GAL20V8
1
12
13
24
I/CLK
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
GND
Vcc
I
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I
I/OE
6
18
CLK
I
I
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I/OE
I/CLK
OE
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
OLMC
OLMC
OLMC
OLMC
OLMC
OLMC
OLMC
IMUX
IMUX
PROGRAMMABLE
AND-ARRAY
(64 X 40)
OLMC
High Performance E2CMOS PLD
Generic Array Logic™
Features
• HIGH PERFORMANCE E2CMOS® TECHNOLOGY
— 5 ns Maximum Propagation Delay
— Fmax = 166 MHz
— 4 ns Maximum from Clock Input to Data Output
— UltraMOS
• 50% to 75% REDUCTION IN POWER FROM BIPOLAR
— 75mA Typ Icc on Low Power Device
— 45mA T yp Icc on Quarter Power Device
• ACTIVE PULL-UPS ON ALL PINS
2
CELL TECHNOLOGY
• E
— Reconfigurable Logic
— Reprogrammable Cells
— 100% Tested/100% Y ields
— High Speed Electrical Erasure (<100ms)
— 20 Year Data Retention
• EIGHT OUTPUT LOGIC MACROCELLS
— Maximum Flexibility for Complex Logic Designs
— Programmable Output Polarity
— Also Emulates 24-pin PAL
Fuse Map/Parametric Compatibility
• PRELOAD AND POWER-ON RESET OF ALL REGISTERS
— 100% Functional Testability
• APPLICATIONS INCLUDE:
— DMA Control
— State Machine Control
— High Speed Graphics Processing
— Standard Logic Speed Upgrade
• ELECTRONIC SIGNA TURE FOR IDENTIFICATION
®
Advanced CMOS Technology
®
Devices with Full Function/
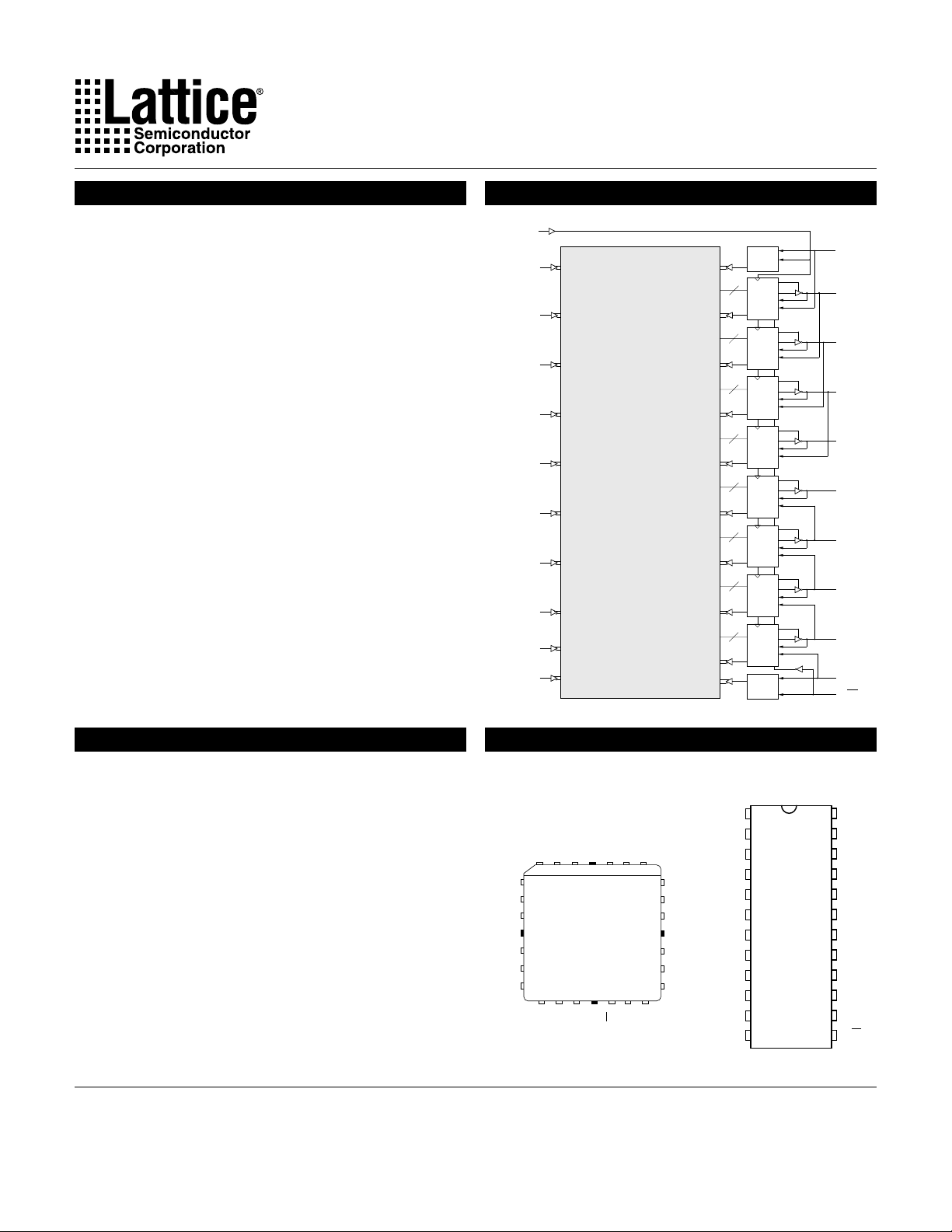
Functional Block Diagram
Description
The GAL20V8C, at 5ns maximum propagation delay time, combines a high performance CMOS process with Electrically Eras-
2
able (E
) floating gate technology to provide the highest speed
performance available in the PLD market. High speed erase times
(<100ms) allow the devices to be reprogrammed quickly and efficiently.
The generic architecture provides maximum design flexibility by
allowing the Output Logic Macrocell (OLMC) to be configured by
the user. An important subset of the many architecture configurations possible with the GAL20V8 are the P AL
in the table of the macrocell description section. GAL20V8 devices
are capable of emulating any of these PAL architectures with full
function/fuse map/parametric compatibility .
Unique test circuitry and reprogrammable cells allow complete AC,
DC, and functional testing during manufacture. As a result, Lattice
Semiconductor delivers 100% field programmability and functionality of all GAL products. In addition, 100 erase/write cycles and
data retention in excess of 20 years are specified.
Copyright © 2000 Lattice Semiconductor Corp. All brand or product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. The specifications and information herein are subject
to change without notice.
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR CORP., 5555 Northeast Moore Ct., Hillsboro, Oregon 97124, U.S.A. August 2000
Tel. (503) 268-8000; 1-800-LATTICE; FAX (503) 268-8556; http://www.latticesemi.com
20v8_04
architectures listed
Pin Configuration
PLCC
I/CLK
I
4
5
I
I
I
7
NC
I
9
I
I
11
12 14 16 18
I
1
NC
I
228
GAL20V8
T op View
I
NC
GND
Vcc
I/OE
DIP
I/O/Q
I
26
25
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
23
I/O/Q
NC
21
I/O/Q
I/O/Q
19
I/O/Q
I
I/O/Q
GAL
20V8
GAL20V8 Ordering Information
Commercial Grade Specifications
)sn(dpT)sn(usT)sn(ocT)Am(ccI#gniredrOegakcaP
534 511JL5-C8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
5.775 511
511PL7-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
511JL7-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
01017 511
511PL01-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
511JL01-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
51210155PQ51-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
55JQ51-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
09PL51-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
09JL51-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
52512155PQ52-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
55JQ52-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
09PL52-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
09JL52-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
8V02LAGCJL7-
8V02LAGCJL01-
Specifications GAL20V8
CCLPdaeL-82
CCLPdaeL-82
Industrial Grade Specifications
)sn(dpT)sn(usT)sn(ocT)Am(ccI#gniredrOegakcaP
01017 031
031IPL01-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
031IJL01-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
512101031IPL51-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
031IJL51-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
02311156IPQ02-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
56IJQ02-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
52512156IPQ52-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
56IJQ52-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
031IPL52-B8V02LAGPIDcitsalPniP-42
031IJL52-B8V02LAGCCLPdaeL-82
8V02LAGCIJL01-
Part Number Description
_
GAL20V8C
GAL20V8B
XXXXXXXX XX X X X
Device Name
CCLPdaeL-82
Speed (ns)
Q = Quarter Power
Grade
Blank = Commercial
I = Industrial
PowerL = Low Power
Package
P = Plastic DIP
J = PLCC
2
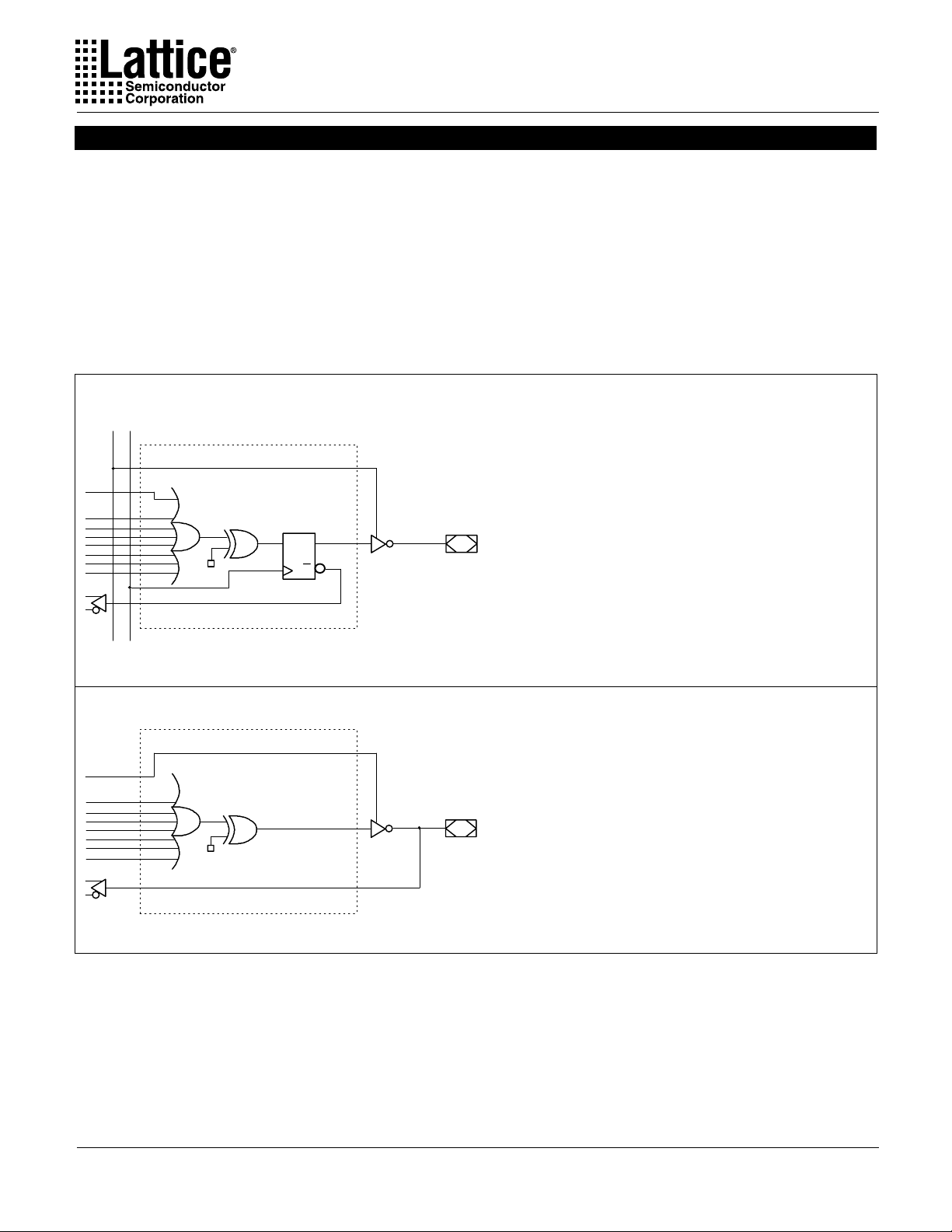
Output Logic Macrocell (OLMC)
The following discussion pertains to configuring the output logic
macrocell. It should be noted that actual implementation is accomplished by development software/hardware and is completely transparent to the user.
There are three global OLMC configuration modes possible:
simple, complex, and registered. Details of each of these modes
is illustrated in the following pages. T wo global bits, SYN and AC0,
control the mode configuration for all macrocells. The XOR bit of
each macrocell controls the polarity of the output in any of the three
modes, while the AC1 bit of each of the macrocells controls the input/output configuration. These two global and 16 individual architecture bits define all possible configurations in a GAL20V8 . The
information given on these architecture bits is only to give a better understanding of the device. Compiler software will transparently set these architecture bits from the pin definitions, so the user
should not need to directly manipulate these architecture bits.
The following is a list of the PAL architectures that the GAL20V8
can emulate. It also shows the OLMC mode under which the
devices emulate the PAL architecture.
Specifications GAL20V8
PAL Architectures GAL20V8
Emulated by GAL20V8 Global OLMC Mode
20R8 Registered
20R6 Registered
20R4 Registered
20RP8 Registered
20RP6 Registered
20RP4 Registered
20L8 Complex
20H8 Complex
20P8 Complex
14L8 Simple
16L6 Simple
18L4 Simple
20L2 Simple
14H8 Simple
16H6 Simple
18H4 Simple
20H2 Simple
14P8 Simple
16P6 Simple
18P4 Simple
20P2 Simple
Compiler Support for OLMC
Software compilers support the three different global OLMC modes
as different device types. These device types are listed in the table
below. Most compilers have the ability to automatically select the
device type, generally based on the register usage and output
enable (OE) usage. Register usage on the device forces the software to choose the registered mode. All combinatorial outputs with
OE controlled by the product term will force the software to choose
the complex mode. The software will choose the simple mode only
when all outputs are dedicated combinatorial without OE control.
The different device types listed in the table can be used to override
the automatic device selection by the software. For further details,
refer to the compiler software manuals.
When using compiler software to configure the device, the user
must pay special attention to the following restrictions in each mode.
In registered mode pin 1 and pin 13 (DIP pinout) are permanently
Registered Complex Simple Auto Mode Select
ABEL P20V8R P20V8C P20V8AS P20V8
CUPL G20V8MS G20V8MA G20V8AS G20V8
LOG/iC GAL20V8_R GAL20V8_C7 GAL20V8_C8 GAL20V8
OrCAD-PLD "Registered"
PLDesigner P20V8R
1
2
"Complex"
P20V8C
TANGO-PLD G20V8R G20V8C G20V8AS
configured as clock and output enable, respectively . These pins
cannot be configured as dedicated inputs in the registered mode.
In complex mode pin 1 and pin 13 become dedicated inputs and
use the feedback paths of pin 22 and pin 15 respectively . Because
of this feedback path usage, pin 22 and pin 15 do not have the
feedback option in this mode.
In simple mode all feedback paths of the output pins are routed
via the adjacent pins. In doing so, the two inner most pins ( pins
18 and 19) will not have the feedback option as these pins are
always configured as dedicated combinatorial output.
1
2
"Simple"
P20V8C
1
2
3
GAL20V8A
P20V8A
G20V8
1) Used with Configuration keyword.
2) Prior to Version 2.0 support.
3) Supported on Version 1.20 or later.
3
Registered Mode
Specifications GAL20V8
In the Registered mode, macrocells are configured as dedicated
registered outputs or as I/O functions.
Architecture configurations available in this mode are similar to the
common 20R8 and 20RP4 devices with various permutations of
polarity , I/O and register placement.
All registered macrocells share common clock and output enable
control pins. Any macrocell can be configured as registered or I/
O. Up to eight registers or up to eight I/Os are possible in this mode.
CLK
DQ
XOR
OE
Q
Dedicated input or output functions can be implemented as subsets of the I/O function.
Registered outputs have eight product terms per output. I/Os have
seven product terms per output.
The JEDEC fuse numbers, including the User Electronic Signature
(UES) fuses and the Product T erm Disable (PTD) fuses, are shown
on the logic diagram on the following page.
Registered Configuration for Registered Mode
- SYN=0.
- AC0=1.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=0 defines this output configuration.
- Pin 1 controls common CLK for the registered outputs.
- Pin 13 controls common OE for the registered outputs.
- Pin 1 & Pin 13 are permanently configured as CLK &
OE for registered output configuration.
Combinatorial Configuration for Registered Mode
- SYN=0.
- AC0=1.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=1 defines this output configuration.
XOR
Note: The development software configures all of the architecture control bits and checks for proper pin usage automatically.
- Pin 1 & Pin 13 are permanently configured as CLK &
OE for registered output configuration..
4
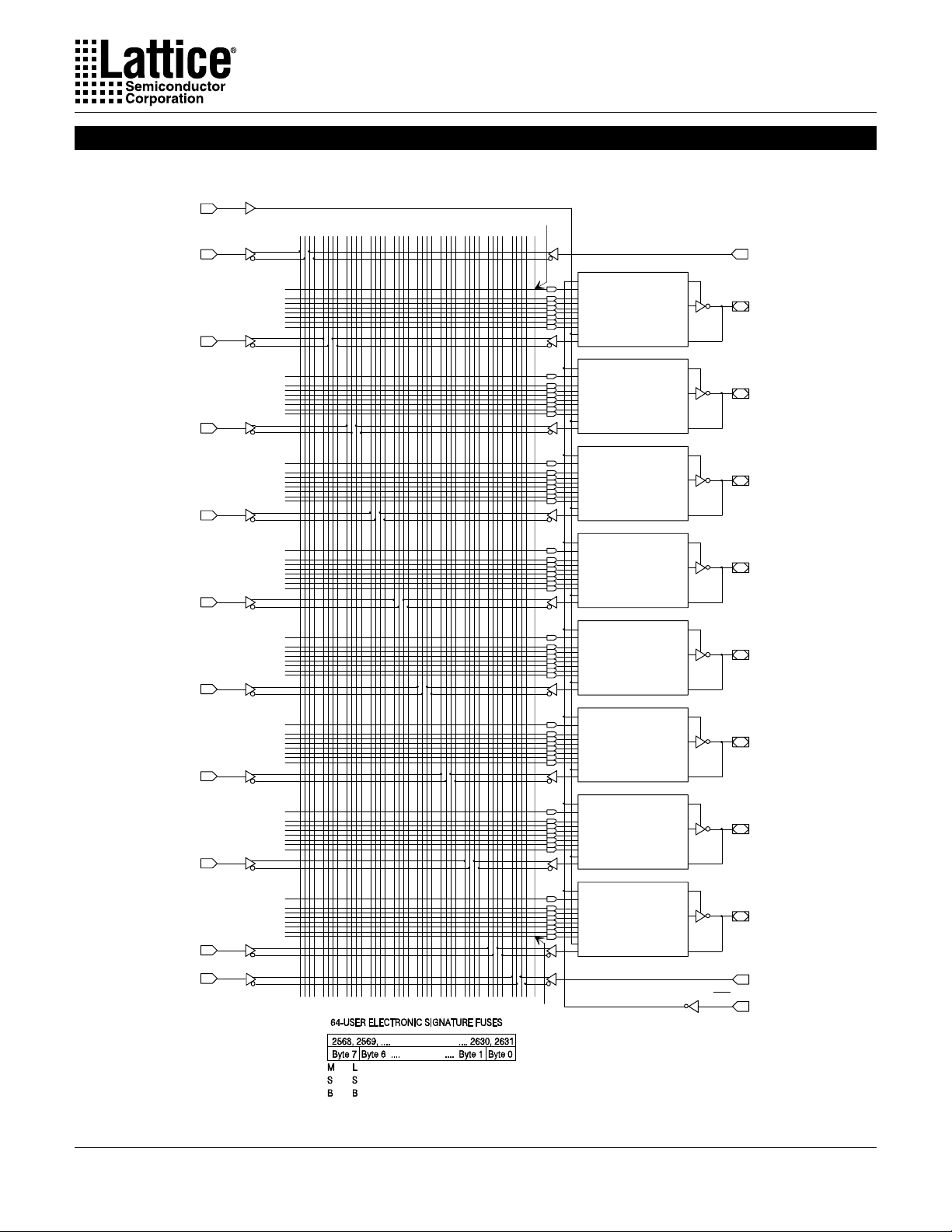
Registered Mode Logic Diagram
Specifications GAL20V8
DIP (PLCC) Package Pinouts
1(2)
2(3)
3(4)
4(5)
5(6)
6(7)
7(9)
0000
0280
0320
0600
0640
0920
0960
1240
1280
1560
28
24
201612840
32
2640
36
PTD
23(27)
OLMC
22(26)
XOR-2560
AC1-2632
OLMC
21(25)
XOR-2561
AC1-2633
OLMC
XOR-2562
AC1-2634
OLMC
XOR-2563
AC1-2635
OLMC
XOR-2564
AC1-2636
20(24)
19(23)
18(21)
8(10)
9(11)
10(12)
11(13)
1600
1880
1920
2200
2240
2520
2703
OLMC
XOR-2565
AC1-2637
OLMC
XOR-2566
AC1-2638
OLMC
XOR-2567
AC1-2639
SYN-2704
AC0-2705
OE
17(20)
16(19)
15(18)
14(17)
13(16)
5
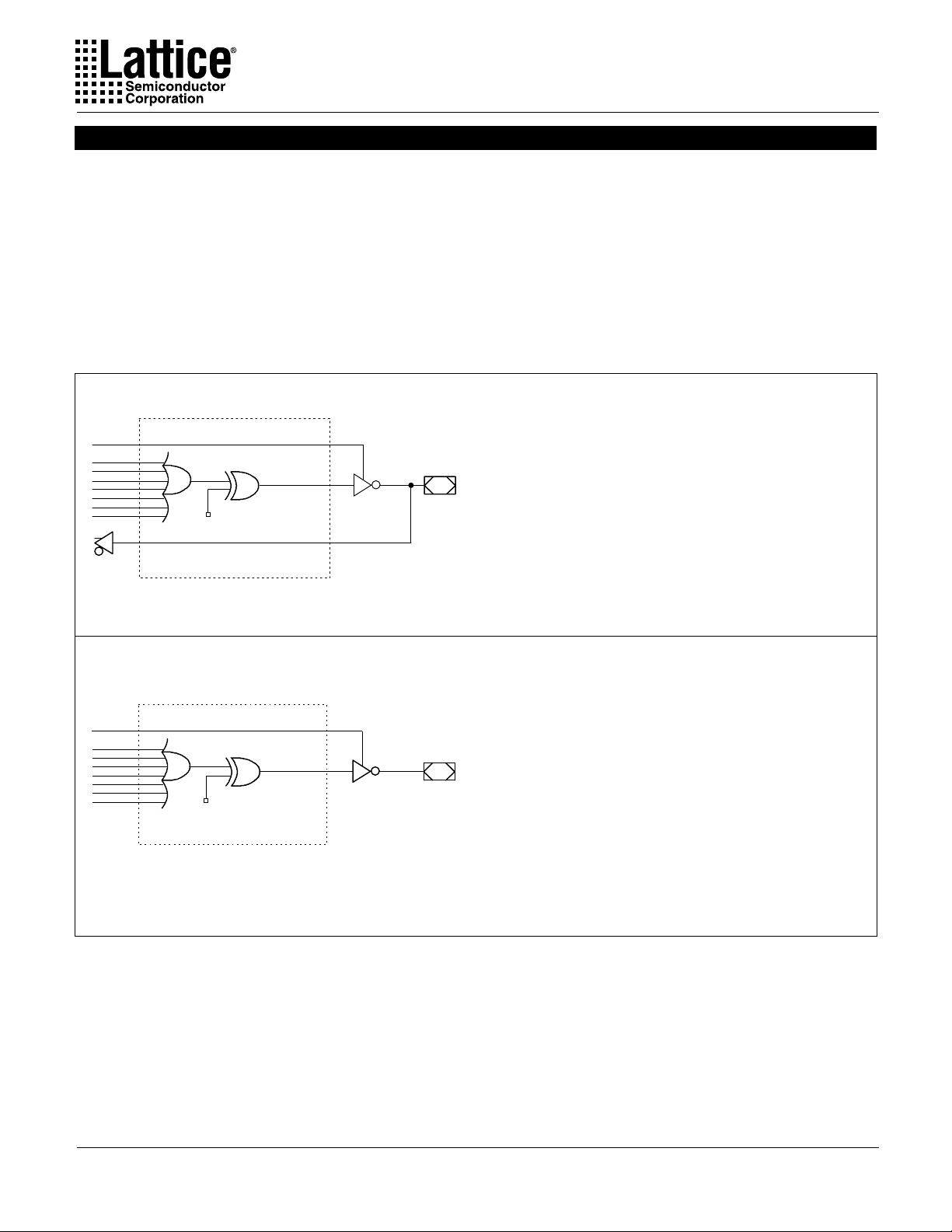
Complex Mode
Specifications GAL20V8
In the Complex mode, macrocells are configured as output only or
I/O functions.
Architecture configurations available in this mode are similar to the
common 20L8 and 20P8 devices with programmable polarity in
each macrocell.
Up to six I/Os are possible in this mode. Dedicated inputs or outputs
can be implemented as subsets of the I/O function. The two outer
most macrocells (pins 15 & 22) do not have input capability . De-
XOR
signs requiring eight I/Os can be implemented in the Registered
mode.
All macrocells have seven product terms per output. One product
term is used for programmable output enable control. Pins 1 and
13 are always available as data inputs into the AND array.
The JEDEC fuse numbers including the UES fuses and PTD fuses
are shown on the logic diagram on the following page.
Combinatorial I/O Configuration for Complex Mode
- SYN=1.
- AC0=1.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=1.
- Pin 16 through Pin 21 are configured to this function.
Combinatorial Output Configuration for Complex Mode
- SYN=1.
- AC0=1.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
XOR
Note: The development software configures all of the architecture control bits and checks for proper pin usage automatically.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=1.
- Pin 15 and Pin 22 are configured to this function.
6
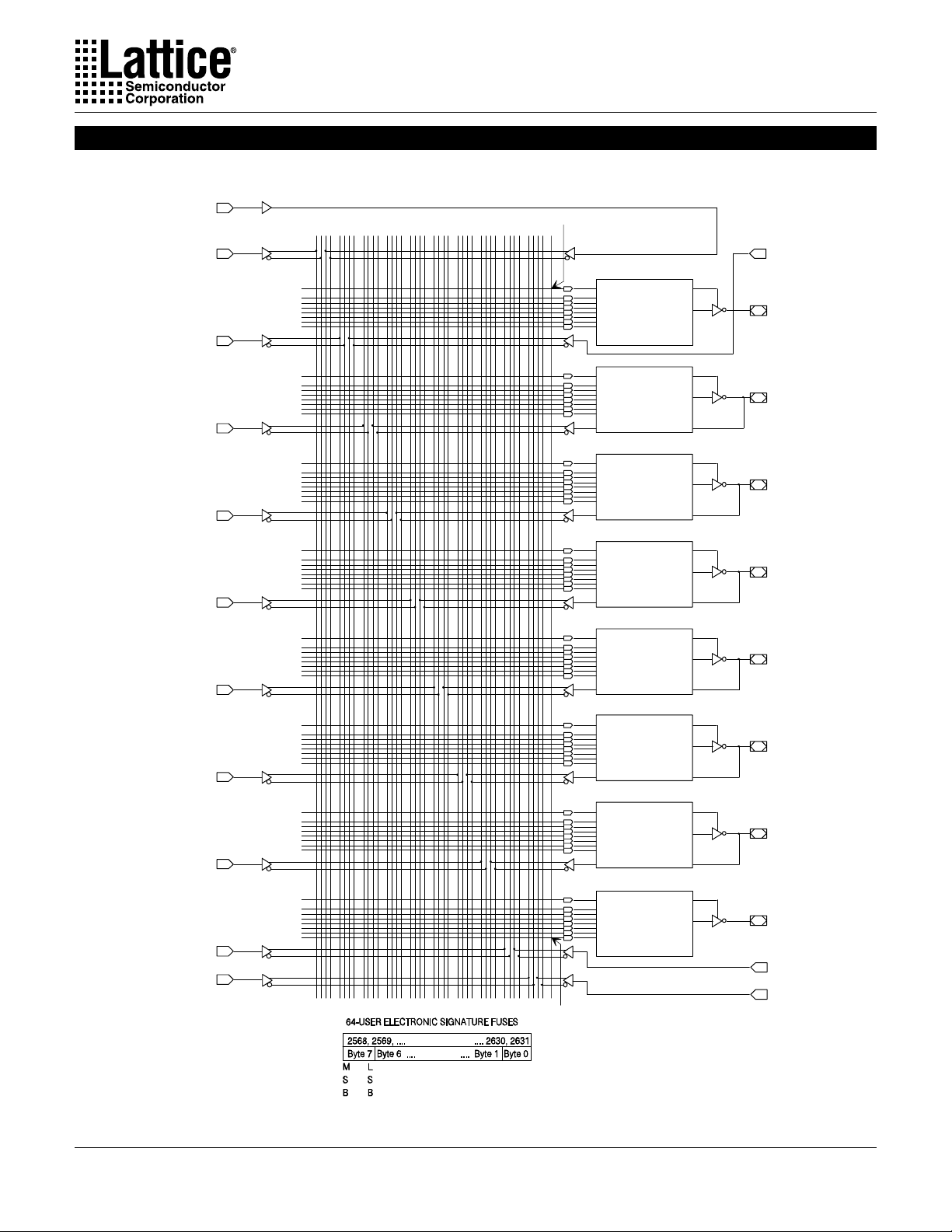
Complex Mode Logic Diagram
Specifications GAL20V8
DIP (PLCC) Package Pinouts
1(2)
2(3)
3(4)
4(5)
5(6)
6(7)
7(9)
0000
0280
0320
0600
0640
0920
0960
1240
1280
1560
24
32
201612840
28
2640
36
PTD
23(27)
OLMC
XOR-2560
22(26)
AC1-2632
OLMC
21(25)
XOR-2561
AC1-2633
OLMC
20(24)
XOR-2562
AC1-2634
OLMC
19(23)
XOR-2563
AC1-2635
OLMC
18(21)
XOR-2564
AC1-2636
8(10)
9(11)
10(12)
11(13)
1600
1880
1920
2200
2240
2520
2703
OLMC
XOR-2565
AC1-2637
OLMC
XOR-2566
AC1-2638
OLMC
XOR-2567
AC1-2639
SYN-2704
AC0-2705
17(20)
16(19)
15(18)
14(17)
13(16)
7

Simple Mode
Specifications GAL20V8
In the Simple mode, pins are configured as dedicated inputs or as
dedicated, always active, combinatorial outputs.
Architecture configurations available in this mode are similar to the
common 14L8 and 16P6 devices with many permutations of generic output polarity or input choices.
All outputs in the simple mode have a maximum of eight product
terms that can control the logic. In addition, each output has programmable polarity .
Vcc
XOR
Pins 1 and 13 are always available as data inputs into the AND
array. The “center” two macrocells (pins 18 and 19) cannot be used
in the input configuration.
The JEDEC fuse numbers including the UES fuses and PTD fuses
are shown on the logic diagram on the following page.
Combinatorial Output with Feedback Configuration
for Simple Mode
- SYN=1.
- AC0=0.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=0 defines this configuration.
- All OLMC except pins 18 & 19 can be configured to
this function.
Combinatorial Output Configuration for Simple Mode
Vcc
XOR
Note: The development software configures all of the architecture control bits and checks for proper pin usage automatically.
- SYN=1.
- AC0=0.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=0 defines this configuration.
- Pins 18 & 19 are permanently configured to this
function.
Dedicated Input Configuration for Simple Mode
- SYN=1.
- AC0=0.
- XOR=0 defines Active Low Output.
- XOR=1 defines Active High Output.
- AC1=1 defines this configuration.
- All OLMC except pins 18 & 19 can be configured to
this function.
8
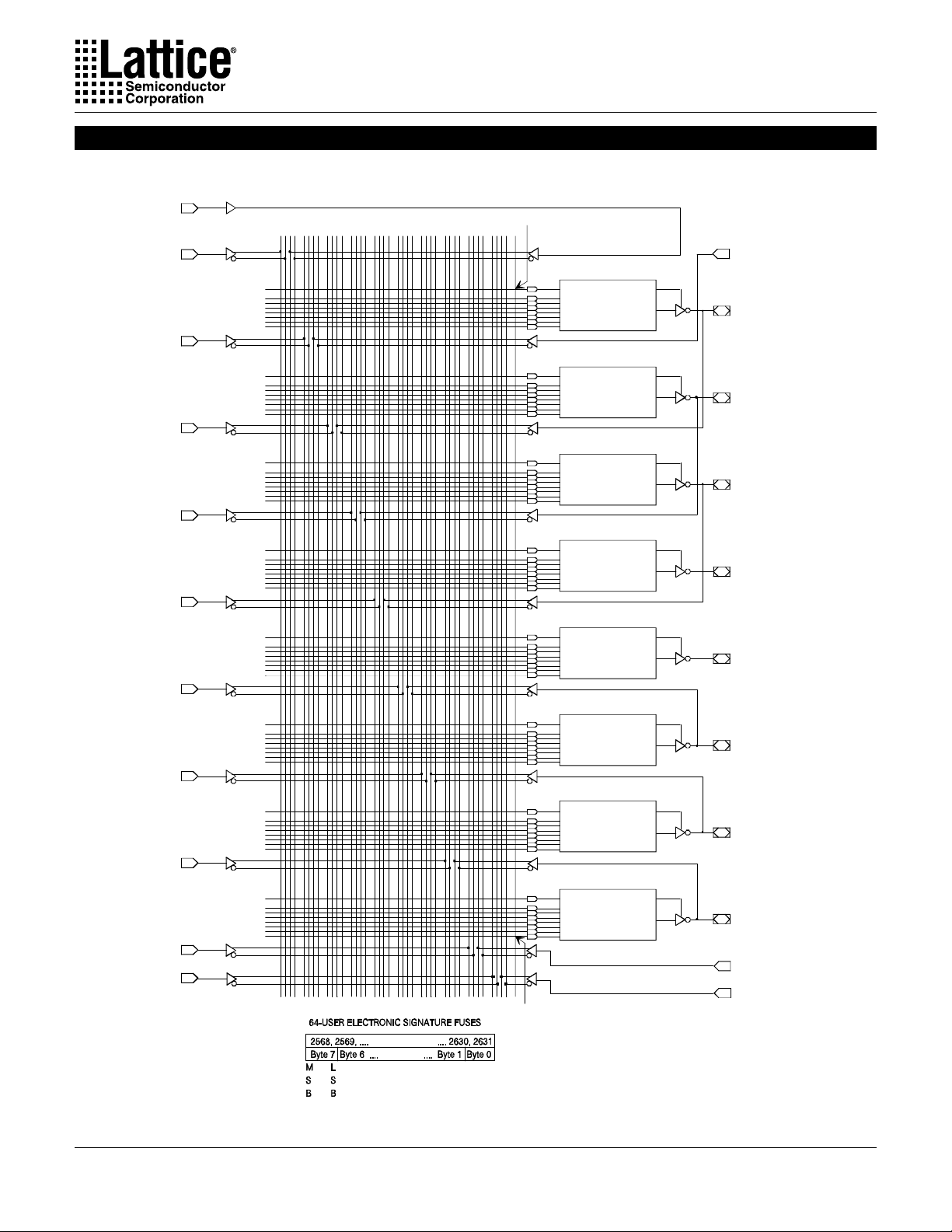
Simple Mode Logic Diagram
Specifications GAL20V8
DIP (PLCC) Package Pinouts
1(2)
2(3)
3(4)
4(5)
5(6)
6(7)
7(9)
0000
0280
0320
0600
0640
0920
0960
1240
1280
1560
24
32
201612840
28
2640
36
PTD
23(27)
OLMC
XOR-2560
AC1-2632
22(26)
OLMC
XOR-2561
AC1-2633
21(25)
OLMC
XOR-2562
AC1-2634
20(24)
OLMC
XOR-2563
AC1-2635
19(23)
OLMC
XOR-2564
AC1-2636
18(21)
8(10)
9(11)
10(12)
11(13)
1600
1880
1920
2200
2240
2520
2703
OLMC
XOR-2565
AC1-2637
OLMC
XOR-2566
AC1-2638
OLMC
XOR-2567
AC1-2639
SYN-2704
AC0-2705
17(20)
16(19)
15(18)
14(17)
13(16)
9

Specifications GAL20V8Specifications GAL20V8C
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply voltage VCC...................................... –0.5 to +7V
Input voltage applied .......................... –2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Off-state output voltage applied .........–2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Storage Temperature ................................ –65 to 150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied ........................................–55 to 125°C
1.Stresses above those listed under the “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These
are stress only ratings and functional operation of the device at
these or at any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied (while
programming, follow the programming specifications).
(1)
Recommended Operating Conditions
Commercial Devices:
Ambient T emperature (TA) ...............................0 to 75°C
Supply voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground ..................... +4.75 to +5.25V
Industrial Devices:
Ambient T emperature (TA) ...........................–40 to 85°C
Supply voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground ..................... +4.50 to +5.50V
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Specified)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN. TYP.3MAX. UNITS
VIL Input Low Voltage Vss – 0.5 — 0.8 V
VIH Input High Voltage 2.0 — Vcc+1 V
1
IIL
Input or I/O Low Leakage Current 0V ≤ VIN ≤ VIL (MAX.) ——–100 µA
IIH Input or I/O High Leakage Current 3.5V ≤ VIN ≤ VCC ——10 µA
VOL Output Low Voltage IOL = MAX. Vin = VIL or VIH ——0.5 V
VOH Output High Voltage IOH = MAX. Vin = VIL or VIH 2.4 ——V
IOL Low Level Output Current ——16 mA
IOH High Level Output Current ——–3.2 mA
2
IOS
Output Short Circuit Current VCC = 5V VOUT = 0.5V TA= 25°C –30 —–150 mA
COMMERCIAL
ICC Operating Power VIL = 0.5V VIH = 3.0V L -5/-7/-10 — 75 115 mA
Supply Current f
toggle = 15MHz Outputs Open
INDUSTRIAL
ICC Operating Power VIL = 0.5V VIH = 3.0V L-10 — 75 130 mA
Supply Current f
1) The leakage current is due to the internal pull-up resistor on all pins. See Input Buffer section for more information.
2) One output at a time for a maximum duration of one second. Vout = 0.5V was selected to avoid test problems caused by tester
ground degradation. Characterized but not 100% tested.
3) T ypical values are at Vcc = 5V and TA = 25 °C
toggle = 15MHz Outputs Open
10

AC Switching Characteristics
Specifications GAL20V8
Specifications GAL20V8C
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
COM/IND
-10
MIN. MAX.
TEST
COND1.
DESCRIPTION
-5
MIN. MAX.
COMCOM
-7
MIN. MAX.
tpd A Input or I/O to 8 outputs switching 1 5 3 7.5 3 10 ns
Comb. Output 1 output switching —— — 7 —— ns
tco A Clock to Output Delay 1 4 2 5 2 7 ns
2
tcf
— Clock to Feedback Delay — 3 — 3 — 6ns
tsu — Setup Time, Input or Feedback before Clock↑ 3 — 5 — 7.5 — ns
th — Hold Time, Input or Feedback after Clock↑ 0 — 0 — 0 — ns
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 142.8 — 100 — 66.7 — MHz
External Feedback, 1/(tsu + tco)
3
fmax
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 166 — 125 — 71.4 — MHz
Internal Feedback, 1/(tsu + tcf)
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 166 — 125 — 83.3 — MHz
No Feedback
twh — Clock Pulse Duration, High 3 — 4 — 6 — ns
twl — Clock Pulse Duration, Low 3 — 4 — 6 — ns
ten B Input or I/O to Output Enabled 1 6 3 9 3 10 ns
B OE to Output Enabled 1 6 2 6 2 10 ns
UNITSPARAMETER
tdis C Input or I/O to Output Disabled 1 5 2 9 2 10 ns
C OE to Output Disabled 1 5 1.5 6 1.5 10 ns
1) Refer to Switching T est Conditions section.
2) Calculated from fmax with internal feedback. Refer to fmax Descriptions section.
3) Refer to fmax Descriptions section. Characterized initially and after any design or process changes that may affect these
parameters.
Capacitance (TA = 25°C, f = 1.0 MHz)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MAXIMUM* UNITS TEST CONDITIONS
C
I
C
I/O
*Characterized but not 100% tested
Input Capacitance 8 pF VCC = 5.0V , VI = 2.0V
I/O Capacitance 8 pF VCC = 5.0V , V
= 2.0V
I/O
11

Specifications GAL20V8Specifications GAL20V8B
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
Supply voltage VCC...................................... –0.5 to +7V
Input voltage applied .......................... –2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Off-state output voltage applied .........–2.5 to VCC +1.0V
Storage Temperature ................................ –65 to 150°C
Recommended Operating Conditions
Commercial Devices:
Ambient T emperature (TA) ...............................0 to 75°C
Supply voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground ..................... +4.75 to +5.25V
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied ........................................–55 to 125°C
1.Stresses above those listed under the “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These
are stress only ratings and functional operation of the device at
these or at any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied (while
programming, follow the programming specifications).
Industrial Devices:
Ambient T emperature (TA) ...........................–40 to 85°C
Supply voltage (VCC)
with Respect to Ground ..................... +4.50 to +5.50V
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Specified)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN. TYP.
3
MAX. UNITS
VIL Input Low Voltage Vss – 0.5 — 0.8 V
VIH Input High Voltage 2.0 — Vcc+1 V
1
IIL
Input or I/O Low Leakage Current 0V ≤ VIN ≤ VIL (MAX.) ——–100 µA
IIH Input or I/O High Leakage Current 3.5V ≤ VIN ≤ VCC ——10 µA
VOL Output Low Voltage IOL = MAX. Vin = VIL or VIH ——0.5 V
VOH Output High Voltage IOH = MAX. Vin = VIL or VIH 2.4 ——V
IOL Low Level Output Current ——24 mA
IOH High Level Output Current ——–3.2 mA
2
IOS
Output Short Circuit Current VCC = 5V VOUT = 0.5V TA= 25°C –30 —–150 mA
COMMERCIAL
ICC Operating Power VIL = 0.5V VIH = 3.0V L -7/-10 — 75 115 mA
Supply Current f
toggle = 15MHz Outputs Open L -15/-25 — 75 90 mA
Q -15/-25 — 45 55 mA
INDUSTRIAL
ICC Operating Power VIL = 0.5V VIH = 3.0V L -10/-15/-25 — 75 130 mA
Supply Current f
1) The leakage current is due to the internal pull-up resistor on all pins. See Input Buffer section for more information.
2) One output at a time for a maximum duration of one second. Vout = 0.5V was selected to avoid test problems caused by tester
ground degradation. Characterized but not 100% tested.
3) Typical values are at Vcc = 5V and TA = 25 °C
toggle = 15MHz Outputs Open Q -20/-25 — 45 65 mA
12

AC Switching Characteristics
Specifications GAL20V8
Specifications GAL20V8B
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
IND COM / IND
-20
MIN. MAX.
-25
MIN. MAX.
PARAM.
TEST
COND
DESCRIPTION
1
.
COM
-7
MIN. MAX.
COM / IND COM / IND
-10
MIN. MAX.
-15
MIN. MAX.
tpd A Input or I/O to 8 outputs switching 3 7.5 3 10 3 15 3 20 3 25 ns
Comb. Output 1 output switching — 7 —— —— —— —— ns
tco A Clock to Output Delay 2 5 2 7 2 10 2 11 2 12 ns
2
tcf
— Clock to Feedback Delay — 3 — 6 — 8 — 9 — 10 ns
tsu — Setup Time, Input or Fdbk before Clk↑ 7 — 10 — 12 — 13 — 15 — ns
th — Hold Time, Input or Fdbk after Clk↑ 0 — 0 — 0 — 0 — 0 — ns
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 83.3 — 58.8 — 45.5 — 41.6 — 37 — MHz
External Feedback, 1/(tsu + tco)
3
fmax
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 100 — 62.5 — 50 — 45.4 — 40 — MHz
Internal Feedback, 1/(tsu + tcf)
A Maximum Clock Frequency with 100 — 62.5 — 62.5 — 50 — 41.7 — MHz
No Feedback
twh — Clock Pulse Duration, High 5 — 8 — 8 — 10 — 12 — ns
twl — Clock Pulse Duration, Low 5 — 8 — 8 — 10 — 12 — ns
ten B Input or I/O to Output Enabled 3 9 3 10 — 15 — 18 — 25 ns
B OE to Output Enabled 2 6 2 10 — 15 — 18 — 20 ns
UNITS
tdis C Input or I/O to Output Disabled 2 9 2 10 — 15 — 18 — 25 ns
C OE to Output Disabled 1.5 6 1.5 10 — 15 — 18 — 20 ns
1) Refer to Switching T est Conditions section.
2) Calculated from fmax with internal feedback. Refer to fmax Descriptions section.
3) Refer to fmax Descriptions section.
Capacitance (TA = 25°C, f = 1.0 MHz)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MAXIMUM* UNITS TEST CONDITIONS
C
I
C
I/O
*Characterized but not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance 8 pF VCC = 5.0V , VI = 2.0V
I/O Capacitance 8 pF VCC = 5.0V , V
= 2.0V
I/O
13

(
)
Switching Waveforms
Specifications GAL20V8
INPUT or
I/O FEEDBACK
COMBINATIONAL
OUTPUT
INPUT or
I/O FEEDBACK
COMBINATIONAL
OUTPUT
VALID INPUT
t
pd
tentdis
INPUT or
I/O FEEDBACK
CLK
REGISTERED
OUTPUT
OE
REGISTERED
OUTPUT
VALID INPUT
su
t
(external fdbk)
h
t
t
co
1/
f
max
Registered OutputCombinatorial Output
dis
t
en
t
OE to Output Enable/DisableInput or I/O to Output Enable/Disable
CLK
wh
t
1/fmax
w/o fb
wl
t
CLK
REGISTERED
FEEDBACK
1/fmax (internal fdbk)
cf
t
su
t
Clock Width
fmax with Feedback
14

fmax Descriptions
Specifications GAL20V8
CLK
LOGIC
ARRAY
t
su
REGISTER
t
co
fmax with External Feedback 1/(tsu+tco)
Note: fmax with external feedback is calculated from measured
tsu and tco.
LOGIC
ARRAY
t
su + th
CLK
REGISTER
fmax with No Feedback
Note: fmax with no feedback may be less than 1/(twh + twl). This
is to allow for a clock duty cycle of other than 50%.
Switching Test Conditions
CLK
LOGIC
ARRAY
REGISTER
t
cf
t
pd
fmax with Internal Feedback 1/(tsu+tcf)
Note: tcf is a calculated value, derived by subtracting tsu from
the period of fmax w/internal feedback (tcf = 1/fmax - tsu). The
value of tcf is used primarily when calculating the delay from
clocking a register to a combinatorial output (through registered
feedback), as shown above. For example, the timing from clock
to a combinatorial output is equal to tcf + tpd.
+5V
Input Pulse Levels GND to 3.0V
Input Rise and GAL20V8B 2 – 3ns 10% – 90%
Fall Times GAL20V8C 1.5ns 10% – 90%
Input Timing Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Timing Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Load See Figure
3-state levels are measured 0.5V from steady-state active
level.
GAL20V8B Output Load Conditions (see figure)
Test Condition R
1 R2 CL
A 200Ω 390Ω 50pF
B Active High ∞ 390Ω 50pF
Active Low 200Ω 390Ω 50pF
C Active High ∞ 390Ω 5pF
Active Low 200Ω 390Ω 5pF
R
1
FROM OUTPUT (O/Q)
UNDER TEST
R
2
*C
INCLUDES TEST FIXTURE AND PROBE CAPACITANCE
L
GAL20V8C Output Load Conditions (see figure)
T est Condition R1 R2 CL
A 200Ω 200Ω 50pF
B Active High ∞ 200Ω 50pF
Active Low 200Ω 200Ω 50pF
C Active High ∞ 200Ω 5pF
Active Low 200Ω 200Ω 5pF
15
C *
L
TEST POINT

Specifications GAL20V8
Electronic Signature
An electronic signature is provided in every GAL20V8 device. It
contains 64 bits of reprogrammable memory that can contain user
defined data. Some uses include user ID codes, revision numbers,
or inventory control. The signature data is always available to the
user independent of the state of the security cell.
NOTE: The electronic signature is included in checksum calculations. Changing the electronic signature will alter the checksum.
Security Cell
A security cell is provided in the GAL20V8 devices to prevent unauthorized copying of the array patterns. Once programmed, this
cell prevents further read access to the functional bits in the device.
This cell can only be erased by re-programming the device, so the
original configuration can never be examined once this cell is programmed. The Electronic Signature is always available to the user ,
regardless of the state of this control cell.
Latch-Up Protection
GAL20V8 devices are designed with an on-board charge pump
to negatively bias the substrate. The negative bias minimizes the
potential of latch-up caused by negative input undershoots. Additionally , outputs are designed with n-channel pull-ups instead of
the traditional p-channel pull-ups in order to eliminate latch-up due
to output overshoots.
Device Programming
Output Register Preload
When testing state machine designs, all possible states and state
transitions must be verified in the design, not just those required
in the normal machine operations. This is because, in system
operation, certain events occur that may throw the logic into an
illegal state (power-up, line voltage glitches, brown-outs, etc.). To
test a design for proper treatment of these conditions, a way must
be provided to break the feedback paths, and force any desired (i.e.,
illegal) state into the registers. Then the machine can be sequenced
and the outputs tested for correct next state conditions.
GAL20V8 devices include circuitry that allows each registered
output to be synchronously set either high or low. Thus, any present
state condition can be forced for test sequencing. If necessary,
approved GAL programmers capable of executing text vectors
perform output register preload automatically .
Input Buffers
GAL20V8 devices are designed with TTL level compatible input
buffers. These buffers have a characteristically high impedance,
and present a much lighter load to the driving logic than bipolar TTL
devices.
The GAL20V8 input and I/O pins have built-in active pull-ups. As
a result, unused inputs and I/O's will float to a TTL "high" (logical
"1"). Lattice Semiconductor recommends that all unused inputs
and tri-stated I/O pins be connected to another active input, VCC,
or Ground. Doing this will tend to improve noise immunity and reduce ICC for the device.
GAL devices are programmed using a Lattice Semiconductorapproved Logic Programmer, available from a number of manufacturers. Complete programming of the device takes only a few
seconds. Erasing of the device is transparent to the user, and is
done automatically as part of the programming cycle.
T ypical Input Pull-up Characteristic
0
-20
-40
Input Current (uA)
-60
0
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
Input Voltage (Volts)
16

Power-Up Reset
Specifications GAL20V8
Vcc
CLK
INTERNAL REGISTER
Q - OUTPUT
FEEDBACK/EXTERNAL
OUTPUT REGISTER
Vcc (min.)
Circuitry within the GAL20V8 provides a reset signal to all registers
during power-up. All internal registers will have their Q outputs set
low after a specified time (
tpr, 1µs MAX). As a result, the state on
the registered output pins (if they are enabled) will always be high
on power-up, regardless of the programmed polarity of the output
pins. This feature can greatly simplify state machine design by providing a known state on power-up. Because of the asynchronous
nature of system power-up, some conditions must be met to provide
Input/Output Equivalent Schematics
t
su
t
wl
t
pr
Internal Register
Reset to Logic "0"
Device P in
Reset to Logic "1"
a valid power-up reset of the device. First, the VCC rise must be
monotonic. Second, the clock input must be at static TTL level as
shown in the diagram during power up. The registers will reset
within a maximum of tpr time. As in normal system operation, avoid
clocking the device until all input and feedback path setup times
have been met. The clock must also meet the minimum pulse width
requirements.
PIN
ESD
Protection
Circuit
PIN
ESD
Protection
Circuit
Typ. V ref = 3.2V
Active Pull-up
Circuit
Vcc
T ypical Input
Vref
Vcc
Vcc
Feedback
Tri-State
Control
Data
Output
Typ. V ref = 3.2V
Active Pull-up
Circuit
Vcc
Vref
Feedback
(To Input Buffer)
T ypical Output
PIN
PIN
17

GAL20V8C: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Specifications GAL20V8
Normalized Tpd vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tpd vs Temp
1.3
-55
-25
PT H->L
PT L->H
0
25
50
75
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
0.7
Temperature (deg. C)
PT H->L
PT L->H
100
125
Normalized Tco vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tco vs Temp
1.3
-25
RISE
FALL
0
25
50
75
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
0.7
-55
Temperature (deg. C)
RISE
FALL
100
125
Normalized Tsu vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
PT H->L
PT L->H
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tsu vs Temp
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
0.7
-55
-25
PT H->L
PT L->H
0
25
50
75
Temperature (deg. C)
100
125
Delta Tpd vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.25
-0.5
-0.75
Delta Tpd (ns)
-1
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tpd vs Output Loading
8
6
4
2
Delta Tpd (ns)
0
-2
0 5 0 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
Delta Tco vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.25
-0.5
-0.75
Delta Tco (ns)
-1
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tco vs Output Loading
8
6
4
2
Delta Tco (ns)
0
-2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
18

Vol vs Iol
Iol (mA)
Vol (V)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00
Voh vs Ioh
Ioh(mA)
Voh (V)
0
1
2
3
4
5
0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00
Voh vs Ioh
Ioh(mA)
Voh (V)
3.25
3.5
3.75
4
4.25
0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00
Normalized Icc vs Vcc
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Icc
0.80
0.90
1.00
1.10
1.20
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Normalized Icc vs Temp
Temperature (deg. C)
Normalized Icc
0.8
0.9
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
-55 -25 0 2 5 50 75 100 1 25
Normalized Icc vs Freq.
Frequency (MHz)
Normalized Icc
0.80
0.90
1.00
1.10
1.20
1.30
1.40
1.50
0 2 5 50 75 100
Delta Icc vs Vin (1 input)
Vin (V)
Delta Icc (mA)
0
2
4
6
8
10
0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00
Input Clamp (Vik)
Vik (V)
Iik (mA)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
-2.00 -1.50 -1.00 -0.50 0.00
GAL20V8C: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Specifications GAL20V8
19

Specifications GAL20V8
GAL20V8B-7/-10: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Normalized Tpd vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tpd vs Temp
1.3
-55
-25
PT H->L
PT L->H
0
25
50
75
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
0.7
Temperature (deg. C)
PT H->L
PT L->H
100
125
Normalized Tco vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tco vs Temp
1.3
-55
-25
RISE
FALL
0
25
50
75
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
0.7
Temperature (deg. C)
RISE
FALL
100
125
Normalized Tsu vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
PT H->L
PT L->H
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tsu vs Temp
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
0.7
-55
-25
PT H->L
PT L->H
0
25
50
75
Temperature (deg. C)
100
125
Delta Tpd vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
Delta Tpd (ns)
-2
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tpd vs Output Loading
10
8
6
4
2
Delta Tpd (ns)
0
-2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
Delta Tco vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
Delta Tco (ns)
-2
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tco vs Output Loading
10
8
6
4
2
Delta Tco (ns)
0
-2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
20

Specifications GAL20V8
GAL20V8B-7/-10: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Vol vs Iol
1
0.75
0.5
Vol (V)
0.25
0
0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00
Iol (mA)
Normalized Icc vs Vcc
1.20
1.10
1.00
0.90
Normalized Icc
0.80
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Voh vs Ioh
5
4
3
2
Voh (V)
1
0
0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 60.00
Ioh(mA)
Normalized Icc vs Temp
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Icc
0.8
-55 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (deg. C)
Voh vs Ioh
4.5
4.25
4
Voh (V)
3.75
3.5
0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00
Ioh(mA)
Normalized Icc vs Freq.
1.30
1.20
1.10
1.00
0.90
Normalized Icc
0.80
0 2 5 50 75 100
Frequency (MHz)
Delta Icc vs Vin (1 input)
10
8
6
4
Delta Icc (mA)
2
0
0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00
Vin (V)
Input Clamp (Vik)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Iik (mA)
70
80
90
100
-2.00 -1.50 -1.00 -0.50 0.00
Vik (V)
21

Specifications GAL20V8
GAL20V8B-15/-25: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Normalized Tpd vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tpd vs Temp
1.3
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tpd
0.8
0.7
-55 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
PT H->L
PT L->H
Temperature (deg. C)
PT H->L
PT L->H
Normalized Tco vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tco vs Temp
1.3
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tco
0.8
0.7
-55 -25 0 25 5 0 75 100 125
RISE
FALL
Temperature (deg. C)
RISE
FALL
Normalized Tsu vs Vcc
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
PT H->L
PT L->H
Supply Voltage (V)
Normalized Tsu vs Temp
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Tsu
0.8
0.7
-55 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
PT H->L
PT L->H
Temperature (deg. C)
Delta Tpd vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
Delta Tpd (ns)
-2
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tpd vs Output Loading
10
8
6
4
2
0
Delta Tpd (ns)
-2
-4
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
Delta Tco vs # of Outputs
Switching
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
Delta Tco (ns)
-2
12345678
Number of Outputs Switching
Delta Tco vs Output Loading
10
8
6
4
2
0
Delta Tco (ns)
-2
-4
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
RISE
FALL
Output Loading (pF)
RISE
FALL
22

Specifications GAL20V8
GAL20V8B-15/-25: Typical AC and DC Characteristic Diagrams
Vol vs Iol
2
1.5
1
Vol (V)
0.5
0
0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00
Iol (mA)
Normalized Icc vs Vcc
1.20
1.10
1.00
0.90
Normalized Icc
0.80
4.50 4.75 5.00 5.25 5.50
Supply Voltage (V)
Voh vs Ioh
5
4
3
2
Voh (V)
1
0
0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 60.00
Ioh(mA)
Normalized Icc vs Temp
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
Normalized Icc
0.8
-55 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (deg. C)
Voh vs Ioh
4.25
4
3.75
Voh (V)
3.5
3.25
0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00
Ioh(mA)
Normalized Icc vs Freq.
1.40
1.30
1.20
1.10
1.00
Normalized Icc
0.90
0.80
0 2 5 50 75 100
Frequency (MHz)
Delta Icc vs Vin (1 input)
12
10
8
6
4
Delta Icc (mA)
2
0
0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00
Vin (V)
Input Clamp (Vik)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Iik (mA)
70
80
90
100
-2.00 -1.50 -1.00 -0.50 0.00
Vik (V)
23
 Loading...
Loading...