Page 1

Operator’s Manual
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
For use with machines having Code Numbers:
12244
Save for future reference
Date Purchased
Code: (ex: 10859)
Serial: (ex: U1060512345)
IM10180 | Issue D ate Nov-13
© Lincoln Global, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Register your machine:
www.lincolnelectric.com/register
Authorized Service and Distributor Locator:
www.lincolnelectric.com/locator
Page 2
THANK YOU FOR SELECTING
AT ALL
TIMES.
SPECIAL SITUATIONS
Additional precautionary measures
A QUALITY PRODUCT BY
LINCOLN ELEC TRIC.
PLEASE EXAMINE CARTON AND EQUIPMENT FOR
DAMAGE IMMEDIATELY
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon
receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims for material damaged in
shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation
company at the time the shipment is received.
SAFETY DEPENDS ON YOU
Lincoln arc welding and cutting equipment is designed and built with
safety in mind. However, your overall safety can be increased by
proper installation ... and thoughtful operation on your part.
DO NOT INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS EQUIPMENT
WITHOUT READING THIS MANUAL AND THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And, most importantly, think before you
act and be careful.
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed
exactly to avoid serious personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to
avoid minor personal injury or damage to this equipment.
SAFETY
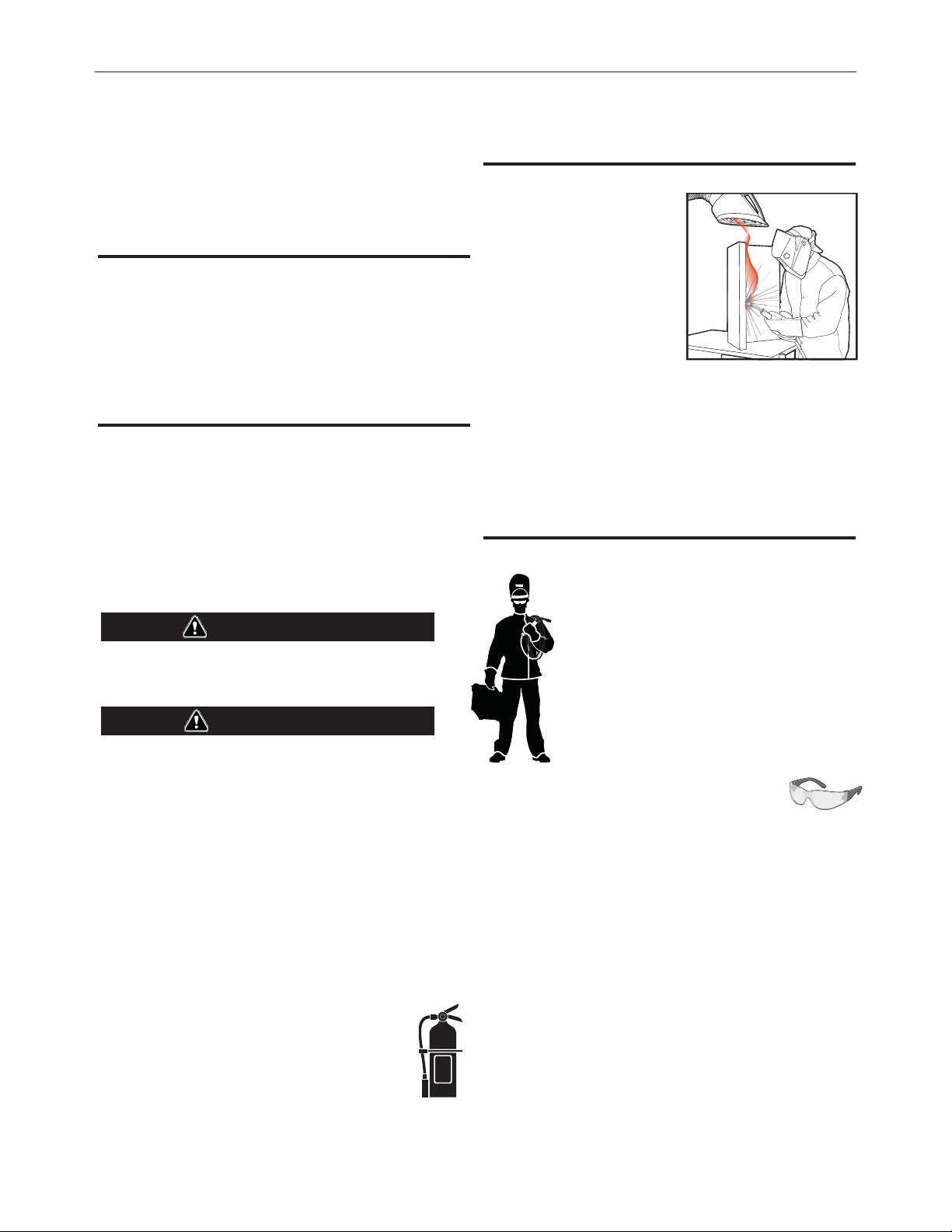
KEEP YOUR HEAD OUT OF THE FUMES.
DON’T get too close to the arc. Use
corrective lenses if necessary to
stay a reasonable distance away
from the arc.
READ and obey the Material Safety
Data Sheet (MSDS) and the warning
label that appears on all containers
of welding materials.
USE ENOUGH VENTILATION or
exhaust at the arc, or both, to keep
the fumes and gases from your breathing zone and the general area.
IN A LARGE ROOM OR OUTDOORS, natural ventilation may be
adequate if you keep your head out of the fumes (See below).
USE NATURAL DRAFTS or fans to keep the fumes away from your
face.
If you de velop unusual symptoms, see your supervisor. Perhaps the
welding atmosphere and ventilation system should be checked.
WEAR CORRECT EYE, EAR & BODY PROTECTION
PROTECT your eyes and face with welding helmet
properly fitted and with proper grade of filter plate
(See ANSI Z49.1).
PROTECT your body from welding spatter and arc
flash with protective clothing including woolen
clothing, flame-proof apron and gloves, leather
leggings, and high boots.
PROTECT others from splatter, flash, and glare with
protective screens or barriers.
IN SOME AREAS, protection from noise may be
appropriate.
BE SURE protective equipment is in good condition.
Also, wear safety glasses in work area
DO NOT WELD OR CUT containers or materials which previously had
been in contact with hazardous substances unless they are properly
cleaned. This is extremely dangerous.
DO NOT WELD OR CUT painted or plated parts unless special
precautions with ventilation have been taken. They can release highly
toxic fumes or gases.
PROTECT compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical
shocks, and arcs; fasten cylinders so they cannot fall.
BE SURE cylinders are never grounded or part of an electrical circuit.
REMOVE all potential fire hazards from welding area.
ALWAYS HAVE FIRE FIGHTING EQUIPMENT READY FOR
IMMEDIATE USE AND KNOW HOW TO USE IT.
i
Page 3

SECTION A:
Diesel Engines
Gasoline Engines
WARNINGS
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other
reproductive harm.
The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm.
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT
YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS
INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR
DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional
safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a
copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the
American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or
CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety”
booklet E205 is available from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801
St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
SAFETY
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and
devices in position and in good repair.Keep
hands, hair, clothing and tools away from
V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts
when starting, operating or repairing
equipment.
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety guards to
perform required maintenance. Remove guards only when
necessary and replace them when the maintenance requiring
their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when
working near moving parts.
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to
override the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control
rods while the engine is running.
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while turning
the engine or welding generator during maintenance work,
disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or magneto wire
as appropriate.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the radiator
pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS MAY
BE DANGEROUS
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor
causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and welding
machines
FOR ENGINE POWERED
EQUIPMENT.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting
and maintenance work unless the
maintenance work requires it to be running.
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes outdoors.
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from
vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts
and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling
tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start engine until
fumes have been eliminated.
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and welders
having a pacemaker should consult their physician before
welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health effects
which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and work
cables. If the electrode cable is on your right side, the
work cable should also be on your right side.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
2
Page 4

SAFETY
ELECTRIC SHOCK
CAN KILL.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are
electrically “hot” when the welder is on. Do
not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin
or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full area
of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if
welding must be performed under electrically
hazardous conditions (in damp locations or while
wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such as
floors, gratings or scaffolds; when in cramped
positions such as sitting, kneeling or lying, if there
is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact
with the workpiece or ground) use the following
equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding
gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection should
be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical (earth)
ground.
3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode
holders connected to two welders because voltage
two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of both
welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
between the
ARC RAYS CAN BURN.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your
eyes from sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or
observing open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens should
conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material
to protect your skin and that of your helpers from the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
CAN BE DANGEROUS.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases. When welding, keep your head out of the fume.
Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep fumes
and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding
with electrodes which require special ventilation
such as stainless or hard facing (see instructions
on container or MSDS) or on lead or cadmium
plated steel and other metals or coatings which
produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low
as possible and within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits using local exhaust or
mechanical ventilation. In confined spaces or in
some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may
be required. Additional precautions are also
required when welding on galvanized steel.
5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected by
various factors including proper use and positioning of the
equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific
welding procedure and application involved. Worker exposure
level should be checked upon installation and periodically
thereafter to be certain it is within applicable OSHA PEL and
ACGIH TLV limits.
5.c. Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The
heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors to form
phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
3.j. Also see It ems 6.c. and 8.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
injury or death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in
confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your employer’s
safety practices. MSDS forms are available from your welding
distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
3
cause
Page 5
SAFETY
WELDING AND CUTTING
SPARKS CAN CAUSE
FIRE OR EXPLOSION.
6.a. Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If
this is not possible, cover them to prevent the
welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that welding
sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through
small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special
precautions should be used to prevent hazardous situations.
Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI Standard Z49.1)
and the operating information for the equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is
touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause
overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures will
not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances inside.
They can cause an explosion even though they have been
“cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended Safe
Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”,
AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society (see address
above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free
protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless
trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs
when welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear
safety glasses with side shields when in a welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area
as practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or
other locations away from the welding area increase the
possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains,
crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire
hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
CYLINDER MAY EXPLODE IF
DAMAGED.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders containing
the correct shielding gas for the process used
and properly operating regulators designed for
the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings,
etc. should be suitable for the application and
maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to
an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected
to physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations
and any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight
except when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l, “Precautions for
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available
from the Compressed Gas Association 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
POWERED EQUIPMENT.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on the
equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National Electrical
Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.I. Read and follow NFPA 51B “ Standard for Fire Prevention During
Welding, Cutting and Other Hot Work”, available from NFPA, 1
Batterymarch Park, PO box 9101, Quincy, Ma 022690-9101.
6.j. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Refer to
http://www.lincolnelectric.com/safety
for additional safety information.
Welding Safety
Interactive Web Guide
for mobile devices
4
Page 6

SAFETY
ELECTROMAGNETIC
COMPATIBILITY (EMC)
CONFORMANCE
Products displaying the CE mark are in conformity with European
Community Council Directive of 3 May 1989 on the approximation of
the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility (89/336/EEC). It was manufactured in conformity with a national
standard that implements a harmonized standard: EN 60974-10
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Product Standard for Arc Welding
Equipment. It is for use with other Lincoln Electric equipment. It is
designed for industrial and professional use.
INTRODUCTION
All electrical equipment generates small amounts of electromagnetic
emission. Electrical emission may be transmitted through power lines
or radiated through space, similar to a radio transmitter. When
emissions are received by other equipment, electrical interference
may result. Electrical emissions may affect many kinds of electrical
equipment; other nearby welding equipment, radio and TV reception,
numerical controlled machines, telephone systems, computers, etc.
Be aware that interference may result and extra precautions may be
required when a welding power source is used in a domestic establishment.
INSTALLATION AND USE
The user is responsible for installing and using the welding equipment
according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then it shall be the responsibility of the user of
the welding equipment to resolve the situation with the technical
assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial action
may be as simple as earthing (grounding) the welding circuit, see
Note. In other cases it could involve construction of an electromagnetic screen enclosing the power source and the work complete with
associated input filters. In all cases electromagnetic disturbances
must be reduced to the point where they are no longer troublesome.
Note: The welding circuit may or may not be earthed for safety reasons
according to national codes. Changing the earthing arrangements should
only be authorized by a person who is competent to access whether the
changes will increase the risk of injury, e.g., by allowing parallel welding
current return paths which may damage the earth circuits of other equipment.
ASSESSMENT OF AREA
Before installing welding equipment the user shall make an
assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in the surrounding
area. The following shall be taken into account:
a. other supply cables, control cables, signaling and telephone cables;
above, below and adjacent to the welding equipment;
b. radio and television transmitters and receivers;
c. computer and other control equipment;
d. safety critical equipment, e.g., guarding of industrial equipment;
e. the health of the people around, e.g., the use of pacemakers and
hearing aids;
f. equipment used for calibration or measurement
g. the immunity of other equipment in the environment. The user shall
ensure that other equipment being used in the environment is
compatible. This may require additional protection measures;
h. the time of day that welding or other activities are to be carried out.
5
The size of the surrounding area to be considered will depend on the
structure of the building and other activities that are taking place. The
surrounding area may extend beyond the boundaries of the premises.
METHODS OF REDUCING EMISSIONS
Mains Supply
Welding equipment should be connected to the mains supply
according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. If interference
occurs, it may be necessary to take additional precautions such as
filtering of the mains supply. Consideration should be given to
shielding the supply cable of permanently installed welding
equipment, in metallic conduit or equivalent. Shielding should be
electrically continuous throughout its length. The shielding should be
connected to the welding power source so that good electrical contact
is maintained between the conduit and the welding power source
enclosure.
Maintenance of the Welding Equipment
The welding equipment should be routinely maintained according to
the manufacturer’s recommendations. All access and service doors
and covers should be closed and properly fastened when the welding
equipment is in operation. The welding equipment should not be
modified in any way except for those changes and adjustments
covered in the manufacturers instructio ns. In particular, the spark
gaps of arc striking and stabilizing devices should be adjusted and
maintained according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Welding Cables
The welding cables should be kept as short as possible and should be
positioned close together, running at or close to floor level.
Equipotential Bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the welding installation and
adjacent to it should be considered. However, metallic components
bonded to the work piece will increase the risk that the operator could
receive a shock by touching these metallic components and the
electrode at the same time. The operator should be insulated from all
such bonded metallic components.
Earthing of the Workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth for electrical safety, not
connected to earth because of its size and position, e.g., ships hull or
building steelwork, a connection bonding the workpiece to earth may
reduce emissions in some, but not all instances. Care should be taken
to prevent the earthing of the work piece increasing the risk of injury
to users, or damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary,
the connection of the workpiece to earth should be made by a direct
connection to the work piece, but in some countries where direct
connection is not permitted, the bonding should be achieved by
suitable capacitance, selected according to national regulations.
Screening and Shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables and equipment in
the surrounding area may alleviate problems of interference.
Screening of the entire welding installation may be considered for
special applications.
1
Portions of the preceding text are contained in EN 60974-10: “Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) product standard for arc welding equipment.”
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Product Description.........................................................................................................................................7
Installation.......................................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications.......................................................................................................A-1
Thumb Screw and Metal Tab of Welding Gun .....................................................................A-2
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................A-3
Location................................................................................................................................A-3
High Frequency Protection...................................................................................................A-3
Cable Connections...............................................................................................................A-3
Arclink Control Cable............................................................................................................A-3
Weld cable Sizes..................................................................................................................A-4
Coaxial Weld Cable..............................................................................................................A-4
Shielding Gas Connection....................................................................................................A-5
Procedure to Install Drive Rolls and Wire Guides ................................................................A-5
Remote Sense Lead Specification .......................................................................................A-6
Loading Spools of Wire ........................................................................................................A-6
Typical System Configurations.............................................................................................A-7
________________________________________________________________________________
Operation.........................................................................................................................Section B
S
afety Precautions ...............................................................................................................B-1
Graphic Symbols that appear on this Machine or in thi
Definition of Welding Terms .................................................................................................B-2
Duty Cycle............................................................................................................................B-2
Recommended Processes, Equipment Limitations, Recommended Power Sources..........B-3
Case Front Controls .............................................................................................................B-4
On-Off Switch.......................................................................................................................B-5
Power Wave System Operation, 2 Step - 4 Step Trigger Operation and Graphics
Set-Up Feature Menu for Parameters and Definition ........................................B-21 thru B-27
Dual Procedure/Memory Buttons .......................................................................B-28 thru B-30
Internal Controls.................................................................................................................B-31
Cold Feed / Gas Purge Switch, Light Switch, Heater Switch, Pressure Arm Adjustment ..B-32
Rear Controls .....................................................................................................................B-33
________________________________________________________________________________
Accessories ....................................................................................................................Section C
Factory Installed Equipment.................................................................................................C-1
Drive Roll Kits ......................................................................................................................C-1
________________________________________________________________________________
Maintenance....................................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions...............................................................................................................D-1
Routine Maintenance ...........................................................................................................D-1
Periodic Maintenance...........................................................................................................D-1
Calibration Specification.......................................................................................................D-1
________________________________________________________________________________
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................Section E
How to Use Troubleshooting Guide .....................................................................................E-1
Error Fault Codes.................................................................................................................E-2
Troubleshooting Guide ...........................................................................................E-3 thru E-4
________________________________________________________________________________
s Manual
.........................................B-1
....B-5 thru B-20
Wiring Diagrams & Dimension Prints ...........................................................................Section F
________________________________________________________________________________
Parts Pages ................................................................................................................P-754 Series
_______________________________________________________________________
________
Page 8

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
General Physical Description
The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is a premium portable wire feeder
for use with the Power Wave products. The wire feeder features a
2 roll MAXtrac™ drive coupled to a powerful motor for driving
wire through difficult situations. The easy-to-use, user interface
provides ready access to all welding modes in the Power Wave.
Built in memories are included with the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
and allows quick recall of favorite weld procedures. Two cases
are available: an engineered aluminum case with replaceable
skids, or an impact resistant polycarbonate plastic case.
The heart of the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is the MAXtrac™ drive.
The patented features on the wire drive offer tool-less changing of
the drive rolls and the wire guides for quick spool changes.
The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS continues Lincoln’s lead role of
environmental protection for electronics. P.C. boards are potted in
epoxy and electrical connections are protected with dielectric
grease. Noise suppression components protect the POWER
FEED™ 25M NNS from stray signals and keep the feeder from
interfering with other digital equipment.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
General Functional Description
The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is best suited for applications were
quality welds are expected. Combined with a Power Wave power
source, the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is great for aluminum, nickel, alloy and other difficult to weld materials. Easy to use controls
make it a great feeder for consistent results with mild steel applications too.
7
Page 9
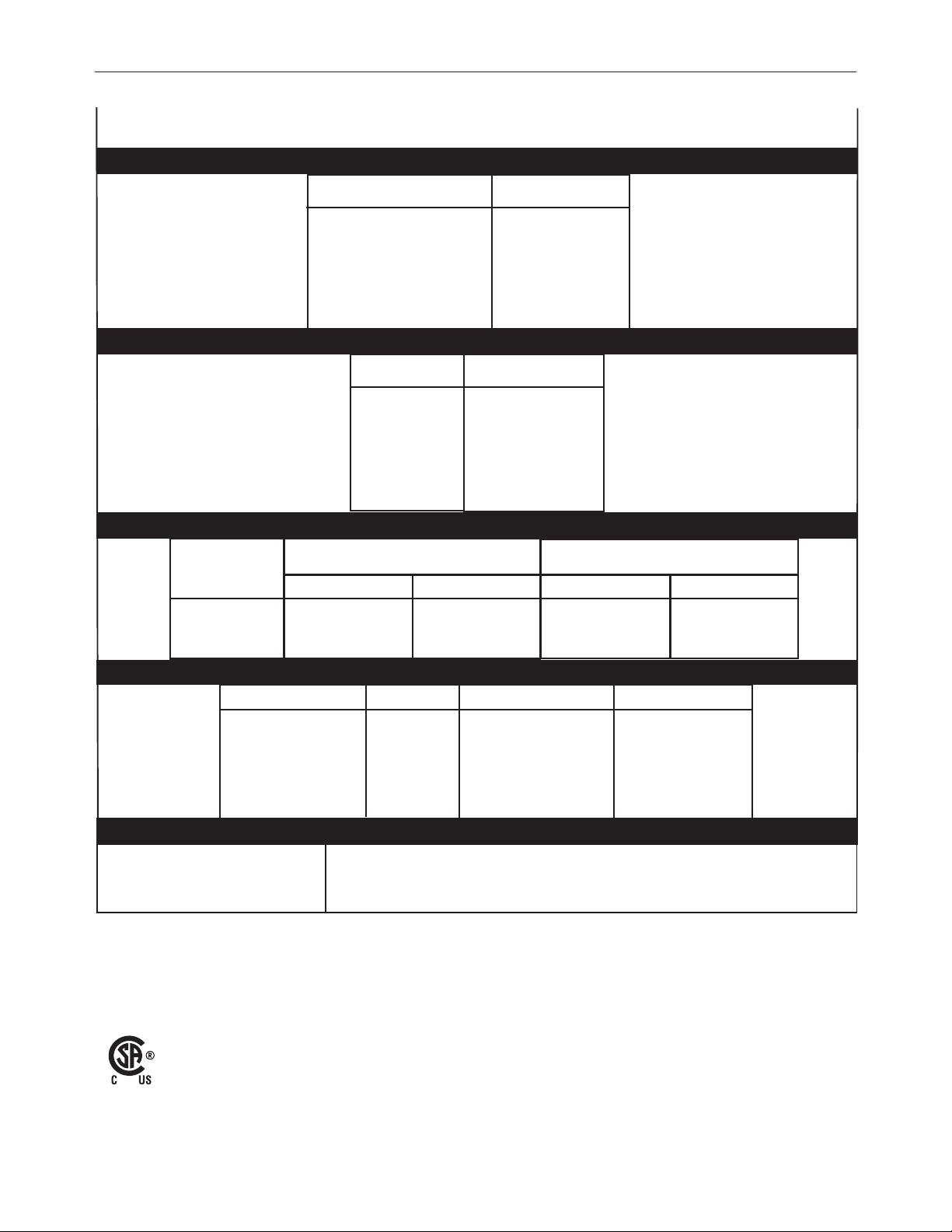
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS –
INPUT VOLTAGE and CURRENT
INPUT VOLTAGE ± 10%
40 VDC
RATED OUTPUT @ 104°F (40°C)
DUTY CYCLE
60% rating
GEARING - WIRE FEED SPEED RANGE-WIRE SIZE
GMAW
POWER FEED™ 25M NNS K2536-6
INPUT AMPERES
4A
INPUT AMPERES
500A
FCAW
GEARING
Normal Speed
(factory setting)
WFS RANGE
50 – 800 ipm
(2.5 – 20.3m/min)
WIRE SIZES
.023 – 1/16"
(0.6 – 1.6mm)
WFS RANGE
50 – 800 ipm
(2.5 – 20.3m/min)
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
HEIGHT WIDTH DEPTH WEIGHT
14.5 Inches 8.5 Inches 23.5 Inches 35 lbs
(368 mm) ( 216 mm) (597 mm) (15.9 kg)
Handle folded down
TEMPERATURE RANGE
OPERATION: -40°F to 122°F (-40°C to 50°C)
STORAGE: -40°F to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C)
WIRE SIZES
.030 – 5/64"
(0.8 – 2.0mm)
IP23
IEC 60974-5
A-1
Page 10

THUMB SCREW AND METAL TAB OF WELDING GUN
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the disconnect switch or fuse box before attempting to
connect or disconnect input power lines, output cables or control cables.
• Only qualified personnel should perform this installation.
• Do not touch the wire drive, drive rolls, wire coil or electrode when welding output is
ON.
• Wire feeder may be connected to a piece of automatic equipment that may be
remotely controlled.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards removed.
• Do not let the electrode or wire spool touch the wire feeder housing.
• Insulate yourself from the work and ground.
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
The metal tab of the welding gun and thumb screw securing the gun are at electrode potential when the
welding output is on. Do not touch the metal tab or thumb screw unless input power is turned OFF. Do
not allow the metal tab or thumb screw to touch other parts of the wire feeder or to touch part at work
potential.(See Figure A.1)
FIGURE A.1
THUMB SCREW
METAL TAB
OF THE WELDING GUN
A-2
Page 11
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding
power source before installation or changing drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and drive mechanism are "hot" to
work and ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger
is released.
• Welding power source must be connected to system ground
per the National Electrical Code or any applicable local
codes.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
LOCATION
For best wire feeding performance, place the POWER FEED™
25M NNS on a stable and dry surface. Keep the wire feeder in
a vertical position. Do not operate the wire feeder on an angled
surface of more than 15 degrees.
Do not submerge the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS.
The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is rated IP23 and is suitable for
outdoor use.
The handle of the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is intended for
moving the wire feeder about the work place only.
CABLE CONNECTION
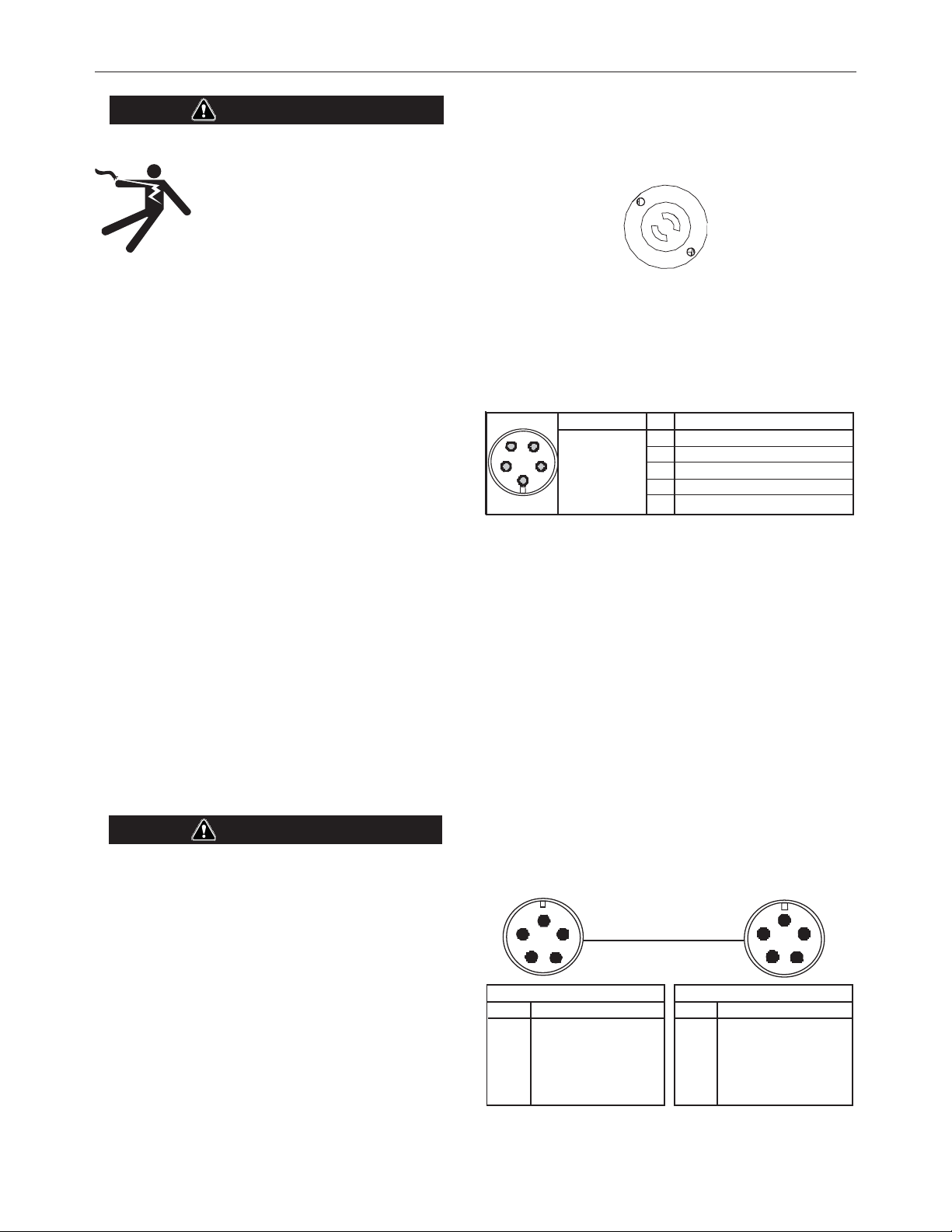
There is one connector on the front of the POWER FEED™ 25M
NNS for the gun trigger. (See 2-prong Figure A.2)
Figure A.2
ARCLINK CONTROL CABLES
There is one circular connector on the rear of the POWER FEED™
25M NNS. Maximum control cable length is 200 ft (61 m). (See
Figure A.3)
FIGURE A.3
Function
5-pin ArcLink
connector.
(See Figure A.4)
ArcLink/LincNet control cables are special high quality cables for
digital communication. The cables are copper 5 conductor cable
in a SO-type rubber jacket. There is one 20 gauge twisted pair for
network communications. This pair has an impedance of approximately 120 ohms and a propagation delay per foot of less than 2.1
nanoseconds. There are two 12 gauge conductors that are used
to supply 40VDC to the network. The fifth wire is 18 gauge and is
used as an electrode sense lead.
PIN
A
B
C
67 Electrode Voltage Sense
D
E
Wiring
ArcLink
ArcLink
40VDC
Common
When suspending a wire feeder, insulate the hanging device
from the wire feeder enclosure.
HIGH FREQUENCY PROTECTION
The control cables connect the power source to the wire feeder,
and the wire feeder to other wire feeders.
Control cables may be connected end to end to extend their
length. Use a maximum of 200 ft. (61.0m) of control cable
CAUTION
between components.
Figure A.4
Locate the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS away from radio controlled
machinery. The normal operation of the POWER FEED™ 25M
POWER SOURCE
WIRE FEEDER
NNS may adversely affect the operation of RF controlled equipment, which may result in bodily injury or damage to the equipment.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Power Source
Pin Function
A ArcLink
B ArcLink
C "67" voltage sense
D40 VDC
E Common
A-3
Wire Feeder
Pin Function
A ArcLink
B ArcLink
C "67" voltage sense
D 40 VDC
E Common
Page 12
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
Electrtrode
Work
Work
El ect r ode
W
or k
El ec t r ode
W
or k
Power Sour ce
Coax i al W
el d Cabl e
Wi r e Feeder
WELD CABLE SIZE
To install:
1. Turn the input power off at the welding power source.
Table A.1 located below are copper cable sizes recommended for different currents
and duty cycles. Lengths stipulated are the distance from the welder to work and
back to the welder again. Cable sizes are increased for greater lengths primarily for
the purpose of minimizing cable drop.
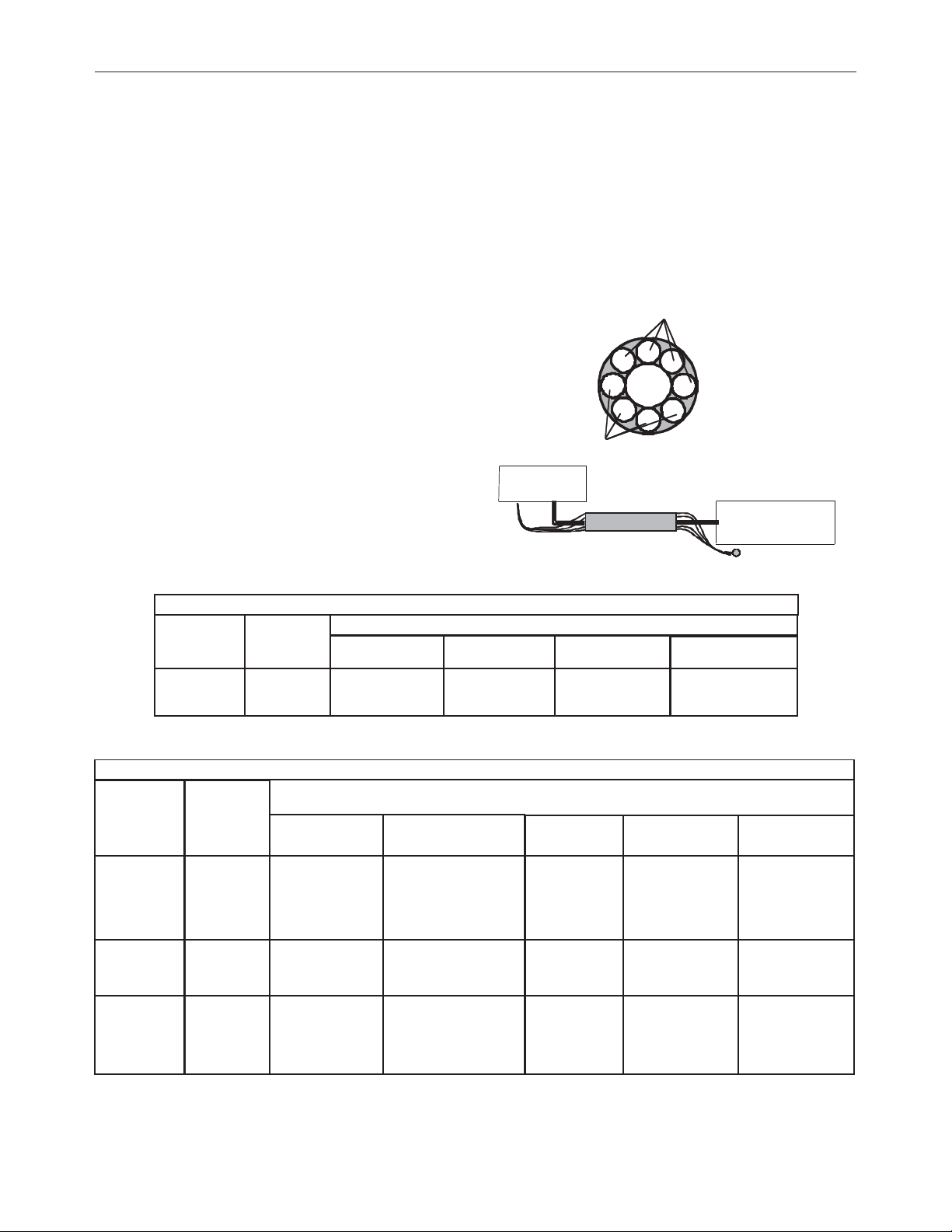
2. Connect one end of the center lead to the power source electrode
connection, and the other end to the wire feeder electrode connection.
3. Connect the outer lead bundle to the power source work connection,
and the other end to the work piece. Minimize the length of any work
COAXIAL WELD CABLE
(See Table A.2)
lead extension for best results.
4. Insulate all connections.
Coaxial welding cables are specially designed welding cables for pulse welding or
STT™ welding. Coaxial weld cables feature low inductance, allowing fast changes
in the weld current. Regular cables have a higher inductance which may distort the
pulse or STT™ wave shape. Inductance becomes more severe as the weld cables
become longer.
Coaxial cables work best for high performance waveforms and when:
• long cables are present.
• the cables are housed in a metal tray.
A coaxial weld cable is constructed with multiple small leads wrapped around one
large lead. The large inner lead connects to the electrode stud on the power source
and the electrode connection on the wire feeder. The small leads combine together
Power Sour c e
or k
El ec t r ode
to form the work lead, one end attached to the power source and the other end to
the work piece. See Figure A.5
FIGURE A.5
Coaxial W
el d Cabl e
El ec t r ode
Wi r e Feeder
or k
TABLE A.2
RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZES (RUBBER COVERED COPPER - RATED 75°C)**
COAXIAL CABLE LENGTH
AMPERES
250
300
350
DUTY
CYCLE
100%
60%
60%
0 to 25Ft.
(0 to7.6M)
1
1
1/0
25 to 50Ft.
(7.6 to 15.2M)
1
1
1/0
50 to 75 Ft.
(15.2 to 22.9M)
1
1
--
75 to 100 Ft.
(22.9 to 30.5M)
1
1/0
--
TABLE A.1
RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZES (RUBBER COVERED COPPER - RATED 167°F or 75°C)**
CABLE SIZES FOR COMBINED LENGTHS OF ELECTRODE AND WORK CABLES
PERCENT
DUTY
CYCLE
60
100
20
40 & 30
30
40
60
100
60
100
60
60
100
60
0 to 50Ft.
(0 to15M)
2
2
4 or 5
3
3
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
50 to 100Ft.
(15 to 30M)
2
2
3
3
3
2
1
1
1
2/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
2/0
100 to 150 Ft.
(30 to 46M)
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
2/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
150 to 200 Ft.
(46 to 61M)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1/0
2/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
3/0
200 to 250 Ft.
(61 to 76M)
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
2/0
3/0
3/0
4/0
4/0
4/0
AMPERES
200
200
225
225
250
250
250
250
300
325
350
400
400
500
** Tabled values are for operation at ambient temperatures of 104°F(40°C) and below. Applications above 104°F(40°C) may require cables
larger than recommended, or cables rated higher than 167°F(75°C).
A-4
Page 13

INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
SHIELDING GAS CONNECTION
WARNING
CYLINDER may explode if damaged.
•Keep cylinder upright and chained
to support.
• Keep cylinder away from areas where it may be damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached.
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from welding or other live electrical
circuits.
• Build up of shielding gas may harm health or kill.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
• See American National Standard Z-49.1, "Safety
in Welding and Cutting” Published by the
American Welding Society.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
M
AXIMUM INLET PRESSURE IS
Install the shielding gas supply as follows:
100
PSI
. (6.9
BAR
.)
PROCEDURE TO INSTALL DRIVE ROLLS AND WIRE
GUIDES
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding
power source before installation or changing
drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode and drive
mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and could remain
energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
1. Turn power off at the welding power source.
2. Release the idle roll pressure arm.
3. Remove the outer wire guide by turning the knurled thumb-
screws counter-clockwise to unscrew them from the feed plate.
4. Rotate the triangular lock and remove the drive rolls.
1. Secure the cylinder to prevent it from falling.
2. Remove the cylinder cap. Inspect the cylinder valves and regulator
for damaged threads, dirt, dust, oil or grease. Remove dust and dirt
with a clean cloth. DO NOT ATTACH THE REGULATOR IF OIL,
GREASE OR DAMAGE IS PRESENT! Inform your gas supplier of this
condition. Oil or grease in the presence of high pressure oxygen is
explosive.
3. Stand to one side away from the outlet and open the cylinder valve
for an instant. This blows away any dust or dirt which may have
accumulated in the valve outlet.
4. Attach the flow regulator to the cylinder valve and tighten the union
nut(s) securely with a wrench. Note: if connecting to 100% CO
cylinder, insert regulator adapter between regulator and cylinder
2
valve. If adapter is equipped with a plastic washer, be sure it is
seated for connection to the CO2cylinder.
5. Attach one end of the inlet hose to the outlet fitting of the flow regulator. Attach the other end to the welding system shielding gas
inlet. Tighten the union nuts with a wrench.
6. Before opening the cylinder valve, turn the regulator adjusting knob
counterclockwise until the adjusting spring pressure is released.
7. Standing to one side, open the cylinder valve slowly a fraction of a
turn. When the cylinder pressure gage stops moving, open the
valve fully.
8. The flow regulator is adjustable. Adjust it to the flow rate recommended for the procedure and process being used before making a
weld.
5. Remove the inner wire guide.
6. Insert the new inner wire guide, groove side out, over the two
locating pins in the feed plate.
7. Install a drive roll on each hub assembly secure with the triangular lock.
8. Install the outer wire guide by aligning it with the pins and tightening the knurled thumbscrews.
9. Close the idle arm and engage the idle roll pressure arm.
Adjust the pressure appropriately
A-5
Page 14
CONNECT AALL SSENSE
LEADS
THE EEND
O
THE WWELD
CONNECT
A
LL
WORK
LEAD
S
AT
THE
BEGINN
IN
G
OF
THE WWELD
DIRE
C
TI ON
OF
TRAVEL
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
• Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from
rotating equipment.
• Do not wear gloves when threadin
g wire or
changing w ir e spool.
• Only qualified personnel should install, use or
servic e this equipment.
REMOTE SENSE LEAD SPECIFICATIONS
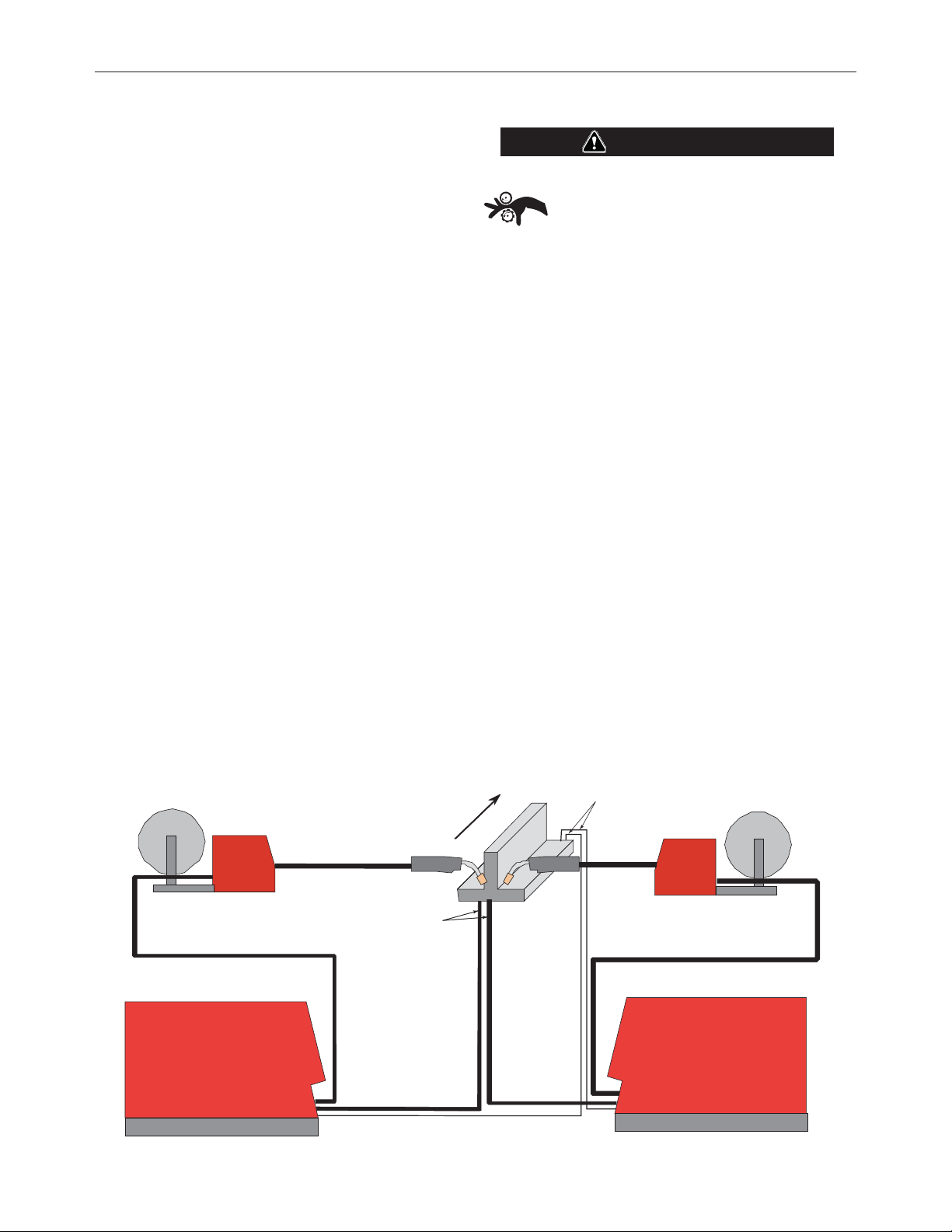
Welding with Multiple Arcs:
( See Figure A.6)
Special care must be taken when more than one arc is welding
imultaneously on a single part. Arc blow and arc interference
s
may occur or be magnified. Each power source requires a work
lead from the work stud to the welding fixture. Do not combine all
of the work leads into one lead. Performing welding in the direction away from the work leads. Connect all of the work sense
leads from each power source to the work piece at the end of the
weld, such that they are out of the path of the weld current. See
Figure A.6
For the best results when pulse welding, set the wire size and
wire feed speed the same for all the arcs. When these parameters
are identical, the pulsing frequency will be the same, helping to
stabilize the arcs.
LOADING SPOOLS OF WIRE
WARNING
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Loading 10 to 15 lb. (4.5 – 6.8kg) Spools.
A K468 spindle adapter is required for loading 2" (51mm) wide
spools on 2" (51mm) spindles. Use a K468 spindle adapter for
loading 2-1/2" (64mm) wide spools.
1. Squeeze the release bar on the retaining collar and remove it
from the spindle.
2. Place the spindle adapter on the spindle, aligning the spindle
brake pin with the hole in the adapter.
3. Place the spool on the spindle and align the adapter brake tab
with one of the holes in the back side of the spool. An indicator
mark on the end of the spindle shows the orientation of the
brake tab. Be certain the wire feeds off of the spool in the
proper direction.
OF
B
TH
OF
L
4. Re-install the retaining collar. Make sure that the release bar
snaps out and that the retaining collar fully engages the groove
on the spindle.
FIGURE A.6
TI O
A
A
G
AAT TH
F FTH
A-6
Page 15

TYPICAL SYSTEM CONFIGURATIONS
STANDARD FEATURES
Arc Performance
• STT™ capable when used with STT™ equipped Power
Waves.
• Waveform Control Technology™ for welds with good appearance and low spatter, even when welding nickel alloys.
Wire Drive
Patented 2 roll drive system. MAXTRAC™ technology delivers
great feeding because:
• The precision machined, rigid aluminum alloy frame results in
maximum drive roll clamping pressure.
• Patented split wire guides fully support the wire and virtually
eliminate birdnesting.
INSTALLATIONPOWER FEED™ 25M NNS
• No tools required to change the drive rolls and wire guides.
• Patented dual spring pressure arms have sensitivity for feeding soft wires without crushing them, and have plenty of compression force for feeding solid or stiff wires.
• All gear driven rolls for more feeding force.
• Powerful, quiet motor with integrated tachometer for accurate
WFS regulation.
Extras:
• Internal heater for keeping condensation off of the spool of
wire.
• Internal lights for illuminating the wire drive compartment.
A-7
Page 16
POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
READ AND UNDERSTAND ENTIRE SECTION
BEFORE OPERATING MACHINE.
WARNING
• ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
Unless using COLD FEED feature, when feeding with gun trigger, the electrode and drive
mechanism are always electrically energized and could
remain energized several seconds after the welding ceases.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power
source before installation or changing drive
rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode
and drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several
seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open.
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
• FUMES AND GASSES can be
dangerous.
• Keep your head out of fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing
zone.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
• WELDING SPARKS can cause
fire or explosion.
• Keep flammable material away.
GRAPHIC SYMBOLS THAT APPEAR ON
THIS MACHINE OR IN THIS MANUAL
INPUT POWER
ON
OFF
WIRE FEEDER
POSITIVE OUTPUT
NEGATIVE OUTPUT
INPUT POWER
DIRECT CURRENT
U
U
0
1
OPEN CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE
INPUT VOLTAGE
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ARC RAYS can burn.
• Wear eye, ear and body protection.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
SEE ADDITIONAL WARNING INFORMATION
UNDER ARC WELDING SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND IN THE FRONT OF THIS OPERATING MANUAL.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
B-1
U
I
I
2
1
2
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
INPUT CURRENT
OUTPUT CURRENT
PROTECTIVE
GROUND
WARNING OR
CAUTION
Page 17

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
DEFINITION OF WELDING TERMS
NON-SYNERGIC WELDING MODES
• A Non-synergic welding mode requires all welding process variables to be set by the operator.
SYNERGIC WELDING MODES
• A Synergic welding mode offers the simplicity of single knob
control. The machine will select the correct voltage and amperage based on the wire feed speed (WFS) set by the operator.
WFS
• Wire Feed Speed
CC
• Constant Current
CV
• Constant Voltage
GMAW
• Gas Metal Arc Welding
DUTY CYCLE
The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS is rated for 500 amps, 60% duty
cycle. The duty cycle is based on a 10 minute cycle.
For example, when welding at 500 amps, the POWER FEED™
25M NNS may run continuously for 6 minutes and then must sit
idle for 4 minutes.
GMAW-P
• Gas Metal Arc Welding-(Pulse Arc)
GMAW-STT
• Gas Metal Arc Welding-(Surface Tension Transfer)
SMAW
• Shielded Metal Arc Welding
FCAW
• Flux Core Arc Welding
CAG
• Carbon Arc Gouging
B-2
Page 18

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES
• GMAW (CV, Synergic CV, Pulse, STT™, Power, Pulse on
Pulse™)
• FCAW
• SMAW
GTAW (Lift Start only)
•
• Solid wires .025" to 1/16"
• Cored wires .035" to 5/64"
EQUIPMENT LIMITATIONS
• Works only on ArcLink®Power Wave power sources.
• Maximum gun length is 25ft.(7.6m) for push-only systems.
• Maximum spool size is 12 in. (305 mm) diameter
• Maximum spool weight is 44 lb (20 kg).
• Maximum control cable length is 200 ft (61 m).
• No more than 2 wire feeders may be connected to one ArcLink
power source at a time.
RECOMMENDED POWER SOURCES
• Power Wave®355M
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
• Power Wave
®
455M
®
455M/STT
®
S350
®
R350
®
i400
OPERATION
B-3
Page 19

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
CASE FRONT CONTROLS
(SEE FIGURE B.1)
OPERATION
10. Gun Trigger Connection
1. Left DISPLAY window
Shows WIRE FEED SPEED or AMPERAGE.
2. Left KNOB
Adjusts values in left display.
3. Main display
Shows detailed welding and diagnostic information.
4. Left Button
Changes the Main display to show the Weld Mode or
UltimArc.
5. Procedure Button
Selects A or B procedure, or gun control.
6. 2-Step/4-Step Button
Toggles between 2-step and 4-step trigger operation.
7. Gun Shielding Gas Connections
8. ON/OFF switch
Controls power to the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS.
9. Gun Electrode Connection
FIGURE B.1
11. Right Display window
Shows VOLTAGE or TRIM.
12. Right Knob
Adjusts values in the right display.
13. Thermal
Lights when the drive overheats.
14. Set-Up
Lights when feeder is set-up.
15. Right Button
Changes the Main display to show Start Options or
End Options.
16. Set Knob
Changes the value on the Main display.
17. Memories Buttons
For selection of common procedures.
18. Gun Conduit Connection
1
2
11
12
3
13
4
14
15
5
6
16
17
7
18
8
9
10
B-4
Page 20

ELECTRI C SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding
pow er source before installation or
chang-
ing drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch el ectrically live parts.
• When inching with the g
un trigger, electrode and drive
mechanism are "hot" to work and ground and could remain
energized sever
al seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Welding power source must be connected to system groun
d
per the National Electrical Code or any applicable loca l
codes.
• Only qualified personnel should perf
orm maintenance work.
The serviceability of a product or structure utilizing the welding
p r o g r a m s is and mus t b e th e so l e r e
s p on s ib i li t y of t he
builder/user. Many variables beyond the control of The Li ncoln
Electric Company aff
ect the results obtained in applying these
programs. These variables include, but are not limited to,
welding proced ur e, plate ch emistry and temperatu r e , weldmen t
design, fabrication methods and service
requirements. The availab le rang e o f a welding p rogr am m ay not be suit able fo r a ll
appli cations, and
the build/user is and must be solely responsi-
ble for welding pro gram selection.
POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
8. ON-OFF SWITCH
The On-Off Switch turns the wire feeder power on and off. It does
not control the power to the welding power source.
WARNING
----------------------------------------------------------------------
POWER WAVE SYSTEM OPERATION
Second, find the program in the welding software that best matches the desired welding process. The standard software shipped
with the Power Waves encompasses a wide range of common
processes and will meet most needs. If a special welding program
is desired, contact the local Lincoln Electric sales representative.
All adjustments are made on the user interface. Because of the
different configuration options your system may not have all of the
following adjustments. Regardless of availability, all controls are
described below.
WARNING
---------------------------------------------------------------------The steps for operating the Power Wave will vary depending upon
the user interface of the welding system. The flexibility of the
Power Wave lets the user customize operation for the best performance.
First, consider the desired welding process and the part to be
welded. Choose an electrode material, diameter, shielding gas and
process (GMAW, GMAW-P, GMAW-STT™, etc.)
B-5
Page 21

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
WIRE FEED SPEED / AMPS DISPLAY AND KNOB
FIGURE B.2
The left display and knob are used to adjust either wire feed
speed or amperage, depending upon the process selected.
While welding, the amps LED lights when amperage is
displayed and the wire feed speed LED lights when WFS is
displayed.
OPERATION
B-6
Page 22
POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
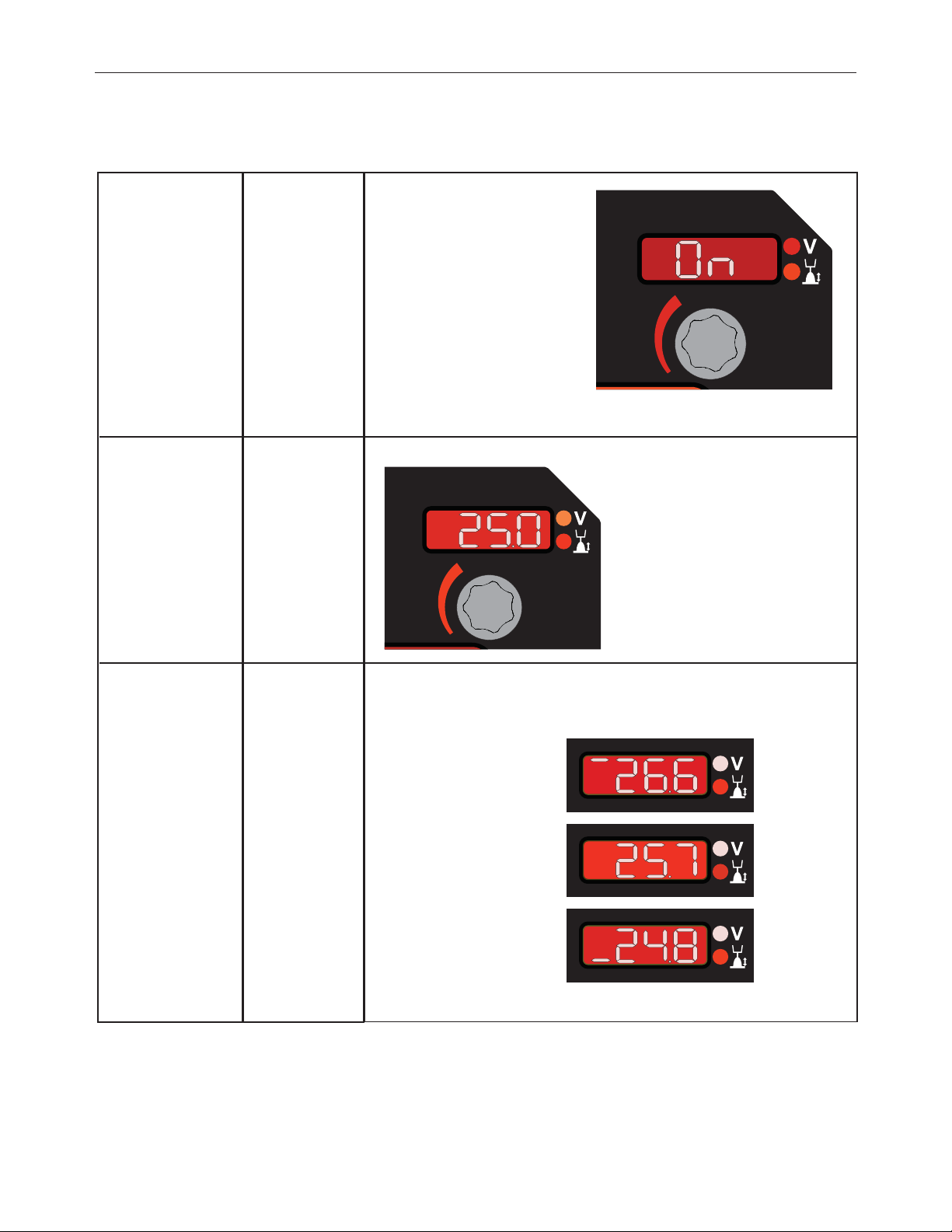
VOLTAGE / TRIM DISPLAY AND KNOB
The right display and knob control voltage, trim or output depending upon the process selected. Once welding is complete, the display
continues to show the welding voltage for 5 seconds.
Process
SMAW
(Stick) and GTAW (TIG)
Non-synergic
GMAW (MIG) and FCAW
(Flux-cored)
Display / Function
Weld Output
Voltage
Description
Rotate clockwise to turn output ON.
Rotate counterclockwise to turn output OFF.
Adjusts the voltage. The display is blank for non-synergic STT modes.
Synergic
GMAW (MIG) and FCAW
(Flux-cored)
When the voltage knob is rotated, the display will show an upper or lower bar indicating if the voltage is above or below the ideal voltage. The display is blank for synergic
STT modes.
• Preset voltage above ideal
voltage. (upper bar displayed).
Voltage
• Preset voltage at idealvoltage.
(no bar displayed).
• Preset voltage below idealvoltage. (lower bar displayed)
B-7
Page 23

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
VOLTAGE / TRIM DISPLAY AND KNOB
OPERATION
Process
Pulse
GMAW (MIG) and FCAW
(Flux-cored)
Display / Function
Trim
Description
Pulse welding controls the arc
length with 'Trim' instead of voltage. When trim (arc length) is
adjusted, the Power Wave automatically recalculates the voltage,
current and time of each part of
the pulse waveform for the best
result. Trim adjusts the arc length and ranges from 0.50 to 1.50. Increasing the trim
value increases the arc length, while decreasing the trim value decreases the arc
length.
Trim .50
Arc Length Short
Trim 1.00
Arc Length Medium
Trim 1.50
Arc Length Long
B-8
Page 24

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
SELECTING A WELD MODE
Weld modes may be selected by mode number or through a search
function.
To select a weld mode:
1. Press the left button until the Weld Mode Menu LED illuminates.
2. Rotate the center knob to select the weld mode.
To enter the search function:
1. Rotate the center knob until “Weld Mode Search” is displayed and
then press the right button.
2. Rotate the center knob to select the wire material. Press the right
button to accept and the left button to cancel.
3. Rotate the center knob to select the wire size. Press the right
button to accept and the left button to cancel.
4. Rotate the center knob to make the final selection about the
process, gas type and waveform. Press the right button to accept
and the left button to cancel.
OPERATION
B-9
Page 25

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
WAVE CONTROL
Wave Control is used to adjust the arc for exact preferences. The wave control functions vary for different processes and weld modes.
Process
SMAW
(Stick)
GMAW
(MIG) and
FCAW
(Flux-cored)
Wave Control
Name
Arc Force
Pinch
Effect / Range
Soft (-10.0) to
Crisp (10.0)
Soft (-10.0) to
Crisp (10.0)
Description
Arc Force adjusts the short circuit current for a soft arc, or for a forceful, driving
arc. It helps to prevent sticking and shorting of organic coated electrodes, particularity globular transfer types such as stainless and low hydrogen. Arc Force is
especially effective for root pass on pipe with stainless electrode and helps to
minimize spatter for certain electrodes and procedure as with low hydrogen, etc.
Pinch controls the arc characteristics when short-arc welding.
Ultimarc regulates the focus or shape of the arc. Ultimarc values greater than
0.0 increase the pulse frequency while decreasing the background current,
resulting in a tight, stiff arc best for high speed sheet metal welding. Ultimarc
values less than 0.0 decrease the pulse frequency while increasing the background current, for a soft arc good for out-of-position welding.
GMAW-P (Pulsed
MIG), Steel and
Stainless
Ultimarc
Soft (-10.0) to
Stiff (10.0)
Arc Control -10.0
Low Frequency, Wide
Arc Control OFF
Medium Frequency and Width
Arc Control +10.0
High Frequency, Focused
For Pulse modes, Arc Control changes the pulsing frequency. When the frequency changes, the Power Wave system automatically adjusts the background current to maintain a similar heat input into the weld. Low frequencies give more
control over the puddle and high frequencies minimize spatter.
B-10
Page 26

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
WAVE CONTROL
OPERATION
Process
GMAW-STT
(Surface Tension
Transfer
Wave Control
Name
Peak Current
Effect / Range
Controls arc
length
Description
Peak Current acts similar to an arc pinch control. Peak Current sets the arc
length and promotes good fusion. Higher peak current levels will cause the arc
to broaden momentarily while increasing arc length. If set too high, globular
transfer may occur. Setting it too low may cause instability and wire stubbing.
Best practice is to adjust for minimum spatter and puddle agitation.
Peak also affects the shape of the root. When using 100% CO2, the peak current will be higher than when welding with blended shielded gases. A longer arc
length is required with CO2 to reduce spatter.
Background current adjusts the overall heat input into the weld. Changing the
background current changes the shape of the back bead. 100% CO2 requires
less background current than when welding with blended shielding gases.
GTAW (TIG)
Background
Current
Tail-out
No wave
controls
available.
Regulates bead
contour
Provides additional power to
the arc.
----
Tail out provides additional power without the molten droplet becoming too
large. Increase as necessary to add heat input without increasing arc length.
Often this results in faster travel speeds. Note that as tail out increases, the peak
current and/or background current may need to be reduced.
----
B-11
Page 27

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
2-St
2- STEP 4- STEP- TRIGGER OPERATION
OPERATION
The 2-Step - 4-Step switch changes the function of the
gun trigger. 2-Step trigger operation switches the welding output ON-OFF in direct response to the trigger. 4Step trigger operation provides 'trigger interlock' capability and gives the ability to control the amount of time
spent in the arc start and arc crater steps.
Press the push button on the case front to toggle
between 2-Step and 4-Step operation.
The 2-Step, 4-Step trigger has no effect when welding
with SMAW or CAG procedures.
2-Step Trigger
2-Step trigger operation is the most common. When the
gun trigger is pulled, the welding system (power source
and wire feeder) cycles through the arc starting
sequence and into the main welding parameters. The
welding system will continue to weld as long as the gun
trigger is activated. Once the trigger is released, the
welding system cycles through the arc ending steps
4-Step Trigger
4-Step trigger operation gives the welder additional
control in the welding sequence. 4-Step trigger allows
the welder to choose the arc start, weld and arc end
time. It may also be set-up to work as a trigger interlock.
ep Trigger
B-12
Page 28

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
2-Step T rigger
2-Step Trigger controls the welding sequence in direct response to the trigger. When the gun trigger is pulled, the welding system
(power source and wire feeder) cycles through the arc starting sequence and into the main welding parameters. The welding system
will continue to weld as long as the gun trigger is activated. Once the trigger is released, the welding system cycles through the arc
ending steps.
Example 1: 2-Step Trigger: Simple operation
The simplest trigger operation occurs with a 2-Step trigger and Start and Crater set to OFF.
For this sequence,
PREFLOW: Shielding gas begins to flow immediately when the gun trigger is pulled.
RUN-IN: After preflow time expires, the power source regulates to the welding output and wire is advanced towards the work piece at
the Run-In WFS. If an arc is not established within 2.0 seconds, the wire feed speed will jump to the welding wire feed
speed.
WELD: The power source output and the wire feed speed continue at the weld settings for as long as the trigger is pulled.
POSTFLOW: As soon as the trigger is released, the power source output and the wire feed speed are turned OFF. Shielding gas
continues until the post flow timer expires.
Trigger Pulled
Arc Established
Trigger Released
B-13
Page 29

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
Trigger Pulled
Arc Established
Trigger Released
OPERATION
2-Step T rigger
Example 2: 2-Step Trigger: Improved Arc Start and Arc End
Tailoring the arc start and arc end is a common method for reducing spatter and improving weld quality. This can be accomplished
with the Start and Burnback functions set to a desired values and Crater set to OFF.
For this sequence,
PREFLOW: Shielding gas begins to flow immediately when the gun trigger is pulled.
RUN-IN: After preflow time expires, the power source regulates to the start output and wire is advanced towards the work piece at
the Run-In WFS. If an arc is not established within 2.0 seconds, the power source output and wire feed speed skips to
the weld settings.
START: Once the wire touches the work and an arc is established, both the machine output and the wire feed speed ramp to the
weld settings throughout the start time. The time period of ramping from the start settings to the weld settings is called
UPSLOPE.
WELD: After upslope, the power source output and the wire feed speed continue at the weld settings.
BURNBACK: As soon as the trigger is released, the wire feed speed is turned OFF and the machine output continues for the burnback
time.
POSTFLOW: Next, the machine output is turned OFF and shielding gas continues until the post flow timer expires.
B-14
Page 30

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
Trigger Pulled
Arc Established
Trigger Released
OPERATION
2-Step T rigger
Example 3: 2-Step Trigger: Customized Arc Start, Crater and Arc End
Aluminum is an example of where start, crater and burnback are commonly used to improve welding performance.
For this sequence,
PREFLOW: Shielding gas begins to flow immediately when the gun trigger is pulled.
RUN-IN: After preflow time expires, the power source regulates to the start output and wire is advanced towards the
work piece at the Run-In WFS. If an arc is not established within 2.0 seconds, the power source output and
wire feed speed skips to the weld settings.
START & UPSLOPE: Once the wire touches the work and an arc is established, both the machine output and the wire feed speed
ramp to the weld settings throughout the start time. The time period of ramping from the start settings to the
weld settings is called UPSLOPE.
WELD: After upslope, the power source output and the wire feed speed continue at the weld settings.
BURNBACK: After the crater time expires, the wire feed speed is turned OFF and the machine output continues for the burn-
back time.
POSTFLOW: Next, the machine output is turned OFF and shielding gas continues until the post flow timer expires.
2-Step trigger: Special considerations
The weld sequence response depends upon when the trigger is pulled and released and whether or not START or CRATER are active.
An example sequence:
Pull the trigger to start feed of wire. When arc is established the sequencer will begin START/UPSLOPE. If trigger is released during
UPSLOPE and CRATER/DOWNSLOPE is active, the machine will begin CRATER/DOWNSLOPE and sloping down over the CRATER time,
regardless of when the trigger release occurred.
If the CRATER is disabled and the trigger is released during START/UPSLOPE, the sequencer will move to the BURNBACK state to end
the weld.
B-15
Page 31

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
4-Step T rigger
4-step trigger allows the operator to release the trigger once an arc has been established. To end the weld, the trigger is pulled and
then released again.
Two types of 4-Step Trigger are available. Use the set-up menu to select the desired type of operation.
With current interlock, if the arc goes out for more than 0.5 seconds while the trigger is released, the welding process stops and goes
to the idle state.
Without the current interlock, if the arc goes out while the trigger is released, output to the power source remains on and the wire
feeder will continue to feed wire.
Example 1: 4-Step Trigger: Trigger Interlock
The 4-Step trigger can be configured as a trigger interlock. Trigger interlock adds to the welder’s comfort when making long welds by
allowing the trigger to be released after an initial trigger pull. Welding stops when the trigger is pulled a second time and then
released, or if the arc is interrupted.
For this sequence,
PREFLOW: Shielding gas begins to flow immediately when the gun trigger is pulled.
RUN-IN: After preflow time expires, the power source regulates to the welding output and wire is advanced towards the work
piece at the Run-In WFS. If an arc is not established within 1.5 seconds, the wire feed speed will jump to the
welding wire feed speed.
WELD: The power source output and the wire feed speed continue at the weld settings. The trigger is released and welding
continues. Welding continues when the trigger is pulled a second time
POSTFLOW: As soon as the trigger is released for the second time, the power source output and the wire feed speed are turned
OFF. Shielding gas flows until the post flow timer expires.
Trigger Pulled
Arc Established
Trigger Released
Trigger Pulled
Trigger Released
B-16
Page 32

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
:
OPERATION
4-Step T rigger
Example 2: 4-Step Trigger: Manual Control of Start and Crater times with Burnback ON.
The 4-Step trigger sequence gives the most flexibility when the Start, Crater and Burnback functions are active. This is a popular
choice when welding aluminum because extra heat may be needed during Start and less heat desired during crater. With 4-Step
trigger, the welder chooses the amount of time to weld at the Start, Weld and Crater settings by using the gun trigger. Burnback
reduces the occurrence of wire to sticking into the weld pool at the end of a weld and conditions the end of the wire for the next arc
start.
In this sequence,
PREFLOW: Shielding gas begins to flow immediately when the gun trigger is pulled.
RUN-IN: After preflow time expires, the power source regulates to the start output and wire is advanced towards the work
piece at the run-in WFS. If an arc is not established within 2.0 seconds, the power source output and wire feed
speed skips to the weld settings.
START: The power source welds at the start WFS and voltage until the trigger is released.
UPSLOPE: During upslope, the power source output and the wire feed speed ramp to the weld settings throughout the start
time. The time period of ramping from the start settings to the weld settings is called UPSLOPE. If the trigger is
pulled before upslope is complete, WELD is skipped and the sequence jumps to DOWNSLOPE.
WELD: After upslope, the power source output and the wire feed speed continue at the weld settings.
DOWNSLOPE
CRATER: During CRATER, the power source continues to supply output at the crater WFS and voltage.
BURNBACK: When the trigger is released, the wire feed speed is turned OFF and the machine output continues for the burnback
POSTFLOW: Next, the machine output is turned OFF and shielding gas continues until the post flow timer expires.
As soon as the trigger is pulled, the wire feed speed and power source output ramp to the crater settings throughout
the crater time. The time period of ramping from the weld settings to the crater settings is called DOWNSLOPE
time.
Trigger Pulled
Arc Established
Trigger Released
Trigger Pulled
Trigger Released
B-17
Page 33

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
Spot T rigger
The Spot Trigger may only be selected if the Spot Time has previously been set to a value other than 0.0 (OFF) and the Start and Crater
are both OFF.
Spot time causes the welding system to turn on for a fixed time, regardless if the trigger is held for a longer period of time. If the trigger is released before the spot timer is complete, welding stops.
If the Spot Time is set to 0.0 (OFF), the left display will be blank and the right display will show “OFF”. The Spot Time LED from the
timer menu will blink twice. After 2.0 seconds,
the trigger menu cycles back to the Cold Feed
Trigger option.
If Start is not set to OFF, the left display will be
blank and the right display will show “On”. The
Start LED from the sequence menu will blink
twice. After 2.0 seconds, the trigger menu
cycles back to the Cold Feed Trigger option.
If Crater is not set to OFF, the left display will be
blank and the right display will show “On”. The
Crater LED from the sequence menu will blink
twice. After 2.0 seconds, the trigger menu
cycles back to the Cold Feed Trigger option.
B-18
Page 34

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
4-Step T rigger: Special Considerations
The response to the trigger with 4-step trigger active is dependent upon when the trigger is pulled/released and the settings for START
and CRATER.
Example 1.
Pull the trigger to start feed of wire. When arc is established the sequencer will remain in START until the trigger is released. When the
trigger is released, UPSLOPE begins. If trigger is pulled again during UPSLOPE and CRATER/DOWNSLOPE is active, the feeder will
begin the DOWNSLOPE, sloping down over the CRATER time, regardless of when the trigger pull occurred.
If the CRATER/DOWNSLOPE state is disabled and the trigger is pulled during UPSLOPE, the sequencer will remain in the UPSLOPE state
and continue with the weld. If the fourth step (trigger release) occurs during UPSLOPE, the sequencer will jump to the BURNBACK to
end the weld.
Example 2:
Pull the trigger to start feed of wire. When arc is established the sequencer will remain in START until the trigger is released. When the
trigger is released, UPSLOPE begins and continues into WELD when the START timer is complete. When the trigger is pulled again
(step 3) and CRATER/DOWNSLOPE is active, DOWNSLOPE begins and continues until the CRATER timer expires, at which time CRATER
will be entered until the trigger is released.
While in DOWNSLOPE, if the trigger is released before the timer expires, the trigger will be ignored and the DOWNSLOPE state will continue until the timer expires, at which point CRATER state will be enabled, check for trigger, and jump to BURNBACK since the trigger
has been released.
While in the DOWNSLOPE state and the trigger is released and then pulled again, it will be ignored. During 4-Step operation in DOWNSLOPE, the trigger will always be ignored.
B-19
Page 35

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
START OPTIONS
The Start Options available depend upon the process and weld mode selected.
OPERATION
Process
SMAW (Stick)
All GMAW (MIG)
and FCAW (Fluxcored)
GTAW (TIG)
END OPTIONS
Start Options
----
Preflow
Time
Run-In WFS
Start time, WFS
and Volts
----
Effect / Range
----
0 – 25.0
seconds
Auto, OFF,
30 in/min to
weld WFS
0 – 10.0 seconds
----
Description
----
Run-In sets the wire feed speed from the time the trigger is pulled until an arc is
established or 2.5 seconds.
Use run-in for softer arc starts.
The Start Procedure controls the WFS and Volts for a specified time at the beginning of the weld. During the start time, the machine will ramp up or
down from the Start Procedure to the preset Welding Procedure.
----
The End Options available depend upon the process and weld mode selected.
Process
SMAW (Stick)
All GMAW (MIG)
and FCAW (Fluxcored)
GTAW (TIG)
Start Options
----
Spot Timer
Crater Time,
WFS and Volts
Burnback Time
Postflow Time
Postflow Time
Effect / Range
----
0 – 10.0
seconds
Auto,
0 – 0.25
seconds
0 – 25.0
seconds
0 – 25.0
seconds
Description
Sets the length of time for welding when the trigger is pulled. If the trigger is
released before the Spot Timer is complete, welding stops.
This option has no effect in 4-Step Trigger Mode.
Crater Procedure controls the WFS and volts for a specified time at the end of
the weld after the trigger is released. During the Crater time, the machine will
ramp up or down from the Weld Procedure to the Crater Procedure.
Crater is not commonly used with STT processes.
The burnback time is the amount of time that the weld output continues after the
wire stops feeding. It prevents the wire from sticking in the puddle and prepares
the end of the wire for the next arc start.
Adjusts the time that shielding gas flows after the welding output turns off.
Adjusts the time that shielding gas flows after the welding output turns off.
----
B-20
Page 36

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
SETUP MENU FEATURES
The Setup Menu gives access to the Setup Configuration. Stored in the setup configuration are user parameters
that generally only need to be set at installation. The parameters are grouped as shown in the following table.
PARAMETER
P.1 through P.99
P.101 through P.199
P.501 through P.599
DEFINITION
Unsecured Parameters (always adjustable)
Diagnostic Parameters (always read only)
Secured Parameters (only accessible through a p.c. or palm application)
GTAW (TIG) WELDING
The POWER FEED™ / Power Wave system is excellent for Touch Start TIG welding.
The system supports TIG torches with or without gas
control valves. TIG torches with gas control valves
connect directly to the gas flow regulator. For TIG
torches without gas control valves, connect the output
gas hose on the wire feeder to the TIG torch gas
hose.
The wire feeder gas solenoid may be enabled or disabled by parameter P.8 in the set-up menu found in
this operations section.
B-21
Page 37

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.0 Exit Setup Menu
This option is used to exit the setup menu. When P.0 is displayed, press the Left Button to exit
the setup menu.
P.1 Wire Feed Speed Units
This option selects which units to use for displaying wire feed speed.
English = inches/minute wire feed speed units (default).
Metric = meters/minute wire feed speed units.
P.2 Arc Display Mode
This option selects what value will be shown on the upper left display while welding.
Amps = The left display shows Amperage while welding (default).
WFS = The left display shows Wire Feed Speed while welding.
P.3 Display Options
This setup parameter was previously named "Display Energy"
If the previous software revision had this parameter set to display energy, that selection will
remain.
OPERATION
This option selects the information displayed on the alphanumeric displays while welding. Not all
P.3 selections will be available on all machines. In order for each selection to be included in the
list, the power source must support that feature. A software update of the power source may be
needed to include the features.
Standard Display = The lower displays will continue to show preset information during and after
a weld (default).
Show Energy = Energy is displayed, along with time in HH:MM:SS format.
Show Weld Score = The accumulative weld score result is shown
P.4 Recall Memory with Trigger
This option allows a memory to be recalled by quickly pulling and releasing the gun trigger. To
recall a memory, quickly pull and release the trigger the number of times that correspond to the
memory number. For example, to recall memory 3, quickly pull and release the trigger 3 times.
To recall memory 1, quickly pull and release the trigger the number of user memories plus 1.
Memories cannot be recalled while the system is welding.
Disabled = The gun trigger cannot be used to recall user memories (default).
Enabled = The gun trigger can be used to recall user memories.
B-22
Page 38

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.8 TIG Gas Control
This option allows control over which gas solenoid actuates while TIG welding.
"Valve (manual)" = No MIG solenoid will actuate while TIG welding, gas flow is manually controlled by an external valve.
"Feeder Solenoid" = The internal (feeder) MIG solenoid will turn on and off automati-
cally while TIG welding.
"Pwr Src Solenoid" = Any gas solenoid connected to the power source will turn on and
off automatically while TIG welding. This selection will not appear in the list if the
power source does not support a gas solenoid.
Notes: Preflow is not available while TIG welding. Postflow is available - the same
postflow time will be used in MIG and TIG. When machine output on/off is controlled via the upper right knob, gas flow will not start until the tungsten touches
the work. Gas flow will continue when the arc is broken until the Postflow time
expires. When machine output on/off is controlled via an arc start switch or foot
Amptrol, gas will begin flowing when the output is turned on and will continue
flowing until the output is turned off and the Postflow time expires.
OPERATION
P.9 Crater Delay
This option is used to skip the Crater sequence when making short tack welds. If the
trigger is released before the timer expires, Crater will be bypassed and the weld will
end. If the trigger is released after the timer expires, the Crater sequence will function
normally (if enabled).
P.14 Reset Consumable Weight
Use this option to reset the initial weight of the consumable package. Press the Right Button to reset the
consumable weight. This option will only appear with systems using Production Monitoring.
P.18 Wire Drive Gear Ratio
This option selects the Wire Drive Gear Ratio that will be used. The possible selectable values
are read from the Wire Drive on startup. For semi-automatic systems, if the feedhead board
has dip switches, this option does not appear in the menu. Gear ratio can be selected using the
dip switches.
Note: Changing this value will cause the system to reset.
P.20 Display Trim as Volts Option
This option determines how trim is displayed.
False = The trim is displayed in the format defined in the weld set (default).
True = All trim values are displayed as a voltage.
Note: This option may not be available on all machines. The power source must support this
functionality, or this option will not appear in the menu.
B-23
Page 39

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.22 Arc Start/Loss Error Time
This option can be used to optionally shut off output if an arc is not established, or is lost for a
specified amount of time. Error 269 will be displayed if the machine times out. If the value is set
to OFF, machine output will not be turned off if an arc is not established nor will output be
turned off if an arc is lost. The trigger can be used to hot feed the wire (default). If a value is
set, the machine output will shut off if an arc is not established within the specified amount of
time after the trigger is pulled or if the trigger remains pulled after an arc is lost. This is disabled
while welding in Stick, TIG or Gouge. To prevent nuisance errors, set Arc Start/Loss Error Time
to an appropriate value after considering all welding parameters (run-in wire feed speed, weld
wire feed speed, electrical stick out, etc). To prevent subsequent changes to Arc Start/Loss
Error Time, the setup menu should be locked out by setting Preference Lock = Yes using the
Power Wave Manager software.
P.27 Language Select
Selects which language will be displayed on the User Interface.
English (Default) Italiano
Deutsch Francais
Polski Espanol
OPERATION
P.28 Display Workpoint as Amps Option
This option determines how workpoint is displayed.
False = The workpoint is displayed in the format defined in the weld set (default).
True = All workpoint values are displayed as an amperage.
Note: This option may not be available on all machines. The power source must support this
functionality, or this option will not appear in the menu.
P.80 Sense From Studs
Use this option for diagnostic purposes only. When power is cycled, this option is automatically
reset to False.
False = Voltage sensing is automatically determined by the selected weld mode and other
machine settings (default).
True = Voltage sensing is forced to "studs".
P.81 Electrode Polarity
Used in place of DIP switches for configuration of the electrode sense lead. This option allows selection of the electrode voltage sense polarity. Most GMAW welding procedures use Electrode Positive
welding. Most GTAW and some inner shield procedures use Electrode Negative welding.
Positive Electrode Welding (default).
Negative Electrode Welding.
This option will only appear in the menu if the feedhead board does not have a dip switch to set the
polarity, and the power source does not support auto-hardware sense lead configuration. If this
option does not apper in the menu, voltage sense polarity can be selected using the dip switches.
B-24
Page 40

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.82 Voltage Sense Display
Allows viewing of Voltage Sense Lead Selection to aid in troubleshooting. The configuration is
displayed as a text string on the lower display whenever the output is enabled. This parameter
is not saved on a power cycle, but will be reset to False.
P.99 Show Test Modes
Most power sources contain weld modes used for calibration and test purposes. By default, the
machine does not include test weld modes in the list of weld modes that are available to the
operator. To manually select a test weld mode, set this option to "Yes". When the power source
is turned off and back on again, the test modes will no longer appear in the mode list. Test weld
modes typically require the machine output to be connected to a grid load and cannot be used
for welding.
P.100 View Diagnostics
Diagnostics are only used for servicing or troubleshooting the Power Wave system. Select
"Yes" to access the diagnostic options in the menu. Additional parameters will now appear in
the setup menu (P.101, P.102, etc).
OPERATION
P.101 View Event Logs
Used for viewing all the system event logs. Press the Right Button to enter the option. Rotate
Control Knob to select the desired event log to read. Press the Right Button again to enter the
selected log. Rotating the Control Knob will scroll through the event log, displaying the log index
number, event code and some other data. Press the Left Button to back out to select another
log. Press the Left Button again to exit this option.
P.102 View Fatal Logs
Used for viewing all the system fatal logs. Press the Right Button to enter the option. Rotate
Control Knob to select the desired fatal log to read. Press the Right Button again to enter that
log. Rotating the Control Knob will scroll through the log, displaying the log index number and
fatal code. Press the Left Button to back out to select another log. Press the Left Button again
to exit this option.
P.103 View Software Version Information
Used for viewing the software versions for each board in the system. Press the Right Button to
enter the option. Rotate Control Knob to select the desired board to read. Press the Right
Button again to read the firmware version. Press the Left Button to back out to select another
board. Rotate the Control Knob to select another board, or press the Left Button to exit this
option.
P.104 View Hardware Version Information
Used for viewing the hardware version for each board in the system. Press the Right Button to
enter the option. Rotate Control Knob to select the desired board to read. Press the Right
Button again to read the hardware version. Press the Left Button to back out to select another
board. Press the Left Button again to exit this option.
P.105 View Welding Software Information
Used for viewing the Weld Set in the Power Source. Press the Right Button to read the Weld
Set version. Press the Left Button to back out and exit this option.
B-25
Page 41

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.106 View Ethernet IP Address
Used for viewing the IP address of Ethernet compatible equipment. Press the Right Button to
read the IP Address. Press the Left Button to back out and exit this option. The IP address cannot be changed using this option.
P.107 View Power Source Protocol
Used for viewing the type of power source the feeder is connected to. Press the Right Button to
identify the power source as either LincNet or ArcLink. Press the Left Button to back out and
exit this option.
P.350 User Interface Group Selection
Used to differentiate multiple PF25M feeders connected to the same power source. Each independent feeder must have a unique selection in order to resolve error 18 problems.
P.500 View Lockout Parameters
Originally used to prevent inadvertent changes of secure setup parameters, P.500 was previously used as a gateway to these parameters. Presently, this option does not exist in any setup
menu.
OPERATION
P.501 Encoder Lockout
Locks one or both of the upper knobs (encoders), preventing the operator from changing wire
feed speed, amps, volts or trim. The function of each upper knob depends on the selected weld
mode. When a constant current weld mode is selected (e.g. Stick, TIG, Gouge), the upper right
knob will always function as an on/off switch. This parameter can only be accessed using
Power Wave Manager software.
P.502 Memory Change Lockout
Determines if the memories can be overwritten with new contents.
• No = Memories can be saved and limits can be configured (default).
• Yes = Memories cannot be changed - saving is prohibited and limits cannot be re-configured.
This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager.
P.503 Memory Button Disable
Disables the specified memory button(s). When a memory is disabled, welding procedures cannot be restored from or saved to that memory. If an attempt is made to save or restore a disabled memory, a message will be displayed on the lower display indicating the memory number
is disabled. In multi-head systems, this parameter disables the same memory buttons on both
feed heads. This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager software.
B-26
Page 42

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
USER DEFINED PARAMETERS
Parameter Definition
P.504 Mode Select Panel Lock
Selects between several Mode Select Panel lockout preferences. When a Mode Select Panel
selection is locked and an attempt is made to change that parameter, a message will be displayed on the lower display indicating the parameter is locked.
• All MSP Options Unlocked = All adjustable parameters on the Mode Select Panel are
unlocked.
• All MSP Options Locked = All knobs and buttons on the Mode Select Panel are locked.
• Start & End Options Locked = The Start and End parameters on the Mode Select Panel are
locked, all others are unlocked.
• Weld Mode Option Locked = The weld mode cannot be changed from the Mode Select Panel,
all others Mode Select Panel settings are unlocked.
• Wave Control Options Locked = The Wave Control parameters on the Mode Select Panel are
locked, all others are unlocked.
• Start, End, Wave Options Locked = The Start, End and Wave Control parameters on the
Mode Select Panel are locked, all others are unlocked.
• Start, End, Mode Options Locked = The Start, End and Weld Mode Select parameters on the
Mode Select Panel are locked, all others are unlocked.
This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager software.
OPERATION
P.505 Setup Menu Lock
Determines if the setup parameters can be modified by the operator without entering a passcode.
• No = The operator can change any set menu parameter without first entering the passcode
even if the passcode is non-zero (default).
• Yes = The operator must enter the passcode (if the passcode is non-zero) in order to change
any setup menu parameters.
This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager.
P.506 Set User Interface Passcode
Prevents unauthorized changes to the equipment. The default passcode is zero which allows
full access. A nonzero passcode will prevent unauthorized:
• changes to memory limits, saving to memory (if P.502 = Yes), changes to setup parameters (if
P.505 = Yes).
This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager software.
P.509 User Interface Master Lockout
Locks all user interface controls, preventing the operator from making any changes. This parameter can only be accessed using Power Wave Manager software.
B-27
Page 43

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
DUAL PROCEDURE/MEMORY PANEL
OPERATION
The Dual Procedure/Memory Panel performs three
functions:
• Weld procedure selection
• Memory save and recall
• Limits setting
There are two procedure memories (A and B) and
eight user memories (1-8).
Procedure Memory vs. User Memory
Procedure memory is used while welding. Changes to
the weld procedure (WFS, voltage, UltimArc™
Controll, etc.) immediately change the contents inside
the selected procedure memory.
PROCEDURE
MEMORY
A
GUN B
1
USER
MEMORIES
ARE COPIED TO
PROCEDURE
MEMORY
M
2
3
(8) USER
MEMORIES
M
4
USER MEMORIES
Recall a memory with memory buttons
To recall a user a memory, press one of the six user
memory buttons. The memory is recalled when the
button is released. Do not hold the button for more
than two seconds when recalling a user memory.
Recall a memory with the gun trigger
If desired, memories 1 through 8 can be recalled with
the gun trigger. For example, to recall memory 3,
quickly pull and release the gun trigger 3 times without
welding. To recall memory 1, quickly pull and release
the gun trigger 9 times without welding. Note: the wire
feeder is factory set with this feature disabled. Use
the SETUP menu and change P.4 to enable memory
recall with the gun trigger.
Note that memories may be locked with P.C. application software to prevent accidental overwrite of the
memories. If an attempt is made to save a memory
when memory saving is locked, the message
"Memory save is Disabled!" will appear briefly in the
MSP4 display.
RECALL:
PRESS
1 SECOND
SAVE:
PRESS
2 SECONDS
5
6
7
8
User memories work by copying the weld procedure
from one of the eight memories into either the “A ” or
“B” procedure. Weld procedures are saved into the
memories only when the operator chooses.
Using Procedure Memories
Procedure memories can be selected by choosing
either "A" or "B" procedure directly with the memory
panel, or by selecting "GUN" and using a dual procedure gun to select between procedure "A" and "B".
When selecting procedures with the gun switch, "A" or
"B" will flash to show which procedure is active.
PRESS
TO SELECT
PROCEDURE
A
GUN B
1
M
2
3
M
4
A
GUN B
1
5
M
2
6
3
7
M
4
8
5
6
7
8
B-28
Page 44

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
OPERATION
LIMITS
Limits allow the welder to adjust the welding procedure only within a defined range.
Each user memory may have a different set of limits.
For example, memory 1 may limit the WFS to 200
through 300 in/min, and memory 2 may limit the WFS
to 275 through 310 in/min, while memory 3 may have
no WFS limits.
Parameters are constrained by machine limits, or by
setting memory limits. When memory limits are
enabled, the parameter will flash whenever an attempt
is made to exceed the memory limit value. The parameter will not flash if an attempt is made to exceed
the machine limit.
The system machine limits are:
Parameter
Wire Feed Speed
Voltage
Trim
UltimArc
Preflow
Start Time
Run-In WFS
Crater Time
Burnback Time
Postflow Time
Range
Weld mode and wire
feeder dependent.
Weld mode dependent
0.50 to 1.50
-10.0 to 10.0
0.0 to 25.0
0.0 to 10.0
Off, 30 to 150
0.0 to 10.0
0.00 to 0.25
0.0 to 25.0
Units
in/min
Volts
--
Weld mode dependent
Seconds
Seconds
in/min
Seconds
Seconds
Seconds
Set Limits:
Press 5
seconds
A
GUN B
1
5
M
2
6
3
7
M
4
8
To set limits, press the desired memory button 1-8
and hold for 5 seconds. Release the memory button
when the LED begins to blink rapidly and the user
interface displays "Memory X Set Limits" as shown
below.
Memory 2
SETUP
Set Limits
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
Limits may be set for:
• Wire Feed Speed/Amperage
• Voltage/Trim
• Arc Control
Weld modes cannot be selected through the Limits
Setup menu, and must be chosen and saved to memory before entering the Limits Setup Menu.
SET
If the passcode does not equal zero (0000), enter the
passcode now. If the passcode has been forgotten, a
p.c. computer application is required to change the
passcode.
B-29
Page 45

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
W
OPERATION
If the passcode does not equal zero (0000), enter the
passcode now. If the passcode has been forgotten, a
p.c. computer application is required to change the
passcode.
High Limit
Memory Value
Low Limit
200
HI = 200 LOW = 180
WELD WFS
WELD MODE
ARC CONTROL
Parameter Name
If the passcode has been set to zero (0000), SETUP will
illuminate on the user interface and the display will show
the following:
Four items show on the user interface.
• Memory Value
• High Limit
• Low Limit
• Parameter Name
One of these items will flash to indicate which item will
change when the user interface encoder is rotated.
Press the right button on the user interface to select the
item to change.
SET
SETUP
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
The memory value must always be less than or equal
to the high limit, and greater than or equal to the low
limit.
After setting limits, press the memory button with the
flashing LED. The display will ask to save or discard
the limit changes just made. Press the left user interface for button (YES) to save and enable the limits
and exit. Press the right button (NO) to exit and leave
limits unchanged.
Enabling/Disabling Limits
Enable/Disable
Limits: Press
10 seconds
A
GUN B
1
5
M
2
6
3
7
M
4
8
Limits for each memory may be enabled or disabled
by pressing and hold the appropriate memory button
for 10 seconds. Release the memory button when the
display shows the following:
200
HI = 200 LOW = 180
WELD WFS
ELD MODE
RC CONTROL
Rotate to
Change
Value.
The Limits Setup menu shows a list of all parameters
available for the weld mode stored in the memory chosen. For example, if limits are being set for a stick
(SMAW) mode, parameters such as Run-in WFS and
Postflow will not appear.
To lock a parameter to a specific value that cannot
be changed, set the high and low limits to the
same value.
SET
SETUP
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
Press to
select item
to change.
MEMORY 2 LIMITS
ENABLE/DISABLE
WELD MODE
ARC CONTROL
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
If the passcode does not equal zero, enter the passcode
now. If the passcode is zero (0000), SETUP will light
and the displays the following:
WELD MODE
ARC CONTROL
ENABLE LIMITS?
Yes No
SET
SETUP
START OPTIONS
END OPTIONS
Press the left button (YES) to enable limits or the right
button (NO) to disable limits. Disabling limits does not
change any limits values that may have been previously set.
B-30
Page 46

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
1
7
6
3
2
4
5
INTERNAL CONTROLS
OPERATION
ITEM DESCRIPTION
1 Cold Feed / Gas Purge Switch
2 Wire Drive Pressure Arm
3 Internal Light Switch
4 Internal Heater Switch
5 Spindle Brake
6 Gun Adapter
7 Thumb Screw for securing the Gun Adapter
B-31
Page 47

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
FCAW
GMAW
AL
OPERATION
COLD FEED/GAS PURGE SWITCH
Cold Feed and Gas Purge are combined into a Rocker switch.
To activate Cold Feeding, push and
hold the Rocker switch in the UP
position. The wire drive will feed
electrode but neither the power
source nor the gas solenoid will be
energized. Adjust the speed of cold
feeding by rotating the WFS knob. Cold feeding, or
"cold inching" the electrode is useful for threading the
electrode through the gun.
Push the Rocker switch in the DOWN position to activate Gas Purge and let the shielding gas flow. The
gas solenoid valve will energize but neither the power
source output nor the drive motor will be turned on.
LIGHT SWITCH
Push the light Rocker switch to illuminate the inside of the POWER FEED™
25M NNS
COLD FEED/GAS PURGE
ROCKER SWITCH
COLD
FEED
GAS
PURGE
LIGHT
ROCKER SWITCH
LIGHTS
ON
G7937-2 VM
OFF
PRESSURE ARM ADJUSTMENT
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Turn the input power OFF at the welding power source before installation or
changing drive rolls and/or guides.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
• When inching with the gun trigger, electrode
and drive mechanism are "hot" to work and
ground and could remain energized several seconds after the gun trigger is released.
• Do not operate with covers, panels or guards
removed or open
• Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance work.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The pressure arm controls the amount of force the drive
rolls exert on the wire. Proper adjustment of pressure
arm gives the best welding performance.
Set the pressure arm as follows (See Figure B.18):
Aluminum wires between 1 and 2
Cored wires between 2 and 3
Steel, Stainless wires between 3 and 5
FIGURE B.18
HEATER SWITCH
Push the heater switch ON to warm the
inside of the POWER FEED™ 25M NNS.
The heater is useful for reducing condensation build-up on the spool of wire.
HEATER
ROCKER SWITCH
HEATER
ON
OFF
1
2
3
4
5
6
AL
FCAW
GMAW
B-32
Page 48

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
REAR CONTROLS:
OPERATION
ITEM DESCRIPTION
1 Shielding Gas Inlet
1
2
3
2 ArcLink Cable Connector
3 Electrode Cable
B-33
Page 49

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
DRIVE ROLL KITS USED
Drive Roll Kits, Steel wires
KP1505-030S .023-.030 (0.6-0.8mm)
KP1505-035S .035 (0.9mm)
KP1505-045S .045 (1.2mm)
KP1505-052S .052 (1.4mm)
KP1505-1/16S 1/16 (1.6mm)
KP1505-1 .035,.045 (0.9, 1.2mm)
KP1505-2 .040 (1.0mm)
Drive Roll Kits, Cored Wires
KP1505-035C .030-.035" (0.8-0.9mm)
KP1505-045C .040-.045" (1.0-1.2mm)
KP1505-052C .052" (1.4mm)
KP1505-1/16C 1/16" (1.6mm)
Drive Roll Kits, Steel or Cored Wires
KP1505-068 .068-.072" (1.8mm)
KP1505-5/64 5/64" (2.0mm)
KP1505-3/32 3/32" (2.4mm)
KP1505-7/64 7/64" (2.8mm)
KP1505-.120 .120" (3.2mm)
ACCESSORIES
Includes: 4 Smooth V groove drive
rolls and inner wire guide.
Includes: 4 Knurled drive rolls
and inner wire guide.
Includes: 4 Knurled drive rolls and
inner wire guide.
Drive Roll Kits, Hardfacing Wires
KP1505-7/64C 7/64" (2.8mm)
Drive Roll Kits, Aluminum Wire
KP1507-035A .035" (0.9 mm)
KP1507-040A .040" (1.0mm)
KP1507-3/64A 3/64" (1.2mm)
KP1507-1/16A 1/16" (1.6mm)
KP1507-3/32A 3/32" (2.4mm)
K2596-2 Plastic Case
K4405-xx
Heavy Duty ArcLink Control Cable
Includes: 2 Knurled drive rolls, 2
Smooth V groove drive rolls and
inner wire guide.
Includes: 4 polished U groove
drive rolls, outer wire guide and
inner wire guide, pressure door
springs, conduit bushing.
Includes: a complete engineered
plastic case. Decals and latches
are all preassembled.
Includes: 5 pin to 5 pin wire feeder
power source to control cable. Cables
may be connected end-to-end to
make a longer cable. The male connector is stainless steel and the
female connector is brass.
Recommended for outdoor applications.
C-1
Page 50

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not operate with covers
removed.
• Turn off power source before
installing or servicing.
• Do not touch electrically hot
parts.
• Turn the input power to the welding power
source off at the fuse box before working in the
terminal strip.
• Only qualified personnel should install, use or
service this equipment.
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
• Check weld cables, control cables and gas hoses
for cuts.
• Clean and tighten all weld terminals.
ACCESSORIES
To verify the voltage display:
• Set the welding power source and POWER FEED™
25M NNS to a CV procedure that gives steady
"spray" transfer in the arc.
• While a weld is being made, measure the voltage
from the feed plate to work with a calibrated volt
meter.
• The displayed voltage on the POWER FEED™ 25M
NNS should be within 2% of the measured value.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
• Motor Brushes:
Inspect the motor brushes every 6 months or every
2.5 million arc starts (whichever comes first).
Replace the brushes if they are less than 0.5” (12.7
mm) long.
CALIBRATION SPECIFICATION
All calibrations are factory set on the POWER FEED™
25M NNS.
To verify the wire feed speed:
• Assemble a .045 (1.2mm) drive roll kit into the
POWER FEED™ 25M NNS.
• Load a spool of .045 (1.2mm) electrode and thread
the electrode through the wire drive.
• Adjust the wire feed speed to 300 in/min
(7.62m/min).
• Press the COLD FEED switch and measure the
actual wire feed speed with a calibrated wire feed
speed tachometer.
• The measured wire feed speed should be within 2%
of the set value.
D-1
Page 51

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
WARNING
Service and Repair should only be performed by Lincoln Electric Factory Trained Personnel.
Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician and
machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid Electrical
Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual.
__________________________________________________________________________
TROUBLE SHOOTING
This Troubleshooting Guide is provided to help you
locate and repair possible machine malfunctions.
Simply follow the three-step procedure listed below.
Step 1. LOCATE PROBLEM (SYMPTOM).
Look under the column labeled “PROBLEM (SYMPTOMS)”. This column describes possible symptoms
that the machine may exhibit. Find the listing that
best describes the symptom that the machine is
exhibiting.
Step 2. POSSIBLE CAUSE.
The second column labeled “POSSIBLE CAUSE” lists
the obvious external possibilities that may contribute
to the machine symptom.
Step 3. RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION
This column provides a course of action for the
Possible Cause, generally it states to contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
If you do not understand or are unable to perform the
Recommended Course of Action safely, contact your
local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
E-1
Page 52

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Fault Code
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
Linc-Net System Error Codes
Description
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
Possible Adjustments
TROUBLE SHOOTING
Err 006
Err 100
Err 53 Voltage sense loss.
Err 81 Motor overload, long term.
1. The wire feeder has not received
a recognition command from the
power source.
1. The power source has issued a
shutdown command.
ArcLink System Error Codes
1. The wire drive motor has overheated.
1. Verify the power source is operating properly. (Status light steady
green.)
2. Check control cable for loose or
broken leads.
3. See power source Instruction
Manual.
1. Verify the power source is operating properly (Status light steady
green.)
2. Check control cable for loose or
broken leads.
3. See power source Instruction
Manual.
1. Check that the electrode slides
easily through the gun and cable.
2. Remove tight bends from the gun
and cable.
3. Check that the spindle brake is
not too tight.
4. Verify a high quality electrode is
being used.
5. Wait for the error to reset and the
motor to cool. (approximately 1
minute).
Err 82 Motor overload, short term.
Err 263 No usable weld modes.
1. The wire drive motor current draw
has exceeded limits, usually
because the motor is in a locked
rotor state.
1. The power source does not have
any welding programs loaded.
1. Check that motor can turn freely
when idle arm is open.
2. Verify that the gears are free of
debris and dirt.
1. See the power source Instruction
Manual for load welding programs.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
E-2
Page 53

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
The feeder does power up - no display, no cold feed.
No shielding gas.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
Output Problems
1. The POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
power switch is OFF.
2. The Power Wave power source is
OFF.
3. The circuit breaker for the wire
feeder on power source have
tripped.
4. The control cable may be loose or
damaged.
5. The power switch is damaged.
1. The gas supply is OFF or empty.
2. The gas hose is cut or crushed.
3. Dirt or debris is in the solenoid.
4. There is a loose solenoid connection or the solenoid has failed.
5. The solenoid has failed.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
1. Turn the POWER FEED™ 25M
NNS power switch ON.
2. Turn ON the Power Wave power
source.
3. Reset the circuit breakers.
4. Tighten, repair or replace the control cable.
5. Replace the power switch.
1. Verify the gas supply is ON and
flowing.
2. Route the gas hose so it avoids
sharp corners and make sure
nothing is on top of it. Repair or
replace damaged hoses.
3. Apply filtered shop at 80psi to the
solenoid to remove dirt.
4. Remove the cover and check that
all connections are in good condition.
5. Replace the solenoid.
Inconsistent wire feeding or wire not
feeding but drive rolls turning.
1. The gun cable is kinked and/or
twisted.
2. The wire is jammed in the gun and
cable.
3. The gun liner is dirty or worn.
4. The electrode is rusty or dirty.
5. The contact tip is partially melted
or has spatter.
6. Improper gun liner, tip, drive rolls
and/or inner wire guide.
7. Incorrect tension arm pressure on
the drive rolls.
8. Worn drive roll.
1. Keep the gun cable as straight as
possible. Avoid sharp corners or
bends in the cable.
2. Remove the gun from the wire
feeder and pull the jammed wire
out of the gun and cable.
3. Blow dirt out of the liner with low
pressure (40psi or less). Replace
the liner if worn.
4. Use only clean electrode. Use
quality electrode, like L-50 or L-56
from Lincoln Electric.
5. Replace the contact tip.
6. Verify the proper parts are
installed.
7. Adjust the tension arm per the
Instruction Manual. Most electrodes feed well at a tension arm
setting of "3".
8. Replace the drive rolls if worn or
filled with dirt.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
E-3
Page 54

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
PROBLEMS
(SYMPTOMS)
Variable or "hunting" arc.
Observe all Safety Guidelines detailed throughout this manual
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
Output Problems
1. Wrong size, worn and/or melted
contact tip.
2. Worn work cable or poor work
connection.
3. Wrong polarity.
4. The gas nozzle is extended
beyond the contact tip or the wire
stickout is too long.
5. Poor gas shielding on processes
requiring gas.
1. Replace the contact tip.
2. Verify all work and electrode con-
3. Adjust polarity to the recommend-
4. Adjust the gas nozzle and shorten
5. Check gas flow and mixture.
RECOMMENDED
COURSE OF ACTION
nections are tight and that the
cables are in good condition.
Clean/replace as necessary.
ed procedure.
the stickout to 3/8 to 1/2 inches.
Remove or block sources of
drafts.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
Poor arc starts with sticking or
"blast-offs", weld porosity, narrow
and ropy looking bead.
The wire feed speed/amperage and
voltage/trim display work during preset but show nothing during welding.
1. Improper procedures or techniques.
1. The software in the POWER
FEED™ 25M NNS must be
upgraded.
1. See "Gas Metal Arc Welding
Guide". (GS-100).
1. Contact the local authorized
Lincoln Field Service Shop.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
E-4
Page 55

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
DIAGRAMS
F-1
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside the
machine on one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number.
Page 56

POWER FEED™ 25M NNS
DIAGRAMS
17.2
14.8
23.1
12 X 18 In. Ellipse
16 In. Circle
8.7
5.7
14.8
17.2
F-2
Page 57

PARTS LIST FOR
Power Feed
P-754 P-754
™
25M NNS
This parts list is provided as an informative guide only.
It was accurate at the time of printing. These pages are only updated on the
Service Navigator DVD and in Lincoln Electricʼs official Parts Book (BK-34).
When ordering parts, always refer to Lincoln Electricʼs official Parts Book
(BK-34) for the latest pages.
POWER FEED™25M NNS
Page 58

2
1
4
3
5
P-754-A
ILLUSTRATION OF SUB-ASSEMBLIES
P-754-A
2
POWER FEED™25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 59

P-754-A.1P-754-A.1
Power Feed™25M NNS
For Code: 12244
Do Not use this Parts List for a machine if its code number is not listed. Contact the Service Department for any
code numbers not listed.
se the Illustration of Sub-Assemblies page and the table below to determine which sub assembly page and
U
column the desired part is located on for your particular code machine.
Sub Assembly Item
No.
SUB ASSEMBLY
PAGE NAME
PAGE NO.
CODE NO.
12244 11111
1
Front Panel Assembly
P-754-C
2
Control Box Assembly
P-754-D
3
Spindle & Mast Assembly
P-754-E
4
Wire Drive Assembly
P-754-F
5
Case Assembly
P-754-G
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 60

Front Panel Assembly
6
7
P-754-CP-754-C
5B
5A
1
4
2
9D
9C
3
9B
9A
10B
8
10A
11B
9
10
11
11A
POWER FEED™25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 61

P-754-C.1
P-754-C.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
Case Front Assembly, Includes: NSS 1X
1 Case Front G5577-5 1 X
2 Nameplate (G7937) NSS 1X
3 Button Cover, Small S23055-1 12 X
4 Potentiometer Insulation S27401 1 X
5A User Interface P.C. Board S28540-[ ] 1 X
5B Sems Screw T10082-12 4 X
6 Shaft Seal T14034-4 2 X
7 Knob M22778-1 3 X
8 Switch, SPST T10800-71 1 X
9 Cam-Lok Receptacle, Includes: M25112 1 X
9A Conduit Lock Nut T14370-3 1 X
9B Plain Washer S9262-120 1 X
9C Lock Washer E106A-16 1 X
9D 3/8-16 Hex Jam Nut CF000121 1 X
10 Female Connector, Includes T14557-3 1 X
10A Lock Washer T9695-8 1 X
10B 1/2-13 Jam Nut CF000054 1 X
11 Receptacle, Includes: S25449 1 X
11A #6-32 HN CF000054 2 X
11B Lock Washer E106A-13 2 X
Note: When ordering new printed circuit boards indicate the dash number [ ] of the “Old” board
that is to be replaced. This will aid Lincoln in supplying the correct and latest board along
with any necessary jumpers or adapters. The dash number brackets [ ] have purposely
been left blank so as to eliminate errors, confusion and updates.
NSS - Not Sold Separately
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 62

Control Box Assembly
7A
7B
3A
3B
1
2A
2C
25A
25B
11D
19A
16A
16C
13A
13B
19E
10
19B
12
19C
19H
19F
19G
11B
11C
9
6A
15A
20
6B
P-754-DP-754-D
6B
6A
20
15A
19G
19F
19B
19C
19H
10
19A
19E
7A
2C
7B
2A
12
13B
25A
16C
16A
13A
3A
3B
11D
11C
11B
25B
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 63

P-754-D.1
P-754-D.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
Control Box Assembly, Includes: NSS 1X
1 Control Box G5584-8 1 X
2A Control Box Decal M22570 1 X
2B Mast Decal (Not Shown) M22570-1 1 X
2C Insulation S25126 1 X
3A Wire Drive P.C. Board Assembly S28539-[ ] 1 X
3B #10-24 HLN T9187-13 4 X
6A Flex Tube T10642-265 1 X
6B Hose Clamp (Not Shown) T13777-8 1 X
7A Spindle & Mast Assembly (G5572-2) See P-754-E 1 X
7B #10-24 HLN T9187-13 4 X
7C Self Tapping Screw (Not Shown) S9225-99 1 X
9 Insulated Mounting Block M21096 1 X
10 Self Tapping Screw S9225-99 2 X
11A 1/2-13 HN (Not Shown) CF000027 1 X
11B Plain Washer S9262-80 1 X
11C Lock Washer E106A-15 1 X
11D 1/2-13 x 1.5 HHCS CF000052 1 X
12 Bus Bar M21006-6 1 X
12A Sleeving (Not Shown) E1159/B-.875-10.00 CS000902 1 X
13 Weld Cable, Includes: M21463-4 1 X
13A Cord Grip Connector S19999 1 X
13B Conduit Lock Nut T14370-3 1 X
13C Cam-Lok Welding Plug (Not Shown) M25115 1 X
14 Harness (Not Shown) G5599-2 1 X
15A Solenoid Assembly M17294-8 1 X
15B Plain Washer (Not Shown) S9262-149 1 X
15C Conduit Lock Nut (Not Shown) T14370-1 1 X
16A Control Box Panel S26587-7 1 X
16B #10-24 HLN (Not Shown) T9187-13 4 X
16C Cable Connection Assembly M21501-4 1 X
19 Resistor Bank Asbly, Includes: NSS 1X
19A Resistor S10404-95 2 X
19B Resistor Bracket M21144-1 1 X
19C Insulating Washer T4479-A 4 X
19D Lock Washer (Not Shown) T9695-1 2 X
19E #10-24 x 5.00 RHS CF000045 2 X
19F Lock Washer E106A-1 2 X
19G #10-24 HN CF000010 2 X
19H Voltage Sense Select P.C. Board M19540-[ ] 1 X
19J Self Tapping Screw (Not Shown) S9225-99 2 X
20 Shielding Gas Filter S28863 1 X
22 Bypass Assembly (Not Shown) S22969-12 1 X
25A Control Box Cover M21011-2 1 X
25B Thread Forming Screw S9225-99 4 X
26 Sems Screw (Not Shown) T10082-12 1 X
NSS - Not Sold Separately
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 64

Spindle & Mast Assembly
1
7
8
8
9
10
11
12
2
3A
3B
15
5
3B
P-754-EP-754-E
3A
10
11
12
15
Jan-14
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Page 65

P-754-E.1
P-754-E.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
Spindle & Mast Assembly (G5572-2), Includes: NSS 1X
1 Spindle Mast G5571-2 1 X
2 Spindle Shaft M20990-1 1 X
3A Thread Forming Screw S9225-102 2 X
3B External Tooth Lock Washer T9860-6 2 X
5 Bushing T12380-1 3 X
7 Spindle L10560-2 1 X
8 Friction Washer S17435-3 2 X
9 Keyed Washer T12965-2 1 X
10 Compression Spring T11862-14 1 X
11 Thumb Screw T14813-A 1 X
12 Retaining Collar Assembly S23811 1 X
15 Bushing T12380-1 2 X
NSS - Not Sold Separately
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 66

Wire Drive Assembly
1
3B
P-754-FP-754-F
13B
13A
3A
2C
15A
15B
17
16
15C
7
3H
2B
4A
2D
10
4B
4C
10A
11
5B
4D
2A
18
3G
POWER FEED™25M NNS
5A
6
6A
Jan-14
Page 67

P-754-F.1
P-754-F.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
Wire Drive Assembly, Includes: M21079-10 1 X
1 Wire Drive Panel G5569-2 1 X
Feed Plate Assembly, Includes: M19932-8 1 X
2A Idle Arm NSS 1X
2B Adjustment Arm Assembly M20593-3 1 X
2C Self Tapping Screw S9225-102 4 X
2D Set Screw S11604-21 1 X
3 Motor Gearbox Assembly, Includes: L12081-1 1 X
3A Drive Motor NSS 1X
3B Connector, Molex S24018-8 1 X
3C Locking Post (Not Shown) S24019-8 1 X
3D Woodruff Key (Not Shown) S24170-1 1 X
3E Snap Ring (Not Shown) S9776-27 1 X
3F Motor Brush & Brush Cap (Not Shown) S28460 1 X
3G Lock Washer E106A-2 3 X
3H M6 x 1.00 PPHS T14731-18 3 X
4A Drive Gear M19870 1 X
4B Collar S25414 1 X
4C Lock Washer T4291-A 1 X
4D Metric Screw T14731-47 1 X
5A Cover M19999 1 X
5B Self Tapping Screw S9225-102 1 X
6 Wire Guide Assembly (Outer), Includes: KP2071-3 1 X
6A Wire Guide Knob S24396 2 X
7 Ball Housing M18946 1 X
10 Drive Roll Shaft Assembly, Includes: S25638 2 X
10A Twist Lock Ring S25308 2 X
11 Retainer S25403 2 X
12 Plug and Lead Assembly (switch & LEDs) (Not Shown) M22587 1 X
13A LED Lens, Clear S23093-1 2 X
13B O Ring T13483-7 2 X
14 Thread Forming Screw S9225-99 4 X
15A Switch Panel S25706-1 1 X
15B Decal, Switch Panel (G7937-2) (Part of G7937) NSS 1X
15C Thread Forming Screw S9225-99 2 X
16 Rocker Switch T10800-71 2 X
17 Momentary Rocker Switch T10800-76 1 X
18 Plug Button T10397-3 1 X
NSS - Not Sold Separately
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 68

P-754-F.2
P-754-F.2
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
2 Roll Kits, 2 Roll Drive
Drive Roll Kits, Steel Wires
KP1696-030S .023-.030 (0.6-0.8mm)
KP1696-035S .035 (0.9mm)
KP1696-045S .045 (1.2mm)
KP1696-052S .052 (1.4mm)
KP1696-1/16S 1/16 (1.6mm)
KP1696-1 .035-.045 (0.9-1.2mm)
KP1696-2 .040 (1.0mm)
Drive Roll Kits, Cored Wires
KP1697-035C .030-.035 (0.8-0.9mm)
KP1697-045C .040-.045 (1.0-1.2mm)
KP1697-052C .052 (1.4mm)
KP1697-1/16C 1/16 (1.6mm)
KP1697-068 .068-.072 (1.7-1.8mm)
KP1697-5/64 5/64 (2.0mm)
Includes: 2 V groove drive
rolls and inner wire guide.
Includes: 2 V Knurled drive
rolls and inner wire guide.
Drive Roll Kits, Aluminum Wire
KP1695-035A .035 (0.9mm)
KP1695-040A .040 (1.0mm)
KP1695-3/64A 3/64 (1.2mm)
KP1695-1/16A 1/16 (1.6mm)
Includes: 2 polished U groove
drive rolls, outer wire guide
and inner wire guide.
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 69

NOTES
POWER FEED™25M NNS
Page 70

Case Assembly
P-754-GP-754-G
12A
9
10
4
2
8
3
7
6
5
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 71

P-754-G.1
P-754-G.1
# Indicates a change this printing.
Use only the parts marked “x” in the column under the
heading number called for in the model index page.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY. 123456789
Case Assembly (G5661-2), Includes: K2596-2 1 X
1 Plastic Case Asbly (G5660) NSS 1X
2 Warning Decal (S20601-2A)(Part of S20601-2) NSS 1X
3 Case Logo Decal S11893-9 1 X
4 Warning Decal (S20601-2B)(Part of S20601-2) NSS 1X
5 Warning Decal S25536-1 1 X
6 Door Logo Decal S11893-8 1 X
7 Decal - Crossed Out Wheeled Bin T13086-201 1 X
8 Plug Button T10397-6 2 X
9 Plug Button T10397-19 2 X
10 Gasket S26924 1 X
11A Insulated Fastener (Not Shown) T15088-2 6 X
11B Thread Forming Screw (Not Shown) S9225-102 2 X
12A Handle Assembly S18170 1 X
12B Plain Washer (Not Shown) S9262-98 2 X
12C Plain Washer (Not Shown) S9262-113 1 X
12D Lock Washer (Not Shown) E106A-2 2 X
12E 1/4-20 x .625 HHCS (Not Shown) CF000013 2 X
NSS - Not Sold Separately
POWER FEED
™
25M NNS
Jan-14
Page 72

CUSTOMER ASSISTANCE POLICY
The business of The Lincoln Electric Company is manufacturing and
selling high quality welding equipment, consumables, and cutting
equipment. Our challenge is to meet the needs of our customers and
to exceed their expectations. On occasion, purchasers may ask
Lincoln Electric for advice or information about their use of our
products. We respond to our customers based on the best information
in our possession at that time. Lincoln Electric is not in a position to
warrant or guarantee such advice, and assumes no liability, with
respect to such information or advice. We expressly disclaim any
warranty of any kind, including any warranty of fitness for any
customer’s particular purpose, with respect to such information or
advice. As a matter of practical consideration, we also cannot assume
any responsibility for updating or correcting any such information or
advice once it has been given, nor does the provision of information
or advice create, expand or alter any warranty with respect to the sale
of our products.
Lincoln Electric is a responsive manufacturer, but the selection and
use of specific products sold by Lincoln Electric is solely within the
control of, and remains the sole responsibility of the customer. Many
variables beyond the control of Lincoln Electric affect the results
obtained in applying these types of fabrication methods and service
requirements.
Subject to Change – This information is accurate to the best of our
knowledge at the time of printing. Please refer to
www.lincolnelectric.com for any updated information.
 Loading...
Loading...