisted.
2.
The wire may be jammed in the gun
cable, or gun cable may be dirty.
3. Check drive roll tension and
position of grooves.
4.
Check for worn or loose drive rolls.
5.
The electrode may be rusty or dirty.
6. Check for damaged or incorrect
contact tip.
7. Check wire spindle for ease of
rotation and adjust break tension knob if necessary.
8. Check that the gun is pushed all
the way into gun mount and
properly seated.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
If all recommended possible areas
of misadjustment have been
checked and the problem persists,
Contact your local Lincoln
Authorized Field Service Facility.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
LOCAL AUTHORIZED LINCOLN ELECTRIC FIELD SERVICE FACILITY for assistance before you proceed.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 28
E-4 E-4
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
TROUBLESHOOTING
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
The wire feed stops while welding.
When trigger is released and
pulled again the wire feed starts.
No control of wire feed speed.
Other machine functions are normal.
Gas does not flow when gun trigger
is pulled.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
FEEDING PROBLEMS
1. Check the wire feed drive rolls
and motor for smooth operation.
2. Check for restrictions in the wire
feed path. Check the gun and
cable for restrictions.
3. Make sure gun liner and tip are
correct for wire size being used.
4.
Make sure drive rolls and guide plates
are clean and are the correct size.
5. Check spindle for ease of rotation.
1. The wire feed speed control may
be dirty. Rotate several times
and check if problem is resolved.
GAS FLOW PROBLEMS
1. Make sure gas supply is connected properly and turned
“ON”.
2. If the gas solenoid does actuate
(click) when the gun trigger is
pulled, there may be a restriction
in the gas supply line.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
If all recommended possible areas
of misadjustment have been
checked and the problem persists,
Contact your local Lincoln
Authorized Field Service Facility.
3. The gun cable assembly may be
faulty. Check or replace.
4. If gas solenoid does not operate
when gun trigger is pulled, the
problem is within the POWER
MIG® 216.
5. Make sure the gun is pushed all
the way into gun mount and is
properly seated.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
LOCAL AUTHORIZED LINCOLN ELECTRIC FIELD SERVICE FACILITY for assistance before you proceed.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 29
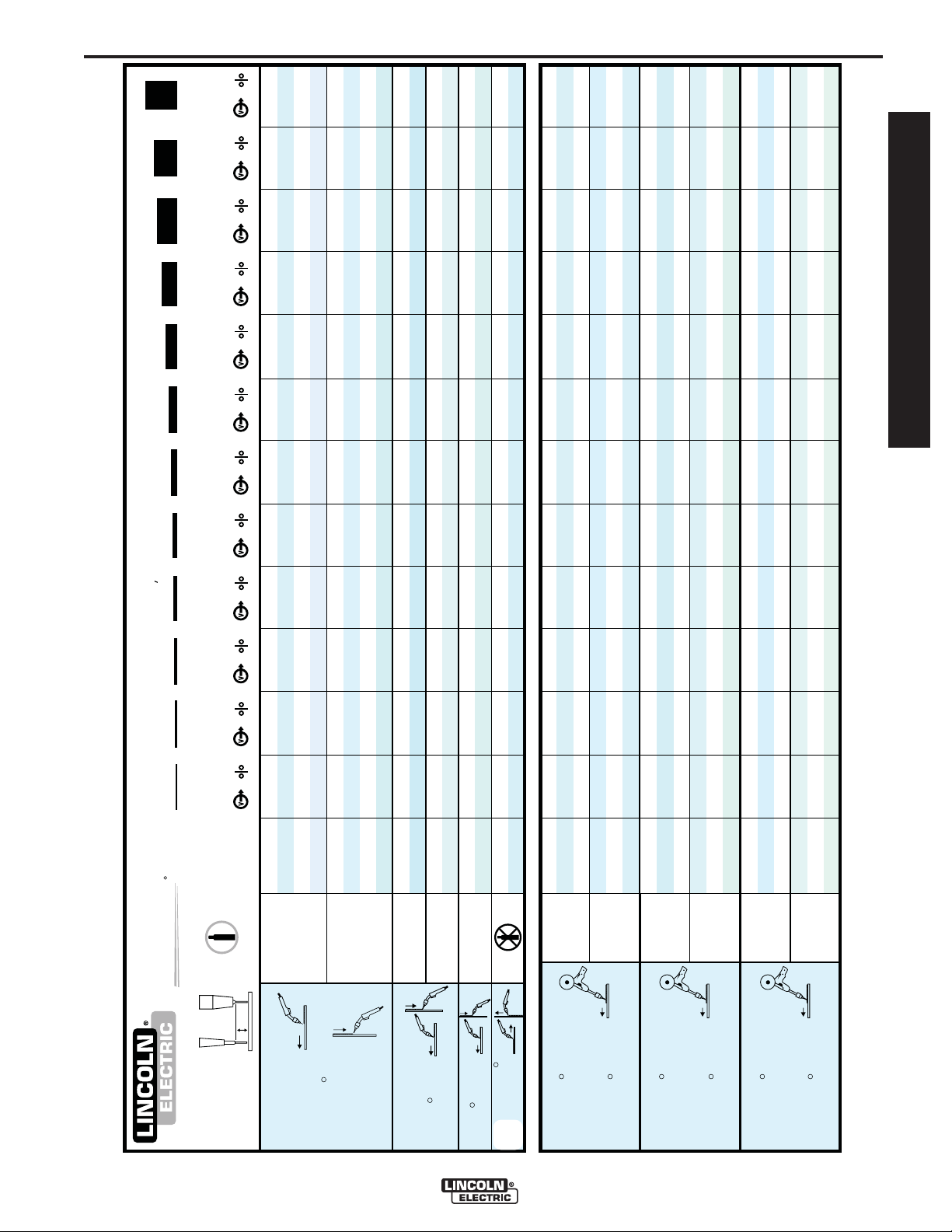
½”
APPLICATION CHART
F-1 F-1
G / 500
G / 425
E / 325 F / 375
E / 400
E / 570
E / 400
E / 575
G / 500
G / 500
G / 350 G / 350 G / 400
F / 375
F / 320
E / 280
E / 170
E / 160
G / 500
G / 300
G / 270
G / 475
F / 350
E / 320
E / 200E / 160
E / 330
D / 280
3/ 16” 1/ 4” 5/ 16” 3/ 8”
E / 180
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
E / 250 F / 300
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 425
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
F / 230
D / 250 E / 300 F / 350
D / 200
E / 300
E / 300
D / 225 D / 350 E / 375 E / 400 F / 500
C / 180
E / 265 E / 280
C / 130 D / 150
D / 130
C / 90 C / 100
B / 80
B / 75
C / 70 C / 90 D / 110 D / 130
B / 70
D / 280
D / 300
C / 230
C / 225
C / 180
C / 175
B / 130
M at erial Thickness/ Espesor de el
material/ Lépaisseur de matériel
B / 11O
B / 90 B / 120 C / 160 C / 200 D / 240
B / 150
C / 110 D / 120 D / 140
C / 8 0
E / 400
D / 285
C / 200
C / 175
E / 350
D / 250
D / 200
C / 175
C / 140
E / 240
D / 200
D / 160
C / 120
C / 9 0
E / 150
D / 125
D / 110
D / 90
C / 7 5
E / 570
D / 485
C / 475
B / 300
A / 300
E / 390 F / 410
B / 500 C / 500 D / 450 E / 500 E / 550
B / 475
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
E / 575
D / 485
C / 475
B / 325
A / 300
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 475
E / 250 F / 300
B / 325 B / 350 B / 450 C / 375 D / 375 E / 400
E / 575 E / 575
D / 485
A / 300 B / 300 C / 475
E / 390 F / 410
22 ga 20 ga 18 ga 16 ga 14 ga 12 ga 10 ga
R
16
2
POWER M IG
/ / / / / / / / / / /
A / 1OO
B / 125
/
.030 in .036 in .048 in .060 in .075 in .105 in .135 in .187 in .250 in .312 in .375 in .500 in
Wire Di ameter
(0.8mm) (0.9mm) (1.2mm) (1.6mm) (2.0mm) (2.5mm) (3.5mm) (4.8mm) (6.4mm) (7.9mm) (9.5mm) (12.7mm)
Dia. du f il
Dia. de alam bre
- 3/8 in.
(mm)
In.
30-40 CFH
B / 125
(0.6)
0.025
A / 75
(0.8)0.030
75%/ 25%
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
C / 150
C / 125
(0.8)0.030
(0.6)0.0
(0.9)0.0
25
35
0.045 (1.1)
2
100% CO
R
MIG
(DC+)
Super Arc
(1.1)0.0
45
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
75%/ 25%
Gas-Shielded
(1.1)0.045
Outer shield 7 1 M
(0.9)0.035
R
UltraCore 71A75
(0.9)
90%/ 7.5%/ 2.5%
BlueMax 308 LS
0.035
He/ Ar/ CO
(DC+)
(1.1)
(0.9)0.0
35
2
R
Innershield
0.045
& 212
NR-211-MP
(DC-)
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
M AGN UM SG GUN (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
R
Aluminum
(0.9)0.035
(1.2)
3/64
100% Ar
SuperGlaze 5356
M AGN UM SG GUN (DC+)
(0.8)0.030
R
Aluminum
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
(0.9)0.0
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
35
100% Ar
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
(0.9)0.035(1.2)
3/64
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
(0.8)0.030
2
Tr i -M ix
100% CO
R
St ainless
DUAL (DC+)
POWER MIG® 216
Page 30
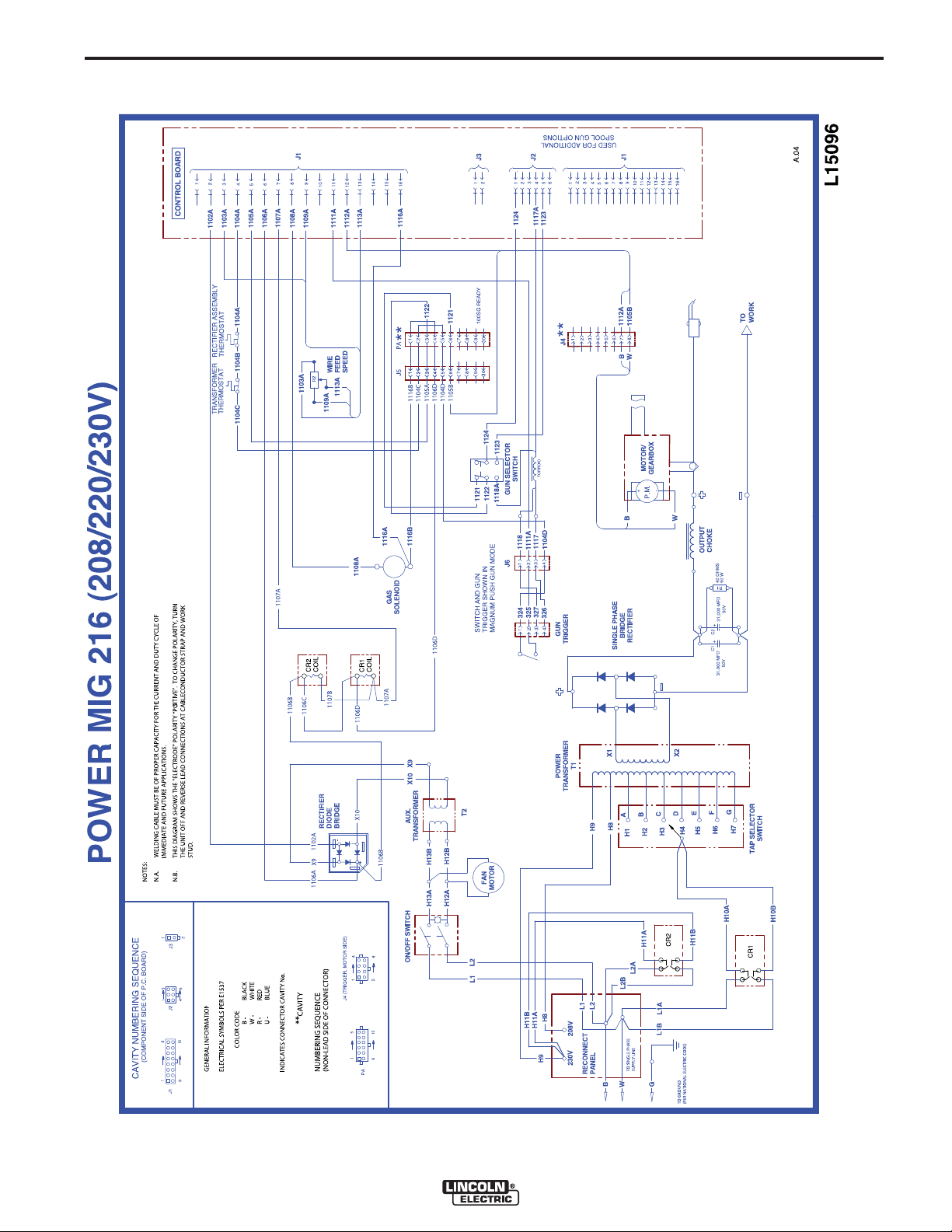
WIRING DIAGRAMS
ENHANCED DIAGRAM
F-2 F-2
POWER MIG® 216
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside the machine on
one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number.
Page 31

DIMENSION PRINT
F-3F-3
A.01
M22179
20.12
19.15
17.47
OPERATORʼS MANUAL
32.56
39.92
38.58
12.00
29.73
30.43
POWER MIG® 216
Page 32

NOTES
Page 33

POWER MIG ®216
Para usarse con máquinas con Número de Código
La seguridad depende de
usted
El equipo de soldadura por arco
y de corte Lincoln está diseñado
y construido teniendo la seguridad en mente. Sin embargo, su
seguridad general puede incrementarse por medio de una instalación adecuada… y una operación cuidadosa de su parte.
NO INSTALE, OPERE O REPARE ESTE EQUIPO SIN LEER
ESTE MANUAL Y LAS PRECAUCIONES DE SE GURIDAD
CONTENIDAS EN EL MISMO.
Y, lo más importante, piense
antes de actuar y sea cuidadoso.
11817
For use with machine Code Numbers
MANUAL DEL OPERADOR
Copyright © Lincoln Global Inc.
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Page 34

i-SP
SEGURIDAD
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA DE LA LEY 65 DE CALIFORNIA
En el es ta do de Ca li for nia, se con si de ra a las emi sio nes del motor de die sel y al gu nos de sus com po nen tes
como da ñi nas para la salud, ya que pro vo can cán cer,
de fec tos de na ci mien to y otros daños re pro duc ti vos.
i-SP
Las emi sio nes de este tipo de pro duc tos con tie nen
químicos que, para el es ta do de Ca li for nia, pro vo can
cáncer, de fec tos de na ci mien to y otros daños
reproduc tivos.
Lo anterior aplica a los motores Diesel
Lo anterior aplica a los motores de gasolina
LA SOLDADURA AL ARCO PUEDE SER PELIGROSA. PROTEJASE USTED Y A LOS DEMAS CONTRA
POSIBLES LESIONES DE DIFERENTE GRAVEDAD, INCLUSO MORTALES. NO PERMITA QUE LOS NIÑOS
SE ACERQUEN AL EQUIPO. LAS PERSONAS CON MARCAPASOS DEBEN CONSULTAR A SU MEDICO
ANTES DE USAR ESTE EQUIPO.
Lea y entienda los siguientes mensajes de seguridad. Para más información acerca de la seguridad, se recomienda comprar un ejemplar
de "Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANIS Standard Z49.1" de la Sociedad Norteamericana de Soldadura, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135
ó CSA Norma W117.2-1974. Un ejemplar gratis del folleto "Arc Welding Safety" (Seguridad de la soldadura al arco) E205 está disponible de
Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
ASEGURESE QUE TODOS LOS TRABAJOS DE INSTALACION, FUNCIONAMIENTO, MANTENIMIENTO Y
REPARACION SEAN HECHOS POR PERSONAS CAPACITADAS PARA ELLO.
Para equipos accionados
por MOTOR.
1.a.
Apagar el motor antes de hacer trabajos de localización de
averías y de mantenimiento, salvo en el caso que el trabajo
de mantenimiento requiera que el motor esté funcionando.
____________________________________________________
1.b. Los motores deben funcionar en lugares
abiertos bien ventilados, o expulsar los
gases de escape del motor al exterior.
1.h. Para evitar quemarse con agua caliente,
no quitar la tapa a presión del radiador
mientras el motor está caliente.
LOS CAMPOS
ELECTRICOS Y
MAGNETICOS pueden ser
____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
1.d. Mantener todos los protectores, cubiertas y dispositivos de
seguridad del equipo en su lugar y en buenas condiciones. No
acercar las manos, cabello, ropa y herramientas a las correas en
V, engranajes, ventiladores y todas las demás piezas móviles
durante el arranque, funcionamiento o reparación del equipo.
____________________________________________________
1.e. En algunos casos puede ser necesario quitar los protectores
para hacer algún trabajo de mantenimiento requerido.
Quitarlos solamente cuando sea necesario y volver a colocar-
los después de terminado el trabajo de mantenimiento. Tener
siempre el máximo cuidado cuando se trabaje cerca de piezas
en movimiento.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
1.g. Para impedir el arranque accidental de los motores de
gasolina mientras se hace girar el motor o generador de la
soldadura durante el trabajo de mantenimiento, desconectar
los cables de las bujías, tapa del distribuidor o cable del
magneto, según corresponda.
1.c. No cargar combustible cerca de un arco de
soldadura cuando el motor esté funcionando. Apagar el motor y dejar que se enfríe
antes de rellenar de combustible para
impedir que el combustible derramado se
vaporice al quedar en contacto con las
piezas del motor caliente. No derramar combustible al llenar el tanque. Si se derrama,
limpiarlo con un trapo y no arrancar el motor
hasta que los vapores se hayan eliminado.
1.f. No poner las manos cerca
del ventilador del motor. No
tratar de sobrecontrolar el
regulador de velocidad en
vacío empujando las varillas de control del acelerador mientras el motor está
funcionando.
2.a. La corriente eléctrica que circula a través de un conductor
origina campos eléctricos y magnéticos (EMF) localizados. La
corriente de soldadura crea campos EMF alrededor de los
cables y los equipos de soldadura.
2.b. Los campos EMF pueden interferir con los marcapasos y en
otros equipos médicos individuales, de manera que los
operarios que utilicen estos aparatos deben consultar a su
médico antes de trabajar con una máquina de soldar.
2.c. La exposición a los campos EMF en soldadura puede tener
otros efectos sobre la salud que se desconocen.
2.d. Todo soldador debe emplear los procedimientos siguientes
para reducir al mínimo la exposición a los campos EMF del
circuito de soldadura:
2.d.1. Pasar los cables de pinza y de trabajo juntos -
2.d.2. Nunca enrollarse el cable de electrodo alrededor del
2.d.3. No colocar el cuerpo entre los cables de electrodo y
2.d.4. Conectar el cable de trabajo a la pieza de trabajo lo más
2.d.5. No trabajar al lado de la fuente de corriente.
peligrosos
Encintarlos juntos siempre que sea posible.
cuerpo.
trabajo. Si el cable del electrodo está en el lado derecho,
el cable de trabajotambién debe estar en el lado derecho.
cerca posible del área que se va a soldar.
Page 35

ii-SP
SEGURIDAD
ii-SP
La DESCARGA
ELÉCTRICA puede
causar la muerte.
3.a.
3.b. Aislarse del circuito de trabajo y de tierra con la ayuda de
material aislante seco. Asegurarse de que el aislante es suficiente
para protegerle completamente de todo contacto físico con el circuito de trabajo y tierra.
3.c. En la soldadura semiautomática o automática con alambre
3.d. Asegurar siempre que el cable de trabajo tenga una buena
3.e. Conectar el trabajo o metal que se va a soldar a una buena
3.f. Mantener el portaelectrodo, pinza de trabajo, cable de soldadura
3.g. Nunca sumergir el electrodo en agua para enfriarlo.
3.h. Nunca tocar simultáneamente la piezas con tensión de los
3.i. Cuando se trabaje en alturas, usar un cinturón de seguridad
3.j. Ver también 6.c. y 8.
Los circuitos del electrodo y de trabajo están eléctricamente con tensión cuando el equipo de soldadura está
encendido. No tocar esas piezas con tensión con la piel
desnuda o con ropa mojada. Usar guantes secos sin agujeros para aislar las manos.
Además de las medidas de seguridad normales, si es
necesario soldar en condiciones eléctricamente
peligrosas (en lugares húmedos o mientras se está
usando ropa mojada; en las estructuras metálicas tales
como suelos, emparrillados o andamios; estando en
posiciones apretujadas tales como sentado, arrodillado o
acostado, si existe un gran riesgo de que ocurra contacto
inevitable o accidental con la pieza de trabajo o con tierra,
usar el equipo siguiente:
• Equipo de soldadura semiautomática de C.C. a tensión
constante.
• Equipo de soldadura manual C.C.
• Equipo de soldadura de C.A. con control de voltaje
reducido.
continuo, el electrodo, carrete de alambre, cabezal de
soldadura, boquilla o pistola para soldar semiautomática
también están eléctricamente con tensión.
conexión eléctrica con el metal que se está soldando. La
conexión debe ser lo más cercana posible al área donde se va a
soldar.
toma de tierra eléctrica.
y equipo de soldadura en unas condiciones de trabajo buenas
y seguras. Cambiar el aislante si está dañado.
portaelectrodos conectados a dos equipos de soldadura
porque el voltaje entre los dos puede ser el total de la tensión
en vacío de ambos equipos.
para protegerse de una caída si hubiera descarga eléctrica.
Los RAYOS DEL ARCO
pueden quemar.
4.a.
Colocarse una pantalla de protección con el filtro adecuado para protegerse los ojos de las
chispas y rayos del arco cuando se suelde o
se observe un soldadura por arco abierto.
Cristal y pantalla han de satisfacer las normas
ANSI Z87.I.
4.b. Usar ropa adecuada hecha de material resistente a la flama
durable para protegerse la piel propia y la de los ayudantes de
los rayos del arco.
4.c. Proteger a otras personas que se encuentren cerca del arco,
y/o advertirles que no miren directamente al arco ni se
expongan a los rayos del arco o a las salpicaduras.
Los HUMOS Y GASES
pueden ser peligrosos.
5.a. La soldadura puede producir humos y gases
peligrosos para la salud. Evite respirarlos.
Durante la soldadura, mantenga la cabeza alejada de los humos. Utilice ventilación y/o extrac-
ción de humos junto al arco para mantener los humos y gases
alejados de la zona de respiración. Cuando se suelda con elec-
trodos que requieren ventilación especial (Ver instrucciones
en el contenedor o la MSDS) o cuando se suelda con chapa
galvanizada u otros metales o revestimeintos que producen
humos tóxicos, evite exponerse lo más posible y dentro de
los límites aplicables según OSHA PEL y ACGIH TLV utilizando un sistema de ventilación de extracción o mecánica
local. En espacios confinados y a la intemperie, puede ser
necesario el uso de respiración asistida. Asimismo se deben
tomar precauciones al soldar con acero galvanizado.
5.b. La operación de equipo de control de humos de soldadura se
ve afectada por diversos factores incluyendo el uso adecuado
y el posicionamiento del equipo así como el procedimiento de
soldadura específico y la aplicación utilizada. El nivel de
exposición del trabajador deberá ser verificado durante la
instalación y después periodicamente a fin de asegurar que
está dentro de los límites OSHA PEL y ACGIH TLV
permisibles.
5.c No soldar en lugares cerca de una fuente de vapores de
hidrocarburos clorados provenientes de las operaciones de
desengrase, limpieza o pulverización. El calor y los rayos del
arco puede reaccionar con los vapores de solventes para
formar fosgeno, un gas altamente tóxico, y otros productos
irritantes.
5.c. Los gases protectores usados para la soldadura por arco
pueden desplazar el aire y causar lesiones graves, incluso la
muerte. Tenga siempre suficiente ventilación, especialmente
en las áreas confinadas, para tener la seguridad de que se
respira aire fresco.
5.d. Lea atentamente las instrucciones del fabricante de este
equipo y el material consumible que se va a usar, incluyendo la
hoja de datos de seguridad del material (MSDS) y siga las
reglas de seguridad del empleado, distribuidor de material de
soldadura o del fabricante.
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
5.e. Ver también 1.b.
Page 36

iii-SP
SEGURIDAD
iii-SP
Las CHISPAS DE
SOLDADURA pueden
provocar un incendio o
una explosión.
6.a.
Quitar todas las cosas que presenten riesgo de incendio del
lugar de soldadura. Si esto no es posible, taparlas para
impedir que las chispas de la soldadura inicien un incendio.
Recordar que las chispas y los materiales calientes de la
soldadura puede pasar fácilmente por las grietas pequeñas
y aberturas adyacentes al área. No soldar cerca de tuberías
hidráulicas. Tener un extintor de incendios a mano.
6.b. En los lugares donde se van a usar gases comprimidos, se
deben tomar precauciones especiales para prevenir
situaciones de riesgo. Consultar “Seguridad en Soldadura y
Corte“ (ANSI Estándar Z49.1) y la información de operación
para el equipo que se esté utilizando.
6.c Cuando no esté soldando, asegúrese de que ninguna parte del
circuito del electrodo haga contacto con el trabajo o tierra. El
contacto accidental podría ocasionar sobrecalentamiento de la
máquina y riesgo de incendio.
6.d. No calentar, cortar o soldar tanques, tambores o contenedores
hasta haber tomado los pasos necesarios para asegurar que
tales procedimientos no van a causar vapores inflamables o
tóxicos de las sustancias en su interior. Pueden causar una
explosión incluso después de haberse “limpiado”. Para más
información, consultar “Recommended Safe Practices for the
Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping
That Have Held Hazardous Substances”, AWS F4.1 de la
American Welding Society .
6.e. Ventilar las piezas fundidas huecas o contenedores antes de
calentar, cortar o soldar. Pueden explotar.
6.f. Las chispas y salpicaduras son lanzadas por el arco de
soldadura. Usar ropa adecuada que proteja, libre de aceites,
como guantes de cuero, camisa gruesa, pantalones sin bastillas,
zapatos de caña alta y una gorra. Ponerse tapones en los oídos
cuando se suelde fuera de posición o en lugares confinados.
Siempre usar gafas protectoras con protecciones laterales
cuando se esté en un área de soldadura.
6.g. Conectar el cable de trabajo a la pieza tan cerca del área de
soldadura como sea posible. Los cables de la pieza de trabajo
conectados a la estructura del edificio o a otros lugares
alejados del área de soldadura aumentan la posibilidad de que
la corriente para soldar traspase a otros circuitos alternativos
como cadenas y cables de elevación. Esto puede crear riesgos
de incendio o sobrecalentar estas cadenas o cables de izar
hasta hacer que fallen.
6.h. Ver también 1.c.
6.i. Lea y siga el NFPA 51B “ Estándar para Prevención de
Incendios Durante la Soldadura, Corte y otros Trabajos
Calientes”, disponible de NFPA, 1 Batterymarch Park, PO box
9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
La BOTELLA de gas
puede explotar si está
dañada.
7.a.
Emplear únicamente botellas que contengan el gas de protección adecuado
en buenas condiciones de funcionamiento diseñados para el
tipo de gas y la presión utilizados. Todas las mangueras,
rácores, etc. deben ser adecuados para la aplicación y estar
en buenas condiciones.
7.b. Mantener siempre las botellas en posición vertical sujetas
firmemente con una cadena a la parte inferior del carro o a un
soporte fijo.
7.c. Las botellas de gas deben estar ubicadas:
• Lejos de las áreas donde puedan ser golpeados o estén
sujetos a daño físico.
• A una distancia segura de las operaciones de corte o
soldadura por arco y de cualquier fuente de calor, chispas o
llamas.
7.d. Nunca permitir que el electrodo, portaelectrodo o cualquier otra
pieza con tensión toque la botella de gas.
7.e. Mantener la cabeza y la cara lejos de la salida de la válvula de
la botella de gas cuando se abra.
7.f. Los capuchones de protección de la válvula siempre deben
estar colocados y apretados a mano, excepto cuando la botella
está en uso o conectada para uso.
7.g. Leer y seguir las instrucciones de manipulación en las botellas
de gas y el equipamiento asociado, y la publicación P-I de
CGA, “Precauciones para un Manejo Seguro de los Gases
Comprimidos en los Cilindros“, publicado por Compressed Gas
Association 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA
22202.
para el proceso utilizado, y reguladores
PARA equipos
ELÉCTRICOS
8.a. Cortar la electricidad entrante usando el interruptor de desconexión en la caja de fusibles
antes de trabajar en el equipo.
8.b. Conectar el equipo a la red de acuerdo con U.S. National
Electrical Code, todos los códigos y las recomendaciones del
fabricante.
8.c. Conectar el equipo a tierra de acuerdo con U.S. National
Electrical Code, todos los códigos y las recomendaciones del
fabricante.
6.j. No utilice una fuente de poder de soldadura para
descongelación de tuberías.
Visite http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety para obtener información adicional.
Page 37

NOTAS
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Page 38

Gracias
v-SPv-SP
por seleccionar un producto de CALIDAD fabricado por Lincoln
Electric. Queremos que esté orgulloso al operar este producto de
Lincoln Electric Company••• tan orgulloso como lo estamos como lo
estamos nosotros al ofrecerle este producto.
El negocio de la Lincoln Electric Company es fabricar y vender equipo de soldadura, consumibles y equipo de corte de alta calidad, Nuestro
reto es satisfacer las necesidades de nuestros clientes y exceder sus expectativas. A veces, los compradores pueden pedir consejo o información a Lincoln Electric sobre el uso de sus productos. Les respondemos con base en la mejor información que tengamos en ese momento. Lincoln Electric no está en posición de garantizar o avalar dicho consejo, y no asume ninguna responsabilidad con respecto a dicha información o guía. Expresamente declinamos cualquier garantía de cualquier tipo, incluyendo cualquier garantía de conveniencia para el fin particular de algún cliente, con respecto a dicha información o consejo. Como un asunto de consideración práctica, tampoco podemos asumir
ninguna responsabilidad por actualizar o corregir dicha información o consejo una vez que se ha dado, ni tampoco el hecho de proporcionar
la información o consejo crea, amplía o altera ninguna garantía en relación con la venta de nuestros productos.
Lincoln Electric es un fabricante responsable, pero la selección y uso de productos específicos vendidos por el mismo está únicamente dentro del control del cliente, y permanece su sola responsabilidad. Varias variables más allá del control de Lincoln Electric afectan los resultados obtenidos al aplicar estos tipos de métodos de fabricación y requerimientos de servicio.
Sujeto a Cambio – Esta información es precisa en nuestro mejor leal saber y entender al momento de la impresión. Sírvase consultar
www.lincolnelectric.com para cualquier información actualizada.
POLÍTICA DE ASISTENCIA AL CLIENTE
Favor de Examinar Inmediatamente el Cartón y el Equipo para Verificar si Existe Algún Daño
Cuando este equipo se envía, el título pasa al comprador en el momento que éste recibe el producto del transportista. Por lo tanto, las reclamaciones por material dañado en el envío las debe realizar el comprador en contra de la compañía de transporte en el momento en el que recibe la mercancía.
Por favor registre la información de identificación del equipo que se presenta a continuación para referencia
futura. Esta información se puede encontrar en la placa de identificación de la máquina.
Producto _________________________________________________________________________________
Número de Modelo _________________________________________________________________________
Número de Código o Código de Fecha__________________________________________________________
Número de Serie___________________________________________________________________________
Fecha de Compra__________________________________________________________________________
Lugar de Compra_________________________________________________________________________
En cualquier momento en que usted solicite alguna refacción o información acerca de este equipo proporcione
siempre la información que se registró anteriormente. El número de código es especialmente importante al
identificar las partes de reemplazo correctas.
Registro del Producto En Línea
- Registre su máquina con Lincoln Electric ya sea vía fax o a través de Internet.
• Para envío por fax: Llene la forma en la parte posterior de la declaración de garantía incluida en el paquete de literatura
que acompaña esta máquina y envíe por fax la forma de acuerdo con las instrucciones impresas en
ella.
• Para registro en línea: Visite nuestro
“Registro de Producto”. Por favor llene la forma y presente su registro.
Lea este Manual del Operador completamente antes de empezar a trabajar con este equipo. Guarde este manual y téngalo a mano para cualquier consulta rápida. Ponga especial atención a las diferentes consignas de seguridad que aparecen a lo
largo de este manual, por su propia seguridad. El grado de importancia a considerar en cada caso se indica a continuación.
SITIO WEB en www.lincolnelectric.com. Seleccione “Vínculos Rápidos” y después
ADVERTENCIA
Este mensaje aparece cuando la información que acompaña debe ser seguida exactamente para evitar daños personales graves o incluso la pérdidad de la vida.
PRECAUCIÓN
Este mensaje aparece cuando la información que acompaña debe ser seguida
o daños a este equipo.
para evitar daños personales menos graves
Page 39

TABLA DE CONTENIDO
Página
________________________________________________________________________
Instalación......................................................................................................Sección A
Especificaciones Técnicas....................................................................................A-1
Precauciones de Seguridad...................................................................................A-2
Desembalaje de la POWER MIG® 216.................................................................A-2
Colocación.............................................................................................................A-2
Alimentación, Aterrizamiento y Diagrama de Conexión.................................A-2, A-3
Conexiones de Polaridad de Salida.......................................................................A-3
Instalación de la Pistola y Cable............................................................................A-4
Gas Protector.........................................................................................................A-4
Instalación de Claw™ de la Bobina.......................................................................A-5
________________________________________________________________________
Operación.......................................................................................................Sección B
Precauciones de Seguridad...................................................................................B-1
Descripción del Producto.......................................................................................B-2
Procesos y Equipo Recomendados.......................................................................B-2
Capacidad de Soldadura .......................................................................................B-2
Limitaciones...........................................................................................................B-2
Descripción de los Controles.................................................................................B-2
Rodillos del Mecanismo de Alimentación ..............................................................B-3
Partes de Conversión de Tamaños de Alambre....................................................B-3
Procedimiento para Cambiar Rodillos Impulsores y de Presión............................B-3
Carga del Carrete de Alambre...............................................................................B-3
Montaje de Carretes de 10 a 30 libras...................................................................B-3
Cómo Encender la Soldadora................................................................................B-4
Alimentación del Electrodo ....................................................................................B-4
Ajuste de Presión del Rodillo de Presión...............................................................B-4
Configuración del Mecanismo de Alimentación .............................................B-4, B-5
Cómo Hacer una Soldadura ..................................................................................B-5
Cómo Evitar Problemas de Alimentación de Alambre...........................................B-6
Control del Ventilador ............................................................................................B-6
Protección de Voltaje de Línea de Entrada ...........................................................B-6
Protecciòn Contra Sobrecarga De Alimentaciòn De Alambre ...............................B-6
Protección Contra Sobrecarga Térmica de Soldadura..........................................B-6
Información sobre Procedimientos de Soldadura..................................................B-6
Aprendizaje soldar.................................................................................................B-6
________________________________________________________________________
vi -SPvi-SP
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Accesorios.....................................................................................................Sección C
Kits de Rodillos Impulsores ...................................................................................C-1
Kit de Montaje de Cilindro Dual ............................................................................C-1
Ensambles Alternativos de Pistola y Cable GMAW Magnum ...............................C-1
Kit de Conexión de Pistola Mágnum ....................................................................C-1
Antorchas “Spool Gun” y Adaptadores Opcionales...............................................C-1
Cómo Hacer una Soldadura con el Kit de Adaptador de Antorcha “Spool Gun” y la Antorcha “Spool Gun” Instalados
________________________________________________________________________
................C-2
Page 40

vii-SP vii-SP
TABLA DE CONTENIDO
Página
Mantenimiento...............................................................................................Sección D
Precauciones de Seguridad ..................................................................................D-1
Mantenimiento General .........................................................................................D-1
Rodillos Impulsores y Tubos Guía.........................................................................D-1
Instalación de la Punta de Contacto y Tobera de Gas..........................................D-1
Tubos y Toberas de la Pistola...............................................................................D-1
Limpieza del Cable de la Pistola ...........................................................................D-1
Remoción y Reemplazo de Guías de Alambre .....................................................D-2
Desensamblaje de la Manija de la Pistola.............................................................D-3
Localización de Averías................................................................................Sección E
Cómo Usar la Guía de Localización de Averías....................................................E-1
Guía de Localización de Averías ................................................................E-2 a E-4
Diagrama de Cableado y Dibujo de Dimensión ..........................................Sección F
Manual de Partes.............................................................................................Apèndice
POWER MIG® 216......................................................................................P-611 (S)
Pistola Magnum Pro 250L ....................................................................P-202-AH (S)
Page 41

A-1-SP
INSTALACIÓN
ESPECIFICACIONES TÉCNICAS – POWER MIG® 216
ENTRADA – MONOFÁSICA ÚNICAMENTE
Voltaje/Fase/Frecuencia Estándar
208/230/1/60 Hz 33/29 Amps 40/36 Amps
220/1/50 Hz 30 Amps 37 Amps
Ciclo de Trabajo Amps Voltios a Amperios Nominales
30% 216 Amps 22 Voltios
40% 190 Amps 23 Voltios
60% 170 Amps 24
Corriente de Entrada a Salida Nominal de 170 Amps Corriente de Entrada a Salida Nominal de 216 Amps
SALIDA NOMINAL
SALIDA
A-1-SP
* Voltios
Rango de Corriente de Soldadura
30 – 250Amps 35 Voltios 13-24 Voltios
Voltaje Máximo de Circuito Abierto
Rango de Voltaje de Soldadura
TAMAÑOS RECOMENDADOS DE ALAMBRES DE ENTRADA Y FUSIBLES
Capacidad Nominal
Voltaje de Entrada/
Frecuencia (Hz)
208/60 50 40A 50 Amp, 250V
230/60 50 36A Enchufe de Tres Dientes
220/50 50 37A (NEMA Type 6-50P)
Tamaño de Fusible de Alambre
o Disyuntor (Quemado Lento)
NOTA: Utilice Alambre de Aterrizamiento AWG #10
de Amperios de Entrada
en Placa de Identificación
(Ciclo de deber del 30%
)
Cable Eléctrico
RANGO DE VELOCIDAD DE ALAMBRE
Velocidad de Alambre 50 – 700 IPM (1.27 – 17.8 m/minuto)
DIMENSIONES FÍSICAS
Altura Ancho Profundidad Pesot
Con la garra Sin la garra
de la bobina de la bobina y el cable del trabajo y el cable del trabajo
32.56 in. 20.12 in. 19.15 in. 39.92 in. 215.5 Ibs. 206.5 lbs.
827 mm 512 mm 487 mm 1014 mm 97.8 kg. 93.7 kg.
Con el arma y el cable Sin el arma y el cableik
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
RANGOS DE TEMPERATURA
RANGO DE TEMPERATURA DE OPERACIÓN
-4°F a 104°F(-20°C a +40°C)
* 23 Voltios at 50 Hz.
RANGO DE TEMPERATURA DE ALMACENAMIENTO
-40°F a 185°F(-40°C a +40°C)
POWER MIG® 216
Page 42

A-2-SP
INSTALACIÓN
A-2-SP
Lea por completo la sección de instalación antes
de iniciar la misma.
PRECAUCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
ADVERTENCIA
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA puede causar la muerte.
• Sólo personal calificado deberá
realizar esta instalación.
• Sólo personal que ha leído y comprendido el Manual de Operación
de la POWER MIG® 216 deberá
instalar y operar este equipo
• La máquina deberá aterrizarse
conforme a todos los códigos
eléctricos nacionales, locales u
otros que apliquen.
• El interruptor de encendido de la
POWER MIG deberá estar en la
posición de APAGADO cuando
instale el cable de trabajo y pistola, y al conectar otro equipo.
DESEMBALAJE DE LA POWER
MIG® 216
Corte las cintas y levante la caja de cartón.
Asimismo, corte las ataduras que sujetan la máquina
a la tarima. Remueva el unicel y material de empaquetamiento corrugado. Retire la cinta adhesiva de
los accesorios de la Plataforma de la Botella de Gas.
Desatornille los dos tornillos de madera (en dicha
Plataforma) que sujetan la máquina a la tarima.
Ruede la máquina fuera del ensamble de la tarima.
UBICACIÓN
Localice el soldador en una localización seca donde
hay circulación libre del aire limpio en el ladrillo en la
parte posterior y las lumbreras hacia fuera el frente.
Una localización que reduce al mínimo la cantidad de
humo y de suciedad dibujados dentro del ladrillo posterior reduce la ocasión de la acumulación de la
suciedad que puede bloquear pasos de aire y causar
el recalentamiento.
ALIMENTACIÓN DE ENTRADA,
ATERRIZAMIENTO Y DIAGRAMA DE
CONEXIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA puede causar la muerte.
• No toque las partes eléctricamente vivas como
las terminales de salida o cableado interno.
• Deberá desconectarse eléctricamente toda la
alimentación antes de proceder.
1. Antes de comenzar la instalación, el cheque con la
empresa eléctrica local si hay cualquier pregunta
sobre si su fuente de alimentación es adecuada
para el voltaje, los amperios, la fase, y la frecuencia especificó en la placa de datos de servicio del
soldador. Asimismo, asegúrese de que la instalación planeada satisface los requerimientos del
Código Eléctrico Nacional de los E.U.A. y código
local. Esta soldadora puede operarse desde una
línea monofásica o desde una fase de una línea
bifásica o trifásica.
2. Se envían los modelos que tienen voltajes de
entrada múltiples especificados en la placa de
datos de servicio (e.g. 208/230) conectaron para el
voltaje más alto. Si la soldadora debe operarse a
un voltaje inferior, deberá reconectarse conforme a
las instrucciones en la Figura A.1 para máquinas
de voltaje dual.
ADVERTENCIA
Asegúrese de que la alimentación está eléctricamente desconectada antes de remover el tornillo
en la cubierta de acceso del panel de reconexión.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 43

INSTALACIÓN
FIGURA A.1 — Conexiones de Entrada para Máquinas de Voltaje Dual
WARNING ADVERTISSEMENT ADVERTENCIA
Disconnect input power before inspecting
or servicing machine.
Do not operate with covers removed.
Do not touch electrically live parts.
Use CU wire only .
Install and Ground machine per National Electrical Code and local codes. Use Grounding Stud or Lug inside.
Only qualified persons should install, use, or service this equipment.
Consult instruction manual before installing or operating.
Débrancher l’alimentation d’entrée avant de réaliser l’inspection ou l’entretien de la machine.
Ne pas faire fonctionner sans les couvercles.
Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique.
Utiliser uniquement du fil CU.
Installer et mettre la machine à la terre conformément au Code Électrique National et aux réglementations locales.
Utiliser une Borne ou un Ergot de Terre à l’intérieur.
Seules des personnes qualifiées peuvent installer
Consulter le Manuel d’Instructions avant d’installer ou de faire fonctionner la machine.
Desconecte elcable de alimentación antes de iniciar caulquier inspeccion ó servicio.
No opere la máquina con las cubiertas removidas.
No toque las partes elécticas vivas.
Use solo cable con alambre de cobre.
Instale y aterrice la máquina de acuerdo a las normas eléctricas locales y nacionales. Use el Tornillo de
Tierra de la máquina.
Únicamente personal calificado debe instalar
Antes de instaler u poerar éste equipo consulte el Manual de Intruccion.
INPUT SUPPLY CONNECTION DIAGRAM
DIAGRAMME DE CONNEXION DE L’ALIMENTATION D’ENTRÉE
DIAGRAMA DE CONEXION DE LA FUENTE DE ENTRADA
Connect leads for
desired voltage range
Connecter les câbles
pour obtenir la tension
désirée.
Conecte cable selector
para el voltage de
alimentacion deseado.
, utilizar ó dar servicio a éste equipo.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels
DESCARGAS ELECTRICAS pueden matar
, utiliser ou réaliser l’entretien de cet appareil.
SINGLE PHASE
MONOPHASE
MONOFASICO
A-3-SPA-3-SP
RECONNECT
RECONEXION
REBRANCHER
INPUT
ALIMENTACION
ENTRÉE
3. La POWER MIG modelo de 208/230 voltios, 50/60
Hz se envía con un cable de entrada de 3.0m (10
pies) y enchufe conectados a la soldadora.
4. Haga que un electricista calificado conecte un
receptáculo (Proporcionado por el Cliente) o cable
a las líneas de alimentación y al aterrizamiento del
sistema conforme al Código Eléctrico Nacional de
los E.U.A. y cualquier código local aplicable.
CONEXIONES DE POLARIDAD DE
SALIDA
La soldadora, como se envía de fábrica, está conectada para polaridad positiva (+) de electrodo. Esta es la
polaridad normal para la soldadura GMAW.
Si se requiere polaridad negativa (–), intercambie la
conexión de los dos cables localizados en el compartimiento del mecanismo de alimentación cerca del
panel frontal. El cable del electrodo, que está conectado al mecanismo de alimentación, deberá conectarse a la terminal etiquetada negativa (-) y al cable
de trabajo, que está conectado a la pinza de trabajo,
deberá conectarse a la terminal etiquetada positiva
(+).
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
POWER MIG® 216
Page 44

A-4-SP
INSTALACIÓN
A-4-SP
INSTALACIÓN DE LA PISTOLA Y CABLE
La pistola y cable Magnum Pro 250L que se proporcionan con la POWER MIG® 216 están instalados de
fábrica con una guía de alambre para un electrodo de
0.9-1.1 mm (.035-.045") y una punta de contacto de
0.9mm (.035”). Asegúrese de que la punta de contacto, guía de alambre y rodillos impulsores correspondan todos con el tamaño del alambre que se está uti-
lizando.
ADVERTENCIA
Apague el interruptor de encendido de la soldadora antes de instalar la pistola y cable.
1. Ponga el cable hacia fuera recto.
2. Desatornille el tornillo de la mano en las partes frontales
de la unidad de impulsión (compartimiento de la alimentación del alambre del interior) hasta que la extremidad del tornillo resalte no más en la abertura del adapta-
dor del pistola según lo considerado del frente de la
máquina. (Véase la figura A.2)
3. Inserte el extremo masculino del cable del arma en el
adaptador del pistola con la abertura en panel de
delante. Cerciórese de que el conectador esté insertado
completamente y apriete el tornillo de la mano.
4. Conecte el conectador del disparador de pistola del
pistolay del cable con el receptáculo de acoplamiento
fuera del compartimiento situado a la izquierda de la
abertura en el panel de delante. Cerciórese de que las
chaveteras están alineados, inserte y apriete el anillo de
retención.
GAS PROTECTOR
[Para los procesos de la soldadura al arco de metal de
gas (GMAW)]
El cliente deberá proporcionar un cilindro de gas protector
de tipo adecuado para el proceso que se está utilizando.
La POWER MIG® 216 incluye de fábrica un regulador
de flujo de gas, para gas de mezcla de Argón, y una
manguera de gas de entrada. Para utilizar 100%
CO2 se requiere un adaptador adicional para conec-
tar el regulador al gas bottle.
ADVERTENCIA
Si sufre algún daño, el CILINDRO
puede explotar.
• El gas bajo presión es explosivo. Siempre conserve los cilindros de gas en una posición vertical y encadenados al carro de transporte o
soporte estacionario. Vea el Estándar Nacional
Estadounidense Z-49.1, “Seguridad en
Soldadura y Corte” publicado por la Sociedad
Estadounidense de Soldadura.
or de la soldadora.
2. Remueva el tapón del cilindro. Inspeccione las
válvulas del cilindro y regulador en busca de
roscas dañadas, suciedad, polvo, aceite o grasa.
Elimine el polvo y suciedad con un trapo limpio.
¡NO CONECTE EL REGULADOR SI HAY PRESENCIA DE ACEITE, GRASA O DAÑOS! Informe
esta condición a su proveedor de gas. El aceite o
grasa en presencia de oxígeno de alta presión es
explosivo.
3. Párese a un lado lejos de la salida, y abra la válvula del cilindro por un instante. Esto elimina
cualquier polvo o suciedad que pudiera haberse
acumulado en la salida de la
válvula.
ADVERTENCIA
Asegúrese de mantener alejada su cara de la salida de la válvula cuando “destape” la válvula.
4. Conecte el regulador de flujo a la válvula del cilindro
y apriete muy bien las tuercas de unión con una
llave.
NOTA: Si se hace una conexión a un cilindro con
100% de CO2, deberá instalarse un adaptador de
regulador adicional entre el regulador y la válvula del
cilindro. Si el adaptador está equipado con una
roldana de plástico, asegúrese de que esté instalada
para conexión a un cilindro de CO2.
5. Conecte un extremo de la manguera de gas de
entrada al conector de salida del regulador de flujo, y
el otro extremo al conector posterior de la POWER
MIG® 216; apriete bien las tuercas de unión con una
llav.
6. Antes de abrir la válvula del cilindro, gire la perilla de
ajuste del regulador a la izquierda hasta que la presión del resorte de ajuste se libere.
7. Permaneciendo a un lado, abra la válvula del cilindro
lentamente una fracción de vuelta. Cuando el medidor de presión del cilindro deje de moverse, abra la
válvula totalmente.
ADVERTENCIA
Nunca se pare directamente en frente o detrás del
regulador de flujo cuando abra la válvula del cilindro. Siempre permanezca a un lado.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
8. El regulador de flujo es ajustable. Ajústelo a la
velocidad de flujo recomendada para el procedimiento y proceso que se están usando antes de
TORNILLO DE
LA MANO
ADAPTADOR
DEL PISTOLA
PISTOLA Y CABLE
MASCULINOS
DEL EXTREMO
Instale el suministro de gas protector en la siguiente forma:
1.
Coloque el cilindro de gas en la plataforma trasera
de la POWER MIG® 216. Enganche la cadena en
su lugar para asegurar el cilindro a la parte posteri-
POWER MIG® 216
CONECTADOR DEL
DISPARADOR
DE PISTOLA
RECEPTÁCULO
Page 45

A-5-SP
INSTALACIÓN
INSTALACIÓN DE LA BOBINA
CLAW™
La Bobina Claw™ y los tornillos de montaje se pro-
porcionan como accesorio opcional para la POWER
MIG® 216. Esto usuario-instala el accesorio proporciona la gerencia del cable para la máquina.
WARNING
Dé vuelta al interruptor del soldador
APAGADO antes de instalar la Bobina
Claw™.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Desempaquete la Bobina Claw™ de su papel pro-
tector y quite el bolso de los tornillos de montaje
de la parte posterior de la Bobina Claw™.
2
. Monte la Bobina Claw™ usando los tornillos de
montaje proporcionados al lado izquierdo de la
máquina, cuando está visto del frente. Cerciórese
de que la Bobina Claw™ esté montada firmemente. (Véase la figura A.3)
A-5-SP
TORNILLOS
DE MONTAJE
FIGURA A.3
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
BOBINA CLAW™
POWER MIG® 216
Page 46

B-1-SP
OPERACIÓN
Lea toda la sección de Operación antes
de operar la POWER MIG® 216.
ADVERTENCIA
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA
puede causar la muerte.
• No toque partes eléctricamente
vivas o electrodos con la piel o
ropa mojada. Aíslese del trabajo y
tierra.
• Siempre utilice guantes aislantes
secos.
Los HUMOS Y GASES
pueden resultar peligrosos.
• Mantenga su cabeza alejada de
los humos.
• Use ventilación o escape para
eliminar los humos y gases de su
zona de respiración.
B-1-SP
Las CHISPAS DE SOLDADURA pueden provocar un
incendio o explosión.
• Mantenga alejado al material
inflamable.
• No suelde en contenedores cerrados.
Los RAYOS DEL ARCO
pueden quemar los ojos y
piel.
• Utilice protección para los ojos,
oídos y cuerpo.
Observe toda la información de seguridad
a lo largo de este manual.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 47

B-2-SP B-2-SP
5
OPERACIÓN
DESCRIPCIÓN DEL PRODUCTO
La
POWER MIG® 216
automática de soldadura de arco de voltaje de CD fabricada para satisfacer las especificaciones NEMA. Combina
una fuente de poder de voltaje de transformador con
tomas de regulación con un alimentador de alambre de
velocidad constante para formar un sistema de soldadura
de desempeño robusto y confiable. Un simple esquema de
control, que consiste de un control de velocidad de alimentación de alambre de rango completo, y 7 selecciones
de tomas de voltaje de salida proporcionan versatilidad
con facilidad de uso y precisión. Una función mejorada de
POWER MIG® 216
la
“Spool Gun” Magnum 100SG.
Otras funciones incluyen un eje de carrete de alambre
O.D. de 51 mm (2") con freno ajustable, un carro de transporte de montaje de cilindro de gas integral, un regulador
de flujo de mezcla de Argón con medidor de presión de
cilindro y manguera de entrada, una pistola GMAW
Magnum Pro 250L de 3.6 m (15 pies) y cable con tobera
fija (al ras), un cable de alimentación de 3.0 m (10 pies)
con enchufe, y un cable de trabajo de 3.0 m (10 pies) con
pinza.
Los kits opcionales del arma, del adaptador del carrete de
la botella doble y el kit dual del montaje del cilindro para el
empuje que alimenta con el estándar construido en alimentador están también disponibles.
es una máquina completa semi-
, es que está lista para la Antorcha
LIMITACIONES
El voltaje/corriente de salida de la POWER MIG® 216 está
sujeto a variar si la alimentación a la máquina cambia debido a
su topología de alimentación de transformador con tomas de
regulación. En algunos casos, puede ser necesario un ajuste a
la preconfiguración de WFS y/o selección de toma de voltaje
para amoldarse a una variación importante en la alimentación.
DESCRIPCIÓN DE LOS CONTROLES
Vea la Figura B.1
1. Interruptor de ENCENDIDO/APAGADO - Presione el inter-
ruptor al " ON" posición para energizar la POWER MIG®
216.
2. Control de Voltaje - Se proporcionan siete selecciones de
toma de voltaje etiquetadas de la “A” (voltaje mínimo) a la
"G" (voltaje máximo). Sólo deberá ser ajustado cuando NO
se esté soldando. La selección del control se puede
preestablecer al ajuste especificado en la etiqueta de la
carta/del procedimiento del uso en el interior de la puerta de
compartimiento del alambre o de la sección F de este manual de la instrucción.
3. Control de Velocidad de Alambre - Controla la velocidad
de alimentación de alambre de 50 – 700 pulgadas por minuto
(1.2 – 17.8 m/min). La velocidad de alambre no se ve afectada cuando se hacen cambios en el control de voltaje.
4. Conectador 4-Pin - Para las operaciones del arma del
empuje y del arma del carrete.
FIGURA B.1
PROCESOS Y EQUIPO RECOMENDADOS
POWER MIG® 216
CAPACIDAD DE SOLDADURA
La POWER MIG® 216 está clasificada a 215 amps a 22
voltios, a un ciclo de trabajo del 30% con base en un
ciclo de diez minutos. Es capaz de ciclos de trabajo más
altos a corrientes de salida inferiores. El diseño de
transformador con tomas de regulación la hace conveniente para utilizarse con la mayoría de los sistemas
generadores portátiles o en planta.
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
5. Interruptor eléctrico del Pistola del empuje de la
botella doble y del Pistola del carrete - Accione
la palanca del interruptor (El punto 5 considera la
figura B.2) para seleccionar entre el arma del
empuje y el arma del carrete. Cuando se selecciona cualquier operación, inserte el cable al
conectador de perno 4. (El punto 4, considera la
figura B.1)
FIGURA B.2
POWER MIG® 216
Page 48

OPERACIÓN
B-3-SPB-3-SP
RODILLOS DEL MECANISMO DE
ALIMENTACIÓN
Los rodillos impulsores instalados con la POWER MIG®
216 tienen dos ranuras, una para electrodos de acero sólido de 0.9mm (.035") y otra para electrodos de 1.2mm
(.045”). El tamaño real del rodillo impulsor está marcado en
el lado expuesto del mismo.
PARTES DE CONVERSIÓN DE
TAMAÑOS DE ALAMBRE
La POWER MIG® 216 está clasificada para alimentar
tamaños de electrodo sólido o tubular de 0.6 a 1.2 mm (.025
- .045").
Las partes de los kits de rodillos impulsores, y de pistola y
cable Magnum Pro 250L están disponibles para alimentar
diferentes tamaños y tipos de electrodos. Vea la sección de
Accesorios.
PROCEDIMIENTO PARA CAMBIAR JUEGOS DE RODILLOS IMPULSORES Y DE
PRESIÓN
1. Usted apaga la fuente de energía.
2. Libere la presión en el rodillo de presión columpiando el
brazo de presión ajustable hacia abajo y en dirección a
la parte posterior de la máquina. Levante el ensamble de
rodillo de presión fundido y permita que se asiente en
una posición vertical.
3. Remueva la placa de retención de la guía de alambre
externa, aflojando los dos tornillos estriados grandes.
4. Gire el mecanismo de retención del rodillo impulsor hacia
la posición sin asegurar como se muestra a continuación,
y remueva los rodillos impulsores. (Vea la Figura B.3)
CARGA DEL CARRETE DE ALAMBRE CARRETES O BOBINAS
Montaje de carretes de 4.5-20 kg (10 a 44 Lb.) (Diámetro de
12"/350MP mm) o Bobinas Innershield de 6 kg (14Lb.):
(Para bobinas Innershield de 6 Kg (13-14 lb.), se debe utilizar un
Adaptador de Bobina K435).
1. Abra la Puerta del Compartimiento del Mecanismo de Alimentación
2. Aplane la Barra de Liberación en el Collarín de Retención, y remuévala del eje.
3. Coloque el carrete en el eje asegurándose de que el pin de frenado
del eje entra en uno de los orificios en la parte posterior del carrete
(NOTA: Una marca de flecha en el eje se alinea con el pin de sujeción del freno para ayudar a alinear un orificio). Asegúrese de que el
alambre sale del carrete en la dirección que permita que se
desenrede desde la parte superior de la bobina.
4. Reinstale el Collarín de Retención. Asegúrese de que la Barra de
Liberación se “expande” y de que los retenedores del collarín encajan totalmente en las ranuras del anillo de retención en el eje.
FIGURA B.3
POSICIÓN SIN ASEGURAR
5. Remueva la placa de la guía de alambre interna.
6. Reemplace los rodillos impulsores y la guía de alambre
interna por un juego adecuado para el nuevo tamaño de
alambre.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que la guía y punta de contacto
también tengan un tamaño adecuado para el tamaño de
alambre seleccionado.
7. Alimente manualmente el alambre desde el carrete de
alambre, a través de la ranura del rodillo impulsor y guía
de alambre, y de ahí a través del buje de bronce del
ensamble de la pistola y cable.
8. Vuelva a colocar la placa de retención de la guía de
alambre externa apretando los dos tornillos estriados
grandes. Vuelva a colocar el brazo de presión ajustable
en su posición original para aplicar presión. Ajuste la
presión según sea necesario.
POSICIÓN ASEGURADA
POWER MIG® 216
Page 49

OPERACIÓN
CÓMO ENCENDER LA SOLDADORA
Coloque el “Interruptor de Encendido” en “ENCENDIDO”. Con el voltaje deseado y la velocidad de alambre seleccionada, opere el gatillo de la pistola para
obtener salida de soldadura y energizar el motor de alimentación de alambre.
ALIMENTACIÓN DEL ELECTRODO
ADVERTENCIA
Cuando se activa, el electrodo y mecanismo de
impulsión están eléctricamente “calientes” en
relación al trabajo y aterrizamiento, y permanecen “calientes” varios segundos después
de que se soltó el gatillo.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
NOTA: Revise que los rodillos impulsores, placas guía y
partes de la pistola sean adecuados para el tamaño y tipo de
alambre que se está utilizando. Consulte la Tabla C.1 en la
sección de Accesorios.
1. Gire el carrete hasta que el extremo libre del electrodo
esté accesible.
2. Mientras sujeta firmemente el electrodo, corte el extremo
doblado y enderece las primeras seis pulgadas. Si el electrodo no está enderezado adecuadamente, no se alimentará correctamente a través del sistema del mecanismo de
alimentación.
3. Libere la presión en el rodillo de presión columpiando el
brazo de presión ajustable hacia abajo y en dirección a la
parte posterior de la máquina. Levante el ensamble de
rodillo de presión fundido y permita que se asiente en una
posición vertical. Deje la placa de guía de alambre externa
instalada. Alimente manualmente el alambre a través del
buje de guía de entrada y a través de las placas guía
(sobre la ranura del rodillo impulsor). Empuje una longitud
suficiente de alambre para asegurar que éste se ha alimentado al ensamble de la pistola y cable sin restricciones. Vuelva a colocar el brazo de presión ajustable a
su posición original para aplicar presión al alambre.
4. Oprima el gatillo de la pistola para alimentar el alambre
del electrodo a través de la pistola.
AJUSTE DE PRESIÓN DEL RODILLO DE PRESIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
El brazo de presión controla la cantidad de fuerza que
los rodillos impulsores ejercen sobre el alambre. Un
ajuste adecuado del brazo de presión brinda el mejor
desempeño de soldadura. Para mejores resultados,
establezca ambos brazos en el mismo valor..
Establezca el brazo de presión en la siguiente forma
(Vea la Figura B.5):
Alambres de aluminio entre 1 y 3
Alambres tubulares entre 3 y 4
Alambres de Acero, Inoxidable entre 4 y 6
FIGURA B.4
ALAMBRES TUBULARES
OUTERSHIELD
METALSHIELD
INERSHIELD
CONFIGURACIÓN DEL MECANISMO DE ALIMENTACIÓN
Vea la Figura B.5
Cambio del adaptador de Pistola
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA puede causar la muerte.
• APAGUE la alimentación de la fuente
de poder de soldadura antes de instalar o cambiar rodillos impulsores y/o
guías.
• No toque partes eléctricamente vivas.
• Cuando desplaza con el gatillo de la pistola, el
electrodo y mecanismo de impulsión están
“calientes” para trabajar y hacer tierra, y
podrían permanecer energizados por varios
segundos después de que se suelta el gatillo.
• Sólo personal calificado deberá realizar trabajo
de mantenimiento.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Herramientas requeridas:
• Llave hexagonal de 1/4".
ALAMBRES SÓLIDOS
1
3
5
2
4
6
ALUMINIO
ACERO
INOXIDABLE
ADVERTENCIA
B-4-SPB-4-SP
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA puede causar la
muerte.
• APAGUE la alimentación de entrada de la
fuente de poder de soldadura antes de instalar
o cambiar rodillos impulsores y/o guías.
• No toque partes eléctricamente vivas.
• Cuando desplaza con el gatillo de la pistola, el electrodo
y mecanismo de impulsión están “calientes” para trabajar y hacer tierra, y podrían permanecer energizados por
varios segundos después de que se suelta el gatillo.
• Sólo personal calificado deberá realizar trabajo de mantenimiento.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Nota: Algunos adaptadores del arma no requieren el uso del tornil-
lo de la mano.
1. Apague la alimentación de la fuente de poder de soldadura.
2. Remueva el alambre de soldadura del mecanismo de ali
mentación.
3. Remueva el tornillo mariposa del mecanismo de alimentación.
4. Remueva la pistola de soldadura del mecanismo de alimentación.
Page 50

B-5-SP
A
5. Afloje el tornillo de casquillo de la cabeza de zócalo que
sostiene la barra del conectador contra el adaptador del
la
.
Importante: no intente remover completamente el tornillo
Allen guía.
OPERACIÓN
pisto-
3. Oprima el gatillo para alimentar el electrodo de alambre a
través de la pistola y cable. Para alambre sólido, corte el
electrodo dentro de aproximadamente 10 mm (3/8") del
final de la punta de contacto [20 mm (3/4") para
Outershield®].
B-5-SP
6. Quite la guía de alambre externa, y empuje el adaptador del
arma de la impulsión del alambre. Debido a el ajuste de la precisión, el golpear ligeramente ligero se puede requerir para
quitar el adaptador del
pistola
.
7. Desconecte la manguera del gas que blinda del adaptador del
pistola
, si procede.
8. Conecte la manguera del gas que blinda con el nuevo adaptador
del
pistola
, si procede.
4. Cuando suelde con gas, encienda el suministro de gas y
establezca la velocidad de flujo requerida (normalmente
30-40 CFH; 14-19 litros/min).
5. Conecte el cable de trabajo al metal a soldarse. La pinza
de trabajo debe hacer buen contacto eléctrico con el trabajo. El trabajo también debe aterrizarse como se establece
en “Precauciones de Seguridad de Soldadura de Arco”
9. Gire el adaptador pistola hasta que el agujero tornillo de pulga
alinee con el agujero del Tornillo de la mano en la placa de la
alimentación. Resbale el adaptador del pistola dentro de la
impulsión alambre y verifiqúelo que los agujeros del tornillo de la
mano están alineados.
10. Apriete el tornillo del zoquet..
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
6. Posicione el electrodo sobre la junta. El extremo del
11. Inserte el arma de la soldadura en el adaptador del
pistola
y
electrodo puede tocar ligeramente el trabajo.
apriete el Tornillo de la mano.
7. Baje la careta, apriete el gatillo y empiece a soldar.
CÓMO HACER UNA SOLDADURA
Sostenga la pistola en tal forma que la distancia de la
punta de contacto al trabajo sea de 10 mm (3/8") [20
1. Revise que la polaridad del electrodo sea la correcta para el pro-
mm (3/4") para Outershield®].
ceso que se está utilizando; después, coloque el interruptor de
encendido en ENCENDIDO.
8. Para detener la soldadura, suelte el gatillo de la pistola
y aleje ésta del trabajo después de que se extinga el
2. Establezca la toma de voltaje de arco y velocidad de alambre
arco.
deseadas para el alambre de electrodo, tipo de material y grosor,
y gas (para MIG y Outershield®) en particular que se está utilizando. Utilice la Tabla de Aplicaciones en la puerta dentro del
compartimiento de alambre como una referencia rápida para
algunos procedimientos de soldadura comunes.
NOTA: La carta del uso se puede también encontrar en la sección
F de este manual de la instrucción.
Figura B.5
ADVERTENCIA
• Cuando utilice un proceso de arco
abierto, es necesario utilizar protección correcta para ojos, cabeza y
cuerpo.
BUJE DEL RECEPTOR DEL ARMA
BLOQUE DE CONECTADOR
TORNILLO DE
CASQUILLO DE LA
CABEZA DE ZÓCALO
AFLOJE APRIETE
POWER MIG® 216
GUÍA DE ALAMBRE EXTERN
TORNILLO DE LA MANO
Page 51

OPERACIÓN
9. Cuando no haya nada más que soldar, cierre la válvula en
el cilindro de gas (si se utiliza), opere momentáneamente
el gatillo de la pistola para liberar la presión del gas, y
apague la POWER MIG® 216.
PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGA DE ALIMENTACIÓN DE
ALAMBRE
B-6-SPB-6-SP
NOTA: Cuando utilice el electrodo Innershield, puede remover
la tobera de gas del aislamiento en el extremo de la
pistola y reemplazarla con la tobera sin gas. Esto
brindará visibilidad mejorada y eliminará la posibilidad
de sobrecalentamiento de la tobera de gas.
CÓMO EVITAR PROBLEMAS DE
ALIMENTACIÓN DE ALAMBRE
Los problemas de alimentación de alambre pueden evitarse
observando los siguientes procedimientos de manejo de la pistola:
1. No tuerza o jale el cable alrededor de esquinas puntiagudas.
2. Mantenga el cable de la pistola tan recto como sea posible
cuando suelde o cargue el electrodo a través del cable.
3. No permita que carretillas o camiones pasen por encima de
los cables.
4. Mantenga el cable limpio siguiendo las instrucciones de
mantenimiento.
5. Use sólo electrodos limpios y libres de óxido. Los electro-
dos de Lincoln tienen lubricación adecuada de superficie.
6. Reemplace la punta de contacto cuando el arco empiece a
perder estabilidad o cuando el extremo de la punta de contacto está fundida o deformada.
7. Mantenga la tensión de frenado del eje del carrete de alam-
bre al mínimo requerido, a fin de evitar recorrido excesivo
del carrete que puede causar que el alambre se
“desenrede” de la bobina.
8. Utilice rodillos impulsores y una presión de mecanismo de
alimentación/rodillo de presión adecuados para el tamaño y
tipo de alambre que se está utilizando.
La POWER MIG cuenta con protección de estado sólido
contra sobrecarga del motor del mecanismo de alimentación. Si el motor se sobrecarga, el trazado de circuito
de la protección apaga el solenoide del motor impulsor y del
gas del alambre. Revise que el tamaño de la punta, guía de
alambre y rodillos impulsores sea el correcto, y si hay
obstrucciones o dobleces en el cable de la pistola, o
cualquier otro factor que podría impedir la alimentación del
alambre. A fin de continuar con la soldadura, simplemente
jale el gatillo. No existe un interruptor automático a
restablecer ya que la protección se hace con partes electrónicas confiables de estado sólido.
PROTECCIÓN CONTRA SOBRECARGA TÉRMICA DE SOLDADURA
La POWER MIG® 216 cuenta con termostatos protectores
integrados que responden ante una temperatura excesiva.
Éstos abren los circuitos de alimentación de alambre y salida de la soldadora si la máquina excede la temperatura de
operación segura máxima debido a una sobrecarga frecuente, o a alta temperatura ambiente más sobrecarga.
Los termostatos se restablecen automáticamente cuando la
temperatura alcanza un nivel de operación seguro y la soldadura y alimentación se permiten otra vez, cuando se
vuelve a apretar el gatillo de la pistola.
INFORMACIÓN SOBRE
PROCEDIMIENTOS DE SOLDADURA
CONTROL DEL VENTILADOR
El ventilador está diseñado para encenderse cuando
se aplica alimentación a la POWER MIG® 216 y apagarse cuando ésta se interrumpe.
VARIACIONES DE VOLTAJE DE LA
LÍNEA DE ENTRADA
Alto Voltaje de Línea — Un voltaje de entrada mayor que el
nominal dará como resultado voltajes de salida mayores que
los normales para una configuración de toma dada. Si su línea
de entrada es alta, es mejor que seleccione una toma de voltaje
más baja que la recomendada en la tabla de procedimientos.
Bajo Voltaje de Línea — Tal vez no pueda obtener una salida
máxima de la máquina si el voltaje de línea es menor que la
entrada nominal. La unidad continuará soldando, pero la salida
puede ser menor que la normal para una configuración de toma
dada. Si su línea de entrada es baja, es mejor que seleccione
una toma de voltaje más alta que la recomendada en la tabla
de procedimientos.
POWER MIG® 216
NOTA: Vea la cubierta interior de la máquina o de la
sección F de este manual de la instrucción para el
procedimiento de soldadura adicional, de uso general.
APRENDIZAJE SOLDAR CON AUTÓGENA
La soldadura es una destreza que puede ser
aprendida solamente practicando. Nadie puede
convertirse en soldador realizado
simplemente leyendo sobre ellos. El
acoplamiento siguiente “que aprende soldar ” el
documento ayudará al operador inexperto a
entender los fundamentos sobre la soldadura
del alambre y a proporcionar la dirección para
ayudar a desarrollar esta capacidad.
“Aprendiendo soldar” acoplamiento:
http://content.lincolnelectric.com/pdfs/products/
navigator/im/LTW1tri.pdf
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Page 52

C-1-SP C-1-SP
ACCESORIOS
KITS DE RODILLOS IMPULSORES
Consulte la Tabla C.1 para informarse sobre los distintos
kits de rodillos impulsores que están disponibles para la
POWER MIG® 216. El elemento en negritas se proporciona
en forma estándar con la POWER MIG® 216
TABLA C.1
Alambre Tamaño
.023”-.030” (0.6-0.8 mm)
Acero
Sólido
Tubular
Aluminio
.035” (0.9 mm) KP1696-035S
.045” (1.1 mm) KP1696-045S
.035-.045 (0.9-1.1mm) KP1696-1
.040 (1.0mm) KP1696-2
.035” (0.9 mm) KP1697-035C
.045” (1.1 mm) KP1697-045C
3/64” (1.2 mm) KP1695-3/64A
.
Kit de Rodillos Impulsores
KP1696-030S
KIT DE MONTAJE DE CILINDRO
DUAL (K1702-1)
Permite el montaje lado a lado de dos cilindros de gas
de tamaño total (9" de diámetro x 5' de alto) con
carga “sin elevación”. La instalación es simple y las
instrucciones fáciles. Incluye soportes de cilindro
inferior y superior, ejes de ruedas y hardware de montaje.
ENSAMBLES ALTERNATIVOS DE
CABLE Y PISTOLA GMAW MAGNUM
Los siguientes ensambles de pistola y cable Magnum
Pro 250L se encuentran disponibles en forma separada para usarse con la POWER MIG® 216. Cada uno
está clasificado a un ciclo de trabajo del 40%, 250
amps y están equipados con un conector integrado,
conector de gatillo twist-lock, tobera fija y aislador, así
como con una guía, difusor y puntas de contacto para
los tamaños de alambre especificados:
Longitud
10' (3.0 m)
12' (3,6 m)
15' (4.5 m)
Núm. de Parte
KP42-4045-15
Tamaño Inglés Tamaño Métrico
del Alambre del Alambre
035” – .045" 0.9 – 1.1 mm
ADVERTENCIA
• Desenchufe o desconecte la energìa
de limentaciòn de la POWER MIG®
216 antes de instalar la Spool Gun y
el Kit.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
KIT DE CONEXIÓN DE PISTOLA
MAGNUM (Opcional K466-6)
Utilizar el Kit de Conexión Magnum K466-6 Opcional
para la POWER MIG® 216 permite el uso de los
ensambles de pistola y cable estándar Magnum 200,
300 ó 400.
ADAPTADOR DE EJE DE CARRETE
PEQUEÑO (K468)
El adaptador de eje K468 permite el uso de carretes
de diámetro pequeño de 8".
ADAPTADOR DEL HUSO PARA 14
LIBRAS. BOBINAS (K435)
El adaptador del huso K435 permite 14lbs. (6kg.)
Innershield arrolla para ser montado en huso de 2” (51m
m) O.D.
ANTORCHAS “SPOOL GUN” Y ADAPTADORES OPCIONALES
La
POWER MIG® 216
ientes antorchas “spool gun” opcionales:
ANTORCHA
“SPOOL GUN”
Magnum 100SG
(K2532-1)
Magnum SG
(K487-25)
Magnum 250LX
(K2490-1)
Adaptador de Antorcha “Spool Gun” (K2703-1)
Este kit está diseñado para permitir que la pistola “spool
gun” Magnum SG ó Magnum 250LX opere con la
MIG® 216
arnés de cableado y panel de conexión de pistola. Este
panel ofrece un conector tipo ms de 6 pines para la antorcha “spool gun” Magnum SG y un conector tipo ms de 7
pines para la antorcha “spool gun” Magnum 250LX, y un
interruptor selector para seleccionar qué pistola estás utilizando.
NOTA: Que el adaptador de antorcha spool gun K2703-1
inhabilita la capacidad para Magnum 100SG.
CAPACIDAD NOMINAL
Ciclo de Trabajo del 30%, 130 amps
Ciclo de Trabajo del 60%, 250 amps
Ciclo de Trabajo del 60%, 300 amps
. El kit incluye el gas solenoide, líneas de gas,
es capaz de operar con las sigu-
ADAPTADOR
Trabajo Ligero
Trabajo Mediano
Trabajo Pesado
Fábrica lista
No requiere adapta-
dor
Adaptador Spool
Gun 2703-1
POWER
POWER MIG® 216
Page 53

C-2-SP
ACCESORIOS
CÓMO HACER UNA SOLDADURA CON EL
KIT DE ADAPTADOR DE ANTORCHA
“SPOOL GUN” Y LA ANTORCHA “SPOOL
GUN” INSTALADOS
PRECAUCIÓN
En cualquiera de las posiciones del interruptor de
palanca, apretar cualquier gatillo hará que el electrodo de ambas pistolas se vuelva eléctricamente
“CALIENTE”. Asegúrese de que una pistola sin utilizar esté posicionada en tal forma que el electrodo o
punta no haga contacto con el gabinete metálico u
otro metal común al trabajo.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Fijando el interruptor eléctrico “para empujar el arma”
coloque las neutralizaciones la válvula electromagnética del gas del arma de la operación y del carrete
del arma del carrete. El cierre del disparador de arma
permite la soldadura del arma del empuje y ambos
electrodos serán eléctricamente “CALIENTES”.
2. Fijando el interruptor eléctrico al “arma del carrete”
coloque las neutralizaciones la válvula electromagnética incorporada del gas de la operación y del
alimentador del arma del empuje. También permite
la válvula electromagnética del gas del arma de la
operación y del carrete del arma del carrete. El
cierre del disparador de arma del carrete permite la
soldadura del arma del carrete y ambos electrodos
serán eléctricamente “CALIENTES”.
C-2-SP
3. Operación con la POWER MIG® 216:
• ENCIENDA la alimentación de la POWER
MIG® 216.
• Ajustar el control de la toma de voltaje aumen-
tará o disminuirá su voltaje de soldadura.
• Ajustar el control de la velocidad de alambre en
la antorcha “spool gun” aumentará o disminuirá
la velocidad de la alimentación de alambre de
la antorcha “spool gun”.
NOTA: Ajustar el control de la velocidad de alimentación de alambre en el Panel de la máquina no
tiene efecto en la velocidad de alimentación de alambre de la antorcha “spool gun”.
4. Refiera al procedimiento de soldadura en la
máquina o la sección F de este manual de la
instrucción para los ajustes de aluminio iniciales.
Haga que una prueba suelda con autógena para
determinar los ajustes finales.
5. Fije el interruptor de selector del pistola del carrete
“a la posición del pistola del empuje” para volver a
la operación del pistola del empuje.
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
POWER MIG® 216
Page 54

D-1-SP
MANTENIMIENTO
D-1-SP
PRECAUCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
ADVERTENCIA
La DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA puede causar la muerte.
• Haga que un electricista instale y
dé servicio a este equipo.
• APAGUE la alimentación de la
caja de fusibles antes de trabajar
en el equipo
• No toque las partes eléctricamente calientes.
MANTENIMIENTO GENERAL
En ubicaciones con cantidad extrema de polvo, la
suciedad puede obstruir los pasajes de aire causando
que la soldadora se sobrecaliente. Elimine la
suciedad de la soldadora aplicando aire de baja presión a intervalos regulares para eliminar la suciedad
excesiva y acumulación de polvo en las partes internas.
Los motores de ventilador cuentan con rodamientos
de bolas sellados que no requieren servicio.
RODILLOS IMPULSORES Y PLACAS GUÍA
Después de cada bobina de alambre, inspeccione el
mecanismo de alimentación. Límpielo según sea
necesario aplicando aire comprimido de baja presión.
No utilice solventes para limpiar el rodillo de presión
porque pueden eliminar el lubricante del rodamiento.
Todos los rodillos impulsores tienen estampados los
tamaños de alambre que alimentarán. Si se utiliza un
tamaño de alambre diferente al marcado en el rodillo,
se deberá cambiar el rodillo impulsor.
TUBOS Y TOBERAS DE LA PISTOLA
1. Reemplace las puntas de contacto desgastadas
según se requiera.
2. Remueva la salpicadura dentro de la tobera de gas y
de la punta después de cada 10 minutos de tiempo
de arco o según se requiera.
LIMPIEZA DEL CABLE DE LA PISTOLA
A fin de ayudar a evitar problemas de alimentación,
limpie la guía del cable después de usar aproximadamente 136 kg (350MP libras) de electrodo. Remueva
el cable del alimentador de alambre y colóquelo en
forma recta sobre el piso. Retire la punta de contacto
de la pistola. Usando una manguera de aire y sólo
presión parcial, remueva suavemente la guía del
cable del extremo del difusor de gas.
PRECAUCIÓN
Presión excesiva en el arranque puede causar que
la suciedad forme una obstrucción.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Doble el cable a la mitad y de nuevo aplique aire
sobre el mismo. Repita este procedimiento hasta que
ya no salga más suciedad. Si ya ha hecho esto y se
experimentan problemas de alimentación, pruebe
reemplazando la guía y consulte la sección de localización de averías en el rubro de Alimentación de
Alambre Irregular.
Para instrucciones sobre cómo reemplazar o cambiar
un rodillo impulsor, vea “Rodillos del Mecanismo de
Alimentación” en la sección de Operación.
INSTALACIÓN DE LA PUNTA DE
CONTACTO Y TOBERA DE GAS
1. Elija la punta de contacto del tamaño correcto para
el electrodo que se está utilizando (el tamaño del
alambre está marcado en el lado de la punta de
contacto) y atorníllelo ajustadamente en el difusor
de gas.
2. Atornille la tobera de gas fija apropiada sobre el
difusor. Es posible utilizar la tobera al ras estándar
de 12.7 mm (.50") u otros tamaños opcionales de
toberas al ras 9arco de rociado) o retraídas. (Vea
la Tabla D.2 en esta sección.)
POWER MIG® 216
Page 55

D-2-SP
MANTENIMIENTO
D-2-SP
REMOCIÓN Y REEMPLAZO DE LA
GUÍA DE ALAMBRE
NOTA: Cambiar la guía de alambre por un tamaño de
alambre diferente requiere reemplazar el difusor de
gas conforme a la Tabla D.1, a fin de asegurar adecuadamente la guía de alambre diferente.
TABLA D.1
Núm. de Parte
Número de Parte
Diámetro de los Alambre de
Electrodos Utilizados
Acero de 0.6-0.8 mm
(.025”-.030")
Acero de 0.9-1.2 mm
(.025”-.030")
Aluminio de 1.2 mm
(3/64")
de la Guía de
Reemplazo Buje de la Guía (y Esténcil)
KP42-25-15 .030 (0.8 mm)
KP42-4045-15 .045 (1.2 mm) KP2746-1
KP42-4045-15 3/64" (1.2 mm)
Tamaño Marcado
en el Extremo del
INSTRUCCIONES DE REMOCIÓN, INSTALACIÓN Y
CORTE DE LA GUÍA DE ALAMBRE PARA MAGNUM PRO 2
50L
NOTA: La variación de longitudes de cables evita la
intercambiabilidad de guías de alambre entre pistolas.
Una vez que una guía ha sido cortada para una pistola
en particular, no deberá instalarse en otra pistola a
menos que pueda satisfacer el requerimiento de longitud
cortada de la guía. Las guías de alambre se envían con
sus cubiertas extendidas en la cantidad adecuada.
1. Remueva la tobera de gas, si se utiliza, para localizar
el tornillo de fijación en el difusor de gas que sirve
para mantener a la guía de alambre anterior en su
lugar. Afloje el tornillo de fijación con una llave Allen
de 2.0 mm (5/64”).
del Difusor
de Gas de la
Tobera Fija
7. Atornille el difusor de gas en el extremo del tubo
de la pistola y apriete bien. Asegúrese de que el
difusor de gas es correcto para la guía de alambre
que se está utilizando. (Vea la tabla y esténcil del
difusor).
8. Apriete el tornillo de fijación en el lado del difusor
de gas contra la guía de alambre del cable utilizando una llave Allen de 2.0 mm (5/64”).
FIGURA D.1
TORNILLO DE FIJACIÓN
CONECTOR DEL CABLE DE BRONCE
AISLADOR
TORNILLO DE FIJACIÓN
DIFUSOR DE GAS
TOBERA DE GAS
LONGITUD
A CORTAR
DE LA GUÍA
DE ALAMBRE
31.8mm (1-1/4)
PRECAUCIÓN
Este tornillo sólo deberá apretarse suavemente.
Apretar de más dividirá o colapsará la guía, lo que
a su vez provocará una alimentación de alambre
deficiente.
2. Remueva el difusor de gas y aislador del tubo de la
pistola.
3. Coloque la pistola y cable en forma recta sobre una
superficie plana. Afloje el tornillo de fijación del
conector localizado en el conector de metal en el lado
de alimentador del cable y jale la guía de alambre
fuera del cable.
4. Inserte la nueva guía de alambre sin cortar en el lado
de conector del cable. Asegúrese de que el buje de
la guía esté marcado apropiadamente para el tamaño
de alambre que se está utilizando.
5. Coloque completamente el buje de la guía de alambre en el conector; apriete el tornillo de fijación en el
conector de metal del cable. En este punto, el difusor
de gas no deberá estar instalado sobre el extremo
del tubo de la pistola.
6. Todavía sin el difusor de gas sobre el tubo de la pistola, asegúrese de que el cable está derecho y
después corte la guía de alambre en la longitud que
se muestra en la Figura D.1. Remueva cualquier
desecho del extremo de la guía de alambre.
POWER MIG® 216
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Page 56

D-3-SP D-3-SP
DESENSAMBLE DE LA MANIJA DE LA PISTOLA
Las partes internas de la manija de la pistola
pueden inspeccionarse o recibir servicio si es
necesario.
La manija de la pistola consiste de dos mitades
que están unidas por un collarín en cada
extremo. A fin de abrir la manija, gire los collarines aproximadamente 60 grados a la
izquierda (la misma dirección a seguir al
remover una rosca derecha) hasta que el collarín se detenga. Después, jale el collarín fuera
de la manija de la pistola. Si los collarines son
difíciles de girar, posiciones la manija de la pistola contra una esquina, coloque un desatornillador sobre la saliente del collarín y pegue
sobre el desatornillador para que el collarín
gire y se libere de una varilla de bloqueo interno.
A la izquierda
MANTENIMIENTO
ACCESORIOS Y PARTES DE REEMPLAZO DISPONIBLES PARA LA
PISTOLA MAGNUM PRO 250L Y ENSAMBLES DE CABLES
Descripción Parte Núm. Inglés Métrico
GUIA DE ALAMBRE DE CABLE
Para cable de 4.5 m KP42-25-15 .025" – .030" 0.6 – 0.8 mm
(15') ó más corto KP42-4045-15 .035" – .045" 0.9 – 1.1 mm
KP42-4045-15 3/64" 1.2 mm
PUNTAS DE CONTACTO
Trabajo Estánda KP2744-025 .025" 0.6 mm
Cónica KP2744-030T .030" 0.8 mm
Saliente (para Aluminio)
TOBERAS DE GAS
Fijas (Al Ras) KP2742-1-38F 3/8" 9.5 mm
Fixed(Retraídas) KP2742-1-38R 3/8" 9.5 mm
Requiere: Gas
Ensamble del Difusor
KP2744-030 .030" 0.8 mm
KP2744-035 .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045 .045" 1.1 mm
KP2744-035T* .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045T .045" 1.1 mm
KP2744-364A 3/64" 1.2 mm
KP2742-1-50F* 1/2" 12.7 mm
KP2742-1-62F 5/8" 15.9 mm
KP2742-1-50R 1/2" 12.7 mm
KP2742-1-62R 5/8" 15.9 mm
KP2746-1* .025" – .045" 0.6 – 1.1 mm
TABLA D.2
(Alambre de Aluminio)
Tamaño Tamaño
(Alambre de Aluminio)
(Alum. Wire) (Alum. Wire)
Aislador KP2773-2*
MONTAJES DE TUBO
DEL ARMA
Estándar (60°) KP3078-60*
45° KP3078-45*
* Se incluye con la POWER MIG® 216
** Las extremidades afiladas se requieren con 3/8 identificación de la” identifi-
cación y del 1/2”. Inyectores.
Vea www.lincolnelectric.com para el ofrecimiento completo de los favorables
materiales consumibles de la botella doble.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 57

LOCALIZACIÓN DE AVERÍAS
CÓMO UTILIZAR LA GUÍA DE LOCALIZACIÓN DE AVERÍAS
ADVERTENCIA
El servicio y la reparación sólo debe de ser realizado por Personal Capacitado por la Fábrica Lincoln
Electric. Reparaciones no autorizadas llevadas a cabo en este equipo pueden resultar peligrosas
para el técnico y el operador de la máquina, e invalidará su garantía de fábrica. Por su seguridad y
para evitar una descarga eléctrica, por favor tome en cuenta todas las notas de seguridad y precauciones detalladas a lo largo de este manual.
__________________________________________________________________________
Esta guía de detección de problemas se proporciona
para ayudarle a localizar y a reparar posibles averías
de la máquina. Simplemente siga el procedimiento de
tres pasos que se da enseguida.
Paso 1.LOCALIZACIÓN DEL PROBLEMA
(SÍNTOMA).
Observe debajo de la columna llamada “PROBLEMA
(SÍNTOMAS)”. Esta columna describe los síntomas
posibles que la máquina pueda presentar. Encuentre
la lista que describa de la mejor manera el síntoma
que la máquina está presentando.
Paso 3.ACCIÓN RECOMENDADA
Esta columna proporciona una acción para la Causa
Posible, generalmente recomienda que establezca
contacto con su Taller de Servicio de Campo
Autorizado por Lincoln local.
Si no entiende o no puede llevar a cabo la Acción
Recomendada de manera segura, contacte su Taller
de Servicio de Campo Lincoln Autorizado
E-1-SPE-1-SP
Paso 2. CAUSA POSIBLE.
En la segunda columna llamada “CAUSA POSIBLE”
se enumeran los factores que pueden originar el síntoma en la máquina.
PRECAUCIÓN
Si por alguna razón usted no entiende los procedimientos de prueba o es incapaz de efectuar las pruebas y
reparaciones de manera segura, contacte su Taller de Servicio de Campo Lincoln Autorizado para asistencia
en la localización de fallas técnicas antes de proceder.
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
POWER MIG® 216
Page 58

SOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
Observe todos los lineamientos de seguridad que se detallan en el presente manual
E-2-SPE-2-SP
PROBLEMAS
(SÍNTOMAS)
PROBLEMAS DE SALIDA
Daño físico o eléctrico relevante es
evidente
No hay presencia de voltaje de circuito abierto ni de alimentación de
alambre cuando se jala el gatillo.
Se aplica alimentación a la
POWER MIG® 216.
Hay presencia de voltaje de salida
y alimentación de alambre cuando
no se jala el gatillo
(no activado).
CAUSA
POSIBLE
1. Póngase en contacto con su
Taller Local de Servicio
Autorizado de Lincoln.
1 El gatillo de la pistola o cable puede
tener falla. Revise o reemplace el
ensamble de la pistola.
2. El circuito de protección térmica
puede estar activado. Si este es el
caso, permitir que la máquina se
enfríe eliminará la condición de error.
3. Asegúrese de que el voltaje de entrada sea el correcto y que corresponda
a la capacidad nominal en la placa
de identificación; reconecte la configuración del panel.
4. Si el kit opcional de antorcha “spool
gun” está instalado, revise para ver
que esté establecido en “Empuje el
Pistola” si se aprieta el gatillo asociado con el alimentador integrado, y en
“Spool Gun” si se aprieta el gatillo de
la antorcha “spool gun”.
1. Remueva el ensamble de la pistola de la máquina. Si el problema
se resuelve, el ensamble de la pistola tiene falla. Repare o reemplace.
2. Si el problema persiste cuando se
remueve el ensamble de la pistola, entonces el problema está dentro de la POWER MIG® 216
.
CURSO DE ACCION
RECOMENDADO
Si todas las áreas posibles de
desajuste han sido revisadas y el
problema persiste, Póngase en
Contacto con su Taller de
Servicio de Campo Autorizado
de Lincoln local.
La salida de la máquina es baja.
Las soldaduras están “frías” y el
cordón de soldadura está
redondeado o con protuberancias
demostrando un mojado pobre en
la placa.
1. Revise el voltaje de entrada.
Asegúrese de que el voltaje de
entrada corresponde a la capacidad nominal de la placa de identificación y reconecte la configuración del panel.
2. Asegúrese de que las configuraciones de la velocidad de alimentación de alambre y voltaje
sean las correctas para el proceso que se está utilizando.
3. Asegúrese de que la polaridad
de salida sea la correcta para el
proceso que se está utilizando..
4. Revise los cables de soldadura y
ensamble de la pistola en busca
de conexiones sueltas o con
falla.
PRECAUCIÓN
Si por alguna razón usted no entiende los procedimientos de prueba o es incapaz de efectuar las pruebas y reparaciones de manera segura,
contacte su Taller de Servicio de Campo Lincoln Autorizado para asistencia en la localización de fallas técnicas antes de proceder.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 59

SOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
Observe todos los lineamientos de seguridad que se detallan en el presente manual
E-3-SPE-3-SP
PROBLEMAS
(SÍNTOMAS)
PROBLEMAS DE SALIDA
Pobre formación de arco con electrodo pegándose o explotando.
PROBLEMAS DE ALIMENTACIÓN
Alimentación de alambre irregular
o el alambre no se alimenta pero
los rodillos impulsores están girando.
CAUSA
POSIBLE
1. Asegúrese de que las configuraciones de
velocidad de alimentación de alambre y voltaje sean las correctas para el proceso que se
está utilizando.
2. La protección de gas puede no ser la adecuada para el proceso que se está utilizando.
3. Revise el voltaje de línea de entrada para
estar dentro del rango nominal recomendado
de la máquina.
4. Revise que el panel de reconexión de la
máquina esté configurado adecuadamente
para el voltaje aplicado.
1. El cable de la pistola puede estar doblado o
retorcido.
2. El alambre puede estar atorado en el cable de
la pistola, o el cable de la pistola puede estar
sucio.
3. Revise la tensión del rodillo impulsor y la posición de las ranuras.
4. Revise si hay rodillos impulsores gastados o
sueltos.
5. El electrodo puede estar oxidado o sucio.
6. Revise si la punta de contacto está dañada o
es incorrecta.
7. Revise si el eje del alambre gira fácilmente y
ajuste la perilla de tensión de frenado si es
necesario.
8. Revise que la pistola esté totalmente dentro
de su montaje y asentada adecuadamente.
CURSO DE ACCION
RECOMENDADO
Si todas las áreas posibles de
desajuste han sido revisadas y el
problema persiste, Póngase en
Contacto con su Taller de
Servicio de Campo Autorizado
de Lincoln local.
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
PRECAUCIÓN
Si por alguna razón usted no entiende los procedimientos de prueba o es incapaz de efectuar las pruebas y reparaciones de manera segura,
contacte su Taller de Servicio de Campo Lincoln Autorizado para asistencia en la localización de fallas técnicas antes de proceder.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 60

E-4-SP E-4-SP
Observe todos los lineamientos de seguridad que se detallan en el presente manual
SOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
PROBLEMAS
(SÍNTOMAS)
PROBLEMAS DE ALIMENTACIÓN
La alimentación de alambre se
detiene durante la soldadura.
Cuando el gatillo se libera y se jala
de nuevo, la alimentación de
alambre empieza otra vez.
No hay control de la velocidad de
alimentación de alambre. Otras
funciones de la máquina son normales.
ÁREAS POSIBLES DE
DESAJUSTE(S)
1. Revise que los rodillos impulsores de alimentación de alambre y el motor funcionen sin
problemas.
2. Revise si hay restricciones en la
ruta de alimentación de alambre.
Revise si hay obstrucciones en
la pistola y cable.
3. Asegúrese de que la guía de
alambre de la pistola y punta
sean correctas para el tamaño
de alambre que se está utilizando.
4. Asegúrese de que los rodillos
impulsores y placas guía estén
limpios y sean del tamaño correcto.
5. Revise si el eje gira fácilment
1. El control de velocidad de alimentación
de alambre puede estar sucio. Gire
varias veces y revise si el problema
está resuelto.
CURSO DE ACCION
RECOMENDADO
Si todas las áreas posibles de
desajuste han sido revisadas y el
problema persiste, Póngase en
Contacto con su Taller de
e.
Servicio de Campo Autorizado
de Lincoln local.
PROBLEMAS DE FLUJO DE GAS
El gas no fluye cuando se jala el
gatillo de la pistola.
1. Asegúrese de que el suministro
de gas este conectado adecuadamente y “ENCENDIDO”.
2. Si el solenoide de gas se active
(hace clic) cuando se aprieta el
gatillo de la pistola, puede haber
una restricción en la línea de
suministro de gas.
3. El ensamble del cable de la pistola puede tener falla. Revise o
reemplace.
4. Si el solenoide de gas no opera
cuando se aprieta el gatillo de la
pistola, el problema está dentro
de la POWER MIG® 216.
5. Asegúrese de que la pistola
esté totalmente dentro de su
montaje y asentada adecuadamente.
PRECAUCIÓN
Si por alguna razón usted no entiende los procedimientos de prueba o es incapaz de efectuar las pruebas y reparaciones de manera segura,
contacte su Taller de Servicio de Campo Lincoln Autorizado para asistencia en la localización de fallas técnicas antes de proceder.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 61

F-1-SP
½”
CARTA DEL USO
F-1-SP
G / 500
D / 225 D / 350 E / 375 E / 400 F / 500
C / 180
G / 425
E / 325 F / 375
E / 265 E / 280
C / 130 D / 150
D / 130
C / 90 C / 100
B / 80
B / 75
C / 70 C / 90 D / 110 D / 130
B / 70
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 425
E / 400
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
E / 250 F / 300
E / 570
E / 570
D / 485
C / 475
B / 300
A / 300
E / 390 F / 410
B / 500 C / 500 D / 450 E / 500 E / 550
B / 475
E / 400
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
E / 575
E / 575
D / 485
C / 475
B / 325
A / 300
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 475
B / 325 B / 350 B / 450 C / 375 D / 375 E / 400
E / 250 F / 300
E / 575 E / 575
D / 485
A / 300 B / 300 C / 475
E / 390 F / 410
G / 500
G / 500
G / 350 G / 350 G / 400
E / 400
D / 285
C / 200
C / 175
F / 375
E / 350
D / 250
D / 200
C / 175
C / 140
F / 320
E / 280
E / 240
D / 200
D / 160
C / 120
C / 9 0
E / 170
E / 160
E / 150
D / 125
D / 110
D / 90
C / 7 5
G / 500
D / 250 E / 300 F / 350
G / 300
G / 270
F / 230
D / 200
G / 475
F / 350
E / 300
E / 300
E / 320
E / 200E / 160
E / 330
D / 280
D / 280
C / 230
C / 180
B / 130
B / 11O
B / 90 B / 120 C / 160 C / 200 D / 240
E / 180
C / 110 D / 120 D / 140
C / 8 0
3/ 16” 1/ 4” 5/ 16” 3/ 8”
D / 300
C / 225
C / 175
M at erial Thickness/ Espesor de el
material/ Lépaisseur de matériel
B / 150
22 ga 20 ga 18 ga 16 ga 14 ga 12 ga 10 ga
R
16
2
POWER M IG
/ / / / / / / / / / /
A / 1OO
B / 125
/
.030 in .036 in .048 in .060 in .075 in .105 in .135 in .187 in .250 in .312 in .375 in .500 in
Wire Di ameter
(0.8mm) (0.9mm) (1.2mm) (1.6mm) (2.0mm) (2.5mm) (3.5mm) (4.8mm) (6.4mm) (7.9mm) (9.5mm) (12.7mm)
Dia. du f il
Dia. de alam bre
- 3/8 in.
(mm)
In.
30-40 CFH
B / 125
(0.6)
0.025
A / 75
(0.8)0.030
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
75%/ 25%
C / 150
C / 125
(0.8)0.030
(0.6)0.0
(0.9)0.0
25
35
0.045 (1.1)
2
100% CO
R
MIG
(DC+)
Super Arc
(1.1)0.0
45
(1.1)0.045
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
75%/ 25%
Gas-Shielded
(0.9)0.035
R
Outer shield 7 1 M
UltraCore 71A75
(0.9)
90%/ 7.5%/ 2.5%
BlueMax 308 LSI
0.035
He/ Ar/ CO
(DC+)
(1.1)
(0.9)0.0
35
2
R
Innershield
0.045
& 212
NR-211-MP
(DC-)
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
M AGN U M SG GUN (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
M AGN U M SG GUN (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
(0.8)0.030
R
Aluminum
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
(0.9)0.0
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
35
100% Ar
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
(0.9)0.035(1.2)
(1.2)
3/64
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
3/64
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
(0.8)0.030
2
Tr i -M ix
100% CO
R
St ainles s
DUAL (DC+)
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
POWER MIG® 216
Page 62

TARJETA DE CONTROL
TERMOSTATO DEL
ENSAMBLE DEL RECTIFICADOR
DIAGRAMAS DE CABLEADO
DE ANTORCHA “SPOOL GUN” ADICIONALES
SE UTILIZA PARA OPCIONES
DE ALAMBRE
VELOCIDAD DE
ALIMENTACIÓN
LISTO 100SG
AL
TRABAJO
F-2-SPF-2-SP
4
TRANSFORMADOR
TERMOSTATO DEL
BOBINA
BOBINA
DIODO DE
PUENTE DEL
RECTIFICADOR
EL INTERRUPTOR Y GATILLO DE LA
PISTOLA SE MUESTRAN EN EL MODO
DE PISTOLA DE CONTRAFASE MAGNUM
DEL ARMA
SELECTOR SWITH
100 L
TOROIDE
GATILLO DE
LA PISTOLA
DE POTENCIA
TRANSFORMADOR
TOROIDE
H9
RECTIFICAR
DEL PUENTE
MONOFÁSICO
A
H8
DE
MOTOR/CAJA
ENGRANAJES
DE SALIDA
INDUCTOR
F
G
E
D
C
B
H7
H6
H5
H4
H3
H2
H1
INTERRUPTOR
SELECTOR DE TOMA
N.B. ESTE DIAGRAMA MUESTRA LA POLARIDAD DEL ELECTRODO COMO “POSITIVA”. A FIN
DE CAMBIAR LA POLARIDAD, APAGUE LA UNIDAD E INVIERTA LAS CONEXIONES DE
N.A. EL CABLE DE SOLDADURA DEBE SER DE CAPACIDAD ADECUADA PARA LA CORRIENTE
Y CICLO DE TRABAJO DE LAS APLICACIONES INMEDIATAS Y FUTURAS.
CABLES EN LA TERMINAL DEL CONDUCTOR DEL CABLE Y BORNE DE TRABAJO
NOTAS:
SECUENCIA DE NUMERACIÓN
(LADO DEL COMPONENTE DE LA TARJETA DE P.C.)
B- NEGRO
W – BALNCO
R- ROJO
U- AZUL
CÓDIGO DE COLOR
INFORMACIÓN GENERAL
SÍMBOLOS ELÉCTRICOS CONFORME A E1537
INDICA CAVIDA DE CONECTOR NÚM.
CAVIDAD
SECUENCIA DE NUMERACIÓN
(LADO NO DE CABLE DEL CONECTOR)
J4 (GATILLO
LADO DEL MONITOR)
TACÓMETRO
Motor de
Ventilador
DE LÍNEA
INTERRUPTOR
POWER MIG® 216
H11B
H10A
H11B
CR2
H11A
H10B
CR1
L2A
L2B
L2
L1
H8
H11A
208V
H9
230V
PANEL DE
RECONEXIÓN
B
A LÍNEA DE
W
SUMINISTRO
MONOFÁSICA
L1A
L1B
G
NACIONAL
A TIERRA CONFORME
AL CÓDIGO ELÉCTRICO
NOTA: Este diagrama es sólo para referencia. Tal vez no sea exacto para todas las máquinas que cubre este manual. El diagrama específico para un código particular está pegado dentro de la máquina en
uno de los páneles de la cubierta. Si el diagrama es ilegible, escriba al Departamento de Servicio para un reemplazo. Proporcione el número de código del equipo.
Page 63

DIBUJO DE DIMENSIÓN
F-3-SPF-3-SP
A.01
M22179
20.12
19.15
17.47
32.68
40.20
12.00
29.73
30.43
POWER MIG® 216
38.58
MANUAL DE OPERACIÓN
Page 64

NOTAS
Page 65

POWER MIG®216
Sʼapplique aux machines dont le numéro de code est
La sécurité dépend de vous
Le matériel de soudage et de
coupage à l'arc Lincoln est
conçu et construit en tenant
compte de la sécurité. Toutefois,
la sécurité en général peut être
accrue grâce à une bonne installation... et à la plus grande prudence de votre part. NE PAS
INSTALLER, UTILISER OU
RÉPARER CE MATÉRIEL
SANS AVOIR LU CE MANUEL
ET LES MESURES DE
SÉCURITÉ QU'IL CONTIENT.
Et, par dessus tout, réfléchir
avant d'agir et exercer la plus
grande prudence
11817
For use with machine Code Numbers
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Copyright © Lincoln Global Inc.
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 66

i-Fr
SÉCURITÉ
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT DE LA PROPOSITION DE CALIFORNIE 65
Les gaz dʼéchappement du moteur diesel et certains de
leurs constituants sont connus par lʼÉtat de Californie
pour provoquer le cancer, des malformations ou autres
dangers pour la reproduction.
i-Fr
Les gaz dʼéchappement de ce produit contiennent des
produits chimiques connus par lʼÉtat de Californie pour
provoquer le cancer, des malformations et des dangers
pour la reproduction.
Ceci sʼapplique aux moteurs diesel.
Ceci sʼapplique aux moteurs à essence.
LE SOUDAGE À LʼARC PEUT ÊTRE DANGEREUX. SE PROTÉGER ET PROTÉGER LES AUTRES CONTRE LES BLESSURES
GRAVES VOIRE MORTELLES. ÉLOIGNER LES ENFANTS. LES PERSONNES QUI PORTENT UN STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE
DEVRAIENT CONSULTER LEUR MÉDECIN AVANT DʼUTILISER LʼAPPAREIL.
Prendre connaissance des caractéristiques de sécurité suivantes. Pour obtenir des renseignements supplémentaires sur la
sécurité, on recommande vivement dʼacheter un exemplaire de la norme Z49.1, de lʼANSI auprès de lʼAmerican Welding
Society, P.O. Box 350140, Miami, Floride 33135 ou la norme CSA W117.2-1974. On peut se procurer un exemplaire gratuit
du livret «Arc Welding Safety» E205 auprès de la société Lincoln Electric, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-
1199.
SʼASSURER QUE LES ÉTAPES DʼINSTALLATION, DʼUTILISATION, DʼENTRETIEN ET DE RÉPARATION
NE SONT CONFIÉES QUʼÀ DES PERSONNES QUALIFIÉES.
POUR LES GROUPES
ÉLECTROGÈNES
1.a. Arrêter le moteur avant de dépanner et dʼentretenir à moins
quʼil ne soit nécessaire que le moteur tourne pour effectuer
lʼentretien.
_____________________________________________________
1.b. Ne faire fonctionner les moteurs quʼà lʼextérieur ou dans des endroits bien aérés
ou encore évacuer les gaz dʼéchappement du moteur à lʼextérieur.
1.h. Pour éviter de sʼébouillanter, ne pas
enlever le bouchon sous pression du
radiateur quand le moteur est chaud.
LES CHAMPS
ÉLECTROMAGNÉTIQUES
_____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
1.d. Les protecteurs, bouchons, panneaux et dispositifs de sécurité doivent être toujours en place et en bon état. Tenir les
mains, les cheveux, les vêtements et les outils éloignés des
courroies trapézoïdales, des engrenages, des ventilateurs et
dʼautres pièces en mouvement quand on met en marche,
utilise ou répare le matériel.
____________________________________________________
1.e. Dans certains cas, il peut être nécessaire de déposer les
protecteurs de sécurité pour effectuer lʼentretien prescrit. Ne
déposer les protecteurs que quand cʼest nécessaire et les
remettre en place quand lʼentretien prescrit est terminé.
Toujours agir avec la plus grande prudence quand on travaille près de pièces en mouvement.
____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
1.g.Pour ne pas faire démarrer accidentellement les moteurs à
essence en effectuant un réglage du moteur ou en entretenant
le groupe électrogène de soudage, de connecter les fils des
bougies, le chapeau de distributeur ou la magnéto
1.c. Ne pas faire le plein de carburant près dʼune
flamme nue, dʼun arc de soudage ou si le
moteur tourne. Arrêter le moteur et le laisser
refroidir avant de faire le plein pour empêcher
que du carburant renversé ne se vaporise au
contact de pièces du moteur chaudes et ne
sʼenflamme. Ne pas renverser du carburant
quand on fait le plein. Si du carburant sʼest
renversé, lʼessuyer et ne pas remettre le
moteur en marche tant que les vapeurs nʼont
pas été éliminées.
1.f. Ne pas mettre les mains près du ventilateur
du moteur. Ne pas appuyer sur la tige de
commande des gaz pendant que le moteur
tourne.
2.a. Le courant électrique qui circule dans les conducteurs crée
des champs électromagnétiques locaux. Le courant de
soudage crée des champs magnétiques autour des câbles et
des machines de soudage.
2.b. Les champs électromagnétiques peuvent créer des interférences pour les stimulateurs cardiaques, et les soudeurs
qui portent un stimulateur cardiaque devraient consulter leur
médecin avant dʼentreprendre le soudage
2.c. Lʼexposition aux champs électromagnétiques lors du soudage
peut avoir dʼautres effets sur la santé que lʼon ne connaît pas
encore.
2.d. Les soudeurs devraient suivre les consignes suivantes afin
de réduire au minimum lʼexposition aux champs électromagnétiques du circuit de soudage:
2.d.1.
si possible avec du ruban adhésif.
2.d.2.Ne jamais entourer le câble électrode autour du corps.
2.d.3.Ne pas se tenir entre les câbles dʼélectrode et de retour.
Si le câble dʼélectrode se trouve à droite, le câble de retour
doit également se trouver à droite.
2.d.4.Connecter le câble de retour à la pièce le plus près possible de la zone de soudage.
2.d.5.Ne pas travailler juste à côté de la source de courant de
soudage.
peuvent être dangereux
Regrouper les câbles dʼélectrode et de retour. Les fixer
Page 67

ii-Fr
SÉCURITÉ
ii-Fr
LES CHOCS
ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent
être mortels.
3.a. Les circuits de lʼélectrode et de retour (ou
masse) sont sous tension quand la source de
courant est en marche. Ne pas toucher ces
pièces sous tension les mains nues ou si lʼon porte des vêtements mouillés. Porter des gants isolants secs et ne comportant
pas de trous.
3.b. S'isoler de la pièce et de la terre en utilisant un moyen d'iso-
lation sec. S'assurer que l'isolation est de dimensions suffisantes pour couvrir entièrement la zone de contact
physique avec la pièce et la terre.
En plus des consignes de sécurité normales, si l'on doit
effectuer le soudage dans des conditions dangereuses
au point de vue électrique (dans les endroits humides
ou si l'on porte des vêtements mouillés; sur les constructions métalliques comme les sols, les grilles ou les
échafaudages; dans une mauvaise position par exemple
assis, à genoux ou couché, sʼil y a un risque élevé de
contact inévitable ou accidentel avec la pièce ou la
terre) utiliser le matériel suivant :
• Source de courant (fil) à tension constante c.c. semiautomatique.
• Source de courant (électrode enrobée) manuelle c.c.
• Source de courant c.a. à tension réduite.
3.c. En soudage semi-automatique ou automatique, le fil, le dévi-
doir, la tête de soudage, la buse ou le pistolet de soudage
semi-automatique sont également sous tension.
3.d. Toujours s'assurer que le câble de retour est bien connecté
au métal soudé. Le point de connexion devrait être le plus
près possible de la zone soudée.
3.e. Raccorder la pièce ou le métal à souder à une bonne prise
de terre.
LE RAYONNEMENT DE
L'ARC peut brûler.
4.a. Utiliser un masque à serre-tête avec oculaire
filtrant adéquat et protège-oculaire pour se protéger les yeux contre les étincelles et le rayon-
observe l'arc de soudage. Le masque à serre-tête et les oculaires filtrants doivent être conformes aux normes ANSI Z87.1.
4.b. Utiliser des vêtements adéquats en tissu ignifugé pour se
protéger et protéger les aides contre le rayonnement de
l'arc.
4.c. Protéger les autres employés à proximité en utilisant des
paravents ininflammables convenables ou les avertir de ne
pas regarder l'arc ou de ne pas s'exposer au rayonnement
de l'arc ou aux projections ou au métal chaud.
nement de l'arc quand on soude ou quand on
L
ES FUMÉES ET
LES GAZ peuvent
être dangereux.
des gaz dangereux pour la santé. Éviter de respirer ces fumées
et ces gaz. Pendant lesoudage, maintenir sa tête hors des
fumées. Utiliser suffisamment de ventilation et/ou d'échappement
au niveau de l'arc pour tenir les fumées et les gaz hors de la
zone de respiration. Lorsqu'on soude avec des électrodes
ayant besoin d'une ventilation spéciale telles que celles en
acier inoxydable ou pour le rechargement dur (voir les
instructions ou le conteneur ou la MSDS)ou sur le plomb ou
de l'acier cadmié ou sur d'autres métaux ou recouvrements
produisant des vapeurs très toxiques, maintenir le niveau
d'exposition aussi bas que possible et dans les limites
OHAS-PEL et ACGIH TLV au moyen de l'échappement local
ou d'une ventilation mécanique. Dans des espaces confinés
ou dans certaines circonstances à l'extérieur, un respirateur
peut s'avérer nécessaire. Des précautions supplémentaires
doivent également être prises pour souder sur de l'acier galvanisé.
5.a. Le soudage peut produire des fumées et
3.f.
Tenir le porte-électrode, le connecteur de pièce, le câble de
soudage et l'appareil de soudage dans un bon état de fonctionnement. Remplacer l'isolation endommagée.
3.g. Ne jamais tremper l'électrode dans l'eau pour la refroidir.
3.h. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les pièces sous tension
des porte-électrodes connectés à deux sources de courant
de soudage parce que la tension entre les deux peut correspondre à la tension à vide totale des deux appareils.
3.i. Quand on travaille au-dessus du niveau du sol, utiliser une
ceinture de sécurité pour se protéger contre les chutes en
cas de choc.
3.j. Voir également les points 6.c. et 8.
5.b. Le fonctionnement de lʼappareil de contrôle des vapeurs de
soudage est affecté par plusieurs facteurs y compris lʼutilisation et le positionnement corrects de lʼappareil, son entretien
ainsi que la procédure de soudage et lʼapplication concernées. Le niveau dʼexposition aux limites décrites par
OSHA PEL et ACGIH TLV pour les ouvriers doit être vérifié
au moment de lʼinstallation et de façon périodique par la
suite afin dʼavoir la certitude quʼil se trouve dans lʼintervalle
en vigueur.
5.c.
Ne pas souder dans les endroits à proximité des vapeurs
d'hydrocarbures chlorés provenant des opérations de
dégraissage, de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et
le rayonnement de l'arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs de
solvant pour former du phosgène, gaz très toxique, et
d'autres produits irritants.
5.d. Les gaz de protection utilisés pour le soudage à l'arc peuvent chasser l'air et provoquer des blessures graves voire
mortelles. Toujours utiliser une ventilation suffisante, spécialement dans les espaces clos pour s'assurer que l'air
inhalé ne présente pas de danger.
5.e. Lire et comprendre les instructions du fabricant pour cet
appareil et le matériel de réserve à utiliser, y compris la
fiche de données de sécurité des matériaux (MSDS) et suivre les pratiques de sécurité de lʼemployeur. Les fiches
MSDS sont disponibles auprès du distributeur de matériel
de soudage ou auprès du fabricant.
5.f. Voir également le point 1.b.
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 68

iii-Fr
SÉCURITÉ
iii-Fr
LES ÉTINCELLES DE
SOUDAGE peuvent
provoquer un incendie
ou une explosion.
6.a.
zone de soudage. Si ce n'est pas possible, les recouvrir
pour empêcher que les étincelles de soudage ne les
atteignent. Les étincelles et projections de soudage peuvent
facilement s'infiltrer dans les petites fissures ou ouvertures
des zones environnantes. Éviter de souder près des conduites hydrauliques. On doit toujours avoir un extincteur à
portée de la main.
6.b. Quand on doit utiliser des gaz comprimés sur les lieux de
travail, on doit prendre des précautions spéciales pour éviter
les dangers. Se référer à la “Sécurité pour le Soudage et le
Coupage” (ANSI Z49.1) et les consignes d'utilisation relatives au matériel.
6.c. Quand on ne soude pas, s'assurer qu'aucune partie du circuit de l'électrode ne touche la pièce ou la terre. Un contact
accidentel peut produire une surchauffe et créer un risque
d'incendie.
6.d. Ne pas chauffer, couper ou souder des réservoirs, des fûts
ou des contenants sans avoir pris les mesures qui s'imposent pour s'assurer que ces opérations ne produiront pas
des vapeurs inflammables ou toxiques provenant des substances à l'intérieur. Elles peuvent provoquer une explosion
même si elles ont été «nettoyées». For information, purchase “Recommended Safe Practices for the
Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That Have
Held Hazardous Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American
Welding Society
6.e. Mettre à l'air libre les pièces moulées creuses ou les contenants avant de souder, de couper ou de chauffer. Elles
peuvent exploser.
Les étincelles et les projections sont expulsées de l'arc de
6.f.
soudage. Porter des vêtements de protection exempts
d'huile comme des gants en cuir, une chemise épaisse, un
pantalon sans revers, des chaussures montantes et un
casque ou autre pour se protéger les cheveux. Utiliser des
bouche-oreilles quand on soude hors position ou dans des
espaces clos. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité avec
écrans latéraux quand on se trouve dans la zone de
soudage.
6.g. Connecter le câble de retour à la pièce le plus près possible
de la zone de soudage. Si les câbles de retour sont connectés à la charpente du bâtiment ou à d'autres endroits
éloignés de la zone de soudage cela augmente le risque
que le courant de soudage passe dans les chaînes de levage, les câbles de grue ou autres circuits auxiliaires. Cela
peut créer un risque d'incendie ou surchauffer les chaînes
de levage ou les câbles et entraîner leur défaillance.
6.h. Voir également le point 1.c.
6.i. Lire et appliquer la Norme NFPA 51B “pour la Prévention
des Incendies Pendant le Soudage, le Coupage et dʼAutres
Travaux Impliquant de la Chaleur”, disponible auprès de
NFPA, 1 Batterymarch Park,PO Box 9101, Quincy, Ma
022690-9101.
Enlever les matières inflammables de la
Preparation
(see address above).
for
LES BOUTEILLES peuvent exploser si elles
sont endommagées.
7.a. N'utiliser que des bouteilles de gaz comprimé contenant le gaz de protection convenant pour le procédé utilisé ainsi que des
détendeurs en bon état conçus pour les gaz et la pression utilisés. Choisir les tuyaux souples, raccords, etc. en fonction de
l'application et les tenir en bon état.
7.b. Toujours tenir les bouteilles droites, bien fixées par une
chaîne à un chariot ou à support fixe.
7.c. On doit placer les bouteilles :
• Loin des endroits où elles peuvent être frappées ou
endommagées.
• À une distance de sécurité des opérations de soudage à
l'arc ou de coupage et de toute autre source de chaleur,
d'étincelles ou de flammes.
7.d. Ne jamais laisser l'électrode, le porte-électrode ou toute
autre pièce sous tension toucher une bouteille.
7.e. Éloigner la tête et le visage de la sortie du robinet de la
bouteille quand on l'ouvre.
7.f. Les bouchons de protection des robinets doivent toujours
être en place et serrés à la main sauf quand la bouteille est
utilisée ou raccordée en vue de son utilisation.
7.g. Lire et suivre les instructions sur les bouteilles de gaz com-
primé, et le matériel associé, ainsi que la publication P-1 de
la CGA “Précautions pour le Maniement en toute Sécurité de
Gaz Comprimés dans des Cylindres », que l'on peut se procurer auprès de la Compressed Gas Association, 1235
Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA22202.
Pour des Appareils à
Puissance ÉLECTRIQUE
8.a. Couper l'alimentation d'entrée en utilisant
le disjoncteur à la boîte de fusibles avant
de travailler sur le matériel.
8.b. Installer le matériel conformément au
Code Électrique National des États Unis,
à tous les codes locaux et aux recommandations du fabricant.
8.c. Mettre à la terre le matériel conformément au Code Électrique National des États Unis et aux recommandations du
fabricant.
6.j. Ne pas utiliser de source de puissance de soudage pour le
dégel des tuyauteries.
Visitez http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety pour obtenir l´information additionnelle.
Page 69

NOTES
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 70

Merci
v-Frv-Fr
dʼavoir choisi un produit de QUALITÉ Lincoln Electric. Nous tenons à ce
que vous soyez fier dʼutiliser ce produit Lincoln Electric ••• tout comme
nous sommes fiers de vous livrer ce produit.
Les activités commerciales de The Lincoln Electric Company sont la fabrication et la vente dʼappareils de soudage de grande qualité, les
pièces de rechange et les appareils de coupage. Notre défi est de satisfaire les besoins de nos clients et de dépasser leur attente.
Quelquefois, les acheteurs peuvent demander à Lincoln Electric de les conseiller ou de les informer sur lʼutilisation de nos produits. Nous
répondons à nos clients en nous basant sur la meilleure information que nous possédons sur le moment. Lincoln Electric nʼest pas en mesure
de garantir de tels conseils et nʼassume aucune responsabilité à lʼégard de ces informations ou conseils. Nous dénions expressément toute
garantie de quelque sorte quʼelle soit, y compris toute garantie de compatibilité avec lʼobjectif particulier du client, quant à ces informations ou
conseils. En tant que considération pratique, de même, nous ne pouvons assumer aucune responsabilité par rapport à la mise à jour ou à la
correction de ces informations ou conseils une fois que nous les avons fournis, et le fait de fournir ces informations ou conseils ne créé, ni
étend ni altère aucune garantie concernant la vente de nos produits.
Lincoln Electric est un fabricant sensible, mais le choix et lʼutilisation de produits spécifiques vendus par Lincoln Electric relève uniquement du
contrôle du client et demeure uniquement de sa responsabilité. De nombreuses variables au-delà du contrôle de Lincoln Electric affectent les
résultats obtenus en appliquant ces types de méthodes de fabrication et dʼexigences de service.
Susceptible dʼêtre Modifié - Autant que nous le sachons, cette information est exacte au moment de lʼimpression. Prière de visiter le site
www.lincolnelectric.com pour la mise à jour de ces info
Veuillez examiner immédiatement le carton et le matériel
Quand ce matériel est expédié, son titre passe à lʼacheteur dès que le transporteur le reçoit. Par conséquent, les
réclamations pour matériel endommagé au cours du transport doivent êtes faites par lʼacheteur contre la société
de transport au moment de la réception.
Veuillez inscrire ci-dessous les informations sur lʼidentification du matériel pour pouvoir sʼy reporter ultérieurement. Vous trouverez cette information sur la plaque signalétique de votre machine.
Produit _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Numéro de Modèle _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
POLITIQUE DʼASSISTANCE AU CLIENT
Numéro e code / Code dʼachat _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Numéro de série _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Date dʼachat _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Lieu dʼachat _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Chaque fois que vous désirez des pièces de rechange ou des informations sur ce matériel, indiquez toujours les
informations que vous avez inscrites ci-dessus.
Inscription en Ligne
- Inscrivez votre machine chez Lincoln Electric soit par fax soit sur Internet.
• Par fax : Remplissez le formulaire au dos du bon de garantie inclus dans la paquet de documentation qui
accompagne cette machine et envoyez-le en suivant les instructions qui y sont imprimées.
• Pour une inscription en Ligne: Visitez notre
Rapides » et ensuite « Inscription de Produit ». Veuillez remplir le formulaire puis
lʼenvoyer.
Lisez complètement ce Manuel de lʼOpérateur avant dʼessayer dʼutiliser cet appareil. Gardez ce manuel et maintenez-le à
portée de la main pour pouvoir le consultez rapidement. Prêtez une attention toute particulière aux consignes de sécurité que
nous vous fournissons pour votre protection. Le niveau dʼimportance à attacher à chacune dʼelle est expliqué ci-après :
WEB SITE www.lincolnelectric.com. Choisissez lʼoption « Liens
AVERTISSEMENT
Cet avis apparaît quand on doit suivre scrupuleusement les informations pour éviter les blessures graves voire mortelles.
ATTENTION
Cet avis apparaît quand on doit suivre les informations pour éviter les blessures légères ou les dommages du matériel.
Page 71

TABLE DES MATIÈRES
Page
________________________________________________________________________
Installation .......................................................................................................Section A
Spécifications Techniques.....................................................................................A-1
Mesures De Sécurité .............................................................................................A-2
Déballage De La POWER MIG® 216....................................................................A-2
Emplacement.........................................................................................................A-2
Puissance Dʼentrée, Mise A La Terre Et Diagramme De Connexion.............A-2, A-3
Branchements Pour La Polarité De Sortie.............................................................A-3
Installation Du Pistolet Et Du Câble.......................................................................A-4
Ecran De Gaz Inerte..............................................................................................A-4
Installation de Claw™ D'enroulement....................................................................A-5
________________________________________________________________________
Fonctionnement ..............................................................................................Section B
Mesures De Sécurité .............................................................................................B-1
Description Du Produit...........................................................................................B-2
Procédés Et Equipement Recommandés..............................................................B-2
Capacité De Soudage............................................................................................B-2
Limites ...................................................................................................................B-2
Description Des Contrôles.....................................................................................B-2
Rouleau Conducteur De Fil ...................................................................................B-3
Pièces De Conversion De Taille De Fil..................................................................B-3
Procédure Pour Le Changement Des Jeux De Rouleaux Conducteurs Et De Cylindres Dʼappui
Chargement Des Tambours De Fil 10 à 30 lbs. ....................................................B-3
Pour Faire Démarrer La Soudeuse........................................................................B-4
Alimentation Du Fil Dʼélectrode .............................................................................B-4
Réglage De La Pression Du Cylindre Dʼappui.......................................................B-4
Configuration De Lʼentraîneur De Fil..............................................................B-4, B-5
Réalisation Dʼune Soudure....................................................................................B-5
Comment Eviter Les Problèmes Dʼalimentation Du Fil..........................................B-6
Contrôle Du Ventilateur .........................................................................................B-6
Ligne d'entrée protection de tension......................................................................B-6
Protection Contre Les Surcharges Dʼalimentation Du Fil ......................................B-6
Protection Thermique Contre Les Surcharges De Soudage .................................B-6
L'information de procédé de soudure ....................................................................B-6
Information Concernant Les Procédures De Soudage..........................................B-6
________________________________________________________________________
......................B-3
vi-Frvi-Fr
Accessoires.....................................................................................................Section C
Kits De Rouleaux Conducteurs .............................................................................C-1
Kit De Montage Du Cylindre Double .....................................................................C-1
Ensembles Alternatifs De Pistolet Magnum Gmaw Et Câble ................................C-1
Kit De Connexion De Pistolet Magnum ...............................................................C-1
Pistolets A Bobine Et Adaptateurs.........................................................................C-1
Réalisation Dʼune Soudure Avec Le Kit De Lʼadaptateur De Pistolet A Bobine Et Le Pistolet A Bobine Installés
________________________________________________________________________
........C-2
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 72

vii-Fr vii-Fr
TABLE DES MATIÈRES
Page
Entretien...........................................................................................................Section D
Mesures De Sécurité.............................................................................................D-1
Entretien Général ..................................................................................................D-1
Rouleaux Conducteurs Et Plaques Guides ...........................................................D-1
Installation De La Pointe De Contact Et Du Bec De Gaz ......................................D-1
Tubes De Pistolet Et Becs.....................................................................................D-1
Nettoyage Du Câble Du Pistolet............................................................................D-1
Retrait Et Changement De La Bande De Remplissage.........................................D-2
Démontage De La Poignée Du Pistolet.................................................................D-3
Guide Dépannage............................................................................................Section E
Comment Utiliser Le Guide De Dépannage ..........................................................E-1
Guide De Dépannage ..................................................................................E-2
Diagrammes De Câblage et Schéma Dimensionnel.....................................Section F
Liste de Pièces ................................................................................................Appendix
POWER MIG® 216
Magnum Pro 250L Gun .........................................................................P-202-AH (F)
......................................................................................P-611 (F)
à E-4
Page 73

A-1-Fr
INSTALLATION
SPÉCIFICATIONS TECHNIQUES - POWER MIG® 216
ENTRÉE – UNIQUEMENT MONOPHASÉE
Tension / Phase / Fréquence Standard
208/230/1/60 Hz 33/29 Amps 40/36 Amps
220/1/50 Hz 30 Amps 37 Amps
Facteur de Marche Amps Volts à Ampérage Nominal
30% 216 Amps 22 Volts
40% 190 Amps 23 Volts
60% 170 Amps 24
Courant dʼEntrée @ 170 Amp de Sortie Nominale
SORTIE NOMINALE
SORTIE
A-1-Fr
Courant dʼEntrée @ 216 Amp de Sortie Nominale
* Volts
Registre de Courant de Soudage
30 – 250Amps 35 Volts 13.5-24 Volts
Tension Maximum de Circuit Ouvert Registre de Tension de Soudage
TAILLES RECOMMANDÉES DE CÂBLES DʼENTRÉE ET DE FUSIBLES
Ampérage Nominal Cordon de Secteur
Tension dʼEntrée / Taille de Fusibles dʼEntrée sur
Fréquence (Hz) ou de Disjoncteurs Plaque Nominative
(Coefficient d'utilisation de 30%)
208/60 50 40A 50 Amp, 250V
230/60 50 36A Bouchon de trois dents
220/50 50 37A (NEMA Type 6-50P)
REGISTRE DE VITESSE DʼALIMENTATION DU FIL
Vitesse du Fil 50 - 70 IPM (1,27 – 17,8 m/minute)
DIMENSIONS PHYSIQUES
Hauteur Largeur Profondeur Poids
Avec l'enroulemen Sans enroulement Avec le pistolet et le câble Sans pistolet et câble
Claw™ Claw™
32.56 in. 20.12 in. 19.15 in. 39.92 in. 215.5 Ibs. 206.5 lbs
827 mm 512 mm 487 mm 1014 mm 97.8 kg. 93.7 kg.
et le câble de travail
et câble de travail
REGISTRES DE TEMPÉRATURES
REGISTRE DE TEMPÉRATURE DE FONCTIONNEMENT
-4°F à 104°F (-20°C à +40°C)
* 23 Volts at 50 Hz.
POWER MIG® 216
REGISTRE DE TEMPÉRATURE DʼENTREPOSAGE
-40°F à 185°F (-40°C à +85°C)
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 74

A-2-Fr
INSTALLATION
A-2-Fr
Lire complètement la section « Installation » avant
de commencer lʼinstallation.
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
• Seul le personnel qualifié doit réaliser cette installation.
• Seul le personnel ayant lu et compris
le Manuel dʼOpération de la POWER
MIG® 216 est à même dʼinstaller et
de faire fonctionner cet appareil.
• La machine doit être raccordée à
terre conformément aux codes électriques nationaux et locaux et à toute
autre régulation applicable.
• Lʼinterrupteur de puissance de la
POWER MIG doit se trouver sur la
position ÉTEINT pour installer le
câble de travail et le pistolet ainsi
que pour raccorder tout autre
appareil.
DEBALLAGE DE LA POWER MIG® 216
Couper les liens et soulever le carton. Couper les
liens qui maintiennent la machine sur le patin. Retirer
la mousse et le matériel dʼemballage gaufré. Décoller
les Accessoires de la Plateforme de la Bouteille de
Gaz. Dévisser les deux vis en bois (sur la Plateforme
de la Bouteille de Gaz) qui maintiennent la machine
sur le patin. Faire rouler la machine pour la faire
descendre du patin.
PUISSANCE DʼENTRÉE, MISE À LA
TERRE ET DIAGRAMME DE CONNEXION
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
• Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation
électrique telles que les terminales de sortie ou
le câblage interne.
• Toute la puissance dʼentrée doit être débranchée
électriquement avant de continuer.
1. Avant de commencer lʼinstallation, vérifier auprès de
la compagnie électrique locale si lʼalimentation en
puissance est appropriée pour la tension, lʼampérage,
la phase et la fréquence spécifiés sur la plaque nominative de la soudeuse. Sʼassurer également que lʼinstallation planifiée soit conforme au Code Électrique
National Américain et aux exigences des régulations
locales. Cette soudeuse peut être opérée depuis une
ligne monophasée ou depuis une phase dʼune ligne
biphasée ou triphasée.
2. Les modèles ayant des tensions dʼentrée multiples
spécifiées sur la plaque nominative (par exemple
208/230) sont livrés avec les branchements effectués
pour la tension la plus élevée. Si la soudeuse doit
fonctionner sur une tension inférieure, les branchements doivent être refaits conformément aux instructions de la Figure A.1 pour les machines à tension
double.
AVERTISSEMENT
EMPLACEMENT
Placer la soudeuse dans un endroit sec où lʼair propre
circule librement dans les évents arrière vers lʼintérieur et dans les claires-voies avant vers lʼextérieur.
Un emplacement qui minimise la quantité de fumée et
de saleté pénétrant dans les claires-voies arrière
réduit les possibilités dʼaccumulation de saleté qui
pourrait bloquer le passage de lʼair et provoquer une
surchauffe.
Vérifier que la puissance dʼentrée soit débranchée
électriquement avant de retirer la vis du couvercle
dʼaccès au panneau de reconnexion.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 75

INSTALLATION
FIGURE A.1 — Connexions dʼEntrée pour Machine à Tension Double
WARNING ADVERTISSEMENT ADVERTENCIA
Disconnect input power before inspecting
or servicing machine.
Do not operate with covers removed.
Do not touch electrically live parts.
Use CU wire only .
Install and Ground machine per National Electrical Code and local codes. Use Grounding Stud or Lug inside.
Only qualified persons should install, use, or service this equipment.
Consult instruction manual before installing or operating.
Débrancher l’alimentation d’entrée avant de réaliser l’inspection ou l’entretien de la machine.
Ne pas faire fonctionner sans les couvercles.
Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique.
Utiliser uniquement du fil CU.
Installer et mettre la machine à la terre conformément au Code Électrique National et aux réglementations locales.
Utiliser une Borne ou un Ergot de Terre à l’intérieur.
Seules des personnes qualifiées peuvent installer
Consulter le Manuel d’Instructions avant d’installer ou de faire fonctionner la machine.
Desconecte elcable de alimentación antes de iniciar caulquier inspeccion ó servicio.
No opere la máquina con las cubiertas removidas.
No toque las partes elécticas vivas.
Use solo cable con alambre de cobre.
Instale y aterrice la máquina de acuerdo a las normas eléctricas locales y nacionales. Use el Tornillo de
Tierra de la máquina.
Únicamente personal calificado debe instalar
Antes de instaler u poerar éste equipo consulte el Manual de Intruccion.
INPUT SUPPLY CONNECTION DIAGRAM
DIAGRAMME DE CONNEXION DE L’ALIMENTATION D’ENTRÉE
DIAGRAMA DE CONEXION DE LA FUENTE DE ENTRADA
Connect leads for
desired voltage range
Connecter les câbles
pour obtenir la tension
désirée.
Conecte cable selector
para el voltage de
alimentacion deseado.
, utilizar ó dar servicio a éste equipo.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels
DESCARGAS ELECTRICAS pueden matar
, utiliser ou réaliser l’entretien de cet appareil.
SINGLE PHASE
MONOPHASE
MONOFASICO
A-3-FrA-3-Fr
RECONNECT
RECONEXION
REBRANCHER
INPUT
ALIMENTACION
ENTRÉE
3. Le modèle de POWER MIG à 208/230 volts 50/60
Hz est livré avec un câble d'entrée de 10ft.(3.0m)et
une prise branchés sur la soudeuse.
4. Demander à un électricien qualifié de brancher le réceptacle ou le câble sur les lignes de puissance dʼentrée et
la masse du système conformément au Code Électrique
National des États-Unis et à toute régulation locale
applicable.
BRANCHEMENTS POUR LA
POLARITÉ DE SORTIE
Telle quʼelle est livrée par lʼusine, la soudeuse est
branchée pour la polarité positive (+) de lʼélectrode. Il
sʼagit là de la polarité normale pour le GMAW.
Si la polarité négative (-) est nécessaire, inverser les
branchements des deux câbles situés dans le compartiment de lʼentraîneur de fil près du panneau avant.
Le câble dʼélectrode, qui est fixé sur lʼentraîneur de fil,
doit être branché sur la terminale étiquetée négative () et le fil de travail, qui est fixé sur lʼagrafe de travail,
doit être branché sur la terminale étiquetée positive
(+).
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 76

A-4-Fr
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION DU PISTOLET ET DU CÂBLE
Un pistolet Magnum Pro 250L et un câble fourni avec la
POWER MIG® 216 est installé en usine avec une bande de
remplissage pour électrode de 0,035-0,045" (0,9-1,1mm) et
pointe de contact de 0,035" (0,9mm). Vérifier que la pointe de
contact, la bande de remplissage et les rouleaux conducteurs
correspondent tous à la taille du fil utilisé.
AVERTISSEMENT
Placer lʼinterrupteur de puissance de la soudeuse sur la
position « éteint » avant dʼinstaller le pistolet et le câble.
1. Étirer le câble bien droit.
2. Dévissez la Vis de Main sur l'embout avant d'unité d'en-
traînement (compartiment d'alimentation de fil d'intérieur)
jusqu'à ce que le bout de la vis ne dépasse plus dans l'ouverture Adapteur de Pistolet comme vu de l'avant de la
machine. (Voir la figure A.2)
3. Passez extrémité masculine du câble de pistolet dans
Adapteur de Pistolet dans ouverture dans le panneau
avant. Assurez-vous que le connecteur est entièrement
inséré et serrez la vis de main.
4. Branchez le Connecteur de Déclenchement de Pistolet
du pistolet et du câble au Réceptacle de accouplement
en dehors du compartiment situé à gauche de ouverture
sur le panneau avant. Assurez-vous que les rainures de
clavette sont alignés, insérez et serrez le circlip.
ÉCRAN DE GAZ INERTE
(Pour Procédés de Soudage à lʼArc Gaz - Métal)
Le client doit fournir un cylindre de gaz de protection de type
approprié pour le procédé utilisé.
A-4-Fr
2. Retirer le bouchon du cylindre. Vérifier que les soupapes
et le régulateur du cylindre ne présentent pas de filetages
endommagés, de saleté, de poussière, dʼhuile ou de
graisse. Retirer la poussière et saleté avec un chiffon propre.
NE PAS FIXER LE RÉGULATEUR SʼIL Y A PRÉSENCE
DʼHULE, DE GRAISSE OU DE DOMMAGE ! En informer
le fournisseur de gaz. Lʼhuile ou la graisse sont explosives
en présence dʼoxygène à haute pression.
3. Se placer sur un côté loin de lʼéchappement et ouvrir la
soupape du cylindre pendant un instant. Ceci permet de
souffler vers lʼextérieur toute poussière ou saleté qui aurait
pu sʼaccumuler dans lʼéchappement de la soupape.
AVERTISSEMENT
Faire attention dʼavoir le visage loin de lʼéchappement de
la soupape au moment de lʼouverture de celle-ci.
4. Fixer le régulateur de flux sur la soupape du cylindre et
bien serrer les écrous dʼunion au moyen dʼune clef.
NOTE: Pour le brancher sur un cylindre 100% CO
adaptateur de régulateur supplémentaire doit être installé
entre le régulateur et la soupape du cylindre. Si lʼadaptateur est équipé dʼune rondelle en plastique, sʼassurer
quʼelle ait une bonne assise pour la connexion sur le cylindre de CO2.
5. Fixer une extrémité du tuyau dʼadmission de gaz sur lʼaccessoire dʼéchappement du régulateur de flux, et lʼautre
extrémité sur le raccord arrière de la POWER MIG® 216,
puis bien serrer les écrous dʼunion au moyen dʼune clef.
6. Avant dʼouvrir la soupape du cylindre, tourner le bouton de
réglage du régulateur dans le sens contraire à celui des
aiguilles dʼune montre jusquʼà ce que la pression du
ressort de réglage soit relâchée.
7. En se plaçant sur un côté, ouvrir doucement la soupape
du cylindre une fraction de tour. Lorsque lʼaiguille de la
jauge de pression du cylindre cesse de bouger, ouvrir la
soupape complètement.
, un
2
Un régulateur de flux de gaz, pour mélange dʼArgon, ainsi
quʼun tuyau dʼadmission de gaz sont fournis par lʼusine avec
la POWER MIG® 216. Pour utiliser un gaz 100% CO
, un
2
adaptateur supplémentaire est requis pour brancher le régulateur sur le gaz.
AVERTISSEMENT
LE CYLINDRE peut exploser sʼil est
endommagé.
• Le gaz sous pression est explosif. Toujours
maintenir les cylindres de gaz en position verticale et enchaînés au chariot ou à un support
stationnaire. Voir la Norme Nationale
Américaine 2-49.1 « Sécurité pour le Soudage et
le Découpage » publiée par la Société
Américaine de Soudage.
Installer lʼalimentation de lʼécran de gaz inerte comme
suit
:
1. Installer le cylindre de gaz sur la plateforme arrière
de la POWER MIG® 216. Accrocher la chaîne pour
fixer le cylindre sur lʼarrière de la soudeuse.
POWER MIG® 216
AVERTISSEMENT
Ne jamais se placer directement devant ou derrière le
régulateur de flux lorsquʼon ouvre la soupape du cylindre. Toujours se placer sur un côté.
___________________________________________
8. Le régulateur de flux est réglable. Avant dʼeffectuer
la soudure, lʼajuster sur le débit recommandé pour
la procédure et le procédé utilisés.
FIGURE A.2
Vis de Main
Adapteur de Pistolet
Pistolet et Câble
Masculins D’extrémité
Réceptacle
Connecteur de
déclenchement
Page 77

A-5-Fr
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION DE L'ENROULEMENT CLAW™
L'enroulement Claw™ et des vis de support sont donnés comme accessoire facultatif pour la
216
. Ceci utilisateur-installent l'accessoire fournit la
gestion de câble pour la machine.
POWER MIG®
WARNING
Tournez le commutateur électrique de
soudeuse AU LOIN avant d'installer l'enroulement Claw™
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Déroulez l'enroulement Claw™ de son papier pro-
tecteur et enlevez le sac des vis de support du dos
de l'enroulement Claw™.
2. Montez l'enroulement Claw™ utilisant les vis de
support fournies à l'aile gauche de la machine, une
fois vu de l'avant. Assurez-vous que l'enroulement
Claw™ est fermement monté. (Voir la figure A.3)
A-5-Fr
VIS DE
SUPPORT
FIGURE A.3
L'ENROULEMENT
CLAW™
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 78

B-1-Fr
FONCTIONNEMENT
Lire la section de « Fonctionnement »
dans sa totalité avant de faire fonctionner la POWER MIG® 216.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
• Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique ou les électrodes les mains nues ou avec des
vêtements humides. Sʼisoler du travail et du sol.
• Toujours porter des gants isolants
secs.
LES VAPEURS ET LES GAZ
peuvent être dangereux.
• Maintenir la tête hors des vapeurs.
• Utiliser la ventilation ou un système
dʼéchappement pour évacuer les
vapeurs de la zone de respiration.
B-1-Fr
LES ÉTINCELLES DE SOUDURE
peuvent provoquer des incendies ou
des explosions.
• Tenir les matériaux inflammables
éloignés.
• Ne pas souder sur des récipients
fermés
.
LES RAYONS DES ARCS
peuvent causer des brûlures.
• Porter des protections pour les
yeux, les oreilles et le corps.
Suivre toutes les instructions de Sécurité
tout au long de ce manuel.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
Page 79

B-2-Fr B-2-Fr
5
FONCTIONNEMENT
DESCRIPTION DU PRODUIT
La POWER MIG® 216 est une machine de soudage à lʼarc c.c.
semi-automatique complète construite de sorte quʼelle soit conforme aux spécifications NEMA. Elle combine une source de
puissance à tension de transformateur à prises et un chargeur
de fil à vitesse constante afin de former un système de soudage
fiable, robuste et performant. Un schéma de contrôle simple,
qui consiste en un contrôle de la vitesse dʼalimentation du fil
continu à registre complet, et 7 sélections de prise de tension
de sortie apportent une certaine versatilité ainsi quʼune grande
exactitude et une utilisation facile. Une fonctionnalité importante
de la POWER MIG® 216 est quʼelle est prête pour fonctionner
avec un Pistolet à Bobine Magnum 100SG.
Dʼautres fonctionnalités comprennent un axe de dévidoir de fil
de 2" (51 mm) de diamètre extérieur avec un frein réglable, un
chariot de montage intégral pour cylindre de gaz, un régulateur
de flux réglable pour mélange dʼArgon avec jauge de pression
de cylindre et tuyau dʼadmission, un pistolet Magnum Pro 250L
pour GMAW avec câble de 15 ft. (3,6 m) avec bec fixé (encastré), un câble dʼalimentation de
câble de travail de 10 ft. (3,0 m) avec agrafe.
Les kits facultatifs de pistolet, d'adapteur de bobine de magnum
et le kit duel de support de cylindre pour la poussée alimentant
avec la norme établie dans le conducteur sont également
disponibles.
10 ft. (3.0 m)
avec fiche, et un
LIMITES
La tension / courant de sortie de la POWER MIG® 216 peut
varier si la puissance dʼentrée vers la machine varie, du fait de
sa topologie de puissance de transformateur à prises. Dans
certains cas, un réglage de la WFS pré-établie et/ou de la
sélection de la prise de tension peut sʼavérer nécessaire pour
placer un déport du foret significatif dans la puissance dʼentrée.
DESCRIPTION DES CONTRÔLES
Voir la Figure B.1
1. Interrupteur de Puissance MARCHE / ARRÊT - Appuyez
2. Contrôle de la Tension - Sept sélections de prises de ten-
3. Contrôle de la Vitesse du Fil - Il contrôle la vitesse dʼali-
4. Connecteur 4-Pin - Pour des opérations de pistolet de
PROCÉDÉS ET ÉQUIPEMENT
RECOMMANDÉS
sur le commutateur à « MARCHE » (« ON ») pour placer la
POWER MIG® 216 sous énergie.
sion sont étiquetées de « A » (tension minimale) à « G » (tension maximale). Elles ne doivent être ajustées que
lorsquʼaucun soudage nʼest effectué. Le choix de commande peut être préréglé à l'arrangement spécifique sur le
décalque de diagramme/procédé d'application sur l'intérieur
de la porte de soute de fil ou de la section F de ce manuel
d'instruction.
mentation du fil de 50 à 700 pouces par minute (1,2 – 17,8
m/min). La vitesse du fil nʼest pas affectée lorsque des
changements sont effectués au niveau du contrôle de la tension.
poussée et de pistolet de bobine.
FIGURE B.1
La POWER MIG® 216 est recommandée pour les procédés de
soudage GMA fonctionnant avec des bobines de 10 à 44 lb (4,5
à 20 kg) de 2" (51 mm) de diamètre intérieur ou dʼélectrodes
auto - blindées de fil solide de 0,025" à 0,045" (0,6 – 1,1 mm),
dʼacier inoxydable de 0,035" (0,9 mm), dʼaluminium de 3/64"
(1,1 mm), dʼOutershield® de 0,035" (0,9 mm) ou de 0,045" (1,1
mm), dʼUltracore® de 0,045" (1,1 mm) ainsi que dʼInnershield®
de 0,045" (1,1 mm).
La POWER MIG® 216 est équipée depuis lʼusine pour alimenter des électrodes de 0,035" (0,9 mm). Elle comprend
également un ensemble de pistolet GMAW à régime nominal de
200A, 60% de facteur de marche (ou 250A, 40% de facteur de
marche) et câble de 15 ft. (3,6 m) équipé pour trois tailles de
fils. Lʼutilisation de procédés GMAW requiert une alimentation
pour écran de gaz inerte.
5. Interruptor eléctrico del Pistolet del empuje de la Botella
CAPACITÉ DE SOUDAGE
La POWER MIG® 216 a un régime nominal de 216 amps @ 22
volts, avec un facteur de marche de 30% sur la base dʼun cycle
de dix minutes. Elle est capable de facteurs de marche
supérieurs avec des courants de sortie inférieurs. La conception
de transformateur à prises le rend tout à fait adapté à lʼutilisation de la plupart des systèmes générateurs portables ou
internes.
Doble y del Pistolet del carrete - Basculez le commutateur
(Le Point 5 voient la figure B.2) pour choisir entre le pistolet
de poussée et le pistolet de bobine. Quand l'une ou l'autre
opération est choisie, insérer le câble sur du Connecteur à 4
goupilles. (Le Point 4, voient la figure B.1)
FIGURE B.2
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 80

FONCTIONNEMENT
B-3-FrB-3-Fr
ROULEAU CONDUCTEUR DE FIL
CHARGEMENT DES TAMBOURS DE FIL –
BOBINES OU ENROULEMENTS
Les rouleaux conducteurs installés sur la POWER MIG® 216
possèdent deux rainures, lʼune pour les fils de 0,035"
(0,9mm) et lʼautre pour les fils de 0,045" (1,2mm). La taille du
rouleau conducteur est gravée sur le côté exposé du rouleau
conducteur.
PIÈCES DE CONVERSION DE TAILLE DE FIL
La POWER MIG® 216 est conçue pour alimenter des électrodes solides ou fourrées allant de 0,025 à 0,045" (0,6 – 1,2
mm).
Les kits de rouleaux conducteurs et les pièces pour pistolet
Magnum Pro 250L et câble sont disponibles pour alimenter
différentes tailles et types dʼélectrodes. Voir la section «
Accessoires ».
PROCÉDURE POUR LE CHANGEMENT DES JEUX DE
ROULEAUX CONDUCTEURS ET DE CYLINDRES DʼAPPUI
1. Arrêtez la source d'énergie.
2. Relâcher la pression sur le cylindre dʼappui en faisant balancer le bras de pression ajustable vers le bas en direction
de lʼarrière de la machine. Lever lʼensemble du cylindre
dʼappui en fonte et lui permettre de prendre assise en position verticale.
3. Retirer la plaque de retenue du guide-fil externe en desserrant les deux grandes vis moletées.
4. Faire tourner le mécanisme de retenue du rouleau conduc-
teur sur la position déverrouillée comme illustré ci-dessous
puis retirer le rouleau conducteur. (Voir la Figure B.3)
FIGURE B.3
Pour Monter des Bobines de 10 à 44 lb (4,5 – 20 kg) (12”/300
mm de diamètre) ou des Rouleaux Innershield de 14 lb (6 kg):
(Pour des rouleaux Innershield de 13-14 lb (6 kg), un Adaptateur de
Rouleau K435 doit être utilisé).
1. Ouvrir la Porte du Compartiment de lʼEntraîneur de Fil.
2. Appuyer sur la Barre de Libération sur le Collier de Retenue
et la retirer de lʼaxe.
3. Placer la bobine sur lʼaxe de sorte que la goupille du frein de
lʼaxe pénètre dans lʼun des orifices sur lʼarrière de la bobine.
(Note : une flèche qui se trouve sur lʼaxe sʼaligne avec la
goupille de support du frein afin dʼaider à aligner lʼorifice).
Sʼassurer que le fil sorte du tambour de sorte quʼil se déroule
depuis le haut du rouleau.
4. Remettre en place le Collier de Retenue. Sʼassurer que la
Barre de Libération soit « éjectée » et que les bagues de
retenue du collier sʼengagent à fond dans la rainure de lʼanneau de retenue sur lʼaxe.
POSITION DÉVERROUILLÉE
5. Retirer la plaque du guide-fil interne.
6. Remplacer les rouleaux conducteurs, les cylindres dʼappui
et les guide-fil internes par un jeu de la taille du nouveau
fil.
NOTE: Vérifier que la taille de la bande de remplissage du
pistolet et de la pointe de contact corresponde aussi à la
taille du fil sélectionné.
7. Alimenter le fil manuellement depuis le dévidoir de fil, en
passant par dessus la rainure du rouleau conducteur et au
travers du guide-fil puis dans le coussinet en laiton de
lʼensemble du pistolet et du câble.
8. Remettre en place la plaque de retenue du guide-fil
externe en serrant les deux grandes vis moletées.
Remettre le bras à pression ajustable sur sa position dʼorigine afin dʼappliquer la pression. Ajuster la pression en
fonction des besoins.
POSITION VERROUILLÉE
POWER MIG® 216
Page 81

FONCTIONNEMENT
POUR FAIRE DÉMARRER LA SOUDEUSE
Placer lʼinterrupteur de puissance sur la position « ALLUMÉ » (« ON »). Une fois
que la tension et la vitesse du fil souhaitées ont été sélectionnées, faire fonctionner
la gâchette du pistolet pour la sortie de la soudeuse et afin de placer sous énergie
le moteur dʼalimentation du fil.
ALIMENTATION DU FIL DʼÉLECTRODE
AVERTISSEMENT
Lorsque lʼon appuie sur la gâchette, lʼélectrode et
le mécanisme de traction se trouvent sous alimentation électrique par rapport au travail et à la
masse et ils le restent pendant plusieurs secondes après que la gâchette du pistolet ait été
relâchée.
------------------------------
NOTE: Vérifier que les rouleaux conducteurs, les plaques
guides et les pièces du pistolet soient appropriés pour la taille et
le type de fil utilisé. Se reporter au Tableau C.1 dans la section
« Accessoires ».
1. Faire tourner la la bobine jusquʼà ce que lʼextrémité libre de
lʼélectrode soit accessible..
------------------------------------------------
Le bras de pression contrôle la quantité de force que les
rouleaux conducteurs exercent sur le fil. Un ajustement
approprié des deux bras de pression permet un meilleur
soudage. Pour de meilleurs résultats, régler les deux bras de
pression sur la même valeur.
Régler le bras de pression comme suit (Voir la Figure B.5):
Fils en Aluminium entre 1 et 3
Fils Fourrés entre 3 et 4
Fils Fourrés entre 3 et 4
FIGURE B.4
FILS FOURRÉS
OUTERSHIELD
METALSHIELD
INERSHIELD
B-4-FrB-4-Fr
FILS SOLIDES
1
3
5
2
4
6
ALUMINIUM
ACIER
ACIER INOXYDABLE
2. Tout en tenant fermement lʼélectrode, couper lʼextrémité
courbée et redresser les six premiers pouces. Si lʼélectrode
nʼest pas correctement redressée, elle peut ne pas bien alimenter à travers le système de traction du fil.
3. Relâcher la pression sur le cylindre dʼappui en faisant balancer le bras de pression ajustable vers le bas en direction
de lʼarrière de la machine. Lever lʼensemble du cylindre
dʼappui en fonte et lui permettre de prendre assise en position verticale. Laisser la plaque du guide-fil externe installée.
Alimenter le fil manuellement à travers le coussinet du guide
entrant et à travers les plaques guides (par dessus la rainure
du rouleau conducteur). Pousser une longueur de fil suffisante pour garantir que le fil soit alimenté sans restriction
dans lʼensemble du pistolet et du câble. Remettre le bras de
pression ajustable dans sa position dʼorigine afin dʼappliquer
la pression sur le fil.
4. Appuyer sur la gâchette du pistolet pour alimenter le fil
dʼélectrode à travers le pistolet.
RÉGLAGE DE LA PRESSION DU CYLINDRE DʼAPPUI
CONFIGURATION DE LʼENTRAÎNEUR DE FIL
Voir la Figure B.5
Changement de l'adapteur de pistolet
• Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique.
• En marche par à-coups avec la gâchette du pistolet,
• Seul le personnel qualifié peut réaliser le travail de
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Outils requis:
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
•
Couper la puissance dʼentrée au niveau de la
source de puissance de soudage avant lʼinstallation ou le changement des rouleaux conducteurs et/ou des guides.
• Ne pas toucher les pièces sous alimentation électrique.
• En marche par à-coups avec la gâchette du pistolet,
lʼélectrode et le mécanisme de traction sont sous tension
par rapport au travail et à la masse et ils peuvent rester
sous énergie plusieurs secondes après que la gâchette
du pistolet ait été relâchée.
• Seul le personnel qualifié peut réaliser le travail de maintenance.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER MIG® 216
1. Couper la puissance au niveau de la source de puissance de
2. Retirer le fil de soudage de lʼentraîneur de fil.
3. Retirer la vis de pression de lʼentraîneur de fil.
4. Retirer le pistolet de soudage de lʼentraîneur de fil.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
• Couper la puissance dʼentrée au niveau de la
source de puissance de soudage avant lʼinstallation ou le changement des rouleaux
conducteurs et/ou des guides.
lʼélectrode et le mécanisme de traction sont sous tension par rapport au travail et à la masse et ils peuvent
rester sous énergie plusieurs secondes après que la
gâchette du pistolet ait été relâchée.
maintenance.
• Llave hexagonal de 1/4".
NOTE: Quelques adapteurs de pistolet exigent pas utilisa-
tion de la vis de main.
soudage.
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 82

B-5-Fr B-5-Fr
SS
5. Desserrez la vis à tête cylindrique à empreinte qui tient la barre
de connecteur contre l'adapteur de pistolet.
Important : Ne pas essayer de retirer complètement la vis
dʼassemblage à six pans creux.
6. Enlevez le guide de câblage externe, et poussez l'adapteur de
pistolet hors de la commande de fil. En raison de l'ajustement de
précision, le tapement léger peut être exigé pour enlever l'adapteur de pistolet.
FONCTIONNEMENT
3. Appuyer sur la gâchette pour alimenter le fil dʼélectrode
au travers du pistolet et du câble. Pour un fil solide,
couper lʼélectrode à environ 3/8" (10 mm) de lʼextrémité
de la pointe de contact (3/4" (20 mm) pour
Outershield®)..
4. Pour souder avec du gaz, ouvrir lʼalimentation du gaz et
établir le débit requis (typiquement 30-40 CFH ; 14-19
litres/min.).
7. Démontez le tuyau de armature de gaz de l'adapteur de pistolet,
s'il y a lieu.
5. Raccorder le câble de travail au métal à souder. Lʼagrafe
du travail doit établir un bon contact électrique avec le travail. Le travail doit également être mis à la terre confor-
8. Reliez le tuyau de armature de gaz au nouvel adapteur de pistolet, s'il y a lieu.
mément aux « Mesures de Sécurité pour le Soudage à
lʼArc ».
9. Tournez l'adapteur de pistolet jusqu'à ce que le trou de vis de
main aligne avec le trou de vis de main dans le plat d'alimentation. Glissez l'adapteur de pistolet dans la commande de fil et le
vérifiez que les trous de vis de main sont alignés.
10. Serrez la vis à tête cylindrique à empreinte.
11. Insérez le pistolet de soudure dans l'adapteur de pistolet et serrez la vis de main.
RÉALISATION DʼUNE SOUDURE
1. Vérifier que la polarité de lʼélectrode soit correcte pour le procédé
utilisé, puis placer lʼinterrupteur de puissance sur la position
ALLUMÉ.
2. Régler la prise de tension de lʼarc et la vitesse du fil en fonction
du fil dʼélectrode particulier, du type de matériau et de son épaisseur et du gaz (pour MIG et Outershield®) utilisés. Se baser sur
le Tableau des Applications qui se trouve sur la porte à lʼintérieur
du compartiment du fil comme référence rapide pour certaines
------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. Placer lʼélectrode sur le joint. Lʼextrémité de lʼélectrode peut toucher légèrement le travail.
7. Baisser le casque de soudage, fermer la gâchette
et commencer à souder. Tenir le pistolet de telle
sorte que la distance entre la pointe de contact et
le travail soit dʼenviron 3/8" (10 mm) (3/4" (20 mm)
pour Outershield®).
8. Pour cesser de souder, relâcher la gâchette du
pistolet puis éloigner le pistolet du travail une fois
que lʻarc a disparu.
procédures de soudage communes.
NOTE : Le diagramme d'application peut également
être trouvé dans la section F de ce manuel d'instruction.
Figure B.5
AVERTISSEMENT
• Lorsquʼun procédé à arc ouvert est
utilisé, il est nécessaire de porter de
bonnes protections pour les yeux, la
tête et le corps.
PALLIER RECEPTEUR DU PISTOLET
CONNECTEUR
POWER MIG® 216
VIS DE PRESSION
T ETE CREUSE
VIS D`ASSEMBLAGE
E
ERREZ SERREZ
GUIDE DE FIL
Page 83

FONCTIONNEMENT
9. Lorsque le soudage est terminé, fermer la
soupape se trouvant sur le cylindre de gaz (sʼil
était utilisé), faire fonctionner momentanément la
gâchette du pistolet pour libérer la pression du
gaz et éteindre la POWER MIG® 216.
NOTE: Lorsquʼune électrode Innershield est utilisée,
le bec de gaz peut être retiré de lʼisolation de
lʼextrémité du pistolet puis remplacée par le
bec sans gaz. Ceci améliore la visibilité et
élimine la possibilité de surchauffe du bec de
gaz.
COMMENT ÉVITER LES PROBLÈMES
DʼALIMENTATION DU FIL
Les problèmes dʼalimentation du fil peuvent être évités en
suivant les procédures de maniement du pistolet suivantes:
1. Ne pas entortiller ni tirer le câble autour de coins
anguleux.
2. Maintenir le câble du pistolet aussi droit que possible pen-
dant le soudage ou le chargement de lʼélectrode au travers du câble.
3. Ne pas permettre que les roues des chariots ou des
camions passer sur les câble.
4. Conserver la propreté du câble en suivant les instructions
de maintenance.
5. Nʼutiliser que des électrodes propres et sans rouille. Les
électrodes Lincoln possèdent une lubrification de surface
appropriée.
6. Changer la pointe de contact lorsque lʼarc commence à
devenir instable ou lorsque lʼextrémité de la pointe de contact est fondue ou déformée.
7. Maintenir la tension du frein de lʼaxe du dévidoir de fil sur
le minimum requis afin dʼéviter un excès de parcours du
dévidoir, qui pourrait faire sortir le fil bouclé de la bobine.
8. Maintenir la tension du frein de lʼaxe du dévidoir de fil sur
le minimum requis afin dʼéviter un excès de parcours du
dévidoir, qui pourrait faire sortir le fil bouclé de la bobine.
CONTRÔLE DU VENTILATEUR
Le ventilateur est conçu pour se mettre en marche lorsque la
puissance dʼentrée est appliquée à la POWER MIG® 216 et
pour sʼéteindre lorsque la puissance est coupée.
VARIATIONS DE LA TENSION DE
LA LIGNE DʼENTRÉE
Tension de Ligne Élevée — Une tension dʼentrée
supérieure à la tension nominale provoquerait des tensions
de sortie supérieures à la normale pour un réglage de prise
donné. Si la ligne dʼentrée est élevée, il est conseillé de
sélectionner une prise de tension plus faible que celle
indiquée sur le tableau de procédure recommandée.
Tension de Ligne Faible — Il peut sʼavérer impossible
dʼobtenir la sortie maximum de la machine si la tension de
ligne est inférieure à lʼentrée nominale. Lʼappareil continue à
souder, mais il se peut que la sortie soit inférieure à la normale pour un réglage de prise donné. Si la ligne dʼentrée est
faible, il est conseillé de sélectionner une prise de tension
plus élevée que celle indiquée sur le tableau de procédure
recommandée.
POWER MIG® 216
B-6-FrB-6-Fr
PROTECTION CONTRE LES SURCHARGES DʼALIMENTATION DU FIL
La POWER MIG® 216 est équipée dʼune protection à
transistor contre les surcharges du moteur de lʼentraîneur de fil. Si le moteur devient surchargé, les circuits de protection arrêtent le moteur et de gaz
solénoïde d'entraînement de fil. Vérifier que la pointe,
la bande de remplissage et les rouleaux conducteurs
soient de la bonne taille, quʼil nʼy ait aucune obstruction ni courbure au niveau du câble du pistolet et tout
autre facteur pouvant empêcher lʼalimentation du fil.
Pour reprendre le soudage, il suffit de tirer sur la
gâchette. Il nʼy a aucun disjoncteur à rétablir car la
protection est effectuée au moyen dʼun dispositif électronique à transistor fiable.
PROTECTION THERMIQUE CONTRE LES SURCHARGES DE
SOUDAGE
La POWER MIG® 216 est équipée de thermostats
protecteurs intégrés qui répondent aux températures
excessives. Ils ouvrent les circuits de sortie dʼalimentation du fil et de soudage si la machine dépasse la
température de fonctionnement maximum recommandée du fait dʼune surcharge fréquente ou dʼune
température ambiante élevée plus une surcharge. Les
thermostats se rétablissent automatiquement lorsque
la température atteint un niveau de fonctionnement
sûr et le soudage et lʼalimentation du fil reprennent
lorsquʼon appuie à nouveau sur la gâchette.
INFORMATION CONCERNANT LES
PROCÉDURES DE SOUDAGE
NOTE: Voir la couverture intérieure de la machine ou de
la section F de ce manuel d'instruction pour le procédé
de soudure additionnel et utilisé généralement.
ÉTUDE POUR SOUDER
La soudure est une compétence qui peut seulement
être apprise par la pratique. Personne ne peuvent
devenir une soudeuse accomplie simplement en
ayant connaissance de eux. Le lien suivant «
apprenant à souder » le document aidera l'opérateur
inexpérimenté à comprendre les fondations au sujet
de la soudure de fil et à fournir des conseils pour aider
à développer cette compétence.
« Apprenant à souder » le lien : http://content.lincolnelectric.com/pdfs/products/navigator/im/LTW1tri.pdf
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 84

C-1-Fr C-1-Fr
ACCESSOIRES
KITS DE ROULEAUX CONDUCTEURS
Se reporter au Tableau C.1 pour connaître les divers
kits de rouleaux conducteurs disponibles pour la
POWER MIG® 216. Lʼarticle en caractère gras est
fourni normalement avec la POWER MIG® 216.
TABLE C.1
Fil Taille
0,023"-0,030" (0,6-0,8 mm)
Acier
dur
À Noyau
Aluminium
0,035" (0,9 mm) KP1696-035S
0,045" (1,1 mm) KP1696-045S
0,035-0,045" (0,9-1,1 mm)
0,040" (1,0 mm) KP1696-2
0,035" (0,9 mm) KP1697-035C
0,045" (1,1 mm) KP1697-045C
3/64" (1,2 mm) KP1695-3/64A
Kit Rouleau Conducteur
KP1696-030S
KP1696-1
KIT DE MONTAGE DU CYLINDRE
DOUBLE (K1702-1)
Il permet le montage stable côte à côte de deux cylindres de
gaz de grande taille de 228,6 mm de diamètre x 1,524 m de
haut (9" de diamètre x 5" de haut) avec chargement « sans
levage ». Installation simple et instructions faciles fournies.
Comprend les supports de cylindre supérieur et inférieur, les
essieux des roues et la visserie de montage.
ENSEMBLES ALTERNATIFS DE PISTOLET MAGNUM GMAW ET CÂBLE
Les ensembles suivants de pistolet Magnum Pro 250ML et
câble sont disponibles séparément pour leur utilisation avec
la POWER MIG® 216. Chacun a un régime nominal de 250
amps à 40% de facteur de marche et est équipé du connecteur intégré, du connecteur de gâchette à verrouillage
tournant, du bec fixe et de lʼisolant, et il comprend une bande
de remplissage, un diffuseur et des pointes de contact pour
les tailles de fil spécifiées:
Longueur Pièce No.
10' (3,0 m)
12' (3,6 m)
15' (4,5 m)
KP42-4045-15
Taille de Fil Taille de Fil
Système Anglais
0,035” –0,045" 0,9 – 1,1 mm
Système Métrique
AVERTISSEMENT
• Débrancher toute la puissance dʼentrée provenant de la POWER MIG®
216 avant dʼinstaller le Pistolet à
Bobine et le Kit.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
KIT DE CONNEXION DE PISTOLET
MAGNUM (K466-6 en Option)
Lʼutilisation du Kit de Connexion Magnum K466-6 en Option
avec la POWER MIG® 216 permet dʼutiliser les ensembles
ordinaires de pistolet et câble Magnum 200, 300 ou 400.
ADAPTATEUR DʼAXE POUR PETITE
BOBINE (K468)
Lʼadaptateur dʼaxe K468 permet dʼutiliser des petites
bobines de 8" de diamètre.
ADAPTEUR D'AXE POUR 14 LIVRES.
ENROULEMENTS (K435)
L'adapteur de l'axe K435 permet 14lbs. (6kg.) Innershield
love pour être monté sur l'axe de 2 » (51mm) O.D.
PISTOLETS À BOBINE ET ADAPTATEURS EN OPTION
La
POWER MIG® 216
pistolets à bobine suivants:
PISTOLET À BOBINE
Magnum 100SG
(K2532-1)
Magnum SG
(K487-25)
Magnum 250LX
(K2490-1)
Adaptateur de Pistolet à Bobine (K2703-1)
Ce kit est conçu pour permettre aux pistolets à bobine
Magnum SG ou Magnum 250LX de fonctionner avec la
POWER MIG® 216
conduits à gaz, les harnais de câblage et le panneau de
connexion du pistolet. Le panneau de connexion du pistolet
est équipé dʼun connecteur de type MS à 6 goupilles pour le
pistolet à bobine Magnum SG et dʼun connecteur de type
MS à 7 goupilles pour le pistolet à bobine Magnum 250LX,
ainsi que dʼun interrupteur de sélection permettant de
choisir le pistolet à utiliser.
est capable de fonctionner avec les
RÉGIME NOMINAL
Série Légère
130 amp 30% de Facteur de Marche
Série Moyenne
250 amp 60% de Facteur de Marche
Série Lourde
300 amp 60% de Facteur de Marche
. Ce kit comprend le gaz solénoïde, les
ADAPTATEUR
Usine prête
Aucun adapteur a exigé
Adaptateur de Pistolet à
Bobine K2703-1
K2703-1
Remarquer que lʼadaptateur de pistolet à bobine K27031 inhabilite lʼutilisation dʼun Magnum 100SG.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 85

C-2-Fr
ACCESSOIRES
RÉALISATION DʼUNE SOUDURE AVEC LE KIT
DE LʼADAPTATEUR DE PISTOLET À BOBINE ET
LE PISTOLET À BOBINE INSTALLÉS
ATTENTION
Dans nʼimporte laquelle des positions du commutateur,
la fermeture de lʼune des gâchettes de pistolet mettra
lʼélectrode des deux pistolets sous alimentation électrique. Vérifier que le pistolet inutilisé soit positionné de
telle sorte que ni lʼélectrode ni la pointe nʼentrent en contact avec la console en métal ou tout autre métal commun au travail.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. En plaçant l'interrupteur à bascule « pour pousser
le pistolet » placez les débronchements la vanne
électromagnétique de gaz de pistolet d'opération et
de bobine de pistolet de bobine. La fermeture du
déclenchement de pistolet permet la soudure de
pistolet de poussée et les deux électrodes seront
électriquement « CHAUDES ».
2. En plaçant l'interrupteur à bascule au « pistolet de
bobine » placez les débronchements la vanne
électromagnétique intégrée de gaz d'opération et
de conducteur de pistolet de poussée. Elle permet
également la vanne électromagnétique de gaz de
pistolet d'opération et de bobine de pistolet de
bobine. La fermeture du déclenchement de pistolet
de bobine permet la soudure de pistolet de bobine
et les deux électrodes seront électriquement «
CHAUDES »..
C-2-Fr
3. Fonctionnement avec la POWER MIG® 216:
• ALLUMER la puissance dʼentrée de la POWER
MIG® 216.
• Lʼajustement du contrôle de la prise de tension
fait augmenter ou diminuer la tension de
soudage.
• Lʼajustement du contrôle de la vitesse du fil sur
le pistolet à bobine fait augmenter ou diminuer
la vitesse dʼalimentation du fil du pistolet à
bobine.
NOTE : Lʼajustement du contrôle de la vitesse dʼalimentation du fil sur le Panneau de la machine nʼa
aucun effet sur la vitesse dʼalimentation du fil du pistolet à bobine.
4. Référez-vous au procédé de soudure sur la
machine ou la section F de ce manuel d'instruction
pour les arrangements en aluminium initiaux. Faites
un essai souder pour déterminer les arrangements
finaux.
5. Placez le sélecteur de pistolet de bobine dans la
position « de pistolet de poussée » pour retourner à
l'opération de pistolet de poussée.
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 86

D-1-Fr
ENTRETIEN
D-1-Fr
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES peuvent être mortels.
• Faire installer et effectuer lʼentretien de cet appareil par un électricien.
• Couper la puissance DʼENTRÉE
au niveau de la boîte à fusibles
avant de travailler sur lʼappareil
• Ne pas toucher les pièces sous
alimentation électrique.
ENTRETIEN GÉNÉRAL
Dans des emplacements extrêmement poussiéreux, la
saleté peut obstruer les passages dʼair, ce qui ferait chauffer
la soudeuse. À des intervalles réguliers, souffler de lʼair à
faible pression pour faire sortir la saleté de la soudeuse afin
dʼéliminer lʼaccumulation excessive de saleté et de poussière sur les pièces internes.
Les moteurs du ventilateur possèdent des roulements à
billes hermétiques qui ne requièrent aucun entretien.
DRIVE ROLLS AND GUIDE PLATES
Après chaque bobine de fil, réaliser une inspection du
mécanisme de lʼentraîneur de fil. Le nettoyer, si nécessaire,
en soufflant de lʼair comprimé à faible pression. Ne pas
utiliser de solvants pour nettoyer le cylindre dʼappui car cela
pourrait éliminer le lubrifiant du roulement. Tous les
rouleaux conducteurs portent la marque des tailles de fil
quʼils peuvent alimenter. Si une taille de fil différente à celles
qui sont marquées doit être utilisée, le rouleau conducteur
doit être changé.
TUBES DE PISTOLET ET BECS
1. Changer les pointes de contact usées selon les
besoins.
2. Retirer les éclaboussures de lʼintérieur du bec de gaz
et de la pointe de contact toutes les 10 minutes de
temps dʼarc ou en fonction des besoins.
NETTOYAGE DU CÂBLE DU PISTOLET
Afin de prévenir les problèmes dʼalimentation, nettoyer la
gaine du câble en utilisant environ 300 livres (136 kg)
dʼélectrode. Retirer le câble du chargeur de fil et lʼétendre bien droit sur le sol. Retirer la pointe de contact du
pistolet. Au moyen dʼun tuyau à air et seulement une
pression partielle, souffler doucement dans la gaine du
câble depuis lʼextrémité du diffuseur de gaz.
ATTENTION
Si une pression excessive est appliquée au début
de la procédure de nettoyage, la saleté peut former un bouchon.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Plier le câble sur toute sa longueur puis y souffler à
nouveau de lʼair. Répéter la procédure jusquʼà ce quʼil
nʼy ait plus de saleté qui sorte. Si après ceci les problèmes dʼalimentation persistent, essayer un changement de bande de remplissage et se reporter à la section de Dépannage concernant lʼalimentation
irrégulière du fil.
Pour obtenir des instructions sur la remise en place ou le
changement du rouleau conducteur, voir les « Rouleaux
Entraîneurs de Fil » dans la section de « Fonctionnement ».
INSTALLATION DE LA POINTE DE
CONTACT ET DU BEC DE GAZ
1. Choisir la taille correcte de pointe de contact pour
lʼélectrode utilisée (la taille du fil est gravée sur le
côté de la pointe de contact) et bien la visser dans
le diffuseur de gaz.
2. Visser à fond le bec de gaz fixe approprié sur le
diffuseur. On peut utiliser soit le bec standard
affleuré de 0,50" (12,7 mm) soit dʼautres tailles de
becs affleurés ou encastrés (arc de pulvérisation)
en option. (Voir le Tableau D.2 dans cette section)
POWER MIG® 216
Page 87

D-2-Fr
ENTRETIEN
D-2-Fr
RETRAIT ET CHANGEMENT DE LA
BANDE DE REMPLISSAGE
NOTE: le changement de la bande de remplissage
pour une taille de fil différente requiert le changement
du diffuseur de gaz conformément au Tableau D.1
afin de bien fixer la bande de remplissage différente.
TABLEAU D.1
Diamètre des
Électrodes Utilisées
Acier 0,025”-0,030" KP42-25-15 .030 (0.8 mm)
(0,6-0,8 mm)
Acier 0,035”-0,045" KP42-4045-15 .045 (1.2 mm) KP2746-1
(0,9-1,1 mm)
Aluminium 3/64" KP42-4045-15 3/64" (1.2 mm)
(1,2 mm)
Numéro de Pièce de la
Bande de Remplissage
de Rechange
Taille Gravée sur
lʼExtrémité du Coussinet
de la Bande de
Remplissage
INSTRUCTIONS DE RETRAIT, INSTALLATION ET
ÉBARBURAGE DE LA BANDE DE REMPLISSAGE
POUR MAGNUM PRO 250L
NOTE: Les variations de longueur de câble empêchent lʼinterchangeabilité des bandes de remplissage entre pistolets. Une
fois quʼune bande de remplissage a été coupée pour un pistolet particulier, elle ne doit pas être installée sur un autre pistolet à moins quʼil ne remplisse les conditions de longueur de
coupure de la bande de remplissage. Les bandes de remplissage sont livrées avec lʼenveloppe de la bande de remplissage allongée et en quantité appropriée.
Bec Fixe
No. de Pièce
pour Diffuseur
de Gaz
(et Pochoir)
7. Visser le diffuseur de gaz sur lʼextrémité du tube du
pistolet et bien serrer. Vérifier quʼil sʼagisse dʼun
diffuseur de gaz approprié pour la gaine utilisée.
(Voir le tableau et la gravure du diffuseur)
8. Serrer la vis de réglage sur le côté du diffuseur de
gaz contre la gaine du câble au moyen dʼune clef
hexagonale de 5/64" (2,0 mm).
FIGURE D.1
VIS DE RÉGLAGE
CONNECTEUR DE CÂBLE EN LAITON
ISOLATEUR
VIS DE RÉGLAGE
DIFFUSEUR DE GAZ
BEC DE GAZ
LONGUEUR
ÉBAVURÉE
DE LA GAINE
1-1/4" (31,8 mm)
ATTENTION
Cette vis doit être légèrement serrée. Si elle est
trop serrée, la bande de remplissage se séparera
en deux ou se brisera, ce qui aura pour conséquence une mauvaise alimentation du fil.
1. Retirer le bec de gaz, si on lʼutilise, pour repérer la vis de
réglage du diffuseur de gaz utilisée pour maintenir en
place lʼancienne bande de remplissage. Dévisser la vis de
réglage avec une clef hexagonale de 5/64" (2,0 mm).
2. Retirer le diffuseur de gaz et isolateur du tube du pistolet.
3. Étendre le pistolet et le câble bien droits sur une surface
plate. Desserrer la vis de réglage du connecteur en laiton
du côté chargeur du câble et tirer sur la bande de remplissage pour la faire sortir du câble.
4. Insérer une nouvelle bande de remplissage non ébavurée
sur lʼextrémité connecteur du câble. Vérifier que le
coussinet de la bande de remplissage soit bien gravé pour
la taille du fil utilisé.
5. Obtenir une assise complète de la bande de remplissage
dans le connecteur. Serrer la vis de réglage sur le connecteur de câble en laiton. A ce moment-là, le diffuseur de
gaz ne doit pas être installé sur lʼextrémité du tube du pistolet.
6. Tandis que le diffuseur de gaz est encore retiré du tube
du pistolet, vérifier que le câble soit droit puis ébarber la
gaine à la longueur illustrée sur la Figure D.1. Retirer
toute bavure de lʼextrémité de la gaine.
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
POWER MIG® 216
Page 88

D-3-Fr D-3-Fr
DÉMONTAGE DE LA POIGNÉE
DU PISTOLET
Une inspection ou un entretien des pièces internes de
la poignée du pistolet peut être réalisée en cas de
besoin.
La poignée du pistolet se compose de deux moitiés
maintenues ensemble au moyen dʼun collier à chaque
extrémité. Pour ouvrir la poignée, faire tourner les colliers sur environ 60 degrés dans le sens contraire à
ENTRETIEN
TABLEAU D.2
ACCESSOIRES ET PIÈCES DE RECHANGE CONSOMMABLES
POUR ENSEMBLES DE PISTOLET MAGNUM PRO 250L ET
CÂBLE
Taille Taille
Description Pièce No. Anglaise Métrique
GAINE DU CÂBLE
Pour Câble de KP42-25-15 .025" – .030" 0.6 – 0.8 mm
15ʼ (4,5 m) ou KP42-4045-15 .035" – .045" 0.9 – 1.1 mm
plus court KP42-4045-15 3/64" 1.2 mm
(Fil en Aluminium) (Fil en Aluminium)
celui des aiguilles dʼune montre (dans la même direction que pour retirer un filetage à droite) jusquʼà ce
que le collier sʼarrête. Ensuite tirer sur le collier pour
le retirer de la poignée du pistolet. Si les colliers sont
difficiles à faire tourner, positionner la poignée du pistolet contre un coin, placer un tournevis contre la
languette du collier puis donner un coup sec sur le
tournevis pour faire tourner le collier jusquʼà ce quʼil
dépasse un épaulement de verrouillage interne.
Sens contraire à
celui des aiguilles
dʼune montre
¢
POINTES DE CONTACT
Régime Standard KP2744-025 .025" 0.6 mm
Coniques KP2744-030T .030" 0.8 mm
Tab (For Aluminum) KP2744-364A 3/64" 1.2 mm
BECS DE GAZ
Fixes (Affleurés) KP2742-1-38F 3/8" 9.5 mm
Fixed (Encastrés) KP2742-1-38R 3/8" 9.5 mm
Requiert: Ensemble
de Diffuseur de Gaz
KP2744-030 .030" 0.8 mm
KP2744-035 .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045 .045" 1.1 mm
KP2744-035T* .035" 0.9 mm
KP2744-045T .045" 1.1 mm
(Fil en Aluminium) (Fil en Aluminium)
KP2742-1-50F* 1/2" 12.7 mm
KP2742-1-62F 5/8" 15.9 mm
KP2742-1-50R 1/2" 12.7 mm
KP2742-1-62R 5/8" 15.9 mm
KP2746-1* .025" – .045" 0.6 – 1.1 mm
Isolateur
TUBES de PISTOLET
standard
(60°) KP3078-60*
45° KP3078-45*
* Compris avec la POWER MIG® 216
** Des bouts coniques sont exigés avec 3/8 identification de » identification et de
1/2 » Becs.
Voir le www.lincolnelectric.com pour l'offre complète de pro consommables de
magnum.
KP2773-2*
POWER MIG® 216
Page 89

E-1-Fr
DÉPANNAGE
COMMENT UTILISER LE GUIDE DE DÉPANNAGE
AVERTISSEMENT
Lʼentretien et les réparations ne doivent être effectués que par le personnel de Lincoln Electric ayant
reçu une formation en usine. Les réparations non autorisées effectuées sur ce matériel peuvent
entraîner un danger pour le technicien et lʼopérateur de la machine et annulent la garantie dʼusine. Par
ATTENTION et pour éviter un choc électrique, veuillez observer toutes les notes de sécurité et les
mises en garde données en détail dans ce manuel.
__________________________________________________________________________
E-1-Fr
Ce guide de dépannage a pour but de vous aider à
localiser les problèmes éventuels dʼinstallation et de
fonctionnement de la machine et à y remédier. Suivre
simplement la méthode en trois étapes donnée ci-après.
Étape 1. REPÉRER LE PROBLÈME (SYMPTÔME).
Regarder dans la colonne «PROBLÈMES
(SYMPTÔMES)». Cette colonne décrit les symptômes
éventuels que peut présenter la machine. Trouver la
phrase qui décrit le mieux le symptôme que présente
la machine. Les symptômes sont groupés en trois
catégories principales: problèmes de sortie, problèmes
de fonctionnement, problèmes de soudage.
Étape 2. CAUSES POSSIBLES.
La deuxième colonne «CAUSES POSSIBLES» donne
la liste des possibilités externes évidentes qui peuvent
contribuer au symptôme de la machine.
Étape 3. MESURES À PRENDRE RECOMMANDÉES
La dernière colonne «Mesures à prendre
recommandées» donne la liste des mesures à prendre
recommandées.
Si pour une raison ou une autre vous ne comprenez
pas les modes opératoires d'essai ou êtes incapable
d'effectuer les essais ou les réparations en toute sécurité, communiquez avant de poursuivre avec votre service après-vente local agréé Lincoln.
ATTENTION
Si pour une raison ou une autre vous ne comprenez pas les modes opératoires d'essai ou êtes incapable
d'effectuer les essais ou les réparations en toute sécurité, communiquez avant de poursuivre avec votre service
après-vente local agréé Lincoln qui vous prêtera assistance.
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 90

DÉPANNAGE
Suivre les Instructions de Sécurité détaillées au début de ce manuel
E-2 -FrE-2-Fr
PROBLÈMES
(SYMPTOMES)
PROBLÈMES DE SORTIE
Dommage physique ou électrique
majeur évident
Il nʼy a pas dʼalimentation du fil ni
de tension de circuit ouvert
lorsquʼon tire sur la gâchette. La
puissance dʼentrée est appliquée
sur la POWER MIG® 216.
La tension de sortie et lʼalimentation du fil sont présentes alors
quʼon nʼa pas tiré sur la gâchette du
pistolet (elle nʼest pas activée).
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
1. Contacter le concessionnaire
autorisé de Service sur le
Terrain Lincoln le plus proche.
1 La gâchette ou le câble du pistolet
est défectueux. Réviser ou changer
lʼensemble du pistolet.
2. Le circuit de protection thermique
est peut-être activé. Si cʼest le cas, il
suffit de laisser la machine refroidir
pour que lʼétat dʼerreur sʼefface.
3. Vérifier que la tension dʼentrée soit
correcte et quʼelle corresponde au
régime nominal de la plaque nominative et à la configuration du panneau de reconnexion.
4. Si le kit pour pistolet à bobine en
option est installé, vérifier quʼil soit
réglé sur « Poussez le Pistolet » si
lʼon tire sur la gâchette du pistolet
associé au chargeur intégré, et sur «
Pistolet à Bobine » si lʼon tire sur la
gâchette du pistolet à bobine.
1. Retirer lʼensemble du pistolet de la
machine. Si le problème est résolu,
lʼensemble du pistolet est défectueux.
Le réparer ou le remplacer.
2. Si le problème persiste lorsque
lʼensemble du pistolet est retiré de la
machine, le problème se situe à lʼintérieur de la POWER MIG® 216.
ACTION
RECOMMANDÉE
Si toutes les zones de déréglage
possibles recommandées ont été
révisées et le problème persiste,
contacter le concessionnaire
autorisé de Service sur le Terrain
Lincoln Electric le plus proche.
La sortie de la machine est faible.
Les soudures sont « froides », le
cordon de soudure est arrondi ou
comporte des bosses, ce qui
indique quʼil y a peu de mouillage
dans la plaque.
1. Vérifier la tension dʼentrée. Vérifier
que la tension dʼentrée corresponde
au régime nominal de la plaque
nominative et à la configuration du
panneau de reconnexion.
2. Vérifier que les réglages pour la
vitesse dʼalimentation du fil et la tension soient corrects pour le procédé
utilisé.
3. Vérifier que la polarité de la sortie
soit correcte pour le procédé utilisé.
4. Vérifier que les câbles de soudage
et lʼensemble du pistolet ne présentent pas de connexions desserrées
ou défectueuses.
ATTENTION
Si pour une raison quelconque vous ne comprenez pas les procédures de tests ou si vous nʼêtes pas en mesure de réaliser les tests/réparations
de façon sûre, avant de continuer, contactez le Service sur le Terrain Lincoln autorisé le plus proche pour obtenir une assistance technique.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 91

DÉPANNAGE
Suivre les Instructions de Sécurité détaillées au début de ce manuel
E-3-FrE-3-Fr
PROBLÈMES
(SYMPTOMES)
PROBLÈMES DE SORTIE
Faible démarrage dʼarc avec électrode collante ou mise à feu.
PROBLÈMES DʼALIMENTATION
Alimentation du fil irrégulière ou fil
qui ne sʼalimente pas mais les
rouleaux conducteurs tournent.
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
1. Vérifier que les réglages pour la vitesse
dʼalimentation du fil et la tension soient
corrects pour le procédé utilis.
2. Le gaz de protection nʼest pas approprié
pour le procédé utilisé.
3. Vérifier que la tension de ligne dʼentrée
se trouve dans lʼintervalle du régime
nominal recommandé de la machine.
4. Vérifier que le panneau de reconnexion
de la machine soit configuré correctement pour la tension appliquée.
1. Le câble du pistolet fait des coques ou est
tordu.
2. Le fil peut être coincé dans le câble du pisto-
let ou le câble du pistolet est sale.
3. Vérifier la tension des rouleaux conducteurs
et la position des rainures.
4. Vérifier que les rouleaux conducteurs ne
soient pas usés ni desserrés.
5. Lʼélectrode peut être rouillée ou sale.
6. Vérifier que la pointe de contact ne soit pas
endommagée ni incorrecte.
7. Vérifier la facilité de rotation de lʼaxe du fil et
ajuster le bouton de tension du frein si nécessaire.
8. Vérifier que le pistolet soit poussé à fond dans
le montage de pistolet et quʼil y soit bien en
place
.
ACTION
RECOMMANDÉE
Si toutes les zones de déréglage
possibles recommandées ont été
révisées et le problème persiste,
contacter le concessionnaire
autorisé de Service sur le Terrain
Lincoln Electric le plus proche.
ATTENTION
Si pour une raison quelconque vous ne comprenez pas les procédures de tests ou si vous nʼêtes pas en mesure de réaliser les tests/réparations
de façon sûre, avant de continuer, contactez le Service sur le Terrain Lincoln autorisé le plus proche pour obtenir une assistance technique.
POWER MIG® 216
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 92

E-4-Fr E-4-Fr
Suivre les Instructions de Sécurité détaillées au début de ce manuel
DÉPANNAGE
PROBLÈMES
(SYMPTOMES)
PROBLÈMES DʼALIMENTATION
Lʼalimentation du fil cesse pendant
le soudage. Lorsque lʼon relâche
la gâchette puis que lʼon tire à
nouveau dessus, lʼalimentation du
fil démarre.
Pas de contrôle de la vitesse dʼalimentation du fil. Les autres fonctions de la
machine sont normales. Other machine
functions are normal.
PROBLÈMES DE CIRCULATION DU GAZ
Le gaz ne circule pas lorsquʼon tire
sur la gâchette.
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
1. Vérifier que les rouleaux conducteurs dʼalimentation
du fil et le moteur aient un fonctionnement régulier.
2. Vérifier quʼil nʼy ait pas dʼobstruction sur le passage
du fil alimenté. Vérifier quʼil nʼy ait pas dʼobstruction
dans le pistolet et le câble.
3. Vérifier que la bande de remplissage du pistolet et
la pointe soient appropriées pour la taille de fil utilisé.
4. Vérifier que les rouleaux conducteurs et les plaques
guides soient propres et de la taille correcte.
5. Vérifier la facilité de rotation de lʼaxe.
1. Le contrôle de la vitesse dʼalimentation du
fil est sale. Le faire tourner plusieurs fois
et vérifier que le problème soit résolu.
1. Sʼassurer que lʼalimentation du
gaz soit connectée correctement
et ”SUR”.
ACTION
RECOMMANDÉE
Si toutes les zones de déréglage
possibles recommandées ont été
révisées et le problème persiste,
contacter le concessionnaire
autorisé de Service sur le Terrain
Lincoln Electric le plus proche.
2. Si le solénoïde de gaz agit (click)
lorsquʼon tire sur la gâchette, il
peut y avoir une obstruction
dans la ligne dʼalimentation du
gaz.
3. Lʼensemble du câble du pistolet
est défectueux. Le réviser ou le
changer.
4. Si le solénoïde de gaz ne fonctionne pas lorsquʼon tire sur la
gâchette, le problème se situe à
lʼintérieur de la POWER MIG®
216.
5. Vérifier que le pistolet soit
poussé à fond dans le montage
de pistolet et quʼil y soit bien en
place.
ATTENTION
Si pour une raison quelconque vous ne comprenez pas les procédures de tests ou si vous nʼêtes pas en mesure de réaliser les tests/réparations
de façon sûre, avant de continuer, contactez le Service sur le Terrain Lincoln autorisé le plus proche pour obtenir une assistance technique.
POWER MIG® 216
Page 93

F-1-Fr
½”
DIAGRAMME D'APPLICATION
F-1-Fr
G / 500
D / 225 D / 350 E / 375 E / 400 F / 500
C / 180
G / 425
E / 325 F / 375
E / 265 E / 280
C / 130 D / 150
D / 130
C / 90 C / 100
B / 80
B / 75
C / 70 C / 90 D / 110 D / 130
B / 70
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 425
E / 400
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
E / 250 F / 300
E / 570
E / 570
D / 485
C / 475
B / 300
A / 300
E / 390 F / 410
B / 500 C / 500 D / 450 E / 500 E / 550
B / 475
E / 400
D / 375
C / 375
B / 450
B / 350
B / 325
E / 575
E / 575
D / 485
C / 475
B / 325
A / 300
B / 500 C / 500 D / 400 D / 410 E / 425
B / 475
B / 325 B / 350 B / 450 C / 375 D / 375 E / 400
E / 250 F / 300
E / 575 E / 575
D / 485
A / 300 B / 300 C / 475
E / 390 F / 410
G / 500
G / 500
G / 350 G / 350 G / 400
E / 400
D / 285
C / 200
C / 175
F / 375
E / 350
D / 250
D / 200
C / 175
C / 140
F / 320
E / 280
E / 240
D / 200
D / 160
C / 120
C / 9 0
E / 170
E / 160
E / 150
D / 125
D / 110
D / 90
C / 7 5
G / 500
D / 250 E / 300 F / 350
G / 300
G / 270
F / 230
D / 200
G / 475
F / 350
E / 300
E / 300
E / 320
E / 200E / 160
E / 330
D / 280
D / 280
C / 230
C / 180
B / 130
B / 11O
B / 90 B / 120 C / 160 C / 200 D / 240
E / 180
C / 110 D / 120 D / 140
C / 8 0
3/ 16” 1/ 4” 5/ 16” 3/ 8”
D / 300
C / 225
C / 175
M at erial Thickness/ Espesor de el
material/ Lépaisseur de matériel
B / 150
22 ga 20 ga 18 ga 16 ga 14 ga 12 ga 10 ga
R
16
2
POWER M IG
/ / / / / / / / / / /
A / 1OO
B / 125
/
.030 in .036 in .048 in .060 in .075 in .105 in .135 in .187 in .250 in .312 in .375 in .500 in
Wire Di ameter
(0.8mm) (0.9mm) (1.2mm) (1.6mm) (2.0mm) (2.5mm) (3.5mm) (4.8mm) (6.4mm) (7.9mm) (9.5mm) (12.7mm)
Dia. du f il
Dia. de alam bre
- 3/8 in.
(mm)
In.
30-40 CFH
B / 125
(0.6)
0.025
A / 75
(0.8)0.030
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
75%/ 25%
C / 150
C / 125
(0.8)0.030
(0.6)0.0
(0.9)0.0
25
35
0.045 (1.1)
2
100% CO
R
MIG
(DC+)
Super Arc
(1.1)0.0
45
(1.1)0.045
0.035 (0.9)
2
Ar/ CO
75%/ 25%
Gas-Shielded
(0.9)0.035
R
Outer shield 7 1 M
UltraCore 71A75
(0.9)
90%/ 7.5%/ 2.5%
BlueMax 308 LSI
0.035
(1.1)
(0.9)0.0
35
2
He/ Ar/ CO
R
Innershield
(DC+)
0.045
& 212
NR-211-MP
(DC-)
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
M AGN U M SG GUN (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
M AGN U M SG GUN (DC+)
(1.2)
3/64
(0.8)0.030
R
Aluminum
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
(0.9)0.0
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
35
100% Ar
(0.8)0.030
(0.9)0.035
100% Ar
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 4043
MAGNUM 100 SG (DC+)
(0.9)0.035(1.2)
(1.2)
3/64
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
R
Aluminum
SuperGlaze 5356
3/64
100% Ar
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
MAGNUM 250 LX (DC+)
(0.8)0.030
2
Tr i -M ix
100% CO
R
St ainles s
DUAL (DC+)
POWER MIG® 216
Page 94

TABLEAU DE COMMANDE
DIAGRAMMES DE CÂBLAGE
SUPPLÉMENTAIRES DE PISTOLET À BOBINES
UTILISÉ POUR DES OPTIONS
F-2-FrF-2-Fr
4
THERMOSTAT DE
L’ENSEMBLE DU REDRESSEUR
THERMOSTAT
DU TRANSFORMATEUR
N.B. CE DIAGRAMME ILLUSTRE LA POLARITÉ « POSITIVE » DE L’ÉLECTRODE. POUR CHANGER
LA POLARITÉ, ÉTEINDRE L’APPAREIL ET INVERSER LES BRANCHEMENTS DES FILS AU
NOTES:
NIVEAU DE LA BARRETTE DU CONDUCTEUR DU CÂBLEET DE LA BORNE DE TRAVAIL.
N.A. LE CÂBLE DE SOUDAGE DOIT ÊTRE DE LA CAPACITÉ APPROPRIÉE POUR LE COURANT
ET LE FACTEUR DE MARCHE DES APPLICATIONS IMMÉDIATES ET FUTURES
DU FIL
VITESSE
D’ALIMENTATION
ENROULEMENT
ENROULEMENT
PONT EN DIODE
DE REDRESSEUR
DE GAZ
SOLÉNOÏDE
LISTO 100SG
INTERRUPTEUR
INTERRUPTEUR ET GÂCHETTE DU PISTOLET
ILLUSTRÉS EN MODE DE PISTOLET À
POUSSOIR MAGNUM 100 L
DE PUISSANCE
TRANSFORMATEUR
TORE
GÂCHETTE DU
PISTOLET
DE PUISSANCE
TRANSFORMATEUR
TORE
H9
DE PONT
MONOPHASÉ
REDRESSEUR
B
A
H8
H1
MOTEUR/BOÎTE
D’ENGRENAGES
C
H3
H2
VERS LE TRAVAIL
DE SORTIE
ÉTRANGLEUR
F
G
E
D
H7
H6
H5
H4
INTERRUPTEUR DE
SÉLECTION DE PRISE
INFORMATION GÉNÉRALE
SÉQUENCE DE NUMÉRATION DE LA CAVITÉ
(CÔTÉ COMPOSANTS DU TABLEAU DE CIRCUITS IMPRIMÉS)
SYMBOLES ÉLECTRIQUES D’APRÈS E1537
B = NOIR
W = BLANC
R = ROUGE
U = BLEU
CODE DE COULEUR
J4 (GÂCHETTE
CAVITÉ
INDIQUE LE No. DE CAVITÉ DU CONNECTEUR
SÉQUENCE DE NUMÉRATION
(CÔTÉ SANS FIL DU CONNECTEUR)
CÔTÉ MOTEUR)
TACHYMÈTRE,
MOTEUR DU
VENTILATEUR
DE LIGNE
INTERRUPTEUR
POWER MIG® 216
H11B
H10A
H10B
H11B
CR2
H11A
CR1
L2A
L2B
L2
L1
H8
H11A
208V
H9
230V
PANNEAU DE
RECONNEXION
B
VERS LIGNE
D’ALIMENTATION
W
MONOPHASÉE
G
L1A
L1B
VERS LA MASSE
D’APRÈS LE CODE
ÉLECTRIQUE NATIONAL
NOTE: Ce diagramme a valeur de référence uniquement. Il peut ne pas être exact pour toutes les machines couvertes par ce manuel. Le diagramme spécifique pour un code particulier est collé à lʼintérieur de la
machine sur lʼun des panneaux de la console. Si le diagramme est illisible, écrire au Département de Service afin dʼen obtenir un autre en remplacement. Donner le numéro de code de lʼappareil.
Page 95

SCHÉMA DIMENSIONNEL
F-3-FrF-3-Fr
A.01
M22179
20.12
19.15
17.47
32.68
40.20
12.00
29.73
30.43
POWER MIG® 216
38.58
MANUEL DE LʼOPÉRATEUR
Page 96

NOTES
Page 97

NOTES
Page 98

G Keep your head out of fumes.
G Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing zone.
G Turn power off before servicing.
G Do not operate with panel open or
guards off.
WARNING
G Los humos fuera de la zona de res-
piración.
G Mantenga la cabeza fuera de los
humos. Utilice ventilación o
aspiración para gases.
G Gardez la tête à l’écart des fumées.
G Utilisez un ventilateur ou un aspira-
teur pour ôter les fumées des zones
de travail.
G Vermeiden Sie das Einatmen von
Schweibrauch!
G Sorgen Sie für gute Be- und
Entlüftung des Arbeitsplatzes!
G Mantenha seu rosto da fumaça.
G Use ventilação e exhaustão para
remover fumo da zona respiratória.
G Desconectar el cable de ali-
mentación de poder de la máquina
antes de iniciar cualquier servicio.
G Débranchez le courant avant l’entre-
tien.
G Strom vor Wartungsarbeiten
abschalten! (Netzstrom völlig öffnen; Maschine anhalten!)
G Não opere com as tampas removidas.
G Desligue a corrente antes de fazer
serviço.
G Não toque as partes elétricas nuas.
G No operar con panel abierto o
guardas quitadas.
G N’opérez pas avec les panneaux
ouverts ou avec les dispositifs de
protection enlevés.
G Anlage nie ohne Schutzgehäuse
oder Innenschutzverkleidung in
Betrieb setzen!
G Mantenha-se afastado das partes
moventes.
G Não opere com os paineis abertos
ou guardas removidas.
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
LEIA E COMPREENDA AS INSTRUÇÕES DO FABRICANTE PARA ESTE EQUIPAMENTO E AS PARTES DE USO, E SIGA AS
PRÁTICAS DE SEGURANÇA DO EMPREGADOR.
Page 99

WARNING
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
G Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
G Insulate yourself from work and
ground.
G No toque las partes o los electrodos
bajo carga con la piel o ropa mojada.
G Aislese del trabajo y de la tierra.
G Keep flammable materials away.
G Mantenga el material combustible
fuera del área de trabajo.
G Wear eye, ear and body protection.
G Protéjase los ojos, los oídos y el
cuerpo.
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
G Ne laissez ni la peau ni des vête-
ments mouillés entrer en contact
avec des pièces sous tension.
G Isolez-vous du travail et de la terre.
G Berühren Sie keine stromführenden
Teile oder Elektroden mit Ihrem
Körper oder feuchter Kleidung!
G Isolieren Sie sich von den
Elektroden und dem Erdboden!
G Não toque partes elétricas e elec-
trodos com a pele ou roupa molhada.
G Isole-se da peça e terra.
G Gardez à l’écart de tout matériel
inflammable.
G Entfernen Sie brennbarres Material!
G Mantenha inflamáveis bem guarda-
dos.
G Protégez vos yeux, vos oreilles et
votre corps.
G Tragen Sie Augen-, Ohren- und Kör-
perschutz!
G Use proteção para a vista, ouvido e
corpo.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE MANUFACTURER’S INSTRUCTION FOR THIS EQUIPMENT AND THE CONSUMABLES TO BE
USED AND FOLLOW YOUR EMPLOYER’S SAFETY PRACTICES.
SE RECOMIENDA LEER Y ENTENDER LAS INSTRUCCIONES DEL FABRICANTE PARA EL USO DE ESTE EQUIPO Y LOS
CONSUMIBLES QUE VA A UTILIZAR, SIGA LAS MEDIDAS DE SEGURIDAD DE SU SUPERVISOR.
LISEZ ET COMPRENEZ LES INSTRUCTIONS DU FABRICANT EN CE QUI REGARDE CET EQUIPMENT ET LES PRODUITS A
ETRE EMPLOYES ET SUIVEZ LES PROCEDURES DE SECURITE DE VOTRE EMPLOYEUR.
LESEN SIE UND BEFOLGEN SIE DIE BETRIEBSANLEITUNG DER ANLAGE UND DEN ELEKTRODENEINSATZ DES HERSTELLERS. DIE UNFALLVERHÜTUNGSVORSCHRIFTEN DES ARBEITGEBERS SIND EBENFALLS ZU BEACHTEN.
Page 100

• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
 Loading...
Loading...