LG LSO-43 User Manual

HOMEOWNER'S CARE AND
OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
OASIS SERIES
43" Wood Burning Outdoor Fireplaces
P/N 875,019M REV. B 03/2007
MODELS
LSO-43 LSO-43-H
The information contained in this manual applies to all model fireplaces
identified on this page. This information will help you obtain safe and
dependable service from your Lennox fireplace system. Keep this document in a safe place for future reference.
Before you start your first fire, read this Care and Operations Manual
carefully to be sure you understand your fireplace system completely.
Failure to follow these suggestions could result in hazardous operation or
fireplace malfunction, creating a serious potential for personal injury and/
or property damage.
RETAIN THESE INSTRUCTIONS
FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
If you have any questions regarding the safe use or operation of your
fireplace, contact your local Lennox Dealer or your contractor/builder.
WARNING: EXERCISE CAUTION WHEN OPERATING YOUR
OUTDOOR FIREPLACE. DO NOT BURN LARGE FIRES.
ATMOSPHERIC CHANGES MAY CAUSE UNEXPECTED
GUSTS OF WIND. FLAMES AND ASHES MAY BE BLOWN
OUT OF THE FIREPLACE. KEEP THE SCREEN CURTAINS
CLOSED AT ALL TIMES.
OTL Report No. 116-F-01-2
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Safety Precautions................ page 2
General Information........................... page 2
Fuels .................................................. page 2
Gas Logs ........................................... page 2
Disposal of Ashes .............................. page 3
Softwood vs Hardwood ..................... page 3
Starting a Fire .................................... page 4
Damper.............................................. page 4
Glass Door Operating Safety
Precautions and Instructions ........... page 4
Air Inlet .............................................. page 4
Refractories ....................................... page 5
Maintenance Guidelines..................... page 5
Twice a Year Check-Up ...................... page 6
Cleanout Panel................................... page 6
Creosote Formation and Removal...... page 6
Troubleshooting ................................ page 6
Warranty............................................ page 7
Product Reference Information ......... page 7
Replacement Parts ............................ page 7
Accessory Components ..................... page 7
Replacement Parts List...................... page 8
GENERAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IMPORTANT! READ AND UNDERSTAND BEFORE YOUR FIRST FIRE.
1. Use SOLID WOOD only for fuel. It is best to
use dry and well seasoned hardwood. Soft
woods tend to burn very quickly. Solid scrap
construction lumber produces excessive
sparks. DO NOT use treated wood, artificial
wax based logs, charcoal, coal, trash, driftwood or woods that have been dipped in tar,
pitch, pine tar, creosote, etc. Wood products
made with synthetic binders, such as plywood, produce abnormally high temperatures
and sputtering, smoking fires.
2. NEVER use gasoline, gasoline-type lantern
fuel, kerosene, charcoal lighter fluid, or similar
liquids to start or “freshen up” a fire in this
fireplace. Keep any flammable liquids a safe
distance from the fireplace.
3. NEVER leave children unattended when
there is a fire burning in the fireplace.
4. Always ensure that the air inlet to the
fireplace is free from debris and any other
obstructions that can block the entrance of air.
5. With the fire burning, close the protective
mesh screens to keep sparks and embers INSIDE the firebox.
6. Keep any combustible furniture or decorative objects at least 60" (1524 mm) from the
fireplace opening.
7. Never leave your fireplace unattended while
it is burning.
8. Be careful adding wood fuel to the fire or
handling fireplace tools such as shovels, tongs
or pokers.
9. Never modify or alter your fireplace system
in any way. To do so may create a potential fire
hazard and void the Limited Warranty.
10. The bottom refractory can be cracked by
excessive abuse such as tossing heavy logs
onto the grate or gouging with fireplace tools.
Exercise caution when adding wood to your
fireplace.
11. DO NOT use a fireplace insert or any other
product not specified by the manufacturer for
use with this fireplace.
12. Neither the manufacturer nor the seller
warrants "smoke free" operation nor are they
responsible for inadequate system draft caused
by mechanical systems, general construction
conditions, inadequate chimney heights, adverse wind conditions and/or unusual
environmental factors or conditions beyond
our control.
WARNING: TO AVOID THE RISK OF
DAMAGING FIREPLACE MATERIALS
AND INCREASING THE RISK OF FIRE,
DO NOT USE THE FIREPLACE TO COOK
OR WARM FOOD.
GENERAL INFORMATION
1. The all-steel, multi-wall firebox is the heat
center of the system. It is constructed for safe
clearance to combustibles.
2. The hearth floor and sidewalls of the
firebox are lined with a brick pattern reinforced refractory for the look of authenticity
and to provide safety.
3. The metal chimney sections extending from
the firebox top to beyond your roof are two
walled and air-cooled. The inner passage, or
flue, provides the exit for smoke and gases.
4. This fireplace does not have a damper.
There is a flue strainer provided at the flue
entrance to keep debris from entering the
chimney. Before you start a fire, the strainer
must be checked to ensure that it is free of
obstructions.
5. Closed screens prevent fire, sparks and
embers from popping out of the firebox while
a fire is burning. Pull screens back when
adding wood to the firebox.
6. Why use a fuel grate? Besides positioning
the firebed properly, it protects the refractory
floor, back and sides of the fireplace. Further,
it ensures a proper flow of combustion air into
and around the firebed. The grate must be
used at all times when burning. Your warranty
may be voided without the use of this grate.
7. This fireplace is not a heater. It is designed
to ensure homeowner comfort by providing
supplemental heat to its immediate area.
FUELS
Never Use Coal in Your Fireplace
Your fireplace system is not designed to be
used with coal derivative products. The combustion process of certain types of coal can
deposit corrosive materials in the fireplace and
chimney system which can lead to premature
product failure. Never use coal as a fuel in this
fireplace system.
Gas Logs
If your fireplace system was installed with a
gas line, you may wish to install one of two
types of gas log sets.
This fireplace has been tested and approved
for use with a decorative gas appliance incorporating an automatic shut-off device and
complying with the Standard for Decorative
Gas Appliances for installation in vented fireplaces, ANSI Z21.60 (1991). Decorative gas
appliances may be installed in these fireplaces.
Installation must be in accordance with the
national Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 for compliance with the revised U.L. 127 Standard.
2
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
WARNING: THIS FIREPLACE HAS NOT
BEEN TESTED WITH AN UNVENTED GAS
LOG SET. TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
FIRE OR INJURY, DO NOT INSTALL AN
UNVENTED GAS LOG SET INTO THIS
FIREPLACE.
Prior to installing any gas log set, refer to the
fireplace installation instructions for verification of mantle heights and placement of
combustible materials around the firebox opening. Vented gas log sets do not have restrictions
placed upon their BTU rating.
Wood Fuel Pointers
SOFTWOOD VS HARDWOOD
Softwoods contain about 15 percent highly
flammable resin which generates creosote soot
in the chimney flue. Burning softwood exclusively may not be as desirable nor as safe as
burning denser hardwoods. Many experienced
fire-builders use small amounts of softwood
kindling and newspaper in conjunction with
starting a fire with split hardwood logs. Here are
some guidelines to remember:
1. Softwoods produce fast warming and shorter
fires. Hardwoods burn less vigorously, have
shorter flames and produce steady, glowing
coals.
8. Be a knowledgeable wood buyer. There is a
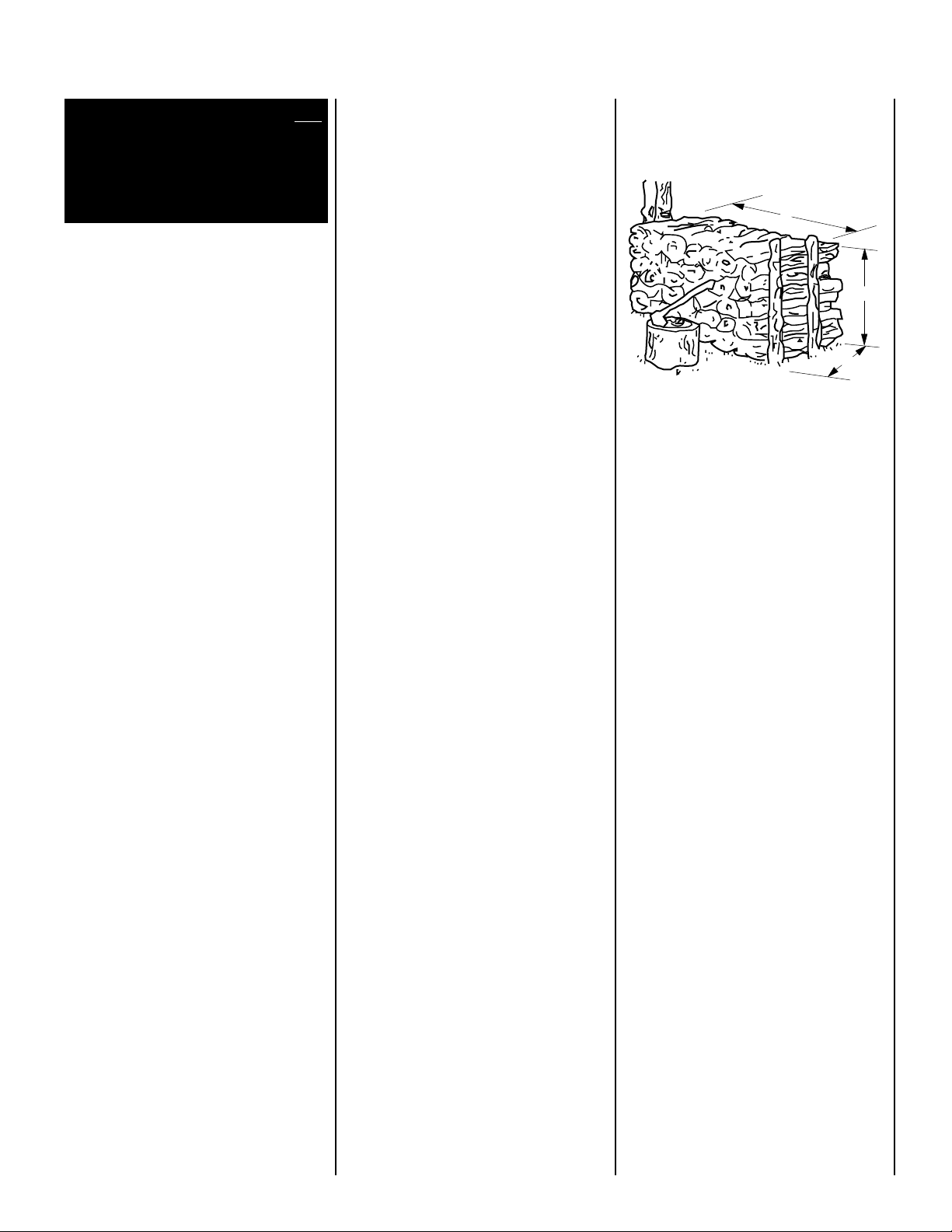
difference in cord sizes. A standard cord stack
of logs is 4 ft. high by 8 ft. long by 4 ft. deep or
the equivalent of this cubic footage, (
Figure 1
Standard
Cord of
8'
Wood
4'
4'
).
Wood is a wonderful renewable fuel source.
Normally it burns clean, leaving only a minimum of waste ash, provides comforting heat
and can provide a variety of aromas and visual
images.
You will want to know which woods are best for
use. Sometimes you may want a quick, short
fire to offset a morning chill. Soft woods are
preferable in this case. Other times you would
want more slow burning and a uniform heat
output. Hardwoods are preferable for this use.
The amount of heat available from the logs will
be about equal on a weight basis. However,
logs are generally not weighed so the amount
of heat will depend on:
1. The type of wood used.
2. How dry it is.
3. How many logs you put in.
4. The size of the logs.
The last statement means that one big log
weighing 10 pounds has as much heating potential as 10 pounds of twigs. However, air
cannot get at the solid log to feed the fire so the
solid log will burn slowly. While you would get
the same amount of heat out of either fire, the
smaller the pieces of wood and the more air
space around them, the faster the fire will burn.
DISPOSAL OF ASHES
Ashes should be placed in a metal container
with a tight fitting lid. The closed container of
ashes should be placed on a noncombustible
floor or on the ground, well away from all
combustible materials, pending final disposal.
If the ashes are to be disposed of by burial in
soil or other wise locally dispersed, they should
be retained in the closed container until all
cinders have thoroughly cooled.
2. As a general rule, denser woods contain
more potential heat per pound. Most softwoods
offer moderate heat value per pound.
3. Different woods vary widely in flame heights,
flame intensities, smoke characteristics and in
sparking. Most hardwoods do not spark.
4. Most freshly cut “green” wood will not burn
well and will smoke. Green wood can be from
10 to 40 percent less efficient than air-dried
seasoned wood.
5. Moisture and resin found inside unseasoned
wood cells will build up pressure under heat
and explode as sparks.
6. Most wood needs to be seasoned 9 to 12
months to reduce the moisture content and
produce good steady fires. When moisture
content is reduced from 60 to 20%, the gain in
heat potential is nearly 7%.
7. Proper storage of wood, especially during
seasoning, is essential. We recommend that
you:
a. Never store wood on the ground. This will
cause rotting and insect infiltration. Raise wood
on flat rock or scrap wood.
b. Stack wood loosely to allow air circulation.
c. Store wood where it will not be excessively
exposed to weather, such as under a tarp or
under a roof.
d. Do not stack wood directly against the walls
of your home.
Figure 1
A face cord is the same height and length as a
standard cord but the depth is only the length
of the logs (12, 18 or 24 inches). A face cord
can contain as little as 25% of the wood found
in a standard cord.
If you buy by the ton, remember that wood
becomes lighter as it dries. When buying green
or wet wood, ask for some extra poundage to
allow for the extra water you will be getting.
9. When comparing woods of the same moisture content and same species, we find most
woods have approximately the same heating
potential per pound.
However, most wood is sold by volume, not by
weight. To determine the best heating source,
look at the density of various wood types.
(Density is the weight for a given size.) The
higher the density, the more potential heat
output. A standard cord has a volume of 128
cubic feet. This figure also includes the air
space between and around the wood. The actual volume in a standard cord is between 60
and 100 cubic feet; depending on how tightly
the wood is packed.
Assuming that you are comparing two standard
cords of different species but the same volume
and moisture content, the denser species will
provide more BTU’s. The table of wood species/
densities reveals more helpful guidelines.
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
3
 Loading...
Loading...