Page 1
CAUTION
BEFORE SERVICING THE UNIT, READ THE "SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS" IN THIS MANUAL.
MODEL: GR-S552 / GR-S592
REFRIGERATOR
SERVICE MANUAL
http://biz.lgservice.com
Page 2

CONTENTS............................................................................................................................................................................. 2
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS.................................................................................................................................................. 3
SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................................................................................... 4
PARTS IDENTIFICATION....................................................................................................................................................... 5
DISASSEMBLY.................................................................................................................................................................... 6-7
DOOR................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
DOOR SWITCH.................................................................................................................................................................... 6
FAN AND FAN MOTOR........................................................................................................................................................ 6
DEF' CONTROL ASM .......................................................................................................................................................... 7
LAMP.................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
CONTROL BOX-R................................................................................................................................................................ 7
ADJUSTMENT..................................................................................................................................................................... 8-9
COMPRESSOR.................................................................................................................................................................... 8
PTC-STARTER..................................................................................................................................................................... 8
OLP (OVER LOAD PROTECTOR)....................................................................................................................................... 9
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM................................................................................................................................................................ 9
TROUBLESHOOTING..................................................................................................................................................... 10-15
COMPRESSOR AND ELECTRIC COMPONENTS ........................................................................................................... 10
PTC AND OLP.................................................................................................................................................................... 11
ANOTHER ELECTRIC COMPONENT............................................................................................................................... 12
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS CHART.......................................................................................................................................... 13
REFRIGERATING CYCLE............................................................................................................................................ 14-15
DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION & CIRCUIT OF MICOM ................................................................................................ 16-32
EXPLODED VIEW & REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST.......................................................................................................... 33-
Please read the followings before servicing your refrigerator.
1. Check if an electric leakage occurs in the set.
2. To prevent electric shock, unplug prior to servicing.
3. In case of testing with power on, wear rubber gloves to
prevent electric shock.
4. If you use any appliances, check regular current, voltage
and capacity.
5. Don't touch metal products in cold freezer with wet hand.
It may cause frostbite.
6. Prevent water flowing to electric elements in mechanical
parts.
7. When you stand up during observing the lower part
with the upper door open, move with care to prevent
head wound which may happen by hitting the upper
door.
8. When sloping the set, remove any materials on the set,
especially thin plate type. (ex.: glass shelf or books.)
9. When servicing evaporator part, wear cotton gloves
without fail. It is to prevent wound by sharp fin of
evaporator.
10. Leave a breakage of refrigerating cycle to a heavy
service center. The gas in cycle inside may soil
ambient air.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CONTENTS
- 2 -
Page 3

- 3 -
Air Recharging in Compressor
Test the refrigeration by connecting it electrically before
refilling operation. It is necessary to ascertain the function
of the motor-compressor and identify the defects
immediately. If the defects have been found, empty the old
system of eventual R-134a residue by breaking off the end
of the extension piece at its narrow point. (Figure 1)
Replace the filter and any damaged components. Unsolder
and pull off the piece remaining inside the service tube and
then attach an extension completely with male Hansen and
last, solder it to the same tube again. (Figure 2)
It is necessary to execute the soldering operation with
valve open so that the fumes caused by oil residue can
come out freely without blowholes between two tubes
during heating the point to be soldered.
The extension fitted with the male Hansen is connected to
the female fitting of the vacuum pump tube. (Figure 3)
Air evacuating from the system begins so soon as the
pump starts. The refrigeration system must be kept under
vacuum until the reading on the low-pressure gauge
indicates vacuum (0 absolute, -1 atm., -760 mm hg) in any
case it is advisable to keep the pump running for about 60
minutes. (Figure 3)
In case that a considerable leakage occurs and to stop the
vacuum pump will be necessary and add a small quantity
of Freon to the system, if vacuum should not be obtained
(pressure gauge can't fall to 1 atmosphere), start the
refrigeration unit and find the leakage with the special leakfinder. When the defective soldering point is visible, re-do it
after opening the extension tube valve and reestablishing
the normal outside pressure inside the group.
Because the melted alloy is sucked into the tubes and
block them, the pressure must be rebalanced when
vacuum is in the system in soldering. As soon as the
vacuum operation is over, add the quantity in grams of
R-134a to the refrigerant system. Remember that every
system has an exact quantity of R-134a with a tolerance of
±5 grams that can be added. (Figure 4)
Before performing this operation (if the vacuum pump and
refilling cylinder are connected), make sure that the valve
placed between the vacuum pump and refilling tube are
closed to keep the Freon for adding to the system. (Figure 5)
In addition, check the graduated scale on the cylinder for
the quantity of R-134a to be added, for example, if we
have 750 grams of Freon in the cylinder and must add 165
grams to the group, this amount will be reached when
R-134a has dropped to 585 grams, remembering that the
indicator shows a lower limit of meniscus. Do this after
choosing the scale corresponding to the gas pressure
different scales reported as the same gas pressure
indicated by the pressure gauge on the top of the column.
To make R-134a flow into the system, open the valve
placed at the base of the cylinder and connected to the
filling tube. The amount of Freon cannot be added to the
system all at once because it may cause a blocking of
motor-compressor. Therefore, proceed by adding original
quantity of about 20-30 grams and close the valve
immediately.
The pressure rises and the motor-compressor must start,
sucking the gas and making the pressure go down again.
Regulate the valve again, maintaining the same manner
until reaching to the quantity of R-134a established for the
system being charged. When the system is running, the
suction pressure must be stabilized between 0.10 to 0.4
atmosphere.
POINT TO BE
BROKEN
CHARGE TUBE
EXTENSION
FEMALE
HANSEN
MALE HANSEN
SOLDERING POINTSERVICE TUBE EXTENSION
Figure 1 Figure 2
TO THE VACUUM
PUMP
PRESSURE
GAUGE
Figure 3
TO THE R-134a CYLINDER
TO THE REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM
Figure 4
FILLING OR
CHARGE TUBE
VALVE TO BE OPENED
WHEN REFILLING
VALVE TO BE CLOSED
AFTER VACUUM
TO THE VACUUM PUMP
TO THE REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM
TO THE CHARGE
CYLINDER
Figure 5
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
Page 4
- 4 -
ITEMS SPECIFICATIONS
FREEZER 114
NET CAPACITY
REFRIGERATOR 306
TOTAL 420
DIMENSIONS (mm) 755(W)
X
689(D)X1777(H)
NET WEIGHT (kg) 79
COOLING SYSTEM Fan Cooling
TEMPERATURE CONTROL Micom Control
Full Automatic
DEFROSTING SYSTEM
Heater Defrost
OUT CASE Pre Coated Metal
INNER CASE A B S
INSULATION Polyurethane Foam
( l )
ITEMS SPECIFICATIONS
FREEZER 1 EA
REFRIGERATOR 2 EA
VEGETABLE TRAY Drawer Type
EGG TRAY 2 Pieces
ICE TRAY 2 Pieces (Plastic)
ICE BANK 1 Piece
COMPRESSOR P.T.C Starting Type
EVAPORATOR Fin Tube Type
CONDENSER Wire Condenser
REFRIGERANT R-134a (135g)
DEFROSTING DEVICE HEATER
SHELF
1. SPECIFICATIONS
1-1 GR-S552
ITEMS SPECIFICATIONS
FREEZER 126
NET CAPACITY
REFRIGERATOR 334
TOTAL 460
DIMENSIONS (mm) 755(W)
X
719(D)X1777(H)
NET WEIGHT (kg) 81
COOLING SYSTEM Fan Cooling
TEMPERATURE CONTROL Micom Control
Full Automatic
DEFROSTING SYSTEM
Heater Defrost
OUT CASE Pre Coated Metal
INNER CASE A B S
INSULATION Polyurethane Foam
( l )
ITEMS SPECIFICATIONS
FREEZER 1 EA
REFRIGERATOR 2 EA
VEGETABLE TRAY Drawer Type
EGG TRAY 2 Pieces
ICE TRAY 2 Pieces (Plastic)
ICE BANK 1 Piece
COMPRESSOR P.T.C Starting Type
EVAPORATOR Fin Tube Type
CONDENSER Wire Condenser
REFRIGERANT R-134a (135g)
DEFROSTING DEVICE HEATER
SHELF
1-2 GR-S592
Page 5
- 5 -
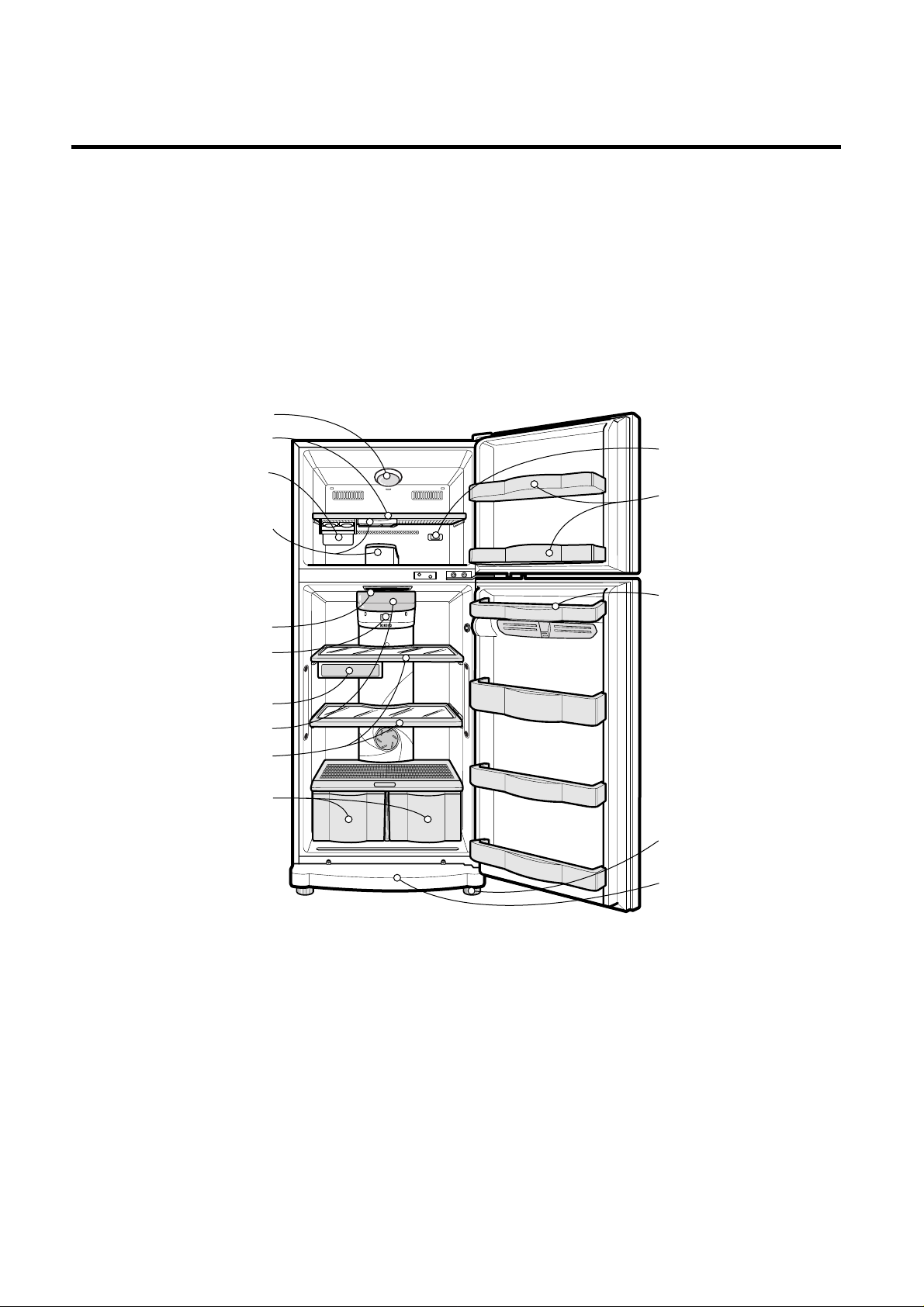
2-1 FEATURE CHART
NOTE : This is a basic model. The shape of refrigerator is subject to change.
2. PARTS IDENTIFICATION
Egg Storage Rack
Freezer Door Rack
Freezer Temperature
Control Dial
Leveling Screw
Vegetable Drawer
Used to keep fruits
and vegetables, etc.
fresh and crisp.
Shelves
Lamp
Fresh Meat
Base Cover
FREEZER
COMPARTMENT
Lamp
Shelf
Twisting Ice
Serve(Option)
or
General Type
Ice Making
Deodorizer
REFRIGERATOR
COMPARTMENT
Refrigerator
Temperature
Electronic Control
Page 6

- 6 -
3-1 DOOR
● Freezer Door
1. Remove the hinge cover by pulling it upwards.
2. Loosen hexagonal bolts fixing the upper hinge to the
body and lift the freezer door.
3. Pull out the door gasket to remove from the door foam
Ass'y.
● Refrigerator Door
1. Loosen hexagonal bolts fixing the lower hinge to the
body to remove the refrigerator door only.
2. Pull out the door gasket to remove from the door foam
Ass'y.
3-2 DOOR SWITCH
1. To remove the door switch, pull out it with a '—' type
driver as shown in (figure 9).
2. Disconnect the lead wire from the switch.
3-3 FAN AND FAN MOTOR
1. Remove the freezer shelf.
2. Remove the Cover Lamp-F and Case Lamp by
loosening 1 screw fixed to ceiling of Inner Case.
3. Remove the Grille by pulling it out.
4. Pull out the Shroud and remove the Fan Motor Assy by
loosening 2 screws.
5. Pull out the fan and, separate the Fan Motor, Brackets
and the Guide Fan.
BOLT
HINGE
HINGE COVER
Figure 6
GASKET
Figure 7
LOWER HINGE
BOLT
Figure 8
Figure 9
3. DISASSEMBLY
GUIDE FAN
FAN
SHROUD
GRILLE
FAN MOTOR
Figure 12
Figure 11
Page 7
- 7 -
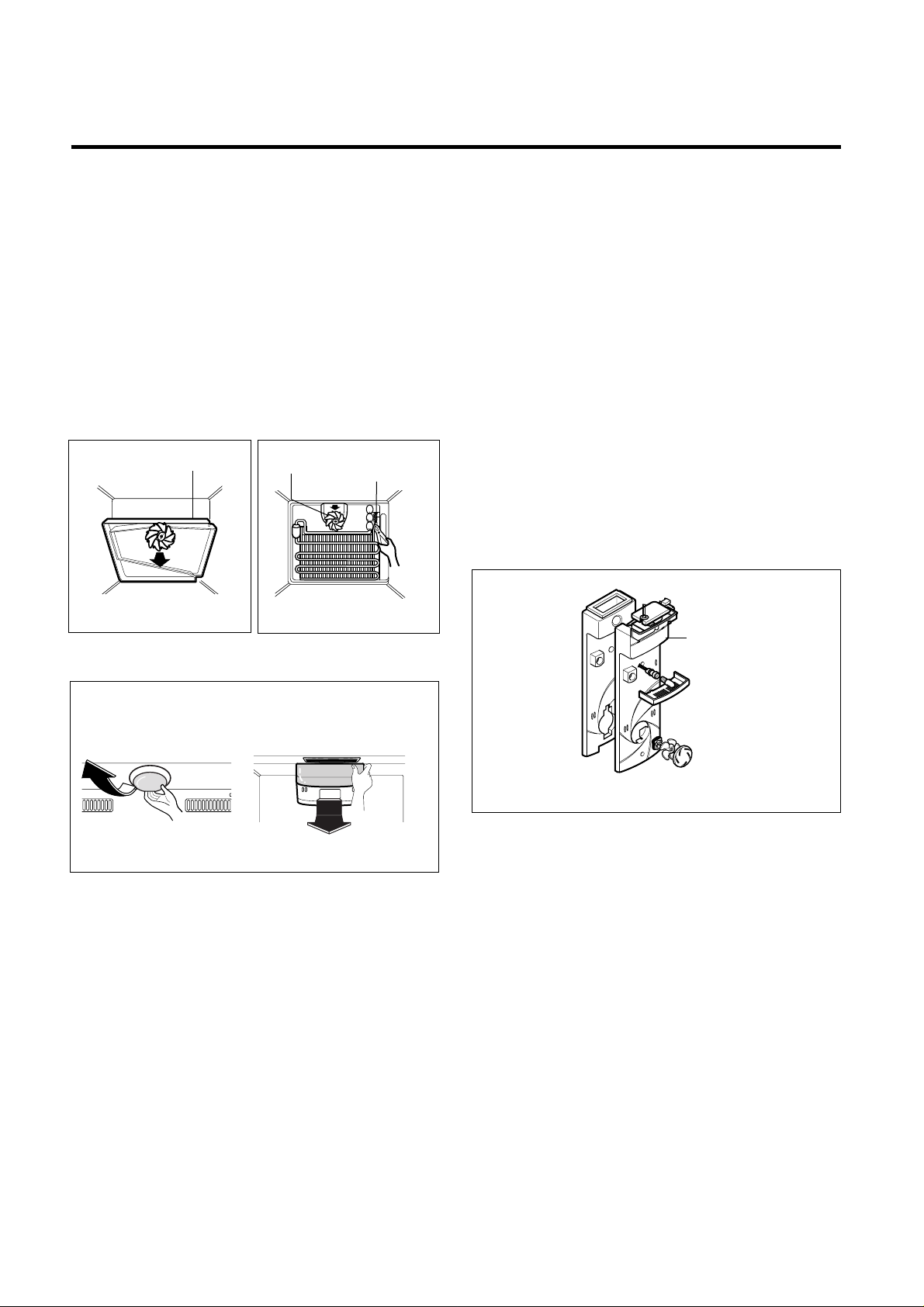
3-4 DEF' CONTROL ASSY
Def control ASM consists of Defrost Sensor and FUSE–M.
Defrost
Sensor
functions to defrost automatically and it is
attached to the Evaporator and the metal side of the case
senses Temp.
Fuse-M is a kind of safety device for preventing overheating of the Heater when defrosting.
At the temperature of 77°C, it stops the emission of TEMP
from the Defrost Heater.
1. Pull out the shroud-F after removing the Grille Fan.
(Figure 13)
2. Separate the connectors connected with the Def Control
ASM and replace the Def Control ASM after cutting the
Tie Wrap. (Figure 14)
3-5 LAMP
3-5-1 Freezer room lamp
1. Unplug the power cord from the outlet.
2. Remove the room lamp lid by taking down while pulling
it forward with your hand after inserting finger into the
inside hole as shown in (figure 16).
3. Remove the lamp by turning it counterclockwise.
4. Assemble in reverse order of disassembly. Replacement
bulb must be the same specication as original.
3-5-2 Refrigerator room lamp
1. Unplug the power cord from the outlet.
2. Remove refrigerator shelves.
3. Remove the room lamp lid by taking down while pulling
forward with your hands as shown in (figure 17).
4. Turn the lamp counterclockwise.
5. Assemble in reverse order of disassembly. Replacement
bulb must be the same specification as original.
3-6 CONTROL BOX-R
1. First, remove all shelves in the refrigerator and Control
Box-R by loosening 1 screw.
2. Loosen 2 screws fixing the Control Box-R to the Inner
Case after detaching the cap screw.
3. Remove the Control Box-R by pulling it downward.
SHROUD-F
Figure 13
FAN
DEF CONTROL ASM
Figure 14
FREEZER ROOM LAMP REFRIGERATOR ROOM LAMP
Figure 16
Figure 17
MULTI FLOW
DUCT
Figure 18
Page 8

- 8 -
4-1 COMPRESSOR
4-1-1 Role
The compressor inhales low temperature and low pressure
gas evaporated from Evaporator of the Refrigerator, and
condenses this gas to high temperature and high pressure
gas, and then plays delivering role to Condenser.
4-1-2 Composition
The Compressor is Composed of Compressor Apparatus
compressing gas, Compressor Motor moving Compressor
Apparatus and Case protecting Compressor Apparatus
and Motor. There are PTC-Starter, and Over Load
Protector (OLP) in the Compressor outside.
On the other
hand, because the Compressor consists of 1/1000mm processing
precision components and is sealed after producing without dust
or humidity, deal and repair with care.
4-1-3 Note to Use
(1) Be careful not to allow over-voltage and over-current.
(2) No Strike
If applying forcible power or strike (dropping or careless
dealing), poor operation and noise may occur.
(3) Use proper electric components appropriate to the
Compressor.
(4) Note to Keep Compressor.
If Compressor gets wet in the rain and rust in the pin of
Hermetic Terminal, poor operation and poor contact
may cause.
(5) Be careful that dust, humidity, and flux due to welding
don't inflow in Compressor inside in replacing
Compressor. Dust, humidity, and flux due to welding
which inflows to Cylinder may cause lock and noise.
4-2 PTC-STARTER
4-2-1 Composition of PTC-Starter
(1) PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) is no-contact
semiconductor starting device which uses ceramic
material and the material consists of BaTiO
3.
(2) The higher the temperature is, the higher resistance
value becomes . These features are used as starting
device of Motor.
4-2-2 Role of PTC-Starter
(1) PTC is attached to Hermetic Compressor used for
Refrigerator, Show Case and starts Motor.
(2) Compressor for household refrigerator applies single-
phase induction Motor.
For normal operation of single-phase induction motor, in
the starting operation flows in both main coil and subcoil. After the starting is over, the current is cut off in
subcoil. The proper features of PTC play the above all
roles. So, PTC is used as a starting device of motor.
4-2-3 PTC-Applied Circuit Diagram
● According to Starting Method of Motor
4-2-4 Motor Restarting and PTC Cooling
(1) For restarting after power off during normal
Compressor Motor operation, plug the power cord after
5 min. for pressure balance of Refrigerating Cycle and
PTC cooling.
(2) During normal operation of Compressor Motor, PTC
elements generate heat continuously. Therefore,
if PTC isn't cooled for a while after power off, Motor
can't operate again.
4-2-5 Relation of PTC-Starter and OLP
(1) If power off during operation of Compressor and power
on before PTC is cooled, (instant shut-off within 2 min.
or reconnect a power plug due to misconnecting),
PTC isn't cooled and a resistance value grows. As a
result, current can't flow to the sub-coil and Motor can't
operate and OLP operates by flowing over current in
only main-coil.
(2) While the OLP repeats on and off operation about 3-5
times, PTC is cooled and Compressor Motor performs
normal operation.
If OLP doesn't operate when PTC is not cooled,
Compressor Motor is worn away and causes circuitshort and fire. Therefore, use a proper fixed OLP
without fail.
4-2-6 Note to Use PTC-Starter
(1) Be careful not to allow over-voltage and over-current.
(2) No Strike
Don't apply a forcible power or strike.
(3) Keep apart from any liquid.
If liquid such as oil or water inflows into PTC,
PTC materials it may break due to insulation
breakdown of material itself.
(4) Don't change PTC at your convenience.
Don't disassemble PTC and mold. If damaging to
outside of PTC-starter, resistance value alters and poor
starting of compressor motor may cause.
(5) Use a properly fixed PTC.
PTC STARTER
HERMETIC
TERMINAL
COMPRESSOR
MOTOR
C
M
S
M
3
6
5
S
PTC
OVERLOAD PROTECTOR
RSIR
Figure 20
4. ADJUSTMENT
Page 9

- 9 -
4-3 OLP (OVER LOAD PROTECTOR)
4-3-1 Definition of OLP
(1) OLP (OVER LOAD PROTECTOR) is attached to
Hermetic Compressor and protects Motor by cutting off
current in Compressor Motor by Bimetal in the OLP in
case of over-rising temperature.
(2) When over-voltage flows to Compressor motor, Bimetal
works by heating the heater inside OLP,
and OLP protects Motor by cutting off current which
flows to Compressor Motor.
4-3-2 Role of OLP
(1) OLP is attached to Hermetic Compressor used to
Refrigerator and Show Case and prevents Motor Coil
from being started in the Compressor.
(2) Do not turn the Adjust Screw of OLP in any way for
normal operation of OLP.
(Composition and connection Diagram of OLP)
5. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
CONTACTING
POINT
COVER
BIMETAL
CONTACTING
POINT
HEATER
TERMINALS
ADJUST
SCREW
HEATER
BIMETAL
Figure 21
NOTE : 1. This is a basic diagram and specifications vary in different localities.
Page 10

- 10 -
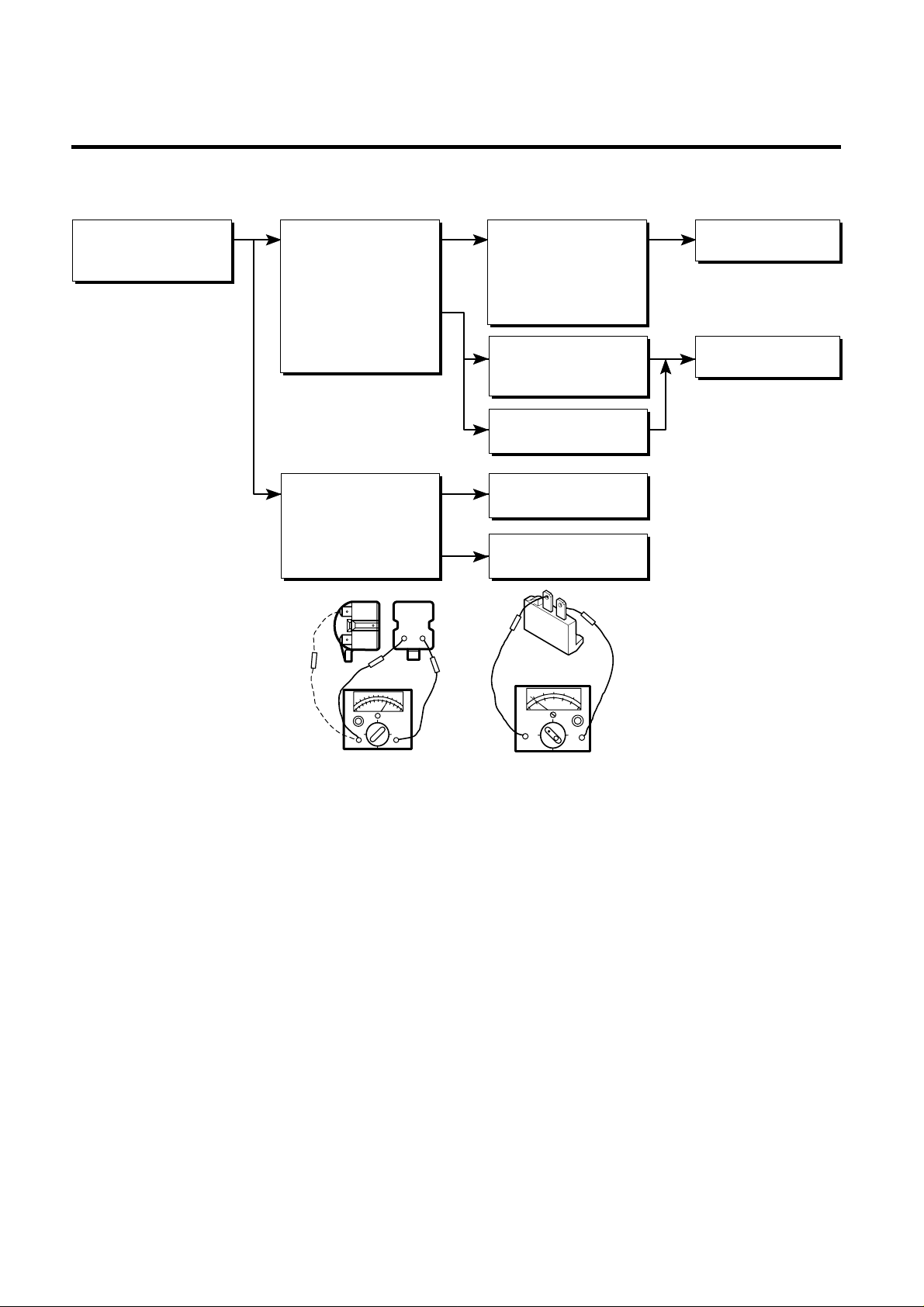
6-1 COMPRESSOR AND ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
6. TROUBLESHOOTING
1
2
3
4
5
2
5
5
3
5
4
5
5
1
43
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
Power Source.
Remove the PTC-Starter
from the Compressor
and measure the voltage
between Terminal C of
Compressor and
Terminals 5 or 6 of PTC.
No Voltage.
(Rating Voltage
±10%)?
Replace OLP.
Reconnect.
Replace
PTC-Starter.
Replace OLP.
O.K.
Check connection
condition.
OLP disconnected?
Advise the customer
to use a regular
Trans.
Replace Compressor.
OLP works within
30 sec. in forcible
OLP operation by
turning instant power
on and off.
Components start in
the voltage of Rating
Voltage ±10%
below.
Applied voltage isn't
in the range of Rating
Voltage ±10%.
Check the resistance
among M-C, S-C and
M-S in Motor
Compressor.
Check the resistance
of two terminals in
PTC-Starter.
Check if applying
a regular OLP.
Measure minimum
starting voltage after 5
min. for balancing cycle
pressure and cooling
the PTC.
Check the
resistance of
Motor
Compressor.
Check the
resistance of
PTC-Starter.
Check OLP.
Check
starting state.
Page 11
- 11 -
6-2 PTC AND OLP
65
3
4
YES
NO
Normal operation of
Compressor is
impossible or poor.
Separate the PTC from
Compressor and
measure the resistance
between No. 5 and 6
(only RSIR Type) or No.
4 and 5 of PTC with a
Tester or Whistone
Bridge. (Figure 22)
Separate the OLP
from Compressor and
check resistance
value between two
terminals of OLP with
a Tester. (Figure 23)
Observation value is
220V/50Hz : 47Ω ± 30%
220 - 240V/50Hz : 47Ω ±30%
110 -115V/60Hz : 6.8Ω ± 30%
220V/60Hz : 47Ω ± 30%
127V/60Hz : 22Ω ± 30%
The resistance value is
0 or several
hundreds Ω.
The value is ∞.
Check another
electric components.
Replace OLP.
Check another
electric components.
Replace
PTC.
Figure 23
Figure 22
Page 12

- 12 -
6-3 ANOTHER ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
▼ Cooling is impossible
Compressor
doesn't run.
Running state of
Compressor is poor.
Check a starting
voltage.
Check if current flows to
the following
components.
a. Thermistor
b. Starting devices
c. OLP
d. Compressor coil
e. Circuit Parts
Low voltage.
Poor contacting.
Shorted or broken.
Poor contacting
or shorted.
Coil shorted.
Poor contacting
or shorted.
Poor contacting
and broken.
Shorted.
Lack of capacity.
Coil of motor
Compressor.
Replace
the compressor.
Replace
each component.
Raise the voltage.
Replace
each component.
Cause.
Check if current flows
to starting devices.
Check current flowing
in sub-coil of
Compressor.
Check capacity of OLP.
The items described
above are normal.
▼ Cooling ability is poor
Fan motor
doesn't run.
Much frost are sticked
to the EVAPORATOR.
Poor contacting.
Coil is shorted.
Shorted.
Replace
each component.
Replace
each component.
Replace
each component.
Check current flowing
in door S/W.
Check current flowing
in the Fan Motor.
Check current flowing
of the following
components.
• Def. Sensor
• FUSE-M
Check current flowing
of the following
components.
• Sheath Heater
Page 13

- 13 -
COMPLAINT POINTS TO BE CHECKED REMEDY
Cooling is • Is the power cord unplugged from the outlet? • Plug to the outlet.
impossible. • Check if the power S/W is set to OFF. • Set the switch to ON.
• Check if the fuse of power S/W is shorted. • Replace a regular fuse.
• Measure the voltage of power outlet. • If voltage is low, wire newly.
Cooling ability • Check if the set is placed close to wall. • Place the set with the space of about 10cm.
is poor. • Check if the set is placed close to stove, gas • Place the set apart from these heat
• cooker and direct rays. • appliances.
• Is the ambient temperature high or • Make the ambient temperature below.
• the room door closed?
• Check if putting in hot foods. • Put in foods after they get cold.
• Did you open the door of the set too often • Don't open the door too often and close
• or check if the door is closed up? • it firmly.
• Check if the Control is set to "Min". • Set the control to mid-position.
Foods in the • Are foods placed in cooling air outlet? • Place foods in high temperature section.
Refrigerator • (Front Part)
are frozen. • Check if the Display LED is set to "Max". • Set the Display LED to "Mid".
• Is the ambient temperature below 5°C? • Set the Display LED to "Min".
Dew or ice • Is watery foods kept? • Seal up watery foods with wrap.
forms in the • Check if putting in hot foods. • Put in foods after they get cold.
chamber of • Did you open the door of the set too • Don't open the door too often and close
the set. • often or check if the door is closed up. • it firmly.
Dew forms • Check if ambient temperature and humidity • Wipe dew with a dry cloth. This happening
in the Out Case. of surroumcling air are high. • is solved in low temperature and humidity
• naturally.
• Is the gap in the door packed? • Fill up the gap.
Abnormal • Is the set positioned in a firm and even place? • Adjust the Adjust Screw, and position
noise generates. • in the firm place.
• Does any unnecessary objects exist • Remove the objects.
• in the back side of the set?
• Check if the Drip Tray is not firmly fixed. • Fix it firmly on an original position.
• Check if the cover of mechanical room • Place the cover at an original position.
• in below and front side is taken out.
To close the door • Check if the door packing becomes dirty • Clean the door packing.
is not handy. • by filth such as juice.
• Is the set positioned in a firm and even place? • Position in the firm place and adjust the
• Adjust Screw.
• Is too much food putted in the set? • Keep foods not to reach the door.
Ice and foods • Check if the inside of the set becomes dirty. • Clean the inside of the set.
smell unpleasant. • Did you keep smelly foods without wraping? • Wrap smelly foods.
• It smells plastic. • The new products smell plastic, but it is
• removed after 1-2 weeks.
● In addition to the items described left, refer to the followings to solve the complaint.
Check if dew forms in
the Freezer.
Replace the
Components of
defrosting circuit.
Check Refrigerating
Cycle.
Check the
Thermistor
Defrosting
is poor.
The cycle
is faulty.
Repair the cycle.
Replace the
Thermistor.
The operation of
the Thermistor is
poor.
6-4 SERVICE DIAGNOSIS CHART
Page 14

- 14 -
6-5 REFRIGERATING CYCLE
▼ Troubleshooting Chart
▼ Leakage Detection
Observe discharging point of refrigerant which may be in oil discharging part in compressor and hole of evaporator.
YES
YES
Whether Compressor
runs or not.
Whether frost
forms or not in
Evaporator.
Observe the discharging
amount of Refrigerant.
Inject Refrigerant to
Compressor and check
cooling operation.
Clogged by dust. Gas leakage.
Faulty
Compressor.
Moisture Clog.
Whether oil leaks
or not.
Normal formed frost
Normal amount
No or much amount
(Check the leakage point)
Normal formed
frost in Evaporator
No frost or forms
in inlet only
Check Comprossor
PARTIAL Freezer and Low flowing sound of A little high • A little Refrigerant
LEAKAGE Refrigerator Refrigerant is heard and more than • discharges.
don't get cold frost forms in inlet only ambient • Normal cooling is possible
normally. temperature. • when injecting Refrigerant
• of regular amount.
WHOLE Freezer and Flowing sound of Refrigerant Equal to ambient • No discharging of Refrigerant.
LEAKAGE Refrigerator is not heard and frost isn't temperature. • Normal cooling is possible
don't get cold formed. • when injecting Refrigerant
at all. • of regular amount.
PARTIAL Freeze room and Flowing sound of Refrigerant A little high • Normal discharging of
CLOG Refrigerator is heard and frost forms more than • refrigerant.
don't get cold in inlet only. ambient • The capillary tube is faulty.
normally. temperature.
WHOLE Freezer and Flowing sound of Refrigerant Equal to ambient • Normal discharging of
CLOG Refrigerator is not heard and frost isn't temperature. • Refrigerant.
don't get cold. formed.
MOISTURE Cooling operation Flowing sound of Refrigerant Low than • Cooling operation restarts
CLOG stops periodically. is not heard and frost melts. ambient • when heating the inlet of
temperature • capillary tube.
COMP- Freezer and Low flowing sound of A little high • The pressure of high
RESSION Refrigerator Refrigerant is heard and than ambient • pressure part in
don't get cold. frost forms in inlet only. temperature. • compressor is low.
NO COMP- No compressing Flowing sound of Refrigerant Equal to ambient • No pressure of high pressure
RESSION operation. is not heard and no frost. temperature. • part in compressor.
CAUSE
TEMPERATURE
OF THE
COMPRESSOR
REMARKS
STATE OF
THE SET
STATE OF THE
EVAPORATOR
LEAKAGE
CLOGGED BY DUST
DEFECTIVE
COMPRESSION
Page 15

- 15 -
NO. ITEMS CONTENTS AND SPECIFICATIONS REMARKS
WELDING (1) H 30
ROD (1) • Chemical Ingredients • Recommend H34 containing 34% Ag in the
(1) • Ag: 30%, Cu: 27%, Zn: 23%, Cd: 20% • Service Center.
(1) • Brazing Temperature: 710~840°C
(2) Bcup-2
(1) • Chemical Ingredients
(1) • Cu: About 93%
(1) • P: 6.8~7.5%
(1) • The rest: within 0.2%
(1) • Brazing Temperature: 735~840°C
FLUX (1) • Ingredients and how to make • Make amount for only a day. (1)
(1) ••Borax 30% • Holding period: 1 day
(1) ••Borax 35% • Close the cover of container to prevent dust
(1) • Fluoridation kalium: 35% • putting in the FLUX.
(1) • Water: 4% • Keep it in a stainless steel container.
(1) • Mix the above ingredients and boil until
(1) • they are transformed into liquid.
DRIER (1) Assemble the drier within 30min. • Don't keep the drier in a outdoor because
ASM (1) after unpacking. • humidity damages to it.
(2) Keep the unpacked drier at the temperature
of 80~100°C.
VACUUM (1) When measuring with pirant Vacuum • Apply M/C Vacuum Gauge without fail.
(1 )gauge of charging M/C, vacuum • Perform vacuum operation until a proper
(1 )degree is within 1 Torr. • vacuum degree is built up.
(2) If the vacuum degree of the cycle inside is • If a proper vacuum degree isn't built up,•
(2) 10 Torr. below for low pressure and 20 Torr. • check the leakage from
(2) for high pressure, it says no vacuum • the Cycle Pipe line part and
(2) leakage state. • Quick Coupler Connecting part.
(3) Vacuum degree of vacuum pump must be
(3) 0.05 Torr. below after 5 min.
(4) Vacuum degree must be same to the
value described item (2) above for more than
20 min.
(1) The pressure of dry air must be more
than 12~16Kg/cm
2
(2) Temperature must be more than
-20~-70°C.
(3) Keep the pressure to 12~6Kg/cm
2
also
(3) when substituting dry air for Nitrogen Gas.
NIPPLE (1) Check if gas leaks with soapy water. • Check if gas leaks from connecting part of
AND (2) Replace Quick Coupler in case of leakage. • Coupler.
COUPLER
PIPE (1)• Put all Joint Pipe in a clean box and
(1)• cover tightly with the lid so that dust or
(1)• humidity is not inserted.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DRY AND
AIR
NITROGEN
GAS
▼ General Control of Refrigerating Cycle
Page 16

The following description is basically for GR-S552/GR-S592. For the other models, refer to the diagram of the entire PCB
circuit.
7-1 FUNCTION
7-1-1 FUNCTION
1. When the appliance is plugged in, it is set to ‘Medium’. Each time the button is pushed, it is set to
‘Medium’→‘Medium/High’→‘High’→‘Low’→‘Medium/Low’→‘Medium’ in order.
2. When the power is initially applied or restored after a power failure, it is automatically set to ‘Medium’.
7-1-2 CONTROL OF VARIABLE SPEED FAN IN THE FREEZER COMPARTMENT
1. Fan motor in the freezer compartment shall change from standard to high speed rpm in order to increase cooling speed
and load corresponding speed.
2. High speed rpm is only used for the initial power application and load corresponding operation. But standard rpm is used
in the general working condition.
3. When the door of freezer room or refrigerator room is opened, the fan motor is stoped immediately, then when the door is
closed, the fan motor is operated.
7-1-3 CONTROL OF DOUBLE COOLING FAN IN THE REFRIGERATOR COMPARTMENT
1. To raise the refrigerating speed, fan motor in the refrigerator compartment is operated when the door of freezer room or
refrigerator room is opened and then closed.
2. The fan motor is stoped after 20 sec. When the door is dosed.
7. DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION & CIRCUIT OF MICOM
- 16 -
Temp
Control
Low MediumMedium/Low Medium/High High
TEMP(°C)
ROOM
6 4.5 2.5 0.5 -1
REFRIGERATOR
Page 17

7-1-4 DEFROSTING
1. The defrosting is performed each time when the total running time of the compressor reaches 7 hours.
2. After the power is turned on (or restored after a power failure), the defrosting starts when the total running time of the
compressor reaches 4 hours.
3. When the temperature of the defrosting sensor reaches 10 °C or above, the defrosting stops. If the temperature does not
reach 10 °C in 2 hours after the defrosting starts, the defrosting error code is displayed.
(Refer to 7-1-6 Error Diagnostic Mode.)
4. With the defective defrosting sensor (cut or short-circuited wire), the defrosting will not be performed.
7-1-5 SEQUENTIAL OPERATION OF ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
The electric components, such as the comp, defrosting heater, and cooling fan, start sequentially to avoid the noise and
damage to the part, which may result from the simultaneous start of various components on turning the power on or after
the completion of a test.
Condition of Operation Operating Sequence
If the temp of the defrosting
sensor is 45 °C or above
(For the initial use after the
purchase or grounding)
If the temp of the defrosting
sensor is below 45 °C
(After a power failure or SVC)
- 17 -
POWER in 0.5 sec COMP & COOLING FAN
ON ON
POWER in 0.5 sec DEFROSTING in 10 sec DEFROSTING
ON HEATER ON HEATER OFF
in 0.5 sec COMP & COOLING FAN
ON
When the power is turned on
Page 18

7-1-6 ERROR DIAGNOSTIC MODE
1. The error diagnostic mode allows the SVC when a fault that may affect the performance of the product occurs while
operating the product.
2. Even if the function control button is pushed when an error occurs, the function will not be performed.
3. When the error is cleared while the error code is displayed due to a fault, the appliance returns to the normal condition
(Reset).
4. The error code is displayed by the refrigerator temp indication LED on the display of the refrigerator while the remaining
LEDs are off.
- 18 -
R1 R2 R3 R4
NO Error
Error Code Display
Cause
State of Operation with Error
R1 R2 R3 R4
Comp / Cooling fan
Defrosting heater
: ON : OFF
1.
2.
3.
Faulty refrigerator(R)
sensor (on the control
box of the refrigerator)
Faulty defrosting sensor
Defrosting failure
Cut or short-circuited wire of
refrigerator sensor
Cut or short-circuited wire of
defrosting sensor
Cut or disconnected wire of
defrosting heater or temperature
fuse(indicated at least 2 hours
later after the error occurs)
15 min ON/
15 min OFF
No defrosting
Page 19

7-2 PCB FUNCTION
7-2-1 POWER CIRCUIT
The secondary part of the TRANS is composed of the power supply for the display and relay drive (12Vdc) and that for the
MICOM and IC (5Vdc).
The voltage for each part is as follows.
VA1 is a part for preventing the over voltage and noise. When 385V or higher power is applied, the inside elements are
short-circuited and broken, resulting in the blowout of the fuse in order to protect the elements of the secondary part of the
TRANS.
- 19 -
PART VA 1 CE 2 CE3
VOLTAGE 220 Vac 12 Vdc 5 Vdc
Page 20

7-2-2 OSCILLATION CIRCUIT
This circuit is to generate the base clock for calculating time and the synchro clock for transmitting data from and to the
inside logic elements of the IC1(MICOM). Be sure to use the authentic parts since the calculating time by the IC1 may be
changed or it will not work if the OSC1 SPEC is changed.
7-2-3 RESET CIRCUIT
The RESET circuit is for allowing all the functions to start at the initial conditions by initializing various parts including the
RAM inside the MICOM (IC1) when the power is initially supplied or the power supply to the MICOM is restored after a
momentary power failure. For the initial 10ms of power supply, ‘LOW’ voltage is applied to the MICOM RESET terminal.
During a normal operation, 5V is applied to the RESET terminal. (If a trouble occurs in the RESET IC, the MICOM will not
work.)
- 20 -
Page 21

7-2-4 LOAD DRIVE CIRCUIT
1. Load Drive Condition Check
- 21 -
Load Type
Measurement Location (IC5) No. 16 No. 13 No. 15 No. 14 No. 12
ON 1V or below
Condition
OFF 12V
Comp
Defrosting
Heater
Freezer Fan Motor
High RPM
Fan Motor (R-Fan)
Standard RPM
Double Cooling
Page 22

7-2-5 TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
The upper CIRCUIT reads REFRIGERATOR temperature and DEF-SENSOR temperature for defrosting into MICOM.
OPENING or SHORT state of each TEMPERATURE SENSOR are as follows.
7-2-6 DOOR OPEN DETECTION CIRCUIT
- 22 -
SENSOR CHECK POINT NORMAL(-30 °C ~ 50 °C)
SHORT-CIRCUITED
OPEN
Refrigerator Sensor POINT Voltage
0.5 V ~ 4.5 V 0 V 5 V
Defrosting Sensor POINT Voltage
A
B
Closed 0V
Open 5V
Measurement Location
Freezer / Refrigerator Door
(Pin No.13)
Page 23

- 23 -
7-2-7 TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION & OVERCOOLING/UNDERCOOLING COMPENSATION CIRCUIT
1. Refrigerator Temperature Compensation
➧ Table of Temperature Compensation by adjusting the resistance (Difference with the current temperature)
E.g.) If the refrigerator compensation resistance (RCR1) is changed from 10K (the current resistance) to 18K
(the adjustment resistance), the temperature of the refrigerator rises +1.0 °C.
Refrigerator
Resistance Temperature Remark
(RCR1) Compensation
180 KΩ +2.5 °C Compensation by
56 KΩ +2.0 °C
raising the
33 KΩ +1.5 °C
temperature
18 KΩ +1.0 °C
12 KΩ +0.5 °C
10 KΩ 0 °C
Standard Temperature
8.2 KΩ -0.5 °C Compensation by
5.6 KΩ -1.0 °C
lowering the
3.3 KΩ -1.5 °C
temperature
2 KΩ -2.0 °C
470 Ω -2.5 °C
Page 24

7-2-8 KEY BUTTON INPUT & DISPLAY LIGHT ON CIRCUIT
➧ The circuit shown above is to determine whether a function control key on the operation display is pushed and to turn on
the corresponding function indication LED. The drive type is the scan type.
- 24 -
Page 25

- 25 -
7-3 RESISTANCE SPECIFICATION OF SENSOR
• The resistance of SENSOR has ±5% common difference.
• Measure the resistance of SENSOR after leaving it over 3 minutes in measuring temperature.
This postponing is necessary because of perceiving speed.
• Measure the F-SENSOR, SUPER FROST SENSOR, R1, R2-SENSOR after disconnect CON5 of PWB ASSY, MAIN.
TEMPERATURE SENSOR RESISTANCE OF REFRIGERATOR
(DEFROST) SENSOR
- 20 ˚C 77 KΩ
- 15 ˚C 60 KΩ
- 10 ˚C 47.3 KΩ
- 5 ˚C 38.4 KΩ
0 ˚C 30 KΩ
+ 5 ˚C 24.1 KΩ
+ 10 ˚C 19.5 KΩ
+ 15 ˚C 15.9 KΩ
+ 20 ˚C 13 KΩ
+ 25 ˚C 11 KΩ
+ 30 ˚C 8.9 KΩ
+ 40 ˚C 6.2 KΩ
+ 50 ˚C 4.3 KΩ
Page 26

- 26 -
7-4 TROUBLE SHOOTING
• Replace PCB when no trouble after checking the contents of trouble.
CLASSIFICATION
STATE OF TROUBLE
POINT BE CHECKED CHECKING METHOD CONTENT REMEDY
POWER SOURCE 1. All the DISPLAY 1. FREEZER/ FREEZER/REFRIGERATOR POWER SOURCE is poor Certify Fuse.
is poor LED OFF REFRIGERATOR DOOR OPEN Certify outlet Voltage.
2. DISPLAY LED 2. LAMP is dim. CHECK with the naked. Applied voltage mistake Use boosting TRANS.
represents abnormal 3. The connection of Certify connection of CONNECTOR connection Reconnect CONNECTOR.
operation. CONNECTOR of MAIN PWB. CONNECTOR. is poor.
TRANS FUSE open. Replace TRANS.
COOLING is poor NO COOLING 1. COMPRESSOR operates? Check the MAIN PCB. COMPRESSOR lock or Replace COMPRESSOR.
blocked.
OLP, PTC is poor. Replace OLP, PTC.
COMPRESSOR RELAY is Replace MAIN PWB RY1
poor
THE CONNECTING WIRE Certify the black wire of MAIN
is poor. PWB CONNECTOR (CON1)
2. Whether refrigerant leaks or Measure the amount of frost Refrigerant leakage. Remedy the leaking part
leaks or not. sticking on EVA and the and reaching Refrigerant.
surface temperature of
condenser pipe.
FREEZER 1. Whether FAN MOTOR Check the MAIN PCB. FAN MOTOR is poor Replace FAN MOTOR.
TEMPERATURE is poor operates or not. DOOR LINE contact. Replace DOOR LINER.
CONETTING WIRE is poor. Certify MOTOR and the
connection of the black wire
of MAIN PWB CONNECTOR.
(CON1)
2. DEFROSTING normal? Certify the amount of frost DEFROSTING is poor. See the DEFROSTING
sticking on EVA. trouble.
3. SENSOR normal? Check resistance the SENSOR RESISTANCE is Replace SENSOR
SENSOR in the poor.
Refrigerator
Page 27

- 27 -
CLASSIFICATION
STATE OF TROUBLE
POINT BE CHECKED CHECKING METHOD CONTENT REMEDY
COOLING is poor. REFRIGERATOR 1. FREEZER TEMPERATURE See "FREEZER Certify the attaching state
TEMPERATURE is is normal? TEMPERATURE is poor". of DOOR.
poor. 2. Cool air of FAN MOTOR is Certify the amount of cool air FAN MOTOR is poor. Replace FAN MOTOR.
is sufficient? and its speed touching check Passage of cool air blocking. Remove impurities.
supplied into
REFRIGERATOR EVA frozen. See "DEFROSTING is poor".
DEFROSTING is NO DEFROSTING. 1. HEATER emit heat? Check the MAIN PCB. HEATER disconnection. Replace HEATER.
poor.
TEMPERATURE FUSE Replace TEMPERATURE
disconnection. FUSE.
Connection is poor. Certify EVA connection and
wire of MAIN PWB
CONNECTOR (CON1)
DEF-SENSOR is poor. Replace DEF-SENSOR.
HEATER RELAY is poor. Replace RY4 of MAIN PWB.
2. DRAIN PIPE blocking? Certify DRAIN PIPE. DRAIN PIPE blocking. Remove ice and impurities.
Certify HEATER PLATE
resistance.
3. Remain ice at Certify the attaching Attaching is poor. Reassemble DEF-SENSOR.
DEFROSTING? of DEF-SENSOR.
Certify the attaching DOOR sticking is poor. Reassemble DOOR.
state(gap) of FREEZER/ Replace GASKET.
REFRIGERATOR DOOR.
Page 28

7-5 MAIN PWB ASS'Y AND PARTS LIST
7-5-1 MAIN PWB ASS'Y
- 28 -
1. R-B52DZ/R-B55DZ
Page 29

7-5-2 REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST
- 29 -
Page 30

7-5-3 PWB ASS'Y, DISPLAY AND PARTS LIST
- 30 -
Page 31

7-6 PWB DIAGRAM
- 31 -
Page 32

- 32 -
Page 33

- 33 -
8. EXPLODED VIEW
104A
106A
310A
308A
314A
307A
309A
312A
328B
315A
281C
281B
281A
282A
282B
103C
318A
317A
304A
323B
328A
329C
420A
319A
105A
315B
327A
315C
319C
106A
283B
120A
158F
329D
409B
158C
410J
158A
158B
409A
401A
301A
418A
406B
103B
103A
410G*
410H*
501A
501F
411A
501K
324A
129A
▼ The parts of refrigerator and the shape of each part are subject to change in different localities.
*
: optional parts
Page 34

*
: optional parts
- 34 -
151A
151A
155K
154A
233B
*
149C
*
149C
*
140A
*
149A
241A
205A
or
205A
or
241D
241C
235A
205A
205A
*
131A
405C
404A
405C 405A
*
131C
233A
230A
203A
200A
201A
*
136A
*
136B
*
136N
*
136P
*
136Q
*
136R
241A
210A
210B
243A
243B
231A
*
149B
*
125A
*
125A
*
131A
*
125A
*
125H
*
149A
234B
*
149B
*
212G
329A
212C
212A
244A
244C
330B
332A
 Loading...
Loading...