LG VN270 Service Manual
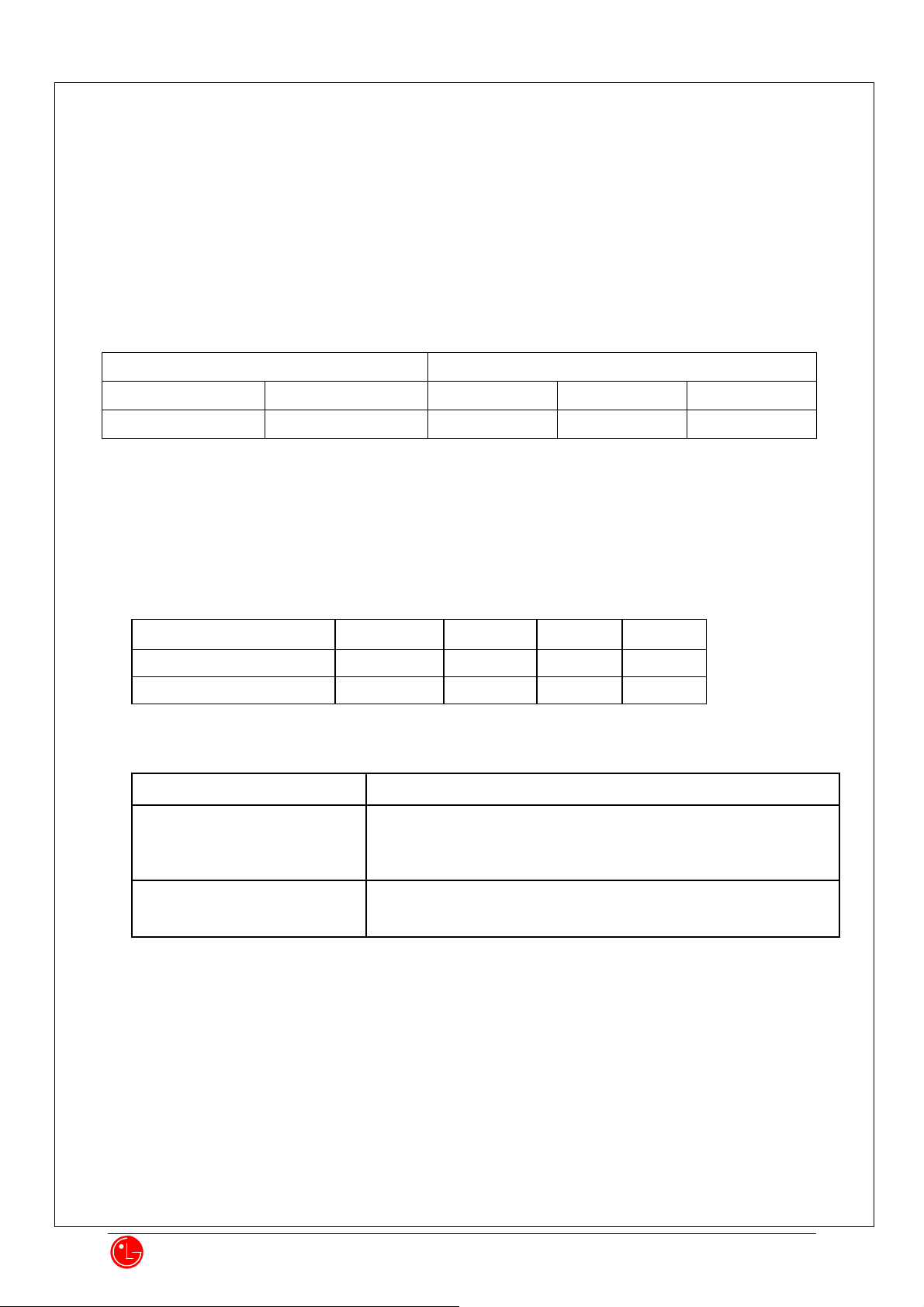
Transmit Frequency (MHz)
Receive Frequency (MHz)
CELLULAR
PCS
CELLULAR
PCS
GPS
824.82 ~ 848.19
1850~1910
869.82~893.19
1930~1990
1575.42
MODE
Part Name
Voltage
Current
Power
CELLULAR
ACPM-7354
4.2V
600mA
0.251W
PCS
ACPM-7354
4.2V
600mA
0.240W
Classification
Function
QSC6055
Terminal operation control and digital signal processing
Converts RF signal to baseband signal
Converts baseband signal to RF signal
MCP (
H8BCS0SIBAR-46M)
NAND (2Gbit) + DDR (1Gbit)
Storing of terminal operation program
Features of VN270
1. Wave Type
CELLULAR : G7W
PCS : G7W
2. Frequency Scope
3. Rated Output Power : CELLULAR = 0.251W / PCS = 0.240W
4. Output Conversion Method : This is possible by correcting the key board channel.
5. Voltage and Current Value of Termination Part Amplifier (Catalogue included)
6. Functions of Major Semi-Conductors
7. Frequency Stability
CELLULAR : ±0.5PPM
PCS : ±0.1PPM
LG Electronics Inc.

VN270
SERVICE MANUAL
CDMA Mobile Subscriber Unit
VN270
TRIPLE BAND, TRIPLE MODE
[PCS/GPS/CELLULAR]
CDMA MOBILE PHONE
1 LG Electronics Inc.

VN270
Table of Contents
General Introduction .................................. 2
CHAPTER 1. System Introduction
1. CDMA Abstract ................................................3
1.1 CDMA Abstract ..........................................3
2. Features and Advantages of CDMA Mobile
Phone ..............................................................5
2.1 Various Types of Diversities ......................5
2.2 Power Control ............................................5
2.3 Voice Encoder and Variable Data Speed ..6
2.4 Protecting Call Confidentiality....................6
2.5 Soft Handoff...............................................6
2.6 Frequency Re-Use and Sector
Segmentation.............................................6
2.7 Soft Capacity .............................................7
3. Structure and Functions of Tri-band CDMA
Mobile Phone...................................................8
4. Specification ....................................................9
4.1 General Specification.................................9
4.2 Receive Specification ..............................10
4.3 Transmit Specification .............................11
4.4 MS (Mobile Station) Transmitter
Frequency................................................12
4.5 MS (Mobile Station) Receiver Frequency 13
4.6 AC Adaptor : See Appendix.....................14
4.7 Cigar Lighter Charger : See Appendix.....14
4.8 Hand-Free Kit : See Appendix .................14
5. Installation .....................................................14
5.1 Installing a Battery Pack ..........................14
5.2 For Adapter Use ......................................14
5.3 For Mobile Mount.....................................14
CHAPTER 2. NAM Input Method ............. 16
CHAPTER 3. Circuit Description
1. RF Transmit/Receive Part .............................26
1.1 Overview..................................................26
1.2 Description of Rx Part Circuit...................27
1.3 Description of Transmit Part Circuit .........31
1.4 Description of Frequency Synthesizer
Circuit.......................................................34
2. Digital/Voice Processing Part ........................34
2.1 Overview..................................................34
2.2 Configuration ...........................................34
2.3 Circuit Description....................................35
Chapter 4. Trouble Shooting
1. Rx Part Trouble .............................................38
1.1 DCN & PCS Rx Trouble...........................38
2. Tx Part Trouble..............................................44
2.1 DCN & PCS Tx Trouble ...........................44
3. Power ............................................................52
3.1 Power On Trouble....................................52
3.2 Charging Trouble .....................................55
4. Logic Part Trouble .........................................57
4.1 LCD Trouble ............................................57
4.2 Camera Trouble.......................................60
4.3 Audio Trouble ..........................................63
4.4 Vibrator Trouble .......................................71
4.5 USB Trouble ............................................74
Appendix .................................................. 75
1. Block Diagram ...............................................75
2. Circuit diagram ..............................................76
2-1. Main PCB ...............................................76
2-2. KEY-PCB................................................76
2-3. MAIN F-PCB...........................................76
3. BGA Pin Map.................................................87
3-1. EUSY0336202(QSG055) .......................87
3-2. EUSY03487506
(H8BCSOSIOBAR-46M).........................88
3-3. EUSY0418701 (BCM2070B2KUBXG) ...89
3-4. EUSY0403901 (WM9093ECS-R)...........90
4. PCB Layout ...................................................91
4-1. Main PCB ...............................................91
5. Ass’y Exploded Diagram ...............................93
6. Part List .........................................................95
6-1. Main PCB Top ........................................95
6-2. Main PCB Bottom ...................................96
6-3. Full BOM List ........................................124
CHAPTER 6. Safety ................................ 160
CHAPTER 7. Glossary............................ 163
1 LG Electronics Inc.
1
VN270
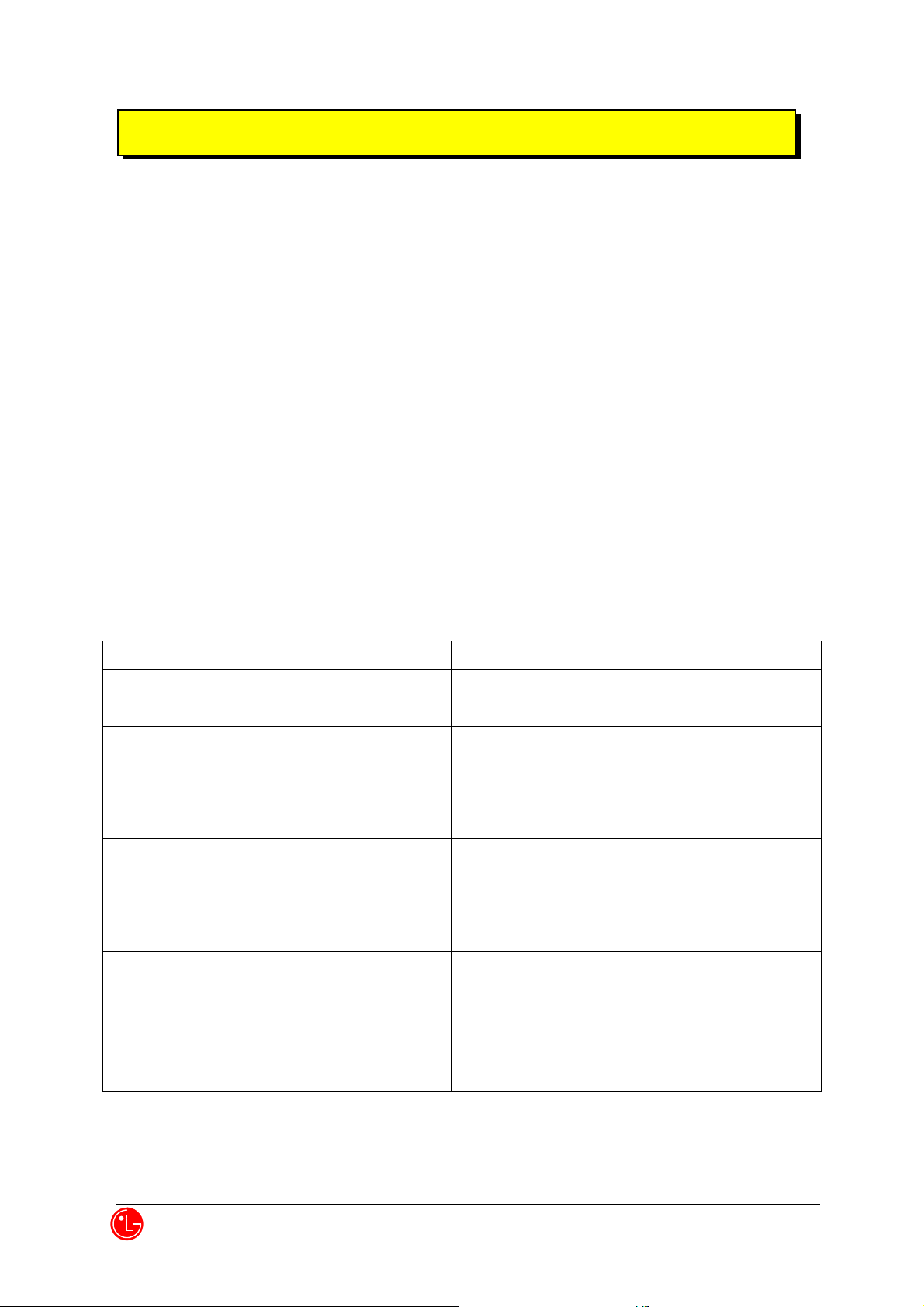
CDMA Standard
Designator
Description
Basic air interface
TIA/EIA/IS-95-A/B/C
ANSI J-STD-008
Protocol between MS and BTS for Cellular & AMPS
Protocol between MS and BTS for PCS
Network
TIA/EIA/IS-634
TIA/EIA/IS/651
TIA/EIA/IS-41-C
TIA/EIA/IS-124
MAS-BS
PCSC-RS
Intersystem operations
Nom-signaling data comm.
Service
TIA/EIA/IS-96-B
TIA/EIA/IS-99
TIA/EIA/IS-637
TIA/EIA/IS-657
Speech CODEC
Assign data and fax
Short message service
Packet data
Performance
TIA/EIA/IS-97
TIA/EIA/IS-98
ANSI J-STD-018
ANSI J-STD-019
TIA/EIA/IS-125
Cellular base station
Cellular mobile station
PCS personal station
PCS base station
Speech CODEC
General Introduction
The VN270 phone has been designed to operate on the latest digital mobile communication technology, Code Division
Multiple Access (CDMA). This CDMA digital technology has greatly enhanced voice clarity and can provide a
variety of advanced features. Currently, CDMA mobile communication technology has been commercially used in
Cellular and Personal Communication Service (PCS). The difference between them is the operating frequency
spectrum. Cellular uses 800MHz and PCS uses 1.9GHz. The VN270 support GPS Mode, we usually call it tri-band
phone. We call it tri-mode phone. If one of the Cellular and PCS base stations is located nearby, Call fail rate of
triple-mode phone is less than dual-mode phone or single-mode phone.
The CDMA technology adopts DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum). This feature of DSSS enables the phone
to keep communication from being crossed and to use one frequency channel by multiple users in the same specific
area, resulting that it increases the capacity 10 times more compared with that in the analog mode currently used.
Soft/Softer Handoff, Hard Handoff, and Dynamic RF power Control technologies are combined into this phone to
reduce the call being interrupted in a middle of talking over the phone.
Cellular and PCS CDMA network consists of MSO (Mobile Switching Office), BSC (Base Station Controller), BTS
(Base station Transmission System), and MS (Mobile Station). The following table lists some major CDMA
Standards.
* TSB –74: Protocol between an IS-95A system and ANSI J-STD-008
2 LG Electronics Inc.
2

VN270
Chapter 1. System Introduction
1. System Introduction
1.1 CDMA Abstract
The CDMA mobile communication system has a channel hand-off function that is used for collecting the information
on the locations and movements of mobile telephones from the cell site by automatically controlling several cell site
through the setup of data transmission routes, and then enabling one switching system to carry out the automatic
remote adjustment. This is to maintain continuously the call state through the automatic location confirmation and
automatic radio channel conversion when the busy subscriber moves from the service area of one cell site to that of
another by using automatic location confirmation and automatic radio channel conversion functions. The call state can
be maintained continuously by the information exchange between switching systems when the busy subscriber moves
from one cellular system area to the other cellular system area.
In the cellular system, the cell site is a small-sized low output type and utilizes a frequency allocation system that
considers mutual interference, in an effort to enable the re-use of corresponding frequency from a cell site separated
more than a certain distance. The analog cellular systems are classified further into an AMPS system, E-AMPS System,
NMT system, ETACS system, and JTACS system depending on technologies used.
Unlike the time division multiple access (TDMA) or frequency division multiple access (FDMA) used in the band
limited environment, the Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) system which is one of digital cellular systems is a
multi-access technology under the interference limited environment. It can process more number of subscribers
compared to other systems (TDMA system has the processing capacity three times greater than the existing FDMA
system whereas CDMA system, about 12~15 times of that of the existing system).
CDMA system can be explained as follows; TDMA or CDMA can be used to enable each person to talk alternately or
provide a separate room for each person when two persons desire to talk with each other at the same time, whereas
FDMA can be used to enable one person to talk in soprano, whereas the other in bass (one of the two talkers can carry
out synchronization for hearing in case there is a bandpass filter function in the area of the hearer). Another available
method is to make two persons to sing in different languages at the same time, space, and frequency when wishing to
let the audience hear the singing without being confused. This is the characteristic of CDMA.
On the other hand, when employing the CDMA technology, each signal has a different pseudo-random binary
sequence used to spread the spectrum of carrier. A great number of CDMA signals share the same frequency spectrum.
In the perspective of frequency area or time area, several CDMA signals are overlapped. Among these types of signals,
only desired signal energy is selected and received through the use of pre-determined binary sequence; desired signals
can be separated, and then received with the correlator used for recovering the spectrum into its original state. At this
3 LG Electronics Inc.
3

VN270
time, the spectrums of other signals that have different codes are not recovered into its original state, and appears as
the self-interference of the system.
4 LG Electronics Inc.
4

VN270
2. Features and Advantages of CDMA Mobile Phone
2.1 Various Types of Diversities
When employing the narrow band modulation (30kHz band) that is the same as the analog FM modulation system
used in the existing cellular system, the multi-paths of radio waves create a serious fading. However, in the CDMA
broadband modulation (1.25MHz band), three types of diversities (time, frequency, and space) are used to reduce
serious fading problems generated from radio channels in order to obtain high-quality calls.
Time diversity can be obtained through the use of code interleaving and error correction code whereas frequency
diversity can be obtained by spreading signal energy to wider frequency band. The fading related to normal frequency
can affect the normal 200~300kHz among signal bands and accordingly, serious effect can be avoided. Moreover,
space diversity (also called path diversity) can be realized with the following three types of methods.
First, it can be obtained by the duplication of cell site receive antenna. Second, it can be obtained through the use of
multi-signal processing device that receives a transmit signal having each different transmission delay time and then,
combines them. Third, it can be obtained through the multiple cell site connection (Soft Handoff) that connects the
mobile station with more than two cell sites at the same time.
2.2 Power Control
The CDMA system utilizes the forward (from a base station to mobile stations) and backward (from the mobile station
to the base station) power control in order to increase the call processing capacity and obtain high-quality calls. In case
the originating signals of mobile stations are received by the cell site in the minimum call quality level (signal to
interference) through the use of transmit power control on all the mobile stations, the system capacity can be
maximized. If the signal power of mobile station is received too strong, the performance of that mobile station is
improved. However, because of this, the interference on other mobile stations using the same channel is increased and
accordingly, the call quality of other subscribers is reduced unless the maximum accommodation capacity is reduced.
In the CDMA system, forward power control, backward open loop power control, and closed loop power control
methods are used. The forward power control is carried out in the cell site to reduce the transmit power on mobile
stations less affected by the multi-path fading and shadow phenomenon and the interference of other cell sites when
the mobile station is not engaged in the call or is relatively nearer to the corresponding cell site. This is also used to
provide additional power to mobile stations having high call error rates, located in bad reception areas or far away
from the cell site.
The backward open loop power control is carried out in a corresponding mobile station; the mobile station measures
power received from the cell site and then, reversely increases/decreases transmit power in order to compensate
channel changes caused by the forward link path loss and terrain characteristics in relation to the mobile station in the
cell site. By doing so, all the mobile transmit signals received by the base station have same strength.
Moreover, the backward closed loop power control used by the mobile station is performed to control power using
the commands issued out by the cell site. The cell site receives the signal of each corresponding mobile station and
compares this with the pre-set threshold value and then, issues out power increase/decrease commands to the
corresponding mobile station every 1.25msec (800 times per second). By doing so, the gain tolerance and the different
5 LG Electronics Inc.
5

VN270
radio propagation loss on the forward/backward link are complemented.
2.3 Voice Encoder and Variable Data Speed
The bi-directional voice service having variable data speed provides voice communication which employs voice
encoder algorithm having power variable data rate between the base station and the mobile station. On the other hand,
the transmit voice encoder performs voice sampling and then, creates encoded voice packets to be sent out to the
receive voice encoder, whereas the receive voice encoder demodulates the received voice packets into voice samples.
One of the two voice encoders described in the above is selected for use depending on inputted automatic conditions
and message/data; both of them utilize four-stage frames of 9600, 4800, 2400, and 1200 bits per second for cellular
and 14400,7200,3600,1800 bits per second for PCS, so PCS provide relatively better voice quality (almost twice
better than the existing cellular system). In addition, this type of variable voice encoder utilizes adaptive threshold
values on selecting required data rate. It is adjusted in accordance with the size of background noise and the data rate
is increased to high rate only when the voice of caller is inputted.
Therefore, background noise is suppressed and high-quality voice transmission is possible under the environment
experiencing serious noise. In addition, in case the caller does not talk, data transmission rate is reduced so that the
transmission is carried out in low energy. This will reduce the interference on other CDMA signals and as a result,
improve system performance (capacity increased by about two times).
2.4 Protecting Call Confidentiality
Voice privacy is provided in the CDMA system by means of the private long code mask used for PN spreading. Voice
privacy can be applied on the traffic channels only. All calls are initiated using the public long code mask for PN
spreading. The mobile station user may request voice privacy during call setup using the origination message or page
response message, and during traffic channel operation using the long code transition request order.
The Transition to private long code mask will not be performed if authentication is not performed. To initiate a
transition to the private or public long code mask, either the base station or the mobile station sends a long code
transition request order on the traffic channel.
2.5 Soft Handoff
A handoff in which the mobile station commences communications with a new base station without interrupting
communications with the old base station. Soft handoff can only be used between CDMA channels having identical
freqeuncy assignments.
2.6 Frequency Re-Use and Sector Segmentation
Unlike the existing analog cellular system, the CDMA system can reuse the same frequency at the adjacent cell. there
6 LG Electronics Inc.
6

VN270
is no need to prepare a separate frequency plan. Total interference generated on mobile station signals received from
the cell site is the sum of interference generated from other mobile stations in the same cell site and interference
generated from the mobile station of adjacent cell site. That is, each mobile station signal generates interference in
relation to the signals of all the other mobile stations.
Total interference from all the adjacent cell sites is the ratio of interference from all the cell sites versus total
interference from other mobile stations in the same cell site (about 65%). In the case of directional cell site, one cell
normally uses a 120°sector antenna in order to divide the sector into three. In this case, each antenna is used only for
1/3 of mobile stations in the cell site and accordingly, interference is reduced by 1/3 on the average and the capacity
that can be supported by the entire system is increased by three times.
2.7 Soft Capacity
The subscriber capacity of the CDMA system is flexible depending on the relation between the number of users and
service classes. For example, the system operator can increase the number of channels available for use during the
busy hour despite the drop in call quality. This type of function requires 40% of normal call channels in the standby
mode during the handoff, in an effort to avoid call disconnection resulting from the lack of channels.
In addition, in the CDMA system, services and service charges are classified further into different classes so that more
transmit power can be allocated to high class service users for easier call set-up; they can also be given higher priority
of using hand-off function than the general users.
7 LG Electronics Inc.
7

VN270
3. Structure and Functions of tri-band CDMA Mobile
Phone
The hardware structure of CDMA mobile phone is made up of radio frequency (RF) part and logic part. The RF part
is composed of Receiver part (Rx), Transmitter part (Tx) and Local part (LO). For the purpose of operating on
tri-band, It is necessary dual Tx path, tri Rx path, dual PLL and switching system for band selection. The mobile
phone antenna is connected with quadplexer which divides antenna input/output signals between cellular frequency
band (824~894 MHz) and PCS frequency band (1850~1990MHz). Quadplexer carries out separating Rx band and Tx
band. The Rx signals from the antenna are directly converted into baseband signal by the frequency synthesizer and
frequency down converter. And then, are converted into digital signals via Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). In
front of the ADC, switching system is required to choose which band path should be open. The digital signals send to
5 correlators in each CDMA de-modulator. Of these, one is called a searcher whereas the remaining 4 are called data
receivers (fingers). Digitalized signals include a great number of call signals that have been sent out by the adjacent
cells. These signals are detected with pseudo-noise sequence (PN Sequence). Signal to interference ratio (C/I) on
signals that match the desired PN sequence are increased through this type of correlation detection process, but other
signals obtain processing gain by not increasing the ratio. The carrier wave of pilot channel from the cell site most
adjacently located is demodulated in order to obtain the sequence of encoded data symbols. During the operation with
one cell site, the searcher searches out multi-paths in accordance with terrain and building reflections. On three data
receivers, the most powerful 3 paths are allocated for the parallel tracing and receiving. Fading resistance can be
improved a great deal by obtaining the diversity combined output for de-modulation. Moreover, the searcher can be
used to determine the most powerful path from the cell sites even during the soft handoff between the two cell sites.
Moreover, 3 data receivers are allocated in order to carry out the de-modulation of these paths. Output data that has
been demodulated changes the data string in the combined data row as in the case of original signals(deinterleaving),
and then, are demodulated by the forward error correction decoder which uses the Viterbi algorithm.
Mobile station user information send out from the mobile station to the cell site pass through the digital voice
encoder via a mike. Then, they are encoded and forward errors are corrected through the use of convolution encoder.
Then, the order of code rows is changed in accordance with a certain regulation in order to remove any errors in the
interleaver. Symbols made through the above process are spread after being loaded onto PN carrier waves. At this
time, PN sequence is selected by each address designated in each call.
Signals that have been code spread as above are digital modulated (QPSK) and then, power controlled at the automatic
gain control amplifier (AGC Amp). Then, they are converted into RF band by the frequency synthesizer synchronizing
these signals to proper output frequencies.
Transmit signals obtained pass through the quadplexer filter and then, are sent out to the cell site via the antenna.
8 LG Electronics Inc.
8
VN270
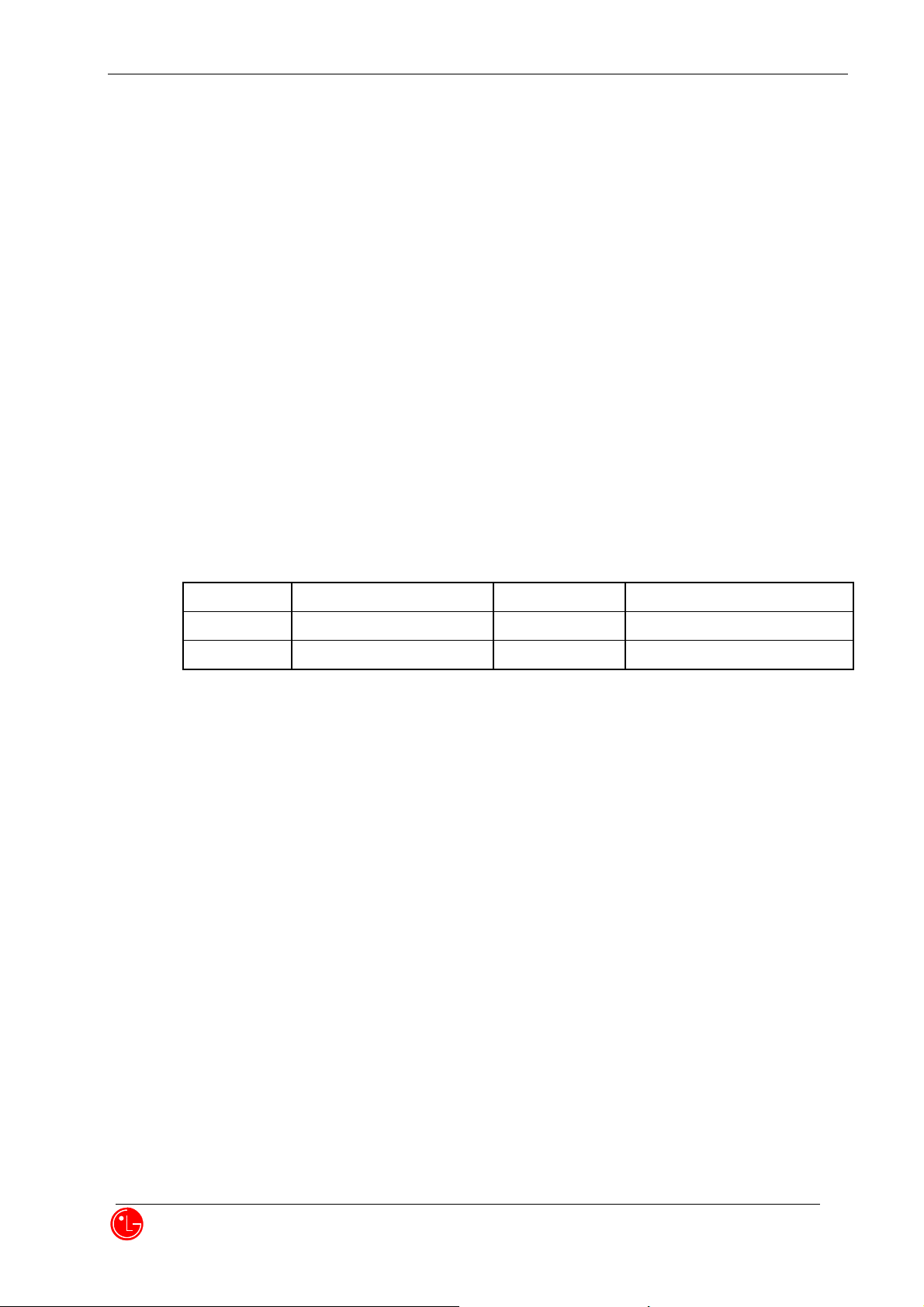
SLEEP
IDLE
MAX POWER
CELLULAR
1.0mA
80~90mA
550 mA (24.5 dBm)
PCS
1.0 mA
80~90mA
600 mA (24.5 dBm)
4. Specification
4.1 General Specification
4.1.1 Transmit/Receive Frequency Interval
1) CELLULAR : 45 MHz
2) PCS : 80 MHz
4.1.2 Number of Channels (Channel Bandwidth)
1) CELLULAR : 20 Channels
2) PCS : 48 Channels
4.1.3 Operating Voltage
DC 3.3~4.2V
4.1.4 Battery Power Consumption
DC 3.7V
4.1.5 Operating Temperature
-20C ~ +50C
4.1.6 Frequency Stability
1) CDMA : ±0.5PPM
2) PCS : ±0.1PPM
4.1.7 Antenna
Fixed Type (Internal Antenna), 50Ω
4.1.8 Size and Weight
4.1.9 Channel Spacing
9 LG Electronics Inc.
1) Size : W x H x D : 103 x 52 x 16.6mm
2) Weight : 120.8g
1) CELLULAR : 1.25MHz
2) PCS: 1.25 MHz
9
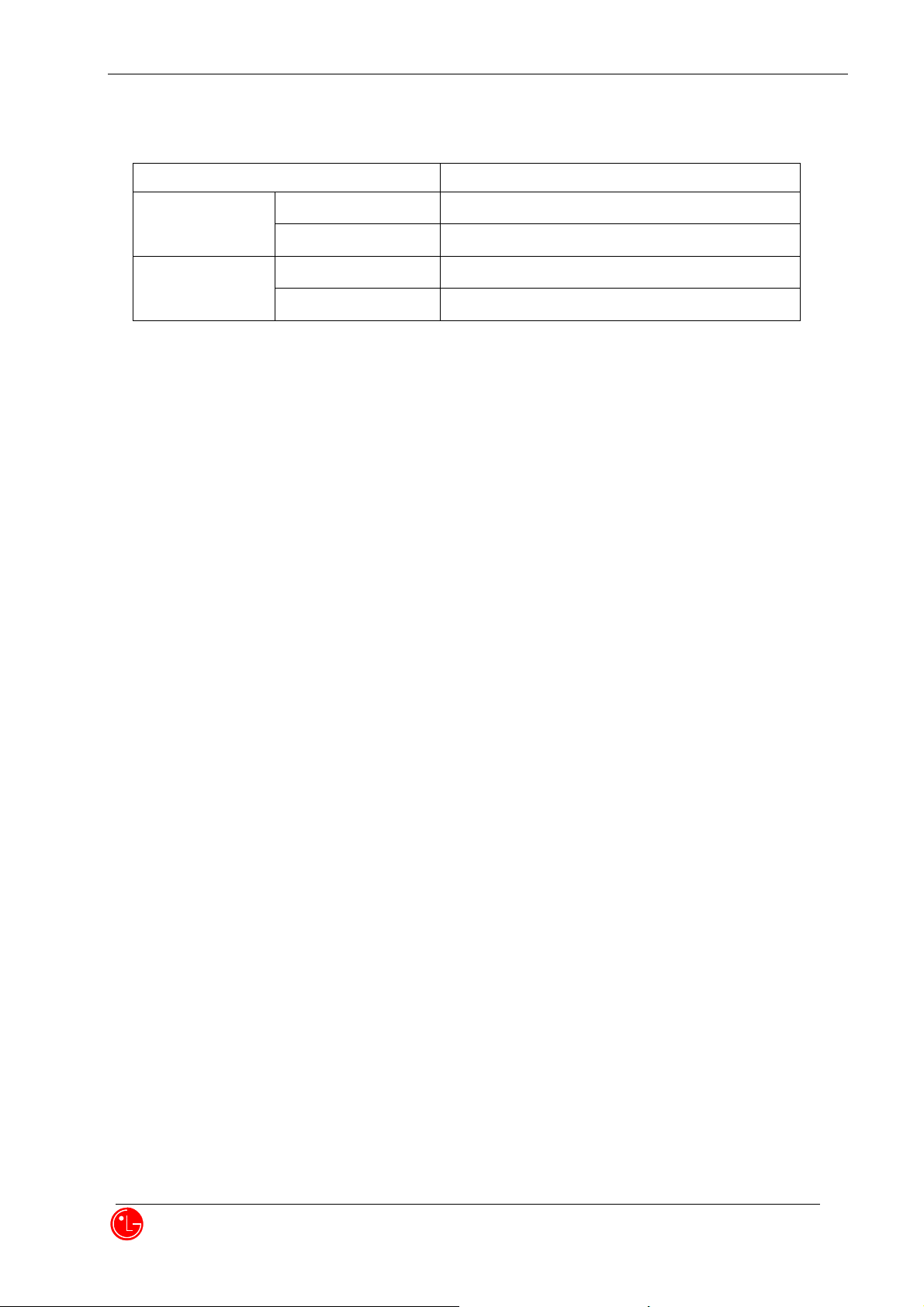
VN270
Standard (1000mAh)
Stand-by Time
PCS(Slot Cycle 2)
About 500 Hrs (SCI=2)
Cellular (Slot Cycle 2)
About 500 Hrs (SCI=2)
Talk Time
PCS(Slot Cycle 2)
About 360 Min.(typical Quadplexer, -92dBm Input)
Cellular (Slot Cycle 2)
About 350 Min.(typical Quadplexer, -92dBm Input)
4.1.10 Battery Type, Capacity and Orerating Time
Unit = Hours, Minutes
4.2 Receive Specification
4.2.1 Frequency Range
1) CELLULAR : 869.820 MHz ~ 893.190 MHz
2) PCS : 1930 MHz ~ 1990 MHz
3) GPS : 1575.42 MHz
4.2.2 Local Oscillating Frequency Range
1) CELLULAR : 1738.08MHz ~ 1787.94MHz
2) PCS : 1715.56MHz 1768.89MHz
3) GPS : 3150.84MHz
4.2.3 Sensitivity
1) CELLULAR : -104dBm (C/N 12dB or more)
2) PCS : -104dBm (C/N 12dB or more)
3) GPS : -148.5dBm
4.2.4 Selectivity
1) CELLULAR : 3dB C/N Degration (With Fch±1.25 kHz : -30dBm)
2) PCS : 3dB C/N Degration (With Fch±1.25 kHz : -30dBm)
4.2.5 Interference Rejection
1) Single Tone : -30dBm at 900 kHz (CELLULAR), -30dBm at 1.25MHz(PCS)
2) Two Tone : -43dBm at 900 kHz & 1700kHz(CELLULAR), -43dBm at 1.25 MHz & 2.05 MHz
4.2.6 Spurious Wave Suppression
Maximum of -80dB
10 LG Electronics Inc.
10

VN270
4.2.7 CDMA Input Signal Range
Dynamic area of more than -104~ -25 dB: 79dB at the 1.23MHz band.
4.3 Transmit Specification
4.3.1 Frequency Range
1) CELLULAR : 824.820MHz ~ 848.190MHz
2) PCS : 1850 MHz ~ 1910 MHz
4.3.2 Local Oscillating Frequency Range
1) CELLULAR : 1738.08MHz ~ 1787.94MHz
2) PCS : 1715.56MHz 1768.89MHz
4.3.3 Intermediate Frequency
Direct Conversion
4.3.4 Output Power
1) CELLULAR : 0.251W
2) PCS: 0.240W
4.3.5 CDMA TX Frequency Deviation
1) CELLULAR: +300Hz or less
2) PCS: 150Hz
4.3.6 CDMA TX Conducted Spurious Emissions
1) CELLULAR : 900kHz : - 42 dBc/30kHz below
1.98MHz : - 54 dBc/30kHz below
2) PCS : -42 dBc / 30KHz below
4.3.7 CDMA Minimum TX Power Control
1) CELLULAR : - 50dBm below
2) PCS: -50dBm below
11 LG Electronics Inc.
11
VN270
Ch #
Center Freq. (MHz)
Ch #
Center Freq. (MHz)
1011
29
70
111
152
193
234
275
316
363
824.640
825.870
827.100
828.330
829.560
830.790
832.020
833.250
834.480
835.890
404
445
486
527
568
609
650
697
738
779
837.120
838.350
839.580
840.810
842.040
843.270
844.500
845.910
847.140
848.370
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
25
1851.25
425
1871.25
825
1891.25
50
1852.50
450
1872.50
850
1892.50
75
1853.75
475
1873.75
875
1893.75
100
1855.00
500
1875.00
900
1895.00
125
1856.25
525
1876.25
925
1896.25
150
1857.50
550
1877.50
950
1897.50
175
1858.75
575
1878.75
975
1898.75
200
1860.00
600
1880.00
1000
1900.00
225
1861.25
625
1881.25
1025
1901.25
250
1862.50
650
1882.50
1050
1902.50
275
1863.75
675
1883.75
1075
1903.75
300
1865.00
700
1885.00
1100
1905.00
325
1866.25
725
1886.25
1125
1906.25
350
1867.50
750
1887.50
1150
1907.50
375
1868.75
775
1888.75
1175
1908.75
4.4 MS (Mobile Station) Transmitter Frequency
4.4.1 CELLULAR mode
4.4.2 PCS mode
12 LG Electronics Inc.
12
VN270
Ch. #
Center Freq. (MHz)
Ch. #
Center Freq. (MHz)
1011
29
70
111
152
193
234
275
316
363
869.640
870.870
872.100
873.330
874.560
875.790
877.020
878.250
879.480
880.890
404
445
486
527
568
609
650
697
738
779
882.120
883.350
884.580
885.810
887.040
888.270
889.500
890.910
892.140
893.370
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
Ch #
Center Freq (MHz)
25
1931.25
425
1951.25
825
1971.25
50
1932.50
450
1952.50
850
1972.50
75
1933.75
475
1953.75
875
1973.75
100
1935.00
500
1955.00
900
1975.00
125
1936.25
525
1956.25
925
1976.25
150
1937.50
550
1957.50
950
1977.50
175
1938.75
575
1958.75
975
1978.75
200
1940.00
600
1960.00
1000
1980.00
225
1941.25
625
1961.25
1025
1981.25
250
1942.50
650
1962.50
1050
1982.50
275
1943.75
675
1963.75
1075
1983.75
300
1945.00
700
1965.00
1100
1985.00
325
1946.25
725
1966.25
1125
1986.25
350
1947.50
750
1967.50
1150
1987.50
375
1948.75
775
1968.75
1175
1988.75
4.5 MS (Mobile Station) Receiver Frequency
4.5.1 CELLULAR mode
4.5.2 PCS mode
4.5.3 GPS mode : 1575.42MHz
4.5.4 Bluetooth mode : 2400MHz ~ 2483.5MHz
13 LG Electronics Inc.
13

VN270
4.6 AC Adaptor
See Appendix
4.7 Cigar Lighter Charger
See Appendix
4.8 Hands-Free Kit
See Appendix
5. Installation
5.1 Installing a Battery Pack
1) The Battery pack is keyed so it can only fit one way. Align the groove in the battery pack with the rail
on the back of the phone until the battery pack rests flush with the back of the phone.
2) Slide the battery pack forward until you hear a “click”, which locks the battery in place.
5.2 For Adapter Use
1) Plug the adapter into a wall outlet. The adapter can be operated from a 110V source.
When AC power is connected to the adapter.
2) Insert the adapter jack into the phone with the installed battery pack.
Red light indicates battery is being charged.. Green light indicates battery is fully charged.
5.3 For Mobile Mount
5.3.1 Installation Position
In order to reduce echo sound when using the Hands-Free Kit, make sure that the speaker and microphone are not
facing each other and keep microphone a generous distance from the speaker.
5.3.2 Cradle Installation
Choose an appropriate flat surface where the unit will not interface with driver‟s movement or passenger‟s comfort.
The driver/user should be able to access the phone with ease. Using the four self-tapping screws provided, mount the
supplied bracket on the selected area. Then with the four machine screws provided, mount the counterpart on the
reverse side of the reverse side of the cradle. Secure the two brackets firmly together by using the two bracket joint
screws provide.
14 LG Electronics Inc.
14

VN270
The distance between the cradle and the interface box must not exceed the length of the main cable.
5.3.3 Interface Box
Choose an appropriate flat surface ( somewhere under the dash on the passenger side is preferred ) and mount the IB
bracket with the four self-tapping screws provided. Clip the IB into the IB bracket.
5.3.4. Microphone Installation
Install the microphone either by clipping I onto the sun visor (driver‟s side) or by attaching it to door post (driver‟s
side), using a Velcro adhesive tape (not included).
5.3.5 Cable Connections
5.3.5.1 Power and Ignition Cables
Connect the red wire to the car battery positive terminal and the black wire to the car ground. Connect the green wire
to the car ignition sensor terminal. ( In order to operate HFK please make sure to connect green wire to ignition sensor
terminal.) Connect the kit‟s power cable connector to the interface box power receptacle.
5.3.5.2 Antenna Cable Connection
Connect the antenna coupler cable connector from the cradle to the external antenna connector. ( Antenna is not
included.)
15 LG Electronics Inc.
15
VN270
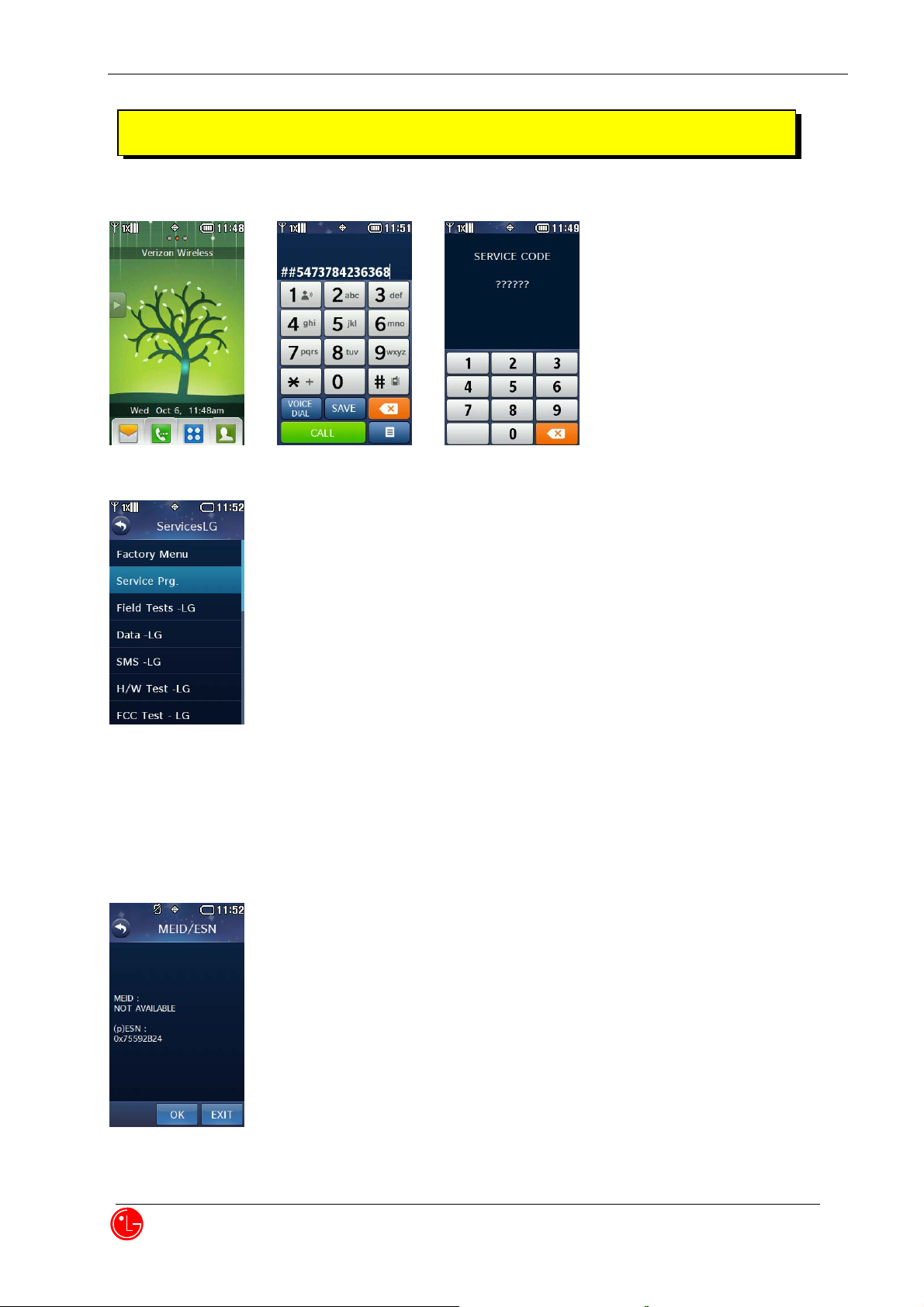
Chapter 2. NAM Input Method
1) Press “##5473784236368 + CALL” and then, press “000000”
2) Select “Service Prg.” to enter service programming menu.
By pressing „OK‟ soft key on every menu, changes will be saved automatically.
By pressing „END‟ key, you can exit service programming menu at any time.
3) MEID/ESN
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “Exit” to exit from service programming menu.
16 LG Electronics Inc.
16
VN270
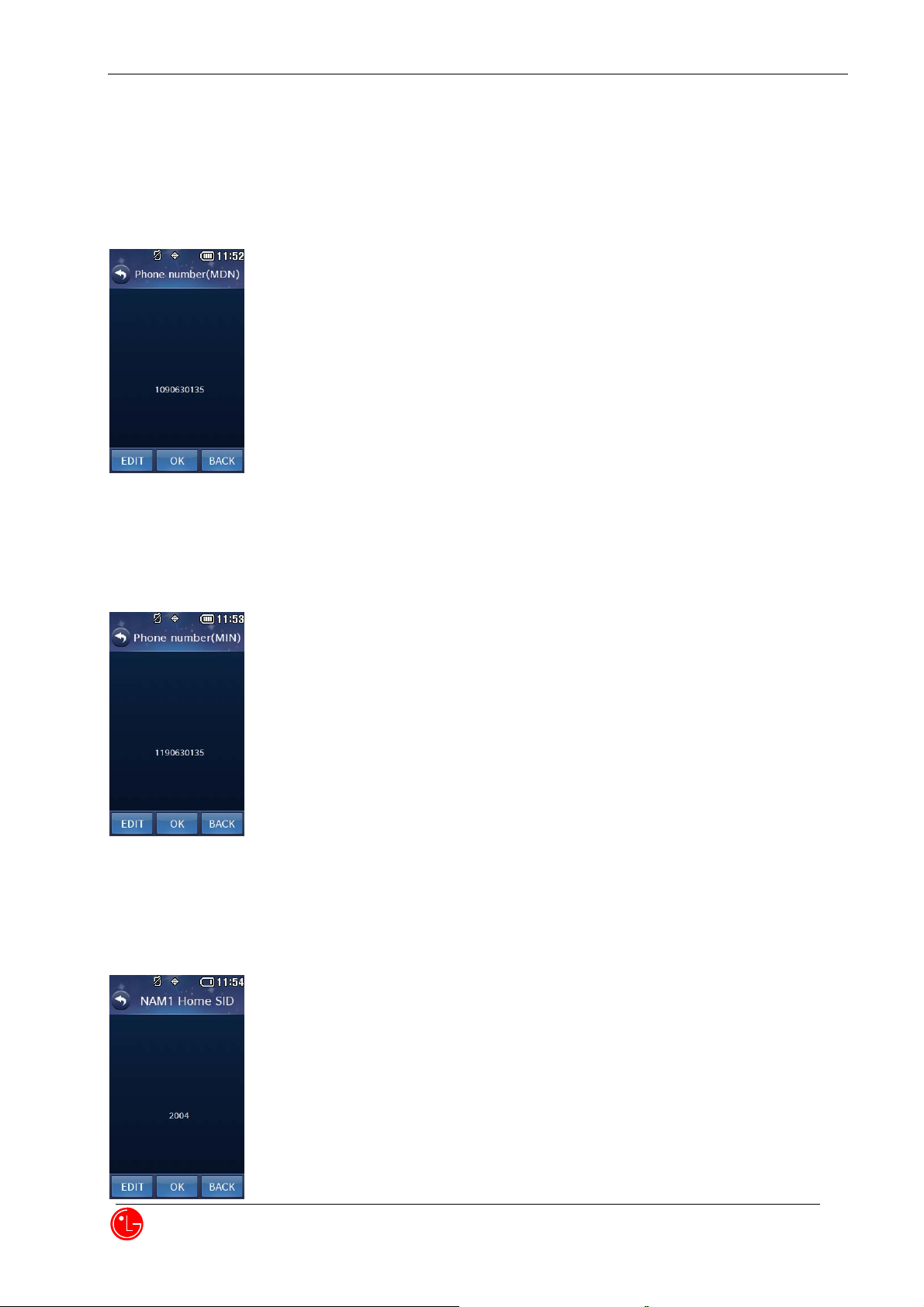
4) NAM 1 Phone Number (MDN)
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
5) NAM1 Phone Number (MIN)
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
6) NAM1 Home SID
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
17 LG Electronics Inc.
17
VN270
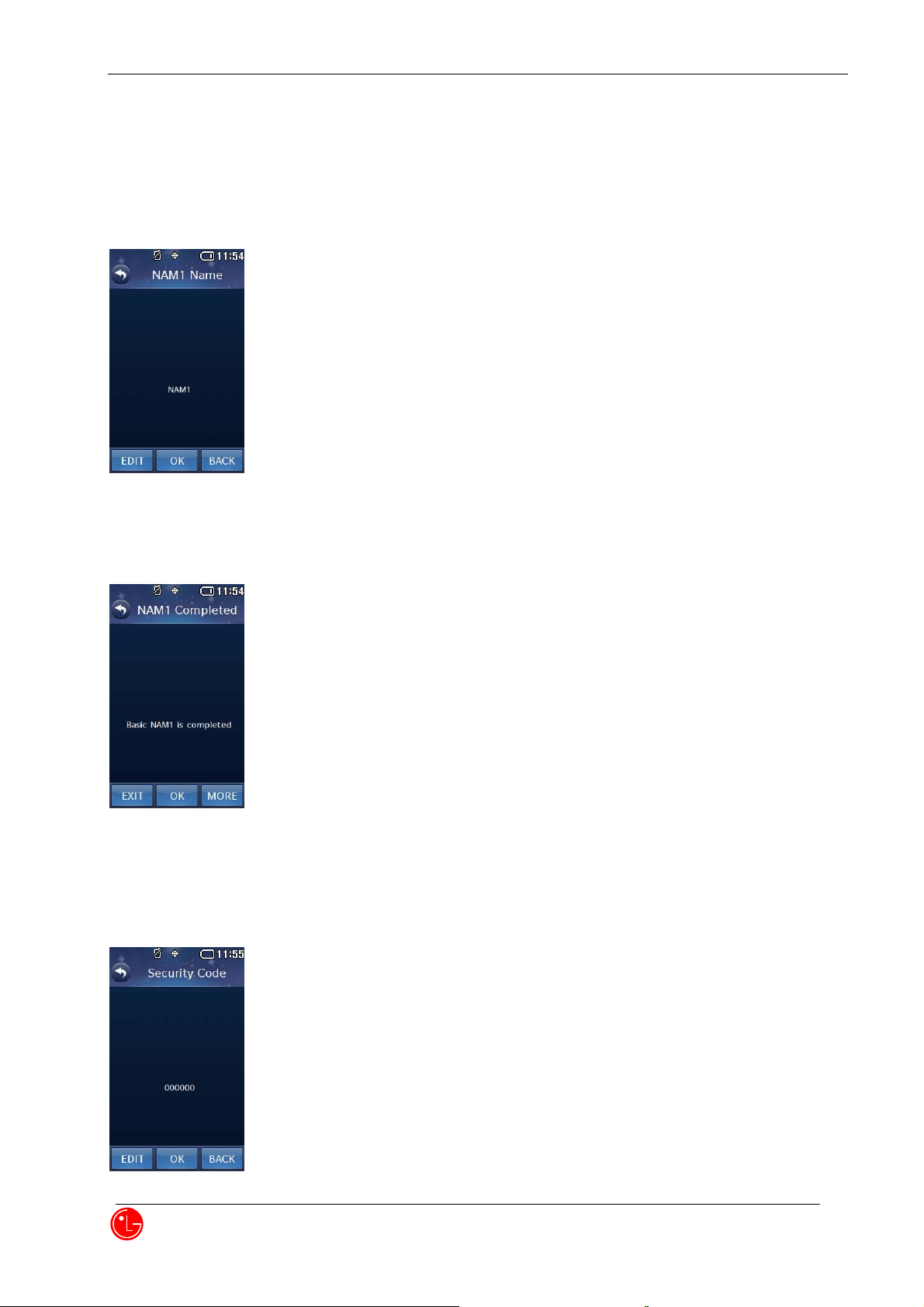
7) NAM1 Name
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
8) More NAM1 Programming
Press “EXIT” or “OK” to exit NAM1 item editing.
Press “MORE” for further service programming menu editing.
9) Security Code
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item. Save and Repress “EDIT” to confirm new security code.
18 LG Electronics Inc.
18
VN270
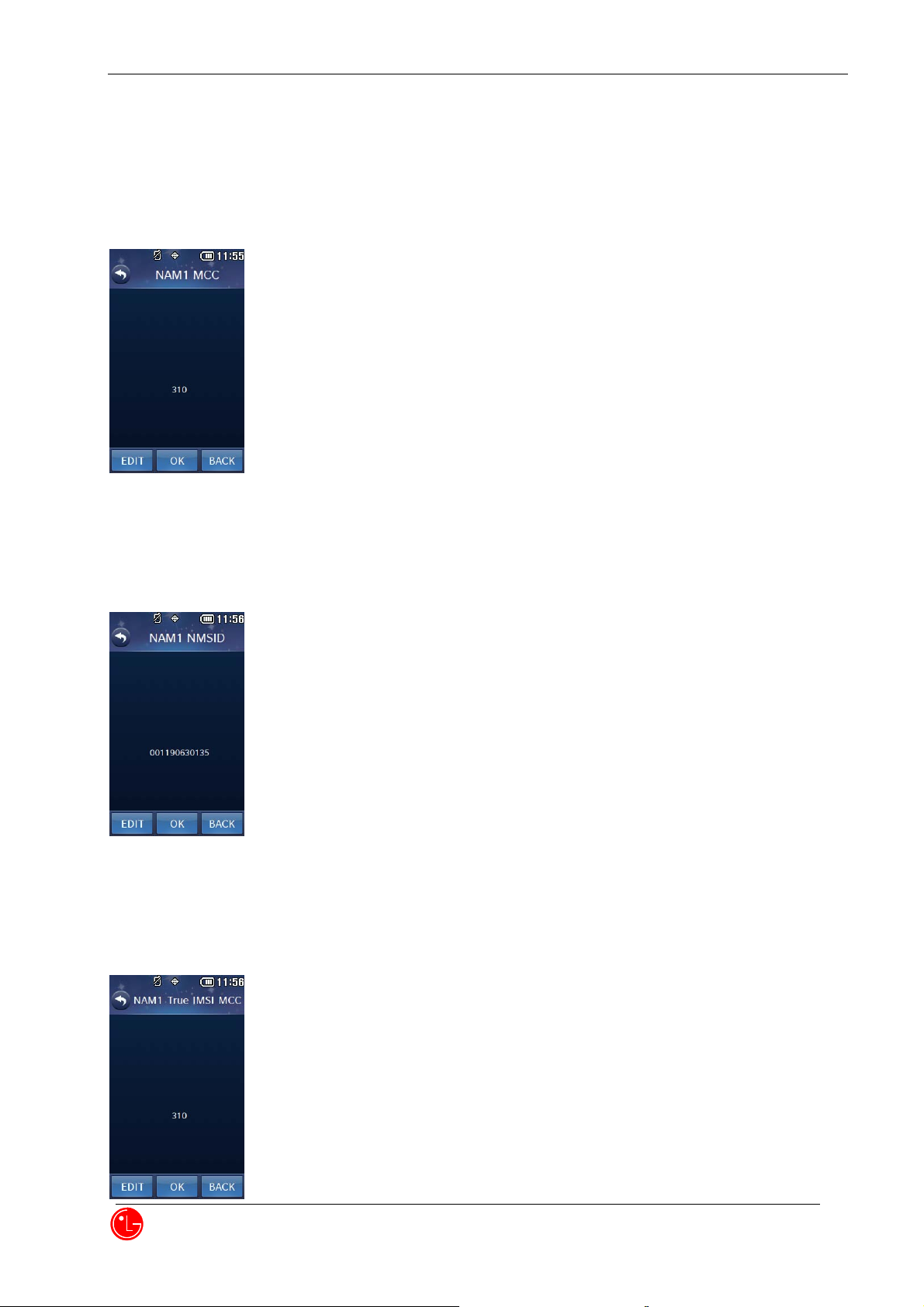
10) NAM1 MCC
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
11) NAM1 NMSID
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
12) NAM1 True IMSI MCC
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
19 LG Electronics Inc.
19

VN270
13) NAM1 True IMSI NMSID
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
14) NAM1 PRL Enabled
Press “OK” to proceed next item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
15) CDMA Home SID/NID
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
20 LG Electronics Inc.
20
VN270
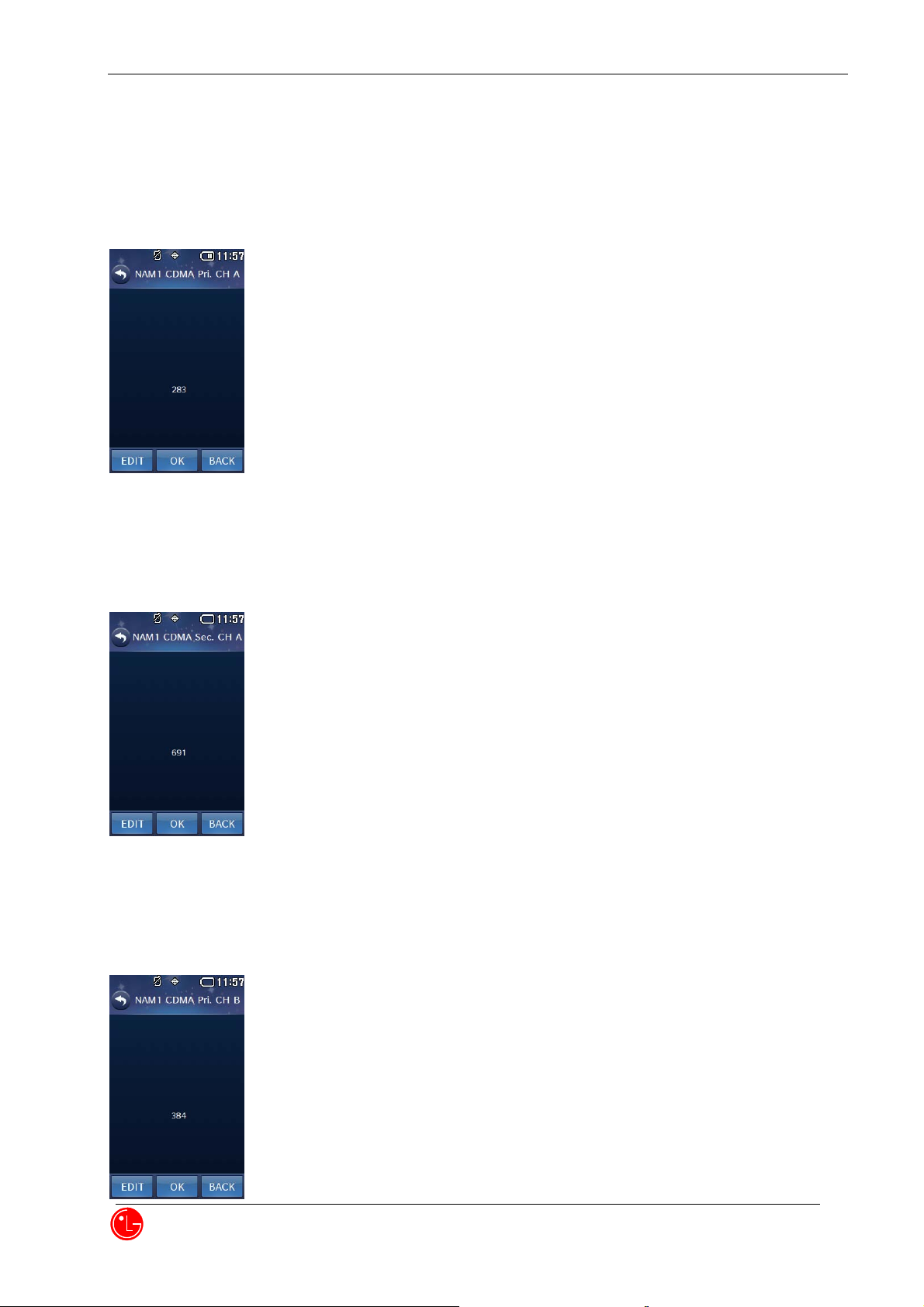
16) NAM1 CDMA Pri.CH A
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
17) NAM1 CDMA Sec. CH A
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
18) NAM1 CDMA Pri. CH B
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
21 LG Electronics Inc.
21
VN270
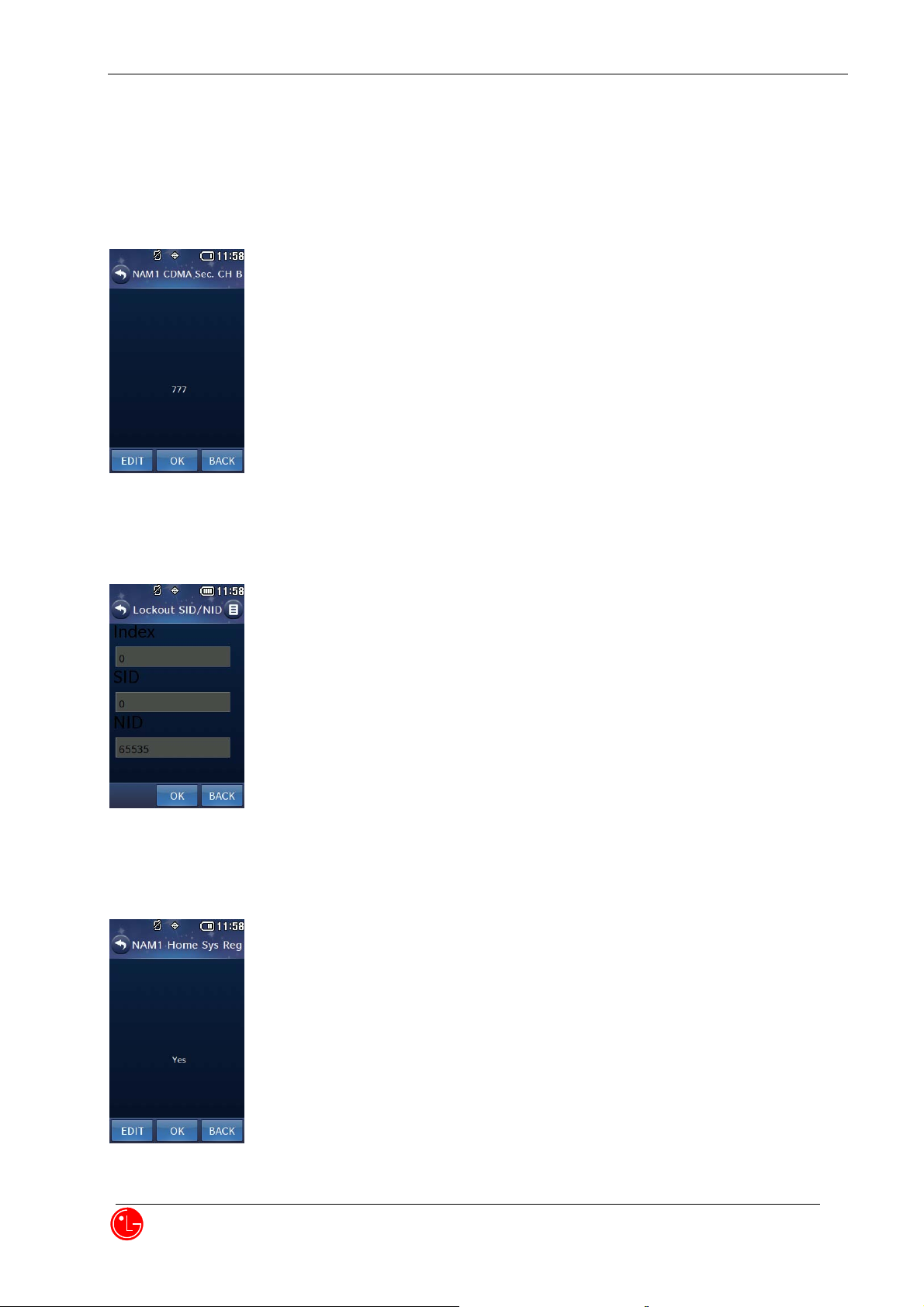
19) NAM1 CDMA Sec. CH B
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
20) Lockout SID/NID
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
21) NAM1 Home Sys Reg
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
22 LG Electronics Inc.
22
VN270
22) NAM1 Forn SID Reg
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
23) NAM1 Forn NID Reg
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
24) NAM1 ACC Ovld Class
Press “OK” to proceed next item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
23 LG Electronics Inc.
23
VN270
25) NAM2 Setting
Press “OK” to proceed next item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
26) Phone Model
Press “OK” to proceed next NAM1 item editing.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
27) Slot Cycle Index
Press “OK” to end service programming.
Press “BACK” to return to the previous menu.
Press “EDIT” to edit this item.
24 LG Electronics Inc.
24

VN270
28) Powering Down
Phone restarts.
25 LG Electronics Inc.
25
VN270
26 LG Electronics Inc.
26
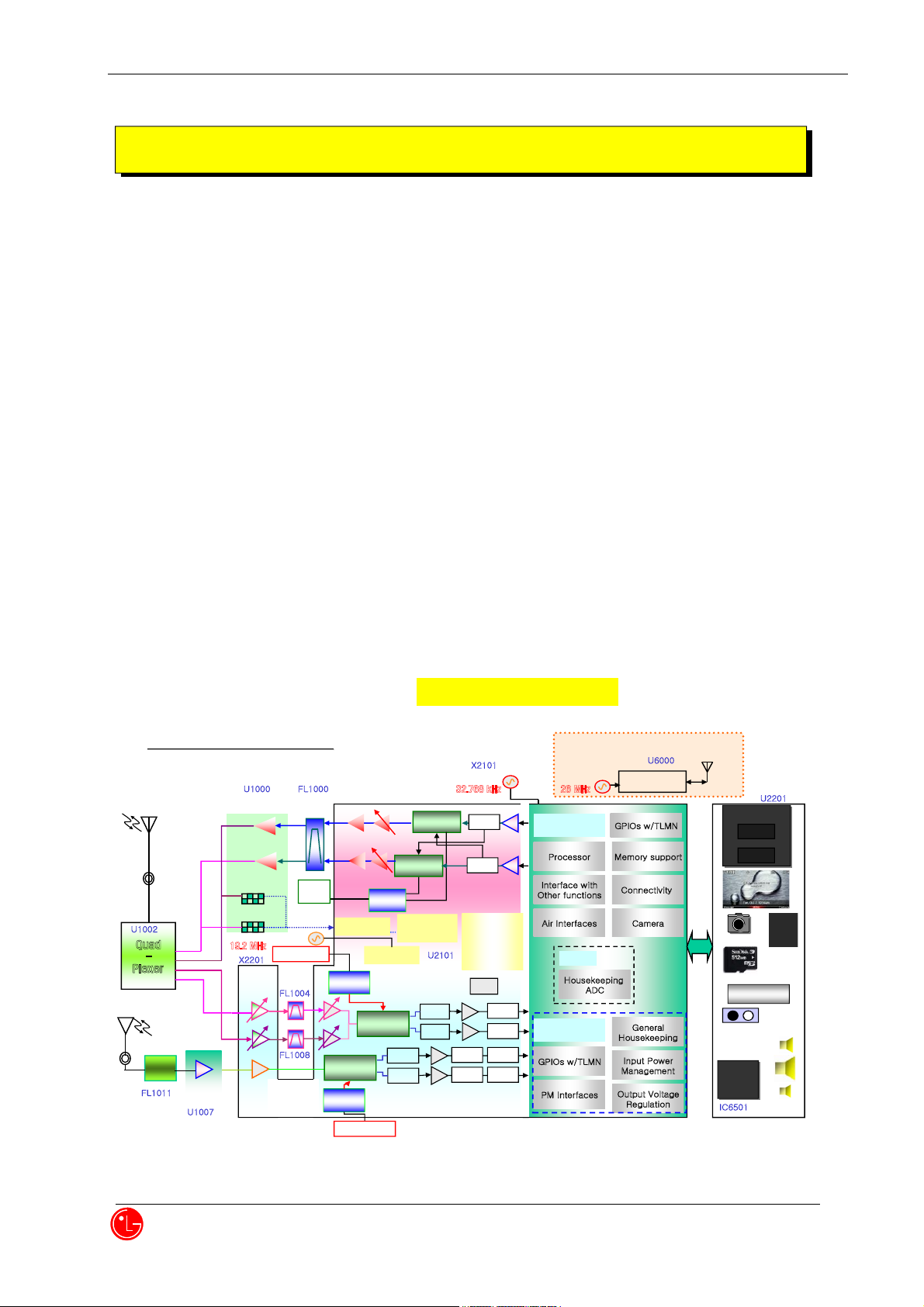
1. RF Transmit/Receive Part
1.1 Overview
The Tx and Rx part employs the Direct Conversion system. The Tx and Rx frequencies are respectively
824.04~848.97MHz and 869.04~893.97MHz for cellular and 1850~1910MHz and 1930~1990MHz for PCS. The
block diagram is shown in [Figure 1-1]. RF signals received through the antenna are seperated by quadplexer.
RF Signal fed into the low noise amplifier (in QSC6055) through the quadplexer. Then, they are combined with the
signals of local oscillator (VCO) at the down conversion mixer(in QSC6055) in order to create Base-band frequency.
Then, this signal is changed into digital signal by the analog to digital converter (ADC, A/D Converter), and the digital
circuit part of the QSC(Qualcomm Single Chip)6055 processes the data from ADC. The digital processing part is a
demodulator.
In the case of transmission, RF Transmitter(in QSC6055) receives QPSK-modulated anlog signal from the QSC6055.
In QSC6055, the baseband quadrature signals are upconverted to the Cellular or PCS frequency bands and amplified
to provide signal drive capability to the power amp.
After that, the RF signal is amplified by the Power Amp in order to have enough power for radiation.
Finally, the RF signal is sent out to the cell site via the antenna after going through the coupler and quadplexer.
[Figure 1-1] Block Diagram Of LG-VN270
Mobile
S/W
Main ANT
Dual-band Ant.
Quad
-
Plexer
SBI
LPF
LPF
VN270 Block Diagram
VN270 Block Diagram
Loop Filter
DCN/PCS
Tx RF BPF
GPS LNA
Dual PAM
(DCN, PCS)
Quad
D’convert
LPF
LPF
Quad
Up-convert
CRX LO
Circuit
GPS LO
Circuit
GPS
BPF
Detector
coupler
Pre- LNA
Quad
D’convert
Loop Filter
Quad
Up-convert
TX _ Gain
Control
LPF
LPF
Baseband
Processor Memory support
Interface with
Other functions
Connectivity
Air Interfaces Camera
GPIOs w/ TLMN
PMIC
GPIOs w/ TLMN
PM Interfaces
Output Voltage
Regulation
ADCLPF
ADCLPF
ADC
ADC
General
Housekeeping
Input Power
Management
QSC
6055
Loop
Filter
TX LO
Circuit
Audio
Housekeeping
A
DC
BLUETOOTH
Module
BLUETOO TH ANT
BCM2070
2.4~2.48G
Buffer
VCTCXO
19.2 MHz
26 MHz
Sleep Crystal
32.768 kHz
Mobile
S/W
GPS ANT
Touch Scre en
Proxi Sensor
Receiver
Audio
AMP
Audio
AMP
Ear jack
1GB
DDR SDRAM
2GB
FLASH
MCP
1.3M cam
SD-card
U1002
U1007
U1000
U2101
U6000
FL1000
FL1004
FL1008
FL1011
X2201
X2101
U2201
IC6501
Chapter 3. Circuit Description

VN270
1.2 Description of Rx Part Circuit
1.2.1 Quadplexer (U102)
The ACFM-7107 is a quadplexer that combines a US PCS duplexer, a cellular band duplexer and a S-GPS
band filter into a single, miniature package with a single antenna port.
The main function of quadplexer is to prohibit the other band signals from flowing into the
one band circuit and vice versa. RF designer can use common tri-band antenna regardless of frequency band
(800, 1575 and 1900 MHz).
27 LG Electronics Inc.
27

VN270
1.2.2 LNAs (U2101)
The QSC6055 has cellular and PCS LNAs, respectively. The characteristics of Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) are low
noise figure, high gain, high intercept point and high reverse isolation.
The frequency selectivity characteristic of mobile phone is mostly determined by LNA.
The specification of VN270 LNAs are described below:
28 LG Electronics Inc.
28
 Loading...
Loading...