Page 1

P4I845D
Socket 478 Motherboard
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright © 2002 by Leadtek Research Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any
means without the prior written consent of Leadtek Research Inc.
Leadtek makes no warranties with respect to this documentation and disclaims
any implied warranties of merchantability, quality, or fitness for any particular
purpose. The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Leadtek reserves the right to make revisions to this publication without obligation
to notify any person or entity of any such changes.
WinFast
or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.
®
is a registered trademark of Leadtek Research Inc. Other trademarks
Leadtek Research Inc.
International Headquarters
18th Fl., 166, Chien-Yi Rd., Chung Ho
Taipei Hsien, Taiwan (235)
Tel: +886 (0)2 8226 5800
Fax: +886 (0)2 8226 5801
http://www.leadtek.com.tw
E-Mail: service@leadtek.com.tw
Europe Headquarters
United States Headquarters
46732 Lakeview Blvd.
Fremont, CA 94538, U.S.A.
Tel: +1 510 490 8076
Fax: +1 510 490 7759
http://www.leadtek.com
Antennestraat 16 1322 AB
Almere, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0)36 536 5578
Fax: +31 (0)36 536 2215
http://www.leadtek.nl
WinFast P4I845D User’s Manual
Version A CODE: LR5760
January 2002 P/N: W0500540
Page 3

Table of Contents
1.
Introduction ............................................................................ 1
1.1 Package Content........................................................................ 1
1.2 Specifications ............................................................................. 2
2. Quick Setting.......................................................................... 3
2.1 Jumper Position ......................................................................... 3
2.2 Jumper/Connector Listing .......................................................... 4
2.3 Jumper Settings ......................................................................... 5
3. Hardware Setup...................................................................... 7
3.1 CPU Installation ......................................................................... 7
3.2 Memory Installation .................................................................... 7
3.3 AGP Display Adapter Installation............................................... 8
3.4 Connecting Instructions.............................................................. 8
4. BIOS Setup ........................................................................... 13
4.1 Main Menu................................................................................ 14
4.2 Standard CMOS Features........................................................ 14
4.3 Advanced BIOS Features ........................................................ 17
4.4 Advanced Chipset Features..................................................... 20
4.5 Integrated Peripherals.............................................................. 22
4.6 Power Management Setup....................................................... 26
4.7 PnP/PCI Configurations ........................................................... 28
4.8 PC Health Status (O.T.S.) ........................................................ 30
4.9 X-BIOS II < Over Clocking > .................................................... 31
4.10 Load Basic Defaults ................................................................. 32
4.11 Load Best Defaults ................................................................... 32
4.12 Set Supervisor/User Password ................................................ 32
4.13 Save & Exit Setup .................................................................... 33
4.14 Exit Without Saving .................................................................. 33
5. Driver Installation................................................................. 34
5.1 Installing Chipset Driver ........................................................... 34
Page 4

5.1.1
Windows 95/98/ME/2000 ........................................................34
5.2 Installing Audio Driver .............................................................. 35
5.3 Installing LAN Driver ................................................................ 35
5.3.1 Under Windows 95/98............................................................. 35
5.3.2 Under Windows NT 4.0........................................................... 37
5.3.3 Under Windows ME/2000/XP..................................................38
5.4 Installing Speed Gear Utility..................................................... 38
5.5 Installing DirectX 8 ................................................................... 39
5.6 Installing Acrobat Utility............................................................ 39
6. Speed Gear Operation ......................................................... 40
Appendix..................................................................................... 42
Appendix A. BIOS Flash Utility ............................................... 42
Appendix B. Troubleshooting Procedures ............................ 43
Appendix C. Troubleshooting Flowchart ............................... 44
Appendix D. Calling for Technical Support............................ 45
Appendix E. FCC Statement.................................................... 45
Appendix F. Limited Warranty ................................................ 46
Page 5

1. Introduction
WinFast P4I845D is a compelling Desktop solution as a Socket 478/Pentium 4
based ATX motherboard.
WinFast P4I845D, integrating Intel 845 chipset, supports the Intel Pentium 4
processor whose performance will exceed expectation of both consumer and
corporate users alike. The WinFast P4I845D also supports a 400 MHz system
bus, PC266 DDR memory, and the latest graphics devices through the 1.5
AGP4X interface; and allows a direct connection to the graphics and memory for
faster access to peripherals.
WinFast P4I845D also supports four USB ports for peripherals with 24Mbps of
bandwidth; the LAN Connect Interface (LCI); with The Intel SingleDriver™
Technology, all three network options; Communications and Network Riser (CNR)
card, and Dual Ultra ATA/100 controllers.
The Intel Application Accelerator software provides additional performance over
native ATA drivers. The Intel Application Accelerator improves system
performance by improving I/O transfer rates and enables faster O/S load time
resulting in accelerated boot times.
WinFast P4I845D offers innovative design, support for high-volume DDR memory,
and configuration options that optimize performance and provide a robust,
mainstream platform.
1.1 Package Content
Accessories:
6X Sound module x 1
Flat Cable x 1
CPU heat sink mount x 1
Fiber Optics Cable x1
Ultra ATA 66/100 IDE cable x 1
FDD cable x 1
This user’s manual
USB module and cable (optional)
Motherboard & SCSI Software Pack
CD:
Chipset Driver
6X Sound audio driver
IDE driver
Built-in LAN driver
AWARD flash utility
User’s manual
Technical support request form
MS or SD and SCR drivers
1
Page 6

1.2 Specifications
CPU Support
♦ Intel Pentium 4 (478 pin package)
Chip Set
♦ Intel 845D
Cache
♦ L2 Cache is CPU built-in
Memory
♦ Two 184-pin DDR DIMM slots
♦ Up to 2 GB
On Board I/O
♦ Support two PCI Enhanced IDEs
PIO Mode3, Mode4 and Ultra
DMA 33/66/100 channels
♦ Twin headers for four IDE devices
including IDE HDDs and
CD-ROMs
♦ Suppors two FDDs of 360KB,
720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB or
2.88MB
♦ One ECP/EPP Parallel Port, two
16550A UART Serial Ports, four
USB ports, PS/2 mouse port, PS/2
keyboard port, LAN port (optional)
♦ MS or SD and SCR ports
On Board Sound
♦ CMI8738 chipset
♦ PnP, Full-Duplex, Sound Blaster,
Direct Sound Ready
♦ Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in and
MIDI/Game port (optional)
Hardware Monitoring (Optional)
♦ Voltage, temperature, fan speed
monitoring, CPU over heat
protection
Expansion Slot
♦ Five PCI bus slots
♦ One Accelerated Graphics Port
(AGP)
♦ One Communication and
Networking Riser (CNR)
Plug and Play
♦ Plug and Play Specification 1.1
♦ Plug and Play for DOS, Windows
3.x, and Windows 95/98/2000
Power Management
♦ Supports SMM, APM and ACPI
♦ Complies to Energy Star "Green
PC" program
♦ Supports Wake-On-LAN (WOL)
♦ Supports Modem Ring-in Wake up
On Board LAN (Optional)
♦ 10/100 Mb/s LAN
AGP
♦ AGP 2.0 (1.5V AGP4X only)
VRM
♦ On Board VRM 9.0
Battery
♦ On-board Lithium battery
Features
♦ Alarm Wake-up
Board Size
♦ ATX form Factor/12" x 9.6"
(304.8mm x 243.8mm)
2
Page 7
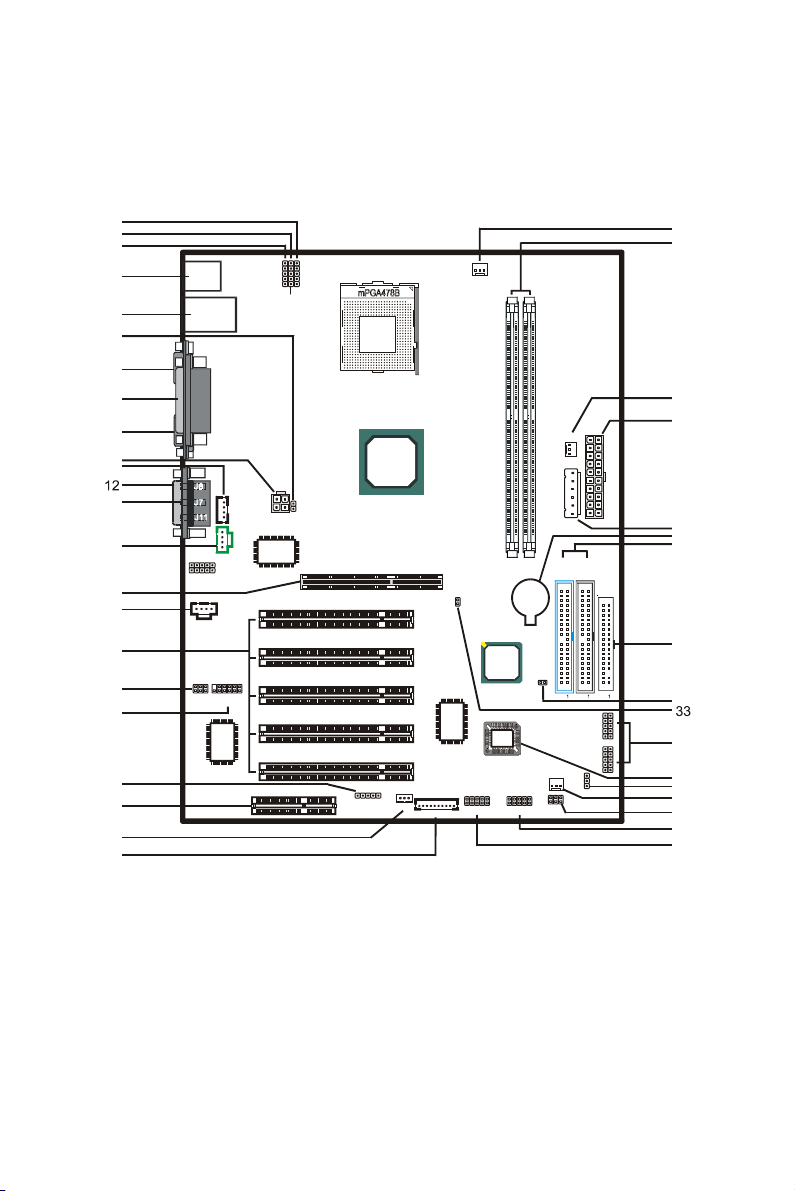
2. Quick Setting
1
3
726
6
7
1
2.1 Jumper Position
2
3
JP9
PWR_12V_CON
RTL8100B
J21
JP11
JP10
Intel
AGP
CIR1
845
PCI1J14
PCI2J16
PCI3J17
PCI4J18
PCI5J19
WOL1
IR1
J8
JP19
J13
CNR
JP12 JP13
MS/CF
JP18
MART
SIO
129
SMART CARD
FAN1
CPU FAN
D
5
4
8
I
P4
t
s
a
F
n
i
W
intel
U18
J51 JP7
10
DIM0 DIM1
BATTERY
BAT1
129
USB CON
FAN3
J5
FAN2
PWR FAN
J4
IDE2
IDE1
FDD
JP1
12
FP1
109
12
FP2
SYS FAN
10
125
JP8
109
JP6
6
4
5
6
KB1
J1
1
M
O
C
7
8
LPT1
9
10
11
13
14
15
16
COM2
J9
CD_IN
JP20
210
19
AUDIO
FRONT PANEL
RGGL
AUX_IN
J10
CD_IN
LGGR
J12
J15
17
JP4
JP3
2
6
18
19
2
11121
1
5
AUDIO-CON
CMI8738
20
21
22
2
24
25
2
ATX_PWR_CON
28
29
30
3
32
34
35
3
3
38
39
40
1. JP11 11. J10 21. J21 31. FDD
2. JP10 12. J9 22. WOL1 32. JP1
3. JP9 13. J6, J7, J11 23. JP12, JP13 33. JP18
4. KB1 14. J12 24. FAN1 34. FP1, FP2
5. J1 15. J13 25. DIM0, DIM1 35. U18
6. JP19 16. J15 26. FAN2 36. JP6
7. COM1 17. J14, J16-19 27. J5 37. FAN3
8. LPT1 18. JP3 28. J4 38. JP8
9. COM2 19. JP4 29. BAT1 39. JP7
10. J8 20. CIR1 30. IDE1, IDE2 40. J51
3
Page 8
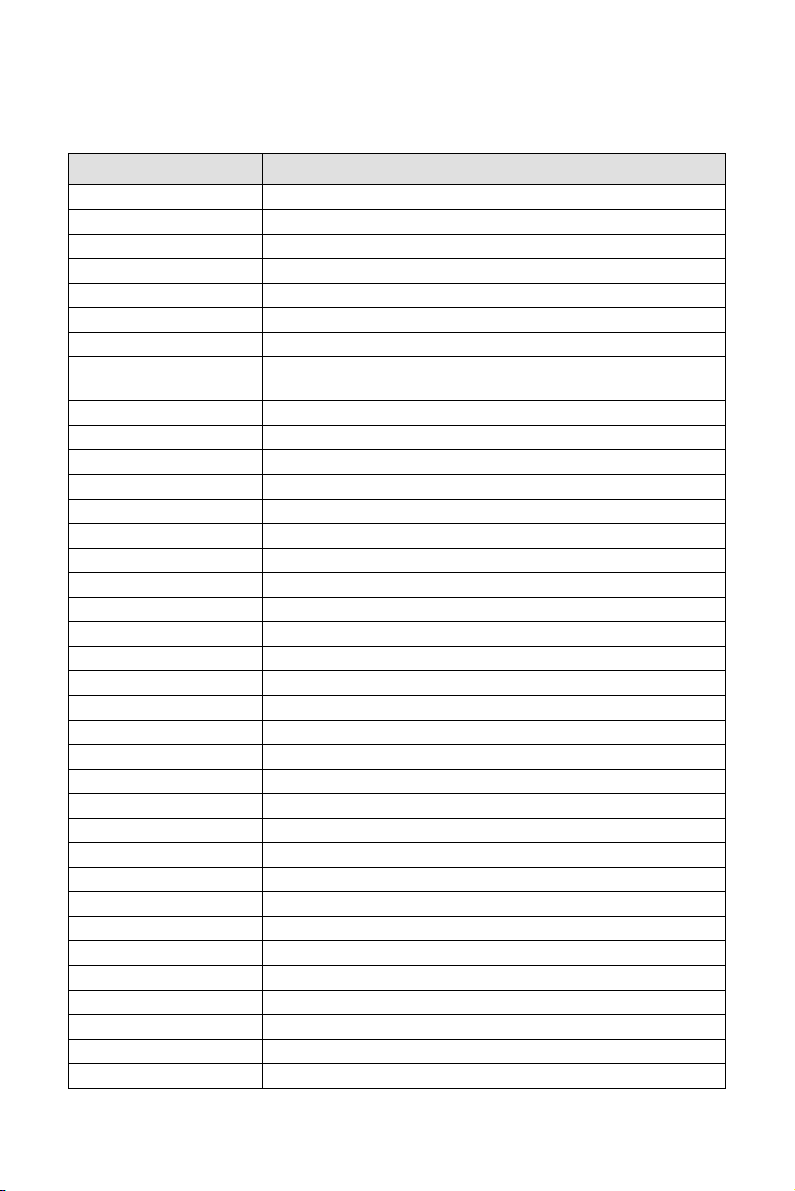
2.2 Jumper/Connector Listing
Jumper/Connector Description
BAT1 Battery
COM1, COM2 COM1, COM2 connector
DIM0, DIM1 Memory module connectors
FAN1 CPU fan connector
FAN2 Power fan connector
FAN3 System fan connector
FDD Floppy disk connector
FP1, FP2 Case Signal Connector: PWRBTN, RESET, KEY LOCK,
IDE1/IDE2 Hard disk connectors (Primary IDE/Secondary IDE)
CIR1 CIR connector
J1 USB ports and 10/100 LAN connector
J4 AUX power connector
J5 ATX power connector
J6, J7, J11 Mic In, Line In, Line Out ports
J8 12V CPU Vcore power connector
J9 MIDI/Joystick port
J10, J12 CD input connectors
J13 AGP slot
J14, 16-19 PCI slot
J15 AUX input connector
J21 CNR slot
J51 Smart Card connector
JP1 Clear CMOS
JP3 Center/Bass Convert
JP4 Audio Connector
JP6 Voice alert language selection
JP7 USB module connector, providing the 3rd and 4th USBs
JP8 USB module selection
JP9-11 VID 0-4: Vcore voltage selection
JP12, JP13 MS/CF connector
JP18 CPU/DIMM frequency selection
JP19 CPU voltage selection
KB1 PS2 keyboard and mouse ports
LPT1 Printer port
U18 LPC Flash
WOL1 Wake on LAN
SPEAKER, HDD_LED, POWER_LED, ACPILED
4
Page 9
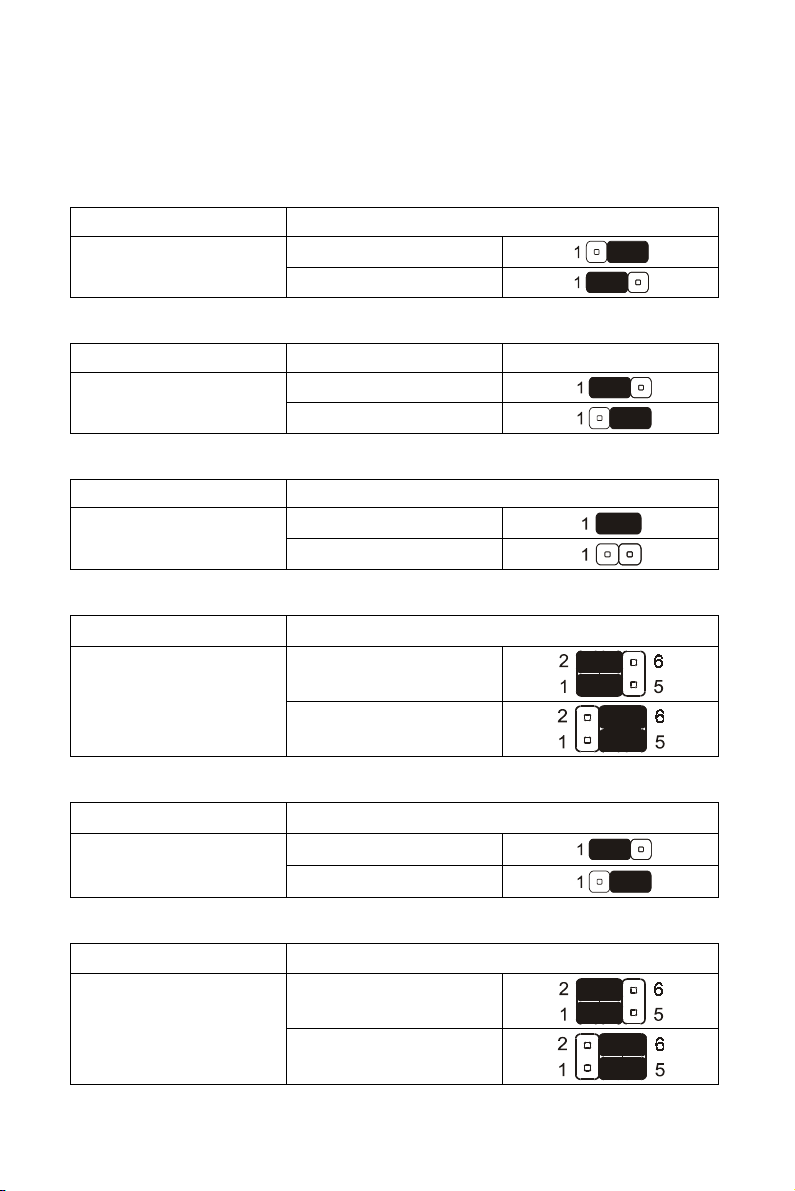
2.3 Jumper Settings
Clear CMOS Data
Jumper Setting
JP1
CPU/DIMM Frequency
Jumper Frequency Setting
JP51
CPU Voltage Selection
Jumper Setting
JP19
Center/Bass Convert
Jumper Setting
Increase voltage by 0.15V
Clear CMOS
Normal (Default)
Auto detect
133/133 MHz
Normal (Default)
Normal
JP3
Inverse
Voice Alert Language Selection
Jumper Setting
JP6
English
Chinese
USB selection
Jumper Setting
USB4
JP8
CNR USB
5
Page 10
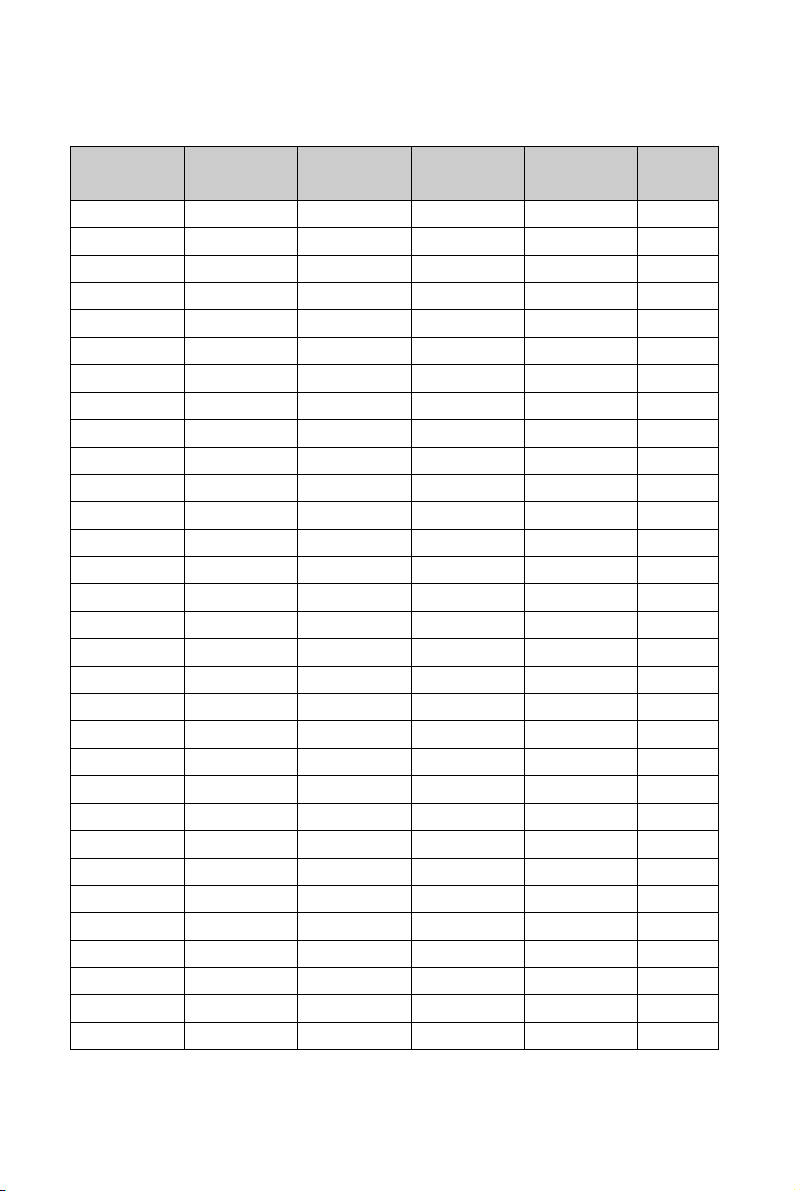
Vcore Voltage Selection (VID 0-4)
VID0 VID1 VID2 VID3 VID4
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.1V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.125V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.15V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.175V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.2V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.225V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.25V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.275V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.3V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.325V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.35V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.375V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.4V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.425V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1.45V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.475V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.5V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.525V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.55V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.575V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.6V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.625V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.65V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.675V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.7V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.725V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.75V
1-2 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.775V
2-3 pins short 1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.8V
1-2 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.825V
2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 2-3 pins short 1.85V
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
6
Page 11

3. Hardware Setup
Static Precautions
Static discharge can damage electronic components. To prevent that, it is
important to handle it carefully. The following measures will suffice your
equipment from static.
Use a grounded wrist strap designed for static discharge.
Touch a grounded metal object before you remove the board from the
anti-static bag.
Handle the board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral
chips, memory modules, or gold contacts. Do not touch pins on chips or
modules.
Put the system board and peripherals back into their anti-static bags when not
in use.
For grounding purposes, be sure your computer chassis provides excellent
conductivity between its power supply, case, the mounting fasteners, and the
system board.
3.1 CPU Installation
Please refer to the instruction manual of the CPU for how to install the CPU.
3.2 Memory Installation
The motherboard provides two 184-pin DIMM (Double In-Line Memory Module)
slots, DIM0 and DIM1. You can use DDR SDRAM modules of 8MB, 16MB, 32MB,
64MB, 128MB, 256MB, or 512MB per DIMM slot.
IF you choose DDR200 in the Memory Frequency option in BIOS, you must use
the qualified DDR SDRAM that meets PC200 specifications.
IF you choose DDR266 in the Memory Frequency option in BIOS, you must use
the qualified DDR SDRAM that meets PC266 specifications.
DIMM Installation Procedures
The DIMM slot has a key marked “VOLT”, thus making the module only fit in one
direction. Note that the module must
be a 3.3V unbuffered DIMM
Step 1:
Insert the module vertically
into the DIMM slot, and then
Step 2:
push it in.
The plastic clips at the side of
the DIMM slot will
automatically close.
7
Page 12
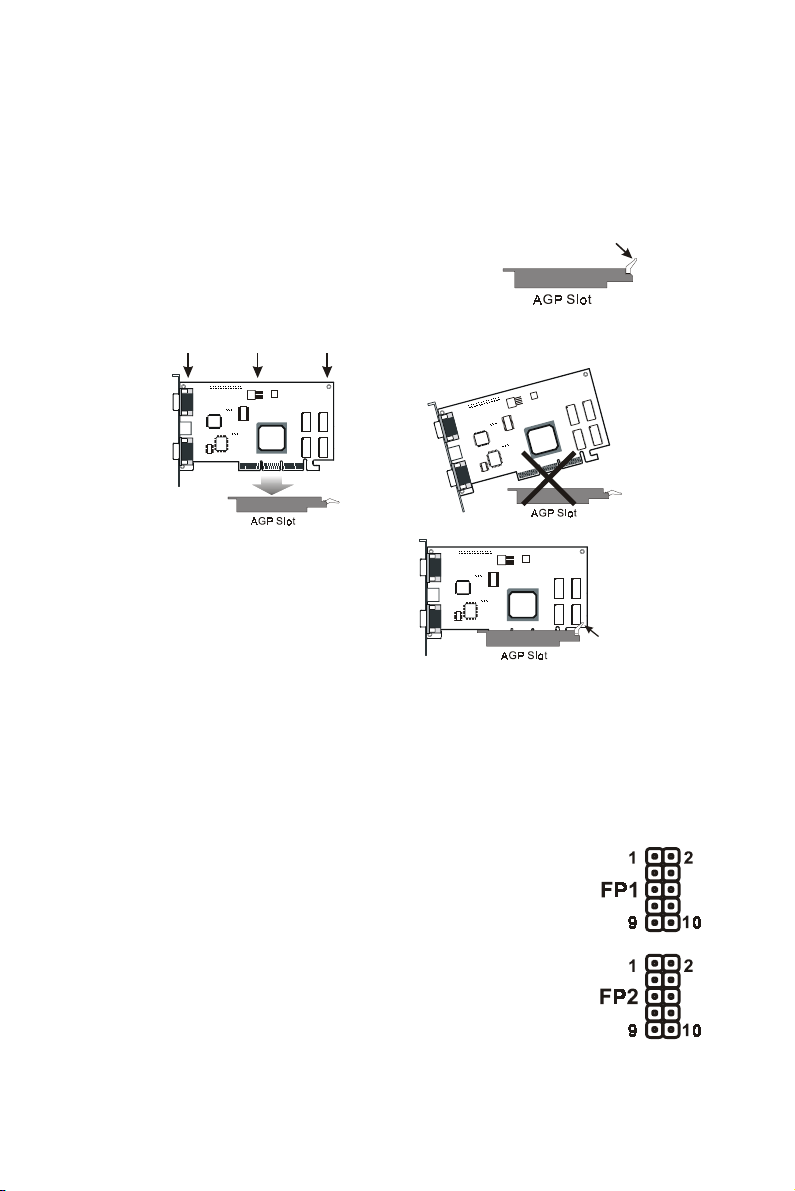
3.3 AGP Display Adapter Installation
The AGP slot on WinFast P4I845D only supports 1.5V AGP4X devices. To install
an AGP display adapter, follow these steps:
Step 1:
Step 2:
Push the clip at the end of AGP slot.
Position the AGP card horizontally over the
AGP slot. Do not tilt the card. Insert the
bus connector in the slot and gently press the bus connector down.
Step 3:
Push the clip back to close it
.
3.4 Connecting Instructions
How each connector is connected and what it does is described here in detail.
See Chapter 2 to locate connectors.
Case Signal Connector (FP1 and FP2)
FP1:
Pins [1 & 3] IDE-LED: IDE hard disk LED shows the activity
of a hard disk drive. Avoid turning the power off while the
HDD LED is lit.
Pins [2 & 4] ACPI-LED: For ACPI LED connection on the
case.
Pins [5 & 7] RESET: Connects to the reset button on the
system’s case. The reset button is used to “cold-boot” the
system without actually turning off the power, reducing wear
and tear on the power supply. Avoid rebooting the system
when the HDD LED is blinking.
Pins [6 & 8] PW_SW: Allows connecting to the power button on the system’s
case.
8
Page 13
FP2:
Pins [1 & 3] KEYLOCK: Keyboard lock switch lead. It connects to the
case-mounted keylock switch, allowing you to disable the keyboard function for
security purpose.
Pins [5 & 7 & 9] PW-LED: Power LED. It is always lit when the system power
is on.
Pins [2 & 4 & 6 & 8] SPEAKER: Connects to the speaker on the system’s
case.
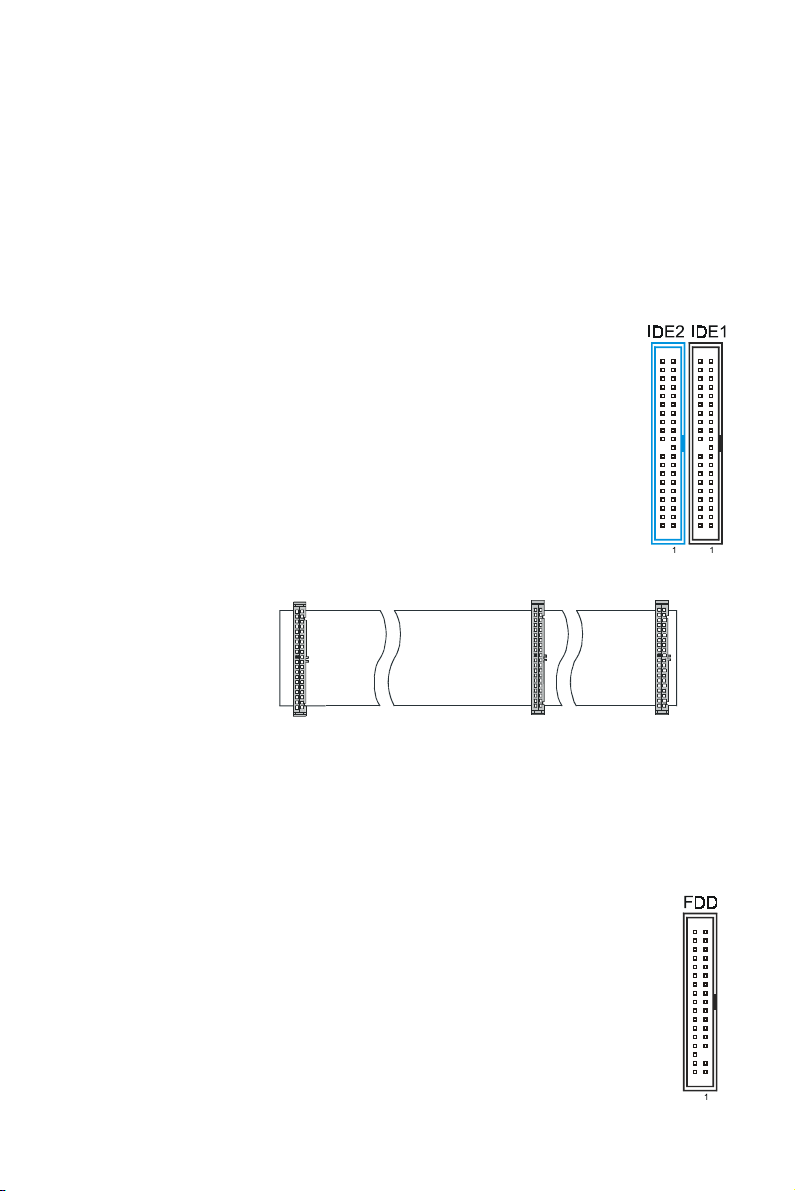
Hard Disk Connector
The on-board Enhanced IDE controller can support up to 4 IDE hard
drives or other ATAPI devices, such as CD-ROMs. This controller, as
with all Enhanced IDE controllers, consists of both Primary (IDE 1)
and Secondary (IDE 2) ports. Each port has an associated connector
and cable, which can support up to 2 ATAPI devices each.
All IDE devices have jumpers, which allow the user to configure the
device as either “Master” or “Slave”. A Master device is one that is
ALONE on the IDE cable, whereas a Slave device is installed as a
SECOND device on the same cable. Keep in mind that the Master
device will appear before the Slave device in the CMOS Setup, as
well as the Operating System software. *Refer to the device
documentation for jumper settings.
The Secondary IDE
port can be used for
Mainboard IDE Port
Slave Drive
Master Drive
up to 2 additional
ATAPI devices.
Make sure to align
the RED stripe on the
ribbon cable with
Blue
Connector
Gray
Connector
Black
Connector
Pin-1 on the
motherboard IDE connector. On most hard drives and CD-ROMs, the RED stripe
should be oriented towards the power connector of the device.
When using Ultra ATA 66/100 IDE cable (as shown above), the black color
connector on the cable is for Master drive, gray color is for Slave drive and blue
color is for connecting to IDE port onboard.
Note that Ultra ATA 66/100 devices must be connected to IDE2 (the blue
connector).
Floppy Disk Connector (FDD)
The on-board floppy controller supports 2 floppy disk drives. Make sure
the RED stripe on the ribbon cable is oriented towards Pin-1. Notice the
“twist” between the sets of connectors on the floppy cable. The floppy
drive “A” position is at the END of the cable, whereas floppy drive “B” is
hooked to one of the connectors on the other side of the twist.
9
Page 14
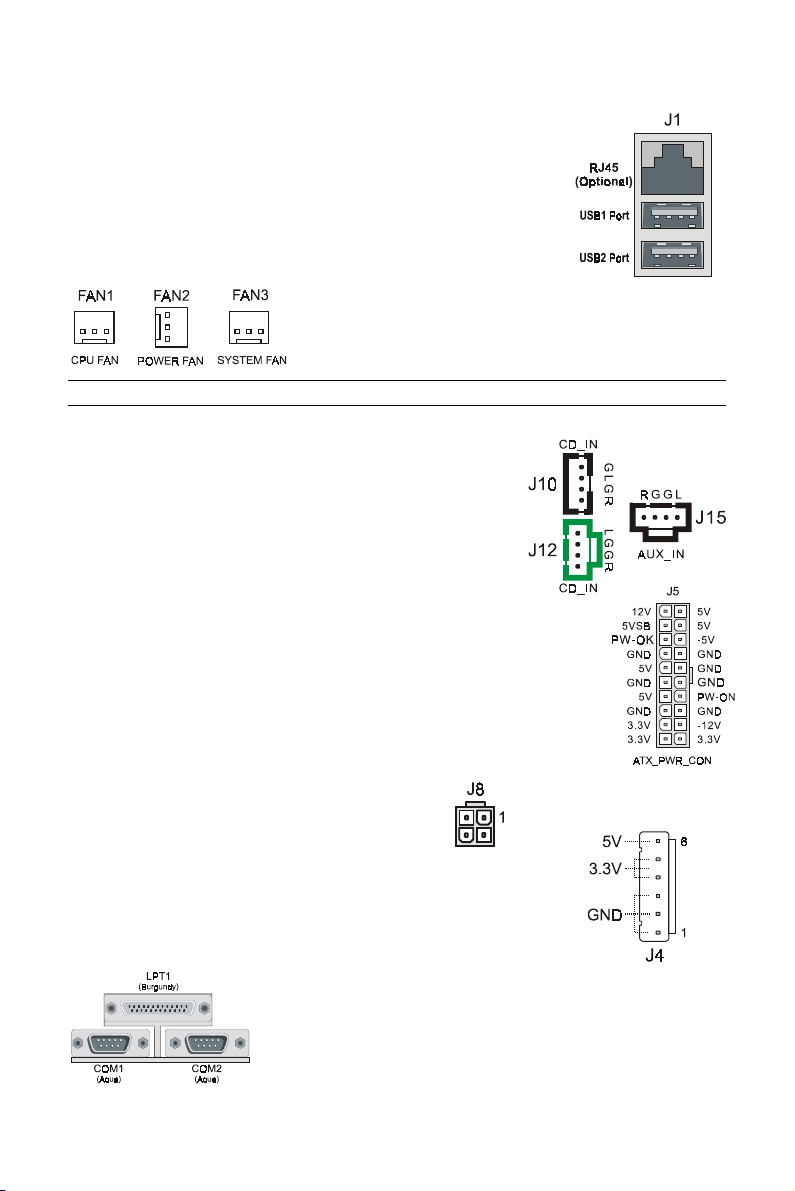
RJ45 Ethernet Connector and USB Connectors (J1)
RJ45 LAN connector and two USB peripheral devices
connectors.
Cooling Fans (FAN1, FAN2, FAN3)
CPU fan (FAN1), power fan (FAN2), and system fan
(FAN3) are small 3-pin Header Connectors that
provide 12-Volt power for CPU fan, power fan, and
system fan. Plug in the fan cable to the connector.
NOTE:
Stereo Audio/Video In Connectors (J10, J12, J15)
J10 and J12 allow you to receive stereo audio input
from internal CD ROM drives. J15 is for connecting
other auxiliary audio sources.
Power Supply Connector (J5)
This motherboard features an ATX-style Power Supply
Connector. This connector is keyed to prevent connection in the
wrong direction. Line up the locking mechanism on the connector
from the Power Supply with the tab on the motherboard
connector. Press down until the two connectors are locked.
12V Power Connector (J8)
J8 connects the 12V power input.
AUX Power Connector (J4)
J4 connects AUX power.
The power fan speed is not monitored in the BIOS.
Serial and Parallel Ports
A 25-pin D-Sub header is provided on the back panel for
a multi-mode bi-directional parallel port. Two 9-pin D-Sub
headers are provided on the back panel for serial port
COM1 and COM2.
10
Page 15
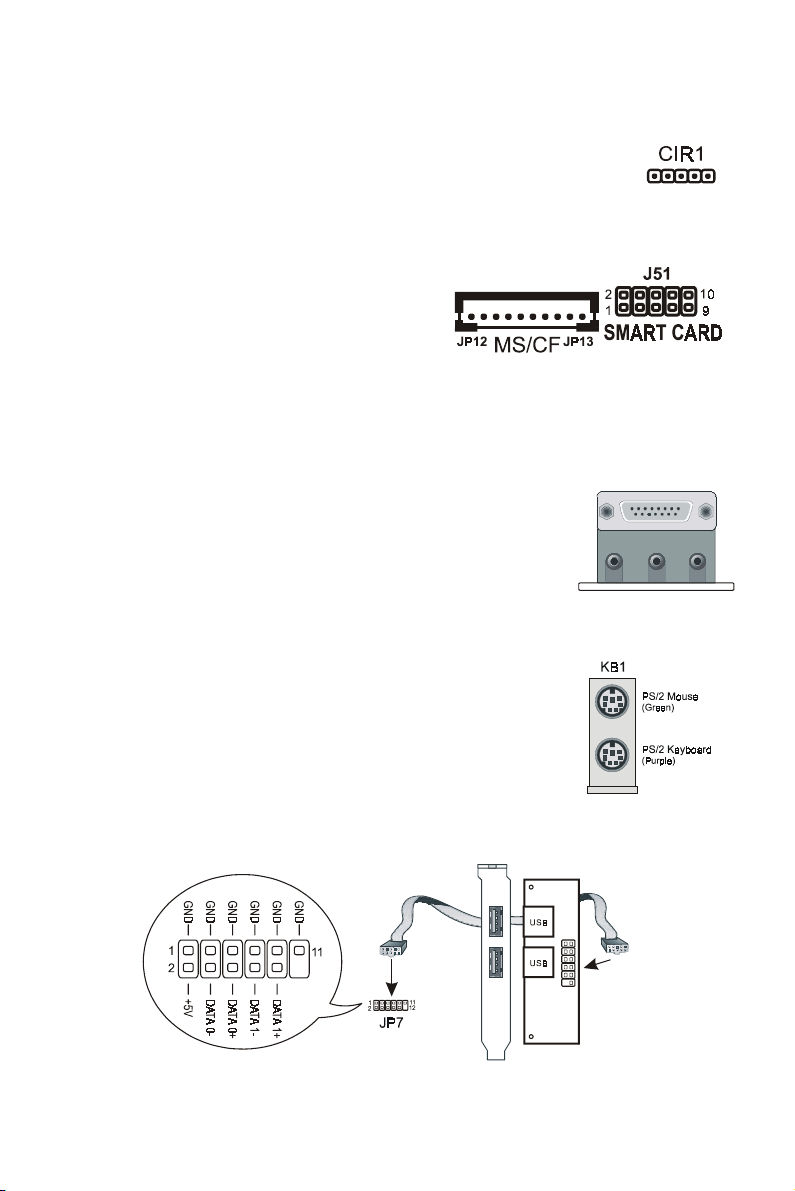
IrDA-Compliant Infrared Module Connector (CIR1)
(
)
(Lig
)
The IrDA connector brackets hook directly to this connector on the
motherboard. This connector provides support for the optional
wireless transmitting and receiving infrared module.
MS or SD and Smart Card connectors
(JP12, JP13, J51)
These two connectors are for connecting the
optional reader that can accommodate an MS
(Memory Stick) or an SD (Secure Digital) as
well as a Smart Card.
Midi/Joystick, MIC, Line In, Line Out
Midi/Joystick: Allow you to connect game joystick or
game pad for playing games or connect Midi devices for
playing or editing audio.
Mic: Allows microphones to be connected for inputting
sound.
Line In: Allows tape players or other audio sources to be
recorded by your computer or played through the Line Out.
Line Out: Connected to headphones or speakers with
amplifier.
PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector (KB1)
These two connectors are located on the back panel of the
motherboard.
Game Port
Line Out
(Lime)
(Gol d)
Line In
ht Blue
MIC
Pink
USB Connector (JP7)
This is for connecting an optional USB module to provide two additional USB
connectors.
11
Page 16

Audio Connector (JP4)
JP4 is for connecting to the sound module that comes with the package. See the
following figure for how to connect the sound module.
12
Page 17

4. BIOS Setup
The BIOS Setup (also called CMOS Setup) is where many hardware
configurations are done and stored. This configuration information will remain in
the BIOS until it is changed, or cleared. CMOS refers to the chip in which the
BIOS information is stored, even when the power is turned off.
AwardBIOS CMOS setup utility allows you to change hardware settings in the
BIOS. This chapter gives a detailed description of each setup item as to what
function it controls and how one can modify its setting.
This motherboard also features a Flash BIOS. A Flash BIOS can be upgraded by
software programs.
The AwardBIOS is activated once you boot the computer. The BIOS reads CMOS
for system configuration information, and begins the process of checking out the
system and configuring it through the power-on self test (POST).
When three preliminaries are finished, the BIOS seeks an OS on one of the data
storage devices (hard drive, floppy disk, etc.) and launch it.
During POST, you can start the Setup program by pressing Del.
The AwardBIOS supports an override to CMOS settings, which will reset your
system to its default configuration if your computer can no longer boot up after
making changes.
We suggest you to only alter settings you have thorough knowledge of. Do not change
settings without a good reason.
To enter the Award BIOS program's main menu:
Turn on or reboot the system.
After the diagnostic checks, press the [Del] to enter the Award BIOS Setup
Utility.
To select items:
Use the arrow keys to move between items and select fields.
From the Main Menu, press arrow keys to enter the selected submenu.
To modify selected items:
Use the [Up]/[Down] keys to modify values within the selected fields. Some
fields let you enter values directly.
13
Page 18

4.1 Main Menu
Once you enter the AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu appears on
the screen. Main Menu presents you the Setup functions included two exit
choices. You could use the arrow keys to select among the items and then press
Enter to the submenu.
* Description of selected item is shown in the column on the bottom of the screen.
4.2 Standard CMOS Features
The Standard CMOS Features allows you to choose the options in the setting
item for basic system configuration.
14
Page 19

* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
Date [mm:dd:yy]
The BIOS determines the day of the week from the other date information. It is for
information only.
Time [hh:mm:ss]
The time format is <hour> <minute> <second>. The time is calculated based on
the 24-hour military-time clock. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00.
IDE Primary Master/ Primary Slave/Secondary Master/Secondary Slave
After pressing [Enter], a menu window appears as shown on below:
The BIOS supports up to four IDE drives. This section does not show information
about other IDE devices, such as a CD-ROM and SCSI drives.
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
IDE HDD Auto-Detection
The “IDE HDD Auto-Detection” utility is a very useful tool especially when you do
not know the type of hard disk you are using. You can use this utility to detect the
correct disk type installed in the system automatically. The BIOS will
automatically detect the hard disk size and model during POST.
The AwardBIOS supports 3
The Generic access mode, neither BIOS nor IDE controller, will make
transformations during accessing.
15
HDD modes: NORMAL, LBA and LARGE modes.
Page 20

NOTE: There must be some software involved to support LBA or LARGE mode of
HDDs. All the software needed is located in the Award HDD Service Routine
(INT 13h). It may fail to access a HDD with LBA (LARGE) mode selected if
you are running under an Operating System, which replaces the whole INT
13h. UNIX operating system do not support either LBA or LARGE, and must
utilize the Standard mode. UNIX can support drives larger than 528MB.
AUTO Mode:
The BIOS can automatically detect the specifications and optimal operating mode
of almost all IDE drives. When you select type Auto for a hard drive, the BIOS
detects its specifications during POST, every time the system boots.
IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT YOU SELECT THE TYPE AUTO FOR ALL DRIVES.
Drive A /Drive B [1.44M, 3.5 in.]
Select the correct specifications for the diskette drive(s) installed on your system.
Floppy 3 Mode Support [Disabled]
This setting item supports the floppy disk drives (FDD) which are 3 1/2" drives
used in Japanese computer system.
Video [EGA/VGA]
Select the type of primary video subsystem on your system. The BIOS usually
detects the correct video type automatically, and supports a secondary video
subsystem that cannot be selected in Setup.
Halt On [All, But Keyboard]
During the power-on self test (POST), the system stops if the BIOS detects a
hardware error. You can ask the BIOS to ignore certain errors and continue the
process. There are the options:
All Errors: If the BIOS detects any non-fatal error, POST stops and
prompts you to take corrective action.
No Errors: POST does not stop for any error.
All, But Keyboard: POST does not stop for keyboard error, but stops for all
other errors.
All, But Diskette: POST does not stop for diskette drive errors, but stops
for all other errors.
All, But Disk/Key: POST does not stop for a keyboard or disk error, but
stops for all other errors.
Memory
You can not change the value in the Memory fields which are information only.
The setting item shows the total installed random access memory (RAM) and
amounts allocated to base memory, extended memory, and other (high) memory.
RAM is the computer’s working memory where the computer stores programs
and data currently being used, so they are accessible to CPU.
16
Page 21

Base Memory: Typically 640 KB is also called conventional memory. The
DOS operating system and conventional applications use this area.
Extended Memory: The memory over the 1MB boundary.
Total Memory: Total memory available from the system.
4.3 Advanced BIOS Features
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
Virus Warning [Disabled]
The BIOS will halt on the system. Then the warning message appears as follows
if there is virus.
!PBVA WARNING!
Paragon Boot Virus analyzer has
detected virus activity on hard disk
We recommend you to press:
[Enter] Boot from clean disk
NOTE: When this item is enabled, the monitoring boot sector virus only happens at the
booting period. After you enter the system, this function is disabled automatically.
So you can run any kind of program, such as many disk diagnostic programs,
which attempt to access boot sectors or the partition table of hard disk drive when
it is running.
[C] Continue Boot
CPU L1 & L2 Cache [Enabled]
Cache memory is an additional memory that is much faster than conventional
DRAM (system memory). When the CPU requests data, the system transfers the
requested data from the main DRAM into the cache memory, for even faster
17
Page 22

access by the CPU.
Quick Power On Self Test [Enabled]
Select Enabled to reduce the amount of time required to run the POST. A quick
POST skips certain steps. We recommend that you normally disable quick POST.
Better to find a problem during POST than lose data during your work.
First, Second, Third, Fourth Boot Device [HDD-0, Floppy, SCSI, Disabled]
This category determines which drive to be searched first, second or third for the
disk operating system (i.e. DOS). You can use these settings to select your
Priority Boot Up drives for Floppy drive A, IDE Hard Disk Drive C, D, E, F, or
SCSI.
Swap Floppy Drive [Disabled]
This field is effective only in system with two floppy drives. This item allows you to
determine whether to enable the swap floppy drive or not (i.e. physical floppy disk
A assigned to logical drive B or physical drive B to logical drive A).
Boot Up Floppy Seek [Enabled]
During the “POST” process, BIOS will determine if the floppy disk drive installed
is 40 or 80 tracks. 360K-type is 40 tracks while 760K, 1.2M and 1.44M are all 80
tracks. Because few modern PCs have 40-track floppy drives, we recommend
that you set this field to Disabled to save time.
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
This field allows you to determine the default state of the numeric keypad. “On”:
keypad is number keys after boot up. “Off”: keypad is arrow keys after boot up.
Gate A20 Option [Fast]
Gate A20 refers to the way the system addresses memory above 1MB (extended
memory). When set to Fast, the system chipset controls Gate A20. When set to
Normal, a pin in the keyboard controller controls Gate A20. Setting to Fast
improves system speed, particularly with OS/2 and Windows.
The options are: Fast and Normal.
Typematic Rate Setting [Enabled]
Setting Enabled allows you to adjust both settings. You can use this feature to
accelerate cursor movement with the arrow keys. When this item is set Disabled,
keep holding down a key will let the system to use the default typematic rate
delay of 250 msec, and typematic rate of 6 chars/sec to input repeatedly.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) [6]
When “Typematic Rate Setting” is Enabled, its selections allow you to select the
rate at which character repeats when you hold down a key.
18
Page 23

Typematic Delay (Msec) [250]
When “Typematic Rate Setting” is Enabled, its selections allow you to select the
delay before key strokes begin to repeat.
Security Option [Setup]
If you have set a password at USER PASSWORD option in main menu, select
whether the password is required every time the System boots, or only when you
enter Setup.
The options are: System and Setup.
APIC Mode [Enabled]
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB [Non-OS2]
Allow you to access memory that is over 64MB in OS/2. Choose OS2 when you
are using OS2 and SDRAM size greater than 64 MB. Choose Non-OS2 for other
operating systems.
The choice: Non-OS2, OS2.
Report No FDD for Win95
Select Yes to release IRQ6 when the system contains no floppy drive, for
compatibility with Windows 95 logo certification. In the Integrated Peripherals
screen, select Disabled for the Onboard FDC Controller field. You should choose
“Yes” if your operating system is Windows 95 and without a floppy disk equipped
in your computer.
The options are: Yes and No.
Small Logo (EPA) Show [Enabled]
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
19
Page 24

4.4 Advanced Chipset Features
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
This section allows you to configure the system based on the specific features of
the installed chipset. This chipset manages bus speeds and access to system
memory resources, such as DRAM and the external cache. It also coordinates
communications between the conventional ISA bus and the PCI bus. It must be
stated that these items should never need to be altered.
The default settings have been chosen because they provide the best operating
conditions for your system. The only time you might consider making any
changes would be if you discovered that data was being lost while using your
system.
DRAM Timing Selectable [By SPD]
The options are: By SPD and Manual.
DRAM CAS Latency Time [3]
The default setting is 3. You can select this setting item according to your
SDRAM specification.
Active to Precharge Delay [7]
The options are: 7, 6, and 5.
DRAM RAS# toCAS# Delay [3]
Be sure the DRAM is installed in your system before you choose the options in
this field. This setting item allows you to insert a timing delay between the RAS
and CAS strobe signals.
20
Page 25

DRAM RAS Precharge [3]
The precharge time is the number of cycles it takes for the RAS to accumulate its
charge before SDRAM refreshes. If insufficient time is allowed, refresh may be
incomplete and the SDRAM may fail to retain data.
The options are: 2 and 3.
DRAM Data Integrity Mode [Non-ECC]
The options are: ECC and Non-ECC.
Memory Frequency for [Auto]
The options are: Auto, DDR200, and DDR266.
DRAM Read Thermal Mgmt [Disabled]
The options are: Disabled and Enabled.
System BIOS Cacheable [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the system BIOS ROM at F0000h-FFFFFh,
resulting in better system performance. However, if any program writes to this
memory area, a system error may result.
The options are: Disabled and Enabled.
Video BIOS Cacheable [Disabled]
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the video memory (RAM) at
A0000h-AFFFFh, resulting in better system performance. However, if any
program writes to this memory area, a system error may result.
The options are: Disabled and Enabled.
Video RAM Cacheable [Disabled]
The options are: Disabled and Enabled.
Delayed Transaction [Enabled]
If the chipset of your motherboard has an embedded 32-bit write buffer to support
delay transaction cycles, you can enable this setting item to provide compliance
with PCI Ver. 2.1.
The options are: Disabled and Enabled.
AGP Aperture Size [64]
This setting item allows you to select the size of the Accelerated Graphics Port
(AGP) aperture. The aperture is a portion of the PCI memory address range
dedicated for graphics memory address space.
The options are: 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256.
Delay Prior to Thermal [16 Min]
The options are: 4 Min, 8 Min, 16 Min, and 32 Min.
21
Page 26

4.5 Integrated Peripherals
This Menu Setup allows you to configure your IDE, USB keyboard, Floppy Drive,
Parallel Port, Serial Port, and IR function.
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
On-Chip Primary PCI IDE [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows you to adjust the functions of Primary PIO and UDMA.
On-Chip Second PCI IDE [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows you to adjust the functions of Second PIO and UDMA.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO [Auto]
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4)
for each of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes
0 through 4 provide successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the
system automatically determines the best mode for each device.
The options are: Auto, Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3, and Mode 4.
22
Page 27

IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA [Auto]
Ultra ATA 66/100 implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive supports
it and the operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a
third-party IDE bus master driver). If your hard drive and your system software
both support Ultra ATA 66/100, select Auto to enable BIOS support.
The options are: Auto and Disabled.
USB Controller [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows the system Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller when
you have USB peripherals.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
USB Keyboard Support [Disabled]
If you use USB keyboard, please choose Enabled.
CNR Audio [Auto]
Selecting Auto allows the BIOS to detect the audio device you use.
The options are: Auto and Disabled.
CNR Modem [Auto]
The options are: Auto and Disabled.
OnBoard 6Xsound Chip [Enabled]
Choose to enable or disable the onboard CMI8738 audio device.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
OnBoard Lan Chip [Enabled]
Choose to enable or disable the onboard Realtek 8100B LAN chip.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Init Display First [AGP]
If you install one AGP and one PCI video card, you can choose which one to be
initialized first as the primary display.
The options are: AGP and PCI Slot.
IDE HDD Block Mode [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows automatic detection of the optimal number of block
read/writes per sector the drive can support.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Power ON Function [BUTTON ONLY]
This setting item allows you to choose a way to power on.
23
Page 28

The options are: Password, Hot KEY, Mouse Left, Mouse right, Any KEY,
BUTTON-ONLY, and Keyboard 98.
KB Power ON Password [Enter]
This setting item allows you to set a password for keyboard powering on.
Hot Key Power ON [Ctrl-F1]
This setting item allows you to choose one of the hot keys to power on from F1 to
F12.
Onboard FDC Controller [Enabled]
This setting item allows you to enable or disable the onboard FDC controller.
Onboard Serial Port 1/Port 2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and second serial
ports.
The choices: 3F8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, Disabled, and Auto.
UART Mode Select
Select an infrared port mode.
The options are: Normal, IrDA, and ASKIR.
RxD, TxD Active
The options are: Hi,Hi, Hi,Lo, Lo,Hi, and Lo,Lo.
IR Transmission Delay
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
UR2 Duplex Mode
This item selects the IR function when the choice of the UART mode is ASKIR.
The options are: Full and Half.
Use IR Pins
The options are: RxD2,TxD2 and IR-Rx2Tx2
Onboard Parallel Port
This item allows you to determine access onboard parallel port controller with
which I/O address.
The options are: 378/IRQ7, 278/IRQ5, 3BC/IRQ7, and Disabled.
Parallel Port Mode
Select an operating mode for the onboard parallel (printer) port. Normal EPP
(Extended Parallel Port) ECP (Extended Capabilities Port) ECP+EPP PC AT
parallel port Bi-directional port Fast, buffered port Fast, buffered, bi-directional
port.
24
Page 29

Select Normal unless you are certain your hardware and software both support
EPP or ECP mode.
The options are: Normal, SPP, EPP, ECP, and ECP+EPP.
EPP Mode Select
The options are: EPP 1.7 and EPP 1.9
ECP Mode Use DMA
This field allows you to select a DMA channel for the port.
The options are: 1 and 3.
PWRON After PWR-Fail
The options are: Off, On, and Former-Sts
CIR Port Address [Disabled]
Select an address for the CIR port.
The options are: Disabled, 3F8, 2F8, 3E8, 2E8.
CIR Port IRQ
This setting field provides options for CIR Port IRQ when the CIR Port Address is
enabled and set at 3F8, 2F8, 3E8, or 2E8.
The options are: 11 and 5.
SCR Port Address [Disabled]
Select an address for the SCR port.
The options are: Disabled, 3E0, 2E0, 320, and 298.
SCR Port IRQ
This setting field provides options for SCR Port IRQ when the SCIR Port Address
is enabled and set at 3E0, 2E0, 320, or 298.
The options are: 11, 5, 3, and 4.
MS/SD Port Address [Disabled]
Select an address for the MS/SD port.
The options are: Disabled, 3E0, 2E0, 320, and 298.
MS/SD Port Mode
Choose to enable the port for use with MS or SD.
The options are: MS Socket and SD Socket.
MS/SD Port IRQ
This setting field provides options for MS/SD Port IRQ when the MS/SD Port
Address is enabled and set at 3E0, 2E0, 320, or 298.
The options are: 11, 5, 3, and 4.
25
Page 30

4.6 Power Management Setup
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
ACPI Function [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows this function if you use ACPI compliant OS, such as
Windows 98 or Windows 2000.
ACPI Suspend Type [S1(POS)]
Two options are available: S1 (POS) and S3 (STR). POS stands for Power On
Suspend. STR stands for Suspend To RAM.
Power Management [User Define]
This category allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving and is
directly related to the following modes:
There are 4 selections for Power Management, three of which have fixed mode
settings.
Disable (default) No power management. Disables all four modes
User Defined Allows you to set each mode individually. When not disabled,
Min. Power Saving Minimum power management. Doze Mode = 1 hr. Standby Mode
Max. Power Saving Maximum power management -- ONLY AVAILABLE FOR SL
Only Power Management field on the Power Management Setup menu is set to
User Defined will the following fields be user configurable.
each of the ranges are from 1 min. to 1 hr. except for HDD Power
Down which ranges from 1 min. to 15 min. and disable.
= 1 hr., Suspend Mode = 1 hr., and HDD Power Down = 15 min.
CPU’S. Doze Mode = 1 min., Standby Mode = 1 min., Suspend
Mode = 1 min., and HDD Power Down = 1 min.
26
Page 31

Video Off Method [DPMS]
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked:
Blank Screen: This option only writes blanks to the video buffer.
V/H SYNC+Blank: This selection will cause the system to turn off the vertical
and horizontal synchronization ports and write blanks to the
video buffer.
DPMS Supported: Select this option if your monitor supports the Display Power
Management Signaling (DPMS) standard of the Video
Electronics Standards.
Video Off In Suspend [Yes]
This setting item determines the manner in which the monitor is blacked.
Suspend Type [Stop Grant]
The default setting is Stop Grant.
MODEM Use IRQ [3]
Name the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to the modem (if any) on your
system. Activity of the selected IRQ always awakens the system.
Suspend Mode [Disabled]
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
HDD Power Down [Disabled]
This setting item will be able to change when Power Management is set to User
Define.
Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN [Instant-Off]
This item allows you to set the off function of power button by software control.
The options are: Instant-Off and Delay 4 Sec.
Wake-Up by PCI card [Disabled]
This setting item allows you to wake-up your system by PCI devices.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Power On by Ring [Enabled]
When you connect an external modem to the onboard serial port, the system can
be powered on by ring.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
USB KB Wake-Up From S3 (S4) [Disabled]
The default setting is Disabled.
27
Page 32

Resume by Alarm [Disabled]
Enable this item to set a date and time alarm that will automatically resume the
system from a software power down.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Date (of Month) Alarm [0]
Set a date from 0 to 31.
Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm [0 0 0]
Set a time for the alarm in hours, minutes, and seconds.
** Reload Global Timer Events **
Primary/Secondary IDE 0/1
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
FDD, COM, LPT Port
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
4.7 PnP/PCI Configurations
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
28
Page 33

The PCI, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect, was developed
primarily to address two important issues: (a) How to allow peripheral devices to
take the fullest advantage of the power of CPU technology, and (b) Provide a
simpler installation process for peripheral devices, such as Network cards, EIDE
or SCSI controllers.
PCI accomplishes these goals with its 32-bit Data path Local Bus design, and
support for Plug & Play. Unlike older expansion bus architectures, PCI provides
peripherals with a direct connection to the CPU and memory. The PCI bus runs at
33Mhz and has a maximum transfer capability of 132MBps. With Plug & Play, the
system BIOS automatically determines hardware resources for new peripherals,
simplifying installation of multiple interface cards.
This Setup Menu provides configuration options for the PCI Bus and its assigned
resources.
Reset Configuration Data [Disabled]
Disabled: Normal Setting
Enabled: Select Enabled to reset Extended System Configuration Data
(ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have installed a new add-on
and the system reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict
that the operating system cannot boot.
Resource Controlled By [Auto (ESCD)]
Manual: The field defines that the PNP Card's resource is controlled by
manual. You can setup whether IRQ-X or DMA-X is assigned to
PCI/ISA PnP or Legacy ISA Cards.
Auto: If your ISA card and PCI card are all PNP cards. Set this field to
"Auto". The BIOS will assign the interrupt resource automatically.
IRQ Resources [Press Enter]
Pressing Enter will take you to the IRQ Resources setup screen that allows you to
assign each IRQ to a device. When the resources are controlled manually,
pressing Enter will take you to the IRQ Resources setup screen that allows you to
assign each system interrupt as a PCI device or reserve the IRQ, depending on
the type of device using the interrupt:
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop [Disabled]
Selecting Enabled allows the BIOS to preview VGA Status, and to modify the
information delivered from the feature connector of the VGA card to the MPEG
card.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Assign IRQ for VGA [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows the BIOS to automatically assign an IRQ for the video
card.
29
Page 34

The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Assign IRQ for USB [Enabled]
Selecting Enabled allows the BIOS to automatically assign IRQ for USB devices.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
4.8 PC Health Status (O.T.S.)
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
This section helps you to get more information about your system including CPU
temperature, FAN speed and voltages. It is recommended that you contact with
your motherboard supplier to get proper value about your setting of the CPU
temperature.
30
Page 35

4.9 X-BIOS II < Over Clocking >
* The Item Help column contains the description of selected item.
CPU Clock Ratio [10X]
The options are: 10X, 11X, 12X,… 24X.
NOTE: This item is effective only when the clock-multiplier of the CPU is not locked.
Auto Detect PCI Clk [Disabled]
Enable or Disable the automatic detection of the PCI frequency clock.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
Spread Spectrum [Disabled]
When the system clock generator pulses, the extreme values of the pulse
generate excess EMI. Enabling pulse spectrum spread modulation changes the
extreme values from spikes to flat curves, thus reducing EMI. This benefit may in
some cases be outweighed by problems with timing-critical devices, such as a
clock-sensitive SCSI device. You can reduce EMI by setting this item to turn on
the clock signal with spread spectrum support.
The options are: Enabled and Disabled.
CPU Clock [100MHz]
For setting the CPU clock frequency. The options range from 100 to 250 MHz.
CPU Vcore Select [Default]
The options are: Default, and from 1.100V, to 1.850V at 0.025V increments.
AGP Slot Vddq [Default]
The options are: +0.1V, +0.2V, +0.3V, and Default.
31
Page 36

System Memory Vmem [Default]
The options are: +0.1V, +0.2V, +0.3V, and Default.
AGP Skew Adjust [Default]
The options are: Default, +250PS, +500PS, and +750PS.
PCI Skew Adjust [Default]
The options are: Default, and from –400PS to +1100PS at 100PS increments.
ICH Skew Adjust [Default]
The options are: Default, and from –400PS to +1100PS at 100PS increments.
4.10 Load Basic Defaults
The BASIC Defaults have been set to provide the minimum requirements for your
system to operate. Its performance is lower than the “Load Best Defaults”. We
suggest you use “Load Best Default”. If your system card has compatibility
issues, use the “Load Basic Defaults”.
4.11 Load Best Defaults
The “Load Best Defaults” function loads the system manufacture default data.
This is the default setting from Leadtek. This function will be necessary when the
system CMOS data is corrupted or you forget your settings.
4.12 Set Supervisor/User Password
Passwords can be set to provide protection for the BIOS configuration options, or
to restrict access to the computer itself.
When enabled, User Password will require all users to enter a password in order
to use the system, and/or enter the BIOS setup (but can’t change its contents). A
Supervisor Password is used to protect the stored CMOS options from being
changed by unauthorized users.
Keep in mind that when set, a password is required only when booting the
system. It will not provide protection to a system that is already booted.
The password check option is set in BIOS FEATURES SETUP by choosing either
System (the password prompt appears every time the system is powered on) or
Setup (the password prompt appears only when the user enters the BIOS Setup).
The password is stored in CMOS RAM, and can be cleared by removing the
battery for a while and then re-installing it back.
32
Page 37

To set a password:
You must first set the Supervisor password by choosing Supervisor Password
and pressing [ENTER]. Setup prompts for a password.
Enter a 1~8 character password using letters, numbers, or a combination of
both. The specific characters are not shown as you enter them. Press
[ENTER].
A confirmation box appears asking you to re-enter the password. Enter the
password again. Press [ENTER]. Follow the same procedure to set the User
Password.
To change a password:
Select the appropriate password option (Supervisor or User) from the main menu
and press [ENTER]. Enter the current password and press [Enter]. The screen
does not display the characters entered. Enter in the new password, then the
confirmation. You cannot change the current password unless you know it.
To erase a password:
If you know the current password, but want to disable password checking,
follow the procedure for changing the password. When the Setup prompts for
the new password, simply press [ENTER]. You will see a message indicating
that the password is disabled.
If you do not know the current password, you can clear the CMOS data by
removing the battery for a while and then re-installing it back (this will clear all
the user-defined BIOS).
4.13 Save & Exit Setup
The “SAVE & EXIT SETUP” option will bring you back to boot up procedure with
all the changes you just recorded in the CMOS RAM.
4.14 Exit Without Saving
The “EXIT WITHOUT SAVING” option will bring you back to normal boot up
procedure without saving any data into CMOS RAM, and will not destroy all the
old data in CMOS
33
.
Page 38

5. Driver Installation
5.1 Installing Chipset Driver
5.1.1 Windows 95/98/ME/2000
Step 4:
Step 5:
Insert the “WinFast Motherboard &
SCSI Software Pack CD” into the
CD-ROM drive.
The “Autorun” will be automatically
executed and the “WinFast
9600QSA P4I845D Setup” window
will appear on screen with
selectable menus.
Step 6:
Step 7:
Step 8:
Step 9:
34
Select and click on “Chipset Driver
Setup”.
A window asking you to choose the
setup language will appear. Check
“English” and click on “Next”.
A welcome window appears. Click
on “Next” to continue.
The software license agreement
window appears. Click on “Yes”.
Page 39

Step 10:
The content of the readme.txt file will be displayed on screen. Click
on ”Next”.
Step 11:
Once the installation is complete, you will be asked to restart Windows or
your computer. Click on “Finish” to restart your computer.
5.2 Installing Audio Driver
Step 1:
Insert the “WinFast Motherboard & SCSI Software Pack CD” into the
CD-ROM drive.
Step 2:
The “Autorun” will be automatically executed and the “WinFast 9600QSA
P4I845D Setup” window will appear on screen with selectable menus.
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 5:
Select and click on “Audio Driver Setup”.
Follow the on-screen instructions to finish the installation.
When all drivers and application software have been installed, please
shut down Windows and reboot your system for new drivers installation.
System will install device drivers automatically.
5.3 Installing LAN Driver
5.3.1 Under Windows 95/98
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Insert the “WinFast Software Pack
CD” into the CD-ROM drive.
“Autorun” will be automatically
executed and the “WinFast
P4I845D 9600QSA Setup” window
will be displayed. Close the
window.
Open the “Control Panel” window
by selecting “Setup” from the
“Start” menu.
Double click on “System”, and a
dialog box appears as shown in
the figure to the right. Click on the
“Device Manager” tab.
35
Page 40
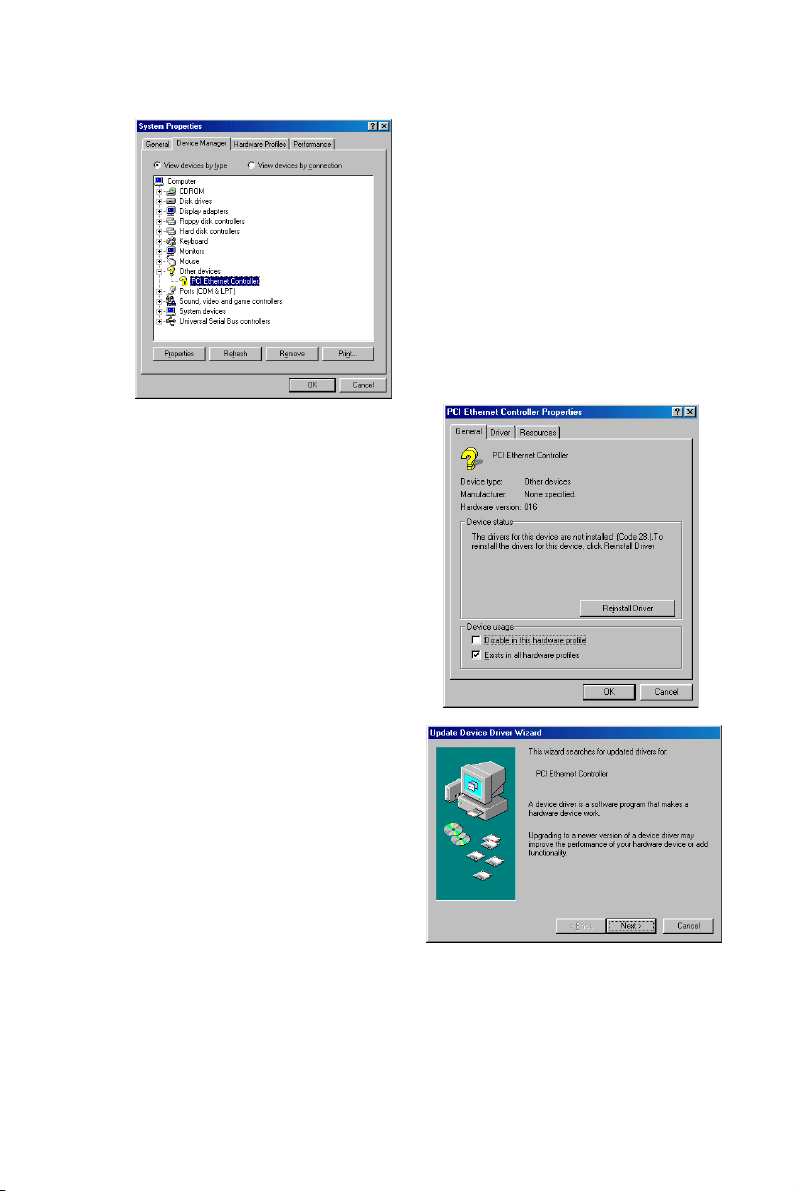
Step 6:
Double click on the “Other
Devices” option. The second level
of the list will be displayed and you
can see a list of unknown devices.
Double click on “PCI Ethernet
Controller".
Step 7:
Another dialog box appears as
shown in the figure to the right.
Click on the “Reinstall Driver”
button.
Step 8:
The “Update Device Driver
Wizard” dialog box pops up on the
screen as shown in the first figure
to the right, ready to guide you
through the installation.
Step 9:
The “Update Device Driver
Wizard” tells you, “This wizard
searches for updated driver for:
PCI Ethernet Controller,….” Click
“Next”.
Step 10:
Another dialog box appears with 2
installation options as shown in
the second figure to the right.
Select “Search for a better driver
than the one your device is using
now…” Then click “Next”.
Step 11:
The wizard will now ask you to
help him search for the driver.
Step 5:
Another dialog box appears
with a list of devices as the
figure to the left.
36
Page 41

Step 12:
Step 13:
(See the figure to the right) Select
“Specify a location” and type in the
field
“E:\Driver\Lan\Realtek\Rtl8139\La
n_inf\Win98”, or browse for it
(assuming E is the letter of your
CD-ROM drive). Then click “Next”.
The system will then search for
the device the driver is for. The
wizard will let you know when the
device is found. Click “Next” when
you see the dialog box as shown
below. The system is now
updating your driver.
When the updated driver is
installed successfully, the wizard
dialog box will tell you so as
shown in the figure below.
5.3.2 Under Windows NT 4.0
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 5:
37
Open the Control Panel, which is found in the Main program group of the
Program Manager.
Start the Network control panel item.
Select the "Add Adapter..." option. In the list that appears, scroll to the
bottom and select the option "<Other> Requires disk from manufacturer".
Click on "Continue".
Put the "WinFast Software Package CD" in your CD-ROM drive and
specify the path: "X:\Driver\Lan\Realtek\Rtl8139\Lan_inf\Winnt4" (X is the
letter of your CD-ROM drive), then click “OK”.
In the list that appears, double-click on "Realtek 8139 PCI Fast Ethernet
Page 42

Adapter".
Step 6:
In the dialog box that appears, select the Media Type and enter the
Network address for the adapter if necessary (You can click Help for
more detailed information about these settings). Click “OK” to complete
this dialog box (or “Cancel” to terminate the configuration without
completing it).
Step 7:
Exit the Network control panel window. Windows NT asks if you wish to
reboot. You must reboot before the adapter will function properly.
5.3.3 Under Windows ME/2000/XP
Windows ME/2000/XP users do not need to install the LAN driver as the LAN can be
detected by Windows ME/2000/XP and the built-in driver will be automatically installed.
5.4 Installing Speed Gear Utility
Step 1:
Put the software CD in the CD-ROM drive. The “WinFast P4I845D
9600QSA Setup” window will appear on screen.
Step 2
Step 2:
Step 3:
Click on “Install Speed gear Utility for Windows 95/98/ME”.
You have to choose a Setup language. Click “OK”.
Step 3
Step 4 Step 5
38
Page 43

Step 4:
Step 5:
The wizard will install Speed Gear. Click “Next”.
The installation is completed. Click “Finish”.
5.5 Installing DirectX 8
Step 1:
Put the software CD in the CD-ROM drive. The “WinFast P4I845D
9600QSA Setup” window will appear on screen.
Step 2:
Click on “Install DirectX 8.1”, and a dialog box will appear. Click on “Yes”
to continue.
Step 3:
Step 4:
The license agreement window appears. Click on “Yes”.
Once the installation is complete, you will be asked to restart your
machine. Click on “OK” to restart your computer.
5.6 Installing Acrobat Utility
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 5:
Put the software CD in the CD-ROM drive. The “WinFast P4I845D
9600QSA Setup” window will appear on the screen.
Click on “Install Acrobat Utility”, and a welcome window will appear. Click
on “Next” to continue.
The software license agreement window appears. Click on “Accept”.
A window will ask you to choose
the destination location. Click on
“Next”.
When the installation is complete,
a dialog box will appear. Click on
“OK”.
39
Page 44

6. Speed Gear Operation
Speed Gear is an over-clocking
tool developed by Leadtek,
which you can use to
conveniently adjust the speeds
of your CPU, memory, and
PCI. You can install Speed
Gear from the software CD.
Once it is installed, you can
double click the icon in the
system tray to bring up the
menu. The operation is
described below:
1. When this indicator is yellow, the changes are applied to every bootup. When it is
red, the setting changes only affect this boot session. You can click on the indicator
to switch between yellow and red.
2. The number shows the speed of CPU’s FSB. The default value is determined by the
value in the <<< X-BIOS II >>> setup screen in BIOS Setup.
3. The ID of the speed combination of CPU’s FSB, memory, and PCI as a group. There
are three groups: A, B, and C.
4. The number shows the speed of memory. This value changes in proportion to the
changes of CPU’s FSB.
5. <HM> button: Click to bring up a on-screen
control panel of four buttons as shown in
the first figure to the right.
<System Voltage>:
Clicking on the <System Voltage> button
brings up another control panel as shown in
the figure below.
There are three meters showing the current
Vcore, Vddq, and Vmem, each with a reading
on the bottom. There is a small yellow
triangle arrow below one of the meters. You
can click on the handle bar on the right and
hold the mouse button down to change the
voltage of the meter pointed at by the triangle.
If you wish to make changes to a different
meter, simply click on such a meter, then the
triangle will move under the meter you just
clicked on.
40
Page 45

<Temperature>:
Click on the <Temperature> button. There
will be an information box, as shown in the
first figure to the right, showing you the
current CPU Shutdown temperature, CPU
temperature and System temperature.
<Power Supply>:
Click on the <Power Supply> button. There
will be an information box, as shown in the
second figure to the right, showing you the
current power supply status.
<Fan Speed>
Click on the <Fan Speed> button. There will
be an information box, as shown in the third
figure to the right, showing you the current
CPU fan speed and system fan speed.
6. The power switch of the Speed Gear utility.
Click to close this application.
7. The speed of AGP bus. This value changes in
proportion to the change of CPU’s FSB.
8. The <help> button. Clicking here will bring
up a table as shown in the last figure to the
right. It shows the range of each group in
Freq/Volt Control
9. Click on the lever and pull it up or down to
increase or decrease the CPU’s FSB by 1
MHz at a time. When you pull the lever here
and hold down the mouse button, the speed
will keep on changing.
10. When the settings are confirmed, click here to
apply the setting.
11. Click here to restore the default value of the
CPU’s FSB and the related settings.
12. The speed of the CPU. This value is
generated by multiplying the value of CPU’s
FSB and the value of Ratio.
13. The Vcore of the CPU. This can only be
altered in <<< X-BIOS >>> menu.
14. As the clock-multiplier of the CPU is locked,
the CPU ratio cannot be changed.
15. The speed of PCI bus. This value changes in
proportion to the change of CPU’s FSB.
41
Page 46

Appendix
Appendix A. BIOS Flash Utility
If you get a new floppy disk or CD_ROM from your local dealer which contains a
new version of the BIOS binary file, or you obtain the new BIOS binary file directly
from our Web Site (www.leadtek.com.tw), please follow the steps below to update
the BIOS.
NOTE: Please contact your dealer first to see if you need to update your BIOS. If you
Step 1: Reboot into DOS or “Command Prompt Only” of Windows95/98
Step 2: Insert the accompany CD into CD-ROM (or floppy disk to Drive A)
Step 3: Copy “AWDFLASH.EXE” to a new directory from X:\FLASH sub-directory (X:
Step 4: Copy the new BIOS binary file to the above said new directory.
Step 5: Change to the new directory and type the following command:
Step 6: A message will display on your screen. Follow the instruction to update BIOS.
NOTE: Do not take any action before finishing the updating, otherwise you may
Step 7: You can also use “AWDFLASH /?” command for help messages.
NOTE: 1. It is recommended that the application is run under DOS prompt. Please do the
update BIOS without contacting your dealer, you might encounter problems and
are unable to start the computer.
being your CD-ROM drive).
AWDFLASH [Filename] ([Filename] means the file name of BIOS binary file)
encounter severe problems and need to have it sent for repair.
following to go to DOS prompt. Start your system. Press and hold Ctrl key before
Windows starts, and the Startup Menu will appear. Select the “Command Prompt
Only” option.
2. Windows users can update your BIOS in Windows by running the program,
winflash.exe, at X:\Flash (X: being your CD-ROM drive).
42
Page 47

Appendix B. Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures and flowchart to troubleshoot your system. If you
have followed all of the procedures below and still need assistance, refer to the
Technical Support Procedures and/or Returning Merchandise for Service
section(s) in this chapter.
Before Power On
Step 1: Make sure there is no short circuit between the motherboard and chassis.
Step 2: Disconnect all the ribbon/wire cables from the motherboard.
Step 3: Remove all the add-on cards except the video graphics card (Make sure the
Step 4: Install a CPU, the chassis speaker and the power LED to the motherboard (Check
Step 5: Install a memory module into one bank.
Step 6: Check the power supply voltage monitor 115V/230V switch.
No Power
Step 1: Make sure the default jumper is on and the CPU is correctly set up.
Step 2: Turn power switch on and off to test system.
Step 3: If still not power, turn it off and change the setting on JP26 to short 2-3 pins.
Step 4: If it does not help by moving the jumper setting, clear the CMOS data.
Step 5: Check the power supply voltage monitor, specifically, the power supply
No Video
Use the following steps for troubleshooting your system configuration.
Step 1: If the power is on but you have no video, remove all the add-on cards and cables.
Step 2: Check for shorted connections, especially under the motherboard.
Step 3: Check the jumpers’ settings, clock speed, and voltage settings.
Step 4: Use the speaker to determine if any beep codes exist.
Step 5: If you are a system integrator, VAR or OEM, a POST diagnostics card is
Memory Errors
If you encounter a memory error, follow the procedures below.
Step 1: Check to determine if the DIMM modules are improperly installed.
Step 2: Determine if different speeds of DIMMs have been installed and verify that the
Step 3: Check for bad DIMM modules or chips.
Losing the System Setup Configuration
Step 1: Check the jumper JP26 setting. Ensure that you are using a high quality power
Step 2: If you still cannot resolve the problem, contact your vendor for repairs.
video/graphics card is inserted properly).
all the jumper settings as well).
115V/230V switch.
recommended. For port 80h codes.
BIOS setup is configured for the fastest speed of RAM used. It is recommended to
use the same RAM speed for DIMMs in the system.
supply. A poor quality power supply may cause the system to lose the CMOS
setup information. Refer to Chapter 2 of this manual for details.
43
Page 48

Appendix C. Troubleshooting Flowchart
Power On
System
N
Power LED
On
Power
Supply OK?
Y
N
Replace Power
Supply
Y
Video
Display
N
Speaker
Beeps
N
Check Cable &
Jumper Settings
Y
System
Y
N
Hold
Check
BIOS Setting &
Add-on Card
N
Y
Mainboad Good
44
Remove Memory
Y
Speaker
Beeps
Check CPU &
BIOS
Y
Speaker
Beeps
Replace
Mainboard
N
N
Number of
Beeps
1long beep intervals
Memory Problem
Check Memory
Correct Setting &
Reboot OK
Y
Mainboard Good
1long 3 short beeps
Video Card
Problem
Page 49

Appendix D. Calling for Technical Support
In the event of not finding the solution for your problem, please contact our technical
support staff, or E-mail to <service@leadtek.com.tw>, with the following information:
Product name: It will be easier for our staff to answer your question if you know the
name of the product. The name of the product is displayed during system booting.
Software driver version: We are updating the version of utilities and drivers from time
to time, so it will be a great help for us to understand where the problem lies in. The
version number is printed on the diskette label.
Motherboard manufacturer, BIOS version and chipset: It is important to know who
manufactured your motherboard, which system BIOS are you using, and what types of
chipset are being used on your motherboard.
Computer type and speed: The type of processor you are using and its speed.
Monitor manufacturer and model: Please advise the type and supporting mode of the
monitor you are using.
Detailed description of your problem: Please describe in detail all the problems you
encountered, including the kind of software and hardware you are using, and the contents
of your system files.
Appendix E. FCC Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communi-cations. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
45
Page 50

Appendix F. Limited Warranty
Leadtek warrants to the original purchaser of this product that it shall be free of defects
resulting from workmanship or components for a period of one (1) year from the date of
sale. Defects covered by this Limited Warranty shall be corrected either by repair or, at
Leadtek’s discretion by replacement. In the event of replacement, the replacement unit
will be warranted for the remainder of the original one (1) year period or thirty (30) days,
whichever is longer.
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
This Limited Warranty is nontransferable and does not apply if the product has been
damaged by negligence, accident, abuse, misuse, modification, misapplication, shipment
to the Manufacturer or service by someone other than the Leadtek Transportation charges
to Leadtek are not covered by this Limited Warranty. To be eligible for warranty service, a
defective product must be sent to and received by Leadtek within fifteen (15) months of the date
of sale and be accompanied with proof of purchase. Leadtek does not warrant that this product
will meet your requirements; it is your sole responsibility to determine the suitability of this
product for your purposes. Leadtek does not warrant the compatibility of this product with
LEADTEK’S SOLE OBLIGATION AND LIABILITY UNDER THIS WARRANTY IS
LIMITED TO THE REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT OF A DEFECTIVE PRODUCT.
THE MANUFACTURER SHALL NOT, IN ANY EVENT, BE LIABLE TO THE
PURCHASER OR ANY THIRD PARTY FOR ANY INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LIABILITY IN TORT RELATING TO THIS
PRODUCT OR RESULTING FROM ITS USE OR POSSESSION.
This limited warranty is governed by the laws of Taiwan.
THERE ARE NO OTHER ORAL OR WRITTEN WARRANTIES,
.
your computer or related peripherals, software.
46
 Loading...
Loading...