LG B2070 Service Manual
launaM ecivreS
: l
edoM B2000
Service Manual
B2000
P/N : MMBD0047201 Date : March 2005 / Issue 1.0
Date: October, 2005 / Issue 1.0
Service Manual
B2070
Model : B2070

Table Of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION..........................2
1.1 Purpose ...........................................2
1.2 Regulatory Information ....................2
1.3 Abbreviations ..................................4
2. PERFORMANCE ........................ 6
2.1 H/W Feature ...................................6
2.2 Technical Specification ..................8
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF ..................13
3.1 Transceiver ...................................13
3.2 Power Amplifier Module ..................19
3.3 13 MHz Clock ............................... 20
3.4 Power Supplies of RF circuits ........20
3.5 Digital Main Processor ...................22
3.6 Analog Main & Power
Management Processor ................28
3.7 Display Interface ............................. 38
3.8 Radio Interface ..............................40
3.9 Keypad Switches and Scanning .... 41
3.10 Microphone ..................................42
3.11 Main Speaker ............................. 42
3.12 Headset interface ........................43
3.13 Key Back-light Illumination .......... 44
3.14 Vibrator ........................................45
4. TROUBLE SHOOTING ............. 46
4.1 RX Trouble ................................... 46
4.2 TX Trouble ................................... 53
4.3 Power On Trouble .........................61
4.4 Charging Trouble........................... 63
4.5 Vibrator Trouble..............................65
4.6 LCD Trouble.................................. 67
4.7 Radio Trouble ................................69
4.8 Speaker Trouble.............................71
4.9 SIM card interface trouble ............ 74
4.10 Earphone Trouble .........................76
4.11 Key Backlight Trouble ..................78
4.12 Receiver Trouble ..........................80
4.13 Microphone Trouble .................... 82
4.14 RTC Trouble .................................84
4.15 Indication LED Trouble..................86
4.16 PTT Trouble .................................88
4.17 Speakerphone Trouble..................89
5. DOWNLOAD AND
CALIBRATION .......................91
5.1 Download .......................................91
5.2 Calibration .......................................96
6. BLOCK DIAGRAM.....................99
7. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM .................101
8. PCB LAYOUT .........................106
9. ENGINEERING MODE .............109
9.1 BB Test [MENU 1] .........................110
9.2 RF Test [MENU 2] .........................111
9.3 MF mode [MENU 3].......................112
9.4 Trace option [MENU 4]..................113
9.5 Call timer [MENU 5] ......................113
9.6 Fact. Reset [MENU 6] ...................113
9.7 S/W version [MENU 7] ..................113
10. STAND ALONE TEST.............114
10.1 Introduction ...............................114
10.2 Setting Method............................114
10.3 Means of Test ............................115
11. AUTO CALIBRATION ...........117
11.1 Overview.....................................117
11.2 Requirements..............................117
11.3 Menu and Settings ......................117
11.4 AGC............................................119
11.5 APC............................................119
11.6 ADC............................................119
11.7 Setting........................................119
11.8 How to do calibration...................119
12. EXPLODED VIEW &
REPLACEMENT PART LIST ..121
12.1 Exploded View............................121
12.2 Replacement Parts
<Mechanic component>...............123
<Main component>......................125
12.3 Accessory ....................................138

- 2 -
1. INTRODUCTION
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Purpose
This manual provides the information necessary to repair, calibration, description and download the
features of this model.
1.2 Regulatory Information
A. Security
To ll fraud, the unauthorized use of telecommunications system byan unauthorized part (for
example, persons other than your company’s employees, agents, subcontractors, or person
working on your company’s behalf) can result in substantial additional charges for your
telecommunications services. System users are responsible for the security of own system.
There are may be risks of toll fraud associated with your telecommunications system. System
users are responsible for programming and configuring the equipment to prevent unauthorized
use. The manufacturer does not warrant that this product is immune from the above case but will
prevent unauthorized use of common-carrier telecommunication service of facilities accessed
through or connected to it.
The manufacturer will not be responsible for any charges that result from such unauthorized use.
B. Incidence of Harm
If a telephone company determines that the equipment provided to customer is faulty and
possibly causing harm or interruption in service to the telephone network, it should disconnect
telephone service until repair can be done. A telephone company may temporarily disconnect
service as long as repair is not done.
C. Changes in Service
Alocal telephone company may make changes in its communications facilities or procedure.
If these changes could reasonably be expected to affect the use of the this phone or
compatibility with the network, the telephone company is required to give advanced written
notice to the user, allowing the user to take appropriate steps to maintain telephone service.
D. Maintenance Limitations
Maintenance limitations on this model must be performed only by the manufacturer or its
authorized agent. The user may not make any changes and/or repairs expect as specifically
noted in this manual. Therefore, note that unauthorized alternations or repair may affect the
regulatory status of the system and may void any remaining warranty.

- 3 -
1. INTRODUCTION
E. Notice of Radiated Emissions
This model complies with rules regarding radiation and radio frequency emission as defined by
local regulatory agencies. In accordance with these agencies, you may be required to provide
information such as the following to the end user.
F. Pictures
The pictures in this manual are for illustrative purposes only; your actual hardware may look
slightly different.
G. Interference and Attenuation
Phone may interfere with sensitive laboratory equipment, medical equipment, etc.Interference
from unsuppressed engines or electric motors may cause problems.
H. Electrostatic Sensitive Devices
ATTENTION
Boards, which contain Electrostatic Sensitive Device (ESD), are indicated by the sign.
Following information is ESD handling:
• Service personnel should ground themselves by using a wrist strap when exchange
systemboards.
• When repairs are made to a system board, they should spread the floor with anti-static mat
which is also grounded.
• Use a suitable, grounded soldering iron.
• Keep sensitive parts in these protective packages until these are used.
• When returning system boards or parts like EEPROM to the factory, use the protective package
as described.
- 4 -
1. INTRODUCTION
1.3 Abbreviations
For the purposes of this manual, following abbreviations apply:
APC Automatic Power Control
BB Baseband
BER Bit Error Ratio
CC-CV Constant Current – Constant Voltage
DAC Digital to Analog Converter
DCS Digital Communication System
dBm dB relative to 1 milli watt
DSP Digital Signal Processing
EEPROM Electrical Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
FPCB Flexible Printed Circuit Board
GMSK Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying
GPIB General Purpose Interface Bus
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
IPUI International Portable User Identity
IF Intermediate Frequency
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LDO Low Drop Output
LED Light Emitting Diode
OPLL Offset Phase Locked Loop
- 5 -
1. INTRODUCTION
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SLR Sending Loudness Rating
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
PSRAM Pseudo SRAM
STMR Side Tone Masking Rating
TA Travel Adapter
TDD Time Division Duplex
TDMA Time Division Multiple Access
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
VCTCXO Voltage Control Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator
WAP Wireless Application Protocol
SAW Surface Acoustic Wave
PAM Power Amplifier Module
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PGA Programmable Gain Amplifier
PLL Phase Locked Loop
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
RF Radio Frequency
RLR Receiving Loudness Rating
RMS Root Mean Square
RTC Real Time Clock

- 6 -
2. PERFORMANCE
2. PERFORMANCE
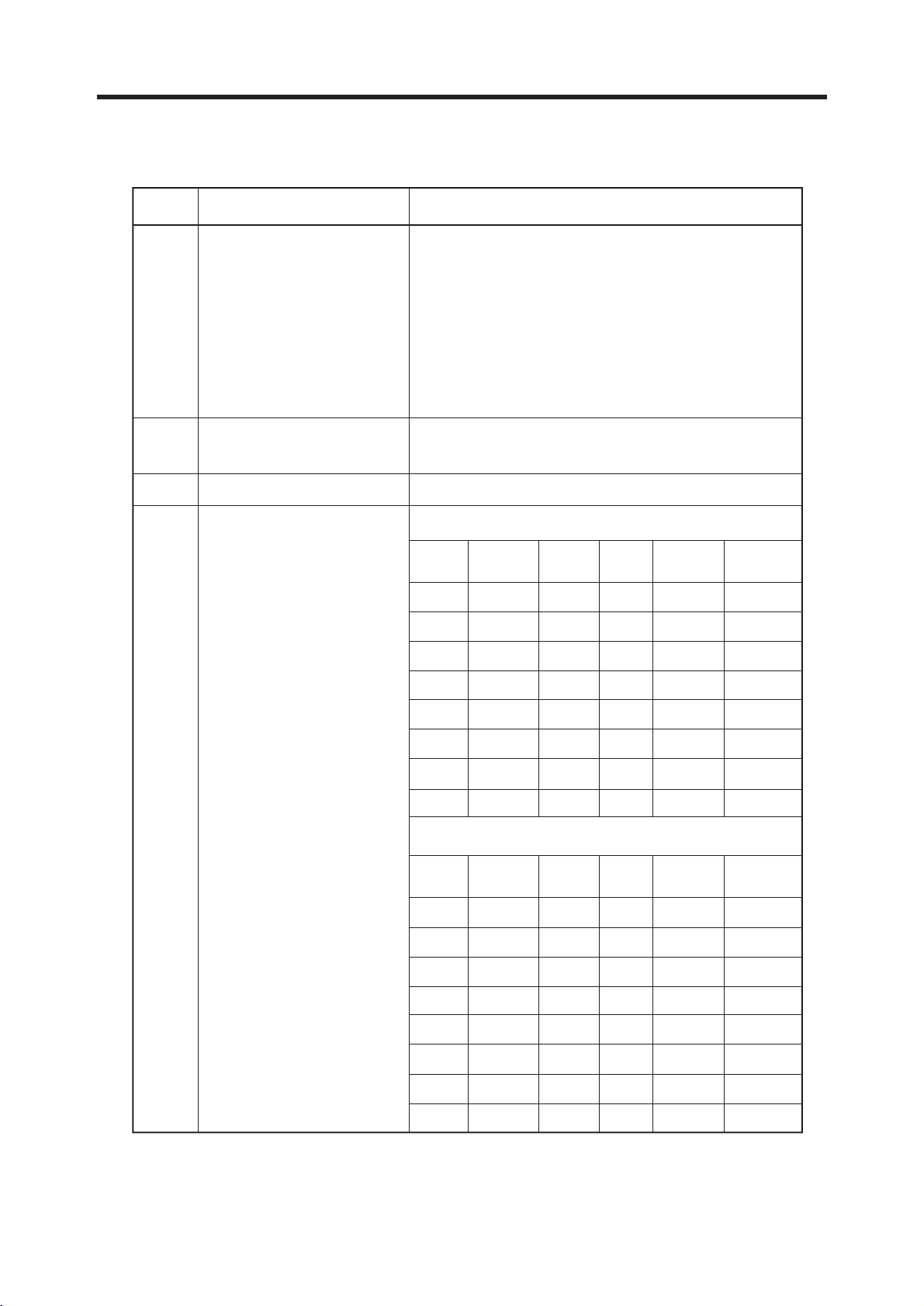
2.1 H/W Features
Item Feature Comment
Li-ion, 780 mAh
Standard Battery Battery Size: 105.5(W) x 44(H) x 15.8(T) [mm]
Battery Weight: TBD
Under the minimum current consumption environment
Stand by Current (such as paging period 9), the level of standby current
is below 4mA.
Stand by time Up to 200 hours (Paging Period: 9, RSSI: -85 dBm)
Charging time Approx. Under 3.75 hours
RX Sensitivity GSM, EGSM: –104dBm, DCS: –104dBm
TX output power
GSM, EGSM: 33dBm (Level 5),
DCS PCS: 30dBm (Level 0)
GPRS compatibility Class 10
SIM card type 3V Small Only
Display Main LCD : CSTN 128 x 128 pixel 65K Color
Hard icons. Key Pad
Status Indicator
0 ~ 9, #, *, 4
Menu Key, Clear Key
Send Key, END/PWR Key
ANT Internal
EAR Phone Jack Yes
PC Synchronization Yes
Speech coding EFR/FR/HR
Data and Fax
Vibrator Yes
Yes
Loud Speaker No
Voice Recording Yes
Soft Key(Left/Right)
(stereo)
Microphone Yes
Talk time Up to 2 hours (GSM TX Level 5)
- 7 -
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Feature Comment
Speaker / Receiver One way dual speaker
Travel Adapter Yes
MIDI 40 Poly (Mono SPK)
MP3/AAC
Options Data Cable
No
- 8 -
2. PERFORMANCE
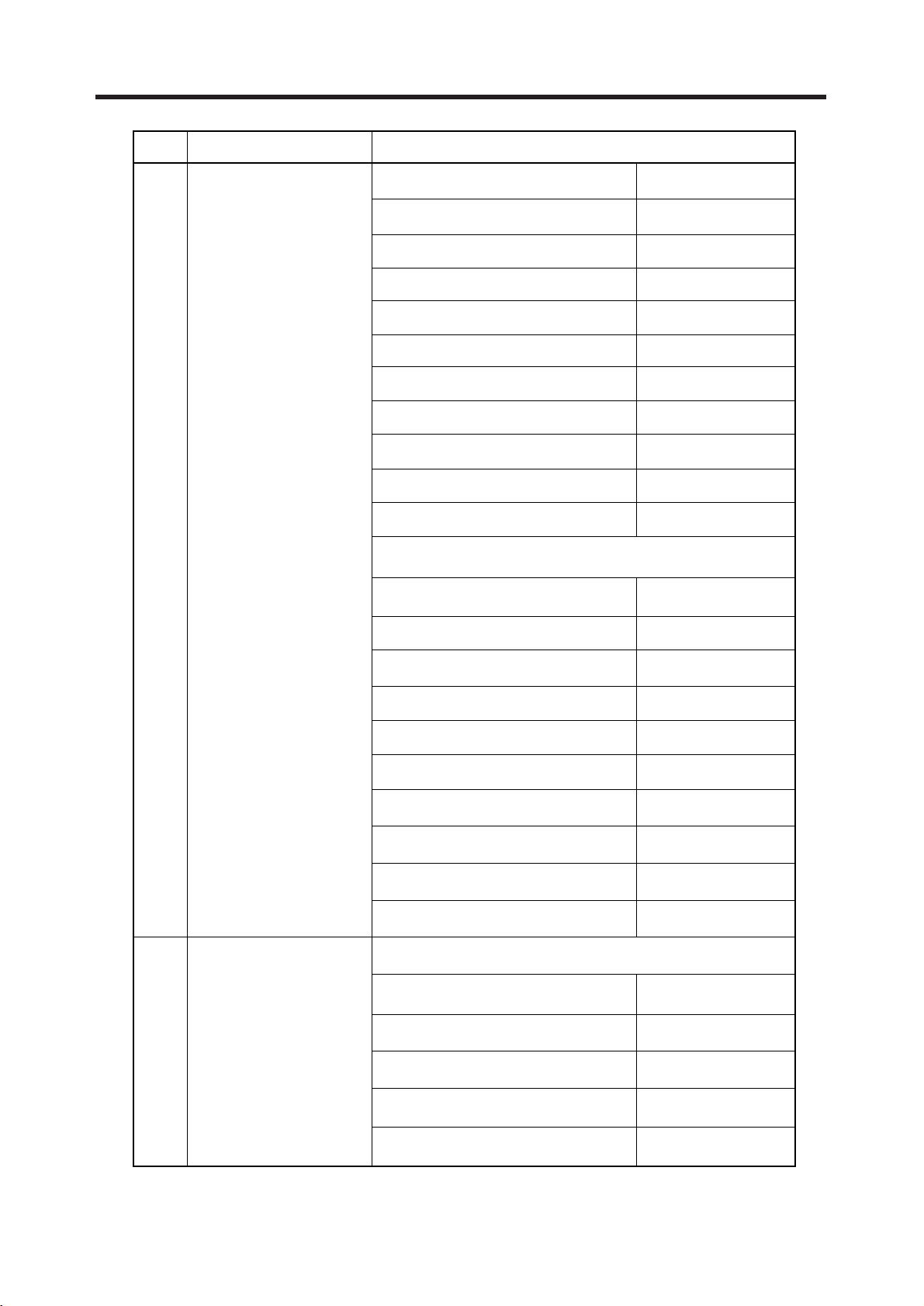
2.2 Technical Specification
EGSM
SCS
IItem Description Specification
1Frequency Band
EGSM
TX : 890 + (n-1024) × 0.2 MHz
RX : 935 + (n-1024) × 0.2 MHz (n=975~1024)
DPCS
TX : 1710 + (n -512) × 0.2 M z
RX : 1805 + (n –512) x 0.2 MHz (n=512~885)
CS
TX : 1810 + (n-512) × 0.2 MHz
RX : 1905 + (n-512) × 0.2 MHz (n=512~885)
2 Phase Error
3Frequency Error < 0.1 ppm
4Power Level
RMS < 5 degrees
Peak < 20 degrees
GSM, EGSM
Level Power Toler. Level Power Toler.
DCS
Level Power Toler. Level Power Toler.
5 33dBm ±2dB 13 17dBm ± 3dB
6 31dBm ±3dB 14 15dBm ± 3dB
7 29dBm ±3dB 15 13dBm ± 3dB
8 27dBm ±3dB 16 11dBm ± 5dB
9 25dBm ±3dB 17 9dBm ± 5dB
10 23dBm ±3dB 18 7dBm ± 5dB
11 21dBm ±3dB 19 5dBm ± 5dB
12 19dBm ±3dB
PCS
,
0 30dBm ±2dB 8 14dBm ± 3dB
1 28dBm ±3dB 9 12dBm ± 4dB
2 26dBm ±3dB 10 10dBm ± 4dB
3 24dBm ±3dB 11 8dBm ± 4dB
4 22dBm ±3dB 12 6dBm ± 4dB
5 20dBm ±3dB 13 4dBm ± 4dB
6 18dBm ±3dB 14 2dBm ± 5dB
7 16dBm ±3dB 15 0dBm ± 5dB
- 9 -
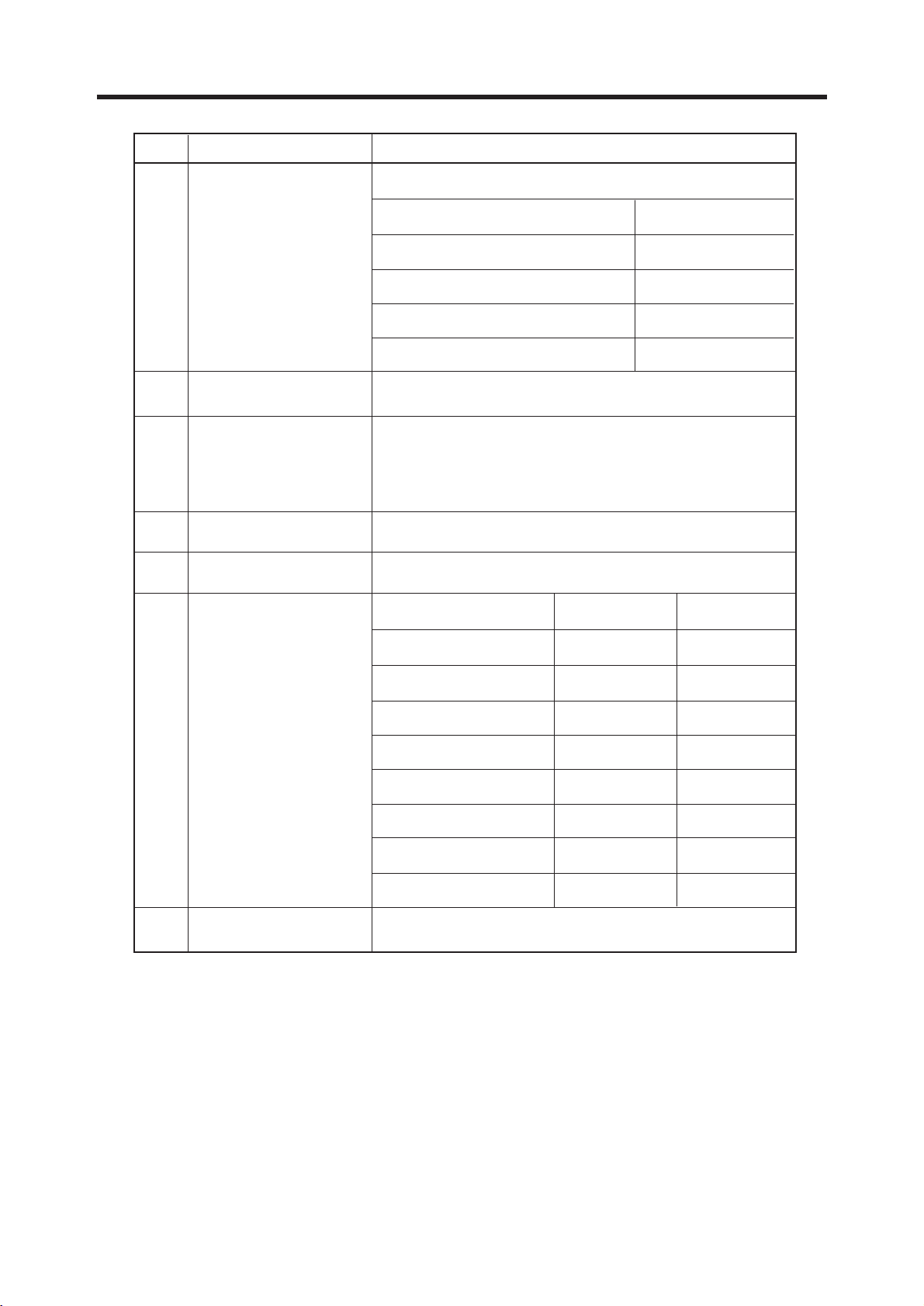
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Description Specification
GSM, EGSM
Offset from Carrier (kHz). Max. dBc
100
200
250
400
600 ~ <1,200
1,200 ~ <1,800
1,800 ~ <3,000
3,000 ~ <6,000
5 Output RF Spectrum 6,000
(due to modulation)
DCS, PCS,
Offset from Carrier (kHz). Max. dBc
100
200
250
400
600 ~ <1,200
1,200 ~ <1,800
1,800 ~ <3,000
3,000 ~ <6,000
6,000
GSM, EGSM
Offset from Carrier (kHz). Max. dBm
400
600
1,200
1,800
(due to switching
transient)
6 Output RF Spectrum
–30
–33
–60
–60
–60
–63
–65
–71
+0.5
–30
–33
–60
–60
–60
–65
–65
–73
+0.5
–19
–21
–21
–24
- 10 -
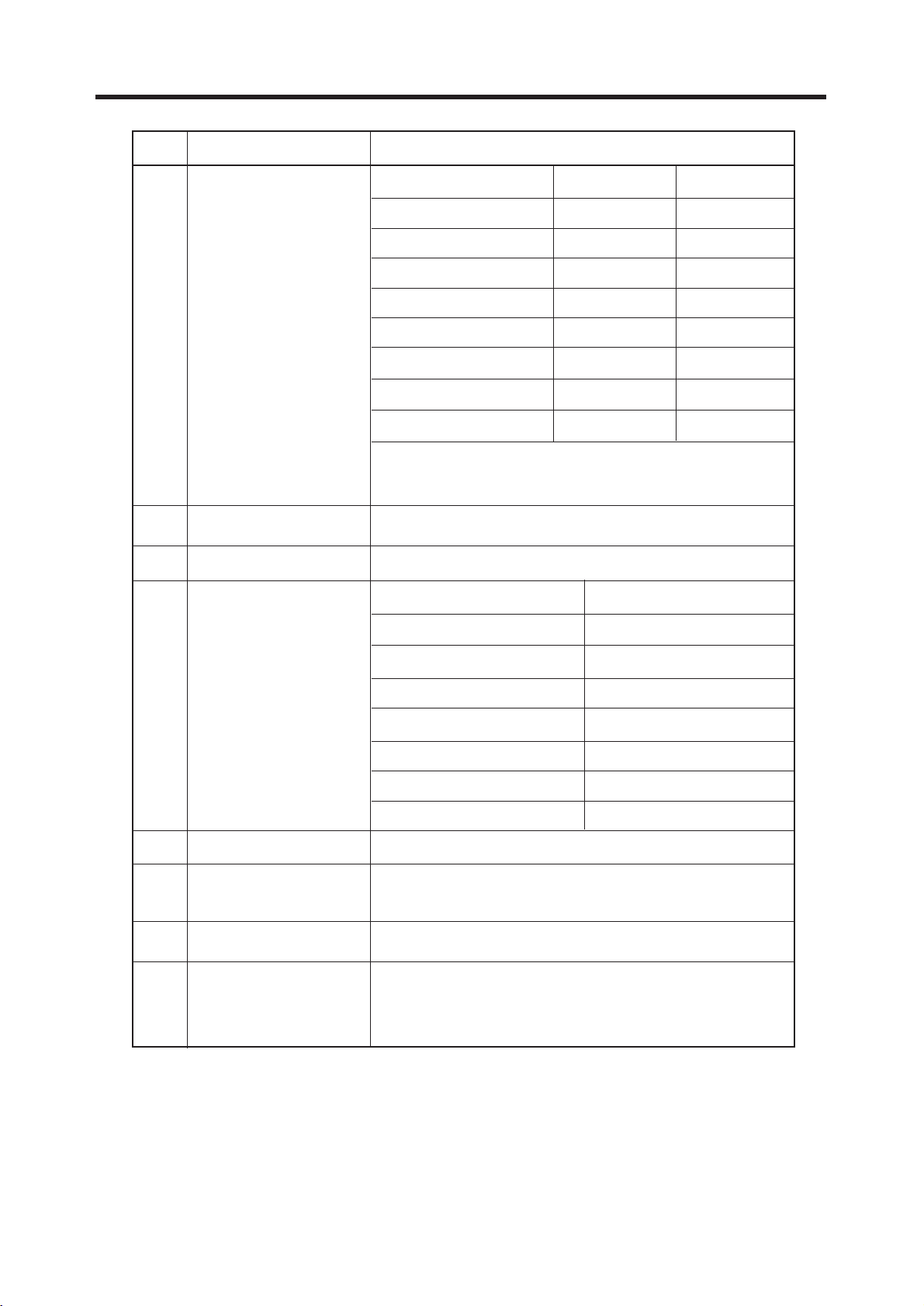
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Description Specification
GSM, EGSM
, EGSM
8 Bit Error Ratio
BER (Class II) < 2.439% @–102 dBm
DCS
BER (Class II) < 2.439% @–100 dBm
9
RX Level Report Accuracy
3 dB
10 SLR 8 3 dB
Frequency (Hz) Max.(dB) Min.(dB)
100 –12 –
200 0 –
300 0 –12
11 Sending Response 1,000 0 –6
2,000 4 –6
3,000 4 –6
3,400 4 –9
4,000 0 –
12 RLR 2 3 dB
+
_
+
_
+
_
7 Spurious Emissions Conduction, Emission Status
(due to switching
DCS, PCS
transient)
Offset from Carrier (kHz). Max. dBm
400 –22
600 –24
1,200 –24
1,800 –27
6 Output RF Spectrum
- 11 -
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Description Specification
Frequency (Hz) Max. (dB) Min. (dB)
100 –12 –
200 0 –
300 2 –7
500 –5
13 Receiving Respons 1,000 0 –5
3,000 2 –5
3,400 2 –10
4,000 2
Mean that Adopt a straight line in between 300 Hz
and 1,000 Hz to be Max. level in the range.
14 STMR 13
5 dB
15 Stability Margin > 6 dB
dB to ARL (dB) Level Ratio (dB)
–35 17.5
–30 22.5
16 Distortion
–20 30.7
–10 33.3
0 33.7
7 31.7
10 25.5
17 Side Tone Distortion Three stage distortion < 10%
18
System Frequency
≤ 2.5 ppm
(13 MHz) Tolerance
19 32.768KHz Tolerance
≤ 30 ppm
+
_
At least 65 dBspl under below conditions:
20 Ringer Volume 1. Ringer set as ringer.
2. Test distance set as 50 cm.
*
*
- 12 -
2. PERFORMANCE
Item Description Specification
21 Charge Current
Fast Charge : < 430 mA
Slow Charge : < 160 mA
Antenna Bar Number Power
5 –85 dBm ~
4 –90 dBm ~ –86 dBm
22 Antenna Display 3 –95 dBm ~ –91 dBm
2 –100 dBm ~ –96 dBm
1 –105 dBm ~ –101 dBm
0~ –105 dBm
Battery Bar Number Voltage
0 3.36 ~ 3.58V
23 Battery Indicator
1 3.59 ~ 3.66V
2 3.67 ~ 3.73V
3 3.74V ~ 3.87V
24 Low Voltage Warning
3.50 0.03V (Standby)
3.59 0.03V (Call)
25 Forced shut down
3.35 0.03V
Voltage
1 Li-ion Battery
26 Battery Type
Standard Voltage = 3.7V
Battery full charge voltage = 4.2V
Capacity : 780mAh
Switching-mode charger
27 Travel Charger Input : 100 ~ 240V, 50/60 Hz
Output : 5.2V, 800 mA
4 3.88V ~
+
_
+
_
+
_
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 13 -
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
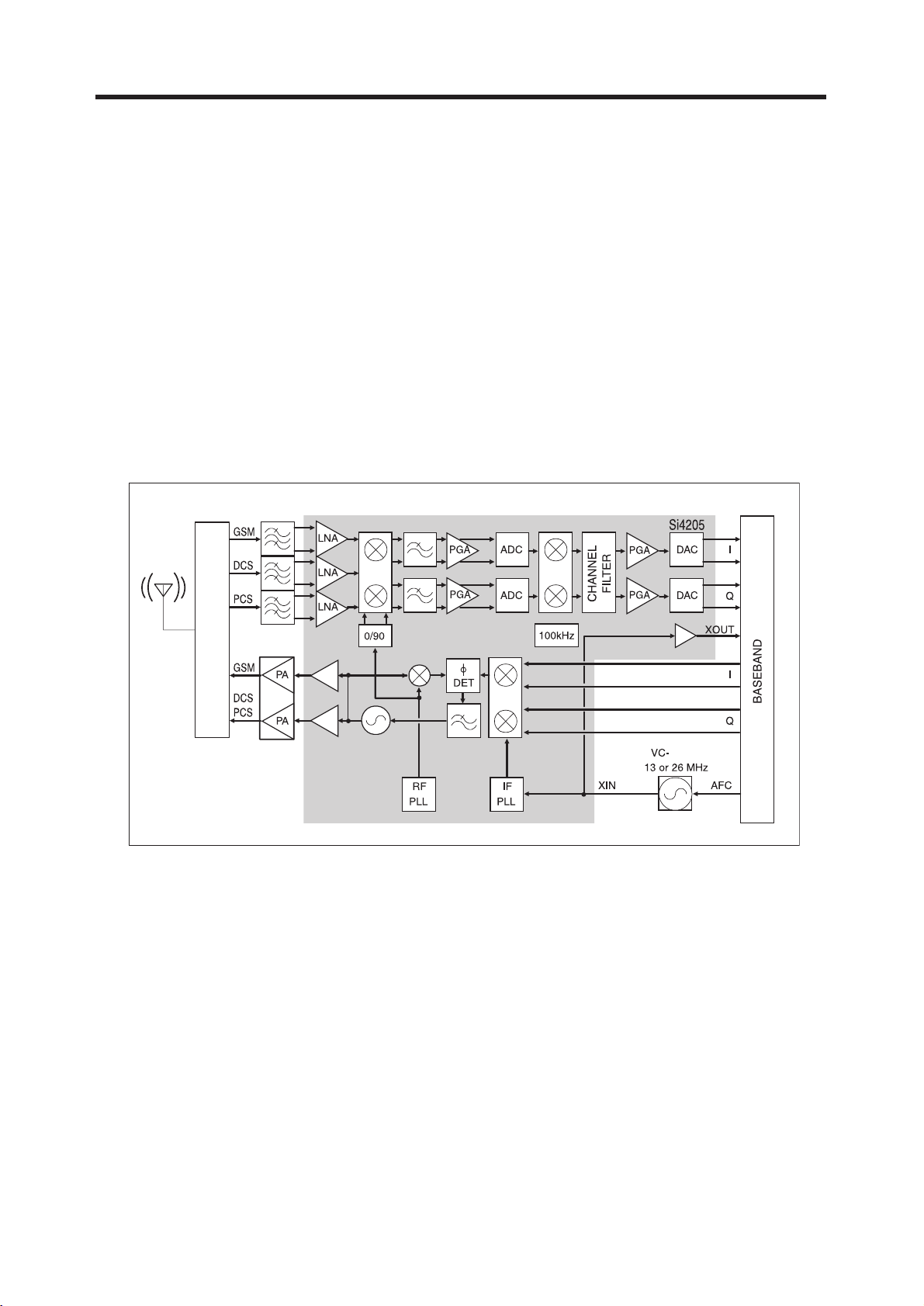
3.1 Transceiver (SI4205-BM, U500)
The RF parts consist of a transmitter part, a receiver part, a frequency synthesizer part, a
voltagesupply part, and a VCTCXO part.
The Aero I transceiver is the integrated RF front end for multi-band GSM/GPRS digital cellular
handsets and wireless data modems. The integrated solution eliminates the IF SAW filter, external
low noise amplifier (LNAs) for three bands, transmit and RF voltage controlled oscillator(VCO
modules, and other discrete components found in conventional designs.
Figure 3-1 RECEIVER FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
HCTIWS ANNETNA
TCXO
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 14 -
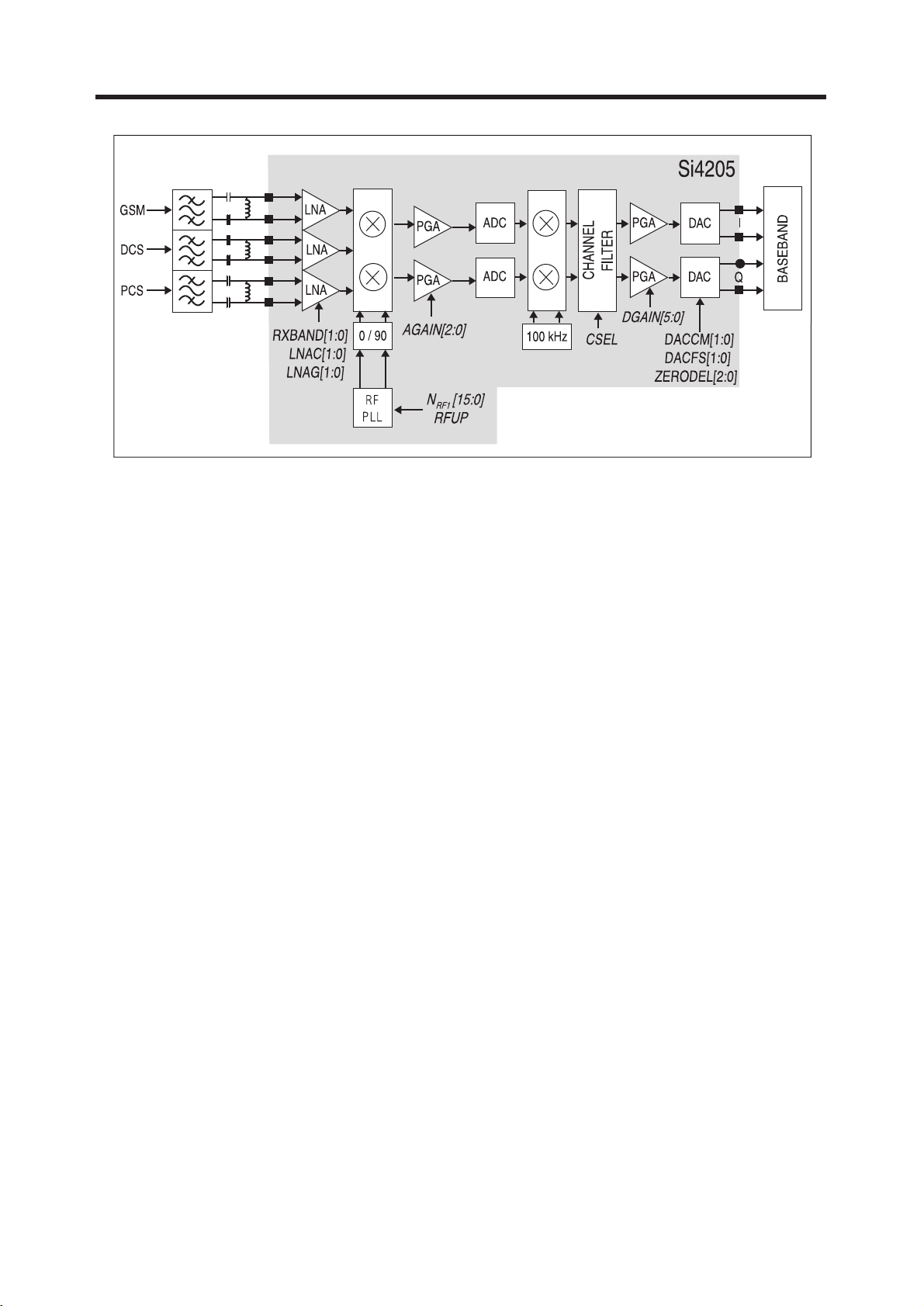
(1) Receiver Part
The Aero I transceiver uses a low-IF receiver architecture which allows for the on chip integration
of the channel selection filters, eliminating the external RF imagereject filters and the IF SAW
filter required in conventional super-heterodyne architectures.
A. RF front end
RF front end consists of Front End Module(FL500) and Quad band LNAs integrated in
transceiver (U500).
The Received RF signals(GSM 925MHz ~ 960MHz, DCS 1805MHz ~ 1880MHzPCS
1930MHz ~ 1990MHz) are fed into the antenna or Mobile switch. The Front End
Module(FL500) is used to control the Rx and Tx paths. And, the input signals VC1, VC2,
VC3 of a FL501 are directly connected to baseband controller to switch either Tx or Rx path
on.
The logic and current is given below Table 3-1.
Three differential-input LNAs are integrated in SI4205. The GSM input supports the
GSM850 (869-849 MHz) or E-GSM 900 (925-960MHz) bands. The DCS input supports
theDCS 1800 (1805-1880 MHz) band. The PCS input supports the PCS 1900 (19301990MHz) band.
The LNA inputs are matched to the 150Ω balanced output SAW filters through external LC
matching networks. The LNA gain is controlled with the LNAG[1:0] and LNAC[1:0] bits in
register 05h (Figure 3-2).
VC1 VC2 VC3
GSM Tx
DCS, PCS Tx
GSM / DCS Rx
PCS / DCS Rx
0 V
0 V
0 V
2.5 ~ 3.0 V
Table 3-1 THE LOGIC AND CURRENT
0 V
2.5 ~ 3.0 V
0 V
0 V
2.5 ~ 3.0 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 15 -
Figure 3-2 SI4205 RECEIVER PART
B. Intermediate frequency (IF) and Demodulation
A quadrature image-reject mixer downconvertsthe RF signal to a 100KHz intermediate
frequency (IF) with the RFLO from the frequency synthesizer. The RFLO frequency is
between 1737.8 to 1989.9 MHz, and is internally divided by 2 for GSM 850 and E-GSM 900
modes. The mixer output is amplified with an analog programmable gain amplifier (PGA),
which is controlled with the AGAIN[2:0] bits in register 05h (Figure3-2). The quadrature IF
signal is digitized with high resolution A/D converters (ADCs).
The ADC output is downconverted to baseband with a digital 100KHz quadrature LO signal.
Digital decimation and IIR filters perform channel selection to remove blocking and
reference interference signals. The selectivity setting (CSEL=0) or a low selectivity setting
(CSEL=1). The low selectivity filter has a flatter group channelization filter is in the
baseband chip. After channel selection, the digital output is scaled with a digital PGA, which
is controlled with the DGAIN [5:0] bits in register 05h.
The amplified digital output signal go through with DACs that drive a differential analog
signal onto the RXIP,RXIN,RXQP and RXQN pins to interface to standard analog ADC input
baseband ICs. No special processing is required in the baseband for offset compensation
or extended dynamic range.
Compared to a direct-conversion architecture, the low-IF architecture has a much greater
degree of immunity to dc offsets that can arise from RF local oscillator(RFLO) self-mixing,
2nd order distortion of blockers, and device 1/f noise.
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 16 -
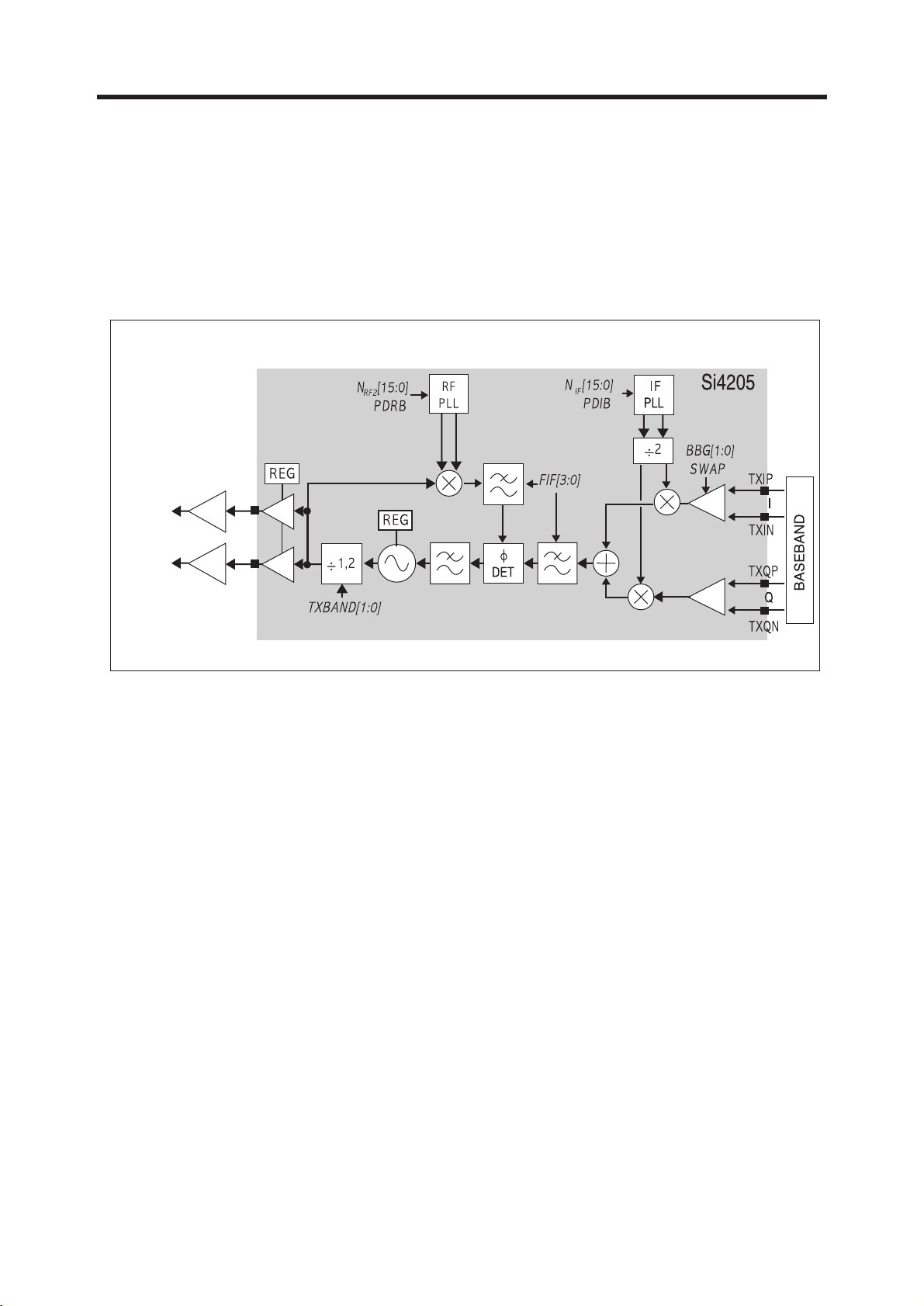
(2) Transmitter Part
The transmit (Tx) section consists of an I/Q baseband upconverter, and offset phase-locked loop
(OPLL) and two output buffers that can drive external poweramplifiers (PA), one for the GSM 850
(824-849 MHz) and E-GSM 900 (880-915 MHz) bands and one for the DCS 1800 (1710-1785
MHz) and PCS 1900 (1850-1910MHz) bands.
A. IF Modulator
The baseband converter(BBC) within the GSM chipset generates I and Q baseband signals
for the Transmit vector modulator. The modulator provides more than 40dBc of carrier and
unwanted sideband rejection and produces a GMSK modulated signal. The baseband
software is able to cancel out differential DC offsets in the I/Q baseband signals caused by
imperfections in the D/A converters.
The Tx-Modulator implements a quadrature modulator. A quadrature mixer upconverts the
differential in-phase (TXIP, TXIN) and quadrature(TXQP, TXQN) signals with the IFLO to
generate a SSB IF signal that is filtered and used as the reference input to the OPLL.
The IFLO frequency is generated between 766 and 896 MHz and internally divided by 2 to
generate the quadrature LO signals for the quadrature modulator, resulting in an IF between
383 and 448 MHz. For the E-GSM 900 band, two different IFLO frequencies are required for
spur management. Therefore, the IF PLL must be programmed per channel in the E-GSM
900 band.
GSM PA
DCS/PCS
RFOG
RFOG
PA
Figure 3-3 SI4205 TRANSMITTER PART

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 17 -
B. OPLL
The OPLL consists of a feedback mixer, a phase detector, a loop filter, and a fully integrated
TXVCO. The TXVCO is centered between the DCS 1800 and PCS 1900 bands, and its
output is
divided by 2 for the GSM 850 and E-GSM 900 bands. The RFLO frequency is generated
between 1272 and 1483 MHz. To allow a single VCO to be used for the RFLO, high-side
injection is used for the GSM 850 and E-GSM 900 bands, and low-side injection is used for
the DCS 1800 and PCS 1900 bands. The I and Q signals are automatically swapped when
switching bands. Additionally, the SWAP bit in register 03h can be used to manually
exchange the I and Qsignals.
Low-pass filters before the OPLL phase detector reduce the harmonic content of the
quadrature modulator and feedback mixer outputs. The cutoff frequency of the filters is
programmable with the FIF[3:0] bits in register 04h (Figure 3-3), and should be set to the
recommended settings detailed in the register description.
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 18 -
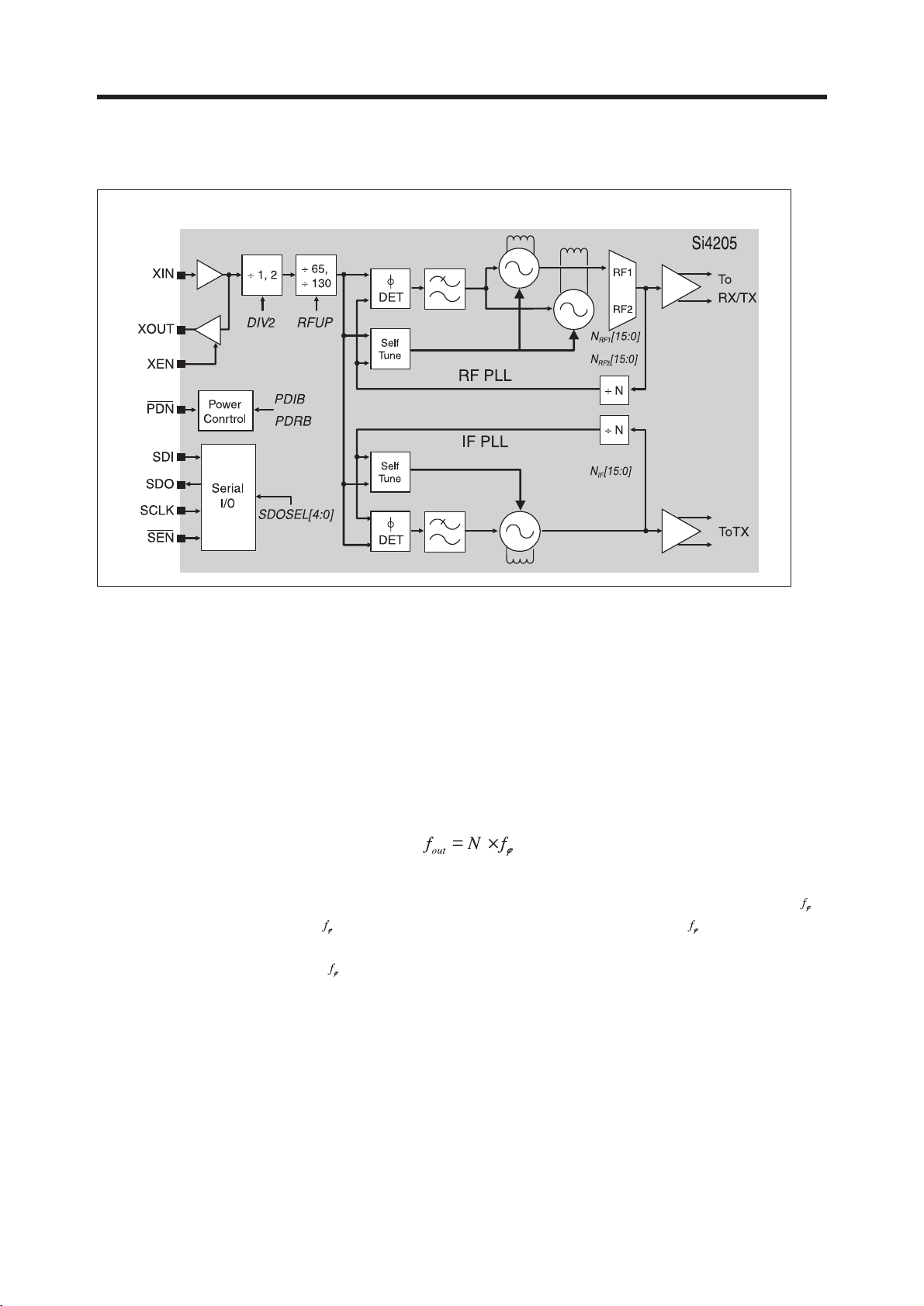
The Aero I transceiver integrates two complete PLLs including VCOs, varactors, resonators, loop
filters, reference and VCO dividers, and phase detectors. The RF PLL uses two multiplexed
VCOs. The RF1 VCO is used for receive mode, and the RF2 VCO is used for transmit mode.
The IF PLL is used only during transmit mode. All VCO tuning inductors are also integrated. The
IF and RF output frequencies are set by programming the N-Divider registers, N
RF1
, N
RF2
and
NIF. Programming the N-Divider register for either RF1 or RF2 automatically selects the proper
VCO. The output frequency of each PLL is as follows:
The DIV2 bit in register 31h controls a programmable divider at the XIN pin to allow either a 13
or 26 MHz reference frequency. For receive mode, the RF1 PLL phase detector update rate ( )
should be programmed = 100 kHz for DCS 1800 or PCS 1900 bands, and = 200 kHz for
GSM 850 and E-GSM 900 bands. For transmit mode, the RF2 and IF PLL phase detector
update rates are always =200 kHz.
(3) Frequency Synthesizer
Figure 3-4 SI4205 FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER PART
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 19 -
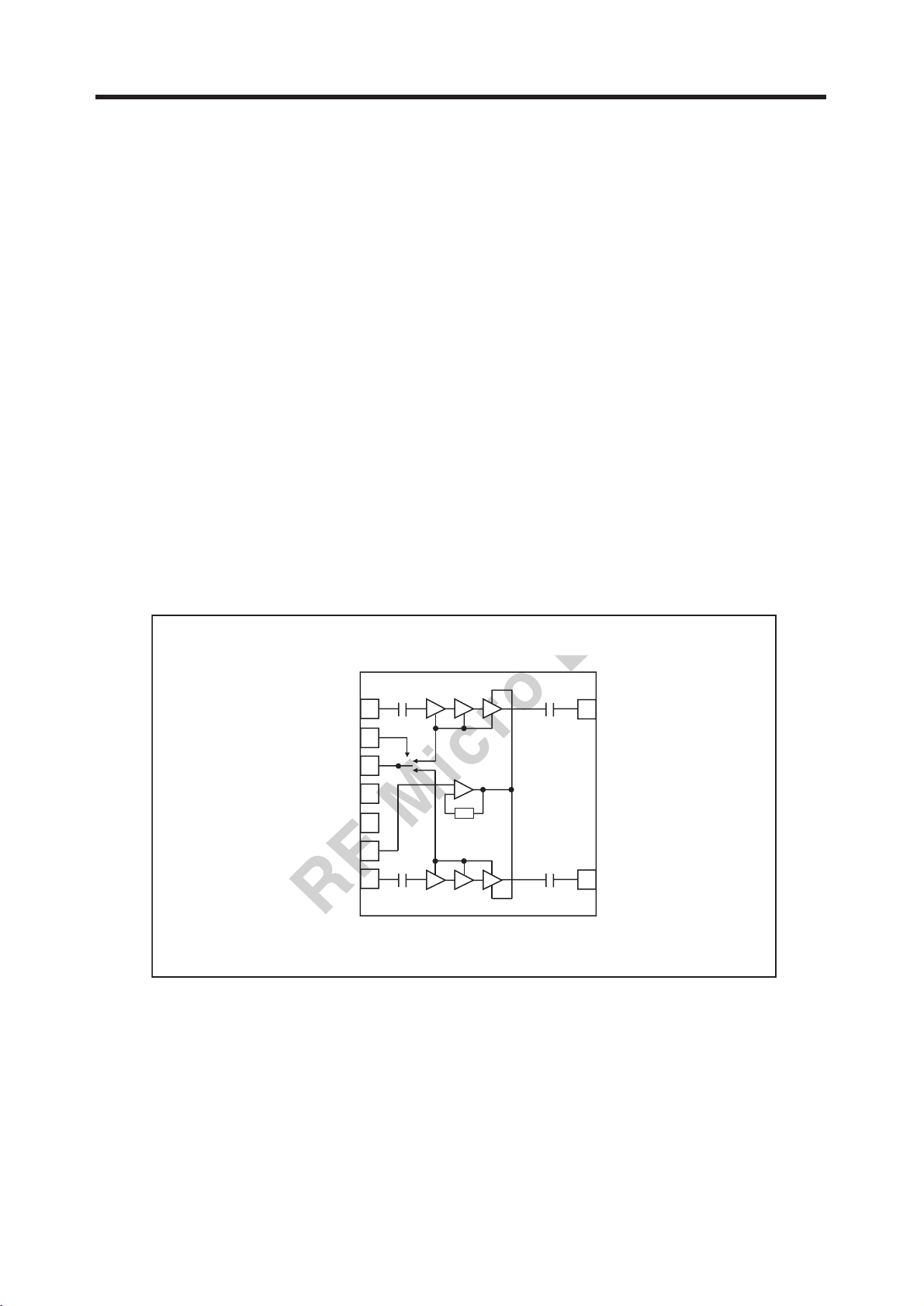
3.2 Power Amplifier Module (RF3166, U501)
The RF3166 is a high-power, high-efficiency power amplifier module with integrated power control
that provides over 50dB of control range. The device is a self-contained 6mmx6mm module with
50Ω input and output terminals.
The device is designed for use as the final RF amplifier in GSM850, EGSM900, DCS and PCS
handheld digital cellular equipment and other applications in the 824MHz to 849MHz, 880MHz to
915MHz, 1710MHz to 1785MHz and 1850MHz to 1910MHz bands. The RF3166 incorporates
RFMD’s latest VBATT tracking circuit, which monitors battery voltage and prevents the power
control loop From reaching saturation. The VBATT tracking circuit eliminates the need to monitor
battery voltage, thereby minimizing switching transients. The RF3166 requires no external routing
or external components, simplifying layout and reducing board space.
DCS/PCS
BAND SELECT
TX ENABLE
VBATT
VRAMP
RFIN
GND
GSM
RFIN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Figure 3-5 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DCS/PCS
9
RFOUT
GSM
8
RFOUT
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 20 -
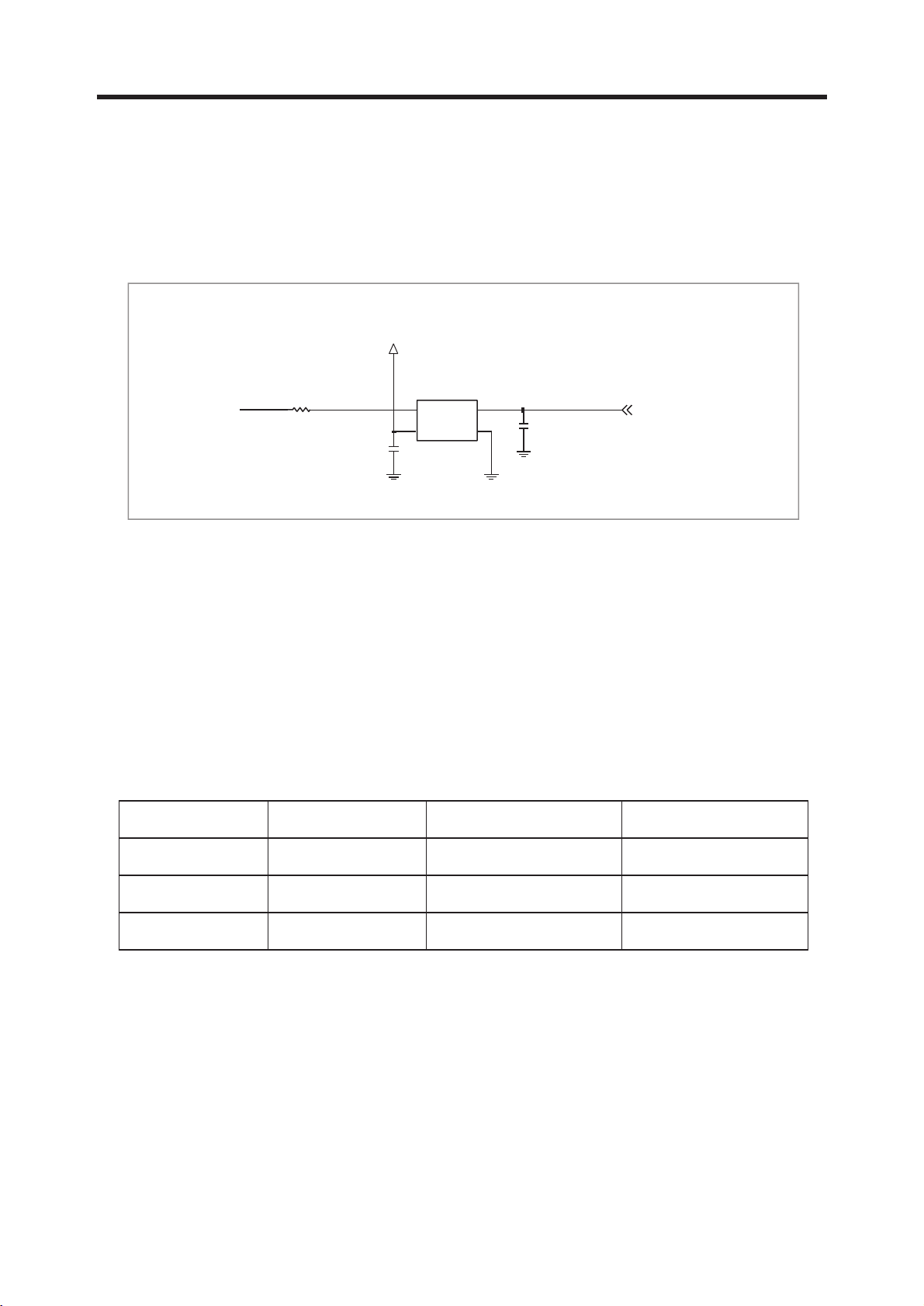
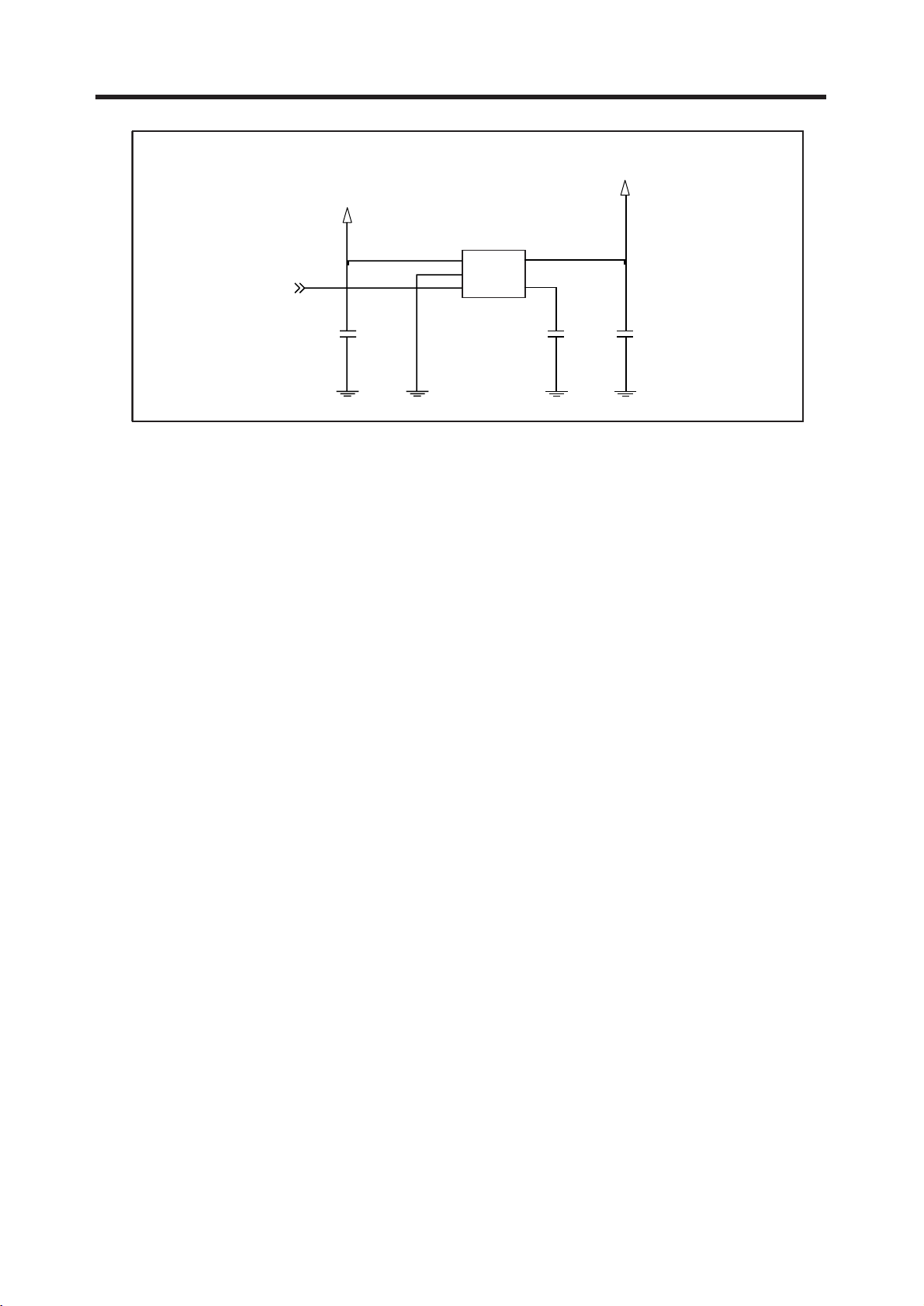
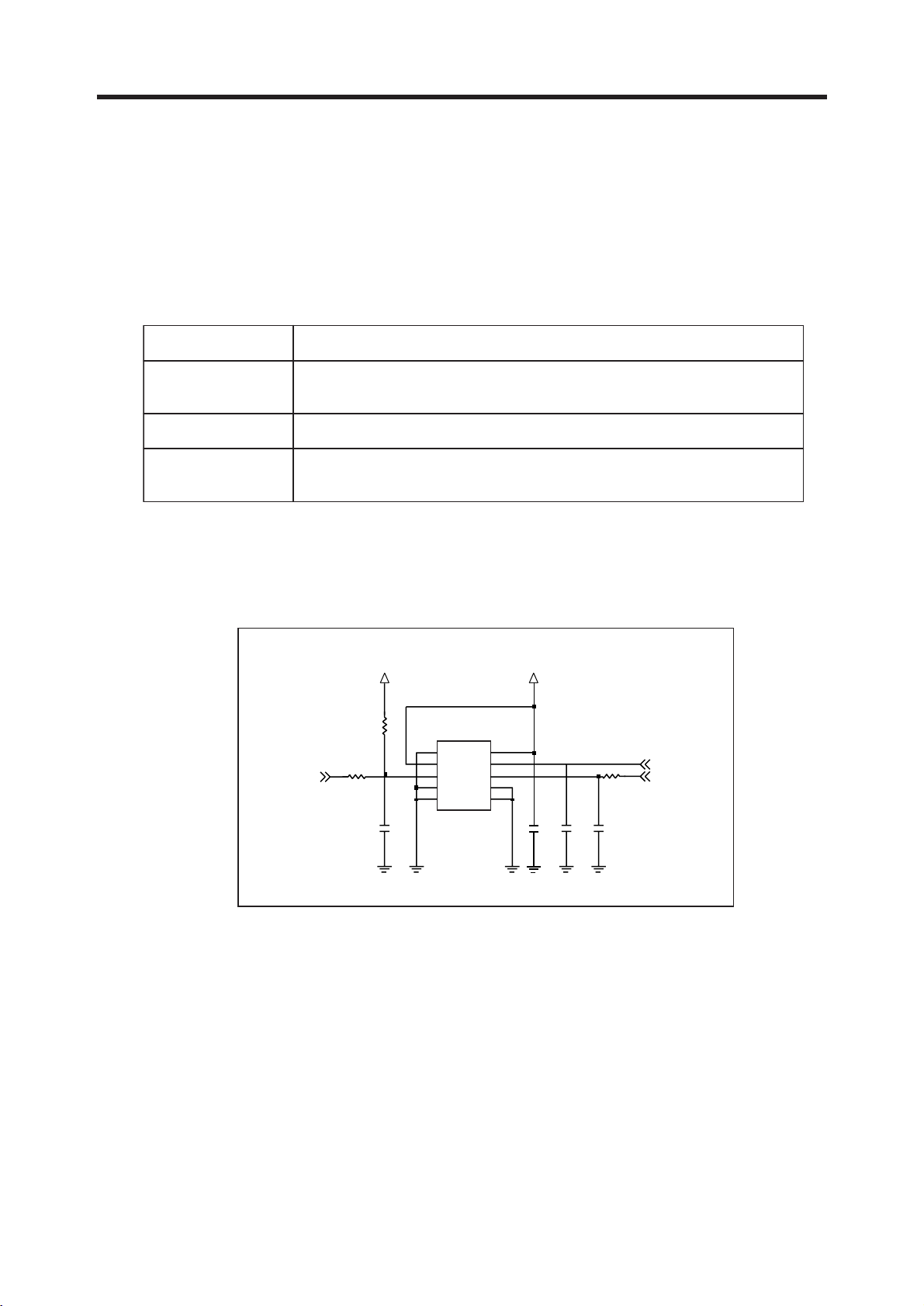
3.3 13 MHz Clock (VCTCXO, X500)
The 13 MHz clock(X500) consists of a TCXO(Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator) which
oscillates at a frequency of 13 MHz. It is used within the Si4205, analog base band chipset
(U101, AD6537B), digital base band chipset (U100, AD6527).
3.4 Power Supplies for RF Circuits (RF LDO, U702)
Two regulators are used for RF circuits. One is MIC5255 (U702), and the other is one port of
AD6537B (U101).
MIC5255 (U702) supplies power to transceiver (SI4205, U500). One port of AD6537B supplies
power to VCTCXO (X500).
2V75_VVCXO
100
R514
C536
22u
3
OUT VCONT
4
VCC
X500
ONG
13MHz
1
2
C538
1000p
R516
15K
APC
Figure 3-6 VCTCXO CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Supplier
Voltage
Powers
enabled signal
U702(VRF)
U101(VVCXO)
Battery(VBAT)
2.85 V
2.75 V
3.4 ~ 4.2 V
U501, U702
Table 3-2 RF POWER SUPPLIERS
U500
X500
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 21 -
CLKON
VBAT
U702 MIC5255-85BM5
1
IN
2
GNO
3
EN
OUT
BYP
5
4
RF2VBS
C533
10u
C734 C534
Table 3-7 RF LDO CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
10u0.01u
(1608)
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 22 -
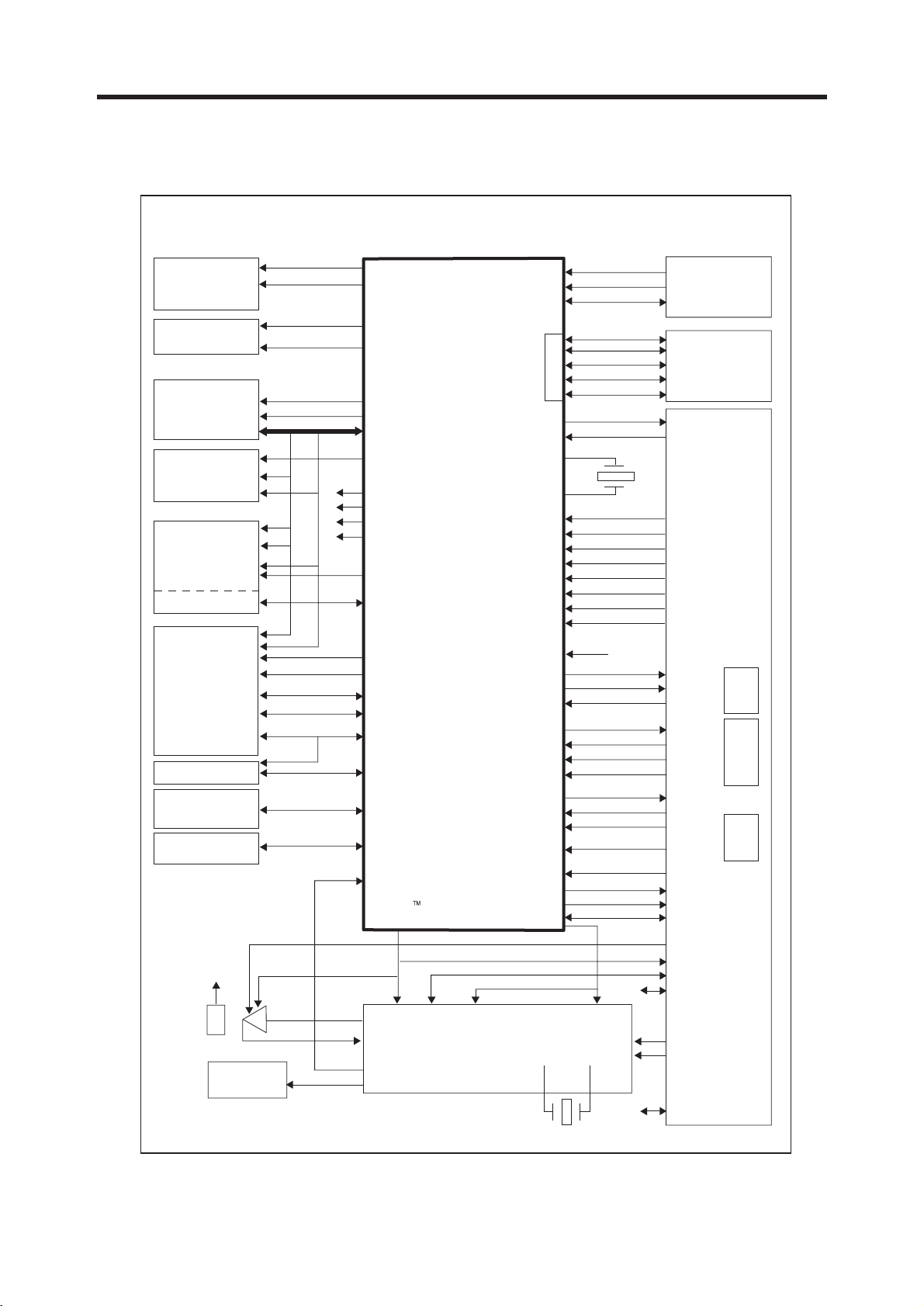
3.5 Digital Main Processor (AD6527, U100)
AD6527/AD6527B GSM-PROCESSOR
Keypad
Matrix
KEYPADCOL[7:0]
KEYPADROW[7:0]
TCK, TMS
JTAGEN
JTAG
TDI, TDO
Backlight/
Service Light
Flash
16-bit
SRAM
8 or 16 bit
(optional)
DISPLAY
(Parallel)
serial display
Accessory
Devices
e.g
BATTERY
SIM
Application
Processor
USB Host
BACKLIGHT[3.0]
Servicelight
JTAG, HSL, GPIO
USCTX/RX/CLK
Enhaoced Generic serial port A
ROMCS[1:0]
ADD[24:0]
DATA[15:0]
RAMCS[1:0]
RD
WR
HWR/UBS
LWR /LBS
Generic serial port B
Generic serial port D
PWRON
RESET
OSCIN
OSCOUT
VDDRTC
VMEM
VEXT
DISPLAYCS[1:0]
Generic Serial
Port C
GPCS[1:0]
AUXCS[1:0]
Generic Serial Port D-A
Generic Serial Port D-B
GPIO[ ] / IRQ
SIM serial
Interface
SPI
USB Interface
*(AD6527B only)
CLKIN
CLKOUT_GATE
MicroSM
RF Interface
VCC
VMMC
VINT
VDDUSB
VSIM
GND
ASDO
ASFS
ASDI
BSDO
BSOFS
BSDI
BSIFS
CSDO
CSDI
CSFS
ABB_INT
CLKOUT
ABBRESET
USC
Management
32KHz
ASDI
ASFS
ASDO
BSDI
BSIFS
BSDO
BSOFS
CSDI
CSDO
CSFS
INT
MCLKEN
MCLK
RESET
VCXOEN
Universal
System
Connector
(USC)
Power
Processor
AD6535 Audio & Base band
Audio
Data
Port
BASE
BAND
I/Q
Serial
Port
control
serial
port
RAMP
RF Timing
I/Q Interface
VOICE i/f &
Buzzer
VOSC
AFC
JTAG
PA S u pply
Enable
DRV-OUT
LNA IN
RADIO
AD6534
AGC Synthesizer
VCO
13/
26MHz
Figure 3-8 SYSTEM INTERCONNECTION OF AD6527 EXTERNAL INTERFACE

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 23 -
• AD6527 is an ADI designed processor
• AD6527 consists of
1. Control Processor Subsystem
• 32-bit ARM7TDMI Control Processor
• 58.5 MHz operation at 1.7V
• On-board 16KB instruction/Data Cache
• 1 Mbitsof on-chip System SRAM
2. DSP Subsystem
• 16-bit Fixed Point DSP Processor
• 91 MIPS at 1.7V
• 16K word Data and 16K word Program SRAM
• 4K word Program Instruction Cache
• Architecture supports Full Rate, Enhanced Full Rate, Half Rate, and AMR speech
Encoding/Decoding Algorithms
3. Peripheral Subsystem
• Shared on-chip peripheral and off-chip interface:
• Support for Burst and Page Mode Flash
• Support for Pseudo SRAM
• Ciphering module for GPRS supporting GAE1 and GAE2 encryption algorithms
• Parallel and Serial Display Interface
• 8 x 8 Keypad Interface
• Four independent programmable backlight plus One Service Light
• 1.8V and 3.0V, 64 kbps SIM interface
• Universal System Connector Interface
• Slow, Medium and Fast IrDA transceiver interface
• Enhanced Generic Serial Port
• Dedicated SPI interface
• Thumbwheel Interface
• JTAG Interface for Test and In-Circuit Emulation
4. Other
• Supports 13 MHz and 26 MHz Input Clocks
• 1.8V Typical Core Operating Voltages
• 204-Ball LFBGA(mini-BGA) Package
5. Applications
• GSM900/DCS1800/PCS1900/PCS850 Wireless Terminals
• GSM Phase 2+ Compliant
• GPRS Class 12 Compliant
• Multimedia Services(MMS)
• Extended Messaging System(EMS)
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 24 -
3.5.1 Interconnection with external devices
A. RTC block interface
Countered by external X-TAL
The X-TAL oscillates 32.768KHz
B. LCD module interface
The LCD module is controlled by AD6527(U100),DBB.
In operating mode, the AD6527(U100) controls the LCD module through _LCD_CS,
LCD_DIM_CTRL, LCD_RESET, _WR, 2V8_VMEM, LCD_ID, LCD_BL_EN.
Signals
_LCD_CS
LCD_DIM_CTRL
LCD_RESET
(GPIO 15)
_WR
2V8_VMEM
LCD_ID
(GPIO 16)
LCD_BL_EN
Description
MAIN LCD driver chip enable. MAIN LCD driver IC has own CS pin
It controls dimming mode of LCD module. (GPIO_5)
This pin resets LCD module. This signal comes from DBB directly
Enable writing to LCD Driver.
2.8V voltage is supplied to LCD driver IC
It determines the maker of LCD module.
It controls back-light of LCD module. (GPO_23)
Table 3-3 LCD CONTRON SIGNALS DISCRIPTION
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 25 -
The backlight of LCD module is controlled by DBB via TPS60230RGTR , U400.
The control signals related to Backlight LED are given bellow.
Signals Description
LCD_DIM_CTL
(GPO 5)
LCD_LED_CTL
LCD_LED_GND
LCD_BL_EN
Control LCD backlight level in 16 steps
Control LCD LED
It Controls back-light of LCD module. (GPO_223)
Table 3-4 DESCRIPTION OF LCD BACKLIGHT LED CONTROL
C. RF interface
The AD6527 control RF parts through PA_BAND, ANT_SW1, ANT_SW2, ANT_SW2,
CLKON, PA_EN, S_EN, S_DATA, S_CLK, RF_PWR_DWN.
Signal Description
PA_BAND (GPO 17) PAM Band Select
ANT_SW3 (GPO 11) Antenna switch Band Select
PA_EN (GPO 16) PAM Enable/Disable
S_DATA (GPO 20) Serial Data to PLL
S_CLK (GPO 21) Clock to PLL
S_EN (GPO 19) PLL Enable/Disable
RF_PWR_DWN(GPO 4) Power down Input
ANT_SW1 (GPO 9) Antenna switch Band Select
ANT_SW2 (GPO 10) Antenna switch Band Select
CLKON RF LDO Enable/Disable
Table 3-5 RF CONTRON SIGNALS DISCRIPTION
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 26 -
D. SIM interface
The AD6527 provides SIM Interface Module. The AD6527 checks status periodically during
established call mode whether SIM card is inserted or not, but it doesn't check during deep
Sleep mode. In order to communicate with SIM card, 3 signals SIM_DATA, SIM_CLK,
SIM_RST(GPIO_23) are required.
The descriptions about the signals are given by bellow Table 3-6 in detail.
E. Key interface
Include 5 column, 5 row and additional GPIO 35 for KEY_ROW5.
The AD6527 detects whetherkey is pressed or not by using interrupt method.
F. AD6537B Interrupt
AD6537B provides an active-high interrupt output signal.
Interrupt signals are generated by the Auxiliary ADC, audio, and charger modules.
Signals Description
LCD_DATA
LCD_CLK
SIM_RST
(GPIO_23)
This pin receives and sends data to SIM card.
This model can support only 3.0 volt interface SIM card.
Clock 3.25MHz frequency.
Reset SIM block
Table 3-6 SIM CONTRON SIGNALS DISCRIPTION
J300
VCC
RST
CLK
OND2
OND3
2V85_VSIM
1
2
3
7
8
C315C314
R338
C316 C317
1000p
SIM_DATA
2V85_VSIM
R336
20K
R337
0
NA
4
OND1
5
VPP
6
IO
10
OND5
9
OND4
SIM_RST
0
SIM_CLK
NA220n
Figure 3-9 SIM Interface of AD6527
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 27 -
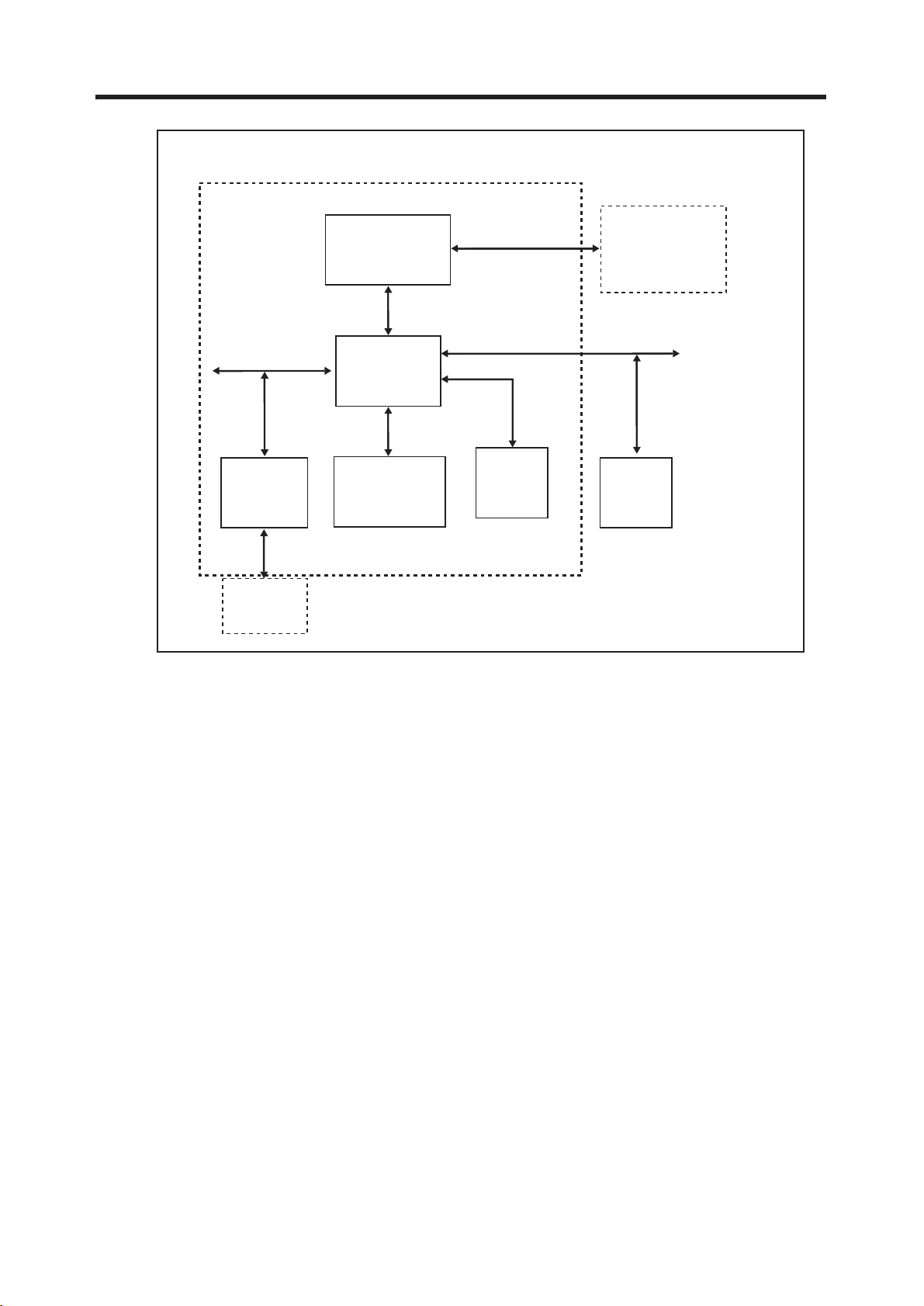
PBUS
The internal architecture of AD6527 is shown above Figure 3-10. AD6527 regroups three main
subsystems connected together through a dynamic and flexible communication bus network.
It also includes onboard system RAM (SRAM) and interfaces with external Flash Memory,
Baseband converter functions, and terminal functions like MMI, SIM and Universal System
Connector (USC).
The Digital Signal Processing (DSP) subsystem primarily hosts all the speech processing,
channel equalization and channel codec functions. The code used to implement such functions
can be stored in external Flash Memory and dynamically downloaded on demand into the DSP’s
program RAM and Instruction Cache.
The micro-controller subsystem supports all the GSM terminal software, including the layer 1, 2
and 3 of the GSM protocol stack, the MMI, and applications software such as data services, test
and maintenance. It is tightly associated with on-chip system SRAM and also includes boot ROM
memory with a small dedicated routine to facilitate the initialization of the external Flash Memory
via code download using the on-chip serial interface to the external Flash Memory interface.
The peripheral subsystem is composed of system peripherals such as interrupt controller, real
time clock, watch dog timer, power management and a timing and control module. It also includes
peripheral interfaces to the terminal functions: keyboard, battery supervision, radio and display.
Both the DSP and the MCU can access the peripheral subsystem via the peripheral bus (PBUS).
For program and data storage, both the MCU subsystem and the DSP subsystem can access
the on chip system SRAM and external memory such Flash Memory. The access to the SRAM
module is made through the RAM Bus (RBUS) under the control of the bus arbitration logic.
Similarly, access to the Flash Memory is through the parallel External Bus (EBUS).
AD6527/AD6527B
DSP
Subsystem
DSP BUS
DMA and BUS
ARBITRATION
SBUS
Serial Link
RBUS IM
AD6535
Audio Baseband
and Power
Management
EBUS
Peripheral
Subsystem
RF-Control
MMI
USC
MUC
Subsystem
(ARM7TDMI
®
)
SRAM
FLASH
Figure 3-10 AD6527 ARCHITECTURE
3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 28 -
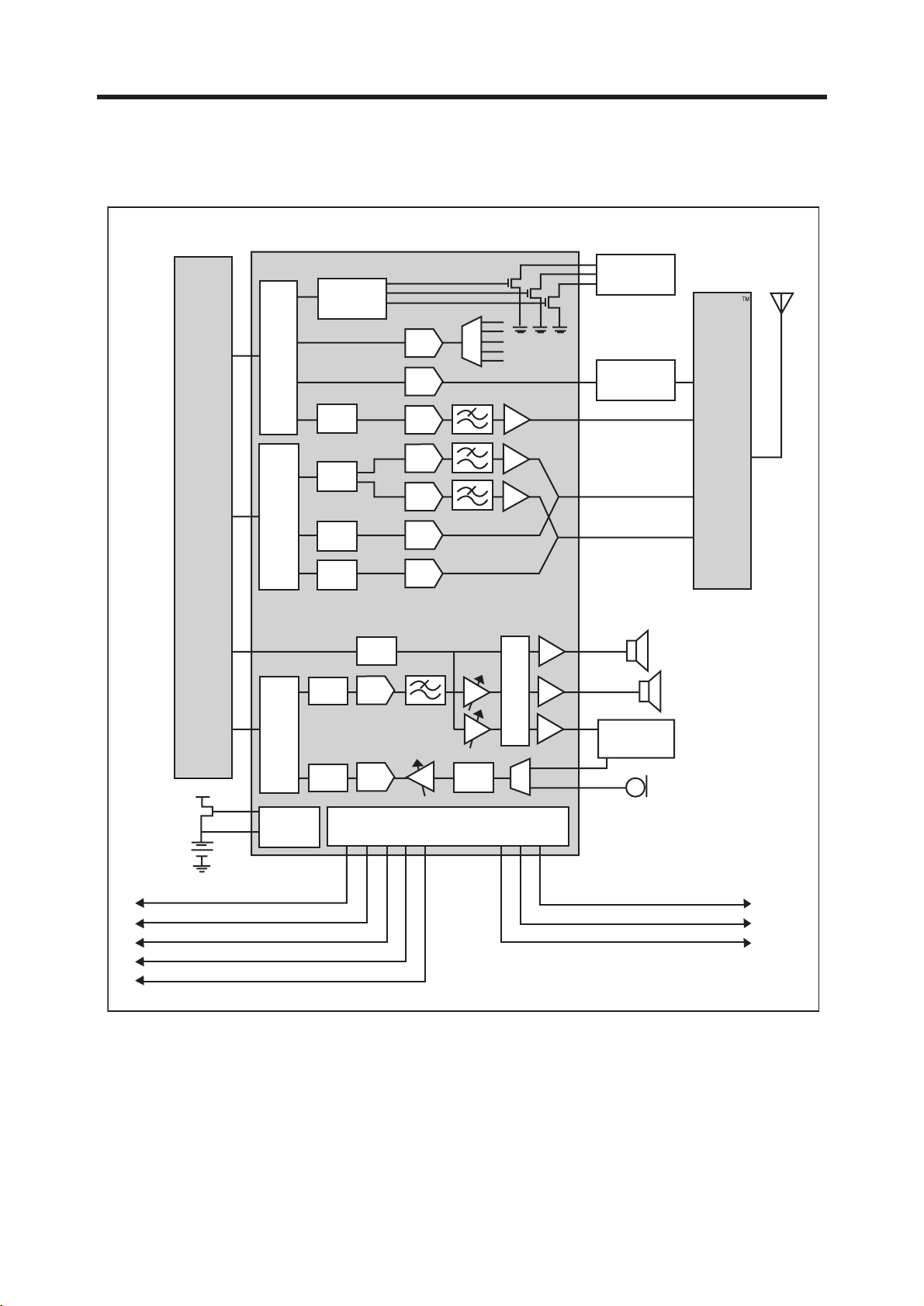
3.6 Analog Main & Power Management Processor (AD6537B, U101)
AD6525
or
AD6526
AD6537B
TROPSC
TROP
S
B
T
R
O
PSA
Light
Controllers
Ram
GMSK
Filter
Filter
Filter
Tone
DAC
ADC
DAC
DAC
DAC
DAC
ADC
ADC
LEDs
Othello
Crystal &
Var act or
hctiwS
Headphones
or Headset
Battery
Charger
VCORE: 1.8 V, 80mA
VMEM: 1.8 or 2.8V, 150mA
VEXT: 2.8V, 170mA
VSIM: 1.8 or 2.85V, 20mA
VRTC: 1.8V, 200 µA
Figure 3-11 AD6537B FUNCTION BLOCK DIAGRAM
Filter
ADC
8 Voltage Regulators
Mic
VAB B
VMIC: 2.5V, 1mA
VVCXO: 2.75V, 10mA

3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 29 -
• AD6537B is an ADI designed Analog Baseband processor. AD6537B covers the processing
GMSK modulation interface, Aux ADC, Voice signal processing and Power Management.
• AD6537B consists of
1. BB Transmit section
• GMSK Modulation
• I-channel & Q-channel Transmit DACs and Filters
• Power Ramping DAC
2. BB Receive section
• I-channel & Q-channel Receive ADCs and Filters
3. Auxiliary section
• Voltage Reference
• Automatic Frequency Control DAC
• Auxiliary ADC
• Light Controllers
4. Audio Section
• 8 kHz & 16 kHz Voiceband Codec
• 48 kHz Monophonic DAC
• Power Amplifiers
5. Power Management section
• Voltage Regulators
• Battery Charger
• Battery Protection
6. Digital Processor section
• Control, Baseband, and Audio Serial Ports
• Interrupt Logic
 Loading...
Loading...