Page 1
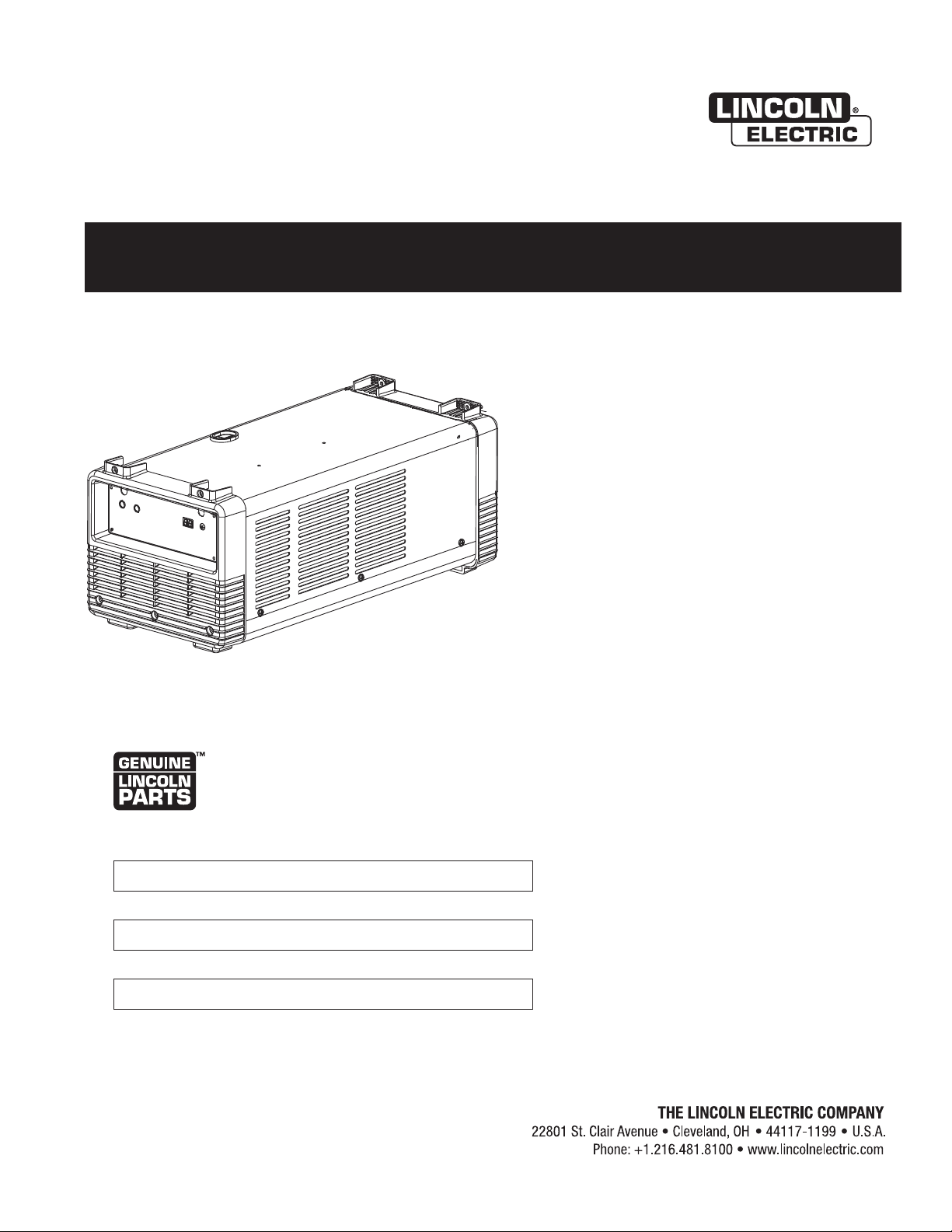
Operator’s Manual
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
COOL ARC ®35
For use with machines having Code Numbers:
11427
Save for future reference
Date Purchased
Code: (ex: 10859)
Serial: (ex: U1060512345)
IM959 | Issue D ate Oct- 13
© Lincoln Global, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Register your machine:
www.lincolnelectric.com/register
Authorized Service and Distributor Locator:
www.lincolnelectric.com/locator
Page 2

THANK YOU FOR SELECTING
AT ALL
TIMES.
SPECIAL SITUATIONS
Additional precautionary measures
A QUALITY PRODUCT BY
LINCOLN ELEC TRIC.
PLEASE EXAMINE CARTON AND EQUIPMENT FOR
DAMAGE IMMEDIATELY
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon
receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims for material damaged in
shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation
company at the time the shipment is received.
SAFETY DEPENDS ON YOU
Lincoln arc welding and cutting equipment is designed and built with
safety in mind. However, your overall safety can be increased by
proper installation ... and thoughtful operation on your part.
DO NOT INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS EQUIPMENT
WITHOUT READING THIS MANUAL AND THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And, most importantly, think before you
act and be careful.
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed
exactly to avoid serious personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to
avoid minor personal injury or damage to this equipment.
KEEP YOUR HEAD OUT OF THE FUMES.
DON’T get too close to the arc. Use
corrective lenses if necessary to
stay a reasonable distance away
from the arc.
READ and obey the Material Safety
Data Sheet (MSDS) and the warning
label that appears on all containers
of welding materials.
USE ENOUGH VENTILATION or
exhaust at the arc, or both, to keep
the fumes and gases from your breathing zone and the general area.
IN A LARGE ROOM OR OUTDOORS, natural ventilation may be
adequate if you keep your head out of the fumes (See below).
USE NATURAL DRAFTS or fans to keep the fumes away from your
face.
If you de velop unusual symptoms, see your supervisor. Perhaps the
welding atmosphere and ventilation system should be checked.
WEAR CORRECT EYE, EAR & BODY PROTECTION
PROTECT your eyes and face with welding helmet
properly fitted and with proper grade of filter plate
(See ANSI Z49.1).
PROTECT your body from welding spatter and arc
flash with protective clothing including woolen
clothing, flame-proof apron and gloves, leather
leggings, and high boots.
PROTECT others from splatter, flash, and glare with
protective screens or barriers.
IN SOME AREAS, protection from noise may be
appropriate.
BE SURE protective equipment is in good condition.
Also, wear safety glasses in work area
DO NOT WELD OR CUT containers or materials which previously had
been in contact with hazardous substances unless they are properly
cleaned. This is extremely dangerous.
DO NOT WELD OR CUT painted or plated parts unless special
precautions with ventilation have been taken. They can release highly
toxic fumes or gases.
PROTECT compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical
shocks, and arcs; fasten cylinders so they cannot fall.
BE SURE cylinders are never grounded or part of an electrical circuit.
REMOVE all potential fire hazards from welding area.
ALWAYS HAVE FIRE FIGHTING EQUIPMENT READY FOR
IMMEDIATE USE AND KNOW HOW TO USE IT.
Page 3

SECTION A:
Diesel Engines
Gasoline Engines
WARNINGS
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other
reproductive harm.
The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm.
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT
YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS
INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR
DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional
safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a
copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the
American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or
CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety”
booklet E205 is available from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801
St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
SAFETY
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and
devices in position and in good repair.Keep
hands, hair, clothing and tools away from
V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts
when starting, operating or repairing
equipment.
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety guards to
perform required maintenance. Remove guards only when
necessary and replace them when the maintenance requiring
their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when
working near moving parts.
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to
override the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control
rods while the engine is running.
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while turning
the engine or welding generator during maintenance work,
disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or magneto wire
as appropriate.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the radiator
pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS MAY
BE DANGEROUS
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor
causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and welding
machines
FOR ENGINE POWERED
EQUIPMENT.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting
and maintenance work unless the
maintenance work requires it to be running.
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes outdoors.
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from
vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts
and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling
tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start engine until
fumes have been eliminated.
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and welders
having a pacemaker should consult their physician before
welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health effects
which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and work
cables. If the electrode cable is on your right side, the
work cable should also be on your right side.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
3
Page 4
SAFETY
ELECTRIC SHOCK
CAN KILL.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are
electrically “hot” when the welder is on. Do
not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin
or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full area
of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if
welding must be performed under electrically
hazardous conditions (in damp locations or while
wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such as
floors, gratings or scaffolds; when in cramped
positions such as sitting, kneeling or lying, if there
is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact
with the workpiece or ground) use the following
equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding
gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection should
be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical (earth)
ground.
3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode
holders connected to two welders because voltage
two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of both
welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
between the
ARC RAYS CAN BURN.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your
eyes from sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or
observing open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens should
conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material
to protect your skin and that of your helpers from the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
CAN BE DANGEROUS.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep your head out of the fume.
Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep fumes
and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding
with electrodes which require special ventilation
such as stainless or hard facing (see instructions
on container or MSDS) or on lead or cadmium
plated steel and other metals or coatings which
produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low
as possible and within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits using local exhaust or
mechanical ventilation. In confined spaces or in
some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may
be required. Additional precautions are also
required when welding on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected by
various factors including proper use and positioning of the
equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific
welding procedure and application involved. Worker exposure
level should be checked upon installation and periodically
thereafter to be certain it is within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c. Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The
heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors to form
phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
3.j. Also see It ems 6.c. and 8.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
injury or death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in
confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your employer’s
safety practices. MSDS forms are available from your welding
distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
4
cause
Page 5

SAFETY
WELDING AND CUTTING
SPARKS CAN CAUSE
FIRE OR EXPLOSION.
6.a. Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If
this is not possible, cover them to prevent the
welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that welding
sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through
small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special
precautions should be used to prevent hazardous situations.
Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI Standard Z49.1)
and the operating information for the equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is
touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause
overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures will
not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances inside.
They can cause an explosion even though they have been
“cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended Safe
Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”,
AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society (see address
above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free
protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless
trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs
when welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear
safety glasses with side shields when in a welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area
as practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or
other locations away from the welding area increase the
possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains,
crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire
hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
CYLINDER MAY EXPLODE IF
DAMAGED.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders containing
the correct shielding gas for the process used
and properly operating regulators designed for
the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings,
etc. should be suitable for the application and
maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to
an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected
to physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations
and any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight
except when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l, “Precautions for
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available
from the Compressed Gas Association 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
POWERED EQUIPMENT.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on the
equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National Electrical
Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.I. Read and follow NFPA 51B “ Standard for Fire Prevention During
Welding, Cutting and Other Hot Work”, available from NFPA, 1
Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
6.j. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Refer to
http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety
for additional safety information.
Welding Safety
Interactive Web Guide
for mobile devices
5
Page 6

vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Installation .......................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications ........................................................................................A-1
Safety Precautions.................................................................................................A-2
Connecting the COOL ARC
Connecting a water-cooled torch ....................................................................A-2
Operation .........................................................................................................Section B
Product Description
Front Panel......................................................................................................B-1
User Interface Display.....................................................................................B-2
User Interface Push Button .............................................................................B-3
Maintenance ....................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions ................................................................................................D-1
Routine Maintenance ......................................................................................D-1
Periodic Maintenance .....................................................................................D-1
Heat Exchanger ..............................................................................................D-1
Reservoir Coolant Level..................................................................................D-1
Coolant Treatment Recommendation .............................................................D-1
Inspect Condition of Coolant...........................................................................D-2
...............................................................................B-1
®
35 to a power source ........................................A-2
vi
Troubleshooting ..............................................................................................Section E
Safety Precautions.................................................................................................E-1
How to Use Troubleshooting Guide ................................................................E-1
Troubleshooting Guide ..........................................................................................E-2
Wiring Diagrams ..............................................................................................Section F
Wiring Diagram ......................................................................................................F-1
Parts List.................................................................................................................P-573
Page 7
A-1
INSTALLATION
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – COOL ARC®35
A-1
Product No. / Model
Input
Current Draw
Maximum Operating Pressure and Flow Rate
(Open Flow, Without Welding Torch Restriction)
Typical Operating Pressure and Flow Rate
(With Welding Torch Restriction)
Reservoir Size
For Use Above Freezing: Clean tap, distilled or de-ionized water.
For Use Below Freezing:
DO NOT USE: Automotive anti-freeze that contains rust inhibitors or leak stoppers.
Recommended Coolant
Shipping
Weight
Reservoir
Full (Water)
These coolants will damage the pump and block the small internal passageways of
the heat exchanger, affecting cooling performance. To acquire the proper coolant
contact a local welding distributor.
DO NOT USE: Pre-packaged welding industry coolants
oil-based substances, which attack the plastic components of the cooler. Once added
to the cooler, these substances are virtually impossible to purge from the water lines
and heat exchanger.
◊
Magnum Pro AL coolant may be used.
K2630-1 COOL ARC®35
350VDC (From V310-T AC/DC & V311-T AC/DC)
0.35 Amps
50 psi (345 kPa) (3.5 bar)Max.
1.2 gal/min. (4.6 liter/min) Max.
53-57 psi (365-393 kPa)
.45-.60 gal/min. (1.7-2.3 liter/min)
1.3 gal. ( 5 liters)
50% water and 50% pure ethylene glycol (reagent
or industrial grade) mixture.
◊
. These coolants may contain
29.8 lbs. (13.5 kg)
42.0 lbs. (19.0 kg)
Dimensions
IP 21S
IEC 60974-2
L
W
H
Temperature Conversion
Chart
Celcius ºC*
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Fahrenheit ºF
68
86
104
122
140
158
176
194
COOL ARC®35
24.5 in. (622 mm)
11.0 in. (280 mm)
10.0 in. (256 mm)
Page 8

A-2
INSTALLATION
A-2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
Connecting a water-cooled torch:
1. Disconnect all power to the power source.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Disconnect input power by removing plug from V310-T/V311-T before
working inside Cooler.
• Do not touch electrically “hot”
parts inside Cooler.
• Have qualified personnel do the installation,
maintenance and troubleshooting work.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Connecting the COOL ARC®35 to a power
source:
1. Disconnect all power to the power source.
2. Turn the power source on its side revealing the Cooler
Access Panel on the bottom.
3. Loosen the fasteners and remove the Panel. Keep the fas-
teners to reattach the Panel.
®
4. Place the COOL ARC
the lead harness from the cooler through the grommet in the
Access Panel that was just removed from the power source
(making sure that the direction of the leads going through the
panel is correct).
5. Attach the two plugs from the COOL ARC
the mating receptacles inside the power source where the
Cooler Access Panel was removed (making sure that these
connectors “lock” into the mating receptacles).
6. Slide the Access Panel up the harness toward the power
source and reattach using the fasteners that were removed.
NOTE: Make sure that the grommet or the harness itself does
not put any stress on the connectors when closing up the Panel.
35 near the V310-T/V311-T and push
®
35 harness into
2. Assemble the torch per the instructions included
with the torch and Twist-mate Adapter.
3. Connect the HOT water return hose (normally RED)
to the Coolant Inlet on the front of the cooler.
Depending on the type of hose connectors on the
torch, it may be necessary to use brass couplers
that are included with the cooler.
4. Connect the COLD water to the torch hose (normally BLUE) to the Coolant Outlet on the front of the
cooler.
5. Attach the twist-mate from the torch to the DC negative (-) Electrode/Gas output terminal on the power
source.
6. Turn the power ON to the power source.
7. The cooler Display will illuminate and go through
initialization. The cooler will enter into standby
mode if a Stick welding mode is selected.
8. Press the push button on the cooler to begin the
priming procedure. The cooler display will show
dashed lines moving in a circular motion.
9. The torch is now ready for water-cooled welding
applications.
Note: If E43 alarm codes are encountered, the torch
has not been properly primed. Run the priming
procedure again by pressing the cooler push
button.
7. Place the power source on top of the cooler locating the feet
of the power source into the mating foot prints in the cooler
case front and back.
8. Secure the power source to the cooler with the four fasteners
that were included with the cooler.
9. Unscrew the coolant reservoir cap and remove the clear plug
(keep for transporting the cooler when filled with coolant).
The clear plug should never be installed when operating the
cooler - it will prevent proper venting. Fill the reservoir with
coolant per the Recommended Coolant section on the TECH-
NICAL SPECIFICATIONS page. The reservoir is full when
the coolant reaches a level just below the cap.
10. The system is now ready for water cooled torch
applications.
COOL ARC®35
Page 9

B-1
OPERATION
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The new COOL ARC®35 is an intelligent cooling unit
equipped with a variable speed three phase rotary
pump and an embedded microprocessor PC board
which controls the pump operation, fan operation, and
the overall functioning of the unit.
The cooler operation is enabled by the power source
and utilizes a “cool as needed” approach, so the pump
and fan speed vary based on real coolant temperature. Furthermore, error signals and related codes are
managed by the power source.
®
The COOL ARC
perature and pressure in order to maximize the cooling of the torch, while using as little energy as possible. If the coolant temperature goes above the maximum limit 185°F (85°C) or the coolant flow is stopped
or the coolant is missing, an alarm is generated and
an error code is sent to the power source. The power
source, consequently, displays the alarm ID code on
the user interface and places the power source and
cooler in a safe condition in order to avoid any damage being done to the cooling components or to the
welding torch. Any alarm condition must be reset by
the user by clearing the alarm code at the power
source user interface before restarting operation, otherwise; the overall welding system is kept in a standby
condition (safety mode).
35 manages both the coolant tem-
B-1
FRONT PANEL
(See Figure B.1)
®
The COOL ARC
AC TIG modes are selected. The cooler does not
operate when STICK modes are selected.
Due to the “cool as needed” functionality (when the
coolant temperature increases passed the maximum
set point) the pump speed is modulated by coolant
temperature feedback. This keeps the cooler noise
levels to a minimum.
The pump starts operating when any TIG welding
mode has been selected and the welder output is
enabled. The pump is kept on until the coolant temperature goes below 175°F (80°C) or for at least 3
minutes after welding has ceased if the cooler was
running while welding.
35 is enabled only when DC TIG or
If a coolant over temperature is detected, welding is
stopped and the cooler is programmed to run at maximum speed in order to recover from the high temperature condition as soon as possible. Welding operation
cannot be restarted before the coolant temperature
has reached a temperature value below 175°F (80°C).
FIGURE B.1
COOLANT OUTLET
COOLANT INLET
DISPLAY
PUSH BUTTON
COOL ARC
®
35
Page 10

B-2
OPERATION
B-2
USER INTERFACE DISPLAY
The 7 segment display shows the coolant temperature during normal operation, but also displays additional cooler status information.
Status indications:
Display
oo
- -
AA
xx
Meaning
OFF mode. The cooler has been turned off by
the user.
Stand-by mode. The cooler has power and is
ready to function, but the selected weld mode is
not a water cooled operation (STICK modes), or
the unit is initiating at power up.
Alarm mode. The cooler is powered and ready to
start, but operation is prevented due to an alarm
condition being detected. The alarm ID code is
displayed by the power source UI. The alarm
codes displayed on the cooler are:
E43 - coolant stoppage - clogged or broken
hose, torch or bypass hose missing.
E44 - coolant temperature upper limit.
Flashing value during power up - indicates the
cooler software version.
yy
nC
Two digit value during normal operation - displays the coolant temperature (°C).
This message is displayed if no communication
between the cooler and the power source is
detected.
Scrolling dashed line (clockwise) is displayed
during torch priming operation.
®
COOL ARC
35
Page 11

B-3
OPERATION
USER INTERFACE PUSH BUTTON
The push button on the user interface of the cooler
has two different functions:
Holding the push button in for 3 seconds toggles the
cooler ON and OFF. When the cooler is turned OFF,
the display will shown “oo”. In this condition, the
cooler can only be turned ON again by pressing the
push button for 3 seconds again, or by cycling input
power to the power source. The power source has no
control over the cooler when it is OFF. It begins communicating with the cooler when the cooler is turned
ON again. If the cooler is OFF when the power source
is turned OFF, it will begin operation in the ON condition when the power source is turned on again, and
must be turned OFF if the user does not want the
cooler to operate during welding.
B-3
Momentarily pressing the COOL ARC
will begin the torch priming procedure and override
any current cooler operation. The cooler will ramp up
the pump speed to maximum and hold it for 30 seconds to allow the torch to be filled with coolant.
During the priming procedure the temperature and
flow/pressure sensing are disabled. To stop the priming procedure before the 30 second time limit the
push button must be pressed again - this places the
cooler back into normal operating mode.
®
35 push button
COOL ARC
®
35
Page 12

D-1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
MAINTENANCE
RESERVOIR COOLANT LEVEL
D-1
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Disconnect input power by removing plug from V310-T/V311-T before
working inside Cooler.
• Do not touch electrically “hot” parts
inside Cooler.
• Have qualified personnel do the installation,
maintenance and troubleshooting work.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
Remove accumulated dust and dirt from the internal
components of the cooler by blowing it out with a lowpressure air hose or removing the dust and dirt with a
vacuum hose.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
In dirty or dusty environments or if biological growth
occurs in the coolant, it may be necessary to flush the
coolant reservoir. Drain the old coolant, rinse the
inside of the reservoir and circulate rinsing solution
through the coolant system. Add new coolant when
cleaning is finished. It is recommended to flush the
coolant at least once a year. A cooling system free
from debris offers increased cooling efficiency and
longer pump and torch life. See the Coolant
Treatment Recommendation in this “Maintenance
Section”.
NOTE: Pure solutions and mixtures of, or materials
(i.e. towels wetted) with ethylene glycol are toxic to
humans and animals. Special precautions should be
taken when discarding toxic material, do not pour this
mixture down any drain. Contact the local EPA office
for responsible disposal methods or for recycling information.
The reservoir volume should be checked daily before
using the cooler. Remove the reservoir fill cap and
check the coolant level. The reservoir is full when the
coolant level is just below the reservoir fill opening.
Keep the reservoir full, especially after disconnecting
the water lines or changing the accessory being
cooled.
COOLANT TREATMENT
RECOMMENDATION
This procedure is intended to provide a means of
reducing the objectionable amount of fungal and bacterial contamination that has occurred in COOL ARC
35 water coolers and cooling systems.
Additive:
The recommended additive can be purchased at local
pool supply stores. An example is "Maintain Pool Pro
30% Non-Foam Algaecide".
Limitations:
• The additive should be used with fresh coolants containing only pure water.
• This additive should not be used with coolants containing any other substance, including antifreeze
substances.
• No other additives shall be used with the specified
coolant that has been treated with the recommended
additive.
• This procedure is no permanent substitute for a periodic maintenance schedule for the specified coolers
• A 1-quart bottle of additive is sufficient to disinfect
and treat about 1000 coolers.
• Check with the manufacturer of your guns or
torches to be sure that this procedure is compatible with your equipment.
®
HEAT EXCHANGER
To maintain maximum cooler efficiency, the heat
exchanger should be kept free of dust and dirt buildup. Clean the heat exchanger periodically using a vacuum hose or a low-pressure air line. Avoid placing the
unit near a flux hopper or a flux waste container. A
clean heat exchanger offers better cooling performance and longer product life. In extremely dirty environments, it may be necessary to remove the heat
exchanger completely from the cooler and clean the
fins with soap and water. Use care to avoid damaging
the fins.
COOL ARC
®
35
Page 13

D-2
Prepare the disinfectant:
Make a quantity of only what is needed to avoid an
excess Bulk preparation (for coolers serviced in quantity):
5.7L (1.5 gals.) of pure, fresh water per cooler and
1.0 ml of additive per cooler. Example: for 100 coolers, add 100 ml to 150 gals. of pure fresh water, Pour
5.0L (1.3 gals.) of disinfectant into the empty reservoir. Recap the reservoir. Prime the cooling system by
positioning cooler horizontally and circulate disinfectant through it for 10 to 15 minutes. Drain disinfectant
from the cooling system. Do not reuse this solution.
Add new, fresh coolant to the cooling system. Add 1L
(0.3 gals.) of fresh disinfectant to the system by pouring it into the reservoir, then reduce the concentration
to the nominal 30 ppm:
Add the balance 4.0L (1.0 gals.) of fresh, pure water
to the reservoir to create the treated coolant concentration. Prime the cooling system.
MAINTENANCE
D-2
INSPECT CONDITION OF COOLANT
If coolant is contaminated or old:
• Drain the system of coolant and dispose of it in an
environmentally specified manner.
• Flush system of old coolant.
• Fill with fresh tap or distilled water, run for ten minutes, and drain.
• Proceed to adding coolant.
Check coolant level. Add more fresh, pure water if
required, without adding more than 0.3L (0.1 gal.) of
pure water to prevent diluting the coolant additive.
Procedure and Preparation:
WARNING
®
• Always disconnect the COOL ARC
from service input power by disconnecting the
V310-T/V311-T from input power.
• Always allow the coolant in the system to cool
enough to avoid burn injuries.
• Avoid contact with contaminated coolant. Wear
waterproof gloves and protective eye wear.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
35 machine
COOL ARC
®
35
Page 14

E-1
TROUBLESHOOTING
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
WARNING
Service and Repair should only be performed by Lincoln Electric Factory Trained Personnel.
Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician and
machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid Electrical
Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual.
__________________________________________________________________________
E-1
This Troubleshooting Guide is provided to help you
locate and repair possible machine malfunctions.
Simply follow the three-step procedure listed below.
Step 1. LOCATE PROBLEM (SYMPTOM).
Look under the column labeled “PROBLEM (SYMPTOMS)”. This column describes possible symptoms
that the machine may exhibit. Find the listing that
best describes the symptom that the machine is
exhibiting.
Step 2. POSSIBLE CAUSE.
The second column labeled “POSSIBLE CAUSE” lists
the obvious external possibilities that may contribute
to the machine symptom.
Step 3. RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION
This column provides a course of action for the
Possible Cause, generally it states to contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
If you do not understand or are unable to perform the
Recommended Course of Action safely, contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
COOL ARC®35
Page 15

E-2
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
TROUBLESHOOTING
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
E-2
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
E43 alarm after initial installation of
power source and cooler, or when
attaching a water cooled torch.
1. Torch water hoses need to be
primed.
2. There is a blockage in the path of
the coolant.
1. After turning the system ON,
press the COOL ARC
button to begin priming procedure.
2. Verify that the coolant path is
clear – that there are no twists,
kinks, or pinch-points in the
coolant hoses.
®
35 push
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
COOL ARC®35
Page 16

F-1
Power Supply
360VDC
DIAGRAMS
10k NTC
the rmistor
BLACK
BROWN
24VDC brushless
fan
F-1
12/13/07
WIRING DIAGRAM
BLACK
RED
BLUE
230VAC 3-Phase
Motor Pump
CAN bus
signals
COOL ARC®35
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside the
machine on one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number.
Page 17

PARTS LIST FOR
P-573P-573
COOL ARC
®
35
This parts list is provided as an informative guide only.
This information was accurate at the time of printing. However, since these
pages are regularly updated in Lincoln Electricʼs official Parts Book (BK-34),
always check with your Lincoln parts supplier for the latest parts information.
®
COOL ARC
35
Page 18

P-573-A.1P-573-A.1
COOL ARC®35
For Code: 11427
Do Not use this Parts List for a machine if its code number is not listed. Contact the Service Department for any
code numbers not listed.
Use the Illustration of Sub-Assemblies page and the table below to determine which sub assembly page and
column the desired part is located on for your particular code machine.
Sub Assembly Item
No.
SUB ASSEMBL Y
PAGE NAME
PAGE NO.
CODE NO.
11427 1
General Assembly
P-573-C
COOL ARC® 35
12-03-2008
Page 19

NOTES
COOL ARC® 35
Page 20

General Assembly
10
12
6
4
5
7
15
9
5
1
8
14
11
3
2
P-573-CP-573-C
15
12
10
14
11
COOL ARC® 35
12-03-2008
Page 21

P-573-C.1
P-573-C.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
1 Base S27342-1 1 X
2 Top Cover S27342-2 1 X
3 Left Cover S27342-3 1 X
4 Right Cover S27342-4 1 X
5 Front/Rear Cover S27342-5 2 X
6 Rear Nameplate S27342-6 1 X
7 Fan S27342-7 1 X
8 Pump S27342-8 1 X
9 Pump Control P.C. Board S27342-9 1 X
10 Control Panel (Display & Control) S27342-10 1 X
11 Cooler S27342-11 1 X
12 Quick Connect S27342-12 2 X
13 Ribbon Cable (Display to Pump Control) (Not Shown) S27342-13 1 X
14 Coolant Temperature Sensor S27342-14 1 X
15 Reservoir S27342-15 1 X
16 Quick Connect (5/8-18 LH Coupler) (Not Shown) S27342-16 2 X
20 Wiring Diagram (Not Shown) S27342-20 1 X
21 Rating Plate (Not Shown) S27342-21 1 X
(Item 22 Connects Cooler to the Power Source)
22 M5 x 35mm Cap Screw (Not Shown) S27342-22 4 X
COOL ARC® 35
12-03-2008
Page 22

NOTES
COOL ARC® 35
Page 23

NOTES
COOL ARC®35
Page 24

CUSTOMER ASSISTANCE POLICY
The business of The Lincoln Electric Company is manufacturing and
selling high quality welding equipment, consumables, and cutting
equipment. Our challenge is to meet the needs of our customers and
to exceed their expectations. On occasion, purchasers may ask
Lincoln Electric for advice or information about their use of our
products. We respond to our customers based on the best information
in our possession at that time. Lincoln Electric is not in a position to
warrant or guarantee such advice, and assumes no liability, with
respect to such information or advice. We expressly disclaim any
warranty of any kind, including any warranty of fitness for any
customer’s particular purpose, with respect to such information or
advice. As a matter of practical consideration, we also cannot assume
any responsibility for updating or correcting any such information or
advice once it has been given, nor does the provision of information
or advice create, expand or alter any warranty with respect to the sale
of our products.
Lincoln Electric is a responsive manufacturer, but the selection and
use of specific products sold by Lincoln Electric is solely within the
control of, and remains the sole responsibility of the customer. Many
variables beyond the control of Lincoln Electric affect the results
obtained in applying these types of fabrication methods and service
requirements.
Subject to Change – This information is accurate to the best of our
knowledge at the time of printing. Please refer to
www.lincolnelectric.com for any updated information.
 Loading...
Loading...