Page 1

LMa
Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Featuring
Digital Hybrid Wireless™ Technology
US Patent 7,225,135
Fill in for your records:
Serial Number:
Purchase Date:
Rio Rancho, NM, USA
www.lectrosonics.com
Page 2

LMa
2
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 3

Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Table of Contents
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................................................................4
Digital Hybrid Technology .....................................................................................................................................................................4
Frequency Agility...................................................................................................................................................................................4
Wide-Band Deviation ............................................................................................................................................................................4
Long Battery Life ...................................................................................................................................................................................4
Servo Bias Input and Wiring .................................................................................................................................................................4
Input Limiter ..........................................................................................................................................................................................5
No Pre-Emphasis/De-Emphasis ...........................................................................................................................................................5
Pilot Tone Squelch ................................................................................................................................................................................5
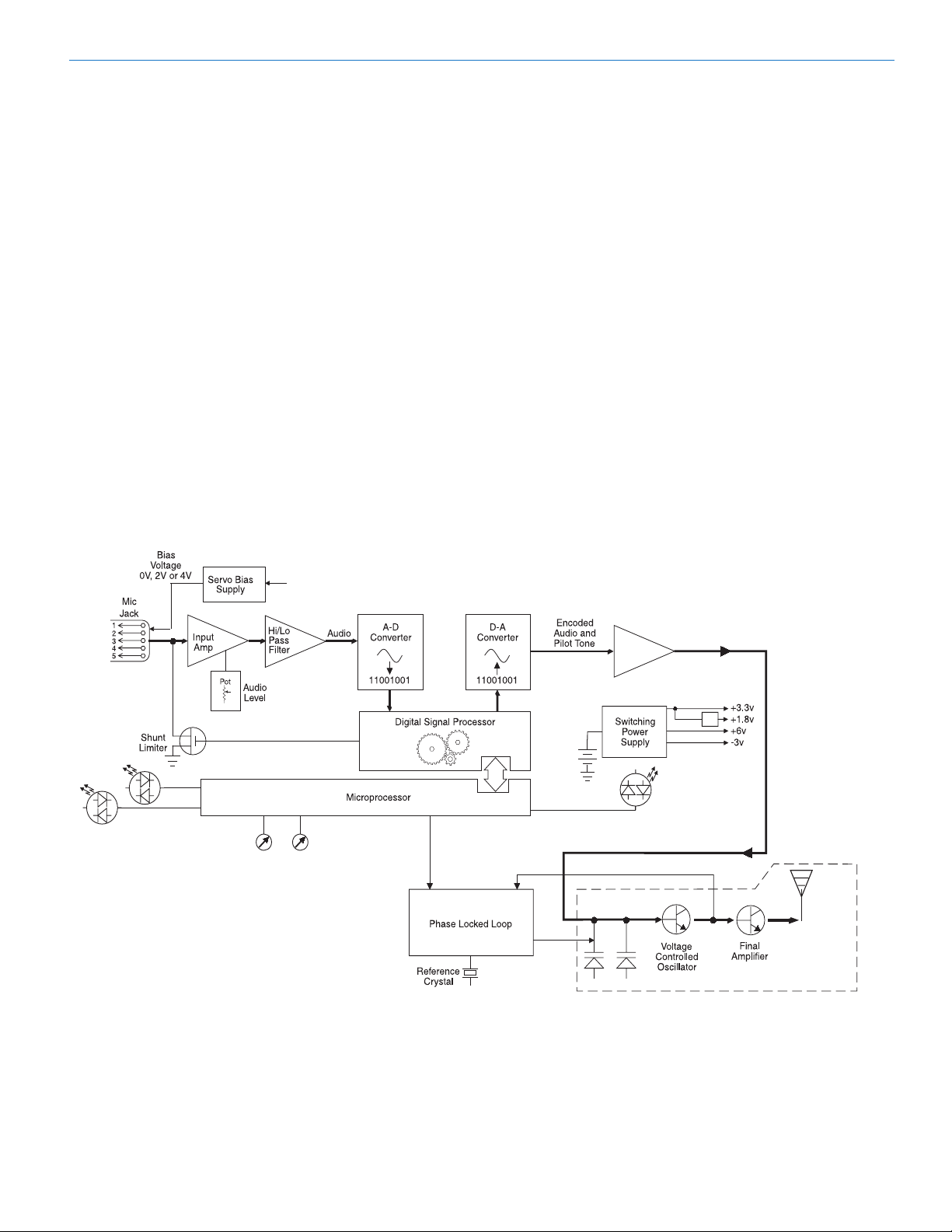
LMa Block Diagram ...............................................................................................................................................................................5
Controls and Functions .........................................................................................................................................................................6
Input Jack ..............................................................................................................................................................................................6
Power ON/OFF Switch ..........................................................................................................................................................................6
Power LED ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
Frequency Select Switches ...................................................................................................................................................................6
Modulation LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................................................6
Audio Level ...........................................................................................................................................................................................6
Antenna .................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Belt Clip .................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Battery Installation .................................................................................................................................................................................7
Operating Instructions ...........................................................................................................................................................................8
Selecting the Compatibility Mode ..........................................................................................................................................................8
Attaching a Microphone or Musical Instrument and Adjusting Audio Levels .........................................................................................8
Adjusting the Transmitter Frequency .....................................................................................................................................................9
5-Pin Input Jack Wiring ........................................................................................................................................................................ 10
Microphone RF Bypassing .................................................................................................................................................................. 10
Line Level Signals ...............................................................................................................................................................................10
Microphone Cable Terminationfor Non-Lectrosonics Microphones ................................................................................................11
Wiring Hookups for Different Sources ...............................................................................................................................................12
Compatible Wiring for Both Servo Bias Inputs and Earlier Transmitters: ............................................................................................12
Simple Wiring for Servo Bias Inputs Only: ..........................................................................................................................................12
Wiring Diagram for MI33A Instrument Cable ......................................................................................................................................13
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................................................................................15
Specifications and Features ................................................................................................................................................................ 16
Service and Repair ...............................................................................................................................................................................17
Returning Units for Repair ..................................................................................................................................................................17
Rio Rancho, NM
3
Page 4

LMa
Introduction
The design of the LMa transmitter introduces the
advanced technology and features of Digital Hybrid
WirelessTM in a Lectrosonics belt-pack transmitter at
a modest cost. Digital Hybrid Wireless™ combines a
24-bit digital audio chain with an analog FM radio link
to eliminate a compandor and its artifacts, yet preserve
the extended operating range and noise rejection of
the finest analog wireless systems. DSP “compatibility modes” allow the LMa to be used with a variety of
analog receivers in addition to its native hybrid mode by
emulating the compandors found in Lectrosonics 100
Series, 200 Series and IFB transmitters, and certain
receivers from other manufacturers (contact the factory
for details). Changing the compatibility mode is accomplished with a simple procedure using the frequency
switches and power switch.
The housing is a rugged, machined aluminum package
with removable, stainless steel wire belt clip. The input
jack is a standard Lectrosonics 5-pin type for use with
electret lavaliere mics, dynamic mics, musical instrument pickups and line level signals. The LEDs on the
front panel allow quick and accurate level settings without having to view the receiver. The battery compartment accepts any 9 volt battery and makes a positive
connection via self-adjusting contacts. The antenna is
a super-rugged, permanently attached 1/4 wavelength
design made of flexible galvanized steel cable.
The switching power supplies in the LMa provide
constant voltages to the transmitter circuits from the
beginning (9.3 VDC) to the end (5.5 VDC) of battery life,
with output power remaining constant over the life of the
battery. The input amplifier uses an ultra low noise op
amp for quiet operation. Input gain is adjustable over a
43 dB range, with a DSP controlled dual envelope input
limiter to cleanly handle signal peaks over 30 dB above
full modulation.
Digital Hybrid Technology
All wireless links suffer from channel noise to some
degree, and all wireless microphone systems seek to
minimize the impact of that noise on the desired signal.
Conventional analog systems use compandors for
enhanced dynamic range, at the cost of subtle artifacts
(known as “pumping” and “breathing”). Wholly digital
systems defeat the noise by sending the audio information in digital form, at the cost of some combination of
power, bandwidth, operating range and resistance to
interference.
The Lectrosonics Digital Hybrid Wireless™ system
overcomes channel noise in a dramatically new way,
digitally encoding the audio in the transmitter and
decoding it in the receiver, yet still sending the encoded
information via an analog FM wireless link. This proprietary algorithm is not a digital implementation of an
analog compandor but a technique which can be accomplished only in the digital domain.
4
Since the RF link between transmitter and receiver
is FM, channel noise will increase gradually with
increased operating range and weak signal conditions, however, the hybrid system handles this situation elegantly with rarely audible audio artifacts as the
receiver approaches its squelch threshold. In contrast,
a purely digital system tends to drop the audio suddenly
during brief dropouts and weak signal conditions. The
Digital Hybrid Wireless™
signal to use a noisy channel as efficiently and robustly
as possible, yielding audio performance that rivals
that of purely digital systems, without the power, noise
and bandwidth problems inherent in digital transmission. Because it uses an analog FM link, Digital Hybrid
Wireless™ enjoys all the benefits of conventional FM
wireless systems, such as excellent range, efficient use
of RF spectrum, and long battery life.
system simply encodes the
Frequency Agility
The transmitter section uses a synthesized, frequency
selectable main oscillator. The frequency is extremely
stable over a wide temperature range and over time.
Two rotary switches, located on the side panel provide
256 frequencies in 100 kHz steps over a 25.6 MHz
bandwidth.
Wide-Band Deviation
In the Digital Hybrid and 200 Series modes, the system uses ±75 kHz deviation to dramatically improve
the capture ratio, and signal to noise ratio of the overall
wireless system.
Long Battery Life
The use of switching power supplies throughout the
design allows over 6 hours of operation using a single 9
volt alkaline battery and over 7 hours of operation with
a 9 volt LiPolymer rechargeable battery. The battery
contacts are spring loaded to prevent “rattle” as the unit
is handled.
Servo Bias Input and Wiring
The LMa input preamp is a radically different design than
previous Lectrosonics transmitter inputs. The improvements are audible and make the transmitters easier to
use and much harder to overload. It is no longer necessary on some mics to introduce pads to prevent overload of the input stage, divide the bias voltage down for
some low voltage mics, or reduce the limiter range at
minimum gain settings.
Two different microphone wiring schemes are now
available to simplify and standardize the configuration.
Simplified 2-wire and 3-wire configurations for the servo
bias input only take full advantage of the preamp circuitry to maximize the signal to noise ratio, and several
other configurations are available that are compatible
with the servo bias input and earlier types.
The input will automatically switch the low frequency
roll-off to 35 Hz when the MI33ARA and MI33AST
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 5
Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Freq
Switches
Bicolor
Modulation
LEDs
9V
Battery
Bicolor
Power
LED
+5v
instrument cables are connected.
Input Limiter
The transmitter employs a digitally-controlled analog
audio limiter prior to the analog-to-digital converter.
The limiter has a range greater than 30 dB for excellent
overload protection. A dual release envelope makes the
limiter acoustically transparent while maintaining low
distortion. It can be thought of as two limiters in series,
connected as a fast attack and release limiter followed
by a slow attack and release limiter. The limiter recovers
quickly from brief transients, so that its action is hidden
from the listener, but recovers slowly from sustained
high levels to keep audio distortion low and preserve
short term dynamic changes in the audio.
No Pre-Emphasis/De-Emphasis
Because the signal to noise ratio of the hybrid system is
so high, there is no need for conventional pre-emphasis
(HF boost) in the transmitter and de-emphasis (HF roll
off) in the receiver. Thus, the possible distortion problems associated with pre-emphasis and de-emphasis
LMa Block Diagram
are eliminated.
Pilot Tone Squelch
The DSP in the transmitter generates one of 256 different ultrasonic tones between 25 and 32 kHz to operate
the receiver squelch (audio muting). The benefit of a
pilot tone squelch system is that the receiver will remain
quiet until it receives the pilot tone from the matching
transmitter, even if a strong RF signal is present on
the carrier frequency of the system. The pilot tone also
eliminates noise (pops, thumps, etc.) from occurring
when the transmitter is powered on and off.
The pilot tone frequency is chosen according to which
of the 256 channels has been selected by the frequency switch setting. This ensures that all transmitters in
a system have different pilot tone frequencies so even
spurious RF from the wrong transmitters can’t open the
receiver squelch.
Rio Rancho, NM
5
Page 6
LMa
Controls and Functions
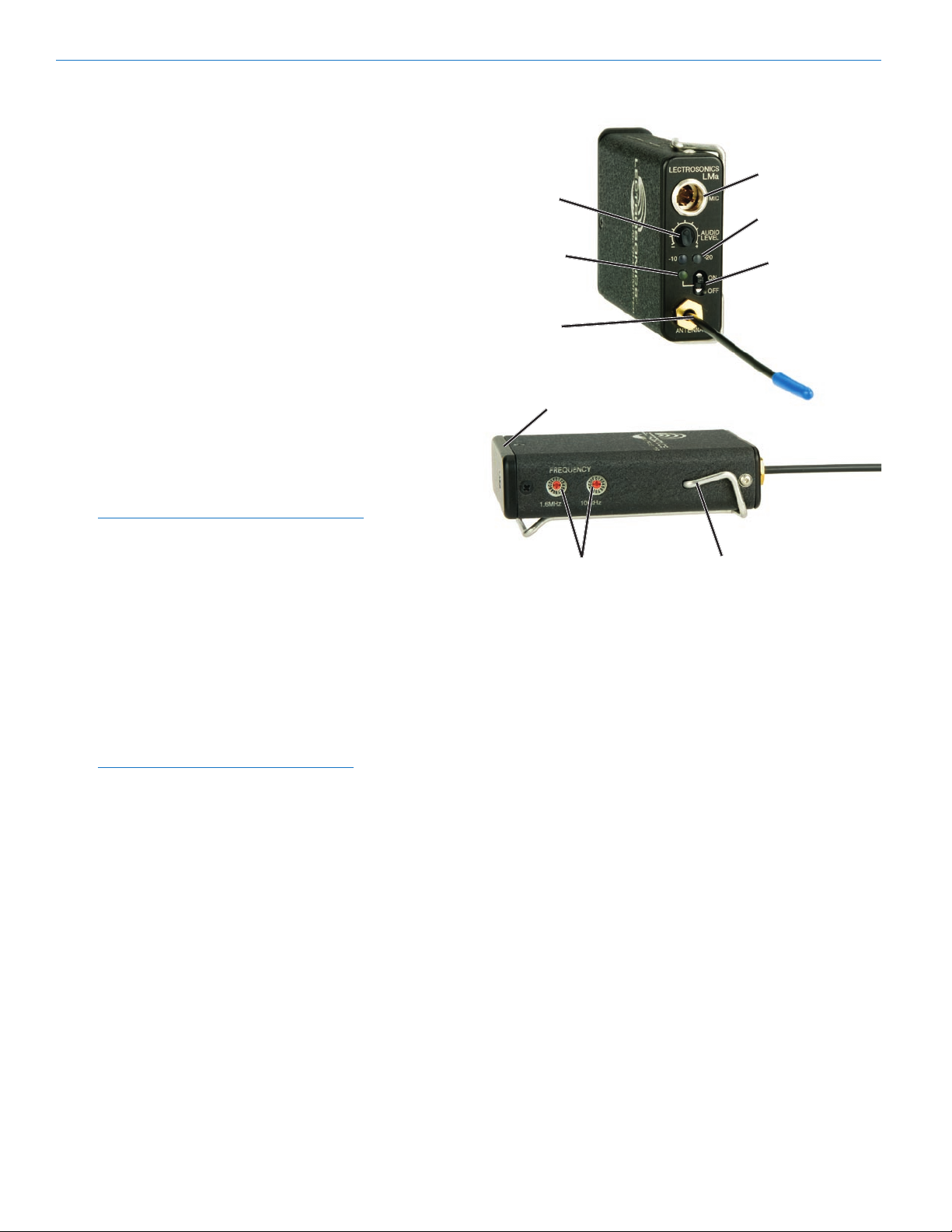
Input Jack
The 5-pin (Switchcraft TA5F compatible) input accommodates virtually every lavaliere, hand-held or shotgun
microphone available, and most musical instrument
signals. Line level signals can also be accommodated.
(See 5-Pin Input Jack Wiring.)
Power ON/OFF Switch
The Power ON/OFF switch turns the transmitter on and
off. The pilot tone muting system prevents transient
noise (pops, thumps, etc.) from occurring at the receiver
even if the transmitter is abruptly switched on or off.
Power LED
The Power LED glows green when the transmitter is
operating and the battery is good. It turns red when the
battery voltage drops to 6.1 VDC and starts blinking
red when the voltage drops to 5.6 VDC. When using a
recommended lithium or alkaline battery, there will be
about 30 minutes of operating time remaining when the
Power LED first begins blinking red.
AUDIO LEVEL
control
Power LED
Antenna
Battery Compartment Door
Input Jack
Modulation
LEDs
Power
ON/OFF
Note: A weak battery will sometimes cause
the Power LED to glow green, but it will soon
discharge to the point where it will turn red or go
out completely. If in doubt, replace the battery with
a known new battery. If the Power LED fails to
glow when the transmitter is turned on, replace the
battery.
LiPolymer rechargeable batteries give little or no warning when they are depleted. If you wish to use these
batteries in the transmitter, you will need to manually
keep track of the operating time to prevent interruptions
caused by dead batteries. Start with a fully charged battery, then measure the time it takes for the Power LED
to go out completely.
Note: A number of Lectrosonics receivers
incorporate a Battery Timer function which tracks
the amount of time the transmitter signal is
detected. See your receiver manual to determine if
this function is available and, if so, the instructions
on measuring the actual run time of the battery.
Frequency Select Switches
Two 16-position rotary Frequency Select Switches, accessed through the left side panel, are used to adjust
the transmitter’s operating frequency. These switches
are labeled 1.6M and 100K. The 1.6M switch is used for
coarse frequency adjustments and the 100K is used for
fine frequency adjustment.
Modulation LEDs
The Modulation LEDs provide a visual indication of the
input audio signal level from the microphone or musical
instrument. These two bicolor LEDs can glow either red
or green to indicate modulation levels.
Frequency Select
Switches
The Modulation LEDs are also used to indicate the
Compatibility Mode when the transmitter is initially
turned on. The Modulation LEDs will blink simultaneously:
• Oncefor100Seriesmode
•Twotimesfor200Seriesmode
•Threetimesformode3
•FourtimesforDigitalHybridWireless
or 400 Series mode
•FivetimesforIFBmode
•Sixtimesformode6
Belt Clip
Attachment Holes
™
Audio Level
The AUDIO LEVEL control is used to set the input gain
for the proper modulation.
Antenna
The flexible, insulated galvanized steel cable antenna
supplied with the transmitter is cut to 1/4 wavelength of
the center of the frequency block (the frequency range)
of the transmitter.
Belt Clip
The belt clip may be removed for special applications
by pulling the ends out of the holes in the sides of the
case. An optional hinged belt clip (P/N BCHINGED) is
also available. Contact a Lectrosonics sales representative, or visit our web site (www.lectrosonics.com) for
more details.
6
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 7

Battery Installation
The transmitter is powered by a standard 9 volt battery.
We recommend using alkaline, lithium, or rechargeable
LiPolymer batteries for longest life. Standard zinc-carbon batteries marked “heavy-duty” or “long-lasting”
are not adequate. Alkaline batteries provide over six
hours of operation at room temperature. LiPolymer batteries will last about 7 hours per charge, and Lithium
batteries can provide up to 13 hours. The battery status
circuitry is designed for the voltage drop over the life of
alkaline batteries. Because rechargeable LiPolymer batteries run down quite abruptly, using the Power LED to
verify battery status is not reliable with LiPolymer batteries. However, it may be possible to track battery status
using the Battery Timer function available in a number
of Lectrosonics receivers. (Refer to the associated
receiver manual to determine if this function is available
in your situation.)
Warning: Care should be taken not to leave
a fully discharged lithium battery in the
transmitter, as swelling of the battery can make
it difficult to remove from the compartment.
To replace the battery, push up on the Battery Compartment Door and rotate it clockwise. (See photo.)
Remove the old battery and take note of the polarity
marked inside showing the location of the positive (+)
and negative ( -) terminals. (You can see the large and
small contact holes inside the battery compartment with
the door open.)
Insert the new battery correctly and rotate the door to
snap flush against the housing. If the battery is inserted
incorrectly, the door will not fully close. Do not force the
door closed.
Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Rio Rancho, NM
7
Page 8

LMa
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Operating Instructions
Selecting the Compatibility Mode
The LMa transmitter is capable of working with Lectrosonics 400 Series Digital Hybrid Wireless™, 200
Series analog, 100 Series analog and some non-Lectrosonics analog wireless receivers (contact the factory
for details). The transmitter must be set to the operating
mode of the matching receiver, which is easily done using the supplied screwdriver and a battery.
NOTE: The unit is supplied from the factory as a
400 series transmitter.
1) Ensure the battery is good.
2) Turn OFF the transmitter.
3) With a small screwdriver (one is included with your
unit), set the Frequency Select Switches to CC. (for
Change, Change).
4) Toggle the power switch ON briefly – just long
enough for the LED’s to light up and then turn it
OFF.
5) Change the Frequency Select Switches to one of
the following settings:
•100Seriesmode: 1,1
•200Seriesmode: 2,2
•Mode3: 3,3
•400Seriesmode: 4,4
•IFBSeriesmode: 5,5
•Mode6: 6,6
6) Toggle the power switch ON, then OFF again.
7) Change the Frequency Select Switches to 0,0.
8) Turn the transmitter ON to complete the operation.
The LEDS will blink to indicate the selected compatibility mode. Immediately after power up, all
LEDs will blink together red, then green, followed
by the audio level LEDs (-20 and -10) blinking to
indicate the mode.
The LEDs will blink:
•Oncefor100Seriesmode
•Twotimesfor200Seriesmode
•Threetimesforsomeotherreceivers
•Fourtimesfor400Seriesmode
•FivetimesforIFBmode
•SixtimesforMode6
Note: Each time the transmitter is turned on, the
Modulation LEDs will confirm the current operating
mode with the number of blinks listed in Step 2.
The mode setting will not change until it is reset
with the procedure listed above.
Attention: During the procedure to set the
compatibility mode, each step between toggles
of the power switch must be performed within
ten seconds, or the procedure must be started
from the beginning.
Frequency Select Switch Settings (C,C)
1.6M 100K
Attaching a Microphone or Musical
Instrument and Adjusting Audio Levels
The front panel Modulation LEDs indicate input level
and limiter activity. (See Modulation LED Signal Level
Table.) Since the distortion introduced by the limiter is
minimal and full modulation is assured, occasional red
flickering of the -20 LED is desirable.
Different voices or instruments will usually require different settings of the AUDIO LEVEL control, so check
this adjustment as each new person uses the system.
If several different people will be using the transmitter
and there is not time to make the adjustment for each
individual, adjust it for the loudest voice.
Musicians also vary their volume depending on the nature of the music. It is suggested that the transmitter be
adjusted for the passage with the loudest volume.
1) If necessary, install a fresh battery.
2) Insert the 5-pin into the input jack. Ensure the pins
are aligned and the connector locks in (it will click).
For those using a musical instrument, insert the 1/4
inch plug on the other end of the instrument cable
into the appropriate jack on your musical instrument.
3) Mute the main sound system or amplifier and rotate
the AUDIO LEVEL control on the transmitter to
maximum counterclockwise (Off).
4) Set the transmitter Power switch to ON.
5) For microphone users, position the microphone in
the location where it will be used in actual operation.
For musicians, adjust the instrument volume con-
trols to the highest levels that would be used during
a performance.
8
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 9

Input Jack
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
AUDIO LEVEL
Control
-20 LED
-10 LED
Modulation LED Signal Level Table
Signal Level -20 LED -10 LED
Less than -20 dB Off Off
-20 dB to -10 dB Green Off
-10 dB to +0 dB Green Green
+0 dB to +10 dB Red Green
Greater than +10 db Red Red
6) For microphone users, observe the Modulation
LEDs while speaking or singing at the same voice
level that will be used during the program. Gradually rotate the AUDIO LEVEL control clockwise until
the -10 LED glows green and the -20 dB glows
green with occasional red flickers. This indicates
full modulation and is the optimum setting for the
transmitter’s gain.
For musicians, gradually rotate the AUDIO LEVEL
control clockwise while playing the loudest notes
that will be played during the performance. It is ideal
for the -20 LED to briefly flicker red during the loudest passages.
7) Once the transmitter’s audio gain has been set, the
remaining components of the audio system can be
energized and adjusted.
Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Adjusting the Transmitter Frequency
Frequency Select Switch Settings
1.6M 100K
The left switch adjusts the operating frequency of the
transmitter up or down in 1.6 MHz steps. The right
switch adjusts the operating frequency of the transmitter up or down in 100 kHz steps. It is suggested to use
the metering on the associated receiver to find a clear
channel. Turn the transmitter off and leave the receiver
turned on.
All 400 Series (and a number of earlier receivers) offer
front panel LCDs that indicate the correct transmitter
switch settings, and built in scanning functions to help
locate clear channels. Use the scanning functions on
these receivers to find a clear channel, then switch the
transmitter to the frequency settings indicated in the
receiver’s display.
The R400A, Venue Series and other Lectrosonics
receivers have an automatic scanning function called
SmartTune
ing channels. If your receiver does not have a built in
scanning function, manually tune the receiver across its
band and find a frequency where little or no RF activity
is indicated.
After finding a clear channel, set the transmitter to this
new frequency, then turn it on and make sure the RF
signal is strongly indicated at the receiver. Be sure the
switch settings between the receiver and transmitter are
set exactly the same. If, for example, the 100K switch
is one click above or below the desired frequency, the
receiver will indicate RF, but no audio (or severely distorted audio) will be produced.
TM
that automatically locates clear operat-
Warning: DO NOT use the audio level control
for controlling the volume of your sound
system or recorder levels. This gain adjustment
matches the transmitter gain with the user’s
voice level and microphone positioning, or the
instrument output level.
Rio Rancho, NM
9
Page 10

LMa
10k
1k
5
4
3
2
1
To Virtual Ground
Audio Amplifier
BIAS
MIC
BIAS SELECT
LINE IN
GND
+
30uF
+5 VDC
Servo Bias
Pin 4 to Pin 1 = 0 V
Pin 4 Open = 2 V
Pin 4 to Pin 2 = 4 V
+
To Limiter Control
30uF
500 Ohm
100 Ohm
2.7K
200 Ohm
+
3.3uF
100 Ohm
3 WIRE MIC2 WIRE MIC
CAPSULE
CAPSULE
SHIELD
AUDIO
SHIELD
AUDIO
BIAS
Alternate locations for bypass capacitors
TA5F
CONNECTOR
TA 5F
CONNECTOR
Preferred locations for bypass capacitors
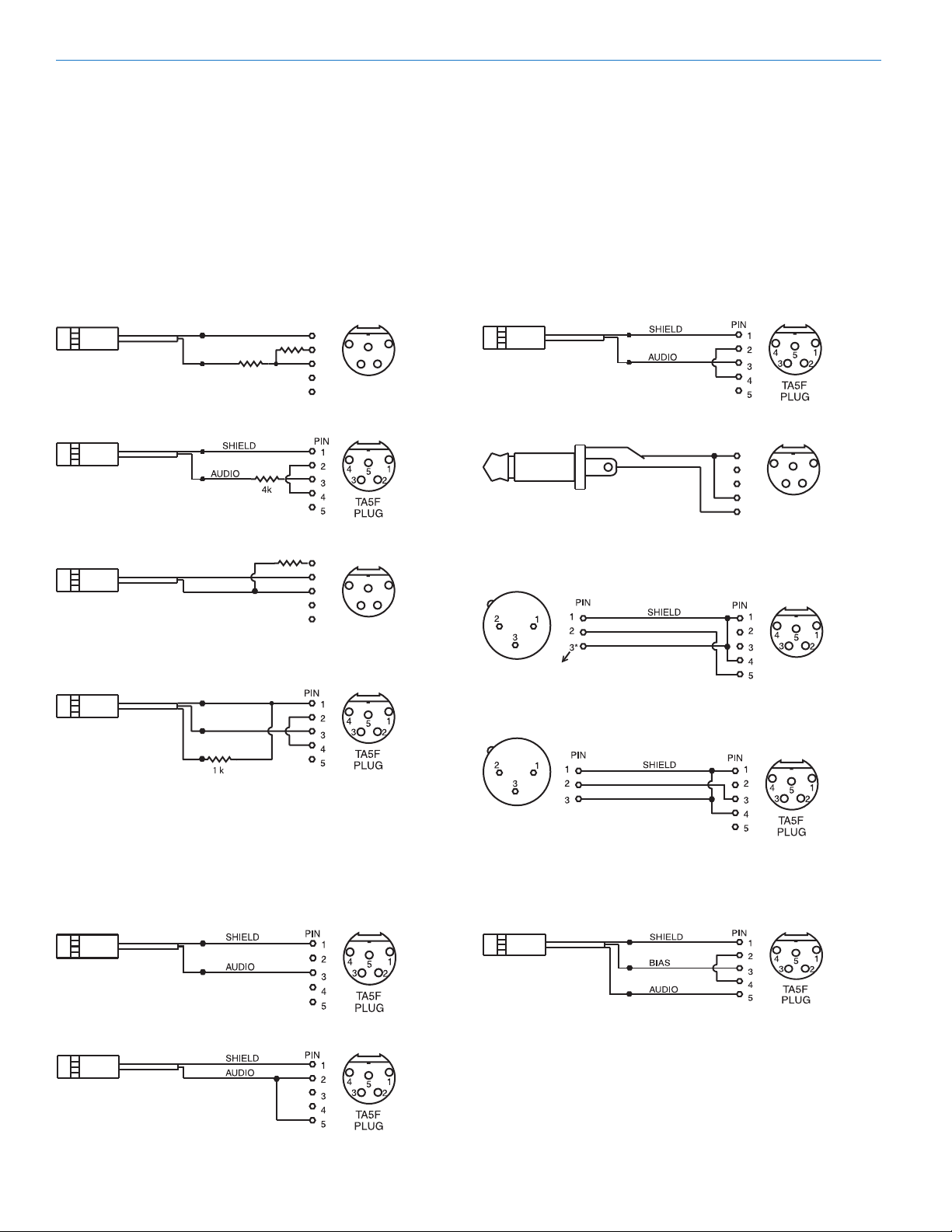
5-Pin Input Jack Wiring
The wiring diagrams included in this section represent
the basic wiring necessary for the most common types
of microphones and other audio inputs. Some microphones may require extra jumpers or a slight variation
on the diagrams shown.
It is virtually impossible to keep completely up to date
on changes that other manufacturers make to their
products, thus you may encounter a microphone that
differs from these instructions. If this occurs please call
our toll-free number listed under Service and Repair in
this manual or visit our web site at:
www.lectrosonics.com
Some mics require RF protection to keep the radio
signal from affecting the capsule, even though the
transmitter input circuitry is already RF bypassed (see
schematic diagram).
If the mic is wired as directed, and you are having difficulty with squealing, high noise, or poor frequency
response, RF is likely to be the cause.
The best RF protection is accomplished by installing RF
bypass capacitors at the mic capsule. If this is not possible, or if you are still having problems, capacitors can
be installed on the mic pins inside the TA5F connector
housing.
Audio input jack wiring:
PIN 1 Shield (ground) for positive biased electret lava-
liere microphones. Shield (ground) for dynamic
microphones and line level inputs.
PIN 2 Bias voltage source for positive biased electret
lavaliere microphones.
PIN 3 Low impedance microphone level input for
dynamic microphones. Also accepts hand-held
electret microphones provided the microphone
has its own built-in battery.
PIN 4 Bias voltage selector for Pin 3. Pin 3 voltage (0, 2
or 4 volts) depends on Pin 4 connection.
Pin 4 tied to Pin 1: 0 V
Pin 4 Open: 2 V
Pin 4 to Pin 2: 4 V
PIN 5 High impedance, line level input for tape decks,
mixer outputs, musical instruments, etc.
Microphone RF Bypassing
When used on a wireless transmitter, the microphone
element is in the proximity of the RF coming from the
transmitter. The nature of electret microphones makes
them sensitive to RF, which can cause problems with
the microphone/transmitter compatibility. If the electret
microphone is not designed properly for use with wireless transmitters, it may be necessary to install a chip
capacitor in the mic capsule or connector to block the
RF from entering the electret capsule.
10
Install the capacitors as follows: Use 330 pF capacitors. Capacitors are available from Lectrosonics. Please
specify the part number for the desired lead style.
Leaded capacitors: P/N 15117
Leadless capacitors: P/N SCC330P
All Lectrosonics lavaliere mics are already bypassed
and do not need any additional capacitors installed for
proper operation.
Line Level Signals
The normal hookup for line level signals is: Signal Hot
to pin 5, Signal Gnd to pin 1 and pin 4 jumped to pin 1.
This allows signal levels up to 3V RMS to be applied
without limiting.
If more headroom is needed, insert a 20 k resistor in
series with pin 5. Put this resistor inside the TA5F connector to minimize noise pickup.
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 11

Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
1
23
4
5
VIEW FROM SOLDER
SIDE OF PINS
0.3"
0.15"
Microphone Cable Termination
for Non-Lectrosonics Microphones
TA5F Connector Assembly
Mic Cord Stripping Instructions
Crimping to Shield and Insulation
Strip and position the cable so that the clamp
can be crimped to contact both the mic cable
shield and the insulation. The shield contact
reduces noise with some microphones and the
insulation clamp increases ruggedness.
Insulation
Shield
Crimp these
fingers to
contact the
shield
Crimp these
fingers to
clamp the
insulation
NOTE: This termination is intended for UHF
transmitters only. VHF transmitters with 5-pin
jacks require a different termination. Lectrosonics
lavaliere microphones are terminated for
compatibility with VHF and UHF transmitters,
which is different than what is shown here.
Rio Rancho, NM
11
Page 12
LMa
2 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET
Simplified wiring for microphones
such as Countryman B6 Lavalier
and E6 Earset models and others.
NOTE: This servo bias wiring is not compatible with earlier
versions of Lectrosonics transmitters. Check with the factor y
to confirm which models can use this wiring.
4 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 3-WIRE ELECTRET
NOTE: This servo bias wiring is not compatible with earlier
versions of Lectrosonics transmitters. Check with the factory
to confirm which models can use this wiring.
1
2
3
4
5
PIN
SHIELD
A UDI O
1
2
3
4
5
T A5 F
PLUG
3.3 k
1.5 k
2 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET
Compatible wiring for microphones such as
Countryman E6 headworn and B6 lavaliere.
4 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET
Most common type of wiring for lavaliere mics.
Fully compatible with 5-pin inputs on Lectrosonics
transmitters such as the LM and UM Series.
DRAIN (BIAS)
SOURCE (AUDIO)
SHIELD
4 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 3-WIRE ELECTRET
WITH EXTERNAL RESISTOR
This wiring is fully compatible with 5-pin inputs on Lectrosonics
transmitters such as the LM and UM Series. This is the wiring
for the Lectrosonics M152 lavaliere microphone.
Used for 3-wire lavaliere
microphones that require an
external resistor such as the
Sanken COS-11.
SHIELD
TIP
PIN
5
4
3
2
1
SLEEVE
LINE LEVEL
RCA or 1/4” PLUG
A UDI O
1
2
3
4
5
T A5 F
PLUG
UNBALANCED LINE LEVEL SIGNALS
For signal levels up to 3V (+12 dBu) before limiting. Fully
compatible with 5-pin inputs on other Lectrosonics transmitters
such as the LM and UM Series. A 20k ohm resistor can be
inserted in series with Pin 5 for an additional 20 dB of
attenuation to handle up to 30V (+32 dBu).
BALANCED AND FLOATING LINE LEVEL SIGNALS
*NOTE: If the output is balanced but center
tapped to ground, such as on all Lectrosonics
receivers, do not connect Pin 3 of the XLR jack
to Pin 4 of the TA5F connector.
TA5F
PLUG
XLR JACK
LO-Z MICROPHONE LEVEL SIGNALS
For low impedance dynamic mics or electret
mics with internal battery or power supply.
XLR JACK
2 VOLT POSITIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET - DPA MICROPHONES
This wiring is for DPA lavalier
and headset microphones.
NOTE: The resistor value can range from 3k to 4k ohms.
2 VOLT NEGATIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET
Simplified wiring for microphones such as negative bias TRAM.
NOTE: This servo bias wiring is not compatible with earlier
versions of Lectrosonics transmitters. Check with the factory
to confirm which models can use this wiring.
1
2
3
4
5
PIN
SHIELD
AUDIO
1
2
3
4
5
T A5 F
PLUG
2.7 k
2 VOLT NEGATIVE BIAS 2-WIRE ELECTRET
Compatible wiring for microphones
such as negative bias TRAM models.
NOTE: The resistor value can range from 2k to 4k ohms.
Wiring Hookups for Different Sources
In addition to the microphone and line level wiring hookups illustrated below, Lectrosonics makes a number of
cables and adapters for other situations such as connecting musical instruments (guitars, bass guitars, etc.)
to the transmitter. Visit www.lectrosonics.com and
click on Accessories, or download the master catalog.
A lot of information regarding microphone wiring is also
available in the FAQ section of the web site at:
http://www.lectrosonics.com/faq.htm
Follow the instructions to search by model number or
other search options.
Compatible Wiring for Both Servo Bias Inputs and Earlier Transmitters:
Simple Wiring for Servo Bias Inputs Only:
12
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 13

Wiring Diagram for MI33A Instrument Cable
SHIELD
TIP
PIN
5
4
3
2
1
SLEEVE
1/4 " PLUG
1
2
3
4
5
Preamp
AUDIO
TA 5F
PLUG
SHIELD
AUDIO
PWR
3 k
The MI33ARA and MI33AST instrument cable assemblies allow an optimum match between musical instrument pickups and Lectrosonics transmitters with 5-pin
input connectors. The low frequency roll-off in the LMa
will be set to 35 Hz automatically when these cables
are connected.
The active preamp and low noise wire cable provide a
“same as wire” experience in a wireless environment.
The 30 inch long cable offers enough cable to comfortably link the instrument to the wireless transmitter
without being excessive.
Note: This cable is prewired and cannot be
field modified. The cable is available in two
configurations, MI33ARA (right angle) and
MI33AST (straight).
Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Rio Rancho, NM
13
Page 14

LMa
Troubleshooting
It is important that you follow these steps in the sequence listed.
Symptom: Possible Cause:
Transmitter Battery LED off 1. Battery is inserted backwards.
when Power Switch “ON” 2. Battery is dead.
No Transmitter Modulation LEDs 1. Gain control turned all the way down.
when Signal Should be Present 2. Battery is in backwards. Check power LED.
3. Mic capsule is damaged or malfunctioning.
4. Mic cable damaged or miswired.
5. Instrument Cable damaged or not plugged in.
6. Musical instrument output level set too low.
Receiver Indicates RF But No Audio 1. Audio source or cable connected to transmitter is defective. Try
using an alternate source or cable.
2. Make sure the compatibility mode is the same on transmitter and
receiver.
3. Ensure musical instrument volume control is not set to minimum.
Receiver RF Indicator Off 1. Ensure that the transmitter and receiver Frequency Select
Switches are set to the same frequency.
2. Transmitter not turned on, or battery is dead.
3. Receiver antenna missing or improperly positioned.
4. Transmitter and receiver not on same frequency.
Check switches/display on transmitter and receiver.
5. Operating distance is too great.
No Sound (Or Low Sound Level), Receiver 1. Receiver output level set too low.
Indicates Proper Audio Modulation 2. Receiver output is disconnected; cable is defective or miswired.
3. Sound system or recorder input is turned down.
Distorted Sound 1. Transmitter gain (audio level) is too high. Check Modulation
LEDs on transmitter and receiver while distortion is being heard.
2. Receiver output level may be mismatched with the sound
system or recorder input. Adjust output level on receiver to the
correct level for the recorder, mixer or sound system.
3. Transmitter and receiver may not be set to the same compatibility
mode. Some mis-matched combinations will pass audio.
4. RF interference. Reset both transmitter and receiver to a clear
channel.
Wind Noise or Breath “Pops’” 1. Reposition microphone, or use a larger windscreen, or both.
2. Omni-directional mics produce less wind noise and breath pops
than directional types.
Hiss and Noise -- Audible Dropouts 1. Transmitter gain (audio level) far too low.
2. Receiver antenna missing or obstructed.
3. Operating distance too great.
4. RF interference. Reset both transmitter and receiver to a
clear channel.
5. Musical instrument volume set too low.
ExcessiveFeedback(WithMicrophone) 1. Transmitter gain (audio level) too high. Check gain adjustment
and/or reduce receiver output level.
2. Microphone too close to speaker system.
3. Microphone is too far from user’s mouth.
14
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 15

Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Specifications and Features
Operating frequencies:
Block 470 470.100 - 495.600
Block 19 486.400 - 511.900
Block 20 512.000 - 537.500
Block 21 537.600 - 563.100
Block 22 563.200 - 588.700
Block 23 588.800 - 607.900 and
614.100 - 614.300
Block 24 614.400 - 639.900
Block 25 640.000 - 665.500
Block 26 665.600 - 691.100
Block 27 691.200 - 716.700
Block 28 716.800 - 742.300
Block 29 742.400 - 767.900
(Frequency usage varies by country
Frequency Selection: 256 frequencies in 100 kHz steps
Channel Separation: 100 kHz
Compatibility Modes: Lectrosonics 400 Series (Digital Hybrid), 200 Series, 100 Series, and IFB.
Mode 3, Mode 6 (Other brands).
RF Power output: Greater than 50 mW
Pilot tone: 25 to 32 kHz frequency; 5 kHz deviation (400 Series only)
Frequency stability: ± 0.002%
Deviation: ± 75 kHz max. (200 & 400 Series Modes)
Spurious radiation: 60 dB below carrier
Equivalent input noise: –120 dBV, A-weighted
Input level:
If set for dynamic mic: 0.5 mV to 50 mV before limiting.
Greater than 1 V with limiting.
If set for electret lavaliere mic: 1.7 uA to 170 uA before limiting.
Greater than 5000 uA (5 mA) with limiting.
Line level input: 5.0 mV to 6 V before limiting.
Greater than 15 V with limiting.
Input impedance:
Dynamic mic: 300 Ohms
Electret lavaliere: Input is virtual ground with servo adjusted
constant current bias
Line level: 2.7 k Ohms
Input limiter: Dual envelope, >30 dB range
(Note: The dual envelope “soft” limiter provides exceptionally good handling of transients using variable attack and release time constraints.)
Gain control range: 43 dB; semi-log rotary control
Modulation indicators: Dual bicolor LEDs indicate modulation of -20, -10, 0, +10 dB referenced to full modulation.
Low frequency roll-off: Microphone: –12 dB/octave; -3 dB @ 70 Hz
Instrument Cable: –12 dB/octave; -3 dB @ 35 Hz
Audio frequency response (overall system): Microphone : 90 Hz to 20 kHz (+/- 1 dB) with the 70Hz low frequency roll-off filter.
Instrument Cable : 40 Hz to 20 kHz (+/- 1 dB)
Controls: 2 position “OFF-ON” slide switch for noiseless turn on/turn off operation.
Front panel audio gain control.
Rotary switches on side panel adjust transmitter frequency.
Audio Input Jack: Switchcraft 5 pin locking (TA5F)
Antenna: Galvanized steel, flexible wire.
Battery: Precision compartment auto-adjusts to accept any known alkaline 9 volt battery.
Battery Life: 6 hours (alkaline); 7 hours (LiPolymer); 13 hours continuous (lithium)
Weight: 6.3 ozs. including battery
Dimensions: 3.1 x 2.4 x .75 inches
Emission Designator: 180KF3E
The FCC requires that the following statement be included in this manual:
This device complies with FCC radiation exposure limits as set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This device
should be installed and operated so that its antenna(s) are not co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
Specifications subject to change without notice
Rio Rancho, NM
15
Page 16

LMa
Service and Repair
If your system malfunctions, you should attempt to correct or isolate the trouble before concluding that the equipment
needs repair. Make sure you have followed the setup procedure and operating instructions. Check the interconnecting
cables and then go through the Troubleshooting section in this manual.
We strongly recommend that you do not try to repair the equipment yourself and do not have the local repair shop attempt anything other than the simplest repair. If the repair is more complicated than a broken wire or loose connection,
send the unit to the factory for repair and service. Don’t attempt to adjust any controls inside the units. Once set at the
factory, the various controls and trimmers do not drift with age or vibration and never require readjustment. There are
no adjustments inside that will make a malfunctioning unit start working.
LECTROSONICS’ Service Department is equipped and staffed to quickly repair your equipment. In warranty repairs
are made at no charge in accordance with the terms of the warranty. Out-of-warranty repairs are charged at a modest
flat rate plus parts and shipping. Since it takes almost as much time and effort to determine what is wrong as it does
to make the repair, there is a charge for an exact quotation. We will be happy to quote approximate charges by phone
for out-of-warranty repairs.
Returning Units for Repair
For timely service, please follow the steps below:
A. DO NOT return equipment to the factory for repair without first contacting us by email or by phone. We need
to know the nature of the problem, the model number and the serial number of the equipment. We also need a
phone number where you can be reached 8 A.M. to 4 P.M. (U.S. Mountain Standard Time).
B. After receiving your request, we will issue you a return authorization number (R.A.). This number will help speed
your repair through our receiving and repair departments. The return authorization number must be clearly shown
on the outside of the shipping container.
C. Pack the equipment carefully and ship to us, shipping costs prepaid. If necessary, we can provide you with the
proper packing materials. UPS is usually the best way to ship the units. Heavy units should be “double-boxed” for
safe transport.
D. We also strongly recommend that you insure the equipment, since we cannot be responsible for loss of or dam-
age to equipment that you ship. Of course, we insure the equipment when we ship it back to you.
Lectrosonics USA:
Mailing address: Shipping address: Telephone:
Lectrosonics, Inc. Lectrosonics, Inc. (505) 892-4501
PO Box 15900 581 Laser Rd. (800) 821-1121 Toll-free
Rio Rancho, NM 87174 Rio Rancho, NM 87124 (505) 892-6243 Fax
USA USA
Web: E-mail:
www.lectrosonics.com sales@lectrosonics.com
Lectrosonics Canada:
Mailing Address: Telephone: E-mail:
49 Spadina Avenue, (416) 596-2202 Sales: colinb@lectrosonics.com
Suite 303A (877) 753-2876 Toll-free Service: joeb@lectrosonics.com
Toronto, Ontario M5V 2J1 (877-7LECTRO)
(416) 596-6648 Fax
16
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 17

Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Rio Rancho, NM
17
Page 18

LMa
18
LECTROSONICS, INC.
Page 19

Frequency-Agile UHF Belt-Pack Transmitter
Rio Rancho, NM
19
Page 20

LMa
581 Laser Road NE • Rio Rancho, NM 87124 USA • www.lectrosonics.com
(505) 892-4501 • (800) 821-1121 • fax (505) 892-6243 • sales@lectrosonics.com
LIMITED ONE YEAR WARRANTY
The equipment is warranted for one year from date of purchase against defects in
materials or workmanship provided it was purchased from an authorized dealer. This
warranty does not cover equipment which has been abused or damaged by careless
handling or shipping. This warranty does not apply to used or demonstrator equipment.
Should any defect develop, Lectrosonics, Inc. will, at our option, repair or replace any
defective parts without charge for either parts or labor. If Lectrosonics, Inc. cannot
correct the defect in your equipment, it will be replaced at no charge with a similar new
item. Lectrosonics, Inc. will pay for the cost of returning your equipment to you.
This warranty applies only to items returned to Lectrosonics, Inc. or an authorized
dealer, shipping costs prepaid, within one year from the date of purchase.
This Limited Warranty is governed by the laws of the State of New Mexico. It states the
entire liablility of Lectrosonics Inc. and the entire remedy of the purchaser for any
breach of warranty as outlined above. NEITHER LECTROSONICS, INC. NOR
ANYONE INVOLVED IN THE PRODUCTION OR DELIVERY OF THE EQUIPMENT
SHALL BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE, CONSEQUENTIAL,
OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE
THIS EQUIPMENT EVEN IF LECTROSONICS, INC. HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE LIABILITY OF
LECTROSONICS, INC. EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE OF ANY DEFECTIVE
EQUIPMENT.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may have additional legal rights which
vary from state to state.
6 Mar 2008
 Loading...
Loading...