Page 1

™
8
+
•
L
e
e
f
t
i
j
d
e
n
•
A
g
e
s
•
Â
g
e
s
•
I
d
a
d
e
s
•
E
d
a
d
e
s
•
A
l
t
e
r
Multilingual Guide
LER 3209
Page 2
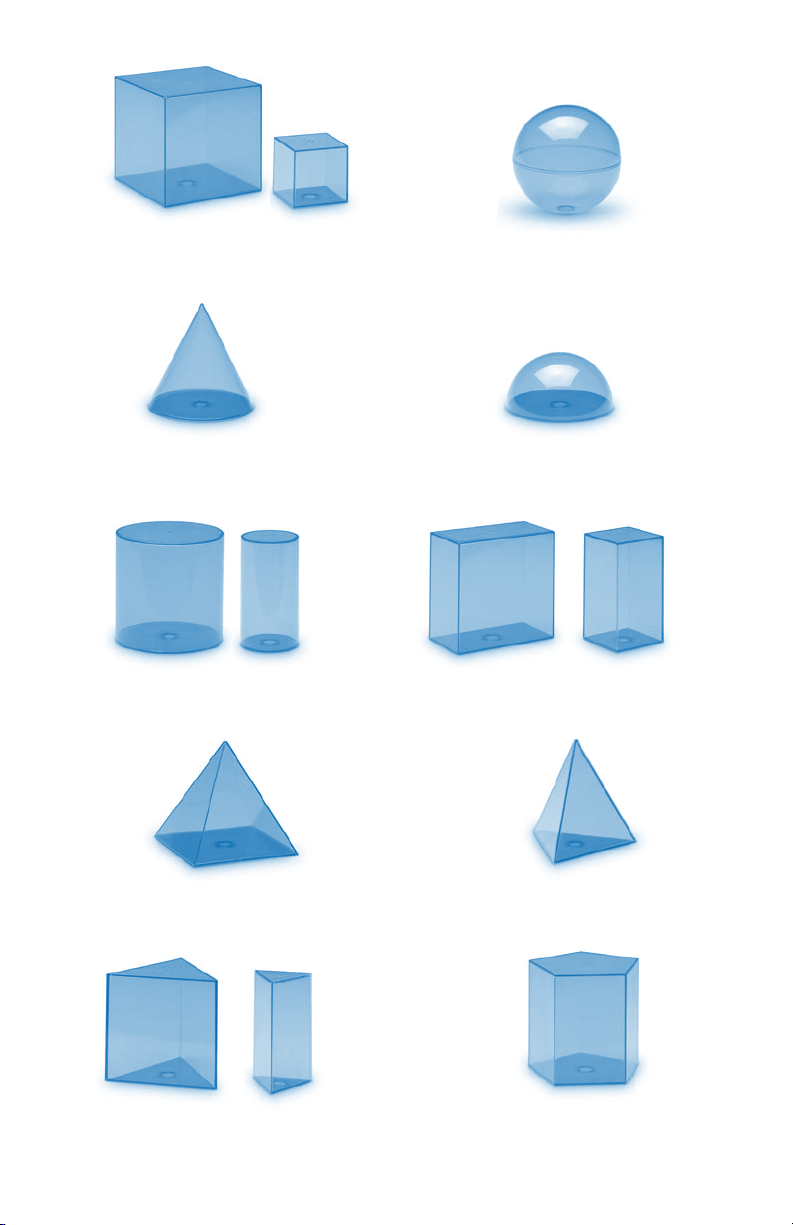
Cube • Cube
Cubo • Würfel
Cubo
Sphere • Sphère
Esfera • Kugel
Esfera
Cone • Cône
Cono • Konus
Cone
Cylinder • Cylindre
Cilindro • Zylinder
Cilindro
Square pyramid • Pyramide carrée
Pirámide cuadrada • Rechtwinklige Pyramide
Pirâmide quadrangular
Hemisphere • Hémisphère
Semiesfera • Halbkugel
Hemisfério
Rectangle prism • Prisme rectangulaire
Prisma rectangular • Rechtwinkliges Prisma
Prisma rectangular
Triangle pyramid • Pyramide triangulaire
Pirámide triangular • Dreieckige Pyramide
Pirâmide triangular
Triangle prism • Prisme triangulaire
Prisma triangular • Dreieckiges Prisma
Prisma triangular
Pentagonal prism • Prisme pentagonal
Prisma pentagonal • Fünfeckiges Prisma
Prisma pentagonal
Page 3

Introduce concepts of volume relationship between solid shapes with this set
of fourteen large View-Thru™ geometric solids. Use the shapes to estimate,
measure and compare volumes in a small group or demonstration setting.
Volume Estimation
Have students list, from least to greatest, the estimated volume of each solid.
Students should check estimates by calculating the volume or lling each shape
with a graduated cylinder and recording the results beside each listed shape.
Volume Formulas
v – volume r – radius
b – base l – length
w – width h – height
s – side length of base
a – apothem (length from the center of a polygon to one side)
Cube – v = l ³ Sphere – v = (4/3) πr ³
Hemisphere – v = (2/3) πr ³ Cone – v = 1/3 (πr²h)
Cylinder – v = πr²h Rectangle prism – v = lwh
Square pyramid – v = 1/3 (lw) h Triangle pyramid – v = 1/3 (1/2 bh) h
Triangle prism – v = (1/2 bh) h Pentagonal prism – v = 5/2 ash
Terminology of Solid Geometry
base face of a geometric shape; bases of the View-Thru™ geometric solids are
blue
polyhedron solid gures with polygon faces
face polygon surface of a polyhedron; shapes in this set are either at or curved
edge intersection of two faces of a polyhedron where they meet at a line
vertex intersection of three or more faces of a polyhedron where they meet at a
point, or corner
prism polyhedron with two congruent, parallel bases and rectangles for the
remaining faces; named for the shape of its bases
pyramid polyhedron with one base and triangles for the remaining faces; named
for the shape of its bases
cylinder two congruent, parallel circular bases and a single curved, lateral face
sphere the set of all points in space equidistant from a given point called the
center
Page 4

FR
Introduisez des concepts concernant les rapports de volumes entre des formes
solides avec cet ensemble de quatorze grands solides géométriques ViewThru™. Utilisez les formes pour estimer, mesurer et comparer des volumes soit
pour les démontrer à vos élèves soit au sein d’un petit groupe.
Estimation du volume
Demandez à vos élèves de faire la liste, en allant du plus petit au plus grand, du
volume estimé de chaque solide. Les élèves devraient vérier les estimations
en calculant le volume ou en remplissant chaque forme au moyen d’un cylindre
gradué et en notant les résultats à côté de chaque forme sur leur liste.
Formules pour les volumes
v – volume r – rayon b – base
L – longueur l – largeur h – hauteur
c – longueur du côté de la base
a – apothème (longueur du centre d’un polygone à l’un des côtés)
Cube – v = l ³ Sphère – v = (4/3) πr ³
Hémisphère – v = (2/3) πr ³ Cône – v = 1/3 (πr²h)
Cylindre – v = πr²h Prisme rectangulaire – v = Llh
Pyramide carrée – v = 1/3 (Ll) h Pyramide triangulaire – v = 1/3 (1/2 bh) h
Prisme triangulaire – v = (1/2 bh) h Prisme pentagonal – v = 5/2 ach
Terminologie de la géométrie des solides
Base face d’une forme géométrique, les bases des solides géométriques ViewThru™ sont bleues
Polyèdre gures solides avec des faces polygonales
Face surface polygonale d’un polyèdre; les formes de cet ensemble sont soit
plates soit courbes
Arête intersection de deux faces d’un polyèdre où elles se rencontrent sur une
ligne
Sommet intersection de trois ou plus de trois faces d’un polyèdre où elles se
rencontrent sur un point ou un coin
Prisme polyèdre ayant deux bases parallèles congruentes et des rectangles pour
les autres faces, ainsi nommé pour les formes de ses bases
Pyramide polyèdre ayant une base et des triangles pour les autres faces, ainsi
nommée pour la forme des ses bases
Cylindre deux bases circulaires parallèles et congruentes et une seule face
latérale courbe
Sphère l’ensemble de tous les points dans un espace équidistants d’un point
donné intitulé le centre
Page 5

ES
Introduce los conceptos de relaciones de volúmenes entre las formas sólidas
con este juego de catorce grandes cuerpos geométricos View-Thru™. Usa las
formas para calcular, medir y comparar volúmenes en un pequeño grupo de
demostración.
Cálculo del volumen
Haz que los alumnos calculen el volumen de cada cuerpo y los enumeren desde
el más pequeño hasta el más grande. Luego, deberán vericar sus respuestas
calculando el volumen o rellenando cada cuerpo con una probeta graduada y
anotando los resultados al lado de cada forma de la lista.
Fórmulas de volúmenes
v – volumen r – radio b – base
l – longitud w – anchura h – altura
s – longitud de un lado de la base
a – apotema (longitud desde el centro de un polígono hasta un lado)
Cubo – v = l ³ Esfera – v = (4/3) πr ³
Semiesfera – v = (2/3) πr ³ Cono – v = 1/3 (πr²h)
Cilindro – v = πr²h Prisma rectangular – v = lwh
Pirámide cuadrada – v = 1/3 (lw) h Pirámide triangular – v = 1/3 (1/2 bh) h
Prisma triangular – v = (1/2 bh) h Prisma pentagonal – v = 5/2 ash
Terminología de cuerpos geométricos
base cara de una forma geométrica; las bases de los cuerpos geométricos ViewThru™ son azules.
poliedro cuerpo sólido con caras poligonales.
cara supercie poligonal de un poliedro; las formas en este juego son planas o
curvas.
arista intersección de dos caras de un poliedro que coinciden en una línea.
vértice intersección de tres o más caras de un poliedro que coinciden en un
punto, o en un ángulo.
prisma poliedro con dos bases congruentes y paralelas y rectángulos para el
resto de las caras; se nombran en función de la forma de sus bases.
pirámide poliedro con una base y triángulos para el resto de las caras; se
nombran en función de la forma de sus bases.
cilindro dos bases circulares congruentes y paralelas, y una sola cara lateral
curvada.
esfera el conjunto de todos los puntos equidistantes en el espacio a un
determinado punto llamado centro.
Page 6

DE
Stellen Sie mit diesem Set aus vierzehn großen geometrischen ViewThru™ Massivformen die Grundlagen des Volumenverhältnisses zwischen
Massivformen dar. Verwenden Sie die Formen, um das Volumen in kleinen
Gruppen oder Demonstrationen zu schätzen, zu messen und zu vergleichen.
Schätzung des Volumens
Fordern Sie die Schüler auf, das geschätzte Volumen der einzelnen
Massivformen aufsteigend aufzulisten. Die Schüler sollen dann ihre
Schätzungen durch Berechnung des Volumens oder durch Befüllen der einzelnen
Formen mit einem Messzylinder überprüfen und die Ergebnisse neben den
aufgeführten Formen notieren.
Formeln zur Berechnung des Volumens
v – Volumen r – Radius b – Grundäche l – Länge
w – Breite h – Höhe s – Seitenlänge der Grundäche
a – Apothem (Länge vom Mittelpunkt eines Polygons zu einer Seite)
Würfel – v = l ³ Kugel– v = (4/3) πr ³
Halbkugel – v = (2/3) πr ³ Konus – v = 1/3 (πr²h)
Zylinder – v = πr²h Rechtwinkliges Prisma – v = lwh
Rechtwinklige Pyramide – v = 1/3 (lw) h
Dreieckige Pyramide– v = 1/3 (1/2 bh) h
Dreieckiges Prisma– v = (1/2 bh) h Fünfeckiges Prisma– v = 5/2 ash
Terminologie der Massiv-Geometrie
Grundäche - Stirnäche einer geometrischen Figur; die Grundächen der
geometrischen View-Thru™ Massivformen sind blau
Polyeder - massive Figuren mit vieleckigen Seiten
Seite - Vieleckige Oberäche eines Polyeders; die Formen in diesem Set sind
entweder ach oder gebogen
Kante - Schnittpunkt von zwei Seiten eines Polyeders, an dem sie sich in einer
Linie treffen
Spitze – Schnittpunkt von drei oder mehr Seiten eines Polyeders, an dem sie
sich an einem Punkt oder einer Ecke treffen
Prisma - Polyeder mit zwei kongruenten, parallelen Grundächen und rechten
Winkeln an den übrigen Seiten; bezeichnet durch die Form seiner Grundächen
Pyramide - Polyeder mit einer Grundäche und Dreiecken an den übrigen
Seiten; bezeichnet durch die Form seiner Grundächen.
Zylinder - zwei kongruente, parallele und runde Grundächen und eine
gebogene Seite
Kugel - die Summe aller Punkte im Raum, die die gleiche Entfernung von
einem bestimmten Punkt haben, der als Mittelpunkt bezeichnet wird.
Page 7

POR
Introduza conceitos de relações entre formas sólidas com este conjunto de
catorze sólidos geométricos grandes View-Thru™. Use as formas sólidas para
calcular, medir e comparar volumes com um grupo pequeno de alunos ou numa
aula de demonstração.
Cálculo de Volumes
Peça aos alunos para listarem, do menor ao maior, o volume calculado de
cada sólido. Os alunos devem vericar estes valores calculando o volume
ou enchendo cada forma sólida, usando para isso um cilindro graduado, e
registando os resultados para cada sólido da lista.
Fórmulas de Volumes
v – volume r – raio b – base l – comprimento
w – largura h – altura s – comprimento do lado da base
a – apótema (comprimento da perpendicular baixada do centro de um polígono
sobre um dos seus lados)
Cubo – v = l ³ Esfera – v = (4/3) πr ³
Hemisfério – v = (2/3) πr ³ Cone – v = 1/3 (πr²h)
Cilindro – v = πr²h Prisma rectangular – v = lwh
Pirâmide quadrangular – v = 1/3 (lw) h
Pirâmide triangular – v = 1/3 (1/2 bh) h
Prisma triangular – v = (1/2 bh) h Prisma pentagonal – v = 5/2 ash
Terminologia da Geometria de Sólidos
base, face de uma forma geométrica; as bases dos sólidos geométricos ViewThru™ são azuis
poliedro, guras sólidas com faces poligonais
face, superfície poligonal de um poliedro; as formas deste conjunto são planas
ou curvas
aresta, intersecção de duas faces de um poliedro, onde se unem ao longo de uma
linha
vértice, intersecção de três ou mais faces de um poliedro, onde convergem num
ponto ou canto
prisma, poliedro com duas bases paralelas congruentes e em que as faces
restantes são rectângulos; a forma da base dá o nome ao prisma
pirâmide, poliedro com uma base e em que as faces restantes são triângulos; a
forma da base dá o nome à pirâmide
cilindro, duas bases circulares, paralelas e congruentes e uma única face lateral
curva
esfera, conjunto de todos os pontos do espaço equidistantes de um dado ponto
designado o centro
Page 8
Look for these other great products from
Learning Resources®!
LER 1206 Liter Set
LER 1207 Gallon Set
LER 2906 Graduated Cylinder Set
For a dealer near you, call:
(847) 573-8400 (U.S. & Int’l)
(800) 222-3909 (U.S. & Canada)
+44 (0)1553 762276 (U.K. & Europe)
© Learning Resources, Inc., Vernon Hills, IL (U.S.A.)
Learning Resources Ltd., King’s Lynn, Norfolk (U.K.)
Please retain our address for future reference.
Made in China. LRM3209-GUD
 Loading...
Loading...