Lattice Semiconductor Corporation pLSI1032-60LJI, pLSI1032-60LT, pLSI1032-80LJ, pLSI1032-80LT, pLSI1032-90LJ Datasheet
...
Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
ispLSI® and pLSI® 1032
High-Density Programmable Logic
Features
• HIGH-DENSITY PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC
— High Speed Global Interconnect
— 6000 PLD Gates
— 64 I/O Pins, Eight Dedicated Inputs
— 192 Registers
— Wide Input Gating for Fast Counters, State
Machines, Address Decoders, etc.
— Small Logic Block Size for Fast Random Logic
— Security Cell Prevents Unauthorized Copying
2
• HIGH PERFORMANCE E
fmax = 90 MHz Maximum Operating Frequency
—
fmax = 60 MHz for Industrial and Military/883 Devices
—
— tpd = 12 ns Propagation Delay
— TTL Compatible Inputs and Outputs
— Electrically Erasable and Reprogrammable
— Non-Volatile E
— 100% Tested
• ispLSI OFFERS THE FOLLOWING ADDED FEATURES
— In-System Programmable™ (ISP™) 5-Volt Only
— Increased Manufacturing Yields, Reduced Time-to-
Market, and Improved Product Quality
— Reprogram Soldered Devices for Faster Prototyping
• COMBINES EASE OF USE AND THE FAST SYSTEM
SPEED OF PLDs WITH THE DENSITY AND FLEX-
IBILITY OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS
— Complete Programmable Device Can Combine Glue
Logic and Structured Designs
— Four Dedicated Clock Input Pins
— Synchronous and Asynchronous Clocks
— Flexible Pin Placement
— Optimized Global Routing Pool Provides Global
Interconnectivity
• ispLSI AND pLSI DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
®
Software
pDS
— Easy to Use PC Windows™ Interface
— Boolean Logic Compiler
— Manual Partitioning
— Automatic Place and Route
— Static Timing Table
ispDS+™ Software
— Industry Standard, Third Party Design
Environments
— Schematic Capture, State Machine, HDL
— Automatic Partitioning and Place and Route
— Comprehensive Logic and Timing Simulation
— PC and Workstation Platforms
2
CMOS Technology
CMOS® TECHNOLOGY
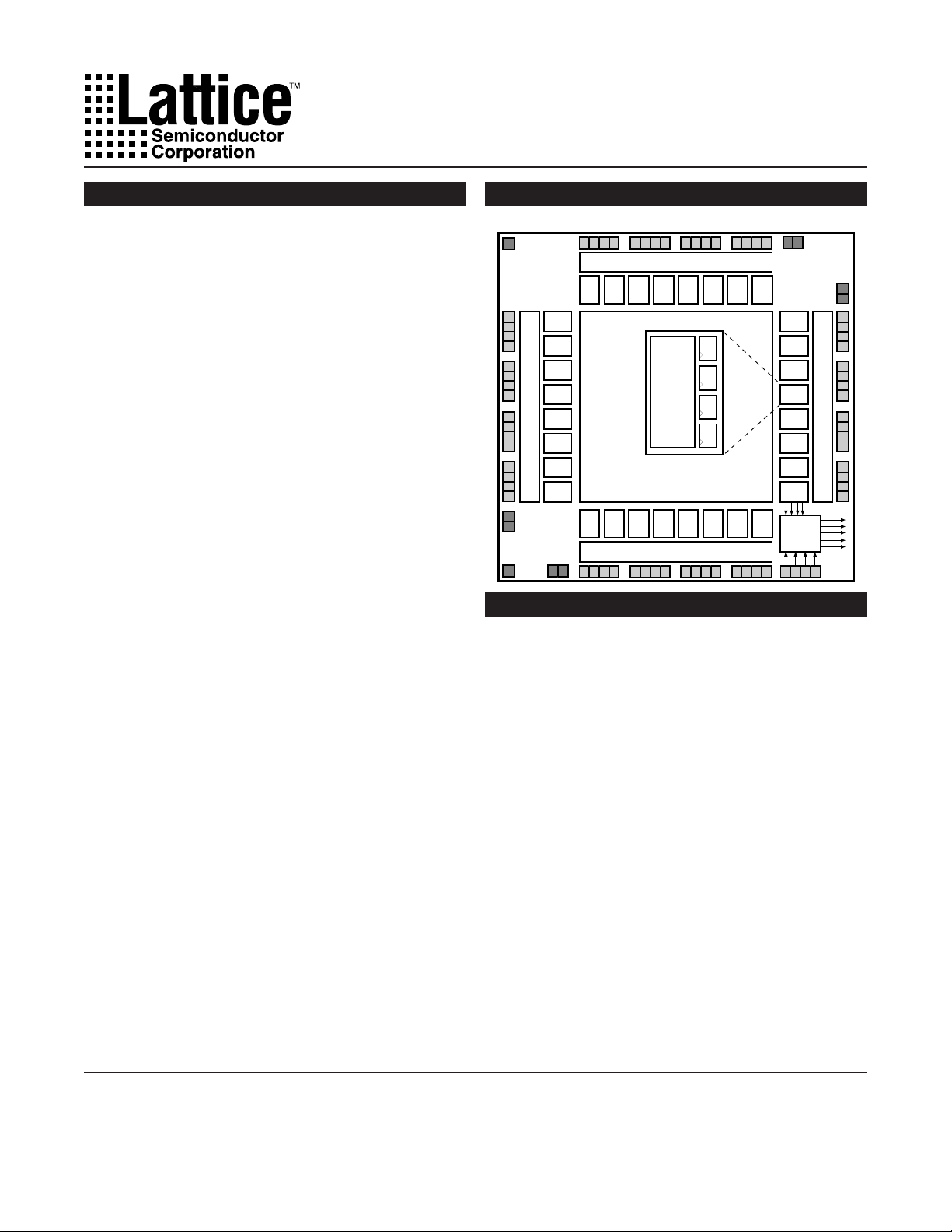
Functional Block Diagram
Output Routing Pool
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
Output Routing Pool
A6
Global Routing Pool (GRP)
A7
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7
Logic
Array
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
GLB
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
Output Routing Pool
C0
CLK
Output Routing Pool
Description
The ispLSI and pLSI 1032 are High-Density Programmable Logic Devices containing 192 Registers, 64
Universal I/O pins, eight Dedicated Input pins, four Dedicated Clock Input pins and a Global Routing Pool (GRP).
The GRP provides complete interconnectivity between
all of these elements. The ispLSI 1032 features 5-Volt insystem programming and in-system diagnostic
capabilities. It is the first device which offers non-volatile
"on-the-fly" reprogrammability of the logic, as well as the
interconnect to provide truly reconfigurable systems. It is
architecturally and parametrically compatible to the pLSI
1032 device, but multiplexes four of the dedicated input
pins to control in-system programming.
The basic unit of logic on the ispLSI and pLSI 1032
devices is the Generic Logic Block (GLB). The GLBs are
labeled A0, A1 .. D7 (see figure 1). There are a total of
32 GLBs in the ispLSI and pLSI 1032 devices. Each GLB
has 18 inputs, a programmable AND/OR/XOR array, and
four outputs which can be configured to be either combinatorial or registered. Inputs to the GLB come from the
GRP and dedicated inputs. All of the GLB outputs are
brought back into the GRP so that they can be connected
to the inputs of any other GLB on the device.
Copyright © 1997 Lattice Semiconductor Corp. All brand or product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. The specifications and information herein are subject
to change without notice.
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR CORP., 5555 Northeast Moore Ct., Hillsboro, Oregon 97124, U.S.A. February 1997
Tel. (503) 681-0118; 1-800-LATTICE; FAX (503) 681-3037; http://www.latticesemi.com 1996 ISP Encyclopedia
1 1996 ISP Encyclopedia1032_02
Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
Functional Block Diagram
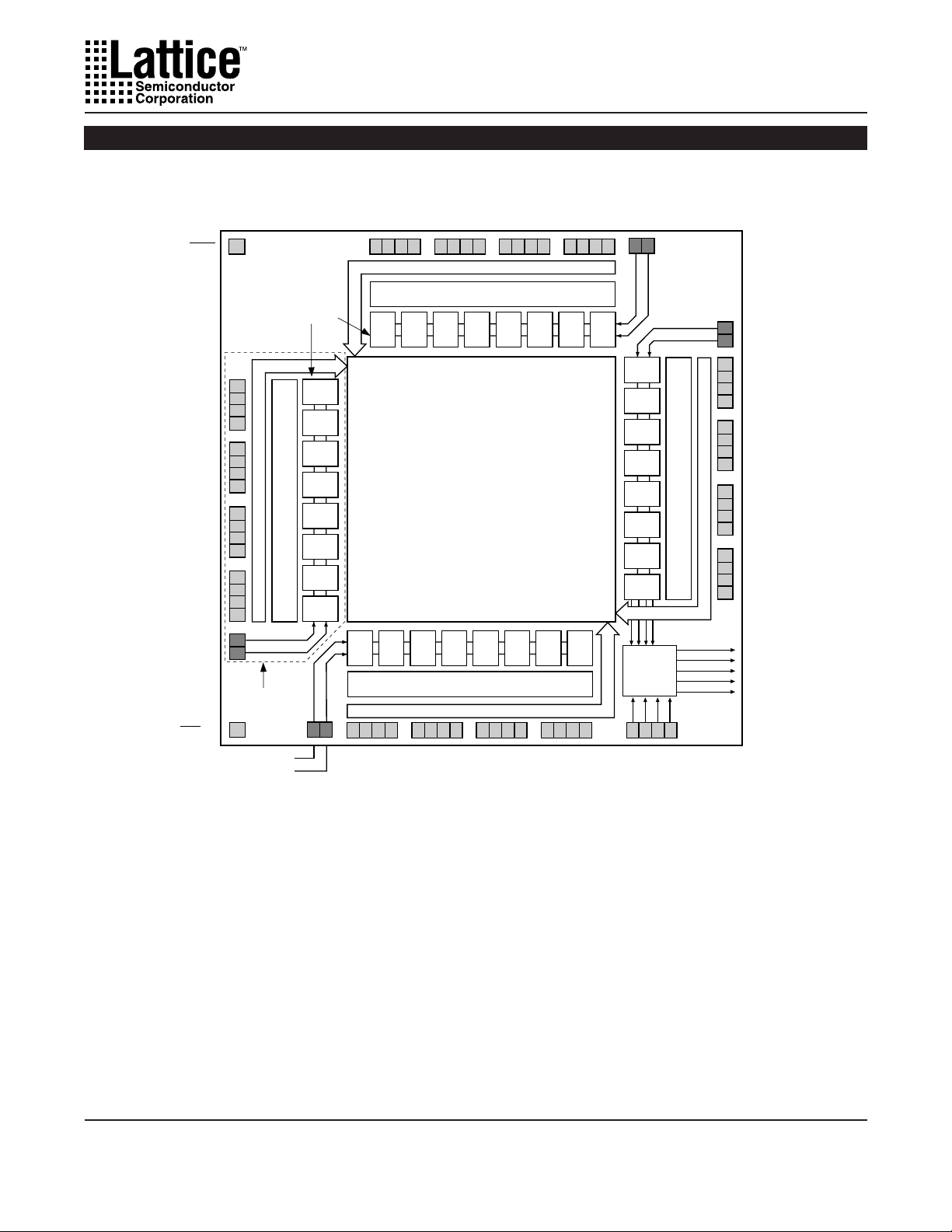
Figure 1. ispLSI and pLSI 1032 Functional Block Diagram
RESET
I/O 0
I/O 1
I/O 2
I/O 3
I/O 4
I/O 5
I/O 6
I/O 7
I/O 8
I/O 9
I/O 10
I/O 11
I/O 12
I/O 13
I/O 14
I/O 15
*SDI/IN 0
*MODE/IN 1
*ispEN/NC
I/O62I/O63I/O61I/O60I/O59I/O58I/O57I/O56I/O55I/O54I/O53I/O52I/O51I/O50I/O49I/O
Generic
Logic Blocks
(GLBs)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
A0
A1
A2
A3
Input Bus
Megablock
*SDO/IN 2
*SCLK/IN 3
*ISP Control Functions for ispLSI 1032 Only
A4
A5
Output Routing Pool (ORP)
A6
A7
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7
Output Routing Pool (ORP)
I/O17I/O16I/O18I/O19I/O20I/O21I/O22I/O23I/O24I/O25I/O26I/O27I/O28I/O29I/O30I/O
Input Bus
Output Routing Pool (ORP)
Global
Routing
Pool
(GRP)
Input Bus
IN7IN
6
48
IN 5
IN 4
lnput Bus
0139(1)-32-isp
I/O 47
I/O 46
I/O 45
I/O 44
I/O 43
I/O 42
I/O 41
I/O 40
I/O 39
I/O 38
I/O 37
I/O 36
I/O 35
I/O 34
I/O 33
I/O 32
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
Output Routing Pool (ORP)
C1
C0
CLK 0
Clock
Distribution
Network
31
Y0Y1Y2Y
CLK 1
CLK 2
IOCLK 0
IOCLK 1
3
The devices also have 64 I/O cells, each of which is
directly connected to an I/O pin. Each I/O cell can be
individually programmed to be a combinatorial input,
registered input, latched input, output or bi-directional
I/O pin with 3-state control. Additionally, all outputs are
polarity selectable, active high or active low. The signal
levels are TTL compatible voltages and the output drivers
can source 4 mA or sink 8 mA.
Eight GLBs, 16 I/O cells, two dedicated inputs and one
ORP are connected together to make a Megablock (see
figure 1). The outputs of the eight GLBs are connected to
a set of 16 universal I/O cells by the ORP. The I/O cells
within the Megablock also share a common Output
Enable (OE) signal. The ispLSI and pLSI 1032 devices
contain four of these Megablocks.
The GRP has as its inputs the outputs from all of the GLBs
and all of the inputs from the bi-directional I/O cells. All of
these signals are made available to the inputs of the
GLBs. Delays through the GRP have been equalized to
minimize timing skew.
Clocks in the ispLSI and pLSI 1032 devices are selected
using the Clock Distribution Network. Four dedicated
clock pins (Y0, Y1, Y2 and Y3) are brought into the
distribution network, and five clock outputs (CLK 0, CLK
1, CLK 2, IOCLK 0 and IOCLK 1) are provided to route
clocks to the GLBs and I/O cells. The Clock Distribution
Network can also be driven from a special clock GLB (C0
on the ispLSI and pLSI 1032 devices). The logic of this
GLB allows the user to create an internal clock from a
combination of internal signals within the device.
2 1996 ISP Encyclopedia

Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
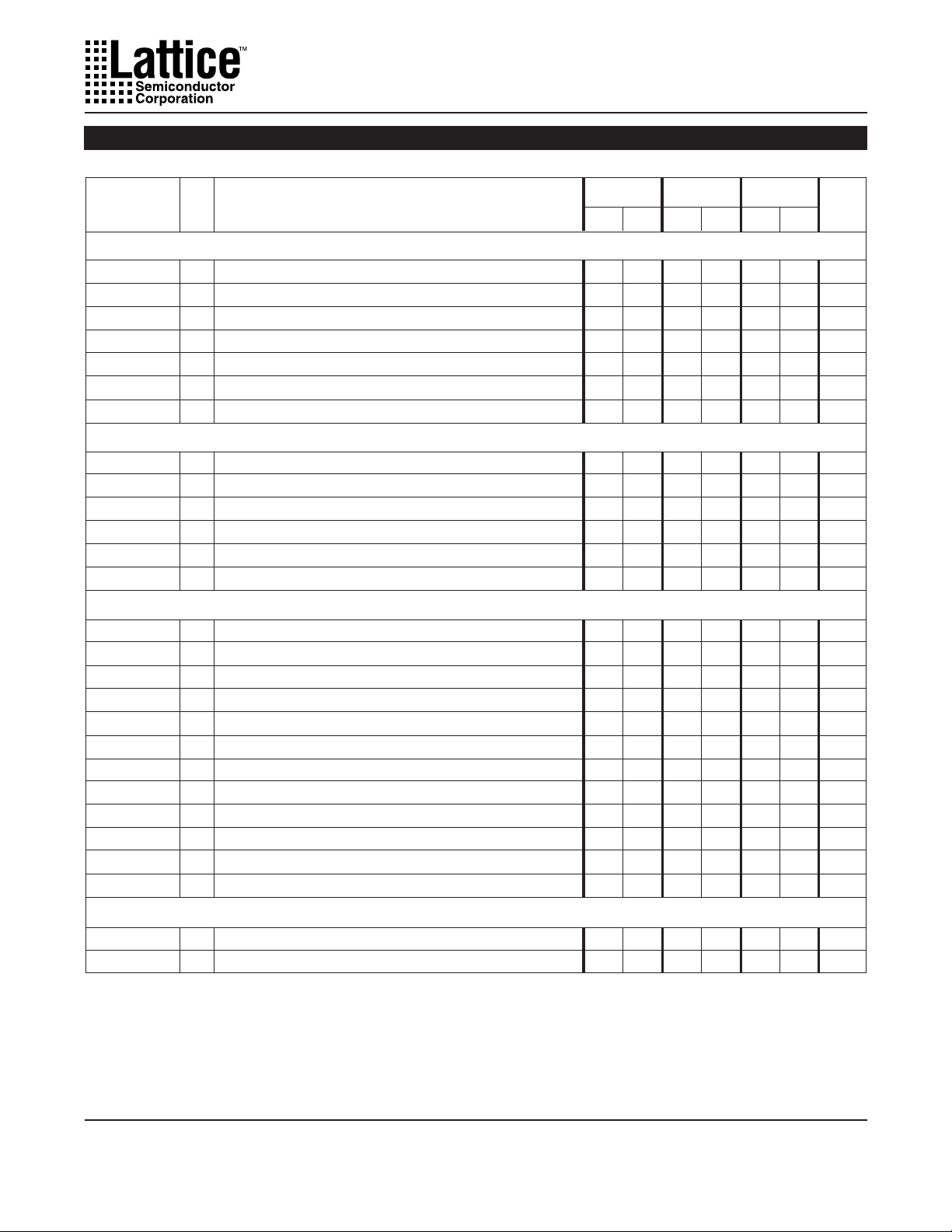
Absolute Maximum Ratings
1
Supply Voltage Vcc...................................-0.5 to +7.0V
Input Voltage Applied........................ -2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Off-State Output Voltage Applied ..... -2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Storage Temperature................................ -65 to 150°C
Case Temp. with Power Applied .............. -55 to 125°C
Max. Junction Temp. (TJ) with Power Applied ... 150°C
1. Stresses above those listed under the “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. Functional
operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification
is not implied (while programming, follow the programming specifications).
DC Recommended Operating Conditions
PARAMETERSYMBOL MIN. MAX. UNITS
5.25
5.5
5.5
0.8
V
V
V
V
CC
IL
Commercial TA = 0°C to +70°C
Supply Voltage
Industrial T
Military/883 T
Input Low Voltage
= -40°C to +85°C
A
= -55°C to +125°C
C
4.75
4.5
4.5
0
V
IH
Input High Voltage
Capacitance (TA=25oC, f=1.0 MHz)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MAXIMUM
C
1
C
2
1
.
Guaranteed but not 100% tested.
Commercial/Industrial 8 pf VCC=5.0V, VIN=2.0V
Dedicated Input Capacitance
Military 10 pf V
I/O and Clock Capacitance 10 pf VCC=5.0V, V
Data Retention Specifications
PARAMETER
Data Retention
ispLSI Erase/Reprogram Cycles
pLSI Erase/Reprogram Cycles
MINIMUM MAXIMUM UNITS
20
10000
100
2.0
1
UNITS TEST CONDITIONS
–
–
–
Vcc + 1
=5.0V, VIN=2.0V
CC
V
Table 2- 0005Aisp w/mil.eps
, VY=2.0V
I/O
Table 2- 0006
Years
Cycles
Cycles
Table 2- 0008B
3 1996 ISP Encyclopedia
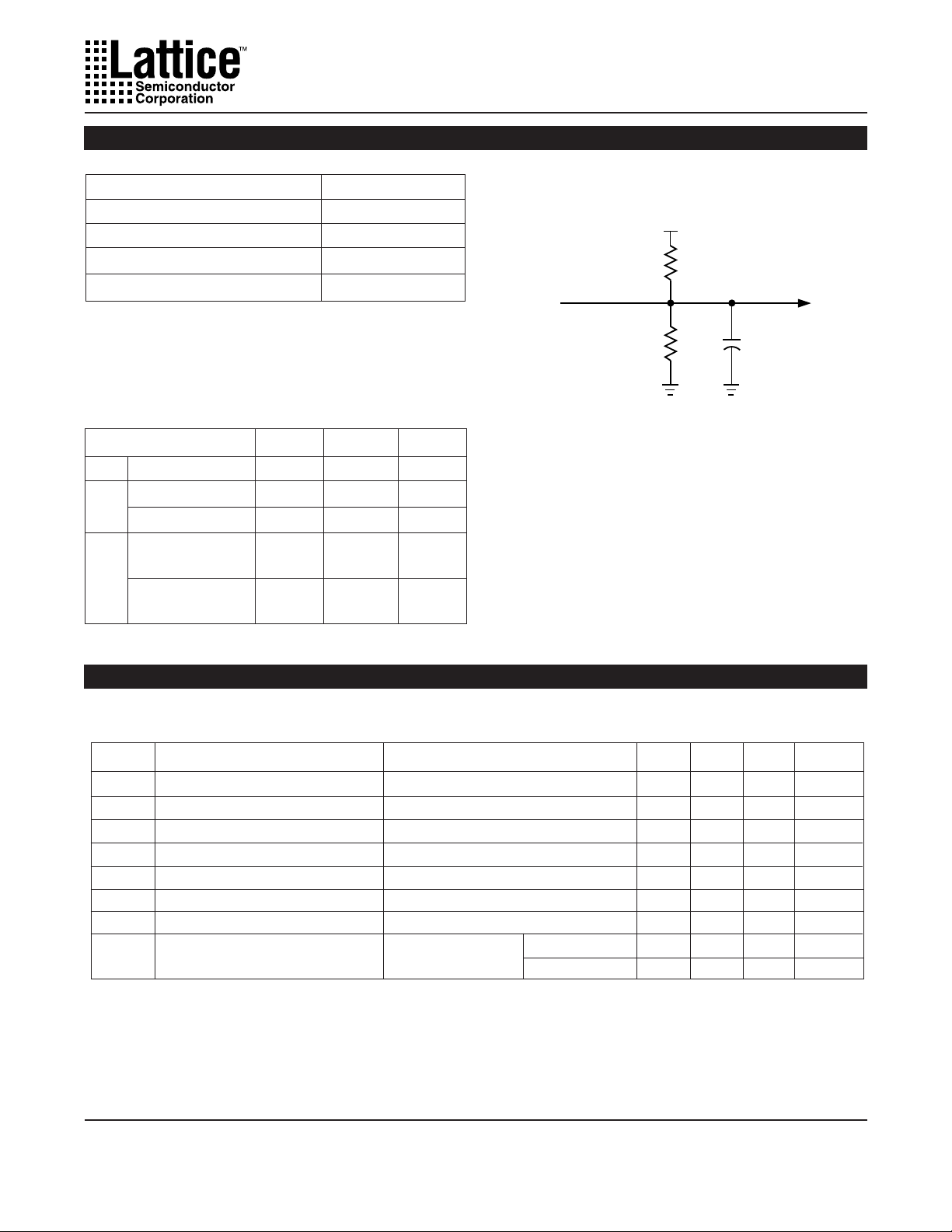
Switching Test Conditions
Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
Input Pulse Levels GND to 3.0V
Input Rise and Fall Time ≤ 3ns 10% to 90%
Input Timing Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Timing Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Load See figure 2
3-state levels are measured 0.5V from steady-state
active level.
-
Output Load Conditions (see figure 2)
Test Condition R1 R2 CL
A 470Ω 390Ω 35pF
B Active High 390Ω 35pF
Active Low 470Ω 390Ω 35pF
Active High to Z 390Ω 5pF
Cat V
- 0.5V
OH
Active Low to Z 470Ω 390Ω 5pF
+ 0.5V
at V
OL
∞
∞
Figure 2. Test Load
+ 5V
R
1
Device
Output
R
2
*
CL includes Test Fixture and Probe Capacitance.
C
Test
Point
*
L
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
130
135
3
MAX.TYP.
0.4
–
-10
10
-150
-150
-200
190
220
UNITS
V
V
µA
µA
µA
µA
mA
mA
mA
Table 2- 0007A-32-isp
SYMBOL
V
OL
V
OH
I
IL
I
IH
I
IL-isp
I
IL-PU
I
OS
I
CC
1. One output at a time for a maximum duration of one second.
2. Measured using eight 16-bit counters.
3. Typical values are at V
4. Maximum ICC varies widely with specific device configuration and operating frequency . Refer to the Power Consumption section of this datasheet and Thermal Management section of this Data Book to estimate maximum ICC.
Output Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Input or I/O Low Leakage Current
Input or I/O High Leakage Current
isp Input Low Leakage Current
I/O Active Pull-Up Current
1
Output Short Circuit Current
2,4
Operating Power Supply Current
PARAMETER CONDITION
IOL =8 mA
=-4 mA
I
OH
≤ VIL (MAX.)
IN
≤ V
IN
CC
≤ V
IN
IL
= 0.5V
OUT
= 0.5V, V
IL
= 1 MHz Industrial/Military
TOGGLE
= 3.0V Commercial
IH
= 5V and TA = 25oC.
CC
0V ≤ V
3.5V ≤ V
0V ≤ VIN ≤ VIL (MAX.)
0V ≤ V
VCC = 5V, V
V
f
MIN.
–
2.4
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
4 1996 ISP Encyclopedia
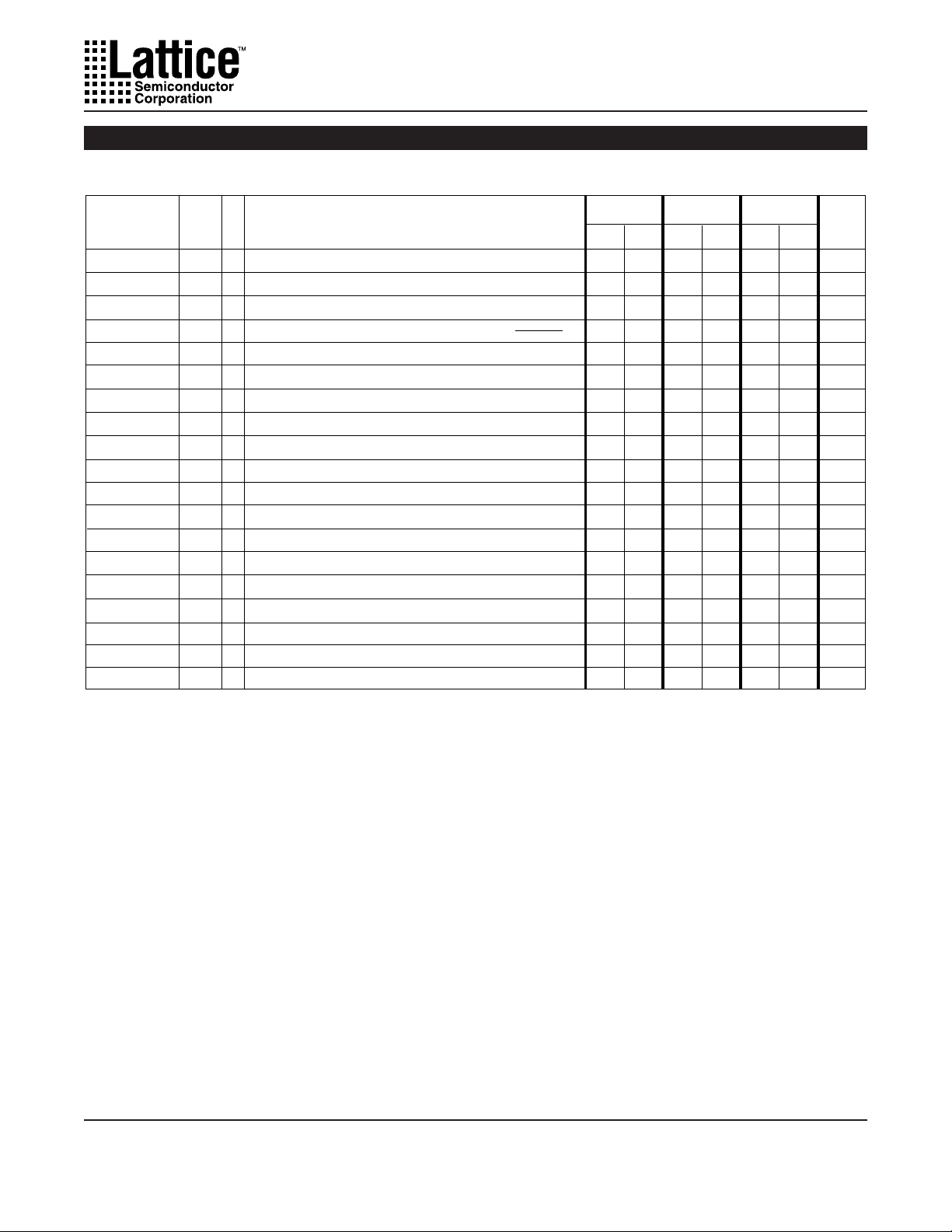
External Timing Parameters
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
5
PARAMETER #
t
pd1
t
pd2
f
max (Int.)
f
max (Ext.)
f
max (Tog.)
t
su1
t
co1
t
h1
t
su2
t
co2
t
h2
t
r1
t
rw1
t
en
t
dis
t
wh
t
wl
t
su5
t
h5
1. Unless noted otherwise, all parameters use a GRP load of 4 GLBs, ORP and Y0 clock.
2. Refer to Timing Model in this data sheet for further details.
3. Standard 16-Bit counter using GRP feedback.
4. fmax (Toggle) may be less than 1/(twh + twl). This is to allow for a clock duty cycle of other than 50%.
5. Reference Switching Test Conditions section.
TEST
COND.
2
DESCRIPTION
A
1
Data Propagation Delay, 4PT bypass, ORP bypass
A
2
Data Propagation Delay, Worst Case Path
A
3
Clock Frequency with Internal Feedback
–
4
Clock Frequency with External Feedback
–
5
Clock Frequency, Max Toggle
–
6
GLB Reg. Setup Time before Clock, 4PT bypass
A
7
GLB Reg. Clock to Output Delay, ORP bypass
–
8
GLB Reg.
–
9
GLB Reg. Setup Time before Clock
–
10
GLB Reg. Clock to Output Delay
–
11
GLB Reg. Hold Time after Clock
A
12
Ext. Reset Pin to Output Delay
–
13
Ext. Reset Pulse Duration
B
14
Input to Output Enable
C
15
Input to Output Disable
–
16
Ext. Sync. Clock Pulse Duration, High
–
17
Ext. Sync. Clock Pulse Duration, Low
–
18
I/O Reg. Setup Time before Ext. Sync. Clock (Y2, Y3)
–
19
I/O Reg. Hold Time after Ext. Sync. Clock (Y2, Y3)
1
3
( )
4
Hold Time after Clock, 4 PT bypass
tsu2 + tco1
1
-90
MIN. MAX.
12
–
17
–
90.9
58.8
–
–
–
125
–
6
8
–
–
0
–
9
10
–
–
0
15
–
–
10
USE 1032E-80
15
–
FOR NEW DESIGNS
15
–
–
4
–
4
–
2
–
6.5
-80 -60
MIN. MAX.
–
–
80
50
100
7
–
0
10
–
0
–
10
USE 1032E-70
–
–
5
5
2
6.5
MIN. MAX.
–
15
–
20
60
–
38
–
83
–
9
–
–
10
0
–
13
–
–
12
0
–
–
17
13
–
–
18
FOR NEW DESIGNS
–
18
6
–
6
–
2.5
–
8.5
–
Table 2-0030-32/90,80,60C
20
25
–
–
–
–
13
–
–
16
–
22.5
–
24
24
–
–
–
–
UNITS
ns
ns
MHz
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
5 1996 ISP Encyclopedia
Specifications ispLSI and pLSI 1032
Internal Timing Parameters
2
DESCRIPTIONPARAMETER UNITS
#
Inputs
t
iobp
t
iolat
t
iosu
t
ioh
t
ioco
t
ior
t
din
I/O Register Bypass
20
I/O Latch Delay
21
I/O Register Setup Time before Clock
22
I/O Register Hold Time after Clock
23
I/O Register Clock to Out Delay
24
I/O Register Reset to Out Delay
25
Dedicated Input Delay
26
GRP
t
grp1
t
grp4
t
grp8
t
grp12
t
grp16
t
grp32
GRP Delay, 1 GLB Load
27
GRP Delay, 4 GLB Loads
28
GRP Delay, 8 GLB Loads
29
GRP Delay, 12 GLB Loads
30
GRP Delay, 16 GLB Loads
31
GRP Delay, 32 GLB Loads
32
1
-90
MIN. MAX.
1.6
–
2.4
–
–
4.8
–
2.1
2.4
–
2.8
–
3.2
–
1.2
–
1.6
–
2.4
–
3.0
–
3.6
–
6.4
–
-80
MIN. MAX.
2.0
–
3.0
–
–
5.5
–
1.0
3.0
–
2.5
–
4.0
–
1.5
–
2.0
–
3.0
–
3.8
–
4.5
–
8.0
–
-60
MIN. MAX.
2.7
–
4.0
–
–
7.3
–
1.3
4.0
–
3.3
–
5.3
–
2.0
–
2.7
–
4.0
–
5.0
–
6.0
–
10.6
–
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
GLB
4 Product Term Bypass Path Delay
t
4ptbp
t
1ptxor
t
20ptxor
t
xoradj
t
gbp
t
gsu
t
gh
t
gco
t
gr
t
ptre
t
ptoe
t
ptck
33
1 Product Term/XOR Path Delay
34
20 Product Term/XOR Path Delay
35
XOR Adjacent Path Delay
36
GLB Register Bypass Delay
37
GLB Register Setup Time before Clock
38
GLB Register Hold Time after Clock
39
GLB Register Clock to Output Delay
40
GLB Register Reset to Output Delay
41
GLB Product Term Reset to Register Delay
42
GLB Product Term Output Enable to I/O Cell Delay
43
GLB Product Term Clock Delay
44
3
ORP
t
orp
t
orpbp
1. Internal Timing Parameters are not tested and are for reference only.
2. Refer to Timing Model in this data sheet for further details.
3. The XOR adjacent path can only be used by hard macros.
ORP Delay
45
ORP Bypass Delay
46
5.2
–
5.7
–
7.0
–
8.2
–
0.8
–
–
1.2
–
3.6
1.6
–
USE 1032E-80 FOR NEW DESIGNS
2.0
–
8.0
–
7.8
–
6.0
2.8
2.4
–
0.4
–
6.5
–
7.0
–
8.0
–
9.5
–
1.0
–
–
1.0
–
4.5
2.0
–
USE 1032E-70 FOR NEW DESIGNS
2.5
–
10.0
–
9.0
–
7.5
3.5
2.5
–
0.5
–
–
–
–
–
–
1.3
6.0
–
–
–
–
4.6
–
–
8.6
9.3
10.6
12.7
1.3
–
–
2.7
3.3
13.3
12.0
9.9
3.3
0.7
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
6 1996 ISP Encyclopedia
 Loading...
Loading...