Service Manual Model : KB775f
Internal Use Only
Service Manual
KB775f
Date: April, 2009 / Issue 1.0

Table Of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ...............................................5
1.1 Purpose ......................................................................5
1.2 Regulatory Information .................................................5
2. PERFORMANCE ...............................................7
2.1 System Overview .........................................................7
2.2 Usable environment .....................................................8
2.3 Radio Performance ......................................................8
2.4 Current Consumption .................................................14
2.5 RSSI BAR ..................................................................14
2.6 Battery BAR ..............................................................14
2.7 Sound Pressure Level ................................................15
2.8 Charging ...................................................................16
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF .........................................17
3.1 General Description ...................................................17
3.2 GSM Mode ................................................................19
3.3 UMTS Mode ..............................................................23
3.4 LO generation and distribution circuits ........................26
3.5 Off-chip RF Components ............................................26
3.6 Digital Baseband (MSM6280) .....................................40
3.7 Subsystem(MSM6280) ..............................................42
3.8 Power Block ..............................................................49
3.9 External memory interface .........................................54
3.10 H/W Sub System .....................................................56
3.11 MAIN Features ........................................................72
4.15 Keypad Backlight Troubleshooting ...........................113
4.16 LCD Troubleshooting ..............................................115
4.17 Receiver Path ........................................................116
4.18 Headset path.........................................................118
4.17 Speaker phone path ..............................................120
4.18 Main microphone ..................................................122
4.19 Headset microphone ..............................................124
4.20 Vibrator .................................................................126
4.21 ISDB-T Circuit diagram, ISN7200 & ISDB-T RF ........127
5. DOWNLOAD .................................................129
5.1 Introduction .............................................................129
5.2 Downloading Procedure ...........................................130
5.3 Troubleshooting Download Errors ..............................146
5.4 Caution ...................................................................153
6. BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................ 154
7. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ...................................... 163
8. BGA Pin Map .............................................. 175
9. PCB LAYOUT ...............................................179
10. Hotkimchi .................................................187
10.1 Usage of Hot-Kimchi ..............................................187
11. TEST MODE ............................................... 190
4. TROUBLE SHOOTING ..................................... 77
4.1 RF Component ..........................................................77
4.2 Component Description ..............................................80
4.3 WCDMA RF Signal Path .............................................81
4.4 GSM RF Signal Path ..................................................82
4.5 Checking VCTCXO Block ............................................83
4.6 Checking Front-End Module Block ..............................86
4.7 Checking WCDMA Block ............................................88
4.8 Checking GSM Block .................................................95
4.9 Checking Bluetooth Block ........................................100
4.10 Power ON Troubleshooting .....................................103
4.11 Charger Troubleshooting ........................................105
4.12 USB Troubleshooting ..............................................107
4.13 USIM Detect Troubleshooting ..................................109
4.14 Camera Troubleshooting ........................................111
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
12. EXPLODED VIEW & REPLACEMENT
PART LIST ................................................ 195
12.1 EXPLODED VIEW ...................................................195
12.2 Replacement Parts ................................................197
12.3 Accessory ............................................................. 221
- 3 -
LGE Internal Use Only

LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 4 -
Only for training and service purposes

1. INTRODUCTION
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Purpose
This manual provides the information necessary to repair, calibration, description and download the features
of this model.
1.2 Regulatory Information
A. Security
Toll fraud, the unauthorized use of telecommunications system by an unauthorized part (for example,
persons other than your company’s employees, agents, subcontractors, or person working on your
company’s behalf) can result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications services. System
users are responsible for the security of own system. There are may be risks of toll fraud associated with your
telecommunications system. System users are responsible for programming and configuring the equipment
to prevent unauthorized use. The manufacturer does not warrant that this product is immune from the
above case but will prevent unauthorized use of common-carrier telecommunication service of facilities
accessed through or connected to it. The manufacturer will not be responsible for any charges that result
from such unauthorized use.
B. Incidence of Harm
If a telephone company determines that the equipment provided to customer is faulty and possibly causing
harm or interruption in service to the telephone network, it should disconnect telephone service until repair
can be done. A telephone company may temporarily disconnect service as long as repair is not done.
C. Changes in Service
A local telephone company may make changes in its communications facilities or procedure. If these
changes could reasonably be expected to affect the use of the phones or compatibility with the net work, the
telephone company is required to give advanced written notice to the user, allowing the user to take
appropriate steps to maintain telephone service.
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 5 -
LGE Internal Use Only

1. INTRODUCTION
D. Maintenance Limitations
Maintenance limitations on the phones must be performed only by the manufacturer or its authorized agent.
The user may not make any changes and/or repairs expect as specifically noted in this manual. Therefore,
note that unauthorized alternations or repair may affect the regulatory status of the system and may void
any remaining warranty.
E. Notice of Radiated Emissions
This model complies with rules regarding radiation and radio frequency emission as defined by local
regulatory agencies. In accordance with these agencies, you may be required to provide information such as
the following to the end user.
F. Pictures
The pictures in this manual are for illustrative purposes only; your actual hardware may look slightly different.
G. Interference and Attenuation
A phone may interfere with sensitive laboratory equipment, medical equipment, etc. Interference from
unsuppressed engines or electric motors may cause problems.
H. Electrostatic Sensitive Devices
ATTENTION
Boards, which contain Electrostatic Sensitive Device (ESD), are indicated by the sign. Following
information is ESD handling:
• Service personnel should ground themselves by using a wrist strap when exchange system boards.
• When repairs are made to a system board, they should spread the floor with anti-static mat which is also
grounded.
• Use a suitable, grounded soldering iron.
• Keep sensitive parts in these protective packages until these are used.
• When returning system boards or parts like EEPROM to the factory, use the protective package as described.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 6 -
Only for training and service purposes
2. PERFORMANCE
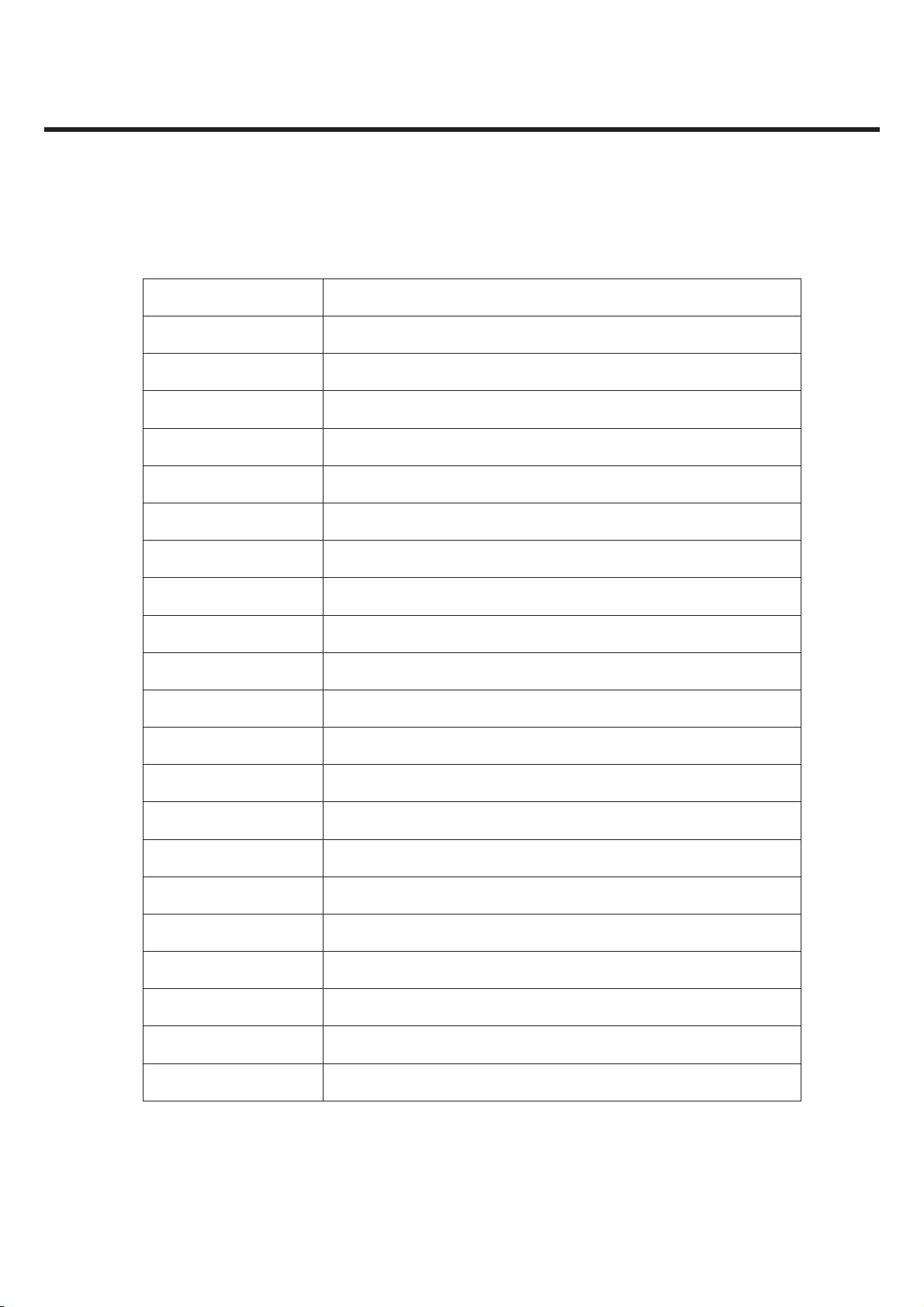
2.1 System Overview
Item Specification
Shape GSM850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA 850/2100 bar type Handset
Size 111 X 54.8 X 11.9 mm
Weight 93 g (with 1000mAh Battery)
Power 4.0V normal, 1000 mAh(Li-ion) inner-pack
Talk Time Over 180 min (WCDMA, Tx=12 dBm, Voice)
(with 1000mAh) Over 180 min (GSM, Tx=Max, Voice)
2. PERFORMANCE
Standby Time Over 250 Hrs (WCDMA, DRX=1.28)
(with 1000mAh) Over 320 Hrs (GSM, Paging period=5)
Antenna Internal type
LCD 400 x 240 pixel (TFT)
LCD Backlight White LED Back Light
Camera 3.0 Mega (CMOS) / VGA (CMOS).
Vibrator Yes
LED Indicator No
MIC Yes
Receiver Yes
Earphone Jack Yes (18 pin)
Connectivity Bluetooth, USB
Volume Key Push Type(+, -)
External Memory Trans-Flash
I/O Connect 18 Pin
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 7 -
LGE Internal Use Only
2. PERFORMANCE
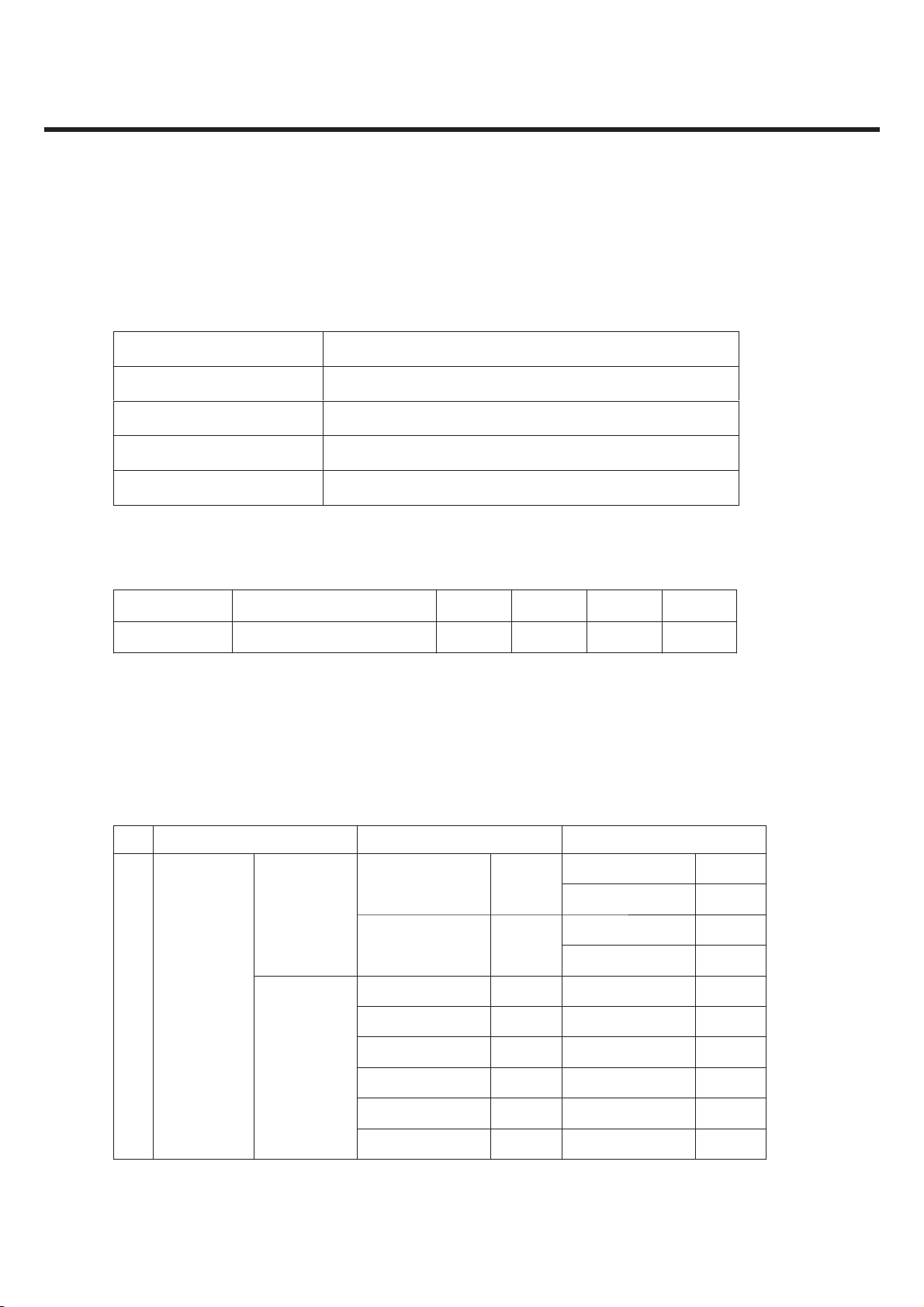
2.2 Usable environment
1) Environment
Item Specification
Voltage 4.0 V(Typ), 3.28 V(Min), [Shut Down : 3.25 V]
Operation Temp -20 ~ +60 °C
Storage Temp -20 ~ +70 °C
Humidity 85 % (Max)
2) Environment (Accessory)
Reference Spec. Min Typ. Max Unit
TA Power Available power 100 220 240 Vac
* CLA : 12 ~ 24 V(DC)
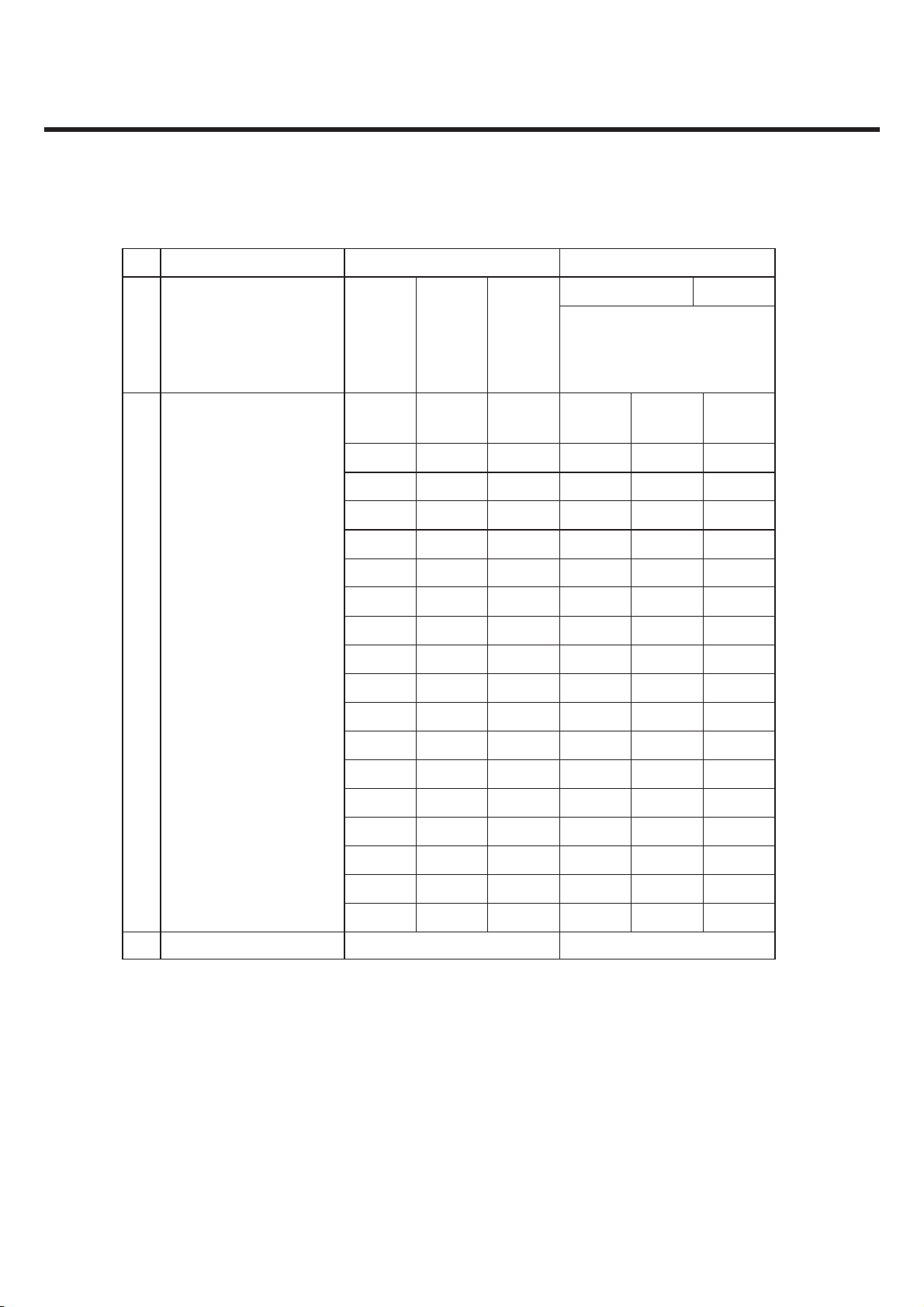
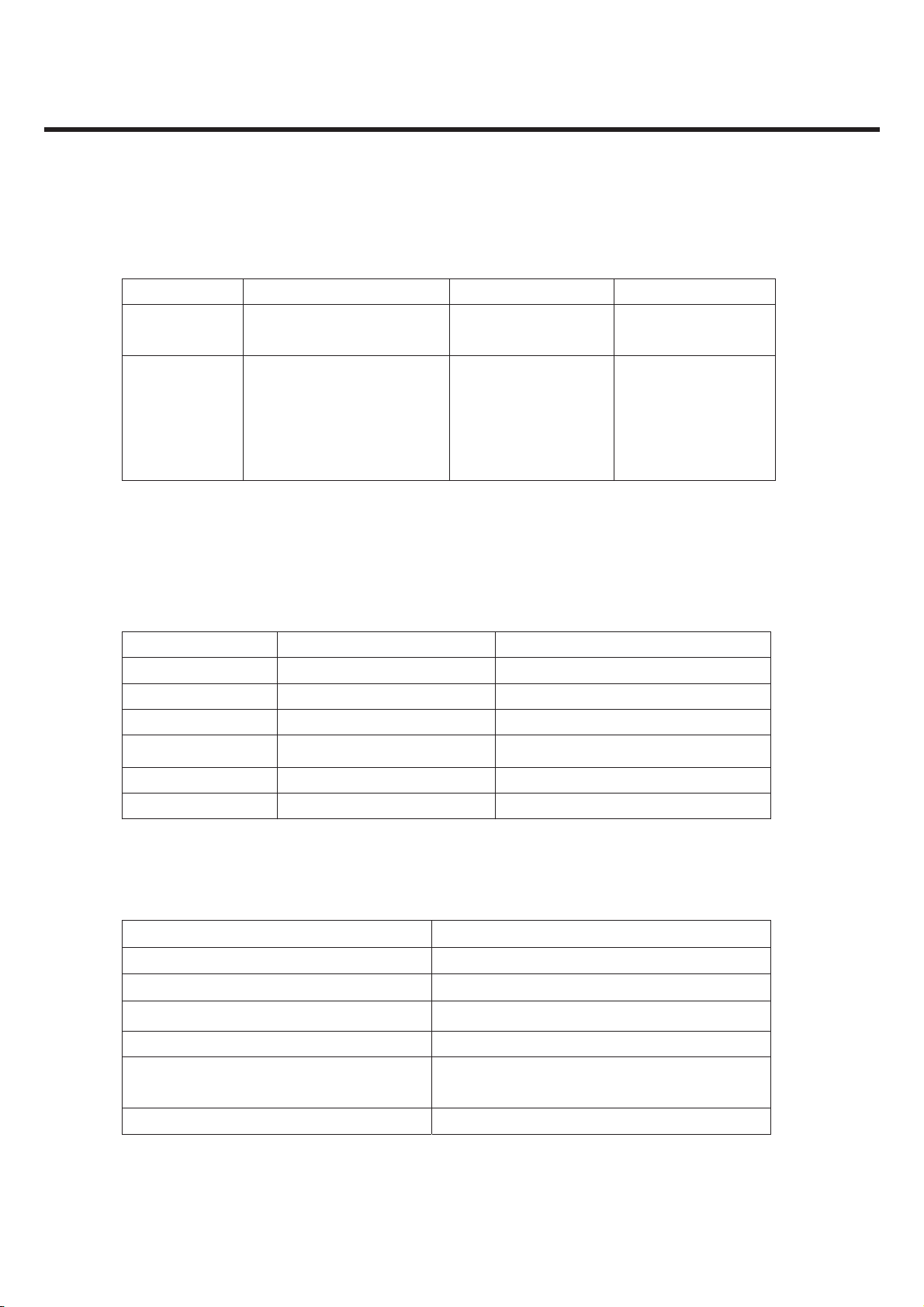
2.3 Radio Performance
1) Transmitter - GSM Mode
No Item GSM DCS & PCS
9k ~ 1GHz -39dBm
1G~[A]MHz -33dBm
[A]M~[B]MHz -39dBm
[B]M~12.75GHz -33dBm
1
Conducted
Spurious
Emission
MS allocated
Channel
Idle Mode
100k~1GHz -39dBm
1G~12.75GHz -33dBm
100k~880MHz -60dBm 100k~880MHz -60dBm
880M~915MHz -62dBm 880M~915MHz -62dBm
915M~1GHz -60dBm 915M~1GHz -60dBm
1G~[A]MHz -50dBm 1G~[A]MHz -50dBm
[A]M~[B]MHz -56dBm [A]M~[B]MHz -56dBm
[B]M~12.5GHz -50dBm [B]M~12.5GHz -50dBm
* In case of DCS : [A] -> 1710, [B] -> 1785 * In case of PCS : [A] -> 1850, [B] -> 1910
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 8 -
Only for training and service purposes
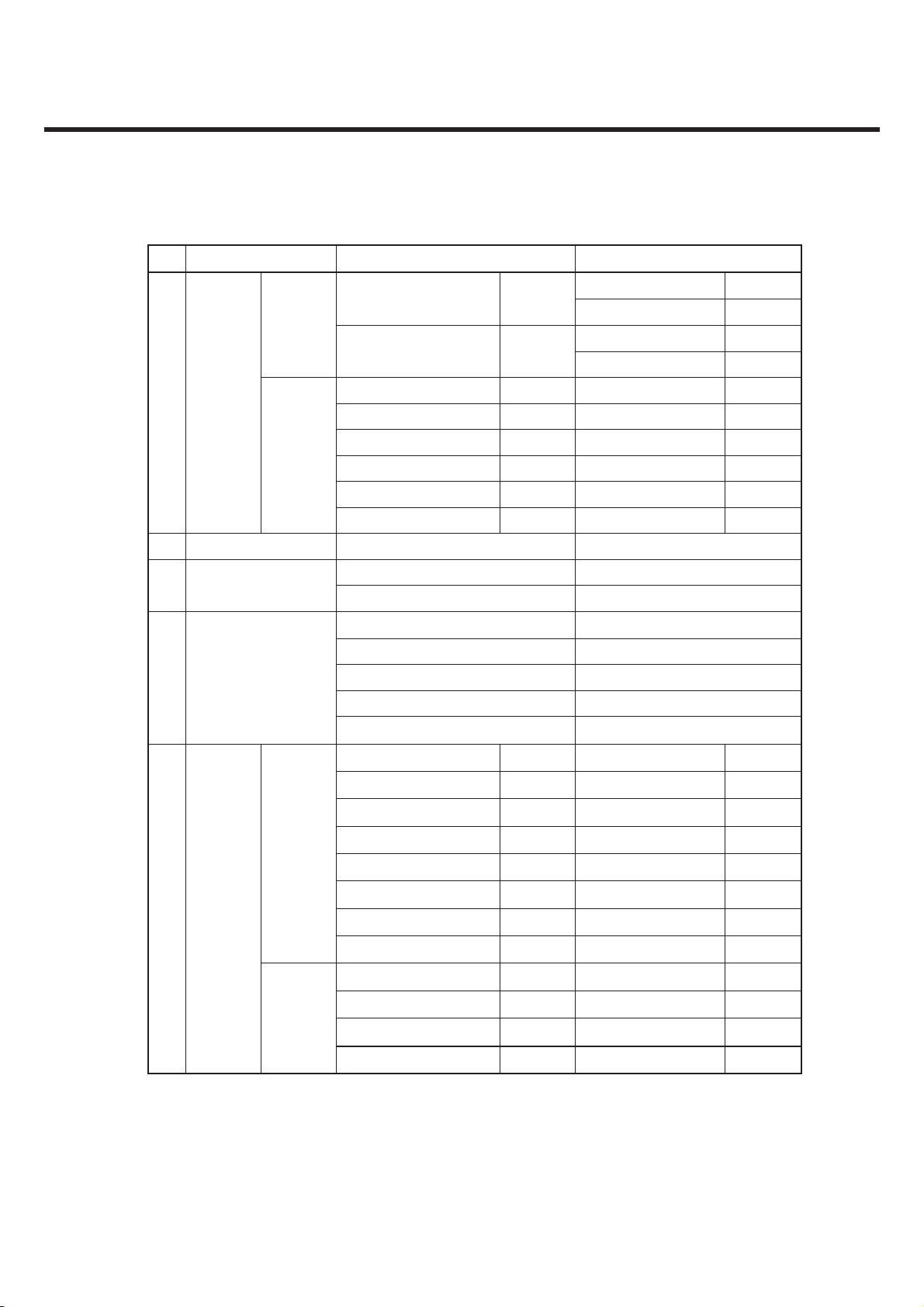
2. PERFORMANCE
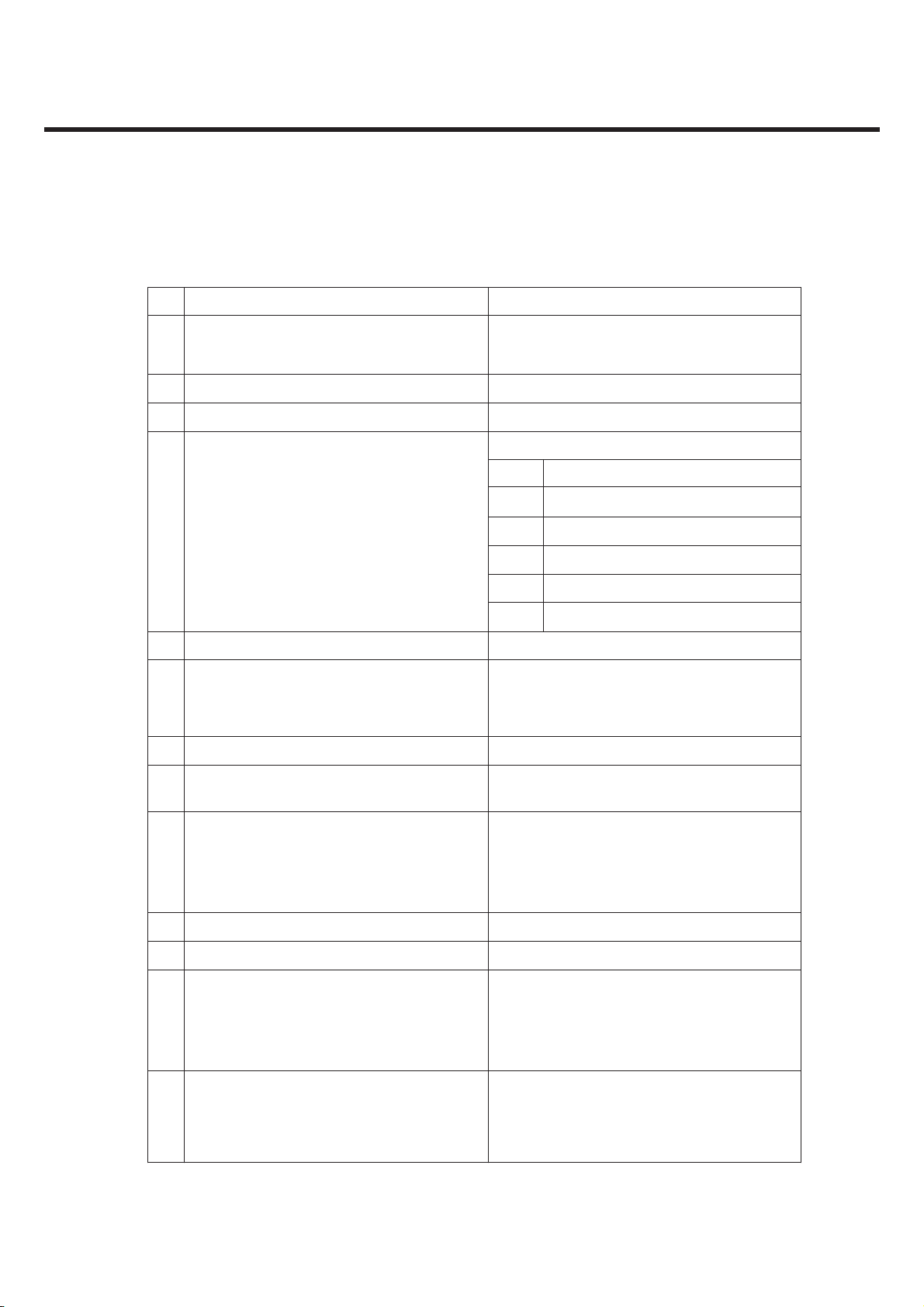
No Item GSM DCS & PCS
MS
allocated
Channel
Radiated
Spurious
2
Emission
3 Frequency Error ±0.1ppm ±0.1ppm
4 Phase Error
Under Multipath and
5
Interference Condition
Idle Mode
Frequency Error
30M ~ 1GHz -36dBm
1G ~ 4GHz -30dBm
30M ~ 880MHz -57dBm 30M~880MHz -57dBm
880M ~ 915MHz -59dBm 880M~915MHz -59dBm
915M~1GHz -57dBm 915M~1GHz -57dBm
1G~[A]MHz -47dBm 1G~[A]MHz -47dBm
[A]M~[B]MHz -53dBm [A]M~[B]MHz -53dBm
[B]M~4GHz -47dBm [B]M~4GHz -47dBm
±5(RMS) ±5(RMS)
±20(PEAK) ±20(PEAK)
3dB below reference sensitivity 3dB below reference sensitivity
RA250 : ±200Hz RA250: ±250Hz
HT100 : ±100Hz HT100: ±250Hz
TU50 : ±100Hz TU50: ±150Hz
TU3 : ±150Hz TU1.5: ±200Hz
30M~1GHz -36dBm
1G~[A]MHz -30dBm
[A]M~[B]MHz -36dBm
[B]M~4GHz -30dBm
0 ~ 100kHz +0.5dB 0 ~ 100kHz +0.5dB
200kHz -30dB 200kHz -30dB
Due to
modulati
on
Output RF
6
Spectrum
*In case of DCS : [A] -> 1710, [B] -> 1785 * In case of PCS : [A] -> 1850, [B] -> 1910
Due to
Switching
transient
250kHz -33dB 250kHz -33dB
400kHz -60dB 400kHz -60dB
600 ~ 1800kHz -66dB 600 ~ 1800kHz -60dB
1800 ~ 3000kHz -69dB 1800 ~ 6000kHz -65dB
3000 ~ 6000kHz -71dB ≥6000kHz -73dB
≥6000kHz -77dB
400kHz -19dB 400kHz -22dB
600kHz -21dB 600kHz -24dB
1200kHz -21dB 1200kHz -24dB
1800kHz -24dB 1800kHz -27dB
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 9 -
LGE Internal Use Only
2. PERFORMANCE
No Item GSM DCS & PCS
Frequency offset 800kHz
7
Intermodulation attenuation
8 Transmitter Output Power
Power
control
Level (dBm) (dB) Level (dBm) (dB)
5 33 ±3 0 30 ±3
6 31 ±3 1 28 ±3
7 29 ±3 2 26 ±3
8 27 ±3 3 24 ±3
9 25 ±3 4 22 ±3
10 23 ±3 5 20 ±3
11 21 ±3 6 18 ±3
12 19 ±3 7 16 ±3
13 17 ±3 8 14 ±3
14 15 ±3 9 12 ±4
15 13 ±3 10 10 ±4
–
Power
Tolerance Power
Intermodulation product should
be Less than 55dB below the
level of Wanted signal
control
Power
Toleranc
e
16 11 ±5 11 8 ±4
17 9 ±5 12 6 ±4
18 7 ±5 13 4 ±4
19 5 ±5 14 2 ±5
9 Burst timing Mask IN Mask IN
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 10 -
15 0 ±5
Only for training and service purposes
2. PERFORMANCE
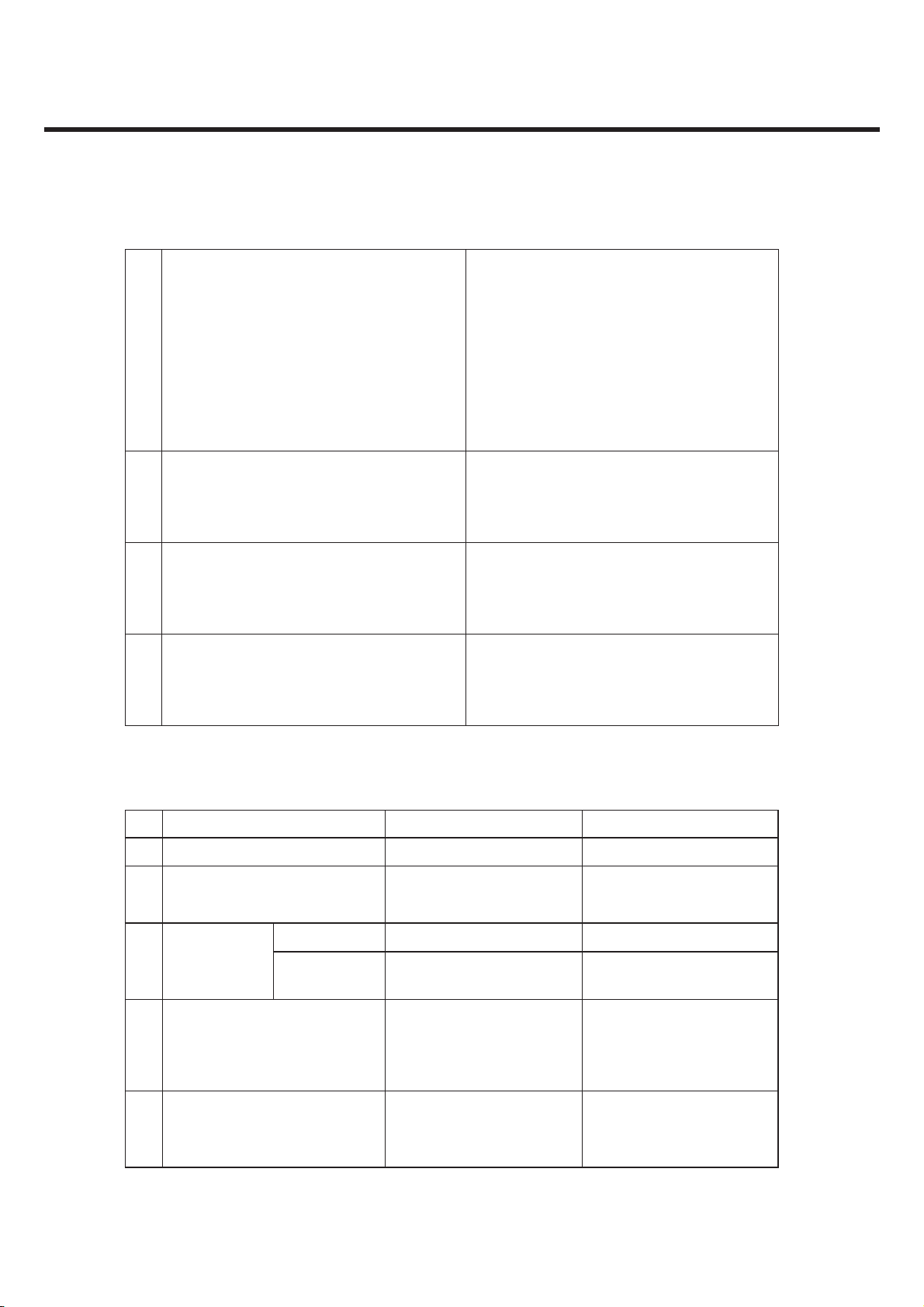
2) Transmitter – WCDMA Mode
No Item Specification
1 Maximum Output Power
2 Frequency Error ±0.1ppm
3 Open Loop Power control in uplink ±9dB@normal, ±12dB@extreme
Inner Loop Power control in uplink
4
5 Minimum Output Power -50dBm(3.84MHz)
Out-of-synchronization handling of output
6
power
7 Transmit OFF Power -56dBm(3.84MHz)
Class3: +24dBm(+1/-3dB)
Class 4 : +21dBm(±2dB)
Adjust output(TPC command)
cmd 1dB 2dB 3dB
+1 +0.5/1.5 +1/3 +1.5/4.5
0 -0.5/+0.5 -0.5/+0.5 -0.5/+0.5
-1 -0.5/-1.5 -1/-3 -1.5/-4.5
Group (10 equel command group)
+1 +8/+12 +16/+24
Qin/Qout : PCCH quality levels
Toff@DPCCH/Ior : -22 -> -28dB
Ton@DPCCH/Ior : -24 -> -18dB
8 Transmit ON/OFF Time Mask ±25us PRACH,CPCH,uplinlk compressed mode
±25us
9
Change of TFC
10 Power setting in uplink compressed ±3dB(after 14slots transmission gap)
11 Occupied Bandwidth(OBW) 5MHz(99%)
12
Spectrum emission Mask
13 Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio(ACLR)
Power varies according to the data rate DTX : DPCH
off
(minimize interference between UE)
-35-15*(Δf-2.5)dBc@Δf=2.5~3.5MHz,30k
-35-1*(Δf-3.5)dBc@Δf=3.5~7.5MHz,1M
-39-10*(Δf-7.5)dBc@Δf=7.5~8.5MHz,1M
-49dBc@Δf=8.5~12.5MHz,1M
33dB@5MHz, ACP>-50dBm
43dB@10MHz, ACP>-50dBm
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 11 -
LGE Internal Use Only
2. PERFORMANCE
Spurious Emissions
14
(*:additional requirement)
-36dBm@f=9~150KHz, 1K BW
-36dBm@f=50KHz~30MHz, 10K BW
-36dBm@f=30MHz~1000MHz, 100K BW
-30dBm@f=1~12.5GHz,1M BW
(*)-41dBm@f=1893.5~1919.6MHz, 300K
(*)-67dBm@f=925~935MHz, 100K BW
(*)-79dBm@f=935~960MHz, 100K BW
(*)-71dBm@f=1805~1880MHz, 100K BW
15 Transmit Intermodulation
16 Error Vector Magnitude (EVM)
17 Transmit OFF Power
-31dBc@5MHz,Interferer -40dBc
-41dBc@10MHz, Interferer -40dBc
17.5%(>-20dBm)
(@12.2K, 1DPDCH+1DPCCH)
-15dB@SF=4.768Kbps,
Multi-code transmission
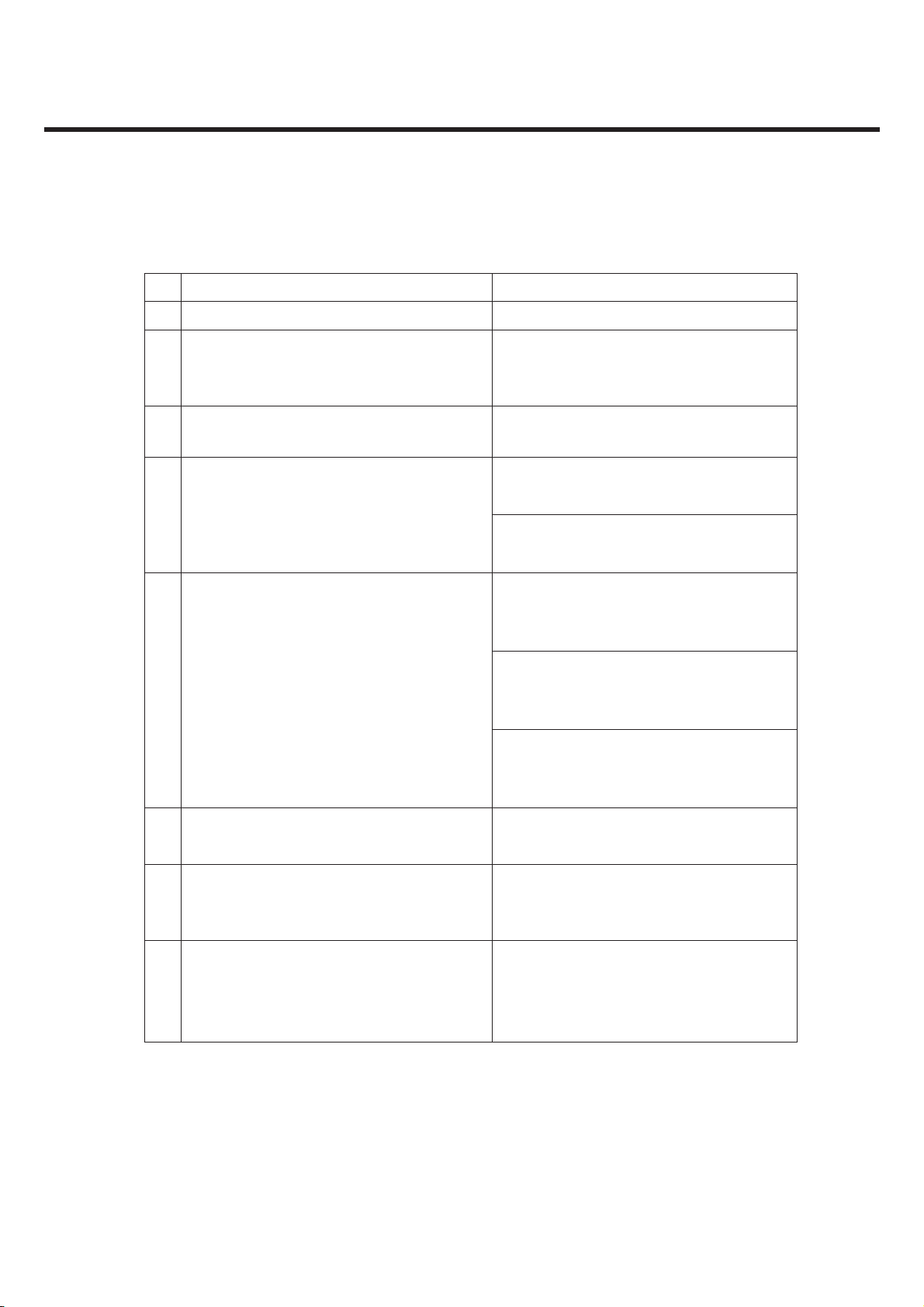
3) Receiver - GSM Mode
No Item GSM DCS & PCS
1 Sensitivity (TCH/FS Class II) -105dBm -105dBm
Co-Channel Rejection (TCH/FS Class
2
II, RBER, TU high/FH)
C/Ic=7dB Storage -30 ~ +85
Adjacent
3
Channel
Rejection
Intermodulation Rejection
4
Blocking Response
5
(TCH/FS Class II, RBER)
200kHz C/Ia1=-12dB C/Ia1=-12dB
400kHz C/Ia2=-44dB C/Ia2=-44dB
Wanted Signal :-98dBm
1st interferer:-44dBm
2nd interferer:-45dBm
Wanted Signal :-101dBm
Unwanted : Depend on
Frequency
Wanted Signal :-96dBm
1st interferer:-44dBm
2nd interferer:-44dBm
Wanted Signal :-101dBm
Unwanted : Depend on
Frequency
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 12 -
Only for training and service purposes
2. PERFORMANCE
4) Receiver - WCDMA Mode
No Item Specification
1 Reference Sensitivity Level -106.7 dBm(3.84 MHz)
-25dBm(3.84MHz)
2
Maximum Input Level
3 Adjacent Channel Selectivity (ACS)
4
In-band Blocking
-44dBm/3.84MHz(DPCH_Ec)
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
33dB
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-56dBm/3.84MHz@10MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-44dBm/3.84MHz@15MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
Out-band Blocking
5
6 Spurious Response
7
Intermodulation Characteristic
8
Spurious Emissions
-44dBm/3.84MHz@f=2050~2095 and
2185~2230MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-30dBm/3.84MHz@f=2025~2050 and
2230~2255MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-15dBm/3.84MHz@f=1~2025 and
2255~12500MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-44dBm CW
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-46dBm CW@10MHz
-46dBm/3.84MHz@20MHz
UE@+20dBm output power(Class3)
-57dBm@f=9KHz~1GHz, 100K BW
-47dBm@f=1~12.5GHz, 1M BW
-60dBm@f=1920MHz~1980MHz, 3.84M BW
-60dBm@f=2110MHz~2170MHz, 3.84M BW
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 13 -
LGE Internal Use Only
2. PERFORMANCE
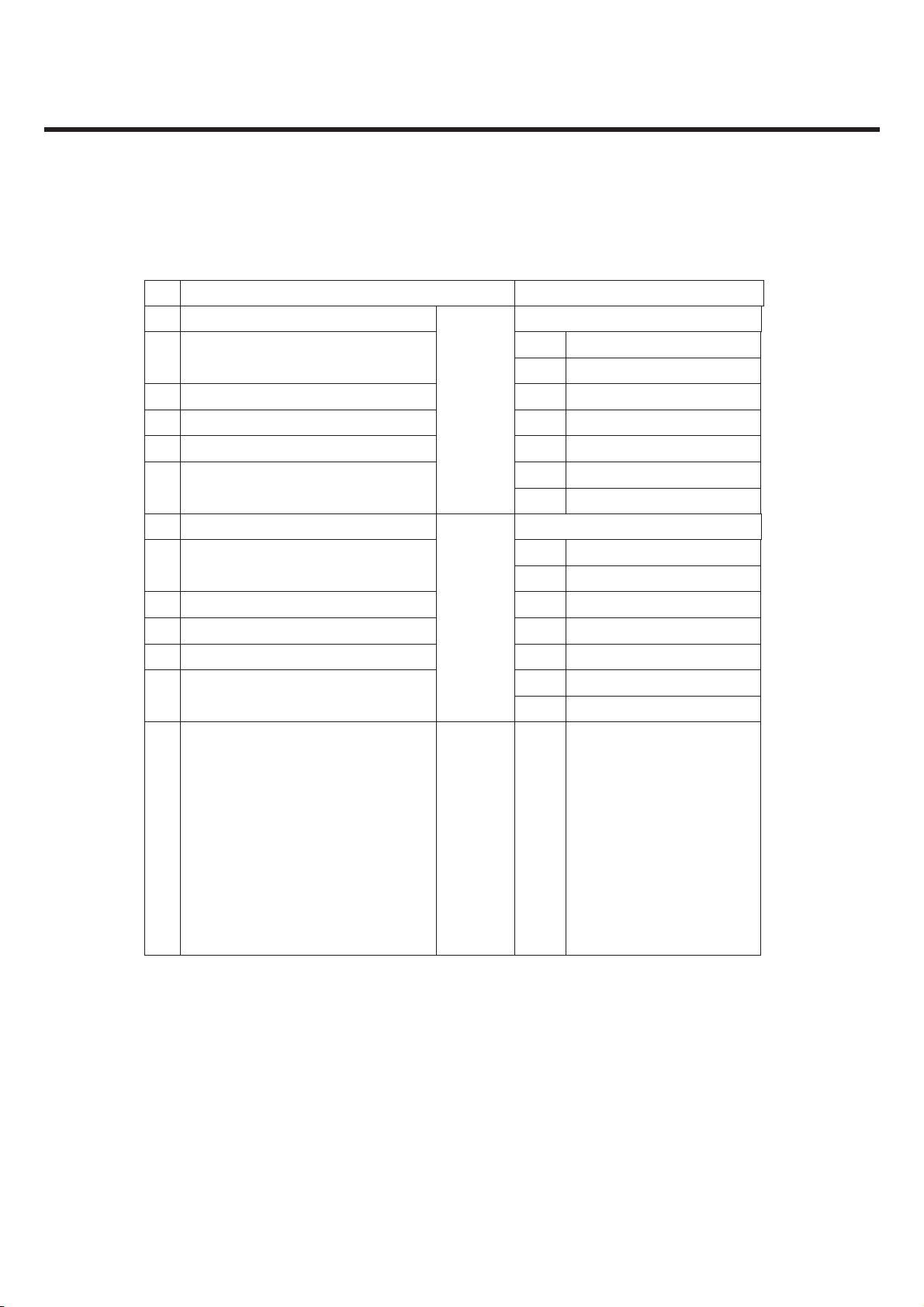
2.4 Current Consumption
Stand by(BT Off condition) Voice Call VT
WCDMA
Under 3.5 mA
(DRX=1.28)
Under 320 mA
(Tx=12dBm)
Under 430mA
(Tx=0dBm)
GSM
(Stand by and Voice Call Test Condition : LCD backlight Off)
(VT Test Condition : Speaker off, LCD backlight On)
Under 3.5 mA
(Paging=5period)
Under 300 mA
(Tx=Max)
2.5 RSSI BAR
Level Change WCDMA GSM
BAR 7 >= -91 dBm >= -92 dBm
BAR 7 → 6,5 -93 ± 2 dBm -94 ± 2 dBm
BAR 6,5 → 4 -105 ± 2 dBm -98 ± 2 dBm
BAR 4 → 3,2 -110 ± 2 dBm -102 ± 2 dBm
BAR 3,2 → 1 -112 ± 2 dBm -105 ± 2 dBm
BAR 1 → 0 -114 ± 2 dBm -107 ± 2 dBm
2.6 Battery BAR
Indication Standby
Bar 3 Over 3.72 ± 0.05V
Bar 3 → 2 3.72 ± 0.05V
Bar 2 → 1 3.60 ± 0.05V
Bar 1 → Empty 3.45 ± 0.05V
Low Voltage,
Warning message + Blinking
Power off 3.25 ± 0.05V
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 14 -
[Interval: 3min(Stand by)/1min(talk)]
3.45 ± 0.05V
Only for training and service purposes
2. PERFORMANCE
2.7 Sound Pressure Level
No Test Item Specification
1 Sending Loudness Rating (SLR)
2 Receiving Loudness Rating (RLR)
3 Side Tone Masking Rating (STMR) Min 17 dB
MS
4 Echo Loss (EL) Min 40 dB
5 Idle Noise-Sending (INS) Max -64 dBm0p
6 Idle Noise-Receiving (INR)
7 Sending Loudness Rating (SLR)
8 Receiving Loudness Rating (RLR)
9 Side Tone Masking Rating (STMR) Min 25 dB
Headset
10 Echo Loss (EL) Min 40 dB
11 Idle Noise-Sending (INS) Max -55 dBm0p
12 Idle Noise-Receiving (INR)
Nor
Max
Nor Under -58 dBPA
Max Under -58 dBPA
Nor
Max
Nor Under -45 dBPA
Max Under -40 dBPA
± 3 dB
8
2±3 dB
-8
7
-6
-13
±3 dB
±3 dB
±3 dB
±3 dB
TDMA Noise
-. GSM : Power Level : 5
DCS/PCS : Power Level : 0
(Cell Power : -90 ~ -105 dBm)
13
-. Acoustic (Max Vol.)
MS/Headset SLR : 8 3dB
MS/Headset RLR : -15 3dB / -12dB
(SLR/RLR : Mid-value setting)
MS and
Headset
Max Under -62 dBm
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 15 -
LGE Internal Use Only

2. PERFORMANCE
2.8 Charging
• Charging Method : CC & CV (Constant Current and Constant Voltage)
• Maximum Charging Voltage : 4.2 V
• Maximum Charging Current : 600 mA
• Normal Battery Capacity : 1000 mAh
• Charging Time : Max 3 hours (except for trickle charging time)
• Full charging indication current (charging icon stop current) : 80mA
• Cut-off voltage : 3.2 V
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 16 -
Only for training and service purposes
2. SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.1 General Description
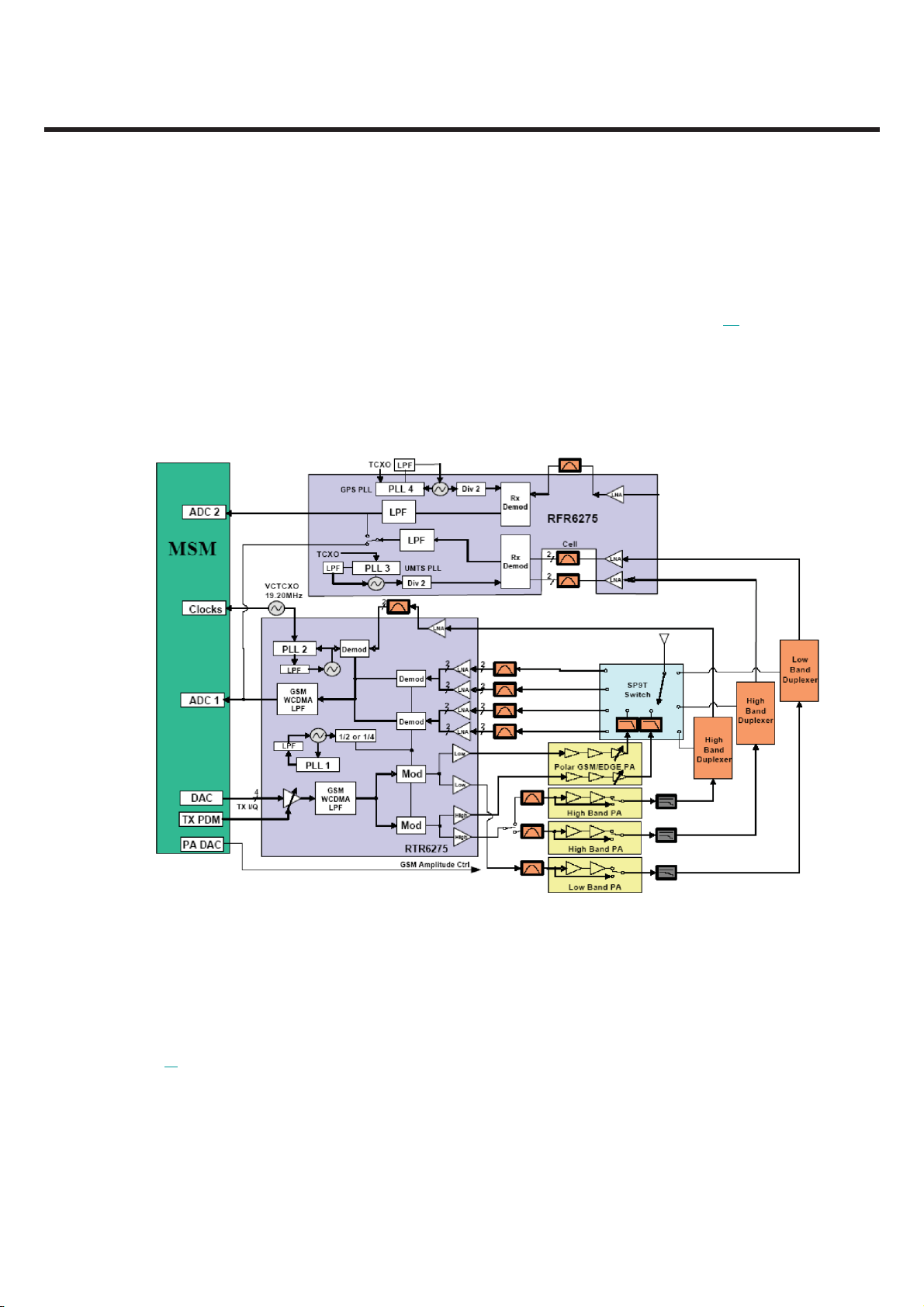
The KB775 supports UMTS-2100,UMTS-850, GSM-850,GSM-900, DCS-1800, and PCS-1900
based GSM/GPRS/EDGE/UMTS. All receivers and the UMTS transmitter use the radioOne[1]
IF architecture to eliminate intermediate frequencies, directly converting signals between RF and
baseband. The quad-band GSM transmitters use a baseband-to-IF up-conversion followed by an
offset phase-locked loop that translates the GMSK-modulated or 8-PSK-modulated signal to RF.
Zero-
Figure 3.1 Block diagram of RF part
A generic, high-level functional block diagram of KB775 is shown in Figure 3.1. One antenna
collects base station forward link signals and radiates handset reverse link signals. The antenna
connects with
[1] QUALCOMM’s branded chipset that implements a Zero-IF radio architecture.
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 17 -
LGE Internal Use Only

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
receive and transmit paths through a FEM(Front End Module)
The UMTS receive paths each include an LNA, an RF band-pass filter, and a downconverter that
translate the signal directly from RF-to-baseband using radioOne ZIF techniques. The RFIC’s Rx
analog baseband outputs, for the receive chains, connect to the MSM IC. The UMTS and GSM Rx
baseband outputs share the same inputs to the MSM IC.
For the transmit chains, the RTR6275 IC directly translates the Tx baseband signals (from the
MSM device) to an RF signal using an internal LO generated by integrated on-chip PLL and VCO.
The RTR6275 IC outputs deliver fairly high-level RF signals that are first filtered by Tx SAWs and
then amplified by their respective UMTS PAs. The high- and low-band UMTS RF transmit signals
emerge from the RTR6275 transceiver.
In the GSM receive path, the received RF signals are applied through their band-pass filters and
down-converted directly to baseband in the RTR6275 transceiver IC. These baseband outputs are
shared with the UMTS receiver and routed to the MSM IC for further signal processing.
The GSM/EDGE transmit path employs one stage of up-conversion and, in order to improve
efficiency, is divided into phase and amplitude components to produce an open-loop Polar topology:
1. The on-chip quadrature up-converter translates the GMSK-modulated signal or 8-PSK
modulated signal, to a constant envelope phase signal at RF;
2. The amplitude-modulated (AM) component is applied to the ramping control pin of Polar power
amplifier from a DAC within the MSM
KB775 power supply voltages are managed and regulated by the PM6650 Power Management IC.
This versatile device integrates all wireless handset power management, general housekeeping,
and user interface support functions into a single mixed signal IC. It monitors and controls the
external power source and coordinates battery recharging while maintaining the handset supply
voltages using low dropout, programmable regulators.
The device’s general housekeeping functions include an ADC and analog multiplexer circuit for
monitoring on-chip voltage sources, charging status, and current flow, as well as user-defined off-
chip variables such as temperature, RF output power, and battery ID. Various oscillator, clock, and
counter circuits support IC and higher-level handset functions. Key parameters such as under-
voltage lockout and crystal oscillator signal presence are monitored to protect against detrimental
conditions.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 18 -
Only for training and service purposes
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.2 GSM Mode
3.2.1 GSM Receiver
The Dual-mode KB775’s receiver functions are split between the three RFICs as follows:
■ GSM-850,EGSM-900(GSM900), DCS-1800, and PCS-1900 modes use the RTR6275 IC only.
Each mode has independent front-end circuits and down-converters, but they share common
baseband circuits (with only one mode active at a time). All receiver control functions are beginning
2
with SBI
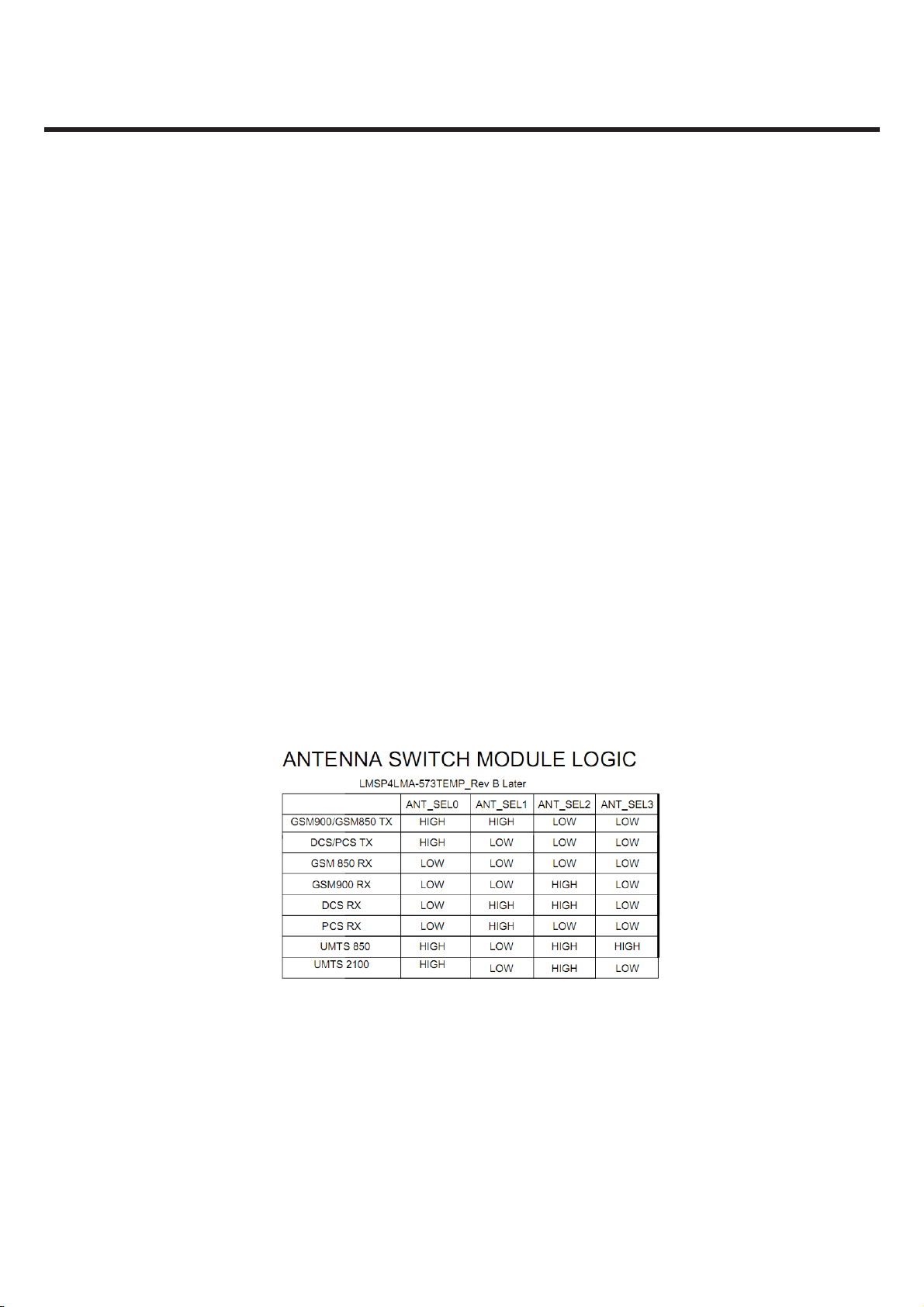
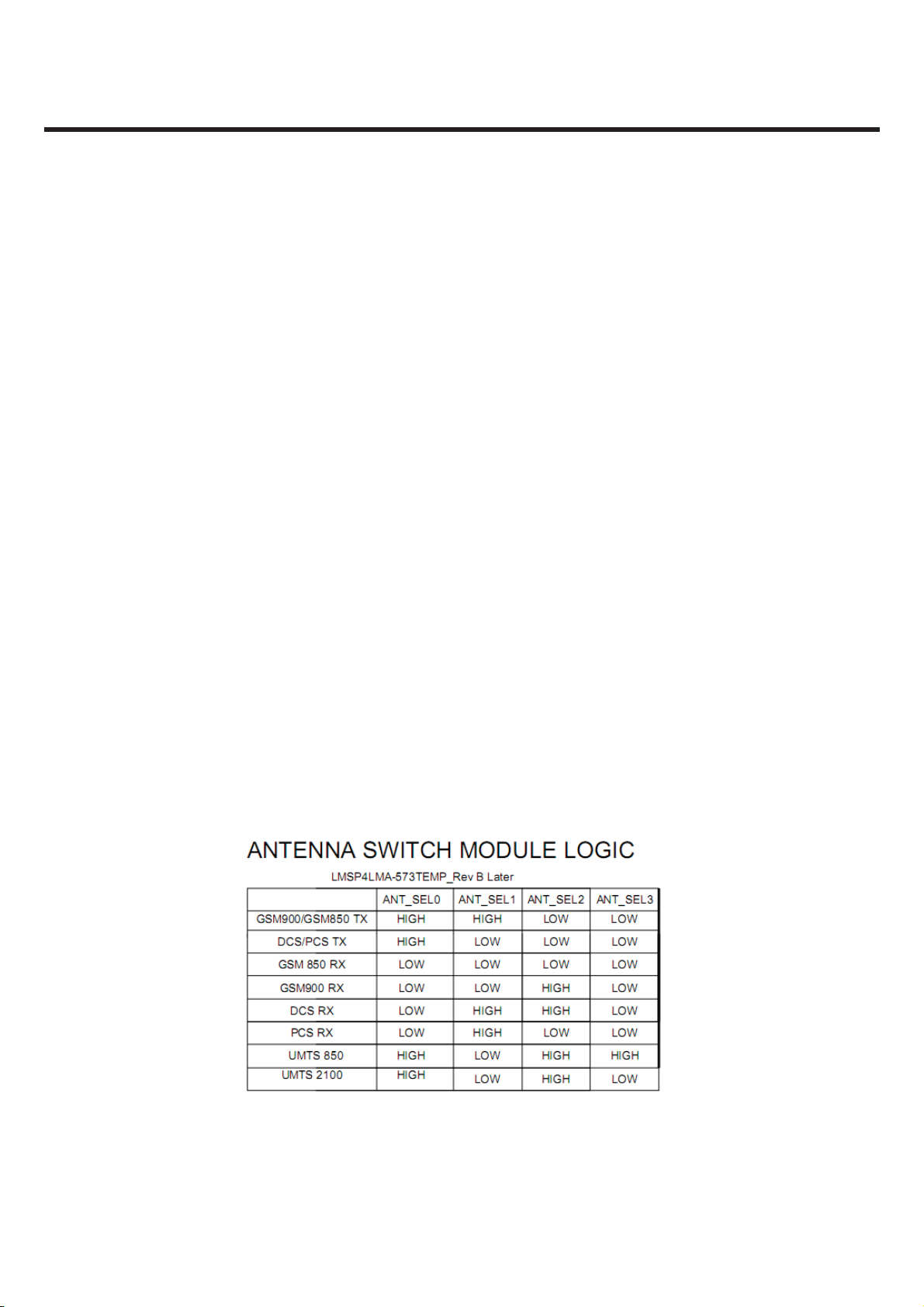
RF Front end consists of antenna, antenna switch module (LMSP4LMA-573TEMP) which includes
four RX saw filters (GSM-850,EGSM-900, DCS-1800 and PCS-1900). The antenna switch module
allows multiple operating bands and modes to share the same antenna. In KB775, a common
antenna connects to one of eight paths: 1) GSM900/GMS850 TX, 2)DCS/PCS TX , 3)GSM850 RX,
4)GSM900 RX, 5)DCS RX, 6)PCS RX, 7)UMTS 850, 8)UMTS 2100. UMTS operation requires
simultaneous reception and transmission, so the UMTS Rx/Tx connection is routed to a duplexer that
separates receive and transmit signals. GSM850,GSM900, DCS1800, and PCS1900 operation is
time division duplexed, so only the receiver or transmitter is active at any time and a frequency
duplexer is not required.
-controlled parameters.
Table 3.2.1 Antenna Switch Module Control logic
2 The RFIC operating modes and circuit parameters are MSM-controlled through the proprietary 3-line
Serial Bus Interface (SBI). The Application Programming Interface (API) is used to implement SBI
commands. The API is documented in AMSS Software – please see applicable AMSS Software
documentation for details.
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 19 -
LGE Internal Use Only

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
The GSM850,GSM900, DCS1800, and PCS1900 receiver inputs of RTR6275 are connected
directly to the transceiver front-end circuits(filters and antenna switch module). GSM850,GSM900,
DCS1800, and PCS1900 receiver inputs use differential configurations to improve common-mode
rejection and second-order non-linearity performance. The balance between the complementary
signals is critical and must be maintained from the RF filter outputs all the way into the IC pins.
Since GSM850,GSM900, DCS1800, and PCS1900 signals are time-division duplex (the handset
can only receive or transmit at one time), switches are used to separate Rx and Tx signals in place
of frequency duplexers – this is accomplished in the switch module.
The GSM850,GSM900, DCS1800, and PCS1900 receive signals are routed to the RTR6275
through band selection filters and matching networks that transform single-ended 50W sources to
differential impedances optimized for gain and noise figure. The RTR input uses a differential
configuration to improve second-order inter-modulation and common mode rejection performance.
The RTR6275 input stages include MSM-controlled gain adjustments that maximize receiver
dynamic range.
The amplifier outputs drive the RF ports of the quadrature RF-to-baseband downconverters. The
downconverted baseband outputs are multiplexed and routed to lowpass filters (one I and one Q)
having passband and stopband characteristics suitable for GMSK or 8-PSK processing. These filter
circuits include DC offset corrections. The filter outputs are buffered and passed on to the
MSM6280 IC for further processing.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 20 -
Only for training and service purposes
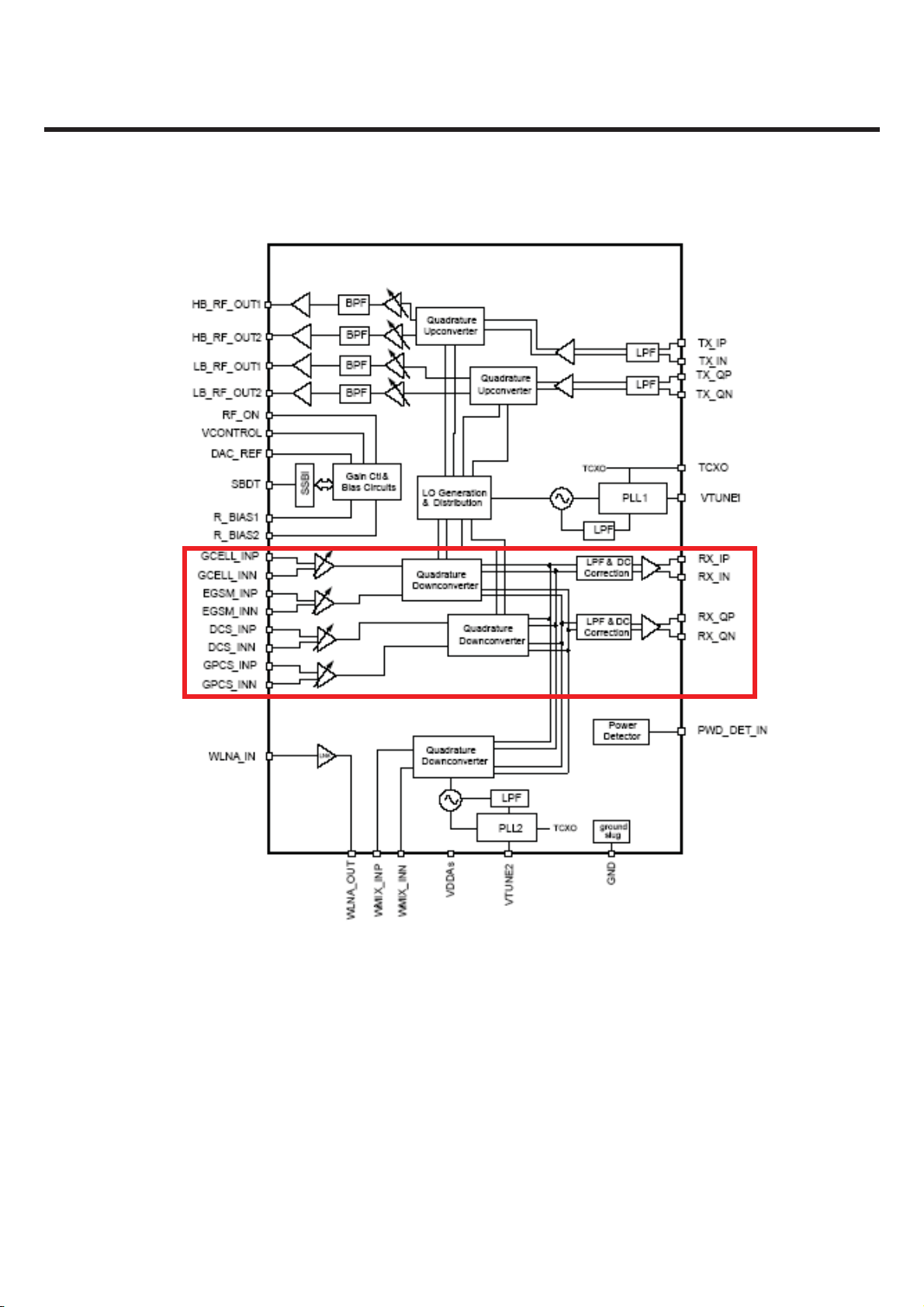
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
Figure 3.2.1 RTR6275 RX featur e
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 21 -
LGE Internal Use Only
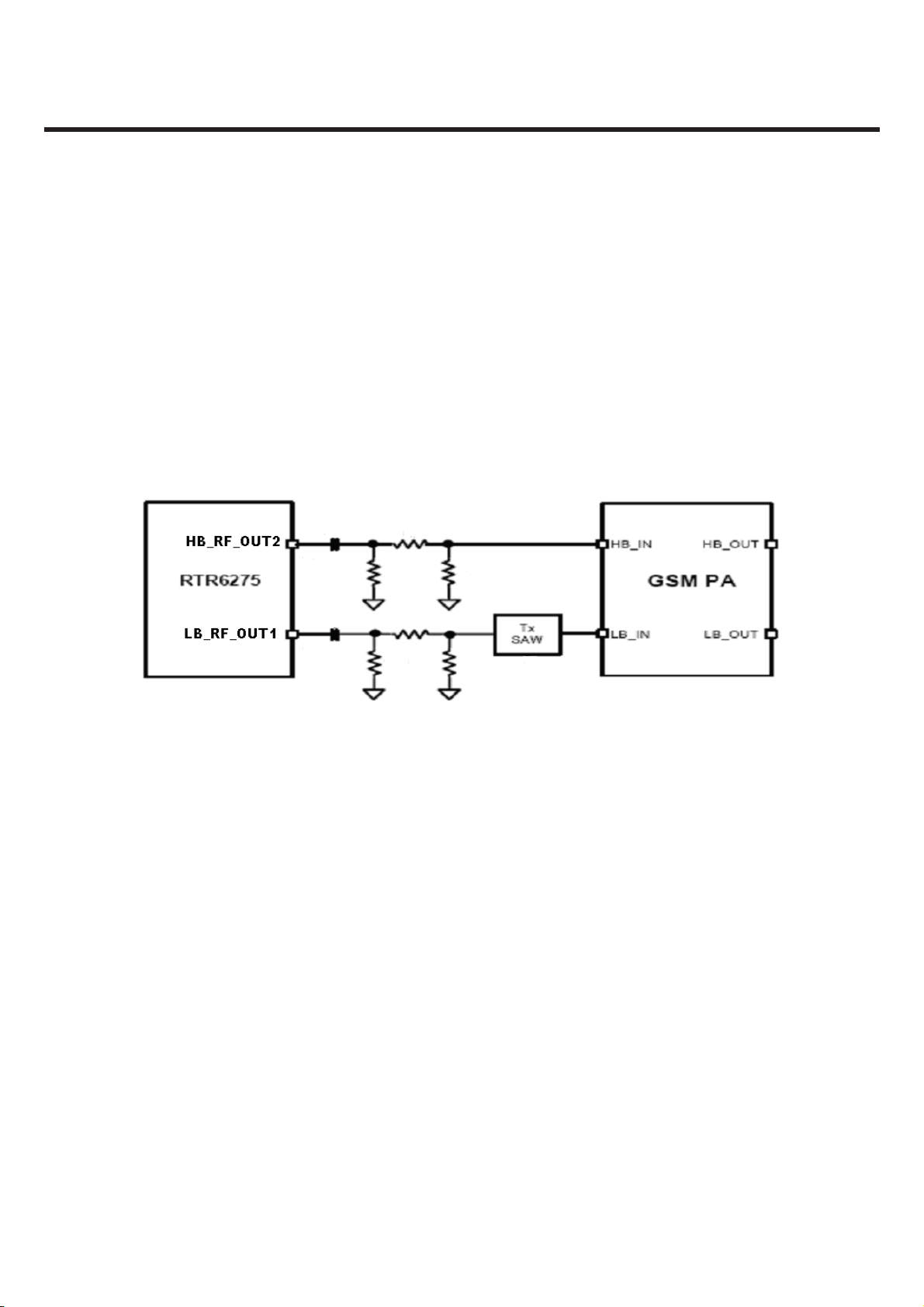
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.2.2 GSM Transmitter
The RTR6275 transmitter outputs (HB_RF_OUT2 and LB_RF_OUT1) include on-chip output matching
inductors. 50ohm output impedance is achieved by adding a series capacitor at the output pins. The
capacitor value may be optimized for specific applications and PCB characteristics based on pass-band
symmetry about the band center frequency. The suggested circuit is shown in Fig.3.2.2
Figure 3.2.2 GSM Transmitter matching
The RTR6275 IC is able to support GSM850/GSM900 and DCS1800/PCS1900 mode transmitting.
This design guideline shows a tri-band GSM application.
Both high-band and low band outputs are followed by resistive pads to ensure that the load Presented
to the outputs remains close to 50ohm. The low-band GSM Tx path also includes a Tx-band SAW filter
to remove noise-spurious components and noise that would be amplified by the PA and appear in the
GSM Rx band.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 22 -
Only for training and service purposes
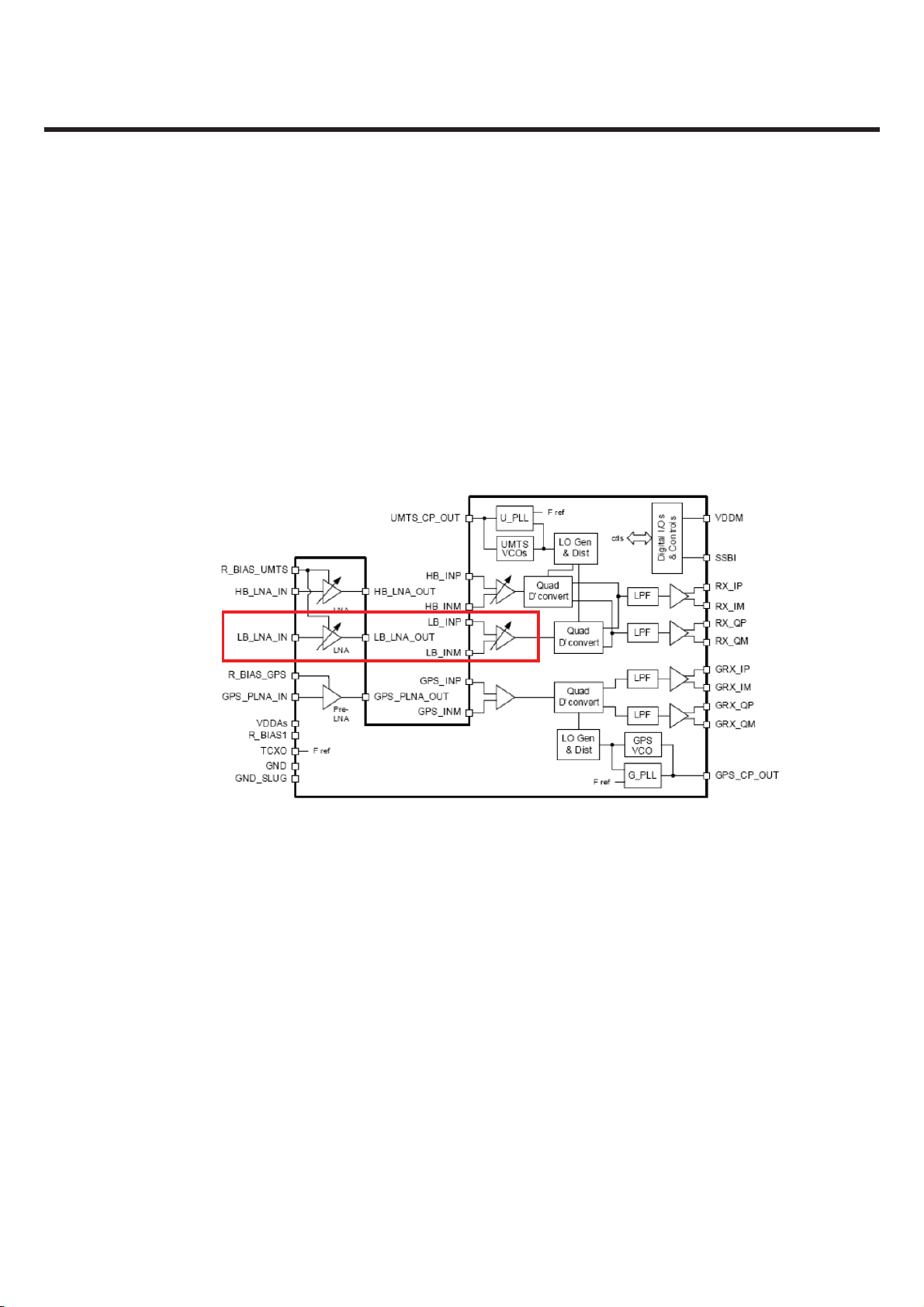
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
UMTS_850_RX
3.3 UMTS Mode
3.3.1 Receiver
The UMTS duplexer receiver output is routed to LNA circuits within the RFR6275 device.
UMTS LNA circuits(one for low-band UMTS and one for high-ban UMTS path) separated from all other
receive functions contained within the RFR6275 receiver IC to improve mixer LO to RF isolation a
critical parameter in the ZIF architecture. Isolation is further improved using high-reverse isolation
circuits into the LNA designes.
The LNA gains are stepped via API control. The IC operating mode and LNA bias currents reautomatically adjusted via software to minimize DC power consumption.
[Figure 3.3.1] RFR6275 IC functional bloc k di ag ra m
The UMTS Rx input is provided with an on-chip LNA that amplifies the signal before a second stage
filter that provides differential downconverter. This second stage input is configured differentially to
optimize second-order intermodulation and common mode rejection performance. The gain of the
UMTS frontend amplifier and the UMTS second stage differential amplifier are adjustable, under MSM
control, to extend the dynamic range of the receivers. The second stage UMTS Rx amplifiers drive the
RF ports of the quadrature RF-to-baseband downconverters. The downconverted UMTS Rx baseband
outputs are routed to lowpass filters having passband and stopband characteristics suitable for UMTS
Rx processing. These filter circuits allow DC offset corrections, and their differential outputs are
buffered to interface shared with GSM Rx to the MSM IC. The UMTS baseband outputs are turned off
when the RTR6275 is downconverting GSM signals and on when the UMTS is operating.
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 23 -
LGE Internal Use Only

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.3.2 Transmitter
The UMTS Tx path begins with differential baseband signals (I and Q) from the MSM device.
These analog input signals are amplified, filtered, and applied to the quadrature up-converter mixers.
The up-converter output is amplified by multiple variable gain stages that provide transmit AGC control.
The AGC output is filtered and applied to the driver amplifier; this output stage includes an integrated
matching inductor that simplifies the external matching network to a single series capacitor to achieve
the desired 50-Ω interface.
The RTR6275 UMTS output is routed to its power amplifier through a bandpass filter, and delivers fairly
high-level signals that are filtered and applied to the PA. Transmit power is delivered from the duplexer
to the antenna through the switch module.
The transceiver LO synthesizer is contained within the RTR6275 IC with the exception of the off-chip
loop filter components and the VC-TCXO. This provides a simplified design for multimode applications.
The PLL circuits include a reference divider, phase detector, charge pump, feedback divider, and digital
logic generator.
UMTS Tx. Using only PLL1, the LO generation and distribution circuits create the necessary LO signals
for nine different frequency converters. The UMTS transmitter also employs the ZIF architecture to
translate the signal directly from baseband to RF. This requires FLO to equal FRF, and the RTR6275 IC
design achieves this without allowing FVCO to equal FRF.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 24 -
Only for training and service purposes
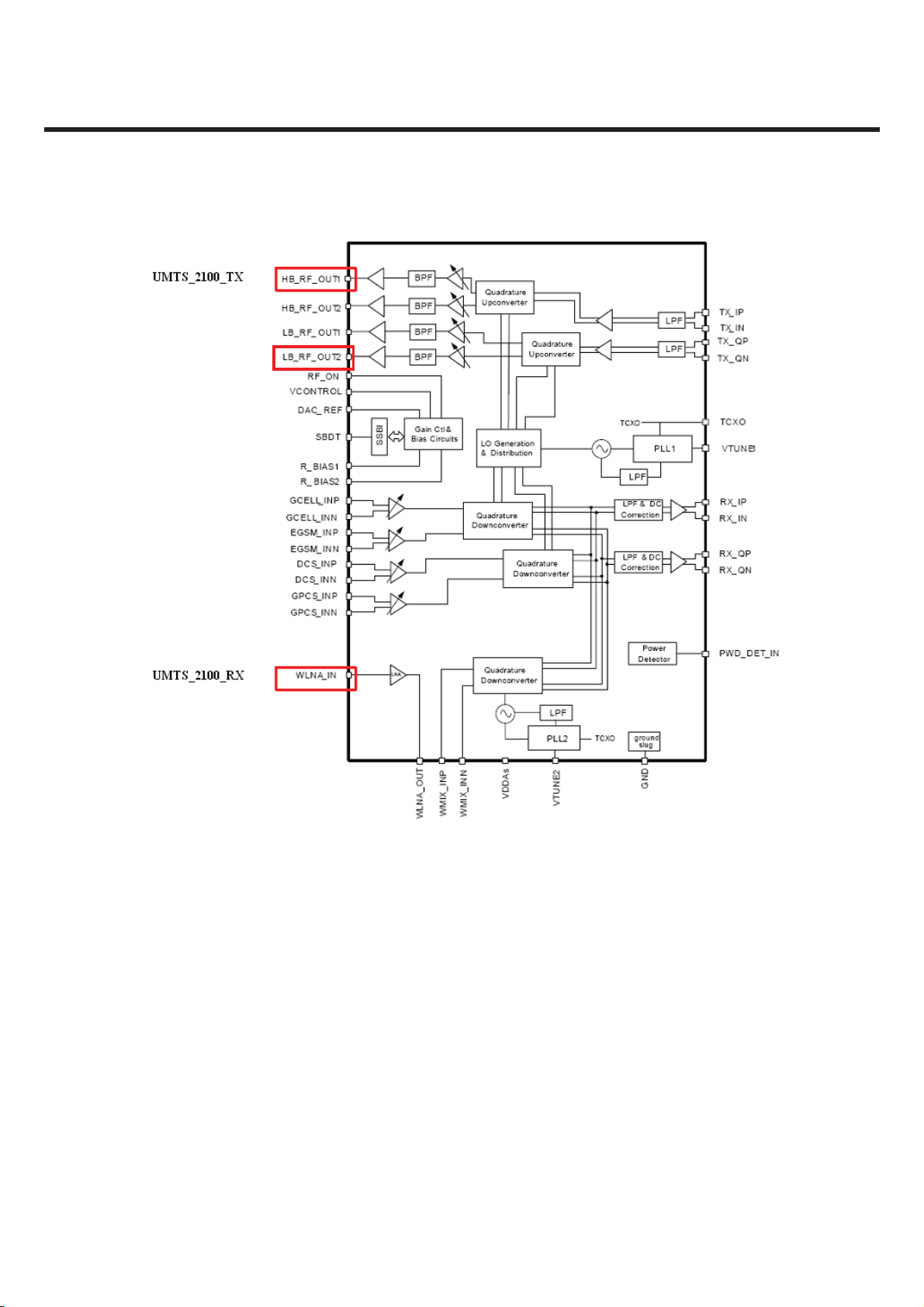
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
UMTS_850_TX
Figure 3.3.2 RTR6275 IC functional block diagr am
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 25 -
LGE Internal Use Only
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.4 LO generation and distribution circuits
The integrated LO generation and distribution circuits are driven by internal VCOs to support various
modes to yield highly flexible quadrature LO outputs that drive all GSM/EDGE and UMTS band
upconverters and downconverters; with the help of these LO generation and distribution circuits, true
zero-IF architecture is employed in all GSM and UMTS band receivers and transmitters to translate the
signal directly from RF to baseband and from baseband to RF.
Two fully functional fractional-N synthesizers, including VCOs and loop filters, are integrated within the
RTR6275 IC. The first synthesizer (PLL1) creates the transceiver LOs that support the UMTS
2100/1900/1800 transmitter, and all four GSM band receivers and transmitters including: GSM 850, GSM
900, GSM 1800, and GSM 1900. The second synthesizer (PLL2) provides the LO for the UMTS
2100/1900/1800 receiver. An external TCXO input signal is required to provide the synthesizer frequency
reference to which the PLL is phase and frequency locked. The RTR6275 IC integrates most of PLL loop
filter components on-chip except two off-chip loop filter series capacitors, and significantly reduces offchip component requirement. With the integrated fractional-N PLL synthesizers, the RTR6275 has the
advantages of more flexible loop bandwidth control, fast lock time, and low-integrated phase error
3.5 Off-chip RF Components
3.5.1 Front-End Module(FL1000 : LMSP4LMA-573TEMP)
This equipment uses a single antenna to support all handset operating modes, with an antenna switch
module select the operating frequency and band. UMTS operation requires simultaneous reception
and transmission, so the UMTS Rx/Tx connection is routed to a duplexer that separates receive and
transmit signals. The active connection is MSM-selected by three control lines (GPIO[9], GPIO[10],
GPIO[11], GPIO[12]). These GPIOs are programmed to be ANT_SEL0, ANT_SEL1, ANT_SEL2,
ANT_SEL3 respectively.
Table 3.5.1 Antenna Switch Module Control logic
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 26 -
Only for training and service purposes

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.5.2 UMTS Dupexer(U1003,FL1003)
A UMTS duplexer splits a single operating band into receive and transmit paths. Important performance
requirements include;
Insertion loss, this component is also in the receive and transmit paths ;
In the KB775 typical losses : UMTS2100_ Tx = 1.5 dB, UMTS2100_ Rx = 1.8 dB
UMTS850 _ Tx = 1.8 dB, UMTS2100_ Rx = 2.2 dB
Out-of-band rejection or attenuation, the duplexer provides input selectivity for the receiver, output
filtering for the transmitter, and isolation between the two. Rejection levels for both paths are specified
over a number of frequency ranges. Two Tx-to-Rx isolation levels are critical to receiver performance:
Rx-band isolation, the transmitter is specified for out-of-band noise falling into the Rx band. This noise
leaks from the transmit path into the receive path, and must be limited to avoid degrading receiver
sensitivity. The required Rx-band isolation depends on the PA out of-band noise levels and Rx-band
losses between the PA and LNA. Minimum duplexer Rx band isolation value is about 46.7 dB.
Tx-band isolation, the transmit channel power also leaks into the receiver. In this case, the leakage is
outside the receiver passband but at a relatively high level. It combines with Rx band jammers to create
cross-modulation products that fall in-band to desensitize the receiver. The required Tx-band isolation
depends on the PA channel power and Tx-band losses between the PA and LNA. Minimum duplexer
Tx-band isolation value is about 51.7dB.
Passband ripple, the loss of this fairly narrowband device is not flat across its passband. Passband
ripple increases the receive or transmit insertion loss at specific frequencies, creating performance
variations across the band.s channels, and should be controlled.
Return loss, minimize mismatch losses with typical return losses of 10 dB or more (VSWR <2:1).
Power handling, high power levels in the transmit path must be accommodated without degraded
performance. The specified level depends on the operating band class and mobile station class (per the
applicable standard), as well as circuit losses and antenna EIRP. Several duplexer characteristics
depend upon its source and load impedances. QUALCOMM strongly recommends an isolator be used
between the UMTS PA and duplexer to assure proper performance.
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 27 -
LGE Internal Use Only
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
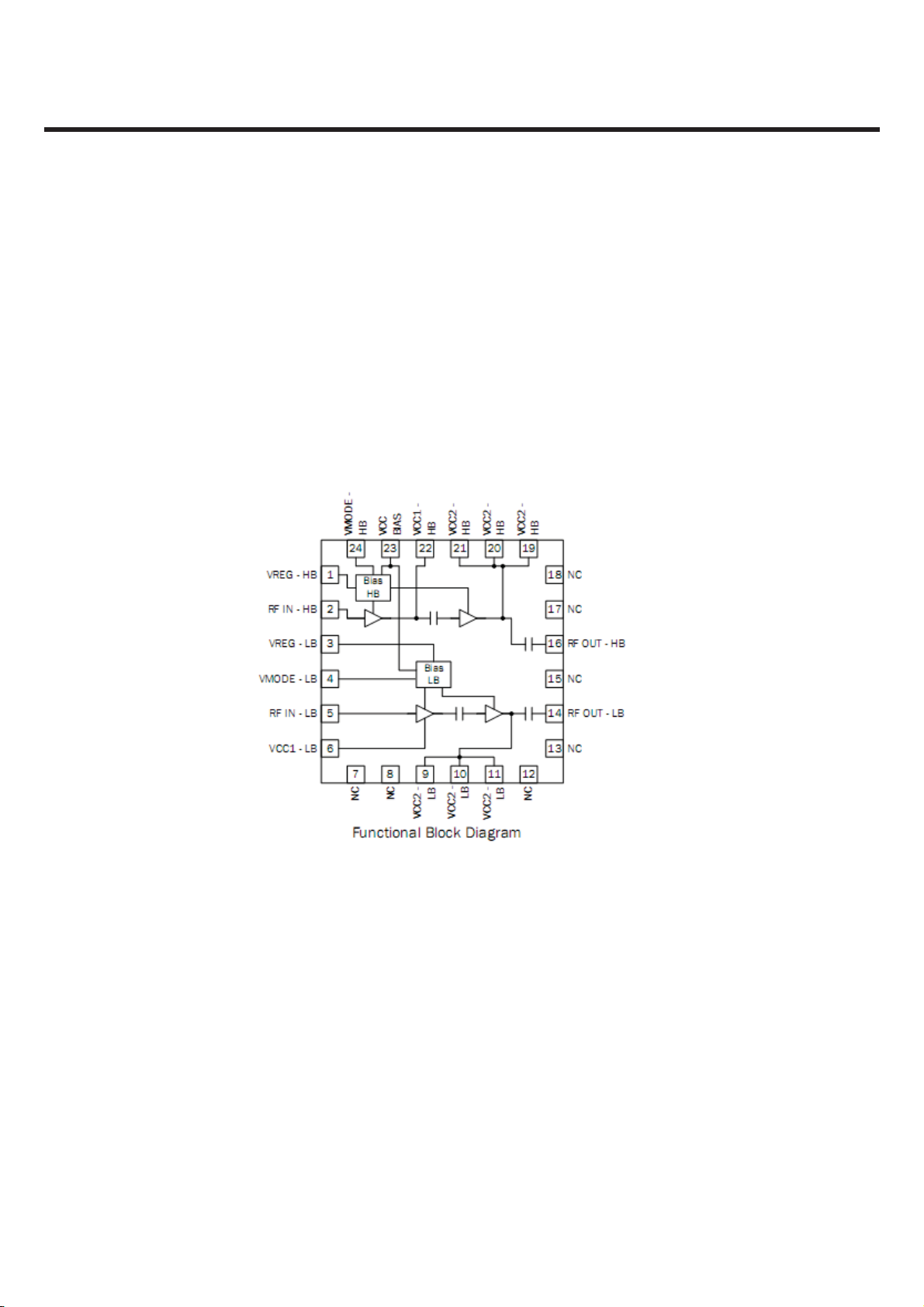
3.5.3 UMTS PAM(U1004 :RF5184)
UMTS850/UMTS 2100 Power Amplifier Module
The RF5184 is a high-power, high-efficiency linear amplifier module specifically designed for 3V
handheld systems. The device is manufactured on an advanced third generation GaAs HBT
process, and was designed for use as the final RF amplifier in UMTS handheld digital cellular
equipment, spread-spectrum systems, and other applications in the 824 MHz to 915 MHz band
(Band V and VIII) and 1850 MHz to 1980 MHz band (Band II and I). The RF5184 is assembled in a
24 pin, 4mm * 4mm, QFN package.
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 28 -
Only for training and service purposes

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
3.5.4 VCTCXO(X1000 : TG-5010LH_19_2M_75A)
The Voltage Controlled Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator (VCTCXO) provides the
reference frequency for all RFIC synthesizers as well as clock generation functions within the
MSM6280 IC. The oscillator frequency is controlled by the MSM6280 IC.s TRK_LO_ADJ pulse density
modulated signal in the same manner as the transmit gain control TX_AGC_ADJ. A two-pole RC
lowpass filter is recommended on this control line.
The PM6650 IC controls the handset power-up sequence, including a special VCTCXO warm-up
interval before other circuits are turned on. This warm-up interval (as well as other TCXO controller
functions) is enabled by the MSM TCXO_EN line . The PM6650 IC VREG_TCXO regulated output
voltage is used to power the VCTCXO and is enabled before most other regulated outputs.
Any GSM mode power control circuits within the MSM6280 IC require a reference voltage for proper
operation and sufficient accuracy. Connecting the PM6650 IC REF_OUT directly to the MSM6275 IC
GSM_PA_PWR_CTL_REF provides this reference. This sensitive analog signal needs a 0.1 μF low
frequency filter near to MSM side, and isolate from digital logic and clock traces with ground on both
sides, plus ground above and below if routed on internal layers
3.5.5 PMIC Functional Block Diagram(U601 : PM6650-3P)
Input power management
- Valid external supply attachment and removal detection
- Supports unregulated (closed-loop) external charger supplies and USB supplies as input power sources
- Supports lithium-ion main batteries
- Trickle, constant current, constant voltage, and pulsed charging of the main battery
- Supports coin cell backup battery (including charging)
- Battery voltage detectors with programmable thresholds
- VDD collapse protection
- Charger current regulation and real-time monitoring for over-current protection
- Charger transistor protection by power limit control
- Control drivers for two external pass transistors and one external battery MOSFET—MOSFET is optional
- Voltage, current, and power control loops
-Automated recovery from sudden momentary power loss
Output voltage regulation
- One boost (step-up) switched-mode power supply (SMPS) for driving white LEDs and hosting USBOTG
- Three buck (step-down) switched-mode power supplies that efficiently generate MSMC, MSME, and PA
(or second MSMC) supply voltages
- Supports dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) for MSMC and PA
- Eleven low dropout regulator circuits with programmable output voltages, implemented using three
different current ratings: 300 mA (two), 150 mA (six), and 50 mA (three). These can be used to power
MSMA, MSMP, RFRX1, RFRX2, RFTX, SYNT, TCXO, WLAN, MMC, USB, and RUIM circuits.
- All regulators can be individually enabled/disabled for power savings
- Low power mode available on MSMA and MSMP regulators
- All regulated outputs are derived from a common bandgap reference—close tracking
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 29 -
LGE Internal Use Only

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- Integrated handset-level housekeeping functions reduces external parts count, size, cost
- Analog multiplexer selects from 8 internal and up to 18 external inputs
- Multiplexer output’s offset and gain are adjusted, increasing the effective ADC resolution
- Adjusted multiplexer output is buffered and routed to an MSM device ADC
- Dual oscillators – 32.768 kHz off-chip crystal and on-chip RC assures MSM device sleep clock
- Crystal oscillator detector and automated switch-over upon lost oscillation
- Real time clock for tracking time and generating associated alarms
- On-chip adjustments minimize crystal oscillator frequency errors
- Circuits control TCXO warm-up and synchronize, deglitch, and buffer the TCXO signal
- TCXO buffer control for optimal QPH/catnap timing
-Three-stage over-temperature protection (smart thermal control)
Integrated handset-level user interfaces
- Four programmable current sinks recommended as keypad backlight, LCD backlight, camera flash,
and general-purpose drivers
- Vibration motor driver programmable from 1.2 to 3.1V in 100 mV increments
-Speaker driver with programmable gain, turn-on time, and muting; differential operation (drives
external 8 Ω speakers with volume controlled 500 mW)
IC-level interfaces
- MSM device-compatible 3-line SBI for efficient initialization, status, and control
- Supports the MSM device’s interrupt processing with an internal interrupt manager
- Many functions monitored and reported through real-time and interrupt status signals
- Dedicated circuits for controlled power-on sequencing, including the MSM device’s reset signal
- Several events continuously monitored for triggering power-on/power-off sequences
- Supports and orchestrates soft resets
- USB-OTG transceiver for full-speed (12 Mb/s) and low speed (1.5 Mb/s) interfacing of the MSM
device to computers as a USB peripheral, or connecting the MSM device to other peripherals
-RUIM level translators enable MSM device interfacing with external modules
Twelve multi-purpose pins that can be configured as digital or analog I/Os, bi-directional I/Os, or
current sinks. Default functions support the RUIM level translators, power-on circuits, analog
multiplexer inputs, an LED driver, and a reference voltage buffer.
Highly integrated functionality in a small package – 84-pin BCCS with a large center slug for electrical
ground, mechanical stability, and thermal relief
LGE Internal Use Only Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
- 30 -
Only for training and service purposes

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
Figure 3.5.5.1 PM6650 Interface with MSM
Copyright © 2009 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 31 -
LGE Internal Use Only
 Loading...
Loading...