Lincoln Electric CLASSIC III 10156, CLASSIC III 10061, CLASSIC III 10033, CLASSIC III 10072 User Manual
Page 1

CLASSIC ®III & CLASSIC ®III D
RETURN TO MAIN MENU
For Machines with Code Numbers 10033, 10061, 10072 or 10156
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding equipment
is designed and built with safety
in mind. However, your overall
safety can be increased by
proper installation ... and
thoughtful operation on your
part. DO NOT INSTALL,
OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS
EQUIPMENT WITHOUT
READING THIS MANUAL AND
THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINED THROUGHOUT.
And, most importantly, think
before you act and be careful.
IM529-A
October, 1999
Supersedes IM482
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
Page 2
i
SAFETY
i
WARNING
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents
are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
The Above For Diesel Engines
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you
purchase a copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box
351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available
from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
The engine exhaust from this product contains
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
The Above For Gasoline Engines
FOR ENGINE
powered equipment.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance
work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running.
____________________________________________________
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes
outdoors.
____________________________________________________
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts and
igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If
fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start
engine until fumes have been eliminated.
____________________________________________________
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in
position and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and
tools away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving
parts when starting, operating or repairing equipment.
____________________________________________________
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety
guards to perform required maintenance. Remove
guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete.
Always use the greatest care when working near moving
parts.
___________________________________________________
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan.
Do not attempt to override the governor or
idler by pushing on the throttle control rods
while the engine is running.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the
radiator pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and
welding machines
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and
welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician
before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health
effects which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1.
Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and
work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right
side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
___________________________________________________
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while
turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance
work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magneto wire as appropriate.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
Mar ‘95
Page 3
ii
SAFETY
ii
ELECTRIC SHOCK can
kill.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits
are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare
skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full
area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding
must be performed under electrically hazardous
conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet
clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or
scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use
the following equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic
welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection
should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover
plates to protect your eyes from sparks and
the rays of the arc when welding or observing
open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens
should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
FUMES AND GASES
can be dangerous.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases.When welding, keep
your head out of the fume. Use enough
ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When
welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see
instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or
cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as
low as possible and below Threshold Limit Values (TLV)
using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In
confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a
respirator may be required. Additional precautions are
also required when welding on galvanized steel.
3.f.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of
electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage
between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage
of both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8.
5.b.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations.
The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating
products.
5.c. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation,
especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.d. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your
employer’s safety practices. MSDS forms are available from
your welding distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.e. Also see item 1.b.
Mar ‘95
vapors
to
Page 4
iii
SAFETY
iii
WELDING SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
6.a.
Remove fire hazards from the welding area.
If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
the welding sparks from starting a fire.
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI
Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the
equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact
can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures
will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even
been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended
Safe Practices for the
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous
Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society
(see address above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil
6.f.
free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt,
cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear
ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places.
Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding
area as practical. Work cables connected to the building
framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing
through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains
or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
Remember that welding sparks and hot
though
they have
Preparation
for Welding and Cutting of
CYLINDER may explode
if damaged.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders
containing the correct shielding gas for the
process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for
the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and
any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas
cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l,
“Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
FOR ELECTRICALLY
powered equipment.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on
the equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Mar ‘95
Page 5
iv
SAFETY
iv
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ
Pour votre propre protection lire et observer toutes les instructions
et les précautions de sûreté specifiques qui parraissent dans ce
manuel aussi bien que les précautions de sûreté générales suivantes:
Sûreté Pour Soudage A L’Arc
1. Protegez-vous contre la secousse électrique:
a. Les circuits à l’électrode et à la piéce sont sous tension
quand la machine à souder est en marche. Eviter toujours
tout contact entre les parties sous tension et la peau nue
ou les vétements mouillés. Porter des gants secs et sans
trous pour isoler les mains.
b. Faire trés attention de bien s’isoler de la masse quand on
soude dans des endroits humides, ou sur un plancher
metallique ou des grilles metalliques, principalement dans
les positions assis ou couché pour lesquelles une grande
partie du corps peut être en contact avec la masse.
c. Maintenir le porte-électrode, la pince de masse, le câble
de soudage et la machine à souder en bon et sûr état
defonctionnement.
d.Ne jamais plonger le porte-électrode dans l’eau pour le
refroidir.
e. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les parties sous tension
des porte-électrodes connectés à deux machines à souder
parce que la tension entre les deux pinces peut être le
total de la tension à vide des deux machines.
f. Si on utilise la machine à souder comme une source de
courant pour soudage semi-automatique, ces precautions
pour le porte-électrode s’applicuent aussi au pistolet de
soudage.
zones où l’on pique le laitier.
6. Eloigner les matériaux inflammables ou les recouvrir afin de
prévenir tout risque d’incendie dû aux étincelles.
7. Quand on ne soude pas, poser la pince à une endroit isolé de
la masse. Un court-circuit accidental peut provoquer un
échauffement et un risque d’incendie.
8. S’assurer que la masse est connectée le plus prés possible
de la zone de travail qu’il est pratique de le faire. Si on place
la masse sur la charpente de la construction ou d’autres
endroits éloignés de la zone de travail, on augmente le risque
de voir passer le courant de soudage par les chaines de levage, câbles de grue, ou autres circuits. Cela peut provoquer
des risques d’incendie ou d’echauffement des chaines et des
câbles jusqu’à ce qu’ils se rompent.
9. Assurer une ventilation suffisante dans la zone de soudage.
Ceci est particuliérement important pour le soudage de tôles
galvanisées plombées, ou cadmiées ou tout autre métal qui
produit des fumeés toxiques.
10. Ne pas souder en présence de vapeurs de chlore provenant
d’opérations de dégraissage, nettoyage ou pistolage. La
chaleur ou les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs
du solvant pour produire du phosgéne (gas fortement toxique)
ou autres produits irritants.
11. Pour obtenir de plus amples renseignements sur la sûreté,
voir le code “Code for safety in welding and cutting” CSA
Standard W 117.2-1974.
2. Dans le cas de travail au dessus du niveau du sol, se protéger
contre les chutes dans le cas ou on recoit un choc. Ne jamais
enrouler le câble-électrode autour de n’importe quelle partie
du corps.
3. Un coup d’arc peut être plus sévère qu’un coup de soliel,
donc:
a. Utiliser un bon masque avec un verre filtrant approprié
ainsi qu’un verre blanc afin de se protéger les yeux du rayonnement de l’arc et des projections quand on soude ou
quand on regarde l’arc.
b. Porter des vêtements convenables afin de protéger la
peau de soudeur et des aides contre le rayonnement de
l‘arc.
c. Protéger l’autre personnel travaillant à proximité au
soudage à l’aide d’écrans appropriés et non-inflammables.
4. Des gouttes de laitier en fusion sont émises de l’arc de
soudage. Se protéger avec des vêtements de protection libres
de l’huile, tels que les gants en cuir, chemise épaisse, pantalons sans revers, et chaussures montantes.
5. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité dans la zone de
soudage. Utiliser des lunettes avec écrans lateraux dans les
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ POUR
LES MACHINES À SOUDER À
TRANSFORMATEUR ET À
REDRESSEUR
1. Relier à la terre le chassis du poste conformement au code de
l’électricité et aux recommendations du fabricant. Le dispositif
de montage ou la piece à souder doit être branché à une
bonne mise à la terre.
2. Autant que possible, I’installation et l’entretien du poste seront
effectués par un électricien qualifié.
3. Avant de faires des travaux à l’interieur de poste, la debrancher à l’interrupteur à la boite de fusibles.
4. Garder tous les couvercles et dispositifs de sûreté à leur
place.
Mar. ‘93
Page 6
for selecting a QUALITY product by Lincoln Electric. We want you
Thank You
to take pride in operating this Lincoln Electric Company product
••• as much pride as we have in bringing this product to you!
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims
for material damaged in shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation company at the
time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This information can be
found on your machine nameplate.
Model Name & Number _____________________________________
Code & Serial Number _____________________________________
Date of Purchase _____________________________________
Whenever you request replacement parts for or information on this equipment always supply the information
you have recorded above.
vv
Read this Operators Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual and keep it
handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection.
The level of seriousness to be applied to each is explained below:
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed exactly to avoid serious personal injury or
loss of life.
CAUTION
This statement appears where the information must be followed to avoid minor personal injury or damage to
this equipment.
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Installation.......................................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications.......................................................................................................A-1
General Description..............................................................................................................A-2
Design Features ...................................................................................................................A-2
Pre-Operation Installation.....................................................................................................A-3
Safety Precautions ........................................................................................................A-3
Exhaust Spark Arrester .................................................................................................A-3
Location/Ventilation.......................................................................................................A-3
Stacking ........................................................................................................................A-3
Angle of Operation ........................................................................................................A-3
Machine Grounding.......................................................................................................A-3
Lift Bail ..........................................................................................................................A-4
Trailers ..........................................................................................................................A-4
Polarity Control and Cable Sizes ..................................................................................A-4
Pre-Operation Service..........................................................................................................A-5
Oil..................................................................................................................................A-5
Fuel ...............................................................................................................................A-5
Cooling System .............................................................................................................A-5
Battery Charging ...........................................................................................................A-5
vi
Operation.........................................................................................................................Section B
Engine Operation .................................................................................................................B-1
Starting The Continental TM27 Engine ................................................................................B-1
Starting The Continental TMD27 Engine..............................................................................B-1
Stopping the engine .............................................................................................................B-1
Welder Operation .................................................................................................................B-2
Duty Cycle ............................................................................................................................B-2
Control of Welding Current...................................................................................................B-2
Idler Operation......................................................................................................................B-2
Auxiliary Power .............................................................................................................B-3
Carburetor Deicing Kit
Accessories ....................................................................................................................Section C
Optional Features (Field Installed) .......................................................................................C-1
Maintenance....................................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................D-1
General Instructions..............................................................................................................D-1
Cooling System.....................................................................................................................D-1
Bearings................................................................................................................................D-1
Commutator and Brushes .....................................................................................................D-1
Idler Maintenance .................................................................................................................D-2
Nameplates...........................................................................................................................D-2
Engine Service Chart ............................................................................................................D-3
...............................................................................................B-3
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................................Section E
Safety Precautions ...............................................................................................................E-1
Welder Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................E-2
Electronic Idler Troubleshooting Guide .................................................................................E-3
Engine Troubleshooting Guide (TM27 Only) ................................................................E-4, E-5
Diagrams..........................................................................................................................Section F
Wiring Diagram (Classic III)..................................................................................................F-1
Wiring Diagram (Classic III D) ..............................................................................................F-2
Dimension Print ....................................................................................................................F-3
Parts Manual..............................................................................P232 Series (IIID), P302 Series (III)
Page 8
A-1
INSTALLATION
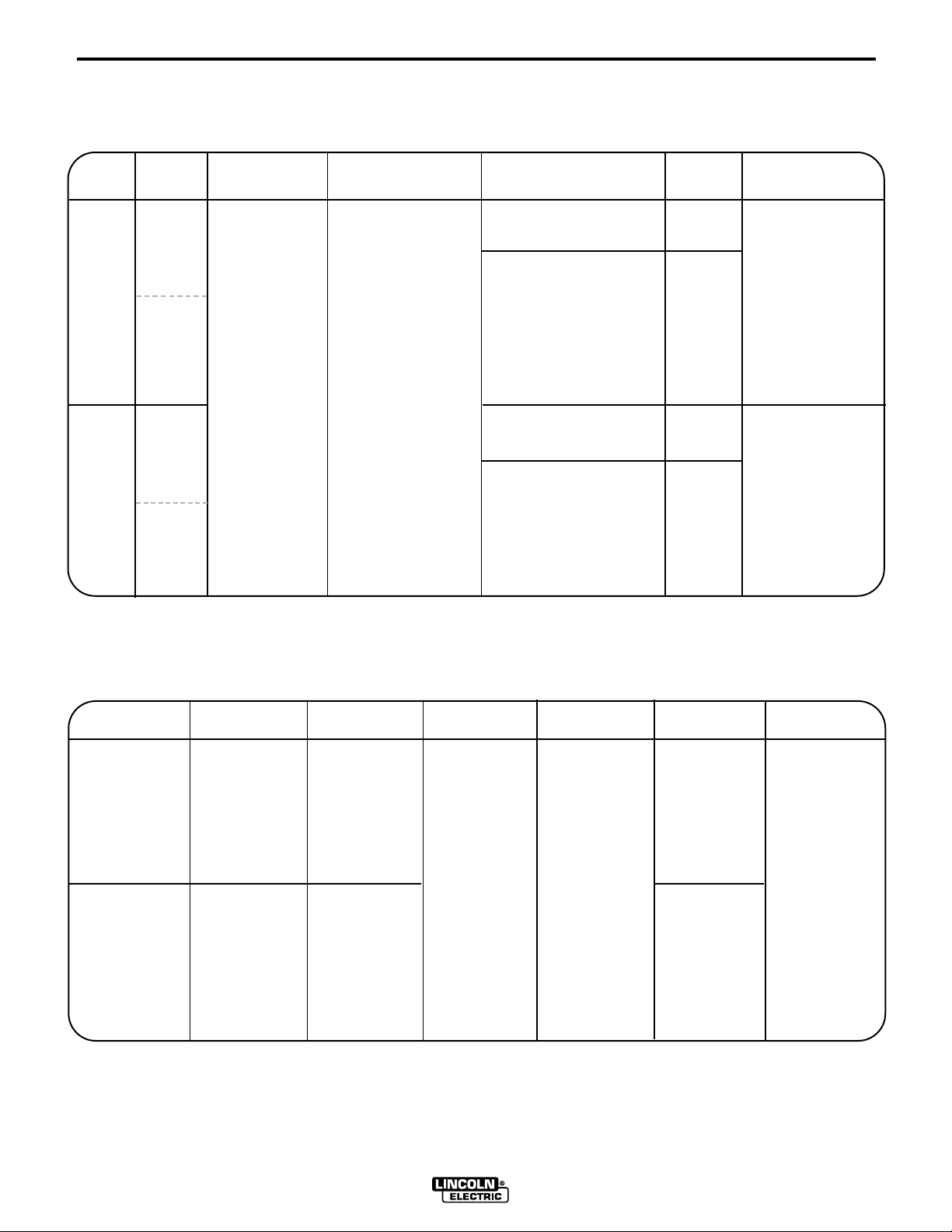
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – CLASSIC III AND IIID
Machine
A-1
Product
Name
Classic III
Classic III D
Ordering
Information
K1428-2
@
CSA
w/o Wire Feed
Module
K1428-3
@
CSA
w/ Wire Feed
Module
K1433-1
@
CSA
w/o Wire Feed
Module
K1433-2
@
CSA
w/ Wire Feed
Module
@
Meets Canadian Standards
Description
300 Amp DC
Arc Welder
All Copper
Windings
Pure DC Power
Generator
Rated DC Output *
Amps / Volts / Duty Cycle
225A / 29V / 100%
300A / 32V / 50%
350A / 34V / 30%
* Based on a 10 min. period.
DC Current Range
(Fine Adjustment in Each Range)
40 - 350 Amps
220 - Max
160 - 240
120 - 190
80 - 130
Min - 90
40 - 350 Amps
220 - Max
160 - 240
120 - 190
80 - 130
Min - 90
Auxiliary
Power
3000 Watts,
60 Hz. AC
26 Amps @
115V
13 Amps @
230V
3000 Watts,
60 Hz. AC
26 Amps @
115V
13 Amps @
230V
Dimensions
& Weight
40.94 x 24.0 x 66.25in
(1040 x 610 x 1683 mm)
1406 lbs (638 kg)
40.94 x 24.0 x 66.25 in
(1040 x 610 x 1683mm)
1445 lbs (657 kg)
Engine
Product
Name
Classic III
Classic III D
Description Horsepower Operating
4 Cylinder
4 Cycle
Water-Cooled
Gasoline Engine
Cast Iron Cylinder,
Block/Crankcase
4 Cylinder
4 Cycle
Water-Cooled
Diesel Engine
Cast Iron Cylinder,
Block/Crankcase
45 HP
@ 1700 RPM
38.9 HP
@ 1700 RPM
Speeds
Full Load:
1725 RPM
High Idle:
1800 RPM
Low Idle:
1350 RPM
Displacement Ignition Capacities
Distributor Type
Electronic
164.7 Cu In
(2.7 ltrs)
Diesel
Fuel:
15 Gals (57 Ltrs)
Lubricating Oil:
7.0 Qts (6.7 Ltrs)
Coolant:
9.3 Qts (8.8 Ltrs)
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 9
A-2
INSTALLATION
A-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Classic®III and Classic®III D are heavy duty,
engine driven, DC arc welding power sources capable
of providing constant current output for stick welding
or DC TIG welding. These welders are wound with all
copper coils, rated at 300 amps/32 Volts, and provide
other Classic features such as improved door latches
and stainless hinges. With the addition of the optional
K623-1 Wire Feed Module™, the Classic III or Classic
III D will provide constant voltage output for running
the LN-7, LN-23P, or LN-25 wire feeders. (The Wire
Feed Module is factory installed on the K1428-3 and
K1433-2).
The Classic III D has Diesel Engine Protection. In the
event of sudden low oil pressure or high coolant temperature, the engine immediately shuts down. The
Classic III & Classic III D have a current range of 40350 DC amps with output ratings as follows:
RATED OUTPUT DUTY CYCLE
225A @ 29V
300A @ 32V
350A @ 34V
These units are also capable of providing 3 kVA of
115/230 volts of 60 cycle AC auxiliary power.
100%
50%
30%
DESIGN FEATURES
Control Panel
Both the engine and the welder controls are located
on one recessed panel at the exciter end of the
machine. The welder controls consist of a five step
“Current Range Selector” switch and a “Fine Current
Adjustment” rheostat. Each welder is equipped with a
“Start” button, an “Ignition” switch and an “Idler” control switch. The diesel version comes with a “Glow
Plug” feature for easier cold weather starting.
The control panels also contain an engine temperature gauge (diesel only), a battery charging ammeter,
an oil pressure gauge (oil pressure light on the gasoline version), two three prong grounding type receptacles and circuit breakers for auxiliary power, and a
choke control (gasoline version only).
All Copper Windings - For long life and dependable
operation.
Engine Idler - Both the Classic III & III D are
equipped with an electronic automatic engine idler. It
automatically increases and decreases engine speed
when starting and stopping welding or using auxiliary power. A built-in time delay permits changing
electrodes before the engine slows to its low idle
speed. The “Idler” control switch on the panel locks
the idler in full speed position when desired.
The Classic III unit uses the Continental TM27
industrial water-cooled Gasoline engine, while the
Classic III D uses the Continental TMD27®industrial
water-cooled Diesel engine.
Auxiliary Power - 3.0 kVA of nominal 115/230V,
®
60Hz, AC. Output voltage is maintained within ± 10%
at all loads up to rated capacity. (See Optional
Features for Power Plug Kits.)
Welder Enclosure - The complete welders are rubber
mounted on a rugged steel “C” channel base.
The output terminals are placed at the side of the
machines so that they are protected by the door. The
output terminals are labeled (+) and (-).
Cranking System - A 12 volt electric starter is standard.
Air Cleaner - Heavy duty two stage dry type.
Muffler - A muffler and rain cap are standard.
Engine Hour Meter - A meter to record hours of oper-
ation.
Diesel Engine Protection - The system shuts the
diesel engine down in the event of sudden low oil
pressure or high coolant temperature.
Carburetor Deicing Kit
Classic III Welders are equipped with a kit, that
prevents carburetor icing when outside temperature is
60°F/15.5°C or lower.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 10

A-3
INSTALLATION
A-3
PRE-OPERATION INSTALLATION
WARNING
Do not attempt to use this equipment until you
have thoroughly read the engine manufacturer’s
manual supplied with your welder. It includes
important safety precautions, detailed engine
starting, operating and maintenance instructions,
and parts lists.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and
ground
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
ENGINE EXHAUST can kill.
• Use in open, well ventilated areas or
vent exhaust outside.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Do not operate with doors open or
guards off.
• Stop engine before servicing.
• Keep away from moving parts.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
See additional warning information at the
front of this operator’s manual.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Exhaust Spark Arrester
Some federal, state or local laws may require that
engines be equipped with exhaust spark arresters
when they are operated in certain locations where
unarrested sparks may present a fire hazard. The
standard mufflers included with these welders do not
qualify as spark arresters. When required by local
regulations, suitable spark arresters must be installed
and properly maintained.
CAUTION
Use of an incorrect arrester may lead to engine damage
or performance loss. Contact the engine manufacturer
for specific recommendations.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Location / Ventilation
STACKING
Classic III and III D machines cannot be stacked.
ANGLE OF OPERATION
To achieve optimum engine performance the Classic
III and III D should be run in a level position. The maximum angle of operation for the TM27 and TMD27
engines is 60 degrees in a direction to cause the air
intake manifold to be angled up, 45 degrees for the air
intake manifold to be angled down, and 50 degrees
for the welder control panel to be angled up or down.
If the engine is to be operated at an angle, provisions
must be made for checking and maintaining the oil
level at the normal (FULL) oil capacity in the
crankcase. When operating the welder at an angle,
the effective fuel capacity will be less than the specified 15 gallons (57 Ltrs.).
Machine Grounding
According to the United States National Electrical
Code, the frame of this portable generator is not
required to be grounded and is permitted to serve as
the grounding means for cord connected equipment
plugged into its receptacle.
Some state, local, or other codes or unusual operating
circumstances may require the machine frame to be
grounded. It is recommended that you determine the
extent to which such requirements may apply to your
particular situation and follow them explicitly. A
machine grounding stud marked with the symbol is
provided on the welding generator frame foot. (If an
older portable welder does not have a grounding stud,
connect the ground wire to an unpainted frame screw
or bolt.) In general, if the machine is to be grounded,
it should be connected with a #8 or larger copper wire
to a solid earth ground such as a metal water pipe
going into the ground for at least ten feet and having
no insulated joints, or to the metal framework of a
building which has been effectively grounded. The
U.S. National Code lists a number of alternate means
of grounding electrical equipment.
Always operate the welder with the doors closed.
Leaving the doors open changes the designed air flow
and may cause overheating.
The welder should be located to provide an unrestricted flow of clean, cool air. Also, locate the welder so
that engine exhaust fumes are properly vented to an
outside area.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 11
A-4
INSTALLATION
A-4
Lift Bail
A lift bail is provided for lifting with a hoist.
WARNING
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause
injury.
• Do not lift this machine using lift bale if
it is equipped with a heavy accessory
such as a trailer or gas cylinder.
• Lift only with equipment of adequate lifting capacity.
• Be sure machine is stable when lifting.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Trailer (See Optional Features)
If the user adapts a non-Lincoln trailer, he must
assume responsibility that the method of attachment
and usage does not result in a safety hazard nor damage the welding equipment. Some of the factors to be
considered are as follows:
Polarity Control and Cable Sizes
With the engine off, route the electrode and work
cables through the strain relief bracket on the base
and connect to the studs located below the fuel tank
mounting rail. (See size recommendations below.)
For positive polarity, connect the electrode cable to
the terminal marked “+”. For Negative polarity, connect the electrode cable to the “-” stud. These connections should be checked periodically and tightened
if necessary.
When welding at a considerable distance from the
welder, be sure you use ample size welding cables.
RECOMMENDED COPPER CABLE SIZES
Cables Sizes for Combined Length
of Electrode Plus Work Cable
Amps Duty Cycle Up to 200 ft. 200 to 250 ft.
225 100% 1 1/0
300 50% 1/0 2/0
350 30% 2/0 3/0
1. Design capacity of trailer vs. weight of Lincoln
equipment and likely additional attachments.
2. Proper support of, and attachment to, the base of
the welding equipment so there will be no undue
stress to the framework.
3. Proper placement of the equipment on the trailer to
ensure stability side to side and front to back when
being moved and when standing by itself while being
operated or serviced.
4. Typical conditions of use, i.e., travel speed, rough-
ness of surface on which the trailer will be operated;
environmental conditions, likely maintenance.
5. Conformance with federal, state and local laws.
(1)
Consult applicable federal, state and local laws regarding specific
requirements for use on public highways.
(1)
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 12

A-5
INSTALLATION
A-5
PRE-OPERATION SERVICE
CAUTION
READ the engine operating and maintenance instruc-
tions supplied with this machine.
WARNING
can cause fire or explosion.
Fuel
-
• Stop engine while fueling.
• Do not smoke when fueling.
• Do not overfill tank.
• Keep sparks and flame away from tank.
• Wipe up spilled fuel and allow fumes to clear
before starting engine.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Oil
This unit is supplied from the factory with the engine
crankcase filled with a high quality SAE 10W/30 oil.
This oil should be acceptable for most typical ambient
temperatures. Consult the engine operation manual
for specific engine manufacturer’s recommendations.
Upon receipt of the welder, check the engine dipstick
to be sure the oil is at the “full” mark. DO NOT overfill.
Fuel
Fill the fuel tank with the grade of fuel recommended
in the Engine Operator’s manual. Make sure fuel
valve on the sediment bowl is in the open position.
Battery Charging
WARNING
GASES FROM BATTERY can explode.
• Keep sparks, flame and cigarettes
away.
BATTERY ACID can burn eyes and
skin.
• Wear gloves and eye protection and
be careful when boosting, charging or
working near battery.
To prevent EXPLOSION when:
a) Installing a new battery - disconnect the
negative cable from the old battery first and
connect the negative cable to the new battery
last.
b) Connecting a battery charger - remove the
battery from the welder by disconnecting the
negative cable first, then the positive cable and
battery clamp. When reinstalling, connect the
negative cable last.
c) Using a booster - connect the positive lead to
the battery first, then connect the negative lead to
the ground lead on the base.
To prevent ELECTRICAL DAMAGE when:
a) Installing a new battery.
b) Using a booster.
Use correct polarity - Negative Ground.
To prevent BATTERY DISCHARGE, if you have an
ignition switch, turn it off when engine is not
running.
Cooling System
The radiator has been filled at the factory with a 50-50
mixture of ethylene glycol antifreeze and water.
Check the radiator level and add a 50-50 solution as
needed (see engine manual or antifreeze container for
alternate antifreeze recommendations).
CLASSIC III AND IIID
• To prevent BATTERY BUCKLING, tighten nuts on
battery clamp until snug.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The Classic III & Classic III D are each equipped with
a wet charged battery. The charging current is automatically regulated when the battery is low (after starting the engine) to a trickle current when the battery is
fully charged.
When replacing, jumping or otherwise connecting the
battery to the battery cables, the proper polarity must
be observed. This system is NEGATIVE GROUND.
Page 13

B-1
OPERATION
B-1
ENGINE OPERATION
WARNING
Do not attempt to use this equipment until you
have thoroughly read the engine manufacturer’s
manual supplied with your welder. It includes
important safety precautions, detailed engine
starting, operating and maintenance instructions,
and parts lists.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and
ground
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
ENGINE EXHAUST can kill.
• Use in open, well ventilated areas or
vent exhaust outside.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Do not operate with doors open or
guards off.
• Stop engine before servicing.
• Keep away from moving parts.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
See additional warning information at the
front of this operator’s manual.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Starting the Classic III D Continental TMD27
Diesel Engine
1. Turn the Idler control switch to “High”.
2. Turn the Ignition control switch to “On”.
3. Push the reset button.
4. Press the Glow Plug button for 10 to 20 seconds.
5. Press the Start button. Release both buttons
when engine starts.
6. If engine fails to start in 60 seconds, the reset
button will pop out. Wait 30 seconds, reset
and repeat the above procedure.
7. Allow engine to run at high idle speed for several
minutes to warm the engine. Cold engines tend
to run at a speed too slow to supply the voltage
required for proper idler operation.
Note: Extreme cold weather starting may require
longer glow plug operation.
WARNING
Under NO
starting fluids be used in conjunction with the
glow plugs. This may cause an explosion or fire!
------------------------------------------------------------------------
conditions should ether or other
Operate the welder with the doors closed. Leaving
the doors open changes the designed air flow and can
cause overheating.
Starting the Classic III Continental TM27
Gasoline Engine
1. Turn the Idler control switch to “High”.
2. Turn the Ignition control switch to “On”.
3. Pull out the choke control.
4. Press the Start button.
5. If the engine fails to start in 60 seconds, wait 30
seconds before repeating the above procedure.
6. Allow engine to run at high idle speed for several
minutes to warm the engine. Cold engines tend
to run at a speed too slow to supply the voltage
required for proper idler operation.
7. As engine warms, slowly return the choke control
to the in (off) position.
Stopping the Engine
1. Turn the Ignition control switch “Off”
At the end of each day’s welding, refill the fuel tank to
minimize moisture condensation in the tank. Also,
running out of fuel tends to draw dirt into the fuel system.
When hauling the welder between job sites, close the
fuel feed valve beneath the fuel tank. In gasoline
engines, failure to turn fuel off when traveling can
cause carburetor flooding and difficult starting at the
new job site.
In diesel engines, if the fuel supply is cut off or runs
out while the fuel pump is operating, air may be
entrapped in the fuel distribution system. If this
happens, bleeding of the fuel system may be
necessary. See the Engine Operating Manual.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 14

B-2
WELDER OPERATION
OPERATION
Range Selector” to the 190-120 position and then
adjust the “Fine Current Adjustment” for 175 amps.
B-2
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and ground.
FUMES & GASES can be dangerous.
• Keep your head out of the fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to remove
fumes from breathing zone.
WELDING SPARKS can cause fire or
explosion.
• Keep flammable material away.
ARC RAYS can burn.
• Wear eye, ear, and body protection.
Duty Cycle
The NEMA output rating of the Classic III &
Classic III D are each 300 amperes at 32 arc volts on
a 50% duty cycle (consult Specifications in this manual
for alternate ratings). Duty cycle is based on a ten
minute period; thus, the welder can be loaded at rated
output for five minutes out of every ten minute period.
When a forceful “digging” arc is required, usually for
vertical and overhead welding, use a higher “Current
Range Selector” setting and lower open circuit voltage. For example: to obtain 175 amps and a forceful
arc, set the “Current Range Selector” to the 240-160
position and the “Fine Current Adjustment” setting to
get 175 amps.
Some arc instability may be experienced with EXX10
electrodes when trying to operate with long arc techniques at settings at the lower end of the open circuit
voltage range.
CAUTION
DO NOT attempt to set the “Current Range Selector”
between the five points designated on the nameplate.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
These switches have a spring loaded cam which
almost eliminates the possibility of setting this switch
between the designated points.
Idler Operation
Start the engine with the “Idler” switch in the “High”
position. Allow it to run at high idle speed for several
minutes to warm the engine. See Specifications for
operating speeds.
Control of Welding Current
CAUTION
DO NOT TURN THE “CURRENT RANGE SELECTOR” WHILE WELDING because the current may
arc between the contacts and damage the switch.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The “Current Range Selector” provides five overlapping current ranges. The “Fine Current Adjustment”
adjusts the current from minimum to maximum within
each range. Open circuit voltage is also controlled by
the “Fine Current Adjustment” permitting control of the
arc characteristics.
A high open circuit voltage setting provides the soft
“buttering” arc with best resistance to pop-outs preferred for most welding. To get this characteristic, set
the “Current Range Selector” to the lowest setting that
still provides the current you need and set the “Fine
Current Adjustment” near maximum. For example: to
obtain 175 amps and a soft arc, set the “Current
The idler is controlled by the “Idler” toggle switch on
the welder control panel. The switch has two positions as follows:
1. In the “High” position, the idler is off, and the
engine high speed is controlled by the governor.
2. In the “Auto” / position, the idler oper-
ates as follows:
a. When welding or drawing power for lights or tools
(approximately 100-150 watts minimum) from the
receptacles, the engine operates at full speed.
b. When welding ceases or the power load is turned
off, a preset time delay of about 15 seconds
starts. This time delay cannot be adjusted.
c. If the welding or power load is not re-started
before the end of the time delay, the idler reduces
the engine to low idle speed.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 15

B-3
Auxiliary Power
The AC auxiliary power, supplied as a standard, has a
rating of 3.0 kVA of 115/230 VAC (60 hertz).
With the 3.0 kVA, 115/230 VAC auxiliary power, one
115V duplex and one 230V grounding type receptacle
are provided. The circuit is protected with circuit
breakers.
The rating of 3.0 kVA permits a maximum continuous
current of 13 amps to be drawn from the 230 volt
duplex receptacle. Or a total of 26 amps can be
drawn from the 115 volt duplex receptacle. The 115
volt duplex receptacle has a configuration which permits 15 amps to be drawn from either half. The total
combined load of all receptacles is not to exceed 3.0
kVA.
An optional power plug kit is available. When this kit
is specified, the customer is supplied with a plug for
each receptacle.
OPERATION
Carburetor Deicing Kit
A carburetor deicing kit is installed on Classic lll
welders leaving the factory. The purpose of the
Carburetor Deicing Kit is to prevent carburetor icing
when the outside temperature is 60°F/15.5°c or lower.
See Carburetor Deicing Kit Usage Instructions For
Seasonal Change Over on page B4.
To obtain REPLACEMENT PARTS for the Carburetor
Deicing Kit contact WIS-CON TOTAL POWER CORPORATION.
Wis-Con Part# Description
10221023 Complete Carburetor Deicing Kit
10220028 Angled Heat Collector Shield
10060025 2”x18” Flexible Hose (Gates 28095)
X02355 #36 1.56”-2.50” Gear Clamp
XM32067 M10X70 Bolt
XM37004 3/8” Flat Washer
10250021 Notice Decal
LIT10278 Installation Instructions
CARBURETOR DEICING KIT
USAGE INSTRUCTIONS FOR SEASONAL CHANGE OVER
WARNING
B-3
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Keep guards in place.
• Keep away from moving parts.
• Only qualified personnel should
install, use or service this equipment.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The engine MUST
change over of the carburetor deicing kit.
When the AVERAGE AIR INTAKE TEMPERATURE
(Average Ambient) is:
BE COLD before seasonal
Below 60°F / 15.5°C (Winter Season
Configuration)
1. With the engine OFF, remove the negative cable
from the battery.
2. Push the FLEXIBLE HOSE fully onto the HEAT
COLLECTOR SHIELD outlet tube, see Figure 1.
3. Reconnect negative battery cable.
FIGURE 1
E
D
C
A
A. FUEL TANK
B. HEAT COLLECTOR SHIELD
C. FLEXIBLE HOSE
D. GEAR CLAMP
E. AIR FILTER
B
Above 60°F / 15.5°C (Summer Season
Configuration)
1. With the engine OFF, remove the negative cable
from the battery.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not operate with panels open.
• Disconnect NEGATIVE(-) BATTERY
LEAD before servicing.
• Do not touch electrically live parts.
2. Remove the FLEXIBLE HOSE from the HEAT
COLLECTOR SHIELD outlet tube.
3. The FLEXIBLE HOSE is to be positioned per figure 2.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 16

B-4
IMPORTANT: 1/2” clearance between the FLEXIBLE
HOSE and the fuel tank edge is required. Also 2”
clearance between FLEXIBLE HOSE and roof.
4. Reconnect negative battery cable.
OPERATION
FIGURE 2
B-4
A
A. FLEXIBLE HOSE
B. HEAT COLLECTOR SHIELD
C. AIR FILTER
NOTE: On welders received directly from the factory,
the “Deicing” kit is configured for “summer Seasons”
B
C
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 17

C-1
ACCESSORIES
OPTIONAL FEATURES (Field Installed)
C-1
Accessory Set (K703) - Includes electrode and work
cables, headshield, work clamp and electrode holder.
Hi-Freq™(K799) - Provides high frequency plus gas
valve for DC TIG welding.
Linc-Thaw™ (L2964-1) - Includes meter and fuses to
protect welder when thawing frozen water pipes.
WARNING
Pipe Thawing IS
If not done properly, it can result in fire, explosion,
damage to wiring which may make it unsafe, damage to pipes, burning up the welder, or other hazards.
Do not use a welder to thaw pipe before reviewing
Lincoln Bulletin E695.1 (dated October 1987 or later.)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Power Plug Kit (K802C) - A power plug kit for the
auxiliary power receptacles is available. (Provides a
plug for each receptacle.)
Remote Control Kit (K924-4) - Contains switch,
receptacle, remote control rheostat, and 100 ft
(30.5m) cable for adjusting the OCV at the welding
site.
NOT a CSA approved procedure.
Wire Feed Module (K623-1) - Provides constant
voltage (CV) output with improved arc stability for
Innershield welding. Excellent for MIG welding.
Recommended wire feeders are the LN-7, LN-23P
and LN-25. (Factory installed on the K1428-3 and
K1433-2).
Trailer (K768) - Two-wheeled trailer for in-plant and
yard towing at speeds under 10 mph only.
Trailer (K780) - Two-wheeled trailer with brakes,
lights and fenders. (For highway use, consult applicable federal, state and local laws regarding possible
additional requirements.)
Trailer - Two-wheeled trailer with steel, torsion-bar
axle, 54” (137cm) wheel track. Low sway, low centerof-gravity. Sturdy tread plate platform. Choice of 3
hitches. Add on fender & light package. For highway
use, consult applicable federal, state, and local laws
regarding possible additional requirements. Order:
K913-1 Trailer, K913-2 Ball Hitch, K913-3 Lunette
Eye Hitch, K913-4 Clevis Pin Hitch, K913-5
Fender & Light Kit.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 18

D-1
MAINTENANCE
D-1
MAINTENANCE
WARNING
Have qualified personnel do the maintenance
work. Turn the engine off before working inside
the machine. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove safety guards to perform
required maintenance. Remove guards only
when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when working near moving parts.
Do not put your hands near the engine cooling
blower fan. If a problem cannot be corrected by
following the instructions, take the machine to
the nearest Lincoln Field Service Shop.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and
ground
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
--------------------------------------------------------
----------------
ENGINE EXHAUST can kill.
• Use in open, well ventilated areas or
vent exhaust outside.
--------------------------------------------------------
----------------
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Do not operate with doors open or
guards off.
• Stop engine before servicing.
• Keep away from moving parts.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
See additional warning information at
front of this operator’s manual.
-----------------------------------------------------------
General Instructions
1. Blow out the welder and controls with an air hose
at least once every two months. In particularly dirty
locations, this cleaning may be necessary once a
week. Use low pressure air to avoid driving dirt into
the insulation.
2. ”Current Range Selector” contacts should not be
greased. To keep the contacts clean, rotate the current control through its entire range frequently. Good
practice is to turn the handle from maximum to minimum setting twice each morning before starting to
weld.
3. Put a drop of oil on the “Current Range Selector”
shaft at least once every month.
4. When necessary, remove the sediment bowl, if so
equipped, from beneath the fuel tank and clean out
any accumulated dirt and water.
5. Follow the engine service schedule in this manual
and the detailed maintenance and troubleshooting in
the engine manufacturer’s manual.
Cooling System
The Classic III & III D are each equipped with a pressure radiator. Keep the radiator cap tight to prevent
loss of coolant. Clean and flush the cooling system
periodically to prevent clogging the passage and overheating the engine. When antifreeze is needed,
always use the permanent type. Capacity = 9.3 qts.
Bearings
This welder is equipped with a double-shielded ball
bearing having sufficient grease to last indefinitely
under normal service. Where the welder is used constantly or in excessively dirty locations, it may be necessary to add one half ounce of grease per year. A
pad of grease one inch wide, one inch long, and one
inch high weighs approximately one half ounce. Overgreasing is far worse than insufficient greasing.
When greasing the bearings, keep all dirt out of the
area. Wipe the fittings completely clean and use
clean equipment. More bearing failures are caused
by dirt introduced during greasing than from insufficient grease.
Commutator and Brushes
WARNING
Uncovered rotating equipment can be dangerous.
Use care so your hands, hair, clothing or tools do
not catch in the rotating parts. Protect yourself
from particles that may be thrown out by the rotating armature when stoning the commutator.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Shifting of the commutator brushes may result in:
- Change in machine output
- Commutator damage
- Excessive brush wear
Periodically inspect the commutator, slip rings, and
brushes by removing the covers. DO NOT remove or
replace these covers while the machine is running.
Commutators and slip rings require little attention.
However, if they are black or appear uneven, have
them cleaned by an experienced maintenance man
using fine sandpaper or a commutator stone. Never
use emery cloth or paper for this purpose. NOTE: If
the welder is used in dirty or dusty locations, or if the
welder is not used for prolonged periods of time, it
may be necessary to clean the commutator and slip
rings more often.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 19

D-2
MAINTENANCE
D-2
Replace brushes when they wear within 1/4” of the
pigtail. A complete set of replacement brushes should
be kept on hand. Lincoln brushes have a curved face
to fit the commutator. Have an experienced maintenance man seat these brushes by lightly stoning the
commutator as the armature rotates at full speed until
contact is made across the full face of the brushes.
After stoning, blow out the dust with low pressure air.
To seat slip ring brushes, position the brushes in
place. Then slide one end of a piece of fine sandpaper between slip rings and brushes with the coarse
side against the brushes. With slight additional finger
pressure on top of the brushes, pull the sandpaper
around the circumference of the rings - in direction of
rotation only - until brushes seat properly. In addition,
stone slip ring with a fine stone. Brushes must be
seated 100%.
Arcing or excessive exciter brush wear indicates a
possible misaligned shaft. Have an authorized Field
Service Shop check and realign the shaft.
Idler Maintenance
Nameplates
Whenever routine maintenance is performed on this
machine - or at least yearly - inspect all nameplates
and labels for legibility. Replace those which are no
longer clear. Refer to the parts list for the replacement item number.
CAUTION
Before doing electrical work on the idler printed
circuit board, disconnect the battery.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
When installing a new battery or using a jumper battery to start the engine, be sure the battery polarity is
connected properly. The correct polarity is negative
ground. Damage to the engine alternator and the
printed circuit board can result from incorrect connection.
1. The solenoid plunger must work freely and not
bind. Dust the plunger about once a year with
graphite powder.
2. Proper operation of the idler requires good grounding of the printed circuit board, reed switch, and battery.
3. If desired, the welder can be used without automatic idling by setting the “Idler” switch to the “High”
position.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 20

Hours Between Servicing
MAINTENANCE
ENGINE SERVICE
D-3D-3
Daily 50
I Engine Oil (1)
R Engine Oil (1) 7 qts (Including Filter)
R Oil Filter Fram #PH-8A Purolator #PER-1A
I Air Cleaner
C Air Cleaner
C PCV System
I Fan Belt Tension
I Cooling System
250 500
R Air Cleaner Cartridge
C Throttle or Governor Linkage
C or R Spark Plugs (Gap=.032”) (4) Champion #RN12YC
Maintenance Item Type or Capacity
Donaldson #P181050 Nelson #70206N
C Cooling System 9.3 qts
R Fuel Filter (4) Lincoln #S17753 (2)
R Fuel Filter (5) Continental #TMD27F00506
R Fuel Filter (6) Continental #TMD20F00400
(3) I Valve Clearance Intake=0.14”; Exhaust=.018”
I Battery BCI Group 24
I = Inspect C = Clean R = Replace
NOTES:
(1) Consult Engine Operators Manual for oil recommendations.
(2) Or equivalent.
(3) First inspection after 50 hours; every 500 thereafter.
(4) Gasoline engine only.
(5) Diesel engine only. (Welder Code Numbers 10061 and below)
(6) Diesel engine only. (Welder Code Numbers above 10061)
(7) Consult Engine Operators Manual for additional maintenance schedule information.
5-6-94C
S20919-1
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 21

E-1
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
E-1
WARNING
Have qualified personnel do the troubleshooting
work. Turn the engine off before working inside
the machine. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove safety guards to perform
required maintenance. Remove guards only
when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when working near moving parts.
Do not put your hands near the engine cooling
blower fan. If a problem cannot be corrected by
following the instructions, take the machine to
the nearest Lincoln Field Service Shop.
------------------------------------------------------------
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
• Insulate yourself from work and
ground
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
ENGINE EXHAUST can kill.
• Use in open, well ventilated areas or
vent exhaust outside.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Do not operate with doors open or
guards off.
• Stop engine before servicing.
• Keep away from moving parts.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
See additional warning information at the
front of this operator’s manual
------------------------------------------------------------
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 22

E-2
TROUBLESHOOTING
WELDER TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLE CAUSES WHAT TO DO
1. Machine fails to hold a. Rough or dirty commutator. a. Commutator should be turned or
the heat consistently. cleaned.
b. Brushes may be worn down to b. Replace brushes.
limit.
c. Field circuit may have variable c. Check field current with ammeter to
resistance connection or discover varying current. This
intermittent open circuit due to applies to both the main generator
loose connection or broken wire. and exciter.
d. Electrode lead or work lead d. Tighten all connections.
connection may be poor.
e. Wrong grade of brushes may e. Use Lincoln brushes.
have been installed on generator.
f. Field rheostat may be making f. Inspect and clean the rheostat.
poor contact and overheating.
2. Welder starts but fails a. Generator or exciter brushes a. Be sure that all brushes bear on the
to generate current. may be loose or missing. commutator and have proper spring
tension.
E-2
b. Exciter may not be operating. b. Check exciter output voltage with
voltmeter or lamp.
c. Field circuit of generator or c. Check for open circuits in rheostat,
exciter may be open. field leads, and field coils. Check
rectifier bridge.
d. Exciter may have lost excitation. d. Flash fields. (1) Check flashing
diode at 5 o’clock brushholder in
generator.
e. Series field and armature circuit e. Check circuit with ringer or voltmeter.
may be open-circuited.
(1) FLASHING THE FIELDS:
1. Stop the engine welder and remove the cover from the exciter.
2. Turn the “Fine Adjustment Control” (rheostat) to “100” on the dial.
3. Using a 12 volt automotive battery, connect it’s negative terminal to the negative brushholder. The
negative brushholder is the one nearest to the rotor lamination. See the wiring diagram. With the
engine NOT running, touch the positive battery terminal to the positive brushholder. Remove the
battery from the circuit.
4. Replace the exciter cover. Start the welder and the generator voltage should build up.
3. Welding arc is loud and a. Current setting may be too high. a. Check setting and current output with ammeter.
spatters excessively
b. Polarity may be wrong. b. Check polarity. Try reversing polarity or try an
electrode of the opposite polarity.
4. Welding current too great or too a. Exciter output low causing low output a. Check exciter field circuit.
small compared to indication on compared to dial indication.
the dial.
b. Operating speed too low or too high. b. Adjust speed screw on governor for 1800 rpm
operating speed.
5. Arc continuously pops out. a. “Current Range Selector” switch may be a. Set the switch at the center of the current range
set at an intermediate position. desired.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 23

E-3
TROUBLESHOOTING
ELECTRONIC IDLER TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Engine Will Not Return to Idle
in Approximately 15 Seconds
Set Idler Control Switch
to the Auto Position
Check Continuity of Idler
Control Switch
Continuity Good Open
1. Reed Switch in Weld Circuit May be Replace Switch
Closed.
2. Check Continuity of Idler Solenoid Coil
(8.5 - 9.0 ohms) & Leads.
3. Check Ground Connections in Idle Circuit.
4. Replace P.C. Board.
E-3
The Arc is Struck
Reed Switch in Weld Circuit
Defective -- Will Not Close
To Check: Short the Red Lead
on P.C. Board to Welder Frame.
Engine Picks Up Speed
1. Check for Break in
Red Lead and Repair
2. Replace Reed Switch
in Weld Circuit.
Engine Will Not Pick Up Speed When:
The Auxiliary Power is Loaded
Power Load Too Small
Try Load Above 150 Watts
Engine Does Not Pick Up Speed
Check Connections and Continuity of
Current Transformer.
Replace P.C. Board
Engine Does Not Pick
Up Speed
Replace P.C. Board
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 24

E-4
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING -
TROUBLESHOOTING
(TM27 Gasoline Engine Only)
TROUBLE CAUSES WHAT TO DO
1. Engine fails to start a. Out of fuel. a. Fill with gasoline.
b. Clogged fuel system. b. Check all lines to the carburetor.
c. Choke not closing tightly. c. Loosen choke cable screw and slack off choke wire.
d. Ignition switch shorted or open. d. Replace.
e. Moisture or carbon on spark plugs. e. Remove plugs, clean and adjust gap.
(See Engine Service Chart)
f. Defective distributor. f. Replace.
2. Low oil pressure. Light not lit a. Oil too light. a. Drain; refill with proper grade.
when engine is running.
b. Oil too low. b. Fill to “Full” mark on bayonet gage. Do not overfill.
c. Defective oil pressure switch or light. c. Replace.
E-4
3. Lack of power. a. Carbon deposits causing pre-ignition. a. Run engine under full load for a short time.
b. Incorrect timing. b. Time ignition. **
4. Overheating. a. No water in radiator or clogged cooling system. a. Check throughout for dirty or broken hoses, clogged
radiator, or defective water pump.
b. Late timing. b. Time ignition. **
c. Improper valve clearance. c. Adjust valve tappets. (See Engine Service Chart
for settings).
d. Fan belt too loose. d. Adjust for 3/4” to 1” deflection.
5. Knocking. a. Poor grade of gasoline. a. Use at least 87 octane gasoline.
b. Spark advanced too far. b. Retime ignition. **
6. Surging. a. Governor and carburetor toggles and butterfly a. Clean and lubricate. Replace toggles if worn.
valve shaft lever are dirty and sticking.
b. Dirty air filter. b. Remove and clean according to instructions on unit.
c. Governor spring adjusting screw misadjusted. c. Adjust screw enough to eliminate surge. **
d. Governor control rod wrong length. d. Adjust length of control rod so that there is from
1/32” to 1/16” clearance between the stop pin
and the stop when the engine is shut off and the
regulator expanded. **
** See engine manual.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 25

E-5
TROUBLESHOOTING
E-5
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING -
(TM27 Gasoline Engine Only)
TROUBLE CAUSES WHAT TO DO
7. Large decrease in speed. a. Misadjusted governor spring adjusting screw. a. Adjust screw until speed does not drop more than
100 rpm ± 25 rpm when arc is struck. If surge
occurs, eliminate it with the control rod. If high
idle speed changes, readjust the high idle
speed screw. **
8. Unable to strike an arc. a. Idle speed screw is misadjusted. a. Idle speed is set too low so idler fails to operate
when arc is struck. Adjust low idle speed
screw for 1350 ± 25 rpm.
9. Engine runs irregularly. a. Carburetor set too lean. a. Adjust carburetor adjusting screw so engine will
run smoothly at idle speed. **
b. Carburetor Deicing Kit in wrong configuration. b. Carburetor Deicing Kit per instructions on page B3
10. Engine fails to pick up speed a. Check the idler.
when arc is struck.
and B4
.
** See engine manual.
CAUTION
If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the tests/repairs safely, contact your
Local Lincoln Authorized Field Service Facility for technical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed.
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 26

F-1
P10
NEUTRAL BONDED TO FRAME
SHOWN AS VEIWED FROM REAR.
CONTROL PANEL COMPONENTS
ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS
PER E1537
1
+Y
2
-W
U
3
456
N
7
89
10
11
12
J5
ROTOR
610
610
+
B
+
ALTERNATOR
B
W
NEUTRE RACCORDE AU BATI
LEAD COLOR CODE
B-BLACK
G-GREEN
H-BROWN
N-BROWN
&WHITE
SLIP RING
SLIP RINGS
EARLIER UNITS ONLY)
(LEADS APPEAR ON
602B
600B
AC
AC
R
NEAREST
TO IRON
B
W
1
41
3
2
42
600A
-
230 VOLT
RECEPTACLE
115 VOLT
RECEPTACLE
5
4
602A
Y
15A.
FUSE
G
P9
6
J8
RHEOSTAT
Y
SWITCH
SELECTOR
R
DIAGRAMS
GENERATOR
A
ALTERNATOR
AUXILIARY
POWER
WINDINGS
W
CB3
CB4
G
CB1
G
CB2
B
B
G
1
2
3
54
B
WELDER
CR2 REED
CURRENT
+Y
-W
U
N
LEAD BLOCK
R
RELAY
TRANSFORMER
U
U
SEE
P11
*
1
3
5
6
2
7
4
BELOW
*
X
W
Y
B
G
POSITIVE
(CC+) & (CV+ WITH W.F.M.)
(CC-)
N
NEGATIVE
RESISTORS
PLUG FOR REMOTE
CONTROL POTENTIOMETER
Y
X
W
K924-4 REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
REMOTE CONTROL RECEPTACLE & SWITCH
42
602
41
600
R
B
1
3
5
2
4
BELOW
SEE
BELOW
SEE
*
*
PLUG
(P5)
8
9
6
WIRE
#8 LEAD
11
12
10
REMOTE CONTROL
CONNECT
TO CASE
P8
SWITCH FOR LOCAL OR
REMOTE CONTROL SHOWN
FEED
MODULE
NEG.
POS.
F-1
10-31-97L
L9263
POTENTIOMETER BOX
IN LOCAL POSITION.
ON REMOTE CONTROL KIT TO CONNECTOR "J8" ON MACHINE.
WITH MACHINE OFF, REMOVE PLUG "P9" ON MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J8". THEN CONNECT PLUG "P8"
*
609
#2 HEAVY LEAD
608
DAMAGE CAN OCCUR TO THE REMOTE CONTROL SWITCH IF IT IS USED WITHOUT THE "P11"
MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J5". CONNECT PLUG "P11" FROM THE REMOTE CONTROL KIT TO CONNECTOR
UNCONNECTED.
PLUG "P10" (IF ONE IS ON THE MACHINE). FASTEN THE NEW PLUG "P11" NEARBY, LEAVING IT
IF NO WIRE FEED MODULE IS INSTALLED, WITH THE MACHINE OFF, DISCONNECT PLUG "P10" ON THE
IF A WIRE FEED MODULE IS INSTALLED, WITH THE MACHINE OFF, DISPOSE OF THE UNCONNECTED
*
*
#2 HEAVY LEAD
MACHINE. DAMAGE TO THE REMOTE CONTROL AND/OR MACHINE WILL RESULT IF THE RED AND BLACK
LEADS ARE CONNECTED IN THE CLASSIC III.
PLUG INSTALLED OR A WIRE FEED MODULE INSTALLED.
"J5" ON THE MACHINE.
THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE USED ON CLASSIC I MACHINES ONLY AND ARE NOT CONNECTED ON THIS
CAUTION:
MACHINE MUST NOT BE RUNNING
WHEN MAKING THESE CONNECTIONS.
*
Y
W
R
U
P.C.
BOARD
IDLER
U
CLASSIC III - WIRING DIAGRAM
TO PLUGS
DISTRIBUTOR
R
COIL
B
IGNITION
-
+
TO PLUGS
DISTRIBUTOR
W
56A
R
R
OIL
ENGINE
HOUR
IDLER
SOLENOID
N
PRESSURE
LIGHT
-
+
METER
IDLER
SWITCH
IGNITION
SWITCH
G
G
Y
U
OIL PRESSURE
50A
START
R
COIL
B
IGNITION
-
+
ON EARLIER ENGINES
(WITH RESISTOR) SUPPLIED
ALTERNATE IGNITION CIRCUIT
IGNITION
RESISTOR
R
BAT
CARBURETOR
R
FUEL SHUT-OFF
SWITCH
WIRE FEED MODULE (OPTIONAL)
250 AMP
THERMOSTAT
BRUSH HOLDER
REMOTE CONTROL
POTENTIOMETER BOX
ASSEMBLY
INLINE
CONNECTORS
ON MACHINE, REMOVE PLUG "P10" FROM CONNECTOR "J5".
CONNECT PLUG "P5" ON W.F.M. TO CONNECTOR "J5" ON MACHINE.
X
Y
PLUG FOR
REMOTE CONTROL
POTENTIOMETER
W.F.M.
CONTROL
PANEL
OUTPUT TERMINALS
CONNECT TO POS. & NEG.
W
B
NEGATIVE CV
OUTPUT TERMINAL
PANEL
CONNECT TO NEG.
RESISTORS
Y
ALTERNATOR
R
EXC
+
60D
U
A
+
B
CONNECT
TO CASE
B
S
H
MOTOR
STARTING
G
Y
X
W
+
R
SWITCH FOR LOCAL OR
REMOTE CONTROL SHOWN
IN LOCAL POSITION.
K924-1 REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
REMOTE CONTROL RECEPTACLE & SWITCH
42
602
41
600
R
B
1
3
5
6
2
4
P8
BELOW
SEE
BELOW
SEE
*
*
WILL RESULT IF THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE CONNECTED IN THE CLASSIC III.
CONNECTED ON THIS MACHINE. DAMAGE TO THE REMOTE CONTROL AND/OR MACHINE
THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE USED ON CLASSIC I MACHINES ONLY AND ARE NOT
CONNECTOR "J8" ON MACHINE.
PLUG "P8" ON REMOTE CONTROL TO
WITH MACHINE NOT RUNNING, REMOVE PLUG "P9" ON
MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J8". THEN CONNECT
*
GROUND
GROUND
TO BASE
TO ENGINE
CLASSIC III AND IIID
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside
the machine on one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number..
Page 27

F-2
1
+Y
2
-W
3
U
456
N
7
89
10
11
12
J5
P10
ROTOR
’
-
ALTERNATOR
B
W
NEUTRAL BONDED TO FRAME
NEUTRE RACCORDE AU BATI
SHOWN AS VIEWED FROM REAR.
CONTROL PANEL COMPONENTS
SLIP RINGS
EARLIER UNITS ONLY)
(LEADS APPEAR ON
LEAD COLOR CODE
B-BLACK
G-GREEN
PER E1537
N-BROWN
ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS
610
610
+
B
+
SLIP RING
NEAREST
602B
AC
AC
R
TO IRON
B
W
600B
1
41
3
2
42
600A
-
230 VOLT
RECEPTACLE
115 VOLT
RECEPTACLE
B
5
4
602A
Y
15A.
FUSE
G
P9
6
J8
RHEOSTAT
Y
B
SWITCH
SELECTOR
R
B
DIAGRAMS
ALTERNATOR
AUXILIARY
POWER
W
CB3
CB4
G
CB1
CB2
GENERATOR
WINDINGS
G
B
A
B
NEAR FUSE)
(GROUND SCREW
G
1
2
3
54
B
N
LEAD BLOCK
WELDER
CR2 REED
RELAY
TRANSFORMER
CURRENT
U
U
+Y
-W
U
POSITIVE
(CC+) & (CV+ WITH W.F.M.)
R
N
NEGATIVE
(CC-)
SEE
P11
*
1
3
8
5
6
2
7
4
BELOW
*
X
Y
G
RESISTORS
PLUG FOR REMOTE
CONTROL POTENTIOMETER
X
K924-4 REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
R
B
REMOTE CONTROL RECEPTACLE & SWITCH
BELOW
SEE
*
9
11
12
10
W
B
REMOTE CONTROL
POTENTIOMETER BOX
CONNECT
TO CASE
Y
W
42
602
41
600
1
3
5
6
2
4
P8
SWITCH FOR LOCAL OR
REMOTE CONTROL SHOWN
IN LOCAL POSITION.
BELOW
SEE
*
WIRE
#8 LEAD
PLUG
(P5)
POS.
WITH MACHINE OFF, REMOVE PLUG "P9" ON MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J8". THEN CONNECT PLUG "P8"
*
FEED
MODULE
#2 HEAVY LEAD
NEG.
608
F-2
10-31-97L
L9260
DAMAGE CAN OCCUR TO THE REMOTE CONTROL SWITCH IF IT IS USED WITHOUT THE "P11"
MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J5". CONNECT PLUG "P11" FROM THE REMOTE CONTROL KIT TO CONNECTOR
ON REMOTE CONTROL KIT TO CONNECTOR "J8" ON MACHINE.
UNCONNECTED.
PLUG "P10" (IF ONE IS ON THE MACHINE). FASTEN THE NEW PLUG "P11" NEARBY, LEAVING IT
IF NO WIRE FEED MODULE IS INSTALLED, WITH THE MACHINE OFF, DISCONNECT PLUG "P10" ON THE
IF A WIRE FEED MODULE IS INSTALLED, WITH THE MACHINE OFF, DISPOSE OF THE UNCONNECTED
*
*
#2 HEAVY LEAD
609
MACHINE. DAMAGE TO THE REMOTE CONTROL AND/OR MACHINE WILL RESULT IF THE RED AND BLACK
LEADS ARE CONNECTED IN THE CLASSIC III D.
PLUG INSTALLED OR A WIRE FEED MODULE INSTALLED.
"J5" ON THE MACHINE.
THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE USED ON CLASSIC I MACHINES ONLY AND ARE NOT CONNECTED ON THIS
CAUTION:
MACHINE MUST NOT BE RUNNING
WHEN MAKING THESE CONNECTIONS.
*
Y
W
R
U
P.C.
BOARD
IDLER
U
56A
57
IDLER
SOLENOID
PUMP SOLENOID
FUEL LIFT PUMP
56
CLASSIC IIID WIRING DIAGRAM
IDLER
SWITCH
IGNITION
SWITCH
58A
54
58
50C
GLOW PLUGS
ENGINE
PROTECTION
RELAY
HOUR
ENGINE
(SFE-14)
FUSE
METER
GLOW
-
+
START
PLUG
58B
GNONCS B
60A
60
58B
52
50B
53
OIL PRESSURE
B
50A
SWITCH(N.C.)
GAUGE
TEMPERATURE
SWITCH(N.O.)
OIL PRESSURE
51A
MOTOR
STARTING
WIRE FEED MODULE (OPTIONAL)
250 AMP
THERMOSTAT
INLINE
CONNECTORS
ON MACHINE, REMOVE PLUG "P10" FROM CONNECTOR "J5".
CONNECT PLUG "P5" ON W.F.M. TO CONNECTOR "J5" ON MACHINE.
X
Y
PLUG FOR
REMOTE CONTROL
POTENTIOMETER
W.F.M.
CONTROL
PANEL
CONNECT TO POS. & NEG.
OUTPUT TERMINALS
W
B
NEGATIVE CV
OUTPUT TERMINAL
PANEL
CONNECT TO NEG.
59A
ALTERNATOR
59C
EXC
+
60D
51
A
+
ENGINE GAUGES)
(GROUND SCREW NEAR
X
50
GROUND
S
+
B
TO ENGINE
K924-1 REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
GROUND
TO BASE
R
B
REMOTE CONTROL RECEPTACLE & SWITCH
BELOW
SEE
*
CONNECT
TO CASE
G
Y
W
R
SWITCH FOR LOCAL OR
REMOTE CONTROL SHOWN
IN LOCAL POSITION.
42
602
41
600
1
3
5
6
2
4
P8
BELOW
SEE
*
ASSEMBLY
BRUSH HOLDER
REMOTE CONTROL
POTENTIOMETER BOX
WILL RESULT IF THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE CONNECTED IN THE CLASSIC III D.
CONNECTED ON THIS MACHINE. DAMAGE TO THE REMOTE CONTROL AND/OR MACHINE
THE RED AND BLACK LEADS ARE USED ON CLASSIC I MACHINES ONLY AND ARE NOT
CONNECTOR "J8" ON MACHINE.
PLUG "P8" ON REMOTE CONTROL TO
WITH MACHINE NOT RUNNING, REMOVE PLUG "P9" ON
MACHINE FROM CONNECTOR "J8". THEN CONNECT
*
CLASSIC III AND IIID
NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The specific diagram for a particular code is pasted inside
the machine on one of the enclosure panels. If the diagram is illegible, write to the Service Department for a replacement. Give the equipment code number..
Page 28

F-3
61.0
(24.00)
DIAGRAMS
104.0
(40.94)
47.0
(18.50)
52.4
(20.62)
F-3
S10766
2-18-94
K
A
DIMENSION PRINT
CONTROL PANEL
N.A.
94.3
(37.12)
HOLE
1.54 (.56) SKID
O
MOUNTING
10.2
(4.00)
8.26
105.8
32.6
J
(3.25)
H
(41.66)
G
(12.82)
F
D
B
N.B.
E C
F
10.2
(4.00)
H
K
71.0
(27.94)
58.4
(23.00)
22.1
(8.70)
E
D
C
G
OIL AND WATER IN ENGINE,
NOTES:
N.A. CENTER OF GRAVITY WITH
MOUNTING HOLES.
BUT NO FUEL.
O
N.B. 1.54 (.56) TRAILER
CLASSIC III AND IIID
1.54 (.56)
SKID MOUNTING
O
HOLE
J
146.6
(57.70)
METRIC cm (ENGLISH in.)
168.3
(66.25)
WELDER A B
CLASSIC III & IIID
PART NO.
S10766-5
Page 29

NOTES
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 30

NOTES
CLASSIC III AND IIID
Page 31

Now Available...12th Edition
VISA
®
MasterCardMasterCard
®
The Procedure Handbook of Arc Welding
With over 500,000 copies of previous editions published
since 1933, the Procedure Handbook is considered by many to
be the “Bible” of the arc welding industry.
This printing will go fast so don’t delay. Place your
order now using the coupon below.
The hardbound book contains over 750 pages of welding
information, techniques and procedures. Much of this material
has never been included in any other book.
A must for all welders, supervisors, engineers and
designers. Many welding instructors will want to use the book
as a reference for all students by taking advantage of the low
quantity discount prices which include shipping by
4th class parcel post.
$15.00 postage paid U.S.A. Mainland
How To Read Shop Drawings
The book contains the latest information and application
data on the American Welding Society Standard Welding
Symbols. Detailed discussion tells how engineers and
draftsmen use the “short-cut” language of symbols to pass
on assembly and welding information to shop personnel.
New Lessons in Arc Welding
Lessons, simply written, cover manipulatory techniques;
machine and electrode characteristics; related subjects,
such as distortion; and supplemental information on arc
welding applications, speeds and costs. Practice materials,
exercises, questions and answers are suggested for each
lesson.
528 pages, well illustrated, 6” x 9” size, bound in simulated,
gold embossed leather.
$5.00 postage paid U.S.A.
Mainland
Need WeldingTraining?
The Lincoln Electric Company operates the oldest and
most respected Arc Welding School in the United States at its
corporate
dents have graduated. Tuition is low and the training is
“hands on”
For details write: Lincoln Welding School
headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio. Over 100,000 stu-
22801 St. Clair Ave.
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
Practical exercises and examples develop the reader’s
to visualize mechanically drawn objects as they will appear
in their assembled form.
187 pages with more than 100 illustrations. Size 8-1/2” x
Durable, cloth-covered board binding.
$4.50 postage paid U.S.A.
ability
11”
Mainland
and ask for bulletin ED-80 or call 216-383-2259 and ask
for the
Welding School Registrar.
Lincoln Welding School
BASIC COURSE $700.00
5 weeks of fundamentals
There is a 10% discount on all orders of $50.00 or more for shipment at one time to one location.
Orders of $50 or less before discount or orders outside of North America must be prepaid with charge, check or money order in U.S. Funds Only.
Prices include shipment by 4 th Class Book Rate for U.S.A. Mainland Only. Please allow up to 4 weeks for delivery.
UPS Shipping for North America Only. All prepaid orders that request UPS shipment please add:
$5.00 For order value up to $49.99
$10.00 For order value between $50.00 & $99.99
$15.00 For order value between $100.00 & $149.00
For North America invoiced orders over $50.00 & credit card orders, if UPS is requested, it will be invoiced or charged to you at cost.
Outside U.S.A. Mainland order must be prepaid in U.S. Funds. Please add $2.00 per book for surface mail or $15.00 per book for air parcel post shipment.
METHOD OF PAYMENT: (Sorry, No C.O.D. Orders)
CHECK ONE:
Please Invoice (only if order is over $50.00)
Check or Money Order Enclosed, U.S. Funds only
Credit Card - Telephone: _______________________________________________
Account No.
USE THIS FORM TO ORDER:
BOOKS OR FREE INFORMATIVE CATALOGS Telephone: 216-383-2211 or, for fastest service, FAX this completed form to: 216-361-5901.
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| Exp Date |_|_| |_|_|
Order from: BOOK DIVISION, The Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199
Name: _______________________________________________
Address: _______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Signature as it appears on Charge Card:
Month Year
______________________
Lincoln Welding School Titles: Price Code Quantity Cost
(ED-80)
Seminar Information Procedure Handbook “Twelfth Edition” $15.00 PH
(ED-45)
Educational Video Information Incentive Management $5.00 IM
(ED-93)
James F. Lincoln Arc Welding The American Century of John C. Lincoln $5.00 AC
Foundation Book Information Welding Preheat Calculator $3.00 WC-8
(JFLF-515)
New Lessons in Arc Welding $5.00 L
How to Read Shop Drawings $4.50 H
A New Approach to Industrial Economics $5.00 NA
Pipe Welding Charts $4.50 ED-89
SUB TOTAL
Additional Shipping Costs if any
TOTAL COST
Page 32

WARNING
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
● Do not touch electrically live parts or
electrode with skin or wet clothing.
● Insulate yourself from work and
ground.
● No toque las partes o los electrodos
bajo carga con la piel o ropa mojada.
● Aislese del trabajo y de la tierra.
● Keep flammable materials away.
● Mantenga el material combustible
fuera del área de trabajo.
● Wear eye, ear and body protection.
● Protéjase los ojos, los oídos y el
cuerpo.
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
● Ne laissez ni la peau ni des vête-
ments mouillés entrer en contact
avec des pièces sous tension.
● Isolez-vous du travail et de la terre.
● Berühren Sie keine stromführenden
Teile oder Elektroden mit Ihrem
Körper oder feuchter Kleidung!
● Isolieren Sie sich von den
Elektroden und dem Erdboden!
● Não toque partes elétricas e elec-
trodos com a pele ou roupa molhada.
● Isole-se da peça e terra.
● Gardez à l’écart de tout matériel
inflammable.
● Entfernen Sie brennbarres Material!
● Mantenha inflamáveis bem guarda-
dos.
● Protégez vos yeux, vos oreilles et
votre corps.
● Tragen Sie Augen-, Ohren- und Kör-
perschutz!
● Use proteção para a vista, ouvido e
corpo.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE MANUFACTURER’S INSTRUCTION FOR THIS EQUIPMENT AND THE CONSUMABLES TO BE
USED AND FOLLOW YOUR EMPLOYER’S SAFETY PRACTICES.
SE RECOMIENDA LEER Y ENTENDER LAS INSTRUCCIONES DEL FABRICANTE PARA EL USO DE ESTE EQUIPO Y LOS
CONSUMIBLES QUE VA A UTILIZAR, SIGA LAS MEDIDAS DE SEGURIDAD DE SU SUPERVISOR.
LISEZ ET COMPRENEZ LES INSTRUCTIONS DU FABRICANT EN CE QUI REGARDE CET EQUIPMENT ET LES PRODUITS A
ETRE EMPLOYES ET SUIVEZ LES PROCEDURES DE SECURITE DE VOTRE EMPLOYEUR.
LESEN SIE UND BEFOLGEN SIE DIE BETRIEBSANLEITUNG DER ANLAGE UND DEN ELEKTRODENEINSATZ DES HERSTELLERS. DIE UNFALLVERHÜTUNGSVORSCHRIFTEN DES ARBEITGEBERS SIND EBENFALLS ZU BEACHTEN.
Page 33

● Keep your head out of fumes.
● Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing zone.
● Turn power off before servicing.
● Do not operate with panel open or
guards off.
WARNING
● Los humos fuera de la zona de res-
piración.
● Mantenga la cabeza fuera de los
humos. Utilice ventilación o
aspiración para gases.
● Gardez la tête à l’écart des fumées.
● Utilisez un ventilateur ou un aspira-
teur pour ôter les fumées des zones
de travail.
● Vermeiden Sie das Einatmen von
Schweibrauch!
● Sorgen Sie für gute Be- und
Entlüftung des Arbeitsplatzes!
● Mantenha seu rosto da fumaça.
● Use ventilação e exhaustão para
remover fumo da zona respiratória.
● Desconectar el cable de ali-
mentación de poder de la máquina
antes de iniciar cualquier servicio.
● Débranchez le courant avant l’entre-
tien.
● Strom vor Wartungsarbeiten
abschalten! (Netzstrom völlig öffnen; Maschine anhalten!)
● Não opere com as tampas removidas.
● Desligue a corrente antes de fazer
serviço.
● Não toque as partes elétricas nuas.
● No operar con panel abierto o
guardas quitadas.
● N’opérez pas avec les panneaux
ouverts ou avec les dispositifs de
protection enlevés.
● Anlage nie ohne Schutzgehäuse
oder Innenschutzverkleidung in
Betrieb setzen!
● Mantenha-se afastado das partes
moventes.
● Não opere com os paineis abertos
ou guardas removidas.
Spanish
AVISO DE
PRECAUCION
French
ATTENTION
German
WARNUNG
Portuguese
ATENÇÃO
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Arabic
LEIA E COMPREENDA AS INSTRUÇÕES DO FABRICANTE PARA ESTE EQUIPAMENTO E AS PARTES DE USO, E SIGA AS
PRÁTICAS DE SEGURANÇA DO EMPREGADOR.
Page 34

• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
 Loading...
Loading...