LG 98UB9800, 98UB9810UB Schematic

Internal Use Only
North/Latin America http://aic.lgservice.com
Europe/Africa http://eic.lgservice.com
Asia/Oceania http://biz.lgservice.com
LED TV
SERVICE MANUAL
CHASSIS : LA41F
MODEL : 98UB9800/9810 98UB9800/9810-UB
CAUTION
BEFORE SERVICING THE CHASSIS,
READ THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS IN THIS MANUAL.
Printed in KoreaP/NO : MFL68086427 (1410-REV01)

CONTENTS
CONTENTS .............................................................................................. 2
PRODUCT SAFETY ................................................................................. 3
SPECIFICATION ....................................................................................... 6
ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTION .............................................................. 13
EXPLODED VIEW .................................................................................. 25
SCHEMATIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ..............................................................
Only for training and service purposes
- 2 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These parts are identified by in the
Schematic Diagram and Exploded View.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as recommended in this manual to prevent
Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
General Guidance
An isolation Transformer should always be used during the
servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not isolated from the AC
power line. Use a transformer of adequate power rating as this
protects the technician from accidents resulting in personal injury
from electrical shocks.
It will also protect the receiver and it's components from being
damaged by accidental shorts of the circuitry that may be
inadvertently introduced during the service operation.
If any fuse (or Fusible Resistor) in this TV receiver is blown,
replace it with the specified.
When replacing a high wattage resistor (Oxide Metal Film Resistor,
over 1 W), keep the resistor 10 mm away from PCB.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature parts.
Before returning the receiver to the customer,
always perform an AC leakage current check on the exposed
metallic parts of the cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, etc., to
be sure the set is safe to operate without damage of electrical
shock.
Leakage Current Cold Check(Antenna Cold Check)
With the instrument AC plug removed from AC source, connect an
electrical jumper across the two AC plug prongs. Place the AC
switch in the on position, connect one lead of ohm-meter to the AC
plug prongs tied together and touch other ohm-meter lead in turn to
each exposed metallic parts such as antenna terminals, phone
jacks, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the
measured resistance should be between 1 MΩ and 5.2 MΩ.
When the exposed metal has no return path to the chassis the
reading must be infinite.
An other abnormality exists that must be corrected before the
receiver is returned to the customer.
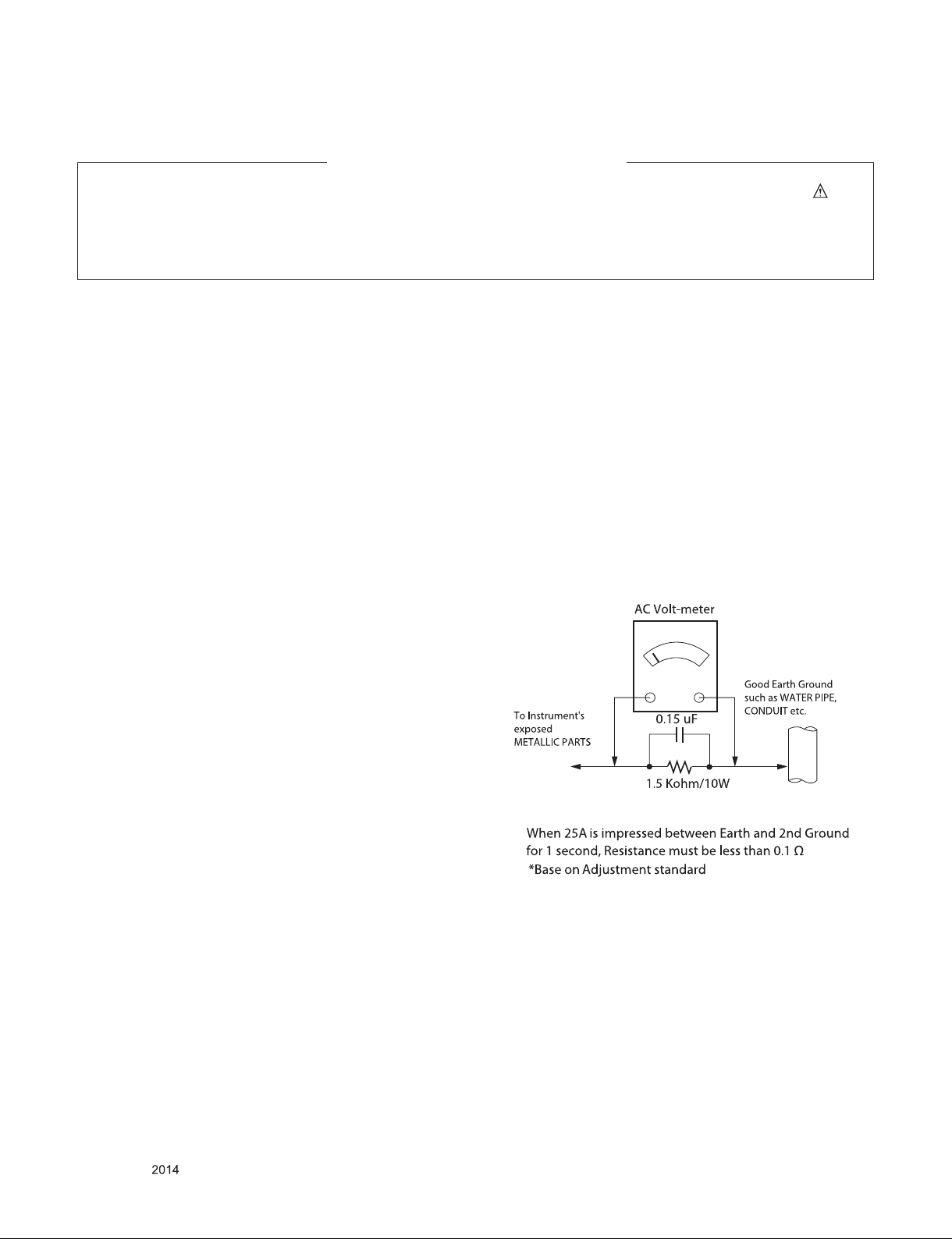
Leakage Current Hot Check (See below Figure)
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet.
Do not use a line Isolation Transformer during this check.
Connect 1.5 K / 10 watt resistor in parallel with a 0.15 uF capacitor
between a known good earth ground (Water Pipe, Conduit, etc.)
and the exposed metallic parts.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor using AC voltmeter
with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity.
Reverse plug the AC cord into the AC outlet and repeat AC voltage
measurements for each exposed metallic part. Any voltage
measured must not exceed 0.75 volt RMS which is corresponds to
0.5 mA.
In case any measurement is out of the limits specified, there is
possibility of shock hazard and the set must be checked and
repaired before it is returned to the customer.
Leakage Current Hot Check circuit
Only for training and service purposes
- 3 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this service
manual and its supplements and addenda, read and follow the
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this publication.
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conict between the
following servicing precautions and any of the safety precautions
on page 3 of this publication, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember: Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power
source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board mod-
ule or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or
other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong part substitution or incorrect polarity
installation of electrolytic capacitors may result in an explosion hazard.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate
high voltage meter or other voltage measuring device (DVM,
FETVOM, etc) equipped with a suitable high voltage probe.
Do not test high voltage by "drawing an arc".
3. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its
assemblies.
4. Unless specied otherwise in this service manual, clean
electrical contacts only by applying the following mixture to the
contacts with a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or comparable
non-abrasive applicator; 10 % (by volume) Acetone and 90 %
(by volume) isopropyl alcohol (90 % - 99 % strength)
CAUTION: This is a ammable mixture.
Unless specied otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of
contacts in not required.
5. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks with which
receivers covered by this service manual might be equipped.
6. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its
electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device heat sinks are
correctly installed.
7. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver
chassis ground before connecting the test receiver positive
lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
8. Use with this receiver only the test xtures specied in this
service manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test xture ground strap to any
heat sink in this receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid-state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES
devices are integrated circuits and some eld-effect transistors
and semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques
should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by static by static electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or
semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any electrostatic
charge on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging
wrist strap device, which should be removed to prevent potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES
devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES
devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device. Some solder
removal devices not classied as “anti-static” can generate
electrical charges sufcient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate
electrical charges sufcient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective
package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or
comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the
leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit,
and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your
foot from a carpeted oor can generate static electricity sufcient to damage an ES device.)
General Soldering Guidelines
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and appropriate
tip size and shape that will maintain tip temperature within the
range or 500 °F to 600 °F.
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder composed
of 60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a mall wirebristle (0.5 inch, or 1.25 cm) brush with a metal handle.
Do not use freon-propelled spray-on cleaners.
5. Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal temperature.
(500 °F to 600 °F)
b. Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static, suction-
type solder removal device or with solder braid.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit
board printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal temperature
(500 °F to 600 °F)
b. First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand against
the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of the
component lead and the printed circuit foil, and hold it there
only until the solder ows onto and around both the component lead and the foil.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit
board printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any excess or
splashed solder with a small wire-bristle brush.
Only for training and service purposes
- 4 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

IC Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong) through
which the IC leads are inserted and then bent at against the circuit foil. When holes are the slotted type, the following technique
should be used to remove and replace the IC. When working with
boards using the familiar round hole, use the standard technique
as outlined in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation by
gently prying up on the lead with the soldering iron tip as the
solder melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static suction-type
solder removal device (or with solder braid) before removing
the IC.
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit board.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad and
solder it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle brush.
(It is not necessary to reapply acrylic coating to the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as close
as possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads remaining
on the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the corresponding
leads extending from the circuit board and crimp the "U" with
long nose pliers to insure metal to metal contact then solder
each connection.
Power Output, Transistor Device
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor leads.
2. Remove the heat sink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the circuit
board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heat sink.
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close as possible to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicular y to the circuit
board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new diode
around the corresponding lead on the circuit board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the solder joints of
the two "original" leads. If they are not shiny, reheat them and if
necessary, apply additional solder.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the replaced
component and adjacent components and the circuit board to
prevent excessive component temperatures.
Circuit Board Foil Repair
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed circuit
board will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to the circuit
board causing the foil to separate from or "lift-off" the board. The
following guidelines and procedures should be followed whenever
this condition is encountered.
At IC Connections
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use the
following procedure to install a jumper wire on the copper pattern
side of the circuit board. (Use this technique only on IC connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a sharp
knife. (Remove only as much copper as absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic coating (if
used) from the end of the remaining copper pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper wire and
carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away copper
pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped end of the
good copper pattern. Solder the overlapped area and clip off
any excess jumper wire.
At Other Connections
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper pattern
at connections other than IC Pins. This technique involves the
installation of a jumper wire on the component side of the circuit
board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp knife.
Remove at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a hazardous
condition will not exist if the jumper wire opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the pattern
break and locate the nearest component that is directly connected to the affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead of the
nearest component on one side of the pattern break to the lead
of the nearest component on the other side.
Carefully crimp and solder the connections.
CAUTION: Be sure the insulated jumper wire is dressed so the
it does not touch components or sharp edges.
Fuse and Conventional Resistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board hollow
stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component around
notch at stake top.
Only for training and service purposes
- 5 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

SPECIFICATION
NOTE : Specifications and others are subject to change without notice for improvement
1. Application range
This spec sheet is applied to the LED TV used LA41F chassis
2. Test condition
Each part is tested as below without special notice.
1) Temperature : 25 ºC ± 5 ºC(77±9ºF), CST : 40 ºC±5 ºC
2) Relative Humidity: 65 % ± 10 %
3) Power Voltage
Standard input voltage (100~240V@ 50/60Hz)
* Standard Voltage of each products is marked by models.
4) Specification and performance of each parts are followed
each drawing and specification by part number in
accordance with BOM.
5) The receiver must be operated for about 20 minutes prior to
the adjustment.
3. Test method
1) Performance: LGE TV test method followed
2) Demanded other specification
- Safety : UL, CSA, CE, IEC specification
- EMC : FCC, ICES, CE, IEC specification
- Wireless : Wireless HD Specification (Option)
.
Only for training and service purposes
- 6 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
4. General Specification
No Item Specication Remark
1. Display Screen Device 98” wide color display module LC980DQD-FGF1(Flat T240)
2. Aspect Ratio 16:9 All
3. LCD Module 98” QWUXGA TFT LCD LC980DQD-FGF1(Flat T240)
4. Operating Environment TFT 1) Temp. : 0 ~ 40 deg
5. Storage Environment ALEF 1) Temp. : 0 ~ 50 deg
6. Input Voltage AC100 ~ 240V, 50/60Hz
7. Power Consumption(Max)
= LCD(Module)
Backlight(LED)
8. LCD Module 2187.8 x1242.8 x 31.0(Size) LC980DQD-FGF1
9. Display Colors 1.06 B (10-bit) Except FHD 60Hz models
Surface Treatment Hard coating (2H), Anti-glare
458.6W Flat Edge LED : LC980DQD-FGF1
0.5622 x 0.5622(Pixel Pitch)
16.7 M (8-bit) Only FHD 60Hz models
2) Humidity : 0 ~ 85%
2) Humidity : 20 ~ 90%
LGE SPEC
Only for training and service purposes
- 7 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
5. External input format
5.1. 2D Mode
5.1.1. Component input(Y, CB/PB, CR/PR)
No
1 720*480 15.73 60 13.5135 SDTV ,DVD 480I
2 720*480 15.73 59.94 13.5 SDTV ,DVD 480I
3 720*480 31.50 60 27.027 SDTV 480P
4 720*480 31.47 59.94 27.0 SDTV 480P
5 1280*720 45.00 60.00 74.25 HDTV 720P
6 1280*720 44.96 59.94 74.176 HDTV 720P
7 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.25 HDTV 1080I
8 1920*1080 33.72 59.94 74.176 HDTV 1080I
9 1920*1080 67.500 60 148.50 HDTV 1080P
10 1920*1080 67.432 59.94 148.352 HDTV 1080P
Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz) Pixel clock(MHz) Proposed
5.1.2. HDMI Input (PC/DTV)
No. Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(kHz) Pixel clock(MHz) Proposed
HDMI-PC DDC
1 640*350 31.468 70.09 25.17 EGA
2 720*400 31.469 70.08 28.32 DOS
3 640*480 31.469 59.94 25.17 VESA(VGA)
4 800*600 37.879 60.31 40.00 VESA(SVGA)
5 1024*768 48.363 60.00 65.00 VESA(XGA)
6 1152*864 54.348 60.053 80.00 VESA
7 1280*1024 63.981 60.02 108.00 VESA (SXGA) Support to HDMI-PC
8 1360*768 47.712 60.015 85.50 VESA (WXGA)
9 1920*1080 67.5 60 148.5
10 3840*2160 54 24.00 297.00
11 3840*2160 56.25 25.00 297.00
12 3840*2160 67.5 30.00 297.00
13 4096*2160 53.95 23.97 296.703
14 4096*2160 54 24.00 297.00
WUXGA(Reduced Blanking)
Only UD Model
Only UD Model
Only UD Model
Only UD Model, Port3
Only UD Model
UHD only
UHD only
UHD only
UHD only
UHD only
Only for training and service purposes
- 8 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
HDMI-DTV
1 640 * 480 31.469 59.94 25.125 SDTV 480P
2 640 * 480 31.5 60 25.125 SDTV 480P
3 720 * 480 15.73 59.94 13.500 SDTV 480I
4 720 * 480 15.75 60.00 13.514 SDTV 480I
5 720 * 480 31.5 60 27.027 SDTV 480P
6 720 * 480 31.47 59.94 27.00 SDTV 480P
7 1280*720 45 60.00 74.25 HDTV 720P
8 1280*720 44.96 59.94 74.176 HDTV 720P
9 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.25 HDTV 1080I
10 1920*1080 33.72 59.94 74.176 HDTV 1080I
11 1920*1080 26.97 23.976 63.296 HDTV 1080P
12 1920*1080 27.00 24.00 63.36 HDTV 1080P
13 1920*1080 33.71 29.97 79.120 HDTV 1080P
14 1920*1080 33.75 30.00 79.20 HDTV 1080P
15 1920*1080 67.432 59.94 148.350 HDTV 1080P
16 1920*1080 67.5 60.00 148.50 HDTV 1080P
17 3840*2160 53.95 23.98 296.703 UDTV 2160P UHD only
18 3840*2160 54 24.00 297.00 UDTV 2160P UHD only
19 3840*2160 56.25 25.00 297.00 UDTV 2160P UHD only
20 3840*2160 61.43 29.97 296.703 UDTV 2160P UHD only
21 3840*2160 67.5 30.00 297.00 UDTV 2160P UHD only
22 3840*2160 135 60.00 594 UDTV 2160P UHD only(Port3)
23 3840*2160 135 59.94 593.407 UDTV 2160P UHD only(Port3)
24 4096*2160 53.95 23.98 296.703 UDTV 2160P UHD only
25 4096*2160 54 24.00 297 UDTV 2160P UHD only
26 4096*2160 56.25 25.00 297 UDTV 2160P UHD only
27 4096*2160 61.43 29.97 296.703 UDTV 2160P UHD only
28 4096*2160 67.5 30.00 297 UDTV 2160P UHD only
29 4096*2160 135 60.00 594 UDTV 2160P UHD only(Port3)
30 4096*2160 135 59.94 593.407 UDTV 2160P UHD only(Port3)
Only for training and service purposes
- 9 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
5.2. 3D Mode
5.2.1. 3D Supported mode (Only for models that support 3D)
Video, which is input as below media contents is switched into the 3D screen automatically.
The method for 3D digital broadcast may differ depending on the signal environment.
If video is not switched automatically into 3D, manually convert the settings to view 3D images.
For models supporting Miracast / Intel® WiDi, you can set the 3D mode
Input Signal Horizontal Frequency
HDMI 480p 31.469 / 31.5 59.94/ 60 Top & Bottom, Side by Side(Half),
62.938 / 63 Frame Packing, Line Alternative
720p 44.96 / 45 59.94 / 60 Top & Bottom, Side by Side(Half),
89.91 / 90 Frame Packing, Line Alternative
1080i 33.72 / 33.75 59.94 / 60 Top & Bottom, Side by Side(Half),
67.432 / 67.5 Frame Packing, Line Alternative
1080p 26.97 / 27 23.97 / 24 Top & Bottom, Side by Side(Half),
28.125 25
33.716/33.75 29.976 / 30
43.94 / 54 23.97 / 24 Frame Packing, Line Alternative
56.25 25
67.432 / 67.5 29.976 / 30
67.432 / 67.5 59.94 / 60 Top & Bottom, Side by Side(Half)
DTV Frame
Compatible
- - Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
(kHz)
Vertical Frequency (Hz) Playable 3D video format
Side by Side(Full)
Side by Side(Full)
Side by Side(Full)
Side by Side(Full)
5.2.2. 3D Supported mode manually(Only for models that support 3D)
Video, which is input as below media contents is switched into the 3D screen automatically.
Signal
Input
DTV HD / SD - - 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
ATV(CVBS/
SCART)
Component 1280 x 720p 45 60
Resolution
SD - -
1920 x 1080i 33.75 60
1920 x 1080p 67.5 60
Horizontal Frequency
(kHz)
44.96 59.94
33.72 59.94
67.432 59.94
27 24
28.12 25
26.97 23.976
33.75 30
33.71 29.97
Vertical Frequency (Hz) Playable 3D video format
- 10 -
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
Signal
Input
HDMI-PC 1024 x 768p 48.36 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
HDMI-DTV 480P 31.5 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom,
USB(Movie) Under 704x480 - - 2D to 3D
USB(Photo) Under 320x240 - - 2D to 3D
Miracast/Intel®
WiDi
Resolution
1360 x 768p 47.71
1920 x 1080p 67.5 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom,
3840 x 2160p
(Ultra HD
model only)
4096 x 2160p
(Ultra HD
model only)
Others - - 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
720p 45 60
1080i 33.75 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
1080p 27 24 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top &
3840 x 2160p
4096 x 2160p
(Ultra HD
model only)
Over 704x480
interlaced
under 1080p
Over 704x480
progressive
under 1080p
Over 704x480
progressive
under 1080p
Over 2160p
(Ultra HD
model only)
Over 320x240 - - 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
1024 x 768p - 30 / 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
1280x720p - 30 / 60
1920 x 1080p - 30 / 60
Others - - 2D to 3D
Horizontal Frequency
(kHz)
54 24 2D to 3D, Top & Bottom(Half), Side by Side(Half)
56.25 24
67.5 30
54 24
28.12 25
33.75 30
67.5 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom,
53.95 23.976 2D to 3D, Top & Bottom(half), Side by Side(half),
54 24
56.25 25
61.43 29.97
67.5 30
135 60(HDMI3 only)
- - 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
- 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top &
- others 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top &
- 24 / 25 / 30 / 60 2D to 3D, Side by Side(Half), Top & Bottom
Vertical Frequency (Hz) Playable 3D video format
Checker Board, Single Frame Sequential, Row
Interleaving, Column Interleaving
Checker Board, Frame Sequential, Row Interleaving, Column Interleaving
Bottom,Checker Board, Row Interleaving, Column
Interleaving
Checker Board, Frame Sequential, Row Interleaving, Column Interleaving
Bottom,Checker Board, Row Interleaving, Column
Interleaving, Frame Sequential
Bottom,Checker Board, Row Interleaving, Column
Interleaving
Only for training and service purposes
- 11 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

**Remark: 3D Input mode
R
L
R
L
No. Side by Side Top & Bottom Checkerboard Single Frame
Sequential
1
Frame Packing Line
Interleaving
Column
Interleaving
Only for training and service purposes
- 12 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTION
1. Application Range
This spec. sheet applies to LA48V Chassis applied LED TV all
models manufactured in TV factory
2. Specification.
(1) Because this is not a hot chassis, it is not necessary to use
an isolation transformer. However, the use of isolation
transformer will help protect test instrument
(2) Adjustment must be done in the correct order.
(3) The adjustment must be performed in the circumstance of
25 ±5ºC of temperature and 65±10% of relative humidity if
there is no specific designation
(4) The input voltage of the receiver must keep 100~240V,
50/60Hz
(5) The receiver must be operated for about 5 minutes prior to
the adjustment when module is in the circumstance of over
15ºC
▪ In case of keeping module is in the circumstance of 0°C, it
should be placed in the circumstance of above 15°C for 2
hours
▪ In case of keeping module is in the circumstance of below
-20°C, it should be placed in the circumstance of above 15°C
for 3 hours
* Caution) When still image is displayed for a period of 20
minutes or longer (especially where W/B scale is
strong. Digital pattern 13ch and/or Cross hatch
pattern 09ch), there can some afterimage in the
black level area.
3. Adjustment items
3.1. PCB assembly adjustment items
1) MAC Address, ESN Key and Wide-vine Key D/L
2) LAN Test( Ping-Test )
3) Main S/W program download : Using USB Memory stick
4) Input Tool - Option
5) Download EDID
6) ADC Calibration – RGB & Component
7) Check SW Version
4. PCB assembly adjustment method
4.1. ADC Calibration : component using internal pattern
- An ADC calibration is needed to fine the optimum black level
and gain in Analog-to-Digital device
.
4.1.1. Adj. method
- Using RS-232C, adjust items listed in “4.1.2”
4.1.2. Adj. protocol
Protocol Command Set ACK
Enter adj. mode aa 00 00 a 00 OK00x
Source change xb 00 40 b 00 OK04x (Adjust 480i, 1080p Comp1 )
Begin adj. ad 00 10 OKx (Case of Success)
Read adj. data ad 00 20 000000000000000000000000007c007b-
Conrm adj. ad 00 99 NG 01 00x (Fail)
End adj. ad 00 90 a 00 OK90x
4.1.3. Adj. Order (TBD)
▪ aa 00 00 [Enter adj. mode]
▪ xb 00 04 [Change input source to Component1(480i&1080p)]
▪ ad 00 10 [Adjust 480i&1080p Comp1]
▪ aa 00 90 [End adj.]
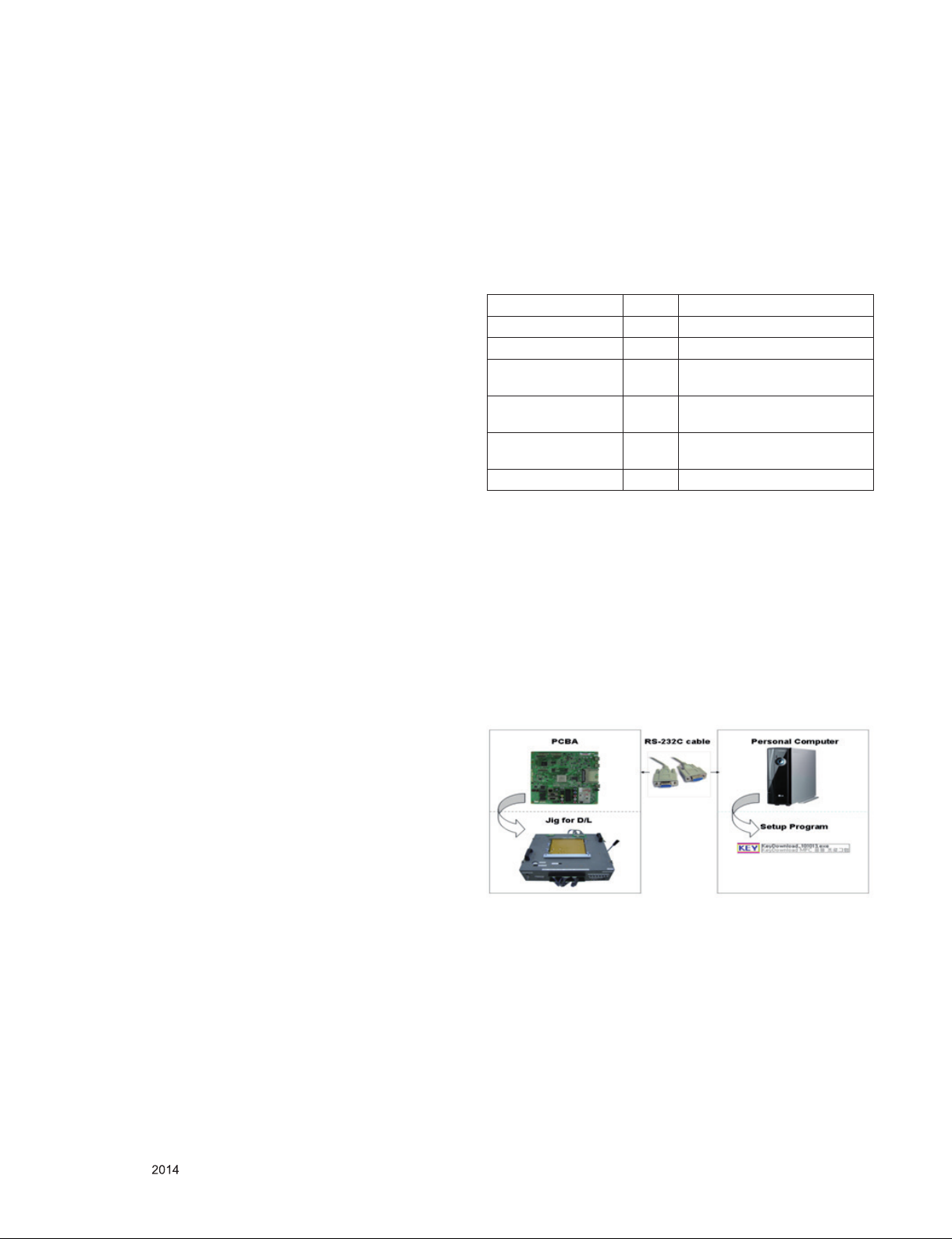
4.2. 4.2.MAC Address, ESN Key and Widevine Key Download
4.2.1. Equipment & Condition
1) Play file: keydownload.exe
2) Key Write: Com 1,2,3,4 and 115200 (Baudrate)
3) Barcode: Com 1,2,3,4 and 9600 (Baudrate)
NGx (Case of Fail)
006dx
OK 01 01x (Success)
3.2. SET assembly adjustment items
1) Input Area option.
2) Adjustment of White Balance : Auto
3) Adjustment of White Balance : Manual
4) Intelligent Sensor Inspection Guide
5) LAN Inspection Guide
6) Widevine Key Inspection Guide
7) Model name & Serial number D/L
8) Wi-Fi MAC Address Check
9) Local Dimming Inspection Guide
10) Preset CH information
11) GND and Internal Pressure check
12) Motion Remote controller Inspection
13) 3D Function test
14) Outgoing Condition Configuration
15) Sound spec
16) Factoring Option Data input.
Only for training and service purposes
- 13 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
4.2.2. Download process (14Y ULTRA HD TV + MAC
+ WIDEVINE + ESN)
1) Execute “keydownload.exe” on PC
2) Select the download items.
3) Mode check : Online only
4) Check the test process
- DETECT -> MAC_WRITE -> ESN_WRITE (only Colombia/
Panama) ->WIDEVINE_WRITE
5) Play: START
6) Check of result: Ready, Test, OK or NG
4.2.3. Inspection : InINSTART menu, check these keys
4.4. Main S/W program download
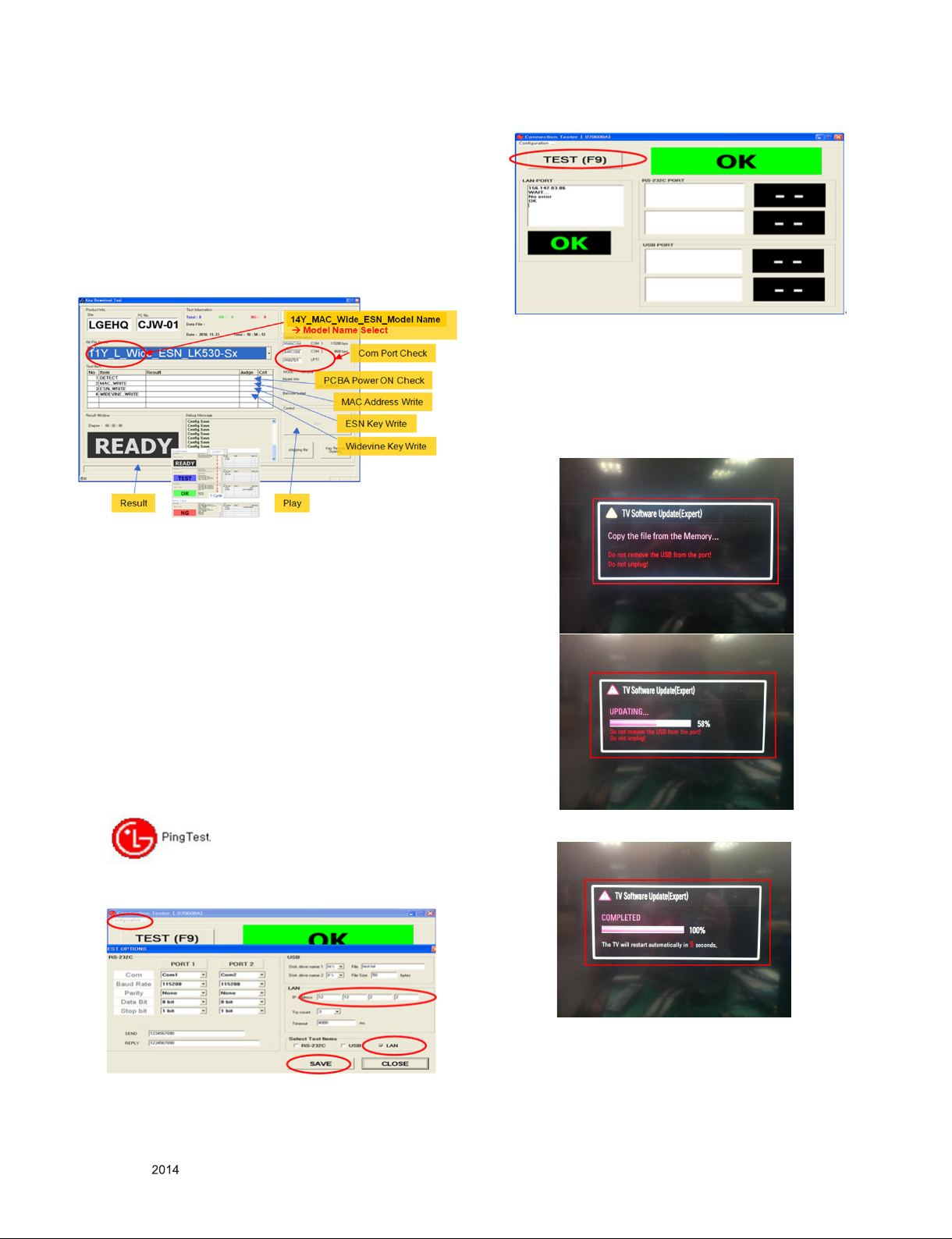
4.4.1. Using the Memory Stick
** USB DOWNLOAD : Service Mode
1) Insert the USB memory Stick to the USB port
2) Automatically detect the SW Version.
-> S/W download process is executed automatically.
3) Show the message “Copy the file from the Memory”
4.3. PING Test(LAN Operating Test)
4.3.1. Check PCBA
1) Connect LAN to PCBA& Power On.(Default IP can be set to
automatic setting. When power ON, IP can be Automatically
be achieved from the router)
2) Push ADJ key on Adjust remote-controller.
3) Enter “13. ACAP PING TEST” & check Network.
4.3.2. Check Set(Manufacturer)
1) Connect TV-Set & PC with Cross LAN cable.(PC IP :
12.12.2.3)
2) Execute “PINT Test program”, Check setting data of
program. (TV-Set IP : 12.12.2.2)
3) Push Power Only key on Adjust remote-controlle.
4) Click “RUN”, Check “OK” or “NG”
4) After Finished the Download, Automatically DC Off -> On
5) If the TV IS Turn On, Check the updated SW Version and
Tool Option.
Only for training and service purposes
- 14 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
4.5. EDID D/L method
Recommend that don’t connect HDMI and RGB(D-SUB) cable
when downloading the EDID.
If not possible, recommend that connect the MSPG equipment.
There are two methods of downloading the edid data
It is a VESA regulation. A PC or a MNT will display an optimal
resolution through information
Sharing without any necessity of user input. It is a realization
of “Plug and Play”
4.5.1. 1st Method
EDID data’s are automatically downloaded when adjusting the
Tool Options.
Automatically downloaded when pushing the enter key in the
EDID D/L menu.
It takes about 2seconds
4.5.2. 2st Method
=> Caution : Must be checked that the tool option is right or
not. If tool option is wrong, HDMI edid data could
not be downloaded well.
1) Press the ADJ key
2) Move to the 13. EDID D/L and Press the right direction
key(►)
3) Press the right direction key(►) at Start.
4) After about a few seconds, appear “Waiting..” => “OK”, then
complete.
ⓐ Product ID
ⓑ Serial No: Controlled on production line.
ⓒ Month, Year: Controlled on production line:
ex) Monthly : ‘01’ -> ‘01’
Year : ‘2014’ -> ‘18
ⓓ Model Name(Hex): LGTV
ⓔ Checksum(LG TV): Changeable by total EDID data.
ⓕ Vendor Specific(HDMI)
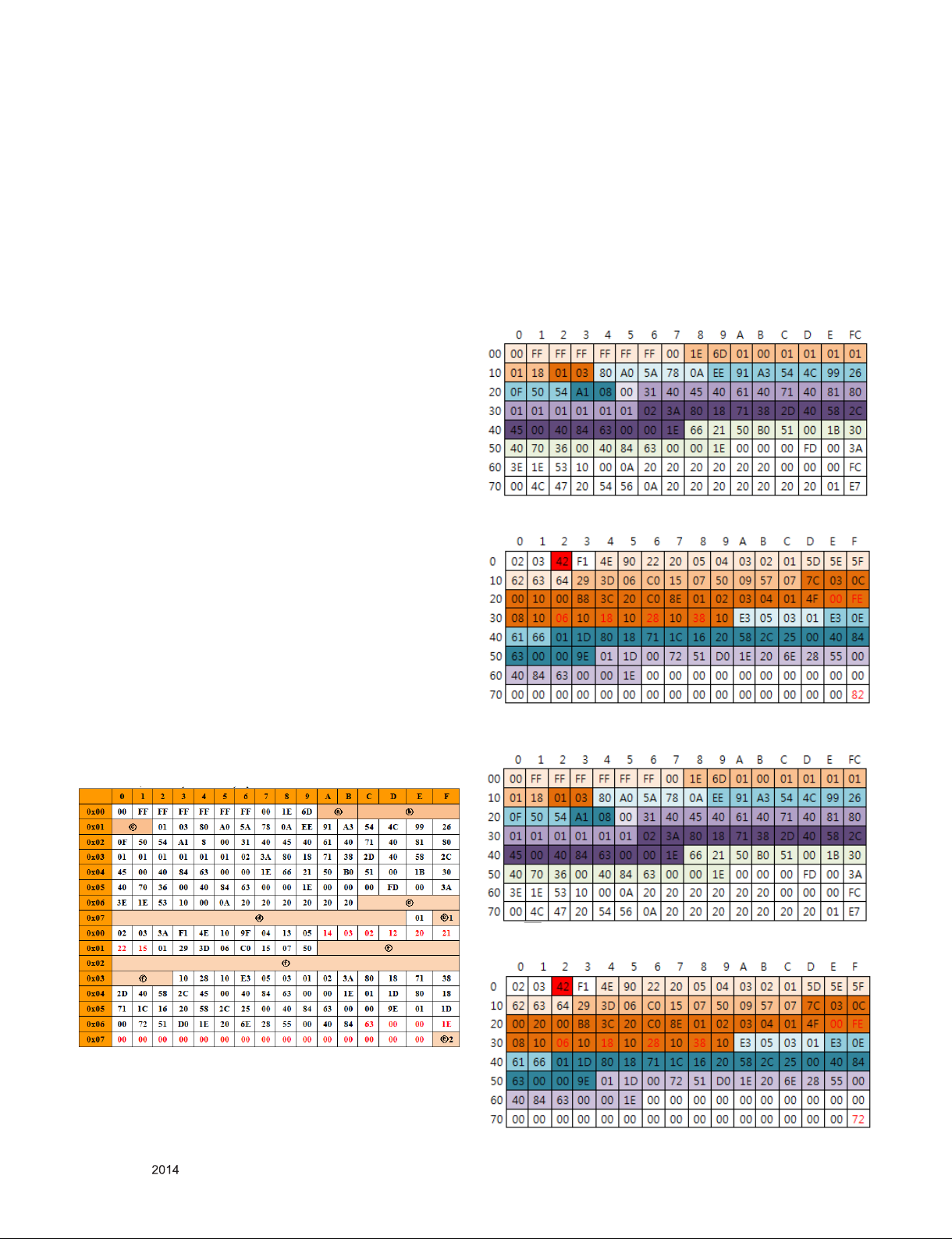
4.5.4.1. EDID
#DTS HDMI1 (C/S: E7 82)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
4.5.3. RS-232C command Method
1) Command : AE 00 10
=> Caution : Don’t connect HDMI and RGB(D-SUB) cable
when downloading the EDID. If the cables are
connected, Downloading of edid could be failed.
4.5.4. EDID DATA
▪ Reference
- HDMI1 ~ HDMI3
- In the data of EDID, bellows may be different by Input mode
#DTS HDMI2 (C/S: E7 72)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-12
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
Only for training and service purposes
- 15 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
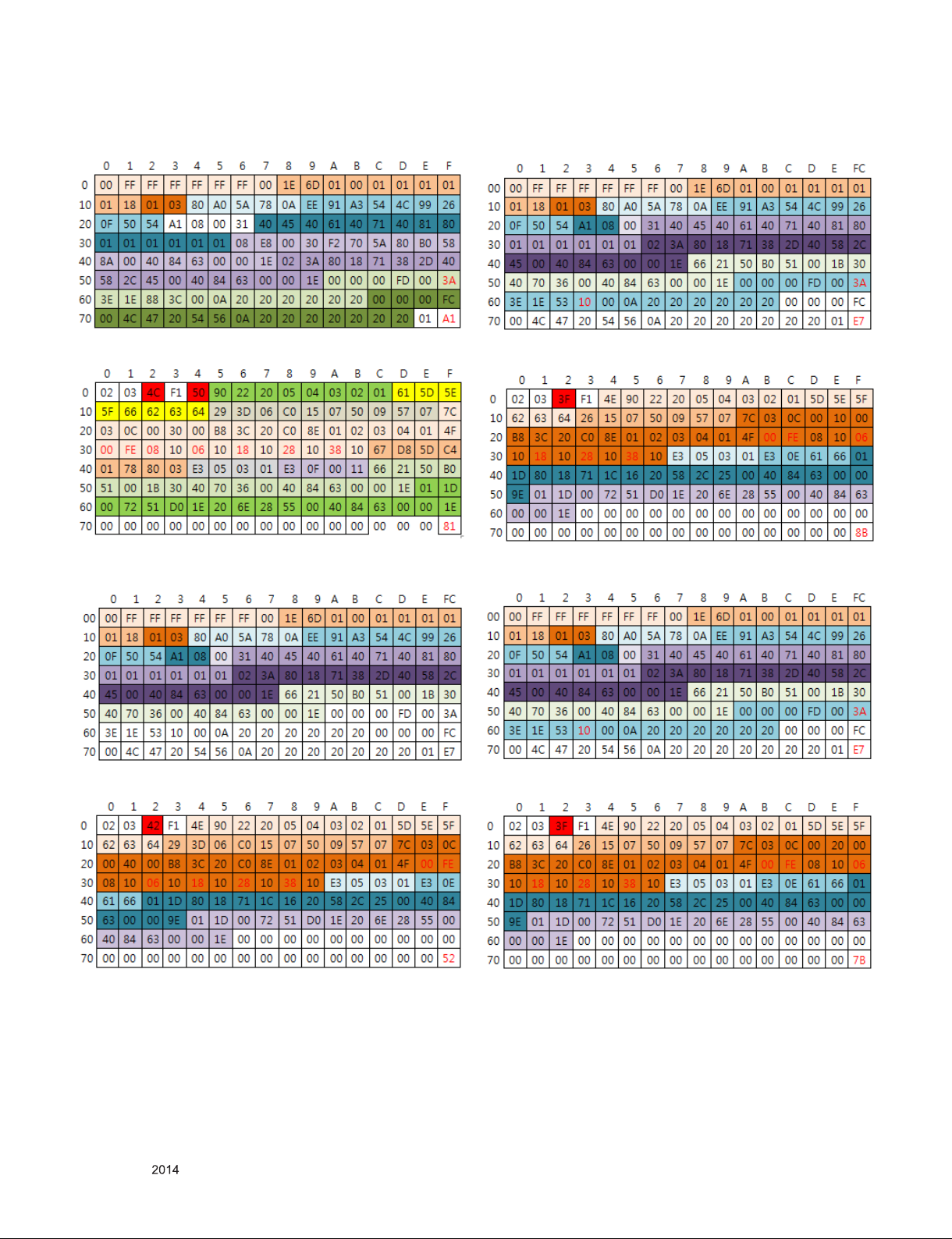
#DTS HDMI3 (C/S: A1 81)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
# AC3 HDMI1 (C/S: E7 8B)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
# DTS HDMI4 (C/S: E7 52)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
# AC3 HDMI2 (C/S: E7 7B)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
Only for training and service purposes
- 16 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

# AC3 HDMI3 (C/S: A1 8A)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
# PCM HDMI1 (C/S: F7 FD)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
# AC3 HDMI4 (C/S: E7 5B)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
# PCM HDMI1(C/S: E7 ED)
Only for training and service purposes
- 17 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
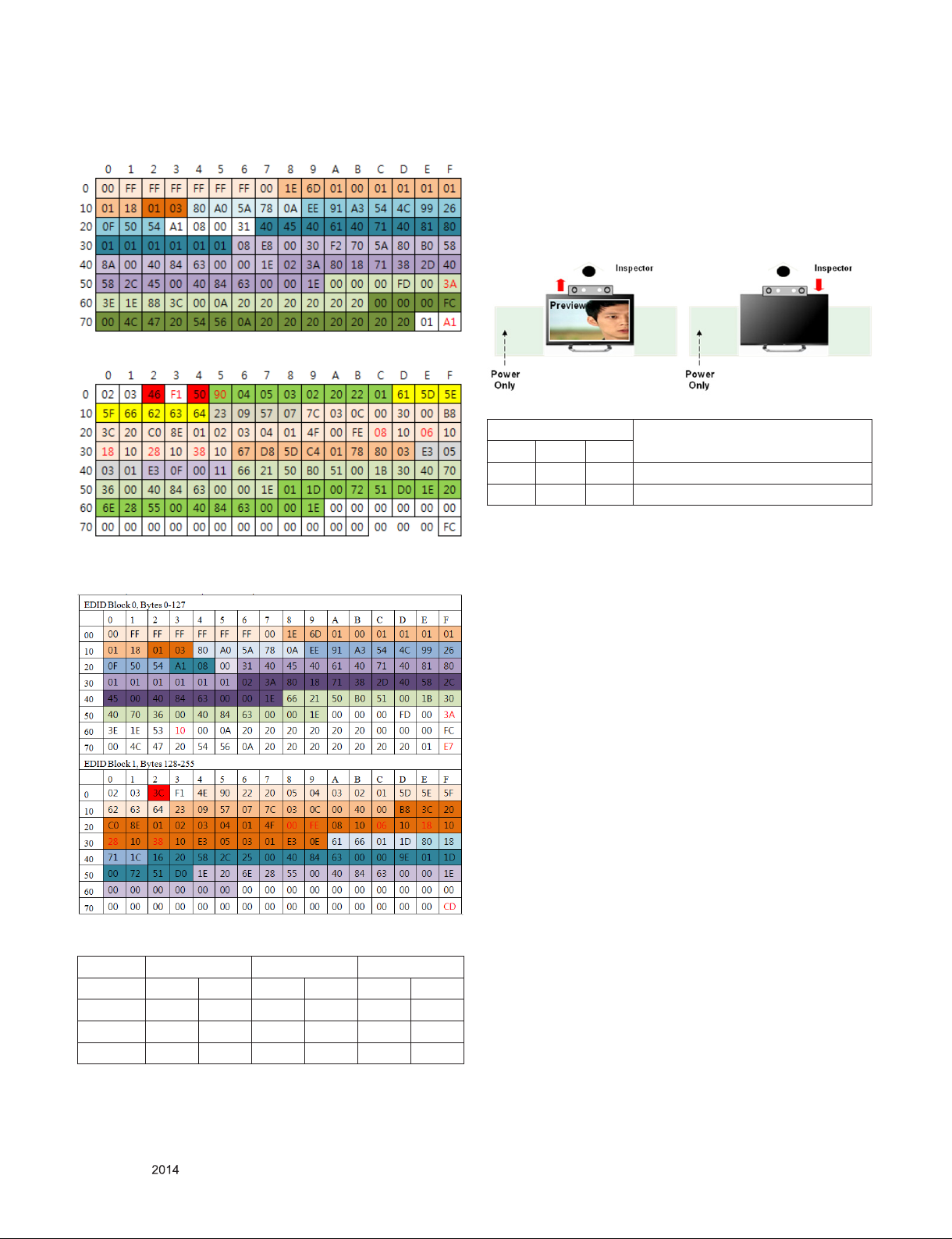
# PCM HDMI3 (C/S: A1 FC)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255
# PCM HDMI4 (C/S: E7 CD)
4.6. Camera Port Inspection
(1) Objective : To check how it connects between Camera and
PCBA normally, and their Function
(2) Test Method : This Inspection is available only Power-Only
Status.
i) Push Camera Up
ii) Camera’s Preview picture appears on TV Set
iii) Push Camera Down
(3) RS-232C Command
RS-232C COMMAND
CMD DATA ID
Ai 00 23 Camera Function Start.
Ai 00 24 Camera Function End.
Explanation
5. SET assembly adjustment method
5.1. Input Area-Option
(1) Profile : Must be changed the Area option value because
being different of each Country’s Language and
signal Condition.
(2) Equipment : adjustment remote control.
(3) Adjustment method
- The input methods are same as other chassis.(Use
IN-START Key on the Adjust Remocon.)
* Checksum (3D HDMI 1/2/3/4)
Input DTS FFh AC3 FFh PCM FFh
HDMI1 E7 82 E7 8B E7 FD
HDMI2 E7 72 E7 7B E7 ED
HDMI3 A1 81 A1 8A A1 FC
HDMI4 E7 52 E7 5B E7 CD
Only for training and service purposes
Refer to Job Expression of each main chassis ass’y
(EBTxxxxxxxx) for Option value.
5.2. Adjustment of White Balance
▪ In case of keeping module is in the circumstance of 0°C, it
should be placed in the circumstance of above 15°C for 2
hours
▪ In case of keeping module is in the circumstance of below
-20°C, it should be placed in the circumstance of above 15°C
for 3 hours.
- Purpose : Adjust the color temperature to reduce the
deviation of the module color temperature.
- Principle : To adjust the white balance without the saturation,
Fix the one of R/G/B gain to 192 (default data) and
decrease the others.
- Adjustment mode : Three modes – Cool / Medium / Warm
- 18 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
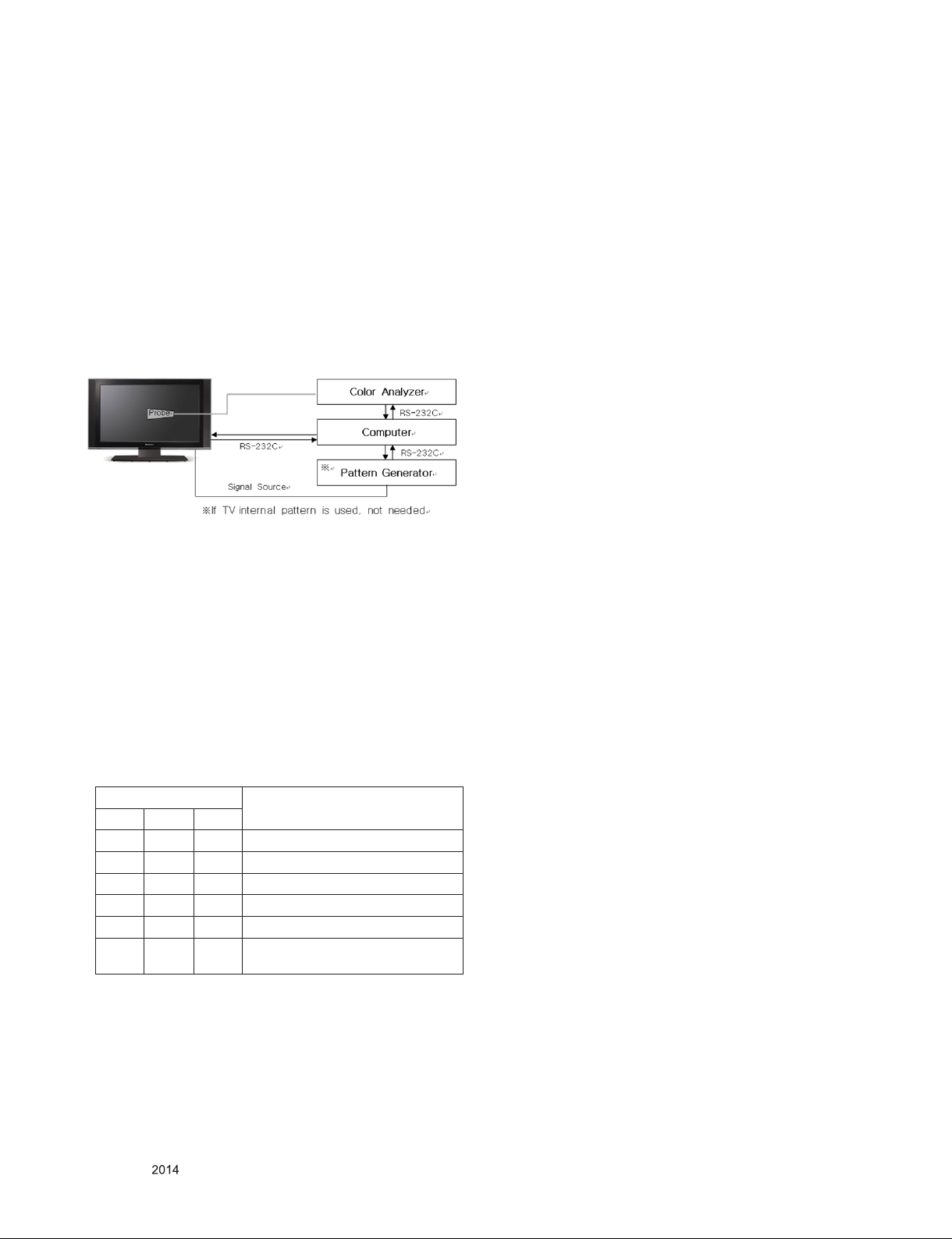
* Required Equipment
▪ Remote controller for adjustment
▪ Color Analyzer : CA100+ or CA-210 or same product (should
be used in the calibrated ch by CS-1000)
- LCD TV : CH-9
- PDP TV : CH-10
- White LED TV : CH-14
- ALEF : CH-18
- RGB LED(MNT) : CH-16
▪ Auto W/B adjustment instrument(only for Auto adjustment)
5.2.1. Adjustment of White Balance :
(For Automatic Adjustment)
Connecting diagram of equipment for measuring (For
Automatic Adjustment)
1) Set TV in ADJ mode using P-ONLY key (or POWER ON
key)
2) Place optical probe on the center of the display
- It need to check probe condition of zero calibration before
adjustment.
3) Connect RS-232C Cable
4) Select mode in ADJ Program and begin a adjustment.
5) When WB adjustment is completed with OK message,
check adjustment status of pre-set mode (Cool, Medium,
Warm)
6) Remove probe and RS-232C cable.
▪ W/B Adj. must begin as start command “wb 00 00” , and
finish as end command “wb 00 ff”, and Adj. offset if need
(1) RS-232C Command used during auto-adj.
RS-232C COMMAND
CMD DATA ID
wb 00 00 Begin White Balance adj.
wb 00 10 Gain adj.(internal white pattern)
wb 00 1f Gain adj. completed
wb 00 20 Offset adj.(internal white pattern)
wb 00 2f Offset adj. completed
wb 00 Ff End White Balance adj.
(internal pattern disappears )
Explanation
5.2.2. Adjustment of White Balance
(For Automatic Adjustment)
5.2.2.1. Adj. condition and cautionary items
1) Lighting condition in surrounding area surrounding lighting
should be lower 10 lux. Try to isolate adj. area into dark
surrounding.
2) Probe location: Color Analyzer (CA-210) probe should be
within 10cm and perpendicular of the module surface (90+/-
2.5°)
3) Aging time
A. After Aging Start, Keep the Power ON status during 5
Minutes.
B. In case of LCD, Back-light on should be checked using
no signal or Full-white pattern.
5.2.2.2. Equipment
1) Color Analyzer: CA-210 (NCG: CH 9 / WCG: CH12 / LED:
CH14)
2) Adj. Computer (During auto adj., RS-232C protocol is
needed)
3) Adjust Remocon
4) Video Signal Generator MSPG-925F 720p/216-Gray
(Model: 217, Pattern: 78)
5.2.2.3. Adjustment
1) Set TV in Adj. mode using POWER ON
2) Zero Calibrate the probe of Color Analyzer, then place it on
the center of LCD module within 10cm of the surface.
3) Press ADJ key -> EZ adjust using adj. R/C > 6. White-
Balance then press the cursor to the right (KEY►). When
KEY(►) is pressed 216 Gray internal pattern will be
displayed.
4) One of R Gain / G Gain / B Gain should be fixed at 192, and
the rest will be lowered to meet the desired value.
5) Adj. is performed in COOL, MEDIUM, WARM 3 modes of
color temperature.
▪ If internal pattern is not available, use RF input. In EZ Adj.
menu 6.White Balance, you can select one of 2 Test-pattern:
ON, OFF. Default is inner(ON). By selecting OFF, you can
adjust using RF signal in 216 Gray pattern.
** R-fix adjustment
Adjust modes (Cool), Fix the R gain to 210 (default data) and
change the others (G/B Gain ).
- Adjust the R gain more than 210 ( If G gain or B gain is less
than 0 , R gain can adjust more than 210 ) and change the
others ( G/B Gain ). Adjust two modes(Medium / Warm), Fix
the one of R/G/B gain to 192 (default data) and decrease the
others.
Only for training and service purposes
- 19 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
5.2.3. LED White balance table
5.2.3.1. Cool Mode
1) Purpose : Especially G-gain fix adjust leads to the
luminance enhancement. Adjust the color
temperature to reduce the deviation of the
module color temperature.
2) Principle : To adjust the white balance without the
saturation, Adjust the G gain more than 172 ( If R
gain or G gain is more than 255 , G gain can
adjust less than 172 ) and change the others (R/B
Gain).
3) Adjustment mode : mode – Cool
5.2.3.2. Medium / Warm Mode
1) Purpose : Adjust the color temperature to reduce the
deviation of the module color temperature.
2) Principle : To adjust the white balance without the
saturation, Fix the one of R/G/B gain to 192
(default data) and decrease the others.
3) Adjustment mode : Two modes – Medium / Warm
▪ Luminance: 204 Gray
▪ Standard color coordinate and temperature using CS-1000
(over 26 inch)
Mode
Cool 0.271 0.270 13,000K 0.0000
Medium 0.286 0.289 9,300K 0.0000
Warm 0.313 0.329 6,500K 0.0000
* Change reason : When vivid mode, more detail than other
▪ Standard color coordinate and temperature using
CA-210(CH-14) – by aging time
(1) Normal line in Korea (From January to February) : LGD
( UB98xxx, UB95/93xxx, UB85xxx, UB83xxx, UC97 Series
models)
1 0-2 286 295 301 314 328 354
2 3-5 284 290 299 309 326 349
3 6-9 282 287 297 306 324 346
4 10-19 279 283 294 302 321 342
5 20-35 276 278 291 297 318 337
6 36-49 274 275 289 294 316 334
7 50-79 273 272 288 291 315 331
8 80-119 272 271 287 290 314 330
9 Over 120 271 270 286 289 313 329
Coordinate
X Y
Aging time
(Min)
Temp △uv
company set.
Cool Medium Warm
X Y X Y X Y
271 270 286 289 313 329
▪ Standard color coordinate and temperature using
CA-210(CH-14) – by aging time
(2) Normal line in Korea (From March to December) : : LGD
(UB98xxx, UB95/93xxx, UB85xxx, UB83xxx, UC97 Series
models)
* Normal line in Mexico : LGD (UB98xxx, UB95/93xxx, UB85xxx,
UB83xxx ,UC97 Series models)
Aging time
(Min)
1 0-2 282 289 297 308 324 348
2 3-5 281 287 296 306 323 346
3 6-9 279 284 294 303 321 343
4 10-19 277 280 292 299 319 339
5 20-35 275 277 290 296 317 336
6 36-49 274 274 289 293 316 333
7 50-79 273 272 288 291 315 331
8 80-119 272 271 287 290 314 330
9 Over 120 271 270 286 289 313 329
Cool Medium Warm
X Y X Y X Y
271 270 286 289 313 329
(3) O/S Module(AUO, INX, Sharp, CSOT, BOE)
Cool Medium Warm
X Y X Y X Y
spec 271 270 286 289 313 329
target 278 280 293 299 320 339
-. To check the Coordinates of White Balance, you have to
measure at the below conditions.
Picture Mode : select Vivid and change
Dynamic Contrast : Off ,
Dynamic Colour : Off,
Clear White : Off
-> Picture Mode change : Vidid -> Vivid(User)
(If you miss the upper condition, the coordinates of W/B can be
lower than the spec.)
Only for training and service purposes
- 20 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

5.3. Model name & Serial number D/L
5.3.1. Notice
1) Serial number D/L is using of scan equipment.
2) Setting of scan equipment operated by Manufacturing
Technology Group.
3) Serial number D/L must be conformed when it is produced
in production line, because serial number D/L is mandatory
by D-book 4.0
4) Check the model name In-start menu -> Factory name
displayed (ex 42LV5500-DD)
5) Check the Diagnostics (DTV country only) -> Buyer model
displayed (ex 42LV5500-DD)
5.3.2. Method : Auto
1) Press “Power on” key of service remocon.(Baud rate :
115200 bps)
2) Connect RS232 Signal Cable to RS-232 Jack
3) Write Serial number by use RS-232.
4) Must check the serial number at Instart menu.
5.4.2. Check the menu on in-start
5.3.3. Method : Manual
* If the TV set is downloaded By OTA or Service man,
Sometimes model name or serial number is initialized.
(Not always) It is impossible to download by bar code scan,
so It need Manual download.
1) Press the ‘instart’ key of ADJ remote controller.
2) Go to the menu ‘6.Model Number D/L’ like below photo.
3) Input the Factory model name or Serial number like photo.
5.4. Wi-Fi MAC Address Check
5.4.1. Using RS232 Command
Command Set ACK
Transmission [A][l][][Set ID][][20][Cr] [O][K][x] or [N][G]
5.5. LAN Inspection
5.5.1. LAN Port connection with PCB
1) Network setting at MENU Mode of TV
2) Setting automatic IP
3) Setting state confirmation
4) If automatic setting is finished, you confirm IP and MAC
Address
5.6. WIDEVINE Key Inspection
1) Confirm Key input Data at the “IN START” MENU Mode
Only for training and service purposes
- 21 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

5.7. Local Dimming Inspection (Optional)
1) Press ‘TILT” key of the Adj. R/C and check moving patterns.
The black bar patterns moves from top left to bottom right. If
local dimming function does not work, a whole screen
shows full white.
5.8. Motion Remote controller Inspection
1) Equipment : Motion remote controller for test, IR-KEYCODE remote controller for test Check battery before test.
(Recommend : Change battery for every Lot.)
2) Process
- If you select the ‘start key(wheel)’ on the controller, you can
pairing with the TV SET.
- You can check the cursor on the TV Screen, when select the
‘Wheel Key’ on the controller
- You must remove the pairing with the TV Set by select ‘Back
+ Home Key’ on the controller
5.9. 3D function test
1) Equipment : Pattern Generator MSHG-600, MSPG-6100
[SUPPORT HDMI1.4, HDMI mode 872, pattern No. 83
2) Process
(A) Please input 3D test pattern like below (HDMI mode NO.
872 , pattern No.83)
(C) Don’t wear a 3D Glasses, Check the picture like below.
5.10. HDMI ARC Function Inspection
5.10.1. Test equipment
- Optic Receiver Speaker
- MSHG-600 (SW: 1220 ↑)
- HDMI Cable (for 1.4 version)
5.10.2. Test method
(1) Insert the HDMI Cable to the HDMI ARC port from the
master equipment (HDMI1)
(2) Check the sound from the TV Set
(B) When 3D OSD appear automatically , then select green
button.
Only for training and service purposes
- 22 -
(3) Check the Sound from the Speaker or using AV & Optic
TEST program (It’s connected to MSHG-600)
* Remark: Inspect in Power Only Mode and check SW version
in master equipment
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

5.11. Eye-Q Green Inspection Guide
(Change to Motion EYE care)
1) Turn on the TV set.
2) Press “EYE” button on the Adjustment remote controller.
3) Block the Intelligent Sensor module on the front C/A about 6
seconds. When the “Sensor Data” is lower than 20, you can
see the “OK” message
=> If it doesn’t show “OK” message, the Sensor Module is
defected one. You have to replace that with a good one.
5.13. Camera Function Inspection
(1) Objective : To check how it connects between Camera and
PCBA normally, and their Function
(2) Test Method : This Inspection is available only Power-Only
Status.
i) Slide Camera Up
ii) Camera’s Preview picture appears on TV Set
iii) Slide Camera Down
5.14. PIP/ W&R Function Inspection
4) After check the “OK” message come out, take out your hand
from the Sensor module.
=> Check “Sensor Data” value change from “0” to “300” or not.
If it doesn’t change the value, the sensor is also defected
one. You have to replace it.
5.12. AUDIO
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1 Audio practical
max Output, L/R
(Distortion=10%
max Output)
2
Speaker
(8Ω Impedance)
*Measurement condition:
(1) RF input: Mono, 1KHz sine wave signal, 100% Modulation
(2) CVBS, Component: 1KHz sine wave signal (0.4Vrms)
(3) RGB PC: 1KHz sine wave signal (0.7Vrms)
9.0 10.0 12.0 W Measurement
condition
8.5 8.9 9.8 Vrms
10.0 15.0 W Measurement
condition
(1) Objective : To check the connection between sub tuner and
PCBA, and their Function
(2) Test Method : This Inspection is available only Power-Only
Status.
1) Press exit key of the Adj. R/C and Press PIP key.
2) Check that the SUB TUNER pop up window on the TV
Set.
3) Check that the normal operation (picture, sound) of DTV
on the TV Set.
Only for training and service purposes
- 23 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.

5.15. Manual ADC Calibration(Optional)
5.15.1. Adjust method
(1) Enter Service Mode by pushing “ADJ” key
(2) Enter ADC Calibration by pushing “►” key at “9. ADC
Calibration”
(3) Select [Reset] button by pressing Enter key
(4) Change “OTP” to “Internal” by pushing “►” key
(5) Select [Start] button by pressing Enter key, then it will
operate ADC adjustment.
5.16.3. Check point
1) Test voltage
(A) 3 Poles
- GND: 1.5KVac/min at 100mA
- SIGNAL: 3KVac/min at 100mA
2) TEST time: 1 second
3) TEST POINT
(B) 3 Poles
- GND Test = POWER CORD GND and SIGNAL CABLE
GND.
- Hi-pot Test = POWER CORD GND and LIVE & NEUTRAL.
4) LEAKAGE CURRENT: At 0.5mArms
5.16. GND and Hi-Pot test
5.16.1. GND & HI-POT auto-check preparation
1) Check the POWER CABLE and SIGNAL CABE insertion
condition
5.16.2. GND & HI-POT auto-check
1) Pallet moves in the station. (POWER CORD / AV CORD is
tightly inserted)
2) Connect the AV JACK Tester.
3) Controller (GWS103-4) on.
4) GND Test (Auto)
- If Test is failed, Buzzer operates.
- If Test is passed, execute next process (Hi-pot test).
(Remove A/V CORD from A/V JACK BOX)
5) HI-POT test (Auto)
- If Test is failed, Buzzer operates.
- If Test is passed, GOOD Lamp on and move to next
process automatically.
Only for training and service purposes
- 24 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
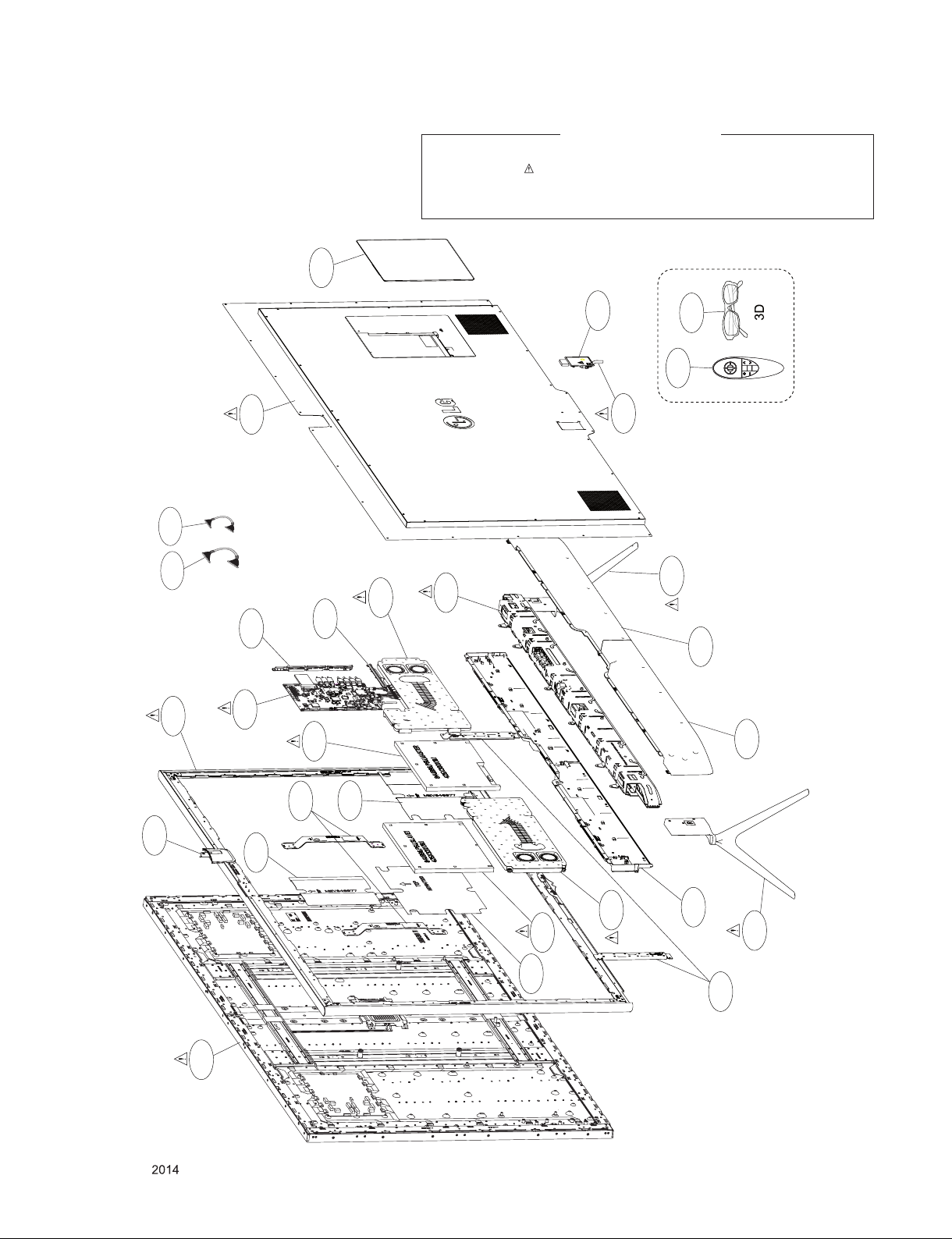
EXPLODED VIEW
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These
parts are identified by in the Schematic Diagram and EXPLODED VIEW.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as
recommended in this manual to prevent X-RADIATION, Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
430
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
LV2
LV1
300
400
521
540
522
530
123
120
710
AG1
A22
700
901
411
410
CAM1
822
200
Only for training and service purposes
420
820
- 25 -
531
821
122
310
900
810
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright © LG Electronics. Inc. All rights reserved.
Clock for LG1154D
Copyright ⓒ 2014 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use Only
For D9 DFT
20131016 version
BIT(0/1)
00
01
10
11
BIT2
BIT3
BIT4
BIT(6/7)
00
01
10
11
BIT8
BIT9
BIT10 Reserved
System Configuration
MAIN Clock(24Mhz)
8pF
C100
8pF
C101
System Clock for Analog block(24Mhz)
OPT
R100 33
R101 33
OPT
T32
0.1uF
P100
12505WS-10A00
T32
11
+3.3V_NORMAL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
X-TAL_1
GND_1
1
2
3
X-TAL_2
OPT
R160 10K
1M
R108
X100
24MHz
4
GND_2
PLL SET[1:0] : internal pull up
"00" : CPU(1200Mhz),M0 / M1 DDR(792,792 Mhz)
PLLSET1
"01" : CPU(1056Mhz),M0 / M1 DDR(672,672 Mhz)
"10" : CPU(1056Mhz),M0 / M1 DDR(792,792 Mhz)
PLLSET0
"11" : CPU( 960Mhz),M0 / M1 DDR(792,792 Mhz)
OPT
R167
33
OPT
OPT
OPT
R163 10K
R166 10K
R168 10K
WebOS UHD HW Option
+3.3V_NORMAL
10K
BIT0_1
BIT1_1
R112
ATSC
KR
BR
High
FHD
U14
D9
AJJA
T/C
T2/C_PIP
T2/C
T2/C/S2
High
OLED
URSA7/URSA9PBIT5
R110 10K
BIT0_0
R109 10K
JP
JP
Low
UHD
Non_U14
Non_D9
T2/C_PIP
Low
LCD
10K
BIT1_0
R111
TW/COL
T/C
T2/C
BIT0
BIT1
BIT2
BIT3
BIT4
BIT5
BIT6
BIT7
BIT8
BIT9
BIT10
DVB
TW/COL
CN/HK
EU
AJJA
Resolution
Support U14
D9 Model
URSA7/URSA9
EU/CIS
T/C
T2/C/S2/ATV_EXT
T2/C
T2/C/S2/AT
Display
Reserved
North.AM.
URSA9
XIN_MAIN
XO_MAIN
Jtag I/F
For Main
TRST_N0
TDI0
TDO0
TMS0
TCK0
SOC_RESET
FHD
U14
R114 10K
UHD
NON_U14
R113 10K
CN/HK
Default
R116 10K
R115 10K
D9
R120 10K
NOT_D9
R119 10K
KR
ATSC_PIP
ATV_SOC
ATV_EXT
URSA9
BIT6_1
R124 10K
R122 10K
BIT6_0
R123 10K
R121 10K
URSA7/URSA9P
North.AM
ATSC_PIP
ATV_SOC
ATV_EXT
NVRAM
EEPROM_RENESAS
IC102
R1EX24256BSAS0A
A0
1
A1
2
A2
A0’h
3
VSS
4
OP MODE[1:0]
"00" : Normal Mode
"01/10/11" : Internal Test mode
+3.3V_NORMAL
OPT
R133 33
R134 33
OPT
OLED
BIT7_1
R126 10K
R128 10K
R129 10K
LCD
OPT
BIT7_0
R125 10K
BR
ISDB_PIP
ISDB
OPT
R130 10K
R127 10K
JP
Default
R131 10K
R132 10K
VCC
8
WP
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
OPM1
OPM0
+3.3V_LNA_TU
C103
0.1uF
D13_INT
EPHY_INT
R135
1.8K
KR_PIP_NOT
1.5K
KR_PIP
R135-*1
+3.3V_NORMAL
Write Protection
- Low : Normal Operation
- High : Write Protection
AR102
+3.3V_NORMAL
OPT
INSTANT_MODE0
+3.3V_NORMAL
R137
1.8K
R136
1.8K
R138
1.8K
KR_PIP_NOT
1.5K
KR_PIP
R136-*1
33
INSTANT boot MODE
"1 : Instant boot
"0 : normal
3.3K
R150
(internal pull down)
R164331/16W
5%
+3.3V_TUNER
R142
1.8K
R141
1.8K
I2C_SCL5
I2C_SDA5
INSTANT_BOOT
SOC_RESET
R149
10K
H13_CONNECT
+3.3V_NORMAL
R144
1.8K
R143
1.8K
EEPROM_ST
M24256-BRMN6TP
E0
1
E1
2
E2
3
VSS
4
EEPROM_ATMEL
AT24C256C-SSHL-T
A0
1
A1
2
A2
3
GND
4
BOOT_MODE0
R151
I2C_SCL_MICOM_SOC
I2C_SDA_MICOM_SOC
I2C PULL UP
R146
1.8K
R147
4.7K
R145
1.8K
I2C_CH1_pullup_4.7K
IC102-*1
VCC
8
WC
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
IC102-*2
VCC
8
WP
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
+3.3V_NORMAL
BOOT MODE
"0 : EMMC
"1 : TEST MODE
3.3K
R117
OPT
3.3K
R118
XIN_MAIN
XO_MAIN
C108
0.1uF
H13A_SCL
H13A_SDA
TRST_N0
PLLSET1
PLLSET0
BOOT_MODE
CAM_TRIGGER_DET
SOC_RX
10K
SOC_TX
M_REMOTE_RX
M_REMOTE_TX
M_REMOTE_RTS
M_REMOTE_CTS
SOC_SPI1_CS
SOC_SPI1_MOSI
SOC_SPI1_MISO
U14 SPI
SOC_SPI1_SCLK
SOC_SPI0_CS0
SOC_SPI0_MOSI
SOC_SPI0_MISO
D13 SPI
SOC_SPI0_SCLK
I2C_SCL1
I2C_SDA1
I2C_SCL2_SOC
I2C_SDA2_SOC
I2C_SCL4
I2C_SDA4
I2C_SCL5
I2C_SDA5
I2C_SCL6
I2C_SDA6
I2C_SDA_MICOM
I2C_SCL_MICOM
I2C_SDA2
I2C_SCL2
I2C_CH1_pullup_4.7K
R148
4.7K
I2C_SDA1
I2C_SCL1
I2C_SDA_MICOM_SOC
I2C_SCL_MICOM_SOC
I2C_SDA2_SOC
I2C_SCL2_SOC
I2C_SDA4
I2C_SCL4
I2C_SDA5
I2C_SCL5
I2C_SDA6
I2C_SCL6
OPM1
TMS0
TCK0
TDI0
TDO0
BOOT_MODE
H13D_XTAL_560ohm
H13D_XTAL_100ohm
R152-*1
AR100
33
0
I2C for tuner
I2C for tuner
560
R152
100
R1020
R104
I2C_CH1_pullup_3.3K
R148-*1
3.3K
R147-*1
3.3K
I2C_CH1_pullup_3.3K
A26
XIN
B26
XOUT
B27
XTAL_BYPASS
AT37
H13DA_XTAL
AU16
PORES_N
AD34
OPM1
AD33
OPM0
AT26
H13DA_SCL
AU26
H13DA_SDA
AP9
TRST_N0
AN9
TMS0
AP11
TCK0
AN11
TDI0
AN10
TDO0
AM10
TRST_N1
AM9
TMS1
AM11
TCK1
AM12
TDI1
AL11
TDO1
AL9
PLLSET1
AL10
PLLSET0
AE34
BOOT_MODE
Y33
EXT_INTR3/GPIO70
W32
EXT_INTR2/GPIO69
W33
EXT_INTR1/GPIO68
W34
EXT_INTR0/GPIO67
AU12
UART0_RXD
AT12
UART0_TXD
AU13
UART1_RXD
AT13
UART1_TXD
AP12
UART1_RTS
AR12
UART1_CTS
AE35
SPI_CS0/GPIO36
AE36
SPI_DO0/GPIO38
AF36
SPI_DI0/GPIO39
AF35
SPI_SCLK0/GPIO37
AG34
SPI_CS1
AF33
SPI_DO1
AG33
SPI_DI1
AG32
SPI_SCLK1
AR15
SCL0/GPIO66
AP15
SDA0/GPIO65
AR16
SCL1/GPIO64
AP16
SDA1/GPIO79
AP17
SCL2/GPIO78
AR17
SDA2/GPIO77
AP6
SCL3
AR6
SDA3
AH32
SCL4
AJ33
SDA4
AH34
SCL5
AH33
SDA5
I2C_SDA_MICOM_SOC
I2C_SCL_MICOM_SOC
I2C_SDA2_SOC
I2C_SCL2_SOC
+3.3V_NORMAL
CAM_CE1_N
CAM_CE2_N
CAM_CD1_N/GPIO76
F33
F34
D32
E32
/PCM_CE1
/PCM_CE2
CAM_CD1_N
CI
USB_CTL3
/USB_OCD3
/USB_OCD2
USB_CTL2
K35
K36
K37
L35
EB_CS3/GPIO93
EB_CS2/GPIO92
EB_CS1/GPIO91
EB_CS0/GPIO90
EB_BE_N1
EB_WE_N
EB_OE_N
H35
H36
J35
J36
H37
EB_WE_N/GPIO95
EB_WAIT/GPIO94
EB_OE_N/GPIO82
EB_BE_N1/GPIO81
EB_ADDR[0-14]
EB_BE_N0
EB_ADDR[14]
EB_ADDR[13]
EB_ADDR[12]
G37
G36
G35
F36
EB_BE_N0/GPIO80
EB_ADDR15/GPIO89
EB_ADDR14/GPIO88
EB_ADDR13/GPIO103
EB_ADDR12/GPIO102
EB_ADDR[6]
EB_ADDR[9]
EB_ADDR[8]
EB_ADDR[7]
EB_ADDR[10]
EB_ADDR[11]
F35
E36
E37
E35
D37
EB_ADDR9/GPIO99
EB_ADDR8/GPIO98
EB_ADDR7/GPIO97
EB_ADDR11/GPIO101
EB_ADDR10/GPIO100
EB_ADDR[3]
EB_ADDR[4]
EB_ADDR[5]
D36
D35
C36
C35
EB_ADDR6/GPIO96
EB_ADDR5/GPIO111
EB_ADDR4/GPIO110
EB_DATA[0-7]
EB_ADDR[2]
EB_ADDR[0]
EB_DATA[6]
EB_DATA[7]
EB_ADDR[1]
B37
B36
B35
C32
B33
EB_ADDR3/GPIO109
EB_ADDR2/GPIO108
EB_ADDR1/GPIO107
EB_ADDR0/GPIO106
EB_DATA7/GPIO105
EB_DATA[5]
A33
EB_DATA6/GPIO104
EB_DATA5/GPIO119
IC100
LG1154D_H13D
CAM_CD2_N/GPIO75
CAM_VS1_N/GPIO86
CAM_VS2_N/GPIO85
CAM_IREQ_N/GPIO73
CAM_RESET
CAM_INPACK/GPIO74
CAM_VCCEN_N/GPIO87
CAM_WAIT_N/GPIO84
CAM_REG_N/GPIO72
CAM_IOIS16_N/GPIO83
SC_CLK/GPIO130
SC_DETECT/GPIO133
SC_VCCEN/GPIO129
SC_VCC_SEL/GPIO128
SC_RST/GPIO131
SC_DATA/GPIO132
SD_CLK/GPIO125
SD_CMD/GPIO124
SD_CD_N/GPIO123
SD_WP_N/GPIO122
SD_DATA3/GPIO121
SD_DATA2/GPIO120
SD_DATA1/GPIO135
SD_DATA0/GPIO134
USB2_2_DP0
USB2_2_DM0
USB2_2_TXRTUNE
G32
G33
F32
G34
D33
H32
E33
D34
H33
T33
U33
T32
V32
V33
V34
A25
C25
B25
E25
D25
E24
D24
C24
L37
L36
K34
1%
200
R157
CAMERA_DP
CAM_CD2_N
R153
10K
PCM_RESET
CAM_IREQ_N
CI
R154
10K
CAM_REG_N
CAM_WAIT_N
PCM_5V_CTL
R155
10K
CI
SMARTCARD_CLK/SD_EMMC_DATA[0]
SMARTCARD_DET/SD_EMMC_DATA[3]
interface
Only SMART CARD
SMARTCARD_PWR_SEL/SD_EMMC_DATA[1]
SMARTCARD_VCC/SD_EMMC_CMD
SMARTCARD_DATA/SD_EMMC_CLK
SMARTCARD_RST/SD_EMMC_DATA[2]
CAMERA_DM
EB_DATA[0]
EB_DATA[2]
EB_DATA[1]
EB_DATA[3]
EB_DATA[4]
C33
A34
B34
C34
A36
EB_DATA4/GPIO118
EB_DATA3/GPIO117
EB_DATA2/GPIO116
EB_DATA1/GPIO115
USB2_1_DP0
USB2_1_DM0
USB2_1_TXRTUNE
M37
M36
K33
AU7
1%
200
HUB_DP
HUB_DM
R159
EMMC_DATA[0-7]
EMMC_CMD
EMMC_CLK
EMMC_RST
EMMC_DATA[7]
Y37
Y36
W35
T36
W36
EMMC_CLK
EMMC_CMD
EMMC_DATA7
EMMC_RESETN
EB_DATA0/GPIO114
USB2_0_DP
USB2_0_DM
USB2_0_TXRTUNE
USB3_DP0
USB3_DM0
AT7
AP7
P37
P36
N36
WIFI_DM
WIFI_DP
R161 200 1%
USB3_DM
USB3_DP
EMMC_DATA[3]
EMMC_DATA[4]
EMMC_DATA[6]
EMMC_DATA[5]
V35
V37
V36
U35
EMMC_DATA6
EMMC_DATA5
EMMC_DATA4
EMMC_DATA3
USB3_RX0P
USB3_RX0M
USB3_TX0P
USB3_TX0M
N37
R36
R37
N34
1%
200
R162
C105 0.1uF
C104 0.1uF
USB3_TX0P
USB3_RX0P
USB3_RX0M
USB3_TX0M
EPHY_MDIO
EPHY_REFCLK
EPHY_CRS_DV
EMMC_DATA[1]
EMMC_DATA[2]
EMMC_DATA[0]
U36
U37
AU11
AU8
AT8
EMMC_DATA2
USB3_RESREF
P33
RMII_MDIO
EMMC_DATA1
EMMC_DATA0
RMII_CRS_DV
RMII_REF_CLK
USB3_REFPADCLKM
USB3_REFPADCLKP
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
P32
L32
L33
M31
AC-coupling CAP
Place near by LG1154D
EPHY_MDC
AR8
AR10
RMII_MDC
NC_4
AJ31
EPHY_EN
AT10
RMII_TXEN
J32
EPHY_TXD1
EPHY_RXD0
EPHY_TXD0
EPHY_RXD1
AU10
AT11
AR11
RMII_TXD1
RMII_TXD0
RMII_RXD1
RMII_RXD0
GPIO23/UART2_TX
GPIO22/UART2_RX
PHY0_ARC_OUT_0
HUB_PORT_OVER0
HUB_VBUS_CTRL0
GPIO136
GPIO137
GPIO138
GPIO139
J33
K32
J34
DPC_CTL
SIL9617_INT
R9531_RESET
R9531_FLASH_WP
GPIO31
GPIO30
GPIO29
GPIO28
GPIO27
GPIO26
GPIO25
GPIO24
GPIO21
GPIO20
GPIO19
GPIO18
GPIO17
GPIO16
GPIO15
GPIO14
GPIO13
GPIO12
GPIO11
GPIO10
GPIO9
GPIO8
GPIO7
GPIO6
GPIO5
GPIO4
GPIO3
GPIO2
GPIO1
GPIO0
DDCD0_CK
DDCD0_DA
HPD0
PHY0_RX0N_0
PHY0_RX0P_0
PHY0_RX1N_0
PHY0_RX1P_0
PHY0_RX2N_0
PHY0_RX2P_0
PHY0_RXCN_0
PHY0_RXCP_0
AL34
AM33
AM32
AF30
AN34
AK34
AL33
AL32
AR9
AM5
AM6
R107 100
AM7
AL6
AK7
AK6
AK5
AJ5
AJ6
AJ7
AH6
AG7
AG6
AG5
AF5
AH30
AG30
AN33
AK33
AE30
AD30
R105 0
AN32
USB3.0_REDRIVER_CTL
AK32
AC32
AC33
AB33
AE37
AC36
AC37
AB36
AB37
AA36
AA37
AD36
AD37
R32
R33
RF_SWITCH_CTL
For connecting
SIC debug tool
CAM_SLIDE_DET
Compensation_Done
/RST_PHY
HDMI_HPD_3
HDMI_HPD_2
AUD_LRCH2
INSTANT_BOOTOPM0
SC_DET
AV1_CVBS_DET
AMP_RESET_N
COMP1_DET
M_RFModule_RESET
HP_DET
SIL9617_RESET
/TU_RESET1
U14_RESET
D14_HWRESET
FRC_FLASH_WP
/RST_HUB
/TU_RESET2
MN864778_RESET
USB3_EN
AMP_RESET_N_1
AR101
3.3K
SPDIF_OUT_ARC
HDMI_RX0-
HDMI_RX0+
HDMI_RX1-
HDMI_RX1+
HDMI_RX2HDMI_RX2+
HDMI_CLK-
HDMI_CLK+
/USB_OCD1
USB_CTL1
+3.3V_NORMAL
R175
3.3K
HDMI_MUX_SEL
To surround amp
local dimming
I2C port
+3.3V_NORMAL
Not Used Net (UB85/95/UC89)
CAM_TRIGGER_DET
H13_CONNECT
SOC_SPI1_CS
SOC_SPI1_MOSI
SOC_SPI1_MISO
SOC_SPI1_SCLK
CAM_SLIDE_DET
AUD_LRCH2
AMP_RESET_N_1
U14_RESET
/RST_HUB
AMP_RESET_N_1
M_REMOTE_RX
M_REMOTE_TX
M_REMOTE_RTS
M_REMOTE_CTS
Not Used Net (Only OLED)
DPC_CTL
Not Used Net (Only OLED 77EC98)
AMP_RESET_N
+3.3V_NORMAL
For ISP
R103
3.3K
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FIRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFACTURES SPECIFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BSD-14Y-UD-001-HD
2013-12-17
H13 D CHIP
LG1154A
Copyright ⓒ 2014 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use Only
LG1154D
AVDD25
VDD25_LTX
VDDC10
AVDD33_CVBS
VDD25_REF
VDD25_LTX
VDD25_AUD
VDD10_XTAL
VDD10_XTAL
VSS25_REF
AVDD33_XTAL
LG1154A
H13A_NON_BRAZIL
E11
F5
F6
F11
G5
H13
J13
P12
P13
R5
R6
N16
T13
T14
N10
N11
N12
N13
U5
N7
N8
N9
F14
M6
N6
M13
F15
F16
H15
J15
J16
K15
K16
R18
G7
G8
G9
H7
H12
J7
J12
K7
K12
L7
L12
M7
M12
T17
T18
M8
G10
G11
G12
V5
C3
D3
D4
D17
E4
F4
F7
F8
F9
F10
F12
F13
F17
F18
G4
G6
G13
G14
G15
G16
G17
G18
H4
H5
H6
H8
H9
H10
H11
VDD33_1
VDD33_2
VDD33_3
VDD33_4
VDD33_5
VDD33_6
VDD33_7
VDD33_8
VDD33_9
VDD33_10
VDD33_11
VDD33_XTAL
AVDD33_CVBS_1
AVDD33_CVBS_2
VDD25_CVBS_1
VDD25_CVBS_2
VDD25_VSB_1
VDD25_VSB_2
VDD25_REF
VDD25_COMP_1
VDD25_COMP_2
VDD25_COMP_3
VDD25_APLL
VDD25_AUD_1
VDD25_AUD_2
VDD25_AAD
LTX_LVDD_1
LTX_LVDD_2
SDRAM_VDDQ_1
SDRAM_VDDQ_2
SDRAM_VDDQ_3
SDRAM_VDDQ_4
SDRAM_VDDQ_5
VDD10_XTAL
VDDC10_1
VDDC10_2
VDDC10_3
VDDC10_4
VDDC10_5
VDDC10_6
VDDC10_7
VDDC10_8
VDDC10_9
VDDC10_10
VDDC10_11
VDDC10_12
VDDC10_13
AVDD10_CVBS
AVDD10_VSB
AVDD10_LLPLL
DVDD10_APLL_1
DVDD10_APLL_2
LTX_VDD
VSS25_REF
GND_1
GND_2
GND_3
GND_4
GND_5
GND_6
GND_7
GND_8
GND_9
GND_10
GND_11
GND_12
GND_13
GND_14
GND_15
GND_16
GND_17
GND_18
GND_19
GND_20
GND_21
GND_22
GND_23
GND_24
GND_25
GND_26
GND_27
GND_28
GND_29
LG1154AN_H13A
AVDD33
IC101
GND_30
GND_31
GND_32
GND_33
GND_34
GND_35
GND_36
GND_37
GND_38
GND_39
GND_40
GND_41
GND_42
GND_43
GND_44
GND_45
GND_46
GND_47
GND_48
GND_49
GND_50
GND_51
GND_52
GND_53
GND_54
GND_55
GND_56
GND_57
GND_58
GND_59
GND_60
GND_61
GND_62
GND_63
GND_64
GND_65
GND_66
GND_67
GND_68
GND_69
GND_70
GND_71
GND_72
GND_73
GND_74
GND_75
GND_76
GND_77
GND_78
GND_79
GND_80
GND_81
GND_82
GND_83
GND_84
GND_85
GND_86
GND_87
GND_88
GND_89
GND_90
GND_91
GND_92
GND_93
GND_94
GND_95
GND_96
GND_97
GND_98
GND_99
GND_100
GND_101
GND_102
GND_103
GND_104
GND_105
GND_106
GND_107
GND_108
GND_109
GND_110
GND_111
GND_112
GND_113
GND_114
GND_115
GND_116
IC100
LG1154D_H13D
A24
M0_DDR_VREF1
A4
M0_DDR_VREF2
A2
M1_DDR_VREF1
Y1
M1_DDR_VREF2
P26
XTAL_VDD
N26
XTAL_VDDP
M21
VDD33_1
Y30
VDD33_2
AA30
VDD33_3
AE8
VDD33_4
AF8
VDD33_5
AK13
VDD33_6
AK24
VDD33_7
AK25
VDD33_8
M22
AVDD33_USB_1
M23
AVDD33_USB_2
AK11
AVDD33_BT_USB_1
AK12
AVDD33_BT_USB_2
AF25
AVDD33_HDMI_1
AF26
AVDD33_HDMI_2
R31
SP_VQPS
AE23
VDD25_LVRX_1
AF23
VDD25_LVRX_2
AE14
VTXPHY_VDD25_1
AF14
VTXPHY_VDD25_2
N25
VDD25_DR3PLL
AD26
GPLL_AVDD25
H10
VDD15_M0_1
H11
VDD15_M0_2
H12
VDD15_M0_3
H13
VDD15_M0_4
H14
VDD15_M0_5
H15
VDD15_M0_6
H16
VDD15_M0_7
H17
VDD15_M0_8
H18
VDD15_M0_9
H19
VDD15_M0_10
H20
VDD15_M0_11
H21
VDD15_M0_12
H22
VDD15_M0_13
H23
VDD15_M0_14
H24
VDD15_M0_15
H25
VDD15_M0_16
H7
VDD15_M1_1
H8
VDD15_M1_2
J8
VDD15_M1_3
K8
VDD15_M1_4
L7
VDD15_M1_5
L8
VDD15_M1_6
M8
VDD15_M1_7
N7
VDD15_M1_8
N8
VDD15_M1_9
P8
VDD15_M1_10
R7
VDD15_M1_11
R8
VDD15_M1_12
T8
VDD15_M1_13
U8
VDD15_M1_14
V8
VDD15_M1_15
W8
VDD15_M1_16
LG1154AN_H13A_ISDB-T (LG1154AN-IT)
P17
P18
J17
N18
D18
M18
M17
U13
V14
V15
V13
U15
U14
U10
V12
V10
U11
V11
U12
E3
K3
K2
A8
B8
U7
V6
V7
T5
T6
U8
V8
V9
U9
H13A_BRAZIL
XIN_SUB
XO_SUB
VSB_AUX_XIN
XTAL_BYPASS
CLK_24M
XTAL_SEL0
XTAL_SEL1
PORES_N
OPM0
OPM1
H13A_SCL
H13A_SDA
CVBS_IN3
CVBS_IN2
CVBS_IN1
CVBS_VCM
BUF_OUT1
BUF_OUT2
REFT
REFB
ADC1_COM
ADC2_COM
ADC3_COM
SC1_SID
SC1_FB
PB1_IN
Y1_IN
SOY1_IN
PR1_IN
PB2_IN
Y2_IN
SOY2_IN
PR2_IN
VTXPHY_VDD11_1
VTXPHY_VDD11_2
VTXPHY_VDD11_3
AVDD11_DR3PLL
IC101-*1
AAD_ADC_SIF
AAD_ADC_SIFM
AUDA_VBG_EXT
AUDA_OUTL
AUDA_OUTR
AUD_SCART_OUTL
AUD_SCART_OUTR
AUAD_L_CH4_IN
AUAD_R_CH4_IN
AUAD_L_CH3_IN
AUAD_R_CH3_IN
AUAD_L_CH2_IN
AUAD_R_CH2_IN
AUAD_L_CH1_IN
AUAD_R_CH1_IN
AUAD_R_REF
AUAD_M_REF
AUAD_L_REF
AUAD_REF_PO
ADC_I_INCOM
ADC_I_INP
ADC_I_INN
VDDC11_1
VDDC11_2
VDDC11_3
VDDC11_4
VDDC11_5
VDDC11_6
VDDC11_7
VDDC11_8
VDDC11_9
VDDC11_10
VDDC11_11
VDDC11_12
VDDC11_13
VDDC11_14
VDDC11_15
VDDC11_16
VDDC11_17
VDDC11_18
VDDC11_19
VDDC11_20
VDDC11_21
VDDC11_22
VDDC11_23
VDDC11_24
VDDC11_25
VDDC11_26
VDDC11_27
VDDC11_28
VDDC11_29
VDDC11_30
VDDC11_31
VDDC11_32
VDDC11_33
VDDC11_34
VDDC11_35
AVDD11_DCO
GPLL_VDD11
H18
H17
P2
N1
N2
N3
P1
P3
R1
R2
T1
U2
U3
V2
V3
U1
T3
T2
R3
K17
ANTCON
K18
RFAGC
J18
IFAGC
U16
U17
V17
F3
GPIO0
F2
GPIO1
F1
GPIO2
G3
GPIO3
G2
GPIO4
G1
GPIO5
H3
GPIO6
H2
GPIO7
H1
GPIO8
J3
GPIO9
E18
GPIO10
E17
GPIO11
H16
GPIO12
J2
GPIO13
J1
GPIO14
K1
GPIO15
N21
N22
N23
P15
P16
P17
P18
R15
T15
T22
T23
T24
U15
U22
U23
U24
V15
V22
V23
V24
W22
W23
W24
AB15
AB24
AC15
AC24
AD15
AD16
AD17
AD18
AD21
AD22
AD23
AD24
AB14
AC14
AD14
P25
AA15
AC26
+1.1V
+1.2V_VDD
VDD12_VTXPHY
VDDC12_XTAL
+1.2V_VDD
(4)
C381 0.1uF
C217 0.1uF
+0.75V
+3.3V
+2.5V
+1.5V
VREF_M1_1
VDDC12_XTAL
VDD25_XTAL
VDD33
VDD25_LVDS
VDD25_XTAL
VREF_M0_1
VREF_M1_0
VDDC15_M0
VDDC15_M1
VREF_M0_0
+3.3V_Bypass Cap
+3.3V_NORMAL
H14
J4
J5
J6
J8
J9
J10
J11
J14
K4
K5
K6
K8
K9
K10
K11
K13
K14
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L8
L9
L10
L11
L13
L14
L15
L16
L17
L18
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M9
M10
M11
M14
M15
M16
N4
N5
N14
N15
N17
P4
P5
P6
P7
P8
P9
P10
P11
P14
P15
P16
R4
R7
R8
R9
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R17
T4
T7
T8
T9
T10
T11
T12
T15
T16
U4
U6
U18
V4
V16
+2.5V_Bypass Cap
+1.0V_Bypass Cap
L209
BLM18PG121SN1D
+2.5V_Normal
+2.5V_Normal
+1.0V_VDD
L211
BLM18PG121SN1D
+1.0V_VDD
L206
BLM18PG121SN1D
AVDD33
(2)
4.7uFC241
L220
BLM18PG121SN1D
L207
BLM18PG121SN1D
C218 0.1uF
4.7uFC211
VDD25_LTX
4.7uFC275
+3.3V_NORMAL
AFE 3CH Power
AVDD25
4.7uFC270
4.7uFC242
Bottom side of chip
4.7uFC216
C223 0.1uF
VDD10_XTAL
4.7uFC239
VDDC10
4.7uFC214
AVDD33_XTAL
L216
BLM18PG121SN1D
4.7uFC255
4.7uFC222
C274 0.1uF
+2.5V_Normal
C246 0.1uF
(1)
C259 0.1uF
BLM15BD121SN1
1uFC224
L200
BLM18PG121SN1D
C251 0.1uF
+3.3V_NORMAL
VDD25_REF
L225
L226
BLM15BD121SN1
1005 size bead
Bottom side of chip
VDD25_AUD
4.7uF
C200
AVDD33_CVBS
L222
BLM18PG121SN1D
0.1uF
C288
VSS25_REF
4.7uF
C202
C204 0.1uF
4.7uFC279
(2)
C283 0.1uF
+1.24V_Bypass Cap
+1.2V_VDD
4.7uFC297
4.7uFC351
C208 0.47uF
C209 0.47uF
Place at the bottom side
+1.2V_VDD
C300 0.1uF
+1.2V_VDD
L227
BLM18PG121SN1D
L201
BLM18PG121SN1D
VDDC12_XTAL
VDD12_VTXPHY
+3.3V_Bypass Cap
+3.3V_NORMAL
L203
BLM18PG121SN1D
+2.5V_Bypass Cap
+2.5V_Normal
L234
BLM18PG121SN1D
4.7uFC298
4.7uFC205
C210 0.47uF
C301 0.1uF
C206 0.1uF
C213 0.47uF
C219 0.47uF
OPT
C207 0.1uF
VDD33
4.7uFC201
C203 0.1uF
C212 0.1uF
C215 0.1uF
Place at the bottom side
VDD25_XTAL
4.7uFC364
C368 0.1uF
+2.5V_Normal
(1)
L238
BLM18PG121SN1D
VDD25_LVDS
4.7uFC378
Place at the bottom side
A27
B5
C5
C26
C27
D5
D26
E5
E6
E7
E8
E22
E23
E26
F7
F8
F22
F23
F24
F25
F26
F27
F31
G7
G8
G9
G10
G11
G12
G13
G14
G15
G16
G17
G18
G19
G20
G21
G22
G23
G24
G25
G26
G27
G28
G29
G30
G31
H9
H26
H27
H28
H29
H30
H31
J7
J30
J31
K7
K30
K31
L30
L31
M7
M12
M13
M14
M15
M16
M17
M18
M19
M20
M24
M25
M26
M30
M32
M33
M34
N12
N13
N14
N15
N16
N17
N18
N19
N20
N24
N30
N31
N32
N33
P7
P12
P13
P14
P19
P20
P21
P22
P23
P24
P30
P31
R12
R13
R14
R16
R17
R18
R19
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
R30
R34
T7
T12
T13
T14
T16
T17
T18
T19
T20
T21
T25
T26
T30
T31
T34
U7
U12
U13
U14
U16
U17
U18
U19
U20
U21
U25
U26
U30
U31
V7
V12
V13
V14
V16
V17
V18
V19
V20
V21
V25
V26
V30
V31
W5
W6
W7
W12
W13
W14
W15
W16
W17
W18
W19
W20
W21
W25
W26
W30
W31
Y3
Y4
LG1154D_H13D
GND_1
GND_2
GND_3
GND_4
GND_5
GND_6
GND_7
GND_8
GND_9
GND_10
GND_11
GND_12
GND_13
GND_14
GND_15
GND_16
GND_17
GND_18
GND_19
GND_20
GND_21
GND_22
GND_23
GND_24
GND_25
GND_26
GND_27
GND_28
GND_29
GND_30
GND_31
GND_32
GND_33
GND_34
GND_35
GND_36
GND_37
GND_38
GND_39
GND_40
GND_41
GND_42
GND_43
GND_44
GND_45
GND_46
GND_47
GND_48
GND_49
GND_50
GND_51
GND_52
GND_53
GND_54
GND_55
GND_56
GND_57
GND_58
GND_59
GND_60
GND_61
GND_62
GND_63
GND_64
GND_65
GND_66
GND_67
GND_68
GND_69
GND_70
GND_71
GND_72
GND_73
GND_74
GND_75
GND_76
GND_77
GND_78
GND_79
GND_80
GND_81
GND_82
GND_83
GND_84
GND_85
GND_86
GND_87
GND_88
GND_89
GND_90
GND_91
GND_92
GND_93
GND_94
GND_95
GND_96
GND_97
GND_98
GND_99
GND_100
GND_101
GND_102
GND_103
GND_104
GND_105
GND_106
GND_107
GND_108
GND_109
GND_110
GND_111
GND_112
GND_113
GND_114
GND_115
GND_116
GND_117
GND_118
GND_119
GND_120
GND_121
GND_122
GND_123
GND_124
GND_125
GND_126
GND_127
GND_128
GND_129
GND_130
GND_131
GND_132
GND_133
GND_134
GND_135
GND_136
GND_137
GND_138
GND_139
GND_140
GND_141
GND_142
GND_143
GND_144
GND_145
GND_146
GND_147
GND_148
GND_149
GND_150
GND_151
GND_152
GND_153
GND_154
GND_155
GND_156
GND_157
GND_158
GND_159
GND_160
GND_161
GND_162
GND_163
GND_164
GND_165
GND_166
GND_167
GND_168
GND_169
GND_170
GND_171
GND_172
GND_173
GND_174
GND_175
GND_176
GND_177
GND_178
GND_179
GND_180
GND_181
GND_182
GND_183
GND_184
IC100
GND_185
GND_186
GND_187
GND_188
GND_189
GND_190
GND_191
GND_192
GND_193
GND_194
GND_195
GND_196
GND_197
GND_198
GND_199
GND_200
GND_201
GND_202
GND_203
GND_204
GND_205
GND_206
GND_207
GND_208
GND_209
GND_210
GND_211
GND_212
GND_213
GND_214
GND_215
GND_216
GND_217
GND_218
GND_219
GND_220
GND_221
GND_222
GND_223
GND_224
GND_225
GND_226
GND_227
GND_228
GND_229
GND_230
GND_231
GND_232
GND_233
GND_234
GND_235
GND_236
GND_237
GND_238
GND_239
GND_240
GND_241
GND_242
GND_243
GND_244
GND_245
GND_246
GND_247
GND_248
GND_249
GND_250
GND_251
GND_252
GND_253
GND_254
GND_255
GND_256
GND_257
GND_258
GND_259
GND_260
GND_261
GND_262
GND_263
GND_264
GND_265
GND_266
GND_267
GND_268
GND_269
GND_270
GND_271
GND_272
GND_273
GND_274
GND_275
GND_276
GND_277
GND_278
GND_279
GND_280
GND_281
GND_282
GND_283
GND_284
GND_285
GND_286
GND_287
GND_288
GND_289
GND_290
GND_291
GND_292
GND_293
GND_294
GND_295
GND_296
GND_297
GND_298
GND_299
GND_300
GND_301
GND_302
GND_303
GND_304
GND_305
GND_306
GND_307
GND_308
GND_309
GND_310
GND_311
GND_312
GND_313
GND_314
GND_315
GND_316
GND_317
GND_318
GND_319
GND_320
GND_321
GND_322
GND_323
GND_324
GND_325
GND_326
GND_327
GND_328
GND_329
GND_330
GND_331
GND_332
GND_333
GND_334
GND_335
GND_336
GND_337
GND_338
GND_339
GND_340
GND_341
GND_342
GND_343
GND_344
GND_345
GND_346
GND_347
GND_348
GND_349
GND_350
GND_351
GND_352
GND_353
GND_354
GND_355
GND_356
GND_357
GND_358
GND_359
GND_360
GND_361
GND_362
GND_363
GND_364
GND_365
GND_366
GND_367
GND_368
Y5
Y8
Y12
Y13
Y14
Y15
Y16
Y17
Y18
Y19
Y20
Y21
Y22
Y23
Y24
Y25
Y26
Y31
Y35
AA8
AA12
AA13
AA14
AA16
AA17
AA18
AA19
AA20
AA21
AA22
AA23
AA24
AA25
AA26
AA31
AB6
AB8
AB12
AB13
AB16
AB17
AB18
AB19
AB20
AB21
AB22
AB23
AB25
AB26
AB30
AB31
AC8
AC12
AC13
AC16
AC17
AC18
AC19
AC20
AC21
AC22
AC23
AC25
AC30
AC31
AD8
AD12
AD13
AD19
AD20
AD25
AD31
AE12
AE13
AE15
AE16
AE17
AE18
AE19
AE20
AE21
AE22
AE24
AE25
AE26
AE31
AF12
AF13
AF15
AF16
AF17
AF18
AF19
AF20
AF21
AF22
AF24
AF31
AG8
AG31
AH8
AH31
AJ8
AJ30
AK8
AK9
AK10
AK14
AK15
AK16
AK17
AK18
AK19
AK20
AK21
AK22
AK23
AK26
AK27
AK28
AK29
AK30
AK31
AL8
AL12
AL13
AL14
AL15
AL16
AL17
AL18
AL19
AL20
AL21
AL22
AL23
AL24
AL25
AL26
AL27
AL28
AL29
AL30
AL31
AM8
AM13
AM14
AM15
AM16
AM17
AM18
AM19
AM20
AM21
AM22
AM23
AM24
AM25
AM26
AM27
AM28
AM29
AM30
AM31
AN6
AN12
AN13
AN15
AN16
AN17
AN18
AN19
AN20
AN21
AN22
AN23
AN24
AN25
AN26
AN27
AN28
AN29
AN30
AN31
GND JIG POINT
JP203
JP204
JP202
JP205
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FIRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFACTURES SPECIFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
11/05/31
SMD TOP for EMI
SMD_GASKET_8.5T
GASKET_8.0X6.0X8.5H
M200
MDS62110209
SMD_GASKET_12.5T
GASKET_8.0X6.0X12.5H
M200-*1
MDS62110217
+1.5V_DDR
L230
BLM18PG121SN1D
22uF
C303
C302
0.1uF
C306
0.1uF
C308
0.1uF
C305
VDDC15_M1
+1.5V_Bypass Cap
VDDC15_M0
R200
OPT
OPT
OPT
0.1uF
C309
0.1uF
C311
0.1uF
C312
OPT
OPT
0.1uF
C313
OPT
0.1uF
C314
C350
0.1uF
C352
0.1uF
0.1uF
C353
0.1uF
C354
0.1uF
C355
0.1uF
C356
0.1uF
C357
0.1uF
C358
0.1uF
C359
0.1uF
C360
0.1uF
C361
0.1uF
C362
0.1uF
C363
0.1uF
C365
0.1uF
C366
0.1uF
C367
0.1uF
C369
0.1uF
C370
0.1uF
C371
0.1uF
C372
0.1uF
R201
VREF_M0_0
1K 1%
1K 1%
C296
OPT
0.1uF
VDDC15_M0
R202
R203
1K 1%
VREF_M0_1
1K 1%
OPT
C344
0.1uF
+1.5V_DDR
L228
BLM18PG121SN1D
22uFC299
C307
0.1uF
VDDC15_M1
R300
R301
VREF_M1_0
1K 1%
1K 1%
C304
OPT
0.1uF
VDDC15_M1VDDC15_M0
VREF_M1_1
R302
1K 1%
OPT
0.1uF
R303
1K 1%
C310
BSD-14Y-UD-003-HD
2013-12-17
MAIN POWER

Place JACK Side
Copyright ⓒ 2014 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use Only
AV1_CVBS_IN
5.5V
D404
SC_CVBS_IN
TU_CVBS
SCART_FB_DIRECT
SC_FB
SC_ID
NON_EU
R422-*1
SC_CVBS_IN_SOY
COMP1_Pb
COMP1_Y
COMP1_Pr
SC_L_IN
SC_R_IN
SCART_Lout
SCART_Rout
HP_LOUT_MAIN
HP_ROUT_MAIN
R423 100
R435
R422
75
0
SCART_FB_DIRECT
SC_B
SC_G
SC_R
5.5V
COMP1/AV1/DVI_L_IN
COMP1/AV1/DVI_R_IN
10pF
C472
D406
D403
D401
5.5V
5.5V
Near Place Scart AMP
EU
4.7uF 10V
C6006
EU
10K
4.7uF 10V
R6005
C6001
+12V
EU
R403
100K
EU
R404
100K
R430
22K
OPT
R445
22K
OPT
C405
150pF
50V
C408
150pF
50V
EU
10K
C473
50V
OPT
EU
10K
R60 06
EU
R408
100K
2.2uF
10V
R409
100K
R6450
C400
0.01uF
OPT
C401
0.01uF
OPT
L408
C402
150pF
50V
OPT
EU
10pF
50V
EU
EU
C403
EU
100
R6451
L409
OPT
C430
1uH
1uH
EU
EU
2.7K
10pF
C474
50V
OPT
10pF
C431
50V
SCART_AMP_R_FB
EU
C406
2.2uF
10V
100
+3.3V_NORMAL
R4641K1/16W
R465
390
1/16W
C410
R410
150pF
75
1%
3216
C462
R411
150pF
75
EU
EU
1%
3216
NON_EU
R436
R436-*1
0
75
75
1%
1%
EU
R414
R412
10pF
10pF
C470
50V
50V
SCART_AMP_L_FB
SCART_Lout_SOC
SCART_Rout_SOC
CLK_54M_VTT
1%
C404
0.01uF
50V
1%
DAC_START_PULLDOWN
R466821/16W
1%
75
EU
EU
1%
R416
75
75
75
1%
1%
1%
R417
R415
R413
AUDA_OUTL
AUDA_OUTR
FOR EMI
R400
R405
R427
R424
R425
1%
R418 27K
1%
R419 27K
1%
R420 27K
1%
R421 27K
SC_FB
Clock for H13A
MAIN Clock(24Mhz)
12pF D13_STPO_SOP
C426
12pF
C427
Place SOC Side
R434
C424 0.047uF
100
EU
R433
R432
EU
EU
EU
C425 0.047uF
100
SC_CVBS_IN_SOY
C423 0.047uF
100
C417 0.047uF
33
C418 0.047uF
33
C428 1000pF
C419 0.047uF
33
C420 0.047uF
33
C421 0.047uF
33
C429 1000pF
C422 0.047uF
33
R431
EU
EU
EU
EU
EU
AUDIO IN
EU
EU
EU
SCART_FB_BUFFER
C432 4.7uF
R437 10K 1%
C433 4.7uF
R438 10K 1%
C434 4.7uF
R439 10K 1%
C435 4.7uF
R440 10K 1%
R401
470
1/16W
5%
R4061K
SCART_FB_BUFFER
EU
EU
EU
+3.3V_NORMAL
R446
4.7K
SCART_FB_BUFFER
C
B
E
1/16W
1%
X-TAL_1
GND_1
1
2
4
3
GND_2
X-TAL_2
AV1_CVBS_IN_SOC
SC_CVBS_IN_SOC
TU_CVBS_SOC
SC_FB_SOC
SC_ID_SOC
COMP1_PB_IN_SOC
COMP1_Y_IN_SOC
COMP1_Y_IN_SOC_SOY
COMP1_PR_IN_SOC
COMP2_PB_IN_SOC
COMP2_Y_IN_SOC
COMP2_Y_IN_SOC_SOY
COMP2_PR_IN_SOC
SC_FB_BUF
MMBT3904(NXP)
Q400
SCART_FB_BUFFER
R441
X400
24MHz
SOC_RESET
AUAD_L_CH3_IN
AUAD_R_CH3_IN
AUAD_L_CH2_IN
AUAD_R_CH2_IN
Tuner IF Filter
1M
COMP1_Y_IN_SOC_SOY
COMP2_Y_IN_SOC_SOY
HP_LOUT_AMP
XIN_SUB
XOUT_SUB
XIN_SUB
XOUT_SUB
XTAL_SEL[0]
XTAL_SEL[1]
C415
OPM[0]
0.1uF
OPM[1]
H13A_SCL
H13A_SDA
AV1_CVBS_IN_SOC
SC_CVBS_IN_SOC
TU_CVBS_SOC
DTV/MNT_V_OUT_SOC
OPT
Placed as close as possible to SOC
REFT
REFB
R447 68
R448 68
R449 68
SC_ID_SOC
SC_FB_SOC
COMP1_PB_IN_SOC
COMP1_Y_IN_SOC
COMP1_PR_IN_SOC
COMP2_PB_IN_SOC
COMP2_Y_IN_SOC
COMP2_PR_IN_SOC
+3.3V_NORMAL
POWER_SAVE
HP_OUT
L400
To ADC
VOUT
VSAG
NON_TU_W_BR/TW
NON_TU_W_BR/TW
NON_TU_W_BR/TW
HP_OUT
C407
0.22uF
10V
DTV/MNT_V_OUT
ADC_I_INN
ADC_I_INP
BLM18PG121SN1D
Place at JACK SIDE
P17
6
5
4
TU_W_BR/TW
R443-*1
220
0.01uF
0.01uF
BLM18PG121SN1D
HP_ROUT_AMP
V+
GND
VIN
C437
C438
P18
J17
N18
D18
M18
M17
E3
K3
K2
A8
B8
U13
V14
V15
V13
U15
U14
U7
V6
V7
U10
V12
T5
T6
U8
V8
V9
U9
V10
U11
V11
U12
L406
OPT
HP_OUT
L401
R453 330
C443 0.047uF
68
R450
C439
100pF
50V
C440 0.047uF
C441 0.047uF
C442 0.047uF
IC400
NJM2561BF1
1
EU
2
3
R443
51
C436
22pF
R444
51
Placed as close as possible to IC100
HP_LOUT
OP MODE Setting
& Select XTAL Input
OP MODE[0:1] : SW[2:1]
00 => Normal Operaiton Mode
/T32 Debug Mode
01 => Internal Test Purpose
10 => Internal Test Purpose
11 => Internal Test Purpose
XTAL SEL[1:0] : SW[4:3]
00 => Xtal Input
01 => CLK 24M from H13D
10 => XTAL Bypass from H13D
IC101
LG1154AN_H13A
XIN_SUB
XO_SUB
VSB_AUX_XIN
XTAL_BYPASS
CLK_24M
XTAL_SEL0
XTAL_SEL1
PORES_N
OPM0
OPM1
H13A_SCL
H13A_SDA
CVBS_IN3
CVBS_IN2
CVBS_IN1
CVBS_VCM
BUF_OUT1
BUF_OUT2
REFT
REFB
ADC1_COM
ADC2_COM
ADC3_COM
SC1_SID
SC1_FB
PB1_IN
Y1_IN
SOY1_IN
PR1_IN
PB2_IN
Y2_IN
SOY2_IN
PR2_IN
H13A_NON_BRAZIL
AAD_ADC_SIF
AAD_ADC_SIFM
AUDA_VBG_EXT
AUDA_OUTL
AUDA_OUTR
AUD_SCART_OUTL
AUD_SCART_OUTR
AUAD_L_CH4_IN
AUAD_R_CH4_IN
AUAD_L_CH3_IN
AUAD_R_CH3_IN
AUAD_L_CH2_IN
AUAD_R_CH2_IN
AUAD_L_CH1_IN
AUAD_R_CH1_IN
AUAD_R_REF
AUAD_M_REF
AUAD_L_REF
AUAD_REF_PO
ANTCON
RFAGC
IFAGC
ADC_I_INCOM
ADC_I_INP
ADC_I_INN
GPIO0
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
GPIO7
GPIO8
GPIO9
GPIO10
GPIO11
GPIO12
GPIO13
GPIO14
GPIO15
H18
H17
P2
N1
N2
N3
P1
P3
R1
R2
T1
U2
U3
V2
V3
U1
T3
T2
R3
K17
K18
J18
U16
U17
V17
F3
F2
F1
G3
G2
G1
H3
H2
H1
J3
E18
E17
H16
J2
J1
K1
Placed as close as possible to IC4300
AUAD_REF_PO
AUAD_L_REF
EU
C412
0.1uF
C414
0.1uF
EU
DTV/MNT_V_OUT_SOC
TU_W_BR/TW
R444-*1
220
TU_W_BR/TW
C436-*1
100pF
IF_N
AUAD_R_REF
AUAD_M_REF
AFE 3CH REF Setting
IF_P
HP_ROUT
HP_OUT
C409
0.22uF
10V
PWM_DIM
PWM_DIM2
+3.3V_NORMAL
10K
10K
10K
10K
OPT
OPT
OPT
OPT
R482
R481
R484
C447
OPT
1uF
25V
R479100
R480100
ADC_I_INP
ADC_I_INN
BIT0
BIT1
BIT2
BIT3
BIT4
BIT5
BIT6
BIT7
BIT8
BIT9
BIT10
SC_FB_BUF
OPT
R45421/10W
C446
0.1uF
NON_OLED
AR402
33
1/16W
R483
R426
22K
EU
1%
R45 5
51K
R45 647K 1 %
5%
C448
OPT
4.7uF
10V
REFT
Must be used
REFB
C457
1000pF
R442
EU
C4494.7uF
100
R459
100
R460
100
R461
100
R462
C450 0.1uF
C451 0.1uF
10uFC452
C453 2.2uF
AUDA_OUTL
AUDA_OUTR
EU
EU
AUAD_L_CH3_IN
AUAD_R_CH3_IN
AUAD_L_CH2_IN
AUAD_R_CH2_IN
AUAD_R_REF
AUAD_M_REF
AUAD_L_REF
AUAD_REF_PO
C454 0.1uF
Placed as close as possible to IC4300
C444
0.1uF
C445
0.1uF
DIMMING
OPM[0]
OPM[1]
XTAL_SEL[0]
XTAL_SEL[1]
TU_SIF
OPT
SCART_Lout_SOC
SCART_Rout_SOC
22K
EU
EU
C458 0.01uF
C460 0.01uF
Close to IC4300
NON_TU_W_BR/TW/CO
R487
0
IF_AGC
C459
0.1uF
TU_W_BR/TW/CO
TU_W_BR/TW/CO
R487-*1
10K
+2.5V_Normal
L407
C455
10uF
1%
R45 7
51K
1%
C456
R45 8
4.7uF
47K
10V
PWM2
PWM1
LG1154AN_H13A
L/DIM0_VS
L/DIM0_SCLK
L/DIM0_MOSI
LG1154A
IC101
INTR_GBB
INTR_AFE3CH
INTR_AGPIO
AUD_FS20CLK
AUD_FS21CLK
AUD_FS23CLK
AUD_FS24CLK
AUD_FS25CLK
AUDCLK_OUT_SUB
AUD_HDMI_MCLK
AUD_DAC1_LRCK
AUD_DAC1_SCK
AUD_DAC1_LRCH
AUD_DAC0_LRCK
AUD_DAC0_SCK
AUD_DAC0_LRCH
AUD_ADC_LRCK
AUD_ADC_SCK
AUD_ADC_LRCH
BB_SCL
BB_SDA
BB_TP_CLK
BB_TP_ERR
BB_TP_SOP
BB_TP_VAL
BB_TP_DATA7
BB_TP_DATA6
BB_TP_DATA5
BB_TP_DATA4
BB_TP_DATA3
BB_TP_DATA2
BB_TP_DATA1
BB_TP_DATA0
CLK_F54M
CVBS_GC2
CVBS_GC1
CVBS_GC0
CVBS_UP
CVBS_DN
FS00CLK
AUDCLK_OUT
DAC_START
DAC_DATA4
DAC_DATA3
DAC_DATA2
DAC_DATA1
DAC_DATA0
AAD_GC4
AAD_GC3
AAD_GC2
AAD_GC1
AAD_GC0
AAD_DATA9
AAD_DATA8
AAD_DATA7
AAD_DATA6
AAD_DATA5
AAD_DATA4
AAD_DATA3
AAD_DATA2
AAD_DATA1
AAD_DATA0
AAD_DATAEN
ADCO_OUT_CLK
HSR_AP0
HSR_AM0
HSR_BP0
HSR_BM0
HSR_CP0
HSR_CM0
HSR_CLKP0
HSR_CLKM0
HSR_DP0
HSR_DM0
HSR_EP0
HSR_EM0
R402 33
AR404
33
L/DIM0_VS
L/DIM0_SCLK
L/DIM0_MOSI
BPL_IN
H13A_NON_BRAZIL
E1
E2
D1
A6
B6
A5
B5
A4
C4
C18
A2
B2
B1
C2
C1
D2
B4
A3
B3
A7
B7
E8
D8
C8
E7
D7
C7
E6
D6
C6
E5
D5
C5
CLK_54M_VTT
1/16W 1%
B10
C9
B9
A9
D9
E9
Close to LG1154A
B11
R492 330
A11
R407 330
D11
C11
E10
D10
C10
A10
R451 330
D13
C13
E12
D12
C12
C17
E16
D16
C16
E15
D15
C15
E14
D14
C14
E13
B18
A12
B12
A13
B13
A14
B14
A15
B15
A16
B16
A17
B17
PWM1
PWM2
BPL_IN
R467 82
DAC_START_PULLDOWN
AT16
INTR_GBB
AU17
INTR_AFE3CH
AT17
INTR_AGPIO
AT24
AUD_FS20CLK
AU24
AUD_FS21CLK
AT23
AUD_FS23CLK
AU23
AUD_FS24CLK
AT22
AUD_FS25CLK
AU36
AUD_HDMI_MCLK
AT20
AUD_DAC1_LRCK
AU20
AUD_DAC1_SCK
AT19
AUD_DAC1_LRCH
AU19
AUD_DAC0_LRCK
AT18
AUD_DAC0_SCK
AU18
AUD_DAC0_LRCH
AU22
AUD_ADC_LRCK
AT21
AUD_ADC_SCK
AU21
AUD_ADC_LRCH
AT25
BB_SCL
AU25
BB_SDA
AP23
BB_TPI_CLK
AR23
BB_TPI_ERR
AP22
BB_TPI_SOP
AR22
BB_TPI_VAL
AP21
BB_TPI_DATA7
AR21
BB_TPI_DATA6
AP20
BB_TPI_DATA5
AR20
BB_TPI_DATA4
AP19
BB_TPI_DATA3
AR19
BB_TPI_DATA2
AP18
BB_TPI_DATA1
AR18
BB_TPI_DATA0
AU28
CLK_54M
AR24
CVBS_GC2
AU27
CVBS_GC1
AT27
CVBS_GC0
AP24
CVBS_UP
AR25
CVBS_DN
AU29
FS00CLK
AT29
H13A_AUDCLK_OUT
AP27
DAC_START
AR27
DAC_DATA4
AP26
DAC_DATA3
AR26
DAC_DATA2
AP25
DAC_DATA1
AT28
DAC_DATA0
AR30
AAD_GC4
AP29
AAD_GC3
AR29
AAD_GC2
AP28
AAD_GC1
AR28
AAD_GC0
AP35
AAD_DATA9
AR35
AAD_DATA8
AP34
AAD_DATA7
AR34
AAD_DATA6
AP33
AAD_DATA5
AR33
AAD_DATA4
AP32
AAD_DATA3
AR32
AAD_DATA2
AP31
AAD_DATA1
AR31
AAD_DATA0
AP30
AAD_DATAEN
AT36
ADCO_OUT_CLK
AT30
HSR_AP
AU30
HSR_AM
AT31
HSR_BP
AU31
HSR_BM
AT32
HSR_CP
AU32
HSR_CM
AT33
HSR_CLKP
AU33
HSR_CLKM
AT34
HSR_DP
AU34
HSR_DM
AT35
HSR_EP
AU35
HSR_EM
AT14
AUD_HPDRV_LRCH
AT15
AUD_HPDRV_LRCK
AU15
NC
AUD_HPDRV_SCK
AC7
FRC_LR_O_SYNC_FLAG
AN5
L_VSOUT_LD
AR14
DIM0_SCLK
AP14
DIM0_MOSI
AN14
DIM1_SCLK
AP13
DIM1_MOSI
AF6
PWM0
AF7
PWM1
AD7
PWM2
AE6
PWM_IN
AP5
EPI_EO
AN8
EPI_VST
AP8
EPI_DPM
AR7
EPI_MCLK
AN7
EPI_GCLK
LG1154D
IC100
LG1154D_H13D
STPI0_CLK/GPIO47
STPI0_SOP/GPIO46
STPI0_VAL/GPIO45
STPI0_ERR/GPIO44
STPI0_DATA/GPIO43
STPI1_CLK/GPIO42
STPI1_SOP/GPIO41
STPI1_VAL/GPIO40
STPI1_ERR/GPIO55
STPI1_DATA/GPIO54
TPIO_DATA0/GPIO58
TPIO_DATA1/GPIO59
TPIO_DATA2/GPIO60
TPIO_DATA3/GPIO61
TPIO_DATA4/GPIO62
TPIO_DATA5/GPIO63
TPIO_DATA6/GPIO48
TPIO_DATA7/GPIO49
DACSLRCH/GPIO127
PCMI3SCK/GPIO112
PCMI3LRCK/GPIO113
DACCLFCH/GPIO126
TP_DVB_CLK
TP_DVB_SOP
TP_DVB_VAL
TP_DVB_ERR
TP_DVB_DATA0
TP_DVB_DATA1
TP_DVB_DATA2
TP_DVB_DATA3
TP_DVB_DATA4
TP_DVB_DATA5
TP_DVB_DATA6
TP_DVB_DATA7
TPI_CLK
TPI_SOP
TPI_VAL
TPI_ERR
TPI_DATA0
TPI_DATA1
TPI_DATA2
TPI_DATA3
TPI_DATA4
TPI_DATA5
TPI_DATA6
TPI_DATA7
TPIO_CLK/GPIO53
TPIO_SOP/GPIO52
TPIO_VAL/GPIO51
TPIO_ERR/GPIO50
AUDCLK_OUT
DACLRCH
DACSCK
DACLRCK
PCMI3LRCH
IEC958OUT
DACSUBMCLK
DACSUBLRCH
DACSUBSCK
DACSUBLRCK
TEST1
TEST2
TX0N
TX0P
TX1N
TX1P
TX2N
TX2P
TX3N
TX3P
TX4N
TX4P
TX5N
TX5P
TX6N
TX6P
TX7N
TX7P
TX8N
TX8P
TX9N
TX9P
TX10N
TX10P
TX11N
TX11P
TX12N
TX12P
TX13N
TX13P
TX14N
TX14P
TX15N
TX15P
TX16N
TX16P
TX17N
TX17P
TX18N
TX18P
TX19N
TX19P
TX20N
TX20P
TX21N
TX21P
TX22N
TX22P
TX23N
TX23P
TX_LOCKN
AK35
AK36
AK37
AJ35
AJ36
AH35
AH37
AH36
AG35
AG36
AM36
AL36
AL35
AL37
AM35
AN36
AN37
AN35
AP37
AP36
AR37
AR36
A28
B29
B28
C28
B32
C31
B31
A31
C30
A30
B30
C29
D30
D31
F30
E31
E30
F29
E29
F28
E28
D28
E27
D27
AD5
AD6
Y6
Y7
AC6
AC5
AA6
AB7
AB5
AU14
AA32
AA34
AA33
AB34
AE32
AE33
AT6
AU6
AT5
AU5
AT4
AU4
AU3
AU2
AT2
AT1
AR4
AR3
AP1
AP2
AP4
AP3
AN4
AN3
AM4
AM3
AL4
AL3
AK1
AK2
AK4
AK3
AJ4
AJ3
AH4
AH3
AG4
AG3
AF1
AF2
AF4
AF3
AE4
AE3
AD4
AD3
AC4
AC3
AB1
AB2
AB4
AB3
AA4
AA3
AR5
FE_DEMOD2_TS_CLK
FE_DEMOD2_TS_SYNC
FE_DEMOD2_TS_VAL
FE_DEMOD2_TS_ERROR
FE_DEMOD2_TS_DATA
D13_STPO_CLK
D13_STPO_VAL
D13_STPO_ERR
D13_STPO_DATA
FE_DEMOD1_TS_CLK
FE_DEMOD1_TS_SYNC
FE_DEMOD1_TS_VAL
FE_DEMOD1_TS_ERROR
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[0]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[1]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[2]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[3]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[4]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[5]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[6]
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[7]
TPI_CLK
TPI_SOP
TPI_VAL
TPI_ERR
TPI_DATA[0]
TPI_DATA[1]
TPI_DATA[2]
TPI_DATA[3]
TPI_DATA[4]
TPI_DATA[5]
TPI_DATA[6]
TPI_DATA[7]
TPO_CLK
TPO_SOP
TPO_VAL
TPO_ERR
TPO_DATA[0]
TPO_DATA[1]
TPO_DATA[2]
TPO_DATA[3]
TPO_DATA[4]
TPO_DATA[5]
TPO_DATA[6]
TPO_DATA[7]
R495 100
R496 100
R452 100
R497 100
R498 100
URSA_RESET_SoC
AR403
33
1/16W
TXB0P/TX5P
TXB0N/TX5N
TXB1P/TX4P
TXB1N/TX4N
TXB2P/TX3P
TXB2N/TX3N
TXBCLKP/TX2P
TXBCLKN/TX2N
TXB3P/TX1P
TXB3N/TX1N
TXB4P/TX0P
TXB4N/TX0N
TXA0P/TX11P
TXA0N/TX11N
TXA1P/TX10P
TXA1N/TX10N
TXA2P/TX9P
TXA2N/TX9N
TXACLKP/TX8P
TXACLKN/TX8N
TXA3P/TX7P
TXA3N/TX7N
TXA4P/TX6P
TXA4N/TX6N
TXD0P/TX17P
TXD0N/TX17N
TXD1P/TX16P
TXD1N/TX16N
TXD2P/TX15P
TXD2N/TX15N
TXDCLKP/TX14P
TXDCLKN/TX14N
TXD3P/TX13P
TXD3N/TX13N
TXD4P/TX12P
TXD4N/TX12N
TXC0P/TX23P
TXC0N/TX23N
TXC1P/TX22P
TXC1N/TX22N
TXC2P/TX21P
TXC2N/TX21N
TXCCLKP/TX20P
TXCCLKN/TX20N
TXC3P/TX19P
TXC3N/TX19N
TXC4P/TX18P
TXC4N/TX18N
TP402
C411
10pF
50V
OPT
FE_DEMOD1_TS_DATA[1-7]
TPI_ERR
TPI_DATA[0-7]
TP400
AUD_MASTER_CLK
AUD_LRCH
AUD_LRCH1
To height amp FOR UB98/UB9
AUD_SCK
AUD_LRCK
SPDIF_OUT
+3.3V_NORMAL
Not Used Net (UB85/95/UC89)
TPO_ERR
TPO_DATA[0-7]
I2S_I/F
To front, woofer,
center amp FOR UB98/UB9
AUD_LRCH1
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FIRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFACTURES SPECIFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BSD-14Y-UD-004-HD
2013-12-17
MAIN AUDIO/VIDEO
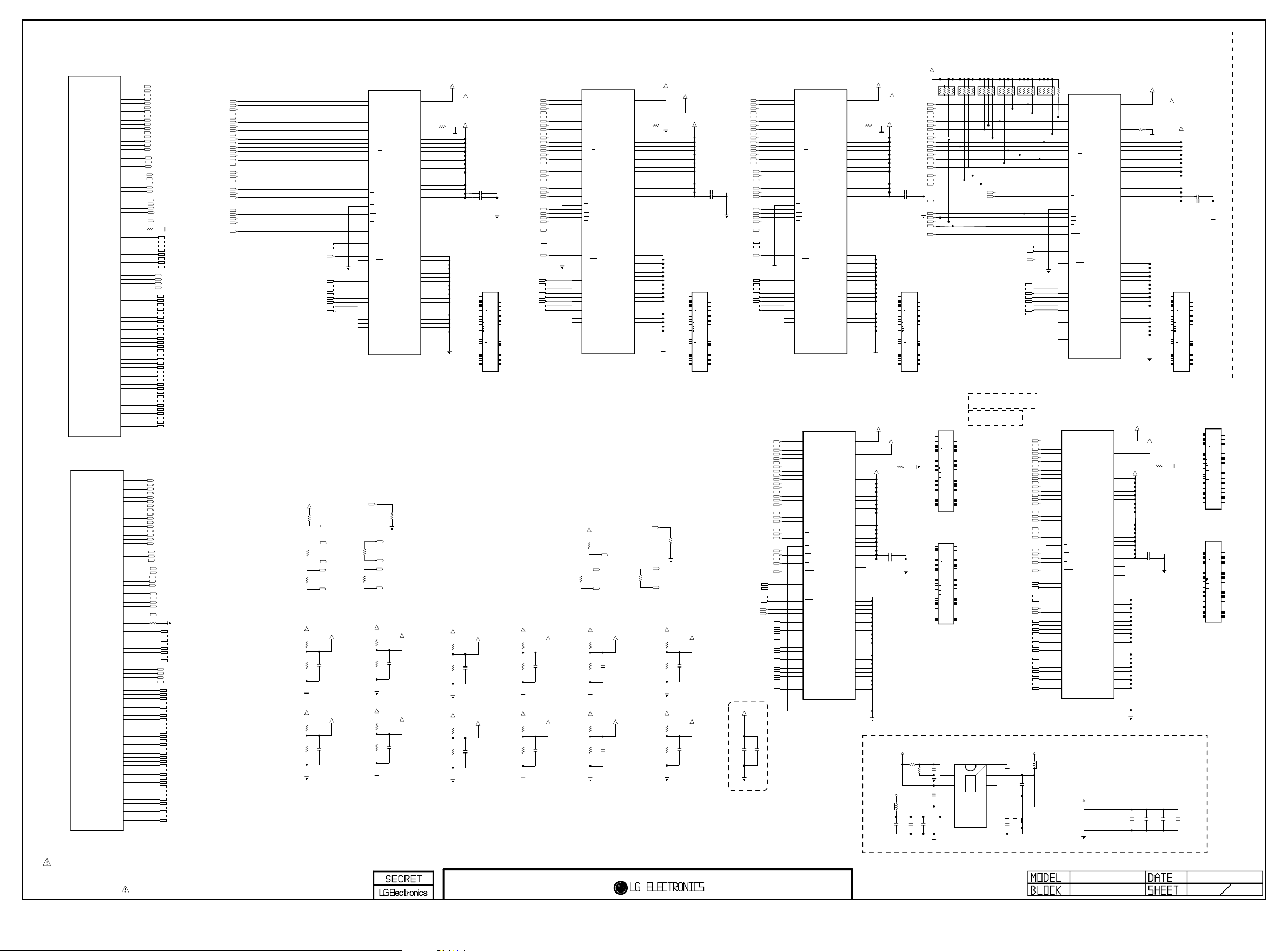
IC100
Copyright ⓒ 2014 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use Only
LG1154D_H13D
M0_DDR_A[10]
M0_DDR_A[11]
M0_DDR_A[12]
M0_DDR_A[13]
M0_DDR_A[14]
M0_DDR_A[15]
M0_DDR_BA[0]
M0_DDR_BA[1]
M0_DDR_BA[2]
M0_DDR_U_CLK
M0_DDR_U_CLKN
M0_DDR_D_CLK
M0_DDR_D_CLKN
M0_DDR_RESET_N
M0_DDR_ZQCAL
M0_DDR_DQS[0]
M0_DDR_DQS_N[0]
M0_DDR_DQS[1]
M0_DDR_DQS_N[1]
M0_DDR_DQS[2]
M0_DDR_DQS_N[2]
M0_DDR_DQS[3]
M0_DDR_DQS_N[3]
M0_DDR_DM[0]
M0_DDR_DM[1]
M0_DDR_DM[2]
M0_DDR_DM[3]
M0_DDR_DQ[0]
M0_DDR_DQ[1]
M0_DDR_DQ[2]
M0_DDR_DQ[3]
M0_DDR_DQ[4]
M0_DDR_DQ[5]
M0_DDR_DQ[6]
M0_DDR_DQ[7]
M0_DDR_DQ[8]
M0_DDR_DQ[9]
M0_DDR_DQ[10]
M0_DDR_DQ[11]
M0_DDR_DQ[12]
M0_DDR_DQ[13]
M0_DDR_DQ[14]
M0_DDR_DQ[15]
M0_DDR_DQ[16]
M0_DDR_DQ[17]
M0_DDR_DQ[18]
M0_DDR_DQ[19]
M0_DDR_DQ[20]
M0_DDR_DQ[21]
M0_DDR_DQ[22]
M0_DDR_DQ[23]
M0_DDR_DQ[24]
M0_DDR_DQ[25]
M0_DDR_DQ[26]
M0_DDR_DQ[27]
M0_DDR_DQ[28]
M0_DDR_DQ[29]
M0_DDR_DQ[30]
M0_DDR_DQ[31]
IC100
LG1154D_H13D
M1_DDR_U_CLKN
M1_DDR_D_CLKN
M1_DDR_RESET_N
M1_DDR_DQS[0]
M1_DDR_DQS_N[0]
M1_DDR_DQS[1]
M1_DDR_DQS_N[1]
M1_DDR_DQS[2]
M1_DDR_DQS_N[2]
M1_DDR_DQS[3]
M1_DDR_DQS_N[3]
M1_DDR_DQ[10]
M1_DDR_DQ[11]
M1_DDR_DQ[12]
M1_DDR_DQ[13]
M1_DDR_DQ[14]
M1_DDR_DQ[15]
M1_DDR_DQ[16]
M1_DDR_DQ[17]
M1_DDR_DQ[18]
M1_DDR_DQ[19]
M1_DDR_DQ[20]
M1_DDR_DQ[21]
M1_DDR_DQ[22]
M1_DDR_DQ[23]
M1_DDR_DQ[24]
M1_DDR_DQ[25]
M1_DDR_DQ[26]
M1_DDR_DQ[27]
M1_DDR_DQ[28]
M1_DDR_DQ[29]
M1_DDR_DQ[30]
M1_DDR_DQ[31]
M0_DDR_A[0]
M0_DDR_A[1]
M0_DDR_A[2]
M0_DDR_A[3]
M0_DDR_A[4]
M0_DDR_A[5]
M0_DDR_A[6]
M0_DDR_A[7]
M0_DDR_A[8]
M0_DDR_A[9]
M0_DDR_CKE
M0_DDR_ODT
M0_DDR_RASN
M0_DDR_CASN
M0_DDR_WEN
M1_DDR_A[0]
M1_DDR_A[1]
M1_DDR_A[2]
M1_DDR_A[3]
M1_DDR_A[4]
M1_DDR_A[5]
M1_DDR_A[6]
M1_DDR_A[7]
M1_DDR_A[8]
M1_DDR_A[9]
M1_DDR_A[10]
M1_DDR_A[11]
M1_DDR_A[12]
M1_DDR_A[13]
M1_DDR_A[14]
M1_DDR_A[15]
M1_DDR_BA[0]
M1_DDR_BA[1]
M1_DDR_BA[2]
M1_DDR_U_CLK
M1_DDR_D_CLK
M1_DDR_CKE
M1_DDR_ODT
M1_DDR_RASN
M1_DDR_CASN
M1_DDR_WEN
M1_DDR_ZQCAL
M1_DDR_DM[0]
M1_DDR_DM[1]
M1_DDR_DM[2]
M1_DDR_DM[3]
M1_DDR_DQ[0]
M1_DDR_DQ[1]
M1_DDR_DQ[2]
M1_DDR_DQ[3]
M1_DDR_DQ[4]
M1_DDR_DQ[5]
M1_DDR_DQ[6]
M1_DDR_DQ[7]
M1_DDR_DQ[8]
M1_DDR_DQ[9]
DDR_HYNIX
F15
M0_DDR_A0
F13
M0_DDR_A1
F17
M0_DDR_A2
F19
M0_DDR_A3
E10
M0_DDR_A4
E18
M0_DDR_A5
E11
M0_DDR_A6
F18
M0_DDR_A7
F11
M0_DDR_A8
F16
M0_DDR_A9
E9
M0_DDR_A10
E12
M0_DDR_A11
E13
M0_DDR_A12
E16
M0_DDR_A13
F12
M0_DDR_A14
F14
M0_DDR_A15
E19
M0_DDR_BA0
F10
M0_DDR_BA1
E15
M0_DDR_BA2
B10
M0_U_CLK
A10
M0_U_CLKN
A19
M0_D_CLK
B19
M0_D_CLKN
E14
M0_DDR_CKE
F21
M0_DDR_ODT
E21
M0_DDR_RASN
E20
M0_DDR_CASN
F20
M0_DDR_WEN
E17
M0_DDR_RESET_N
F9
B20
A20
C19
D19
A11
B11
C10
D10
D18
C20
D9
C11
D22
C15
C23
D16
B24
B15
D23
A15
C16
D21
D17
C22
C18
C21
C17
D20
C13
D7
D13
C6
D14
D6
C14
A5
C7
D12
D8
B13
C9
C12
C8
D11
R500
240
1%
M0_DDR_DQS0
M0_DDR_DQS_N0
M0_DDR_DQS1
M0_DDR_DQS_N1
M0_DDR_DQS2
M0_DDR_DQS_N2
M0_DDR_DQS3
M0_DDR_DQS_N3
M0_DDR_DM0
M0_DDR_DM1
M0_DDR_DM2
M0_DDR_DM3
M0_DDR_DQ0
M0_DDR_DQ1
M0_DDR_DQ2
M0_DDR_DQ3
M0_DDR_DQ4
M0_DDR_DQ5
M0_DDR_DQ6
M0_DDR_DQ7
M0_DDR_DQ8
M0_DDR_DQ9
M0_DDR_DQ10
M0_DDR_DQ11
M0_DDR_DQ12
M0_DDR_DQ13
M0_DDR_DQ14
M0_DDR_DQ15
M0_DDR_DQ16
M0_DDR_DQ17
M0_DDR_DQ18
M0_DDR_DQ19
M0_DDR_DQ20
M0_DDR_DQ21
M0_DDR_DQ22
M0_DDR_DQ23
M0_DDR_DQ24
M0_DDR_DQ25
M0_DDR_DQ26
M0_DDR_DQ27
M0_DDR_DQ28
M0_DDR_DQ29
M0_DDR_DQ30
M0_DDR_DQ31
N6
M1_DDR_A0
R6
M1_DDR_A1
L6
M1_DDR_A2
J6
M1_DDR_A3
U5
M1_DDR_A4
J5
M1_DDR_A5
T5
M1_DDR_A6
K6
M1_DDR_A7
U6
M1_DDR_A8
M6
M1_DDR_A9
V5
M1_DDR_A10
R5
M1_DDR_A11
P5
M1_DDR_A12
L5
M1_DDR_A13
T6
M1_DDR_A14
P6
M1_DDR_A15
H5
M1_DDR_BA0
V6
M1_DDR_BA1
M5
M1_DDR_BA2
R2
R1
F1
F2
N5
G6
F5
G5
H6
K5
F6
E2
E1
F3
F4
P1
P2
R3
R4
G4
E3
T4
P3
C4
K3
B3
J4
A3
K2
B4
K1
J3
D4
H4
C3
G3
D3
H3
E4
M3
V4
M4
W3
L4
W4
L3
Y2
V3
N4
U4
M2
T3
N3
U3
P4
M1_U_CLK
M1_U_CLKN
M1_D_CLK
M1_D_CLKN
M1_DDR_CKE
M1_DDR_ODT
M1_DDR_RASN
M1_DDR_CASN
M1_DDR_WEN
M1_DDR_RESET_N
R501
240
1%
M1_DDR_DQS0
M1_DDR_DQS_N0
M1_DDR_DQS1
M1_DDR_DQS_N1
M1_DDR_DQS2
M1_DDR_DQS_N2
M1_DDR_DQS3
M1_DDR_DQS_N3
M1_DDR_DM0
M1_DDR_DM1
M1_DDR_DM2
M1_DDR_DM3
M1_DDR_DQ0
M1_DDR_DQ1
M1_DDR_DQ2
M1_DDR_DQ3
M1_DDR_DQ4
M1_DDR_DQ5
M1_DDR_DQ6
M1_DDR_DQ7
M1_DDR_DQ8
M1_DDR_DQ9
M1_DDR_DQ10
M1_DDR_DQ11
M1_DDR_DQ12
M1_DDR_DQ13
M1_DDR_DQ14
M1_DDR_DQ15
M1_DDR_DQ16
M1_DDR_DQ17
M1_DDR_DQ18
M1_DDR_DQ19
M1_DDR_DQ20
M1_DDR_DQ21
M1_DDR_DQ22
M1_DDR_DQ23
M1_DDR_DQ24
M1_DDR_DQ25
M1_DDR_DQ26
M1_DDR_DQ27
M1_DDR_DQ28
M1_DDR_DQ29
M1_DDR_DQ30
M1_DDR_DQ31
M0_DDR_A0
M0_DDR_A1
M0_DDR_A2
M0_DDR_A3
M0_DDR_A4
M0_DDR_A5
M0_DDR_A6
M0_DDR_A7
M0_DDR_A8
M0_DDR_A9
M0_DDR_A10
M0_DDR_A11
M0_DDR_A12
M0_DDR_A13
M0_DDR_A14
M0_DDR_A15
M0_DDR_BA0
M0_DDR_BA1
M0_DDR_BA2
M0_D_CLK
M0_D_CLKN
M0_DDR_CKE
M0_DDR_ODT
M0_DDR_RASN
M0_DDR_CASN
M0_DDR_WEN
M0_DDR_RESET_N
M0_DDR_DQS0
M0_DDR_DQS_N0
M0_DDR_DM0
M0_DDR_DQ0
M0_DDR_DQ1
M0_DDR_DQ2
M0_DDR_DQ3
M0_DDR_DQ4
M0_DDR_DQ5
M0_DDR_DQ6
M0_DDR_DQ7
VDDC15_M0
R520
10K
200
R519
200
R580
VDDC15_M0
R514
1K 1%
R515
1K 1%
VDDC15_M0
R516
1K 1%
R517
1K 1%
M0_DDR_RESET_N
M0_DDR_VREFCA
0.1uF
C504
M0_DDR_VREFDQ
0.1uF
C505
M0_D_CLK
M0_D_CLKN
M0_D_CLK
M0_D_CLKN
M0_DDR_CKE
IC500
H5TQ4G83AFR-PBC
DDR3
K3
A0
4Gbit
L7
A1
L3
A2
K2
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
A6
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A9
H7
A10/AP
M7
A11
K7
A12/BC
N3
A13
N7
A14
J7
A15
J2
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
F7
CK
G7
CK
G9
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
B7
DM/TDQS
A7
NF/TDQS
B3
DQ0
C7
DQ1
C2
DQ2
C8
DQ3
E3
DQ4
E8
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
A3
NC_1
F1
NC_2
F9
NC_3
H1
NC_4
H9
NC_5
M0_U_CLK
200
R535
M0_U_CLKN
M0_U_CLK
200
R581
M0_U_CLKN
VDDC15_M0
M0_1_DDR_VREFCA
R536
1K 1%
R537
1K 1%
C512
VDDC15_M0
M0_1_DDR_VREFDQ
R538
1K 1%
R539
1K 1%
C513
0.1uF
0.1uF
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
R541
10K
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
M0_DDR_VREFCA
M0_DDR_VREFDQ
J8
E1
VDDC15_M0
R558
H8
ZQ
240
1%
A2
A9
D7
G2
G8
K1
K9
M1
M9
B9
C1
E2
E9
A1
A8
B1
D8
F2
F8
J1
J9
L1
L9
N1
N9
B2
B8
C9
D1
D9
VDDC15_M0
VDDC15_M0
R550
R551
1K 1%
R552
R553
1K 1%
C559
C560
M0_DDR_VREFCA_T
1K 1%
C550
M0_DDR_VREFDQ_T
1K 1%
C551
0.1uF
0.1uF
0.1uF
0.1uF
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC500-*1
K4B4G0846D-BCK0
K3
A0
L7
A1
L3
A2
K2
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
A6
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A9
H7
A10/AP
M7
A11
K7
A12/BC
N3
A13
N7
A14
J2
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
F7
CK
G7
CK
G9
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
B7
DM/TDQS
A7
NU/TDQS
B3
DQ0
C7
DQ1
C2
DQ2
C8
DQ3
E3
DQ4
E8
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
A3
NC_1
F1
NC_2
F9
NC_3
H1
NC_4
H9
NC_5
J7
NC_6
M0_DDR_A0
M0_DDR_A1
M0_DDR_A2
M0_DDR_A3
M0_DDR_A4
M0_DDR_A5
M0_DDR_A6
M0_DDR_A7
M0_DDR_A8
M0_DDR_A9
M0_DDR_A10
M0_DDR_A11
M0_DDR_A12
M0_DDR_A13
M0_DDR_A14
M0_DDR_A15
M0_DDR_BA0
M0_DDR_BA1
M0_DDR_BA2
M0_D_CLK
M0_D_CLKN
M0_DDR_CKE
M0_DDR_ODT
M0_DDR_RASN
M0_DDR_CASN
M0_DDR_WEN
M0_DDR_RESET_N
M0_DDR_DQS1
M0_DDR_DQS_N1
M0_DDR_DM1
M0_DDR_DQ8
M0_DDR_DQ9
M0_DDR_DQ10
M0_DDR_DQ11
J8
VREFCA
M0_DDR_DQ12
E1
VREFDQ
H8
M0_DDR_DQ13
ZQ
A2
M0_DDR_DQ14
VDD_1
A9
VDD_2
D7
VDD_3
G2
VDD_4
M0_DDR_DQ15
G8
VDD_5
K1
VDD_6
K9
VDD_7
M1
VDD_8
M9
VDD_9
B9
VDDQ_1
C1
VDDQ_2
E2
VDDQ_3
E9
VDDQ_4
A1
VSS_1
A8
VSS_2
B1
VSS_3
D8
VSS_4
F2
VSS_5
F8
VSS_6
J1
VSS_7
J9
VSS_8
L1
VSS_9
L9
VSS_10
N1
VSS_11
N9
VSS_12
B2
VSSQ_1
B8
VSSQ_2
C9
VSSQ_3
D1
VSSQ_4
D9
VSSQ_5
VDDC15_M0
M0_1_DDR_VREFCA_T
R554
1K 1%
0.1uF
R555
1K 1%
C552
VDDC15_M0
M0_1_DDR_VREFDQ_T
R556
1K 1%
0.1uF
R557
1K 1%
C553
DDR_HYNIX
IC502
H5TQ4G83AFR-PBC
DDR3
K3
A0
4Gbit
L7
A1
L3
A2
K2
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
A6
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A9
H7
A10/AP
M7
A11
K7
A12/BC
N3
A13
N7
A14
J7
A15
J2
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
F7
CK
G7
CK
G9
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
B7
DM/TDQS
A7
NF/TDQS
B3
DQ0
C7
DQ1
C2
DQ2
C8
DQ3
E3
DQ4
E8
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
A3
NC_1
F1
NC_2
F9
NC_3
H1
NC_4
H9
NC_5
VDDC15_M1
R521
10K
M1_DDR_RESET_N
M1_D_CLK
100
R518
M1_D_CLKN
VDDC15_M1
M1_DDR_VREFCA
R510
1K 1%
0.1uF
R511
1K 1%
C500
VDDC15_M1
M1_DDR_VREFDQ
R512
1K 1%
0.1uF
R513
1K 1%
C501
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
J8
E1
H8
ZQ
A2
A9
D7
G2
G8
K1
K9
M1
M9
B9
C1
E2
E9
A1
A8
B1
D8
F2
F8
J1
J9
L1
L9
N1
N9
B2
B8
C9
D1
D9
M1_DDR_CKE
M0_1_DDR_VREFCA
R560
240
1%
100
R530
M1_U_CLK
M1_U_CLKN
VDDC15_M1
R531
R532
VDDC15_M1
R533
R534
M0_1_DDR_VREFDQ
R540
10K
M1_1_DDR_VREFCA
1K 1%
0.1uF
1K 1%
C508
M1_1_DDR_VREFDQ
1K 1%
0.1uF
1K 1%
C509
VDDC15_M0
0.1uF
C583
0.1uF
C574
M0_DDR_RESET_N
M0_DDR_DQS_N2
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC502-*1
K4B4G0846D-BCK0
J8
K3
VREFCA
A0
L7
A1
L3
A2
E1
K2
VREFDQ
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
H8
A6
ZQ
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A2
A9
VDD_1
H7
A9
A10/AP
VDD_2
M7
D7
A11
VDD_3
G2
K7
A12/BC
VDD_4
G8
N3
VDD_5
A13
N7
K1
A14
VDD_6
K9
VDD_7
M1
VDD_8
M9
J2
VDD_9
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
B9
VDDQ_1
C1
F7
VDDQ_2
CK
E2
G7
VDDQ_3
CK
E9
G9
VDDQ_4
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
A1
B7
VSS_1
DM/TDQS
A8
A7
VSS_2
NU/TDQS
B1
VSS_3
D8
VSS_4
F2
VSS_5
F8
VSS_6
J1
B3
VSS_7
DQ0
J9
C7
VSS_8
DQ1
L1
C2
VSS_9
DQ2
L9
C8
VSS_10
DQ3
N1
E3
VSS_11
DQ4
N9
E8
VSS_12
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
B2
VSSQ_1
B8
A3
VSSQ_2
NC_1
C9
F1
VSSQ_3
NC_2
D1
F9
VSSQ_4
NC_3
D9
H1
VSSQ_5
NC_4
H9
NC_5
J7
NC_6
Place at the bottom side
M0_DDR_A0
M0_DDR_A1
M0_DDR_A2
M0_DDR_A3
M0_DDR_A4
M0_DDR_A5
M0_DDR_A6
M0_DDR_A7
M0_DDR_A8
M0_DDR_A9
M0_DDR_A10
M0_DDR_A11
M0_DDR_A12
M0_DDR_A13
M0_DDR_A14
M0_DDR_A15
M0_DDR_BA0
M0_DDR_BA1
M0_DDR_BA2
M0_U_CLK
M0_U_CLKN
M0_DDR_CKE
M0_DDR_ODT
M0_DDR_RASN
M0_DDR_CASN
M0_DDR_WEN
M0_DDR_DQS2
M0_DDR_DM2
M0_DDR_DQ16
M0_DDR_DQ17
M0_DDR_DQ18
M0_DDR_DQ19
M0_DDR_DQ20
M0_DDR_DQ21
M0_DDR_DQ22
M0_DDR_DQ23
M1_DDR_DQS0
M1_DDR_DQS_N0
M1_DDR_DQS1
M1_DDR_DQS_N1
M1_DDR_DM0
M1_DDR_DM1
VDDC15_M1
M1_DDR_RASN
M1_DDR_CASN
M1_DDR_RESET_N
M1_DDR_DQ10
M1_DDR_DQ11
M1_DDR_DQ12
M1_DDR_DQ13
M1_DDR_DQ14
M1_DDR_DQ15
1uF
C502
M1_DDR_A0
M1_DDR_A1
M1_DDR_A2
M1_DDR_A3
M1_DDR_A4
M1_DDR_A5
M1_DDR_A6
M1_DDR_A7
M1_DDR_A8
M1_DDR_A9
M1_DDR_A10
M1_DDR_A11
M1_DDR_A12
M1_DDR_A13
M1_DDR_A14
M1_DDR_A15
M1_DDR_BA0
M1_DDR_BA1
M1_DDR_BA2
M1_D_CLK
M1_D_CLKN
M1_DDR_CKE
M1_DDR_ODT
M1_DDR_WEN
M1_DDR_DQ0
M1_DDR_DQ1
M1_DDR_DQ2
M1_DDR_DQ3
M1_DDR_DQ4
M1_DDR_DQ5
M1_DDR_DQ6
M1_DDR_DQ7
M1_DDR_DQ8
M1_DDR_DQ9
1uF
C516
DDR_HYNIX
IC504
H5TQ4G83AFR-PBC
DDR3
K3
4Gbit
A0
L7
A1
L3
A2
K2
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
A6
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A9
H7
A10/AP
M7
A11
K7
A12/BC
N3
A13
N7
A14
J7
A15
J2
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
F7
CK
G7
CK
G9
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
B7
DM/TDQS
A7
NF/TDQS
B3
DQ0
C7
DQ1
C2
DQ2
C8
DQ3
E3
DQ4
E8
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
A3
NC_1
F1
NC_2
F9
NC_3
H1
NC_4
H9
NC_5
OPT
IC501
K4B4G1646B-HCK0
N3
DDR3
A0
P7
4Gbit
A1
P3
(x16)
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12/BC
T3
A13
T7
A14
M7
A15
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
ZQ
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
M0_DDR_VREFCA_T
M0_DDR_VREFDQ_T
J8
E1
VDDC15_M0
R559
H8
240
1%
A2
A9
D7
G2
G8
K1
K9
M1
M9
B9
C1
E2
E9
A1
A8
B1
D8
F2
F8
J1
J9
L1
L9
N1
N9
B2
B8
C9
D1
D9
C568
C569
M1_DDR_VREFCA
M1_DDR_VREFDQ
M8
H1
L8
ZQ
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
R543
VDDC15_M1
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
C529
H9
J1
J9
L1
L9
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
0.1uF
C530
0.1uF
* DDR_VTT
DDR_VTT
DDR_VTT
AR8
AR7
56
56
M0_DDR_A0
M0_DDR_A1
M0_DDR_A2
M0_DDR_A3
M0_DDR_A4
M0_DDR_A5
M0_DDR_A6
M0_DDR_A7
M0_DDR_A8
M0_DDR_A9
M0_DDR_A10
M0_DDR_A11
M0_DDR_A12
M0_DDR_A13
M0_DDR_A14
M0_DDR_A15
M0_DDR_BA0
M0_DDR_BA1
M0_DDR_BA2
0.1uF
0.1uF
M0_DDR_CKE
M0_DDR_ODT
M0_DDR_RASN
M0_DDR_CASN
M0_DDR_WEN
M0_DDR_RESET_N
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC504-*1
K4B4G0846D-BCK0
J8
K3
VREFCA
A0
L7
A1
L3
A2
E1
K2
VREFDQ
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
H8
A6
ZQ
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A2
A9
VDD_1
H7
A9
A10/AP
VDD_2
M7
D7
A11
VDD_3
G2
K7
A12/BC
VDD_4
G8
N3
VDD_5
A13
N7
K1
A14
VDD_6
K9
VDD_7
M1
VDD_8
M9
J2
VDD_9
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
B9
VDDQ_1
C1
F7
VDDQ_2
CK
E2
G7
VDDQ_3
CK
E9
G9
VDDQ_4
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
A1
B7
VSS_1
DM/TDQS
A8
A7
VSS_2
NU/TDQS
B1
VSS_3
D8
VSS_4
F2
VSS_5
F8
VSS_6
J1
B3
VSS_7
DQ0
J9
C7
VSS_8
DQ1
L1
C2
VSS_9
DQ2
L9
C8
VSS_10
DQ3
N1
E3
VSS_11
DQ4
N9
E8
VSS_12
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
B2
VSSQ_1
B8
A3
VSSQ_2
NC_1
C9
F1
VSSQ_3
NC_2
D1
F9
VSSQ_4
NC_3
D9
H1
VSSQ_5
NC_4
H9
NC_5
J7
NC_6
DDR_HYNIX
IC501-*1
H5TQ4G63AFR-PBC
M8
N3
VREFCA
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
H1
A3
VREFDQ
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
L8
A6
ZQ
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
B2
A9
VDD_1
L7
D9
A10/AP
VDD_2
R7
G7
A11
VDD_3
K2
N7
A12/BC
VDD_4
K8
T3
VDD_5
A13
T7
N1
A14
VDD_6
N9
M7
VDD_7
A15
R1
VDD_8
R9
M2
VDD_9
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
J7
VDDQ_2
CK
C1
K7
VDDQ_3
CK
C9
K9
VDDQ_4
CKE
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
L2
VDDQ_6
CS
F1
240
K1
VDDQ_7
ODT
H2
J3
VDDQ_8
RAS
H9
K3
VDDQ_9
CAS
L3
WE
J1
NC_1
J9
T2
NC_2
RESET
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
A9
C7
VSS_1
DQSU
B3
B7
VSS_2
DQSU
E1
VSS_3
G8
E7
VSS_4
DML
J2
D3
VSS_5
DMU
J8
VSS_6
M1
E3
VSS_7
DQL0
M9
F7
VSS_8
DQL1
P1
F2
VSS_9
DQL2
P9
F8
VSS_10
DQL3
T1
H3
VSS_11
DQL4
T9
H8
VSS_12
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
D7
VSSQ_2
DQU0
D1
C3
VSSQ_3
DQU1
D8
C8
VSSQ_4
DQU2
E2
C2
VSSQ_5
DQU3
E8
A7
VSSQ_6
DQU4
F9
A2
VSSQ_7
DQU5
G1
B8
VSSQ_8
DQU6
G9
A3
VSSQ_9
DQU7
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC501-*2
K4B4G1646D-BCK0
M8
N3
VREFCA
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
H1
A3
VREFDQ
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
L8
A6
ZQ
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
B2
A9
VDD_1
L7
D9
A10/AP
VDD_2
R7
G7
A11
VDD_3
N7
K2
A12/BC
VDD_4
T3
K8
A13
VDD_5
T7
N1
A14
VDD_6
N9
M7
VDD_7
A15
R1
VDD_8
R9
M2
VDD_9
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
J7
VDDQ_2
CK
C1
K7
VDDQ_3
CK
C9
K9
VDDQ_4
CKE
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
L2
VDDQ_6
CS
F1
K1
VDDQ_7
ODT
H2
J3
VDDQ_8
RAS
H9
K3
DDR3 1.5V bypass Cap - Place these caps near Memory
VDDQ_9
CAS
L3
WE
J1
NC_1
J9
T2
NC_2
RESET
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
A9
C7
VSS_1
DQSU
B3
B7
VSS_2
DQSU
E1
VSS_3
G8
E7
VSS_4
DML
J2
D3
VSS_5
DMU
J8
VSS_6
M1
E3
VSS_7
DQL0
M9
F7
VSS_8
DQL1
P1
F2
VSS_9
DQL2
P9
F8
VSS_10
DQL3
T1
H3
VSS_11
DQL4
T9
H8
VSS_12
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
D7
VSSQ_2
DQU0
D1
C3
VSSQ_3
DQU1
D8
C8
VSSQ_4
DQU2
E2
C2
VSSQ_5
DQU3
E8
A7
VSSQ_6
DQU4
F9
A2
VSSQ_7
DQU5
G1
B8
VSSQ_8
DQU6
G9
A3
VSSQ_9
DQU7
VDDC15_M0
R546
1%
10K
R549
10K
L500
UBW2012-121F
C503
22uF
10V
C510
1000pF
1%
C511
22uF
10V
C506
C507
22uF
22uF
10V
10V
REFIN
VLDOIN
VOSNS
TPS51200DRCR
1
2
VO
3
PGND
4
5
AR9
56
M0_U_CLK
M0_U_CLKN
Real USE : 1Gbit
H5TQ1G63DFR-PBC(x16)
1Gbit : T7(NC_6)
4Gbit : T7(A14)
IC506
[EP]
VIN
10
PGOOD
11
9
THERMAL
GND
8
EN
7
REFOUT
6
AR10
56
AR11
56
M0_DDR_DQS3
M0_DDR_DQS_N3
M0_DDR_DM3
M0_DDR_DQ24
M0_DDR_DQ25
M0_DDR_DQ26
M0_DDR_DQ27
M0_DDR_DQ28
M0_DDR_DQ29
M0_DDR_DQ30
M0_DDR_DQ31
M1_DDR_A0
M1_DDR_A1
M1_DDR_A2
M1_DDR_A3
M1_DDR_A4
M1_DDR_A5
M1_DDR_A6
M1_DDR_A7
M1_DDR_A8
M1_DDR_A9
M1_DDR_A10
M1_DDR_A11
M1_DDR_A12
M1_DDR_A13
M1_DDR_A14
M1_DDR_A15
M1_DDR_BA0
M1_DDR_BA1
M1_DDR_BA2
M1_U_CLKN
M1_DDR_CKE
M1_DDR_ODT
M1_DDR_RASN
M1_DDR_CASN
M1_DDR_WEN
M1_DDR_RESET_N
M1_DDR_DQS2
M1_DDR_DQS_N2
M1_DDR_DQS3
M1_DDR_DQS_N3
M1_DDR_DM2
M1_DDR_DM3
M1_DDR_DQ16
M1_DDR_DQ17
M1_DDR_DQ18
M1_DDR_DQ19
M1_DDR_DQ20
M1_DDR_DQ21
M1_DDR_DQ22
M1_DDR_DQ23
M1_DDR_DQ24
M1_DDR_DQ25
M1_DDR_DQ26
M1_DDR_DQ27
M1_DDR_DQ28
M1_DDR_DQ29
M1_DDR_DQ30
M1_DDR_DQ31
UBW2012-121F
C514
0.1uF
M1_U_CLK
+3.3V_NORMAL
L501
C515
4700pF
AR12
56
DDR_HYNIX
R3104
IC505
56
H5TQ4G83AFR-PBC
DDR3
K3
A0
4Gbit
L7
A1
L3
A2
K2
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
A6
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A9
H7
A10/AP
M7
A11
K7
A12/BC
N3
A13
N7
A14
J7
A15
J2
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
F7
CK
G7
CK
G9
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
B7
DM/TDQS
A7
NF/TDQS
B3
DQ0
C7
DQ1
C2
DQ2
C8
DQ3
E3
DQ4
E8
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
A3
NC_1
F1
NC_2
F9
NC_3
H1
NC_4
H9
NC_5
OPT
IC503
K4B4G1646B-HCK0
N3
DDR3
A0
P7
4Gbit
A1
P3
(x16)
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12/BC
T3
A13
T7
A14
M7
A15
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
DDR_VTT
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
ZQ
J8
E1
H8
ZQ
A2
A9
D7
G2
G8
K1
K9
M1
M9
B9
C1
E2
E9
A1
A8
B1
D8
F2
F8
J1
J9
L1
L9
N1
N9
B2
B8
C9
D1
D9
M1_1_DDR_VREFCA
M8
H1
L8
VDDC15_M1
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
H9
J1
J9
L1
L9
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
M0_1_DDR_VREFCA_T
R561
240
1%
M1_1_DDR_VREFDQ
R545
C561
0.1uF
C562
0.1uF
C520
C519
0.47uF
0.47uF
6.3V
6.3V
M0_1_DDR_VREFDQ_T
VDDC15_M0
0.1uF
C572
0.1uF
C577
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC505-*1
K4B4G0846D-BCK0
J8
K3
VREFCA
A0
L7
A1
L3
A2
E1
K2
VREFDQ
A3
L8
A4
L2
A5
M8
H8
A6
ZQ
M2
A7
N8
A8
M3
A2
A9
VDD_1
H7
A9
A10/AP
VDD_2
M7
D7
A11
VDD_3
G2
K7
A12/BC
VDD_4
G8
N3
VDD_5
A13
N7
K1
A14
VDD_6
K9
VDD_7
M1
VDD_8
M9
J2
VDD_9
BA0
K8
BA1
J3
BA2
B9
VDDQ_1
C1
F7
VDDQ_2
CK
E2
G7
VDDQ_3
CK
E9
G9
VDDQ_4
CKE
H2
CS
G1
ODT
F3
RAS
G3
CAS
H3
WE
N2
RESET
C3
DQS
D3
DQS
A1
B7
VSS_1
DM/TDQS
A8
A7
VSS_2
NU/TDQS
B1
VSS_3
D8
VSS_4
F2
VSS_5
F8
VSS_6
J1
B3
VSS_7
DQ0
J9
C7
VSS_8
DQ1
L1
C2
VSS_9
DQ2
L9
C8
VSS_10
DQ3
N1
E3
VSS_11
DQ4
N9
E8
VSS_12
DQ5
D2
DQ6
E7
DQ7
B2
VSSQ_1
B8
A3
VSSQ_2
NC_1
C9
F1
VSSQ_3
NC_2
D1
F9
VSSQ_4
NC_3
D9
H1
VSSQ_5
NC_4
H9
NC_5
J7
NC_6
DDR_HYNIX
IC503-*1
H5TQ4G63AFR-PBC
M8
N3
VREFCA
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
H1
A3
VREFDQ
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
L8
A6
ZQ
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
B2
A9
VDD_1
L7
D9
A10/AP
VDD_2
R7
G7
A11
VDD_3
N7
K2
A12/BC
VDD_4
T3
K8
A13
VDD_5
T7
N1
A14
VDD_6
N9
M7
VDD_7
A15
R1
VDD_8
R9
M2
VDD_9
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
J7
VDDQ_2
CK
K7
C1
VDDQ_3
CK
K9
C9
CKE
VDDQ_4
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
L2
VDDQ_6
CS
F1
K1
VDDQ_7
ODT
H2
240
C521
0.47uF
6.3V
J3
VDDQ_8
RAS
H9
K3
VDDQ_9
CAS
L3
WE
J1
NC_1
J9
T2
NC_2
RESET
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
A9
C7
VSS_1
DQSU
B3
B7
VSS_2
DQSU
E1
VSS_3
G8
E7
VSS_4
DML
J2
D3
VSS_5
DMU
J8
VSS_6
M1
E3
VSS_7
DQL0
M9
F7
VSS_8
DQL1
P1
F2
VSS_9
DQL2
P9
F8
VSS_10
DQL3
T1
H3
VSS_11
DQL4
T9
H8
VSS_12
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
D7
VSSQ_2
DQU0
D1
C3
VSSQ_3
DQU1
D8
C8
VSSQ_4
DQU2
E2
C2
VSSQ_5
DQU3
E8
A7
VSSQ_6
DQU4
F9
A2
VSSQ_7
DQU5
G1
B8
VSSQ_8
DQU6
G9
A3
VSSQ_9
DQU7
DDR_SAMSUNG
IC503-*2
K4B4G1646D-BCK0
M8
N3
VREFCA
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
H1
A3
VREFDQ
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
L8
A6
ZQ
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
B2
A9
VDD_1
L7
D9
A10/AP
VDD_2
R7
G7
A11
VDD_3
N7
K2
A12/BC
VDD_4
T3
K8
A13
VDD_5
T7
N1
A14
VDD_6
N9
M7
VDD_7
A15
R1
VDD_8
R9
M2
VDD_9
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
J7
VDDQ_2
CK
C1
K7
VDDQ_3
CK
C9
K9
VDDQ_4
CKE
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
L2
VDDQ_6
CS
F1
K1
VDDQ_7
ODT
H2
J3
VDDQ_8
RAS
H9
K3
VDDQ_9
CAS
L3
DDR3 1.5V bypass Cap - Place these caps near Memory
WE
J1
NC_1
J9
T2
NC_2
RESET
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
A9
C7
VSS_1
DQSU
B3
B7
VSS_2
DQSU
E1
VSS_3
G8
E7
VSS_4
DML
J2
D3
VSS_5
DMU
J8
VSS_6
M1
E3
VSS_7
DQL0
M9
F7
VSS_8
DQL1
P1
F2
VSS_9
DQL2
P9
F8
VSS_10
DQL3
T1
H3
VSS_11
DQL4
T9
H8
VSS_12
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
D7
VSSQ_2
DQU0
D1
C3
VSSQ_3
DQU1
D8
C8
VSSQ_4
DQU2
E2
C2
VSSQ_5
DQU3
E8
A7
VSSQ_6
DQU4
F9
A2
VSSQ_7
DQU5
G1
B8
VSSQ_8
DQU6
G9
A3
VSSQ_9
DQU7
C522
0.47uF
6.3V
Close to REFOUT pin
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FIRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFACTURES SPECIFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BSD-14Y-UD-005-HD
2013-12-17
MAIN DDR
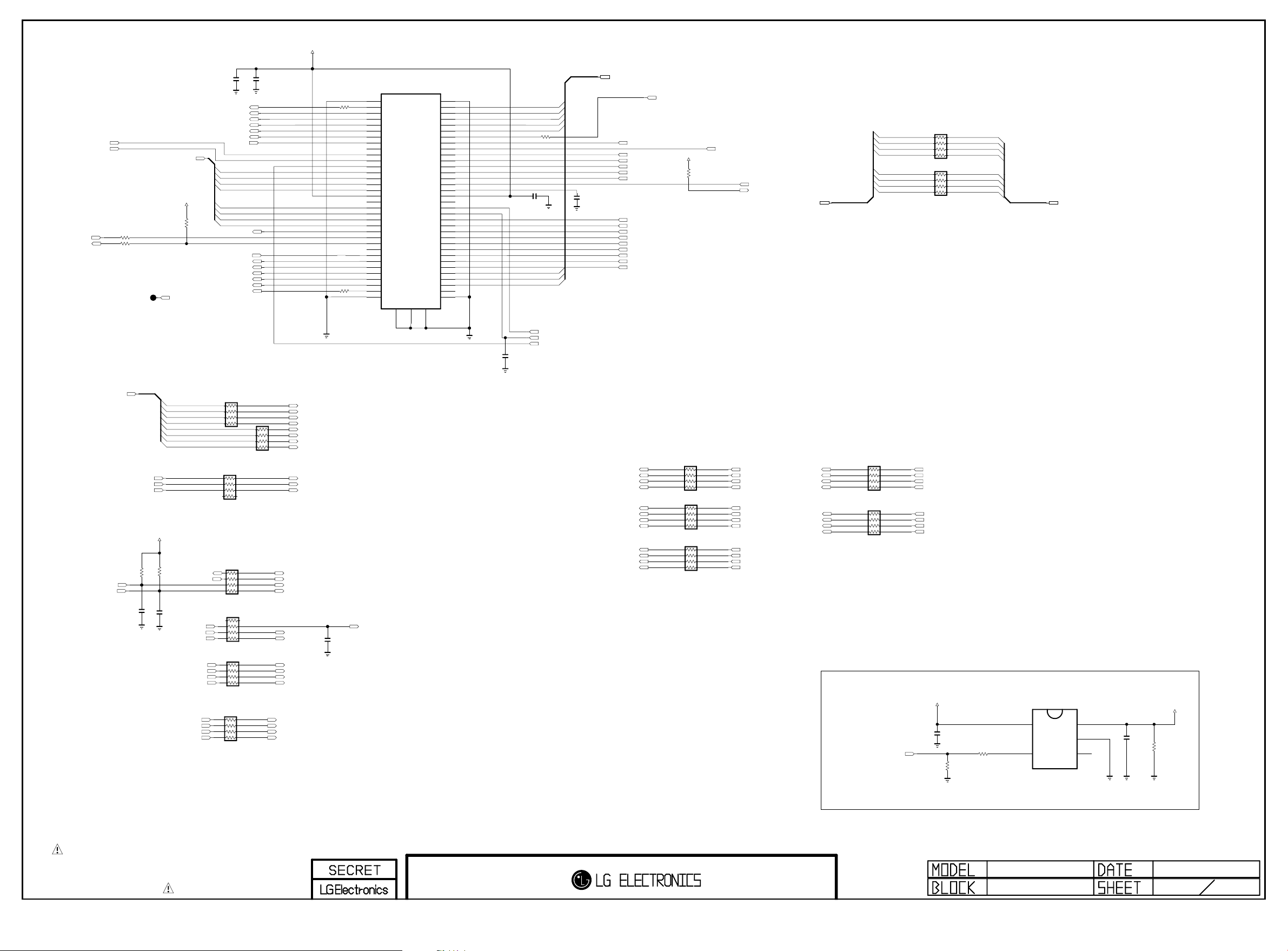
PCM_RESET
Copyright ⓒ 2014 LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
LGE Internal Use Only
/PCM_WAIT
/PCM_IORD
/PCM_IOWR
R701
R702
CI_IN_TS_DATA[0-7]
CI
33
CI
33
+5V_CI_ON
/PCM_CE2
10K
R709
CI
C702
0.1uF
CI
/CI_CD1
CI_TS_DATA[3]
CI_TS_DATA[4]
CI_TS_DATA[5]
CI_TS_DATA[6]
CI_TS_DATA[7]
/PCM_CE2
CI_IN_TS_DATA[0]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[1]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[2]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[3]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[4]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[5]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[6]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[7]
CI_TS_CLK
/PCM_REG
CI_TS_VAL
CI_TS_SYNC
CI_TS_DATA[0]
CI_TS_DATA[1]
CI_TS_DATA[2]
/CI_CD2
C703
4.7uF
10V
CI
+5V_CI_ON
R716
CI
R717 100
CI_ADDR[11]
CI_ADDR[9]
CI_ADDR[13]
C707
0.1uF
16V
CI_ADDR[12]
CI_ADDR[7]
CI_ADDR[6]
CI_ADDR[5]
CI_ADDR[4]
CI_ADDR[3]
CI_ADDR[2]
CI_ADDR[1]
CI_ADDR[0]
CI_DATA[0-7]
CI_ADDR[10]
CI_ADDR[11]
CI_ADDR[9]
CI_ADDR[8]
CI_ADDR[13]
CI_ADDR[14]
CI_ADDR[12]
CI_ADDR[7]
CI_ADDR[6]
CI_ADDR[5]
CI_ADDR[4]
CI_ADDR[3]
CI_ADDR[2]
CI_ADDR[1]
CI_ADDR[0]
/PCM_CE1
+5V_CI_ON
R723
10K
CI
CI_DATA[0]
CI_DATA[1]
/PCM_OE
CI
/PCM_WE
/PCM_IRQA
CI_DATA[0-7]
CI_DATA[2]
CI_DATA[3]
CI_DATA[0-7]
CI_DATA[4]
CI_DATA[5]
CI_DATA[6]
CI_DATA[7]
AR712
33
CI
AR713
33
EB_DATA[0]
EB_DATA[1]
EB_DATA[2]
EB_DATA[3]
EB_DATA[4]
EB_DATA[5]
EB_DATA[6]
EB_DATA[7]
@netLa
EB_DATA[0-7]
CI
JK700
10125901-115LF
100
CI
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
65
66
67
68
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2660
2761
2862
2963
3064
31
32
33
34
G1G2
69
CI_DATA[3]
CI_DATA[4]
CI_DATA[5]
CI_DATA[6]
CI_DATA[7]
CI
C706 0.1uF
C705
12pF
50V
OPT
R721 33
CI
CI_DATA[0]
CI_DATA[1]
CI_DATA[2]
CI_IN_TS_VAL
CI_IN_TS_CLK
CI_IN_TS_SYNC
CI_ADDR[10]
CI_ADDR[8]
CI_ADDR[14]
CI
TPO_DATA[0-7]
/CI_CD2
/CI_CD1
TPO_CLK
TPO_SOP
TPO_VAL
R703
+5V_NORMAL
10K
R705
CI
C700
0.1uF
16V
TPO_DATA[0]
TPO_DATA[1]
TPO_DATA[2]
TPO_DATA[3]
TPO_DATA[4]
TPO_DATA[5]
TPO_DATA[6]
TPO_DATA[7]
10K
/PCM_WAIT
/PCM_IRQA
CI
C701
0.1uF
16V
CI_TS_CLK
CI_TS_VAL
CI_TS_SYNC
CI_TS_DATA[7]
CI_TS_DATA[6]
CI_TS_DATA[5]
CI_TS_DATA[4]
CI_TS_DATA[3]
CI_TS_DATA[2]
CI_TS_DATA[1]
CI_TS_DATA[0]
CI
AR701
33
AR706
CI
AR705
33
AR702
100
AR703
CI
100
AR704
CI
100
CI
AR700
100
CI
33
CAM_WAIT_N
CAM_IREQ_N
CAM_CD2_N
CAM_CD1_N
TPI_VAL
TPI_SOP
TPI_DATA[7]
TPI_DATA[6]
TPI_DATA[5]
TPI_DATA[4]
TPI_DATA[3]
TPI_DATA[2]
TPI_DATA[1]
TPI_DATA[0]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[0]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[1]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[2]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[3]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[4]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[5]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[6]
CI_IN_TS_DATA[7]
CI_IN_TS_CLK
CI_IN_TS_SYNC
CI_IN_TS_VAL
C704
12pF
50V
OPT
TPI_CLK
CI_ADDR[3]
CI_ADDR[0]
CI_ADDR[2]
CI_ADDR[1]
CI_ADDR[4]
CI_ADDR[5]
CI_ADDR[6]
CI_ADDR[7]
CI_ADDR[8]
CI_ADDR[9]
CI_ADDR[10]
CI_ADDR[11]
CI
AR707
33
CI
AR708
33
CI
AR709
33
EB_ADDR[3]
EB_ADDR[0]
EB_ADDR[2]
EB_ADDR[1]
EB_ADDR[4]
EB_ADDR[5]
EB_ADDR[6]
EB_ADDR[7]
EB_ADDR[8]
EB_ADDR[9]
EB_ADDR[10]
EB_ADDR[11]
CI_ADDR[12]
CI_ADDR[13]
CI_ADDR[14]
/PCM_REG
/PCM_OE
/PCM_WE
/PCM_IORD
/PCM_IOWR
CI
AR711
33
CI
AR710
33
EB_ADDR[12]
EB_ADDR[13]
EB_ADDR[14]
CAM_REG_N
EB_OE_N
EB_WE_N
EB_BE_N1
EB_BE_N0
CI POWER ENABLE CONTROL
IN
EN
IC700
AP2151WG-7
5
4
+5V_CI_ON
OUT
1
CI
GND
2
FLG
3
C708
1uF
25V
R706
10K
CI
CI
PCM_5V_CTL
+5V_NORMAL
C709
0.1uF
CI
50V
R700
10K
CI
CI
R704
100
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FIRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFACTURES SPECIFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BSD-14Y-UD-007-HD
2013-12-17
PCMCIA
 Loading...
Loading...