Lattice Semiconductor Corporation M4LV-96-48-7VC, M4LV-96-48-18VI, M4LV-96-48-15VC, M4LV-96-48-14VI, M4LV-96-48-12VI Datasheet
...
Publication#
17466
Rev:
M
Amendment/
0
Issue Date:
March 2000
MACH 4 CPLD Family
High Performance E2CMOS®
In-System Programmable Logic
FEATURES
◆
High-performance, E2CMOS 3.3-V & 5-V CPLD families
◆
Flexible architecture for rapid logic designs
— Excellent First-Time-FitTM and refit feature
— SpeedLocking
TM
performance for guaranteed fixed timing
— Central, input and output switch matrices for 100% routability and 100% pin-out retention
◆
High speed
— 7.5ns tPD Commercial and 10ns t
PD
Industrial
— 111.1MHz f
CNT
◆
32 to 256 macrocells; 32 to 384 registers
◆
44 to 256 pins in PLCC, PQFP, TQFP and BGA packages
◆
Flexible architecture for a wide range of design styles
— D/T registers and latches
— Synchronous or asynchronous mode
— Dedicated input registers
— Programmable polarity
— Reset/ preset swapping
◆
Advanced capabilities for easy system integration
— 3.3-V & 5-V JEDEC-compliant operations
— JTAG (IEEE 1149.1) compliant for boundary scan testing
— 3.3-V & 5-V JTAG in-system programming
— PCI compliant (-7/-10/-12 speed grades)
— Safe for mixed supply voltage system designs
— Bus-Friendly
TM
inputs and I/Os
— Programmable security bit
— Individual output slew rate control
◆
Advanced E
2
CMOS process provides high-performance, cost-effective solutions
◆
Supported by ispDesignEXPERT
TM
software for rapid logic development
— Supports HDL design methodologies with results optimized for MACH 4
— Flexibility to adapt to user requirements
— Software partnerships that ensure customer success
◆
Lattice and third-party hardware programming support
— LatticePRO
TM
software for in-system programmability support on PCs and automated test
equipment
— Programming support on all major programmers including Data I/O, BP Microsystems, Advin,
and System General
2 MACH 4 Family
Notes:
1. For information on the M4-96/96 device, please refer to the M4-96/96 data sheet at www.latticesemi.com.
2. “M4-xxx” is for 5-V devices. “M4LV-xxx” is for 3.3-V devices.
Table 1. MACH 4 Device Features
1, 2
Feature
M4-32/32
M4LV-32/32
M4-64/32
M4LV-64/32
M4-96/48
M4LV-96/48
M4-128/64
M4LV-128/64
M4-128N/64
M4LV-128N/64
M4-192/96
M4LV-192/96
M4-256/128
M4LV-256/128
Macrocells 32 64 96 128 128 192 256
Maximum User I/O Pins 32 32 48 64 64 96 128
t
PD
(ns) 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.5
f
CNT
(MHz) 111 111 111 111 111 111 111
t
COS
(ns) 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5
t
SS
(ns) 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5
Static Power (mA) 25 25 50 70 70 85 100
JTAG Compliant Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
PCI Compliant Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
MACH 4 Family 3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MACH
®
4 family from Lattice offers an exceptionally flexible architecture and delivers a
superior Complex Programmable Logic Device (CPLD) solution of easy-to-use silicon products
and software tools. The overall benefits for users are a guaranteed and predictable CPLD
solution, faster time-to-market, greater flexibility and lower cost. The MACH 4 devices offer
densities ranging from 32 to 256 macrocells with 100% utilization and 100% pin-out retention.
The MACH 4 family offer 5-V (M4-xxx) and 3.3-V (M4LV-xxx) operation.
MACH 4 products are 5-V or 3.3-V in-system programmable through the JT AG (IEEE Std. 1149.1)
interface. JTAG boundary scan testing also allows product testability on automated test
equipment for device connectivity.
All MACH 4 family members deliver First-Time-Fit and easy system integration with pin-out
retention after any design change and refit. For both 3.3-V and 5-V operation, MACH 4 products
can deliver guaranteed fixed timing as fast as 7.5 ns t
PD
and 111 MHz f
CNT
through the
SpeedLocking feature when using up to 20 product terms per output (Table 2).
Note:
1. C = Commercial, I = Industrial
The MACH 4 family offers numerous density-I/O combinations in Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP),
Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP), Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC), and Ball Grid Array (BGA)
packages ranging from 44 to 256 pins (Table 3). It also offers I/O safety features for mixedvoltage designs so that the 3.3-V devices can accept 5-V inputs, and 5-V devices do not overdrive
3.3-V inputs. Additional features include Bus-Friendly inputs and I/Os, a programmable powerdown mode for extra power savings and individual output slew rate control for the highest speed
transition or for the lowest noise transition.
Table 2. MACH 4 Speed Grades
Device
Speed Grade
1
-7 -10 -12 -14 -15 -18
M4-32/32
M4LV-32/32
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-64/32
M4LV-64/32
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-96/48
M4LV-96/48
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-128/64
M4LV-128/64
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-128N/64
M4LV-128N/64
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-192/96
M4LV-192/96
C C, I C, I I C I
M4-256/128
M4LV-256/128
C C, I C, I I C I
4 MACH 4 Family
Table 3. MACH 4 Package and I/O Options (Number of I/Os and dedicated inputs in Table)
Package
M4-32/32
M4LV-32/32
M4-64/32
M4LV-64/32
M4-96/48
M4LV-96/48
M4-128/64
M4LV-128/64
M4-128N/64
M4LV-128N/64
M4-192/96
M4LV-192/96
M4-256/128
M4LV-256/128
44-pin PLCC 32+2 32+2
44-pin TQFP 32+2 32+2
48-pin TQFP 32+2 32+2
84-pin PLCC 64+6
100-pin TQFP 48+8 64+6
100-pin PQFP 64+6
144-pin TQFP 96+16
208-pin PQFP 128+14
256-ball BGA 128+14
MACH 4 Family 5
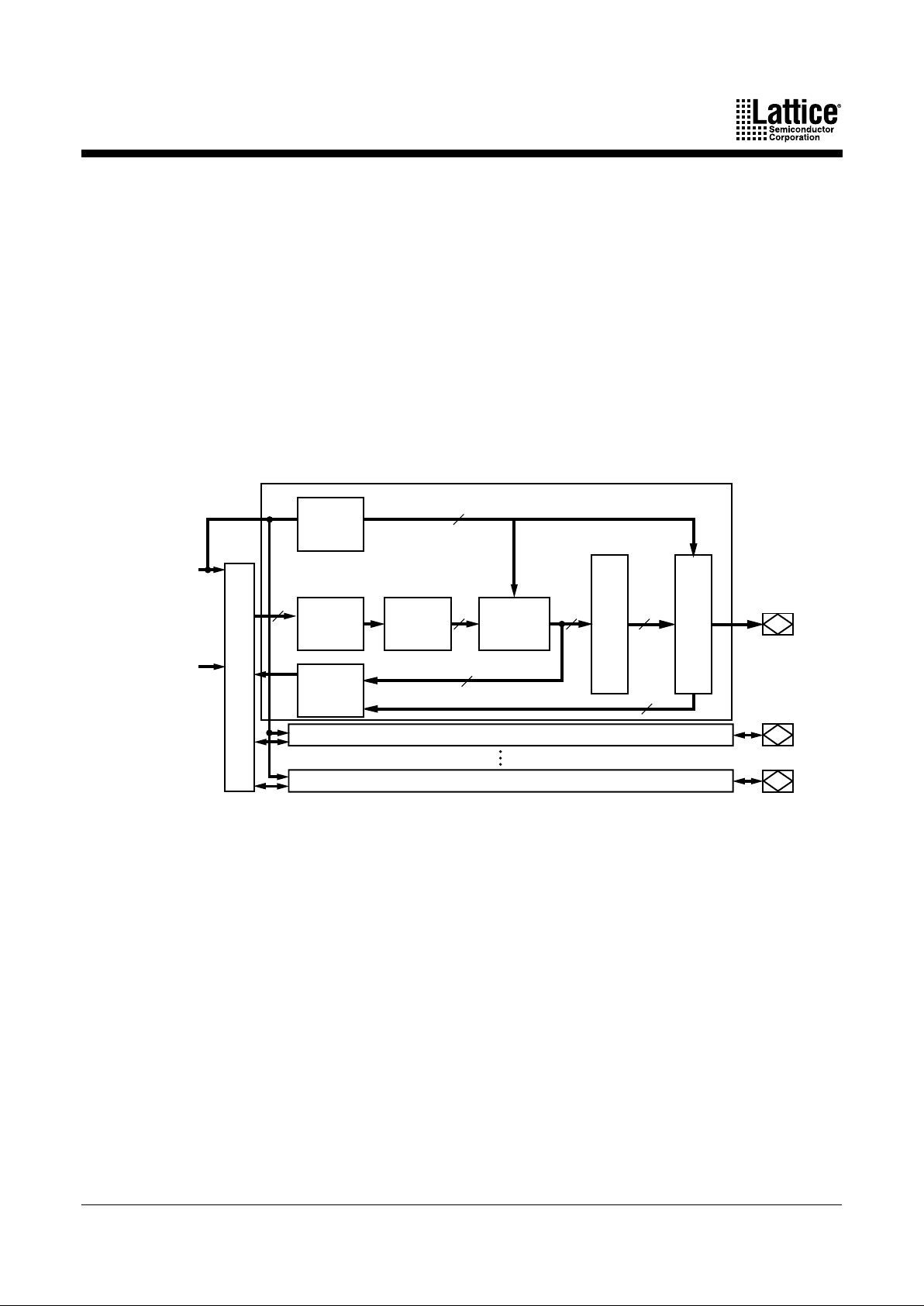
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The fundamental architecture of MACH 4 devices (Figure 1) consists of multiple, optimized P AL
®
blocks interconnected by a central switch matrix. The central switch matrix allows
communication between PAL blocks and routes inputs to the PAL blocks. Together, the PAL
blocks and central switch matrix allow the logic designer to create large designs in a single
device instead of having to use multiple devices.
The key to being able to make effective use of these devices lies in the interconnect schemes.
In MACH 4 architecture, the macrocells are flexibly coupled to the product terms through the
logic allocator, and the I/O pins are flexibly coupled to the macrocells due to the output switch
matrix. In addition, more input routing options are provided by the input switch matrix. These
resources provide the flexibility needed to fit designs efficiently.
Notes:
1. 16 for MACH 4 devices with 1:1 macrocell-I/O cell ratio (see next page).
2. Block clocks do not go to I/O cells in M4(LV)-32/32.
3. M4(LV)-192/96 and M4(L V)-256/128 have dedicated clock pins which cannot be used as inputs and do not connect to the central
switch matrix.
I/O
Pins
Clock/Input
Pins
Central Switch Matrix
I/O
Pins
I/O
Pins
Dedicated
Input Pins
PAL Block
PAL Block
Logic
Allocator
with XOR
Output/
Buried
Macrocells
33/
34/
36
1616
Clock
Generator
Logic
Array
Output Switch Matrix
Input
Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
16
16
8
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
4
PAL Block
17466G-001
Figure 1. MACH 4 Block Diagram and PAL Block Structure
6 MACH 4 Family
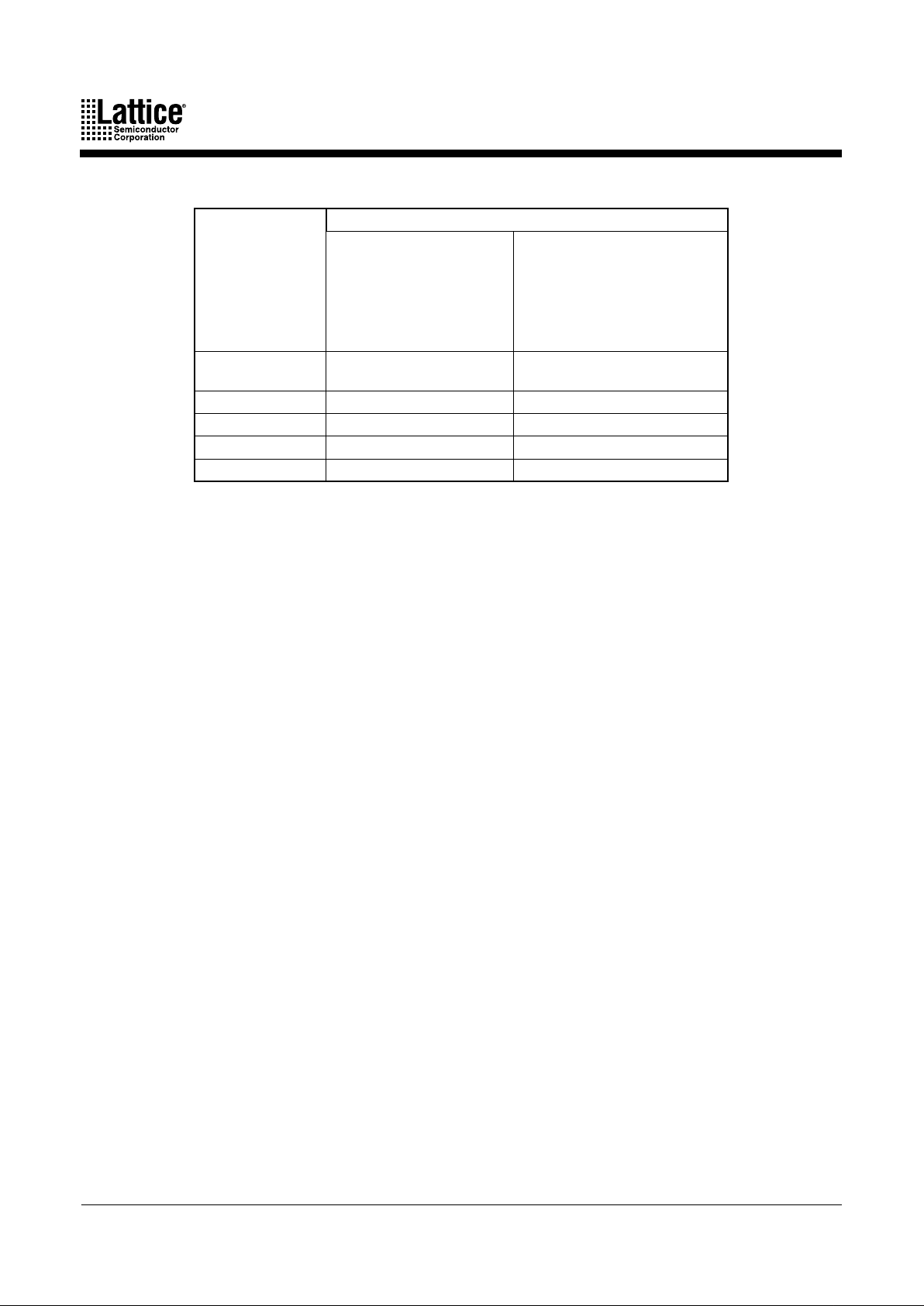
Table 4. Architectural Summary of MACH 4 devices
The Macrocell-I/O cell ratio is defined as the number of macrocells versus the number of I/O
cells internally in a PAL block (Table 4).
The central switch matrix takes all dedicated inputs and signals from the input switch matrices
and routes them as needed to the P AL blocks. Feedback signals that return to the same P AL block
still must go through the central switch matrix. This mechanism ensures that P AL blocks in MACH
4 devices communicate with each other with consistent, predictable delays.
The central switch matrix makes a MACH 4 device more advanced than simply several PAL
devices on a single chip. It allows the designer to think of the device not as a collection of
blocks, but as a single programmable device; the software partitions the design into PAL blocks
through the central switch matrix so that the designer does not have to be concerned with the
internal architecture of the device.
Each PAL block consists of:
◆
Product-term array
◆
Logic allocator
◆
Macrocells
◆
Output switch matrix
◆
I/O cells
◆
Input switch matrix
◆
Clock generator
MACH 4 Devices
M4-64/32, M4LV-64/32
M4-96/48, M4LV-96/48
M4-128/64, M4LV-128/64
M4-128N/64, M4LV-128N/64
M4-192/96, M4LV-192/96
M4-256/128, M4LV-256/128
M4-32/32
M4LV-32/32
Macrocell-I/O Cell
Ratio
2:1 1:1
Input Switch Matrix Yes Yes
Input Registers Yes No
Central Switch Matrix Yes Yes
Output Switch Matrix Yes Yes
MACH 4 Family 7
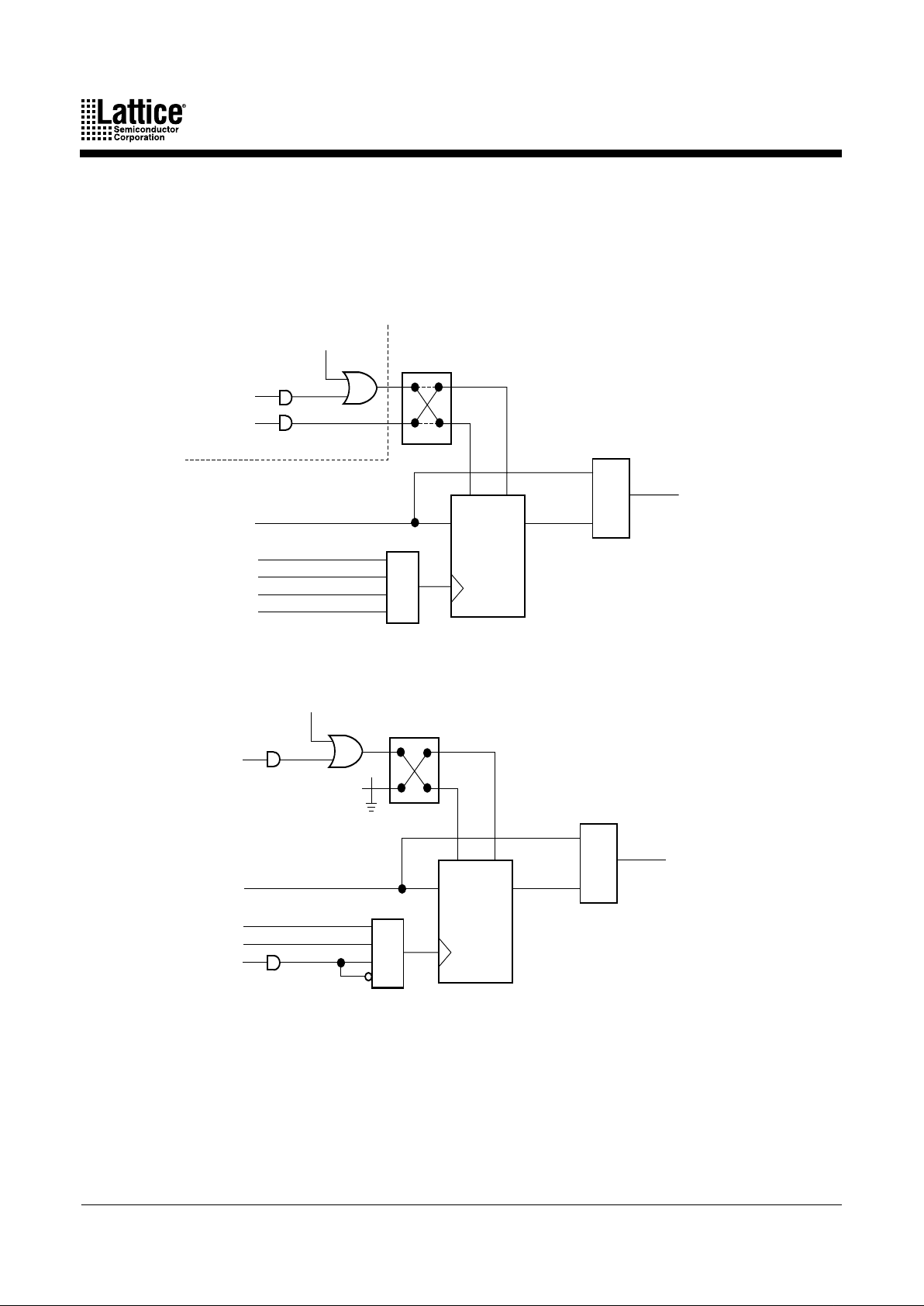
Product-Term Array
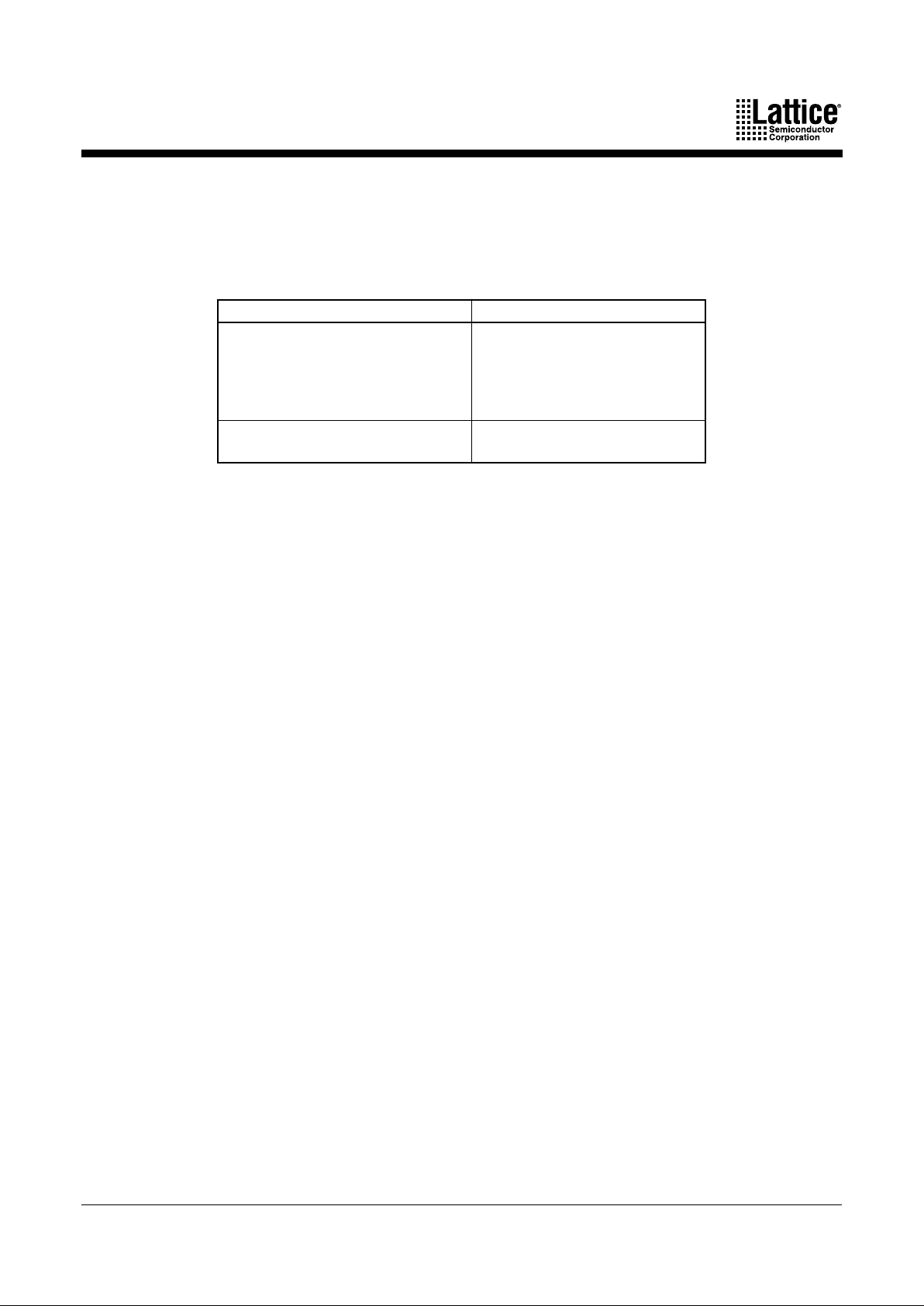
The product-term array consists of a number of product terms that form the basis of the logic
being implemented. The inputs to the AND gates come from the central switch matrix (Table 5),
and are provided in both true and complement forms for efficient logic implementation.
Logic Allocator
Within the logic allocator, product terms are allocated to macrocells in “product term clusters.”
The availability and distribution of product term clusters are automatically considered by the
software as it fits functions within a PAL block. The size of a product term cluster has been
optimized to provide high utilization of product terms, making complex functions using many
product terms possible. Yet when few product terms are used, there will be a minimal number
of unused—or wasted—product terms left over. The product term clusters available to each
macrocell within a PAL block are shown in Tables 6 and 7.
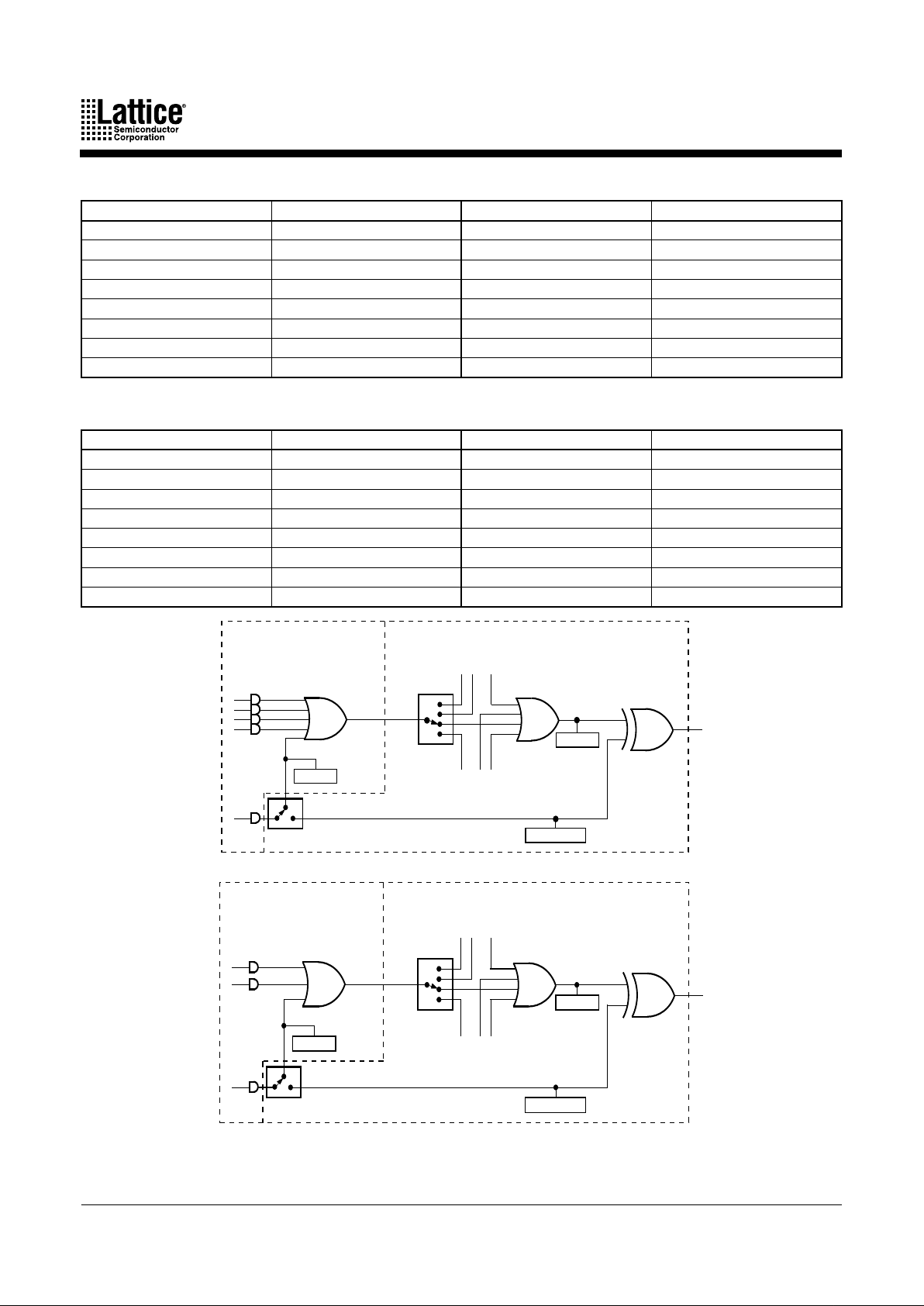
Each product term cluster is associated with a macrocell. The size of a cluster depends on the
configuration of the associated macrocell. When the macrocell is used in synchronous mode
(Figure 2a), the basic cluster has 4 product terms. When the associated macrocell is used in
asynchronous mode (Figure 2b), the cluster has 2 product terms. Note that if the product term
cluster is routed to a different macrocell, the allocator configuration is not determined by the
mode of the macrocell actually being driven. The configuration is always set by the mode of the
macrocell that the cluster will drive if not routed away, regardless of the actual routing.
In addition, there is an extra product term that can either join the basic cluster to give an
extended cluster, or drive the second input of an exclusive-OR gate in the signal path. If included
with the basic cluster, this provides for up to 20 product terms on a synchronous function that
uses four extended 5-product-term clusters. A similar asynchronous function can have up to 18
product terms.
When the extra product term is used to extend the cluster, the value of the second XOR input
can be programmed as a 0 or a 1, giving polarity control. The possible configurations of the logic
allocator are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
Table 5. PAL Block Inputs
Device Number of Inputs to PAL Block
M4-32/32 and M4LV-32/32
M4-64/32 and M4LV-64/32
M4-96/48 and M4LV-96/48
M4-128/64 and M4LV-128/64
M4-128N/64 and M4LV-128N/64
33
33
33
33
33
M4-192/96 and M4LV-192/96
M4-256/128 and M4LV-256/128
34
34
8 MACH 4 Family
Table 6. Logic Allocator for All MACH 4 Devices (except M4(LV)-32/32)
Output Macrocell Available Clusters Output Macrocell Available Clusters
M
0
C
0
, C
1
, C
2
M
8
C
7
,
C
8
, C
9
, C
10
M
1
C
0
, C
1
, C
2
, C
3
M
9
C
8
, C
9
, C
10
, C
11
M
2
C
1
, C
2
, C
3
, C
4
M
10
C
9
, C
10
, C
11
, C
12
M
3
C
2
, C
3
, C
4
, C
5
M
11
C
10
, C
11
, C
12
, C
13
M
4
C
3
, C
4
, C
5
, C
6
M
12
C
11
, C
12
, C
13
, C
14
M
5
C
4
, C
5
, C
6
, C
7
M
13
C
12
, C
13
, C
14
, C
15
M
6
C
5
, C
6
, C
7
,
C
8
M
14
C
13
, C
14
, C
15
M
7
C
6
, C
7
,
C
8
, C
9
M
15
C
14
, C
15
Table 7. Logic Allocator for M4(LV)-32/32
Output Macrocell Available Clusters Output Macrocell Available Clusters
M
0
C
0
, C
1
, C
2
M
8
C
8
, C9, C
10
M
1
C0, C1, C2, C
3
M
9
C8, C9, C10, C
11
M
2
C1, C2, C3, C
4
M
10
C9, C10, C11, C
12
M
3
C2, C3, C4, C
5
M
11
C10, C11, C12, C
13
M
4
C3, C4, C5, C
6
M
12
C11, C12, C13, C
14
M
5
C4, C5, C6, C
7
M
13
C12, C13, C14, C
15
M
6
C5, C6, C
7
M
14
C13, C14, C
15
M
7
C6, C
7
M
15
C14, C
15
0 Default
0 Default
Prog. Polarity
To n-1
To n-2
From n-1
To n+1
From n+1
From n+2
Basic Product
Term Cluster
Extra
Product
Term
Logic Allocator
n
n
To Macrocell
n
0 Default
0 Default
Prog. Polarity
To n-1
To n-2
From n-1
To n+1
From n+1
From n+2
Basic Product
Term Cluster
Extra
Product
Term
Logic Allocator
nn
To Macrocell
n
17466G-006
Figure 2. Logic Allocator: Configuration of Cluster “n” Set by Mode of Macrocell “n”
17466G-005
a. Synchronous Mode
b. Asynchronous Mode
MACH 4 Family 9
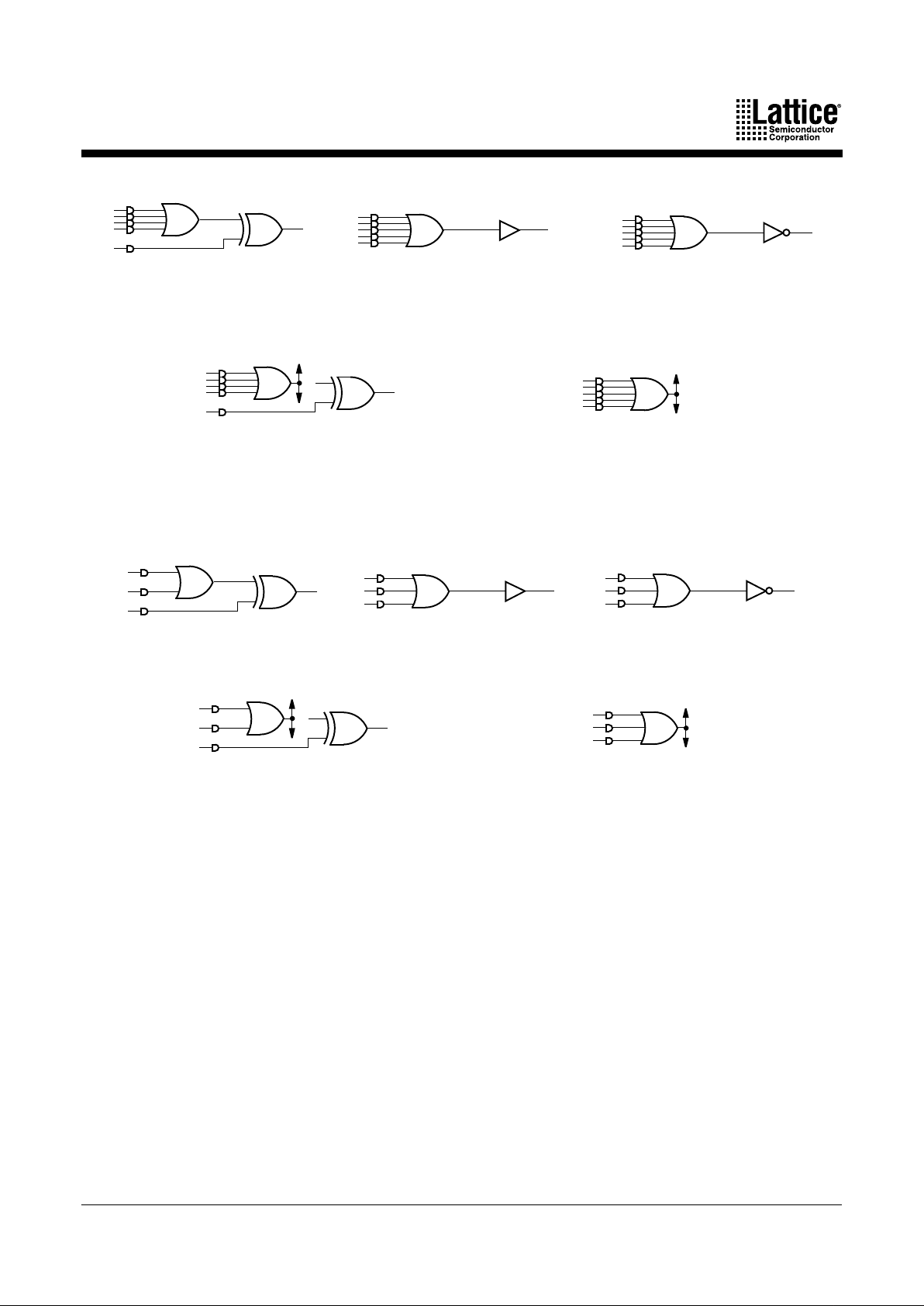
Note that the configuration of the logic allocator has absolutely no impact on the speed of the
signal. All configurations have the same delay. This means that designers do not have to decide
between optimizing resources or speed; both can be optimized.
If not used in the cluster, the extra product term can act in conjunction with the basic cluster to
provide XOR logic for such functions as data comparison, or it can work with the D-,T-type flipflop to provide for J-K, and S-R register operation. In addition, if the basic cluster is routed to
another macrocell, the extra product term is still available for logic. In this case, the first XOR
input will be a logic 0. This circuit has the flexibility to route product terms elsewhere without
giving up the use of the macrocell.
Product term clusters do not “wrap” around a PAL block. This means that the macrocells at the
ends of the block have fewer product terms available.
0
17466G-007
Figure 3. Logic Allocator Configurations: Synchronous Mode
a. Basic cluster with XOR
b. Extended cluster, active high c. Extended cluster, active low
d. Basic cluster routed away;
single-product-term, active high
e. Extended cluster routed away
0
17466G-008
Figure 4. Logic Allocator Configurations: Asynchronous Mode
b. Extended cluster, active high c. Extended cluster, active low
e. Extended cluster routed away
d. Basic cluster routed away;
single-product-term, active high
a. Basic cluster with XOR
10 MACH 4 Family
Macrocell
The macrocell consists of a storage element, routing resources, a clock multiplexer, and
initialization control. The macrocell has two fundamental modes: synchronous and
asynchronous (Figure 5). The mode chosen only affects clocking and initialization in the
macrocell.
In either mode, a combinatorial path can be used. For combinatorial logic, the synchronous
mode will generally be used, since it provides more product terms in the allocator.
SWAP
D/T/L
Q
AP AR
Power-Up
Reset
PAL-Block
Initialization
Product Terms
From Logic Allocator
Block CLK0
Block CLK1
Block CLK2
Block CLK3
To Output and Input
Switch Matrices
Common PAL-block resource
Individual macrocell resources
From
PAL-Clock
Generator
D/T/L
Q
AP AR
Power-Up
Reset
Individual
Initialization
Product Term
From Logic
Allocator
Block CLK0
Block CLK1
To Output and Input
Switch Matrices
Individual Clock
Product Term
From PAL-Block
Clock Generator
17466G-010
Figure 5. Macrocell
17466G-009
a. Synchronous mode
b. Asynchronous mode
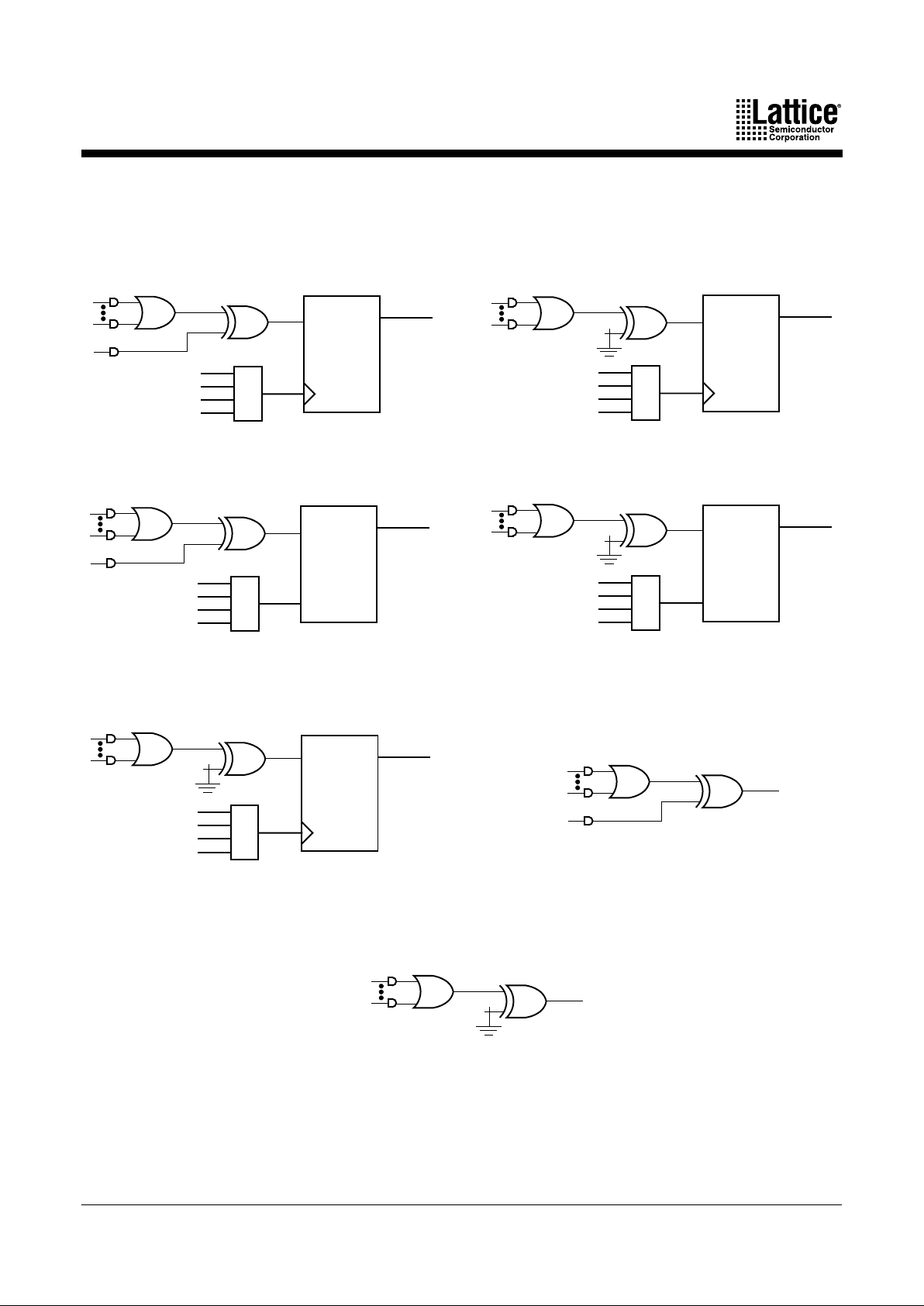
MACH 4 Family 11
The flip-flop can be configured as a D-type or T-type latch. J-K or S-R registers can be
synthesized. The primary flip-flop configurations are shown in Figure 6, although others are
possible. Flip-flop functionality is defined in Table 8. Note that a J-K latch is inadvisable as it will
cause oscillation if both J and K inputs are HIGH.
DQ
AP AR
DQ
AP AR
LQ
AP AR
LQ
AP AR
G
G
TQ
AP AR
17466G-011
Figure 6. Primary Macrocell Configurations
g. Combinatorial with programmable polarity
a. D-type with XOR
b. D-type with programmable D polarity
c. Latch with XOR
d. Latch with programmable D polarity
e. T-type with programmable T polarity
f. Combinatorial with XOR
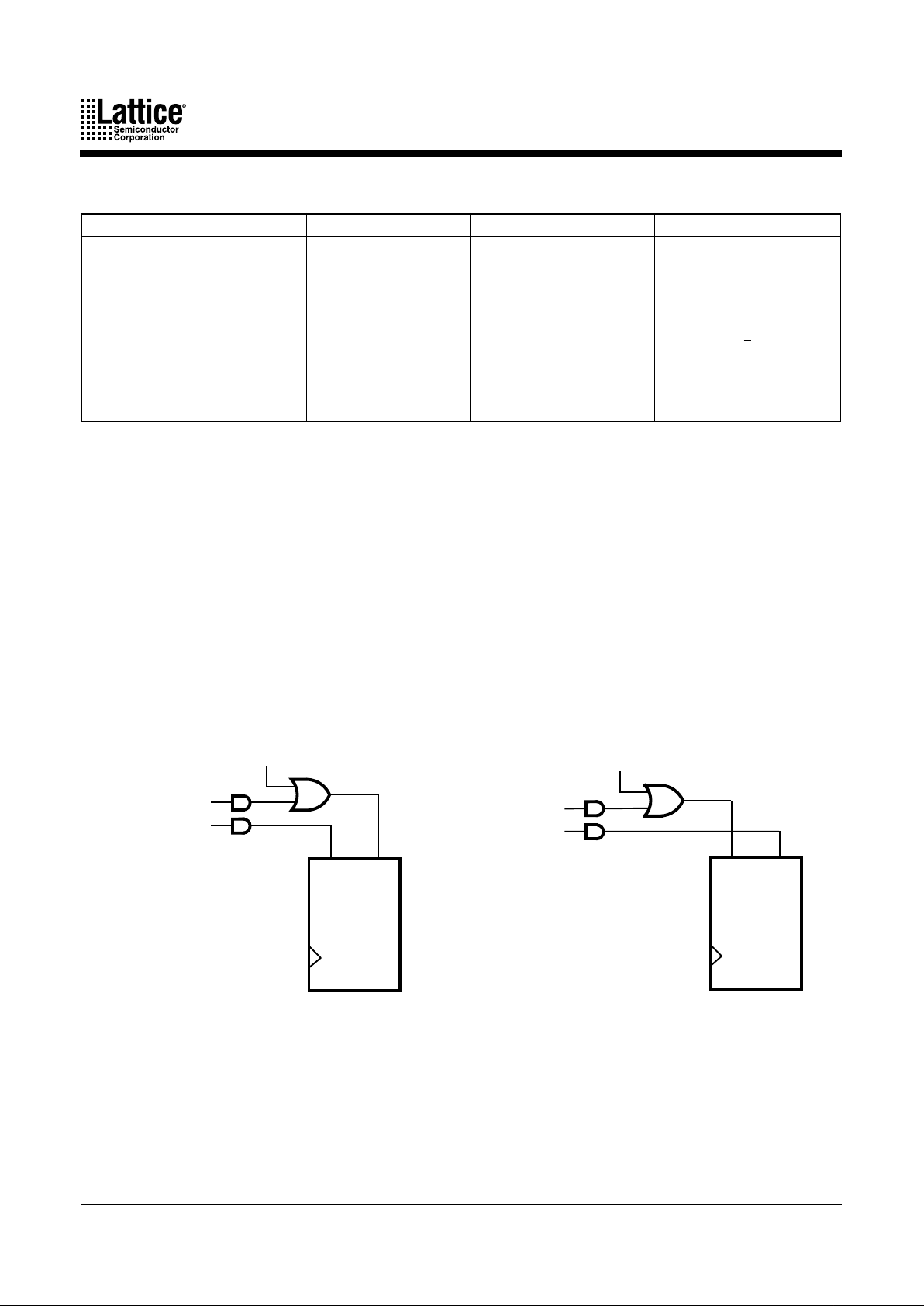
12 MACH 4 Family
Note:
1. Polarity of CLK/LE can be programmed
Although the macrocell shows only one input to the register, the XOR gate in the logic allocator
allows the D-, T-type register to emulate J-K, and S-R behavior. In this case, the available product
terms are divided between J and K (or S and R). When configured as J-K, S-R, or T-type, the
extra product term must be used on the XOR gate input for flip-flop emulation. In any register
type, the polarity of the inputs can be programmed.
The clock input to the flip-flop can select any of the four P AL block clocks in synchronous mode,
with the additional choice of either polarity of an individual product term clock in the
asynchronous mode.
The initialization circuit depends on the mode. In synchronous mode (Figure 7), asynchronous
reset and preset are provided, each driven by a product term common to the entire PAL block.
Table 8. Register/Latch Operation
Configuration Input(s) CLK/LE
1
Q+
D-type Register
D=X
D=0
D=1
0,1, ↓ (↑)
↑ (↓)
↑ (↓)
Q
0
1
T-type Register
T=X
T=0
T=1
0, 1, ↓ (↑)
↑ (↓)
↑ (↓)
Q
Q
Q
D-type Latch
D=X
D=0
D=1
1(0)
0(1)
0(1)
Q
0
1
Power-Up
Reset
AP
D/T/L
AR
Q
PAL-Block
Initialization
Product Terms
a. Power-up reset
Power-Up
Preset
AP
D/L
PAL-Block
Initialization
Product Terms
AR
Q
17466G-012 17466G-013
Figure 7. Synchronous Mode Initialization Configurations
b. Power-up preset
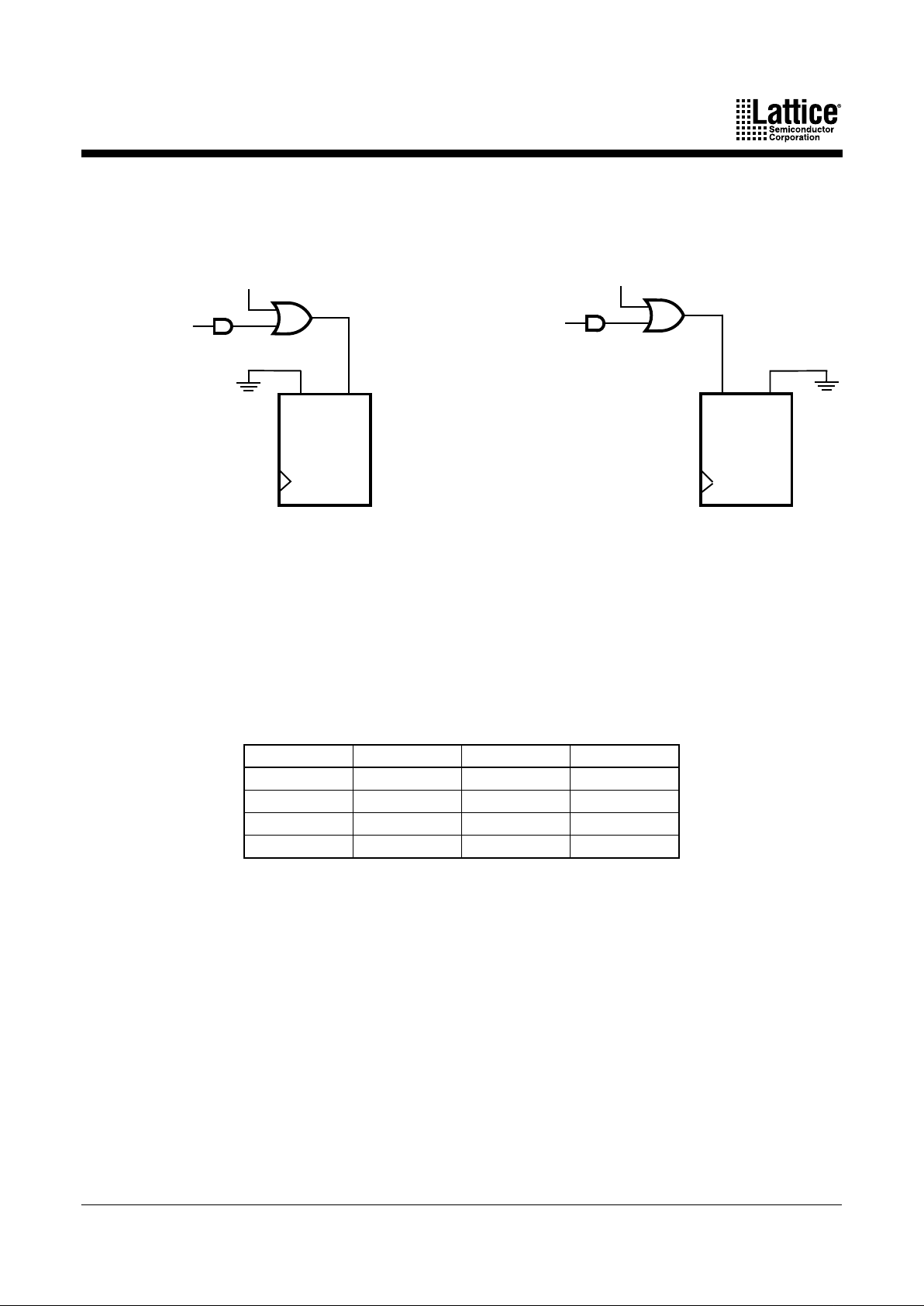
MACH 4 Family 13
A reset/preset swapping feature in each macrocell allows for reset and preset to be exchanged,
providing flexibility. In asynchronous mode (Figure 8), a single individual product term is
provided for initialization. It can be selected to control reset or preset.
Note that the reset/preset swapping selection feature effects power-up reset as well. The
initialization functionality of the flip-flops is illustrated in Table 9. The macrocell sends its data
to the output switch matrix and the input switch matrix. The output switch matrix can route this
data to an output if so desired. The input switch matrix can send the signal back to the central
switch matrix as feedback.
Note:
1. Transparent latch is unaffected by AR, AP
Table 9. Asynchronous Reset/Preset Operation
AR AP CLK/LE
1
Q+
0 0 X See Table 8
01X1
10X0
11X0
Power-Up
Reset
AP
D/L/T
AR
Q
Individual
Reset
Product Term
a. Reset
Power-Up
Preset
AP
D/L/T
AR
Q
Individual
Preset
Product Term
b. Preset
17466G-014 17466G-015
Figure 8. Asynchronous Mode Initialization Configurations
14 MACH 4 Family
Output Switch Matrix
The output switch matrix allows macrocells to be connected to any of several I/O cells within a
PAL block. This provides high flexibility in determining pinout and allows design changes to
occur without effecting pinout.
In MACH 4 devices with 2:1 Macrocell-I/O cell ratio, each PAL block has twice as many
macrocells as I/O cells. The MACH 4 output switch matrix allows for half of the macrocells to
drive I/O cells within a PAL block, in combinations according to Figure 9. Each I/O cell can
choose from eight macrocells; each macrocell has a choice of four I/O cells. The MACH 4 devices
with 1:1 Macrocell-I/O cell ratio allow each macrocell to drive one of eight I/O cells (Figure 9).
M0
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
M15
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
Each macrocell can drive
one of 4 I/O cells in
MACH 4 devices with
2:1 macrocell-I/O cell ratio.
Each I/O cell can
choose one of 8
macrocells in
all MACH 4
devices.
macrocells
MUX
I/O cell
M0
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
M15
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
Each macrocell can drive
one of 8 I/O cells in
M4(LV)-32/32 devices.
Figure 9. MACH 4 Output Switch Matrix

MACH 4 Family 15
Table 10. Output Switch Matrix Combinations for MACH 4 Devices with 2:1
Macrocell-I/O Cell Ratio
Macrocell Routable to I/O Cells
M0, M1 I/O0, I/O5, I/O6, I/O7
M2, M3 I/O0, I/O1, I/O6, I/O7
M4, M5 I/O0, I/O1, I/O2, I/O7
M6, M7 I/O0, I/O1, I/O2, I/O3
M8, M9 I/O1, I/O2, I/O3, I/O4
M10, M11 I/O2, I/O3, I/O4, I/O5
M12, M13 I/O3, I/O4, I/O5, I/O6
M14, M15 I/O4, I/O5, I/O6, I/O7
I/O Cell Available Macrocells
I/O0 M0, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7
I/O1 M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9
I/O2 M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10, M11
I/O3 M6, M7, M8, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13
I/O4 M8, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, M15
I/O5 M0, M1, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, M15
I/O6 M0, M1, M2, M3, M12, M13, M14, M15
I/O7 M0, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M14, M15
Table 11. Output Switch Matrix Combinations for M4(LV)-32/32
Macrocell Routable to I/O Cells
M0, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7 I/O0, I/O1, I/O2, I/O3, I/O4, I/O5, I/O6, I/O7
M8, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, M15 I/O8, I/O9, I/O10, I/O11, I/O12, I/O13, I/O14, I/O15
I/O Cell Available Macrocells
I/O0, I/O1, I/O2, I/O3, I/O4, I/O5, I/O6, I/O7 M0, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7
I/O8, I/O9, I/O10, I/O11, I/O12, I/O13, I/O14, I/O15 M8, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, M15

16 MACH 4 Family
I/O Cell
The I/O cell (Figures 10 and 11) simply consists of a programmable output enable, a feedback
path, and flip-flop (except MACH 4 devices with 1:1 macrocell-I/O cell ratio.) An individual
output enable product term is provided for each I/O cell. The feedback signal drives the input
switch matrix.
The I/O cell (Figure 10) contains a flip-flop, which provides the capability for storing the input
in a D-type register or latch. The clock can be any of the PAL block clocks. Both the direct and
registered versions of the input are sent to the input switch matrix. This allows for such functions
as “time-domain-multiplexed” data comparison, where the first data value is stored, and then the
second data value is put on the I/O pin and compared with the previous stored value.
Note that the flip-flop used in the MACH 4 I/O cell is independent of the flip-flops in the
macrocells. It powers up to a logic low.
Zero-Hold-Time Input Register
The MACH 4 devices have a zero-hold-time (ZHT) fuse which controls the time delay associated
with loading data into all I/O cell registers and latches. When programmed, the ZHT fuse
increases the data path setup delays to input storage elements, matching equivalent delays in
the clock path. When the fuse is erased, the setup time to the input storage element is minimized.
This feature facilitates doing worst-case designs for which data is loaded from sources which
have low (or zero) minimum output propagation delays from clock edges.
Input Switch Matrix
The input switch matrix (Figures 12 and 13) optimizes routing of inputs to the central switch
matrix. Without the input switch matrix, each input and feedback signal has only one way to
enter the central switch matrix. The input switch matrix provides additional ways for these
signals to enter the central switch matrix.
D/L
Q
Block CLK3
Block CLK2
Block CLK1
Block CLK0
To
Input
Switch
Matrix
Individual
Output Enable
Product Term
From Output
Switch Matrix
17466G-017 17466G-018
Figure 10. I/O Cell for MACH 4 Devices with 2:1
Macrocell-I/O Cell Ratio
Figure 11. I/O Cell for MACH 4 Devices with 1:1
Macrocell-I/O Cell Ratio
To
Input
Switch
Matrix
Individual
Output Enable
Product Term
From Output
Switch Matrix
Power-up reset

MACH 4 Family 17
PAL Block Clock Generation
Each MACH 4 device has four clock pins that can also be used as inputs. These pins drive a
clock generator in each PAL block (Figure 14). The clock generator provides four clock signals
that can be used anywhere in the PAL block. These four PAL block clock signals can consist of
a large number of combinations of the true and complement edges of the global clock signals.
Table 12 lists the possible combinations.
Note:
1. M4(LV)-32/32 and M4(LV)-64/32 have only two clock pins, GCLK0 and GCLK1. GCLK2 is tied to GCLK0, and GCLK3 is tied to
GCLK1.
To Central Switch Matrix
From Macrocell 2
From Input Cell
Direct
From Macrocell 1
Registered/Latched
17466G-002 17466G-003
Figure 12. MACH 4 with 2:1 Macrocell-I/O Cell Ratio
- Input Switch Matrix
Figure 13. MACH 4 with 1:1 Macrocell-I/O Cell Ratio
- Input Switch Matrix
To Central Switch Matrix
From Macrocell
From I/O Pin
GCLK0
GCLK1
GCLK2
GCLK3
Block CLK0
(GCLK0 or GCLK1)
Block CLK1
(GCLK1 or GCLK0)
Block CLK2
(GCLK2 or GCLK3)
Block CLK3
(GCLK3 or GCLK2)
17466G-004
Figure 14. PAL Block Clock Generator
1

18 MACH 4 Family
Note:
1. Values in parentheses are for the M4(LV)-32/32 and M4(LV)-64/32.
This feature provides high flexibility for partitioning state machines and dual-phase clocks. It
also allows latches to be driven with either polarity of latch enable, and in a master-slave
configuration.
Table 12. PAL Block Clock Combinations
1
Block CLK0 Block CLK1 Block CLK2 Block CLK3
GCLK0
GCLK1
GCLK0
GCLK1
X
X
X
X
GCLK1
GCLK1
GCLK0
GCLK0
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
GCLK2 (GCLK0)
GCLK3
(GCLK1)
GCLK2 (GCLK0)
GCLK3
(GCLK1)
X
X
X
X
GCLK3 (GCLK1)
GCLK3 (GCLK1)
GCLK2
(GCLK0)
GCLK2
(GCLK0)

MACH 4 Family 19
MACH 4 TIMING MODEL
The primary focus of the MACH 4 timing model is to accurately represent the timing in a MACH
4 device, and at the same time, be easy to understand. This model accurately describes all
combinatorial and registered paths through the device, making a distinction between internal
feedback and external feedback. A signal uses internal feedback when it is fed back into the
switch matrix or block without having to go through the output buffer. The input register
specifications are also reported as internal feedback. When a signal is fed back into the switch
matrix after having gone through the output buffer, it is using external feedback.
The parameter, t
BUF
, is defined as the time it takes to go from feedback through the output buffer
to the I/O pad. If a signal goes to the internal feedback rather than to the I/O pad, the parameter
designator is followed by an “i”. By adding t
BUF
to this internal parameter, the external parameter
is derived. For example, t
PD
= t
PDi
+ t
BUF
. A diagram representing the modularized MACH 4
timing model is shown in Figure 15. Refer to the Technical Note entitled MACH 4 Timing and
High Speed Design for a more detailed discussion about the timing parameters.
SPEEDLOCKING FOR GUARANTEED FIXED TIMING
The MACH 4 architecture allows allocation of up to 20 product terms to an individual macrocell
with the assistance of an XOR gate without incurring additional timing delays.
The design of the switch matrix and PAL blocks guarantee a fixed pin-to-pin delay that is
independent of the logic required by the design. Other competitive CPLDs incur serious timing
delays as product terms expand beyond their typical 4 or 5 product term limits. Speed and
SpeedLocking combine to give designs easy access to the performance required in today’s
designs.
(External Feedback)
(Internal Feedback)
INPUT REG/
INPUT LATCH
t
SIRS
t
HIRS
t
SIL
t
HIL
t
SIRZ
t
HIRZ
t
SILZ
t
HILZ
t
PDILi
t
ICOSi
t
IGOSi
t
PDILZi
Q
t
SS(T)
t
SA(T)
t
H(S/A)
t
S(S/A)L
t
H(S/A)L
t
SRR
t
PDi
t
PDLi
t
CO(S/A)i
t
GO(S/A)i
t
SRi
COMB/DFF/TFF/
LATCH/SR*/JK*
S/R
IN
BLK CLK
OUT
t
PL
t
BUF
t
EA
t
ER
t
SLW
Q
Central
Switch
Matrix
*emulated
17466G-025
Figure 15. MACH 4 Timing Model

20 MACH 4 Family
IEEE 1149.1-COMPLIANT BOUNDARY SCAN TESTABILITY
All MACH 4 devices, except the M4(LV)-128N/64, have boundary scan cells and are compliant
to the IEEE 1149.1 standard. This allows functional testing of the circuit board on which the
device is mounted through a serial scan path that can access all critical logic nodes. Internal
registers are linked internally, allowing test data to be shifted in and loaded directly onto test
nodes, or test node data to be captured and shifted out for verification. In addition, these devices
can be linked into a board-level serial scan path for more complete board-level testing.
IEEE 1149.1-COMPLIANT IN-SYSTEM PROGRAMMING
Programming devices in-system provides a number of significant benefits including: rapid
prototyping, lower inventory levels, higher quality, and the ability to make in-field modifications.
All MACH 4 devices provide In-System Programming (ISP) capability through their Boundary
ScanTest Access Ports. This capability has been implemented in a manner that ensures that the
port remains compliant to the IEEE 1149.1 standard. By using IEEE 1149.1 as the communication
interface through which ISP is achieved, customers get the benefit of a standard, well-defined
interface.
MACH 4 devices can be programmed across the commercial temperature and voltage range. The
PC-based LatticePRO software facilitates in-system programming of MACH 4 devices. LatticePRO
takes the JEDEC file output produced by the design implementation software, along with
information about the JTAG chain, and creates a set of vectors that are used to drive the JTAG
chain. LatticePRO software can use these vectors to drive a JT AG chain via the parallel port of a
PC. Alternatively, LatticePRO software can output files in formats understood by common
automated test equipment. This equpment can then be used to program MACH 4 devices during
the testing of a circuit board.
PCI COMPLIANT
MACH 4 devices in the -7/-10/-12 speed grades are compliant with the PCI Local Bus
Specification version 2.1, published by the PCI Special Interest Group (SIG). The 5-V devices are
fully PCI-compliant. The 3.3-V devices are mostly compliant but do not meet the PCI condition
to clamp the inputs as they rise above V
CC
because of their 5-V input tolerant feature.
SAFE FOR MIXED SUPPLY VOLTAGE SYSTEM DESIGNS
Both the 3.3-V and 5-V VCC MACH 4 devices are safe for mixed supply voltage system designs.
The 5-V devices will not overdrive 3.3-V devices above the output voltage of 3.3 V, while they
accept inputs from other 3.3-V devices. The 3.3-V device will accept inputs up to 5.5 V. Both the
5-V and 3.3-V versions have the same high-speed performance and provide easy-to-use mixedvoltage design capability.
BUS-FRIENDLY INPUTS AND I/OS
All MACH 4 devices have inputs and I/Os which feature the Bus-Friendly circuitry incorporating
two inverters in series which loop back to the input. This double inversion weakly holds the
input at its last driven logic state. While it is good design practice to tie unused pins to a known
state, the Bus-Friendly input structure pulls pins away from the input threshold voltage where
noise can cause high-frequency switching. At power-up, the Bus-Friendly latches are reset to a
logic level “1.” For the circuit diagram, please refer to the document entitled MACH Endurance
Characteristics on the Lattice/Vantis Data Book CD-ROM or Lattice web site.

MACH 4 Family 21
POWER MANAGEMENT
Each individual P AL block in MACH 4 devices features a programmable low-power mode, which
results in power savings of up to 50%. The signal speed paths in the low-power PAL block will
be slower than those in the non-low-power PAL block. This feature allows speed critical paths
to run at maximum frequency while the rest of the signal paths operate in the low-power mode.
PROGRAMMABLE SLEW RATE
Each MACH 4 device I/O has an individually programmable output slew rate control bit. Each
output can be individually configured for the higher speed transition (3 V/ns) or for the lower
noise transition (1 V/ns). For high-speed designs with long, unterminated traces, the slow-slew
rate will introduce fewer reflections, less noise, and keep ground bounce to a minimum. For
designs with short traces or well terminated lines, the fast slew rate can be used to achieve the
highest speed. The slew rate is adjusted independent of power.
POWER-UP RESET/SET
All flip-flops power up to a known state for predictable system initialization. If a macrocell is
configured to SET on a signal from the control generator, then that macrocell will be SET during
device power-up. If a macrocell is configured to RESET on a signal from the control generator
or is not configured for set/reset, then that macrocell will RESET on power-up. To guarantee
initialization values, the V
CC
rise must be monotonic, and the clock must be inactive until the
reset delay time has elapsed.
SECURITY BIT
A programmable security bit is provided on the MACH 4 devices as a deterrent to unauthorized
copying of the array configuration patterns. Once programmed, this bit defeats readback of the
programmed pattern by a device programmer, securing proprietary designs from competitors.
Programming and verification are also defeated by the security bit. The bit can only be reset by
erasing the entire device.

22 MACH 4 Family
MACROCELL
M0
C0
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
M15
B
89
M0
M4(LV)-64/32, M4(LV)-96/48,
M4(LV)-128/64
A
B
16
17
17
17
M4(LV)-192/96, M4(LV)-256/128
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
O0
O1
O2
O3
O4
O5
O6
O7M15
CLK0
CLK1
CLK2
CLK3
I/O
CELL
I/O0
CLOCK
GENERATOR
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
CENTRAL SWITCH MATRIX
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
24
A
0
4
16
16
C1
C2
I/O
CELL
I/O1
C3
C4
I/O
CELL
I/O2
C5
C6
I/O
CELL
I/O3
C7
C8
I/O
CELL
I/O4
C9
C10
I/O
CELL
I/O5
C11
C12
I/O
CELL
I/O6
C13
C14
I/O
CELL
INPUT SWITCH
MATRIX
I/O7
C15
LOGIC ALLOCATOR
OUTPUT SWITCH MATRIX
Figure 16. PAL Block for MACH 4 with 2:1 Macrocell - I/O Cell Ratio

MACH 4 Family 23
17466H-042
MACROCELL
M0
C0
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
M15
17
97
M0
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
M9
M10
M11
M12
M13
M14
O0
O2
O4
O6
O8
O10
O12
O14
M15
I/O
CELL
I/O0
CLOCK
GENERATOR
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
CENTRAL SWITCH MATRIX
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
MACROCELL
O1
I/O
CELL
I/O1
32
16
0
2
16
16
C1
C2
I/O
CELL
I/O2
O3
I/O
CELL
I/O3
O5
I/O
CELL
I/O5
O7
I/O
CELL
I/O7
C3
C4
I/O
CELL
I/O4
C5
C6
I/O
CELL
I/O6
C7
C8
I/O
CELL
I/O8
O9
I/O
CELL
I/O9
O11
I/O
CELL
I/O11
C9
C10
I/O
CELL
I/O10
C11
C12
I/O
CELL
I/O12
O13
I/O
CELL
I/O13
O15
I/O
CELL
I/O15
C13
C14
I/O
CELL
INPUT
SWITCH
MATRIX
I/O14
C15
LOGIC ALLOCATOR
OUTPUT SWITCH MATRIX
OUTPUT SWITCH MATRIX
CLK0/I0 CLK0/I1
Figure 17. PAL Block for M4(LV)-32/32

24 MACH 4 Family
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-32/32
17466H-019
Central Switch Matrix
2
2
CLK0/I0, CLK1/I1
I/O8–I/O15 I/O0–I/O7
I/O16–I/O23 I/O24–I/O31
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
8
8
16
8
8
8
33
4
4 4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 98
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
8
8
16
8
8
8
2
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
8
8
16
8
8
8
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 98
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
8
8
16
8
8
8
2
8
8
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Clock Generator
OE
OE
OE
OE
Block A
Block B
33

MACH 4 Family 25
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-64/32
17466H-020
Central Switch Matrix
2
2
CLK0/I0, CLK1/I1
I/O0–I/O7 I/O24–I/O31
I/O16–I/O23I/O8–I/O15
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
2
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
2
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
2
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
2
8
8
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Clock Generator
Clock Generator
OE
OE
OE
OE
Block A
Block B
Block D
Block C

26 MACH 4 Family
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-96/48
4
4
4
CLK0/I0, CLK1/I1,
CLK2/I4, CLK3/I5
I2, I3, I6, I7
I/O16–I/O23 I/O8–I/O15 I/O0–I/O7
I/O40–I/O47I/O32–I/O39I/O24–I/O31
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
OE
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Clock Generator
Clock Generator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
OE
OE
OE
OE
OE
Block C Block B Block A
Block D Block E Block F
Central Switch Matrix
17466G-021

MACH 4 Family 27
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-128N/64 AND M4(LV)-128/64
Central Switch Matrix
4
4
2
CLK0/I0, CLK1/I1,
CLK2/I3, CLK3/I4
I2, I5
I/O0–I/O7I/O8–I/O15I/O16–I/O23I/O24–I/031
I/O32–I/O39 I/O40–I/O47 I/O48–I/O55 I/O56–I/O63
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
I/O Cells
Output Switch
Matrix
Macrocells
66 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
OE
16
16
24
16
16
8
33
4
4
4
8
8
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Clock Generator
Clock Generator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Input Switch
Matrix
Clock Generator
OE
OE
OE
OE
OE
OE
OE
Block ABlock BBlock CBlock D
Block HBlock GBlock FBlock E
17466H-022

28 MACH 4 Family
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-192/96
Central Switch Matrix
Block B
I/O8–I/O15
CLK0–CLK3
I/O32–I/O39
Block E
I/O56–I/O63
Block H
I/O48–I/O55
Block G
I0–I15
I/O40–I/O47
Block F
Block A
I/O0–I/O7
Block K
I/O80–I/O87
Block L
I/O88–I/O95
Block C I/O16–I/O23
Block D I/O24–I/O31
I/O72–I/O79 Block J
I/O64–I/O71 Block I
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
16
4
4
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
4
4
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
34 34 34 34
34 34 34 34
4
4
OE
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
4
4
8
24
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
8
24
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
OE
4
4
8
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
4
4
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
OE
4
4
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
4
4
8
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
4
4
OE
17466G-067

MACH 4 Family 29
BLOCK DIAGRAM – M4(LV)-256/128
Central Switch Matrix
Block B
I/O8–I/O15
CLK0–CLK3
I/O48–I/O55
Block G
I/O72–I/O79
Block J
I/O64–I/O71
Block I
I0–I13
I/O56–I/O63
Block H
Block A
I/O0–I/O7
Block O
I/O112–I/O119
Block P
I/O120–I/O127
Block C I/O16–I/O23
Block D I/O24–I/O31
Block E I/O32–I/O39
Block F I/O40–I/O47
I/O104–I/O111 Block N
I/O96–I/O103 Block M
I/O88–I/O95 Block L
I/O80–I/O87 Block K
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
I/O Cells
Macrocells
68 X 90
AND Logic Array
and Logic Allocator
Clock Generator
Input Switch
Matrix
Output Switch
Matrix
14
4
4
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
4
4
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
OE
4
4
8
34
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
4
4
34
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
OE
4
4
34
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
4
4
8
34
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
4
4
OE
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
4
4
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
8
24
34
4
8
8
16
16
4
4
16
16
OE
OE
4
4
8
34
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
4
4
34
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
OE
4
4
34
24
16
16
8
16
16
4
8
8
4
4
8
34
24
16
16
8
16
8
4
16
OE
8
16
8
4
16
24
8
16
16
34
4
4
OE
17466G-024

MACH 4 Family 30
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
M4
Storage Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature
with Power Applied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55°C to +100°C
Device Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . +130°C
Supply Voltage
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5 V to +7.0 V
DC Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5 V to V
CC
+ 0.5 V
Static Discharge Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000 V
Latchup Current (TA = -40°C to +85°C). . . . . . . 200 mA
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum
Ratings may cause permanent device failure. Functionality at
or above these limits is not implied. Exposure to Absolute
Maximum Ratings for extended periods may affect device
reliability.
OPERATING RANGES
Commercial (C) Devices
Ambient Temperature (TA)
Operating in Free Air. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
Supply Voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . +4.75 V to +5.25 V
Industrial (I) Devices
Ambient Temperature (TA)
Operating in Free Air. . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40°C to +85°C
Supply Voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . . +4.50 V to +5.5 V
Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the device is guaranteed.
Notes:
1. Total I
OL
for one PAL block should not exceed 64 mA.
2. These are absolute values with respect to device ground, and all overshoots due to system or tester noise are included.
3. I/O pin leakage is the worst case of I
IL
and I
OZL
(or IIH and I
OZH
).
4. Not more than one output should be shorted at a time and duration of the short-circuit should not exceed one second.
V
OUT
= 0.5 V has been chosen to avoid test problems caused by tester ground degradation.
5-V DC CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING RANGES
Parameter
Symbol Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage
I
OH
= –3.2 mA, VCC = Min, VIN = V
IH
or V
IL
2.4 V
I
OH
= 0 mA, VCC = Max, VIN = V
IH
or V
IL
3.3 V
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 24 mA, VCC = Min, VIN = VIH or V
IL
(Note 1) 0.5 V
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage
Guaranteed Input Logical HIGH Voltage for all Inputs
(Note 2)
2.0 V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage
Guaranteed Input Logical LOW Voltage for all Inputs
(Note 2)
0.8 V
I
IH
Input HIGH Leakage Current VIN = 5.25 V, VCC = Max (Note 3) 10 µA
I
IL
Input LOW Leakage Current VIN = 0 V, V
CC
= Max (Note 3) –10 µA
I
OZH
Off-State Output Leakage Current HIGH V
OUT
= 5.25 V, VCC = Max, VIN = V
IH
or VIL (Note 3) 10 µA
I
OZL
Off-State Output Leakage Current LOW V
OUT
= 0 V, VCC = Max , VIN = V
IH
or VIL (Note 3) –10 µA
I
SC
Output Short-Circuit Current V
OUT
= 0.5 V, VCC = Max (Note 4) –30 –160 mA

MACH 4 Family 31
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
M4LV
Storage Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature
with Power Applied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55°C to +100°C
Device Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . +130°C
Supply Voltage
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5 V to +4.5 V
DC Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5 V to 6.0 V
Static Discharge Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000 V
Latchup Current (TA = -40°C to +85°C). . . . . . . 200 mA
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum
Ratings may cause permanent device failure. Functionality at
or above these limits is not implied. Exposure to Absolute
Maximum Ratings for extended periods may affect device
reliability.
OPERATING RANGES
Commercial (C) Devices
Ambient Temperature (TA)
Operating in Free Air. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
Supply Voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . . . +3.0 V to +3.6 V
Industrial (I) Devices
Ambient Temperature (TA)
Operating in Free Air. . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40°C to +85°C
Supply Voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground . . . . . . . . . . . +3.0 V to +3.6 V
Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the device is guaranteed.
Notes:
1. Total I
OL
for one PAL block should not exceed 64 mA.
2. I/O pin leakage is the worst case of I
IL
and I
OZL
(or IIH and I
OZH
).
3. Not more than one output should be shorted at a time and duration of the short-circuit should not exceed one second.
3.3-V DC CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING RANGES
Parameter
Symbol Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage
V
CC
= Min
V
IN
= VIH or V
IL
IOH = –100 µAV
CC
– 0.2 V
I
OH
= –3.2 mA 2.4 V
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage
V
CC
= Min
V
IN
= VIH or V
IL
(Note 1)
I
OL
= 100 µA 0.2 V
I
OL
= 24 mA 0.5 V
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage
Guaranteed Input Logical HIGH Voltage for all
Inputs
2.0 5.5 V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage
Guaranteed Input Logical LOW Voltage for all
Inputs
–0.3 0.8 V
I
IH
Input HIGH Leakage Current VIN = 3.6 V, VCC = Max (Note 2) 5 µA
I
IL
Input LOW Leakage Current VIN = 0 V, V
CC
= Max (Note 2) –5 µA
I
OZH
Off-State Output Leakage Current HIGH
V
OUT
= 3.6 V, VCC = Max
V
IN
= V
IH
or VIL (Note 2)
5 µA
I
OZL
Off-State Output Leakage Current LOW
V
OUT
= 0 V, VCC = Max
V
IN
= V
IH
or VIL (Note 2)
–5 µA
I
SC
Output Short-Circuit Current V
OUT
= 0.5 V, VCC = Max (Note 3) –15 –160 mA

32 MACH 4 Family
MACH 4 TIMING PARAMETERS OVER OPERATING RANGES1
-7 -10 -12 -14 -15 -18
UnitMin Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Combinatorial Delay:
t
PDi
Internal combinatorial propagation delay 5.5 8.0 10.0 12.0 13.0 16.0 ns
t
PD
Combinatorial propagation delay 7.5 10.0 12.0 14.0 15.0 18.0 ns
Registered Delays:
t
SS
Synchronous clock setup time, D-type register 5.5 6.0 7.0 10.0 10.0 12.0 ns
t
SST
Synchronous clock setup time, T-type register 6.5 7.0 8.0 11.0 11.0 13.0 ns
t
SA
Asynchronous clock setup time, D-type register 3.5 4.0 5.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 ns
t
SAT
Asynchronous clock setup time, T-type register 4.5 5.0 6.0 9.0 9.0 11.0 ns
t
HS
Synchronous clock hold time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
t
HA
Asynchronous clock hold time 3.5 4.0 5.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 ns
t
COSi
Synchronous clock to internal output 3.5 4.5 6.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 ns
t
COS
Synchronous clock to output 5.5 6.5 8.0 10.0 10.0 12.0 ns
t
COAi
Asynchronous clock to internal output 7.5 10.0 12.0 16.0 16.0 18.0 ns
t
COA
Asynchronous clock to output 9.5 12.0 14.0 18.0 18.0 20.0 ns
Latched Delays:
t
SSL
Synchronous Latch setup time 6.0 7.0 8.0 10.0 10.0 12.0 ns
t
SAL
Asynchronous Latch setup time 4.0 4.0 5.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 ns
t
HSL
Synchronous Latch hold time 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
t
HAL
Asynchronous Latch hold time 4.0 4.0 5.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 ns
t
PDLi
Transparent latch to internal output 8.0 10.0 12.0 15.0 15.0 18.0 ns
t
PDL
Propagation delay through transparent latch to output 10.0 12.0 14.0 17.0 17.0 20.0 ns
t
GOSi
Synchronous Gate to internal output 4.0 5.5 8.0 9.0 9.0 10.0 ns
t
GOS
Synchronous Gate to output 6.0 7.5 10.0 11.0 11.0 12.0 ns
t
GOAi
Asynchronous Gate to internal output 9.0 11.0 14.0 17.0 17.0 20.0 ns
t
GOA
Asynchronous Gate to output 11.0 13.0 16.0 19.0 19.0 22.0 ns
Input Register Delays:
t
SIRS
Input register setup time 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 ns
t
HIRS
Input register hold time 3.0 3.0 3.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 ns
t
ICOSi
Input register clock to internal feedback 3.5 4.5 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 ns
Input Latch Delays:
t
SIL
Input latch setup time 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 ns
t
HIL
Input latch hold time 3.0 3.0 3.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 ns
t
IGOSi
Input latch gate to internal feedback 4.0 4.0 4.0 5.0 5.0 6.0 ns
t
PDILi
Transparent input latch to internal feedback 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 ns
Input Register Delays with ZHT Option:
t
SIRZ
Input register setup time - ZHT 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 ns
t
HIRZ
Input register hold time - ZHT 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns

MACH 4 Family 33
Input Latch Delays with ZHT Option:
t
SILZ
Input latch setup time - ZHT 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 ns
t
HILZ
Input latch hold time - ZHT 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
t
PDILZi
Transparent input latch to internal feedback - ZHT 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 ns
Output Delays:
t
BUF
Output buffer delay 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 ns
t
SLW
Slow slew rate delay adder 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 ns
t
EA
Output enable time 9.5 10.0 12.0 15.0 15.0 17.0 ns
t
ER
Output disable time 9.5 10.0 12.0 15.0 15.0 17.0 ns
Power Delay:
t
PL
Power-down mode delay adder 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 ns
Reset and Preset Delays:
t
SRi
Asynchronous reset or preset to internal register output 10.0 12.0 14.0 18.0 18.0 20.0 ns
t
SR
Asynchronous reset or preset to register output 12.0 14.0 16.0 20.0 20.0 22.0 ns
t
SRR
Asynchronous reset and preset register recovery time 8.0 8.0 10.0 15.0 15.0 17.0 ns
t
SRW
Asynchronous reset or preset width 10.0 10.0 12.0 15.0 15.0 17.0 ns
Clock/LE Width:
t
WLS
Global clock width low 3.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
t
WHS
Global clock width high 3.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
t
WLA
Product term clock width low 4.0 5.0 8.0 9.0 9.0 10.0 ns
t
WHA
Product term clock width high 4.0 5.0 8.0 9.0 9.0 10.0 ns
t
GWS
Global gate width low (for low transparent) or high
(for high transparent)
5.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
t
GWA
Product term gate width low (for low transparent) or
high (for high transparent)
4.0 5.0 6.0 9.0 9.0 11.0 ns
t
WIRL
Input register clock width low 4.5 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
t
WIRH
Input register clock width high 4.5 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
t
WIL
Input latch gate width 5.0 5.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 7.0 ns
MACH 4 TIMING PARAMETERS OVER OPERATING RANGES1 (CONTINUED)
-7 -10 -12 -14 -15 -18
UnitMin Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max

34 MACH 4 Family
Notes:
1. See “MACH Switching Test Circuit” document on the Literature Download page of the Lattice web site.
2. This parameter does not apply to flip-flops in the emulated mode since the feedback path is required for emulation.
CAPACITANCE
1
Note:
1. These parameters are not 100% tested, but are calculated at initial characterization and at any time the design is modified where
this parameter may be affected.
Frequency:
f
MAXS
External feedback, D-type, Min of 1/(t
WLS
+ t
WHS
) or
1/(t
SS
+ t
COS
)
90.9 80.0 66.7 50.0 50.0 41.7 MHz
External feedback, T-type, Min of 1/(t
WLS
+ t
WHS
) or
1/(t
SST
+ t
COS
)
83.3 74.1 62.5 47.6 47.6 40.0 MHz
Internal feedback (f
CNT
), D-type,
Min of 1/(t
WLS
+ t
WHS
) or 1/(tSS + t
COSi
)
111.1 95.2 76.9 55.6 55.6 45.5 MHz
Internal feedback (f
CNT
), T-type,
Min of 1/(t
WLS
+ t
WHS
) or 1/(t
SST
+ t
COSi
)
100.0 87.0 71.4 52.6 52.6 43.5 MHz
No feedback
2
, Min of 1/(t
WLS
+ t
WHS
), 1/(tSS + tHS) or
1/(t
SST
+ tHS)
153.8 100.0 83.3 83.3 83.3 71.4 MHz
f
MAXA
External feedback, D-type, Min of 1/(t
WLA
+ t
WHA
) or
1/(t
SA
+ t
COA
)
76.9 62.5 52.6 38.5 38.5 33.3 MHz
External feedback, T-type, Min of 1/(t
WLA
+ t
WHA
) or
1/(t
SAT
+ t
COA
)
71.4 58.8 50.0 37.0 37.0 32.3 MHz
Internal feedback (f
CNTA
), D-type,
Min of 1/(t
WLA
+ t
WHA
) or 1/(tSA + t
COAi
)
90.9 71.4 58.8 41.7 41.7 35.7 MHz
Internal feedback (f
CNTA
), T-type,
Min of 1/(t
WLA
+ t
WHA
) or 1/(t
SAT
+ t
COAi
)
83.3 66.7 55.6 40.0 40.0 34.5 MHz
No feedback
2
, Min of 1/(t
WLA
+ t
WHA
),
1/(t
SA
+ tHA) or 1/(t
SAT
+ tHA)
125.0 100.0 62.5 55.6 55.6 50.0 MHz
f
MAXI
Maximum input register frequency,
Min of 1/(t
WIRH
+ t
WIRL
) or 1/(t
SIRS
+ t
HIRS
)
111.0 100.0 83.3 83.3 83.3 71.4 MHz
Parameter Symbol Parameter Description Test Conditions Typ Unit
C
IN
Input capacitance VIN=2.0 V 3.3 V or 5 V, 25°C, 1 MHz 6 pF
C
I/O
Output capacitance V
OUT
=2.0V 3.3 V or 5 V, 25°C, 1 MHz 8 pF
MACH 4 TIMING PARAMETERS OVER OPERATING RANGES1 (CONTINUED)
-7 -10 -12 -14 -15 -18
UnitMin Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max

MACH 4 Family 35
I
CC
vs. FREQUENCY
These curves represent the typical power consumption for a particular device at system frequency. The selected “typical” pattern is a 16-bit up-down counter. This pattern fills the device and
exercises every macrocell. Maximum frequency shown uses internal feedback and a D-type register. Power/Speed are optimized to obtain the highest counter frequency and the lowest power .
The highest frequency (LSBs) is placed in common P AL blocks, which are set to high power . The
lowest frequency signals (MSBs) are placed in a common PAL block and set to lowest power.
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
VCC = 5 V or 3.3 V, TA = 25º C
I
CC
(mA)
Frequency (MHz)
17466G-066
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-96/48
M4(LV)-128/64
M4(LV)-192/96
M4(LV)-256/128
Figure 18. MACH 4 ICC Curves at High Speed Mode
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
VCC = 5 V or 3.3 V, TA = 25º C
M4(LV)-32/32
I
CC
(mA)
Frequency (MHz)
17466G-065
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-96/48
M4(LV)-128/64
M4(LV)-192/96
M4(LV)-256/128
Figure 19. MACH 4 ICC Curves at Low Power Mode

36 MACH 4 Family
44-PIN PLCC CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-32/32 AND M4(LV)-64/32)
Top View
44-Pin PLCC
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
1
44
43
42
5
4
3
2
641
40
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
23
24
25
26
19
20
21
22
18 27
28
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
TDI
CLK0/I0
GND
TCK
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
A2
A1
A0
B0
B1
B2
B3
D3
D2
D1
D0
C0
C1
C2
B3
B2
B1
B0
B8
B9
B10
A2
A1
A0
A8
A9
A10
A11
I/O27
I/O26
I/O25
I/O24
TDO
GND
CLK1/I1
TMS
I/O23
I/O22
I/O21
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
VCC
GND
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
B4B5B6
B7
C7C6C5C4C3
A12
A13
A14
A15
B15
B14
B13
B12
B11
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
GND
VCC
I/O31
I/O30
I/O29
I/O28
A3A4A5A6A7
D7D6D5
D4
A3A4A5A6A7
B7B6B5
B4
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
17466G-026
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-D)
C7

MACH 4 Family 37
44-PIN TQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-32/32 AND M4(LV)-64/32)
Top View
44-Pin TQFP
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
VCC
GND
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
B4B5B6
B7
C7C6C5C4C3
A12
A13
A14
A15
B15
B14
B13
B12
B11
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
GND
VCC
I/O31
I/O30
I/O29
I/O28
A3A4A5A6A7
D7D6D5
D4
A3A4A5A6A7
B7B6B5
B4
I/O27
I/O26
I/O25
I/O24
TDO
GND
CLK1/I1
TMS
I/O23
I/O22
I/O21
D3
D2
D1
D0
C0
C1
C2
B3
B2
B1
B0
B8
B9
B10
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
TDI
CLK0/I0
GND
TCK
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
A2
A1
A0
B0
B1
B2
B3
A2
A1
A0
A8
A9
A10
A11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
4443424140
39
38
373635
34
1213141516
17
18
192021
22
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-D)
C7

38 MACH 4 Family
48-PIN TQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-32/32 AND M4(LV)-64/32)
Top View
48-Pin TQFP
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
NC = No Connect
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
VCC
NC
GND
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
B4B5B6
B7
C7C6C5C4C3
A12
A13
A14
A15
B15
B14
B13
B12
B11
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
GNDNCVCC
I/O31
I/O30
I/O29
I/O28
A3A4A5A6A7
D7D6D5
D4
A3A4A5A6A7
B7B6B5
B4
I/O27
I/O26
I/O25
I/O24
TDO
GND
NC
CLK1/I1
TMS
I/O23
I/O22
I/O21
D3
D2
D1
D0
C0
C1
C2
B3
B2
B1
B0
B8
B9
B10
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
TDI
CLK0/I0
NC
GND
TCK
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
A2
A1
A0
B0
B1
B2
B3
A2
A1
A0
A8
A9
A10
A11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
33
34
35
36
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
44
45
46
47
48
43
424140
39
38
37
13
141516
17
18
192021
222324
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-32/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
M4(LV)-64/32
17466G-028
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-D)
C7

MACH 4 Family 39
100-PIN TQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-96/48)
Top View
100-Pin TQFP
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I = Input
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
NC = No Connect
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
NC
TDI
NC
NC
I/O6
I/O7
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I0/CLK0
V
CC
GND
I1/CLK1
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
I/O16
I/O17
NC
NC
TMS
TCK
NC
A1
A0
B0
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
C0
C1
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
GND
NC
NC
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
NCI2NC
NC
GND
V
CC
I3
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O27
I/O28
I/O29
NC
NC
GND
C2C3C4C5C6
C7
D7D6D5D4D3
D2
100
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
76
GNDNCNC
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0I7V
CC
GNDNCNCI6NC
I/O47
I/O46
I/O45
I/O44
I/O43
I/O42NCNC
GND
A2A3A4A5A6
A7
F7F6F5F4F3
F2
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
NC
TDO
NC
NC
NC
I/O41
I/O40
I/O39
I/O38
I/O37
I/O36
I5/CLK3
GND
V
CC
I4/CLK2
I/O35
I/O34
I/O33
I/O32
I/O31
I/O30
NC
NC
NC
NC
F1
F0
E0
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
D0
D1
17466G-029
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-F)
C7

40 MACH 4 Family
84-PIN PLCC CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-128N/64)
Top View
84-Pin PLCC
Note:
Pin-compatible with the MACH131, MACH231, MACH435.
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I = Input
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
1
2
3
81
82
83
84
6
7
8
9
4
5
80
76
77
78
79
75
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
43
42
41
40
47
46
45
44
37
36
35
34
39
38
33
48
52
51
50
49
102211
32
53
74
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
CLK0/I
0
V
CC
GND
CLK1/I
1
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
GND
I/O8
GND
I/O55
I/O54
I/O53
I/O52
I/O51
I/O50
I/O49
I/O48
CLK3/I
4
V
CC
CLK2/I
3
I/O47
G7
G6
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
G0
F0
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
C0
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
I/O46
I/O45
I/O44
I/O43
I/O42
I/O41
GND
I/O40
GND
V
CC
I/O0
I/O62
I/O63
I
5
V
CC
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O1
I/O2
I/O61
I/O57
I/O58
I/O59
I/O60
I/O56
I/O7
H0H1H2H3H4H5H6
H7
A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
GND
GND
V
CC
I
2
I/O34
I/O33
I/O32
V
CC
I/O29
I/O28
I/O27
I/O26
I/O31
I/O30
I/O35
I/O39
I/O38
I/O37
I/O36
GND
I/O25
I/O24
E0E1E2E3E4E5E6
E7
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
17466G-030
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-H)
C7

MACH 4 Family 41
100-PIN PQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-128/64)
Top View
100-Pin PQFP
Note:
The numbers in parentheses reflect compatible pin numbers for 84-pin PLCC.
PIN DESIGNATIONS
I/CLK = Input or Clock
GND = Ground
I = Input
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
TRST = Test Reset
ENABLE = Program
I/O7 A7
A6A5A4A3A2A1A0
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
V
CC
GND
GND
V
CC
I/O63
I/O62
I/O61
I/O60
I/O59
I/O58
I/O57
I/O56
H0H1H2H3H4H5H6
H7
GND
GND
TDI
I5
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
IO/CLK0
GND
GND
I1/CLK1
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
C0
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
TMS
TCK
GND
GND
28
29
30
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
1
2
3
99
98
100
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
50
9796959493929190898887868584828183
I/O46
I/O45
I/O44
I/O43
I/O42
I/O41
I/O40
I2
ENABLE
GND
GND
GND
TD0
TRST
I/O55
I/O54
I/O53
I/O52
I/O51
I/O50
I/O49
I/O48
G7
G6
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
G0
I4/CLK3
GND
GND
I3/CLK2
I/O47
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F0
GND
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
80
79
78
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O27
I/O28
I/O29
I/O30
I/O31
GND
GND
I/O32
I/O33
I/O34
I/O35
I/O36
I/O37
I/O38
I/O39
E0E1E2E3E4E5E6
E7
(83)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
(23)
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
(28)
(29)
(30)
(31)
(33)
(34)
(35)
(36)
(37)
(38)
(39)
(40)
(45)
(46)
(47)
(48)
(49)
(50)
(51)
(52)
(62)
(61)
(60)
(59)
(58)
(57)
(56)
(55)
(54)
(41)
(73)
(72)
(71)
(70)
(69)
(68)
(67)
(66)
(65)
(10)
(9)
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(82)
(81)
(80)
(79)
(78)
(77)
(76)
(75)
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
17466G-031
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-H)
C7

42 MACH 4 Family
100-PIN TQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-128/64)
Top View
100-Pin TQFP
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK/I = Clock or Input
GND = Ground
I = Input
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
TRST = Test Reset
ENABLE = Program
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
GND
TDI
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
I0/CLK0
V
CC
GND
I1/CLK1
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
TMS
TCK
GND
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
C0
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
GND
GND
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O27
I/O28
I/O29
I/O30
I/O31
I2
V
CC
GND
GND
V
CC
I/O32
I/O33
I/O34
I/O35
I/O36
I/O37
I/O38
I/O39
GND
GND
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
E0E1E2E3E4E5E6
E7
100
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
76
GND
GND
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
VCCGND
GND
VCCI5
I/O63
I/O62
I/O61
I/O60
I/O59
I/O58
I/O57
I/O56
GND
GND
A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
H0H1H2H3H4H5H6
H7
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
GND
TDO
TRST
I/O55
I/O54
I/O53
I/O52
I/O51
I/O50
I/O49
I/O48
I4/CLK3
GND
V
CC
I3/CLK2
I/O47
I/O46
I/O45
I/O44
I/O43
I/O42
I/O41
I/O40
ENABLE
GND
G7
G6
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
G0
F0
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
17466G-032
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-H)
C7

MACH 4 Family 43
144-PIN TQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-192/96)
Top View
144-Pin TQFP
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK = Clock
GND = Ground
I = Input
I/O = Input/Output
V
CC
= Supply Voltage
TDI = Test Data In
TCK = Test Clock
TMS = Test Mode Select
TDO = Test Data Out
17466G-033
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
GND
TDI
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
I2
I3
V
CC
GND
I4
I/O8
I/O9
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
I/O14
I/O15
GND
V
CC
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
TMS
TCK
GND
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
C0
E7
E6
E5
E4
E3
E2
E1
E0
3738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071
72
GND
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O27
I/O28
I/O29
I/O30
I/O31
I5I6I7
CLK1
GND
V
CC
CLK2
I8
I9
I/O32
I/O33
I/O34
I/O35
I/O36
I/O37
I/O38
I/O39
V
CC
GND
I/O40
I/O41
I/O42
I/O43
I/O44
I/O45
I/O46
I/O47
F7F6F5F4F3F2F1
F0
G0G1G2G3G4G5G6
G7
H0H1H2H3H4H5H6
H7
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
I/O95
I/O94
I/O93
I/O92
I/O91
I/O90
I/O89
I/O88
GND
V
CC
I/O87
I/O86
I/O85
I/O84
I/O83
I/O82
I/O81
I/O80I1I0
CLK0
GND
VCCCLK3
I15
I14
I13
I/O79
I/O78
I/O77
I/O76
I/O75
I/O74
I/O73
I/O72
GND
B7B6B5B4B3B2B1
B0A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0
L0L1L2L3L4L5L6
L7
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
GND
TDO
NC
I/O71
I/O70
I/O69
I/O68
I/O67
I/O66
I/O65
I/O64
I12
V
CC
GND
I11
I10
I/O63
I/O62
I/O61
I/O60
I/O59
I/O58
I/O57
I/O56
GND
V
CC
I/O55
I/O54
I/O53
I/O52
I/O51
I/O50
I/O49
I/O48
NC
GND
K0
K1
K2
K3
K4
K5
K6
K7
J0
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
I0
I1
I2
I3
I4
I5
I6
I7
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-L)
C7
17466G-044

44 MACH 4 Family
208-PIN PQFP CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-256/128)
Top View
208-Pin PQFP
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
C0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
E0
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
F0
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
GND
TDI
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O19
I/O20
I/O21
I/O22
I/O23
VCC
GND
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O27
I/O28
I/O29
I/O30
I/O31
I2
I3
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
I4
I/O32
I/O33
I/O34
I/O35
I/O36
I/O37
I/O38
I/O39
GND
VCC
I/O40
I/O41
I/O42
I/O43
I/O44
I/O45
I/O46
I/O47
TMS
TCK
GND
GND
I/O48
I/O49
I/O50
I/O51
I/O52
I/O53
I/O54
I/O55
GND
VCC
I/O56
I/O57
I/O58
I/O59
I/O60
I/O61
I/O62
I/O63
I5
I6
CLK1
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
CLK2
I7
I8
I/O64
I/O66
I/O66
I/O67
I/O68
I/O69
I/O70
I/O71
VCC
GND
I/O72
I/O73
I/O74
I/O75
I/O76
I/O77
I/O78
I/O79
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
G7G6G5G4G3G2G1
G0
H7H6H5H4H3H2H1
H0
I0I1I2I3I4I5I6
I7
J0J1J2J3J4J5J6
J7
5354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
100
101
102
103
104
N7
N6
N5
N4
N3
N2
N1
N0
M7
M6
M5
M4
M3
M2
M1
M0
L0
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L7
K0
K1
K2
K3
K4
K5
K6
K7
B7B6B5B4B3B2B1
B0
A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
P0P1P2P3P4P5P6
P7
O0O1O2O3O4O5O6
O7
GND
I/O15
I/O14
I/O13
I/O12
I/O11
I/O10
I/O9
I/O8
GND
VCC
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0I1I0
CLK0
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
CLK3
I13
I12
I/O127
I/O126
I/O125
I/O124
I/O123
I/O122
I/O121
I/O120
VCC
GND
I/O119
I/O118
I/O117
I/O116
I/O115
I/O114
I/O113
I/O112
GND
GND
TDO
TRST
I/O111
I/O110
I/O109
I/O108
I/O107
I/O106
I/O105
I/O104
VCC
GND
I/O103
I/O102
I/O101
I/O100
I/O99
I/O98
I/O97
I/O96
I11
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
I10
I9
I/O95
I/O94
I/O93
I/O92
I/O91
I/O90
I/O89
I/O88
GND
VCC
I/O87
I/O86
I/O85
I/O84
I/O83
I/O82
I/O81
I/O80
ENABLE
GND
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
208
207
206
205
204
203
202
201
200
199
198
197
196
195
194
193
192
191
190
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
175
174
173
172
171
170
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
158
157
RECOMMEND TO TIE TO VCC
RECOMMEND TO TIE TO GND
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK
GND
I
I/O
N/C
VCC
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
TRST
ENABLE
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-HX)
Clock
Ground
Input
Input/Output
No Connect
Supply Voltage
Test Data In
Test Clock
Test Mode Select
Test Data Out
Test Reset
Program
C7
17466G-044
17466H-066

MACH 4 Family 45
256-BALL BGA CONNECTION DIAGRAM (M4(LV)-256/128)
Bottom View
256-Ball BGA
GND
GND
I/O116
O3
I/O120
P7
I/O123
P4
GND
I12
GND
N/C
GND
N/C
N/C
GND
I1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
N/C
I/O113
O6
N/C
I/O117
O2
I/O119
O0
I/O122
P5
I/O125
P2
I/O127
P0
N/C
CLK3
CLK0
N/C
I/O0
A0
I/O1
A1
GND
N/C
VCC
I/O112
O7
I/O114
O5
I/O118
O1
I/O121
P6
I/O126
P1
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
I/O2
A2
I/O6
A6
I/O108
N4
I/O109
N5
TRST
VCC
TDI
I/O115
O4
VCC
I/O124
P3
I13
N/C
N/C
I0
I/O3
A3
VCC
I/O105
N1
I/O106
N2
I/O111
N7
VCC
GND
I/O103
M7
I/O107
N3
I/O110
N6
I/O100
M4
I/O102
M6
I/O104
N0
VCC
I/O96
M0
I/O98
M2
I/O101
M5
N/C
GND
N/C
I/O97
M1
I/O99
M3
GND
I11
N/C
N/C
GND
N/C
I10
I9
GND
N/C
I/O94
L1
I/O92
L3
GND
I/O82
K5
VCC
I/O79
J7
I/O77
J5
I/O73
J1
I/O70
I6
I/O66
I2
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
I/O61
H2
I/O57
H6
GND
20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
I/O95
L0
I/O93
L2
I/O90
L5
N/C
8
I/O91
L4
I/O89
L6
I/O86
K1
VCC
7
GND
I/O88
L7
I/O84
K3
I/O81
K6
6
I/O87
K0
I/O85
K2
I/O80
K7
VCC
5
N/C
I/O83
K6
ENABLE
VCC
TDO
I/O76
J4
VCC
I/O67
I3
I7
N/C
N/C
I6
I/O60
H3
VCC
43
GND
N/C
I/O78
J6
I/O75
J3
I/O72
J0
I/O69
I5
I/O65
I1
I/O64
I0
N/C
CLK2
CLK1
I/O63
H0
I/O59
H4
I/O58
H5
21
2019181716151413121110987654321
GND
I/O74
J2
I/O71
I7
I/O68
I4
GND
I8
GND
N/C
N/C
GND
I/O62
H1
GND
I5
GND
I/O4
A4
I/O7
A7
I/O5
A5
I/O8
B0
I/O11
B3
I/O9
B1
I/O12
B4
I/O15
B7
N/C
TCK
VCC VCC
I/O18
C5
VCC
I/O24D7I/O29
D2
I2 N/C
I/O35
E3
I/O54
G1
I/O50
G5
I/O48
G7
N/C VCC N/C VCC
I/O51
G4
TMS
VCC
I/O56
H7
I/O55
G0
I/O53
G2
GND
N/C
N/C
I/O10
B2
GND
GND
I/O13
B5
I/O14
B6
GND
VCC
N/C
GND
I/O16
C7
N/C
N/C
I/O17
C6
I/O19
C4
I/O20
C3
I/O21
C2
I/O22
C1
GND
I/O23
C0
I/O25
D6
I/O26
D5
I/O27
D4
I/O28
D3
I/O30
D1
I/O31
D0
N/C
GND
I3
N/C
GND
N/C
I4
GND
I/O33
E1
N/C
GND
VCC
N/C
GND
I/O37
E5
I/O34
E2
I/O32
E0
I/O41
F1
I/O38
E6
I/O36
E4
I/O43
F3
I/O39
E7
GND
I/O46
F6
I/O42
F2
I/O40
F0
I/O47
F7
I/O45
F5
I/O44
F4
I/O52
G3
I/O49
G6
N/C
N/C
GND
GND
PIN DESIGNATIONS
CLK
GND
I
I/O
N/C
VCC
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
TRST
ENABLE
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
I/O Cell (0-7)
PAL Block (A-P)
Clock
Ground
Input
Input/Output
No Connect
Supply Voltage
Test Data In
Test Clock
Test Mode Select
Test Data Out
Test Reset
Program
C7
17466G-045

46 MACH 4 Family
MACH 4 PRODUCT ORDERING INFORMATION
MACH 4 Devices Commercial & Industrial - 3.3V and 5V
Lattice/V antis programmable logic products are available with several ordering options. The order number (V alid Combination) is formed by a combination of:
All MACH devices are dual-marked with both Commercial and
Industrial grades. The Industrial speed grade is slower, i.e.,
M4-256/128-7YC-10YI
Valid Combinations
Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be
supported in volume for this device. Consult the local
Lattice sales office to confirm availability of specific valid
combinations and to check on newly released
combinations.
128
FAMILY TYPE
M
4- = MACH 4 Family (5-V VCC)
M
4LV- = MACH 4 Family Low Voltage (3.3-V VCC)
M4- 256 Y C
MACROCELL DENSITY
32 = 32 Macrocells 128N = 128 Macrocells, Non-ISP
64 = 64 Macrocells 192 = 192 Macrocells
96 = 96 Macrocells 256 = 256 Macrocells
128 = 128 Macrocells
I/Os
/32 = 32 I/Os in 44-pin PLCC, 44-pin TQFP or 48-pin TQFP
/48 = 48 I/Os in 100-pin TQFP
/64 = 64 I/Os in 84-pin PLCC, 100-pin PQFP or 100-pin TQFP
/96 = 96 I/Os in 144-pin TQFP
/
128 = 128 I/Os in 208-pin PQFP or 256-ball BGA
OPERATING CONDITIONS
C = Commercial (0°C to +70°C)
I = Industrial (-40°C to +85°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
A = Ball Grid Array (BGA)
J = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
(PLCC)
V = Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP)
Y = Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP)
SPEED
-7 =7.5 ns t
PD
-10 =10 ns t
PD
-12 =12 ns t
PD
-14 =14 ns tPD
-15 =15 ns t
PD
-18 =18 ns t
PD
-7
48 = 48-pin TQFP for M4(LV)-32/32
or M4(LV)-64/32
/
Valid Combinations
M4-32/32
-7, -10, -12, -15
JC, VC, VC48
M4LV-32/32 JC, VC, VC48
M4-64/32 JC, VC, VC48
M4LV-64/32 JC, VC, VC48
M4-96/48 VC
M4LV-96/48 VC
M4-128/64 YC, VC
M4LV-128/64 YC, VC
M4-128N/64 JC
M4LV-128N/64 JC
M4-192/96 VC
M4LV-192/96 VC
M4-256/128 YC, AC
M4LV-256/128 YC, AC
Valid Combinations
M4-32/32
-10, -12, -14, -18
JI, VI, VI48
M4LV-32/32 JI, VI, VI48
M4-64/32 JI, VI, VI48
M4LV-64/32 JI, VI, VI48
M4-96/48 VI
M4LV-96/48 VI
M4-128/64 YI, VI
M4LV-128/64 YI, VI
M4-128N/64 JI
M4LV-128N/64 JI
M4-192/96 VI
M4LV-192/96 VI
M4-256/128 YI, AI
M4LV-256/128 YI, AI
 Loading...
Loading...