Page 1

Document Title
A7130 Data Sheet, 2.4GHz FSK/GFSK Transceiver with 4Mbps data rate
Revision History
Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark
0.0 Initial issue. Dec, 2009 Objective
0.1 Update ch8 and the application circuit. July, 2011 Preliminary,
0.2 Modify the tape reel information and the add Shenzhen office
address.
0.3 Add Ch20 WOR and Ch21 AES128. Aug., 2011 Preliminary,
0.4 Add section 16.4.3 FIFO extension and Ch21 AES128.
Update sleep cur rent, Xtal start up time and PDL formula, TMOE
timing, WTR Timing, and Ch14.
0.5 Remove 3Mbps data rate
Add descriptions for HECF, FECF and CRCF clear method in 9.2.1
July, 2011 Preliminary,
Apr., 2012 Preliminary,,
Aug.,2012 Preliminary
LBA7130
0.6 Add suggestion in WOR function Oct. 2012 Preliminary
Important Notice:
AMICCOM reserves t he right t o make changes t o its produ cts or to discontinue any integrated circuit product or se rvice
without notice. AMICCOM integrated circuit products are not designed, intended, authorized, or warranted to be suitable for
use in life-support a pplications, de vices o r sys tems or ot her critical ap plications. Use of AM ICCOM products in such
applications is understood to be fully at the risk of the customer.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 1 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 2

LBA7130
Table of Contents
1. General Description....................................................................................................................................................... 5
2. Typical Applications ....................................................................................................................................................... 5
3. Feature......................................................................................................................................................................... 5
4. Pin Configurations......................................................................................................................................................... 6
5. Pin Description (I: input; O: output, I/O: input or output)................................................................................................... 7
6. Chip Block Diagram....................................................................................................................................................... 8
7. Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................................................................................................ 9
8. Electrical Specification..................................................................................................................................................10
9. Control Register ...........................................................................................................................................................12
9.1 Control register table............................................................................................................................................12
9.2 Control register description ..................................................................................................................................15
9.2.1 Mode Register (Address: 00h)....................................................................................................................15
9.2.2 Mode Control Register (Address: 01h)......................................................................................................15
9.2.3 Calibration Control Register (Address: 02h)..............................................................................................16
9.2.4 FIFO Register I (Address: 03h).................................................................................................................16
9.2.5 FIFO Register II (Address: 04h)................................................................................................................16
9.2.6 FIFO DATA Register (Address: 05h) .........................................................................................................16
9.2.7 ID DATA Register (Address: 06h)................................................................................................................16
9.2.8 RC OSC Register I (Address: 07h) .............................................................................................................17
9.2.9 RC OSC Register II (Address: 08h).............................................................................................................17
9.2.10 RC OSC Register III (Address: 09h)..........................................................................................................17
9.2.11 CKO Pin Control Register (Address: 0Ah) .................................................................................................17
9.2.12 GIO1 Pin Control Register I (Address: 0Bh)...............................................................................................18
9.2.13 GIO2 Pin Control Register II (Address: 0Ch) .............................................................................................20
9.2.14 Clock Register (Address: 0Dh)..................................................................................................................21
9.2.15 PLL Register I (Address: 0Eh)...................................................................................................................21
9.2.16 PLL Register II (Address: 0Fh)..................................................................................................................21
9.2.17 PLL Register III (Address: 10h).................................................................................................................22
9.2.18 PLL Register IV (Address: 11h).................................................................................................................22
9.2.19 PLL Register V (Address: 12h)...............................................................................................................22
9.2.20 Channel Group Register I (Address: 13h)..................................................................................................22
9.2.21 Channel Group Register II (Address: 14h).................................................................................................22
9.2.22 TX Register I (Address: 15h).....................................................................................................................23
9.2.23 TX Register II (Address: 16h)....................................................................................................................23
9.2.24 Delay Register I (Address: 17h)................................................................................................................23
9.2.25 Delay Register II (Address: 18h) ...............................................................................................................24
9.2.26 RX Register (Address: 19h)......................................................................................................................24
9.2.27 RX Gain Register I (Address: 1Ah)............................................................................................................25
9.2.28 RX Gain Register II (Address: 1Bh)...........................................................................................................25
9.2.29 RX Gain Register III (Address: 1Ch) .........................................................................................................25
9.2.30 RX Gain Register IV (Address: 1Dh).........................................................................................................26
9.2.31 RSSI Threshold Register (Address: 1Eh) ..................................................................................................26
9.2.32 ADC Control Register (Address: 1Fh)........................................................................................................26
9.2.33 Code Register I (Address: 20h).................................................................................................................26
9.2.34 Code Register II (Address: 21h)................................................................................................................27
9.2.35 Code Register III (Address: 22h)...............................................................................................................27
9.2.36 IF Calibration Register I (Address: 23h).....................................................................................................27
9.2.37 IF Calibration Register II (Address: 24h)....................................................................................................28
9.2.38 VCO current Calibration Register (Address: 25h).......................................................................................28
9.2.39 VCO band Calibration Register I (Address: 26h)........................................................................................28
9.2.40 VCO band Calibration Register II (Address: 27h).......................................................................................29
9.2.41 VCO Deviation Calibration Register I (Address: 28h).................................................................................29
9.2.42 VCO Deviation Calibration Register II (Address: 29h)................................................................................29
9.2.43 DASP0 (Address: 2Ah, Page 0 by AGT [3:0]=0) ........................................................................................30
9.2.43 DASP1 (Address: 2Ah, Page 1 by AGT[3:0]=1) .........................................................................................30
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 2 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 3

LBA7130
9.2.43 DASP2 (Address: 2Ah, Page 2 by AGT[3:0]=2) .........................................................................................30
9.2.43 DASP3 (Address: 2Ah, Page 3 by AGT[3:0]=3) .........................................................................................31
9.2.43 DASP4 (Address: 2Ah, Page 4 by AGT[3:0]=4) .........................................................................................31
9.2.43 DASP5 (Address: 2Ah, Page 5 by AGT[3:0]=5) .........................................................................................31
9.2.43 DASP6 (Address: 2Ah, Page 6 by AGT[3:0]=6) .........................................................................................31
9.2.43 DASP7 (Address: 2Ah, Page 7 by AGT[3:0]=7) .........................................................................................31
9.2.44 VCO Modulation Delay Register (Address: 2Bh)........................................................................................31
9.2.45 Battery detect Register (Address: 2Ch).....................................................................................................32
9.2.46 TX test Register (Address: 2Dh) ...............................................................................................................32
9.2.47 Rx DEM test Register I (Address: 2Eh) .....................................................................................................32
9.2.48 Rx DEM test Register II (Address: 2Fh).....................................................................................................33
9.2.49 Charge Pump Current Register I (Address: 30h) .......................................................................................33
9.2.50 Charge Pump Current Register II (Address: 31h).......................................................................................33
9.2.51 Crystal test Register (Address: 32h)..........................................................................................................33
9.2.52 PLL test Register (Address:33h) ...............................................................................................................34
9.2.53 VCO test Register I (Address:34h)............................................................................................................34
9.2.54 RF Analog Test Register (Address: 35h)....................................................................................................34
9.2.55 AES Key data Register (Address: 36h)......................................................................................................35
9.2.56 Channel Select Register (Address: 37h)....................................................................................................35
9.2.57 ROMP0 (Address: 38h, Page 0 by AGT[3:0]=0).........................................................................................35
9.2.57 ROMP1 (Address: 38h, Page 1 by AGT[3:0]=1).........................................................................................35
9.2.57 ROMP2 (Address: 38h, Page 2 by AGT[3:0]=2).........................................................................................36
9.2.57 ROMP3 (Address: 38h, Page 3 by AGT[3:0]=3).........................................................................................36
9.2.57 ROMP4 (Address: 38h, Page 4 by AGT[3:0]=4).........................................................................................36
9.2.58 Data Rate Clock Register (Address: 39h)..................................................................................................36
9.2.59 FCR Register (Address: 3Ah) ...................................................................................................................36
9.2.60 ARD Register (Address: 3Bh) ...................................................................................................................37
9.2.61 AFEP Register (Address: 3Ch)..................................................................................................................37
9.2.62 FCB Register (Address: 3Dh) ...................................................................................................................37
9.2.63 KEYC Register (Address: 3Eh).................................................................................................................38
9.2.64 USID Register (Address: 3Fh) ..................................................................................................................38
10. SPI.............................................................................................................................................................................39
10.1 SPI Format........................................................................................................................................................40
10.2 SPI Timing Characteristic...................................................................................................................................40
10.3 SPI Timing Chart................................................................................................................................................41
10.3.1 Timing Chart of 3-wire SPI........................................................................................................................41
10.3.2 Timing Chart of 4-wire SPI........................................................................................................................41
10.4 Strobe Commands .............................................................................................................................................42
10.4.1 Strobe Command - Sleep Mode................................................................................................................42
10.4.2 Strobe Command - ldle Mode ...................................................................................................................42
10.4.3 Strobe Command - Standby Mode ............................................................................................................43
10.4.4 Strobe Command - PLL Mode...................................................................................................................43
10.4.5 Strobe Command - RX Mode....................................................................................................................44
10.4.6 Strobe Command - TX Mode ....................................................................................................................44
10.4.7 Strobe Command – FIFO Write Pointer Reset...........................................................................................44
10.4.8 Strobe Command – FIFO Read Pointer Reset...........................................................................................45
10.4.9 Strobe Command – Deep Sleep Mode ......................................................................................................45
10.5 Reset Command................................................................................................................................................46
10.6 ID Accessing Command.....................................................................................................................................46
10.6.1 ID Write Command...................................................................................................................................46
10.6.2 ID Read Command ..................................................................................................................................47
10.7 FIFO Accessing Command.................................................................................................................................47
10.7.1 TX FIFO Write Command .........................................................................................................................47
10.7.2 Rx FIFO Read Command.........................................................................................................................48
11. State machine.............................................................................................................................................................49
11.1 Key states..........................................................................................................................................................49
11.2 FIFO mode ........................................................................................................................................................50
11.3 Direct mode .......................................................................................................................................................51
12. Crystal Oscillator ........................................................................................................................................................54
12.1 Use External Crystal ..........................................................................................................................................54
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 3 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 4

LBA7130
12.2 Use External Clock ............................................................................................................................................54
13. System Clock.............................................................................................................................................................55
13.2 Data Rate Setting ..............................................................................................................................................55
14. Transceiver LO Frequency..........................................................................................................................................56
14.1 LO Frequency Setting........................................................................................................................................56
14.2 IF Side Band Select ...........................................................................................................................................57
14.2.1 Auto IF Exchange.....................................................................................................................................58
14.2.2 Fast Exchange.........................................................................................................................................59
14.3 Auto Frequency Compensation...........................................................................................................................60
15. Calibration..................................................................................................................................................................60
15.1 Calibration Procedure ........................................................................................................................................60
16. FIFO (First In First Out)...............................................................................................................................................61
16.1 TX Packet Format in FIFO mode........................................................................................................................61
16.1.1 Basic FIFO mode.....................................................................................................................................61
16.1.2 Advanced FIFO mode...............................................................................................................................61
16.2 Bit Stream Process in FIFO mode.......................................................................................................................62
16.3 Transmission Time.............................................................................................................................................63
16.4 Usage of TX and RX FIFO .................................................................................................................................63
16.4.1 Easy FIFO ...............................................................................................................................................64
16.4.2 Segment FIFO .........................................................................................................................................65
16.4.3 FIFO Extension........................................................................................................................................67
17. ADC (Analog to Digital Converter)...............................................................................................................................71
17.1 RSSI Measurement............................................................................................................................................71
18. Battery Detect ............................................................................................................................................................73
19. Auto-ack and auto-resend...........................................................................................................................................74
19.1 Basic FIFO plus auto-ack auto-resend................................................................................................................74
19.2 Advanced FIFO plus auto-ack and auto-resend...................................................................................................74
19.3 WTR Behavior during auto-ack and auto-resend.................................................................................................76
19.6 Examples of auto-ack and auto-resend...............................................................................................................77
20. RC Oscillator..............................................................................................................................................................79
20.1 WOR Function...................................................................................................................................................79
20.2 TWOR Function.................................................................................................................................................80
21. AES128 Security Packet .............................................................................................................................................80
22. Application circuit........................................................................................................................................................81
22.1 MD7130-A01 .....................................................................................................................................................81
22.2 MD7130-F07 .....................................................................................................................................................82
23. Abbreviations..............................................................................................................................................................83
24. Ordering Information...................................................................................................................................................83
25. Package Information...................................................................................................................................................84
26. Top Marking Information..............................................................................................................................................85
27. Reflow Profile.............................................................................................................................................................86
28. Tape Reel Information.................................................................................................................................................87
29. Product Status............................................................................................................................................................89
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 4 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 5

LBA7130
1. General Description
A7130 is a high performance and low cost 2.4GHz ISM band wireless transceiver. This device integrates both high sensitivity
receiver (- 88dBm @4Mbps) and programmable power amplifier 5dBm. Based on Data Rate Register (39h), user can
configure on-air data rates to 4Mbps.
A7130 supports fast settling time (90 us) for frequency hopping system. For packet handling, A7130 has b uilt-in separated
64-bytes TX/ RX FIFO (could be logically extended t o 4K b ytes) for da ta buffering and bu rst trans mission, aut o-ack a nd
auto-resend, CRC for error packet filtering, FEC for 1-bit data correction per code word, RSSI for clear channel assessment,
therm al sensor for monitoring relative temperature, WOR (Wake on R X) function to support periodically wake up from sleep
mode to RX mode and listen for incoming packets without MCU interaction, data whitening for data encryption / decryption. In
addition, A7130 ha s bu ilt-in AES128 co -processor (Adva nced Encr yption St andard) for advan ced dat a e ncryption and
decryption which consists of the transformation of a 128-bit block into an encrypted 128-bit block. Those functions are very
easy to use while developing a wireless system. All features are integrated in a small QFN 4X4 20 pins package.
A7130’s control registers ar e a ccessed via 3- wire o r 4-wire S PI interface s uch as TX/RF FIFO, ID r egister, RSSI value,
frequency hopping to chip calibration procedures. Another one, via SPI as well, is the unique Strobe command, A7130 can
be cont rolled f rom power sav ing mode (deep s leep, sleep, idle , standby ), PLL mode, TX mode and R X mode. The o ther
connections between A7130 and MCU are GIO1 and GIO2 (multi-function GPIO) to output A7130’s status so that MCU could
use either polling or int errupt scheme for radio cont rol. Ove rall, this de vice is very easy-to-use for de veloping a w ireless
application with a MCU.
2. Typical Applications
n 2.4GHz video baby monitor
n 2.4GHz PC peripherals
n HiFi quality wireless audio streaming
n 2408 ~ 2468 MHz ISM system
n Wireless metering and building automation
n Wireless toys and game controllers
3. Feature
n Small size (QFN4 X4, 20 pins).
n Frequency band: 2408 ~ 2468MHz.
n FSK or GFSK modulation
n Low current consumption: RX 27mA (4Mbps), TX 29mA (at 5dBm output power).
n Deep sleep current (0.1 uA).
n Sleep current (2.5 uA).
n On chip regulator, support input voltage 2.0 ~ 3.6 V.
n Data rate 4Mbps.
n Programmable TX power level from 5 dBm.
n Ultra High sensitivity:
u -88dBm at 4Mbps on-air data rate.
n Fast settling time (90 us) synthesizer for frequency hopping system.
n On chip low power RC oscillator for WOR (Wake on RX) function.
n Built-in AES128 co-processor
n AGC (Auto Gain Control) for the wide RSSI dynamic range.
n AFC (Auto Frequency Compensation) for frequency drift due to temperature.
n Support low cost crystal (16 / 18 MHz).
n Low Battery Detector indication.
n Easy to use.
u Support 3-wire or 4-wire SPI.
u Unique Strobe command via SPI.
u ONE register setting for new channel frequency.
u CRC Error Packet Filtering.
u Auto-acknowledgement and auto-resend.
u Dynamic FIFO length.
u 8-bits RSSI measurement for clear channel indication.
u Auto Calibrations.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 5 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 6
u Auto IF function.
u Auto FEC by (7, 4) Hamming code (1 bit error correction / code word).
u Separated 64 bytes RX and TX FIFO.
u Easy FIFO / Segment FIFO / FIFO Extension (up to 4K bytes).
u Support FIFO mode frame sync to MCU.
u Support direct mode with recovery clock output to MCU.
4. Pin Configurations
VDD_A
REGI
CKO
GIO2
LBA7130
GIO1
19
RSSI
BP_BG
RFI
RFO
RFC
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
CP
V_VCO
Fig 4-1. A7130 QFN 4x4 Package Top View
17
18
8
9
XI
V_PLL
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
XO
GND
SDIO
VDD_D
SCK
SCS
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 6 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 7
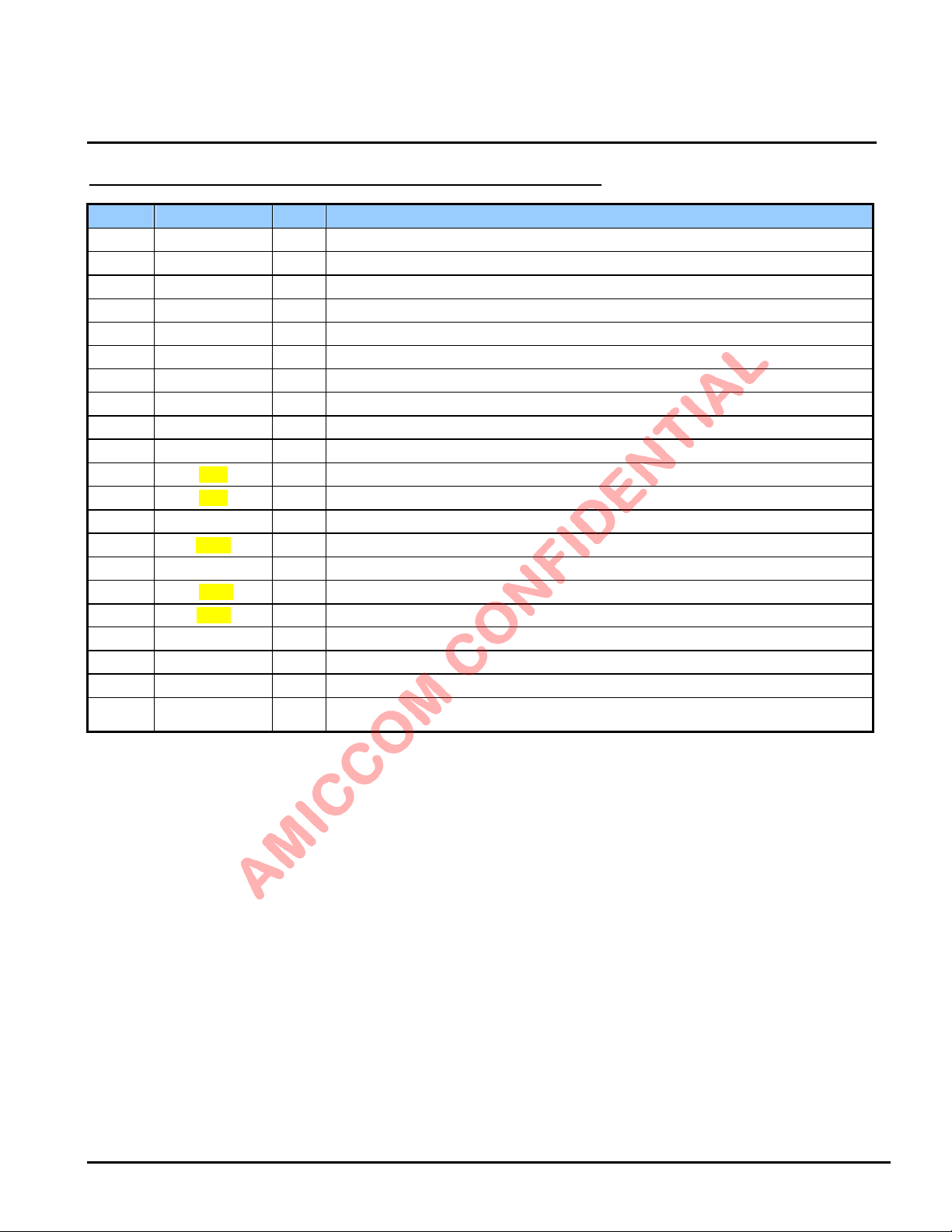
5. Pin Description (I: input; O: output, I/O: input or output)
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function Description
1 RSSI O Connected to a bypass capacitor for RSSI.
2 BP_BG O Connected to a bypass capacitor for internal Regulator bias point.
3 RFI I LNA input. Connected to matching circuit.
4 RFO O PA input. Connected to matching circuit.
5 RFC I RF Choke input. Connected to matching circuit.
6 V_VCO I VCO supply voltage input.
7 CP O Charge-pump. Connected to loop filter.
8 V_PLL I PLL supply voltage input.
9 XI I Crystal oscillator input.
10 XO O Crystal oscillator output.
11 SCS I SPI chip select.
12 SCK I SPI clock input pin.
13 VDD_D I Connected to a bypass capacitor to supply voltage for digital part.
14 SDIO I/O SPI read/write data.
15 GND G G round
16 GIO1 I/O Multi-function GIO1 / 4-wire SPI data output.
17 GIO2 I/O Multi-function GIO2 / 4-wire SPI data output.
18 CKO O
19 REGI I Regulator input (External Power Input)
20 VDD_A O
Back side plate G
Multi-function clock output.
Internal Regulator output to supply V_VCO (pin 6), V_PLL (pin 8) and RFC (pin 5).
Ground.
Back side plate shall be well-solder to ground; otherwise, it will impact RF performance.
LBA7130
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 7 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 8
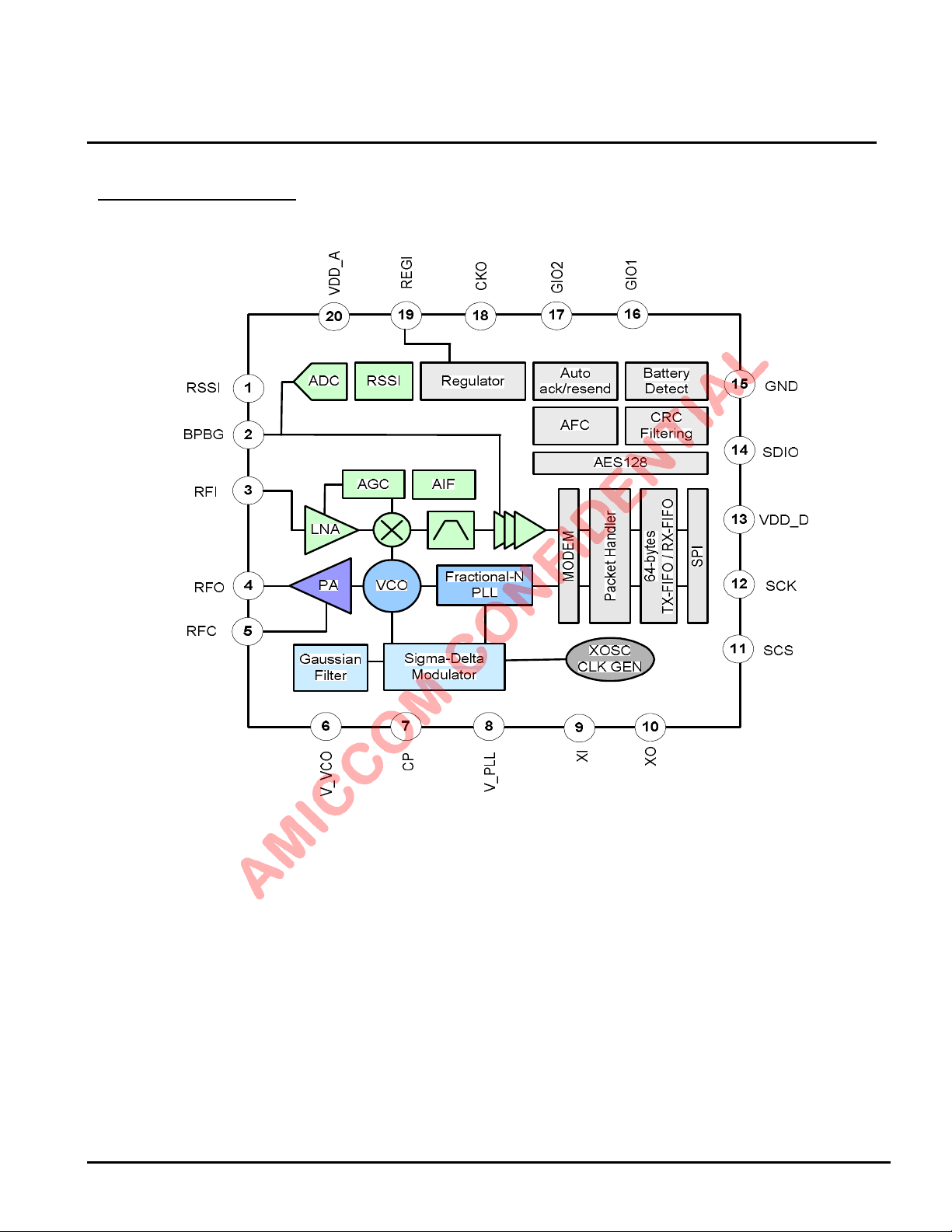
6. Chip Block Diagram
LBA7130
Fig 6-1. A7130 Block Diagram
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 8 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 9
LBA7130
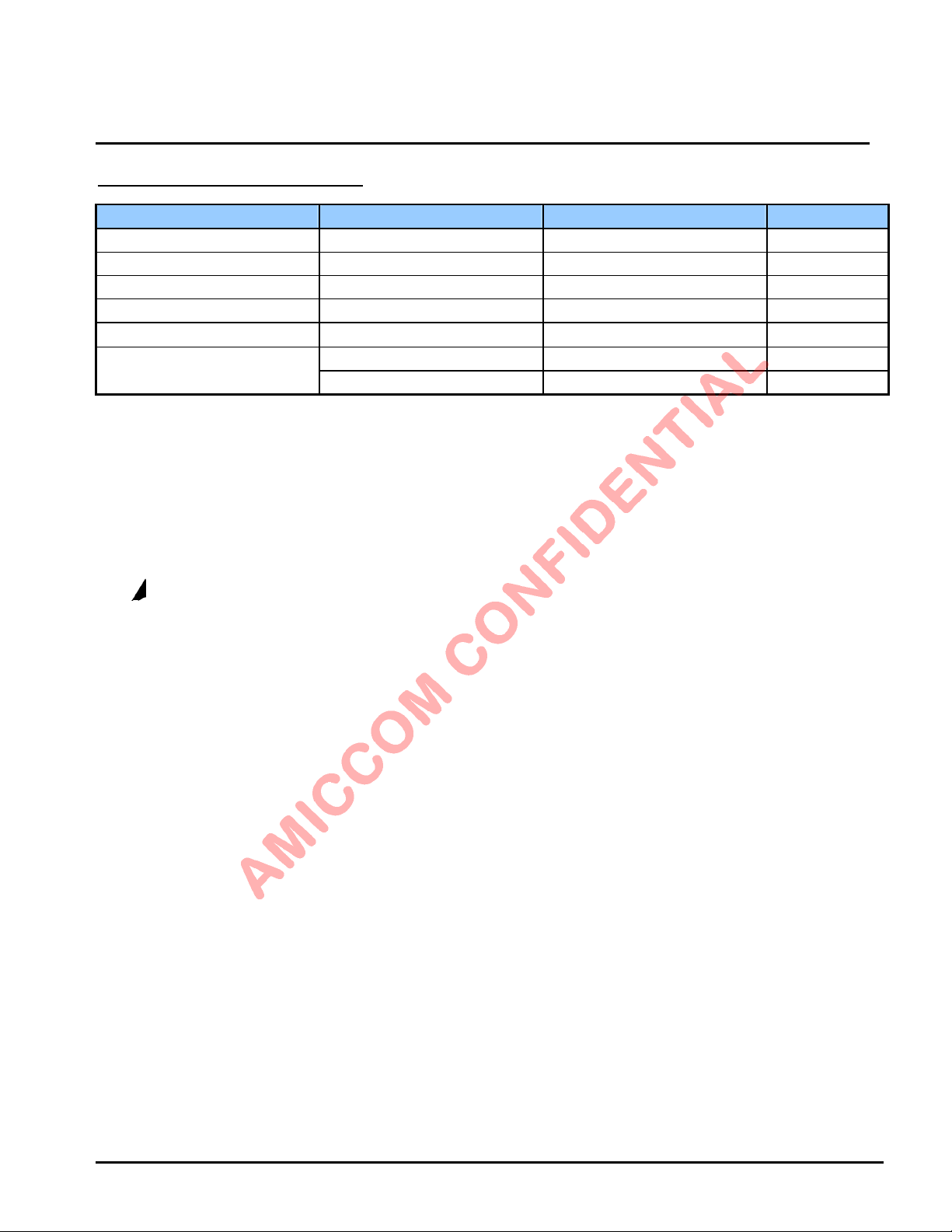
7. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter With respect to Rating Unit
Supply voltage range (VDD) GND -0.3 ~ 3.6 V
Digital IO pins range GND -0.3 ~ VDD+0.3 V
Voltage on the analog pins range GND -0.3 ~ 2.1 V
Input RF level 10 dBm
Storage Temperature range -55 ~ 125
HBM ± 2K VESD Rating
MM ± 100 V
*Stresses above those listed unde r “Absolute M aximum Rating” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are
stress ratings only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
*Device is ESD sensitive. Use appropriate ESD precautions. HBM (Human Body Mode) is tested under MIL-STD-883F
Method 3015.7. MM (Machine Mode) is tested under JEDEC EIA/JESD22-A115-A.
*Device is Moisture Sensitivity Level III (MSL 3).
°C
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 9 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 10
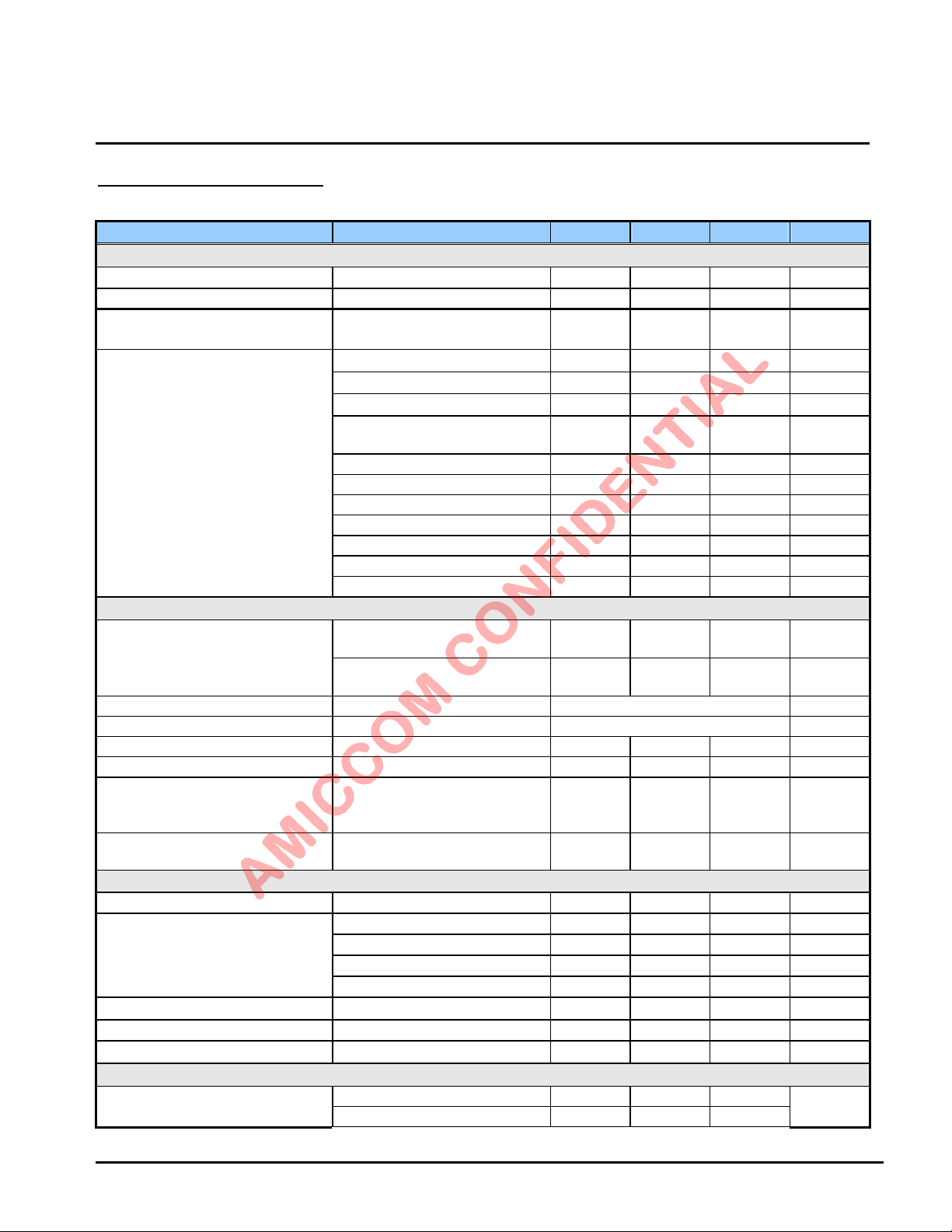
8. Electrical Specification
LBA7130
(Ta=25℃, VDD=3.3V, F
=16MHz, with Match circuit and low pass filter, On Chip Regulator = 1.8V, unless otherwis e noted.)
XTAL
Parameter Description Min. Type Max. Unit
General
Operating Temperature -40 85
Supply Voltage (VDD) with internal regulator 2.0 3.3 3.6 V
Current Consumption
Deep Sleep mode*
1
0.1
(No registers retention)
Current Consumption
(DBL =0 at 0Fh, bit7)
Sleep mode (WOR off) *
Sleep mode (WOR on) *
1
1
Idle Mode (Regulator on) *
Standby Mode
1
2.5
3.5
0.3 mA
2.7 mA
(XOSC on, CLK Gen. on)
PLL mode 12.5 mA
RX Mode (4Mbps) 27 mA
TX Mode (5dBm) 29 mA
TX Mode (3dBm) 24 mA
TX Mode (0dBm) 20 mA
TX Mode ( -5dBm) 18 mA
TX Mode ( -17dBm) 16 mA
°C
mA
mA
mA
PLL block
Crystal start up time*
(3225 SMD type)
2
Crystal frequency Data rate: 4Mbps 16 MHz
Crystal tolerance Data rate: 4M/bps ±50 ppm
Crystal ESR 80 ohm
VCO Operation Frequency 2408 2468 MHz
PLL phase noise Offset 10k
PLL settling time*
3
Idle to standby
(Xtal osc. is stable at 20ppm)
Idle to standby
(Xtal osc. is stable at 10ppm)
Offset 500K
Offset 1M
Loop filter based on app. circuit.
(Standby to PLL)
1 ms
2 ms
75
90
100
30
dBc
mS
Transmitter
Output power range -17 0 5 dBm
Out Band Spurious Emission *
Frequency deviation*
Data rate 4M bps
TX ready time*
6
4
30MHz~1GHz -36
1GHz~12.75GHz -30
1.8GHz~ 1.9GHz -47
5.15GHz~ 5.3GHz -47
5
Data rate 4Mbps
Standby to TX
±1M
90
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
Hz
mS
Receiver
dBm
@ BER = 0.1%
Data rate 4Mbps -88Receiver sensitivity
Data rate 4Mbps (GFSK) -85
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 10 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 11
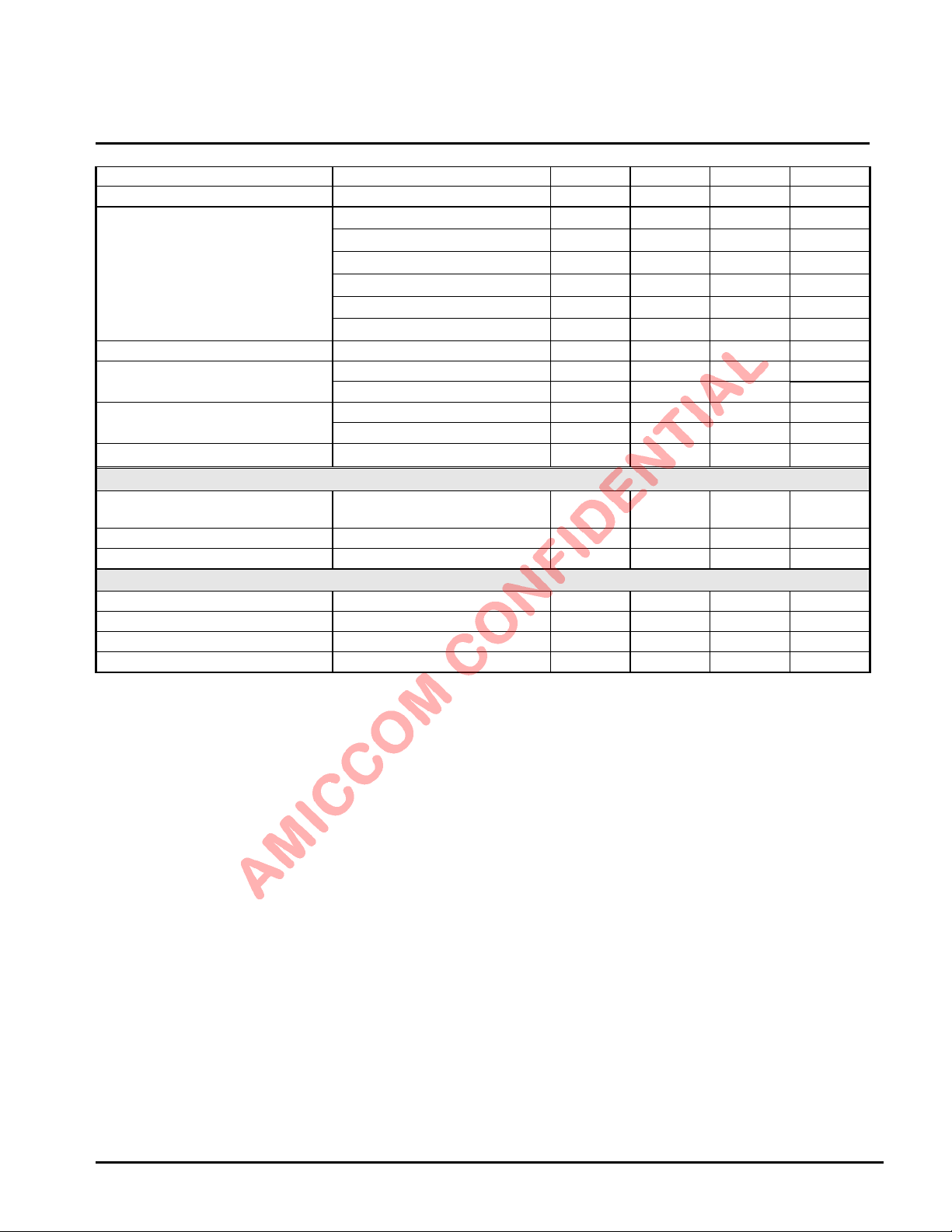
LBA7130
IF Filter bandwidth IFS = [11], 4Mbps 4.8M Hz
IF center frequency IFS = [11], 4Mbps 4M Hz
Interference *
(4Mbps , IF = 4MHz)
Maximum Operating Input Power @RF input (BER=0.1%) 5 dBm
RX Spurious Emission *
RX Ready Time 80
Regulator
Regulator settling time Pin 2 connected to 470pF.
Band-gap reference voltage 1.28 V
Regulator output voltage 1.79 1.8 2.3 V
Digital IO DC characteristics
High Level Input Voltage (VIH) 0.8*VDD VDD V
Low Level Input Voltage (VIL) 0 0.2*VDD V
High Level Output Voltage (VOH) @IOH= -0.5mA VDD-0.4 VDD V
Low Level Output Voltage (VOL) @IOL= 0.5mA 0 0.4 V
7
4
(Sleep to idle).
Co-Channel (C/I0) 11 dB
±4MHz Adjacent Channel
±8MHz Adjacent Channel
±12MHz Adjacent Channel
±16MHz Adjacent Channel
Image (C/IIM) - 10 dB
30MHz~1GHz -57 dBm
1GHz~12.75GHz -47
AGC = 0 -95 -50 dBmRSSI Range
AGC = 1 -95 -20 dBm
0 dB
- 10 dB
- 20 dB
- 30 dB
0.5 ms
ms
Note 1: When digital I/O pins are configured as input, those pins shall NOT be floating but pull either high or low (SCS shall
be pulled high only); otherwise, leakage current will be induced.
Note 2: Xtal settling time is depend on Xtal package type, Xtal ESR and Xtal Cm.
Note 3: Refer to Delay Register I (17h) to set PDL (PLL settling delay).
Note 4: With external RF filter that provides minimum 17dB of attenuation in the band: 30MHz ~ 2GHz and 3GHz ~12.75GHz.
Note 5: Refer to TX Register II (16h) to set FD [7:0].
Note 6: Refer to Delay Register I (17h) to set PDL and TDL.
Note 7: The wanted signal is set above sensitivity level +3dB. The modulation data of wanted signal and interferer
are PN9 and PN15, respectively.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 11 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 12
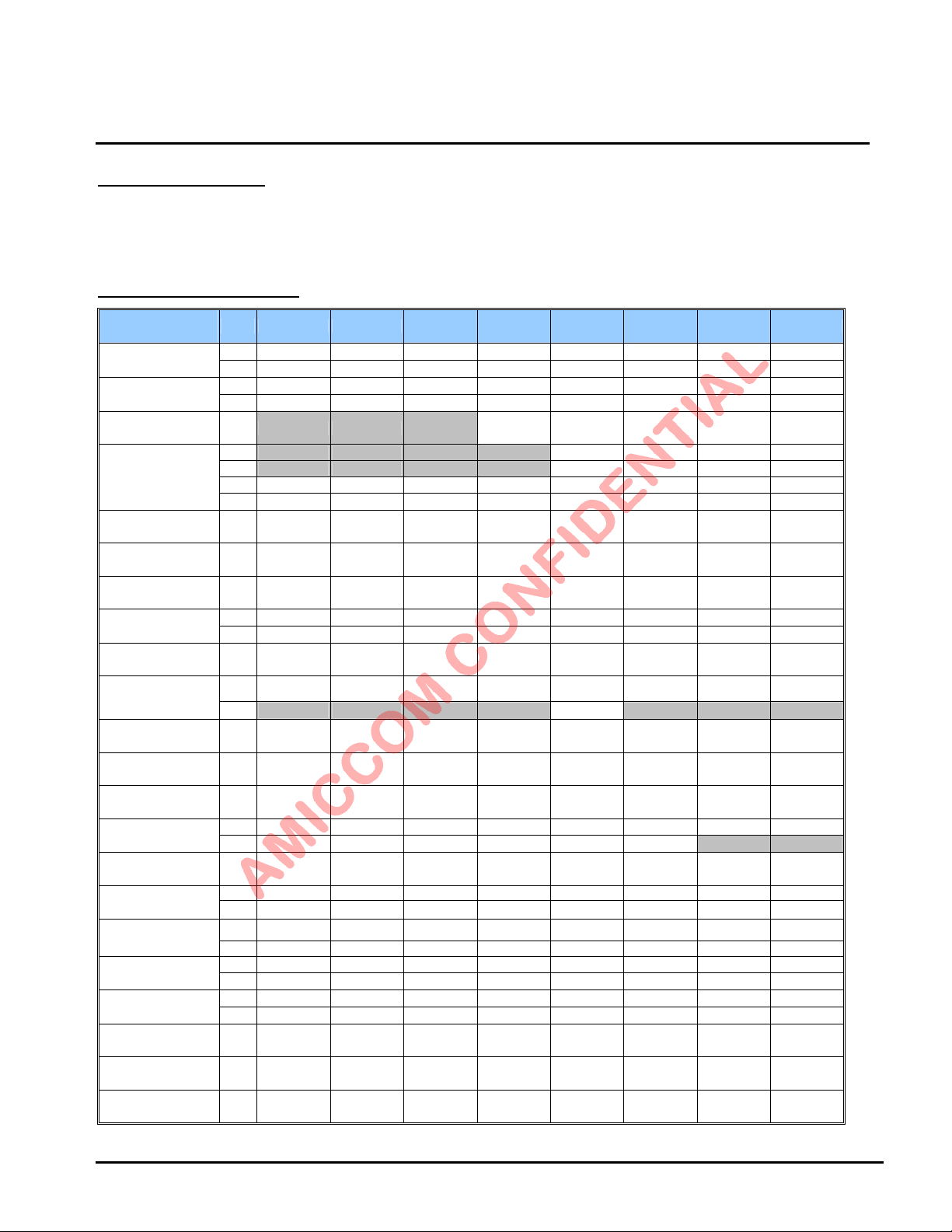
LBA7130
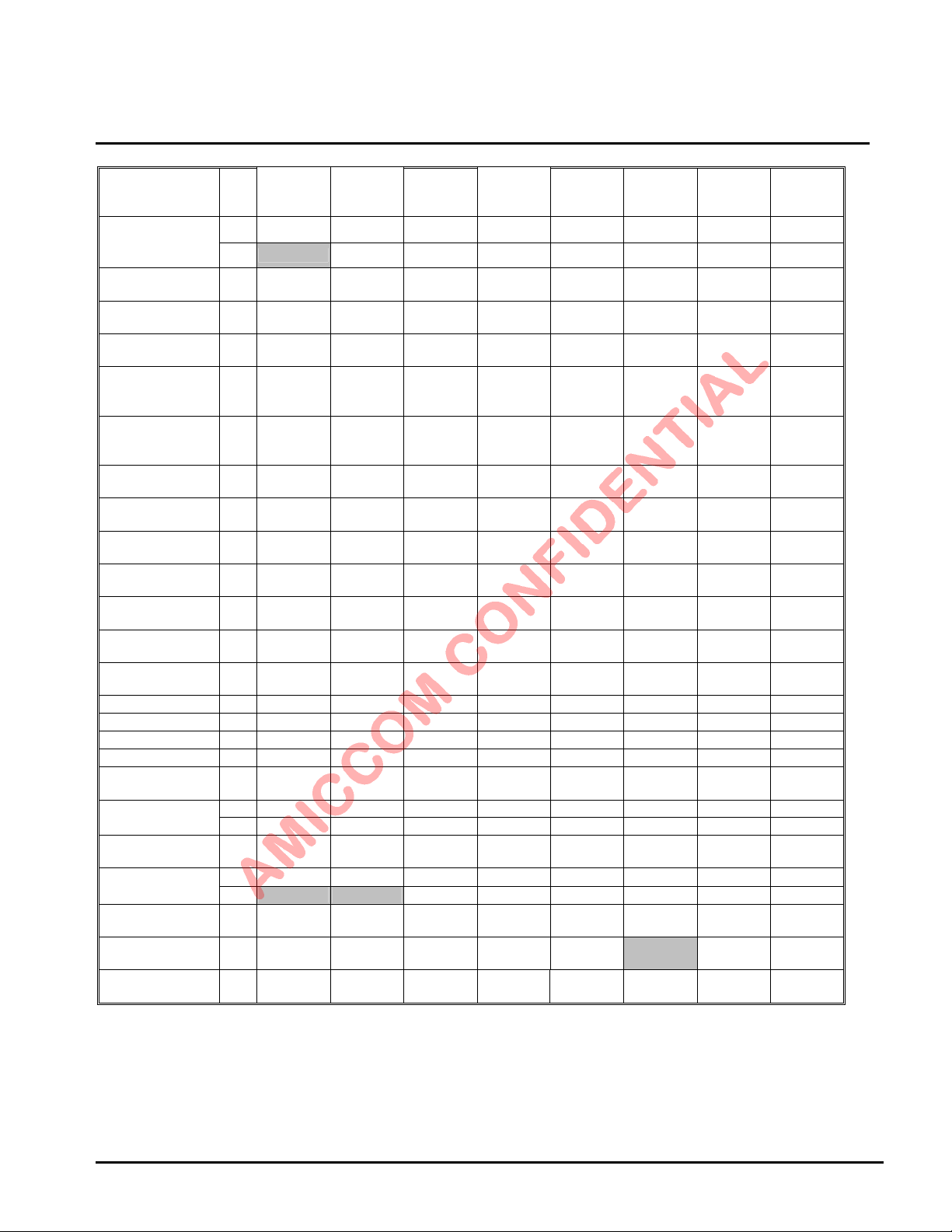
9. Control Register
A7130 contains 69 control registers. MCU can access those control registers via 3-wire (SCS, SCK, SDIO) or 4-wire (SCS,
SCK, SDIO, GIO1/GIO2) SPI interface (max. 15 Mbps). Please refer to Chapter 10 for SPI timing. In general, most of control
registers are just need to configure the recommended values based on A7130 reference code.
9.1 Control register table
Address /
Name
Mode
01h
Mode control
02h
Calc
03h
FIFO I
04h
FIFO II
05h
FIFO Data
06h
ID Data
07h
RC OSC I
08h
RC OSC II
09h
RC OSC III
0Ah
CKO Pin
0Bh
GPIO1 Pin I
0Ch
GPIO2 Pin II
0Dh
Clock
0Eh
PLL I
0Fh
PLL II
10h
PLL III
11h
PLL IV
12h
PLL V
13h
Channel Group I
14h
Channel Group II
15h
TX I
R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
W RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN00h
R HECF FECF CRCF CER XER PLLER TRSR TRER
W DDPC ARSSI AIF DFCD WORE FMT FMS ADCM
R DDPC ARSSI AIF CD WORE FMT FMS ADCM
R/W
W -- -- -- -- FEP11 FEP10 FEP9 FEP8
R -- -- -- -- LENF11 LENF10 LENF9 LENF8
W FEP7 FEP6 FEP5 FEP4 FEP3 FEP2 FEP1 FEP0
R LENF7 LENF6 LENF5 LENF4 LENF3 LENF2 LENF1 LENF0
W
R/W FIFO7 FIFO6 FIFO5 FIFO4 FIFO3 FIFO2 FIFO1 FIFO0
R/W
W WOR_SL7 WOR_SL6 W OR_SL5 WOR_SL4 WOR_SL3 WOR_SL2 WOR_SL1 WOR_SL0
R RCOC7 RCOC6 RCOC5 RCOC4 RCOC3 RCOC2 RCOC1 RCOC0
W
W
R
W
W
W
W CGC1 CGC0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0 CGS XS
R IFS1 IFS0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0
R/W CHN7 CHN6 CHN5 CHN4 CHN3 CHN2 CHN1 CHN0
W DBL RRC1 RRC0 CHR3 CHR2 CHR1 CHR0 BIP8
R DBL RRC1 RRC0 CHR3 CHR2 CHR1 CHR0 IP8
W BIP7 BIP6 BIP5 BIP4 BIP3 BIP2 BIP1 BIP0
R IP7 IP6 IP5 IP4 IP3 IP2 IP1 IP0
W BFP15 BFP14 BFP13 BFP12 BFP11 BFP10 BFP9 BFP8
R FS YN-FP15 AC14-FP14 AC13-FP13 AC12-FP12 AC11-FP11 AC10-FP10 AC9-FP9 AC8-FP8
W BFP7 BFP6 BFP5 BFP4 BFP3 BFP2 BFP1 BFP0
R AC7-FP7
R/W CHGL7 CHGL6 CHGL5 CHGL4 CHGL3 CHGL2 CHGL1 CHGL0
R/W CHGH7 CHGH6 CHGH5 CHGH4 CHGH3 CHGH2 CHGH1 CHGH0
W
-- -- -- VCC VBC VDC FBC RSSC
FPM1 FPM0 PSA5 PSA4 PSA3 PSA2 PSA1 PSA0
ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
WOR_SL9 WOR_SL8 W OR_AC5 WOR_AC4 WOR_AC3 WOR_AC2 WOR_AC1 WOR_AC0
RTCS RCOT2
RCOT1/
RTCC1
RCOT0/
RTCC0
CALWC
RCOSC_E TSEL TWORE
-- -- -- -- CALWR -- -- --
ECKOE CKOS3 CKOS2 CKOS1 CKOS0 CKOI CKOE SCKI
VKM VPM GIO1S3 GIO1S2 GIO1S1 GIO1S0 GIO1I GIO1OE
BBCKS1 BBCKS0 GIO2S3 GIO2S2 GIO2S1 GIO2S0 GIO2I GIO2OE
-- --
AC6-FP6 AC5-FP5 AC4-FP4 AC3-FP3 AC2-FP2 AC1-FP1 AC0-FP0
GDR GF TMDE TXDI TME FDP2 FDP1 FDP0
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 12 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 13
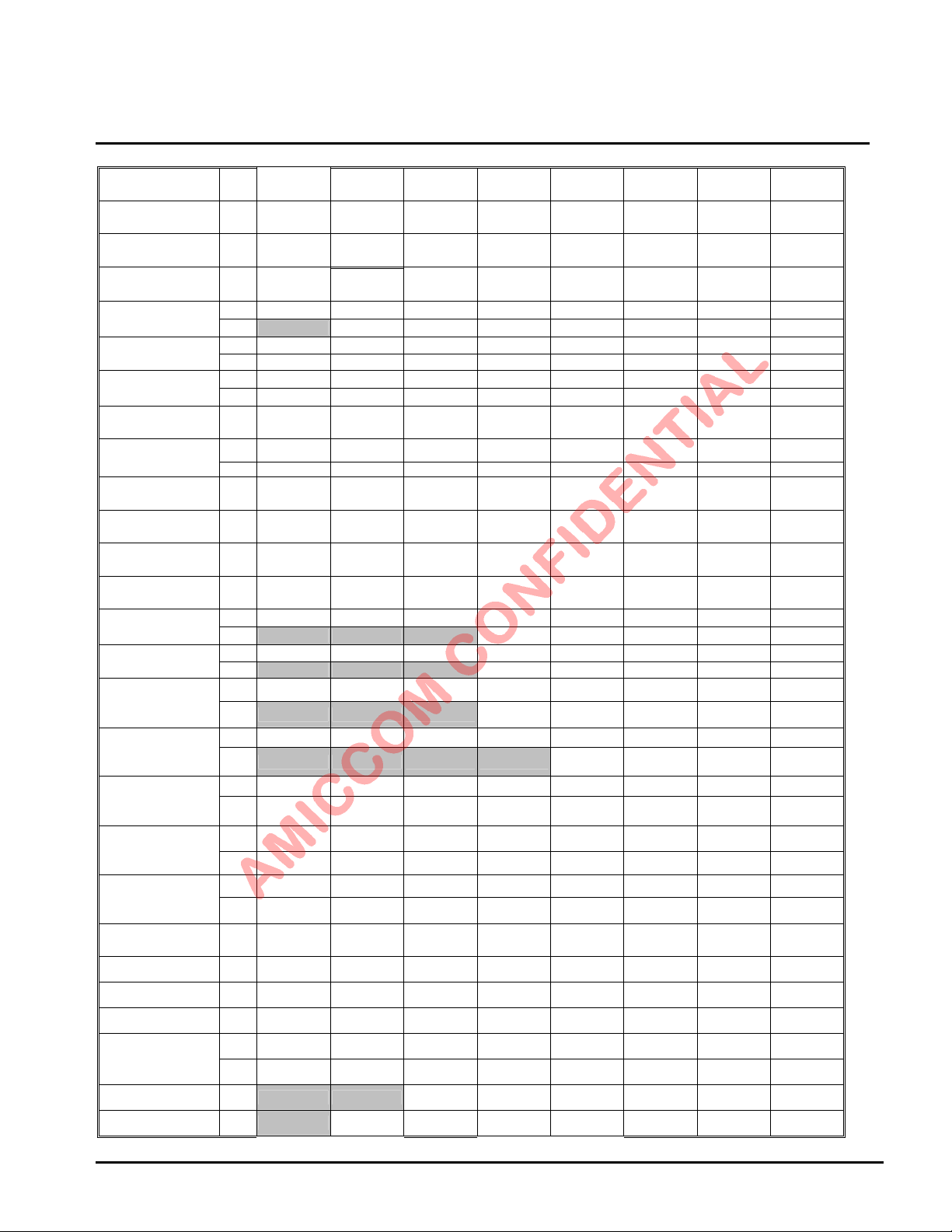
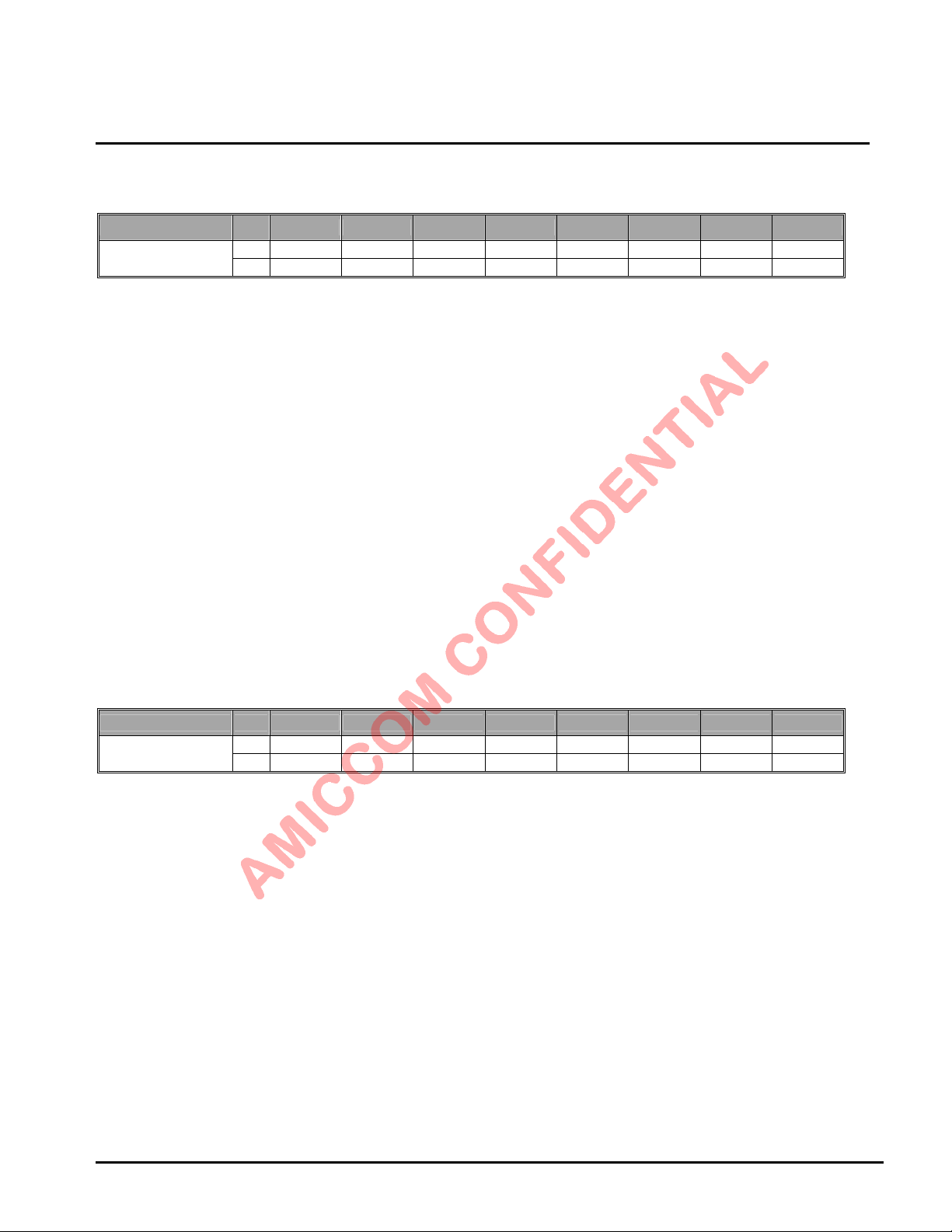
LBA7130
16h
TX II
17h
Delay I
18h
Delay II
19h
RX
1Ah
RX Gain I
1Bh
RX Gain II
1Ch
RX Gain III
1Dh
RX Gain IV
1Eh
RSSI Threshold
1Fh
ADC Control
20h
Code I
21h
Code II
22h
Code III
23h
IF Calibration I
IF Calibration II
25h
VCO current
Calibration
26h
VCO band
Calibration I
27h
VCO band
Calibration II
28h
VCO deviation
Calibration I
29h
VCO deviation
Calibration II
2Ah
DASP0
DASP1
DASP2
DASP3
DASP4
DASP5
DASP6
W
W DPR2 DPR1 DPR0 TDL1 TDL0 PDL2 PDL1 PDL0
W
W
W PRS MIC IGC1 IGC0 MGC1 MGC0 LGC1 LGC0
R
W RSAGC1 RSAGC0 VTL2 VTL1 VTL0 VTH2 VTH1 VTH0
R RH7 RH6 RH5 RH4 RH3 RH2 RH1 RH0
W -- RDU IFS1 IFS0 RSM1 RSM0 ERSSM RSS
R RL7 RL6 RL5 RL4 RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0
W LIMC IFBC1 IFBC0 IFAS MHC1 MHC0 LHC1 LHC0
W RTH7 RTH6 RTH5 RTH4 RTH3 RTH2 RTH1 RTH0
R ADC7 ADC6 ADC5 ADC4 ADC3 ADC2 ADC1 ADC0
W
W
W MSCRC EDRL HECS ETH2 ETH1 ETH0 PMD1 PMD0
W CRCINV WS6 WS5 WS4 WS3 W S2 WS1 WS0
W HFR CKGS1 CKGS0 MFBS MFB3 MFB2 MFB1 MFB0
R
W PWORS
R -- -- -- FCD4 FCD3 FCD2 FCD1 FCD0
W ROSCS RSIS VCRLS MVCS VCOC3 VCOC2 VCOC1 VCOC0
R -- -- -- VCCF VCB3 VCB2 VCB1 VCB0
W DCD1 DCD0 DAGS CWS MVBS MVB2 MVB1 MVB0
R - - - - VBCF VB2 VB1 VB0
W MDAG7 MDAG6 MDAG5 MDAG4 MDAG3 MDAG2 MDAG1 MDAG0
R ADAG7 ADAG6 ADAG5 ADAG4 ADAG3 ADAG2 ADAG1 ADAG0
W DEVS3 DEVS2 DEVS1 DEVS0 DAMR _M VMTE_M VMS_M MSEL
R DEVA7 DEVA6 DEVA5 DEVA4 DEVA3 DEVA2 DEVA1 DEVA0
W MVDS MDEV6 MDEV5 MDEV4 MDEV3 MDEV2 MDEV1 MDEV0
R ADEV7 ADEV6 ADEV5 ADEV4 ADEV3 ADEV2 ADEV1 ADEV0
W
W
W
W DCV7 DCV6 DCV5 DCV4 DCV3 DCV2 DCV1 DCV0
W VMG7 VMG6 VMG5 VMG4 VMG3 VMG2 VMG1 VMG0
R VMG7 VMG6 VMG5 VMG4 VMG3 VMG2 VMG1 VMG0
W -- -- PKT1 PKT0 PKS PKIS1 PKIS0 IFPK
W -- HPLS HRS PACTL IWS CNT MXD LXD
FD7 FD6 FD5 FD4 FD3 FD2 FD1 FD0
WSEL2 WSEL1 WSEL0 RSSC_D1 RSSC_D0 RS_DLY2 RS_DLY1 RS_DLY0
LNAGE AGCE RXSM1 RXSM0 AFCE RXDI DMG ULS
-- MICR IGCR1 IGCR0 MGCR1 MGCR0 LGCR1 LGCR0
AVSEL1 AVSEL0 MVSEL1 MVSEL0 RADC FSARS XADS CDM
MCS WHTS FECS CRCS IDL1 IDL0 PML1 PML0
-- -- -- FBCF FB3 FB2 FB1 FB0
TRT2 TRT1 TRT0 ASMV2
QLIM RFSP
STS CELS
VTRB3 VTRB2 VTRB1 VTRB0 VMRB3 VMRB2 VMRB1 VMRB0
INTRC
(CSXTL5)
CSXTL4 CSXTL3 CSXTL2 CSXTL1 CSXTL0
RGS RGC1 RGC0 VRPL1 VRPL0 INTPRC
ASMV1 ASMV0 AMVS24h
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 13 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 14
2Bh
VCO modulation
W
DMV1 DMV0 DEVFD2 DEVFD1 DEVFD0 DEVD2 DEVD1 DEVD0
Delay
2Ch
Battery detect
2Dh
TX test
2Eh
Rx DEM test I
2Fh
Rx DEM test II
W
W
W DMT DCM1 DCM0 MLP1 MLP0 SLF2 SLF1 SLF0
W DCH1 DCH0 DCL2 DCL1 DCL0 RAW CDTM1 CDTM0
LVR
R -- RGV1 RGV0 BDF BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
RMP1 RMP0 TXCS PAC1 PAC0 TBG2 TBG1 TBG0
RGV1 RGV0 QDS BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
30h
CPM3 CPM2 CPM1 CPM0 CPT3 CPT2 CPT1 CPT0
Charge Pump
W
Current I
31h
Charge Pump
W CPTX3 CPTX2 CPTX1 CPTX0 CPRX3 CPR X2 CPRX1 CPRX0
Current II
32h
Crystal test
33h
PLL test
34h
VCO test
35h
RF Analog test
36h
Key Data
37h
Channel Select
38h
ROM_P0
W
CDPM CPS CPH CPCS DBD XCC XCP1 XCP0
MDEN OLM PRIC1 PRIC0 PRRC1 PRRC0 SDPW NSDO
W
DEVGD2 DEVGD1 DEVGD0 TLB1 TLB0 RLB1 RLB0 VBS
W
AGT3 AGT2 AGT1 AGT0 RFT3 RFT2 RFT1 RFT0
W
W/R
KEY7 KEY6 KE Y5 KE Y4 KEY3 KEY2 KE Y1 KEY0
W CHI3 CHI2 CHI1 CHI0 CHD3 CHD2 CHD1 CHD0
W
MPOR EPRG MIGS MRGS MRSS MTMS MADS MBGS
ROMP1 W APG MPA1 MPA0 FBG4 FBG3 FBG2 FBG1 FBG0
ROMP2 W PTM1 PTM0 CTR5 CTR4 CTR3 CTR2 CTR1 CTR0
ROMP3 W -- -- CRS2 CRS1 CRS0 CTS2 CTS1 CTS0
ROMP4 W -- STMP STM5 STM4 STM3 STM2 ST M1 STM0
39h
Data Rate CLK
3Ah
FCR
3Bh
ARD
3Ch
AFEP
3Dh
FCB
3Eh
KEYC
3Fh
USID
W SDR7 SDR6 SDR5 SDR4 SDR3 SDR2 SDR1 SDR0
W FCL1 FCL0 ARC3 ARC2 ARC1 ARC0 EACKS EARTS
R ARTEF VPOAK
W
ARD7 ARD6 ARD5 ARD4 ARD3 ARD2 ARD1 ARD0
W EACKF SPSS ACKFEP5 ACKFEP4 ACKFEP3 ACKFEP2 ACKFEP1 ACKFEP0
R
W/R
W
W
-- -- EARTS EARTS EARTS TXSID2 TXSID1 TXSID0
F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0
MEDCS AFIDS ARTMS MIDS AESS -- AKFS EDCRS
RND7 RND6 RND5 RND4 RND3 RND2 RND1 RND0
RCR3 RCR2 RCR1 RCR0 EACKS EARTS
Legend: -- = unimplemented
LBA7130
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 14 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 15
9.2 Control register description
9.2.1 Mode Register (Address: 00h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mode
RESETN: Write to this register by 0x00 to issue reset command, then it is auto clear
HECF: Head Control Flag. (HECF will be clear after issue a strobe command.)
HEC is CRC-8 result for the optional Packet Header (Please refer to chapter 16 for details)
[0]: HEC pass. [1]: HEC error.
FECF: FEC flag. (FECF will be clear after issue any strobe command.)
[0]: FEC pass. [1]: FEC error.
CRCF: CRC flag. (CRCF will be clear after issue any strobe command.)
[0]: CRC pass. [1]: CRC error.
CER: RF chip enable status.
[0]: RF chip is disabled. [1]: RF chip is enabled.
XER: Internal crystal oscillator enabled status.
[0]: Crystal oscillator is disabled. [1]: Crystal oscillator is enabled.
PLLE: PLL enabled status.
[0]: PLL is disabled. [1]: PLL is enabled.
TRER: TRX state enabled status.
[0]: TRX is disabled. [1]: TRX is enabled.
TRSR: TRX Status Register.
[0]: RX state. [1]: TX state.
Serviceable if TRER=1 (TRX is enable).
R HECF FECF CRCF CER XER PLLER TRSR TRER
W RESETN
RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN RESETN
LBA7130
9.2.2 Mode Control Register (Address: 01h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mode Control I
DDPC (Direct mode data pin control): Direct mode modem data can be accessed via SDIO pin.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
ARSSI: Auto RSSI measurement while entering RX mode.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
AIF (Auto IF Offset): RF LO frequency will auto offset one IF frequency while entering RX mode.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
CD: Carrier detector (Read only).
[0]: Input power below threshold. [1]: Input power above threshold.
DFCD: Data Filter by CD : The received packet would be filtered if the input power level is below RTH (1Eh).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
WORE: WOR (Wake On RX) Function Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
FMT: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
FMS: Direct/FIFO mode select.
[0]: Direct mode. [1]: FIFO mode.
ADCM: ADC measurement enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable measurement or measurement finished. [1]: Enable measurem ent.
Refer to chapter 17 for details.
R DDPC ARSSI AIF DFCD WORE FMT FMS ADCM
W DDPC ARSSI AIF CD WORE FMT FMS ADCM
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 15 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 16
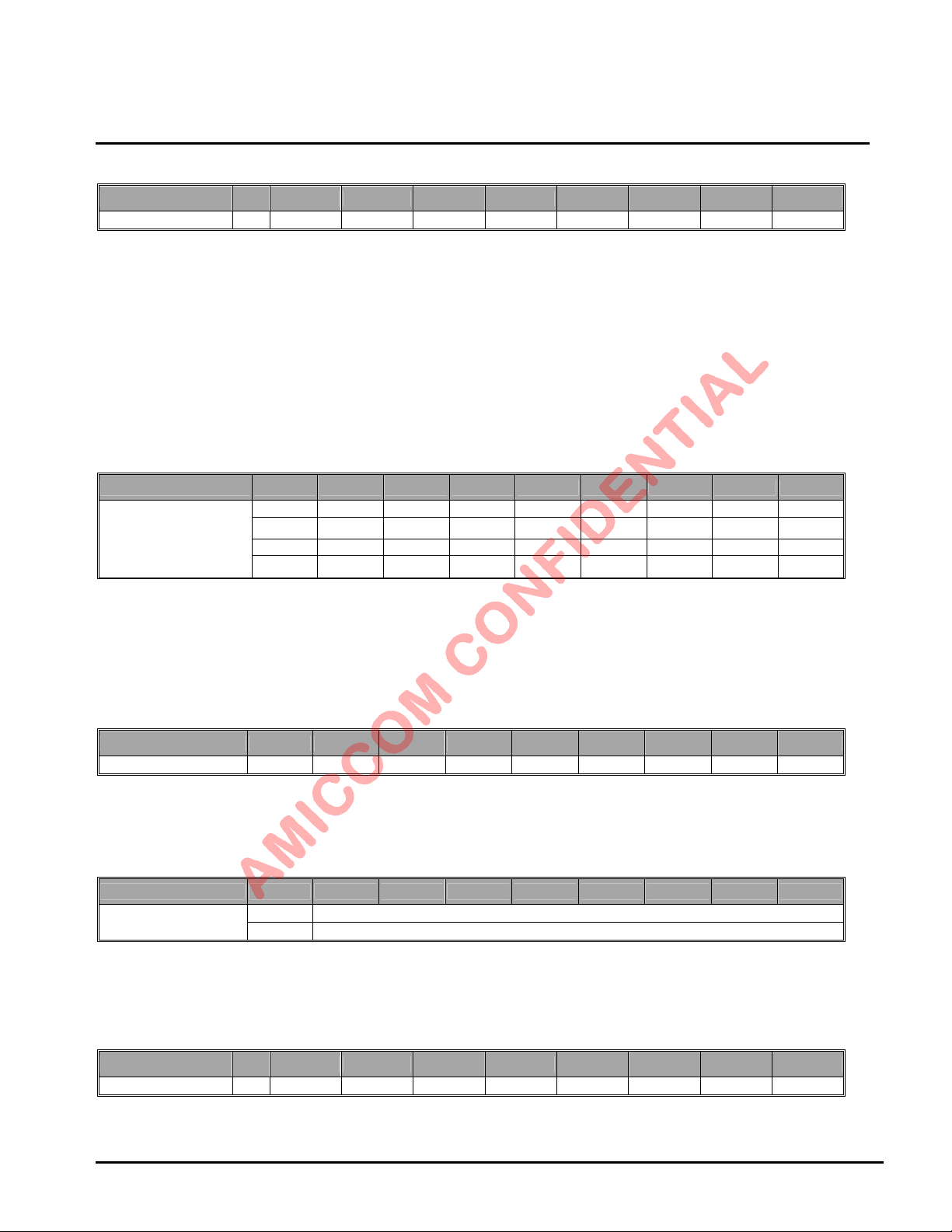
9.2.3 Calibration Control Register (Address: 02h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mode Control II R/W -- -- --
VCC: VCO Current calibration enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
VBC: VCO Bank calibration enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
VDC: VCO Deviation calibration enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
FBC: IF Filter Bank calibration enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
RSSC: RSSI calibration enable (Auto clear when done).
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
VCC VBC VDC FBC RSSC
9.2.4 FIFO Register I (Address: 03h)
Name R/W Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8
W -- -- -- -- FEP11 FEP10 FEP9 FEP8
FIFO I
R -- -- -- -- LENF11 LENF10 LENF9 LENF8
W FEP7 FEP6 FEP5 FEP4 FEP3 FEP2 FEP1 FEP0
R LENF7 LENF6 LENF5 LENF4 LENF3 LENF2 LENF1 LENF0
LBA7130
FEP [11:0]: FIFO End Pointer for TX FIFO and Rx FIFO.
Data Sequence is FEP[7:0] and FEP[15:8].
Please refer to chapter 16 for details.
LENF [11:0]: Received FIFO Length for dynamic FIFO function. (Ready Only)
When EDRL =1, that means dynamic FIFO is enabled, MCU can read LENF [11:0] to know the RX FIFO length of the coming
packet. Please refer to chapter 16 for details.
9.2.5 FIFO Register II (Address: 04h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
FIFO II W FPM1 FPM0 PSA5 PSA4 PSA3 PSA2 PSA1 PSA0
FPM [1:0]: FIFO Pointer Margin
PSA [5:0]: Used for Segment FIFO.
Refer to chapter 16 for details.
9.2.6 FIFO DATA Register (Address: 05h)
Bit R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Name
FIFO [7:0]: TX FIFO / RX FIFO
TX FIFO and RX FIFO share the same address (05h).
TX FIFO and RX FIFO are separated physical 64 Bytes.
Refer to chapter 16 for details.
W TX-FIFO[7:0]
R/W RX-FIFO[7:0]
9.2.7 ID DATA Register (Address: 06h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ID DATA R/W ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
ID [7:0]: ID data.
When this address is accessed, ID Data is input or output sequential (ID Byte 0,1, 2 and 3) corresponding to Write or Read.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 16 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 17
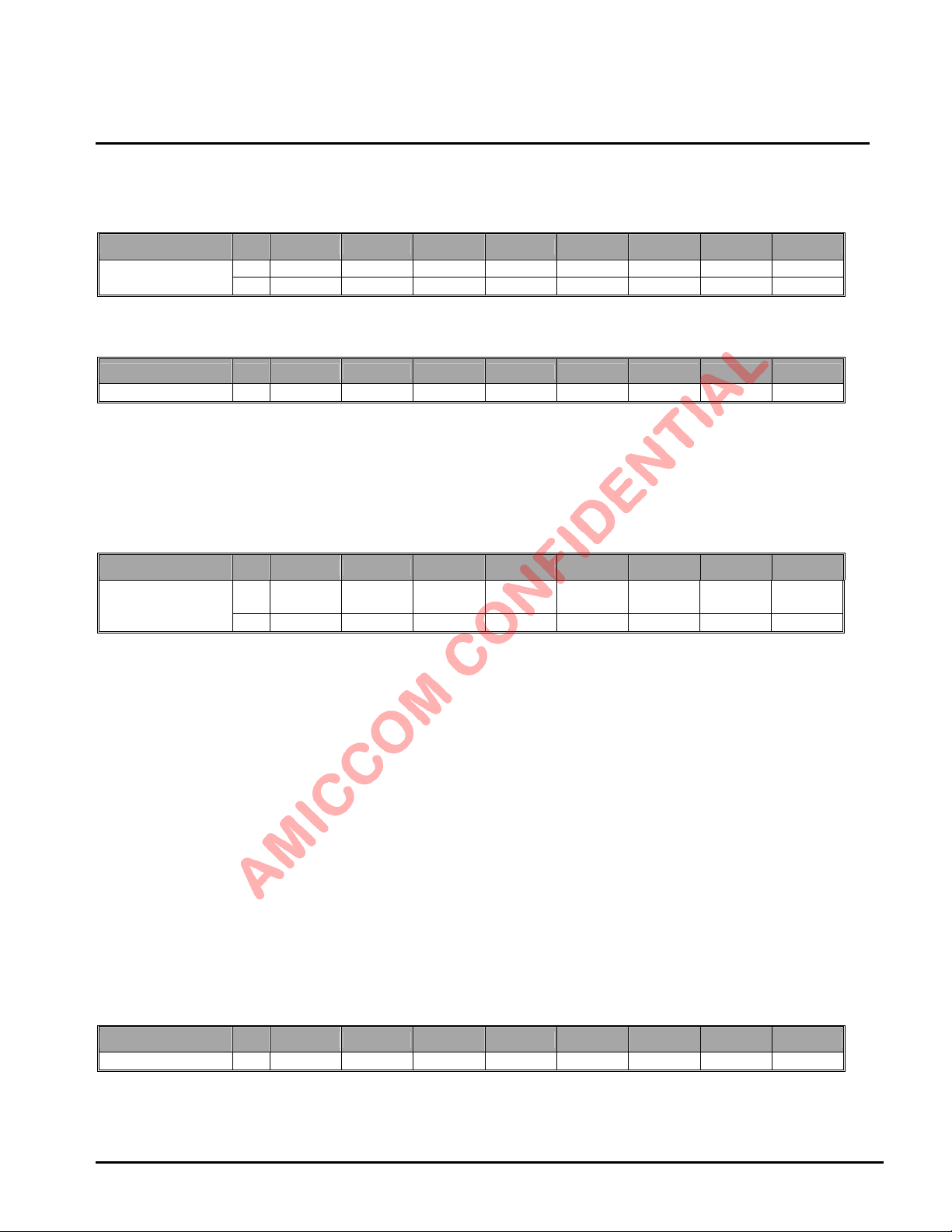
Recommend to set ID Byte 0 = 5xh or Axh.
Refer to section 10.6 for details.
9.2.8 RC OSC Register I (Address: 07h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RCOC7 RCOC6 RCOC5 RCOC4 RCOC3 RCOC2 RCOC1 RCOC0
RC OSC I
RCOC [7:0]: Reserved for internal usage (read only).
R
WOR_SL7 WOR_SL6 WOR_SL5 WOR_SL4 WOR_SL3 WOR_SL2 WOR_SL1 W OR_SL0
W
9.2.9 RC OSC Register II (Address: 08h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RC OSC II W
WOR_AC [5:0]: 6-bits WOR Active Timer for WOR and TWOR Function
WOR_SL [9:0]: 10-bits WOR Sleep Timer for WOR and TWOR Function.
WOR_SL [9:0] are from address (07h) and (08h),
Active period = (WOR_AC+1) x (1/4092).
Sleep period = (WOR_SL+1) x (1/32) x (1/4092).
WOR_SL9 WOR_SL8 WOR_AC5 WOR_AC4 WOR_AC3 WOR_AC2 WOR_AC1 WOR_AC0
LBA7130
9.2.10 RC OSC Register III (Address: 09h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RC OSC III
RTCS: internal Oscillator selection in sleep mode. Recommend RTCS= [0].
[0]: RC oscillator. [1]: RTC oscillator.
RCOT[2:0]: Reserved for internal used. Recommend RCOT= [000].
RCOT[1:0]: RCOSC current select for RC oscillator calibration.
[00]: 240nA [01]: 280nA [10]: 320nA [11]: 360nA
TSEL: Timer select for TWOR function.
[0]: Use WOR_AC. [1]: Use WOR_SL.
CALWC: RC Oscillator Calibration Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
CALWR: RC Oscillator Calibration ending indication.
[0]: ending. [1]: Not ending.
RCOSC_E: RC-oscillator enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
TSEL: Timer Duty select for TWOR function.
[0]: Use WOR_AC. [1]: Use WOR_SL.
TWORE: Enable TWOR function.
[0]: WOR mode. [1]: TWOR mode.
W RTCS RCO T2
R -- -- -- -- CALWR
RCOT1/
RTCC1
RCOT0/
RTCC0
CALWC
RCOSC_E TSEL TW ORE
-- -- --
9.2.11 CKO Pin Control Register (Address: 0Ah)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CKO Pin Control W ECKOE CKOS3 CKOS2 CKOS1 CKOS0 CKOI CKOE SCKI
ECKOE: CKO pin Output Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
CKOS [3:0]: CKO pin output select.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 17 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 18
[0000]: DCK (TX data clock) in TX mode, RCK (RX recovery clock) in RX mode.
[0001]: DCK (TX data clock) in TX mode, RCK (RX recovery clock) in RX mode.
[0010]: FPF (FIFO pointer flag).
[0011]: EOP, EOVBC, EOFBC, EOVCC, EOVDC, RSSC_OK. (Internal usage only).
[0100]: External clock output= F
[0101]: External clock output / 2= F
[0110]: RXD
[0111]: FSYNC.
[1000]: WCK.
[1001]: PF8M.(8Mhz, internal usage)
[1010]: ROSC.
[1011]: MXDEC(SLF[0]=1:~OKADCN, SLF[1]=0: DEC , internal usage)
[1100]: BDF (Battery Detect flag).
[1101]: F
[1110]: VPOAK.
[1111]: WRTC (internal usage)
CKOI: CKO pin output signal invert.
[0]: Non-inverted output. [1]: Inverted output.
CKOE: CKO pin Output Enable.
[0]: High Z. [1]: Enable.
SCKI: SPI clock input invert.
[0]: Non-inverted input. [1]: Inverted input.
SYCK
..
SYCK
/ 2.
SYCK
/ 4.
LBA7130
9.2.12 GIO1 Pin Control Register I (Address: 0Bh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
GIO1 Pin Control I W VKM VPM GIO1S3 GIO1S2 GIO1S1 GIO1S0 GIO1I GI O1OE
VKM: Valid packet mode select.
[0]: by event. [1]: by pulse.
VPM: Valid Pulse width select.
[0]: 20u. [1]: 40u.
TX Mode (disable auto-resend, EAR=0).
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 18 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 19
RX Mode (disable Auto-ack, EAK =0).
LBA7130
Note1, If auto-resend is enabled (EAR = 1), WTR behavior is different while it is output to GIO1 and GIO2.
Note2, If auto-ack is enabled (EAK = 1), WTR behavior is different while it is output to GIO1 and GIO2.
Note3, VPOAK’s behavior is controlled by VPM (0Bh) and VPW (0Bh).
Refer to chapter 19 for details
GIO1S [3:0]: GIO1 pin function select.
GIO1S [3:0] TX state RX state
[0000] WTR (Wait until TX or RX finished)
[0001] EOAC (end of access code) FSYNC (frame sync)
[0010] TMEO (TX modulation enable) CD (carrier detect)
[0011] Preamble Detect Output (PMDO)
[0100] If RCOSC_E =1, output TWOR.
If RCOSC_E =0, output CWTR signal. (internal usage)
[0101] In phase demodulator input(DMII)or VT[0] (internal usage)
[0110] SDO ( 4 wires SPI data out)
[0111] TRXD In/Out (Direct mode)
[1000] RXD (Direct mode)
[1001] TXD (Direct mode)
[1010] PDN_RX
[1011]
[1100] MXINC(SLF[0]=1:EOADC.SLF[1]=0:INC.) (internal usage)
[1101] FPF
[1110] VPOAK (Valid Packet or Auto ACK OK Output)
[1111] FMTDO (internal usage)
If GIO1S = [0100] and RCOSC_E = 0, CWTR is an internal signal to monitor TX/RX cycles of auto-ack and auto-resend.If
GIO1S = [1011] and direct mode is selected, the internal frame sync function will be disabled. In such case, A7130 supports
to accept an external frame sync signal from MCU to feed to GIO1 pi n to determine the timing of fixing DC estimation voltage
of demodulator.
GIO1I: GIO1 pin output signal invert.
[0]: Non-inverted output. [1]: Inverted output.
GIO1OE: GIO1pin output enable.
[0]: High Z. [1]: Enable.
External FS YNC input in RX direct mode (internal usage)
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 19 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 20
LBA7130
9.2.13 GIO2 Pin Control Register II (Address: 0Ch)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
GIO2 Pin Control II W BBCKS1 BBCKS0 GIO2S3 GIO2S2 GIO2S1 GIO2S0 GIO2I GI O2OE
BBCKS [1:0]: Clock select for digital block. Recommend BBCKS = [00].
[00]: F
GIO2S [3:0]: GIO2 pin function select.
If GIO2S = [0100] and RCOSC_E = 0, CWTR is an internal signal to monitor TX/RX cycles of auto-ack and auto-resend.
GIO2I: GIO2 pin output signal invert.
[0]: Non-inverted output. [1]: Inverted output.
GIO2OE: GIO2 pin Output Enable.
[0]: High Z. [1]: Enable.
SYCK
. [01]: F
/ 2. [10]: F
SYCK
/ 4. [11]: F
SYCK
SYCK
/ 8.
GIO2S TX state RX state
[0000] WTR (Wait until TX or RX finished)
[0001] EOAC (end of access code) FSYNC (frame sync)
[0010] TMEO (TX modulation enable) CD (carrier detect)
[0011] Preamble Detect Output (PMDO)
[0100] If RCOSC_E =1, output TWOR.
If RCOSC_E =0, output CWTR signal. (internal usage)
[0101] Quadrature phase demodulator input (DMIQ) (internal usage)
[0110] SDO (4 wires SPI data out)
[0111] TRXD In/Out (Direct mode)
[1000] RXD (Direct mode)
[1001] TXD (Direct mode)
[1010] PDN_TX
[1011] ROMOK(ROM Program OK) (internal usage)
[1100] BDF (Battery Detect Flag)
[1101] FPF
[1110] VPOAK (Valid Packet or Auto ACK OK Output)
[1111] DCK (internal usage)
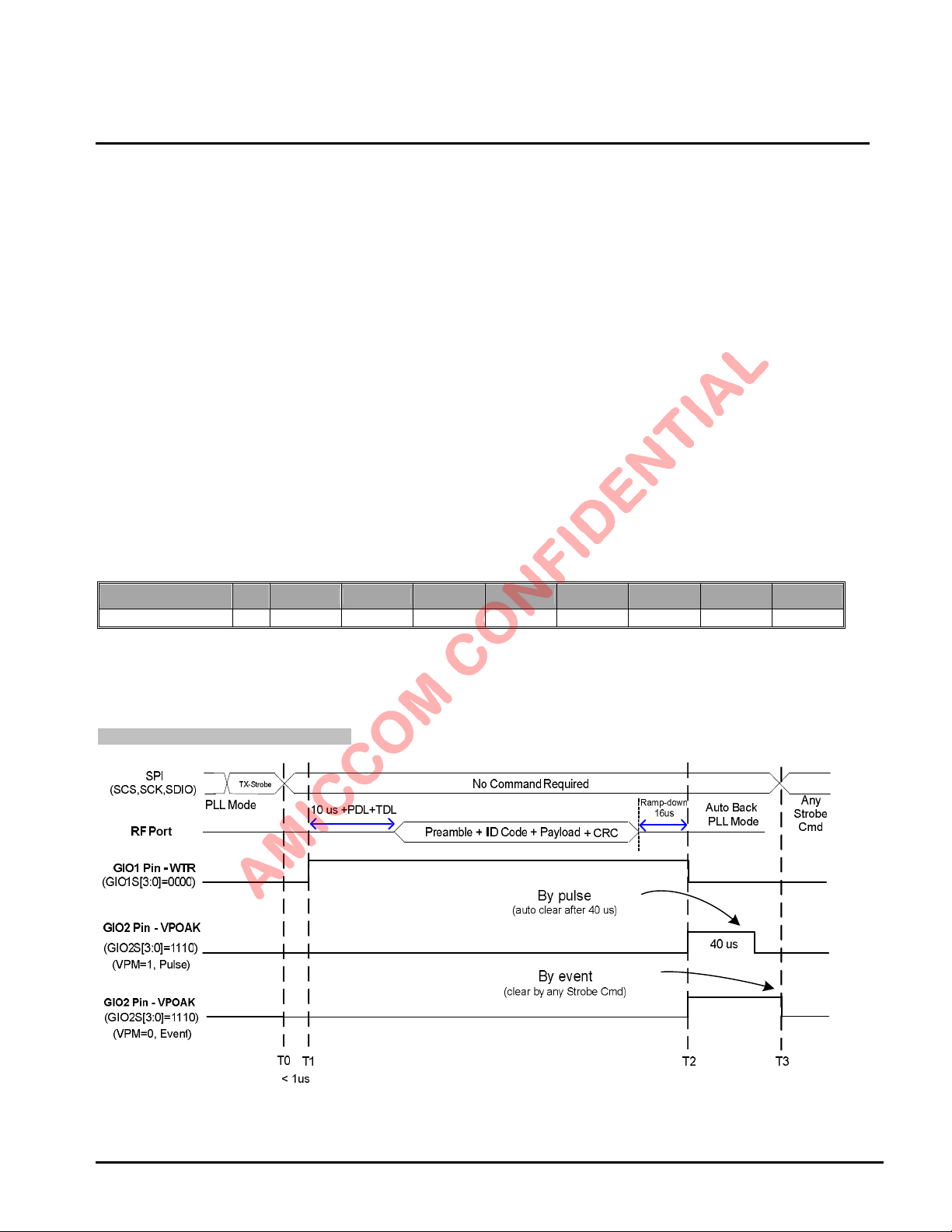
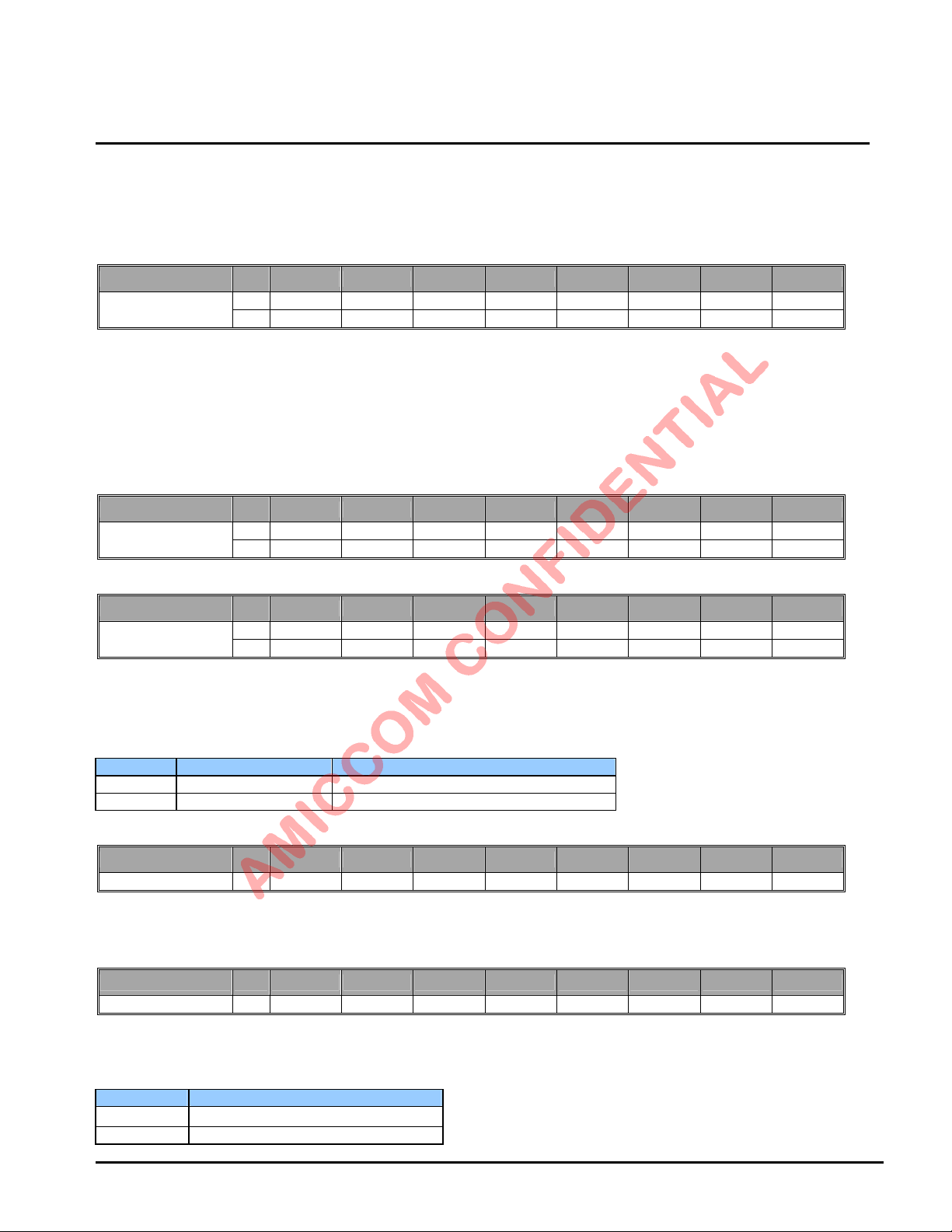
In TX mode
SPI
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RF Port
(Output)
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO2 Pin - TMEO
(GIO2S[3:0]=0010)
TX-Strobe
PLL Mode
10 us + (PDL+TDL)
T0
T1
< 1us
No Command Required
Preamble +
ID Code + Payload
+ CRC
16 us
PA Ramp Down
T2
Next Instruction
Auto Back
PLL Mode
T3
In RX mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 20 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 21
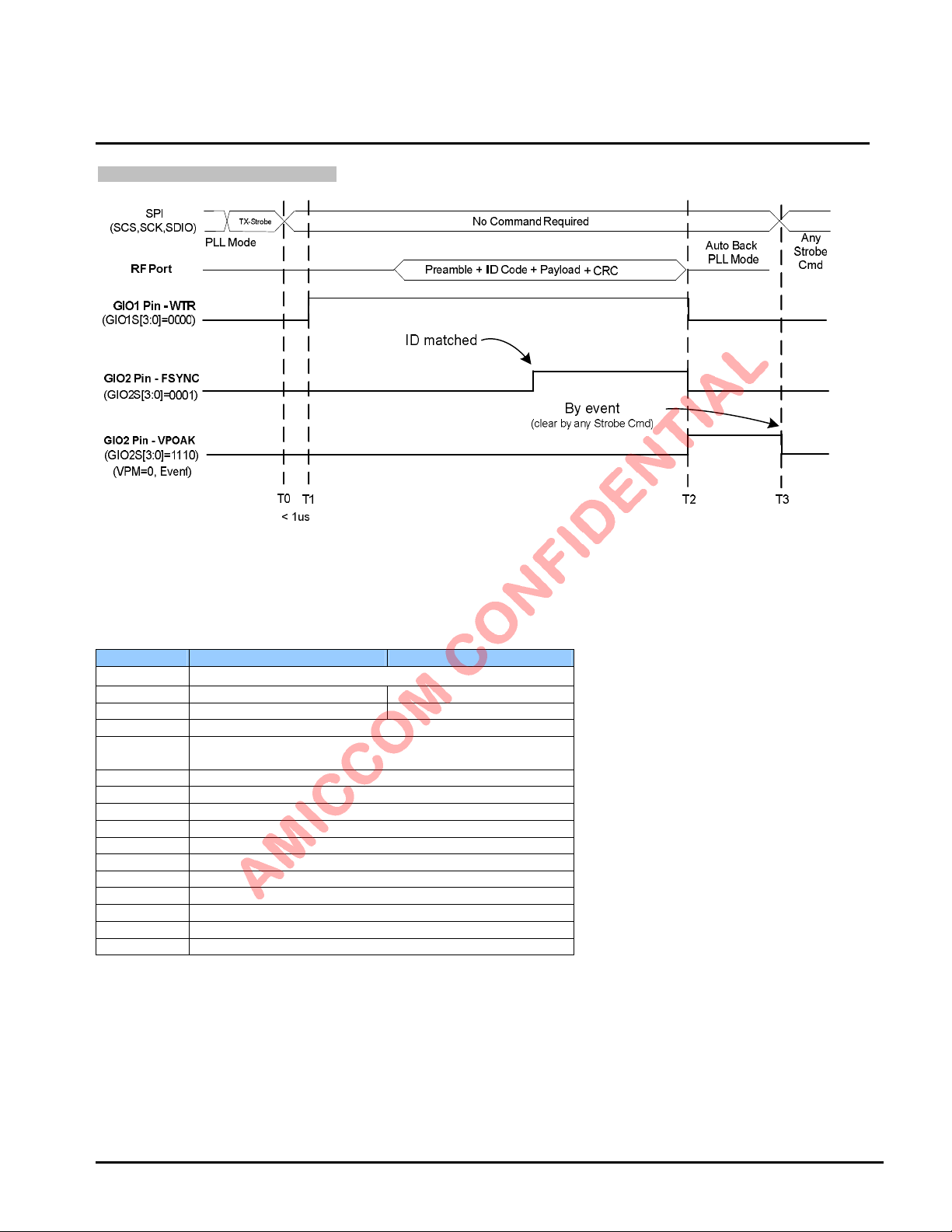
LBA7130
SPI
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RF Po rt
(Input)
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO2 Pin - FSYNC
(GIO2S[3:0]=0001)
RX-Strobe
PLL Mode
T0
< 1us
T1
10us+PDL+TDL
No Command Required
Preamble +
ID Code + Payload
ID-Matched
+ CRC
T2
9.2.14 Clock Register (Address: 0Dh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Clock W
CGC [1:0]: Clock Gen. Current select. Shall be set to [10].
GRC [3:0]: Clock generation reference counter. Recommend GRC = [0111] for 16MHz Xtal.
GRC [3:0] is used to let below formula be true when CGS = 1.
F
x (DBL+1) / (GRC+1) = 2MHz.
XTAL
CGS: Clock generator enable. Recommend CGS = [1]
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
XS: Crystal oscillator select. Recommend XS = [1]
[0]: External clock. [1]: Crystal.
IFS [1:0]: IF band selection. (Ready only)
CGC1 CGC0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0
IFS1 IFS0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0
R
Next Instruction
Auto Back
PLL Mode
CGS XS
-- --
9.2.15 PLL Register I (Address: 0Eh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL I R/W CHN7 CHN6 CHN5 CHN4 CHN3 CHN2 CHN1 CHN0
CHN [7:0]: LO channel number select.
Refer to chapter 14 for details.
9.2.16 PLL Register II (Address: 0Fh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL II
DBL: Crystal frequency doublers selection.
[0]: Disable. F
[1]: Enable. F
XREF
XREF
In FIFO mode, recommend to set DBL =0.
In Direct mode, recommend to set DBL =1.
Please refer to A7130 reference code for details.
RRC [1:0]: RF PLL reference counter setting. Recommend RRC = [00].
The PLL comparison frequency, F
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 21 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
R DBL RRC1 RRC0 CHR3 CHR2 CHR1 CHR0 IP8
W DBL RRC1 RRC0 CHR3 CHR2 CHR1 CHR0 BIP8
= F
.
XTAL
=2 * F
XTAL
.
PFD
= F
*(DBL+1) / (RRC+1).
CRYSTAL
Page 22
CHR [3:0]: PLL channel step setting.
In FIFO mode, recommend to set CHR [3:0] = [0111].
In Direct mode, recommend to set CHR [3:0] = [1111].
Please refer to chapter 14 and A7130 reference code for details.
9.2.17 PLL Register III (Address: 10h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL III
BIP [8:0]: LO base frequency integer part setting. (0Fh and 10h)
In FIFO mode, recommend to set BIP [8:0] = [0x096].
In Direct mode, recommend to set BIP [8:0] = [0x04B].
Please refer to chapter 14 and A7130 reference code for details.
IP [8:0]: LO frequency integer part value.
IP [8:0] are from address (0Fh) and (10h),
Refer to chapter 14 for details.
R IP7 IP6 IP5 IP4 IP3 IP2 IP1 IP0
W BIP7 BIP6 BIP5 BIP4 BIP3 BIP2 BIP1 BIP0
9.2.18 PLL Register IV (Address: 11h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL IV
R RAC15 RAC14 RAC13 RAC12 RAC11 RAC10 RAC9 RAC8
W BFP15 BF P14 BFP13 BFP12 BF P11 BFP10 BFP9 BFP8
LBA7130
9.2.19 PLL Register V (Address: 12h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL V
BFP [15:0]: LO base frequency fractional part setting. (11h and 12h)
In FIFO mode, recommend to set BFP [15:0] = [0x0004].
In Direct mode, recommend to set BFP [15:0] = [0x0002].
Please refer to chapter 14 and A7130 reference code for details.
RAC [15:0]: Auto Frequency compensation value if AFC (19h) =1.
RAC [15:0] Note
AFC = 1 PLLFF [15:0] LO Freq. compensation value
AFC = 0 {SYNCF, AC [14:0]}
R RAC7 RAC6 RAC5 RAC4 RAC3 RAC2 RAC1 RAC0
W BFP7 BFP6 BFP5 BFP4 BFP3 BFP2 BFP1 BFP0
9.2.20 Channel Group Register I (Address: 13h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CHGI R/W
CHGL [7:0]: PLL channel group low boundary setting for auto-calibration. Recommed CHGL[7:0] = 0x3C.
Refer to A7130 reference code for details.
CHGL7 CHGL6 CHGL5 CHGL4 CHGL3 CHGL2 CHGL1 CHGL0
9.2.21 Channel Group Register II (Address: 14h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CHGII R/W
CHGH [7:0]: PLL channel group high boundary setting for auto-calibration. Recommed CHGH[7:0] = 0x78.
Refer to A7130 reference code for details.
CHGH7 CHGH6 CHGH5 CHGH4 CHGH3 CHGH2 CHGH1 CHGH0
PLL calibration frequency is divided into 3 groups by CHGL and CHGH:
Channel
Group1 0 ~ CHGL-1
Group2 CHGL ~ CHGH-1
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 22 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 23
Group3 CHGH ~ 255
9.2.22 TX Register I (Address: 15h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TX I W GDR GF TMDE TXDI TME FDP2 FDP1 FDP0
GDR: Gaussian Filter Over Sampling Rate Select. Recommend GDR = [1].
[0]: BT= 0.7 [1]: BT= 0.5
GF: Gaussian Filter Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
TMDE: TX modulation enable for VCO modulation. Recommend TMDE = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
TXDI: TX data invert. Recommend TXDI = [0].
[0]: Non-invert. [1]: Invert.
TME: TX modulation enable. Recommend TME = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
FDP [2:0]: Frequency deviation power setting. Recommend FDP = [110].
In FIFO mode, recommend to set FDP [2:0] = [111].
In Direct mode, recommend to set FDP [2:0] = [110].
Please refer to chapter 14 and A7130 reference code for details.
LBA7130
9.2.23 TX Register II (Address: 16h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TXI W
FD [7:0]: Frequency deviation setting.
F
= (F
DEV
Where F
/216) x FD[7:0] x 2
PFD
= F
PFD
* (DBL+1) / (RRC [1:0]+1), PLL comparison frequency.
XTAL
FD7 FD6 FD5 FD4 FD3 FD2 FD1 FD0
(FDP-1)
.
Data Rate FDP[2:0] FD[7:0] Fdev
4Mbps FIFO mode 111 0x40 1MHz
4Mbps Direct mode 110 0x40 1MHz
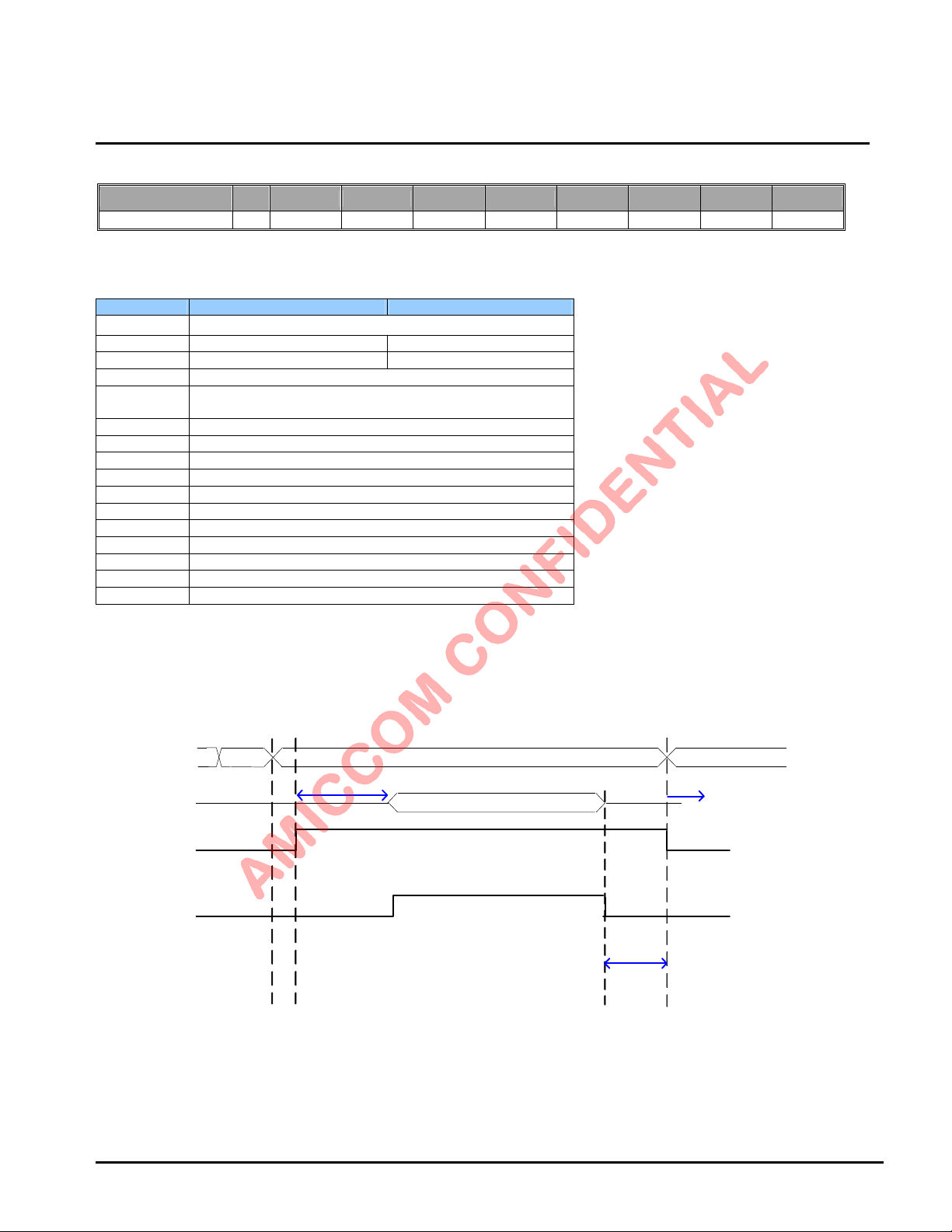
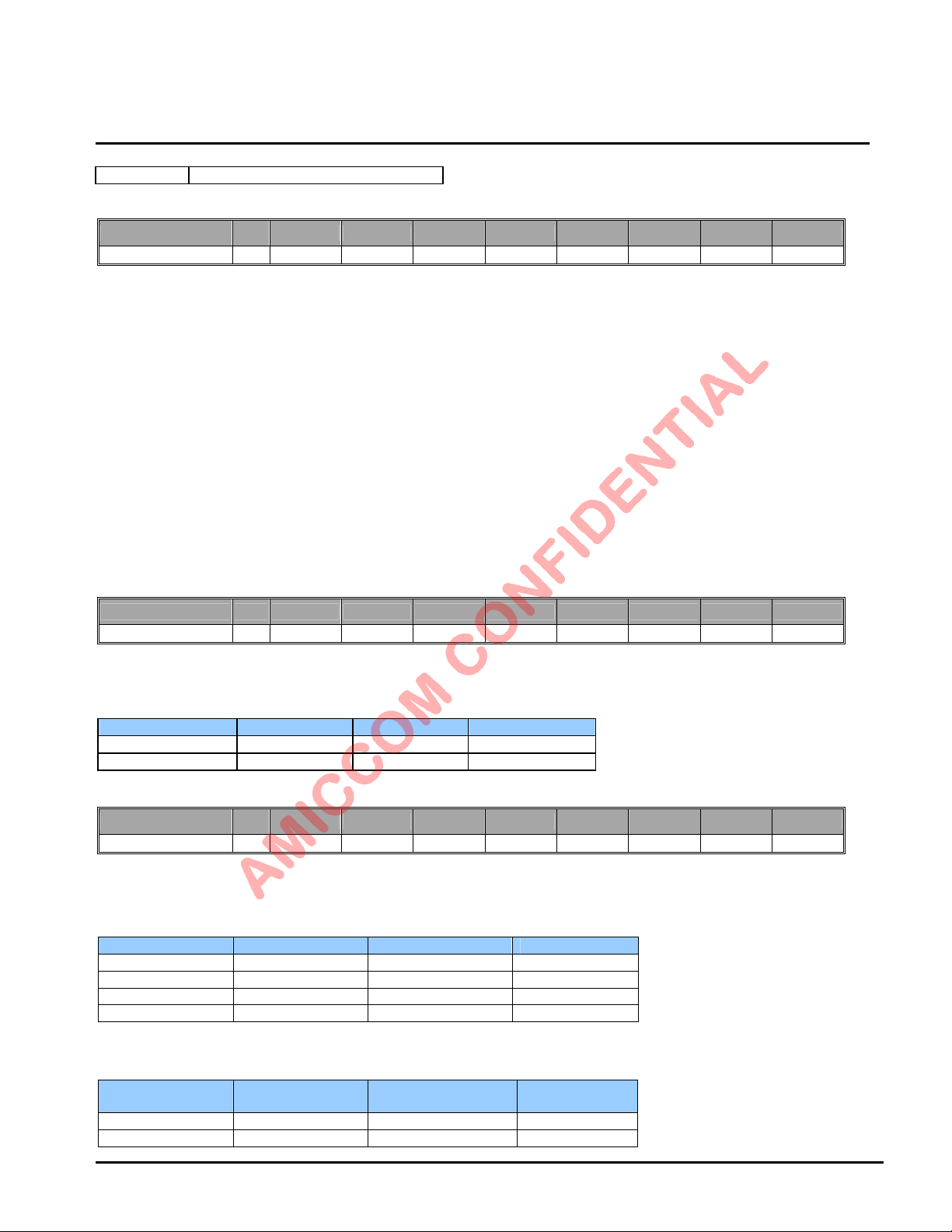
9.2.24 Delay Register I (Address: 17h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Delay W DPR2 DPR1 DPR0 TDL1 TDL0 PDL2 PDL1 PDL0
DPR [2:0]: Delay scale. Recommend DPR = [000].
TDL [1:0]: Delay for TX settling from WPLL to TX.
TDL Delay= 20 * (TDL [1:0]+1)*(DPR [2:0]+1) us.
DPR [2:0] TDL [1:0] WPLL to TX Note
000 00 20 us
000 01 40 us
000 10 60 us Recommend
000 11 80 us
PDL [2:0]: Delay for TX settling from PLL to WPLL.
PDL Delay= 10 + {20 * (PDL [2:0]+1)*(DPR [2:0]+1)} us.
DPR [2:0] PDL [2:0] PLL to WPLL
Note
(LO freq changed)
000 000 30 us Recommend
000 001 50 us
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 23 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 24
000 010 70 us
000 011 90 us
000 100 110 us
LBA7130
G IO 1 P in
(WTR)
R FO Pin
PLL Mode
TX Strobe
10 us + PDL
TDL
TX M ode
Packet
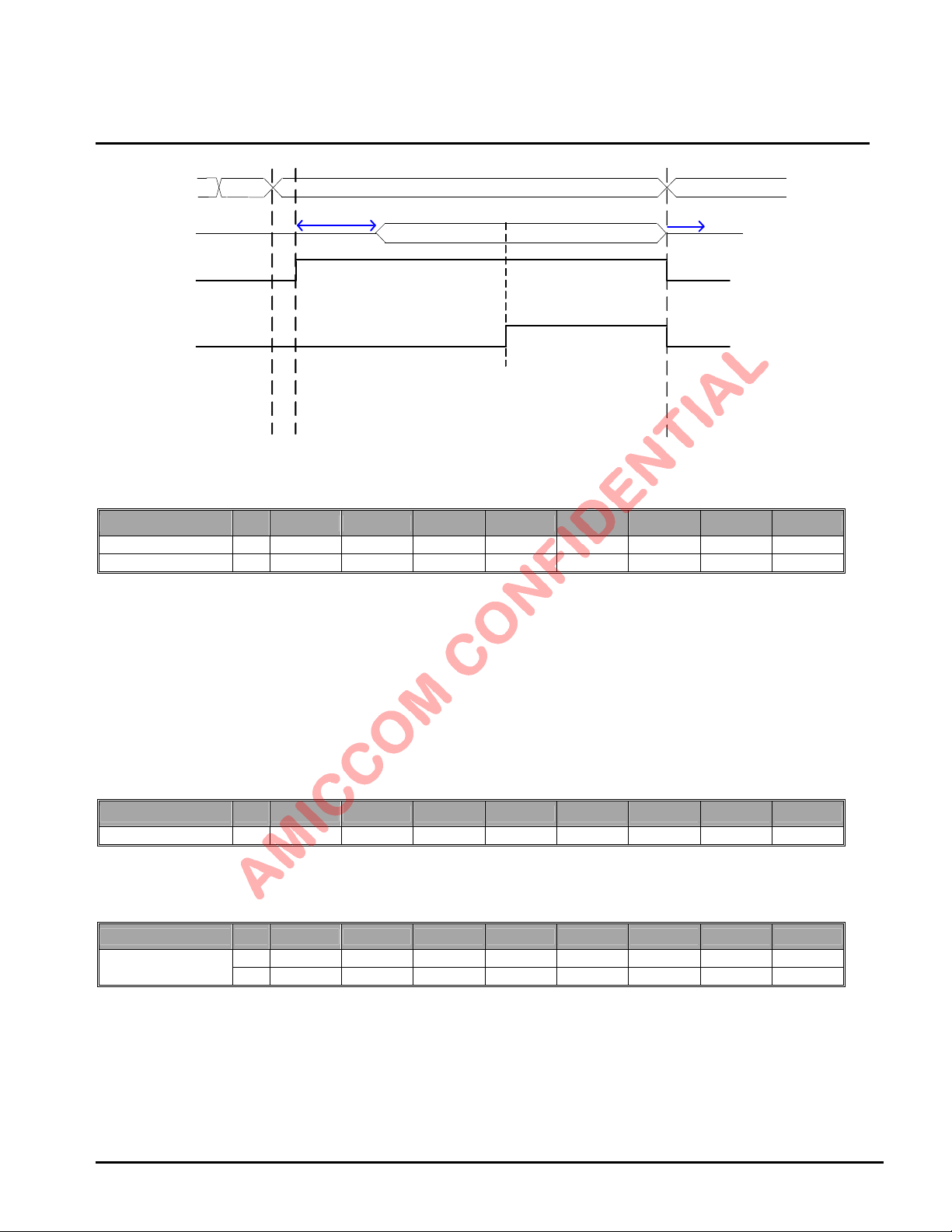
9.2.25 Delay Register II (Address: 18h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Delay W WSEL2 WSEL1 WSEL0 RSSC_D1 RSSC_D0 RS_DLY2 RS_DLY1 RS_DLY0
WSEL [2:0]: XTAL settling delay setting (200us ~ 2.5ms). Recommend WSEL = [011].
[000]: 200us. [001]: 400us. [010]: 600us. [011]: 800us.
[100]: 1ms. [101]: 1.5ms. [110]: 2ms. [111]: 2.5ms.
Crystal
O scilla tor
GIO1 Pin
(WTR)
R FO Pin
RSSC_D [1:0]: RSSI calibration switching time (10us ~ 40us). Recommend RSSC_D = [00].
[00]: 10us. [01]: 20us. [10]: 30us. [11]: 40us.
RS_DLY [2:0]: RSSI measurement delay (10us ~ 80us). Recommend RS_DLY = [000].
[000]: 10us. [001]: 20us. [010]: 30us. [011]: 40us.
[100]: 50us. [101]: 60us. [110]: 70us. [111]: 80us.
Id le
mode
300 us
WSEL
TX or R X S trob e Cm d
10 us + PDL
Packet (Preamble + ID + Payload)
TDL
PA
Ramp Down
16 us
9.2.26 RX Register (Address: 19h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RX W LNAGE AGCE RXSM1 RXSM0 AFCE RXDI DMG ULS
LNAGE: Auto LNA Gain Control Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
AGCE: Auto Front end Gain Control Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
RXSM1: RX clock recovery circuit moving average filter length. Recommend RXSM1 = [1].
[0]: 4 bits. [1]: 8 bits.
RXSM0: Demodulator LPF Bandwidth Select. Recommend RXSM0 = [1].
[0]: 2*IF. [1]: 1*IF.
AFCE: Frequency compensation select.
[0]: Disable. [ 1]: Enable.
RXDI: RX data output invert. Recommend RXDI = [0].
[0]: Non-inverted output. [1]: Inverted output.
DMG: Demodulator Gain Select. Recommend DMG = [1].
[0]: x 1. [1]: x 3.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 24 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 25

ULS: RX Up/Low side band select. Recommend ULS = [0].
[0]: Up side band, [1]: Low side band.
Refer to section 14.2 for details.
9.2.27 RX Gain Register I (Address: 1Ah)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RX Gain I
PRS: Limiter amplifier discharge manual select. Recommend PRS =[0].
MIC: Mixer buffer gain setting. Recommend MIC =[1].
[0]: 0dB. [1]: 6dB.
IGC [1:0]: IFA Attenuation Select. Recommend IGC =[10].
[00]: 0dB. [01]: 6dB. [10]: 12dB. [11]: 18dB.
MGC [1:0]: Mixer Gain Attenuation select. Recommend MGC =[11].
[00]: 0dB. [01]: 6dB. [10]: 12dB. [11]: 18dB.
LGC [1:0]: LNA Gain Attenuation select. Recommend LGC =[11].
[00]: 0dB. [01]: 6dB. [10]: 12dB. [11]: 18dB.
W PRS MIC IGC1 IGC0 MGC1 MGC0 LGC1 LGC0
R -- MICR IGCR1 IGCR0 MGCR1 MGCR0 LGCR1 LGCR0
9.2.28 RX Gain Register II (Address: 1Bh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RX Gain II
R RH7 RH6 RH5 RH4 RH3 RH2 RH1 RH0
W
RSAGC1 RSAGC0 VTL2 VTL1 VTL0 VTH2 VTH1 VTH0
LBA7130
RSAGC [1:0]: AGC clock select. Recommend RSAGC = [11].
[00]: IF / 8. [01]: IF / 4. [10]: IF/ 2. [11]: IF
VTL [2:0]: VCO tuning voltage lower threshold level setting. Recommend VTL = [000].
[000]: 0.1V. [001]: 0.2V. [010]: 0.3V. [011]: 0.4V.
[100]: 0.5V. [101]: 0.6V. [110]: 0.7V. [111]: 0.8V
VTH [2:0]: VCO tuning voltage upper threshold level setting. Recommend VTH = [010].
[000]: VDD_A – 0.6V. [001]: VDD_A – 0.7V. [010]: VDD_A – 0.8V. [011]: VDD_A – 0.9V
[100]: VDD_A – 1.0V. [101]: VDD_A – 1.1V. [110]: VDD_A – 1.2V. [111]: VDD_A – 1.3V
Remark: VDD_A is on chip analog regulator output voltage where is set to 1.8V.
RH [7:0]: RSSI Calibration High Threshold. (Read only)
.
9.2.29 RX Gain Register III (Address: 1Ch)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RX Gain III
RDU: Clock Generator Select. Recommend RDU = [0].
[0]: 128MHZ [1]: 96MHZ.
IFS [1:0]: IF Frequency Select.
[00]: reserved. [01]: reserved. [10]: reserved [11]: 4MHZ.
RSM [1:0]: RSSI Margin = RTH – RTL. Recommend RSM = [11].
[00]: 5. [01]: 10. [10]: 15. [11]: 20.
Refer to chapter 17 for details.
ERSSM: Ending Mode Select in RSSI Measurement. Recommend ERSSM = [0].
[0]: RSSI ending by RX. [1]: RSSI ending by SYNC_Ok.
RSS: RSSI measurement select. (XADS=0, RSS=0, default mode is thermal sensor.)
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable (recomm end).
R RL7 RL6 RL5 RL4 RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0
W
-- RDU IFS1 IFS0 RSM1 RSM0 ERSSM RSS
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 25 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 26
RL [7:0]: RSSI Calibration Low Threshold. (Ready only)
9.2.30 RX Gain Register IV (Address: 1Dh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RX Gain III W LIMC IFBC1 IFBC0 IFAS MHC1 MHC0 LHC1 LHC0
LIMC: IF limiter current select. Recommend LIMC = [1].
[0]: 0.3mA. [1]: 0.6mA.
IFBC [1:0]: IF BPF current Select. Recommend IFBC = [11].
[00]: 0.75 mA.. [01]: 1.4mA. [10]: 2.1mA. [11]: 3.5mA.
IFAS: IF Amp current select. Recommend IFAS = [0].
[0]: 0.3mA. [1]: 0.6mA.
MHC: Mixer Current Select. Recommend MHC = [01].
[00]: 0.6mA. [01]: 1.2mA. [10]: reserved. [11]: reserved.
LHC[1:0]: LNA Current Select. Recommend LHC = [11].
[00]: 0.5mA. [01]: 1mA. [10]: 1.5mA. [11]: 2m A.
9.2.31 RSSI Threshold Register (Address: 1Eh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RSSI Threshold
R ADC7 ADC6 ADC5 ADC4 ADC3 ADC2 ADC1 ADC0
W
RTH7 RTH6 RTH5 RTH4 RTH3 RTH2 RTH1 RTH0
LBA7130
RTH [7:0]: Carrier detect threshold.
Refer to Chapter 17 for details.
CD (Carrier Detect)=1 when RSSI ≧ RT H.
CD (Carrier Detect)=0 when RSSI < RTL.
ADC [7:0]: ADC output value for RSSI measurement.
ADC input voltage= 1.2 * ADC [7:0] / 256 V.
9.2.32 ADC Control Register (Address: 1Fh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ADC Control W AVSEL1 AVSEL0 MVSEL1 MVSEL0 RADC FSARS XADS CDM
AVSEL [1:0]: ADC average times (for Carrier / temeperature sensor / external ADC). Recommend AVSEL = [11].
[00]: No average. [01]: Average 2 times. [10]: Average 4 times. [11]: Average 8 times.
MVSEL [1:0]: ADC average times (for VCO calibration and RSSI ). Recommend MVSEL = [11].
[00]: Average 8 times. [01]: Average 16 times. [10]: Average 32 times. [11]: Average 64 times.
RADC: ADC Read Out Average Mode. Recommend RADC = [0].
[0]: by AVSEL.
[1]: by MVSEL.
FSARS: ADC clock select. Recommend FSARS = [0].
[0]: 4MHz. [1]: 8MHz.
XADS: External ADC Input Signal Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
CDM: RSSI measurement mode. Recommend CDM = [1].
[0]: Single mode. [1]: Continuous mode.
9.2.33 Code Register I (Address: 20h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Code I W MCS WHTS FECS CRCS IDL1 IDL0 PML1 PML0
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 26 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 27
MSC: Manchester Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
WHTS: Data Whitening (Data Encryption) Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable (The data is whitening by multiplying PN7).
FECS: FEC Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable (The FEC is (7, 4) Hamming code).
CRCS: CRC Select. Recommend CRCS = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
IDL [1:0]: ID Code Length Select. Recommend IDL= [01].
[00]: 2 bytes. [01]: 4 bytes. [10]: 6 bytes. [11]: 8 bytes.
PML [1:0]: Preamble Length Select. Recommend PML= [11].
[00]: 1 byte. [01]: 2 bytes. [10]: 3 bytes. [11]: 4 bytes.
9.2.34 Code Register II (Address: 21h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Code II W MSCRC EDRL HECS ETH2 ETH1 ETH0 PMD1 PMD0
MSCRC: Mask CRC (CRC Data Filtering Enable). Recommend MSCRC = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
EDRL: Enable FIFO Dynamic Length
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
Please refer to chapter 16 for details.
HECS: HEC Header CRC-8 select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
Please refer to chapter 16 for details.
ETH [2:0]: Received ID Code Error Tolerance. Recommend ETH = [001].
[000]: 0 bit, [001]: 1 bit. [010]: 2 bit. [011]: 3 bit. [100]: 4 bit, [101]: 5 bit. [110]: 6 bit. [111]: 7 bit.
PMD [1:0]: Preamble pattern detection length. Recommend PMD = [10].
[00]: 0bit. [01]: 4bits. [10]: 8bits. [11]: 16bits.
LBA7130
9.2.35 Code Register III (Address: 22h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Code III W CRCINV WS6 WS5 WS4 W S3 W S2 WS1 WS0
CRCINV: CRC Inverted Select.
[0]: Non-inverted. [1]: inverted.
WS [6:0]: Data Whitening seed setting (data encryption key).
The data is whitened by multiplying with PN7.
Please refer to chapter 16 for details.
9.2.36 IF Calibration Register I (Address: 23h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
IF Calibration I
HFR: Half Rate setting. Recommend HFR = [0].
[0]: Clk gen. by 32 x Data Rate. [1]: Clk gen. by 16 x Data Rate.
CKGS[1:0]: Clock gen. data rate manual setting. Recommend CKGS = [11].
[00]: reserved. [01]: reserved. [10]: reserved. [11]: 4MHZ.
When RDU=0, CKGS[1:0] = IFS[1:0]
When RDU=1, CKGS[1:0] = Manual setting.
MFBS: IF filter calibration value select. Recommend MFBS = [0].
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 27 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
R -- -- -- FBCF FB3 FB2 FB1 FB0
W HFR CKGS1 CKGS0 MFBS MFB3 MFB2 MFB1 MFB0
Page 28

[0]: Auto calibration value. [1]: Manual calibrati on value.
MFB [3:0]: IF filter manual calibration value.
FBCF: IF filter auto calibration flag (read only).
[0]: Pass. [1]: Fail.
FB [3:0]: IF filter calibration value (read only).
MFBS= 0: Auto calibration value (AFB),
MFBS= 1: Manual calibration value (MFB).
9.2.37 IF Calibration Register II (Address: 24h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
IF Calibration II
PWORS: TX high power setting. Recommend PWORS = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
TRT [2:0]: TX Ramp down discharge current select. Recommend TRT = [111].
AMSV [2:0]: TX Ramp up Timing Select. Recommend AMSV = [111].
[000]: 2us, [001]: 4us. [010]: 6us. [011]: 8us. [100]: 10us, [101]: 12us. [110]: 14us. [111]: 16us.
Real case of TX ramping up is AMSV [2:0] multiplied by 2^(RMP[1:0])
AMVS: TX Ramp Up Enable. Recommend AMVS = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
FCD [4:0]: IF filter calibration deviation from goal (read only).
R -- -- FCD4 FCD3 FCD2 FCD1 FCD0
W PWORS TRT2 TRT1 TRT0 ASMV2 ASMV1 ASMV0 AMVS
LBA7130
9.2.38 VCO current Calibration Register (Address: 25h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
VCO current
Calibration
ROSCS: WOR RC select. Recommend ROSCS = [1]
RSIS: WOR current select. Recommend RSIS = [0]
VCRLS: VCO Current Resistor Select. Recommend VCRLS = [0]
[0]: low current select. [1]: high current select.
MVCS: VCO current calibration value select. Recommend MVCS = [0].
[0]: Auto calibration value. [1]: Manual calibrati on value.
VCOC [3:0]: VCO current manual calibration value.
VCCF: VCO Current Auto Calibration Flag (read only).
[0]: Pass. [1]: Fail.
VCB [3:0]: VCO current calibration value (read only).
MVCS= 0: Auto calibration value (VCB).
MVCS= 1: Manual calibration value (VCOC).
R -- -- -- VCCF VCB3 VCB2 VCB1 VCB0
ROSCS RSIS VCRLS MVCS VCO C3 VCOC2 VCOC1 VCOC0
W
9.2.39 VCO band Calibration Register I (Address: 26h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
VCO Single band
Calibration I
DCD [1:0]: VCO Deviation Calibration Delay. Recommend DCD = [11].
Delay time = PDL (Delay Register I, 17h) × ( DDC + 1 ).
DAGS: DAG Calibration Value Select. Recommend DAGS = [0].
[0]: Auto calibration value. [1]: Manual calibration value.
R -- -- -- -- VBCF VB2 VB1 VB0
DCD1 DCD0 DAGS
W
CWS MVBS MVB2 MVB1 MVB0
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 28 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 29

CWS: Clock Disable for VCO Modulation. Recommend CWS = [1].
[0]: Enable. [1]: Disable.
MVBS: VCO bank calibration value select. Recommend MVBS = [0].
[0]: Auto calibration value. [1]: Manual calibrati on value.
MVB [2:0]: VCO band manual calibration value.
VBCF: VCO band auto calibration flag (read only).
[0]: Pass. [1]: Fail.
VB [2:0]: VCO bank calibration value (read only).
MVBS= 0: Auto calibration value (AVB).
MVBS= 1: Manual calibration value (MVB).
9.2.40 VCO band Calibration Register II (Address: 27h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DAGM7 DAGM6 DAGM5 DAGM4 DAGM3 DAGM2 DAGM1 DAGM0
VCO Single band
Calibration II
DAGM [7:0]: DAG Manual Setting Value.
DAGB [7:0]: Auto DAG Calibration Value (read only).
W
DAGB7 DAGB6 DAGB5 DAGB4 DAGB3 DAGB2 DAGB1 DAGB0
R
LBA7130
9.2.41 VCO Deviation Calibration Register I (Address: 28h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DEVA7 DEVA6 DEVA5 DEVA4 DEVA3 DEVA2 DEVA1 DEVA0
VCO Deviation
Calibration I
DEVS [3:0]: Deviation Output Scaling. Recommend DEVS = [0111].
DAMR_M: DAMR Manual Enable. Recommend DAMR_M = [0].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
VMTE_M: VMT Manual Enable. Recommend VMTE_M = [0].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
VMS_M: VM Manual Enable. Recommend VMS_M = [0].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
MSEL: VMS, VMTE and DAMR control select. Recommend MSEL = [0].
[0]: Auto control. [1]: Manual control.
DEVA [7:0]: Deviation Output Value (read only).
MVDS (29h)= 0: Auto calibration value ((DEVC / 8) × (DEVS + 1)),
MVDS (29h)= 1: Manual calibration value (DEVM [6:0]).
R
DEVS3 DEVS2 DEVS1 DEVS0 DAMR_M VMTE_M VMS_M MSEL
W
9.2.42 VCO Deviation Calibration Register II (Address: 29h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DEVC7 DEVC6 DEVC5 DEVC4 DEVC3 DEVC2 DEVC1 DEVC0
VCO Deviation
Calibration II
MVDS: VCO Deviation Calibration Select. Recommend MVDS = [0].
[0]: Auto calibration value. [1]: Manual calibration value.
DEVM [6:0]: VCO Deviation Manual Calibration Value.
DEVC [7:0]: VCO Deviation Auto Calibration Value (read only).
R
MVDS DEVM 6 DEVM5 DEVM4 DEVM3 DEVM2 DEVM1 DEVM0
W
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 29 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 30

LBA7130
9.2.43 DASP0 (Address: 2Ah, Page 0 by AGT [3:0]=0)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP0 W QLIM RFSP
QLIM: quick charge select for IF limiter amp. Recommend QLIM = [0].
[0]: disable. [1]: enable. (QLIM fall down delay 10 us).
RFSP: RF single port Select. Recommend RFSP = [0].
[0]: LNA (RFI) and PA (RFO) are combined internally to RFI pin.
[1]: LNA (RFI) and PA (RFO) are separated to RFI pin and RFO pin.
INTXC: internal crystal oscillator capacitor selection. Recommend INTXC = [1].
[0]: disable. [1]: enable.
CSXTAL[4:0]: On-chip Crystal loading select. Recommend CSXTAL = [10100] if Xtal Cload = 18 pF.
{INTXC,CSXTAL[4:0]} On-chip Xtal Capacitor (pF)
0XXXXX 0
100000 16
100001 17
100010 18
…
111110 46
111111 47
INTXC
(CSXTL5)
CSXTL4 CSXTL3 CSXTL2 CSXTL1 CSXTL0
9.2.43 DASP1 (Address: 2Ah, Page 1 by AGT[3:0]=1)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP1 W STS CELS RGS RGC1 RGC0 VRPL1 VRPL0 INTPRC
STS: Start up mode select. Shall be set to [0].
CELS: Digital voltage select in standby mode. Recommend CELS = [1].
RGS: Low Power Regulator Voltage Select. Recommend RGS = [0].
LVR (2Ch) RGS Low Power Regulator Voltage Note
0 0 3/5 *REGI
0 1 3/4 * REGI
1 0 1.8 V Recommended
1 1 1.6 V
RGC [1:0]: Low power band-gap current select. Recommend RGC = [01].
VRPL [1:0]: internal PLL loop filter resistor value select. Recommend VRPL = [00].
[00]: 500 ohm. [01]: 666 ohm. [10]: 1 K ohm. [11]: 2K ohm.
INTPRC: Internal PLL loop filter resistor and capacitor select. Recommend INTPRC = [1].
[0]: disable. [1]: enable
9.2.43 DASP2 (Address: 2Ah, Page 2 by AGT[3:0]=2)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP2 W VTRB3 VTRB2 VTRB1 VTRB0 VMRB3 VMRB2 VMRB1 VMRB0
VTRB [3:0]: Resistor Bank for VT RC Filtering. Shall be set to [0000].
VMRB [3:0]: Resistor Bank for VM RC Filtering. Shall be set to [0000].
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 30 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 31

9.2.43 DASP3 (Address: 2Ah, Page 3 by AGT[3:0]=3)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP3 W DCV7 DCV6 DCV5 DCV4 DCV3 DCV2 DCV1 DCV0
DCV [7:0]: Demodulator Fix mode DC value. Recommend DCV = [0x80].
9.2.43 DASP4 (Address: 2Ah, Page 4 by AGT[3:0]=4)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP4 W/R VMG7 VMG6 VMG5 VMG4 VMG3 VMG2 VMG1 VMG0
VMG [7:0]: VM Center Value for Deviation Calibration. Recommend VMG [7:0] = [0x80].
9.2.43 DASP5 (Address: 2Ah, Page 5 by AGT[3:0]=5)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP5 W -- -- PKT1 PKT0 PKS PKIS1 PKIS0 IFPK
PKT[1:0]: VCO Peak Detect Current Select. Recommend PKT = [00].
PKS: VCO Current Calibration Mode Select. Recommend PKS = [0].
PKIS[1:0]: AGC Peak Detect Current Select. Recommend PKIS = [00].
IFPK: AGC Amplifier Current Select. Recommend IFPK = [0].
LBA7130
9.2.43 DASP6 (Address: 2Ah, Page 6 by AGT[3:0]=6)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP6 W -- HPLS HRS PACTL IWS CNT M XD LXD
HPLS: High Power LNA Gain Select. Recommend HPLS = [0].
[0]: LGC set to 6dB when in TX Mode. [1]: LGC set to 24dB when in TX Mode.
HRS: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
PACTL: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
IWS: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [1].
CNT: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
MXD: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [1].
LXD: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
9.2.43 DASP7 (Address: 2Ah, Page 7 by AGT[3:0]=7)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
DASP7 W
XDS: VCO Modulation Data Sampling Clock selection. Recommend XDS = [0].
[0]: 8x over-sampling Clock. [ 1]: XCPCK Clock.
VRSEL: AGC Function select. Recommend VRSEL = [1].
[0]: RSSI AGC. [1 ]: Normal AGC.
MS: AGC Manual scale select. Recommend MS = [0].
[0]: By (RH−RL). [ 1]: By MSCL[4:0].
MSCL[4:0]: AGC Manual Scale setting. Recommend MSCL = [00000].
XDS VRSEL MS MSCL4 MSCL3 MSCL2 MSCL1 MSCL0
9.2.44 VCO Modulation Delay Register (Address: 2Bh)
Bit R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Name W DMV1 DMV0 DEVFD2 DEVFD1 DEVFD0 DEVD2 DEVD1 DEVD0
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 31 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 32

DMV [1:0]: Demodulator D/A Voltage Range Select. Recommend DMV = [11].
[00]: 1/32*1.2. [01]: 1/16*1.2. [10]: 1/8*1.2. [11]: 1/4*1.2.
DEVFD [2:0]: VCO Modulation Data Delay by 8x over-sampling Clock. Recommend DEVFD = [011].
DEVD [2:0]: VCO Modulation Data Delay by XCPCK Clock. Recommend DEVD = [100].
9.2.45 Battery detect Register (Address: 2Ch)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Battery detect
LVR: Low Power Bandgap Select. Recommend LVR = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
RGV [1:0]: VDD_D and VDD_A voltage setting in non-Sleep mode. Recommend RGV = [11].
[00]: 2.1V. [01]: 2.0V. [10]: 1.9V. [11]: 1.8V.
QDS: VDD Quick Discharge Select. Recommend QDS = [1].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
BVT [2:0]: Battery voltage detect threshold.
[000]: 2.0V. [001]: 2.1V. [010]: 2.2V. [011]: 2.3V.
[100]: 2.4V. [101]: 2.5V. [110]: 2.6V. [111]: 2.7V.
BD_E: Battery Detect Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable. It will be clear after battery detection is triggered.
BDF: Battery detection flag.
[0]: Battery voltage < BVT [2:0]. [1]: Battery voltage ≧ BVT [2:0].
W LVR RGV1 RGV0 QDS BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
R -- RGV1 RGV0 BDF BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
LBA7130
9.2.46 TX test Register (Address: 2Dh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TX test W RMP1 RMP0 TXCS PAC1 PAC0 TBG2 TBG1 TBG0
RMP [1:0]: PA ramp up timing scale. Recommend RMP = [00].
TXCS: TX Current Setting. Recommend TXCS = [1].
[0]: lowest current. [1]: highest current.
PAC [1:0]: PA Current Setting.
TBG [2:0]: TX Buffer Setting.
RF Band Typical power (dBm) PWORS (24h) TBG TXCS PAC Typical current (mA)
2.4GHz
Refer to A7130 App. Note for more settings.
5 1 7 1 2 29
0 1 0 1 0 20
-5 0 4 1 0 18
-17 0 0 1 0 16
9.2.47 Rx DEM test Register I (Address: 2Eh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Rx DEM test I W DMT DCM1 DCM0 MLP1 MLP0 SLF2 SLF1 SLF0
DMT: Reserved for internal usage only. Shall be set to [0].
DCM [1:0]: Demodulator DC estimation mode. Recommend DCM = [10].
(The average length before hold is selected by DCL in RX DEM Test Register II.)
[00]: Fix mode (For testing only). DC level is set by DCV [7:0].
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 32 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 33

LBA7130
[01]: Preamble hold mode. DC level is preamble average value.
[10]: ID hold mode. DC level is the average value hold about 8 bit data rate later if preamble is detected.
[11]: Payload average mode (For internal usage). DC level is payload data average.
MLP1: Reserved for internal usage. Shall set MLP1 = [0].
MLP0: Reserved for internal usage. Shall set MLP0 = [0].
SLF [2:0]: Symbol Recovery Loop Filter Setting. Shall be SLF[2:0] = [111].
9.2.48 Rx DEM test Register II (Address: 2Fh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Rx DEM test II W DCH1 DCH0 DCL2 DCL1 DCL0 RAW CDTM1 CDTM0
DCH [1:0]: DC Estimation of AGC hold mode. Recommend DCH = [11].
[00]: hold when PMDO. [01]: hold when Fsync. [10]: no hold. [11]: no hold.
DCL [2]: DC Estimation Average Length After ID Detected. Recommend DCL[2] = [1].
[0]: 128 bits. [1]: 256 bits.
DCL [1:0]: DC Estimation Average Length Before ID Detected. Recommend DCL[1:0] = [10].
[00]: 8 bits. [01]: 16 bits. [10]: 32 bits. [11]: 64 bits.
RAW: Raw Data Output Select. Recommend RAW = [1].
[0]: latch data output. [1]: RAW data output.
CDTM [1:0]: Preamble carrier detect setting. Recommend CDTM = [11].
[00]: 12. [01]: 24. [10]: 36. [11]: 48.
9.2.49 Charge Pump Current Register I (Address: 30h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CPC I W
CPM [3:0]: Charge Pump Current Setting for VM loop. Recommend CPM = [1111].
Charge pump current = (CPM + 1) / 16 mA.
CPT [3:0]: Charge Pump Current Setting for VT loop. Recommend CPT = [0000].
Charge pump current = (CPT + 1) / 16 mA.
CPM3 CPM2 CPM1 CPM0 CPT3 CPT2 CPT1 CPT0
9.2.50 Charge Pump Current Register II (Address: 31h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CPC II W
CPTX [3:0]: Charge Pump Current Setting for TX mode. Recommend CPTX = [0011].
Charge pump current = (CPTX + 1) / 16 mA.
CPRX [3:0]: Charge Pump Current Setting for RX mode. Recommend CPRX = [0111].
Charge pump current = (CPRX + 1) / 16 mA.
CPTX3 CPTX2 CPTX1 CPTX0 CPRX3 CPRX2 CPRX1 CPRX0
9.2.51 Crystal test Register (Address: 32h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Crystal test W CDPM CPS CPH CPCS DBD XCC XCP1 XCP0
CDPM:First Time Preamble Detect mode select. Recommend CDPM = [0].
CPS: PLL charge pump enable. Recommend CPS = [1].
[0]: Enable. [1]: Disable.
CPH: Charge Pump High Current. Shall be set to [0].
[0]: Normal. [1]: High.
CPCS: Charge Pump Current Select. Shall be set to [1].
[0]: Use CPM for TX, CPT for RX. [1]: Use CPTX for TX, CPRX for RX.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 33 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 34

DBD: Crystal Frequency Doubler High Level Pulse Width Select. Recommend DBD = [0].
[0]: about 8 ns. [1]: about 16 ns.
XCC: Crystal Startup Current Selection. Recommend XCC = [1].
[0]: about 0.7 mA. [1]: about 1.5 mA.
XCP [1:0]: Crystal Oscillator Regulated Couple Setting. Recommend XCP = [01].
[00]: 1.5mA. [01]: 0.5mA. [10]: 0.35mA. [11]: 0.3mA.
9.2.52 PLL test Register (Address:33h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PLL test W MDEN OLM PRIC1 PRIC0 PRRC1 PRRC0 SDPW NSDO
MDEN : Use for Manual VCO Calibration. Shall be set to [0].
OLM: Open Loop Modulation Enable. Shall be set to [0].
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
PRIC [1:0]: Prescaler IF Part Current Setting. Shall be set to [01].
[00]: 0.95mA. [01]: 1.05mA. [10]: 1.15mA. [11]: 1.25m A.
PRRC [1:0]: Prescaler RF Part Current Setting. Shall be set to [01].
[00]: 1.0mA. [01]: 1.2mA. [10]: 1.4mA. [11]: 1.6mA.
SDPW: Clock Delay For Sigma Delta Modulator. Shall be set to [0].
[0]: 13 ns. [1]: 26 ns.
NSDO: Sigma Delta Order Setting. Shall be set to [1].
[0]: order 2. [1]: order 3.
LBA7130
9.2.53 VCO test Register I (Address:34h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
VCO test I W DEVGD2 DEVGD1 DEVGD0 TLB1 TLB0 RLB1 RLB0 VBS
DEVGD [2:0]: Sigma Delta Modulator Data Delay Setting. Recommend DEVGD = [000].
TLB [1:0]: LO Buffer Current Select. Recommend TLB[1:0] = [10].
[00]: 0.6mA. [01]: 0.75mA. [10]: 0.9mA. [11]: 1.05mA.
RLB [1:0]: RF divider Current Select. Recommend RLB[1:0] = [10].
[00]: 1.2mA. [01]: 1.5mA. [10]: 1.8mA. [11]: 2.1mA.
VBCS : VCO Buffer Current Setting. Recommend VBCS = [1].
[0]: 1mA. [1]: 1.5mA.
9.2.54 RF Analog Test Register (Address: 35h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RFT W AGT3 AGT2 AGT1 AGT0 RFT3 RFT2 RFT1 RFT0
AGT[3:0]:Page selection for both DASP (2Ah) and ROMP (38h).
AGT[3:0]
(35h)
0 DASP0 (page 0) ROMP0 (page 0) Internal usage only
1 DASP1 (page 1) ROMP1 (page 1) Internal usage only
2 DADP2 (page 2) ROMP2 (page 2) Internal usage only
3 DASP3 (page 3) ROMP3 (page 3) Internal usage only
4 DASP4 (page 4) ROMP4 (page 4) Internal usage only
5 DASP5 (page 5)
6 DASP6 (page 6)
DASP Register Group
(2Ah)
ROMP Register Group
(38h)
Note
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 34 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 35

RFT [3:0]: RF analog pin configuration for testing. Recommend RFT= [0000].
9.2.55 AES Key data Register (Address: 36h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Key Data
R KEYO7 KEYO6
W
KEYI7 KEYI6
KEYI [7:0]: AES128 key input, total 16-btyes. (Write only).
KEYO [7:0]: AES128 key output, total 16-bytes. (Read only). Select by KEYOS (3Eh).
A E S K e y D a ta (to ta l 1 6 B y te s )
KEYO5 KEYO4 KEYO3 KEYO2 KEYO1 KEYO0
KEYI5 KEYI4 KEYI3 KEYI2 KEYI1 KEYI0
LBA7130
KEY[7:0] KEY[15:8]
…
KE Y[127:120]
9.2.56 Channel Select Register (Address: 37h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Channel Select W CHI3 CHI2 CHI1 CHI0 CHD3 CHD2 CHD1 CHD0
CHI [3:0]: Auto IF Offset Channel Number Setting. Recommend CHI [3:0] = [0111].
F
× (CHI + 1 ) = F
CHSP
Refer to chapter 14 for F
IF
setting
CHSP
.
CHD [3:0]: Channel Frequency Offset for Deviation Calibration. Recommend CHD [3:0] = [0111].
Offset channel number = +/- (CHD + 1).
9.2.57 ROMP0 (Address: 38h, Page 0 by AGT[3:0]=0)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ROMP0 W MPOR EPRG MIGS MRGS MRSS MTMS MADS MBGS
MPOR: manual SPI read in OTP program cycle.
EPRG: enable OTP program in test mode.
[0]: disable. [1]: enable.
MIGS: IF gain setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
MRGS: LNA and mixer gain setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
MRSS: RSSI voltage fine trim setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
MTMS: Temp voltage fine trim setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
MADS: ADC fine trim setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
MBGS: Bandgap voltage fine trim setting select.
[0]: SPI setting. [1]: OTP setting.
9.2.57 ROMP1 (Address: 38h, Page 1 by AGT[3:0]=1)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ROMP1 W APG MPA1 MPA0 FBG4 FBG3 FBG2 FBG1 FBG0
APG: OTP program select.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 35 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 36

[1]: auto program. [0]: manual SPI setting.
MPA [1:0]: OPT address setting in manual SPI OTP program.
FBG [4:0]: Bandgap voltage SPI fine trim setting.
9.2.57 ROMP2 (Address: 38h, Page 2 by AGT[3:0]=2)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ROMP2 W PTM1 PTM0 CTR5 CTR4 CTR3 CTR2 CTR1 CTR0
PTM [1:0]: OTP program operation mode select. Recommend PTM = [00].
CTR [5:0]: ADC voltage SPI fine trim setting.
9.2.57 ROMP3 (Address: 38h, Page 3 by AGT[3:0]=3)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ROMP3 W FGC1 FGC0 CRS2 CRS1 CRS0 SRS2 SRS1 SRS0
FGC[1:0]: BPF fine gain control.
CRS [2:0]: RSSI voltage offset fine trim setting.
SRS [2:0]: RSSI voltage curve slope fine time setting.
LBA7130
9.2.57 ROMP4 (Address: 38h, Page 4 by AGT[3:0]=4)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ROMP4 W -- STMP STM5 STM4 STM3 ST M2 STM1 STM0
STMP: Temp voltage ADC reading select.
[0]: 1 scale / degree C. [1]: 2 scale/degree C.
STM [5:0]: Temperature voltage SPI fine trim setting.
9.2.58 Data Rate Clock Register (Address: 39h)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Data Rate Clock W
SDR [1:0]: Data Rate Setting. On-air Data rate = FIF/ (SDR+1).
Data Rate FIF (Hz) SDR [7:0] Xtal
4M 4M 0x00 16 MHz
Please refer to chapter 13 for details.
SDR7 SDR6 SDR5 SDR4 SDR3 SDR2 SDR1 SDR0
9.2.59 FCR Register (Address: 3Ah)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
FCR
FCL [1:0] : FCB Length.
[00]: No Fram e Contr ol.
[01]: 1 byte FCB (3Dh).
[10]: 2 byte FCB (3Dh).
[11]: 4 byte FCB (3Dh).
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
ARC [3:0] : Auto Resend Cycle Setting.
[0000]: resend disable.
R ARTEF VPOAK RCR3 RCR2 RCR1 RCR0 EAK EAR
W FCL1 FCL0 ARC3 ARC2 ARC1 ARC0 EAK EAR
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 36 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 37

LBA7130
[0001]: 1 [0010]: 2 [0011]: 3 [0100]: 4 [0101]: 5 [0110]: 6 [0111]: 7 [1000]: 8 [1001]: 9 [1010]: 10
[1011]: 11 [1100]: 12 [1101]: 13 [1110]: 14 [1111]: 15
EAK : Enable Auto ACK.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
EAR : Enable Auto Resend.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
ARTEF: Auto re-transmission ending flag (read only).
[0]: Resend not end [1 ]: Finish resend.
VPOAK : Valid Packet or ACK OK Flag. (read only and auto clear by Strobe command)
[0]: Neither valid packet nor ACK OK. [1]: Valid packet or ACK OK.
RCR [3:0] (read) : Decremented of ARC[3:0].
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
9.2.60 ARD Register (Address: 3Bh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ARD W ARD7 ARD6 ARD5 ARD4 ARD3 ARD2 ARD1 ARD0
ARD[7:0] : Auto Resend Delay
ARD Delay = 200 us * (ARD+1) à (200us ~ 51.2 ms)
[0000-0000]: 200 us.
[0000-0001]: 400 us.
[0000-0010]: 600 us.
…
…
[1111-1111]: 51.2 ms.
Please refer to chapter 19 for details.
9.2.61 AFEP Register (Address: 3Ch)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
AFEP
EAF: Enable ACK FIFO.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
SPSS : Mode Back Select for Auto ACK/Resend.
[0]: Standby mode. [1]: PLL mode.
ACKFEP [5:0]: FIFO Length setting for auto-ack packet.
ACK FIFO Length = (ACKFEP[5:0] + 1)
max. 64 bytes.
EARTS [2:0]: Enable Auto Resend Read.
SID [2:0]: Serial Packet ID.
This device increases SID each time for every new packet and keep the same SID when retransmitting.
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
R 0 0 EARTS2 EARTS1 EARTS0 SID2 SID1 SID0
W EAF SPSS ACKFEP5 ACKFEP4 ACKFEP3 ACKFEP2 ACKFEP1 ACKFEP0
9.2.62 FCB Register (Address: 3Dh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
FCB R/W F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0
FCB [7:0]: Frame Control Buffer, total 20-bytes.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 37 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 38

Byte Name Bit-Map Description Strobe Cmd
0 FCB0 0 0 1 1 1 SID2 SID1 SID0 For auto-resend. NA
1 FCB1 [7:0]
2 FCB2 [7:0]
ACK info
by user’s attaching
NA
3 FCB3 [7:0]
Remark:
1. Please refer to section 10.4.10 for details.
2. SID is auto incremental for every new packet if FCB0 is enabled.
3. FCB0 ~ FCB3 is controlled by FCL[1:0] (3Ah)
4. User can attach wanted ACK information to FCB1 ~ FCB3 if auto-ack is enabled (EAK =1).
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
LBA7130
4 bytes
au to
ack/resend
ID codePreamble Payload (CRC)
4 bytes
FCB
1~4 bytes
M A C H e ader (self-generated )PH Y H ead er (self-generated)
dynamic
FIFO
FEP
12 bits
9.2.63 KEYC Register (Address: 3Eh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
KEYC W KEYOS AFIDS ART MS MIDS AESS -- AKFS EDCRS
KEYOS: AES128 Key source read select.
[0]: If AKFS=1, from RX received encrypted AES128 key data.
If AKFS=0, from SPI write AES128 key data.
[1]: From encrypted/decrypted AES128 key data.
Please refer to chapter 21 for details.
AFIDS: FIFO ID appendixes Select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
ARTMS: auto-resend Interval Mode Select.
[0]: random interval. [1]: fixed interval.
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
MIDS: FIFO control byte address mapping for FIFO ID select.
[0]: Received device ID. [1]: internal FIFO control byte ID.
AESS: encryption format selection.
[1]: Standard AES 128 bit. [0]: proprietary 32 bit.
Please refer to chapter 21 for details.
AKFS: Data packet with decrypted key appendixes select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
EDRCS: Data encrypt or decrypt select.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable.
2 bytesPhy. 64 bytes
9.2.64 USID Register (Address: 3Fh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
USID W RND7 RND6 RND5 RND4 RND3 RND2 RND1 RND0
RND [7:0]: Random seed for auto-resend interval.
Please refer to chapter 16 and 19 for details.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 38 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 39

LBA7130
10. SPI
A7130 only supports one SPI interface with maximum data rate up to 15Mbps. MCU should assert SCS pin low (SPI chip
select) to active accessing of A7130. Via SPI interface, user can access control registers and issue Strobe command.
Figure 10.1 gives an overview of SPI access manners.
3-wire SPI (SCS, SCK and SDIO) or 4-wire SPI (SCS, SCK, SDIO and GIO1/GIO2) configuration is provided. For 3-wire SPI,
SDIO pin is configured as bi-direction to be data input and output. For 4-wire SPI, SDIO pin is data input and GIO1 (or GIO2)
pin is data output. In such case, GIO1S (0bh) or GIO2S (0ch) should be set to [0110].
For SPI write operation, SDIO pin is latched into A7130 at the rising edge of SCK. For SPI read operation, if input address is
latched by A7130, data output is aligned at falling edge of SCK. Therefore, MCU can latch data output at the rising edge of
SCK.
To control A7130’s internal state machine, it is very easy to send Strobe command via SPI interface. The Strobe command is
a unique command set with total 8 commands. See section 10.3, 10.4 and 10.5 for details.
SPI chip select Data In Data Out
3-Wire SPI SCS pin = 0 SDIO pin SDIO pin
4-Wire SPI SCS pin = 0 SDIO pin GIO1 (GIO1S=0110) /
GIO2 (GIO2S=0110)
SCS
Read/Wr ite register
Read/Writ e RF
FIFO
Read/Write ID
register
Sleep Mode
Idle Mode
STBY Mode
PLL Mode
RX Mode
TX Mode
FIFO Write Reset
FIFO Read Reset
ADDR
reg
ADDR
FIFO
ADDR
ID
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Strobe
Command
Data Byte
DataByte
Data Byte
Sleep Mod e
Idle Mode
STBY Mode
PLL Mode
RX Mode
TX Mode
FIFO Write Reset
FIFO Read Reset
ADDR
0
DataByte1DataByte2Data Byte
0
DataByte
Data Byte DataByte
reg
1
Data Byte
3
ADDR
2
reg
DataByte
3
DataByte
n
Figure 10.1 SPI Access Manners
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 39 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 40

LBA7130
10.1 SPI Format
The first bit (A7) is critical to indicate A7130 the following instruction is “Strobe command” or “control register”. See Table 10.1
for SPI format. Based on Table 10.1, To access control registers, just set A7=0, then A6 bit is used to indicate read (A6=1) or
write operation (A6=0). See Figure 10.2 (3-wire SPI) and Figure 10.3 (4-wire SPI) for details.
Address Byte (8 bits) Data Byte (8 bits)
CMD R/W Address Data
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Table 10.1 SPI Format
Address byte:
Bit 7: Command bit
[0]: Control registers.
[1]: Strobe command.
Bit 6: R/W bit
[0]: Write data to control register.
[1]: Read data from control register.
Bit [5:0]: Address of control register
Data Byte:
Bit [7:0]: SPI input or output data, see Figure 10.2 and Figure 10.3 for details.
10.2 SPI Timing Characteristic
No matter 3-wire or 4-wire SPI interface is configured, the maximum SPI data rate is 10 Mbps. To active SPI interface, SCS
pin must be set to low. For correct data latching, user has to take care hold time and setup time between SCK and SDIO. See
Table 10.2 for SPI timing characteristic.
Parameter Description Min. Max. Unit
F
C
T
SE
T
HE
T
SW
T
HW
T
DR
FIFO clock frequency. 10 MHz
Enable setup tim e. 50 ns
Enable hold time. 50 ns
TX Data setup time. 50 ns
TX Data hold time. 50 ns
RX Data delay time. 0 50 ns
Table 10.2 SPI Timing Characteristic
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 40 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 41

10.3 SPI Timing Chart
In this section, 3-wire and 4-wire SPI interface read / write timing are described.
10.3.1 Timing Chart of 3-wire SPI
SCS
SCK
LBA7130
SDIO
SCS
SCK
SDIO
A7 DW7A0A1A2A3A4A5A6 DW0DW5DW6 DW1
RF IC will latch address bit at
rising edge of SCK
A7 DR7A0A1A2A3A4A5A6 DR0DR5DR6 DR1
RF IC will latch address bit at
rising edge of SCK
Figure 10.2 Read/Write Timing Chart of 3-Wire SPI
10.3.2 Timing Chart of 4-wire SPI
SCS
SCK
SDIO
A7 DW7A0A1A2A3A4A5A6 DW0DW5DW6 DW1
RF IC will latch address bit at
rising edge of SCK
RF IC will latch data bit at
the rising edge of SCK
3-Wire serial interface - Write operation
RF IC will change the data
when falling ed ge of SCK
3-Wire serial interface - Read operation
RF IC will latch data bit at rising
edge of SCK
4-Wire serial interface - Writ e operation
MCU can latch data at rising
edge of SCK
SCS
SCK
SDI
GIOx
A7 A0A1A2A3A4A5A6
RF IC will latch address bit at
rising edge of SCK
x
RF IC will change the data
when falling edge of SCK
4-Wire serial interface - Read operation
DR7 DR1DR0DR5DR6 DR2
x
MCU can latch data at the
rising edge of SCK
Figure 10.3 Read/Write Timing Chart of 4-Wire SPI
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 41 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 42

LBA7130
10.4 Strobe Commands
A7130 supports 8 Strobe commands to control internal state machine for chip’s operations. Table 10.3 is the summary of
Strobe commands.
Be notice, Strobe command could be defined by 4-bits (A7~A4) or 8-bits (A7~A0). If 8-bits Strobe command is selected, A3
~ A0 are don’t care conditions. In such case, SCS pin can be remaining low for asserting next commands.
Strobe Command when AFIDS =0 (3Eh) and MIDS =0 (3Eh)
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 Deep Sleep mode (I/Os are in tri-state)
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 Deep Sleep mode (I/Os are pulled high)
1 0 0 0 x x x x Sleep mode
1 0 0 1 x x x x Idle mode
1 0 1 0 x x x x Standby mode
1 0 1 1 x x x x PLL mode
1 1 0 0 x x x x RX mode
1 1 0 1 x x x x TX mode
1 1 1 0 x x x x FIFO write pointer reset
1 1 1 1 x x x x FIFO read pointer reset
Remark: x means “ don’t care”
Description
Table 10.3 Strobe Commands by SPI interface
10.4.1 Strobe Command - Sleep Mode
Refer to Table 10.3 user can issue 4 bits (1000) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into Sleep mode. Below are the
Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 0 0 x X x x Sleep mode
Figure 10.4 Sleep mode Command Timing Chart
Description
10.4.2 Strobe Command - ldle Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1001) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into Idle mode. Below is the Strobe
command table and timing chart.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 42 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 43

Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Description
1 0 0 1 x X x x Idle mode
LBA7130
SCS
SCK
SDIO
A7 A4A5A6
Idle mode
SCS
SCK
SDIO
A7 A4A5A6
A3 A0A1A2
Idle mode
Figure 10.5 Idle mode Command Timing Chart
10.4.3 Strobe Command - Standby Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1010) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into Standby mode. Below is the
Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 1 0 x X x x Standby mode
Description
Figure 10.6 Standby mode Command Timing Chart
10.4.4 Strobe Command - PLL Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1011) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into PLL mode. Below are the
Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 1 1 x X x x PLL mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 43 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Description
Page 44

LBA7130
Figure 10.7 PLL mode Command Timing Chart
10.4.5 Strobe Command - RX Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1100) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into RX mode. Below are the Strobe
command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 1 0 0 x X x x RX mode
Description
Figure 10.8 RX mode Command Timing Chart
10.4.6 Strobe Command - TX Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1101) Strobe command directly to set A7130 into TX mode. Below are the Strobe
command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 1 0 1 x x x x TX mode
Figure 10.9 TX mode Command Timing Chart
Description
10.4.7 Strobe Command – FIFO Write Pointer Reset
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 44 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 45

LBA7130
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1110) Strobe command directly to reset A7130 FIFO write pointer. Below is the
Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 1 1 0 x x x x FIFO write pointer reset
Figure 10.10 FIFO write pointer reset Command Timing Chart
Description
10.4.8 Strobe Command – FIFO Read Pointer Reset
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue 4 bits (1111) Strobe command directly to reset A7130 FIFO read pointer. Below are the
Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 1 1 1 x x x x FIFO read pointer reset
Figure 10.11 FIFO read pointer reset Command Timing Chart
Description
10.4.9 Strobe Command – Deep Sleep Mode
Refer to Table 10.3, user can issue (8 bits) deep sleep Strobe command directly to switch off power supply to A7130.In this
mode, A7130 is staying minimum current consumption. All registers are no data retention and re-calibration flow is
necessary. Below are the Strobe command table and timing chart.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 Tri-state of GIO1 / GIO2 (no register retention)
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 Internal Pull-High of GIO1 / GIO2 (no register retention)
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 45 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Description
Page 46

Figure 10.12 Deep Sleep Mode Timing Chart
LBA7130
10.5 Reset Command
In addition to power on reset (POR), MCU could issue software reset to A7130 by setting Mode Register (00h) through SPI
interface as shown below. As long as 8-bits address (A7~A0) are delivered zero and data (D7~D0) are delivered zero, A7130
is informed to generate internal signal “RESETN” to initial itself. After reset command, A7130 is in standby mode and
calibration procedure shall be issued again.
SCS
SCK
SDIO
RESETN
A7 DW7A0A1A2A3A4A5A6 DW0DW5DW6 DW1
Reset RF ch ip
Figure 10.14 Reset Command Timing Chart
10.6 ID Accessing Command
A7130 has built-in 32-bits ID Registers for customized identification code. It is accessed via SPI interface. ID length is
recommended to be 32 bits by setting IDL (1Fh). Therefore, user can toggle SCS pin to high to terminate ID accessing
command when ID data is output completely.
Figure 10.13 and 10.14 are timing charts of 32-bits ID accessing via 3-wire SPI.
10.6.1 ID Write Command
User can refer to Figure 10.2 for SPI write timing chart in details. Below is the procedure of ID write command.
Step1: Deliver A7~A0 = 00000110 (A6=0 for write, A5~A0 = 000110 for ID addr, 06h).
Step2: By SDIO pin, deliver 32-bits ID into A7130 in sequence by Data Byte 0 (recommend 5xh or Axh), 1, 2 and 3.
Step3: Toggle SCS pin to high when step2 is completed.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 46 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 47

Figure 10.15 ID Write Command Timing Chart
10.6.2 ID Read Command
User can refer to Figure 10.2 for SPI read timing chart in details. Below is the procedure of ID read command.
Step1: Deliver A7~A0 = 01000110 (A6=1 for read, A5~A0 = 000110 for ID addr, 06h).
Step2: SDIO pin outputs 32-bits ID in sequence by Data Byte 0, 1, 2 and 3.
Step3: Toggle SCS pin to high when step2 is completed.
LBA7130
Figure 10.16 ID Read Command Timing Chart
10.7 FIFO Accessing Command
To use A7130’s FIFO mode, enable FMS (01h) =1 via SPI interface. Before TX delivery, just write wanted data into TX FIFO
(05h) then issue TX Strobe command. Similarly, user can read RX FIFO (05h) once payload data is received.
MCU can use polling or interrupt scheme to do FIFO accessing. FIFO status can output to GIO1 (or GIO2) pin by setting
GIO1S (0Bh) or GIO2S (0Ch).
Figure 10.15 and 10.16 are timing charts of FIFO accessing via 3-wire SPI.
10.7.1 TX FIFO Write Command
User can refer to Figure 10.2 for SPI write timing chart in details. Below is the procedure of TX FIFO write command.
Step1: Deliver A7~A0 = 00000101 (A6=0 for write control register and issue FIFO A [5:0] = 05h).
Step2: By SDIO pin, deliver (n+1) bytes TX data into TX FIFO in sequence by Data Byte 0, 1, 2 to n.
Step3: Toggle SCS pin to high when step2 is completed.
Step4: Send Strobe command of TX mode (Figure 10.9) to do TX delivery.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 47 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 48

LBA7130
Figure 10.17 TX FIFO Write Command Timing Chart
10.7.2 Rx FIFO Read Command
User can refer to Figure 10.2 for SPI read timing chart in details. Below is the procedure of RX FIFO read command.
Step1: Deliver A7~A0 = 01000101 (A6=1 for read control register and issue FIFO at address 05h).
Step2: SDIO pin outputs RX data from RX FIFO in sequence by Data Byte 0, 1, 2 to n.
Step3: Toggle SCS pin to high when RX FIFO is read completely.
Figure 10.18 RX FIFO Read Command Timing Chart
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 48 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 49

11. State machine
SPI
From accessing data point of view, if FMS=1, FIFO mode is enabled, otherwise, A7130 is in direct mode.
SPI
chip select
3-Wire SPI
4-Wire SPI
SCS SCK SDIO SDIO FIFO (FMS=1)
SCS SCK SDIO GIO1 or GIO2 FIFO (FMS=1)
From current consumption point of view, A7130 has below 8 operation modes.
(1) Deep Sleep mode
(2) Sleep mode
(3) Idle mode
(4) Standby mode
(5) PLL mode
(6) TX mode
(7) RX mode
(8) Star-networking mode
SPI
Clock
SPI
Data In
FMS register
Data Out
Direct (FMS=0)
Direct (FMS=0)
LBA7130
11.1 Key states
After power on reset or software reset or deep sleep m ode, user has to do c alibration process because all control registers
are in initial values. The calibration process of A7130 is very easy, user only needs to issue Strobe commands and enable
calibration registers. And then, the calibrations are automatically completed by A7130’s internal state machine. Table 11.1
shows a summary of key circuitry among those strobe commands.
Strobe Command when AFIDS =0 (3Eh) and MIDS =0 (3Eh)
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 Deep Sleep mode (I/Os are in tri-state)
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 Deep Sleep mode (I/Os are pulled high)
1 0 0 0 x x x x Sleep mode
1 0 0 1 x x x x Idle mode
1 0 1 0 x x x x Standby mode
1 0 1 1 x x x x PLL mode
1 1 0 0 x x x x RX mode
1 1 0 1 x x x x TX mode
1 1 1 0 x x x x FIFO write pointer reset
1 1 1 1 x x x x FIFO read pointer reset
Mode
Deep Sleep
(Tri-state)
Deep Sleep
(pull-high)
Sleep Yes ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF (1000-xxxx)b
Idle Yes ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF (1001-xxxx)b
Standby Yes ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF (1010-xxxx)b
PLL Yes ON ON ON ON OFF OFF (1011-xxxx)b
TX Yes ON ON ON ON OFF ON (1101-xxxx)b
RX Yes ON ON ON ON ON OFF (1100-xxxx)b
Register
retention
No
No
Regulator Xtal Osc. VCO PLL RX TX Strobe Command
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF (10 00-1000)b
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF (10 00-1011)b
Remark: x means “don’t care”
Table 11.1. Operation mode and strobe command
Description
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 49 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 50

LBA7130
11.2 FIFO mode
This mode is suitable for the requirements of general purpose applications and can be chosen by setting FMS = 1. After
calibration, user can issue Strobe command to enter standby mode where write TX FIFO or read RX FIFO. From standby
mode to packet data transmission, only one Strobe command is needed. Once transmission is done, A7130 is auto back to
standby mode. Figure 11.1 and Figure 11.2 are TX and RX timing diagram respectively. Figure 11.3 illustrates state diagram
of FIFO mode.
Strobe CMD
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RFO Pin
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
Strobe CMD
RFI Pin
TX
Strobe
10us +(PDL+TDL)
T0
RX
strobe
RF settling
Preamble + ID Code + Payload
T1
Figure 11.1 TX timing of FIFO Mode
RX set tling
T0
Wait
Packet
T1
T2
Transmitting Time
Preamble + ID Code + Payload
Receiving Time
Next Instruction
T2
Auto Back
Standby Mode
Next Instruction
Auto Back
Standby Mode
T3
Figure 11.2 RX timing of FIFO Mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 50 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 51

LBA7130
Figure 11.3 State diagram of FIFO Mode
11.3 Direct mode
This mode is suitable to let MCU to drive customized packet to A7130 directly by setting FMS = 0. In TX mode, MCU shall
send customized packet in bit sequence (simply called raw TXD) to GIO1 or GIO2 pin. In RX mode, the receiving raw bit
streams (simply called RXD) can be configured output to GIO1 or GIO2 pin. Be aware that a customized packet shall be
preceded by a 32 bits preamble to let A7130 get a suitable DC estimation voltage. After calibration flow, for every state
transition, user has to issue Strobe command to A7130 for fully manual control. This mode is also suitable for the requirement
of versatile packet format.
Figure 11.4 and Figure 11.5 are TX and RX timing diagram in direct mode respectively. Figure 14.6 illustr ates state diagram
of direct mode.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 51 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 52

LBA7130
Strobe CMD
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RFO Pin
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO1 Pin - TMEO
(GIO1S[3:0]=0010)
GIO2 Pin - TXD
(GIO2S[3:0]=1001)
Strobe CMD
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RFO Pin
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO1 Pin - PMDO
(GIO1S[3:0]=0011)
GIO2 Pin - RXD
(GIO2S[3:0]=1000)
TX
Strobe
RX
Strobe
RF settling
10us+(PDL+TDL)
T0
Carr ier
only
Modulation auto enable
T3
Figure 11.4 TX timing of Direct Mode
RX settling
Wait
packet
Modulated signals
Preamble + customized raw TXD
32-bits
preamble
Coming packet
Preamble + customized raw TXD
Preamble detect output
STB strobe
Manually back
to STB
T4T1
STB strobe
Manually back
to STB
T0
T3
T4T1
Figure 11.5 RX timing of Direct Mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 52 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 53

LBA7130
Figure 11.6 State diagram of Direct Mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 53 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 54

LBA7130
12. Crystal Oscillator
A7130 needs external crystal or external clock that is either 16 MHz (or 18MHz) to generate internal wanted clock.
Relative Control Register
Clock Register (Address: 0Dh)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Clock W
12.1 Use External Crystal
Figure 12.1 shows the connection of crystal network between XI and XO pins. C1 and C2 capacitance built inside A7130 are
used to adjust different crystal loading. User can set INTXC [4:0] to meet crystal loading requirement. A7130 supports low
cost crystal within ± 50 ppm accuracy. Be aware that crystal accuracy requirement includes initial tolerance, temperature drift,
aging and crystal loading.
CGC1 CGC0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0
IFS1 IFS0 GRC3 GRC2 GRC1 GRC0
R
Crystal Accuracy Crystal ESR
±50 ppm ≦80 ohm
CGS XS
-- --
Fig12.1 Crystal oscillator circuit, set INTXC[4:0] for the internal C1 and C2 values.
12.2 Use External Clock
A7130 has built-in AC couple capacitor to support external clock input. Figure 12.2 shows how to connect. In such case, XI pin
is left opened. XS shall be low to select external clock. The frequency accuracy of external clock shall be controlled within ± 50
ppm, and the amplitude of external clock shall be within 1.2 ~ 1.8 V peak-to-peak.
Fig12.2 External clock source. R is used to tune Vpp = 1.2~1.8V
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 54 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 55

LBA7130
13. System Clock
A7130 supports different crystal frequency by programmable “Clock Register”. Based on this, three important internal clocks
F
, FDR and F
CGR
are generated.
SYCK
(1) F
(2) F
(3) F
(4) F
: Crystal frequency.
XTAL
: Crystal Ref. Clock = F
XREF
: Clock Generation Reference = 2MHz = F
CGR
: System Clock is related to FIF and F
SYCK
* (DBL+1).
XREF
(6) FDR: Data Rate Clock = FIF / (SDR+1).
Data Rate DBL (0Fh) F
CGR
4Mbps 0 (FIFO mode) 2MHz F
4Mbps 1 (Direct mode) 2MHz F
Table 13.1 System clock and related clock sources
XI
XS
CE
CE
DBL
F
XREF
0
X 2
1
XO
F
XTAL
/ (GRC+1).
XREF
DR.
CLK Gen. F
X 32 64MHz 4MHz 4MHz
CGR
X 64 128MHz 4MHz 4MHz
CGR
GRC
÷
(GRC+1)
RDU/CGC
PLL
x64/x32
F
= 2MHz
CGR
Clock Generator
F
PFD
/ (RRC+1) VCO
SYCK
F
IF
1
F
SYCK
CGS
F
CE
auto
scaler
DR
F
IF
/ (SDR+1)
F
DR
0
auto
scaler
/ 2
4MHz
8MHz
0
1
FSARS
F
ADC
Fig13.1 System clock block diagram
13.2 Data Rate Setting
User has to choose 16MHz Xtal (or 18M Hz) for 4Mbps applications. For more data rate options, p lease contact AMICCOM
FAE team.
Data rate 4Mbps
Xtal DBL
(0Fh)
16MHz 0 0111 0 1 00 10 1 11 0x00 FIFO mode
16MHz 1 1111 0 1 00 10 1 11 0x00 Direct mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 55 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
GRC
(0Dh)
RDU
(1Ch)
CGS
(0Dh)
RRC
(0Fh)
CGC
(0Dh)
CGS
(0Dh)
IFS
(1Ch)
SDR [7:0]
(39h)
Note
Page 56

LBA7130
F
F
F
14. Transceiver LO Frequency
A7130 is a half-duplex transceiver with embedded PA and LNA. For TX or RX frequency setting, user just needs to set up LO
(Local Oscillator) frequency for two ways radio transmission.
To target full range of 2.4GHz ISM band (2408 MHz to 2468 MHz), A7130 applies offset concept by LO frequency FLO =
F
setting, PLL Register I (CHN [7:0]).
Below is the LO frequency block di agram.
LO_BASE
+ F
Therefore, this device is easy to implement frequency hopping and multi-channels by just ONE register
OFFSET.
F
XTAL
BIP[8:0] +
BFP [15 :0]/ 2
CHN / [4*(CHR+1)]
/ (RRC[1:0]+1)X (DBL+1) PFD
AC[14:0 ]/ 2
16
F
16
0
LO_BASE
+
F
OFFSET
F
PFD
AFC
1
0
F
LO
+
Divider
Fig14.1 Frequency synthesizer block diagram
14.1 LO Frequency Setting
From Figure 14.1, FLO is not only for TX radio frequency but also to be RX LO frequency. To set up F
steps.
1. Set F
2. Set F
3. Set F
4. The LO frequency, FLO = F
~ 2400.001MHz.
LO_BASE
= 500 KHz.
CHSP
= CHN [7:0] x F
OFFSET
CHSP
LO_BASE
+ F
OFFSET
F
LO
VCO
it is easy by below 4
LO,
LO
LO_BASE
OFFSET
F
LO_BASE
BIPFF
PFDLO_BASE
BFP
]0:8[(
2
]0:15[
DBL
)1()
×+=+×=
RRC
F
XTAL
BFP
BIP
+
1]0:1[
+×
]0:8[(
2
]0:15[
)
1616
Base on the above formula, i.e. 16 MHz, please refer to Table 14.1 and 14.2 as a calculation example to get LO frequency.
DBL = 0 for FIFO mode
STEP ITEMS VALUE NOTE
1 F
XTAL
16 MHz Crystal Frequency
2 DBL 0 Disable double function
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 56 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 57

LBA7130
3 RRC 0 If so, F
4 BIP[8:0] 0x096 To get F
5 BFP[15:0] 0x0004 To get F
6 F
LO_BASE
2400.001 MHz LO Base frequency
DBL = 1 for Direct mode
STEP ITEMS VALUE NOTE
1 F
XTAL
16 MHz Crystal Frequency
2 DBL 1 Enable double function
3 RRC 0 If so, F
4 BIP[8:0] 0x04B To get F
5 BFP[15:0] 0x0002 To get F
6 F
LO_BASE
2400.001 MHz LO Base frequency
Table 14.1 How to set F
How to set F
TXRF
= FLO= F
LO_BA SE
+ F
~ 2405.001 MHz
OFFSET
STEP ITEMS VALUE NOTE
1 F
LO_BASE
2400.001 MHz After set up BIP and BFP
[0111] To get F
[1111] To get F
4 CHN[7:0] 0x0A F
6 F
7 F
LO
TXRF
2405.001 MHz Get FLO= F
2405.001 MHz F
Table 14.2 How to set F
LO_BASE
OFFSET
TXRF
TXRF
= 16MHz
PFD
=2400 MHz
LO_BASE
~ 2400.001 MHz
LO_BASE
= 16MHz
PFD
=2400 MHz
LO_BASE
~ 2400.001 MHz
LO_BASE
= 500 KHz if DBL =0 for FIFO mode.2 CHR[3:0]
CHSP
= 500 KHz if DBL =1 for Direct mode.
CHSP
= 500 KHz * (CHN) = 5MHz
+ F
= F
LO_BASE
LO
OFFSET
For 16MHz crystal, below is the calculation detail for F
F
F
F
CHSP
XTAL
=
(MHz)
PFD
[]
( )
CHR
10:34 +×
DBL
(0Fh)
(0Fh)
RRC
F
PFD
and F
FPD
CHSP.
(MHz) CHR [3:0] F
(KHz) Note
CHSP
16 0 00 16 0111 500 Recommend
16 1 00 32 1111 500 Recommend
14.2 IF Side Band Select
Since A7130 is a low-IF TRX, in RX mode, the F
F
. Therefore, A7130 offers two methods to set up FLO while A7130 is exchanging from TX mode to RX mode.
TXRF
AIF register is used to enable Auto IF function for Auto IF exchange mode. And ULS registers is used for fast exchange mode
because of reduction of PLL settling time.
(1) Auto IF exchange mode
AIF (01h) ULS (19h)
1 0 F
1 1 F
F
RXLO
RXLO
RXLO
(2) Fast exchange mode
AIF (01h) ULS (19h)
0 0 F
0 1 F
F
RXLO
RXLO
RXLO
shall be set to shift a FIF (i.e. FIF = 4MHz @ 4Mbps) regarding to coming
RXLO
Formula Note
= FLO- F
= FLO+ F
IF
IF
Auto-minus a FIF because ULS = 0
Auto-plus a FIF because ULS = 1
Formula Note
= F
= F
LO
LO
The coming F
The coming F
TXRF
TXRF
shall be (F
shall be (F
RXLO
RXLO
+ FIF)
- FIF)
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 57 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 58

14.2.1 Auto IF Exchange
F
F
F
F
= FLO=
F
F
F
F
= FLO=
F
F
LBA7130
A7130 supports Auto IF offset function by setting AIF = 1. In such case, F
there is only one carrier frequency (Fcarrier) during communications. Meanwhile, F
between master and slave is the same so that
TXRF
during TRX exchanging is auto shifted
RXLO
FIF. See below Figures and Table 14.3 for details.
Master
AIF=1 and ULS=0, F
is auto shifted lower than F
RXLO
LO_BASE
F
=5MHz
OFFSET
TXRF
RXLO
for a (FIF).
TXRF
IF
Carrier
4MHz @ 4Mbps
Master
AIF ULS CHN[7:0] F
CHSP
(KHz) F
LO_BASE
(MHz) F
TXRF
(MHz)
TX 1 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 2405.001 -RX 1 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 -- 2401.001
Slave
AIF=1 and ULS=0, F
is auto shifted lower than F
RXLO
TXRF
for a (FIF).
F
RXLO
(MHz)
LO_BASE
F
OFFSET
TXRF
RXLO
=5MHz
IF
Carrier
4MHz @ 4Mbps
Slave
AIF ULS CHN[7:0] F
CHSP
(KHz) F
LO_BASE
(MHz) F
TXRF
(MHz)
F
RXLO
TX 1 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 2405.001 -RX 1 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 -- 2401.001
Table 14.3 Auto IF exchange mode while TRX exchanging
(MHz)
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 58 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 59

14.2.2 Fast Exchange
F
F
F
F
F
=
FLO=
F
F
=
FLO=
F
LBA7130
Fast exchange can reduce the PLL settling time during TRX exchanging because F
either master or slave side. However, there are two on-air frequency ( F
Carrier (master),FCarrier (slave)
RXLO
and F
are kept to the same FLOin
TXRF
) during communications. In such
case, user has to control ULS =0 in master side and ULS = 1 in slave side for two ways radio. See below Figures and Table 14.4
for details.
Master
AIF=0 and ULS=0, Master is set to up side band.
LO_BASE
F
=5MHz
OFFSET
Slave
AIF=0 and ULS=1, Slave is set to low side band.
LO_BASE
F
TXLO
RXLO
4MHz @ 4Mbps
IF
TXLO
Carrier (Master)
Carrier (Slave)
RXLO
F
=9MHz
OFFSET
Master
AIF ULS CHN[7:0] F
CHSP
(KHz) F
LO_BASE
(MHz) F
TXRF
(MHz)
F
RXLO
TX 0 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 2405.001 -RX 0 0 0x0A 500 2400.001 -- 2405.001
Slave
AIF ULS CHN[7:0] F
CHSP
(KHz) F
LO_BASE
(MHz) F
TXRF
(MHz)
F
RXLO
TX 0 1 0x12 500 2400.001 2409.001 -RX 0 1 0x12 500 2400.001 -- 2409.001
Table 14.4 Fast exchange mode while TRX exchanging
(MHz)
(MHz)
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 59 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 60

LBA7130
14.3 Auto Frequency Compensation
The AFC function (Auto Frequency Compensation) supports to use low accuracy crystal (±50 ppm) on A7130 without sensitivity
degradation. The AFC concept is automatically fine tune RX LO frequency (F
compensation value of F
RXLO
.
). User can read AC [14:0] to know the
RXLO
F
XTAL
BIP[8:0] +
BFP [15 :0]/ 2
CHN / [4*(CHR+1)]
F
/ (RRC[1:0]+1)X (DBL+1) PFD
LO_BASE
16
0
AFC
AC[14:0 ]/ 2
16
F
+
F
OFFSET
PFD
1
0
F
LO
+
Divider
VCO
F
LO
Figure 14.3 Block Diagram of enabling AFC function
For AFC procedure, please refer to A7130’s reference code and contact AMICCOM FAE team for details.
15. Calibration
A7130 needs calibration process after deep sleep mode or power on reset or software reset. Below are six calibration items
inside the device.
1. VCO Current Calibration.
2. VCO Bank Calibration.
3. VCO Deviation Calibration.
4. IF Filter Bank Calibration.
5. RSSI Calibration.
6. RC Oscillator Calibration.
15.1 Calibration Procedure
The purpose to execute the above calibration items is to deal with Foundry process deviation. After calibrations, A7130 will be
set to the best working conditions without concerning Foundry process deviation to impact A7130’s RF performance.
In general, user can use A7130’s auto calibration function by just enabling calibration items and checking its calibration flag. For
detailed calibration procedures, please refer to A7130 reference code of initRF() subroutine and A7130_Cal() subroutine.
1. Initialize A7130 by calling the subroutine of initRF().
n Initialize all control registers by calling the subroutine of A7130_Config().
n Execute all calibration items by calling the subroutine of A7130_Cal().
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 60 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 61

LBA7130
16. FIFO (First In First Out)
A7130 has the separated physical 64-bytes TX and RX FIFO inside the device. To use A7130’s FIFO mode, user just needs to
enable FMS =1. For FIFO accessing, TX FIFO (write-only) and RX FIFO (read-only) share the same register address 05h. TX
FIFO represents transmitted payload. On the other hand, RX circuitry synchronizes ID Code and stores received payload into
RX FIFO.
16.1 TX Packet Format in FIFO mode
16.1.1 Basic FIFO mode
If FCL[1:0] = 00 and ENRL = 0, A7130 is formed a Basic FIFO mode which can also support Auto-ack/ Auto-resend function.
There is no MAC header in TX packet format. ID code is a PHY header used to be the frame sync to enable RX FIFO receiving.
Data whitening(optional)
FEC encoded/decoded(optional)
CRC -16 calculation(optional)
ID codePreamble Payload (CRC)
4 bytes
Preamble:
The packet is led by a self-generated preamble which is composed of alternate 0 and 1. If the first bit of ID code is 0, preamble
shall be 0101…0101. In the contrast, if the first bit of ID code is 1, preamble shall be 1010…1010.
Pream ble length is recomm ended to set 4 bytes by PML [1:0] (20h).
ID code:
ID code is recommended to set 4 bytes by IDL[1:0] = [01] and ID Code is stored into ID Data register by sequence ID Byte 0, 1,
2 and 3. If RX circuitry check ID code is correct, payload will be written into RX FIFO. In addition, user can set ID code error
tolerance (0~ 7bit error) by setting ETH [2:0] during ID synchronization check.
Payload:
Payload length is programmable by FEP [11:0]. The physical FIFO depth is 64 bytes. A7130 also supports logical FIFO
extension up to 4K bytes.
4 bytes 2 bytesPhy. 64 bytes
ID code
ID Byte 0 ID Byte 1 ID Byte 2 ID Byte 3
Figure 16.1 TX packet format of basic FIFO mode
CRC:
In FIFO mode, if CRC is enabled (CRCS=1), 2-bytes of CRC value is self-generated and attached at the footer of the packet. In
the same way, RX circuitry will check CRC value and show the result to CRC Flag.
16.1.2 Advanced FIFO mode
A7130 supports to self generated MAC header to form an advanced FIFO mode by enabling FCL[1:0], ENRL.. Therefore,
A7130 can support ACK FIFO (FCB1~FCB3) and dynamic FIFO length depending on configurations.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 61 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 62

LBA7130
4 bytes
au to
ack/resend
ID codePreamble Payload (CRC)
4 bytes
FCB
1~4 bytes
M A C H eade r (self-generated)PH Y H ead er (self-generated)
dynamic
FIFO
FEP
1 2 b its
2 bytesPhy. 64 bytes
Figure 16.2 TX packet format of advanced FIFO mode.
FCB:
If FCL[1:0] ≠00, FCB header is enabled to support ACK FIFO by (FCB1~FCB3). The FCB is frame control byte. FCB0 is NOT
allowed to program but carry a dedicated header (00111b) and SID [2:0] (Serial ID of packet number). FCB1~3 are used for
customized information in FCB field.
FCB
FCB 0 FCB 1 FCB 2 FCB 3
Figure 16.3 FCB (Frame Control Field)
FEP:
If ENRL = 1, A7130 supports dynamic FIFO. FEP [11:0] is self-generated to add into TX packet. In RX side, FEP[11:0] of the
coming TX packet will be detected and stored into LENF [11:0] register.
HEC:
If HECS = 1, A7130 supports to self-generated a HEC byte which is a local CRC-8 of the MAC header. This HEC byte is an
optional feature to calculate CRC result of MAC Header. HEC is located at the end of the MAC header.
Header
CRC
HEC
1 b y te
2 bytesPhy. 64 bytes
4 bytes
MAC
header
ID codePreamble Payload (CRC)
4 bytes
FCB
1~4 bytes
M A C H e ader (self-generated )PH Y H ead er (self-generated)
FEP
12 b its
Figure 16.4 HEC (CRC for MAC Header)
16.2 Bit Stream Process in FIFO mode
A7130 supports 3 optional bit stream process for payload in FIFO mode, they are,
(1) CCITT-16 CRC
(2) (7, 4) Hamming FEC
(3) Data Whitening by XOR PN7 (7-bits Pseudo Random Sequence). The initial seed of PN7 is set by WS [6:0]
CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check):
1. CRC is enabled by CRCS= 1. TX circuitry calculates the CRC value of payload (preamble and ID code are excluded) and
transmits 2-bytes CRC value after payload.
2. RX circuitry checks CRC value and shows the result to CRCF. If CRCF=0, received payload is correct, else error
occurred.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 62 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 63

LBA7130
FEC (Forward Error Correction):
1. FEC is enabled by FECS= 1. Payload and CRC value (if CRCS=1) are encoded by (7, 4) Hamming code.
2. Each 4-bits (nibble) of payload is encoded into 7-bits code word and delivered out automatically.
(ex., 64 bytes payload will be encoded to 128 code words, each code word is 7 bits.)
3. RX circuitry decodes received code words automatically. Each code word can correct 1-bit error. Once 1-bit error
occurred, FECF=1 (00h).
Data Whitening:
1. Data whitening is enabled by WHTS= 1. Payload and CRC value (if CRCS=1) or their encoded code words (if FECS=1)
are encrypted by bit XOR operation with PN7. The initial seed of PN7 is set by WS [6:0].
2. RX circuitry decrypts received payload and 2-bytes CRC (if CRCS=1) automatically. Please noted that user shall set the
same WS [6:0] (22h) to TX and RX.
16.3 Transmission Time
Based on CRC and FEC options, the transmission time are different. See table 16.1 for details.
Data Rate = 4 Mbps
Data Rate Preamble
(bits)
4Mbps
32 32 512 Disable Disable 576 bit X 0.25 us = 144 us
32 32 512 16 bits Disable 592 bit X 0.25 us = 148 us
32 32 512 Disable 512 x 7 / 4 960 bit X 0.25 us = 240 us
32 32 512 16 x 7 / 4 512 x 7 / 4 988 bit X 0.25 us = 247 us
ID Code
(bits)
Payload
(bits)
Table 16.1 Transmission time
CRC
(bits)
FEC Transmission
Time / Packet
16.4 Usage of TX and RX FIFO
In application points of view, A7130 supports 2 options of FIFO arrangement.
(1) Easy FIFO
(2) Segment FIFO
(3) FIFO extension
For FIFO operation, A7130 supports Strobe command to reset TX and RX FIFO pointer as shown below. User can refer to
section 10.5 for details.
Strobe Command
Strobe Command
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
1 1 1 0 x x X x FIFO write pointer reset (for TX FIFO)
1 1 1 1 x x X x FIFO read pointer reset (for RX FIFO)
Description
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 63 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 64

LBA7130
16.4.1 Easy FIFO
In Easy FIFO mode, max FIFO length is 64 bytes. FIFO length is equal to ( FEP [11:0] +1 ) where FEP [11:0] is max 0x003F.
User just needs to control FEP [11:0] (03h) and disable PSA and FPM as shown below.
TX-FIFO
(byte)
1 1 0x00 0 0
8 8 0x07 0 0
16 16 0x0F 0 0
32 32 0x1F 0 0
64 64 0x3F 0 0
Table 16.2 Control registers of Easy FIFO
Procedures of TX FIFO Transmitting
1. Initialize all control registers (refer A7130 reference code).
2. Set FEP [11:0] = 0x003F for 64-bytes FIFO.
3. Send Strobe command – TX FIFO write pointer reset.
4. MCU writes 64-bytes data to TX FIFO.
5. Send TX Strobe Command and monitor WTR signal.
6. D one.
Procedures of RX FIFO Reading
1. When RX FIFO is full, WTR (or FSYNC) can be used to trigger MCU for RX FIFO reading.
2. Send Strobe command – RX FIFO read pointer reset.
3. MCU monitors WTR signal and then read 64-bytes from RX FIFO.
4. D one.
RX-FIFO
(byte)
FEP[11:0]
(03h)
PSA[5:0]
(04h)
FPM[1:0]
(04h)
Figure 16.5 Easy FIFO
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 64 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 65

LBA7130
16.4.2 Segment FIFO
In Segment FIFO, TX FIFO length is equal to (FEP [11:0] - PSA [5:0]+1). FPM [1:0] should be zero. This function is very
useful for button applications. In such case, each button is used to transmit fixed code (data) every time. During initialization,
each fixed code is written into corresponding segment FIFO once and for all. Then, if button is triggered, MCU just assigns
corresponding segment FIFO (PSA [5:0] and FEP [11:0]) and issues TX strobe command. Table 16.4 explains the details if TX
FIFO is arranged into 8 segments, each TX segment and RX FIFO length are 8 bytes.
Segment PSA FEP TX FIFO Length PSA[5:0] FEP[11:0] FPM[1:0]
1 PSA1 FEP1 8 bytes 0x00 0x07 0
2 PSA2 FEP2 8 bytes 0x08 0x0F 0
3 PSA3 FEP3 8 bytes 0x10 0x17 0
4 PSA4 FEP4 8 bytes 0x18 0x1F 0
5 PSA5 FEP5 8 bytes 0x20 0x27 0
6 PSA6 FEP6 8 bytes 0x28 0x2F 0
7 PSA7 FEP7 8 bytes 0x30 0x37 0
8 PSA8 FEP8 8 bytes 0x38 0x3F 0
RX FIFO Length PSA[5:0] FEP[11:0] FPM[1:0]
8 bytes 0 0x0007 0
Table 16.3 Segment FIFO is arranged into 8 segments
Procedures of TX FIFO Transmitting
1. Initialize all control registers (refer A7130 reference code).
2. Issue Strobe command – TX FIFO write pointer reset.
3. MCU writes fixed code into corresponding segment FIFO once and for all.
4. To consign Segment 1, set PSA = 0x00 and FEP= 0x0007
To consign Segment 2, set PSA = 0x08 and FEP= 0x000F
To consign Segment 3, set PSA = 0x10 and FEP= 0x0017
To consign Segment 4, set PSA = 0x18 and FEP= 0x001F
To consign Segment 5, set PSA = 0x20 and FEP= 0x0027
To consign Segment 6, set PSA = 0x28 and FEP= 0x002F
To consign Segment 7, set PSA = 0x30 and FEP= 0x0037
To consign Segment 8, set PSA = 0x38 and FEP= 0x003F
5. Issue TX Strobe Command and monitor WTR signal.
6. D one.
Procedures of RX FIFO Reading
1. When RX FIFO is full, WTR (or FSYNC) is used to trigger MCU for RX FIFO reading.
2. Issue Strobe command – RX FIFO read pointer reset.
3. MCU monitors WTR signal and then read 8-bytes from RX FIFO.
4. D one.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 65 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 66

LBA7130
Figure 16.6 Segment FIFO Mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 66 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 67

LBA7130
16.4.3 FIFO Extension
A7130 supports FIFO extension up to 4K bytes from the 64 bytes physical TX FIFO and RX FIFO. The FIFO extension length is
configured by (FEP [11:0] +1 and PSA [5:0] =0). FPM [1:0] is used to set the FPF threshold which FPF is FIFO Pointer Flag to
inform MCU the timing of reading RX FIFO and refilling TX FIFO.
Please be notice, SPI speed is important to prevent error operati on (over-write) in FIFO extension mode. We recommend the
min. SPI speed shall be equal or greater than (A70 on-air data rate + 500Kbps).Please refer to A7130’s reference code
(FIFO extension) for details.
For example, if A7130 data rate = 4Mbps and FIFO extension = 256 bytes.
FIFO
Length
(byte)
256
TX
FPF
Threshold
Delta = 04 10 Mbps Delta = 60 10 Mbps 00 0
Delta = 08 10 Mbps Delta = 56 10 Mbps 01 0
Delta = 12 10 Mbps Delta = 52 10 Mbps 10 0
Delta = 16 8 Mbps
Max. SPI
Data Rate
Table 16.4 How to set FIFO extension when A7130 is at 4Mbps data rate
FIFO
Length
(byte)
256
RX
FPF
Threshold
Delta = 48 8 Mbps
Max. SPI
Data Rate
Control Registers
FEP[7:0] FPM[1:0] PSA[5:0]
0xFF
11 0
Procedures of TX FIFO Extension
1. Initialize all control registers (refer A7130 reference code).
2. Set FEP [11:0] = 0x0FF for 256-bytes FIFO extension.
3. Set FPM [1:0] = 11 for FPF threshold.
4. Set CKO Register = 0x12
5. Issue Strobe command – TX FIFO write pointer reset.
6. MCU writes 1st 64-bytes TX FIFO.
7. Issue TX Strobe command.
8. MCU monitors FPF from A7130’s CKO pin.
9. FPF triggers MCU to write 2nd 48-bytes TX FIFO.
10. Monitor FPF.
11. FPF triggers MCU to write 3rd 48-bytes TX FIFO.
12. Monitor FPF.
13. FPF triggers MCU to write 4th 48-bytes TX FIFO.
14. Monitor FPF.
15. FPF triggers MCU to write 5th 48-bytes TX FIFO.
16. D one.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 67 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 68

LBA7130
Figure 16.7 TX FIFO Extension
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 68 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 69

Procedures of RX FIFO Reading
1. Initialize all control registers (refer A7130 reference code).
2. Set FEP [11:0] = 0x0FF for 256-bytes FIFO extension.
3. Set FPM [1:0] = [11b] for FPF threshold.
4. Set CKO Register = 0x12
5. Issue Strobe command – RX FIFO read pointer reset.
6. Issue RX Strobe command.
7. MCU monitors FPF from A7130’s CKO pin.
8. FPF triggers MCU to read 1st 48-bytes RX FIFO.
9. Monitor FPF.
10. FPF triggers MCU to read 2nd 48-bytes RX FIFO.
11. Monitor FPF.
12. FPF triggers MCU to read 3rd 48-bytes RX FIFO.
13. Monitor FPF.
14. FPF triggers MCU to read 4th 48-bytes RX FIFO.
15. Monitor FPF.
16. FPF triggers MCU to read 5th 48-bytes RX FIFO.
17. Monitor WTR falling edge or WTR = low, read the rest 16-bytes RX FIFO
18. D one.
LBA7130
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 69 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 70

LBA7130
Figure 16.8 RX FIFO Extension Mode
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 70 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 71

LBA7130
ERSSM
17. ADC (Analog to Digital Converter)
A7130 has built-in 8-bits ADC for RSSI measurement and internal the rmal sensor by enabling ADCM. User can just use the
recommended va lues of ADC from Tab le 17.1. Please noted tha t ADC clock can be selected by s etting FSARS (4MHz or
8MHz). The ADC converting time is 20 x ADC clock periods.
XADS
(1Fh)
RSS
(1Ch)
ARSSI
(01h)
ADCM
(01h)
(1Ch)
FSARS
(1Fh)
CDM
(1Fh)
Standby Mode RX Mode
0 1 1 1 1 0 1 Thermal sensor RSSI
Table 17.1 Setting of RSSI measurement
17.1 RSSI Measurement
A7130 supports 8-bits digital RSSI to detect RF signal stre ngth. RSSI value is stored in ADC [7:0] (1Eh ). Fig 17.1 shows a
typical plot of RSSI reading as a function of input power. Be aware RSSI accuracy is about ± 6dBm.
ADC value Curve (AGC on,25℃)
300
250
200
150
100
ADC Value
50
Avera ge
0
-110 -105 -1 00 -95 -9 0 -85 -80 -75 -70 -65 -60 -55 -50 -45 -40 -35 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 1 0
Input Power (dBm)
ADC value Curve (AGC off,25℃)
250
200
150
100
Average
ADC Value
50
0
-110 -105 -100 -95 -90 -85 -80 -75 -70 -65 -60 -55 -50 -45 -4 0 -35 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10
Input Power (dBm)
Figure 17.1 Typical RSSI characteristic
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 71 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 72

Auto RSSI measurement for TX Power of the coming packet:
LBA7130
1. Set wanted F
RXLO
.
2. Set recommend values of Table 17.1.
3. Enable ADCM = 1.
4. Send RX Strobe command.
5. Once frame sync (FSYNC) is detected or exiting RX mode, user can read digital RSSI value from ADC [7:0] for TX power
of the coming packet.
St rob e CMD
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RF-IN
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GPIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO2 Pi n - FSYNC
(GPIO2S[3:0]=0001)
RX-Strobe
RX Ready Ti me
T0
T0-T1: Settling Time
T2-T3: Receivi ng Packet
T3 : Exit RX mode automatically in FIFO mode
T3-T4: MCU read RSSI value @ ADC [7:0]
RX Mode
Received Packet
T1
T2
MCU Read ADC[ 7:0]
Read 8- bits RSSI val ue
T3
T4
Figure 17.2 RSSI Measurement of TX RSSI of the coming packet.
Auto RSSI measurement for Background Power:
1. Set wanted F
RXLO
.
2. Set recommend values of Table 17.1.
3. Enable ADCM = 1.
4. Send RX Strobe command.
5. Stay in RX mode at least 140 us and then exiting RX mode. User can read digital RSSI value from ADC [7:0] for the
background power.
Strobe CMD
(SCS, SCK,SDI O)
RFI Pin
GIO1 Pin - WTR
(GPIO1S[3:0]=0000)
GIO2 Pin - FSYNC
(GPIO2S[3:0]=0001)
RX-Str obe
No Packet
Min. 140 us
MCU reads 8-bits RSSI value that is refresh every 40 us
T0
T0-T1: MCU Delay Loop from PLL to RX mode for RSSI measurment
T1 : Auto RSSI Measurment is done by 8-times average.
MCU can read RSSI value from ADC [7:0]
T1
MCU Read ADC[7:0]
Figure 17.3 Measurement of Background RSSI.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 72 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 73

LBA7130
18. Battery Detect
A7130 has a built-in battery detector to check supply voltage (REGI pin). The detecting range is 2.0V ~ 2.7V into 8 levels.
Battery detect Register (Address: 2Ch)
Name R/W Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Battery detect
BVT [2:0]: Battery voltage detect threshold.
[000]: 2.0V. [001]: 2.1V. [010]: 2.2V. [011]: 2.3V.
[100]: 2.4V. [101]: 2.5V. [110]: 2.6V. [111]: 2.7V.
BD_E: Battery Detect Enable.
[0]: Disable. [1]: Enable. It will be clear after battery detection is triggered.
BDF: Battery detection flag.
[0]: Battery voltage less than threshold. [1]: Battery voltage gr eater than threshold.
Below is the procedure to detect low voltage input (ex. below 2.1V):
1. Set A7130 in standby or PLL mode.
2. Set BVT [2:0] = [001] and enable BD_E = 1.
3. After 5 us, BD_E is auto clear.
4. User can read BDF or output BDF to GIO1 pin or CKO pin.
If REGI pin > 2.1V,
BDF = 1 (battery high). Else, BDF = 0 (battery low).
W LVR RGV1 RGV0 QDS BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
R -- RGV1 RGV0 BDF BVT2 BVT1 BVT0 BD_E
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 73 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 74

LBA7130
19. Auto-ack and auto-resend
A7130 supports auto-resend and auto-ack scheme by enable EAK = 1 (auto-ack) and EAR = 1 (auto-resend). In application
points of view, this feature is also ok to enable together with other feature options like FCB and/or EDRL (dynamic FIFO).
19.1 Basic FIFO plus auto-ack auto-resend
Set EAF = 0, EAK = 1 and EAR = 1 to enable auto-ack and auto-resend. Please refer to the below TX and ACK packet format of
the sender and the receiver site respectively.
19.2 Advanced FIFO plus auto-ack and auto-resend
In addition to set EAF = 0, EAK = 1 and EAR = 1 to enable auto-ack and auto-resend. User can also enable an optional MAC
header (FCB field) in the TX packet together with auto-ack and auto resend scheme. Please refer to the below TX and ACK
packet format of the sender and the receiver site.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 74 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 75

LBA7130
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 75 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 76

LBA7130
19.3 WTR Behavior during auto-ack and auto-resend
If auto-ack and auto-resend are enabled (EAR = EAK = 1), WTR represents a completed transmission period and CWTR is a
debug signal which represents the cyclic TX period and cyclic RX period. Please refer to the below timing diagrams for details.
The sender site (auto-resend)
The receiver site (auto-ack)
Remark: Refer to 3Bh for ARD[7:0] setting (auto resend delay).
Refer to 3Fh for RND[7:0] setting (random seed for resend interval).
Refer to 3Ah for EAK (enable auto-ack).
Refer to 3Ah for EAR (enable auto-resend).
Refer to 0Bh for VKM and VPM.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 76 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 77

LBA7130
19.6 Examples of auto-ack and auto-resend
Once EAK and EAR are enabled, below case 1 ~ case 3 illustrate the most common cases as a timing reference (assume ARD
= 800 us) in two ways radio communications.
<Case1> Always success
<Case2> Success in second packet
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 77 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 78

<Case3> always resend failure
LBA7130
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 78 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 79

LBA7130
20. RC Oscillator
A7130 has an internal RC oscillator to supports WOR (Wake On RX) and TWOR (Timer Wake On RX) function. RCOSC_E
(09h) is used to enable RC oscillator. WORE (01h) is used to enable WOR function and TWORE (09h) is used to enable TWOR
function. After done calibrations of RC oscillator, WOR and TWOR function can be operated from -40℃ to 85℃.
Parameter Min Max Unit Note
Calibrated Freq. 3.8K 4.2K Hz
Sleep period 7.82 8007.68 ms [( WOR_SL [9:0] ) +1] x 7.8 ms
RX period 0.244 ms [( WOR_AC [5:0] ) +1] x 244 us
Operation temperature -40 85 ℃ After calibration.
20.1 WOR Function
When WOR is e nabled (WORE = 1 and RCOSC_E =1), A7130 pe riodically wakes up f rom sleep and li sten (auto-enter RX
mode) for incoming packets without MCU interaction. Therefore, A7130 will stay in sleep mode based on WOR_SL timer and
RX mode based on WOR_AC timer unless a packet is received.
The internal RC oscillator used for the WOR function varies with temperature and CMOS process deviation. In order to keep the
frequency as accurate as possible, the RC oscillator shall be calibrated (CALWC=1) whenever possible. After done calibrations,
MCU shall set WORE=1 and issue sleep strobe command to start WOR function. After a period (WOR_SL) in sleep mode, the
device goes to RX mode to check coming packets. And then, A7130 is back to sleep mode for the next WOR cycle. To end up
WOR function, MCU just needs to set WORE = 0. Beware, please turn on MSCRC (21h, CRC data filtering) when CRCS = 1
(20h, CRC select) in WOR function.
Strobe CMD
(SCS,SCK,SDIO)
RF In Pin
GIO1 -- WTR
GIO1S[3:0]=0000
sleep
Start WOR
(sleep strobe )
Sleep
WOR_SL[9:0]
No Command Required
RX
WOT_SL[9:0]
Sleep
Coming
packet
RX
End of WOR
(set WORE = 0)
Strobe
cmd
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 79 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 80

LBA7130
20.2 TWOR Function
The RC oscillator inside A7130 can also be used to supports programmable TWOR (Timer Wake-On, TWORE=1) function
which enables A7130 to output a periodic square wave from GIO1 (or GIO2). The duty cycle of this square wave is set by
WOR_AC (08h) or WOR_SL (08h and 07h) regarding to TSEL (09h). User can use this square wave to wake up MCU or other
purposes.
21. AES128 Security Packet
A7130 has a built-in AES128 co-processor to generate a security packet by a general purpose MCU. In addition to support
128-bits key length (AES128), A7130 also support a proprietary 32-bits key length called AES32.
Software procedure to use AES128.
Step1: Write 16-bytes AES128 key to KEYI [127:0] (36h)
Step2: Set AESS=1 (3Eh) to select standard AES128
Step3. Set AKFS=0 (3Eh) to disable attaching AES128 KEYI [127:0] into the TX packet.
Step4: Set EDCRS=1 (3Eh) to enable AES co-processor.
Step5: Write plain text to TX FIFO
Step6: Issue TX strobe command and then A7130 will execute AES128 encryption and deliver the cipher text without latency.
Step7: In RX side with the same configurations, A7130 will execute AES128 decryption and store plain text back to RX FIFO.
Remark
1. The unit size of AES128 encryption packet is 16-bytes.
2. In TX side, if plain text is not dividable by 16-bytes, i.e. 5-bytes only, the TX packet is complement to be 16-bytes.
3. In RX side, the coming cipher text will be decrypted and restore 5-bytes plain text back to RX FIFO.
Software procedure to use AES32.
Step1: Write 4-bytes AES128 key to KEYI [31:0] (36h)
Step2: Set AESS=0 (3Eh) to select proprietary AES32.
Step3. Set AKFS=0 (3Eh) to not attach AES128 KEYI [31:0] to the wanted TX packet.
Step4: Set EDCRS=1 (3Eh) to enable AES co-processor.
Step5: Write plain text to TX FIFO
Step6: Issue TX strobe command and then A7130 will execute AES32 encryption and deliver the cipher text without latency.
Step7: In RX side with the same configurations, A7130 will execute AES32 decryption and store plain text back to RX FIFO.
Remark
1. The unit size of AES32 encryption packet is 4-bytes.
2. In TX side, if plain text is not dividable by 4-bytes, i.e. 5-bytes only, the TX packet is complement to 8-bytes.
3. In RX side, the coming cipher text will be decrypted and restore 5-bytes plain text back to RX FIFO.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 80 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 81

22. Application circuit
22.1 MD70-A01
AMICCOM’s ref. design module, MD7130-A01, max 5 dBm output power, application circuit exam ple.
LBA7130
TP1
ANTENNA
ANT
C15
1.8pF
VDD_A
L2
2.7nH
C1
470pF
C2
100pF
C3
4.7uF
C5
100pF
C6
0.1uF
VIN
U1
15
14
13
12
11
A7130
C12
G ND
CKO
G I O2
G I O1
SDIO
SCK
SCS
G ND
G ND
CON/10P 2.0
C4 2.2uF
VDD_A
CKO
GIO2
V IN
19
20
REGI
1
2
3
4
5
R1
NC
VDD_A
BP_RSSI
BP_BG
RFI
RFO
RFC
V DD_ VCO6CP7VDD_PLL8XI9XO
C8
2.2nF
A7130PKG
GIO1
18
16
CKO
GIO217GIO1
GND
SDIO
VDD_D
SCK
SCS
10
C7
2.2uF
Y1 NC
1
J1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
J2
2
CON/2P 2.0
1
J3
2
CON/2P 2.0
SDIO
SCK
SCS
C13
C9
NC
VDD_A
C10
0.1uF
C11
100pF
NC
Y2 NC
4
G ND
1
G ND
3
2
NC
Y3
16M Hz X TA L_ 3. 2*2 . 5
4
G ND
1
G ND
3
2
Remark
1. RF Matching to 50Ω.
2. RX and TX signal are combined internally to RFI pin only so that RFSP bit = 0 (DASP0 register = 0x34).
3. Recommend 16MHz crystal with 18 pF Cload.
4. Recommend to let C12 and C13 NC because of enabling on-chip Xtal Capacitors by (INTXC = 1 and CSXTAL = [10100]).
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 81 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 82

LBA7130
22.2 MD70-F07
AMICCOM’s ref. design module, MD7130-F07, typical 17 dBm output power together with a range extendor A7700.
4321
C18
D
C16
LNA_OUT
PA_IN
C
TP1
TEST POINT
C11
NC
L7
2.4nH
B
A
C6
1.5pF
C19
1.5pF
L8
2.4nH
C25 1pF
C33
8.2pF
C42
NC
1 2 3 4
VDD_PA
L1
4.7nH
1
TRX
2
3
4
REGI33
C8
NC
C12
NC
GND
ANT
NC
VDD_PA
REGI 33
16
C7
8.2pF
TX SW
RX SW
14
HGM
RX SW15TX SW
GND5VDD_BA7VDD _A
NC
6
C13
0.1uF
C15
NC
13
BG
8
BG
BGS
RFO
GND
RFI
REGI33
C57
100pF
U2
12
11
10
9
A7700
R6
6.8K
C36
L3
0R
L2
3nH
NC
RFO
RFI
R1
47
C38 NC
LNA_OUT
PA_IN
C9
1. 2pF
1pF
C10
1pF
C3
1nF
L10
L9
C29
100pF
VDD_A
CKO
3.3nH
3.3nH
R11
R12
4.7uF
C2
100pF
C5
1
2
3
4
5
C14
0.1uF
NC
0R
C32
NC
2.2uF
VDD_A
CKO
GIO2
GIO1
RE GI 33
18
16
19
20
VDD_A
BP_RSSI
BP_ BG
RFI
RFO
RFC
VDD_VCO6CP7VDD_PLL8XI9XO
R10
NC
C1
2.2pF
REGI33
CKO or GND
GIO2
GIO1
SDIO
SCK
SCS
TX SW
RX SW
GND
REGI
A7130P KG
C31
2.2nF
CKO
J2
VDD_A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
GIO217GIO1
10
GND
SDIO
VDD_D
C30
0.1uF
SCK
SCS
U1
15
14
13
12
11
A70
CRYSTAL/5*3 .2
CON/10P 2.0
Title
MD7˄ˆ0-F07-05(2L)
Number Revisi onSize
A4
Date: 1 2-Jan-2 012 She et o f
File: C: \Docu ments and Sett in gs\ac 0086 \桌面\MD7130~2.DDBDrawn By:
2012.01.12
Y2 16MHz
4
1
C34
NC
C20
2.2uF
Y1
1 2
16MHz
1 2
Y3
GND
GND
SDIO
SCK
SCS
D
C
3
2
C37
NC
B
A
Remark
1. RF matching to 50Ω.
2. RX and TX signal are separated to RFI pin and RFO pin so that RFSP bit = 1 (DASP0 register = 0x74).
3. Recommend 16MHz crystal with 18 pF Cload.
4. Recommend to let C34 and C37 NC because of enabling on-chip Xtal Capacitors by (INTXC = 1 and CSXTAL = [10100]).
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 82 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 83

23. Abbreviations
ADC Analog to Digital Converter
AIF Auto IF
FC Frequency Compensation
AGC Automatic Gain Control
BER Bit Error Rate
BW Bandwidth
CD Carrier Detect
CHSP Channel Step
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DC Direct Current
FEC Forward Error Correction
FIFO First in First out
FSK Frequency Shift Keying
ID Identifier
IF Interm ediate Frequency
ISM Industrial, Scientific and Medical
LO Local Oscillator
MCU Micro Controller Unit
PFD Phase Frequency Detector for PLL
PLL Phase Lock Loop
POR Power on Reset
RX Receiver
RXLO Receiver Local Oscillator
RSSI Received Signal Strength Indicator
SPI Serial to Parallel Interface
SYCK System Clock for digital circuit
TX Transmitter
TXRF Transmitter Radio Frequency
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
XOSC Crystal Oscillator
XREF Crystal Reference frequency
XTAL Crystal
LBA7130
24. Ordering Information
Part No. Package Units Per Reel / Tray
A71C30AQFI/Q
A71C30AQFI
A71C30AH
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 83 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
QFN20L, Pb Free, Tape & Reel, -40℃〜85℃
QFN20L, Pb Free, Tray, -40℃〜85℃
Die form, -40℃〜85℃
3K
490EA
100EA
Page 84

25. Package Information
QFN 20L (4 X 4 X 0.8mm) Outline Dimensions
TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW
LBA7130
10
6
0.25 C
10
E2
e
6
0.10// C
A
y C
A3
Dimensions in mm
Max Min Nom Max
11 15
5 1
D
15
16
E
20
1 5
0.25 C
A1
Seating Plane
Symbol
11
C
Dimensions in inches
Min Nom
D2
L
16
20
e
b
C0.10MA B
A 0.028 0.030 0.032 0.70 0.75 0.80
A1 0.000 0.001 0.002 0.00 0.02 0.05
A3 0.008 REF 0.203 REF
b 0.007 0.010 0.012 0.18 0.25 0.30
D 0.154 0.158 0.161 3.90 4.00 4.10
D2 0.075 0.079 0.083 1.90 2.00 2.10
E 0.154 0.158 0.161 3.90 4.00 4.10
E2 0.075 0.079 0.083 1.90 2.00 2.10
e
0.020 BSC 0.50 BSC
L 0.012 0.016 0.020 0.30 0.40 0.50
y 0.003 0.08
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 84 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 85

26. Top Marking Information
A : 0.55
v
A71C30AQFI
¡ Part No. :A71C30AQFI
¡ Pin Count : 20
¡ Package Type : QFN
¡ Dimension :4*4 mm
¡ Mark Method : Laser Mark
¡ Character Type : Arial
LBA7130
J
K
N
F
CHARACTER SIZE : (Unit in mm)
B : 0.36
C1 : 0.25 C2 : 0.3
C3 : 0.2
D : 0.03
Y
N
D
Y
C1
70
N
N
WXW
B
N
N
A
I
Y
X
N N N N N
N
Y W
N
N
W
C2
C3
N
L
G
:DATECODE
: PKG HOUSE
N
N N
: LOT NO.
(max. 9 characters)
F=G
I=J
K=L
0.8
0.6
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 85 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
0.6
5
70
1.6
0
Page 86

27. Reflow Profile
LBA7130
Actual Measurement Graph
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 86 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 87

28. Tape Reel Information
Cover / Carrier Tape Dimension
LBA7130
Unit: mm
TYPE P A0 B0 P0 P1 D0 D1 E F W
20 QFN 4*4 8 4.35 4.35 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.75 5.5 12
24 QFN 4*4 8 4.4 4.4 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.75 5.5 12
32 QFN 5*5 8 5.25 5.25 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.75 5.5 12
QFN3*3 / DFN-10 4 3.2 3.2 4.0 2.0 1.5 - 1.75 1.9 8
20 SSOP 12 8.2 7.5 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.75 7.5 16
24 SSOP 12 8.2 8.8 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.75 7.5 16
TYPE K0 t COVER TAPE WIDTH
20 QFN (4X4) 1.1 0.3 9.2
24 QFN (4X4) 1.4 0.3 9.2
32 QFN (5X5) 1.1 0.3 9.2
QFN3*3 / DFN-10 0.75 0.25 8
20 SSOP 2.5 0.3 13.3
24 SSOP 2.1 0.3 13.3
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 87 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Page 88

REEL DIMENSIONS
UNIT IN mm
TYPE G N T M D K L R
20 QFN(4X4)
24 QFN(4X4)
32 QFN(5X5)
DFN-10
12.8+0.6/-0.4
100
REF
18.2(MAX) 1.75±0.25 13.0+0.5/-0.2 2.0±0.5
330+
0.00/-1.0
LBA7130
20.2
48 QFN(7X7)
28 SSOP (150mil)
20 SSOP
24 SSOP
L R
16.8+0.6/-0.4
20.4+0.6/-0.4
16.4+2.0/-0.0
100
REF
100
REF
100
REF
22.2(MAX) 1.75±0.25 13.0+0.5/-0.2 2.0±0.5
25(MAX) 1.75±0.25 13.0+0.5/-0.2 2.0±0.5
22.4(MAX)
1.75±0.25 13.0+0.2/-0.2 1.9±0.4
D
330+
0.00/-1.0
330+
0.00/-1.0
330+
0.00/-1.0
T
20.2
20.2
20.2
N
M
K
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 88 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
G
Page 89

RF ICs
AMICCOM
29. Product Status
Data Sheet Identification Product Status Definition
Objective Planned or Under Development This data sheet contains the design specifications
for product development. Specifications may
change in any manner without notice.
LBA7130
Preliminary Engineering Samples
and First Production
No Identification Noted Full Production This data sheet contains the final specifications.
Obsolete Not In Production This data sheet contains specifications on a
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and
supplementary data will be published at a later
date. AMICCOM reserves the right to make
changes at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible
product.
AMICCOM reserves the right to make changes at
any time without notice in order to improve design
and supply the best possible product.
product that has been discontinued by AMICCOM.
The data sheet is printed for reference inform ation
only.
Oct., 2012, Version 0.6 (PRELIMINARY) 89 AMICCOM Electronics Corporation
Headquarter
A3, 1F, No.1, Li-Hsin Rd. 1, Hsinchu Science Park,
Taiwan 30078
Tel: 886-3-5785818
Shenzhen Office
Rm., 2003, DongFeng Building, No. 2010,
Shennan Zhonglu Rd., Futian Dist., Shenzhen, China
Post code: 518031
Web Site
http://www.amiccom.com.tw
Page 90

Modular Approal:
The LBA 7130RF module is designed to comply with the FCC statement. FCC ID is OIE51402TR.
The host system using LBA 7130RF, should have label indicated FCC ID: OIE51402TR.
This radio module must not installed to co-locate and operating
Simultaneously with other radios in host system, additional testing
and equipment authorization may be required to operating simultaneously with other radio
FCC Statement:
1. This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1)This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2)This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
2. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
 Loading...
Loading...