Page 1

,
EPA CERTIFIED
WOOD BURNING
STOVE
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
MANUAL
Model CI2000HT Shown
RETAIN THESE
INSTRUCTIONS
Spectra Series Wood Stoves
FOR FUTURE
REFERENCE
THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE INSTALLED BY A QUALIFIED INSTALLER. READ
MODELS CI1000HT and CI2000HT
ENTIRE MANUAL THOROUGHLY BEFORE INSTALLATION.
P/N 775
080M; Rev. F, 3/2005
Page 2

IMPORTANT WARNINGS
PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE MANUAL BEFORE YOU INSTALL AND USE YOUR NEW ROOM HEATER. FOR
YOUR SAFETY, FOLLOW THE INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS EXACTLY,
WITHOUT DEVIATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS MAY RESULT IN PROPERTY DAMAGE,
BODILY INJURY, OR EVEN DEATH. IF THIS APPLIANCE IS NOT PROPERLY INSTALLED, A HOUSE FIRE MAY
RESULT. CONTACT YOUR LOCAL BUILDING OR FIRE OFFICIALS ABOUT RESTRICTIONS AND INSTALLATION INSPECTION REQUIREMENTS IN YOUR AREA.
1. If utilizing an older chimney, it must be inspected
for adequate serviceability. Refer to the heading
Chimney Inspection on page 11 of this manual.
2. The minimum clearances must be maintained for all
combustible surfaces. The following materials
should be kept a minimum of 36 inches (914 mm)
from the heater; furniture, carpet, drapes, clothing,
wood, papers, etc. Do not store firewood within this
clearance space. Failure to maintain clearances to
all combustibles may result in a house fire.
3. This appliance requires floor protection as outlined in this manual (see Floor Protection on
pages 5, 6 and 7).
4. WARNING: improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause injury
or property damage. This appliance must be
properly installed or the listing will be void. Installations other than those specifically covered
herein have not been confirmed by test and are
not covered by the listing.
5. Minimum ceiling height must be 5 feet (measured
from base of appliance to ceiling).
6. DO NOT CONNECT THIS UNIT TO A CHIMNEY
FLUE CONNECTED TO ANOTHER APPLIANCE.
7. Do not connect this appliance to air ducts or any
air distribution system.
8. PREVENT CREOSOTE FIRE: Inspect and clean
chimney connector and chimney daily for creosote build-up until experience shows how often
you need to clean to be safe. Under certain conditions of use, creosote buildup may occur rapidly.
Be aware that the hotter the fire the less creosote
is deposited, and weekly cleaning may be necessary in mild weather even though monthly cleaning may be enough in the coldest months. Using
green or inadequately seasoned wood can greatly
increase creosote buildup. Use dry wood to minimize creosote buildup.
9. USE SOLID WOOD FUEL ONLY: This appliance is approved for burning dry seasoned natural wood only.
CAUTION: BURN UNTREATED WOOD ONLY. DO
NOT BURN GARBAGE OR FLAMMABLE FLUIDS
SUCH AS GASOLINE, NAPHTHA OR ENGINE OIL.
10. Never use gasoline, gasoline-type lantern fuel,
kerosene, charcoal lighter fluid, or similar liquids
to start or "freshen up" a fire in this heater. Keep
all such liquids well away from the heater while it
is in use.
11. DO NOT OVERFIRE: If heater or chimney connector glows, you are overfiring. Overfiring this appliance could cause a house fire. Overfiring is a
condition where the appliance is operated at temperatures above its design capabilities. Overfiring
can be caused by improper installation, improper
PAGE 2
operation, lack of maintenance or improper fuel
usage. Do not operate the stove with the doors
open or ajar, as this will produce extreme temperatures within the stove.
overfiring is NOT covered under the manufacturers limited warranty (see Care and Operation,
pages 15 to 20).
12. NEVER LEAVE AN UNATTENDED STOVE BURNING ON HIGH. Operation of the stove with the
primary air draft control at its highest burn rate
setting for extended periods can cause dangerous overfiring conditions. The primary air draft
control should only be positioned at the highest
setting during start-up procedures (see How to
Start and Maintain a Fire on page 16) and for short
durations. When leaving the stove unattended ensure that the primary air draft control is set to the
low or medium low range.
13. It is imperative that the control compartments and
circulating air passageways of the appliance be
kept clean.
14. Use a metal container with a tight fitting lid to dispose of ashes.
15. IN THE EVENT OF A COMPONENT FAILURE, USE
ONLY COMPONENTS PROVIDED BY THE MANUFACTURER AS REPLACEMENT PARTS.
16. Burning any kind of fuel uses oxygen from the
dwelling. Be sure that you allow an adequate
source of fresh air into the room where the stove
is operating (see Ventilation Requirements on
page 12).
17. CAUTION: HOT WHILE IN OPERATION. An appliance hot enough to warm your home can severely
burn anyone touching it. Keep children, clothing
and furniture away. Contact may cause skin
burns. Do not let children touch the appliance.
Train them to stay a safe distance from the unit.
The use of a fireguard is recommended.
18. Do not operate this appliance without the firebox
baffle brick properly installed.
19. Always build wood fires directly on the firebox
grate. Do not use andirons or any other method
to elevate the fire.
20. Do not install these appliances into a Manufactured (Mobile) Home.
21. See the listing label located on the back of stove
(or see Safety/Listing Labels on pages 35 & 36).
22. These appliances are designed as supplemental
heaters. Therefore, it is advisable to have an alternate heat source when installed in a dwelling.
23. SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. Ensure that this
manual remains with the appliance and passed to
the user after installation.
Damage caused from
Page 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Important Warnings ................................................ 2
Testing/Listing, EPA, Using this Manual.................. 3
Planning Your Installation ..................................... 4-9
Installation ........................................................ 10-14
Care and Operation .......................................... 15-20
Recommended Fuel / Wood Storage ............... 19-20
Maintenance ..................................................... 21-23
Troubleshooting ................................................ 23-24
Specifications.................................................... 25-26
Replacement Parts List..................................... 27-33
Optional Accessories ..............................................34
Safety/Listing Labels......................................... 35-36
EPA Labels .............................................................37
Service and Maintenance Log ................................38
TESTING/LISTING
Models CI1000HT and CI2000HT have been Listed to
UL Standard #1482 and ULC-S627 by OMNI-Test Laboratories, Inc.; Beaverton, OR; Report numbers;
CI1000HT #132-S-03-2 and CI2000HT #132-S-05-2.
EPA CERTIFICATION
This heater meets EPA particulate matter (smoke) control requirements for noncatalytic wood heaters built on
or after July 1, 1990.
CONGRATULATIONS ON THE PURCHASE OF YOUR
NEW WOODSTOVE MANUFACTURED BY LENNOX
HEARTH PRODUCTS.
When you purchased your new woodstove, you
joined the ranks of thousands of concerned individuals whose answer to their home heating needs
reflects their concern for aesthetics, efficiency and
our environment. We extend our continued support
to help you achieve the maximum benefit and enjoyment available from your new wood stove.
It is our goal at Lennox Hearth Products to provide
you, our valued customer, with an appliance that will
ensure you years of trouble free warmth and pleasure.
Thank you for selecting a Lennox Hearth Products
stove as the answer to your home heating needs.
Sincerely,
All of us at Lennox Hearth Products
USING THIS MANUAL
Please carefully read and follow all instructions in this
manual before starting the installation. Please pay special attention to the safety instructions provided in this
manual. The Homeowner’s Care and Operation Instructions included here will assure you have many years of
dependable and enjoyable service from your appliance.
PACKAGING LIST
This appliance is packaged with an accessory package,
which contains the following:
One - Installation and Operation Manual
One - Warranty Certificate
One - Wood and Brass, Removable Door Handle (for
opening the ashpan door, firebox door and side
door)
One - Air Control / Ash Pan Removal Tool
One - Fire Poker
Four - Leg Cushions
One - Spray Can of Charcoal Paint
PAGE 3
Page 4
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION
QUESTIONS TO ASK LOCAL BUILDING OFFICIAL
A correct installation is critical and imperative for reducing fire hazards and perilous conditions that can arise
when wood burning appliances are improperly installed.
The installer must follow all of the manufacturers’ instructions. These models are designed as radiant room
heaters and should be used for no other purpose.
The installation of a wood burning appliance must conform to local codes and applicable state and federal
requirements and a building permit must be obtained
before installing. Familiarity with these requirements
before installation is essential. Important considerations
to discuss with local building officials include:
1. Applicable codes (i.e. Uniform Mechanical Code,
State or Regional Codes.)?
2. Local amendments?
3. Is a permit required - cost?
(You may wish to contact your insurance company
to ask if they require this?).
4. Rooms where the installation is not allowed?
SMOKE DETECTORS
Since there are always several potential sources of fire
in any home, we recommend installing smoke detectors. If possible, install the smoke detector in a hallway
adjacent to the room (to reduce the possibility of occasional false activation from the heat produced by the
stove). If your local code requires a smoke detector be
installed within the same room, you must follow the requirements of your local code. Check with your local
building department for requirements in your area.
NOTE – This appliance is NOT
tion into a Manufactured (Mobile) Home.
SELECTING A LOCATION
The design of your home and where you place your
stove will determine its value as a source of heat. A
wood stove depends primarily on air circulation (convection) to disperse its heat, and therefore, a central
location is often best. There are other practical considerations, which must be considered before a final selection of locations is made.
approved for installa-
♦ Existing Chimneys
♦ Wood Storage
♦ Aesthetic Considerations
♦ Roof Design (Rafter Locations & Roof Pitch)
♦ Room Traffic
♦ Proximity to Combustibles
♦ Electrical Wiring
The installation of this stove will require some research.
Once your options are determined, consult with your
local building department who will be able to give you
the necessary installation requirements for your area (Is
a building permit required?, Rooms where installation
may not be allowed?, etc.).
WARNING: CHECK ALL LOCAL BUILDING AND
SAFETY CODES BEFORE INSTALLATION. THE INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS AND APPROPRIATE
CODE REQUIREMENTS MUST BE FOLLOWED EXACTLY AND WITHOUT COMPROMISE. ALTERATIONS TO THE STOVE ARE NOT ALLOWED. DO
NOT CONNECT THE STOVE TO A CHIMNEY SYSTEM SERVING ANOTHER STOVE, APPLIANCE, OR
ANY AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCT. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS WILL VOID THE
MANUFACTURERS WARRANTY.
If you plan to vent your stove into an existing masonry
chimney, have it inspected by a local fire marshal or
qualified installer. Remember that a stove's performance is heavily influenced by the chimney and its location on the roof. An oversized flue may not provide effective draw, and a flue liner may be required (see Draft
Requirements on page 12). Consult your dealer or
qualified installer before final selection is made.
This stove requires pre-installation work to be completed before installation can take place. This may include modification for flue and chimney.
The appliance should be inspected before use and the
chimney cleaned at least annually. More frequent cleaning may be required due to poor operation, installation,
or low quality fuel.
CAUTION: THE STOVE BODY IS VERY HEAVY. THE
USE OF A HEAVY DUTY ESCALARA (STAIR STEP
HAND TRUCK) IS RECOMMENDED FOR LIFTING
THE STOVE BODY.
PAGE 4
Page 5
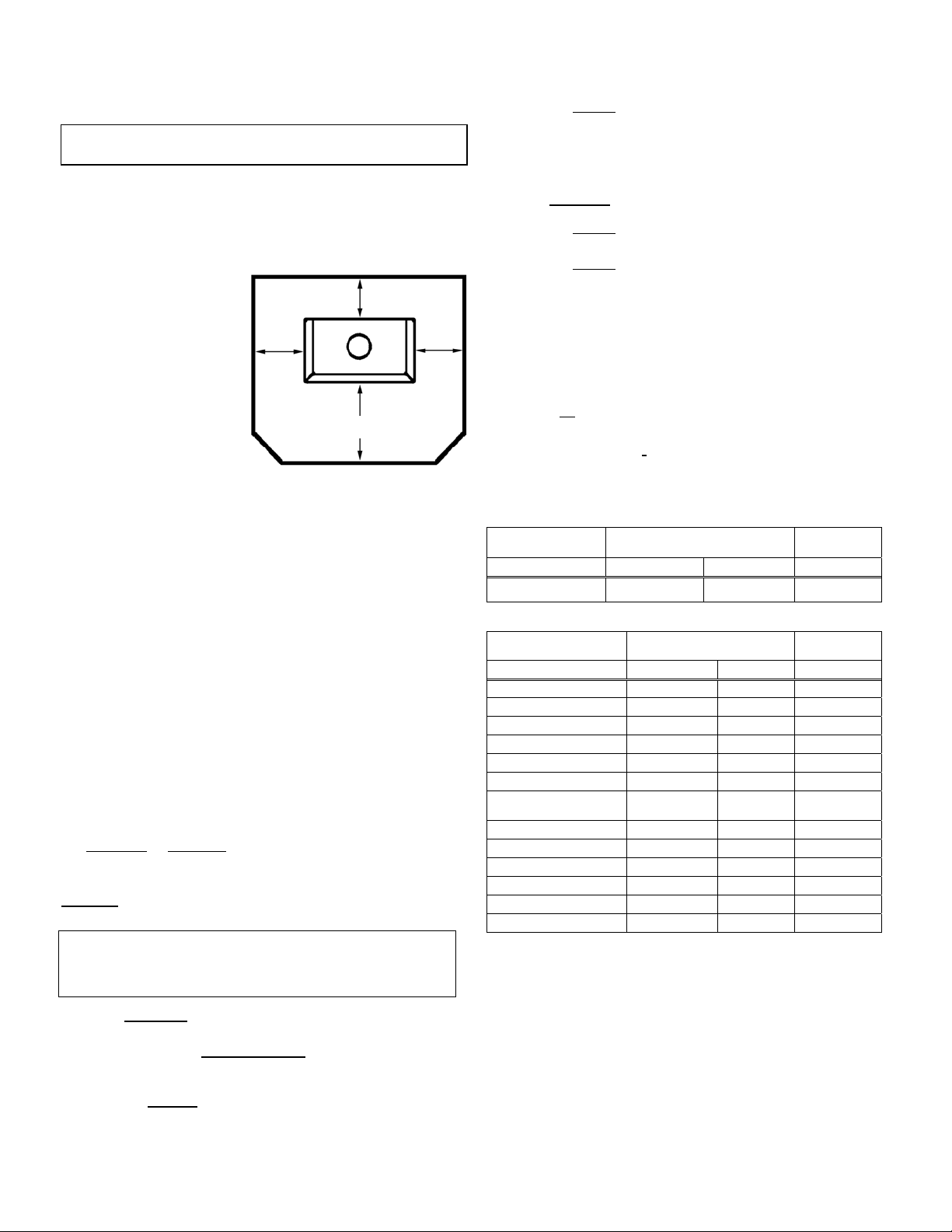
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION – Model CI1000HT
T
aterials
↓
FLOOR PROTECTION
FOR INSTALLATIONS IN THE USA
MODEL CI1000H
The floor protector must meet or exceed the minimum thermal requirements as defined on this page (see Floor Protec-
tion Using Alternate Material As Floor Protector). If the floor
protection is to be stone, tile, brick, etc., it must be mortared
or grouted to form a continuous noncombustible surface. If a
chimney connector extends
horizontally over the floor,
protection must also cover
the floor under the
Top View
0 "
(0 mm)
connector and at least 2"
(51 mm) to either side.
The floor protector must
fully cover the area
beneath the appliance
5.2"
(132 mm)
5.2"
(132 mm)
and extend 18” to the
front, 5.2” to the sides,
and 0” from the back as
18" (457 mm)
shown in the illustration
to the right.
FLOOR PROTECTION
USING ALTERNATE MATERIAL AS FLOOR PROTECTOR
The hearth pad or alternate material used as a floor protector must be constructed of a durable noncombustible material having an equal or better thermal conductivity value
(lower k value) of k = .84 BTU / IN FT
2
HR °F or a thermal
resistance that equals or exceeds r = 1.19 HR °F FT
IN/BTU with a minimum thickness of 1/2”. With these values, determine the minimum thickness of the alternate material required using the formula(s) and the table shown
here (see chart – Approved Alternative Materials for Floor
Protection).
Note: Any noncombustible material having a thickness of
1/2” (13 mm) whose k value is less than .84 or whose r
value is more than 1.19 is acceptable. If the alternate material used has a higher k value or lower r value will require a
greater thickness of the material used. In some cases, if the
k value is less or the r value higher, a thinner material may
be used.
Methods of determining floor protection equivalents:
To determine the thickness required for the alternate material when either the k value or r value is known, use either
the k formula
or r formula:
Example: Durock Cement Board is to be used for the floor
protection. How thick must this material be? The following
formulas
required.
T
M
give the means of determining minimum thickness
= minimum thickness required for alternate material
kM = k value per inch of alternate material
TL = minimum thickness of listed material
rM = r value per inch of alternate material
Using the k formula
Desired Thickness k value of desire Minimu
of the alternate = material (per inch)
material k value of listed of listed
material (per inch) material
(inches) = kM x TL
T
M
.84
:
x thickness
TM (inches) = 1.92 x 1/2”
.84
Answer using k: 2.286 x 0.50” = 1.143 = ~ 1 9/64”
1 9/64” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
Using the r formula:
TM (inches) = 1.19 x TL
r
T
.52
Answer using r: 2.288 x 0.50” = 1.143 = ~ 1 9/64”
1 9/64” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
At times it is important to know what combination of materials are
acceptable for use as floor protection. The “R values” are used to
determine acceptable combinations of materials because “R values” are additive where r and k values are not.
“R value” = 1
k
Example: “R value” = 1/k
that the required “R value” for a suitable floor protector used must be
equal to or greater than:“R” = r x T
2
Note: To convert inches to millimeters divide by .03937.
(*) After minimum thickness is calculated, the thickness can
be no less than 1/2” (13mm).
(**) If the floor protector to be used is a noncombustible material and is NOT listed on this chart on this page, the manufacturer of the material must provide either the listed k-value
per inch or r-value per inch and the minimum thickness will
need to be calculated per instructions on this page.
M
(inches) = 1.19 x .5”
M
= r x thickness of material used
= r x thickness of material used. Given
= 1.19 x .5” = .60.
L
Listed Material
Listed Material Thermal Values Listed Min.
Listed Material → .84 1.19 1/2”
k (per inch) r (per inch) T
Thickness
L
Approved Alternate Materials for Floor Protection (**)
Alternative
M
k (per inch) r ( per i nch) TM
Kaowool M Board .47 2.13 * 1/2”
Micore 160 .35 2.86 * 1/2”
Micore 300 .46 2.18 * 1/2”
Durock Cement Board 1.92 .52 1 3/16”
Hardibacker 1.95 .51 1 3/16”
Hardibacker 500 2.30 .44 1 3/8”
Cultered Stone
Hearthstone
Wonderboard 3.23 0.31 1 15/16”
Face brick 9.00 0.11 5 3/8”
Common brick 5.00 0.20 3”
Cement mortar 5.00 0.20 3”
Ceramic tile 12.5 .08 7 ½”
Marble ~20.0 ~.05 11 15/16”
Thermal Values * Minimum
Thickness
2.82 .35 1 11/16”
PAGE 5
Page 6
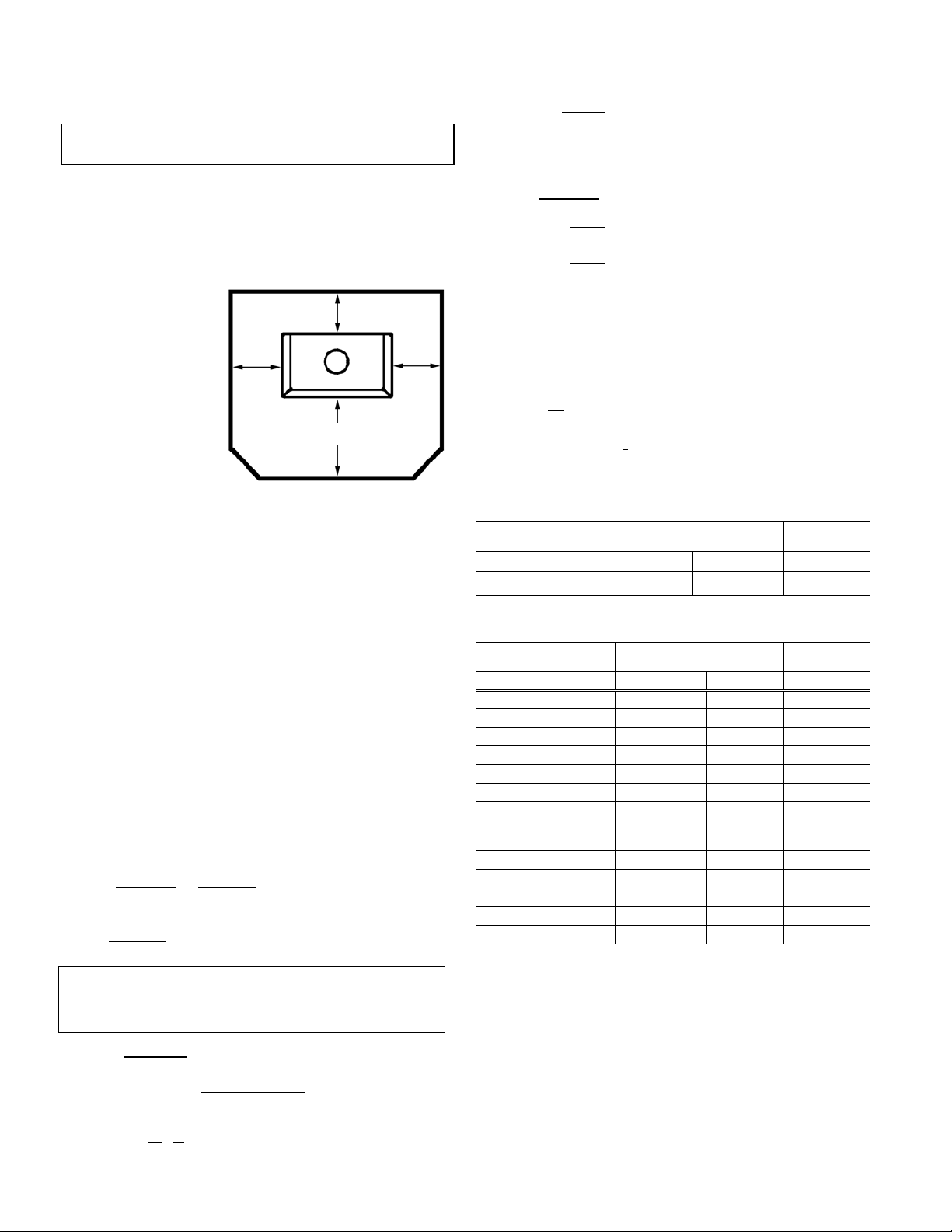
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION – Model CI1000HT
T
aterials
↓
FLOOR PROTECTION
FOR INSTALLATIONS IN CANADA
MODEL CI1000H
The floor protector must meet or exceed the minimum thermal requirements as defined on this page (see Floor Pro-
tection Using Alternate Material As Floor Protector). If the
floor protection is to be stone, tile, brick, etc., it must be
mortared or grouted to form a continuous noncombustible
surface. If a chimney connector extends horizontally over
the floor, protection
must also cover the
floor under connector
and at least 2" (51
mm) to either side.
Top View
8" (203 mm)
The floor protector must
fully cover the area
beneath the appliance
8"
(203 mm)
8"
(203 mm)
and extend 18” to the
front, 8” to the sides,
and 8” from the back as
18" (457 mm)
shown in the illustration
to the right.
FLOOR PROTECTION USING ALTERNATE MATERIAL
AS FLOOR PROTECTOR
The hearth pad or alternate material used as a floor protector must be constructed of a durable noncombustible
material having an equal or better thermal conductivity
value (lower k value) of k = .84 BTU / IN FT
thermal resistance that equals or exceeds r = 1.19 HR °F
2
IN/BTU with a minimum thickness of 1.45”. With these
FT
2
HR °F or a
values, determine the minimum thickness of the alternate
material required using the formula(s) and the table
shown here (see chart – Approved Alternative Materials
for Floor Protection).
Note: Any noncombustible material having a thickness of
1.45" (37 mm) whose k value is less than .84 or whose r
value is more than 1.19 is acceptable. If the alternate material used has a higher k value or lower r value will require a greater thickness of the material used. In some
cases, if the k value is less or the r value higher, a thinner
material may be used.
Methods of determining floor protection equivalents:
To determine the thickness required for the alternate material when either the k value or r value is known, use either the k formula
or r formula:
Example: Durock Cement Board is to be used for the
floor protection. How thick must this material be? The following formulas
thickness required.
= minimum thickness required for alternate material
T
M
give the means of determining minimum
kM = k value per inch of alternate material
TL = minimum thickness of listed material
rM = r value per inch of alternate material
Using the k formula
Desired thickness k value of desire Minimum
of the alternate = material (per inch)
material k value of listed of listed
material (per inch) material
TM (inches) = k
.84
:
x TL
M
x thickness
TM (inches) = 1.92 x .1.45”
.84
Answer using k: ~2.287 x ~1.45” = ~ 3.316” = ~ 3 5/16”
~ 3 5/16” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
Using the r formula:
TM (inches) = 1.19 x TL
r
T
M
.52
Answer using r: ~2.287 x 1.45” = ~3.316 =~ 3 5/16”
~ 3 5/16” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
At times it is important to know what combination of materials are
acceptable for use as floor protection. The “R values” are used to
determine acceptable combinations of materials because “R values” are additive where r and k values are not.
“R value” = 1
k
Example: “R value” = 1/k = r x thickness of material used. Given that
the required “R value” for a suitable floor protector used must be equal to
or greater than:“R” = r x T
Listed Material Thermal Values Listed Min.
Listed Material → .84 1.19 1.45”
Alternative
M
k (per inch) r ( per i nch) TM
Kaowool M Board .47 2.13 * 1.45”
Micore 160 .35 2.86 * 1.45”
Micore 300 .46 2.18 * 1.45”
Durock Cement Board 1.92 .52 3.5/16”
Hardibacker 1.95 .51 3 3/8”
Hardibacker 500 2.30 .44 4”
Cultered Stone
Hearthstone
Wonderboard 3.23 0.31 5 9/16”
Face brick 9.00 0.11 15 9/16”
Common brick 5.00 0.20 8 5/8”
Cement mortar 5.00 0.20 8 5/8”
Ceramic tile 12.5 .08 21 9/16”
Marble ~20.0 ~.05 34 9/16”
Note: To convert inches to millimeters divide by .03937.
(*) After minimum thickness is calculated, the thickness can be
no less than 1.45” (36.8mm).
(**) If the floor protector to be used is a noncombustible material and is NOT listed on this chart on this chart, the manufacturer of the material must provide either the listed k-value per
inch or r-value per inch and the minimum thickness will need to
be calculated per instructions on this page.
PAGE 6
M
(inches) = 1.19 x .1.45”
= r x thickness of material used
= 1.19 x 1.45” = ~ 1.73.
L
Listed Material
k (per inch) r (per inch) T
Approved Alternate Materials for
Floor/Hearth Protection (**)
Thickness
L
Thermal Values * Minimum
2.82 .35 4 7/8”
Thickness
Page 7
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION– Model CI2000HT
aterials
↓
a
a
FLOOR PROTECTION
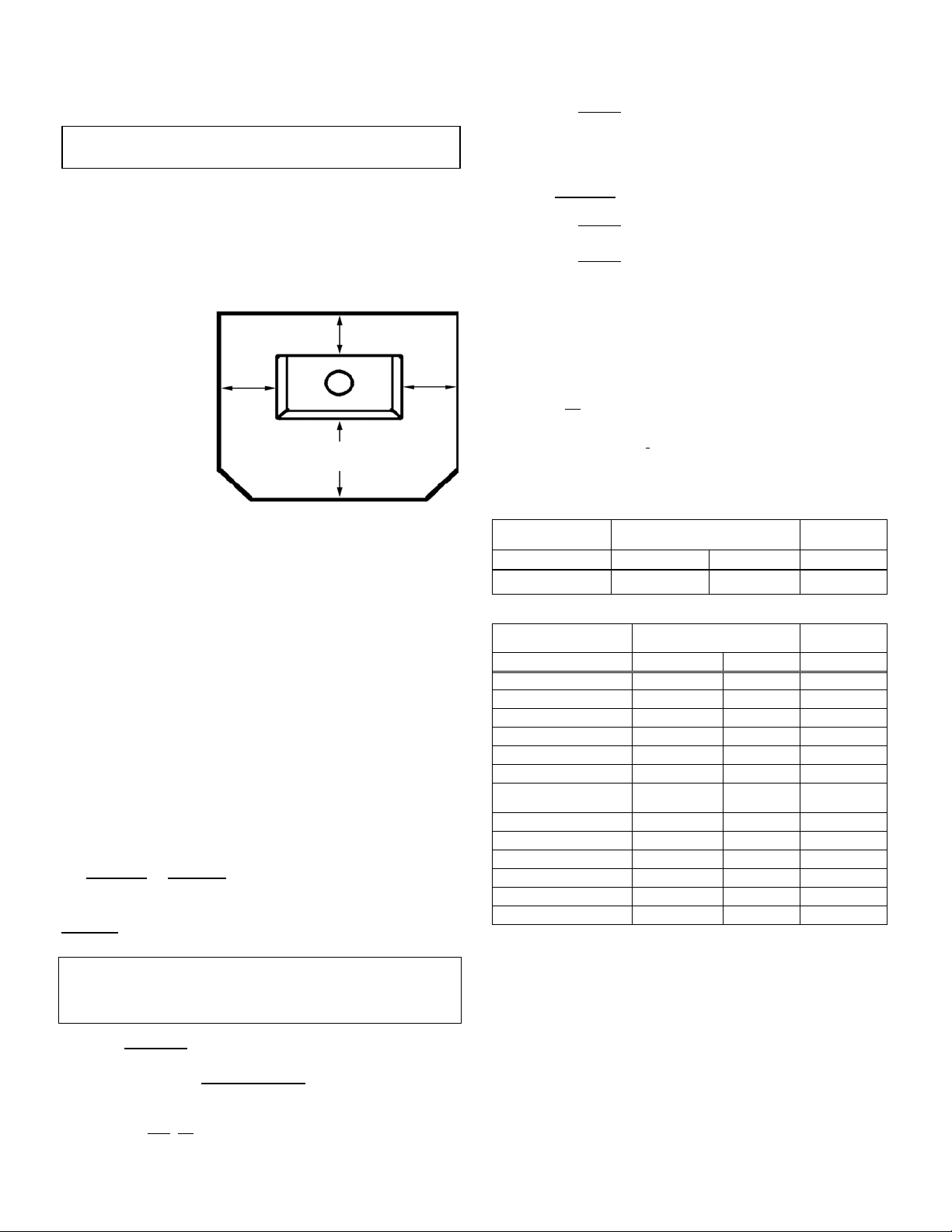
FOR INSTALLATIONS IN THE USA & CANADA
The floor protector must meet or exceed the minimum thermal requirements as defined on this page (see Floor Protec-
tion Using Alternate Material As Floor Protector). If the floor
protection is to be stone, tile, brick, etc., it must be mortared
or grouted to form a continuous noncombustible surface. If a
chimney connector extends horizontally over the floor, protection must also cover the floor under the connector and at
least 2" (51 mm) to
either side.
The floor protector
must fully cover the
area beneath the
appliance and extend
18” to the front, 5”USA and 8”-Canada
to the sides, and 0”USA and 8”-Canada
from the back as
shown in the illustration to the right.
FLOOR PROTECTION USING ALTERNATE MATERIAL AS
FLOOR PROTECTOR
The hearth pad or alternate material used as a floor protector must be constructed of a durable noncombustible material having an equal or better thermal conductivity value
(lower k value) of k = .84 BTU / IN FT
resistance that equals or exceeds r = 1.19 HR °F FT
with a minimum thickness of 1/2”. With these values, determine the minimum thickness of the alternate material required using the formula(s) and the table shown here (see
chart – Approved Alternative Materials for Floor Protection).
Note: Any noncombustible material having a thickness of
1/2” (13 mm) whose k value is less than .84 or whose r value
is more than 1.19 is acceptable. If the alternate material
used has a higher k value or lower r value will require a
greater thickness of the material used. In some cases, if the
k value is less or the r value higher, a thinner material may
be used.
Methods of determining floor protection equivalents:
To determine the thickness required for the alternate material when either the k value or r value is known, use either
the k formula
or r formula:
Example: Durock Cement Board is to be used for the floor
protection. How thick must this material be? The following
formulas
required.
T
M
give the means of determining minimum thickness
= minimum thickness required for alternate material
kM = k value per inch of alternate material
TL = minimum thickness of listed material
rM = r value per inch of alternate material
Using the k formula
Desired thickness k value of desire Minimum
of the alternate = material (per inch)
material k value of listed of listed
material (per inch) material
(inches) = k
T
M
.84
MODEL CI2000HT
Canad
8"/203mm
USA
5" / 127 mm
:
x TL
M
Top View
USA & Canada
18" (457 mm)
2
HR °F or a thermal
x thickness
0" / 0 mm USA
8" / 203mm Canada
Canad
8"/203mm
USA
5" / 127 mm
2
IN/BTU
PAGE 7
T
(inches) = 1.92 x 1/2”
M
.84
Answer using k: 2.286 x 0.50” = 1.143 = ~ 1 9/64”
~1 9/64” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
Using the r formula:
(inches) = 1.19 x TL
T
M
r
(inches) = 1.19 x .5”
T
M
.52
M
Answer using r: 2.288 x 0.50” = 1.143 = ~ 1 9/64”
~1 9/64” thickness Durock Cement Board will be required.
At times it is important to know what combination of materials
are acceptable for use as floor protection. The “R values” are
used to determine acceptable combinations of materials because “R values” are additive where r and k values are not.
“R value” = 1
k
= r x thickness of material used
Example: “R value” = 1/k = r x thickness of material used. Given
that the required “R value” for a suitable floor protector used must be
equal to or greater than:“R” = r x T
= 1.19 x .5” = .60.
L
Listed Material
Listed Material Thermal Values Listed Min.
Listed Material → .84 1.19 1/2”
k (per inch) r (per inch) T
Thickness
L
Approved Alternate Materials for Floor Protection (**)
Alternative
M
k (per inch) r ( per i nch) TM
Kaowool M Board .47 2.13 * 1/2”
Micore 160 .35 2.86 * 1/2”
Micore 300 .46 2.18 * 1/2”
Durock Cement Board 1.92 .52 1 3/16”
Hardibacker 1.95 .51 1 3/16”
Hardibacker 500 2.30 .44 1 3/8”
Cultered Stone
Hearthstone
Wonderboard 3.23 0.31 1 15/16”
Face brick 9.00 0.11 5 3/8”
Common brick 5.00 0.20 3”
Cement mortar 5.00 0.20 3”
Ceramic tile 12.5 .08 7 ½”
Marble ~20.0 ~.05 11 15/16”
Thermal Values * Minimum
Thickness
2.82 .35 1 11/16”
Note: To convert inches to millimeters divide by .03937.
(*) After minimum thickness is calculated, the thickness can
be no less than 1/2” (13mm).
(**) If the floor protector to be used is a noncombustible material and is NOT listed on this chart on this chart, the manufacturer of the material must provide either the listed k-value
per inch or r-value per inch and the minimum thickness will
need to be calculated per instructions on this page.
Page 8
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION– Model CI1000HT
E
MODEL CI1000HT
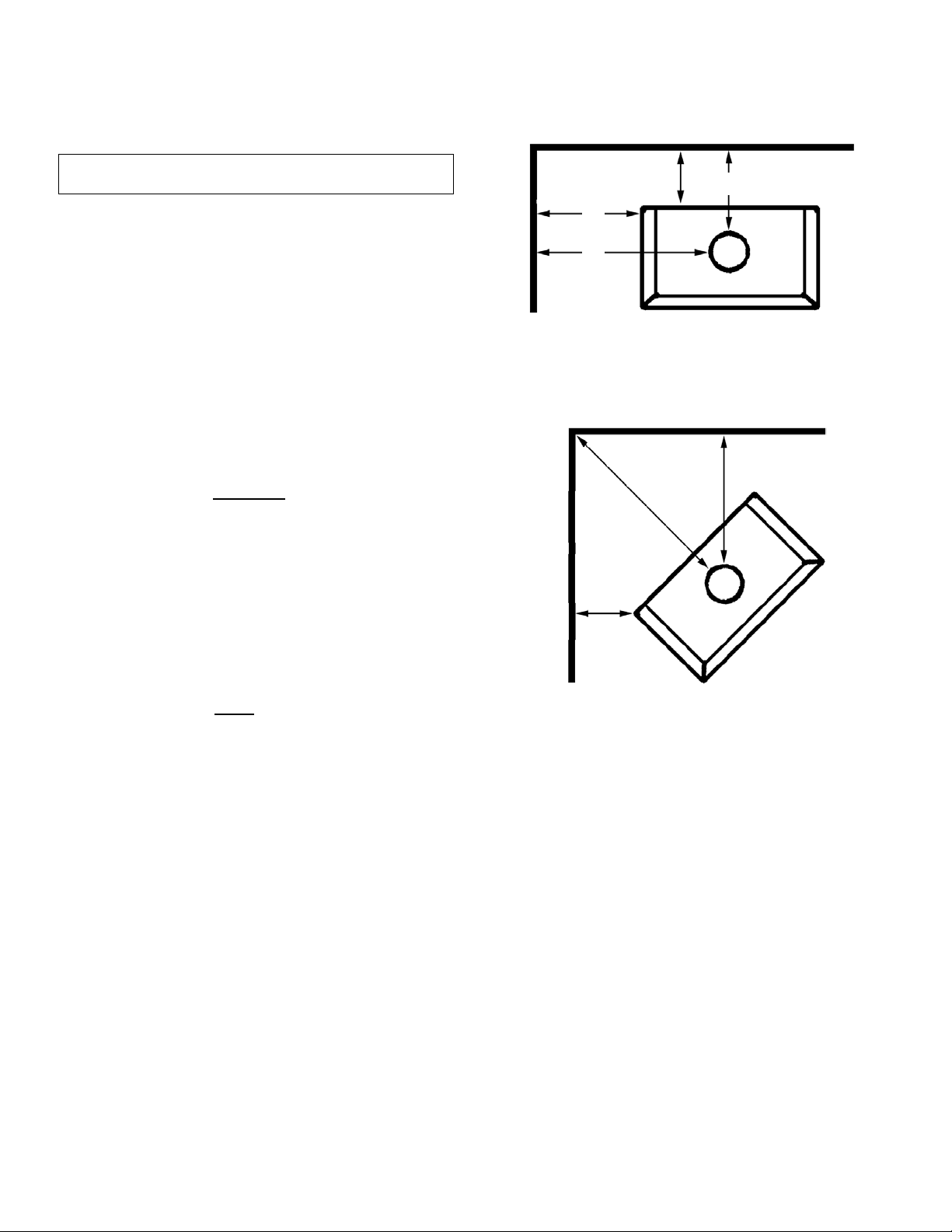
COMBUSTIBLE WALL CLEARANCE – USA & Canada
WARNING: It is very important that you observe the
minimum clearances.
There are listed clearances for your stove which were
determined in a Laboratory test using various "classes"
of stove pipe or chimney. Minimums are first established for the stove itself and increased based on how
much heat is transferred by each class of pipe.
Position the unit no closer than the minimum clearances
to combustible materials. Check that no overhead
cross members in the ceiling or roof will be cut. Reposition unit if necessary being careful not to move closer
than the minimum clearances.
Minimum Ceiling Height – 7 feet / 2133mm from floor
to ceiling.
SINGLE WALL PIPE WITHOUT
Using single wall 24 MSG black or 25 MSG blued steel
connector pipe with factory-built chimney listed to either
UL 103HT or ULC S629.
Minimum Clearances (inches)
A. 27 1/2" / 699mm D. 24" / 610mm
B. 27" / 686mm E. 18" / 457mm
C. 27" / 686mm F. 19" / 483mm
G. 35 3/16” / 894 mm (this is a reference dimension only)
SINGLE WALL PIPE WITH
CLEARANCE
Using single wall 24 MSG black or 25 MSG blued steel
connector pipe with factory-built chimney listed to either
UL 103HT or ULC S629. The use of a pipe shield for 6"
connector with 1" clearance to the pipe is mandatory.
Minimum Clearances (Inches)
A. 21 1/2" / 546mm D. 18" / 457 mm
B. 27" / 686mm E. 18" / 457mm
C. 19" / 483mm F. 11" / 279mm
G. 23 7/8” / 606 mm (this is a reference dimension only)
PROTECTED WALL CLEARANCE
Some local codes will allow reduced clearances when the
stove is installed adjacent to a protected wall system. The
variance must be approved by your local building official.
Normally, the protected wall system is defined as a noncombustible material with a minimum of 1" air space behind. Check your local building codes or with a qualified
installer (Ref. NFPA 211).
PIPE SHIELD
PIPE SHIELD / REDUCED
Parallel Installation
D
B
Corner Installation
G
F
• MODEL CI1000HT IS NOT APPROVED FOR USE
WITH DOUBLE WALL PIPE.
• DO NOT INSTALL THE CI1000HT INTO AN AL-
COVE OR A CONFINED SPACE. This unit has
not been tested or approved for installation into
a confined space such as an alcove (see the national standard below).
NFPA 211-96, 9-2.2: (Applies to Solid Fuel Burn-
ing Appliances, which are not alcove tested) Solid fuel-burning appliances shall not be installed in confined spaces. The space or room
shall be of ample size to allow adequate circulation of heated air. Appliances shall be so located as not to interfere with the proper circulation of air within the heated space.
A
C
PAGE 8
Page 9
PLANNING YOUR INSTALLATION– Model CI2000HT
MODEL CI2000HT
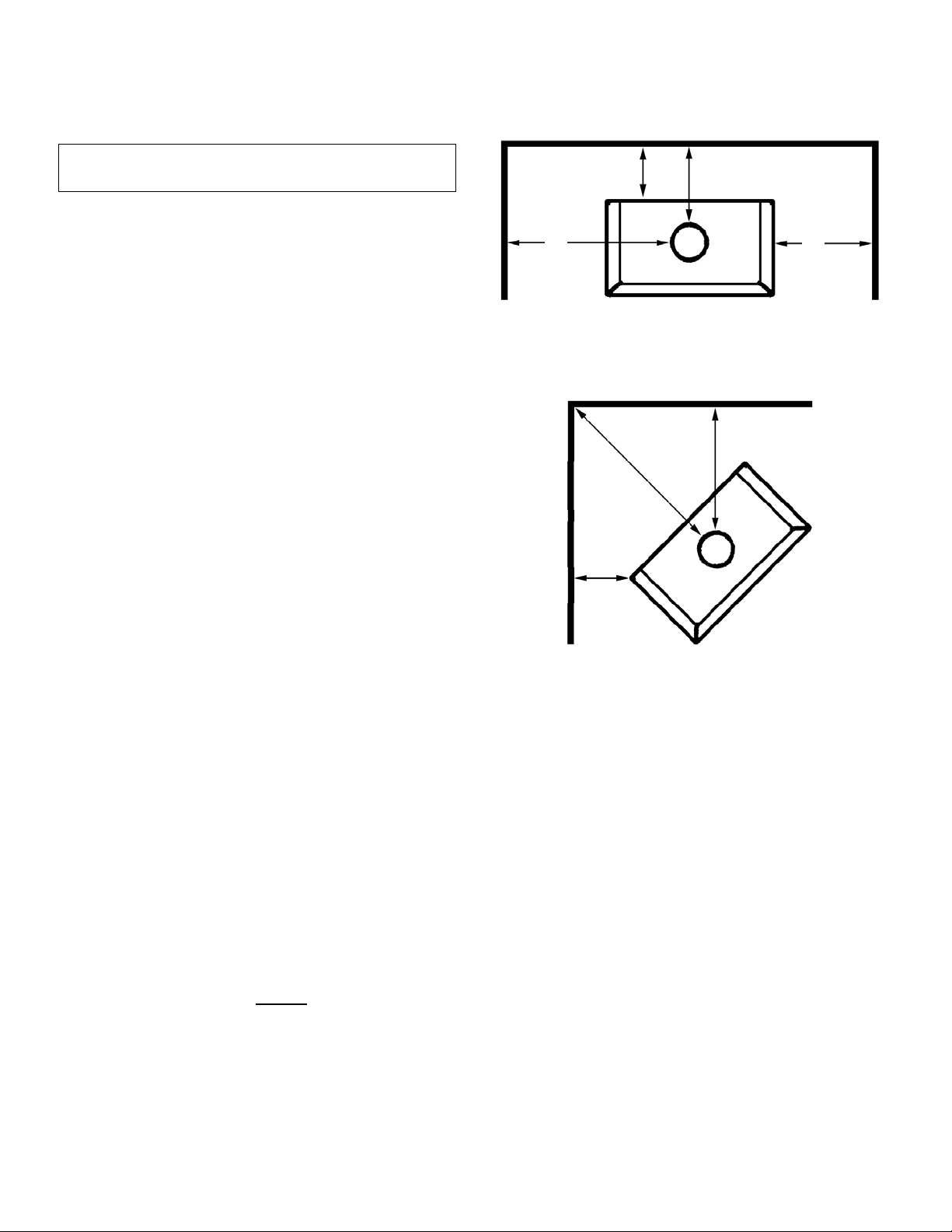
COMBUSTIBLE WALL CLEARANCE – USA & Canada
WARNING: It is very important that you observe the
minimum clearances.
There are listed clearances for your stove which were
determined in a Laboratory test using various "classes"
of stove pipe or chimney. Minimums are first established
for the stove itself and increased based on how much
heat is transferred by each class of pipe.
Position the unit no closer than the minimum clearances
to combustible materials. Check that no overhead cross
members in the ceiling or roof will be cut. Reposition
unit if necessary being careful not to move closer than
the minimum clearances.
SINGLE WALL PIPE (Not approved for alcove installations) Using single wall 24 MSG black or 25 MSG
blued steel connector pipe with factory-built chimney
listed to either UL 103HT or ULC S629.
Minimum Clearances (inches)
A. 18" / 457mm D. 13" / 330mm
B. 32" / 813mm E. 20" / 508mm
C. 27" / 686mm F. 16" / 406mm
G. 35 3/16” / 894 mm (this is a reference dimension only)
DOUBLE WALL PIPE (For alcove installations,
clearances "C" and "F" are not applicable) Use listed
double wall chimney connector or Type L vent pipe to
the top of the stove.
Minimum Clearances (Inches)
A. 14 1/2" / 368mm D. 10" / 254mm
B. 28 1/2" / 724mm E. 17" / 432mm
C. 18" / 457mm F. 7" / 178mm
Minimum Ceiling Height for Single wall pipe and
double wall pipe installations and Alcove Installations – 60" / 1524mm from floor to ceiling and 29" /
737mm from stove top to ceiling.
ALCOVE INSTALLATION CLEARANCES
Alcove Installations Require Double Wall Pipe Only
Use listed double wall chimney connector or Type L
vent pipe to the top of the stove.
Minimum Clearances (Inches)
A. 14 1/2" (368 mm) D. 10" (254 mm)
B. 28 1/2" (724 mm) E. 17" (432 mm)
C. N/A F. N/A
Note: Alcove clearances cannot
wall protection. Maximum alcove depth must be no
more than 48" (1220 mm).
be reduced using
Parallel & Alcove Installations
D
B E
A
Corner Installation
C
G
F
PROTECTED WALL CLEARANCE
Some local codes will allow reduced clearances when the
stove is installed adjacent to a protected wall system. The
variance must be approved by your local building official.
Normally, the protected wall system is defined as a non- combustible material with a minimum of 1" air space behind.
Check your local building codes or with a qualified installer
(Ref. NFPA 211).
PAGE 9
Page 10
INSTALLATION
INSTALLING LEG PADS
The four leg pads (included in accessory package), are
provided for placement under the four legs.
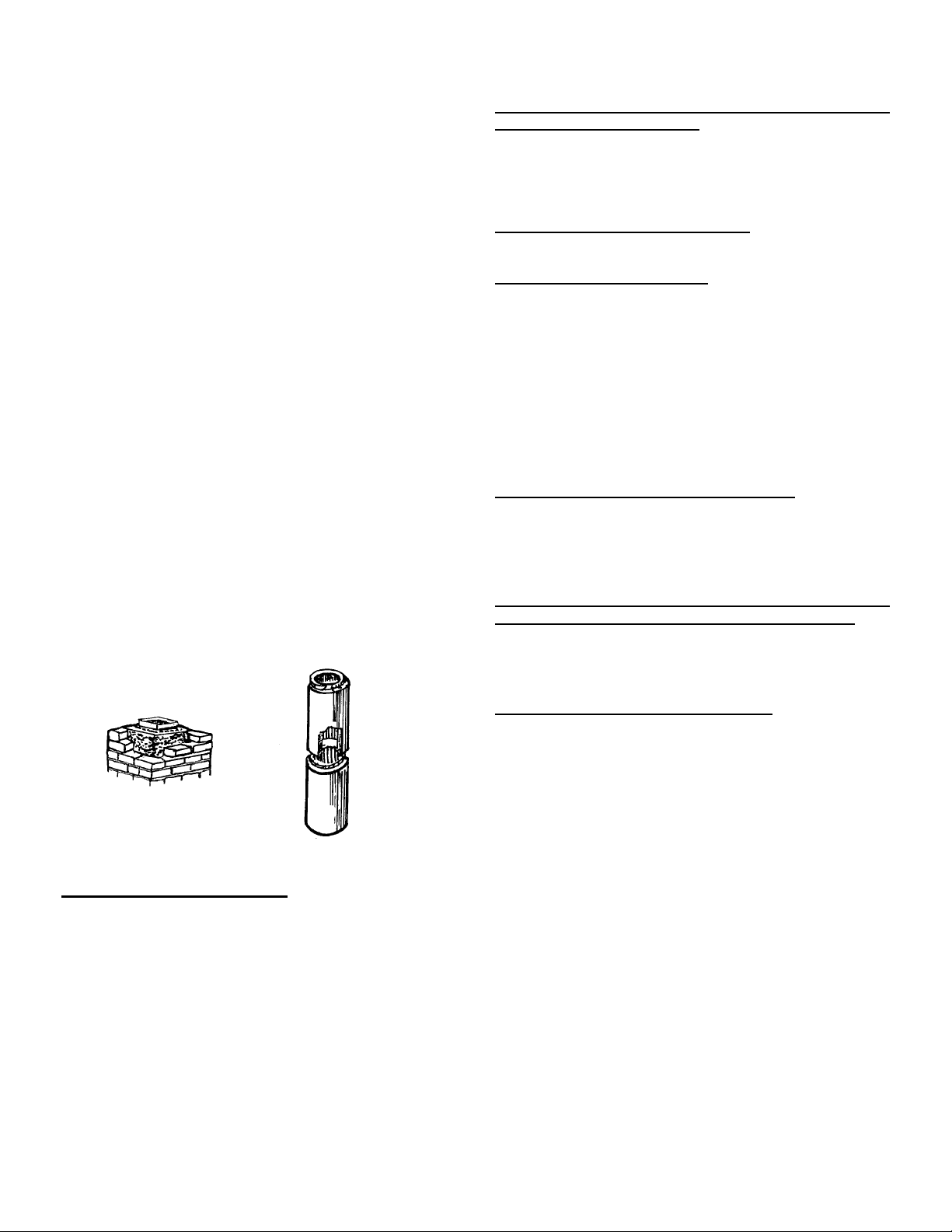
TYPES OF CHIMNEYS
The unit must be connected to either a code-approved
masonry chimney with a flue liner, or a 6 inch diameter
factory-built chimney complying with the requirements for
Type HT chimneys in the standard UL 103.
The chimney is a vital part of your stove installation. A
properly built masonry chimney or a properly installed
factory-built chimney will assure a consistent draft under
a variety of weather conditions (a smoking stove is usually caused by a chimney problem). The stove flue size is
6 inches diameter, which is approximately 28 square
inches minimum. The maximum flue size should be no
more than (3)-three times the cross sectional area of the
size of the stove flue collar. In this case, that would be no
larger than an 10-inch diameter stack, or approximately
85 square inches maximum.
All chimneys must be installed as specified by local
building codes and according to the chimney manufacturer instructions (in the case of a factory-built chimney).
See the chimney manufacturer instructions for exact
specifications. Factory-built chimneys must comply with
UL 103HT or ULC S629. A chimney connector shall not
pass through an attic or roof space, closet or similar concealed space, or a floor, or ceiling. Where passage
through a wall, or partition of combustible construction is
desired, the installation shall conform to CAN/CSA-B365,
Installation Code for Solid-Fuel-Burning Appliances and
Equipment.
Factory
Built
Chimney
Tile-lined
Masonry
ACCEPTABLE CONNECTOR PIPE FOR INSTALLATIONS
When Using Single Wall Pipe:
ameter, single wall, 24 MSG black steel or 26 MSG
blued steel connector pipe on the flue collar of the unit.
When installing pipe, the crimped ends of the pipe
should all point down. Position all seams toward the
back for aesthetics. Three (3) pre-drilled holes are provided in the flue collar for fastening the pipe securely to
the stove. Use sheet metal screws to do this. Additional
sections of single wall pipe should be fastened together
with at least three (3) sheet metal screws each section.
All pipe connections must be sealed (ie. high temperature silicone). When connecting to the factory-built ceiling
support package, use the manufacturer's transition
piece, usually called a dripless connector, to join single
wall pipe to their factory-built chimney section.
Chimney
Install a six (6) inch di-
When Using Approved Double Wall Pipe (Approved
for Model CI2000HT Only): Type L and listed double
wall connector pipe is acceptable. Install any factory-built
brand of pipe according to the manufacturer's instructions. All pipe connections must be sealed (ie. high temperature silicone).
Minimum / Maximim Flue Diameter
Minimum 6", Maximum 10"
Chimney Connector Adapter
tor adapter to connect the chimney connector up to the
chimney. The small ends of the chimney connector
should all point down for a drip free installation. Position
all seams toward the back for aesthetics. The chimney
connector must be 6-inch diameter.
Secure adjoining sections of chimney connector to each
other using three equally spaced sheet metal screws.
Secure the connector pipe to flue collar using three
equally spaced sheet metal screws. DO NOT secure
chimney connector to chimney with screws.
Connection To A Factory-built Chimney
heater is to be connected to a factory-built chimney conforming to CAN / ULC – S629, Standard for 650°C Factory-Built Chimneys. All pipe connections must be sealed
(ie. high temperature silicone).
For Reduced Residential Clearances Using Double
Wall Pipe (Approved for Model CI2000HT Only): Type
L and listed double wall connector pipe is acceptable.
Install any factory-built brand of pipe according to the
manufacturer's instructions.
Vapor Barrier at Chimney Penetration
Install all venting components per the Vent Manufacturers installation instructions. Ensure that there is an effective vapor barrier at the location where the chimney
penetrates to the exterior of the structure. This can be
accomplished by applying a non-hardening waterproof
sealant to the following components:
• Around the chimney at the point where the storm
collar will meet the chimney just above the Flashing.
• Along the vertical seam of the chimney pipe, where it
is exposed to the weather.
• On each nail head on the flashing.
• Around the chimney at the point where the storm
collar will meet the chimney just above the flashing.
Notes:
• On a flat or tarred and graveled roofs, nail and seal
the flat roof flashing to the roof on all sides with roofing compound.
• Do not put screws through the flashing into the chim-
ney pipe.
:
- Use a chimney connec-
- This space
PAGE 10
Page 11
INSTALLATION
CHIMNEY INSPECTION
Existing chimneys must be inspected before installing
your stove. Consult your local building department for
chimney code requirements. A masonry chimney must
have a code approved liner. This liner must not have
broken or missing pieces. Some non-code masonry
chimneys may be brought up to code by being relined.
(Consult your dealer or qualified chimney sweep).
Factory-built chimneys should also be inspected, first
for creosote deposits (which should be removed), and
then for integrity of the stainless steel liner. Look for
obvious bulges in the lining, which may indicate the
need to replace that section (use a bright flashlight).
Also, inspect the attic to see that the chimney has
proper clearance to combustible framing members. For
interior masonry chimneys and most factory-built chimneys, this must be a (2) two inch air space clearance,
which must not be filled with insulation or any other
material. An exterior masonry chimney must have a (1)
one-inch air space clearance.
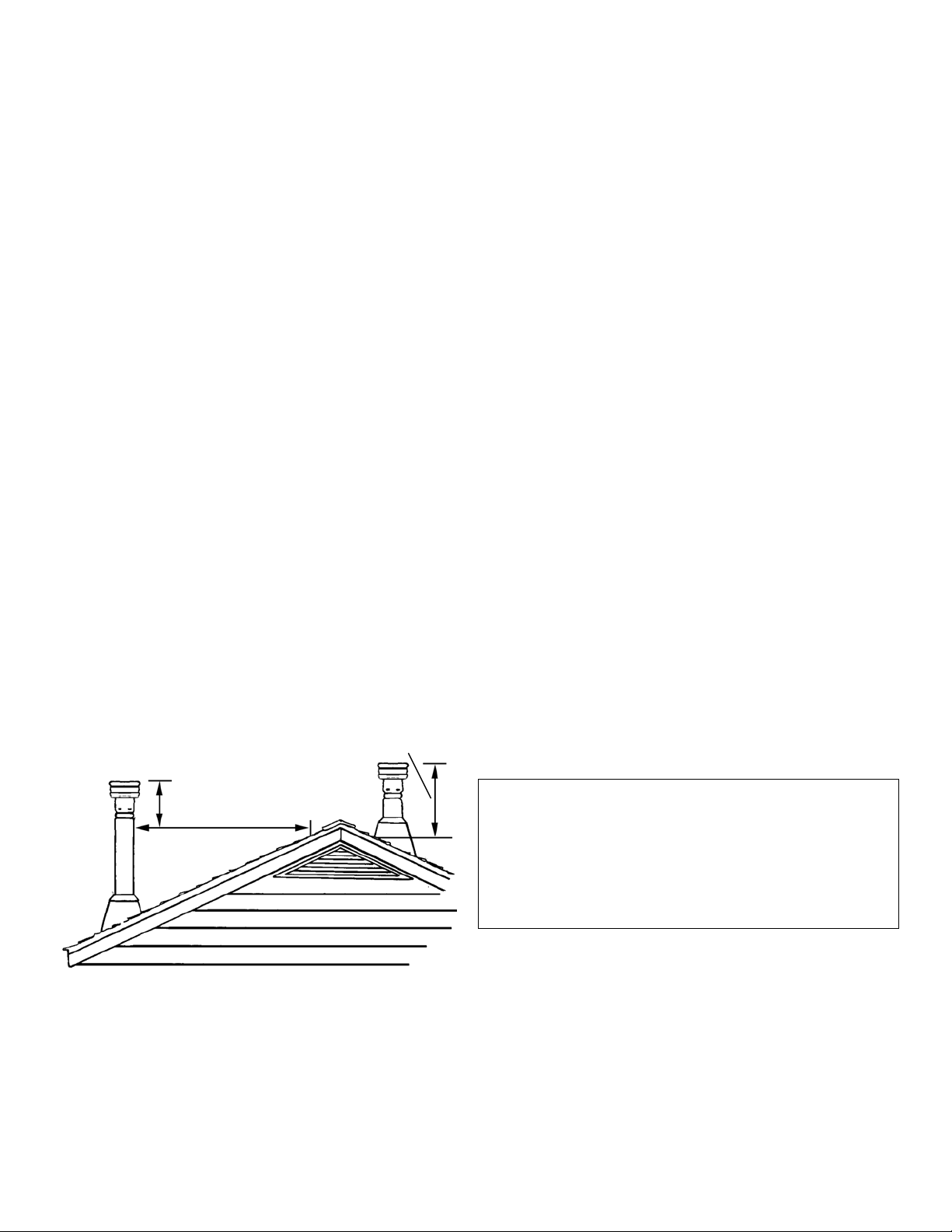
CHIMNEY HEIGHT REQUIREMENTS
The chimney must extend 3 feet above the level of roof
penetration and a minimum of 2 feet higher than any
roof surface within 10 feet (see below). Check with
your local building officials for any additional requirements for your area.
Due to prevailing winds, local terrain, adjacent tall
trees, a hill, or ravine near the home, or adjacent structures, additional chimney height or a special chimney
cap may be required to ensure optimum performance.
The 10’ by 2’ Rule for Vent Termination
Requires A Listed
Termination Cap
2’ (610mm)
10’ (305 cm)
The top of the flue must be 2’ (610 mm) higher than
any part of the roof within 10’ (305 cm) horizontal and a
minimum of 3’ (915 mm) higher than the highest point of roof
penetration.
3’ (915mm)
SPECIAL NOTE:
The installation of a barometric damper is recommended
for all freestanding stoves in areas that may have high
winds, which can effect the draft. The installation must be
only in units with a newly constructed chimney, free of
creosote deposits. The barometric damper is an automatic
device designed to regulate the draft in a heating appliance, which in turn, stabilizes the chimney temperatures,
lessening the potential of over-firing. Do not place the
barometric damper greater than 24 inches (610 mm) above
the unit. Excessive draft will lead to poor control of the
burning rate and possible over-firing of the stove and damage to the cast iron firebox. Most barometric dampers are
calibrated in inches of water column and can be set to draft
requirements of -.03 to -.08 inches (-7.5 to -20 Pa). It is
recommended that the barometric dampers to be set between -.05 and -.06 inches.
THE RECOMMENDED DRAFT REQUIREMENTS FOR
THESE APPLIANCES IS NO LESS THAN -.05 AND NO
GREATER THAN -.06. OPERATION OF YOUR STOVE
WITH A DRAFT GREATER THAN -.06 CAN POSSIBLY
CAUSE DAMAGE TO THE STOVE AND VOID THE
WARRANTY.
Fire intensity is a function of several factors. One of these
factors is DRAFT. Normally, increasing draft increases fire
intensity. Conversely, increasing the fire intensity will increase draft. Draft can also be affected by external factors
such as wind strength and direction, outside temperature,
airflow in or out of the structure, and so forth. If one of
these factors changes, the draft of a low-burning appliance
may increase. This increased draft may cause dangerously high temperature to develop, possibly causing failure
of the unit or flue, or ignition of nearby combustibles. Closing down the combustion airflow ("Primary Air Draft Control") may not guarantee that this will not happen.
CAUTION: MANY STRUCTURE FIRES HAVE RESULTED WHEN A SLOW BURNING FIRE HAS BEEN
LEFT UNATTENDED FOR ANY EXTENDED PERIOD OF
TIME. THESE FIRES NORMALLY OCCUR BECAUSE
COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS CLOSE TO AN APPLIANCE BECOME HEATED TO THE IGNITION POINT BY
AN OVERFIRED APPLIANCE WHICH THE OPERATOR
THOUGHT WAS SAFETY "THROTTLED DOWN."
PAGE 11
Page 12

INSTALLATION
DRAFT REQUIREMENTS
The appliance is merely one component of a larger
system. The other equally important component is the
venting system which is necessary for achieving the
required flow of combustion air to the fire chamber and
for safely removing unwanted combustion byproducts
from the appliance. If the venting system's design does
not promote these ends, the system may not function
properly. Poorly functioning venting systems may create performance problems (i.e. smoking stove, poor
heat output, fire goes out, window blackens, increased
creosote buildup, etc.) as well as be a safety hazard.
Some factors that may lead to performance problems
are as follows:
• Oversized or undersized chimney.
• Excessive offsets in venting.
• Insufficient vertical height of chimney.
• Insufficient chimney termination height in relation-
ship to roof.
• Insufficient ventilation.
• Lack of maintenance.
• Improper operation.
• Burning improper fuel (unit is approved for use with
natural dry well-seasoned wood only).
• Down drafts in the chimney (may need a special wind
cap).
To ensure that the venting system is functioning properly a draft test should be performed (see Draft Test
Procedure on this page).
American National Standards Institute ANSI/NFPA
211-96: A chimney or vent shall be so designed and
constructed to develop a flow sufficient to completely
remove all flue and vent gases to the outside atmosphere. The venting system shall satisfy the draft requirements of the connected appliance in accordance
with the manufacturer instructions.
DRAFT TEST PROCEDURE
After this appliance is installed a draft test should be
performed to ensure proper draft. A qualified technician should perform the draft test procedure as follows:
1) Close all windows and doors in the dwelling.
2) Turn on or operate all appliances which remove air
from the home (such as a furnace, heat pump, air
conditioner, clothes dryer, exhaust fans, fireplaces,
and other fuel burning appliances).
3) Drill a hole in the vent pipe per the draft gauge manufacturers instructions (to create a draft test port). Note:
Hole location should be a minimum of 1 foot above flue
outlet collar.
4) Start a fire (See How To Start And Maintain A Fire on
page 16).
5) After the fire is well established (20-25 minutes) and
burning at a low setting, perform the draft test per the
gauge manufacturer instructions. The draft gauge
should read between .05 and .06” W.C. (inches water column). Excessive draft (above .06 W.C.I.) can result in too
much combustion air to be pulled into the firebox, this will
produce hotter burns and could result in overfiring. Too little draft (below .05” W.C.) will not allow enough combustion air delivery to maintain a fire well or cause performance problems such as smoking (this may result in improper operation of appliance, i.e. will not maintain fire well
unless ash drawer or fuel door is left open).
6) Install a screw to seal the draft test port in the vent pipe. If
the draft test reading was not within the required range,
correct the installation and repeat this procedure.
VENTILATION REQUIREMENTS / PROVIDE ADEQUATE
AIR FOR COMBUSTION
THE FRESH AIR REQUIREMENTS OF THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE MET WITHIN THE SPACE WHERE IT
WILL BE INSTALLED. VENTILATION IS ESSENTIAL
WHEN USING A SOLID FUEL BURNING HEATER.
In well insulated and weather tight homes, it may be difficult to establish a good draft up the chimney (caused by a
shortage of air in the home). The lack of air is caused by
many common household appliances which exhaust air
from the home (such as a furnace, heat pump, air conditioner, clothes dryer, exhaust fans, fireplaces, and other
fuel burning appliances). Also, the combustion process of
this heater uses oxygen from inside the dwelling. If the
available fresh air delivery in the dwelling is insufficient to
support the demands of these appliances, problems can
result (i.e. excessive negative pressure can develop in the
dwelling which will affect the rate at which this appliance
can draft thus resulting in performance problems; See
Draft Requirements on this page). To correct this problem
it may help to open a window (preferably on the windward
side of the house) or install a vent to provide make-up air
into the dwelling.
PAGE 12
Page 13

INSTALLATION
a
e
See Pipe Manufacturers Instructions For Installation Requirements Of Venting Components And Vent Clearances.
SINGLE WALL PIPE
Using 6” Diameter Single Wall Connector Pipe
Storm
Collar
Roof
Flashing
Chimney
Termination
Cap
(Approved for Model CI2000HT Only)
Using 6” Diameter Type L-Vent Connector Pipe
DOUBLE WALL PIPE
3 Feet
Minimum
Termination
Cap with
Spark Arrestor
Storm Collar
Flashing
Ceiling Support
Assembly
Slip
Adapter
6" x 24" 24-gage
black steel or 26 gag
blued steel single wall
pipe
Chimney
Connector
Minimum of 12-15' of
Flue to achieve
stable draft
.
7 Feet
Minimum
Support
Box
DVL Close
Clearance
Connector
Pipe
Floor
Protector
IMPORTANT NOTES:
• Minimize the use of elbows (30°, 45° or 90°) - Offsets in the
venting system are very restrictive and will inhibit the draft
(i.e. You will lose approximately 5 feet of effective draft for
every 90 degrees of direction change). This appliance requires 12 to 15 feet of effective draft for optimum performance (see Draft Requirements on page 12).
• First section of pipe must be vertical - Use as much straight
vertical pipe directly above the appliance as possible before using an elbow (a 2’ to 3’ initial vertical rise is suggested).
PAGE 13
Page 14

INSTALLATION – Combustible Wall Chimney Connector Pass-Throughs
y
d
pp
pp
y
y
A
Min. 12 in. (304.8mm)
to Combustibles
Min. Chimney Clearance from Masonry to Sheet Steel
B
Supports & Combustibles – 2 in. (51mm)
Factory Built
Chimney Length
Air Space – 9 in.
(228.6mm) Min.
C
Min. Chimney Clearance from Masonry to Sheet Steel
Supports & Combustibles – 2 in. (51mm)
2 Ventilated Air
Channels, Each
1 in. (25.4 mm)
Construction of
Sheet Steel
D
Sheet Steel
Supports
Chimney
Section
Air Space – 2 in.
(51mm) Min.
NOTES:
1. Connectors to a masonry chimney, excepting method B, shall extend in one continuous section through the wall
pass-through system and the chimney wall, to but not past the inner flue liner face.
2. A chimney connector shall not pass through an attic
ceiling.
3. Where passage through a wall, or partition of combustible construction is desired, the installation shall conform to
CAN/CSA-B365.
Min. Chimney Clearance to Brick &
Combustibles – 2 in. (51mm)
Min. Clearance 12 in.
(304.8mm) of Brick
Chimney Flue
Fire Clay
Liner
Nonsoluble
Refractory
Cement
Chimney Length
Flush with Inside of Flue
Chimney
Flue
Masonr
Chimney
Sheet Steel Su
Chimney Flue
Sheet Steel Su
Masonr
Chimney
Min. Chimney Clearance from
Masonry to Sheet Steel Supports
& Combustibles – 2 in. (51mm)
Chimney
Connector
Masonr
Chimney
orts
2 Air Channels, Each 1
in. (25.4 mm)
Min. 6 in.
(152.4mm) glass
Fiber Insulation
Min. Clearance
2 in. (51 mm)
Chimney
Length
Sheet
Steel
Supports
Chimney
Connector
Min. Clearance
9 in. (228.6mm)
Chimney
Connector
Use Chimney
Mfrs. Parts to
Attach Connector Securely
-Insulated
Soli
Listed FactoryBuilt Chimney
Length
Chimney
Connector
orts
1 in. (25.4 mm)
Air Space to
Chimney
Length
Chimney
Connector
Method A. 12” (305 mm) Clearance to Combustible Wall Member: Using a minimum thickness 3.5” (89 mm) brick and a 5/8” (16
mm) minimum wall thickness clay liner, construct a wall passthrough. The clay liner must conform to ASTM C315 (Standard
Specification for Clay Fire Linings) or its equivalent. Keep a minimum of 12” (305 mm) of brick masonry between the clay liner and
wall combustibles. The clay liner shall run from the brick masonry
outer surface to the inner surface of the chimney flue liner but not
past the inner surface. Firmly grout or cement the clay liner in
place to the chimney flue liner.
Method B. 9” (229 mm) Clearance to Combustible Wall Member:
Using a 6” (153 mm) inside diameter, listed, factory-built Solid-Pak
chimney section with insulation of 1” (26 mm) or more, build a wall
pass-through with a minimum 9” (229 mm) air space between the
outer wall of the chimney length and wall combustibles. Use sheet
metal supports fastened securely to wall surfaces on all sides, to
maintain the 9” (229 mm) air space. When fastening supports to
chimney length, do not penetrate the chimney liner (the inside wall
of the Solid-Pak chimney). The inner end of the Solid-Pak chimney section shall be flush with the inside of the masonry chimney
flue, and sealed with a non-water soluble refractory cement. Use
this cement to also seal to the brick masonry penetration.
Method C. 6” (153 mm) Clearance to Combustible Wall Member: Starting with a minimum 24 gage (.024” [.61 mm]) 6” (153
mm) metal chimney connector, and a minimum 24 gage ventilated
wall thimble which has two air channels of 1” (26 mm) each, construct a wall pass-through. There shall be a minimum 6” (153 mm)
separation area containing fiberglass insulation, from the outer
surface of the wall thimble to wall combustibles. Support the wall
thimble, and cover its opening with a 24-gage minimum sheet
metal support. Maintain the 6” (153 mm) space. There should
also be a support sized to fit and hold the metal chimney connector. See that the supports are fastened securely to wall surfaces
on all sides. Make sure fasteners used to secure the metal chimney connector do not penetrate chimney flue liner.
Method D. 2” (51 mm) Clearance to Combustible Wall Member: Start with a solid-pak listed factory built chimney section at
least 12” (304 mm) long, with insulation of 1” (26 mm) or more,
and an inside diameter of 8” (2 inches [51 mm] larger than the 6”
[153 mm] chimney connector). Use this as a pass-through for a
minimum 24-gage single wall steel chimney connector. Keep
solid-pak section concentric with and spaced 1” (26 mm) off the
chimney connector by way of sheet metal support plates at both
ends of chimney section. Cover opening with and support chimney section on both sides with 24 gage minimum sheet metal supports. See that the supports are fastened securely to wall surfaces
on all sides. Make sure fasteners used to secure chimney section
do not penetrate chimney flue liner.
or roof space, closet or similar concealed space, or a floor, or
PAGE 14
Page 15

CARE AND OPERATION
PRIMARY AIR DRAFT CONTROL
Use the air control adjustment tool (provided) to adjust
the air controls per the following instructions.
Air Control / Ash Pan Removal Tool
The primary combustion air delivery is controlled by the
Primary Air Draft Control Assembly (located above the
front door). The heat output can be controlled by sliding
the control to a higher or lower heat output setting using
the Air Control Tool Provided (See Primary Air Draft Con-
trol below).
The fuel, the amount of heat and burn times desired, the
type of installation are all variables that will affect the
control setting. The same control settings in a variety of
installations will produce different results. You will need
to try different settings so you can learn how much heat
to expect and how long the fire will burn.
With the air control tool (provided in accessory package)
the control can be adjusted to the heat output desired
(see following illustration).
Primary Air Draft Control
Using the air control tool (provided) slide the control
above door to adjust burn rate.
Lower Burn / Slide Left
Higher Burn / Slide Right
Adjusting Burn Rate:
The primary air draft control located above the front door
can be adjusted to the right for higher temperatures and
to the left for lower temperatures.
Generally, you will want to set the draft control somewhere in the low or medium range
Tips - Adjust the primary air control to a medium to
low setting for a slow and more efficient burn. When
burning on a higher setting, it is more efficient to
burn with a bright but not roaring fire.
START UP AIR CONTROL (IGNITION BOOSTER)
To facilitate lighting, your stove is equipped with an ignition booster, which brings start-up air to the fire for a
short period of time. This can be especially helpful when
your chimney is cold. The ignition booster can also be
used to allow the fire to recover quickly following refuelling.
Start-Up Air Control
PROVIDES SUPPLEMENTAL PRIMARY AIR. DO NOT
LEAVE THE START-UP AIR CONTROL OPEN FOR MORE
THAN FIVE MINUTES.
Slide
to
Open
Before Initial Lighting
1. Using the air control tool open the start-up air control
by pulling the lever outwards (see illustration above).
2. Load fuel into the firebox and light the fire as usual
(see How To Start And Maintain A Fire on page 16)
DO NOT LEAVE THE START-UP AIR CONTOL IN THE
OPEN POSITION FOR MORE THAN FIVE MINUTES
(THIS COULD RESULT IN DANGEROUS OVERFIRING
WHICH IS NOT COVERED UNDER THE WARRANTY).
CLOSE BY PUSHING THE LEVER INWARDS.
See How to Start And Maintain A Fire on page 16
Stove
Back
Start-Up Air
Control Module.
PAGE 15
Page 16

CARE AND OPERATION
HOW TO START AND MAINTAIN A FIRE
1. Using the Air Control Tool (provided), open the
Start-Up Air Control (see Start-Up Air Control, on
page 15).
2. Adjust the primary air draft control to the full open
position (see Primary Air Draft Control on page 15).
3. Open the side fuel loading door and build your fire
directly on the grate in the firebox.
a. Place five or six loosely crumpled sheets of
newspaper in the stove.
b. Add a small amount of dry kindling randomly on
the top of the newspaper.
c. Place a few more loosely crumpled newspapers
on top of the kindling and light the bottom paper
first, then light the top paper. Once the fire is
well underway, close the door. The upper fire
should preheat the chimney and create an effective draft while the lower fire ignites the kindling.
4. After the kindling is burning well, add increasingly
larger pieces of wood until the fire is actively burning (see notes below). Leave the fuel door open
(slightly ajar for 5 minutes). Then close the stove
door. Never leave the stove unattended when the
door is open.
When loading fuel, be careful not to smother
the fire.
Load logs evenly across the base being cau-
tious not to place wood in front of the rear edge
of the log guard.
5. Once a bed of coals has been established, adjust
the primary air control to a lower setting AND
CLOSE THE START-UP AIR CONTROL.
AIR DELIVERY SYSTEMS
Tip – Using the air control tool, adjust the primary air
draft control to a medium to low setting for a slow and
more efficient burn. On higher settings, it is more efficient to burn with a bright but not roaring fire.
When Refueling
1. Follow the normal procedure for refuelling described on page 18. However, instead of cracking the
door open ½ ″, open the start-up air control by pul-
ling the lever outwards. This will supply enough
primary combustion air to allow the fire to recover.
DO NOT LEAVE THE START-UP AIR CONTROL
OPEN FOR MORE THAN FIVE MINUTES. CLOSE BY
PUSHING THE LEVER INWARDS.
Primary Air
Control
Secondary Air
Tubes (2)
Permanent Primary Air Intake.
Supplimental Primary Air is Delivered
through this Small
Opening (to improve
efficiency). There is
no adjustment controls for this intake.
Primary Air
Control
Secondary Air
Tubes (3)
CI1000HT
Side Cut-A-Way View
CI2000HT
Side Cut-A-Way View
Permanent
Secondary
Combustion
Air Intake.
Secondary Air is
Delivered through
this Opening to
ignite secondary
gases. There is no
adjustment control for this intake.
Start-up
Air Control.
See Start-Up Air
Control Illustration on page 15.
Supplemental
Secondary
Air Delivery
Secondary Air is
delivered through
this opening to
ignite secondary
gases. There is no
adjustment control for this intake.
PAGE 16
Page 17

CARE AND OPERATION
FRONT ASH REMOVAL DOOR AND SIDE FUEL LOADING DOOR
CAUTION: When opening the doors, do not extend
them beyond their normal travel. Overextending the
doors to a further open position can put excessive
stress on the hinge area of the doors which may result
in breakage.
Latch Assemblies
(For front ash removal door, side fuel loading door and
ash drawer door).
The door latch assemblies are designed to securely latch
the front door, side door and ash drawer door. To open the
latches, insert the door handle (provided) into hole in the
latch assembly and rotate counterclockwise until door releases. To close and latch, reverse the process
GLASS
The glass is a 5mm super heat resistant ceramic that withstands continuous temperatures up to 1256° F. This temperature is well beyond the temperatures in which you operate your stove.
These models are designed to provide a flow of air over the
inside of the glass, where along with high heat helps keep it
clean. When operating the stove on low for extended periods of time, the glass may get dirty. A short, hot fire (15 20 minutes) will help clean off much of the normal buildup
(see Dirty Glass, page 23). A commercial glass cleaner
designed for stoves is recommended for cleaning.
The glass should be cleaned thoroughly with glass
cleaner and a soft cloth BEFORE the stove is burned.
USE CONTROL SETTINGS THAT WORK FOR YOU
CAUTION: NEVER LEAVE STOVE UNATTENDED ON
HIGH SETTINGS.
The fuel, the amount of heat you want, the type of installation you have and how long you wish the fire to burn
are all variables that will affect the control setting. The
same control settings in a variety of installations will produce different results.
Familiarize yourself with your stove by trying different
settings so you can learn how much heat to expect and
how long the fire will burn. It may take a week or two to
learn but your patience will be rewarded by the warmth
and pleasant satisfaction that only a wood fire can provide.
REPLENISH HUMIDITY LEVEL OF DWELLING
Heating the air in a closed building decreases the relative
humidity of the air, which will dry wood and other combustible materials. This drying lowers the ignition temperature of these materials, thus increasing the fire hazard. To reduce the risk of fire, some provision should be
made for replenishing moisture to the air whenever a
structure is being heated for extended periods.
• BREAK-IN PERIOD
Your stove finish is a high temperature paint that re-
quires time and temperature to completely cure. We
recommend that you ventilate the house during the
initial burns. The paint emits non-toxic odors during
this process.
KEEP YOUR HOUSE WELL VENTILATED DURING
THE CURING PROCESS TO PREVENT ACTIVATION OF YOUR HOME SMOKE DETECTOR.
It will take approximately three burn cycles to cure the
paint. The first two burns should be low heat, approximately 250°F., for 20 minutes each, using paper
and light kindling.
After each 20-minute burn, allow the appliance to cool
completely. The third burn should be at least medium
high or about 450°F. for 45 - 60 minutes. The paint
will become soft and emit non-toxic haze during these
burns. Keep the area well ventilated.
As the paint cures it will become slightly lighter in color.
Eventually the entire surface will become an even color.
Once the paint has been softened and cooled two or
three times, it will harden. Do not place anything on the
stove surface until the paint is completely cured. Do not
attempt to repaint the stove until the paint is completely
cured. If the surface later becomes stained or marred, it
may be lightly sanded and touched up with spray paint
from the same paint (See Small Area Paint Touch-up,
page 21). Paint is available at your local authorized Lennox Hearth Products dealer. Never attempt to paint a
hot stove.
PAGE 17
Page 18

CARE AND OPERATION
FIRST FIRE
NOTE: There is often an unpleasant odor and nontoxic fumes during the first initial burns (this is a
natural result of the paint curing). We recommend
that a window should be left open near the appliance
during this curing process. See Break-In Period on
page 17.
When your installation has been completed and inspected you are ready to build your first fire.
1. Using the air control tool, open the primary air draft
control to the full open position (see Primary Air Draft
Control, page 15).
2. Open fuel loading door and build a small fire in the
stove using tightly rolled paper and dry kindling. Wait
a few minutes for a good updraft to establish the fire.
3. Now place two or three thoroughly dried logs on the
burning kindling and secure door.
5. After about 25-30 minutes of burning (when fire is well
established), slide the primary air draft control to a
medium setting. This will keep the fire burning at a
moderate level so heat is transferred through the
stove rather than up the chimney.
6. Once a bed of coals has been established, adjust the
primary air draft control to a low setting.
7. During the first few fires, keep the combustion rate at
a low to moderate level. Avoid burning fires with the
primary air control wide open for long periods of time.
This results in an updraft fire with most of the heat escaping up the chimney.
WARNING! READ AND USE THE INFORMATION
PROVIDED IN THIS SECTION. TO DISREGARD THIS
MAY CAUSE SERIOUS PERMANENT DAMAGE TO
THE STOVE AND VOID YOUR WARRANTY. IT IS
BEST TO WARM YOUR STOVE UP SLOWLY AND
KEEP IT AT A MODERATE LEVEL.
REFUELING
CAUTION: ALWAYS CHECK FOR HIGH FLAMES
WHEN OPENING A DOOR BY PARTIALLY OPENING
DOOR FOR A FEW SECONDS BEFORE OPENING
FULLY.
To prevent smoke blowing into the room follow these
recommendations:
1. Using the air control tool adjust the primary air draft
control and start-up air control to the full open position and let the fire "liven up" for about one minute
before opening the fuel loading door. Open door
about 1/2" and hold in this position about 30 seconds
or until stove is drafting well, then fully open the door.
2. Rake the embers towards the front of the stove and
spread evenly. If there are logs only partially burned
rake these to the front of stove.
• Feed the logs to the embers. When loading wood,
add one or two logs at a time, depending on size.
Try and use the side fuel loading door as it will allow for cleaner operation. Load logs evenly
across the base being cautious not to place wood
in front of the rear edge of the log guard.
• Close the fuel loading door.
• With the primary air draft control in the full open
position. Crack the door open about ½" and let it
burn for approximately 5 minutes. Then close the
door and adjust the primary air draft control to the
desired setting and CLOSE THE START-UP AIR
CONTROL.
• In order to maintain an attractively burning fire,
logs should be up to 18" (457 mm) long and well
seasoned. Loading the appliance full of damp
wood on a low fire is certain to cause low combustion efficiency resulting in tar and dirty glass.
• High combustion temperatures are the secret to
clean glass operation.
OVERNIGHT BURNING
To inhibit excessive build-up on the glass during a slow
overnight burn, it is recommended that the primary air
draft control be adjusted to at least a slightly open position (the optimum setting will depend on how well your
chimney draws). To achieve a slow burn (the maximum
burn time is 8 hours under optimum conditions - dry,
high BTU wood such as oak and proper draft from the
chimney).
Note: With a good drafting chimney, the primary air
control will need to be closed further than with a poor
drafting chimney.
PAGE 18
Page 19

CARE AND OPERATION
BURN RECOMMENDED FUEL
This appliance is designed for use with natural wellseasoned wood. Do not burn particleboard scraps or
pressed logs because they can produce conditions which
will deteriorate metal. Green or uncured wood does not
work well as fuel, and can cause increased creosote
buildups. The value of green wood as a source of heat is
limited. Do not overload or use kindling wood or mill ends
as primary fuel as this may cause overfiring. Overfiring is
a condition where excessive temperatures are reached,
beyond the design capabilities of the stove. The damage
that occurs from overfiring is not covered under the stove
warranty.
What is the best wood for the fire?
Some woods are easier to light than others (i.e. hornbeam, beech, & oak do not light easily whereas aspen,
birch and lime light easily but they do not last as long).
Then come the softwoods and conifers. Regardless if
you are burning a softer or harder wood, what is most
important is that it is well-seasoned dry wood. Damp
wood has far less heating power, this lowers the combustion temperature of the fire therefore, the output.
Green wood is difficult to light, it burns badly and gives
off smoke and causes the formation of deposits (tarring
and soot staining) in the chimney flue and on the door
glass.
What is tarring and soot staining in the chimney?
When the smoke arrives in the chimney at low temperature, part of the water vapor which they convey condenses. The heaviest constituents are deposited on the
inside of the flue (this is TARRING). The mixture oxidizes
in the air and forms brownish patches (this is SOOT
STAINING). Four essential points for avoiding these
drawbacks, use dry wood, use a stove designed for
wood, connect it to a chimney with thick walls and of suitable cross-section (size and height), and ensure the connecting pipes are as short as possible (horizontal pipes
should be no more than 6" / 150mm).
Flue Gas Temperature
It is recommended to thoroughly heat the flue system
during start-up, before adjusting the burn rate to a medium or low setting (see How To Start And Maintain A
Fire, Page 16). To ensure that the flue system is thoroughly heated, adjust the primary air to a medium/high
position for approximately 20-25 minutes after the startup air is closed before adjusting to a lower setting. This
helps to establish the draft and it reduces creosote deposits on the internal surfaces of the stove, glass and
chimney.
Hints:
Creosote condenses in a cold chimney, not a warm
one. Avoid a smoldering fire for more than a twelvehour period and your chimney will never get cold.
Burn a hot fire for a short period once or twice a day
(and after reloading), and then adjust the primary air
draft module to a medium or low position.
When loading wood, add one or two logs at a time,
depending on size. Loading the appliance full of
damp wood on a low fire is certain to cause poor
combustion efficiency resulting in creosote and dirty
glass.
If the wood is not quite as dry as it should be, to as-
sist for a short period, smokeless coal can be added
with the wood to raise the combustion temperature.
Have the chimney cleaned and inspected by a professional chimney sweep once a year.
WARNING: BURNING IMPROPER FUEL (I.E. CHARCOAL) CAN RESULT IN CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING WHICH MAY LEAD TO DEATH!
CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING – EARLY SIGNS
OF CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING RESEMBLE
THE FLU WITH HEADACHES, DIZZINESS, OR NAUSEA. IF YOU HAVE THESE SIGNS, GET FRESH AIR
AT ONCE! HAVE THE HEATER INSPECTED BY A
QUALIFIED SERVICE TECHNICIAN. SOME PEOPLE
ARE MORE AFFECTED BY CARBON MONOXIDE
THAN OTHERS. THESE INCLUDE PREGNANT
WOMEN, PEOPLE WITH HEART OR LUNG DISEASE
OR ANEMIA, THOSE UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF
ALCOHOL, AND THOSE AT HIGH ALTITUDES.
WHY SEASON WOOD?
The key to the success of a good fire that produces heat
from a woodstove is the wood. It needs to be wellseasoned natural wood.
What does “Well-Seasoned” mean?
When a tree is cut down, the wood is green, full of sap and
moisture. This moisture content can exceed 80%, which
must be reduced to less than 20%. Wood properly seasoned is then capable of generating the heat the stove was
designed to provide.
Green wood does not burn easily. Attempting to burn
green wood often results in a lot of smoke and very little
fire. Time is the most important factor in seasoning wood.
Ideally the moisture content should be reduced to 11-20%,
although very few of us will be able to check that figure.
There are several steps that should be taken to ensure that
you come close to these figures.
PAGE 19
Page 20

CARE AND OPERATION
SEASONING GUIDE
Softwoods – 18 months
Hardwoods – 18 months to 24 months
This period can be shortened (12 to 15 months) if the
wood is cut to the right length and immediately stored
under a ventilated shelter.
Logs that are 5” diameter across or larger should be split in
half, three pieces if over 8 inches, and four pieces when
over a foot across (split wood dries quicker than round
logs). Round logs left in the open for more than a year
end up rotten. If the tree was fell 2 to 4 years ago, it still
needs to be cut, split, and seasoned for 18 to 24 months
depending on the wood.
Wood which is too small to split must be drained, by removing some of the bark.
WOOD STORAGE
Wood to be seasoned should be stacked in an area open
enough to ensure good air circulation on both sides –
leaving adequate space between woodpiles to walk comfortable. Do not stack wood against a wall or building. It
helps to elevate the woodpiles off the ground (two 2 x 4’s
running lengthwise beneath the woodpile works well).
This allows air to flow under the bottom logs.
Store wood in a cool, dry place, well away from any
source of flame or heat. Keep paper, wood, rags and
other easily ignited materials away from the wood. If
wood should become wet, separate it and allow it to dry
naturally; do not mix wet and dry wood or pile wet wood
on top of dry wood. If Wood is kept outdoors, either covered with a tarp, or not covered at all, it will not burn well
until it has been in an enclose space for one to two months.
If stored outside, keep the wood covered to protect from
rain or snow.
Wood supplied in ready-cut lengths stored immediately
under a ventilated shelter dries quicker than wood
stocked in high piles.
PAGE 20
Page 21

MAINTENANCE
DO NOT CLEAN STOVE WHILE HOT
INSPECT THE ENTIRE STOVE FREQUENTLY FOR
PROPER OPERATION, FIT AND SOUNDNESS OF
PARTS. IF ANY MALFUNCTIONING, CRACKED, BROKEN, OR LOOSE PARTS OR OTHER PROBLEMS ARE
NOTED, CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR QUALIFIED
SERVICEMAN TO INSPECT AND REPAIR THE UNIT.
DO NOT OPERATE THE UNIT IF INSTALLED OR
FUNCTIONING IMPROPERLY.
SUMMER SHUT DOWN
Remove ashes and cinders from the stove and dispose of
(see Ash Removal and Disposal on this page). If the room
is damp, place some absorbent crystals inside the stove
and/or disconnect it completely from the chimney. Close
doors and secure the latches closed.
CLEANING HEATER SURFACE
Clean the heater surface with a dry or slightly damp cloth.
In case of condensation, clean the affected areas before
they dry.
SMALL AREA PAINT TOUCH-UP
The stove body is painted with a quality high-temperature
stove paint. Use only Stove Paint, Catalog # 40M68. Do
not touch-up your stove with any other paint.
Using one small piece of 320 grit sand paper and lightly
sand the blemish so that the edges are “feathered” or
smooth to the touch between the painted and bare surfaces. Do not let the sand paper gum up with paint, as this
will cause scratches on the metal surface. If there are any
scratches, use 600 grit sandpaper instead. Mask off surfaces you do not want painted. Paint lightly over the bare
surface first as this will act as an undercoat. Then paint
over a larger area in smooth even strokes to blend.
See Break-In Period on page 17 for information on curing the paint.
ASH REMOVAL AND DISPOSAL
Empty the ash pan regularly to prevent the ash from spilling over. Do not allow the ash to build up and touch the
under side of the grate.
To remove the ash from the stove, operate the firebox
grate using the handle.
A layer of ash left over the grate when burning wood will
protect the grate and retain heat so encouraging clean
combustion.
The tool provided for removal of the ash pan should
not be used to carry the ash pan. Use a leather glove
and hold the ash pan on both sides.
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE FIRE IS OUT AND
THE STOVE IS COLD BEFORE REMOVING ASHES!
Ashes can hold live embers for several days, and must be
disposed of with care.
NEVER place ashes in a cardboard box or any other combustible receptacle.
Proper Disposal of Ashes:
Ashes should be placed in a metal container with a tight
fitting lid. The closed container of ashes should be placed
on a noncombustible floor or on the ground, well away
from all combustible materials, pending final disposal.
If the ashes are disposed of by burial in soil or otherwise
locally dispersed, they should be retained in the closed
container until all cinders have thoroughly cooled.
DOOR, AND GLASS GASKETS
If the gaskets which provide a seal around the doors or
glass should become frayed or damaged they should be
replaced with the same size and type as the original gasket. Contact your dealer for ordering. Use high temperature silicone sealer as an adhesive for the door gasket.
The glass gasket has a self-adhesive backing (see Re-
placement Parts on pages 27-33). If the gasketing is in
good condition, check the closure latch screws; if these
are loose, tighten with a Phillips screwdriver (do not overtighten).
WARNING: THE GASKETS MUST BE KEPT IN GOOD
CONDITION. DO NOT LEAVE THE STOVE BURNING
WITH THE FUEL LOADING DOORS OPEN OR AJAR.
THIS WILL CAUSE EXCESSIVE HEAT BUILD UP IN
THE UNIT AND COULD IGNITE SURROUNDING
COMBUSTIBLES AS WELL AS DAMAGE THE
STOVE BY OVERFIRING IT. OVERFIRING IS A CONDITION WHERE EXCESSIVE TEMPERATURES ARE
REACHED, BEYOND THE DESIGN CAPABILITIES
OF THE STOVE (SUCH DAMAGE IS NOT COVERED
BY THE MANUFACTURERS WARRANTY).
FIREBRICK
The firebrick should be inspected periodically and replaced
if damaged (crumbling or excessively cracked). Through
normal wear and tear, the firebrick may need to be replaced over time (through proper installation, operation,
maintenance and fuel, the longevity of the firebrick will be
increased – see Overfiring Damage, page 24). For information on warranty of the firebrick, see warranty statement
provided with the appliance.
PAGE 21
Page 22

MAINTENANCE
SERVICING GLASS
CAUTION: BE CAREFUL NOT TO ABUSE DOOR
ASSEMBLY BY STRIKING OR SLAMMING IT. IF
THE DOOR ASSEMBLY OR GLASS IS BROKEN OR
DAMAGED, THEY MUST BE REPLACED WITH FACTORY ORIGINAL PARTS BEFORE HEATER CAN BE
SAFELY OPERATED. USE ONLY COMPONENTS
PROVIDED BY THE MANUFACTURER AS REPLACEMENT PARTS.
Cleaning Glass: Ensure stove is cold prior to cleaning
glass. A commercial glass cleaner designed for stoves
is recommended. Do not use abrasive cleaners. Do not
clean with any materials, which may scratch or otherwise damage the glass. Scratches on the glass can
develop into cracks or break. Inspect the glass regularly. If you detect a crack, extinguish the fire and contact your dealer for a replacement.
Replacing Glass:
1. Open the door. Using a phillips screwdriver loosen
the 4 screws which secure the glass then carefully
remove broken glass one piece at a time (protective
leather gloves are recommended).
2. Remove screws and clips from doorframe and set
aside.
DOORFRAME
4 EA. CLIP
GASKETS
4 EA. GLASS
CLIPS
GLASS GASKET
GLASS
3. Clean the area where the glass with gasket will be
installed.
4. Install new glass with gasket (use only factory 4mm glass with glass channel gasket. Do not substitute).
5. Carefully reinstall glass clips with gasket and
screws. Be very careful not to overtighten the
screws (this could result in breakage when stove is
hot).
CREOSOTE FORMATION AND NEED FOR REMOVAL
What is Creosote - When wood is burned slowly, it
produces tar and other organic vapors, which combine
with expelled moisture to form creosote. The creosote
vapors condense in the relatively cool chimney flue of a
slow-burning fire. As a result, creosote residue accumulates on the flue lining. When ignited this creosote
makes an extremely hot fire. Also, creosote deposits
tend to form in long runs of venting where gases be-
4 EA. GLASS CLIP SCREWS
PAGE 22
come too cool prior to exhausting. Note: Single wall
pipe cools rapidly, therefore installations using this type
of flue are more susceptible to creosote deposits.
To inhibit the build up of creosote, adjust the primary air
draft control to a medium-high or high setting for a 10minute period each day. Do not attempt to burn out
heavy creosote accumulations in this manner. This
must be removed from the chimney by scraping or
brushing to reduce the risk of a chimney fire.
Burn Approved Fuel Only - This stove is approved for
burning dry seasoned natural wood only. Using green
or inadequately seasoned wood may increase creosote
buildup.
Inspection Frequency - The chimney connector and
chimney should be inspected at least twice monthly during the heating season to determine if a creosote
buildup has occurred. If creosote has accumulated it
should be removed to reduce the risk of a chimney fire.
If creosote has accumulated (1/8 “(3 mm) or more) it
should be removed to reduce the risk of a chimney fire.
Experienced chimney servicing personnel should be
consulted.
Cleaning - Remove the baffle brick in the firebox prior
to having your chimney cleaned (should be done by a
qualified chimney sweep). See following – Removing
Baffle Brick for Cleaning).
Removing Baffle for Cleaning
Before flue can be cleaned, the baffle in the stove firebox must be removed. The CI1000HT has one vermiculite firebrick, which serves as a baffle for the flue gasses. The CI2000HT has a 5-sided box made of ceramic
fiber brick that serves as a baffle. In both cases, the
baffles are located just above the secondary air tubes
(which must be removed to access the baffle). Suggestion: Wear a pair of leather work gloves when removing
secondary air tube assembly and baffle.
1. To access the baffle, the secondary air tube assembly must be removed. Locate the 4 screws,
which secure the assembly into place (located at
the ceiling of the firebox). Remove the assembly
and set aside. Slide the baffle out and set aside.
2. Once the baffle is removed from the firebox, the flue
can be cleaned. The accumulated soot that is removed by brushing will fall to the firebox floor where
it can be removed and disposed of.
WARNING! DO NOT OPERATE THE STOVE WITHOUT THE BAFFLE BRICK PROPERLY INSTALLED.
THIS WILL VOID THE WARRANTY AND THE STOVE
WILL NOT FUNCTION PROPERLY.
Page 23

MAINTENANCE / TROUBLESHOOTING
IN THE EVENT OF A CHIMNEY FIRE
Make sure the fuel loading doors are securely
closed. Adjust the primary air draft control to the
lowest (most closed) setting and ensure that the
start-up air control is closed. Call the fire department immediately. After a chimney fire, the complete
chimney system should be checked by a qualified
technician before further use.
Consult your dealer for suggestions on proper chimney care. Contact your local municipal or provincial
fire authority for information on how to handle a
chimney fire. Have a clearly understood plan for handling a chimney fire. Establish a routine for the fuel,
stove and firing technique. Check daily for creosote
build-up until experience shows how often you need
to clean to be safe. Be aware that the hotter the fire
the less creosote is deposited, and weekly cleaning
may be necessary in mild weather even though
monthly cleaning may be enough in the coldest
months.
REINSTALL BAFFLE BRICK
After your chimney has been swept, reinstall the baffle
brick. See – Removing Baffle Plates for Cleaning (on
previous page) and reverse steps.
TROUBLESHOOTING
* When Fuel Door Is Opened, Smoke Enters Room.
1. The primary air draft control is closed.
2. The chimney is too cool. Set the primary air draft control on "HIGH" for a few minutes before opening either
fuel loading door.
3. Excess creosote will not only restrict your draft but it
will create a risk of a creosote fire. Strictly adhere to
maintenance requirements as outlined in this manual.
If excess creosote has built up on the inside of the
firebox sides and door, burn a small hot fire at intervals that are more frequent with air control on HIGH
for a few minutes.
4. Deposits may have built up in the chimney and are
restricting the draft, or the spark arrester on top of
the chimney may be plugged.
5. Chimney diameter too large or too small to provide
adequate draft.
6. The house is too airtight (usually takes 20 to 30 min-
utes for problem to appear as stove lowers air pressure in house). Crack a window open or provide an
outside source of air near stove.
7. Insufficient vertical height to chimney to achieve ade-
quate draft.
Does Not Produce Enough Heat
1. Using green or insufficiently cured wood.
2. Excessive draft.
3. High ceilings (heat rises quickly, but can be recirculated by a well-placed ceiling fan with a winter/summer switch).
4. The area to heat is too large (square foot heating
estimates are based on "average" climates and
home design).
5. There is an obstruction in the chimney.
6. The chimney or chimney cap is restricted by creosote preventing enough draw to sustain a "high" heat
output rate.
* Does Not Maintain A Fire
1. Soft wood does not burn as long or as well as seasoned hardwood resulting in a short burn time.
2. Wood size too small. Burns at too rapid a rate.
3. The gasket seal on the fuel loading doors, or glass is
leaking air. Repair or replace it if necessary.
4. Excessive Draft.
5. There may be an obstruction in the chimney.
* Backpuffing
Definition: This is a term describing the condition
when combustible gases remain unlit because of insufficient combustion air delivery which results in
combustible gases building, then flash igniting. If
backpuffing is occurring, it can push some smoke
into the room through the primary or secondary air
openings. The combustion air delivery is dependent
upon the draft of the venting system. The following
are variables, which can negatively affect the draft
resulting in backpuffing.
1. Downdraft in the chimney (a special wind cap may be
needed).
2. The house is too air tight (ventilation is needed).
3. Insufficient vertical height to chimney to achieve ade-
quate draft.
Odors
1. Creosote accumulation in firebox (brush out on next
cleaning).
2. Chimney downdraft when stove is not operating (close
the primary air draft control).
3. Paint curing on first several burns.
* Dirty Glass
1. Poor draft conditions.
2. Long burn periods at low draft settings.
3. Burning wet, pitchy or spongy wood.
4. Poorly arranged logs (too close to glass).
* Draft problems; if installing into a larger flue, it may
be necessary to use a full-length liner to achieve
adequate draft for the appliance. A draft gauge
should read a minimum of .05" W.C. (inches water
column) not to exceed .06" W.C. for optimum performance (See Draft Requirements on 11).
PAGE 23
Page 24

TROUBLESHOOTING
OVERFIRING DAMAGE
If the heater or chimney connector glows, you are overfiring. Other symptoms may include: Cracking, warping or
burning out of components, stove glass may develop a
haze, which will not come off with cleaning.
Overfiring of a stove is a condition where excessive temperatures are reached, beyond the design capabilities of
the appliance. The damage that occurs from overfiring is
not covered under the manufacturers limited warranty.
The following are a few conditions that should be evaluated and (corrected if necessary) if an overfiring condition is suspected:
Overfiring Caused From Improper Installation
Ensure that all installation requirements have been met
as outlined in the installation manual. The chimney
should be clean and in good repair. A draft test should be
performed to determine if the draft requirements of the
appliance are being met. A draft gauge should read between .05 and .06 " W.C. (inches water column). Excessive draft (above .06 " W.C.) will allow too much combustion air to be pulled in which results in hotter burns. Too
little draft (below .05 " W.C.) will not allow enough combustion air delivery to maintain a fire (this may result in
improper operation of appliance, i.e. wont maintain fire
unless fuel loading door is left open. See following, Over-
firing Caused From Improper Operation).
Overfiring Caused From Improper Operation
Operate this appliance only as outlined in this manual.
Never burn the appliance with either fuel loading door
open or ajar. Do not operate this stove with the Primary
Air Draft Control in the full "open" position for extended
periods. This wastes fuel and can cause dangerous
overfiring conditions. NEVER leave the stove unattended
on high settings.
Overfiring Caused From Improper Maintenance
Strictly adhere to all maintenance requirements at frequent intervals as prescribed in this manual including
cleaning of flue and stove. Should either fuel loading
door or glass gaskets become worn or damaged, they
should be replaced.
Overfiring Caused From Improper Fuel
This appliance is approved for use with natural dry wellseasoned wood only (ask your authorized dealer what
are approved fuels for your area). Do not burn garbage,
particleboard scraps, or pressed logs because they can
produce conditions that will deteriorate metal. Do not
overload or use kindling wood or mill ends as primary
fuel as this may cause overfiring.
PAGE 24
Page 25

SPECIFICATIONS - Model CI1000HT
Flue position........................................ Top
Flue collar size .................................... 6" (152 mm)
Approx. burn time..............................6 to 8 hours
Maximum burn rate ...........................87,301 BTU
EPA BTU Range................................. 11,500 – 55,000 BTU
Emissions Rate (grams/hr).............. 4.42 grams
Maximum Log length ........................ 18" (457 mm)
Firebox Size.........................................1.12 cu. feet
Loading................................................. Front & Side
Width (overall)..................................... 23 3/4" (604 mm)
* Shown with optional window trim
FRONT VIEW *
SIDE VIEW
Depth (overall)..................................... 15 5/16" (389 mm)
Height (to flue) .................................... 30" (762 mm)
Height (to stove top)..........................27 1/4" (693 mm)
Back to centerline of flue .................6 7/16" (163 mm)
Approx. weight with brick................ ~280 lbs. (140 kg)
Note: Dimensions shown are approximate only
(+/- ¼”).
PAGE 25
Page 26

SPECIFICATIONS - Model CI2000HT
Flue position........................................ Top
Flue collar size .................................... 6" (152 mm)
Approx. burn time..............................6 to 8 hours
Maximum burn rate ...........................96,662 BTU
EPA BTU Range................................. 11,923 – 60,897 BTU
Emissions Rate (grams/hr).............. 2.72 grams
FRONT VIEW *
Maximum Log length ........................ 22" (559 mm)
Firebox Size.........................................1.97 cu. feet
Loading................................................. Front & Side
Width (overall)..................................... 29 1/8" (740 mm)
Depth (overall)..................................... 18 3/4" (476 mm)
Height (to flue) ....................................32 13/16" (833 mm)
Height (to stove top)..........................29 3/4" (756 mm)
Back to centerline of flue .................7 11/16" (195 mm)
Approx. weight with brick................ ~410 lbs. (205 kg)
* Shown with optional window trim
SIDE VIEW
Note: Dimensions shown are approximate only (+/- ¼”).
PAGE 26
Page 27

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
PART #
(ITEM #)
40M5701 (♦31) Air Column Set, Left & Right (Includes Gaskets & Screws) CI1000HT
40M6901 (♦32) Air Column Set, Left & Right (Includes Gaskets & Screws) CI2000HT
40M2301 (♦33) Air Deflector (Air Wash), Upper (Includes Hardware) CI1000HT
40M9801 (♦34) Air Deflector (Air Wash), Upper (Includes Hardware) CI2000HT
40M2101 (♦35) Ashlip, Charcoal, Painted (Includes Gasket & Screws) CI1000HT
40M8601 (♦35) Ashlip, Charcoal, Painted (Includes Screws) CI2000HT
40M3901 (♦36) Ashpan Assembly CI1000HT
41M0501 (♦36) Ashpan Assembly CI2000HT
40M3601 Back, Steel Stove (Includes Hardware) CI1000HT
41M0301 Back, Steel Stove (Includes Hardware) CI2000HT
40M5101 (♦37) Baffle Assembly, ceramic fiber brick (Baffle Box) CI2000HT
41M0401 (♦38) Channel Assembly, Start-Up Air (Includes Gasket And Hardware) CI2000HT
41M0101 Clip Set, Glass (Includes 4 Ea. Gaskets, Screws & Clips) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M2701 (♦39) Collar Kit, Charcoal Replacement Flue (Includes Gasket & Hardware) CI1000HT
40M9001 (♦40) Collar Kit, Charcoal Replacement Flue (Includes Gasket & Hardware) CI2000HT
40M0701 (♦3) Door, Ashpan, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI1000HT
40M4301 (♦4) Door, Ashpan, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI2000HT
40M1701 (♦1) Door, Firebox, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI1000HT
40M8201 (♦1) Door, Firebox, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI2000HT
40M1201 (♦2) Door, Side Loading, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI1000HT
40M7801 (♦2) Door, Side Loading, Charcoal (Handle Receiver Not Included) CI2000HT
40M3501 (♦47) Draft Module, Air Intake (Slide Assembly) Includes Gasket & Hardware CI1000HT
41M0201 (♦48) Draft Module, Air Intake (Slide Assembly) Includes Gasket & Hardware CI2000HT
41M3901 (♦12) Firebrick, Left CI1000HT
41M3801 (♦13) Firebrick, Lower Rear CI1000HT
41M4001 (♦14) Firebrick, Right CI1000HT
41M3701 (♦15) Firebrick, Baffle (vermiculite) CI1000HT
41M4101 (♦16) Firebrick, Upper Rear CI1000HT
41M5501 (♦5) Firebrick, Bottom Center CI2000HT
41M4901 (♦6) Firebrick, Bottom Side (left or right) CI2000HT
41M5001 (♦7) Firebrick, Left Lower CI2000HT
41M5101 (♦8) Firebrick, Left Upper CI2000HT
41M5401 (♦9) Firebrick, Lower Rear CI2000HT
41M5201 (♦10) Firebrick, Right Lower CI2000HT
41M5301 (♦11) Firebrick, Upper Rear CI2000HT
40M7201 (♦17) Frame, Fuel Grate (bottom) CI1000HT
40M9301 (♦18) Frame, Fuel Grate (bottom) CI2000HT
DESCRIPTION WHERE USED
See Note
PAGE 27
Page 28

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
PART #
(ITEM #)
40M4501 Gasket Kit, 6 mm X 156cm (14979) For Air Intake Slide & Glass & 4 Ea. 6mm
Glass Clip Gaskets (31856)
40M0201 Gasket Kit, Ashpan Door Rope (8mm Dia. X 97 cm) CI1000HT
40M4201 Gasket Kit, Rope (10mm Dia. X 146cm) Ashpan Door-CI2000HT,Side & Front Fire-
box Door-CI1000HT
40M4401 Gasket Kit, Rope (12mm Dia. X 177 Cm) Front & Side Door CI200* CI2000HT
40M4901 (♦19) Gasket Set, Air Column, 70mm X 45mm (Also Includes Start Up Air Channel -
Model CI2000HT Only)
41M3601 Gasket, Flue Outlet CI1000HT
40M5401 Glass, Replacement, 10.39" X 14.02" (Includes Gasket) CI1000HT
41M0801 Glass, Replacement, 18.82" X 12.52" (Includes Gasket) CI2000HT
40M4001 (♦20) Grate Support Bar, Fuel CI1000HT
40M1301 (♦21) Grate, Ash Removal CI1000HT
40M2901 (♦22) Grate, Fuel CI1000HT
40M9601 (♦23) Grate, Fuel CI2000HT
40M5301 (♦24) Hinge Pin Set, Ashpan Door (Includes 2 Hinge Pins, 2 Acorn Nuts & 2 Washers) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M4101 (♦25) Hinge Pin Set, Firebox Door (Includes 2 Hinge Pins, 2 Acorn Nuts & 4 Washers) CI1000HT
40M5601 (♦26) Hinge Pin Set, Firebox Door (Includes 2 Hinge Pins, 2 Acorn Nuts & 4 Washers) CI2000HT
40M5801 (♦27) Hinge Pin Set, Side Door (Includes Hinge Pins, 2 Acorn Nuts & 2 Washers) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
41M0901 (♦28) Leg, Front Left, Charcoal (Includes Gasket & Hardware) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M9501 (♦28) Leg, Front Right, Charcoal (Includes Gasket & Hardware) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
41M3101 (♦28) Leg, Right & Left Rear, Charcoal (Includes Gasket & Hardware) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M2801 (♦29) Log Guard (W/ 2 Andirons) CI1000HT
40M9701 (♦30) Log Guard (W/ 3 Andirons) CI2000HT
40M68 Paint, Touch-Up Spray (Spray, Charcoal) 1 Spray Can CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M6201 (♦41) Poker, Fire CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M5201 (♦42) Receiver Assembly, Ashpan Door Handle (Includes Latch) CI1000HT
40M0301 (♦42) Receiver Assembly, Ashpan Door Handle (Includes Latch) CI2000HT
40M1001 (♦42) Receiver Assembly, Firebox Door Handle (Includes Latch) CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M3801 (♦42) Receiver Assembly, Side Door Handle (Includes Latch) CI2000HT
40M6101 (♦42) Receiver Assembly, Side Door Handle (Includes Latch) CI1000HT
41M5601 (♦49) Retainer Set, Firebrick (Includes 1 Left, 1 Right & 2 Rear Firebrick Retainers &
Hardware)
41M4201 Retainer, Firebrick Steel CI1000HT
40M6001 (♦43) Secondary Air Tube Kit (Includes Screws) CI1000HT
40M0101 (♦44) Secondary Air Tube Kit (Includes Screws & Washers) CI2000HT
41M1001 (♦45) Tool, Ashpan Removal / Air Control CI1000HT & CI2000HT
40M5501 (♦46) Tool, Removable Door Opener CI1000HT &.CI2000HT
41M0601 Tube, Front Air Feed CI2000HT
♦
The numbers in parenthesis correspond to the following component diagrams:
DESCRIPTION WHERE USED
See Note
CI1000HT & CI2000HT
CI1000HT & CI2000HT
CI1000HT & CI2000HT
CI2000HT
PAGE 28
Page 29

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
(
♦1) Front Firebox Door
(
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
♦4) Ashpan Door
(CI2000HT Series)
♦7) Left Lower Firebrick
(
(CI2000HT Series)
7.87” / 200 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
(
♦2) Side Loading Door
(CI1000HT Series)
♦2) Side Loading Door
(
(CI2000HT Series)
(
♦3) Ashpan Door
(CI1000HT Series)
10.08” / 256mm
(
♦5) Bottom Center Firebrick
(CI2000HT Series)
7.87” x 200 mm
♦8) Upper Left Firebrick
(
(CI2000HT Series)
10.43” / 265 mm
4.6” / 117 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
9.25 ´/ 235 mm
♦9) Lower Rear Firebrick
♦6) Bottom Side Firebrick
(
(
(CI2000HT Series)
(CI2000HT Series)
12.36” / 314 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
7.87” / 200 mm
2.87” / 73 mm
13.94” / 354 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
5.51” / 140 mm
7.87” x 200 mm
9.25” / 235 mm
PAGE 29
Page 30

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
♦10) Right Lower Firebrick
(
(CI2000HT Series)
10.43” / 265 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
♦11) Upper Rear Firebrick
(
(CI2000HT Series)
13.93” / 354 mm
.79” / 20 mm thick
4.72” / 120 mm
♦14) Right Firebrick
(
(CI1000HT Series)
8.47” / 215 mm x 5.12” /
130mm (.98” / 25mm thick)
♦17) Fuel Grate Frame
(
(CI1000HT Series)
(
♦18) Fuel Grate Frame
(CI2000HT Series)
♦12) Left Firebrick
(
(CI1000HT Series)
8.47” / 215 mm
x 12” / 305 mm
(.79” / 20mm
thick)
♦13) Lower Rear Firebrick
(
(CI1000HT Series)
6.50” / 165mm
x 12.40” / 315 mm
(.98” / 25 mm thick
7.87” / 200 mm
)
♦15) Baffle Firebrick
(
(above tubes on ceiling)
(CI1000HT Series)
♦16) Upper Rear Firebrick
(
(CI1000HT Series)
5.51” / 140mm
x 12.60” / 320 mm
(.98” / 25 mm thick
5.87” / 149 mm
x 14.36” / 365 mm
(.98” / 25 mm thick
(♦19) Air Column Gasket
)
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
)
(
♦19) Start-up Air Column Gasket
(CI2000HT Series)
PAGE 30
Page 31

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
♦20) Fuel Grate Support Bar
(
(CI1000HT Series)
(♦25) Front Firebox Door Hinge Pin
(CI1000HT Series)
♦29) Log Guard
(
(C1000HT Series)
(
♦21) Ash Removal Grate
(CI1000HT Series)
♦26) Front Firebox Door Hinge Pin
(
(CI2000HT Series)
♦30) Log Guard
(
(CI2000HT Series)
(
♦22) Fuel Grate
(CI1000HT Series)
♦27) Side Door Hinge Pin
(
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
(
♦31) Left Air Column Assembly
(CI1000HT Series)
(
♦23) Fuel Grate
(CI2000HT Series)
(
♦24) Ashpan Door Hinge Pin
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
(
♦28) Stove Leg
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
(
♦31) Right Air Column Assembly
(CI1000HT Series)
PAGE 31
Page 32

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
♦32) Left Air Column Assembly
(
(CI2000HT Series)
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
(♦35) Ashlip
(
♦39) Flue Outlet Collar
(CI1000HT Series)
♦32) Right Air Column Assembly
(
(CI2000HT Series)
(♦33) Upper Air Deflector
(CI1000HT Series)
(
♦34) Upper Air Deflector
(CI2000HT Series)
♦36) Ashpan
(
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
♦37) Baffle Assembly, Ceramic Fiber
(
Brick (above secondary air tubes)
(CI2000HT Series)
(
♦38) Start-up Air Channel Assembly
(CI2000HT Series)
♦40) Flue Outlet Collar
(
(CI2000HT Series)
Side View
Top View
(
♦41) Fire Poker
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
♦42) Ashpan, Side Door and Firebox
(
Door Handle Receivers
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
PAGE 32
Page 33

REPLACEMENT PARTS - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
(
♦43) Secondary Air Tube Assembly
(
(CI1000HT Series)
♦45) Air Control/Ash Pan Removal Tool
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
(♦48) Draft Module (Air Intake Slide)
(CI2000HT Series)
♦44) Secondary Air Tube Assembly
(
(CI2000HT Series)
CI1000HT Firebrick Placement Diagram
CEILING
BACK WALL
LEFT WALL
(12) Left Side
Firebrick
(15) Baffle Firebrick
(16) Upper Rear Firebrick
(13) Lower Rear Firebrick
Note:
CI1000HT does
not have firebrick on firebox floor (fuel
grate & frame
on floor only).
♦46) Removable Door Opener Tool
(
(CI1000HT & CI2000HT Series)
♦49) Rear Firebrick Retainers
(
(CI2000HT Series)
Side Retainers Not Shown
(
♦47) Draft Module (Air Intake Slide)
(CI1000HT Series)
Note: The refractory baffle assembly (37) on ceiling (above tubes), not shown.
CI2000HT Firebrick Placement Diagram
BACK WALL
(11) Upper
Rear Firebrick
LEFT WALL RIGHT WALL
(9) Lower
Rear Firebrick
(8) Upper
RIGHT WALL
Left Firebrick
(7) Lower
Left Firebrick
(6) Bottom
Side
Firebrick
(5) Bottom Center
Firebrick
(6) Bottom
Side
Firebrick
(10) Lower
Right Firebrick
(14) Right Side
Firebrick
FLOOR
PAGE 33
Page 34

OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES - Models: CI1000HT & CI2000HT
Catalog # Model Description Stove Model
H0459 WTK-CI10 Window Trim Kit, Charcoal CI1000HT
H0455 WTK-CI20 Window Trim Kit, Charcoal CI2000HT
Window Trim Kit – CI1000HT & CI2000HT
PAGE 34
Page 35

LABEL, SAFETY / LISTING – Model CI1000HT
PAGE 35
Page 36

SAFETY/LISTING LABEL – Model CI2000HT
PAGE 36
Page 37

EPA LABELS – CI1000HT and CI2000HT
PAGE 37
Page 38

OWNERSHIP RECORDS
Dealer’s Name:
Dealer’s Address:
City: State: Zip Code:
Serial Number: Date of Purchase: Date Installed:
Notes:
SERVICE AND MAINTENANCE LOG
Service Service Service
Date Technician Description
PAGE 38
Page 39

Page 40

NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
LENNOX reserves the right to make changes at any time, without notice, in design, materials,
specifications, prices and also to discontinued colors, styles and products.
Consult your local distributor for fireplace code information
Printed in U.S.A LENNOX HEARTH PRODUCTS 2002
P/N 775,080M Rev. F, 3/2005 1110 West Taft Avenue • Orange, CA 92865
.
 Loading...
Loading...