Page 1

Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters
Product Guide
The Intel X550 10GBASE-T Adapter is a low cost, low power 10 GbE performance adapter suitable for all
data center applications. With support for standard CAT 6a cabling with RJ45 connectors, the X550 offers
a low barrier of entry to 10 Gb Ethernet networking.
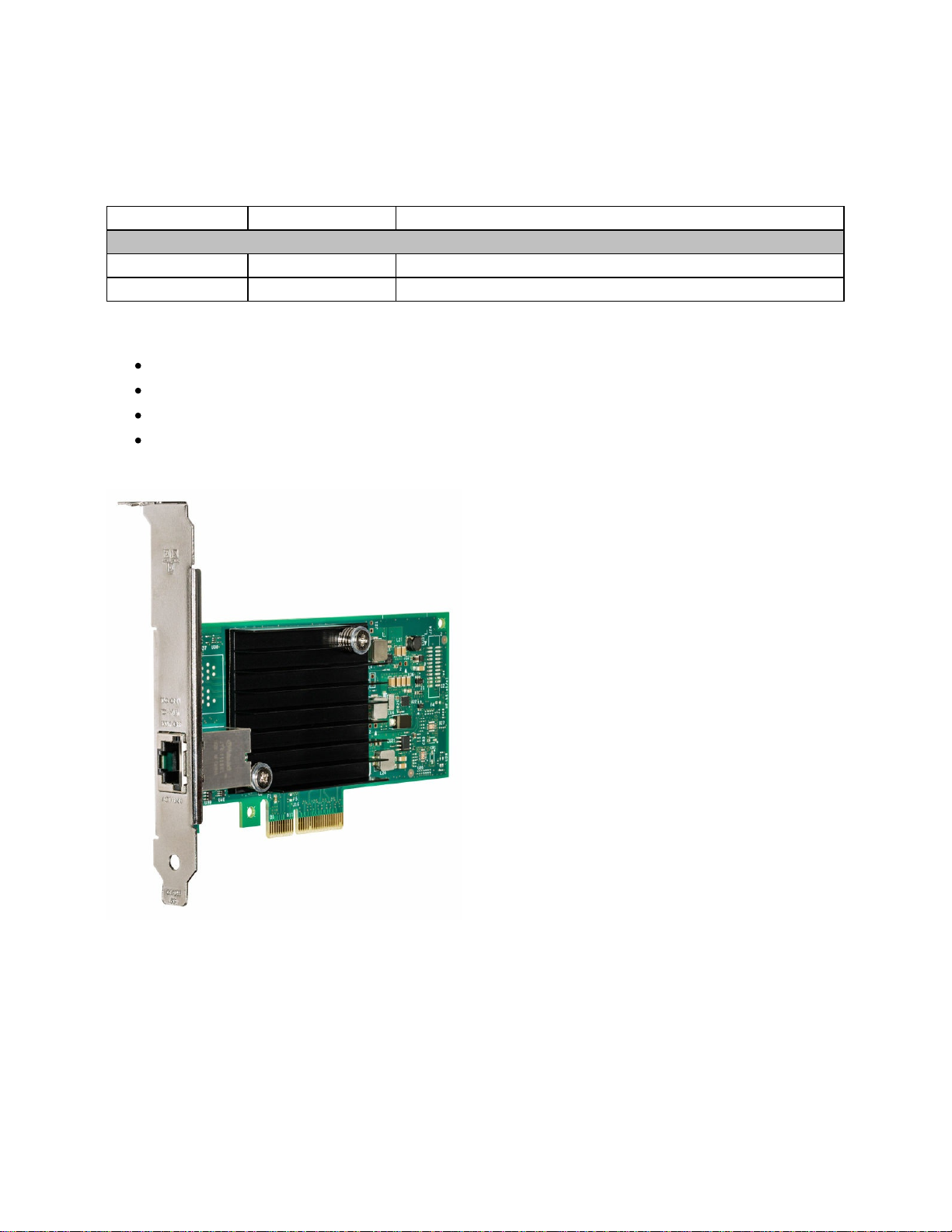
The following figure shows the Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter.
Figure 1. Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter
Did you know?
The Intel X550 is the newest innovation in Intel’s adapter family to drive 10 GbE into the broad server
market. This adapter hosts Intel’s latest Ethernet ASIC, the Intel Ethernet Controller X550, a low-cost
single-chip 10GBASE-T solution for today’s server platforms.
Click here to check for updates
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 1
Page 2
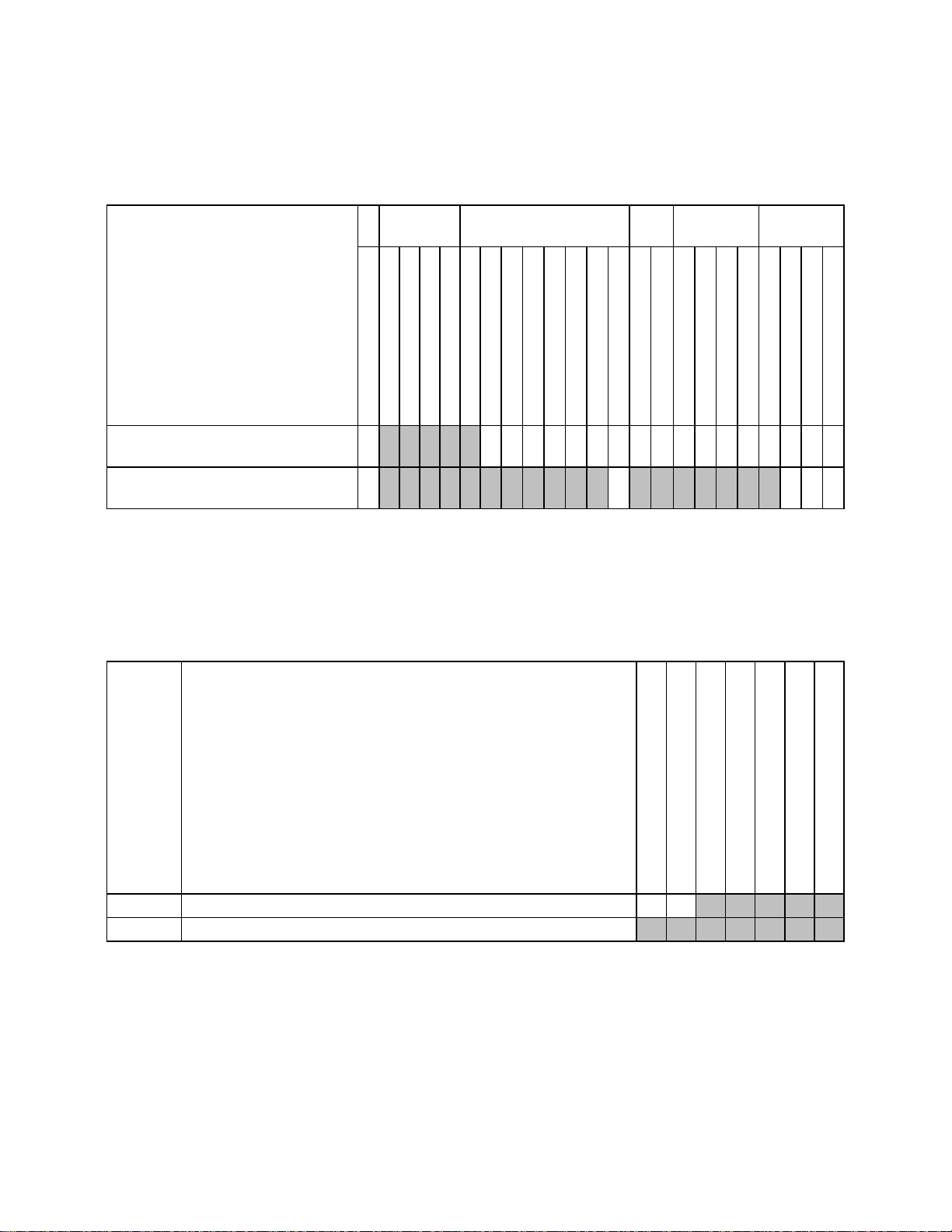
Part number information
The following table provides the ordering part numbers and feature codes for the Intel X550 adapter.
Table 1. Ordering part numbers and feature codes
Part number Feature code Description
System x and ThinkSystem adapters
00MM850 ATRY Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter
00MM860 ATPX Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter
The adapter option part numbers includes the following items:
One Intel 10 Gb Ethernet adapter with a full-height (3U) bracket attached
Low-profile (2U) bracket included in the box
Quick Install Guide
Other documentation
The following figure shows the single-port X550-T1 adapter.
Figure 2. Intel X550-T1 single-port adapter
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 2
Page 3

Features
The Intel X550 adapter has the following features:
Supports Intel Virtualization Technology for connectivity (VT-c), I/O virtualization advances network
connectivity used in today’s servers to more efficient models by providing Flexible Port Partitioning
(FPP), multiple Tx/Rx queues, Tx queue rate-limiting, and on-controller QoS functionality that is
useful for both virtual and non-virtual server deployments.
Supports Virtual Machine Device Queues (VMDq) for NIC-based VM queue sorting, enabling efficient
hypervisor-based switching. VMDq reduces I/O impact on the hypervisor in a virtualized server by
performing data sorting and coalescing in the network adapter.
Supports SR-IOV for direct assignment - NIC-based isolation and switching for various virtual
station instances enabling optimal CPU usage in virtualized environment.
Provides virtual bridging support that delivers both host-side and switch-side control and
management of virtualized I/O as well as the following modes of virtualized operation:
VEPA: IEEE 802.1Qbg support for Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator.
VEB: Virtual Ethernet Bridge support with Intel VT.
Supports VXLAN/NVGRE Hardware Offloads, stateless offloads that preserve application
performance for overlay networks. With these offloads, it is possible to distribute network traffic
across CPU cores. At the same time, the X550 offloads LSO, GSO, and checksum from the host
software, which reduces CPU overhead.
Flexible Port Partitioning (FPP), based on the SR-IOV specification, enables virtual Ethernet
controllers that can be used by a Linux host directly or assigned directly to virtual machines for
hypervisor virtual switch bypass. FPP enables the assignment of up to 64 Linux host processes or
virtual machines per port to virtual functions. FPP can be used to control the partitioning of the
bandwidth across multiple virtual functions. FPP can also provide balanced QoS by giving each
assigned virtual function equal access to 10 Gb/s of bandwidth.
MSI-X interrupts support minimizes the impact of I/O interrupts by load balancing interrupts across
multiple processor cores.
Low-Latency Interrupts: Allows the adapter to bypass the automatic moderation of time intervals
between the interrupts (based on the sensitivity of the incoming data).
Load balancing on multiple processors, which increases performance on multiprocessor systems by
efficiently balancing network loads across processor cores when used with Receive Side Scaling
(RSS) from Microsoft or Scalable I/O on Linux.
Header Splits and Replication in Receive helps the driver focus on the relevant part of the packet
without needing to parse it.
Multiple queues allow packet handling without the waiting/buffer overflow, which provides efficient
packet prioritization.
Mobile and cloud application acceleration: Intel’s Data Plan Development Kit (DPDK) delivers an
open driver where users can fine-tune small packet performance.
Offload features:
IP, TCP, and UDP checksum offload (IPv4 and IPv6)
TCP and UDP segmentation/large send offload (IPv4 and IPv6)
IPsec offload
Receive Side Scaling for Windows and Scalable I/O for Linux (IPv4, IPv6, and TCP/ UDP)
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN support with VLAN tag insertion, with stripping and packet filtering for up to
4096 VLAN tags.
IEEE 802.3x flow control support.
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service/Quality of Service.
Support for Advanced Packet Filtering.
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 3
Page 4

Jumbo frames support (up to 9,500 bytes).
Teaming support:
Adapter Fault Tolerance (AFT)
Switch Fault Tolerance (SFT)
Adaptive Load Balancing (ALB)
Virtual Machine Load Balancing (VMLB)
IEEE 802.3ad (link aggregation control protocol)
Support for both UEFI and PXE boot.
Technical specifications
The Intel X550 adapter has the following specifications:
One or Two 10GBASE-T RJ-45 ports
Supports 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, and 10 Gbps speeds
Standard PCIe low-profile card form factor
PCIe 3.0 x4 host interface
Power consumption (10GBASE-T): 13.0 W (maximum), 11.2 (typical)
Standards supported
The Intel X550 adapter supports the following standards:
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service (CoS) traffic prioritization
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging
IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol
IEEE 802.3x Full-duplex flow control
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T copper twisted pair Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 802.3an 10GBASE-T copper twisted pair 10 Gb Ethernet
IEEE 802.1Qbg Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator
IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) support
IEEE 1588 Precision clock synchronization protocol
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 4
Page 5
Server support - ThinkSystem
The following table lists the ThinkSystem servers that are compatible.
Table 2. ThinkSystem server support
Description and part number
E 1S Intel 2S Intel AMD 4S Intel
Dense/
Blade
Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T
Adapter, 00MM850
N Y Y Y Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T
Adapter, 00MM860
N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N N N
Server support - System x
The following tables list the System x servers that are compatible with the Intel X550 adapter.
Support for System x and dense servers with Xeon E5/E7 v4 and E3 v5 processors
Table 3. Support for System x and dense servers with Xeon E5/E7 v4 and E5 v5 processors
Part
number Description
00MM850 Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter N N Y Y Y Y Y
00MM860 Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SE350 (7Z46/7D1X)
ST50 (7Y48/7Y50)
ST250 (7Y45/7Y46)
SR150 (7Y54)
SR250 (7Y51/7Y52)
ST550 (7X09/7X10)
SR530 (7X07/7X08)
SR550 (7X03/7X04)
SR570 (7Y02/7Y03)
SR590 (7X98/7X99)
SR630 (7X01/7X02)
SR650 (7X05/7X06)
SR670 (7Y36/7Y37/7Y38)
SR635 (7Y98/7Y99)
SR655 (7Y00/7Z01)
SR850 (7X18/7X19)
SR850P (7D2F/2D2G)
SR860 (7X69/7X70)
SR950 (7X11/12/13)
SD530 (7X21)
SD650 (7X58)
SN550 (7X16)
SN850 (7X15)
x3250 M6 (3943)
x3250 M6 (3633)
x3550 M5 (8869)
x3650 M5 (8871)
x3850 X6/x3950 X6 (6241, E7 v4)
nx360 M5 (5465, E5-2600 v4)
sd350 (5493)
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 5
Page 6

Support for System x and dense servers with Intel E5 v3 and E3 v3 processors
Table 4. Support for servers with Intel Xeon v3 processors
Part
number Description
00MM850 Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter N N N N N N N
00MM860 Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter N N N Y Y Y Y
Support for servers with Intel Xeon v2 processors
Table 5. Support for servers with Intel Xeon v2 processors
Part
number Description
00MM850 Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter N N N N N N N N
00MM860 Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter N N N N N N N Y
x3100 M5 (5457)
x3250 M5 (5458)
x3500 M5 (5464)
x3550 M5 (5463)
x3650 M5 (5462)
x3850 X6/x3950 X6 (6241, E7 v3)
nx360 M5 (5465)
x3300 M4 (7382)
x3500 M4 (7383, E5-2600 v2)
x3550 M4 (7914, E5-2600 v2)
x3630 M4 (7158, E5-2400 v2)
x3650 M4 (7915, E5-2600 v2)
x3650 M4 BD (5466)
x3750 M4 (8753)
x3850 X6/x3950 X6 (6241, E7 v2)
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 6
Page 7

Network cabling requirements
The network cables that can be used with the X550 are as follows:
10GBASE-T
UTP Category 7 (100 m maximum)
UTP Category 6a (100 m maximum)
UTP Category 6 (55 m maximum)
1000BASE-T and 100BASE-TX
UTP Category 7 (100 m maximum)
UTP Category 6a (100 m maximum)
UTP Category 6 (100 m maximum)
UTP Category 5e (100 m maximum)
The following table lists the supported Category 6 (CAT 6) cables.
Table 6. CAT6 cables
Part number Feature code Description
CAT6 Green Cables
00WE123 AVFW 0.75m CAT6 Green Cable
00WE127 AVFX 1.0m CAT6 Green Cable
00WE131 AVFY 1.25m CAT6 Green Cable
00WE135 AVFZ 1.5m CAT6 Green Cable
00WE139 AVG0 3m CAT6 Green Cable
90Y3718 A1MT 10m CAT6 Green Cable
90Y3727 A1MW 25m CAT6 Green Cable
CAT6 Blue Cables
90Y3721 A1MU 10m CAT6 Blue Cable
90Y3730 A1MX 25m CAT6 Blue Cable
CAT6 Yellow Cables
90Y3724 A1MV 25m CAT6 Yellow Cable
Operating system support
The following tables list the supported operating systems for the adapters:
Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter, 00MM850
Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter, 00MM860
Tip: These tables are automatically generated based on data from Lenovo ServerProven. Older systems
are not shown in the tables - refer to ServerProven for those systems.
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 7
Page 8

Table 7. Operating system support for Intel X550-T1 Single Port 10GBase-T Adapter, 00MM850
Operating systems
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 N N N N N Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Y Y Y Y Y Y N N Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server version 1709 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server version 1803 N N N N N N N N Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.10 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.9 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5 Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.7 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0 Y Y Y Y Y Y N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1 Y Y Y Y Y Y N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 with Xen N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 with Xen N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 Y Y N N N Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 with Xen Y Y N N N Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 with Xen N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 with Xen Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 Y Y N Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 with Xen Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 with Xen Y Y N Y Y Y N Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 5.5 N N N N N N Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.0 U3 N N N N Y Y Y N Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U2 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SR250
ST250
ST50
ST550 (Gen 2)
ST550 (Gen 1)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v4)
sd350 (5493)
nx360 M5 (5465)
x3550 M5 (8869)
x3650 M5 (8871)
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 8
Page 9

VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 Y Y N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U1 N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U2 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Operating systems
Table 8. Operating system support for Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter, 00MM860 (Part 1 of 2)
Operating systems
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server version 1709 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Microsoft Windows Server version 1803 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.10 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.9 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5 Y Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.7 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 with Xen N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 with Xen N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N Y N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 with Xen Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N Y N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 with Xen N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SR250
ST250
ST50
ST550 (Gen 2)
ST550 (Gen 1)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v4)
sd350 (5493)
nx360 M5 (5465)
x3550 M5 (8869)
x3650 M5 (8871)
SR250
ST250
ST50
SR635
SR655
SD530 (Gen 2)
SR530 (Gen 2)
SR550 (Gen 2)
SR570 (Gen 2)
SR590 (Gen 2)
SR630 (Gen 2)
SR650 (Gen 2)
SR850 (Gen 2)
SR850P
SR860 (Gen 2)
SR950 (Gen 2)
ST550 (Gen 2)
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 9
Page 10

SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 with Xen Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 Y Y N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 with Xen Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 with Xen Y Y N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 5.5 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.0 U3 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U1 N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U2 Y Y Y N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 Y Y N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U1 N N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U2 Y Y Y N N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Operating systems
Table 9. Operating system support for Intel X550-T2 Dual Port 10GBase-T Adapter, 00MM860 (Part 2 of 2)
Operating systems
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 N N N N N N N N N N N Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y N N N Y N Y
Microsoft Windows Server version 1709 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Microsoft Windows Server version 1803 Y N N N N Y Y Y Y Y N N N N N N N Y N Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.10 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.9 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 Y Y Y N N Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SR250
ST250
ST50
SR635
SR655
SD530 (Gen 2)
SR530 (Gen 2)
SR550 (Gen 2)
SR570 (Gen 2)
SR590 (Gen 2)
SR630 (Gen 2)
SR650 (Gen 2)
SR850 (Gen 2)
SR850P
SR860 (Gen 2)
SR950 (Gen 2)
ST550 (Gen 2)
SD530 (Gen 1)
SR530 (Gen 1)
SR550 (Gen 1)
SR570 (Gen 1)
SR590 (Gen 1)
SR630 (Gen 1)
SR650 (Gen 1)
SR850 (Gen 1)
SR860 (Gen 1)
SR950 (Gen 1)
ST550 (Gen 1)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v3)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v4)
x3250 M6 (3633)
sd350 (5493)
nx360 M5 (5465)
x3550 M5 (5463)
x3550 M5 (8869)
x3650 M5 (5462)
x3650 M5 (8871)
1
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 10
Page 11

Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.7 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N N N N N N N
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N N N N N N N
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 with
Xen
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 Y Y Y N N Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2 with
Xen
Y Y Y N N Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP3 with
Xen
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP4 with
Xen
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP5 with
Xen
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N Y N Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N Y N Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 with
Xen
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N Y N Y
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 with Xen Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y N Y N Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 5.5 N N N N N N N N N N N Y N Y Y N Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.0 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N N Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 Y Y Y N N Y Y Y N Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U2 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.5 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y N Y N Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U1 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y N Y N Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U2 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y N Y N Y
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 6.7 U3 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y N Y Y Y Y N Y N Y
Operating systems
[in box driver support only]
SD530 (Gen 1)
SR530 (Gen 1)
SR550 (Gen 1)
SR570 (Gen 1)
SR590 (Gen 1)
SR630 (Gen 1)
SR650 (Gen 1)
SR850 (Gen 1)
SR860 (Gen 1)
SR950 (Gen 1)
ST550 (Gen 1)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v3)
x3850/3950 X6 (6241, E7 v4)
x3250 M6 (3633)
sd350 (5493)
nx360 M5 (5465)
x3550 M5 (5463)
x3550 M5 (8869)
x3650 M5 (5462)
x3650 M5 (8871)
1
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 11
Page 12

Physical specifications
The adapter has the following physical specifications:
Length: 134 mm (5.3 in.)
Width: 16 mm (0.6 in.)
Height: 69 mm (2.7 in.)
Shipping box dimensions (approximate):
Length: 238 mm (9.4 in.)
Width: 143 mm (5.6 in.)
Height: 51 mm (2.0 in.)
Operating environment
These adapters are supported in the following environment:
Operating temperature: 5 - 55 °C (41 - 131 °F)
Storage temperature: -40 - 85 °C (-40 - 185 °F)
Air flow requirement:
40 LFM at 5 °C
150 LFM at 55 °C
Maximum operating altitude: 10,000 feet (3,048 m)
Vibration and shock: IEC 68, FCC Part 68.302, NSTA, 1A
Electrostatic/electromagnetic susceptibility: IEC 801-2, -3, -4, and -5
Warranty
One-year limited warranty. When installed in a System x server, these cards assume the system’s base
warranty and any warranty upgrade.
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 12
Page 13

Agency approvals
The X550 conforms to the following standards:
UL/CSA 60950-1-07, 2nd Edition + amendment 1, dated 2011/12/19
EN60950-1: 2006+A11:2009+A1:2010+A12:2010+A2:2013
USA: FCC, 47 CFR Part 15, Class A digital device (USA)
Canada: ICES-003, class A (CAN)
EN 55032: 2013 Class A Radiated and Conducted Emissions requirements for European Union
EN 55024: 2010 Immunity requirements for European Union (EU)
EN-55022: Class A, 2010 Radiated and Conducted Emissions requirements for European Union (EU)
Korea: KN32 Radiated and Conducted Emissions, KN35 Immunity
Australia/New Zealand: AS/NZS CISPR 22:2009 + A1:2010 Class A and CISPR 32:2012 for
Radiated and Conducted Emissions requirements
CE: Passes CE specification and receives the CE Mark
Japan: VCCI:2014-04 Class A Radiated and Conducted Emissions requirements
Taiwan: BSMI CNS13438: 2006 (complete) Class A Radiated and Conducted Emissions
requirements
EU REACH: Complies with European REACH directive
EU WEEE: Complies with European WEEE directive
EU RoHS: Complies with European RoHS directive
China: RoHS Complies with China RoHS directive
Related publications
For more information, see the following documents:
Lenovo ThinkSystem networking options product page
https://lenovopress.com/lp0765-networking-options-for-thinksystem-servers
Lenovo System x networking options product page
https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/data-center/servers/server-options/system-x-options/networkingadapters/system-x-adapters/c/system-x-adapters
Intel X550 product page
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ethernet-products/converged-network-adapters/ethernetx550.html
Lenovo ServerProven compatibility information for options:
https://static.lenovo.com/us/en/serverproven/options.shtml
Related product families
Product families related to this document are the following:
10 Gb Ethernet Connectivity
Ethernet Adapters
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 13
Page 14

Notices
Lenovo may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in all countries. Consult your
local Lenovo representative for information on the products and services currently available in your area. Any
reference to a Lenovo product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that Lenovo product,
program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product, program, or service that does not infringe any
Lenovo intellectual property right may be used instead. However, it is the user's responsibility to evaluate and verify
the operation of any other product, program, or service. Lenovo may have patents or pending patent applications
covering subject matter described in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license
to these patents. You can send license inquiries, in writing, to:
Lenovo (United States), Inc.
1009 Think Place - Building One
Morrisville, NC 27560
U.S.A.
Attention: Lenovo Director of Licensing
LENOVO PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION ”AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT,
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some jurisdictions do not allow disclaimer of
express or implied warranties in certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This information could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new editions of the publication. Lenovo may make
improvements and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this publication at any time
without notice.
The products described in this document are not intended for use in implantation or other life support applications
where malfunction may result in injury or death to persons. The information contained in this document does not
affect or change Lenovo product specifications or warranties. Nothing in this document shall operate as an express
or implied license or indemnity under the intellectual property rights of Lenovo or third parties. All information
contained in this document was obtained in specific environments and is presented as an illustration. The result
obtained in other operating environments may vary. Lenovo may use or distribute any of the information you supply
in any way it believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you.
Any references in this publication to non-Lenovo Web sites are provided for convenience only and do not in any
manner serve as an endorsement of those Web sites. The materials at those Web sites are not part of the materials
for this Lenovo product, and use of those Web sites is at your own risk. Any performance data contained herein was
determined in a controlled environment. Therefore, the result obtained in other operating environments may vary
significantly. Some measurements may have been made on development-level systems and there is no guarantee
that these measurements will be the same on generally available systems. Furthermore, some measurements may
have been estimated through extrapolation. Actual results may vary. Users of this document should verify the
applicable data for their specific environment.
© Copyright Lenovo 2020. All rights reserved.
This document, LP0097, was created or updated on January 7, 2020.
Send us your comments in one of the following ways:
Use the online Contact us review form found at:
http://lenovopress.com/LP0097
Send your comments in an e-mail to:
comments@lenovopress.com
This document is available online at http://lenovopress.com/LP0097.
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 14
Page 15

Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other
countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at
https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ServerProven®
System x®
ThinkServer®
ThinkSystem
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Intel® and Xeon® are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the
United States and other countries.
Linux® is a trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both.
Microsoft®, Windows Server®, and Windows® are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States, other countries, or both.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
Intel X550 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-T Adapters 15
 Loading...
Loading...