Page 1

DC P
OWER
Helios DC System 4000/48
1500, 3000, 4000 & 6000 A
DC Power System
User
Manual
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.0 A
BOUT THIS DOCUMENT
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.1 Purpose of This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 Applicability of This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2.0 I
NTRODUCTION
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
2.1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2.2 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.3 Control and Distribution Cabinets - Typical Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3.0 S
PECIFICATIONS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
3.1 Framework . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1.1 Mechanical Specifications of a Cabinet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1.2 Electrical Specifications of the Cabinets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.2 Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.2.1 Mechanical Specifications of the Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.2.2 Electrical Specifications of the Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.3 Distribution Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.3.1 Fuse Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.3.2 Circuit Breaker Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.4 Externally Mounted Battery Return Busbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.4.1 Mechanical Specifications of the External Battery Return Busbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.4.2 Electrical Specifications of the External Battery Return Busbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.5 Terminating Assemblies (Optional). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.6 MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.6.1 Mechanical Specifications of the MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.6.2 Electrical Specifications of the Power Shelves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7 Rectifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7.1 Helios Rectifier 100/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7.2 Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.7.3 Electrical Specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.7.4 Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.8 Helios Monitor 3000/48 (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.8.1 Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.8.2 Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.9 600 A and 1200 A Battery Disconnect Unit (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.10 AC Junction Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.10.1 Mechanical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.10.2 Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
i
Page 4

3.11 Overall Power System Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.11.1 Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.11.2 Mechanical Specifications of Fully Equipped Power Cabinets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.11.3 Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.11.4 Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.11.5 Floor and Point Loading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.0 O
PERATION
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.2 Conventional Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.2.1 Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.2.2 Rear Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.3 MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4.4 Rectifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.5 AC Junction Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.6 Distribution Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.7 Terminating Assemblies (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.8 Helios Monitor 3000/48 (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.9 600 A and 1200 Battery Disconnect Units (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5.0 M
AINTENANCE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.1.1 Helios Monitor 3000/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.1.2 Controller and Rectifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.2 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.3 Addition / Replacement Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.3.1 Addition or Replacement of a Rectifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.3.2 Replacing a Rectifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
5.3.3 Adding or Replacing a Battery String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5.3.4 Replacement of a Distribution Fuse Block or Circuit Breaker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
5.3.5 Replacing a Cabinet Alarm Lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
6.0 R
7.0 L
EFERENCE DOCUMENTS
IST OF TERMS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
ii
Page 5

FIGURES
Figure 1 Front view of a typical bottom fed 4000 A Helios DC System 4000/48 power system . . . . . . . 2
Figure 2 Front view of a typical 6000 A Helios DC System 4000/48 power system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 3 Typical configurations for Helios DC System 4000/48 control, distribution and
rectifier cabinets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Figure 4 Front view of the Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 5 Front view of the 20 QFF 0-5 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6 Front view of the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (12) ABS 5-30 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 7 Front view of the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (6) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 8 Front view of the (8) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 9 Front view of the (4) RS100P 70-100 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 10 Front view of the (4) CRS200P 150-200 A /
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load shunts) fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 11 Front view of the (4) TPL 225-600 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 12 Front view of the (18) TPS 1-70 A fuse panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 13 Front view of the (24) Plug-In 1-100 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 14 Front view of the (4) 70-250 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 15 Front view of the (2) 400 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 16 Front view of the (1) 600-700 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 17 Top and side views of the external battery return busbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 18 Perspective view of the a terminating assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 19 Front view of the MPS300 power shelf (shown empty) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 20 Front view of the MPA100 power shelf (shown empty) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 21 Front view of the Helios Rectifier 100/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 22 Front view of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 23 Front view of the Helios Monitor 3000/48 (without the mounting brackets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 24 600 A Battery Disconnect Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 25 Front view of the AC junction box (with the front panel open) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 26 Front view of the Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 27 Shunt range selection settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 28 Equalize voltage and duration settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 29 Terminal blocks and connectors layout at the rear of the Conventional Controller. . . . . . . . 32
Figure 30 Wiring diagram and pin assignment of terminal blocks TB1 to TB4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 31 Wiring diagram and pin assignment of terminal blocks TB5 and TB6, and
connectors P1 to P26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 32 AC connections in a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 33 AC connections in the female receptacle for a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or
a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 34 AC connections inside the junction box (top fed shown) for a Helios Rectifier 200E/48. . . . . 43
Figure 35 AC cable routing for the Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 in a top fed system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 36 AC cable routing for the Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 in a bottom fed system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
iii
Page 6

TABLES
Table 1 Rectifier cabinets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 2 Control and distribution cabinets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 3 Auxiliary distribution cabinets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 4 Mechanical specifications of the cabinet (empty) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 5 Mechanical specifications of the Conventional Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 6 Mechanical specifications of the fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 7 Fuse sizes available for the (20) QFF 0-5 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 8 Fuse sizes available for the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (12) ABS 5-30 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 9 Fuse sizes available for the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (6) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 10 Fuse sizes available for the (8) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 11 Fuse sizes available for the (4) RS100P 70-100 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 12 Fuse sizes available for the (4) CRS200P 150-200 A/
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load shunts) fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 13 Fuse sizes available for the (4) TPL 225-600 A fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 14 Fuse sizes available for the (18) TPS 1-70 A fuse panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 15 Electrical specifications of the fuse panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 16 Mechanical specifications of the circuit breaker panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 17 Plug-in circuit breakers available for the (24) Plug-In 1-100 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . 14
Table 18 Circuit breaker sizes available for the (4) 70-250 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 19 Circuit breaker kits available for the (2) 400 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 20 Circuit breaker kits available for the (1) 600-700 A circuit breaker panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 21 Electrical specifications of the circuit breaker panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 22 Mechanical specifications of a single lamination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 23 Mechanical specifications of the MPS300 and MPA100 power shelves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 24 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 25 Electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 26 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 27 Electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 28 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Monitor 3000/48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 29 Mechanical specifications of the AC junction box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 30 Mechanical specifications of fully equipped power cabinets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 31 Floor and point loading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 32 Visual indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 33 Transmitted alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 34 Potentiometers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 35 Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 36 DIP switch modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 37 Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 38 Test points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 39 Fault diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
iv
Page 7

1.0 A
BOUT THIS DOCUMENT
1.1 Purpose of This Document
This document provides all the necessary information to operate and maintain a Helios DC Sys-
tem 4000/48 power system.
The installation procedures for the Helios DC System 4000/48 power system are covered in instal-
lation manual SL-60034.
1.2 Applicability of This Document
This document applies to Helios DC System 4000/48 power systems having any configuration of
equipment.
About This Document 1
Page 8
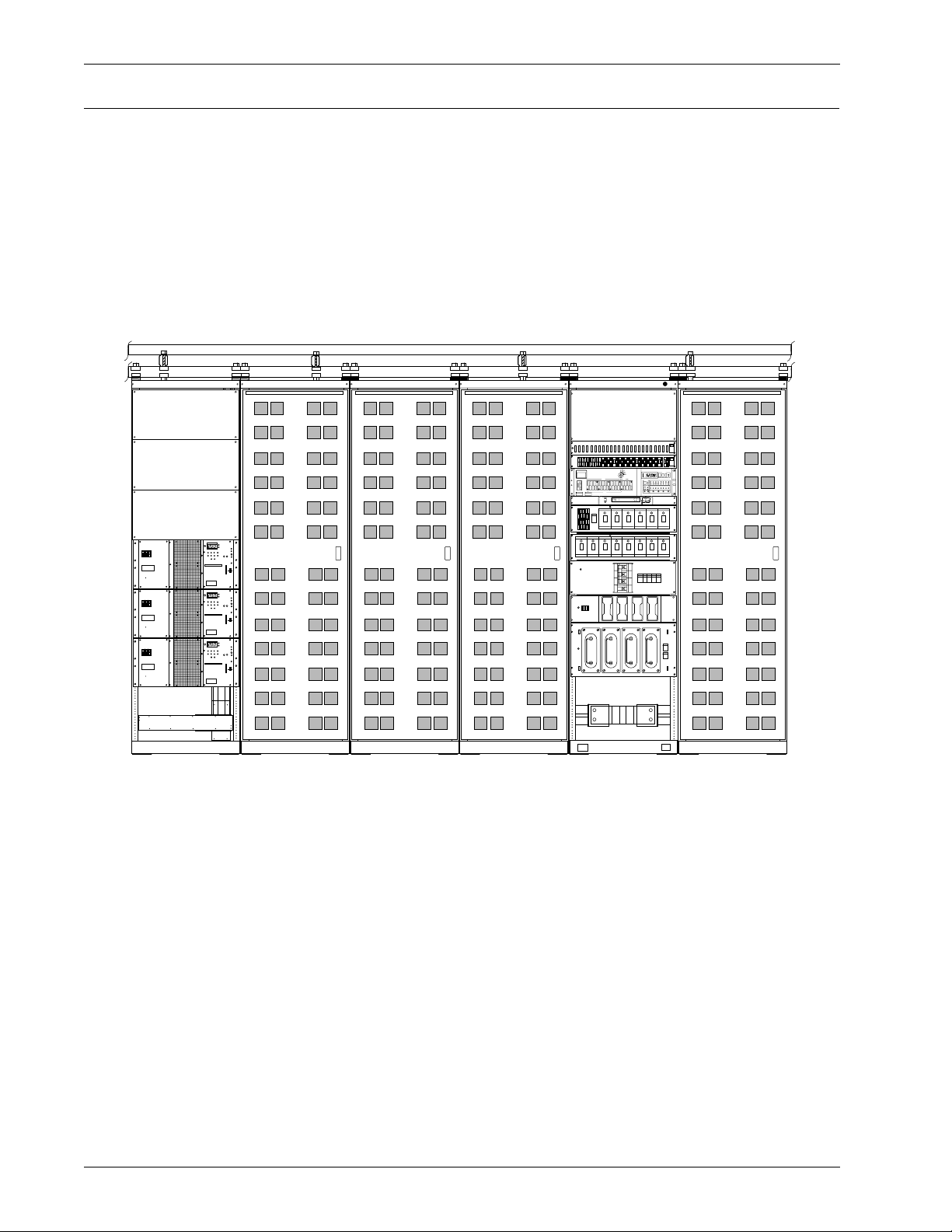
2.0 I
NTRODUCTION
2.1 Description
The Helios DC System 4000/48 is a positive ground, -48 V DC nominal power system consisting of
one control and distribution cabinet and one or more rectifier cabinets. It is available in capacities
of 1500, 3000, 4000 and 6000 A. Auxiliary distribution cabinets can be added as required for additional distribution. Remote monitoring, temperature compensation and battery disconnect
options are also available. The 1500, 3000 and 4000 A versions use internal -48 V bussing and
external BR+ bussing, while the 6000 A version uses overhead bussing.
bottom fed 4000 A system, while
Figure 1 Front view of a typical bottom fed 4000 A Helios DC System 4000/48 power system
Figure 2
shows a typical 6000 A system.
Figure 1
shows a typical
1200 A rectifier cabinets
Main cabinet
Aux dist. cabinet
2 Introduction
Page 9
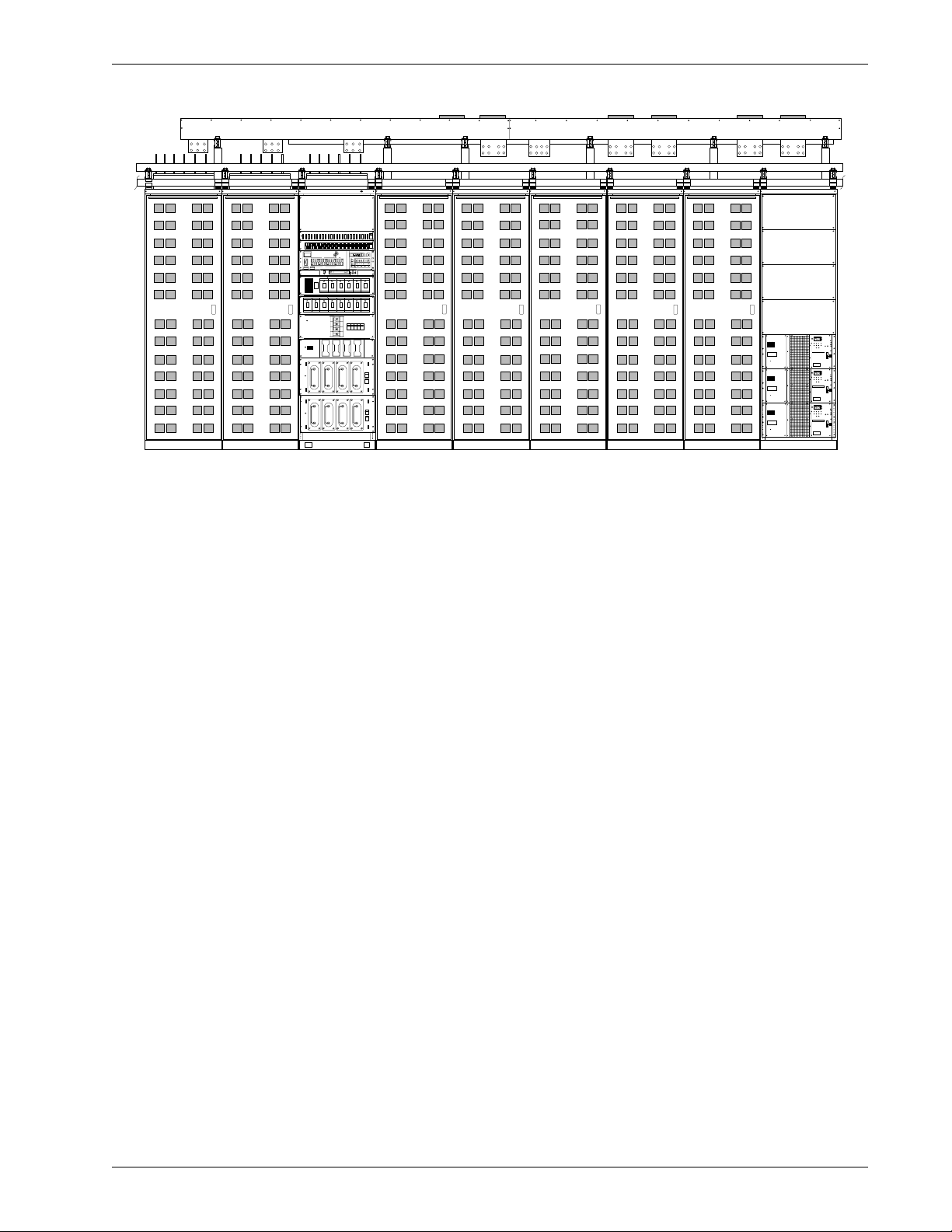
Figure 2 Front view of a typical 6000 A Helios DC System 4000/48 power system
Aux dist. cabinets Main cabinet
Cables are used for inter-cabinet connections (1500, 3000 and 6000 A systems) or connections to
the overhead busbars (6000 A system) for ease of expansion on live systems. In a 1500, 3000 or
4000 A systems, the power system battery return (BR) busbar is mounted externally from the cab-
inet to facilitate the connections of the battery return cables. In a 6000 A system, a separate BR
busbar dedicated to the battery returns for the loads is mounted externally from the overhead
busbar duct to facilitate the connections of the load battery return cables.
The Helios DC System 4000/48 provides a variety of monitoring and alarm features, such as high/
low float and high/low voltage alarm, high voltage shutdown, fuse and breaker alarm and rectifier
failure alarms.
The Helios DC System 4000/48 uses Helios Rectifiers 200I/48, Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 or Helios
Rectifiers 100/48 connected in parallel as building blocks to reach the maximum capacities. The
Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 operate from a 380 V to 415 V three phase, 50 or 60 Hz AC source. The
Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 operate from a 480 V three phase, 50 or 60 Hz AC source. The Helios
Rectifiers 100/operate from a 208 V to 240 V single phase, 50 or 60 Hz AC source.
The 1200 A rectifier cabinet accepts up to six Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 or 200E/48, while the 1000
A rectifier cabinet accepts up to 10 Helios Rectifiers 100/48.
The control and distribution cabinet and the auxiliary distribution cabinets are available with
distribution busbar risers of 2000 A or 3000 A capacity.
The cabinets are seismic qualified to zone 4 (Bellcore) when anchored to a concrete floor whose
compressive strength is at least 2.11 kg/mm
The cabinets are seismic qualified to zone 2 without the seismic kit.
2
(3000 psi) and when equipped with a seismic kit.
1200 A rectifier cabinets
The cabinets are equipped with a ventilated, lockable door, a ventilated top cover and two rear
ventilated panels.
In many applications, such as with DMS, a consistent single-point ground (SPG) topology must be
maintained for all associated equipment. The Helios DC System 4000/48 complies with this
requirements for single-point grounding (the isolation kit is required).
2.2 Applications
The Helios DC System 4000/48 is designed to operate with DMS systems or any other telecommu-
nication systems whose input is nominal -48 V DC and whose current requirements do not exceed
6000 A capacity.
Introduction 3
Page 10
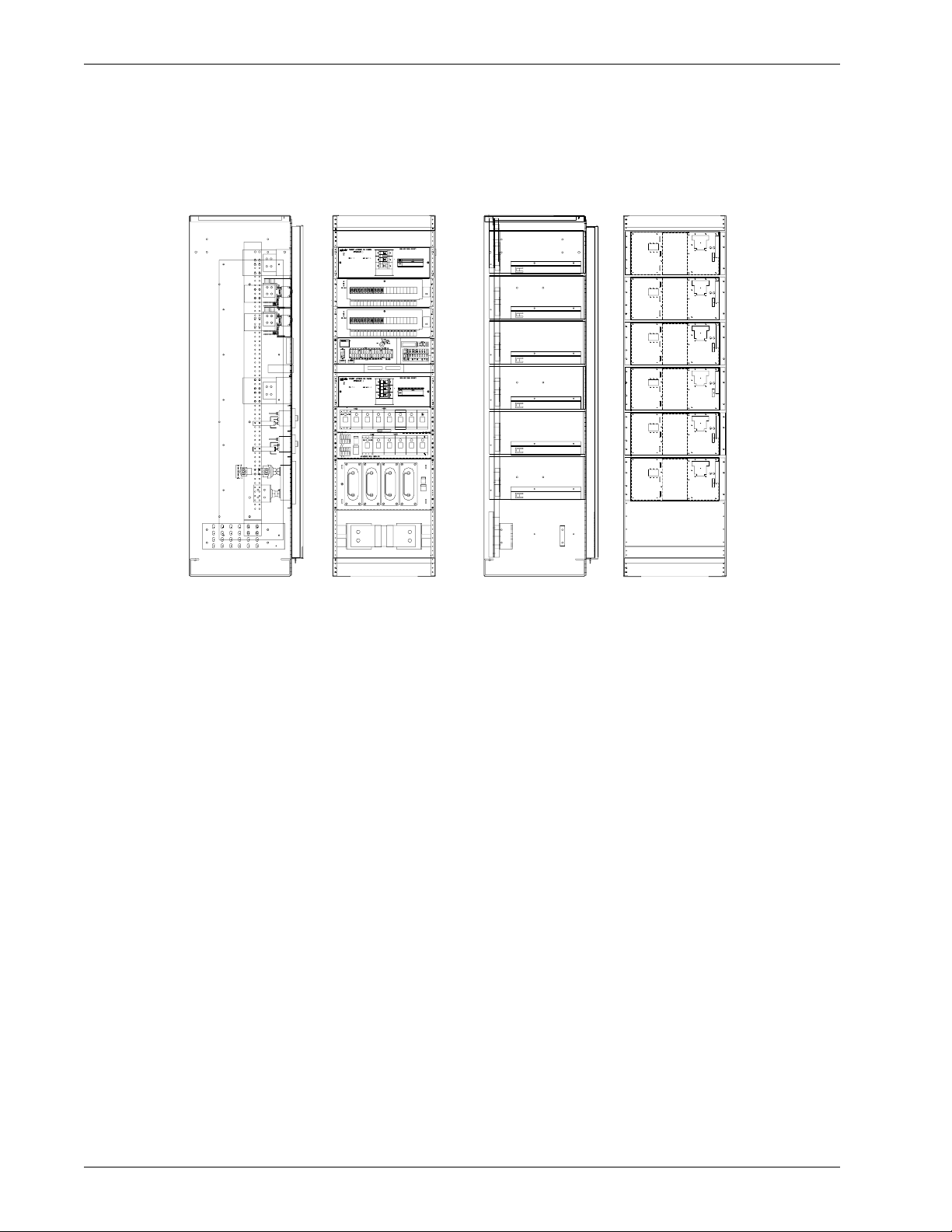
2.3 Control and Distribution Cabinets - Typical Configurations
Figure 3
DC System 4000/48 (bottom cabled cabinets are illustrated - top cabled versions are available).
Figure 3 Typical configurations for Helios DC System 4000/48 control, distribution and rectifier
shows the front and side views of typical rectifier and distribution cabinets for a Helios
cabinets
Control and Distribution cabinet 1200A Rectifier cabinet
4 Introduction
Page 11
Cabinets are available in a variety of configurations as listed in the following tables. Note that for
a 6000 A system, the cabling is always at the top.
Table 1 Rectifier cabinets
Rectifier
Cabinet Capacity
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200I 6 Top
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200I 6 Bottom
1000 A Helios Rectifier 100/48 10 Top or bottom
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200E 6 Top
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200E 6 Bottom
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200E 6 Top
1200 A Helios Rectifier 200E 6 Bottom
Cabled top or bottomType Qty
Table 2 Control and distribution cabinets
Nominal cabinet capacity Shunt capacity Riser busbar capacity Cabled top or bottom
1500 A 2500 A 2000 A Top
3000 A 4000 A 3000 A Top
4000 A 5000 A 3000 A Top
1500 A 2500 A 2000 A Bottom
3000 A 4000 A 3000 A Bottom
4000 A 5000 A 3000 A Bottom
For a 6000 A system, the charge busbars and the shunt are mounted externally from the control and distribution cabinet.
Table 3 Auxiliary distribution cabinets
Nominal cabinet capacity Top busbar capacity Riser busbar capacity Cabled top or bottom
2000 A 3000 A 2000 A Top
2000 A 3000 A 2000 A Bottom
3000 A 4000 A 3000 A Top
3000 A 4000 A 3000 A Bottom
Introduction 5
Page 12
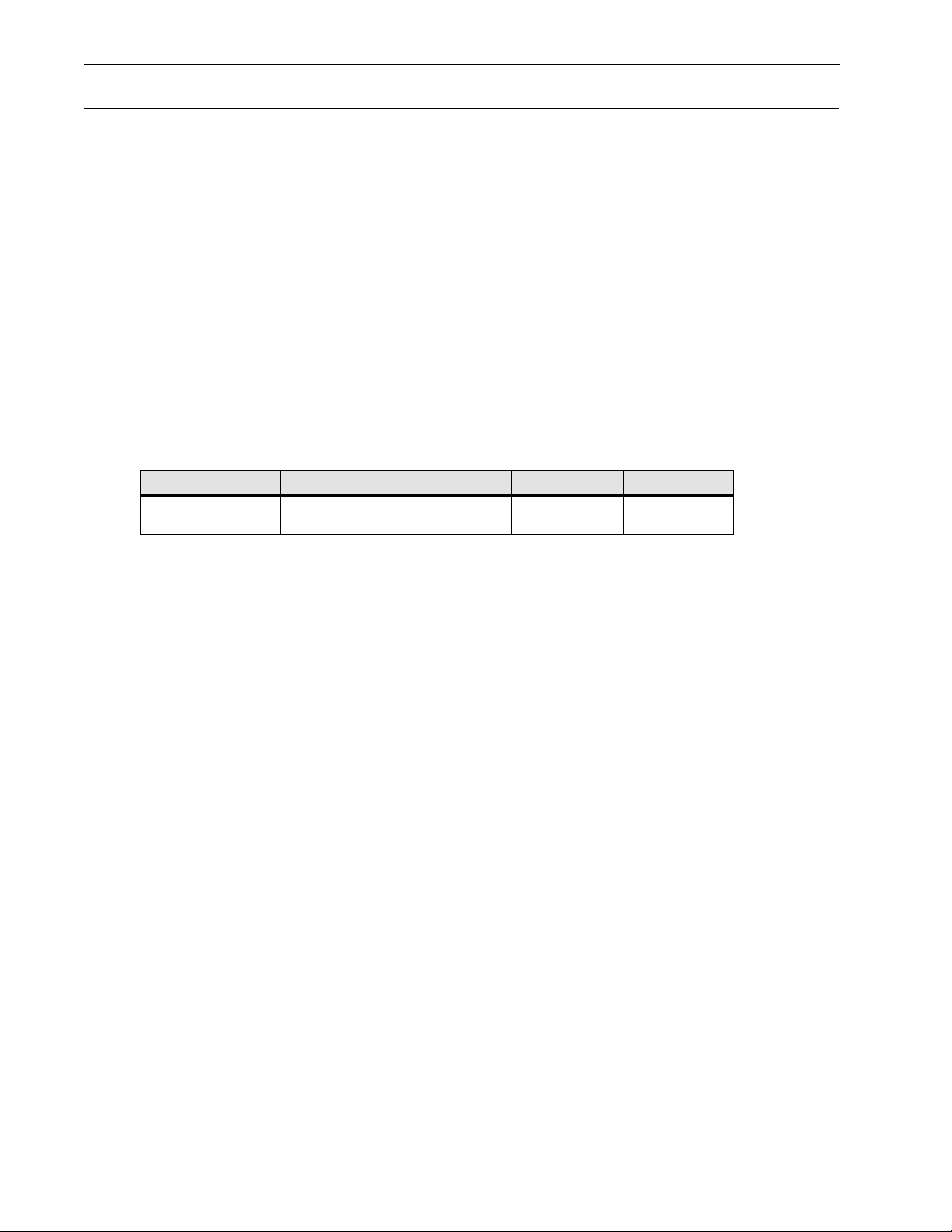
3.0 S
PECIFICATIONS
3.1 Framework
The Helios DC System 4000/48 uses cabinet type frameworks. The same cabinet design is used for
the main control and distribution cabinet, the auxiliary distribution cabinets and the rectifier cabinets. The cabinet is always equipped with a front door and door frame (lockable, equipped with
ground straps, and easily removable for installation or maintenance access), a ventilated top
cover made of non-flammable plastic, and two ventilated rear cover panels (equipped with ground
strap and easily removable for installation and maintenance access). Bussing and equipment
(controller, rectifiers, distribution panels, etc.) are added as required, depending on the use of the
cabinet. Seismic bracing is also available as options.
When using the Cable Trough, overhead cabling cannot enter from the front or rear of the system.
It must be confined to the system foot print and enter at the ends of the lineup.
The cabinets may be either top or bottom cabled as determined by the location of the bussing.
3.1.1 Mechanical Specifications of a Cabinet
The mechanical specifications of an empty cabinet are listed in
Table 4 Mechanical specifications of the cabinet (empty)
Framework type Height Depth Width Weight
Cabinet 2134 mm
Refer to
Figure 3
(84.0 in.)
for typical views of cabinets.
600 mm
(23.6 in.)
3.1.2 Electrical Specifications of the Cabinets
The electrical specifications of equipped cabinets are as follows:
• The main control and distribution cabinet for a 1500 A system has a 2000 A busbar riser and
a common equipment panel e/w one 1500 A CHG and DISCH busbar and a 2500 A system
shunt.
• The main control and distribution cabinet for a 3000A system has a 3000 A busbar riser and a
common equipment panel e/w two 1500 A CHG and DISCH busbars and a 4000 A system
shunt.
• The main control and distribution cabinet for a 4000A system has a 3000 A busbar riser and a
common equipment panel e/w three 1500 A CHG and DISCH busbars and a 5000 A system
shunt.
• A 6000 A system has a 3000 A busbar riser in the main control and distribution cabinet (the
CHG and DISCH busbar and the shunt are external).
• The auxiliary distribution cabinet is available with a 2000 or 3000 A busbar riser.
• A 1200 A rectifier cabinet has 1500 A busbar risers for the DC output of the rectifiers.
600 mm
(23.6 in.)
Table 4.
114 kg
(251 lb)
6 Specifications
Page 13
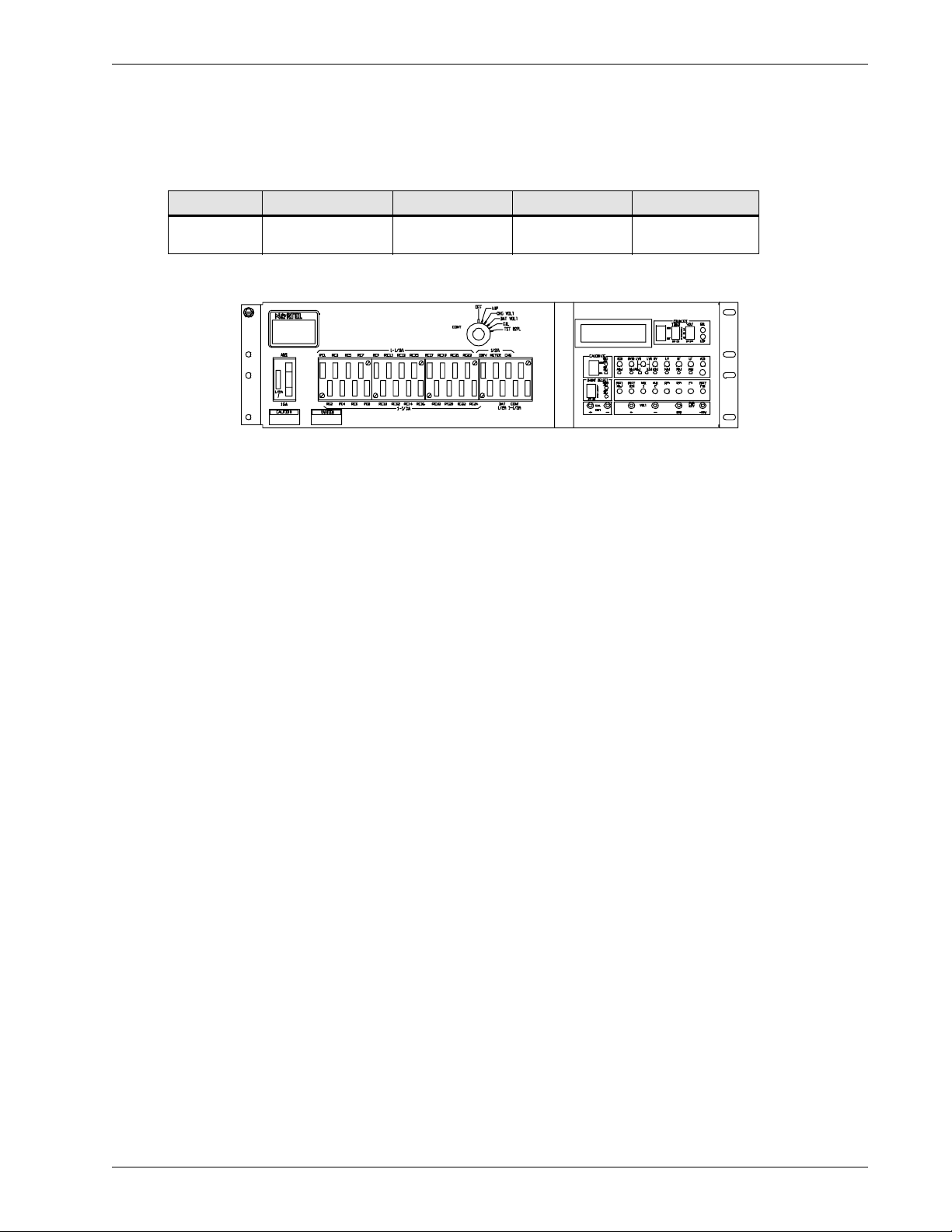
3.2 Conventional Controller
3.2.1 Mechanical Specifications of the Conventional Controller
The mechanical specifications of the Conventional Controller are listed in
Table 5 Mechanical specifications of the Conventional Controller
Figure Height Depth Width Weight
Figure 4
152 mm
(6.0 in.)
76 mm
(3.0 in.)
584 mm
(23 in.)
Figure 4 Front view of the Conventional Controller
3.2.2 Electrical Specifications of the Conventional Controller
The operating voltage is -48 V DC. Refer to the
listed in
6.0 - Reference Documents
for a detailed list of specifications, operating parameters
and features of the Conventional Controller.
4.0 - Operation
Table 5.
4.5 kg
(10 lb)
and the appropriate user manual
Specifications 7
Page 14
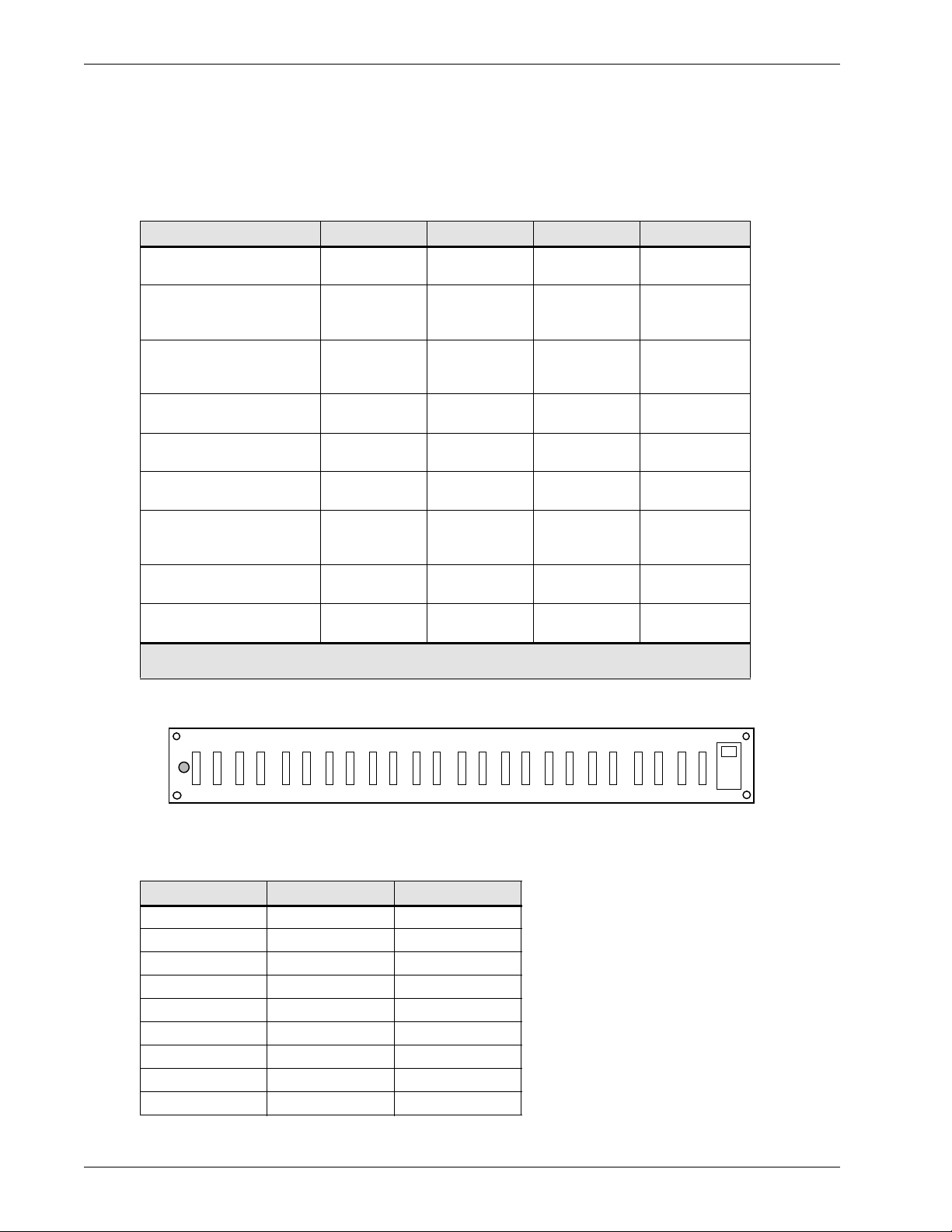
3.3 Distribution Panels
3.3.1 Fuse Panels
Mechanical specifications of the fuse panels
The mechanical specifications of the fuse panels are listed in
Table 6
below.
Table 6 Mechanical specifications of the fuse panels
Panel description Figure Height Width Weight
(20) QFF 0-5 A
60 A max
(16) QFF 0-5 A &
(12) ABS 5-30 A
300 A max
(16) QFF 0-5 A &
(6) TPN 5-30 A
250 A max
(8) TPN 5-30 A
250 A max
(4) RS100P 70-100 A
300 A max
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A
600 A max
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A
(w/load shunts)
600 A max
(4) TPL 225-600 A
1600 A max
(18) TPS 1-70 A
600 A max
An alarm circuit pack with an alarm indication LED is standard on all panels
Note 1:
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load shunts) is equipped with four shunts.
Note 2:
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
Figure 9
Figure 10
Figure 10
Figure 11
Figure 12
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
152.4 mm
(6.0 in.)
152.4 mm
(6.0 in.)
152.4 mm
(6.0 in.)
228.6 mm
(9.0 in.)
228.6 mm
(9.0 in.)
304.8 mm
(12.0 in.)
178 mm
(7.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
3 kg
(6.6 lb)
5 kg
(11.0 lb)
7 kg
(15.4 lb)
7 kg
(15.4 lb)
8 kg
(17.8 lb)
22 kg
(48.4 lb)
24 kg
(52.9 lb)
32 kg
(70.4 lb)
35 kg
(77.0 lb)
Figure 5 Front view of the 20 QFF 0-5 A fuse panels
FA
The DC output connections are wire wrap or solder.
Table 7 Fuse sizes available for the (20) QFF 0-5 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
QFF1A 1.333 A0205202
QFF1B 2 A0205203
QFF1C 3 A0205204
QFF1D 5 A0205205
QFF1E 0.18 A0205206
QFF1F 0.25 A0205207
QFF1G 0.5 A0205208
QFF1H 0.75 A0205209
QFF3A DUMMY A0205210
8 Specifications
Page 15
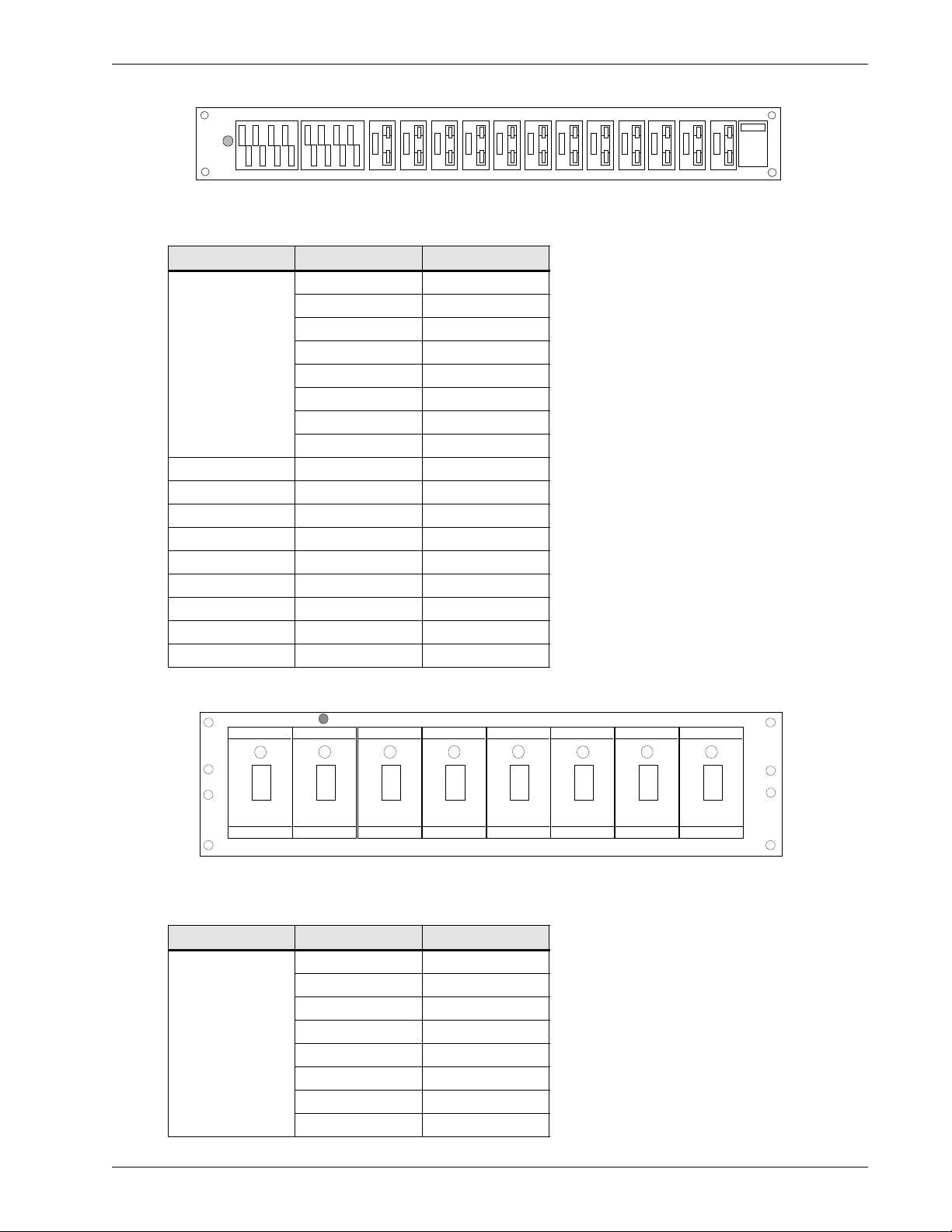
Figure 6 Front view of the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (12) ABS 5-30 A fuse panels
FA
-48 V
The DC output connections are No. 8-32 studs equipped with two hex nuts.
Table 8 Fuse sizes available for the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (12) ABS 5-30 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
5 A0327000
8 A0111415
10 A0315462
4AB (ABS)
QFF1A 1.333 A0205202
QFF1B 2 A0205203
QFF1C 3 A0205204
QFF1D 5 A0205205
QFF1E 0.18 A0205206
QFF1F 0.25 A0205207
QFF1G 0.5 A0205208
QFF1H 0.75 A0205209
QFF3A DUMMY A0205210
12 A0267003
15 A0344157
20 A0314873
25 A0243206
30 A0328460
Figure 7 Front view of the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (6) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels
FA
ALM 1/2 A
-48 V
The DC output connections are 0.250-20 studs equipped with two hex nuts.
Table 9 Fuse sizes available for the (16) QFF 0-5 A & (6) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
1 A0380108
3 A0380109
6 A0380111
DC power (TPN)
10 A0380112
15 A0380113
20 A0380147
25 A0380148
30 A0380149
Specifications 9
Page 16
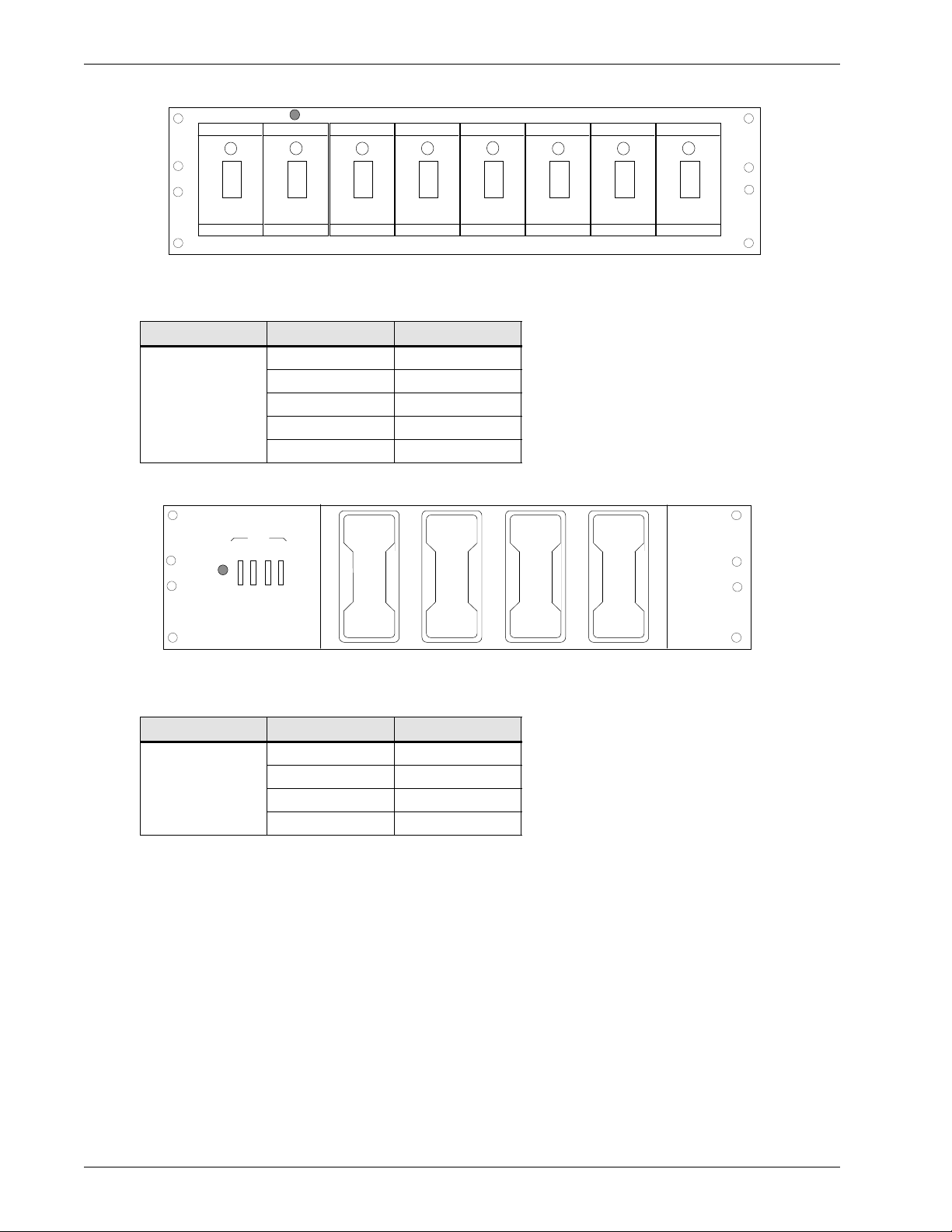
Figure 8 Front view of the (8) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels
FA
ALM 1/2 A
-48 V
The DC output connections are 0.250-20 studs equipped with two hex nuts.
Table 10 Fuse sizes available for the (8) TPN 5-30 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
35 A0380150
40 A0380151
DC power (TPN)
45 A0380152
50 A0380114
60 A0380115
Figure 9 Front view of the (4) RS100P 70-100 A fuse panels
-48 V
FA
ALM
(1) (2) (3) (4)
(1)
(2) (3) (4)
The DC output connections are 0.375-16 studs equipped with two hex nuts.
Table 11 Fuse sizes available for the (4) RS100P 70-100 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
70 A0722046
HRC1-K
80 A0722045
90 A0722044
100 A0722049
10 Specifications
Page 17
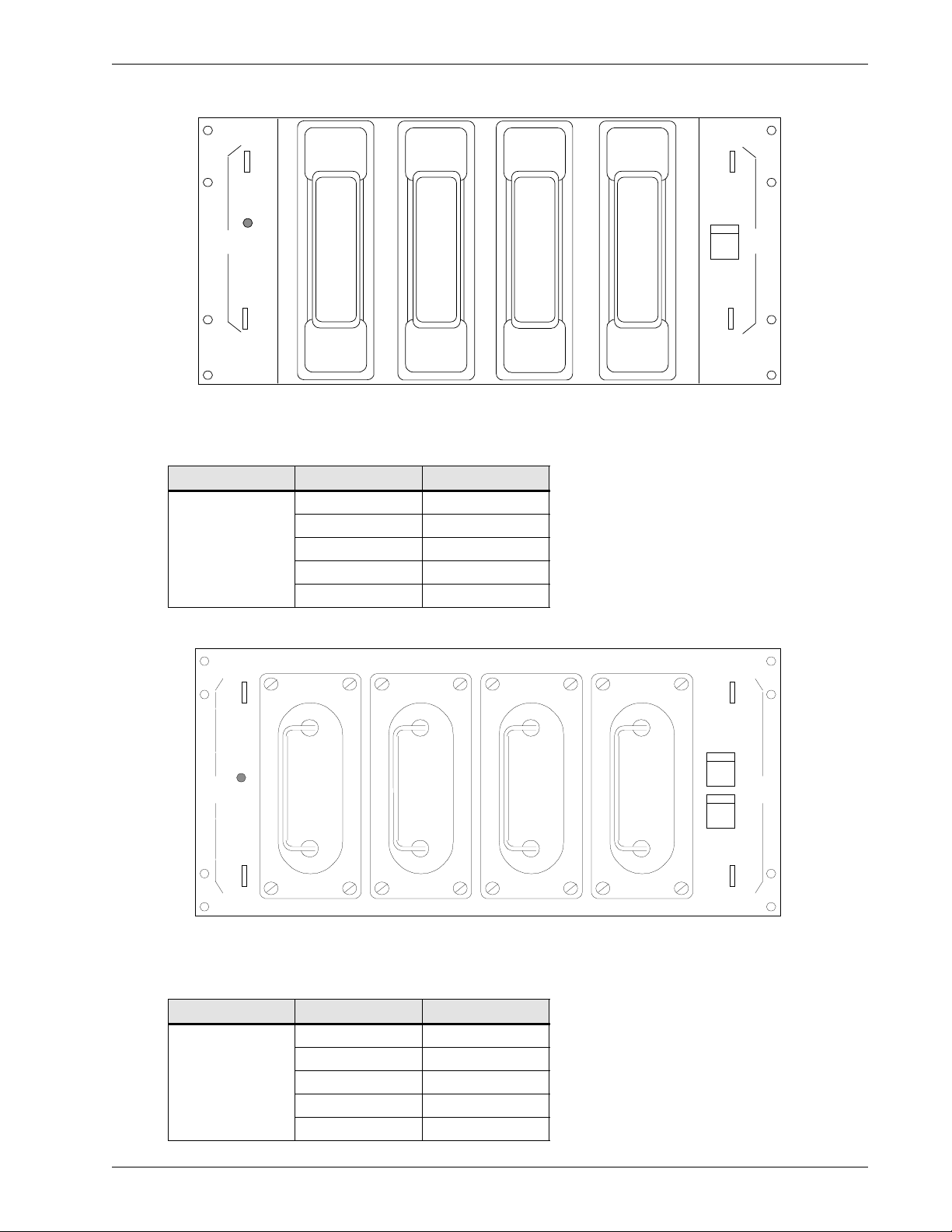
Figure 10 Front view of the (4) CRS200P 150-200 A / (4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load shunts) fuse panels
ALM
FA
(1)
(2)
(2)
(3)
(4)(1)
(3)
ALM
(4)
The DC output connections are 0.50-13 studs equipped with two hex nuts.
Table 12 Fuse sizes available for the (4) CRS200P 150-200 A/(4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load
shunts) fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
110 A0329697
125 A0329696
HRC1-J
150 A0722041
175 A0722038
200 A0614832
Figure 11 Front view of the (4) TPL 225-600 A fuse panels
-48 V
(2)
ALM
(1)
(2)
(1)
FA
The DC output connections are busbar angles that can accept 535MCM or 750MCM cables, or the
metric equivalent. The lugs must be for two 1/2” dia. bolts at 1-3/4” c-c.
Table 13 Fuse sizes available for the (4) TPL 225-600 A fuse panels
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
225 A0380138
300 A0380140
DC power (TPL)
400 A0380141
500 A0380142
600 A0380143
(3)
(4)
(3)
ALM
(4)
Specifications 11
Page 18

Figure 12 Front view of the (18) TPS 1-70 A fuse panel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 UNIT
FA
FUSE PANEL NT6C 21XX
MAX FUSE 70A
AMPS
LOAD
600 A MAX PANEL CAPACITY
Can accept maximum 1/0 AWG cables and requires one-hole lugs for 1/4” diameter studs.
Table 14 Fuse sizes available for the (18) TPS 1-70 A fuse panel
Fuse type Current (A) CPC
1 A0601322
3 A0601323
5 A0601325
6 A0601326
10 A0601327
DC power (TPS)
15 A0601328
25 A0601330
30 A0601331
40 A0601332
50 A0601333
60 A0601334
70 A0601335
12 Specifications
Page 19

Electrical specifications of the fuse panels
The electrical specifications of the fuse panels are described in
Table 15 Electrical specifications of the fuse panels
Panel number Figure
(20) QFF 0-5 A
60 A max
(16) QFF 0-5 A &
(12) ABS 5-30 A
300 A max
(16) QFF 0-5 A &
(6) TPN 5-30 A
250 A max
(8) TPN 5-30 A
250 A max
(4) RS100P 70-100 A
300 A max
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A
600 A max
(4) CRS200P 150-200 A (w/load shunts)
600 A max
(4) TPL 225-600 A
1600 A max
(18) TPS 1-70 A
600 A max
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
Figure 9
Figure 10
Figure 11
Figure 12
Quantity Capacity
20 0-5 A 60 A
16
12
8 0-30 A 250 A
8 31-60 A 300 A
4 70-100 A 300 A
4 101-200 A 600 A
4 225-600 A 1600 A
18 0-70 A 600 A
Table 15.
Fuses
0-30 A
0-5 A
Busbar
capacity
300 A
3.3.2 Circuit Breaker Panels
Mechanical specifications of the circuit breaker panels
The mechanical specifications of the circuit breaker panels are described in
Table 16 Mechanical specifications of the circuit breaker panels
Panel description Figure Height Width Weight
(24) Plug-In 1-100 A
900 A max
(4) 70-250 A
900 A max *
(2) 400 A
(1) 600-700 A
* The 250 A circuit breaker has two poles, thus the panel can accommodate a maximum of two 250 A breakers.
An alarm circuit pack with an alarm indication LED is standard on all panels.
Figure 13
Figure 14
Figure 15
Figure 16
165 mm
(6.5 in.)
178 mm
(7.0 in.)
178 mm
(7.0 in.)
178 mm
(7.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
Table 16.
9.1kg
(20 lb.)
10.5 kg
(25 lb)
10.5 kg
(25 lb)
10.5 kg
(25 lb)
Specifications 13
Page 20

Figure 13 Front view of the (24) Plug-In 1-100 A circuit breaker panel
The DC output connections vary according to the circuit breaker capacity: maximum cable size is
2/0AWG. The lugs must be for 3/8” dia. bolts at 1” c-c.
Refer to
Table 21
for the maximum panel capacity.
Table 17 Plug-in circuit breakers available for the (24) Plug-In 1-100 A circuit breaker panel
Nominal
current
1 A A0723076 A0722751
5 A A0723033 A0722752
10 A A0723035 A0722754
15 A A0723037 A0722755
20 A A0723007 A0722695
25 A A0723039 A0722707
30 A A0723040 A0722715
35 A A0723041 A0722717
40 A A0723042 A0722721
45 A A0723069 A0722722
50 A A0723008 A0722726
60 A A0723070 A0722727
65 A A0723071 A0722497
70 A A0723072 A0722732
80 A A0723074 A0722733
90 A A0723077 A0722750
100 A A0723009 A0722496
CPC Std Trip CPC Mid Trip
14 Specifications
Page 21

Figure 14 Front view of the (4) 70-250 A circuit breaker panel
CIRCUIT BREAKER PANEL
NT6C12EE
(4) 70-250 A
FA
REL ( )
SER NO ( )
900A MAX. PANEL CAPACITY
1
2
UNIT
AMPS
LOAD
3
4
1
225
2
225 225
3
4
225
The DC output connections can accommodate two 4/0 cables back to back for each circuit breaker.
The required lugs can be either for two 3/8” holes at 1” c-c or for two 1/2” holes at 1-3/4” c-c.
Refer to
Table 21
for the maximum panel capacity.
Table 18 Circuit breaker sizes available for the (4) 70-250 A circuit breaker panel
Nominal current CPC
70 A (no shunt) A0617079
70 A (with shunt) A0617080
70 A (with relay trip) A0617081
100 A (no shunt) A0616667
100 A (with shunt) A0616668
100 A (with relay trip) A0616669
150 A (no shunt) A0616670
150 A (with shunt) A0616671
150 A (with relay trip) A0616672
200 A (no shunt) A0616673
200 A (with shunt) A0616674
200 A (with relay trip) A0616675
225 A (no shunt) A0605489
225 A (with shunt) A0605490
225 A (with relay trip) A0605492
250 A (no shunt) A0616676
250 A (with shunt) A0616677
250 A (with relay trip) A0616678
The (4) 70-250 A circuit breaker panel can accept up to:
• four breakers (70 to 225 A) mid trip with or without the metering shunt option (1 pole breakers)
• two breakers (70 to 225 A) mid trip with the relay trip option (takes a 2 pole space)
• two breakers (250 A) mid trip with or without the metering shunt option (takes a two pole
breaker)
• one (250 A) breaker mid trip with the relay trip option (takes a 3 pole space)
Specifications 15
Page 22

Figure 15 Front view of the (2) 400 A circuit breaker panel
CIRCUIT BREAKER PANEL
NT6C12EF
FA
(2) 400 A
REL ( )
SER NO ( )
The DC output connections can accommodate two 750 MCM cables back to back for each circuit
breaker. The required lugs must be for two 1/2” holes at 1-3/4” c-c.
900A MAX. PANEL CAPACITY
1
UNIT
AMPS
LOAD
2
1
400
2
400
Refer to
Table 21
for the maximum panel capacity.
Table 19 Circuit breaker kits available for the (2) 400 A circuit breaker panel
Nominal current CPC
400 A (no shunt) P0748316
400 A (with shunt) P0748317
2 x 400 A (no shunt) P0748318
2 x 400 A (with shunt) P0748319
400 A (with relay trip) P0748320
The panel accepts up to:
• two breakers (400 A) mid trip with or without the metering shunt option
• one breaker (400 A) mid trip with the relay trip option (takes a 3 pole space)
Figure 16 Front view of the (1) 600-700 A circuit breaker panel
CIRCUIT BREAKER PANEL
NT6C12EG
(1) 600-700 A
FA
REL ( )
SER NO ( )
1
2
900A MAX. PANEL CAPACITY
UNIT
AMPS
LOAD
600
1
The DC output connections can accommodate four 750 MCM cables back to back. The lugs must
be for two 1/2” bolts at 1-3/4” c-c.
Refer to
Table 21
Table 20 Circuit breaker kits available for the (1) 600-700 A circuit breaker panel
Nominal current CPC
600 A (no shunt) P0875700
600 A (e/w shunt) P0875701
600 A (e/w relay trip) P0875702
16 Specifications
for the available circuit breakers and the maximum panel capacity.
Page 23

Electrical specifications of the circuit breaker panels
The electrical specifications of the circuit breaker panels are described in
Table 21 Electrical specifications of the circuit breaker panels
Panel description
(24) Plug-In 1-100 A
900 A max
(4) 70-250 A
900 A max
(2) 400 A
(1) 600-700 A
Figure
Figure 13
Figure 14
Figure 15
Figure 16
Circuit breakers
Max. Quantity Capacity
24 1-100 A 900A
4 70-250 A 900 A
2 400 A 900 A
1 600 A 900 A
Busbar
capacity
Table 21.
Specifications 17
Page 24

3.4 Externally Mounted Battery Return Busbar
&
A
A
The battery return busbar is designed to mount on the overhead racking for 6000 A systems and
top cabled 1500, 3000 or 4000 A power systems. It can also be mounted on a wall or on the floor
below the raised floor for bottom cabled 1500, 3000 or 4000 A power systems (which are assumed
to be installed on a raised, computer type floor).
3.4.1 Mechanical Specifications of the External Battery Return Busbar
The external battery return busbar kit consists of a group of single busbar laminations and
attachment hardware assembled as shown in
cally in such a way as to maintain the 3-ft maximum radius grounding requirement. Laminations
are added as required to increase the capacity. The mechanical specifications of a single lamination are listed in
Table 22.
Table 22 Mechanical specifications of a single lamination
Figure Length Width Thickness
Figure 17
863.6 mm
(34 inches)
Figure 17 Top and side views of the external battery return busbar
Figure 17
152.4 mm
(6 inches)
(6000 A shown). The kit can grow verti-
12.7 mm
(0.5 inches)
6” (152 mm)
Top view of the external ground bar
Future growth as required
34” (864 mm)
6”
Smaller busbar for
small wires and cables
Side view of the external ground bar installed on
auxiliary framing above the power system
NOTE
All bars and details are 0.5 in. thick.
* For a 1500 A system, only the bottom level is provided for the external
battery return ground bar.
Available
configurations:
= 1500*
3000 A
= 4000
= 6000
3.4.2 Electrical Specifications of the External Battery Return Busbar
A single busbar lamination has a current carrying capacity of 3000 A.
18 Specifications
Page 25

3.5 Terminating Assemblies (Optional)
The optional terminating assembly allows top access connections for up to six loads. Refer to
Figure 18.
c-c hole spacing, for cables up to 777 kcmil.
The terminating assembly is bolted to the top of the main or auxiliary distribution cabinets and,
therefore, increase the cabinet height by 12 inches. The weight of the terminating assembly is
12.5 kg (27.6 lb).
An optional Lexan
Figure 18 Perspective view of the a terminating assemblies
Glastic
insulating
material
Each load position is rated at 600 A and can accept up to three lugs having 1” or 1-3/4”
™
protective cover is available to protect the connections of the load cables.
Optional
protective
cover
NT6C2625
(for main distribution cabinet)
NT6C2624
(for auxiliary distribution cabinet)
Specifications 19
Page 26

3.6 MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves
The MPS300 and MPA100 power shelves are required for the Helios Rectifier 100/48, which is a
plug-in type rectifier. The MPA100 power shelf supports one Helios Rectifier 100/48, while the
MPS300 shelf can support up to three Helios Rectifiers 100/48.
3.6.1 Mechanical Specifications of the MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves
The mechanical specifications of the power shelves are listed in
Table 23 Mechanical specifications of the MPS300 and MPA100 power shelves
Shelf model Figure Height Depth Width Weight
MPS300
MPA100
Figure 19
Figure 20
533 mm
(21.00 in.)
178 mm
(7.00 in)
381 mm
(15.00 in.)
381 mm
(15.00 in.)
Figure 19 Front view of the MPS300 power shelf (shown empty)
Table 23.
584 mm
(23.00 in.)
584 mm
(23.00 in.)
16.6 kg
(36.5 lb)
5.4 kg
(12 lb)
20 Specifications
Page 27

Figure 20 Front view of the MPA100 power shelf (shown empty)
3.6.2 Electrical Specifications of the Power Shelves
Each rectifier position provides interconnection points for AC input (208 to 240 V nominal), DC
output (-48 V nominal) and control and alarm signals.
3.7 Rectifiers
The Helios system 4000/48 can be equipped with Helios Rectifiers 100/48 for single phase 208/240
V AC operation, with Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 for three phase 380/415 V AC operation, or with
Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 for three phase 480 V AC operation.
3.7.1 Helios Rectifier 100/48
Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48
The mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48 are listed in
Table 24 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48
Figure Height Depth Width Weight
Figure 21
178 mm
(7.0 in.)
305 mm
(12.0 in.)
Figure 21 Front view of the Helios Rectifier 100/48
584 mm
(23.0 in.)
Table 24.
22.2 kg
(49 lb)
Specifications 21
Page 28

Electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48
The electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48 are listed in
Table 25 Electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 100/48
Parameter Specification
Input voltage:
Input current:
Recommended AC
service input:
Output voltage:
Output current:
Input protection:
Output protection:
Output regulation:
Efficiency:
Power factor:
Electromagnetic
interference (EMI):
Heat dissipation:
208/240 V AC, 1-phase, 47-63 Hz
Input voltage range: 176 to 264 V AC
31 A nominal at 208 V AC input and -56 V DC, 100 A output
50 A, two pole AC circuit breaker
Float: -48 to -58 V DC
Equalize: 0 to 4 V DC above Float
Maximum: -59.5 V DC
100 A per rectifier
100 A for a one position shelf
300 A for a three position shelf
A two pole / 45 A circuit breaker opens both lines.
The rectifier is protected by a 120 A circuit breaker at the output. The output current
is limited to a value adjustable from 50% to 105% of the rated capacity of the
rectifier. This circuit is factory set to 105 A.
The rectifier output voltage is automatically regulated to remain within ±0.5% of the
selected value under all load conditions and within the specified input voltage,
frequency, and ambient temperature ranges. And within + 1% for any combinations
of specified input, output and environmental conditions.
Efficiency is better than 88% at a nominal input voltage of 208/240 V AC and an
output load greater than 40 A.
Power factor is 0.99 at a nominal input voltage of 208 V AC and output loads greater
than 40 A.
The rectifier meets the FCC requirements for conducted and radiated EMI for Class
“A” equipment.
763 W (2606 Btu/hr)
Table 25.
3.7.2 Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
The mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifier 200I/48 and 200E/48 are listed in
Table 26 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
Figure Height Depth Width Weight
Figure 22
254 mm
(10 in.)
559 mm
(22 in.)
521 mm
(20.5 in.)
Table 26.
42.3 kg
(93 lb)
22 Specifications
Page 29

Figure 22 Front view of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
VOLT
AMP
1
0
VOLT/AMP
THSD
RFA
FAN
HVSD
ALM
VOUT+
VOLT
CAL
CUR
CAL
SEN
FAIL
AC ON
CL
EQL
VOUTÐ
CL
ADJ
EQL
ADJ
EQL
FFI
FF2
FLT
1.0A
1.0A
FLT
ADJ
HVSD
ADJ
1
ST UP
DLY
FS
SLS
Specifications 23
Page 30

3.7.3 Electrical Specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
The electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48 are listed in
Table 27 Electrical specifications of the Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and 200E/48
Parameter Specification
Input voltage
Input current
Input protection
Recommended AC
service input
Output voltage
Output current
Output protection
Output regulation
Efficiency
Power factor
Electromagnetic
interference (EMI)
Heat dissipation
Total harmonic
distortion (THD)
Helios Rectifier 200I/48:
380/415 V AC, three phase, 47-63 Hz
Input voltage range: 330 to 475 V AC
Helios Rectifier 200E/48:
480 V AC, three phase, 47-63 Hz
Input voltage range: 430 to 520 V AC
Helios Rectifier 200I/48: 18.3 A RMS nominal at 380 V AC input and -54 V DC, 200 A
output (24 A RMS worst case)
Helios Rectifier 200E/48: 15 A RMS nominal at 480 V AC input and -54 V DC, 200 A
output (17 A RMS worst case)
A 3 pole / 25 A circuit breaker opens all three lines.
30 A, 3 pole AC circuit breaker
Float: -46 to -58 V DC
Equalize: 0 to 4 V DC above Float
Maximum: -60 V DC
200 A nominal
Adjustable between 100 and 210 A
The rectifier is protected by a 250 A circuit breaker at the output.
The output current is limited to a value adjustable from 50% to 105% of the rated
capacity of the rectifier. This circuit is factory set to 205 A.
The rectifier output voltage is automatically regulated to remain within ±0.5% of the
selected value under all load conditions and within the specified input voltage,
frequency, and ambient temperature ranges. And within + 1% for any combinations of
specified input, output and environmental conditions.
Efficiency is better than 89% at nominal input voltage and an output load greater than
80 A.
Power factor is better than 0.99 at nominal input voltage and an output load greater
than 80 A.
The rectifier meets the FCC requirements for conducted and radiated EMI for Class
“B” equipment.
1,335 W (4,558 Btu/hr) at -54 V DC, 200 A output
THD is less than 5% between half load and full load at nominal input voltage
Table 27.
3.7.4 Standards
The following standards also apply to the rectifiers:
• ANSI Std. C62.41/IEEE Std. 587-1980, Class A and B lightning surge 6000 V, 3000 A, 1.2 x 50
ms impulse, 10 hits per second
• ANSI Std. C82.41 oscillatory surge 2500 V, 0.5 ms impulse, 100kHz positive/negative oscillating decay
• Bellcore TR-TSY-000947
• IEC-950, VDE EN 60950, EN 41003
• CISPR 22, Class A
• CE mark
24 Specifications
Page 31

3.8 Helios Monitor 3000/48 (Optional)
3.8.1 Mechanical Specifications
The mechanical specifications of the Helios Monitor 3000/48 are listed in
Table 28 Mechanical specifications of the Helios Monitor 3000/48
Figure Height Depth Width Weight
Figure 23
45 mm
(1.75 in.)
222 mm
(8.75 in.)
280 mm
(11.0 in.)
The above dimensions are without the mounting brackets. The weight may vary slightly depending on the number and type of analog interface modules installed in the unit.
Figure 23 Front view of the Helios Monitor 3000/48 (without the mounting brackets)
UNIT
ADRESS
Table 28.
2.8 kg
(6.2 lb)
POWER/FAIL
LED INDICATOR
ROTARY SWITCHES 12 DIGIT ALPHA-NUMERIC DISPLAY 4 PUSH-BUTTON KEYPAD
HELIOS Monitor 3000/48
3.8.2 Electrical Specifications
The input voltage of the Helios Monitor 3000/48 is -48 V DC nominal, with a range of -42 V DC to
-60 V DC.
The input current drain is 400 mA. This current drain may vary slightly depending upon the
number and type of analog interface modules installed in the unit.
For more detailed electrical specifications of the Helios Monitor 3000/48, refer to the appropriate
user manual listed in
6.0 - Reference Documents.
3.9 600 A and 1200 A Battery Disconnect Unit (Optional)
The Battery Disconnect Units are 11 inches high and provides for 500 mm (19 in.) or 600 mm
(23 in.) framework mounting or wall mounting. The units are equipped with a heavy duty circuit
breaker that can be used to manually or automatically disconnect a battery string. Reconnect is
manual only. The breaker is mid trip and equipped with a relay trip feature.
Figure 24 600 A Battery Disconnect Unit
600 A
NT6C18MA
BATTERY DISCONNECT UNIT
: MODE SELECTION
: PARAMETER SELECTION
DISABLE
BDA
AUTODISC
ONOFF ONOFF ONOFF
FA
DSBL SP CAL
TEST
DISC
CALIBRATE
VOLT
ADJ
GRD -48V
F1
3 A
For more detailed electrical specifications of the Battery Disconnect Unit, refer to the user manual, SL-60040.
Specifications 25
Page 32

3.10 AC Junction Box
The AC junction box is required as an AC connection interface in rectifier cabinets where the
Helios Rectifier 200E/48 is used.
Figure 25 Front view of the AC junction box (with the front panel open)
Six receptacles
to plug the
cables from the rectifiers
RECT 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
L1L2L3
RECT 5
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 4
TB1
L1L2L3
GRD
3.10.1 Mechanical Specifications
The junction box is made of zinc plated steel and can accommodate up to six one-inch rigid or flexible conduits. The mechanical specifications are listed in
Table 29 Mechanical specifications of the AC junction box
Figure Height Depth Width
Figure 25
264 mm
(10.4 in.)
3.10.2 Electrical Specifications
The junction box is designed to accommodate six 3-phase circuits (3 wires plus ground) at a maximum voltage of 600 V AC and a capacity of 30 A per circuit.
3.11 Overall Power System Specifications
3.11.1 Standards
The Helios DC System 4000/48 meets the following North American and European standards:
RECT 3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 2
L1L2L3
GRD
TB2
GRD
Table 29.
284 mm
(11.2 in.)
RECT 1
L1L2L3
GRD
521 mm
(20.5 in.)
• UL-1801
• CSA 22.2 (#0.7, #225)
• TR-TSY-000406
•CE
•VDE
3.11.2 Mechanical Specifications of Fully Equipped Power Cabinets
Table 30 Mechanical specifications of fully equipped power cabinets
Height Depth Width
2134 mm
(84 in.)
26 Specifications
600 mm
(23.62 in.)
600 mm
(23.62 in.)
Total weight (4000 A control
and distribution cabinet)
363 kg
(800 lb) approx.
Total weight (1200 A rectifier
cabinet with six rectifiers)
440 kg
(970 lb) approx.
Page 33

3.11.3 Electrical Specifications
Refer to the individual component’s specifications.
Electromagnetic compliance (EMC)
The equipment contained in the power system complies with the specifications of FCC, Part 15,
Subpart B for class A equipment, CSA 108.8 for class A and CISPR 22 for class A.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity
No equipment damage or malfunctions shall occur when electrostatic discharge voltages of severity level 2 and 4, as specified by IEC-801-2, are applied to exposed parts of the power system.
3.11.4 Environmental Specifications
Operating
Temperature:
Humidity:
Altitude:
0° to +50°C (32° to 122°F)
0 to 95% non-condensing
Sea level to 2134 m (7000 ft)
Transportation
NOTE
Do NOT ship with the rectifiers installed in the rectifier cabinet(s).
During transportation the equipment may be subjected to the following conditions without damage:
Temperature:
Humidity:
Vibration:
Shock:
-50° to +75°C (-58° to +167°F)
0 to 95% (non condensing) 4kPa max. WVP for 10 days
TR-NWT-000063 section 5.4.4 Transportation Vibration (packaged equipment)
TR-NWT-000063, Section 5.4.1 Handling Drop Tests, and Section 5.4.3 Installation Shop Tests
Storage
Temperature:
Humidity:
-50° to +75°C (-58° to +167°F)
0 to 95% (non condensing) 4kPa max. WVP for 10 days
Heat dissipation
A Helios DC System 4000/48 rectifier cabinet equipped with six Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/
48 will dissipate a maximum of 8,010 watts or 27,350 Btu/hr.
3.11.5 Floor and Point Loading
The floor loading is based on a footprint of 600 mm x 600 mm (23.6 in. x 23.6 in.) plus a 30-inch
aisle width (15 inches front and rear).
The point loading is based on distributing the cabinet weight over four shims, each with an
assumed area of 25.8 cm
Figure 1
See
for a typical system configuration for floor and point loading calculations.
Table 31 Floor and point loading
Cabinet type Floor loading Point loading
Control and distribution cabinet 41.3 kN/sq m (90.9 lb/sq ft) 34.5 N/sq cm (50 lb/sq in.)
Auxiliary distribution cabinet 32.3 kN/sq m (71 lb/sq ft) 26.9 N/sq cm (39 lb/sq in.)
Rectifier cabinet 50.1 kN/sq m (110.2 lb/sq ft) 41.8 N/sq cm (60.6 lb/sq in.)
2
(4 in.2).
Specifications 27
Page 34

4.0 O
PERATION
4.1 General
This chapter describes the control, adjustment and operational features of the Helios DC System
4000/48.
4.2 Conventional Controller
The Conventional Controller monitors the operation of the entire power plant. It monitors all the
alarms, and it controls and monitors the rectifiers.
Provision is made on the back of the Conventional Controller to extend any occurring alarm to the
alarm center through the facilities provided in the powered equipment.
All of the control switches, potentiometers, operational and alarm visual indications are located at
the front of the Conventional Controller.
4.2.1 Front Panel
The front panel of the Conventional Controller is provided with the control, alarm and operational
features shown in
Figure 26 Front view of the Conventional Controller
Figure 26
and described in the following subsections.
Visual indicators
A 4.5 digit red LED readout to display the system current and voltage, and 18 LEDs to display the
alarm conditions as described in
descent cabinet alarm lamp.
Table 32 Visual indicators
Designation Description Color
RECT FAN Rectifier Fan Failure yellow
EQL Equalize On yellow
FA Fuse Failure Alarm (Internal to the Controller) red
DFA Discharge Fuse Alarm red
CFA (not used) Charge Fuse Alarm red
RFA MIN Rectifier Failure Alarm Minor yellow
RFA MAJ Rectifier Failure Alarm Major red
ACO Alarm cut-off red
HVSD High Voltage Shutdown Alarm red
HV High Voltage Alarm red
LV Low Voltage Alarm red
HF High Float Alarm yellow
LF Low Float Alarm yellow
LVD Low Voltage Disconnect red
BOD Battery On Discharge red
LOP Loss of Phase red
AUX 1 (BDA) Auxiliary Major red
AUX 2 Auxiliary Minor yellow
Table 32.
All alarm conditions are also displayed by a red incan-
28 Operation
Page 35

Table 33 Transmitted alarms
Alarm Description
RECT FAN (1 - Form C contacts)
RFA MIN (1 - Form C contacts)
RFA MAJ (1 - Form C contacts)
H/L FLOAT (2 - Form C contacts)
EQL ALM (1 - Form C contacts)
H/L VOLT (2 - Form C contacts)
FA (1 - Form C contacts)
CHG FUSE (1 - Form C contacts)
DISCH FUSE (1 - Form C contacts)
LVD (1 - Form C contacts)
LOSS OF AC VOLT (1 - Form C contacts)
AUX 1 ALM (2 - Form C contacts)
AUX 2 ALM (2 - Form C contacts)
HVSD (1 - Form C contacts)
BOD (1 - Form C contacts)
MIN VIS (note 2) (2 - Form C contacts)
MAJ VIS (note 2) (2 - Form C contacts)
MIN AUD (2 - Form C contacts)
MAJ AUD (2 - Form C contacts)
NOTE
Form C contacts are rated at 0.5 A, 60 V AC.
MINOR VIS (2) and MAJ VIS (2) are used for the cabinet alarm lamp.
Potentiometers
Twelve potentiometers for the adjustment of alarm and control functions as described in
Table 34.
Table 34 Potentiometers
Designation Description
HVSD High Voltage Shutdown
HV High Voltage Alarm
LV Low Voltage Alarm
HF High Float Alarm
LF Low Float Alarm
LVD Low Voltage Disconnect
BOD Battery On Discharge
VOLT ADJ Plant Voltage Adjustment
REF CAL Reference Calibration
METER ADJ Meter Adjustment
AMP ADJ Ampere Adjustment
LVR Low Voltage Reconnect
Operation 29
Page 36

Switches
Four switches for the control of functions as described in
Table 35 Switches
Designation Description
EQUALIZE MAN/AUTO Used to activate or deactivate the equalize function.
ACO Used to cancel the audible alarm signal.
CALIBRATE NORM/CAL Used to activate or deactivate the calibration function.
CONT rotary switch Six position switch: OFF, AMP, CHG VOLT, BAT VOLT, CAL, TST DISPL
DIP switches
Three DIP switch modules for the setting of functions as described in
Figure 27
Table 36 DIP switch modules
Designation Description
SHUNT SELECT To select the shunt size
TIMER To select the duration of the equalize
VOLT To select the equalize voltage
Figure 27 Shunt range selection settings
and
Figure 28.
123456
S1
Table 35.
RANGE AMPS
MIN-MAX
Table 36
and as shown in
= SWITCH IS ON
55 to 100
100 to 170
170 to 340
340 to 500
500 to 1000
1000 to 1700
1700 to 3400
3400 to 7000
7000 to 14000
30 Operation
Page 37

Figure 28 Equalize voltage and duration settings
TIMER
VOLT
Switch # 1 2 3 4 5 6
OFF ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
10 sec.
20 sec.
38 sec.
1.25 h
3.0 h
5.0 h
LOP enabled
: switch in the ON position
Switch # 1 2 3
0.6V
1.3V
1.9V
2.6V
3.2V
3.9V
4.6V
1
2
3
ON OFF
Fuses
Thirty-four fuses for circuit protection as described in
small tube type (9/32” dia x 1-1/4” long), all fuses are of the QFF type.
Table 37 Fuse
Designation Capacity Description
ABS 15 A -48 V supply for the office alarm circuit(s)
ABS ALM 1/2 A Alarm fuse for the above ABS fuse
RC1 to RC24 1-1/3 A -48 V sense supply for the rectifiers of the system
CONV 1/2 A Protection for the internal converter in the controller
METER 1/2 A Protection for the meter and selector panel if so equipped
CHG 1/2 A Protection for internal circuitry of the controller when the CONT rotary switch
is in the CHG VOLT position
Spare 1 and 2 0 to 5 A For external loads as required (ex.: Helios Monitor)
BAT 1/2 A Protection for internal circuitry of the controller when the CONT rotary switch
is in the BAT VOLT position
CONT 1-1/3 A Protection for the internal circuitry of the controller
Plus one unused position
Table 37.
Except for the ABS fuse, which is
Test points
Three sets of test points for applications as described in
Table 38 Test points
Designation Description
CAL OUT + and - To connect an external meter when calibrating the LED readout for current readings
VOLT + and - To connect an external meter when adjusting the BOD, LF, LV, HF, HV, HVSD, LVD and
LVR thresholds
PWR EXT + and - The connect an external power supply when adjusting the LVR threshold
Table 38.
Operation 31
Page 38

4.2.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Conventional Controller is provided with the connection interface features
shown in
Figure 29 Terminal blocks and connectors layout at the rear of the Conventional Controller
Figure 30
and described in the following subsections.
TB2
TB1
J7 J6
TB3
P25 P23 P21 P19 P17
J5
J4
TB4
TB5
J8
P3P15 P13 P11
J3
J2
J1
TB6
1
P2P10 P8 P6 P4P16 P14 P12P22 P20 P18P24P26
8
P1P9 P7 P5
Terminal blocks
Six terminal blocks to interface with external wiring as follows:
• TB1: various alarm outputs to the office alarm circuits and the cabinet alarm lamp
• TB2: various alarm outputs to the office alarm circuits, and remote equalize signal input
• TB3: various alarm outputs to the office alarm circuits, and charge and discharge fuse alarm
inputs
• TB4: various alarm outputs to the office alarm circuits, and LVD control and alarm
• TB5: various alarm outputs to the office alarm circuits, remote TR signal input, -48 V supply
to cabinet alarm lamp and various small loads, and AUX 1 and AUX 2 alarms inputs
• TB6: -48 V supply to office alarm circuits if required, VR+ and VR- inputs, and -48 V and
ground inputs
Refer to
Figure 30
and
Figure 31
for the pin assignment of terminal blocks TB1 to TB6.
32 Operation
Page 39

Figure 30 Wiring diagram and pin assignment of terminal blocks TB1 to TB4
)
(1)
(1)
v
To office
alarm
circuit
Input from DISCH fuse alarm circuits
Input from CHG fuse alarm circuits
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
H/L FLOAT ALM (1
H/L FLOAT ALM (1)
H/L FLOAT ALM (2)
H/L FLOAT ALM (2)
MIN RECT ALM
MIN RECT ALM
MAJ RECT ALM
MAJ RECT ALM
LVD ALM
LVD ALM
LOSS OF AC VOLT ALM
LOSS OF AC VOLT ALM
DFA
CFA
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
C
C
C
C
C
C
TB3 TB1
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
13
13
14
14
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
20
20
C
NC
NO
BK ALARM VISUAL (C)
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
G ALARM VISUAL (NC)
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
MINOR VIS (1)
MINOR VIS (1)
MAJOR VIS (1)
MAJOR VIS
MINOR AUD (1)
MINOR AUD (1)
MINOR AUD (2)
MINOR AUD (2)
MAJOR AUD (1)
MAJOR AUD (1)
To small internal
battery return
busbar
To cabinet
alarm lamp
To office
alarm
circuit
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
To office
alarm
circuit
Input alarm from LVD circuit
AUX ALM NO.1 (1)
AUX ALM NO.1 (1)
AUX ALM NO.1 (2)
AUX ALM NO.1 (2)
AUX ALM NO.2 (1)
AUX ALM NO.2 (1)
AUX ALM NO.2 (2)
AUX ALM NO.2 (2)
EQUALIZE ALM
EQUALIZE ALM
HVSD ALM
HVSD ALM
To LVD circuit
RLVD
LVDA
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
NC
NO
C
C
C
C
C
C
TB4 TB2
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
13
13
14
14
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
20
20
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
C
NC
NO
REMOTE EQUALIZE START
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
MAJOR AUD (2)
MAJOR AUD (2)
FUSE ALM
FUSE ALM
CHG FUSE ALM
CHG FUSE ALM
DISCH FUSE ALM
DISCH FUSE ALM
H/L VOLT ALM
H/L VOLT ALM (1)
H/L VOLT ALM (2)
H/L VOLT ALM (2)
To office
alarm
circuit
Input from office remote circuit
Operation 33
Page 40

Figure 31 Wiring diagram and pin assignment of terminal blocks TB5 and TB6, and connectors P1 to
P26
22GA 8-conductor
shielded cable
To alarm
To
NT6C43PA
interface
or
board or
NT6C43PB
rectifier
rectifier
interface
interface
card as
card as
required,
required,
or
or directly
directly
to rectifier
to
rectifier
22GA 2-conductor
shielded cable
Main
plant
SHUNT +
shunt
(the shunt
wires should
be fused near
the shunt to
prevent fire
hazard)
To AC
ALM
monitor
circuit
such as
NT6C18BA
EQL ( )
RG+ ( )
RC- ( )
TR ( )
FAN ( )
HVSD ( )
RFA ( )
NC
NC
SHUNT –
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
GRD
P1 TO P24
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
P25
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
P26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TB5
TB6
To office alarm circuit,
ABSF
If required
Input from office
TR
C
NC
NO
RECT FAN
RECT FAN
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
LP (–48V)
–48V (SPARE 2)
-48V (METER)
remote circuit
To office alarm circuit
To cabinet alarm lamp
To load as required
To meter & selector
panel (NT6C10AA),
GRD
C
NC
NO
NE-1451X cable
(or equivalent)
AUX1 INPUT (MAJ)
AUX2 INPUT (MIN)
if so equipped
BOD
To office alarm circuit
BOD
–48 V CHG busbar
GRD alarm signals from
auxiliary equipment as
required
–48 (ABS)
To office alarm circuit
or alarm reporting
circuit, if required
10 AWG
VR–
Battery sense
VR+
leads
GRD
Power plant
–48V
10 AWG
busbars
Connectors
Twenty-six connectors to interface with external equipment as follows:
• P1 to P24: signaling between the controller and the rectifiers
• P25: interface with the main power system shunt
• P26: interface with an AC monitoring device
Refer to
Figure 31
for the pin assignment of connectors P1 to P26.
Eight connectors (J1 to J8) for the interface between the two circuit boards of the controller (for
factory use only).
4.3 MPS300 and MPA100 Power Shelves
The MPS300 power shelf provides the interconnecting points for all the AC, DC and control
cabling and wiring for three Helios Rectifier 100/48. The MPA100 power shelf does the same for
one Helios Rectifier 100/48.
Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual listed in
operation information on the MPS300 and MPA100 power shelves.
34 Operation
6.0 - Reference Documents
for detailed
Page 41

4.4 Rectifiers
The rectifiers provide isolated, filtered and regulated DC power, from either a single-phase AC
source (Helios Rectifier 100/48) or a three-phase AC source (Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48),
for charging a positive grounded battery.
The nominal output is adjustable over the range of -46 to -59.5 V to float a 23 or 24 cell battery
string.
The rectifiers are equipped with AC input and DC output circuit breakers, a digital ammeter,
potentiometers for the adjustment of thresholds, and LED indicators for alarm indications.
The rectifiers use high frequency switching technology and forced air-cooling.
Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual listed in
operation information on the Helios Rectifier 100/48, the Helios Rectifier 200I/48, or the Helios
Rectifier 200E/48.
4.5 AC Junction Box
WARNING
!
PREVENTING ELECTRICAL SHOCKS
WHEN OPENING THE DOOR OR WIRING THE AC INPUT OF
THE RECTIFIERS INSIDE THE JUNCTION BOX, ENSURE THAT
THE ASSOCIATED AC BREAKERS, LOCATED IN THE AC
SERVICE PANEL, ARE IN THE OFF POSITION AND THAT A
WARNING TAG CLEARLY INDICATES THAT THESE BREAKERS
ARE TO REMAIN OFF UNTIL THE AC WIRING HAS BEEN
COMPLETED. DO NOT INSERT FUSES, OR OPERATE CIRCUIT
BREAKER OR SWITCHES TO ON UNTIL THE WIRING IS
COMPLETED AND YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO DO SO.
The AC junction box is part of the rectifier cabinet used for the Helios Rectifier 200E/48. It is
located at the top of the cabinet for top fed systems, or at the bottom of the cabinet for bottom fed
systems.
The AC junction box provides AC connection interface for up to six rectifiers and facilitates the
addition and/or replacement of rectifiers in a working system. The AC supply from the AC service
panel is hard wired inside the box at the time of the initial installation. Detailed cabling and connecting guidelines for the AC junction box can be found in
6.0 - Reference Documents
5.0 - Maintenance.
for detailed
The rectifiers are provided with a factory-installed AC cord equipped with a male connector. This
male connector is plugged into a matching female receptacle at the rear of the AC junction box.
For the complete procedures for adding or replacing a rectifier, refer to
that caps are provided to protect the unused female receptacles.
4.6 Distribution Panels
All distribution panels provide local alarm indication on the panel itself, and alarm extension to
the controller for additional indication on the controller and the cabinet and further extension to
remote alarm facilities.
4.7 Terminating Assemblies (Optional)
Terminating assemblies are optional devices used to facilitate the connecting of loads to distribution fuses or circuit breakers larger than 199 A. These assemblies can be used in top fed systems
only (they cannot be used on bottom fed systems). Each terminating assembly provides connection
facilities for up to six loads without having to route the cables inside the cabinet during installation.
Two terminating assemblies can be used on an auxiliary distribution cabinet, while only one terminating assembly can be used on a main control and distribution cabinet.
5.0 - Maintenance.
Operation 35
Note
Page 42

4.8 Helios Monitor 3000/48 (Optional)
The Helios Monitor 3000/48 is a microprocessor-based unit used to monitor and record power systems operational data. The recorded data is accessible locally by means of the front panel or the
RS-232 port, or remotely through the modem link.
If an Helios Monitor 3000/48 was supplied with your system, refer to the Monitor 3000 user manual, SL-60015, for detailed operational characteristics.
4.9 600 A and 1200 Battery Disconnect Units (Optional)
The 600 A and 1200 A Battery Disconnect Units (BDU) are equipped with a circuit breaker that
provides for automatic or manual disconnect, but only manual reconnect. The automatic disconnect is intended to serve the low voltage disconnect function to prevent batteries from deep discharge that could damage them. The circuit breaker has industrial grade contacts to connect and
disconnect large currents, and it is provided with a relay trip feature.
If battery disconnect unit(s) were supplied with your system, refer to the user manual, SL-60040,
for the detailed operational characteristics of the battery disconnect unit.
36 Operation
Page 43

5.0 M
AINTENANCE
5.1 General
The following is a list of general preventive maintenance procedures which should be performed
periodically as required according to the environmental conditions and customer maintenance
policy to ensure trouble free operation of the Helios DC System 4000/48:
• clean all ventilation openings
• if these are used, clean or replace the air filters on the rectifiers
• tighten all electrical connections
• check for hot fuses or breakers (loose, undersized or overloaded)
• verify alarms and alarm thresholds
• verify calibration settings
• verify rectifier settings
The voltage and alarm settings of the controller and rectifiers are based on the type of batteries
used with the power system. The recommended settings for various types of batteries can be
found in SL-60026, Voltage Level Limits for Power Plants, Rectifiers and Controllers. If unlisted
models of batteries are used, it may be necessary to follow specific customer or manufacturer
requirements.
The following is list of the tools and test equipment required to adjust the equipment in the Helios
DC System 4000/48:
• a potentiometer screwdriver, Bourns No. 60 or equivalent
• a digital voltmeter, Fluke 8050A or equivalent
• a dummy load, 5 kVA
5.1.1 Helios Monitor 3000/48
If the power system is equipped with a Helios Monitor 3000/48, refer to the user manual,
SL-60015, for maintenance and troubleshooting information.
5.1.2 Controller and Rectifiers
The controller and the rectifiers need little maintenance. The following should be checked periodically in order to ensure trouble free operation.
WARNING
!
PREVENTING DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT
DO NOT ATTEMPT ANY OTHER REPAIR THAN THOSE LISTED
BELOW. IF ANY PROBLEM PERSISTS, CONTACT LIEBERT
GLOBAL SERVICES AT 1-800-LIEBERT.
Cleaning
Clean the front panels and the LED display screens with a soft cloth and isopropyl alcohol.
Calibration
Verify the calibration of the alarm and control thresholds at least once a year. Follow the calibration instructions detailed in the appropriate user manual.
Storage
The rectifiers contain aluminum electrolytic capacitors. For this reason, they shall be either kept
in operation, or energized once a year for at least two hours in order to maintain the electrolytic
capacitors in good condition.
Maintenance 37
Page 44

Air filter replacement
In dusty environments, the use of an air filter is strongly recommended. When used, it should be
replaced at least once a year. Do not install a wet filter on a rectifier. To remove the filter, simply
unscrew it. Install the new one by reversing the operation. Contact your local Liebert representative for ordering information on air filters.
Fan unit replacement
Visually inspect the airflow intake for any obstruction by foreign objects or excessive dust and dirt
build-up. Open both AC and DC breakers. If the rectifier is a Helios Rectifier 100/48, remove it
from the power shelf. Inspect the air outlet for obstruction by foreign objects. Visually inspect the
air outlet of the power shelf (Helios Rectifier 100/48) or the cabinet (Helios Rectifiers 200I/48 and
200E/48). The fan unit is field replaceable. Contact your local Liebert representative for ordering
information on replacement fans. To install a new fan unit, refer to the appropriate procedure and
associated figures in the maintenance chapter of the applicable rectifier user manual listed in
6.0 - Reference Documents.
bal Services
1-800-LIEBERT.
at
If a problem is detected inside the rectifier, contact
Do not attempt to open the unit for on-site servicing.
Liebert Glo-
38 Maintenance
Page 45

5.2 Troubleshooting
Table 39
provides a list of the problems that may occur on the Helios DC System 4000/48, along
with their possible causes. Blown fuses and tripped circuit breakers should always be investigated before utilizing
Table 39.
Table 39 Fault diagnosis
Fault symptom Possible causes
No DC output current
Incorrect indication of the DC
output current
Low float voltage
Low recharge voltage
High float or recharge voltage
Failure to generate alarms
during alarm conditions
Failure to generate cabinet
alarm during minor or major
alarm conditions
Failure to generate RFA alarm
under appropriate conditions
Failure to generate FA alarm
HV lamp lit
LV lamp lit
HF lamp lit
LF lamp lit
FA lamp lit
CFA lamp lit
DFA lamp lit
RECT MIN lamp lit
RECT MAJ lamp lit
RECT FAN lamp lit
Open AC circuit breaker
Open DC circuit breaker
Faulty connection between the power shelf and the rectifier (Helios
Rectifier 100/48)
Faulty connection between the rectifier and the power plant
Sense leads opened
Incorrect meter calibration
Loose shunt leads connection
Faulty rectifier(s)
Shorted battery cell(s)
Prolonged power failure
Incorrect float voltage adjustment
Sense leads opened
Incorrect float voltage adjustment
Discharge load greater than the rectifier’s capacity (batteries are
recharging or the system is in manual bypass)
Sense leads opened
Faulty rectifier(s)
Incorrect Float/Equalize adjustment
Incorrect connections between the controller and the rectifiers and
distribution panels
Faulty LP fuse on the controller (F31)
Faulty cabinet alarm lamp
Faulty or loose connection
Faulty rectifier
Faulty wiring
Faulty RFA LED
Faulty wiring
Faulty fuse
Faulty FA LED
Loose connection
High discharge voltage condition
Incorrect HV level adjustment
Low discharge voltage condition
Incorrect LV level adjustment
High discharge voltage condition
Incorrect HF level adjustment
Low discharge voltage condition
Incorrect LF level adjustment
Blown fuse or extended FA alarm
Blown charge fuse
Blown distribution fuse
One rectifier has failed
Two or more rectifiers have failed
Defective rectifier fan(s)
Maintenance 39
Page 46

Table 39 Fault diagnosis
Fault symptom Possible causes
LOP lamp lit
HVSD lamp lit
LVD lamp lit
AUX 1 lamp lit
AUX 2 lamp lit
BOD lamp lit
ACO lamp lit
EQL lamp lit
Rectifiers are not sharing the
load
Meter display is OFF
Loss of one or more phases in the AC supply
High voltage shutdown condition initiated by the controller
Low voltage disconnect condition initiated by the controller
User defined alarm condition
When a Battery Disconnect Unit is present, this lamp will indicate that a
battery disconnect alarm is ongoing.
User defined alarm condition
Low discharge voltage condition
Incorrect BOD level adjustment
ACO switch has been operated during an alarm condition which is still
ongoing
The equalize function has been activated
Incorrect float or equalize adjustment on one of the rectifiers
Sense leads opened on one rectifier
Share mode incorrectly set
Open meter fuse
Meter and display failure
Meter and display rotary switch in the OFF position
5.3 Addition / Replacement Procedures
5.3.1 Addition or Replacement of a Rectifier
WARNING
!
PRECAUTIONS SHALL BE TAKEN TO AVOID SERVICE
INTERRUPTIONS
WHEN INSTALLING A RECTIFIER, THE FLOAT AND EQUALIZE
VOLTAGES MUST BE SET ACCORDING TO THE TYPE OF
BATTERIES USED WITH THE SYSTEM. FAILURE TO SET
THESE VOLTAGES PROPERLY MAY RESULT IN BATTERY
UNDERCHARGING OR OVERCHARGING AND/OR BATTERY
DAMAGE.
WARNING
!
PROTECTING PERSONNEL AGAINST ELECTRICAL SHOCKS
INPUT VOLTAGES TO THE RECTIFIERS ARE AT A
DANGEROUS LEVEL. ENSURE THAT THE CIRCUIT BREAKERS
ARE LOCKED IN THE OFF POSITION AT THE AC SERVICE
PANEL BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO WORK ON THE RECTIFIERS.
DANGEROUS VOLTAGES MAY STILL BE PRESENT AT THE
TERMINALS EVEN IF THE RECTIFIERS ARE OFF. USE A
VOLTMETER TO VERIFY FOR THE PRESENCE OF SUCH
VOLTAGES. DO NOT SWITCH CIRCUIT BREAKERS TO ON
UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO IN THE APPROPRIATE
PROCEDURE.
Add a rectifier as described in the following procedure for a Helios Rectifier 100/48 or as in the
Adding a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48
40 Maintenance
procedure, whichever is applicable.
Page 47

Adding a Helios Rectifier 100/48
1. Remove the rectifier blank panel and store it for future use.
Note:
Should a rectifier be removed at any time, re-install the blank panel to meet the
regulatory requirements.
2. Verify that the AC, DC and signalling cabling for the rectifier shelf has been previously
installed and verified.
3. Ensure that the AC and DC circuit breakers on the front panel of the rectifier are in the OFF
position.
4. Carefully slide the rectifier into position, making sure that it is fully inserted.
5. Install the left and right side clamping brackets supplied with the rectifier to secure it into
position.
6. Operate the AC circuit breaker of the new rectifier to the “ON” position.
7. With the DC breaker in the “OFF” position, adjust the float, equalize and high voltage
shutdown voltage levels as required. Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
8. Install the corresponding sense fuse (RC) on the front of the controller.
9. Ensure that the FLS/FS switch on the rectifier is set to the same position as that of the other
rectifiers in the power system.
10. Operate the DC circuit breaker of the rectifier to the “ON” position.
11. Verify that the rectifier is sharing the load by observing its ammeter. It should display
approximately the same value as the ammeters on the other rectifiers. If not, adjust its float
and equalize voltage levels as described in the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
6.0 -
6.0 -
Adding a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48
1. Ensure that the AC and DC circuit breakers on the front panel of the rectifier are in the OFF
position.
2. Use a manual lift (or at least two people) to lift the rectifier to its position, rest it on the angle
guides, and slide it into the cabinet.
3. Align the mounting holes of the rectifier with those of the cabinet uprights and secure the
rectifier in place using the eight mounting screws provided.
Note:
A star washer must be used on one of the mounting screws.
4. Bring the connectorized AC cord up (top fed) or down (bottom fed) the cabinet and secure as
required.
5. Install the required circuit breaker at the AC service panel.
6. Ensure that the circuit breaker installed per
7. Determine the length of cable (or individual wires in conduit) required to bring the AC supply
from the AC service panel to the rectifier cabinet.
8. Cut the cable (or wires) to the required lengths then run and secure between the AC service
panel and the rectifier cabinet.
9. Strip the sheeting and insulation material away from the ends of the wires to expose the AC
leads
10. For a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 without an AC cord, remove the AC protective cover at the rear
of the rectifier and connect the AC leads inside the rectifier as shown in
reinstall the AC protective cover.
For a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 or a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 equipped with an AC cord, first
connect the associated female receptacle supplied with the rectifier to the cable (or wires)
incoming from the AC service panel (refer to
end of the rectifier AC cord into the female receptacle.
For a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 equipped with an AC cord, feed the cables through the appropriate strain relief connector at the top (top fed) or bottom (bottom fed) of the rectifier AC
junction box inside the cabinet (refer to
the strain relief connector, then connect the wires to the appropriate terminals inside the
junction box as shown in
points (one for each rectifier position) inside the junction box. Plug the male connector at the
Figure 34.
Use plastic cable ties to secure the wires at the tie down
Step 5
Figure 33).
Figure 34).
is locked in the open (OFF) position.
Figure 32,
Then, plug the male connector at the
Use a flat blade screwdriver to tighten
then
Maintenance 41
Page 48

end of the rectifier AC cord into the corresponding female receptacle behind the junction box.
For the specific AC cable routing to be used with the Helios Rectifier 200E/48, refer to
Figure 35
in the case of a top fed system, or to
11. Make the ground and line connections as applicable, at the AC service panel.
12. Install the four bolts for the DC connections to the busbar risers at the rear of the cabinet.
13. Plug one end of the control and signal cable supplied with the rectifier into the DB25
connector at the rear of the rectifier.
14. Plug the other end of the control and signal cable into the corresponding connector on the
interface circuit board at the top (top fed system) or bottom (bottom fed system) of the rectifier
cabinet.
15. Operate the AC circuit breaker of the new rectifier to the “ON” position.
16. With the DC breaker in the “OFF” position, adjust the float, equalize and high voltage
shutdown voltage levels as required. Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
17. Install the corresponding sense fuse (RC) on the front of the controller.
18. Ensure that the FLS/FS switch on the rectifier is set to the same position as that of the other
rectifiers in the power system.
19. Operate the DC circuit breaker of the rectifier to the “ON” position.
20. Verify that the rectifier is sharing the load by observing its ammeter. It should display
approximately the same value as the ammeters on the other rectifiers. If not, adjust its float
and equalize voltage levels as described in the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
Figure 32 AC connections in a Helios Rectifier 200E/48
Figure 36
in the case of a bottom fed system.
6.0 -
6.0 -
L1 L2 L3
Teck cable or
flexible conduit
AC cover
GRD
Partial view of
the rectifier’s
rear panel (right
side as viewed
from the rear)
TB1
42 Maintenance
Page 49

Figure 33 AC connections in the female receptacle for a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or a Helios Rectifier
200E/48
Cover
Phase 2
or L2
Cover
Phase 2
or L2
Phase 3
or L3
Phase 1
or L1
Phase 3
or L3
GRD
Helios Rectifier 200I/48
(380 V ac)
Phase 1
or L1
GRD
Helios Rectifier 200E/48
(480 V ac)
Figure 34 AC connections inside the junction box (top fed shown) for a Helios Rectifier 200E/48
Teck cables or
flexible
conduits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
L1L2L3
Six connectors
to plug the
cables from the rectifiers
RECT 6
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 5
TB1
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 3
TB2
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 2
L1L2L3
GRD
RECT 1
Junction box
shown with
front cover
open
Screw type
terminal block
Tie down
Knockout
GRD
Maintenance 43
Page 50

Figure 35 AC cable routing for the Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 in a top fed system
Junction
box
Partial
view of
junction
RECT 1
RECT 2
RECT 3
RECT 4
RECT 5
RECT 6
Partial view of Rect. 1
box
Rect.
1
Rect.
2
Enlarged view of
routing of the AC
cables from behind
the junction box to
the side of the
rectifiers.
Rect.
Rect.
3
5
4Rect.
Rect.
6
Figure 36 AC cable routing for the Helios Rectifiers 200E/48 in a bottom fed system
Partial view of Rect. 6
Rect.
6
Rect.
5
Rect.
4
Rect.
RECT 1
RECT 2
RECT 3
RECT 4
RECT 5
Enlarged view of
routing of the AC
cables from behind
the junction box to
the side of the
RECT 6
Partial
view of
junction
box
Junction box
See
enlarged view
Rect.
3
rectifiers.
Rect.
2
1
44 Maintenance
Page 51

5.3.2 Replacing a Rectifier
Replace a rectifier as described below for a Helios Rectifier 100/48 or as in
Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48,
whichever is applicable.
Replacing a Helios
Replacing a Helios Rectifier 100/48
1. Notify the alarm center of incoming alarms during this procedure.
2. Turn OFF the AC and DC circuit breakers on the rectifier.
3. Remove the corresponding sense fuse on the front of the controller.
4. Remove the left and right rectifier retaining bars by loosening the screws.
5. Slide the rectifier out of the shelf carefully. Reuse the shipping carton of the new rectifier to
store or ship the removed unit.
6. Ensure that the AC and DC circuit breakers on the new rectifier about to be plugged-in are in
the “OFF” position (down).
7. Carefully slide the new rectifier into the shelf, ensuring that it is fully inserted.
8. Reinstall the left and right side clamping brackets removed in
into position.
9. Operate the AC circuit breaker of the new rectifier to the “ON” position.
10. With the DC breaker in the “OFF” position, adjust the float, equalize and high voltage
shutdown voltage levels as required. Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
11. Reinstall the sense fuse (RC) removed in
12. Ensure that the FLS/FS switch on the rectifier is set to the same position as that of the other
rectifiers in the power system.
13. Operate the DC circuit breaker of the new rectifier to the “ON” position.
14. Verify that the replacement rectifier is sharing the load by observing its ammeter. It should
display approximately the same value as the ammeters on the other rectifiers. If not, adjust
its Float and Equalize voltage levels as described in the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
6.0 - Reference Documents).
15. Notify the alarm center of the end of the procedure.
Step 3.
Step 4
to secure the rectifier
6.0 -
Maintenance 45
Page 52

Replacing a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48
1. Notify the alarm center of incoming alarms during this procedure.
2. Turn OFF the AC and DC circuit breakers on the rectifier to be replaced.
3. Remove the corresponding sense fuse on the front of the controller.
4. At the AC service panel, place the AC circuit breaker associated with this rectifier in the OFF
position.
5. For a Helios Rectifier 200E/48 without an AC cord, remove the AC protective cover at the rear
of the rectifier and disconnect the AC cable inside the rectifier (refer to
For a Helios Rectifier 200I/48 or 200E/48 equipped with an AC cord, unplug the AC cord from
the supply receptacle.
6. Remove the four bolts for the DC connections to the busbar risers at the rear of the cabinet.
7. Disconnect the control and signal cable from the DB25 connector at the rear of the rectifier.
8. Remove the mounting screws securing the rectifier to the cabinet.
9. Carefully slide the rectifier out of the cabinet.
CAUTION:
persons are required to remove the rectifier.
Reuse the shipping carton of the new rectifier to store or ship the removed unit.
10. Ensure that the AC and DC circuit breakers on the front panel of the new rectifier are in the
OFF position.
11. Lift the new rectifier to its position, rest it on the angle guides, and slide it into the cabinet.
CAUTION:
persons are required to install the rectifier.
12. Align the mounting holes of the rectifier with those of the cabinet uprights and secure the
rectifier in place using the eight mounting screws provided.
Note:
13. Reinstall the four bolts for the DC connections to the busbar risers at the rear of the cabinet
(removed in
14. Reconnect the control and signal cable into the DB25 connector at the rear of the rectifier
(disconnected in
15. Reconnect the AC cable disconnected in
16. At the AC service panel, place the AC circuit breaker associated with the rectifier in the ON
position.
17. Operate the AC circuit breaker of the new rectifier to the “ON” position.
18. With the DC breaker in the “OFF” position, adjust the float, equalize and high voltage
shutdown voltage levels as required. Refer to the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
19. Reinstall the sense fuse (RC) removed in
20. Ensure that the FLS/FS switch on the rectifier is set to the same position as that of the other
rectifiers in the power system.
21. Operate the DC circuit breaker of the rectifier to the “ON” position.
22. Verify that the rectifier is sharing the load by observing its ammeter. It should display
approximately the same value as the ammeters on the other rectifiers. If not, adjust its float
and equalize voltage levels as described in the appropriate rectifier user manual (see
Reference Documents).
23. Notify the alarm center of the end of the procedure.
Due to the weight of the rectifier (55 kg - 120 lb) a manual lift or at least two
Due to the weight of the rectifier (55 kg - 120 lb) a manual lift or at least two
A star washer must be used on one of the mounting screws.
Step 6).
Step 7).
Step 5
(or the AC cord that was unplugged).
Step 3.
Figure 32).
6.0 -
6.0 -
46 Maintenance
Page 53

5.3.3 Adding or Replacing a Battery String
For replacements, proceed from
dure.
WARNING
!
THIS PROCEDURE IMPLIES THAT ALL OR PART OF THE
BATTERIES WILL BE MOMENTARILY TAKEN OUT OF
SERVICE.
THIS WORK SHOULD THEN BE COMPLETED DURING
REDUCED TRAFFIC HOURS AND/OR WITH A DIESEL
GENERATOR BACKUP AVAILABLE TO ENSURE NO LOSS OF
SERVICE DURING A POSSIBLE AC OUTAGE. IF MORE THAN
ONE STRING IS TO BE REPLACED, REPLACE ONLY ONE
STRING AT A TIME AND DO NOT DISCONNECT THE NEXT
STRING BEFORE THE PREVIOUS ONE IS RECONNECTED.
Removal of the old string:
1.
Notify the alarm center of the possibility of incoming alarms during this procedure.
2. Above the battery stand, or at the top of the main cabinet for a 1500, 3000 or 4000 A system,
or at the overhead busbars for a 6000 A system, locate, disconnect and isolate the charge leads
(+ and -) coming from the batteries being replaced.
3. Disconnect the inter-cell connectors from the individual battery cells, and insulate each
exposed terminal with electrician tape.
4. The removed batteries shall be disposed of in accordance with local, state and national
environmental legislation.
Installation of the new string:
5.
If this is an addition, locate and install the new battery stand according to the specifications
and drawings. If this is a replacement, install the new battery string in the space vacated by
the removed one.
6. Install the new batteries and use the new connecting material supplied with the batteries to
interconnect them.
7. Perform the initial charging of this new battery string according to the battery
manufacturer’s specifications using an external power supply.
8. Above the battery stand, or at the top of the main cabinet for a 1500, 3000 or 4000 A system,
or at the overhead busbars for a 6000 A system, connect the charge leads (+ and -) coming
from the new batteries.
9. Notify the alarm center of the end of the procedure.
Step 1
below. For new installations, go to
Step 5
of this proce-
Maintenance 47
Page 54

5.3.4 Replacement of a Distribution Fuse Block or Circuit Breaker
CAUTION
!
Precautions must be taken to avoid service interruptions.
Use properly insulated tools when working on the power
distribution panels.
Replace a distribution fuse block as described below.
1. Notify the alarm center of incoming alarms during this procedure.
2. Remove the fuse from the fuse block to be replaced.
3. Remove the rear panels of the cabinet.
4. Carefully remove and insulate any load and alarm leads connected to the fuse block.
5. Carefully remove the fuse block.
6. Ensure that the fuse is removed from the new fuse block.
7. Carefully install the new fuse block.
8. Reconnect the load and alarm leads disconnected in
9. Install the fuse in the fuse block.
10. Notify the alarm center of the end of this procedure.
Step 4.
Replacing a distribution circuit breaker
Replace a distribution circuit breaker as described below.
1. Notify the alarm center of incoming alarms during this procedure.
2. Place the circuit breaker to be replaced in the OFF position.
3. Remove the rear panels of the cabinet.
4. Carefully remove and insulate any load lead and alarm lead connected to the circuit breaker.
5. Carefully remove the circuit breaker.
6. Ensure that the new circuit breaker is in the OFF position before installing it.
7. Carefully install the new circuit breaker.
8. Reconnect the load and alarm leads disconnected in
9. Turn on the circuit breaker
10. Notify the alarm center of the end of this procedure.
Step 4.
5.3.5 Replacing a Cabinet Alarm Lamp
Replace a cabinet alarm lamp as described below.
1. Remove the LP fuse on the controller (F31).
2. Unscrew and remove the lens cap on the cabinet alarm lamp unit.
3. Pull the defective light bulb out.
4. Insert the new light bulb.
5. Screw back the lens cap on the cabinet alarm lamp unit.
6. Reinstall the LP fuse on the controller (F31) removed in
48 Maintenance
Step 1.
Page 55

6.0 R
EFERENCE DOCUMENTS
Manual No. Description
SL-60040 600 A and 1200 A Battery Disconnect Unit
SL-60014 TCM48 temperature compensation module
SL-60026 Voltage level limits for rectifiers and controllers
SL-60015 Helios Monitor 3000/48 remote surveillance unit
SL-60033 Helios DC System 4000/48 Installation manual
SL-60012 Helios Rectifier 100/48
SL-60036 Helios Rectifier 200I/48
SL-60037 Helios Rectifier 200E/48
Reference Documents 49
Page 56

7.0 L
IST OF TERMS
A
ABS
ABSF
AC or ac
ACO
AD
ADJ
ALM
AMP
AUD
AUX
AWG
BAT
BAT RTN
BDA
BDU
BMU
BOD
BODA
BPG
BR
BRR
CAL
CFA
CHG
COM
CONT
CSA
CTRL
DC or dc
DFA
DISCH
DSPL
EB
EMI
EQL
ESD
EXT
F
FA
FG
FGB
FS
ft
ft-lb
GRD or GRND
HF
HV
HVA
ampere
alarm battery supply
alarm battery supply fuse
alternating current
alarm cut-off
Assembly drawing
adjust or adjustment
alarm
ampere
audible
auxiliary
American wire gauging
battery
battery return
battery disconnect alarm
battery disconnect unit
battery management unit
battery on discharge
battery on discharge alarm
building principal ground
battery return
battery return reference
calibrate
charge fuse alarm
charge
common
control
Canadian Standard Association
control
direct current
distribution fuse alarm
discharge
display
earthquake brace
electromagnetic interference
equalize
electrostatic discharge
external
fuse
fuse alarm
frame ground
floor ground bar
forced sharing
foot
foot-pound
ground
high float
high voltage
high voltage alarm
50 List of Terms
Page 57

HVSD
HVSDA
HVSDR
in.
in.-lb
IS
ISG
L
lb
LED
LF
LOP
LV
LVA
LVD
LVDA
LVR
m
MAJ
MGB
MIN
MNL
MOP
MPS
mV
NC
N-m
NO
NORM
psi
PWR
RC
RECT
REF
RFA
RPM
RST
SHT
SLS
SPG
SW
TB
TCM
TP
TR
TST
UL
V
VRLA
WD
WVP
high voltage shutdown
high voltage shutdown alarm
high voltage shutdown reset
inch
inch-pound
interconnect schematic
isolated system ground
line
pound
light emitting diode
low float
loss of phase
low voltage
low voltage alarm
low voltage disconnect
low voltage disconnect alarm
low voltage reconnect
meter
major
main ground bar
minor
manual
method of procedure
modular power shelf
millivolt
normally closed
Newton-meter
normally open
normal
pound per square inch
power
Rectifier control
rectifier
reference
rectifier failure alarm
remote power monitor
reset
shunt
slope load share
single-point ground (connection)
switch
terminal block
temperature compensation module
test point
temporary release
test
Underwriters Laboratories
volt
valve regulated lead acid (batteries)
wiring diagram
water vapor pressure
List of Terms 51
Page 58

52 List of Terms
Page 59

Helios DC System 4000/48
1500, 3000, 4000 & 6000 A
DC Power System
Technical Support
U.S.A. 1-800-222-5877
Outside the U.S.A. 614-841-6755
U.K. +44 (0) 1793 553355
France +33 1 4 87 51 52
Germany +49 89 99 19 220
Italy +39 2 98250 1
Netherlands +00 31 475 503333
E-mail upstech@liebert.com
Web site http://www.liebert.com
Worldwide FAX
tech support
614-841-5471
The Company Behind The Products
With more than 500,000 installations around the globe, Liebert is the world leader in computer
protection systems. Since its founding in 1965, Liebert has developed a complete range of support
and protection systems for sensitive electronics:
• Environmental systems: close-control air conditioning from 1.5 to 60 tons.
• Power conditioning and UPS with power ranges from 250 VA to more than 1000 kVA.
• Integrated systems that provide both environmental and power protection in a single, flexible
package.
• Monitoring and control — on-site or remote — from systems of any size or location
Service and support, through more than 100 service centers around the world, and a 24-hour
Customer Response Center.
While every precaution has been taken to ensure accuracy and completeness of this literature,
Liebert Corporation assumes no responsibility, and disclaims all liability for damages resulting
from use of this information or for any errors or omissions.
© 1998 Liebert Corporation. All rights reserved throughout the world. Specifications subject to
change without notice.
® Liebert and the Liebert logo are registered trademarks of Liebert Corporation. All names
referred to are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Printed in U.S.A.
SL-60030
Revised: June 1999
 Loading...
Loading...