Lincoln Electric IM892 User Manual
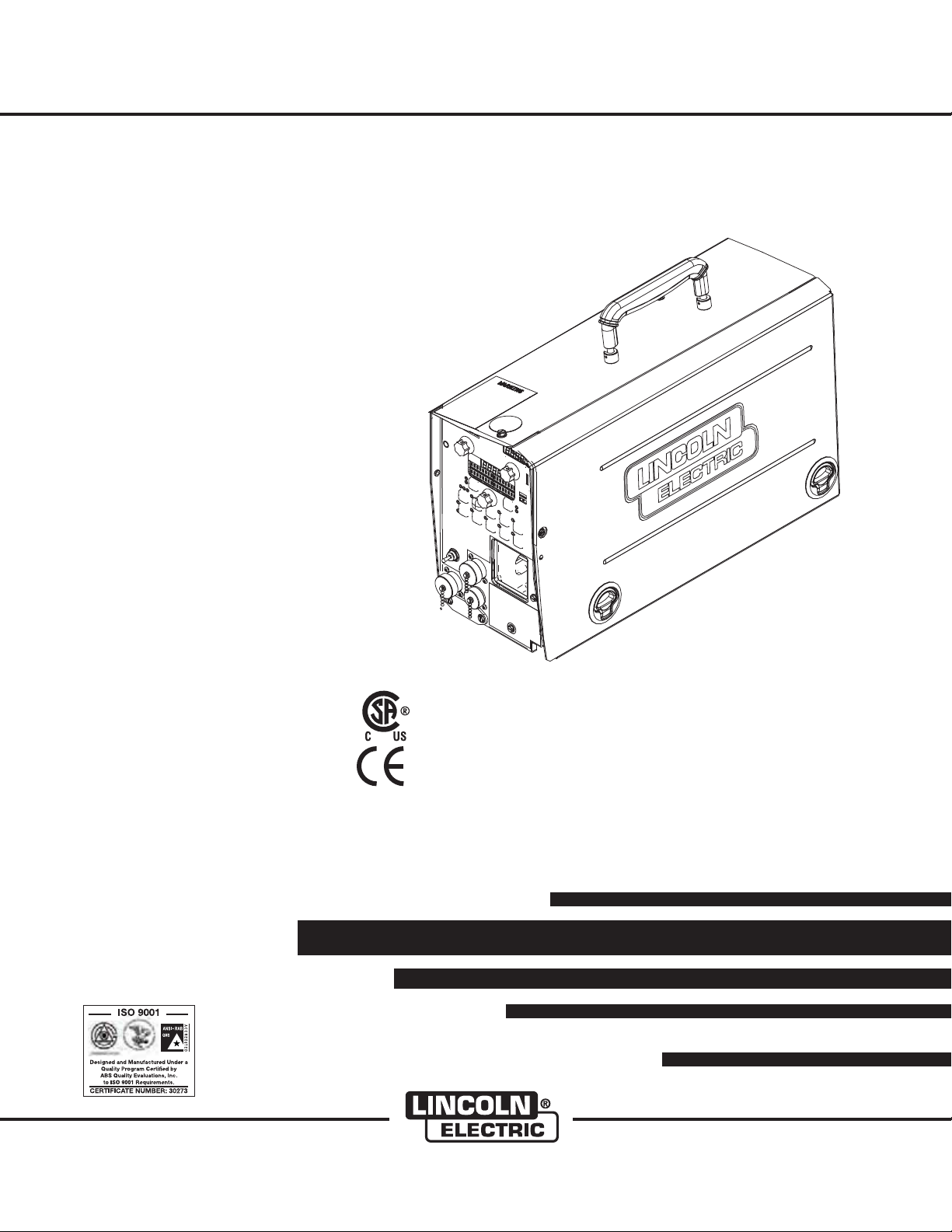
IM892-C
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
POWER FEED
For use with machines having Code Number : 11313, 11456, 11557, 11714, 11715
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding and cutting
equipment is designed and built with
safety in mind. However, your overall
safety can be increased by proper
installation ... and thoughtful operation on your part. DO NOT
INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR
THIS EQUIPMENT WITHOUT
READING THIS MANUAL AND
THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And,
most importantly, think before you
act and be careful.
™
25M
March, 2010
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
IP23
IEC 60974-5
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
Copyright © Lincoln Global Inc.
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
i
SAFETY
WARNING
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents
are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
The Above For Diesel Engines
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you
purchase a copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box
351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available
from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
The engine exhaust from this product contains
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
The Above For Gasoline Engines
i
FOR ENGINE
powered equipment.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance
work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running.
____________________________________________________
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes
outdoors.
____________________________________________________
1.c. Do no t add t he fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts and
igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If
fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start
engine until fumes have been eliminated.
____________________________________________________
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in
position and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and
tools away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving
parts when starting, operating or repairing equipment.
____________________________________________________
1.e. In some c ases i t m ay be ne cessa ry to remove safety
guards to perform required maintenance. Remove
guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete.
Always use the greatest care when working near moving
parts.
___________________________________________________
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan.
Do not attempt to override the governor or
idler by pushing on the throttle control rods
while the engine is running.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the
radiator pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and
welding machines
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and
welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician
before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health
effects which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1.
Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and
work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right
side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
___________________________________________________
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while
turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance
work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magneto wire as appropriate.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
Mar ‘95
ii
SAFETY
ii
ELECTRIC SHOCK can
kill.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits
are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare
skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full
area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding
must be performed under electrically hazardous
conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet
clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or
scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use
the following equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic
welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection
should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
3.f.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of
electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage
between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage
of both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8.
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover
plates to protect your eyes from sparks and
the rays of the arc when welding or observing
open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens
should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
can be dangerous.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep
your head out of the fume. Use enough
ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When
welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see
instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or
cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as
low as possible and within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits using local exhaust or mechanical
ventilation. In confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be required.
Additional precautions are also required when welding
on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected
by various factors including proper use and positioning of
the equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific welding procedure and application involved. Worker
exposure level should be checked upon installation and
periodically thereafter to be certain it is within applicable
OSHA PEL and ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations.
The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation,
especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
vapors
to
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your
employer’s safety practices. MSDS forms are available from
your welding distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
Jan ‘09
iii
SAFETY
iii
WELDING and CUTTING
SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
6.a.
Remove fire hazards from the welding area.
If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
Remember that welding sparks and hot
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI
Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the
equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact
can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures
will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even
been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended
Safe Practices for the
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous
Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society
(see address above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil
6.f.
free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt,
cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear
ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places.
Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding
area as practical. Work cables connected to the building
framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing
through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains
or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
the welding sparks from starting a fire.
though
they have
Preparation
for Welding and Cutting of
CYLINDER may explode
if damaged.
7.a. Us e only compressed gas cylinders
containing the correct shielding gas for the
process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for
the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and
any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas
cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l,
“Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
powered equipment.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on
the equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.I. Read and follow NFPA 51B “ Standard for Fire Prevention
During Welding, Cutting and Other Hot Work”, available
from NFPA, 1 Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma
022690-9101.
6.j. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
Refer to http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety for additional safety information.
Jan ‘09
iv
SAFETY
iv
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ
Pour votre propre protection lire et observer toutes les instructions
et les précautions de sûreté specifiques qui parraissent dans ce
manuel aussi bien que les précautions de sûreté générales suivantes:
Sûreté Pour Soudage A L’Arc
1. Protegez-vous contre la secousse électrique:
a. Les circuits à l’électrode et à la piéce sont sous tension
quand la machine à souder est en marche. Eviter toujours
tout contact entre les parties sous tension et la peau nue
ou les vétements mouillés. Porter des gants secs et sans
trous pour isoler les mains.
b. Faire trés attention de bien s’isoler de la masse quand on
soude dans des endroits humides, ou sur un plancher
metallique ou des grilles metalliques, principalement dans
les positions assis ou couché pour lesquelles une grande
partie du corps peut être en contact avec la masse.
c. Maintenir le porte-électrode, la pince de masse, le câble
de soudage et la machine à souder en bon et sûr état
defonctionnement.
d.Ne jamais plonger le porte-électrode dans l’eau pour le
refroidir.
e. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les parties sous tension
des porte-électrodes connectés à deux machines à souder
parce que la tension entre les deux pinces peut être le
total de la tension à vide des deux machines.
f. Si on utilise la machine à souder comme une source de
courant pour soudage semi-automatique, ces precautions
pour le porte-électrode s’applicuent aussi au pistolet de
soudage.
2. Dans le cas de travail au dessus du niveau du sol, se protéger
contre les chutes dans le cas ou on recoit un choc. Ne jamais
enrouler le câble-électrode autour de n’importe quelle partie
du corps.
5. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité dans la zone de
soudage. Utiliser des lunettes avec écrans lateraux dans les
zones où l’on pique le laitier.
6. Eloigner les matériaux inflammables ou les recouvrir afin de
prévenir tout risque d’incendie dû aux étincelles.
7. Quand on ne soude pas, poser la pince à une endroit isolé de
la masse. Un court-circuit accidental peut provoquer un
échauffement et un risque d’incendie.
8. S’assurer que la masse est connectée le plus prés possible
de la zone de travail qu’il est pratique de le faire. Si on place
la masse sur la charpente de la construction ou d’autres
endroits éloignés de la zone de travail, on augmente le risque
de voir passer le courant de soudage par les chaines de levage, câbles de grue, ou autres circuits. Cela peut provoquer
des risques d’incendie ou d’echauffement des chaines et des
câbles jusqu’à ce qu’ils se rompent.
9. Assurer une ventilation suffisante dans la zone de soudage.
Ceci est particuliérement important pour le soudage de tôles
galvanisées plombées, ou cadmiées ou tout autre métal qui
produit des fumeés toxiques.
10. Ne pas souder en présence de vapeurs de chlore provenant
d’opérations de dégraissage, nettoyage ou pistolage. La
chaleur ou les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs
du solvant pour produire du phosgéne (gas fortement toxique)
ou autres produits irritants.
11. Pour obtenir de plus amples renseignements sur la sûreté,
voir le code “Code for safety in welding and cutting” CSA
Standard W 117.2-1974.
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ POUR
3. Un coup d’arc peut être plus sévère qu’un coup de soliel,
donc:
a. Utiliser un bon masque avec un verre filtrant approprié
ainsi qu’un verre blanc afin de se protéger les yeux du rayonnement de l’arc et des projections quand on soude ou
quand on regarde l’arc.
b. Porter des vêtements convenables afin de protéger la
peau de soudeur et des aides contre le rayonnement de
l‘arc.
c. Protéger l’autre personnel travaillant à proximité au
soudage à l’aide d’écrans appropriés et non-inflammables.
4. Des gouttes de laitier en fusion sont émises de l’arc de
soudage. Se protéger avec des vêtements de protection libres
de l’huile, tels que les gants en cuir, chemise épaisse, pantalons sans revers, et chaussures montantes.
LES MACHINES À SOUDER À
TRANSFORMATEUR ET À
REDRESSEUR
1. Relier à la terre le chassis du poste conformement au code de
l’électricité et aux recommendations du fabricant. Le dispositif
de montage ou la piece à souder doit être branché à une
bonne mise à la terre.
2. Autant que possible, I’installation et l’entretien du poste seront
effectués par un électricien qualifié.
3. Avant de faires des travaux à l’interieur de poste, la debrancher à l’interrupteur à la boite de fusibles.
4. Garder tous les couvercles et dispositifs de sûreté à leur
place.
Mar. ‘93

Thank You
vv
for selecting a QUALITY product by Lincoln Electric. We want you
to take pride in operating this Lincoln Electric Company product
••• as much pride as we have in bringing this product to you!
The business of The Lincoln Electric Company is manufacturing and selling high quality welding equipment, consumables, and cutting equipment. Our challenge is to meet the needs of our customers and to exceed their expectations. On occasion, purchasers may ask Lincoln
Electric for advice or information about their use of our products. We respond to our customers based on the best information in our possession at that time. Lincoln Electric is not in a position to warrant or guarantee such advice, and assumes no liability, with respect to such information or advice. We expressly disclaim any warranty of any kind, including any warranty of fitness for any customer’s particular purpose,
with respect to such information or advice. As a matter of practical consideration, we also cannot assume any responsibility for updating or
correcting any such information or advice once it has been given, nor does the provision of information or advice create, expand or alter any
warranty with respect to the sale of our products.
Lincoln Electric is a responsive manufacturer, but the selection and use of specific products sold by Lincoln Electric is solely within the control
of, and remains the sole responsibility of the customer. Many variables beyond the control of Lincoln Electric affect the results obtained in
applying these types of fabrication methods and service requirements.
Subject to Change – This information is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of printing. Please refer to www.lincolnelectric.com
for any updated information.
CUSTOMER ASSISTANCE POLICY
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims
for material damaged in shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation company at the
time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This information can be
found on your machine nameplate.
Product _________________________________________________________________________________
Model Number ___________________________________________________________________________
Code Number or Date Code_________________________________________________________________
Serial Number____________________________________________________________________________
Date Purchased___________________________________________________________________________
Where Purchased_________________________________________________________________________
Whenever you request replacement parts or information on this equipment, always supply the information you
have recorded above. The code number is especially important when identifying the correct replacement parts.
On-Line Product Registration
- Register your machine with Lincoln Electric either via fax or over the Internet.
• For faxing: Complete the form on the back of the warranty statement included in the literature packet
accompanying this machine and fax the form per the instructions printed on it.
• For On-Line Registration: Go to our
“Product Registration”. Please complete the form and submit your registration.
Read this Operators Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual and keep it
handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection.
The level of seriousness to be applied to each is explained below:
WEB SITE at www.lincolnelectric.com. Choose “Quick Links” and then
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed exactly to avoid serious personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to avoid minor personal injury or damage to this equipment.

vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Installation.......................................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications.......................................................................................................A-1
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................A-2
Location................................................................................................................................A-2
High Frequency Protection...................................................................................................A-2
Arclink Control Cable............................................................................................................A-3
Cable Connections ...............................................................................................................A-3
Weld cable Sizes..................................................................................................................A-4
Coaxial Weld Cable..............................................................................................................A-4
Electrode Polarity .................................................................................................................A-5
Shielding Gas Connection....................................................................................................A-5
Changing The Drive Motor Gears ........................................................................................A-6
Wire Drive Configuration ......................................................................................................A-7
Procedure to Install Drive Rolls and Wire Guides ................................................................A-7
Remote Sense Lead Specification .......................................................................................A-8
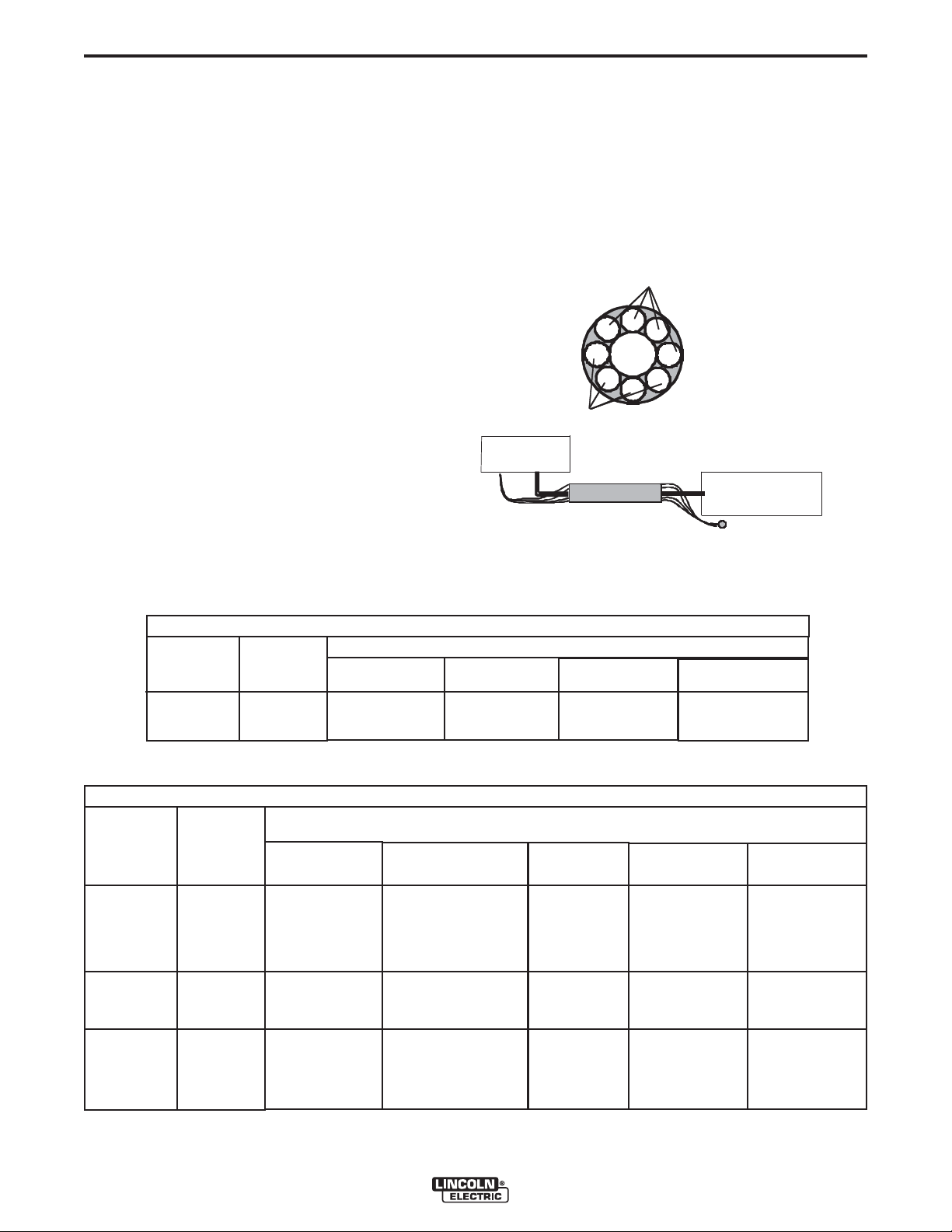
Loading Spools of Wire ........................................................................................................A-8
Typical System Configurations.............................................................................................A-9
________________________________________________________________________________
Operation.........................................................................................................................Section B
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................B-1
Graphic Symbols that appear on this Machine or in this Manual .........................................B-1
Definition of Welding Terms .................................................................................................B-2
General Description..............................................................................................................B-2
Duty Cycle ............................................................................................................................B-2
Recommended Processes, Equipment Limitations, Recommended Power Sources ..........B-3
Case Front Controls.......................................................................................................B-4,B-5
On-Off Switch .......................................................................................................................B-6
Making a Weld with Waveform Technology Power Sources ................................B-7 thru B-24
Set-Up Feature Menu for Parameters and Definition ........................................B-25 thru B-32
Procedure/Memory Panel Operation ..................................................................B-33 thru B-35
Dual Procedure/Memory Operation....................................................................B-36 thru B-38
Internal Controls .......................................................................................................B-39, B-40
Cold Feed / Gas Purge Switch, Light Switch, Heater Switch, Pressure Arm Adjustment ..B-41
2 Step - 4 Step Trigger Operation and Graphics ................................................B-42 thru B-47
Rear Controls .....................................................................................................................B-48
Flow Meter..........................................................................................................................B-49
Operation On Lincnet Power Sources................................................................................B-49
________________________________________________________________________________
Accessories ....................................................................................................................Section C
Factory Installed Equipment.................................................................................................C-1
Drive Roll Kits used..............................................................................................................C-1
Common Packages with Accessories Used...........................................................C-2 thru C-4
Installation of Water Cooling Kit ...........................................................................................C-5
Water Cooled Guns..............................................................................................................C-6
________________________________________________________________________________
Maintenance....................................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................D-1
Routine Maintenance ...........................................................................................................D-1
Periodic Maintenance...........................................................................................................D-1
Calibration Specification.......................................................................................................D-1
________________________________________________________________________________
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................Section E
How to Use Troubleshooting Guide .....................................................................................E-1
Error Fault Codes .................................................................................................................E-2
Troubleshooting Guide ...........................................................................................E-3 thru E-4
________________________________________________________________________________
vi
Wiring Diagrams & Dimension Prints ...........................................................................Section F
________________________________________________________________________________
Parts Pages ................................................................................................................P-534 Series
_______________________________________________________________________
________

A-1
INSTALLATION
A-1
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS –
INPUT VOLTAGE and CURRENT
INPUT VOLTAGE ± 10%
40 VDC
RATED OUTPUT @ 104°F (40°C)
DUTY CYCLE
60% rating
100% rating
GEARING - WIRE FEED SPEED RANGE-WIRE SIZE
GMAW
POWER FEED™ 25M K2536-1, -2, -3
INPUT AMPERES
4A
INPUT AMPERES
500
400
FCAW
GEARING
Normal Speed
(factory setting)
Extra torque
WFS RANGE
50 – 800 ipm
(2.5 – 20.3m/min)
30 – 400 ipm
(1.3 – 10.4m/min)
WIRE SIZES
.023 – 1/16"
(0.6 – 1.6mm)
.023 – 1/16"
(0.6 – 1.6mm)
WFS RANGE
50 – 800 ipm
(2.5 – 20.3m/min)
30 – 400 ipm
(1.3 – 10.4m/min)
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
HEIGHT WIDTH DEPTH WEIGHT
14.5 Inches 8.5 Inches 23.5 Inches 35 lbs
(368 mm) ( 216 mm) (597 mm) (15.9 kg)
Handle folded down Memory Panel Closed
TEMPERATURE RANGE
OPERATION: -40°F to 122°F (-40°C to 50°C)
STORAGE: -40°F to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C)
WIRE SIZES
.030 – 5/64"
(0.8 – 2.0mm)
.030 – 3/32"
(0.8 – 2.4mm)
POWER FEED™ 25M

A-2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
INSTALLATION
HIGH FREQUENCY PROTECTION
A-2
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the
welding power source before
installation or changing drive rolls
and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger,
electrode and drive mechanism are
"hot" to work and ground and
could remain energized several
seconds after the gun trigger is
released.
• Welding power source must be connected to
system ground per the National Electrical Code
or any applicable local codes.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
LOCATION
For best wire feeding performance, place the POWER
FEED™ 25M on a stable and dry surface. Keep the
wire feeder in a vertical position. Do not operate the
wire feeder on an angled surface of more than 15
degrees.
CAUTION
Locate the POWER FEED™ 25M away from radio
controlled machinery. The normal operation of the
POWER FEED™ 25M may adversely affect the operation of RF controlled equipment, which may result
in bodily injury or damage to the equipment.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Do not submerge the POWER FEED™ 25M.
The POWER FEED™ 25M is rated IP23 and is
suitable for outdoor use.
The handle of the POWER FEED™ 25M is intended
for moving the wire feeder about the work place only.
When suspending a wire feeder, insulate the hanging
device from the wire feeder enclosure.
POWER FEED™ 25M

A-3
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
F
E
A
B
G
C
D
F
E
INSTALLATION
ARCLINK CONTROL CABLES
(See Figure A.3)
ArcLink Control Cables are available in two forms:
• K1543-xx series for most indoor or factory installations.
• K2683-xx series for outdoor use or when the equipment is frequently moved.
ArcLink/LincNet control cables are special high quality
cables for digital communication. The cables are copper 5 conductor cable in a SO-type rubber jacket.
There is one 20 gauge twisted pair for network communications. This pair has an impedance of approximately 120 ohms and a propagation delay per foot of
less than 2.1 nanoseconds. There are two 12 gauge
conductors that are used to supply 40VDC to the network. The fifth wire is 18 gauge and is used as an
electrode sense lead.
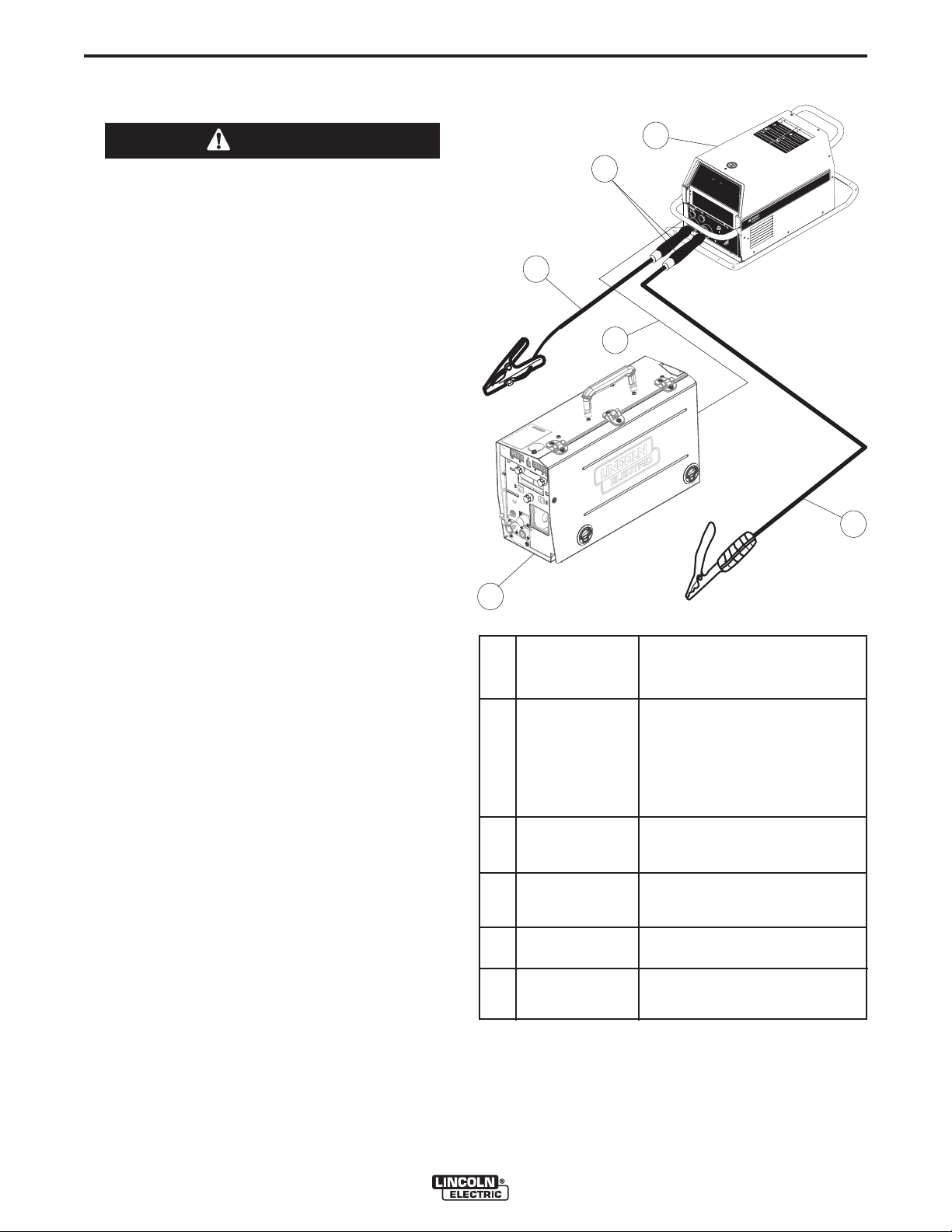
CABLE CONNECTIONS
There are three circular connectors on the front of the
POWER FEED™ 25M.
(See 5-pin, 6-pin and 7-pin- Figure A.1)
FIGURE A.1
Function
PIN
Wiring
A-3
Use of non-standard cables may lead to system shutdowns, poor arc starting and wire feeding problems.
The control cables connect the power source to the
wire feeder, and the wire feeder to other wire feeders.
Control cables may be connected end to end to
extend their length. Use a maximum of 200 ft.
(61.0m) of control cable between components.
Figure A.3
POWER SOURCE
Power Source
Pin Function
A ArcLink
B ArcLink
C "67" voltage sense
D 40 VDC
E Common
Pin Function
A ArcLink
B ArcLink
C "67" voltage sense
D 40 VDC
E Common
WIRE FEEDER
Wire Feeder
5 pin trigger connector for pushonly guns.
6 pin connector for
remote control or
foot/hand amptrol.
7 pin connector for
push-pull guns
A
B
C
D
Dual Procedure Selection
E
A
77 Remote potentiometer, 5K
B
75 Remote potentiometer, common
C
76 Remote potentiometer, wiper
D
E
F
A
B
C
77 Remote potentiometer, 5K
D
76 Remote potentiometer, wiper
E
F
G
75 Remote potentiometer, common
Trigger
Not used
Common
Common
Switch, On/Off
Switch, common
Not used
Motor -
Motor +
Switch, On/Off
Switch, common
There is one circular connector on the rear of the POWER
FEED™ 25M. Maximum control cable length is 200 ft (61 m).
FIGURE A.2
Function
5 pin ArcLink connector.
PIN
A
B
C
67 Electrode Voltage Sense
D
E
Wiring
ArcLink
ArcLink
40VDC
Common
POWER FEED™ 25M
A-4
Electrtrode
Work
Work
Electrode
ork
Electrode
ork
Power Source
Coaxial W
eld Cable
Wire Feeder
WELD CABLE SIZE
INSTALLATION
To install:
1. Turn the input power off at the welding power source.
Table A.1 located below are copper cable sizes recommended for
different currents and duty cycles. Lengths stipulated are the distance from the welder to work and back to the welder again. Cable
sizes are increased for greater lengths primarily for the purpose of
minimizing cable drop.
2. Connect one end of the center lead to the power source
electrode connection, and the other end to the wire feeder electrode connection.
3. Connect the outer lead bundle to the power source work
connection, and the other end to the work piece.
Minimize the length of any work lead extension for best
COAXIAL WELD CABLE
(See Table A.2)
results.
4. Insulate all connections.
Coaxial welding cables are specially designed welding cables for
pulse welding or STT™ welding. Coaxial weld cables feature low
inductance, allowing fast changes in the weld current. Regular
cables have a higher inductance which may distort the pulse or
STT™ wave shape. Inductance becomes more severe as the weld
cables become longer.
Coaxial cables work best for high performance waveforms and
when:
• long cables are present.
P
• the cables are housed in a metal tray.
ower Source
WWork
Electrode
A coaxial weld cable is constructed with multiple small leads
wrapped around one large lead. The large inner lead connects to
the electrode stud on the power source and the electrode connection on the wire feeder. The small leads combine together to form
the work lead, one end attached to the power source and the other
end to the work piece. See Figure A.5
TABLE A.2
RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZES (RUBBER COVERED COPPER - RATED 75°C)**
COAXIAL CABLE LENGTH
AMPERES
250
300
350
DUTY
CYCLE
100%
60%
60%
0 to 25Ft.
(0 to7.6M)
1
1
1/0
25 to 50Ft.
(7.6 to 15.2M)
1
1
1/0
FIGURE A.5
Coaxial W
eld Cable
50 to 75 Ft.
(15.2 to 22.9M)
1
1
--
Electrode
Wire Feeder
WWork
75 to 100 Ft.
(22.9 to 30.5M)
1
1/0
--
A-4
TABLE A.1
RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZES (RUBBER COVERED COPPER - RATED 167°F or 75°C)**
CABLE SIZES FOR COMBINED LENGTHS OF ELECTRODE AND WORK CABLES
PERCENT
DUTY
CYCLE
60
100
20
40 & 30
30
40
60
100
60
100
60
60
100
60
0 to 50Ft.
(0 to15M)
2
2
4 or 5
3
3
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
50 to 100Ft.
(15 to 30M)
2
2
3
3
3
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
100 to 150 Ft.
POWER FEED™ 25M
(30 to 46M)
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
2/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
150 to 200 Ft.
(46 to 61M)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
3/0
200 to 250 Ft.
(61 to 76M)
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
4/0
4/0
4/0
AMPERES
200
200
225
225
250
250
250
250
300
325
350
400
400
500
** Tabled values are for operation at ambient temperatures of 104°F(40°C) and below. Applications above 104°F(40°C) may require cables
larger than recommended, or cables rated higher than 167°F(75°C).

A-5
INSTALLATION
ELECTRODE POLARITY
The wire feeder is factory set for Electrode Positive
welding. Most GMAW welding procedures use
Electrode Positive welding. Most GTAW and some
Innershield procedures use Electrode Negative welding.
CAUTION
When changing the electrode polarity, the weld
cables must be changed at the power source studs
and the DIP switch inside the wire feeder must be
properly set. Operation with the DIP switch in the
wrong position will cause erratic arc performance.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power source before changing
electrode polarity.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Electrode Polarity DIP switch #7 setting
Positive OFF (Factory setting)
Negative ON
Tools required:
• 5/16" nut driver
To change the DIP switch from Electrode Polarity:
1. Turn power off at the welding power source
2. Remove the spool of wire from the feeder.
3. Remove the 4 screws holding the cover. Lift the
cover out of the feeder.
4. Move DIP switch #7 on the feed head board to the
appropriate position.
5. Install the cover and secure with the screws.
A-5
SHIELDING GAS CONNECTION
WARNING
CYLINDER may explode if
damaged.
• Keep cylinder upright and
chained to support.
• Keep cylinder away from areas where it may be
damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached.
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from welding or other live
electrical circuits.
• BUILD UP OF SHIELDING GAS MAY
HARM HEALTH OR KILL.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not
in use.
• See American National Standard Z-49.1, "Safety
in Welding and Cutting” Published by the
American Welding Society.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAXIMUM INLET PRESSURE IS 100 PSI. (6.9 BAR.)
Install the shielding gas supply as follows:
1. Secure the cylinder to prevent it from falling.
2. Remove the cylinder cap. Inspect the cylinder valves
and regulator for damaged threads, dirt, dust, oil or
grease. Remove dust and dirt with a clean cloth. DO
NOT ATTACH THE REGULATOR IF OIL, GREASE
OR DAMAGE IS PRESENT! Inform your gas supplier
of this condition. Oil or grease in the presence of high
pressure oxygen is explosive.
3. Stand to one side away from the outlet and open the
cylinder valve for an instant. This blows away any dust
or dirt which may have accumulated in the valve outlet.
4. Attach the flow regulator to the cylinder valve and
tighten the union nut(s) securely with a wrench. Note:
if connecting to 100% CO2cylinder, insert regulator
adapter between regulator and cylinder valve. If
adapter is equipped with a plastic washer, be sure it is
seated for connection to the CO2cylinder.
5. Attach one end of the inlet hose to the outlet fitting of
the flow regulator. Attach the other end to the welding
system shielding gas inlet. Tighten the union nuts with
a wrench.
6. Before opening the cylinder valve, turn the regulator
adjusting knob counterclockwise until the adjusting
spring pressure is released.
7. Standing to one side, open the cylinder valve slowly a
fraction of a turn. When the cylinder pressure gage
stops moving, open the valve fully.
8. The flow regulator is adjustable. Adjust it to the flow
rate recommended for the procedure and process
being used before making a weld.
POWER FEED™ 25M
A-6
INSTALLATION
CHANGING THE DRIVE MOTOR GEAR RATIO
WARNING
• Turn off input power at the welding power source before installation or changing drive roll and/or
wire guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts
such as the wire drive or internal
wiring.
• When feeding with the gun trigger, the electrode
and wire drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform this
operation.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
A-6
8. Remove the busbar by unscrewing the bolt using a 3/4"
open end wrench.
9. With a 1/4" hex key wrench, loosen the socket head cap
screw securing the gun bushing. Remove the gun bushing from the wire drive.
10. With a 5/16" nut driver remove the five screws securing
the wire drive panel. Lift out the wire drive panel and
disconnect the molex connections.
11. Using a 5/16" nut driver, remove the four screws secur-
ing the cover.
12. With a Phillips screwdriver, remove the three screws
and lock washers securing the motor. Remove the
motor.
13. Place the motor in the new position.
Extra
Torque
Gearing
Feed Force
Extra Torque
Gearing
400
Normal
Speed
Gearing
Normal Speed
Gearing
WFS
800
Tools required:
• 1/4" hex key wrench
• 3/4" open end wrench
• 9/16" socket and ratchet wrench
• 7/16" nut driver
• 5/16" nut driver
• Phillips screw driver
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
. Remove the spool of electrode from the wire feeder.
2
3. Loosen the thumb screw at the wire drive and remove the
welding gun.
4. Remove the outer wire guide, drive rolls and inner wire
guide.
14. Assemble the three screws and lock washer holding the
wire drive motor.
15. Assemble the molex connections and place the wire
drive assembly inside the wire feeder. Route the gas
hose through the opening in the wire drive panel.
16. Move DIP switch #8 on the Feed head board to the
appropriate position.
Gear Select DIP Switch #8 Setting Range
Normal Speed ON 50 – 800 ipm
Extra Torque OFF 30 – 400 ipm
17. Place the gun bushing in the wire drive and align the
threaded hole in the gun bushing with the hole in the
feed plate. With a 1/4" hex key, tighten the socket head
cap screw to secure the bushing in the wire drive.
18. Reassemble the busbar and tighten the mounting hardware with a 3/4" open end wrench.
19. Place the new gear on the motor shaft. Secure the gear
to the motor shaft with the collar, washer and screw.
20. Reassemble the lower drive roll hub and lower drive roll
hub retainer.
21. Reassemble the gear cover.
5. Use a 7/16" nut driver to remove the gear cover.
6. Use 9/16" socket and ratchet wrench to remove the lower
drive roll hub retainer. Remove the lower drive roll hub.
7. With a Phillips screwdriver, remove the screw, washer
and collar holding the pinion gear. Remove the pinion
gear.
POWER FEED™ 25M
22. Reassemble the inner wire guide, drive rolls and outer
wire guide.
23. Place the welding gun into the gun bushing and secure
with the thumb screw.

A-7
INSTALLATION
WIRE DRIVE CONFIGURATION
(See Figure A-6)
Changing the Gun Receiver Bushing
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the
welding power source before installation or changing drive rolls and/or
guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode
and drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tools required:
• 1/4" hex key wrench.
Note: Some gun bushings do not require the use of
the thumb screw.
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
2. Remove the welding wire from the wire drive.
3. Remove the thumb screw from the wire drive.
4. Remove the welding gun from the wire drive.
5. Loosen the socket head cap screw that holds the
connector bar against the gun bushing.
Important: Do not attempt to completely
remove the socket head cap screw.
6. Remove the outer wire guide, and push the gun
bushing out of the wire drive. Because of the precision fit, light tapping may be required to remove
the gun bushing.
7. Disconnect the shielding gas hose from the gun
bushing, if required.
FIGURE A-6
A-7
8. Connect the shielding gas hose to the new gun
bushing, if required.
9. Rotate the gun bushing until the thumb screw hole
aligns with the thumb screw hole in the feed plate.
Slide the gun receiver bushing into the wire drive
and verify the thumb screw holes are aligned.
10. Tighten the socket head cap screw.
11. Insert the welding gun into the gun bushing and
tighten the thumb screw.
PROCEDURE TO INSTALL DRIVE ROLLS
AND WIRE GUIDES
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the
welding power source before installation or changing drive rolls and/or
guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground
and could remain energized several seconds
after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
2. Release the idle roll pressure arm.
3. Remove the outer wire guide by turning the knurled
thumbscrews counter-clockwise to unscrew them
from the feed plate.
4. Rotate the triangular lock and remove the drive
rolls.
GUN RECEIVER BUSHING
CONNECTOR BLOCK
THUMB SCREW
SOCKET HEAD
CAP SCREW
OUTER WIRE GUIDE
LOOSEN TIGHTEN
5. Remove the inner wire guide.
6. Insert the new inner wire guide, groove side out,
over the two locating pins in the feed plate.
7. Install a drive roll on each hub assembly secure
with the triangular lock.
8. Install the outer wire guide by aligning it with the
pins and tightening the knurled thumbscrews.
9. Close the idle arm and engage the idle roll pressure
arm. Adjust the pressure appropriately
POWER FEED™ 25M
A-8
CONNECT AALL SSENSE
LEADS
THE EEND
O
THE WWELD
CONNECT
A
LL
WORK
LEAD
S
AT
THE BBEG
INN
IN
G
OF
THE WWELD
D
IRE
C
TION
OF
TRAVEL
INSTALLATION
A-8
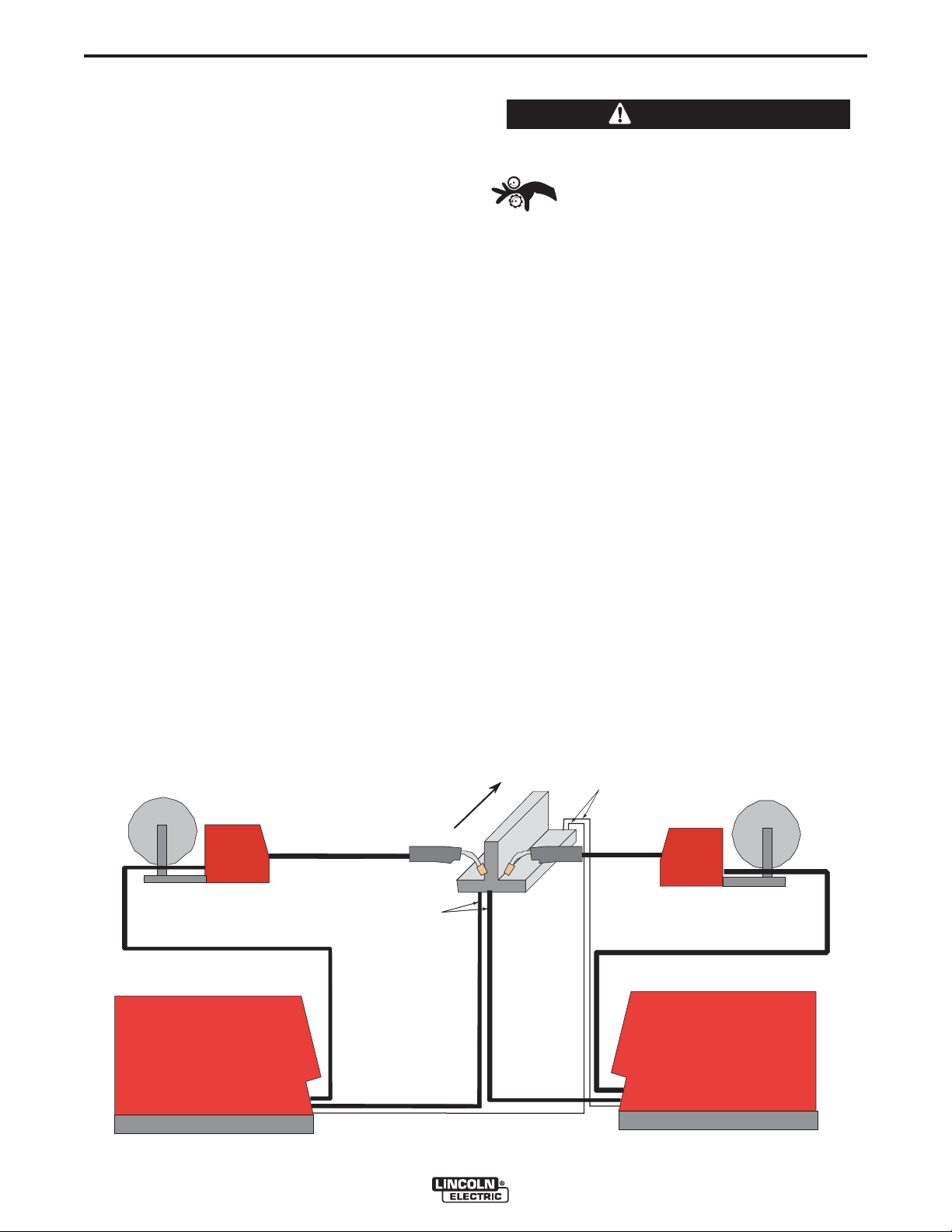
REMOTE SENSE LEAD SPECIFICATIONS
Welding with Multiple Arcs:
( See Figure A.7)
Special care must be taken when more than one arc
is welding simultaneously on a single part. Arc blow
and arc interference may occur or be magnified. Each
power source requires a work lead from the work stud
to the welding fixture. Do not combine all of the work
leads into one lead. Performing welding in the direction away from the work leads. Connect all of the work
sense leads from each power source to the work
piece at the end of the weld, such that they are out of
the path of the weld current. See Figure A.7
For the best results when pulse welding, set the wire
size and wire feed speed the same for all the arcs.
When these parameters are identical, the pulsing frequency will be the same, helping to stabilize the arcs.
LOADING SPOOLS OF WIRE
WARNING
• Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools
away from rotating equipment.
• Do not wear gloves when threading
wire or changing wire spool.
• Only qualified personnel should install,
use or service this equipment.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Loading 10 to 15 lb. (4.5 – 6.8kg) Spools.
A K468 spindle adapter is required for loading 2"
(51mm) wide spools on 2" (51mm) spindles. Use a
K468 spindle adapter for loading 2-1/2" (64mm) wide
spools.
1. Squeeze the release bar on the retaining collar and
remove it from the spindle.
2. Place the spindle adapter on the spindle, aligning
the spindle brake pin with the hole in the adapter.
IRE
OF
L
TH
TH
FIGURE A.7
TIO
TR
A
A
G
INN
3. Place the spool on the spindle and align the
adapter brake tab with one of the holes in the back
side of the spool. An indicator mark on the end of
the spindle shows the orientation of the brake tab.
Be certain the wire feeds off of the spool in the
proper direction.
4. Re-install the retaining collar. Make sure that the
release bar snaps out and that the retaining collar
fully engages the groove on the spindle.
AAT TH
F FTH
POWER FEED™ 25M

A-9
INSTALLATION
TYPICAL SYSTEM CONFIGURATIONS
A-9
Standard Features
Arc Performance
• Push-Pull ready for welding aluminum with Pulse
and Pulse-on-Pulse™ waveforms.
• STT™ capable when used with STT™ equipped
Power Waves.
• Waveform Control Technology™ for welds with
good appearance and low spatter, even when welding nickel alloys.
User Controls
• (code 11313) 6 memories for easily selecting procedures.
• (code 11456 and higher) 8 memories for easily
selecting procedures.
• MSP4 panel located behind the memory panel for
protection.
• Full sequence control for tailoring the weld from
start to end.
• All welding controls located at the wire feeder,
including process selection
• Brass-to-brass connections between the electrode
connection and the gun minimize voltage drop variations, resulting in consistent arc performance all
day, every day.
• Powerful, quiet motor with integrated tachometer for
accurate WFS regulation.
Extras:
• Flowmeter with gas control valve
• Push-Pull ready.
• Remote control / Foot amptrol ready.
• Internal heater for keeping condensation off of the
spool of wire.
• Internal lights for illuminating the wire drive compartment.
Options
• Water cooling kit for use with water cooled guns.
Wire Drive
Patented 2 roll drive system. MAXTRAC™ technology
delivers great feeding because:
• Patent pending drive rolls improve traction on solid
wire by up to 20%.
• The precision machined, rigid aluminum alloy frame
results in maximum drive roll clamping pressure.
• Patented split wire guides fully support the wire and
virtually eliminate birdnesting.
• No tools required to change the drive rolls and wire
guides.
• Patented dual spring pressure arms have sensitivity
for feeding soft wires without crushing them, and
have plenty of compression force for feeding solid or
stiff wires.
• All gear driven rolls for more feeding force.
• Changeable gun bushings easily accept guns from
other manufacturers.
POWER FEED™ 25M

B-1
OPERATION
B-1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
READ AND UNDERSTAND ENTIRE SECTION
BEFORE OPERATING MACHINE.
WARNING
• ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
Unless using COLD FEED feature, when feeding with gun trigger, the electrode and drive
mechanism are always electrically energized and could
remain energized several seconds after the welding ceases..
• Do not touch electrically live part or electrode
with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and ground.
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
• FUMES AND GASSES can be
dangerous.
• Keep your head out of fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing
zone.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
• WELDING SPARKS can cause
fire or explosion.
• Keep flammable material away.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ARC RAYS can burn.
• Wear eye, ear and body protection.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
SEE ADDITIONAL WARNING INFORMATION
UNDER ARC WELDING SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND IN THE FRONT OF THIS OPERATING MANUAL.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
GRAPHIC SYMBOLS THAT APPEAR ON
THIS MACHINE OR IN THIS MANUAL
INPUT POWER
ON
OFF
WIRE FEEDER
POSITIVE OUTPUT
NEGATIVE OUTPUT
INPUT POWER
DIRECT CURRENT
U
U
U
I
0
1
2
1
OPEN CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE
INPUT VOLTAGE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
INPUT CURRENT
I
POWER FEED™ 25M
2
OUTPUT CURRENT
PROTECTIVE
GROUND
WARNING OR
CAUTION

B-2
OPERATION
B-2
DEFINITION OF WELDING TERMS
NON-SYNERGIC WELDING MODES
• A Non-synergic welding mode requires all welding
process variables to be set by the operator.
SYNERGIC WELDING MODES
• A Synergic welding mode offers the simplicity of
single knob control. The machine will select the correct voltage and amperage based on the wire feed
speed (WFS) set by the operator.
WFS
• Wire Feed Speed
CC
• Constant Current
CV
• Constant Voltage
GMAW
• Gas Metal Arc welding
GMAW-P
• Gas Metal Arc welding-(Pulse Arc)
GMAW-STT
• Gas Metal Arc welding-(Surface Tension Transfer)
SMAW
• Shielded Metal Arc welding
FCAW
• Flux Core Arc Welding
CAG
• Carbon Arc Gouging
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
General Physical Description
The POWER FEED™ 25M is a premium portable wire
feeder for use with the Power Wave products. The
wire feeder features a 2 roll MAXtrac™ drive coupled
to a powerful motor for driving wire through difficult situations. The easy-to-use, MSP4 interface provides
ready access to all welding modes in the Power
Wave. A memory panel is included with the POWER
FEED™ 25M and allows quick recall of favorite weld
procedures. Two cases are available: An engineered
aluminum case with replaceable skids, or an impact
resistant polycarbonate plastic case.
The heart of the POWER FEED™ 25M is the
MAXtrac™ drive. The patented features on the wire
drive offer tool-less changing of the drive rolls and the
wire guides for quick spool changes. Plus, the drive
can be configured for extra torque when feeding large
diameter flux cored electrodes.
The POWER FEED™ 25M continues Lincoln’s lead
role of environmental protection for electronics. P.C.
boards are potted in epoxy and electrical connections
are protected with dielectric grease. Noise suppression components protect the POWER FEED™ 25M
from stray signals and keep the feeder from interfering
with other digital equipment.
General Functional Description
The POWER FEED™ 25M is best suited for applications were quality welds are expected. Combined with
a Power Wave power source, the POWER FEED™
25M is great for aluminum, nickel, alloy and other difficult to weld materials. Easy to use controls make it a
great feeder for consistent results with mild steel
applications too.
DUTY CYCLE
The POWER FEED™ 25M is rated for 500 amps,
60% duty cycle and 400 amps, 100% duty. The duty
cycle is based on a 10 minute cycle.
For example, when welding at 500 amps, the POWER
FEED™ 25M may run continuously for 6 minutes and
then must sit idle for 4 minutes.
POWER FEED™ 25M

B-3
OPERATION
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES
• GMAW (CV, Synergic CV, Pulse, STT™, Power,
Pulse on Pulse™, Push-Pull)
• FCAW
• SMAW
• GTAW (Lift Start only)
• Solid wires .025" to 1/16"
• Cored wires .035" to 5/64"
• Cored wires .035" to 3/32" when configured for
"extra torque"
EQUIPMENT LIMITATIONS
• Works only on ArcLink®or LincNet Power Wave
power sources.
• When operating on LincNet power sources, not all
features are available.
• Maximum gun length is 25ft.(7.6m) for push-only
systems.
• Maximum gun length is 50ft.(15.2m) for push-pull
systems.
• Spool guns do not work with the POWER FEED™
25M.
• A remote control/foot amptrol and a push-pull gun
may not be connected to the POWER FEED™ 25M
simultaneously.
• Maximum spool size is 12 in. (305 mm) diameter
• Maximum spool weight is 44 lb (20 kg).
• Maximum control cable length is 200 ft (61 m).
• Other gun bushings are required for welding guns
that do not have a Magnum (Tweco #2-#4 compatible) back end.
• No more than 2 wire feeders may be connected to
one ArcLink power source at a time.
B-3
RECOMMENDED POWER SOURCES
• Power Wave®355M
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
®
455M
®
455M/STT
®
655/R
POWER FEED™ 25M

B-4
OPERATION
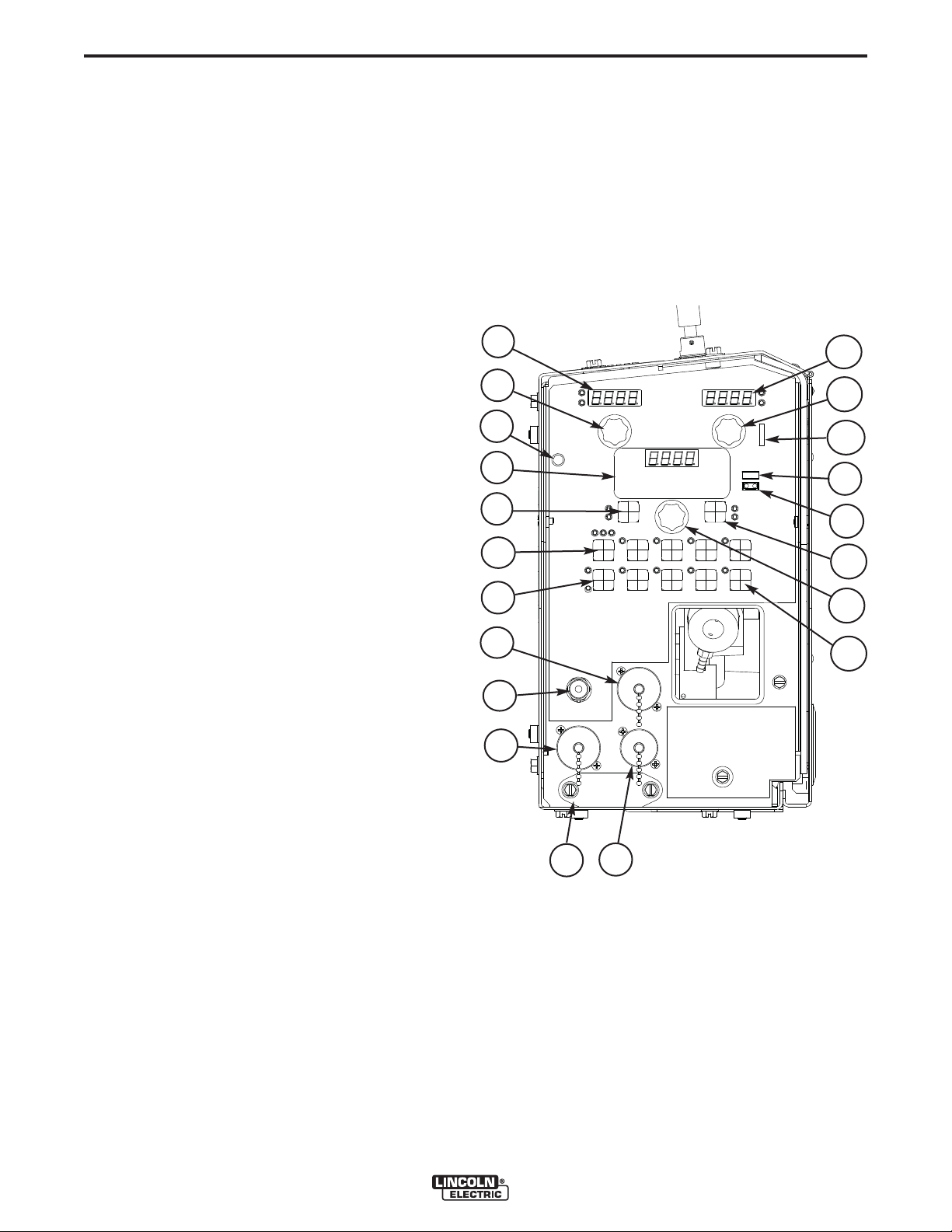
CASE FRONT CONTROLS (CODE 11313)
(SEE FIGURE B.1)
B-4
15. Cover
Covers location for optional water cooling line.
1. Left DISPLAY window
Shows WIRE FEED SPEED or AMPERAGE.
2. Left KNOB
Adjusts values in left display.
3. Right Display window
Shows VOLTAGE or TRIM.
4. Right Knob
Adjusts values in the right display.
5. Status LED
Illuminates a steady green when communicating to
the power source properly.
6. IR port
Used to transfer information to palm computers,
etc.
7. MSP4 display window
Shows detailed welding and diagnostic information.
8. Left Button
Changes the MSP4 display to show the Weld Mode
or Arc Control.
16. Set-Up
Lights when feeder is set-up.
17. Memory Panel Door
(See Memory Panel Operations in this Section)
FIGURE B.1
1
2
5
6
8
10
11
12
3
4
7
16
9
14
9. Right Button
Changes the MSP4 display to show Start Options
or End Options.
10. Set Knob
Changes the value on the MSP4 display.
11. ON/OFF switch
Controls power to the POWER FEED™ 25M.
12. 5-pin connector
Trigger connector for a push-only gun.
13. 6-pin connector
Connector for a remote control.
14. 7- pin connector
Connector for a push-pull gun.
13
17
Fold Out
Memory Panel
15
POWER FEED™ 25M
B-5
OPERATION
B-5
CASE FRONT CONTROLS (CODE 11456 and
higher) (See Figure B.1a)
1. Left DISPLAY window
Shows WIRE FEED SPEED or AMPERAGE.
2. Left KNOB
Adjusts values in left display.
3. Status LED
Illuminates a steady green when communicating to
the power source properly.
4. MSP4 display window
Shows detailed welding and diagnostic information.
5. Left Button
Changes the MSP4 display to show the Weld Mode
or Arc Control.
6. Procedure Button
Selects A or B procedure, or gun control.
7. 2-Step/4-Step Button
Toggles between 2-step and 4-step trigger operation.
8. 5-pin connector
Trigger connector for a push-only gun.
18. Right Button
Changes the MSP4 display to show Start Options
or End Options.
19. Set Knob
Changes the value on the MSP4 display.
20. Memory Buttons
(For selection of common procedures.)
FIGURE B.1a
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
9. ON/OFF switch
Controls power to the POWER FEED™ 25M.
10. 6-pin connector
Connector for a remote control.
11. Cover
Covers location for optional water cooling line.
12. 7- pin connector
Connector for a push-pull gun.
13. Right Display window
Shows VOLTAGE or TRIM.
14. Right Knob
Adjusts values in the right display.
15. Thermal
Lights when the drive overheats.
16. Set-Up
Lights when feeder is set-up
17. IR port
Used to transfer information to palm computers,
etc.
8
9
10
11
20
12
POWER FEED™ 25M
B-6
OPERATION
11. ON-OFF SWITCH
The On-Off Switch turns the wire feeder power on and
off. It does not control the power to the welding power
source.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the
welding power source before
installation or changing drive
rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live
parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and
drive mechanism are "hot" to work and ground
and could remain energized several seconds
after the gun trigger is released.
• Welding power source must be connected to
system ground per the National Electrical Code
or any applicable local codes.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
B-6
LED condition
Steady green
Blinking green.
Blinking green, fast
Blinking green followed by blinking
red.
STATUS LED
(See Table B.1)
The status LED indicates system status. Normal
operation is a steady green light.
Note: During normal power-up, the LED may flash
red and/or green as the equipment performs self tests.
TABLE B.1
Definition
System okay. The power source and wire feeder are communicating normally.
Occurs during a reset and indicates the power source is identifying each component in the system. This is
normal for up to 15 seconds after power-up, or if the system configuration is changed during operation.
Indicates that one or more pieces of ArcLink equipment are not mapping properly. Check the DIP switch setting on the wire feeders.
Non-recoverable system fault. If the power source or wire feeder status LED is flashing any combination of
red and green, errors are present in the system. Read the error code before the machine is turned off.
Error codes are detailed in the Troubleshooting Section E. Individual code digits are flashed in red with a
long pause between digits. After each error code the LED will flash green and codes will repeat. There may
be more than one error code indicated.
STAT
US
To clear the error, turn the power source OFF, and then back ON to reset. See Troubleshooting Section E.
POWER FEED™ 25M
B-7
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
it
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
la
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
iq
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
ct
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
ib
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
si
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
te
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
ia
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
ci
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
ip
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
co
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
sc
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
ia
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
lo
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
su
m
d
o
lo
r
sit
a
m
e
t
co
n
s
e
ct
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
sc
i
n
g
e
l
it
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
ib
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
ti
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
ip
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
si
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
lo
r
s
it
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
se
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
ism
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
iq
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
su
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
ct
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
id
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
iq
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
si
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
se
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
ib
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
ci
d
u
n
t
u
t
la
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
ct
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
ci
d
u
n
t
u
t
la
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
mi
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
rs
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
yn
i
b
he
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
ra
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
yn
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
rs
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
se
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
rs
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
ra
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
yn
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
dt
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
em
a
g
n
aa
l
i
q
u
a
me
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
s
i
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
ct
e
tu
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
in
g
e
l
i
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
c
i
d
u
n
t
u
t
la
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
L
o
r
e
m
i
p
s
u
m
d
o
l
o
r
si
t
a
m
e
t
c
o
n
s
e
c
t
e
t
u
e
r
a
d
i
p
i
s
c
i
n
g
e
li
t
,
e
d
d
i
a
m
n
o
n
u
m
m
y
n
i
b
h
e
u
i
s
m
o
d
t
i
n
ci
d
u
n
t
u
t
l
a
o
r
e
e
t
d
o
l
o
r
e
m
a
g
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
a
m
e
r
a
t
OPERATION
MAKING A WELD WITH WAVEFORM
TECHNOLOGY POWER SOURCES
WARNING
The serviceability of a product or structure utilizing
the welding programs is and must be the sole
responsibility of the builder/user. Many variables
beyond the control of The Lincoln Electric Company
affect the results obtained in applying these programs. These variables include, but are not limited
to, welding procedure, plate chemistry and temperature, weldment design, fabrication methods and service requirements. The available range of a welding
program may not be suitable for all applications, and
the build/user is and must be solely responsible for
welding program selection.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The steps for operating the Power Wave will vary
depending upon the user interface of the welding system. The flexibility of the Power Wave lets the user
customize operation for the best performance.
B-7
FIGURE B.2
!
W
!
A
R
W
N
L
A
o
r
e
m
e
I
l
i
i
t
p
,
RNING
N
s
e
l
u
a
d
m
o
d
r
L
e
i
d
o
a
e
o
r
m
t
e
l
d
G
o
m
e
n
r
o
l
i
o
s
i
l
t
o
p
n
it
,
r
s
u
e
e
la
a
u
m
d
m
m
o
m
m
d
r
e
a
e
L
i
d
t
y
a
g
e
o
o
c
m
n
n
t
r
l
o
e
o
a
i
d
b
n
m
n
r
o
e
h
s
a
o
s
l
l
e
o
l
i
i
n
i
i
e
t
p
t
q
c
,
r
u
u
e
e
s
a
t
u
m
l
e
i
u
m
a
m
a
s
d
t
m
o
m
m
u
m
e
d
a
r
e
t
y
e
o
i
d
g
r
e
a
c
e
d
o
n
n
r
m
a
o
t
t
L
a
l
a
i
d
o
b
n
d
i
o
t
n
n
i
r
h
s
a
o
r
p
c
e
o
e
s
l
l
i
iq
e
i
o
s
m
n
i
c
d
t
e
u
c
r
t
u
u
u
e
a
l
e
i
i
i
i
m
a
n
s
n
t
p
m
t
,
m
m
u
m
g
t
s
m
e
e
e
l
u
u
a
a
o
d
t
r
y
e
t
m
g
o
d
c
r
a
d
n
n
r
a
o
t
e
d
i
d
a
ib
i
t
a
n
n
e
i
!
o
p
m
h
s
c
a
t
l
i
o
e
i
l
s
L
d
d
i
e
n
q
r
ct
c
o
o
u
u
o
u
i
si
r
l
n
e
n
i
o
e
n
a
s
g
t
t
t
r
m
m
u
u
m
e
e
a
u
e
m
l
m
o
t
i
m
i
r
e
t
p
d
m
A
,
e
r
a
s
a
a
e
t
t
l
y
d
u
a
g
i
t
d
n
c
i
m
o
n
n
p
L
o
c
d
r
a
i
i
o
i
b
n
s
e
d
i
d
r
a
c
h
TTE
se
a
e
e
u
o
!
m
i
l
t
n
m
n
l
i
e
e
o
q
c
d
g
t
u
n
l
r
t
u
o
i
i
e
u
i
t
p
o
a
s
s
,
l
t
t
A
o
s
n
m
i
u
m
e
t
la
r
u
u
e
d
e
a
o
m
o
m
r
e
m
d
d
m
r
r
a
m
e
a
i
d
e
t
d
a
a
i
e
t
V
o
n
t
y
i
m
g
p
t
l
c
c
o
n
n
i
d
i
o
s
n
d
r
a
ib
o
n
c
P
o
u
s
l
i
h
s
a
o
n
n
n
i
t
e
L
l
r
g
u
t
i
e
e
IS
a
q
c
o
m
u
u
m
t
u
N
r
m
e
t
i
e
a
m
s
e
t
m
a
m
u
m
e
RECAUCI
t
y
g
e
L
l
o
c
i
i
n
n
t
r
e
p
o
o
L
d
,
a
i
r
a
s
r
b
n
e
a
la
e
o
t
u
d
TI
h
s
a
d
i
t
e
m
n
m
r
i
o
O
e
l
p
i
e
c
e
d
r
l
q
c
i
i
e
e
i
i
u
s
i
t
d
p
d
t
m
u
a
,
e
e
c
i
l
o
s
u
a
s
m
e
i
t
i
t
l
l
t
u
n
a
m
n
u
m
o
d
,
d
i
m
g
o
t
l
e
n
r
p
o
a
o
d
e
r
u
L
r
e
o
s
d
l
s
e
DE
ia
d
o
d
L
u
r
o
e
d
r
e
i
e
a
e
t
m
m
l
d
i
t
o
,
i
n
l
p
l
a
e
o
s
o
d
r
u
e
r
e
m
d
m
e
i
a
t
d
a
m
d
o
o
l
o
n
l
o
r
o
r
n
s
e
i
u
m
m
a
m
g
y
n
n
a
a
l
i
q
u
1
a
6
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
R
E
M
O
T
E
P
O
W
E
R
O
N
O
F
F
O
o
t
o
r
a
n
i
e
t
a
o
r
t
r
d
u
m
i
e
t
e
a
t
l
n
m
i
m
o
p
d
m
m
ci
m
e
n
r
i
o
m
s
l
e
d
o
si
i
a
l
ip
d
c
t
o
t
u
y
n
,
g
t
i
r
s
o
n
c
n
u
e
n
e
n
l
a
N
u
o
a
g
t
m
d
l
a
i
m
m
o
b
n
o
m
u
m
d
h
s
r
a
e
t
r
o
a
e
L
ia
d
e
l
t
y
iq
e
g
e
o
n
s
o
c
c
m
u
n
n
t
r
t
u
l
i
o
u
e
o
e
i
t
a
i
d
a
s
b
n
m
n
r
t
m
o
e
m
u
a
m
s
h
s
a
o
lo
l
e
e
l
it
m
i
n
o
i
m
i
e
p
t
r
e
q
c
,
r
a
u
d
u
e
su
g
l
r
te
u
a
e
e
m
y
L
a
i
a
m
t
a
s
d
d
n
m
i
t
o
t
t
m
o
n
m
m
u
m
i
d
e
n
p
a
r
a
r
ci
c
e
e
t
y
e
o
i
i
d
i
g
s
r
e
a
d
e
o
m
b
co
e
d
a
o
c
n
n
r
m
a
u
t
t
n
h
a
l
i
ip
lo
a
i
l
t
i
n
d
n
b
n
i
d
t
i
t
s
n
q
,
n
g
r
i
t
a
h
s
a
o
p
s
e
l
ci
e
o
e
u
e
sit
u
l
l
u
i
m
a
i
e
o
s
d
u
n
q
t
c
d
c
m
a
o
u
c
r
t
u
u
u
i
O
e
d
a
e
e
t
r
i
i
s
m
m
a
n
s
n
e
e
i
d
m
t
a
t
m
m
m
u
m
g
t
e
o
m
t
m
e
e
u
c
t
u
a
l
o
e
o
i
t
o
r
y
e
t
d
o
g
b
d
e
L
n
r
r
co
r
a
o
d
n
n
a
a
n
o
h
o
r
si
t
d
l
a
ib
i
o
t
r
n
n
n
t
s
i
N
t
t
e
a
p
r
e
u
h
s
c
a
i
e
e
a
m
i
n
d
e
i
e
m
l
sc
u
d
m
i
e
c
m
q
ct
l
c
i
u
i
m
u
i
i
p
t
u
i
e
p
t
s
i
m
n
,
e
n
a
i
e
d
a
s
t
s
y
i
e
g
t
g
t
m
l
s
m
u
u
m
c
t
a
u
d
u
n
n
u
c
o
m
e
e
o
d
o
t
a
o
i
n
b
n
r
e
e
r
i
r
d
n
e
d
t
i
h
d
s
a
r
a
L
a
a
r
a
e
e
ti
o
l
g
d
o
u
m
i
e
t
t
t
q
n
t
c
a
lo
i
r
d
u
p
i
t
e
t
u
c
n
d
e
n
r
i
i
m
o
i
a
s
sc
d
e
t
o
c
s
i
l
m
u
m
p
o
u
l
n
it
i
i
i
i
e
t
n
p
r
d
n
o
u
i
,
e
a
r
e
s
g
su
t
d
m
e
u
u
l
m
r
a
a
c
m
a
d
t
n
m
d
m
o
t
i
e
i
t
n
a
i
n
d
r
t
t
p
y
c
g
e
i
d
g
c
i
a
u
i
s
n
e
n
d
o
o
m
c
a
t
i
t
u
l
b
n
o
i
d
n
n
h
se
a
n
r
o
g
t
l
o
s
iq
e
l
u
c
o
n
i
u
t
t
t
u
r
u
e
ism
e
a
a
L
m
t
m
u
m
m
L
o
m
e
e
o
o
a
r
r
e
t
r
y
d
e
g
e
r
a
c
e
a
n
n
m
t
m
d
o
e
i
t
a
l
i
n
i
b
n
i
l
p
i
t
c
i
h
t
s
a
p
,
i
i
,
i
s
l
e
d
p
e
l
s
a
iq
e
c
e
la
ct
u
u
L
s
u
d
i
o
u
n
d
n
m
o
L
o
e
i
u
a
s
g
t
r
d
r
r
t
o
e
m
e
e
u
m
m
d
u
i
d
a
e
e
m
e
r
t
o
e
o
i
m
e
t
r
a
e
l
li
d
e
o
t
d
d
i
r
a
m
t
m
p
n
a
r
,
l
o
t
d
o
d
s
i
i
o
t
s
e
n
l
t
l
i
u
o
o
l
a
p
n
i
,
d
i
c
o
n
t
l
m
r
p
o
i
u
l
a
id
s
e
e
a
o
d
r
o
r
m
s
d
c
e
m
o
u
i
d
m
r
a
n
i
s
u
e
m
n
n
o
e
r
e
m
i
a
t
u
g
t
e
m
l
d
t
t
y
o
g
d
u
m
m
e
c
n
i
r
a
n
n
o
t
a
o
o
si
t
d
a
i
l
m
a
m
b
o
n
m
n
t
d
o
h
r
s
a
u
g
e
a
e
e
y
l
o
l
m
i
e
n
m
o
n
q
ct
t
m
l
u
m
n
u
a
o
r
o
e
e
c
i
a
a
s
i
t
y
r
tu
n
s
o
g
b
m
m
a
e
c
n
n
i
u
e
n
h
o
t
l
o
a
i
i
r
e
b
n
m
m
se
d
q
a
r
a
e
h
s
a
a
u
t
m
d
e
a
l
m
i
u
t
i
e
n
c
q
i
c
a
p
g
u
c
i
t
u
e
t
y
s
m
i
e
i
i
e
s
n
a
s
d
t
t
m
c
m
u
m
u
t
n
a
in
c
u
e
n
e
o
i
o
o
b
r
e
g
t
e
a
r
d
d
r
a
u
n
a
h
r
l
a
t
d
i
t
i
s
t
t
q
n
t
a
i
e
p
i
e
ci
u
n
d
i
u
s
c
d
a
c
i
c
i
p
u
t
s
i
m
i
e
n
d
n
i
m
s
g
t
t
u
u
u
c
e
o
n
t
e
i
r
n
d
t
a
r
g
u
t
t
a
i
t
n
d
c
i
p
i
d
i
s
u
c
n
i
n
t
g
u
t
5 5
3
E
V
A
W
R
E
W
O
P
4
3
First, consider the desired welding process and the
part to be welded. Choose an electrode material,
diameter, shielding gas and process (GMAW, GMAWP, GMAW-STT™, etc.)
Second, find the program in the welding software that
best matches the desired welding process. The standard software shipped with the Power Waves encompasses a wide range of common processes and will
meet most needs. If a special welding program is
desired, contact the local Lincoln Electric sales representative.
All adjustments are made on the user interface.
Because of the different configuration options your
system may not have all of the following adjustments.
Regardless of availability, all controls are described
below.
SMAW (STICK) WELDING
SMAW is most often used for outdoor construction,
pipe welding and general repairs. The wire feeder
controls Amperage, Output Control and Arc Force during SMAW welding.
During SMAW welding, the wire feeder sets the weld
parameters and the wire drive remains idle.
2
K2368-1 Power Wave®355M
1 K2202-1 Power Wave®455M
K2203-1 Power Wave®455M/STT
K2230-1 POWER FEED™ 10M, Bench
Model
2 K2234-1
Bench Model
K2536-1,-2,-3 POWER FEED™ 25M
3 K1543-xx Digital Control Cable
K2683-xx
4 K1842-xx Weld Power Cable, Lug to Lug
K910-xx Ground Clamp
5 K909-xx Electrode Holder
6 K2176-1 Twist-Mate to Lug Cable
POWER FEED™ 10M Dual,
Adapter
5
The “Volts”-”Trim” control is used to turn the power
Source Output ON or OFF. (See Figure B.3)
SMAW Welding (See Figure B.2)
POWER FEED™ 25M
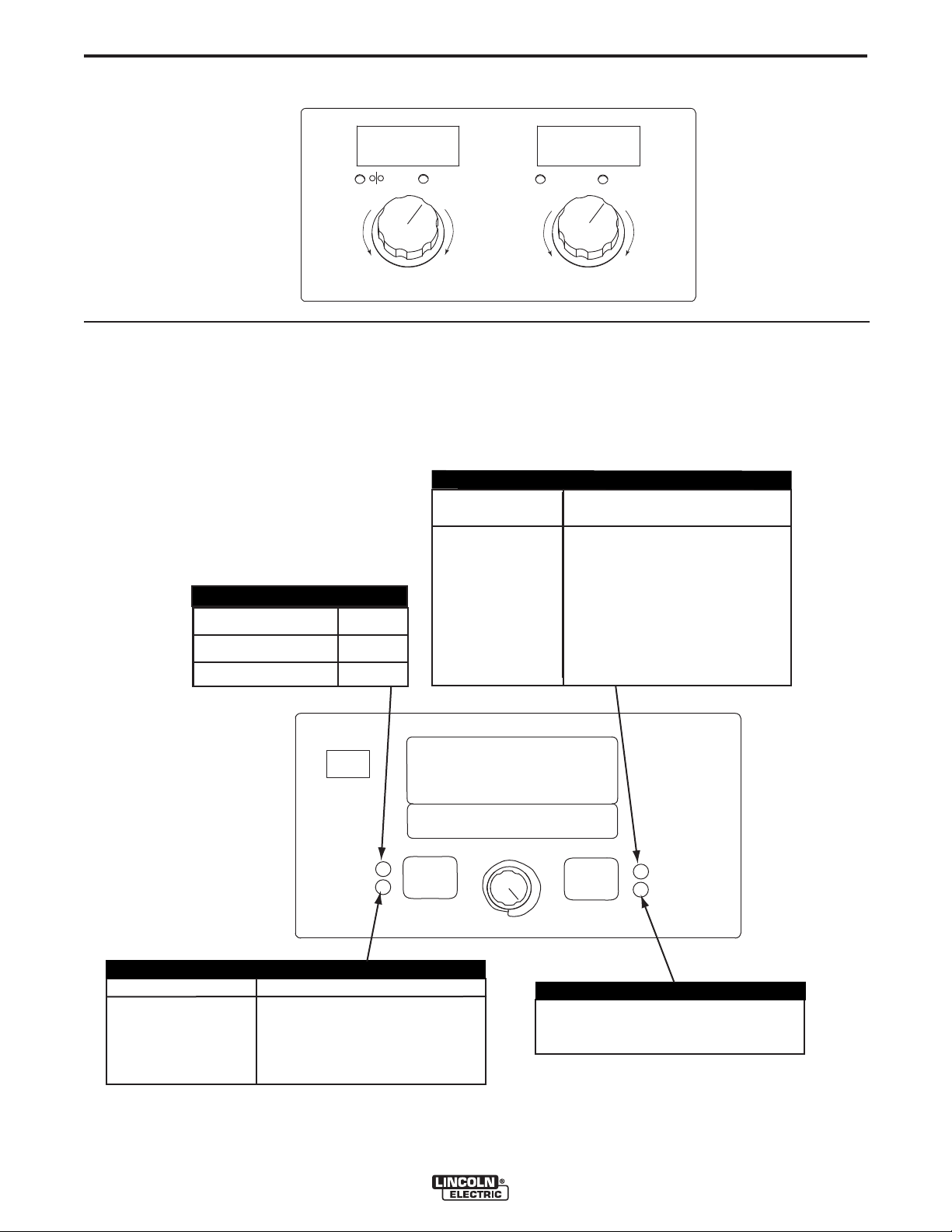
SMAW (Stick) Welding Display
OPERATION
FIGURE B.3
B-8B-8
MSP4 OPERATION
Stick Soft(7018)
Stick Crisp(6010)
CC STICK MODES
PROCESS
194
LESS
AMPS
MODE
1
2
WFS AMPS
MORE
AMPS
START TIME:
0 to 10 seconds
0
n
VOLTS TRIM
OUTPUT
OFF
OUTPUT
ON
START OPTIONS
If no remote control is installed,
this control sets the time for
the weld output to ramp up or
down from a preset Start current to the preset Weld current.
Use the WFS/AMP knob to
adjust Start current while the
Start Options LED is displayed.
FUNCTION
ARC FORCE
(Soft)-10.0 to
(Crisp)+10.0
IR PORT
WELD MODE
ARC CONTROL
ARC CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
Lower values will provide less short
circuit current and a softer arc.
Higher settings will provide a higher
short circuit current, a more forceful
arc and possibly more spatter.
POWER FEED™ 25M
WAVEFORM CONTROLTECHNOLOGY
Stick
I
I
CC Stick Soft
SET
No arc ending options are active for
SMAW
SETUP
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
(Stick) welding modes.

B-9
OPERATION
NON-SYNERGIC GMAW AND FCAW
WELDING
(See Figure B.4)
B-9
Three non-synergic welding modes are available.
Description Mode Used for:
GMAW, Standard CV 5 Best for traditional
MIG welding.
Non-synergic GMAW and FCAW welding mimics the
welding controls of traditional welding power sources.
Voltage and WFS are set as independent variables.
FIGURE B.4
6
4
2
3
GMAW, Power 40 Specialized GMAW
mode.
FCAW 6 Best for self shield-
ed electrodes like
Innershield™.
1
5
K2368-1 Power Wave®355M
1 K2202-1 Power Wave®455M
K2203-1 Power Wave®455M/STT
K2230-1
K2234-1
K2536-1,-2,-3 POWER FEED™ 25M
2 KP1696-xx, Drive Roll Kit, 2 Roll Feeder
KP1697-xx
KP1505-xx, Drive Roll Kit, 4 Roll Feeder
KP1507-xx
3 K1543-xx Digital Control Cable
K2683-xx
4 K1842-xx Weld Power Cable, Lug to Lug
K910-xx Ground Clamp
5 See Magnum MIG gun
Literature
6 K586-1 Shielding Gases
POWER FEED™ 10M, Bench Model
POWER FEED™ 10M Dual, Bench Model
Deluxe Regulator for Mixed
Shielding Gas Hose
POWER FEED™ 25M
 Loading...
Loading...