LG L192WS-BNQ/SNQ, A**JQP/ A**QQP Schematic

E-mail:http://www.LGEservice.com/techsup.html
COLOR MONITOR
SERVICE MANUAL
MODEL:
L192WS-BNQ/SNQ. A**JQP/ A**QQP
( ) **Same model for Service
CAUTION
BEFORE SERVICING THE UNIT,
READ THE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IN THIS MANUAL.
*To apply the MSTAR Chip.
1
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................... 2
PRECAUTIONS ....................................................... 3
TIMING CHART ....................................................... 7
DISASSEMBLY ........................................................ 8
BLOCK DIAGRAM...................................................10
DISCRIPTION OF BLOCK DIAGRAM ................... 11
ADJUSTMENT ...................................................... 13
SPECIFICATIONS
1. LCD CHARACTERISTICS
Type
Active Display Area : 19 inch
Pixel Pitch
Color Depth
Size
Electrical Interface : LVDS
Surface Treatment : Hard-coating(3H), Haze=25%
Operating Mode
Backlight Unit
2. OPTICAL CHARACTERISTICS
2-1. Viewing Angle by Contrast Ratio ≥ 10
(a) For
(b) For CMO M190A1-L02 panel: Left 85°/Right 85°;Top
2-2. Luminance
(a) For
(b)
2-3. Contrast Ratio
(a) For
(b)
Typical
3. SIGNAL (Refer to the Timing Chart)
3-1. Sync Signal Type :
Separate Sync, Composite, SOG (Sync On Green)
InnoLux
80°/Right 80°;Top 80° /Bottom 80° at type CR≥10
80°/Bottom 80° at type CR≥10
InnoLux MT190AW01-V2 panel: 300cd/m2 (Typ.)
220cd/m2 (Min.) (6500k); 170 cd/m2 (Min.)(9300k)
For
CMO M190A1-L02 panel: 300cd/m2 (Typ.)
220cd/m2 (Min.) (6500k);170 cd/m2 (Min.)(9300k)
InnoLux MT190AW01-V2 panel: 500:1 minimum;
700:1 Typical
For
CMO M190A1-L02 panel: 500:1 minimum; 850:1
MT190AW01-V2 panel: Left
3-2. Video Input Signal
1) Type
2) Voltage Level
a) Color 0, 0
b) Color 7, 0
c) Color 15, 0
3) Input Impedance : 75 Ω
3-3. Operating Frequency
Horizontal
Vertical
4
. Max. Resolution
D-sub Analog
: TFT Color LCD Module
: 0.285 (H) x 0.285 (V)
: 16.2M colors
: 427.2 (H) x 277.4 (V) x 17 (D)
: Normally White, Transmissive mode
: Top/Bottom edge side 4-CCFL
(Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp)
: R, G, B Analog
: 0~0.71 V
: 0 Vp-p
: 0.467 Vp-p
: 0.714 Vp-p
: 30 ~ 83kHz
: 50 ~ 77Hz
: 1440 x 900@75Hz
Anti-Glare treatment
CONTENTS
SERVICE OSD .........................................................14
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ............................. 15
WIRING DIAGRAM ............................................... 22
EXPLODED VIEW ................................................... 23
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST .............................. 25
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ...........................................34
5. POWER SUPPLY
5-1. Power
5-2. Power Consumption
MODE H/V SYNC VIDEO POWER CONSUMPTION LED COLOR
POWER ON (TYPICAL) ON/ON ACTIVE 34 W TYPICAL GREEN
POWER S/W OFF - - Less than 1 W OFF
6. ENVIRONMENT
6-1. Operating Temperature : 0°C~40°C
6-2. Relative Humidity
6-3. MTBF
7. DIMENSIONS (with TILT/SWIVEL)
Width
Depth
Height
8. WEIGHT (with TILT/SWIVEL)
Net. Weight
Gross Weight
: AC 90~264V, 50~60Hz , <0.8A
Lamp Life
OFF/ON
ON/OFF
OFF/OFF
OFF Less than 1 W AMBERSLEEP MODE
: 20%~90%
: 50,000 HRS with 90% Confidence
: 50,000 Hours(Min)
: 434.8 mm
: 180 mm
: 370 mm
: 4.2±0.4 kg
: 5.2±0.4 kg
(Ambient)
(Non-condensing)
2
PRECAUTION
WARNING FOR THE SAFETY -RE LATE D C OMPO NENT.
• There are some special components used in LCD
monitor that are important for safety. These parts are
marked on the schematic diagram and
t he replacement parts list. It is essential that these
critical parts should be replaced with the
manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent electric
shock, fire or other hazard.
• Do not modify original design without obtaining written
permission from manufacturer or you will void the
original parts and labor guarantee.
TAKE CARE DURING HANDLING THE LCD MODULE
WITH BACKLIGHT UNIT.
• Must mount the module using mounting holes arranged
in four corners.
• Do not press on the panel, edge of the frame strongly
or electric shock as this will result in damage to the
screen.
• Do not scratch or press on the panel with any sharp
objects, such as pencil or pen as this may result in
damage to the panel.
• Protect the module from the ESD as it may damage the
electronic circuit (C-MOS).
• Make certain that treatment person’s body are
grounded through wrist band.
• Do not leave the module in high temperature and in
areas of high humidity for a long time.
• The module not be exposed to the direct sunlight.
• Avoid contact with water as it may a short circuit within
the module.
• If the surface of panel become dirty, please wipe it off
with a softmaterial. (Cleaning with a dirty or rough cloth
may damage the panel.)
WARNING
BE CAREFUL ELECTRIC SHOCK !
• If you want to replace with the new backlight (CCFL)
or inverter circuit, must disconnect the AC
adapter because high voltage appears at inverter
circuit about
650Vrms.
• Handle with care wires or connectors of the
inverter circuit. If the wires are pressed cause short
and may burn or take fire.
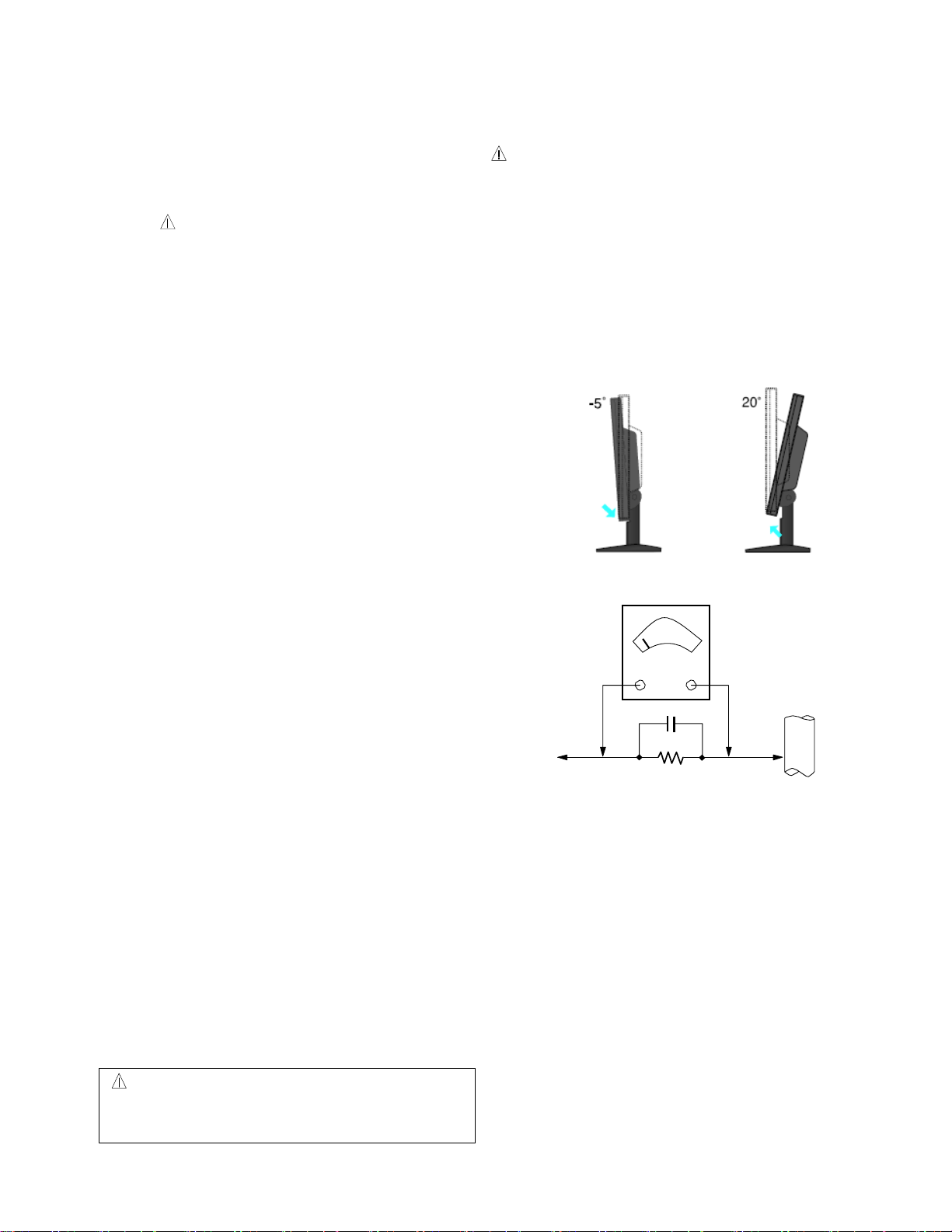
• Be careful while tilting and rotating the monitor to
avoid pinching hand(s)
Leakage Current Hot Check Circuit
AC Volt-meter
Good Earth Ground
To Instrument's
exposed METALLIC
PARTS
1.5 Kohm/10W
such as WATER PIPE,
CONDUIT etc.
CAUT ION
Please use only a plastic screwdriver to protect
yourself from shock hazard during service operation.
3

SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this
service manual and its supplements and addenda, read
and follow the SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this
publication.
NOTE:
between the following servicing precautions and any of the
safety precautions on page 3 of this publication, always
follow the safety precautions. Remember: Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an
3. Discharge the picture tube anode only by (a) first
4. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of
5. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual,
6. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks
7. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of
8. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the
If unforeseen circumstances create conflict
power source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit
board module or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical
plug or other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an
electrolytic capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong part substitution or incorrect
polarity installation of electrolytic capacitors may
result in an explosion hazard.
d. Discharging the picture tube anode.
appropriate high voltage meter or other voltage
measuring device (DVM, FETVOM, etc) equipped with a
suitable high voltage probe.
Do not test high voltage by "drawing an arc".
connecting one end of an insulated clip lead to the
degaussing or kine aquadag grounding system shield
at the point where the picture tube socket ground lead is
connected, and then (b) touch the other end of the
insulated clip lead to the picture tube anode button,
using an insulating handle to avoid personal contact
with high voltage.
its assemblies.
clean electrical contacts only by applying the following
mixture to the contacts with a pipe cleaner, cottontipped stick or comparable non-abrasive applicator;
10% (by volume) Acetone and 90% (by volume)
isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION: This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual,
lubrication of contacts in not required.
with which receivers covered by this service manual
might be equipped.
its electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device
heat sinks are correctly installed.
receiver chassis ground before connecting the test
receiver positive lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
9. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in
this service manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap
to any heat sink in this receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid-state) devices can be
damaged easily by static electricity. Such components
commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES)
Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated
circuits and some field-effect transistors
and semiconductor "chip" components. The
fol l o wi n g techniques should be used to help reduce the
incidence of component damage caused by static by static
electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor
component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain
off any electrostatic charge on your body by touching a
known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a
commercially available discharging wrist strap device,
which should be removed to prevent potential shock
reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with
ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive
surface such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic
charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or
unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device.
Some solder removal devices not classified as "antistatic" can generate electrical charges sufficient to
damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES
devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its
protective package until immediately before you are
ready to install it. (Most replacement ES devices are
packaged with leads electrically shorted together by
conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable
conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material
from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the
protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly
into which the device will be installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis
or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged
replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion
such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or
the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor
can generate static electricity sufficient to damage an
ES device.)
4

General Soldering Guidelines
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and
appropriate tip size and shape that will maintain tip
temperature within the range or 500。F to 600。F.
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder
composed of 60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a
mall wire-bristle (0.5 inch, or 1.25cm) brush with a
metal handle.
Do not use freon-propelled spray-on cleaners.
5. Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal
temperature.
(500。F to 600。F)
b. Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static,
suction-type solder removal device or with solder
braid.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the
circuitboard printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal
temperature (500。F to 600。F)
b. First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand
against the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of
the component lead and the printed circuit foil, and
hold it there only until the solder flows onto and
around both the component lead and the foil.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the
circuit board printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any
excess or splashed solder with a small wire-bristle
brush.
IC Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong)
through which the IC leads are inserted and then bent flat
against the circuit foil. When holes are the slotted type,
the following technique should be used to remove and
replace the IC. When working with boards using the
familiar round hole, use the standard technique as
outlined in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation
by gently prying up on the lead with the soldering iron
tip as the solder melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static
suction-type solder removal device (or with solder
braid) before removing the IC.
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit board.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad
and solder it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle
brush. (It is not necessary to reapply acrylic coating to
the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as
close as possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads
remaining on the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the
corresponding leads extending from the circuit board
and crimp the "U" with long nose pliers to insure metal
to metal contact then solder each connection.
Power Output, Transistor Device
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor
leads.
2. Remove the heat sink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the
circuit board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heat sink.
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close
as possible to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicular y to the
circuit board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new
diode around the corresponding lead on the circuit
board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the
solder joints of the two "original" leads. If they are not
shiny, reheat them and if necessary, apply additional
solder.
Fuse and Conventional Resistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board
hollow stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component
around notch at stake top.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the
replaced component and adjacent components and the
circuit board to prevent excessive component temperatures.
5

Circuit Board Foil Repair
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed
circuit board will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to
the circuit board causing the foil to separate from or
"lift-off" the board. The following guidelines and
procedures should be followed whenever this condition is
encountered.
At IC Connections
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use
the following procedure to install a jumper wire on the
copper pattern side of the circuit board. (Use this
technique only on IC connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a
sharp knife. (Remove only as much copper as
absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic
coating (if used) from the end of the remaining copper
pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper
wire and carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the
IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away
copper pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped
end of the good copper pattern. Solder the overlapped
area and clip off any excess jumper wire.
At Other Connections
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper
pattern at connections other than IC Pins. This technique
involves the installation of a jumper wire on the
component side of the circuit board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp
knife.
Remove at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a
hazardous condition will not exist if the jumper wire
opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the
pattern break and locate the nearest component that is
directly connected to the affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead
of the nearest component on one side of the pattern
break to the lead of the nearest component on the
other side.
Carefully crimp and solder the connections.
CAUTION: Be sure the insulated jumper wire
is dressed so the it does not touch components or
sharp edges.
6
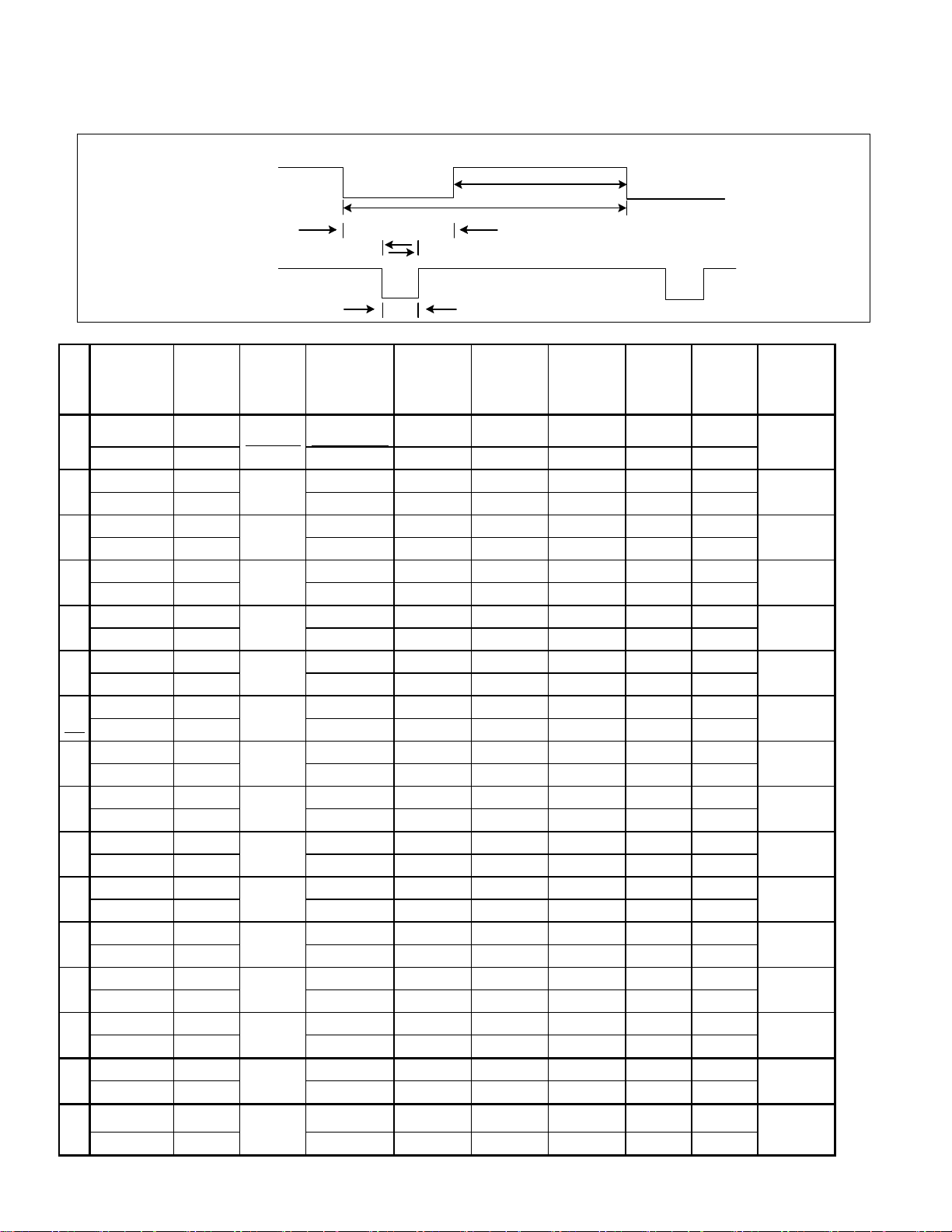
TIMING CHART
VIDEO
distingishme
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
nt
H(Pixels) +
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) - 31.468 900 720 18 108 54
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) - 31.469 800 640 16 96 48
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) - 37.5 840 640 16 64 120
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) + 37.879 1056 800 40 128 88
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) + 46.875 1056 800 16 80 160
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) +/- 49.725 1152 832 32 64 224
V(Lines) +/-
H(Pixels) - 48.363 1344 1024 24 136 160
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) - 60.123 1312 1024 16 96 176
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) +/- 68.681 1456 1152 32 128 144
V(Lines) +/-
H(Pixels) +/- 61.805 1504 1152 18 134 200
V(Lines) +/-
H(Pixels) + 63.981 1688 1280 48 112 248
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) + 79.976 1688 1280 16 144 248
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) + 55.5 1600 1440 48 32 80
V(Lines) -
H(Pixels) - 55.935 1904 1440 80 152 232
V(Lines) +
H(Pixels) - 70.635 1936 1440 96 152 248
V(Lines) +
Polority
SYNC
DOT
CLOCK
[MHz]
25.175
28.321
25.175
31.5
40.0
49.5
57.283
65.0
78.75
100.0
92.978
108.0
135.0
88.750
106.500
136.750
A
E
D B
C
M
Frequency
[kHz]/ [Hz]
31.469
70.8 449 350 37 2 60
70.09 449 400 12 2 35
59.94 525 480 10 2 33
75 500 480 1 3 16
60.317 628 600 1 4 23
75.0 625 600 1 3 21
74.55 667 624 1 3 39
60.0 806 768 3 6 29
75.029 800 768 1 3 28
75.062 915 870 3 3 39
65.96 937 900 2 4 31
60.02 1066 1024 1 3 38
75.035 1066 1024 1 3 38
59.90 926 900 3 6 17
59.887 934 900 3 6 25
74.984 942 900 3 6 33
Total period
(E)
800 640 16 96 48
Display
(A)
Front
Porch
(D)
Sync.
(C)
Back
Porch
(B)
Resolution
640 x 350
720 X 400
640 x 480
640 x 480
800 x 600
800 x 600
832 x 624
1024 x 768
1024 x 768
1152 x 870
1152 x 900
1280 x
1024
1280 x
1024
1440 x 900
1440x 900
1440x 900
7

DISASSEMBLY
#1 #2
Put a soft cushion on the desk and lay the stand on
its side so that the base is accessible.
#4
#3
Pry the hinge cover by flat-tip screw driver or jig and
be careful to prevent from scratching the hinge
cover.
Pull up the front cover side by side(4 sides) and take
away the front cover
8
Twist the stand assy until “click” , then take out the
stand assy into the product in the
correct direction as shown in picture.
Unscrew the 4 screws on the hinge to separate the
hinge neck ass’y
.
#6#5
Turn over the set and pull up the cabinet to separate
the control cable, then take away the back cover

#8#7
Pull out the LVDS cable Pull out the lamp wire.
9
A
A
A
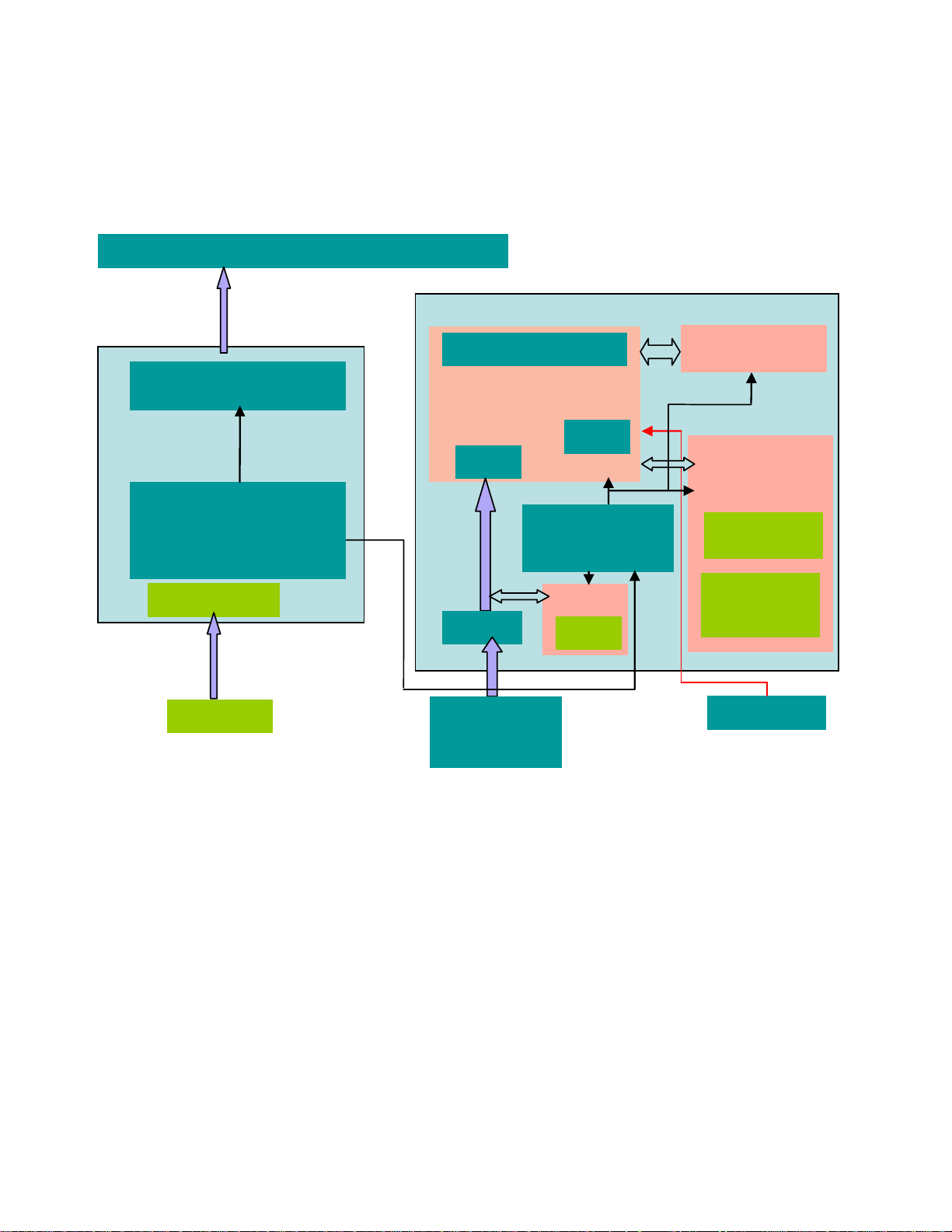
BLOCK DIAGRAM
L192WS consists of a main body and a stand (base). The main body contains a InnoLux (or CMO) LCD
module with 4 CCFL lamps, a power board (includes AC/DC, DC/DC, inverter and panel power source),
a control board (key pad) and an interface board. The block diagram is shown as below.
InnoLux TFT-LCD Module with 4FFCLs
Inverter
14V
Power
AC to DC (14V&5V)
C Socket
C Input
LVDS Transmitter
TSUM16AL-LF-1
DC
1.8V regulator
24C02
D-sub
Analog
RGB Signal
10
MCU
3.3V and
DDC
128KB Flash ROM
EEPROM
24C04
OSD parameters
Timing
parameters
Key pad

DESCRIPTION OF BLOCK DIAGRAM
1. Video Controller Part.
This part amplifies the level of video signal for the digital conversion and converts from the analog video signal to the digital
video signal using a pixel clock.
The pixel clock for each mode is generated by the PLL. The range of the pixel clock is from 25MHz to 135MHz.
This part consists of the Scaler, ADC convertor and LVDS transmitter.
The Scaler gets the video signal converted analog to digital, interpolates input to 1440 X 900 resolution signal and outputs
8-bit R, G, B signal to transmitter.
2. Power Part.
This part consists of the one 3.3V, and one 1.8V regulators to convert power which is provided 5V in Power board.
14V is provided for inverter, 14V is provided for LCD panel and 5V for micom.
Also, 5V is converted 3.3V and 1.8V by regulator. Converted power is provided for IC in the main board. The inverter
converts from DC14V to AC 700Vrms and operates back-light lamps of module.
3. MICOM Part.
This part is include video controller part. And this part consists of EEPROM IC which stores control data, and the Micom
which imbedded in scaler IC.
The Micom distinguishes polarity and frequency of the H/V sync are supplied from signal cable. The controlled data of each
modes is stored in EEPROM.
11
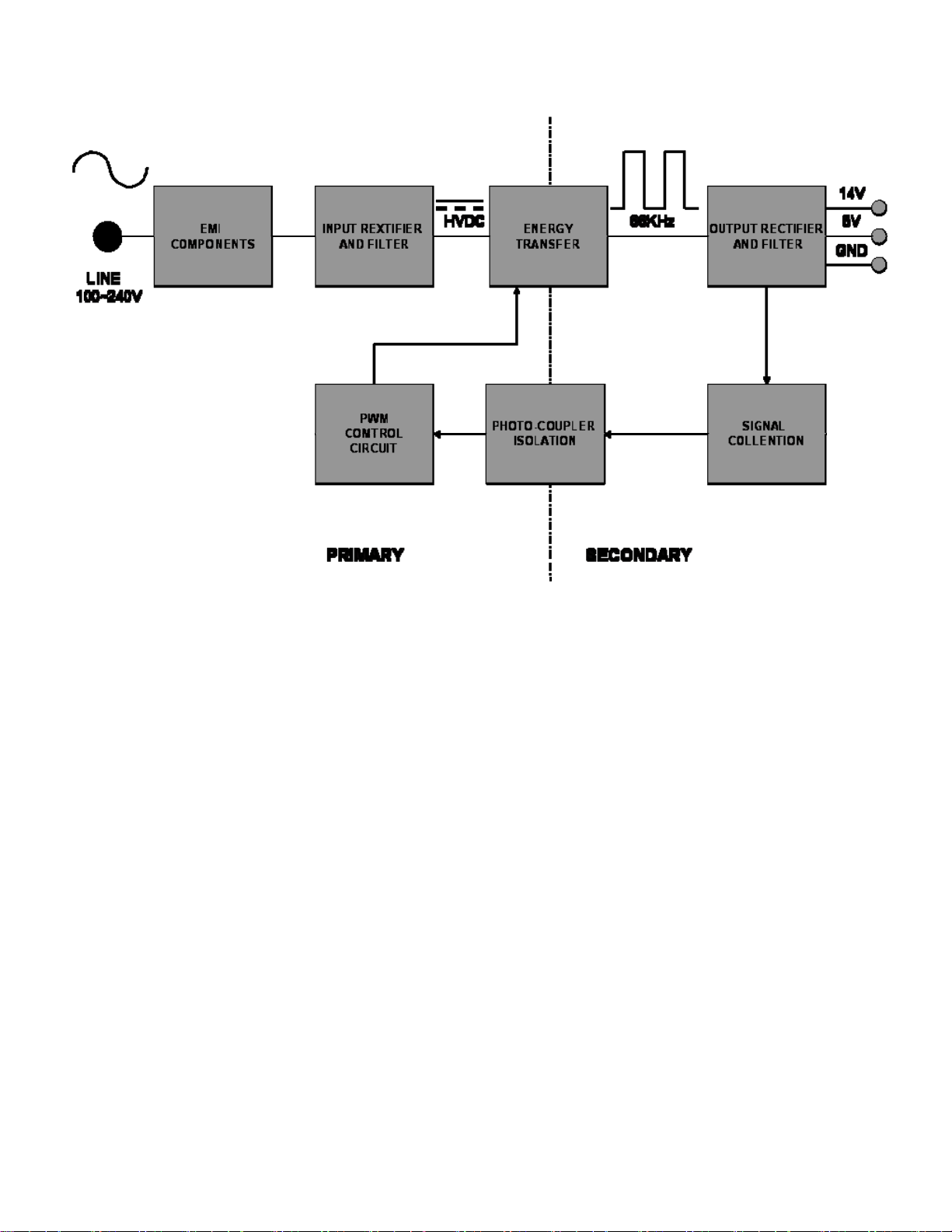
LIPS Board Block Diagram
50~60Hz
Operation description_LIPS
1. EMI components.
This part contains of EMI components to comply with global marketing EMI standards like FCC, VCCI CISPR, the circuit
included a line-filter, across line capacitor and of course the primary protection fuse.
2. Input rectifier and filter.
This part function is for transfer the input AC voltage to a DC voltage through a bridge rectifier and a bulk capacitor.
3. Energy Transfer.
This part function is transfer the primary energy to secondary through a power transformer.
4. Output rectifier and filter.
This part function is to make a pulse width modulation control and to provide the driver signal to power switch, to adjust
the duty cycle during different AC input and output loading condition to achive the dc output stablize, and also the over
power protection is also monitor by this part.
5. Photo-Coupler isolation.
This part function is to feed back the dc output changing status through a photo transistor to primary controller to achieve
the stabilized dc output voltage.
6. Signal collection.
This part function is to collect the any change from the dc output and feed back to the primary through photo transistor.
12
 Loading...
Loading...