Page 1
LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS LINUX V4.39.0 USER GUIDE
FIT – Instituto de Tecnologia
1
Page 2

Title:
Lenovo Diagnostics User Guide
E-mail:
rafael.rodrigues
@
fit-tecnologia
.
org
.br
LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS LINUX USER GUIDE
Author: Rafael Rodrigues
Date:
March 11th, 2021
Platform: Linux
2
Page 3

REVISION HISTORY
Revision
1.0 Elsa Martins Created according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.29 Mar 15, 2019
1.1 Elsa Martins Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.30 May 23, 2019
1.2 Helano Rocha Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.31 Jul 30, 2019
1.3 Helano Rocha Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.32 Oct 15, 2019
1.4 Helano Rocha Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.33 Jan 17, 2020
1.5 Geisiane Almeida Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.34 Feb 20, 2020
1.6 Júlio Oliveira Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.35 Apr 29, 2020
1.7 Geisiane Almeida Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.35.1 Jun 08, 2020
1.8 Geisiane Almeida Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.36 Jun 29, 2020
1.9 Claudio Pereira Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.37 Oct 21, 2020
1.10 Rafael Rodrigues Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.38 Dec 07, 2020
1.11 Rafael Rodrigues Updated according to Lenovo Diagnostics 4.39 Mar 05, 2021
Author Revision History Date
3
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS LINUX V4.39.0 USER GUIDE 1
Lenovo Diagnostics LINUX User Guide 2
Revision History 3
TABLE OF Contents 4
LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS LINUX V4.39.0 USER GUIDE 6
1. Lenovo Diagnostics overview 7
1.1 What is Lenovo Diagnostics? 7
1.2 Understanding the diagnostics 7
2. Performing diagnostics in Lenovo Diagnostics 8
2.1 Lenovo Diagnostics Main screen 8
2.2 Run diagnostic for a module 9
2.2.1 Select Devices and Tests
2.2.3 Run Tests
11
9
2.3 See Execution Log 13
3. Lenovo Diagnostics Modules and Tests 15
3.1 Audio 15
3.2 Audio Controller 16
3.3 Battery 17
3.4 Camera 18
3.5 Fan 18
3.6 Processor 18
3.7 Display 20
3.8 Display Interface 21
3.9 Keyboard 22
3.10 Memory 23
3.11 Motherboard 25
3.12 Optical Drive 26
3.13 PCI Express 27
3.14 Mouse Devices 27
3.15 RAID 29
3.16 Storage 30
3.17 Touchscreen 32
4
Page 5

3.18 Video Card 33
3.19 Wired Ethernet 35
3.20 Wireless 35
3.21 Sensors 35
3.22 Bluetooth 36
3.23 Fingerprint Reader 36
3.24 Touchpad Devices 37
4. EXPLORING LENOVO RUN ALL OPTION 39
4.1 Quick tests 39
4.2 Quick tests (customized option) 40
4.3 Full tests 40
4.4 Full tests (customized option) 41
5. EXPLORING LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS TOOLS 42
5. 1 Diagnostic Script 42
5.1.1 Create a diagnostic script
5.1.2 Edit a diagnostic script
5.1.3 Execute a diagnostic script
5.2 System Information 47
5.3 Log History 47
5.4 Recover Bad Sectors 48
5.5 SMART Tool 48
5.6 Temperature Tool 49
5.7 Temperature Tool 49
6. Glossary 50
43
43
44
5
Page 6

LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS LINUX V4.39.0 USER GUIDE
Note
Before using this information, be sure to read and understand the Lenovo Privacy Statement.
6
Page 7

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
1. LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS OVERVIEW
1.1 What is Lenovo Diagnostics?
Lenovo Diagnostics is a diagnostic tool that tests various devices in Lenovo computers providing feedback to the
users about their machines health. Lenovo Diagnostics is composed by Modules that allows performing diagnostics
for a group of devices and by Tools to create custom executions (diagnostic script), see detailed information about
each device (system information) and consult the results for the tests performed in a machine (Log History).
1.2 Understanding the diagnostics
Each module contains one or more tests that may be performed under one or more devices resulting in a diagnostic.
This structure is displayed in the image below:
When a diagnostic is finished, Lenovo Diagnostics displays the results for each performed test and create two results
codes resuming the test execution.
7
Page 8
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
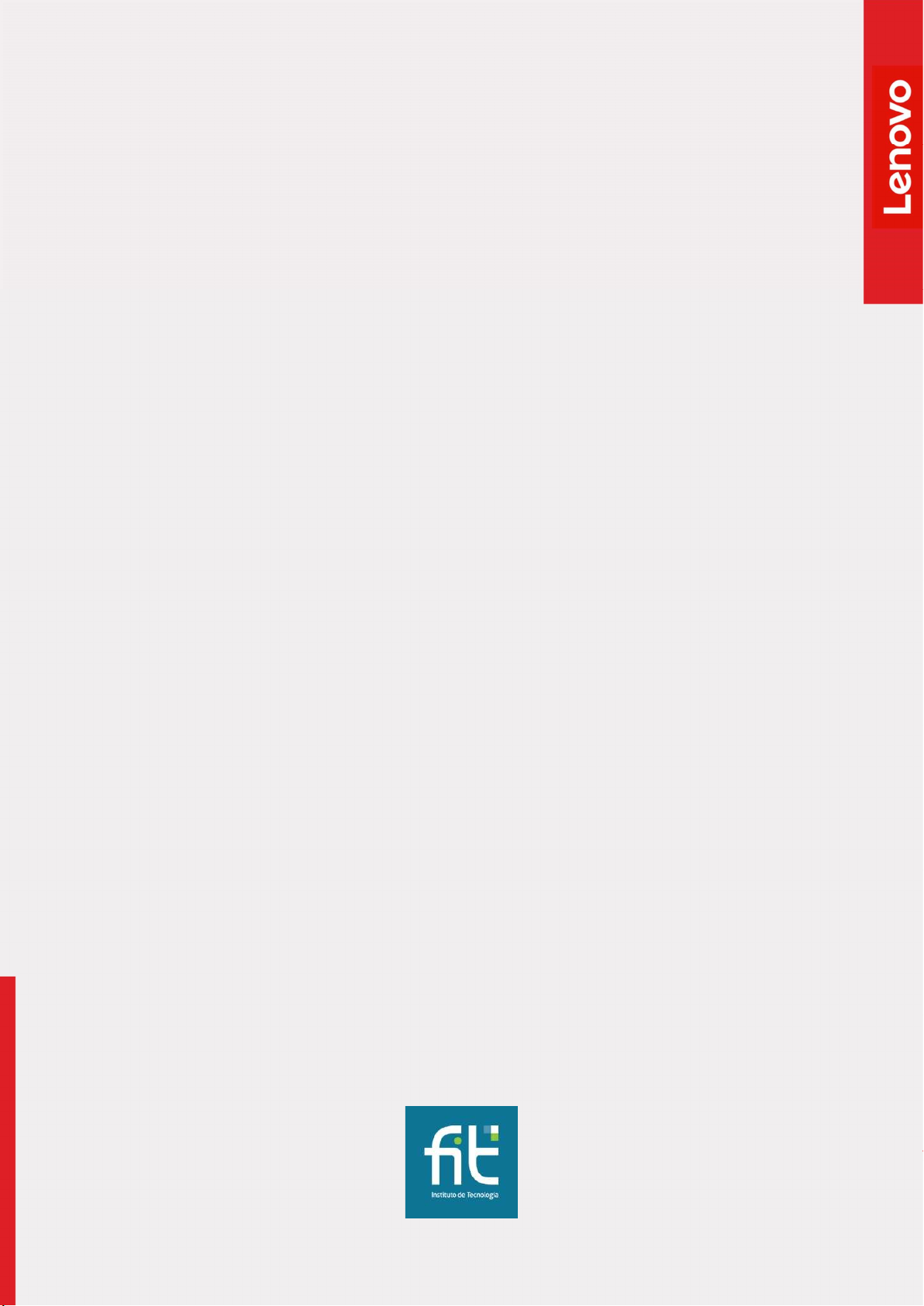
The tests on Lenovo Diagnostics may have the following statuses:
Passed
Failed
Warning
Canceled
Not Applicable
The generated codes are:
Result Code
Final Result Code Contains information about the machine serial number, system platform and execution
On the next section, you will learn how to use Lenovo Diagnostics to perform the diagnostics.
When the test algorithm is executed and no failure is found.
When the test identifies the diagnosed device is defective.
When the test indicates the diagnosed device may have some defect but the
result is not conclusive.
When the test is canceled in the middle of test execution.
When the test is not applicable for the selected device.
Contains information about the machine serial number, system platform and test
execution status and date. This code is generated for each tested device.
date. This code reports also the module where the tests were performed and the tests
with failed status.
2. PERFORMING DIAGNOSTICS IN LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS
2.1 Lenovo Diagnostics Main screen
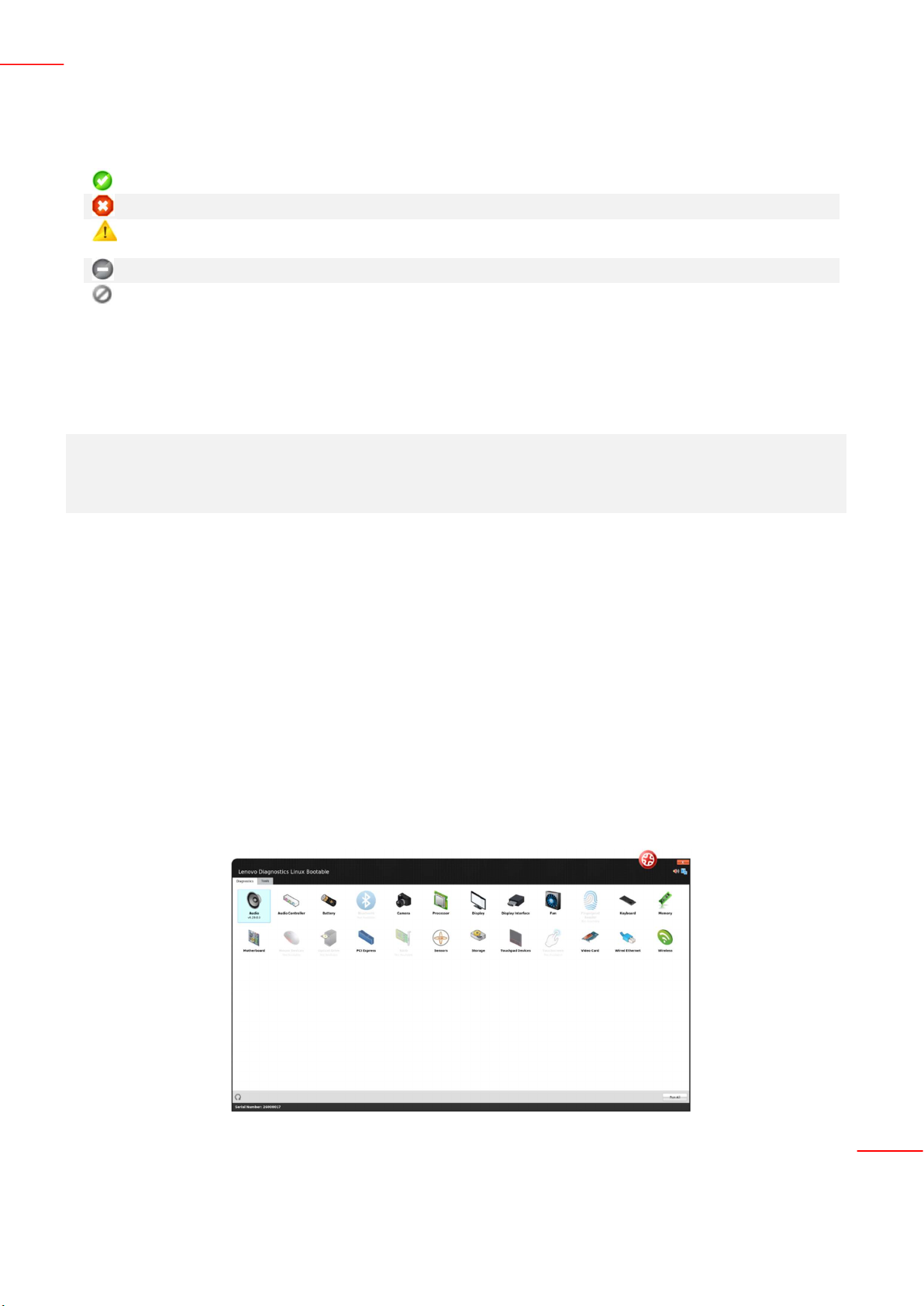
By opening the Lenovo Diagnostics, you will see the main screen with the tabs Diagnostics and Tools.
Diagnostics: here, you can see the modules provided by Lenovo Diagnostics and select one of them to perform
tests. As you will using the application. The modules with not supported devices are disabled, like the modules RAID,
Sensors and Wireless on the image below. On this tab, you can also select the option “Run All” to perform the
diagnostic for all available modules
8
Page 9
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Refresh button : you must update the modules after plug or unplug any device.
Sound Notice button : you must choose if you want to be advised regarding tests execution.
Tools: By selecting this option, you can access additional Lenovo Diagnostics features like Diagnostic Script, System
Information, Log History screen, Recover Bad Sectors and SMART tool.
2.2 Run diagnostic for a module
The diagnostic for a module in Lenovo Diagnostics is based on the following steps:
2.2.1 Select Devices and Tests
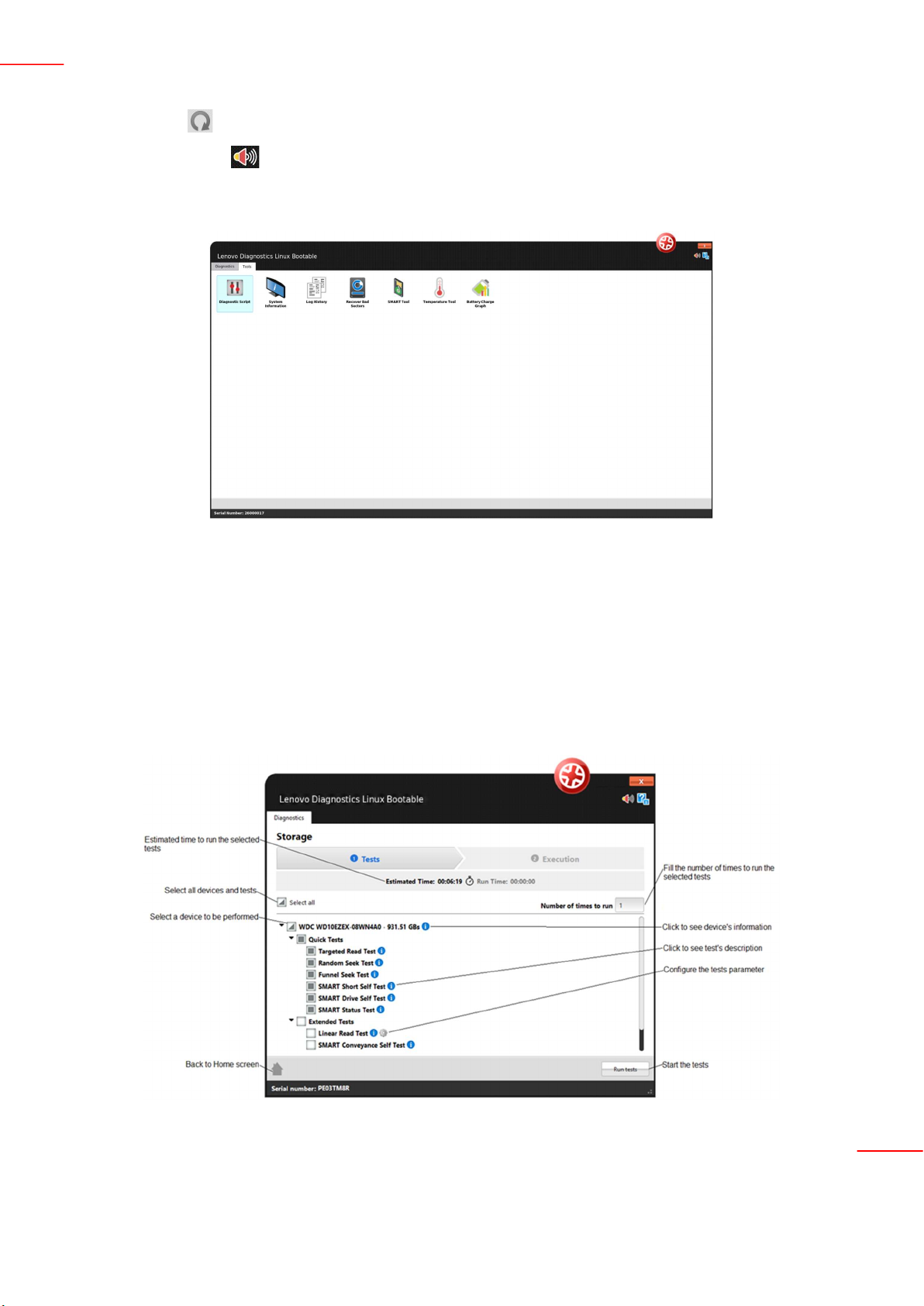
By selecting a module in the Diagnostics tab, you will be directed to a screen where you can select which devices
and tests will be performed. On this step, all devices and tests supported by the selected module are displayed and
you may select one or more of them to perform the tests. It is also possible to select the number of times to run
the set of tests in a range from 1 to 999 times.
9
Page 10
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
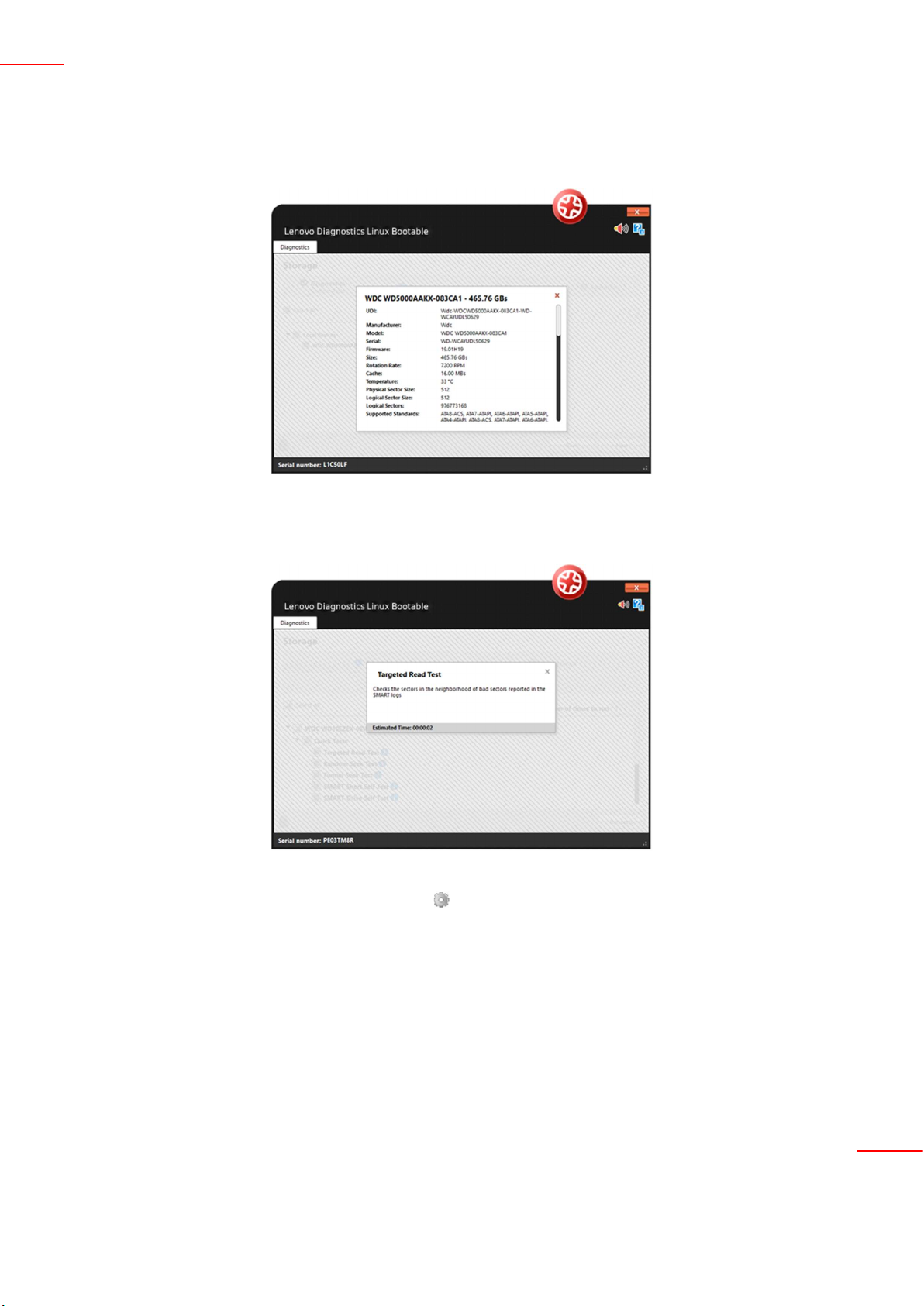
By clicking to See Device Information, you can view detailed information about the device. The properties
displayed depends on the selected module.
By clicking to See test description, you can view a brief description of the test and the estimated time to run the
test, as the screen below.
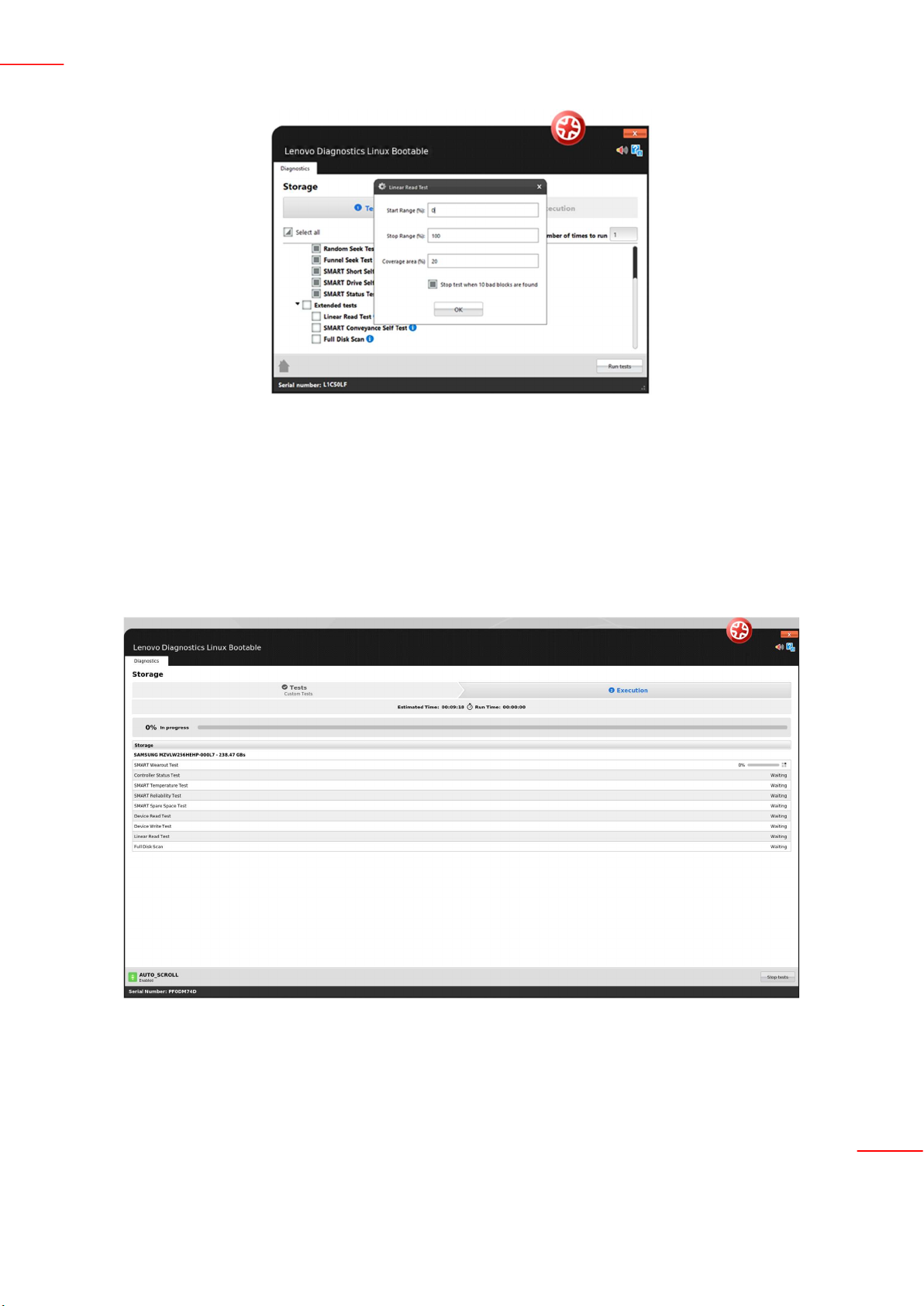
If a test supports parameters customization, the icon is displayed next to the test name. By clicking on this icon,
a popup to set the values is displayed. See in the image below the customization for the Linear Read Test from
Storage module:
10
Page 11
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
After the devices and test selection, you are able to run the diagnostic. The test execution is detailed in the next
section.
2.2.3 Run Tests
After configuring the tests execution and clicking to Run Test, you will be directed to the Execution screen. This
screen is displayed for both Recommended and Custom tests.
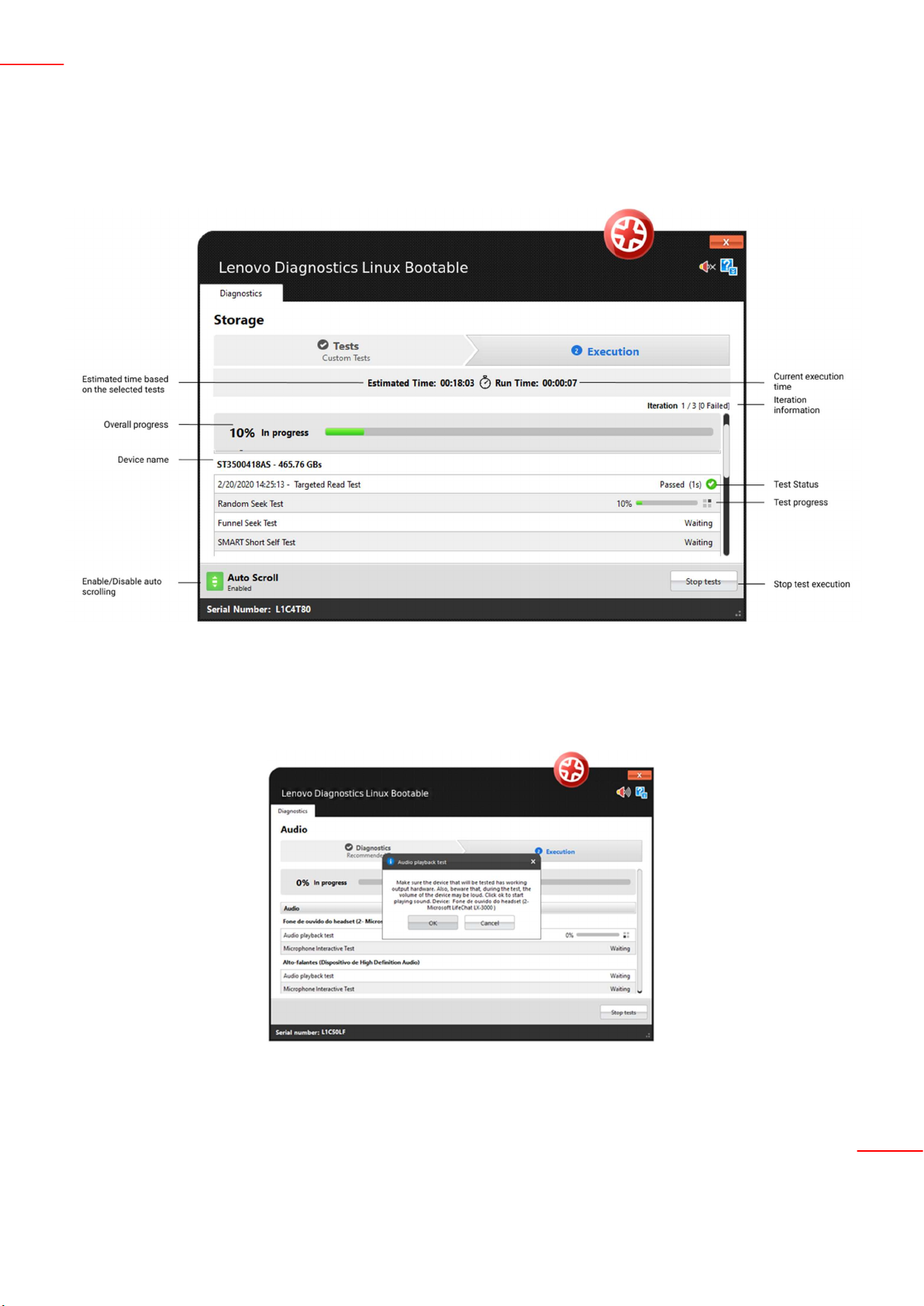
In the image below, you can see a screen of the test execution:
Once you have pressed OK, the tests execution begins. See in the image below that all devices selected in the
previous steps are displayed with their respective tests. You can follow each test execution by tracking the individual
11
Page 12
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
test progress and see the test status of each one. In addition, you can see the overall test progress and time that
reports the progress for all devices and tests selected.
If you have selected Custom Tests with more than one iteration, you will be able to see amount iterations that fail
navigate around these iterations in order to see the executions already finished and the executions not started yet.
Some tests have specific guidelines that should be followed by the user to assure the correct execution. In this case,
before to begin the execution of these tests, the application displays a popup with the test instructions. For instance,
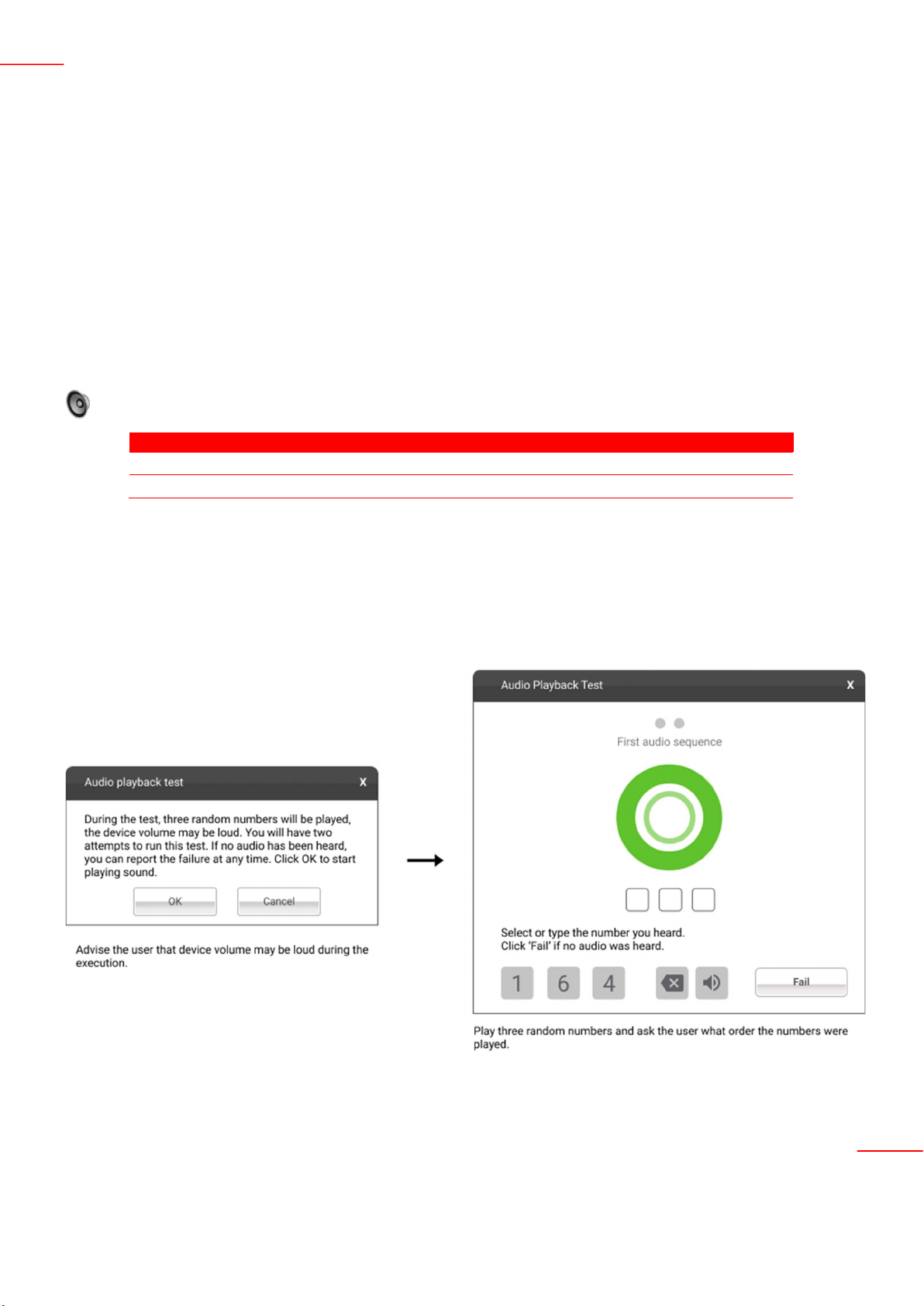
the Audio Playback test asks the user to make sure the output device is working correctly and advises a probably
loud sound will played.
If you chose to continue by pressing the OK button, the execution continues normally. If you clicking on Cancel, the
current test is canceled and the execution proceeds to the other tests not executed yet.
12
Page 13
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
If you want to abort the whole test execution, you can click on Stop tests. In this case, the current test and all
tests waiting for execution are canceled, including those from the next iterations. At the same way, the overall status
for the current iteration and for all next iterations are changed to Canceled.
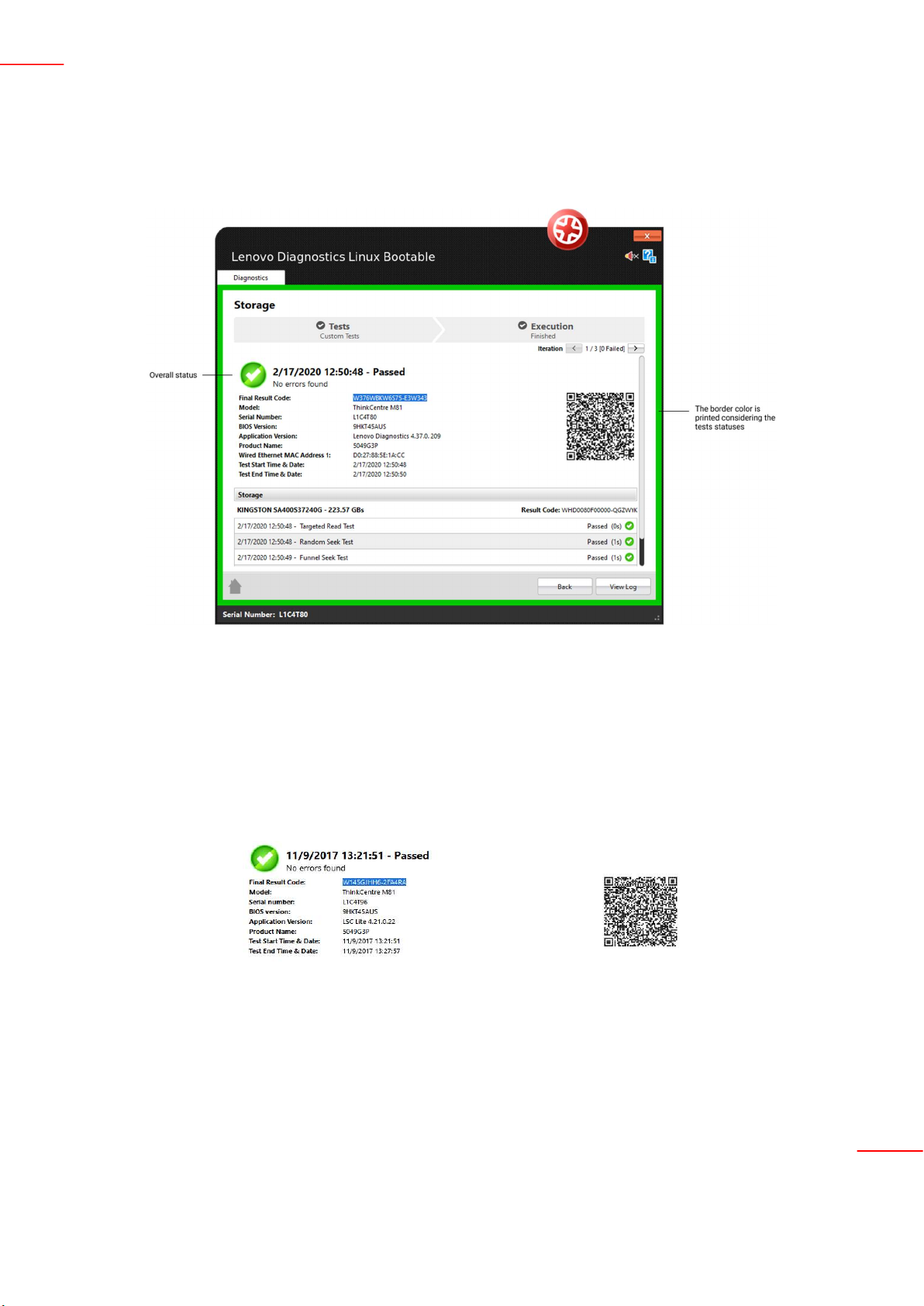
After all tests to being finished, system displays the screen below where is possible to analyze the test results.
In this above image, you can see each test results, information about machine, final result code and test date. This
section also display a QR Code that containing all those information.
2.3 See Execution Log
After a diagnostic execution, Lenovo Diagnostics generates a log with detailed information about the devices and
their test results. This log is composed by the following sections:
General information: contains information about machine, test date and final result. This section also displays a
QR Code containing those information.
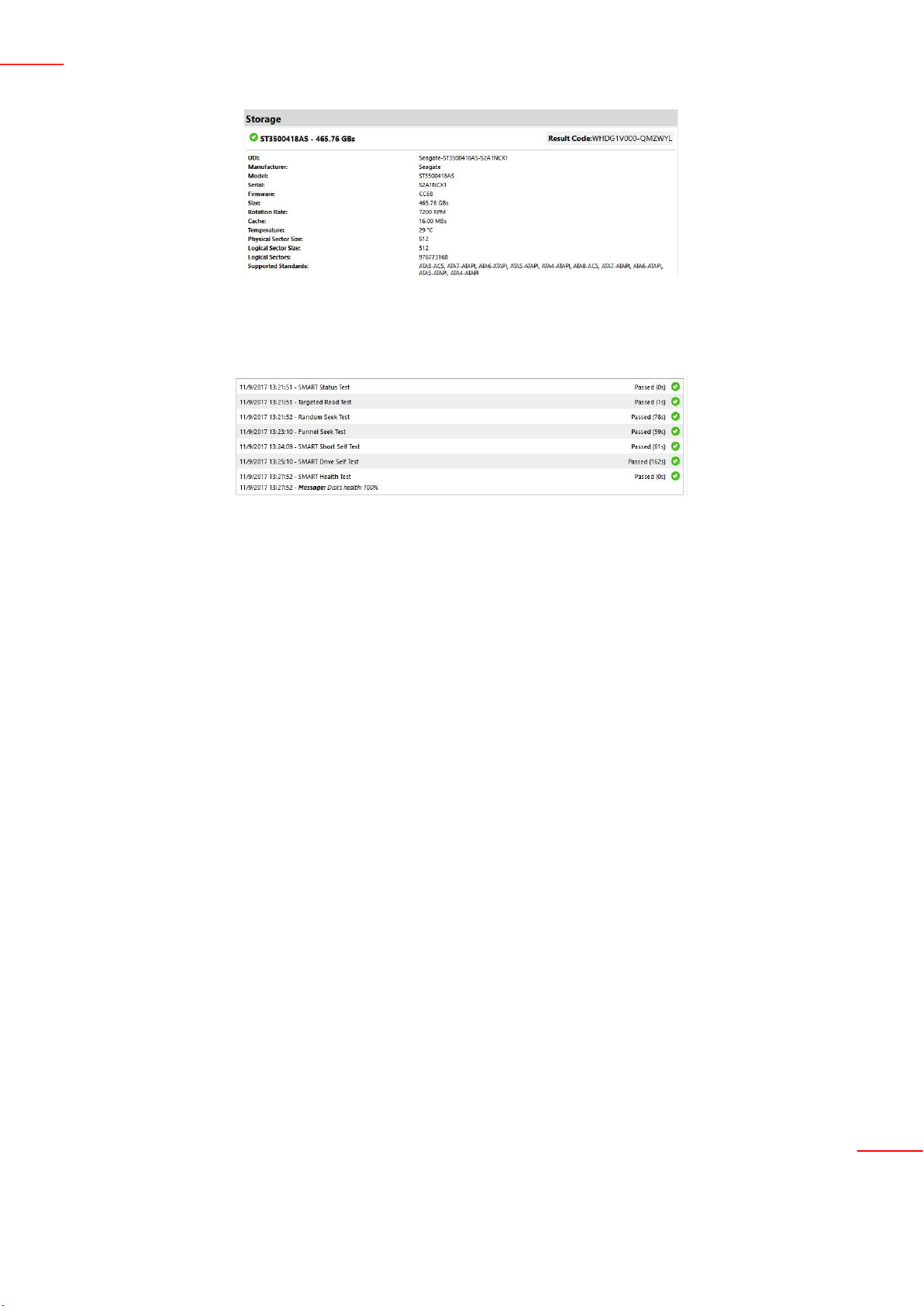
Device information: displays the technical details of each tested device and their respective result codes.
13
Page 14
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Test Results: displays the results and execution time of each performed test.
14
Page 15
Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3. LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS MODULES AND TESTS
This section provides information about all modules available in Lenovo Diagnostics and their respective
tests. Here, you will understand the approach implemented by each test and how these tests should be
performed for assure the correct diagnostic of your machine.
3.1 Audio
The Audio module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
Audio Playback Test Quick Attended
Microphone Interactive Test Quick Attended
Audio Playback Test
The audio playback test tries to play random numbers through the audio hardware and asks the user in what
order the numbers were played.
15
Page 16

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Microphone Interactive Test
This test helps to identify if the microphone is capable of capturing sound properly.
The microphone interactive test is performed according to the following workflow:
3.2 Audio Controller
The Audio Controller module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
CORB Status Test Quick Unattended
Output Stream Test Quick Unattended
Input Stream Test Quick Unattended
Bidirectional Stream Test Quick Unattended
CORB Status Test
This test checks the status of the Command Outbound Ring Buffer (CORB) mechanism.
Output Stream Test
This test checks the status of the output streams. Before starting the test, Lenovo Diagnostics advises the user that
a short audio tune will be played as displayed in the image below.
16
Page 17

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Input Stream Test
This test checks the status of the input streams.
Bidirectional Stream Test
This test checks the status of the bidirectional streams.
3.3 Battery
The Battery module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
Battery Health Test Quick Unattended
Battery Discharge Test Extended Attended
Battery Charge Test Extended Attended
Battery Temperature Test Quick Unattended
Battery Health Test
Battery Health Test checks the device charge capacity and other important battery properties in order to evaluate
device's health.
Battery Discharge Test
Battery Health Test checks the device charge capacity and other important battery properties in order to evaluate
device's health. If there is an AC cable plugged you will must to unplug it before proceeding to the test as displayed
below.
Battery Charge Test
The test checks if the battery charge increases while the AC cable is connected. If there is no AC cable plugged you
should connect it before proceeding to the test.
Battery Temperature Test
Temperature test evaluates if the battery temperature is too high, which may prevent it from charging properly.
17
Page 18

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Test
Test type
Attendance
BT Instruction Test
Quick
Unattended
AES Test
Quick
Unattended
Stress Test
Extended
Unattended
3.4 Camera
The Camera module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
Camera Capture Test Quick Attended
Camera Capture Test
Verifies if the camera device is working properly based on the user’s feedback for the captures images. This test is
performed according to the following workflow:
3.5 Fan
The Fan module is composed by the following test:
‘ Test type Attendance
Control Test Quick Unattended
Control Test
Check if the fan controller is able to work on higher speeds according to predefined levels (0-7) in the firmware.
3.6 Processor
The Processor module is composed by the following tests:
x87 Floating Point Test Quick Unattended
MMX Test Quick Unattended
3dnow! Test Quick Unattended
SSE Family Test Quick Unattended
18
Page 19

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
BT Instruction Test
The test checks the processor support for BT instruction.
x87 Floating Point Test
The test checks the processor support for x87 Floating Point instructions. If the processor does not support such
feature, the test returns unsupported.
MMX Test
The test checks the processor support for MMX instructions. If the processor does not support such feature, the test
returns unsupported.
3dnow! Test
The test checks the processor support for 3Dnow! Instructions. This test only runs in AMD processors. If the processor
does not support such feature, the test returns unsupported.
SSE Test
The test checks the processor support for SSE Family (SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2) instructions. If the
processor does not support such feature, the test returns unsupported.
AES Test
The test checks the processor support for AES instructions. If the processor does not support such feature, the test
returns unsupported.
Stress Test
The stress test performs a sequence of continuous check on all processor cores for 10 minutes. While running this
test, the CPU temperature can increase considerably, to check the temperature a pop-up screen with this information
is displayed.
19
Page 20

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.7 Display
The Display module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
Red Purity test Quick Attended
Green Purity test Quick Attended
Blue Purity test Quick Attended
Black Purity test Quick Attended
White test Quick Attended
Color Transition Test Quick Attended
Monochromatic Mesh Test Quick Attended
Inverted Monochromatic Mesh Test Quick Attended
Sharpness Test Quick Attended
Resolution Fitting Test Quick Unattended
Display Interactive Test Quick Attended
Red Purity test
This test identifies any dead pixel or burn-in problem within the red channel.
Green Purity test
This test identifies any dead pixel or burn-in problem within the green channel.
Blue Purity test
This test identifies any dead pixel or burn-in problem within the blue channel.
Black Purity test
This test identifies any dead pixel or burn-in problem within the black channel.
White Purity test
This test identifies any dead pixel or burn-in problem within the white channel.
Color Transition Test
This test identifies any problem with the display color distinction.
Resolution Fitting Test
This test checks if the system can take full advantage of the display native resolution.
Display Interactive Test
The Display Interactive Test is the combination of all purity tests. The purity tests aim to identify dead pixels or burnin problems in the channels: red, green, blue, black and white.
20
Page 21

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
All Purity tests from Display module are performed according to the following workflow:
3.8 Display Interface
The Display module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
EDID Checksum Test Quick Unattended
Display Communication Test Quick Unattended
EDID Checksum Test
This test checks the integrity of the Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) checksum provided by the monitor.
Display Communication Test
This test checks the communication with the monitor.
21
Page 22

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.9 Keyboard
The Keyboard module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
PS2 Keyboard Test Quick Unattended
USB Keyboard Test Quick Unattended
Keycode Verification Test Quick Attended
Advanced Test Quick Attended
PS2 Keyboard Test
This test tries to identify any defective PS/2 keyboard detected on this machine.
USB Keyboard Test
This test tries to identify any defective USB keyboard detected on this machine.
Keycode Verification Test
Presents the latest pressed key to the user in a legible format and the current state of the toggle keys.
If the user confirms the all keys that him have pressed was displayed, the test is finished as Passed. Otherwise the
test is finished as Failed.
Advanced Test
Interactive test to verify the status of the keyboard keys.
The test will marking the pressed keys until you test all keys. You are able to select the most appropriate keyboard
layout.
22
Page 23

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.10 Memory
The Memory module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type Attendance
Quick Random Pattern Test Quick Unattended
Advanced Integrity Test Extended Unattended
Address Test Extended Unattended
Bit Low Test Extended Unattended
Bit High Test Extended Unattended
Walking Ones Left Test Extended Unattended
Walking Ones Right Test Extended Unattended
Modulo-20 Test Extended Unattended
Moving Inversions 8 Bit Test Extended Unattended
Moving Inversions 32 Bit Test Extended Unattended
Random Pattern Test Extended Unattended
Random Number Sequence Test Extended Unattended
Block Move Test Extended Unattended
Nibble Move Test Extended Unattended
Quick Random Pattern Test
The test consists of filling the memory with a random generated pattern and then checking that the pattern was
correctly written. When checking, it writes the pattern binary complement and checks again. The test is repeated
twice. By default, 15 random patterns are used, therefore, the test runs once for each of these patterns.
Advanced Integrity Test
The test is based on the March C- enhanced algorithm. This test consists of filling the accessible memory with a
pattern, checking it, and writing its complement in an 8 bytes block size (64 bits) and then checking it again. This
procedure is repeated twice, being the first one addressing the accessible memory from the highest position to the
lowest and the second time by doing the inverse path. This test is intended to cover Stuck-At Faults and some
Coupling Faults and Transition Faults.
Address Test
This test consists of writing each memory address its own address. After that, the algorithm reads the memory
previously written and checks if they still store their own address. This test is intended to cover any addressing fault
in the accessible memory range.
Bit Low Test
This test consists of filling the memory buffer with a pattern where all bits are 0 and then checking it. When checking
for this pattern, it writes its binary complement, and finally checks if the complement was stored accordingly. Such
process is repeated 4 times. This test is intended to identify the most serious Stuck-At Faults, some cases of Transition
Faults and some cases of Read Random Faults.
23
Page 24

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Bit High Test
This test consists of filling the memory buffer with a pattern where all bits are 1 and then checking it. When checking
for this pattern, it writes its binary complement, and finally checks if the complement was stored accordingly. Such
process is repeated 4 times. This test is intended to identify the most serious Stuck-At Faults, some cases of Transition
Faults and some cases of Read Random Faults.
Walking Ones Left Test
The Walking Ones Left Test consists of writing a pattern where only the rightmost bit is set (e.g. 00000001), then
shift this pattern to the left (e.g. 00000010) until the end of the size of a byte, writing it again at the same memory
address each time such pattern is shifted. Therefore, the test is intended to cover most of the Stuck-At Faults and
some cases of Coupling Faults, and also testing the data bus by confirming that every bit can be written.
Walking Ones Right Test
The Walking Ones Right Test consists of writing a pattern where only the leftmost bit is set (e.g. 10000000), then
shift this pattern to the right (e.g. 01000000) until the end of the size of a byte, writing it again at the same memory
address each time such pattern is shifted. Therefore, such test is intended to cover most of the Stuck-At Faults and
some cases of Coupling Faults, and also testing the data bus by confirming that every bit can be written.
Modulo-20 Test
The test consists of writing into an interval of 20 memory locations for each block with a pattern and filling all other
locations with its complement 6 times. Unlike the other tests, the Modulo-20 test is not affected by buffering or
caching, so it is able to detect most of the Stuck-At Faults, Coupling Faults, Transition Faults and Read Random
Faults that are not detected by other testing approaches.
Moving Inversions 8 Bit Test
The test consists of filling the memory with the 8-bit wide pattern: 10000000 and then checking that the pattern
was correctly written. When checking, it writes the pattern binary complement (01111111) and checks it again. The
procedure described earlier is repeated 8 times, one for each pattern right shifted: 10000000, 01000000, 00100000,
00010000, 00001000, 00000100, 00000010, 00000001.
Moving Inversions 32 Bit Test
This test fills all the accessible memory with a shifting pattern, that is, a value which is binary left shifted as it is
written out through the accessible memory of every memory block. Once the pattern reaches 0x80000000 (a value
with the left most bit set to 1 only) then the pattern is reset to 0x00000001. After that, it checks the written values
and writes their binary complements, starting from the first memory address to the last one. Finally, the algorithm
checks the memory for the complements written in the previous step, being this checking starting from the last
element down to the first one. Such process is repeated 2 times. This test presents a more thorough approach
intended to cover most of the Stuck-At Faults and Transition Faults and some cases of Coupling Faults and Read
Random Faults...
Random Pattern Test
The test consists of filling the memory with a random generated pattern and then checking that the pattern was
correctly written. When checking, it writes the pattern binary complement and checks it again. This process is
repeated twice. By default, 50 random patterns are used, therefore the test runs once for each of these patterns...
24
Page 25

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Random Number Sequence Test
The test consists of filling the memory with one different random generated pattern for each memory address and
then checking that the pattern was correctly written. In order to check it, the test must generate these numbers
based on a seed that may be reset to reproduce the sequence. When checking, it writes the pattern binary
complement and it checks again. Such process is repeated several times. This test is intended to cover most of the
Stuck-At Faults. Coupling Faults, and some cases of Transition Faults and Read Random Faults.
Block Move Test
The test consists of moving memory data around within memory blocks. It repeats the movements described above
80 times. Finally, the test checks every memory address to verify if it is consistent.
Nibble Move Test
This test consists of writing to a nibble (a nibble is a group of four bits) a pattern value in each memory address,
then it validates every nibble individually. It repeats this process until all nibbles in every address are checked.
3.11 Motherboard
The Motherboard module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Chipset Test Quick Unattended
PCI/PCI-e Test Quick Unattended
RTC Test Quick Unattended
USB Test Quick Unattended
CMOS Pattern Test Quick Unattended
Chipset Test
The test checks the status registers of the controllers that form the foundation of the motherboard chipset. These
controllers are: EHCI, OHCI, xHCI and SATA.
PCI/PCI-e Test
The PCI/PCI-e Test checks the status registers of the PCI Express onboard devices for unexpected errors or power
failure.
RTC Test
The test checks the following RTC (Real Time Clock) properties: accuracy and rollover. The test attempts to
guarantee the correct operation of these properties.
Attendance
USB Test
The test checks the status of USB devices. If any errors are indicated, the test fails.
25
Page 26

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
CMOS Pattern Test
The test saves the CMOS current value and attempts to write predefined pattern values on CMOS, verifying if the
written values are consistent, and then the backup is restored
3.12 Optical Drive
The Optical Drive module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Media-Less Optical Self-Test Quick Attended
Linear Seek Test Quick Attended
Random Seek Test Quick Attended
Funnel Seek Test Quick Attended
Read and Compare Test Quick Attended
Write Test Quick Attended
Media-Less Optical Self-Test
Checks the optical drive internal components. This test requires that no media is inserted into the drive. Therefore
if any media was detected into the drive the application displays the following message:
Linear Seek Test
Checks the integrity of the optical drive mechanism is continuously moving the driver head all around the media.
For execute this test the user must have a media containing at least the following amount of date written on it
according to its type: CD (210 MB), DVD (1000 MB), Blu-Ray (4000 MB).
Attendance
Random Seek Test
Checks the integrity of the optical drive transmission mechanism by moving the driver head through random
positions on the media. For executing this test, the user must have a media containing at least the following
amount of date written on it according to its type: CD (210 MB), DVD (1000 MB), Blu-Ray (4000 MB).
Funnel Seek Test
Checks the integrity of the optical drive mechanism by moving the driver head in a funnel pattern. For executing
this test, the user must have a media containing at least the following amount of date written on it according to its
type: CD (210 MB), DVD (1000 MB), Blu-Ray (4000 MB).
26
Page 27

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Read and Compare Test
Checks the driver ability to make correct read operations. Performs two linear read operations and compares the
information obtained from the two reads. For executing this test, the user must have a media containing at least
the following amount of date written on it according to its type: CD (210 MB), DVD (1000 MB), Blu-Ray (4000 MB).
Write Test
Checks the capability of the drive to write correctly to an optical media. For executing this test, you must have a
blank media (CDR, CD-RW, DVD-R, DVD-RW, BD-R, BD-RE).
Linear Seek Test, Random Seek Test, Funnel Seek Test, Read and Compare Test and Write Test are
performed according the following workflow:
3.13 PCI Express
The PCI Express module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Status Test Quick Attended
Status Test
Verifies that all the PCI Express devices are recognized and communicating with the system.
Attendance
3.14 Mouse Devices
The Mouse Devices module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Click Test Quick Attended
Precision Test Quick Attended
Press Precision Test Quick Attended
Attendance
27
Page 28

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Click Test
It does a check on the device buttons, issuing the user to perform some actions regarding them. The Click Test
execution is based on the workflow below.
The user must perform one by one, the actions issued by the test. Note that the actions requested depends on the
numbers and types of buttons present in your pointing device.
The user has two attempts to execute each requested action. If the requested action was detected by the application,
it is considered as passed. Otherwise the action is considered as “Failed”. The Click Test is considered as “Passed” if
all actions required are passed.
If the user does not perform any action for 30 seconds, the following popup is displayed:
If the user select “Yes”, reporting that the test was performed according to the instructions the test will fail. In this
case, the application assumes that it was not possible to detect the device, indicating a bad working of it. If the user
selects “No”, the test is canceled because the actions required were not properly executed.
Precision Test and Press Precision Test
Tests the device movement precision. The Precision Test execution is based on the following workflow:
28
Page 29

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
If the user gets to move the pointer through the entire depicted area without to reach the outside area the test is
finished as passed. If the outside area was reached two times the test will fail. If the pointer is not moved for more
than 30 seconds the test will be closed and the following message will be displayed to the user:
If the user selects “Yes”, reporting the test was performed according to the instructions, the test will be finished as
“failed”. In this case, the application assumes that it was not possible to detect the device movement, indicating a
bad working of the device. If the user selects “No”, the test is canceled because the required actions were not
properly executed.
Note: For executing Press Precision test, you must press any button from mouse and move the pointer.
3.15 RAID
The RAID module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Battery Status Test Quick Unattended
Enclosure Status Test Quick Unattended
Logical Drive Status Test Quick Unattended
RAID Status Test Quick Unattended
Consistency Check Extended Attended
Battery Status Test
Checks the health of the controller BBU (Battery Backup Unit).
Enclosure Status Test
Checks the status of the enclosures used by a RAID controller.
Logical Drive Status Test
Checks the status of each logical drive in the RAID controller.
RAID Status Test
Checks the status of each RAID volume in the RAID controller.
Consistency Check
Checks the consistency of each controller logical drive. This test might take a few hours to run depending on how
many logical and physical drives are present in the RAID controller.
Attendance
29
Page 30

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.16 Storage
The Storage module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
SMART Status Test Quick Unattended
Targeted Read Test Quick Unattended
Random Seek Test Quick Unattended
Funnel Seek Test Quick Unattended
SMART Short Self Test Quick Unattended
SMART Drive Self Test Quick Unattended
Default Self Test Quick Unattended
Device Read Test Quick Unattended
SMART Wearout Test Quick Unattended
Controller Status Test Quick Unattended
SMART Temperature Test Quick Unattended
SMART Reliability Test Quick Unattended
SMART Spare Space Test Quick Unattended
Extended Random Seek Test Extended Unattended
Extended Funnel Seek Test Extended Unattended
Extended Self Test Extended Unattended
Device Write Test Extended Unattended
Linear Read Test Extended Unattended
SMART Conveyance Test Extended Unattended
Full Disk Scan Test Extended Unattended
SMART Status Test
Checks the status reported by SMART to quickly identify whether a device is defective or not.
Targeted Read Test
Attendance
Checks the sectors in neighborhood of bad sectors reported in the SMART logs.
Random Seek Test
Checks the integrity of the Servomechanism of a device by checking sectors at several randomly chosen addresses.
Funnel Seek Test
Checks the integrity of the Servomechanism of a device by checking sectors following a "funnel" or "butterfly" pattern.
SMART Short Self Test
Checks electrical and mechanical component status as well as the reading ability of the device.
SMART Drive Self Test
Proprietary Lenovo Drive Self-Test (DST) that mixes sequential and random reads to the disk.
Default Self Test
Vendor specific test that runs a quick check.
30
Page 31

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Device Read Test
Tests if it is possible to correctly read sectors in different areas of the storage device.
SMART Wearout Test
SMART Wearout Test checks the wearout level of the attached SSD device by reading SMART attributes and informs
whether the device is in good condition or has reached its wearout limit.
Controller Status Test
This test detects if the device behaves as expected.
SMART Temperature Test
This test detects if the current temperature for the device is in critical state.
SMART Reliability Test
This test detects if the device is still reliable based on SMART metrics.
SMART Spare Space Test
This test detects if the spare space in the device is critically low.
Extended Random Seek Test
Works similar to quick random test, but the number of checked sectors is larger and it does not stop when the first
bad sector is found.
Extended Funnel Seek Test
Works similar to quick funnel test, but the number of checked sectors is larger and it does not stop when the first
bad sector is found.
Extended Self Test
Works similar to a quick short self test, but checks more sectors.
Device Write Test
The Storage Device Write Test will verify if it is possible to write data on different areas of the device and then
read the data correctly.
Linear Read Test
Checks the integrity of the storage device by reading its sectors following a linear pattern.
SMART Conveyance Test
Checks the device integrity through the status returned by SMART Conveyance test.
Full Disk Scan Test
This test performs a full verification of the disk.
31
Page 32

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.17 Touchscreen
The Touchscreen module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Basic Touch Test Quick Attended
Accuracy Test Quick Attended
Diagonal Test Quick Attended
Grid Test Quick Attended
Multi-touch Test Quick Attended
Basic Touch Test
The Basic touch test will verify if the system is receiving touch events. This test is based on the following workflow:
Accuracy test
The Accuracy test will verify if the touchpoints are accurate with the screen mapping. This test is based on the
following workflow:
Attendance
Diagonal Test
The Diagonal test will verify if rows and columns of the touchscreen are sensing through a diagonal gesture on the
screen. This test is based on the following workflow:
32
Page 33

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Grid test
The Grid test will verify if any areas of touchscreen are not able to receive touch events.
Multi-touch Test
The Multi-touch test will verify if the system is receiving multi-touch events.
3.18 Video Card
The Video Card module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Video Memory Test Quick Unattended
Extended Video Memory Test Extended Unattended
Stress Test Extended Unattended
Texture Pipeline Test Quick Unattended
Mathematical Operations Test Quick Unattended
Framebuffer Address Test Quick Unattended
Framebuffer Block Moving Test Quick Unattended
Framebuffer Walking Ones Test Quick Unattended
Framebuffer Deterministic Filling Test Quick Unattended
Framebuffer Random Filling Test Quick Unattended
Video Memory Test
Verifies if some data patterns are consistently read from and written to video card memory.
Extended Video Memory Test
Similar to Video Memory Test, but performs an extended analysis with more data patterns
Attendance
33
Page 34

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Stress Test
Executes heavy operations on the video card for the purpose of stressing the GPU and verifying that the results
remain reliable under stress.
Texture Pipeline Test
Sends texture patterns to be rendered by the graphics pipeline and checks for loss of data when comparing input
and output.
Mathematical Operations Test
Consists in basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division.
Framebuffer Address Test
This test consists in writing to each memory address its own address, foreach memory block.
Framebuffer Block Moving Test
This test fills all the accessible memory with a shifting pattern, that is, a value which is binary left shifted as it is
written out through the accessible memory of every memory block.
Framebuffer Walking Ones Test
Consists on writing a pattern where only the rightmost bit is set (e.g.00000001), then shift this pattern to the left
(e.g.00000010) until the end of the size of a byte, writing it again at the same memory address each time such
pattern is shifted
Framebuffer Deterministic Filling Test
Consists in filling the memory buffer from every block with a pattern where all bits are 1 and then checking it.
When checking for this pattern, it writes its binary complement was stored accordingly.
Framebuffer Random Filling Test
Consists in basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division.
34
Page 35

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
3.19 Wired Ethernet
The Wired Ethernet module is composed by the following test:
Test Test type
Self-Test Quick Unattended
Self-Test
Checks the device’s integrity by performing its driver’s built-in self-tests.
3.20 Wireless
The Wireless module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Radio Enabled Test Quick Unattended
Network Scan Test Quick Unattended
Signal Strength Test Quick Unattended
Connection Test Extended Unattended
Radio Enabled Test
Verifies that the wireless is turned on.
Attendance
Attendance
Network Scan Test
Verifies that the wireless adapter can detect available networks. Make sure that there is a properly configured
router or access point nearby before running this test.
Signal Strength Test
Verifies that the wireless adapter can detect available networks. Make sure that there is a properly configured
router or access point nearby before running this test.
Connection Test
Verifies if it is possible to connect with different SSIDs that already set in advance. Once connected, it tests the
connection on each one of the SSIDs and verifies if it is possible to download and upload from a specific server.
This test is enabled by config.ini parameter ENABLE_CONNECTION_TEST = 1 on Bootable version.
3.21 Sensors
The Sensors module is composed by the following test:
Test Test type
Attendance
35
Page 36

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Lid Closure Test Quick Attended
Lid Closure Test
This test verifies if the lid sensor is capturing the events of closing and opening the lid. The test will fail if these
events are not captured.
The test will ask to the user open and close the notebook lid.
3.22 Bluetooth
The Bluetooth module is composed by the following test:
Test Test type
Scan Test Quick Attended
Scan Test
Scan for nearby active Bluetooth devices.
The test starts by asking you to make sure that the Bluetooth device is enabled and there is another Bluetooth
close and active.
Attendance
3.23 Fingerprint Reader
The Fingerprint reader module is composed by the following test:
36
Page 37

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
Test Test type
Recognition Test Quick Attended
Attendance
Recognition Test
The test prompts the user to swipe or touch a finger on the fingerprint device. The test starts by asking you to swipe
or touch in your device.
If the user does not perform any action for 30 seconds, the following popup is displayed:
If the user selects “Yes”, reporting that the test was performed according to the instructions, the test will fail. In this
case, the application assumes that it was not possible to detect the device, indicating a bad working of it. If the user
selects “No”, the test is canceled because the actions required were not properly executed.
3.24 Touchpad Devices
The Touchpad Devices module is composed by the following tests:
Test Test type
Click Test Quick Attended
Precision Test Quick Attended
Press Precision Test Quick Attended
Click Test
It does a check on the device buttons, issuing the user to perform some actions regarding them. The Click Test
execution is based on the workflow below.
Attendance
37
Page 38

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
The user must perform one by one, the actions issued by the test. Note that the actions requested depends on the
numbers and types of buttons present in your touchpad device.
The user has two attempts to execute each requested action. If the requested action was detected by the application,
it is considered as passed. Otherwise the action is considered as “Failed”. The Click Test is considered as “Passed” if
all actions required are passed.
If the user does not perform any action for 30 seconds, the following popup is displayed:
If the user selects “Yes”, reporting that the test was performed according to the instructions the test will fail. In this
case, the application assumes that it was not possible to detect the device, indicating a bad working of it. If the user
selects “No”, the test is canceled because the actions required were not properly executed.
Precision Test and Press Precision Test
Tests the device movement precision. The Precision Test execution is based on the following workflow:
38
Page 39

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
If the user gets to move the pointer through the entire depicted area without to reach the outside area the test is
finished as passed. If the outside area was reached two times the test will fail. If the pointer is not moved for more
than 30 seconds the test windows is going to be closed and the following message is displaying to the user:
If the user selects “Yes”, reporting the test was performed according to the instructions, the test will be finished as
“failed”. In this case, the application assumes that it was not possible to detect the device movement, indicating a
bad working of the device. If the user selects “No”, the test is canceled because the required actions were not
properly executed.
Note: For executing Press Precision test, you must press any button from touchpad and move the pointer.
4. EXPLORING LENOVO RUN ALL OPTION
Run All option allows to perform all supported tests from all supported modules at the same execution. In this flow
is not possible to select devices, thus all devices will be tested. It is possible to choose if the Attended tests should
be performed or not.
When the checkbox is marked, the application will run Unattended + Attended tests from the test execution option
selected.
4.1 Quick tests
Click on Quick tests button to perform all quick tests.
39
Page 40

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
4.2 Quick tests (customized option)
Click to Customize to remove any module or test from the list of tests that will be performed.
4.3 Full tests
Click on Full Tests button to perform all quick and extended tests.
40
Page 41

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
4.4 Full tests (customized option)
Click to Customize to remove any module or test from the list of tests that will be performed.
41
Page 42

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
5. EXPLORING LENOVO DIAGNOSTICS TOOLS
This section provides information about Tools:
5. 1 Diagnostic Script
The Diagnostic Script is a tool that allows user to create a custom list of tests from any module. By selecting this
tool, the following options are displayed:
● Create: allows to create a new diagnostic script.
● Edit: allows editing a diagnostic script saved previously.
● Execute: allows to perform the tests configured in a diagnostic script.
42
Page 43

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
5.1.1 Create a diagnostic script
By selecting the option “Create” and clicking on the Next button, the screen below will be displayed. This screen
allows selecting a set of tests to be performed from a list with all tests present in Lenovo Diagnostics. The tests not
supported by the tested machine are marked with the icon .
It is also possible to configure the execution of this tests according one of the following parameters:
Number of executions: allows performing the tests according to a specific number of executions in a range from
1 to 999999999. In this case, the diagnostic will be finished when all iterations are completed.
Test duration in minutes: allows performing the tests according to a specific number of minutes in a range from
1 to 999999999. In this case, the diagnostic will be finished when this time is reached and all tests from the current
iteration are finished. Notice that even if the time is reached the tests will be performed until the end in the current
iteration.
Module Execution sequence: allows you to select the order in which the modules will be executed by dragging
and dropping the modules in the list. The list will be filled according to the selected modules.
5.1.2 Edit a diagnostic script
By selecting the option “Edit”, the Lenovo Diagnostics displays a field where is possible to select an existing diagnostic
script to be edited.
43
Page 44

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
By selecting this file and clicking on the Next button, a screen is displayed with the configuration from the selected
diagnostic script. Here it is possible to modify this configuration by changing the list of tests, modify the number of
executions or duration minutes and change the order of modules execution. By clicking on Save button all changes
are saved in the current file and clicking on Save as it is possible to create a new file with the current configuration.
5.1.3 Execute a diagnostic script
By selecting the option “Execute”, the Lenovo Diagnostics displays a field where is possible to select an existing
diagnostic script to be performed.
44
Page 45

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
By selecting a valid diagnostic script file and clicking on the Next button, a screen is displayed with the configuration
from the selected diagnostic script. All selected tests are listed selected and the not supported one are marked with
the icon .
By clicking to Run Tests, the diagnostic script execution screen is displayed, and all supported tests are performed.
The not supported tests that do not have an associated device are filtered on this execution. It is possible to finish
the execution anytime by clicking on Stop Test.
45
Page 46

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
When the diagnostic is finished, the following popup is displayed with the execution summary.
The user can view the execution log by clicking View log.
It is also possible to export all executions log to a PDF file by clicking Export all log or export a specific iteration by
clicking on Export log.
46
Page 47

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
5.2 System Information
The system information tool allows the user to see general information about the system and the available modules
devices. See in the screen below that is possible navigating between the modules and export the information by
module or export all information at the same time.
5.3 Log History
The Log History tool allows the user to see the logs of all executions performed in a machine. See in the image below
it is possible to find logs by informing a period and export all logs.
47
Page 48

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
5.4 Recover Bad Sectors
The Recover Bad Sectors tool allows the user to scan HDD/SSD devices for bad sectors and fix them whenever
possible.
Be aware to perform a backup of your disk before performing this operation. The recovery operation can cause data
loss and requires your confirmation.
5.5 SMART Tool
SMART tool provides a list of storage devices and shows, for each one, the SMART attributes and its information.
You are able to export those information to a PDF or HTML file. It is possible to export information for each storage
device separately or for all available devices in the same file.
48
Page 49

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
5.6 Temperature Tool
The Temperature Tool shows in real time the temperature information of machine devices.
5.7 Battery Charge Graph
See battery information, including real time charge graph.
49
Page 50

Lenovo Diagnostics Linux v4.39.0 – User Guide
6. GLOSSARY
Extended Test: type of test that is performed in some hours.
Quick test: type of test that is performed in some minutes.
Unattended test: It is a test that does not depend on user actions to be executed. All steps are performed
automatically by the application.
Attended test: It is a test that depends on some user action to be executed.
Module: a module contains a set of tests that can be performed for a type of devices. It is enabled in the application
only if the tested machine has at least one device supported by the module.
50
 Loading...
Loading...