Page 1

xSenso
User Guide
xSenso 2100
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21R2
Part Number 900-629-R
Revision B March 2013
Page 2

Copyright & Trademark
© 2013 Lantronix, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be transmitted
or reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of Lantronix.
Lantronix® is a registered trademark and DeviceInstaller and xSenso are trademarks of
Lantronix, Inc.
Windows® and Internet Explorer® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Mozilla®
and Firefox® are registered trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation. Chrome™ is a trademark of
Google. Opera™ is a trademark of Opera Software ASA. Tera Termâ is a registered trademark of
Vector, Inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the property of their respective holders.
Warranty
For details on the Lantronix warranty policy, please go to our web site at
www.lantronix.com/support/warranty
Contacts
.
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
167 Technology Drive
Irvine, CA 92618, USA
Toll Free: 800-526-8766
Phone: 949-453-3990
Fax: 949-450-7249
Technical Support
Online: www.lantronix.com/support
Sales Offices
For a current list of our domestic and international sales offices, go to the Lantronix web site at
www.lantronix.com/about/contact
Disclaimer
The information in this guide may change without notice. The manufacturer assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this guide.
Revision History
Date Rev. Comments
July 2012 A Initial document for firmware release 7.4.0.0.
March 2013 B Updated for firmware release 7.6.0.0R10 and added xSenso 21A2 and
.
xSenso 21R2.
xSenso User Guide 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Copyright & Trademark ______________________________________________________2
Warranty _________________________________________________________________2
Contacts _________________________________________________________________2
Disclaimer ________________________________________________________________2
Revision History ___________________________________________________________2
List of Figures ____________________________________________________________10
List of Tables _____________________________________________________________11
1: Using This Guide 13
Purpose and Audience _____________________________________________________13
Summary of Chapters ______________________________________________________13
Additional Documentation ___________________________________________________14
2: Introduction 15
Key Features _____________________________________________________________15
Applications ______________________________________________________________16
Sample Applications ____________________________________________________16
Protocol Support _________________________________________________________17
Troubleshooting Capabilities _________________________________________________18
Configuration Methods _____________________________________________________18
Configuration Using the MGMT (USB) Port __________________________________18
xSenso Wiring Example ____________________________________________________19
Addresses and Port Numbers ________________________________________________20
Hardware Address _________________________________ ____________________20
IP Address ___________________________________________________________20
Port Numbers _________________________________________________________20
Product Information Label ___________________________________________________20
3: Installation of xSenso 22
Package Contents _________________________________________________________22
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________22
xSenso 2100 Isolation Block Diagram _________________________________________23
Hardware Components _____________________________________________________23
Front/Top Panel _______________________________________________________23
Right Side Panel _______________________________________________________25
Back Panel ___________________________________________________________26
Installing the xSenso _______________________________________________________26
xSenso User Guide 3
Page 4

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2 28
Package Contents _________________________________________________________28
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________28
xSenso 21A2 Isolation Block Diagram _________________________________________29
Hardware Components _____________________________________________________29
Front/Top Panel _______________________________________________________29
Side Panels __________________________________________________________32
Back Panel ___________________________________________________________32
Installing the xSenso _______________________________________________________33
5: Installation of xSenso 21R2 34
Package Contents _________________________________________________________34
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________34
xSenso 21R2 Block Diagram ________________________________________________35
Hardware Components _____________________________________________________35
Front/Top Panel _______________________________________________________35
Side Panels __________________________________________________________38
Back Panel ___________________________________________________________38
Installing the xSenso _______________________________________________________39
6: Using DeviceInstaller 40
Accessing xSenso Using DeviceInstaller _______________________________________40
Device Detail Summary _____________________________________________________40
7: Configuration Using Web Manager 42
Accessing Web Manager ___________________________________________________42
xSenso Home and Device Status Pages ____________________________________45
Live Reading Pages and Configuration Pages ___________________________________46
Web Manager Components _________________________________________________47
Navigating Web Manager ___________________________________________________48
8: Network Settings 50
Network Interface Settings __________________________________________________50
To Configure Network Interface Settings ____________________________________51
To View Network Interface Status _________________________________________51
Network Link Settings __________________________________________________ ____52
To Configure Network Link Settings ________________________________________52
xSenso User Guide 4
Page 5

9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings 53
DAQ Format _____________________________________________________________53
To Configure DAQ Settings ______________________________________________54
Analog Input _____________________________________________________________55
To Configure Analog Settings _____________________________________________56
Analog Output ____________________________________________________________56
To Configure Analog Output Settings _______________________________________57
Relay Output _____________________________________________________________57
To Configure Relay Settings ______________________________________________58
10: Chart 59
Data Chart Configuration ___________________________________________________60
To Configure Data Chart Settings _________________________________________60
11: Logging 61
Data Logging Configuration _________________________________________________63
To Configure Data Logging Settings _______________________________________63
12: Reading 64
Data Reading Configuration _________________________________________________65
To View Data Reading Settings ___________________________________________65
13: Action Settings 66
Alarms and Reports _______________________________________________________66
Actions Available for Alarms and Reports _______________________________________66
To Configure Terminal Block Power Alarm Settings ____________________________71
To Configure Barrel Connector Power Alarm Settings __________________________71
To Configure Input 1 and 2 Alarm Settings __________________________________72
To Configure Status Reports 1 and 2 Settings ________________________________72
To Configure Output 1 and 2 Alarm Settings _________________________________72
14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings 73
Tunnel Settings ___________________________________________________________73
Accept Mode ________________________________________________ __________73
To Configure Tunnel Accept Mode Settings __________________________________74
Modbus Settings __________________________________________________________75
To Configure Modbus Settings ____________________________________________75
Supported Modbus TCP/IP Functions and Registers ___________________________75
xSenso User Guide 5
Page 6

15: Services Settings 77
DNS Settings _____________________________________________________________77
To View or Configure DNS Settings: _______________________________________77
FTP Settings _____________________________________________________________78
To Configure FTP Settings _______________________________________________78
Syslog Settings ___________________________________________________________78
To View or Configure Syslog Settings: ______________________________________79
HTTP Settings ________________________________ ____________________________79
To Configure HTTP Settings ___________________________________ __________80
To Configure HTTP Authentication _________________________________________81
RSS Settings _____________________________________________________________81
To Configure RSS Settings ______________________________________________82
SNMP Settings ___________________________________________________________82
To Configure SNMP Settings _____________________________________________83
SMTP Settings ___________________________________________________________83
To Configure SMTP Network Stack Settings _________________________________84
16: Security Settings 85
SSH Settings _____________________________________________________________85
SSH Server Host Keys __________________________________________________ 85
SSH Client Known Hosts ________________________________________________86
SSH Server Authorized Users ____________________________________________86
SSH Client Users ______________________________________________________87
To Configure SSH Settings ______________________________________________88
SSL Settings _____________________________________________________________88
Certificate and Key Generation ___________________________________________89
To Create a New Credential ______________________________________________89
Certificate Upload Settings _______________________________________________90
To Configure an Existing SSL Credential ____________________________________90
Trusted Authorities _____________________________________________________91
To Upload an Authority Certificate _________________________________________91
17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings 92
Filesystem Settings ________________________________________________________92
File Display ___________________________________________________________ 92
To Display Files _______________________________________________________92
File Modification _______________________________________________________93
File Transfer __________________________________________________________93
To Transfer or Modify Filesystem Files ______________________________________94
Protocol Stack Settings _____________________________________________________94
IP Settings ___________________________________________________________94
To Configure IP Network Stack Settings ____________________________________94
xSenso User Guide 6
Page 7

ICMP Settings _________________________________________________________95
To Configure ICMP Network Stack Settings __________________________________95
ARP Settings _________________________________________________________95
To Configure ARP Network Stack Settings __________________________________95
SMTP Settings ________________________________________________________96
To Configure ARP Network Stack Settings __________________________________96
Diagnostics ______________________________________________________________96
Hardware ____________________________________________________________96
To View Hardware Information ____________________________________________96
IP Sockets ___________________________________________________________97
To View the List of IP Sockets ____________________________________________97
Ping ________________________________________________________________97
To Ping a Remote Host _________________________________________________97
Traceroute ___________________________________________________________98
To Perform a Traceroute ________________________________________________98
Log _________________________________________________________________98
To Configure the Diagnostic Log Output ____________________________________98
Memory ______________________________________________________________ 99
To View Memory Usage _________________________________________________99
Processes ____________________________________________________________ 99
To View Process Information _____________________________________________99
Threads ________________________________________________________________ 100
To View Thread Information _____________________________________________100
Clock __________________________________________________________________100
To Configure the Clock _________________________________________________101
System Settings _________________________________________________________101
To Reboot or Restore Factory Defaults ___________________ _________________101
Discovery and Query Port __________________________________________________102
To Configure Discovery ________________________________________________102
18: Advanced Settings 103
Email Settings ___________________________________________________________103
To View, Configure and Send Email _______________________________________103
Command Line Interface Settings ____________________________________________104
Basic CLI Settings ____________________________________________________104
To View and Configure Basic CLI Settings __________________________________104
Telnet Settings ____________________________________________________ ___105
To Configure Telnet Settings ____________________________________________105
SSH Settings ________________________________________________________105
To Configure SSH Settings _____________________________________________106
XML Settings ____________________________________________________________106
XML: Export Configuration ______________________________________________106
To Export Configuration in XML Format ____________________________________107
xSenso User Guide 7
Page 8

XML: Export Status ____________________________________________________107
To Export in XML Format _______________________________________________107
XML: Import Configuration ______________________________________________108
Import Configuration from External File ____________________________________108
Import Configuration from the Filesystem ___________________________________108
To Import Configuration in XML Format ____________________________________108
19: Security in Detail 109
Public Key Infrastructure ___________________________________________________109
TLS (SSL) ______________________________________________________________109
Digital Certificates ________________________________________________________109
Trusted Authorities _________________________________________ ______________109
Obtaining Certificates _____________________________________________________110
Self-Signed Certificates ____________________________________________________110
Certificate Formats _______________________________________________________110
OpenSSL _______________________________________________________________ 110
Steel Belted RADIUS _____________________________________________________111
Free RADIUS ___________________________________________________________111
20: Updating Firmware 112
Obtaining Firmware _______________________________________________________112
Loading New Firmware through Web Manager _________________________________ 112
To upload new firmware: ___________________________________ ___________112
Loading New Firmware through FTP _________________________________________113
21: Branding the xSenso 114
Web Manager Customization _______________________________________________114
Short and Long Name Customization ______________________ ___________________115
To Customize Short or Long Names ______________________________________115
xSenso User Guide 8
Page 9

Appendix A: Technical Specifications 116
Analog Inputs ________________________________________________________ 116
Analog Outputs _______________________________________________________116
Relay Ports __________________________________________________________116
Architecture _________________________________________________________117
Network Interface _____________________________________________________117
Management _________________________________________________________ 117
Security _____________________________________________________________ 117
DAQ _______________________________________________________________118
Software ____________________________________________________________118
Power* _____________________________________________________________118
Environmental ________________________________________________________ 118
Physical Characteristics ________________________________________________118
Appendix B: Technical Support 119
Appendix C: Binary to Hexadecimal Conversions 120
Converting Binary to Hexadecimal ___________________________________________120
Conversion Table _____________________________________________________120
Scientific Calculator ___________________________________________________120
Appendix D: Compliance 122
Appendix E: USB-CDC-ACM Device Driver File
for Windows Hosts 124
xSenso User Guide 9
Page 10

List of Figures
Figure 2-1 Sample xSenso Configuration______________________________________________16
Figure 2-2 Sample Applications _____________________________________________________17
Figure 2-3 xSenso Wiring Diagram___________________________________________________19
Figure 2-4 xSenso Product Label ____________________________________________________21
Figure 3-1 xSenso 2100 Isolation Block Diagram________________________________________23
Figure 3-2 xSenso , Front View______________________________________________________23
Figure 3-3 xSenso Top/Front View __________________________________________________24
Figure 3-6 xSenso, Side View_______________________________________________________26
Figure 3-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View ___________________________________________26
Figure 4-1 xSenso 21A2 Isolation Block Diagram________________________________________29
Figure 4-2 xSenso 21A2, Front View _________________________________________________30
Figure 4-3 xSenso 21A2 Top/Front View ______________________________________________30
Figure 4-6 xSenso, Side Views______________________________________________________32
Figure 4-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View ___________________________________________33
Figure 5-1 xSenso 21R2 Isolation Block Diagram _______________________________________35
Figure 5-2 xSenso 21R2, Front View _________________________________________________36
Figure 5-3 xSenso 21R2 Top/Front View ______________________________________________36
Figure 5-6 xSenso, Side Views______________________________________________________38
Figure 5-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View ___________________________________________39
Figure 7-1 xSenso Home Pages_____________________________________________________43
Figure 7-2 Device Status Pages_____________________________________________________ 44
Figure 7-4 Live Reading vs. Configuration Pages________________________________________46
Figure 7-5 Components of the Web Manager Page______________________________________47
Figure 9-1 Analog Inputs 1 and 2 for xSenso ___________________________________________ 53
Figure 10-1 Charting Options in the Chart Tab by xSenso Model ___________________________59
Figure 11-1 xSenso 2100 Logging Tab________________________________________________61
Figure 11-2 xSenso 21A2 Logging Tab _____________________________________________ __62
Figure 11-3 xSenso 21R2 Logging Tab _______________________________________________62
Figure 12-1 xSenso 2100 Reading Tab _______________________________________________64
Figure 12-2 xSenso 21A2 Reading Tab _______________________________________________65
Figure 12-3 xSenso 21R2 Reading Tab _______________________________________________65
Figure 20-1 Uploading New Firmware _______________________________________________112
xSenso User Guide 10
Page 11

List of Tables
Table 3-4 Analog Input LEDs _______________________________________________________24
Table 3-5 Ethernet LEDs __________________________________________________________25
Table 4-4 Analog Input and Analog Output LEDs _______________________________________31
Table 4-5 Ethernet LEDs __________________________________________________________31
Table 5-4 Analog Input and Relay Output LEDs ________________________________________37
Table 5-5 Ethernet LEDs __________________________________________________________37
Table 7-3 Comparing xSenso Home Page and Device Status Page Information _______________45
Table 8-1 Network Interface Settings _________________________________________________50
Table 8-2 Network 1 (eth0) Link Settings ______________________________________________52
Table 9-2 xSenso DAQ Command ___________________________________________________53
Table 9-3 DAQ Settings ___________________________________________________________54
Table 9-4 Analog Input Settings _____________________________________________________55
Table 9-5 Analog Output Settings ___________________________________________________56
Table 9-6 Relay Output Settings ____________________________________________________57
Table 10-2 Data Chart Settings _____________________________________________________60
Table 11-4 Data Logging Settings ___________________________________________________63
Table 13-1 xSenso Alarms and Reports ______________________________________________66
Table 13-2 Control Analog Output Settings __________________________________ __________66
Table 13-3 Make Connection Settings ________________________________________________67
Table 13-4 Send Email Settings _____________________________________________________68
Table 13-5 FTP Put Settings _______________________________________________________69
Table 13-6 HTTP Post Settings _____________________________________________________70
Table 13-7 Control Relay Settings ___________________________________________________70
Table 13-8 SNMP Trap Settings ____________________________________________________71
Table 14-1 Tunnel Accept Mode Settings ___________________________ __________________73
Table 14-2 Modbus Settings _______________________________________________________75
Table 14-3 0xxxx Read/Write Coils (Function Codes 1, 5 and 15) __________________________75
Table 14-4 3xxxx Read Only Registers (Function Codes 4 and 23) _____________________ ____76
Table 14-5 4xxxx Read/Write Holding Registers (Function Codes 3, 16 and 23) _______________76
Table 15-1 DNS Settings __________________________________________________________77
Table 15-2 FTP Settings __________________________________________________________78
Table 15-3 Syslog Settings ________________________________________________________78
Table 15-4 HTTP Settings _________________________________________________________79
Table 15-5 HTTP Authentication Settings _____________________________________________81
Table 15-6 RSS Settings __________________________________________________________81
Table 15-7 SNMP Settings _________________________________________________________82
xSenso User Guide 11
Page 12

Table 15-8 SMTP Network Stack Settings _____________________________________________83
Table 16-1 SSH Server Host Keys ___________________________________________________85
Table 16-2 SSH Client Known Hosts _________________________________________________86
Table 16-3 SSH Server Authorized Users _____________________________________________87
Table 16-4 SSH Client Users _______________________________________________________87
Table 16-5 Certificate and Key Generation Settings _____________________________________89
Table 16-6 Upload Certificate Settings _______________________________________________90
Table 16-7 Trusted Authority Settings ________________________________________________91
Table 17-1 File Display Settings ____________________________________________________92
Table 17-2 File Modification Settings _________________________________________________93
Table 17-3 File Transfer Settings ____________________________________________________93
Table 17-4 IP Network Stack Settings ________________________________________________94
Table 17-5 ICMP Network Stack Settings _____________________________________________95
Table 17-6 ARP Network Stack Settings ______________________________________________95
Table 17-7 SMTP Settings _________________________________________________________96
Table 17-8 Ping Settings __________________________________________________________97
Table 17-9 Traceroute Settings _____________________________________________________98
Table 17-10 Log Settings __________________________________________________________98
Table 17-11 Clock Settings _______________________________________________________100
Table 17-12 System Settings ______________________________________________________101
Table 17-13 Discovery Settings _________ ___________________________________________102
Table 18-1 Email Configuration ____________________________________________________103
Table 18-2 CLI Configuration Settings _______________________________________________104
Table 18-3 Telnet Settings _______________________________________________________105
Table 18-4 SSH Settings _________________________________________________________105
Table 18-5 XML Exporting Configuration _____________________________________________106
Table 18-6 Exporting Status _______________________________________________________107
Table 18-7 Import Configuration from Filesystem Settings _______________________________108
Table 21-1 Short and Long Name Settings ___________________________________________115
xSenso User Guide 12
Page 13
1: Using This Guide
Purpose and Audience
This guide provides the information needed to configure, use, and update the xSenso. It is
intended for software developers and system integrators who are installing this product into their
designs.
Summary of Chapters
The remaining chapters in this guide include:
Chapter Description
2: Introduction Main features of the product and the protocols it supports.
3: Installation of xSenso Instructions for installing the xSenso 2100.
4: Installation of xSenso 21A2 Instructions for installing the xSenso 21A2.
5: Installation of xSenso 21R2 Instructions for installing the xSenso 21R2.
6: Using DeviceInstaller Instructions for viewing the current configuration using
7: Configuration Using Web Manager Instructions for accessing Web Manager and using it to configure
8: Network Settings Instructions for configuring network settings.
9: Analog Input, Output and Relay
Settings
10: Chart Instructions for viewing and configuring live analog chart data on
11: Logging Instructions for running and configuring live data logs on the
12: Reading Instructions for reading live analog data on the Reading page.
13: Action Settings Instructions for configuring action for reports and alarms settings.
14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings Instructions for configuring modbus and tunnel settings.
15: Services Settings Instructions for configuring DNS, FTP, HTTP and Syslog settings.
16: Security Settings Instructions for configuring SSL security settings.
17: Maintenance and Diagnostics
Settings
18: Advanced Settings Instructions for configuring email, CLI and XML settings.
19: Security in Detail Provides additional information on security settings available.
20: Updating Firmware Instructions for obtaining the latest firmware and updating the .
21: Branding the xSenso Instructions on how to brand your device.
Appendix A: Technical Specifications Technical specifications for the device.
Appendix B: Technical Support Instructions for contacting Lantronix Technical Support.
Includes technical specifications.
DeviceInstaller.
settings for the device.
Instructions for configuring analog and relay settings.
the Chart page.
Logging page.
Instructions to maintain the , view statistics, files, and diagnose
problems.
xSenso User Guide 13
Page 14

Chapter (continued) Description
Appendix C: Binary to Hexadecimal
Conversions
Appendix D: Compliance Lantronix compliance information.
Appendix E: USB-CDC-ACM Device
Driver File for Windows Hosts
Additional Documentation
Visit the Lantronix Web site at www.lantronix.com/support/documentation for the latest
documentation and the following additional documentation.
Document Description
xSenso Command Reference Instructions for accessing Command Mode (the command line
xSenso Quick Start Guide Instructions for getting the xSenso up and running.
1: Using This Guide
Instructions for converting binary values to hexadecimals.
Information about the device driver file for windows host.
interface) using a Telnet connection, SSH connection or through the
USB port. Detailed information about the commands. Also provides
details for XML configuration and status.
DeviceInstaller Online Help Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to locate the
xSenso and to view its current settings.
xSenso User Guide 14
Page 15

2: Introduction
xSenso is a compact DIN-rail or wall mount solution that enables sensors with analog outputs
(voltage or current) to easily and transparently send real-time data to any node on the network or
over the Internet. xSenso is an ideal solution for remote monitoring and data logging of critical
events in process control and automation applications. With its low port density, xSenso can be
affordably installed in dispersed locations. In applications where analog sensors and controllers
are used, xSenso can be configured to send alarms via emails or text messages when readings
are outside predefined ranges. These alarms allow control engineers to take immediate corrective
action when certain thresholds are met. Its embed ded web server makes it p ossible to monitor the
input readings, chart or log the data using browsers on computers, smartphones, and tablets fr om
anywhere in the world.
There are three Lantronix xSenso device servers:
xSenso 2100 with two analog inputs (part number XSO210000-01-S)
xSenso 21A2 with two analog inputs and two analog output (part number XSO21A200-01-S)
xSenso 21R2 with two analog inputs and two relay outputs (part number XSO21R200-01-S)
Key Features
Power Supply: 9-30 VDC input voltage (1 terminal screw block and 1 locking barrel jack,
where when both are used, may operate as red unda n cy an d fa ilover)
Ethernet: 1 Port Ethernet 10Base-T or 100Base-TX (auto-sensing for speed, duplex and
cross-over CAT5 cable)
Analog Inputs (All Models): 2 configurable analog inputs with available ranges: ±100mV,
±1V, ±10V or ±20mA
Analog Outputs (xSenso 21A2): 2 configurable isolated analog outputs with available ranges:
0-10V, 0-20mA
Relay Outputs (xSenso 21R2): 2 independently isolated mechanical form-C relays
Wireless:USB Ports: One 2.0 full speed USB port for device management and configuration
Temperature Range: Storage and operating temperature between -40° to +85°C
Note: UL-certified operating temperature is -40° to +7 5° C
xSenso User Guide 15
Page 16
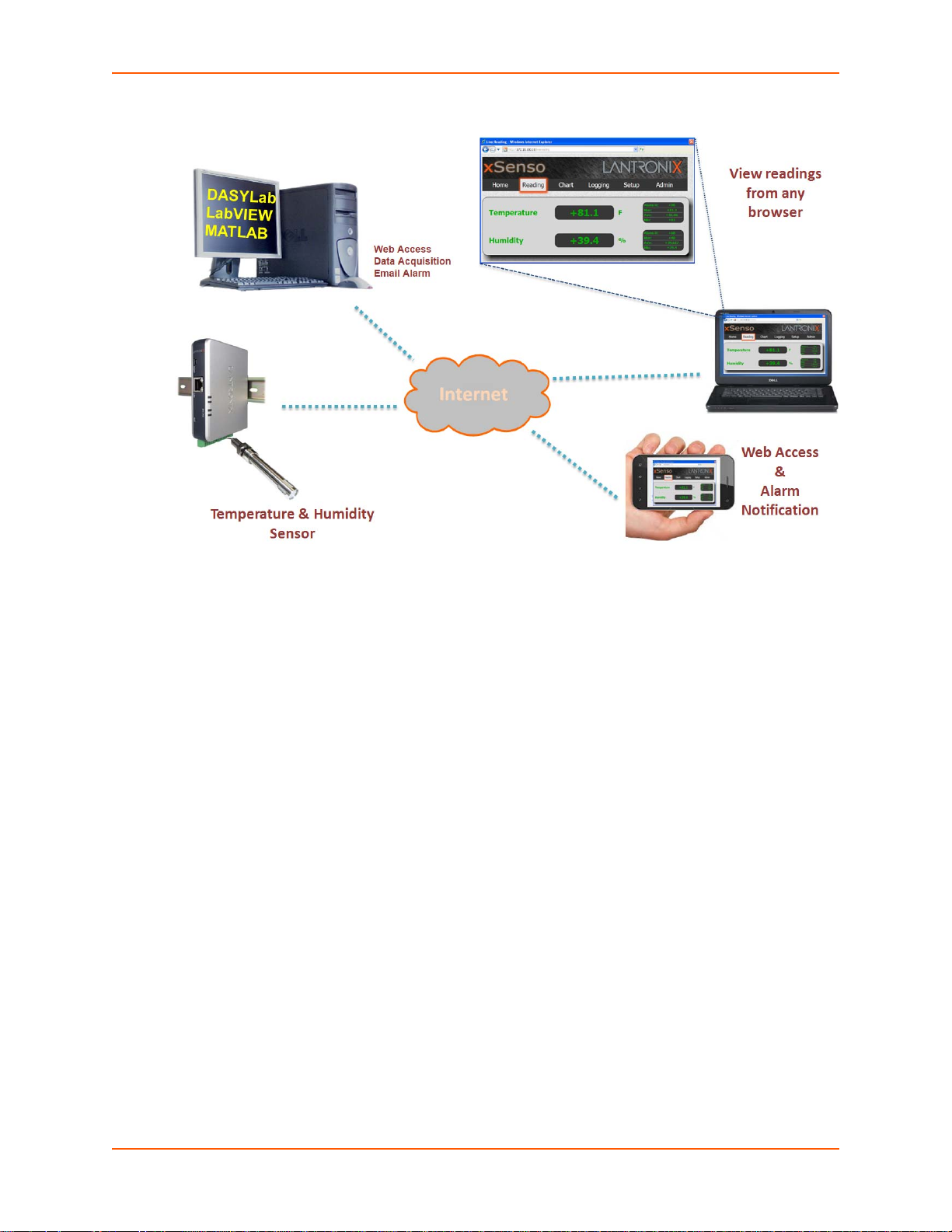
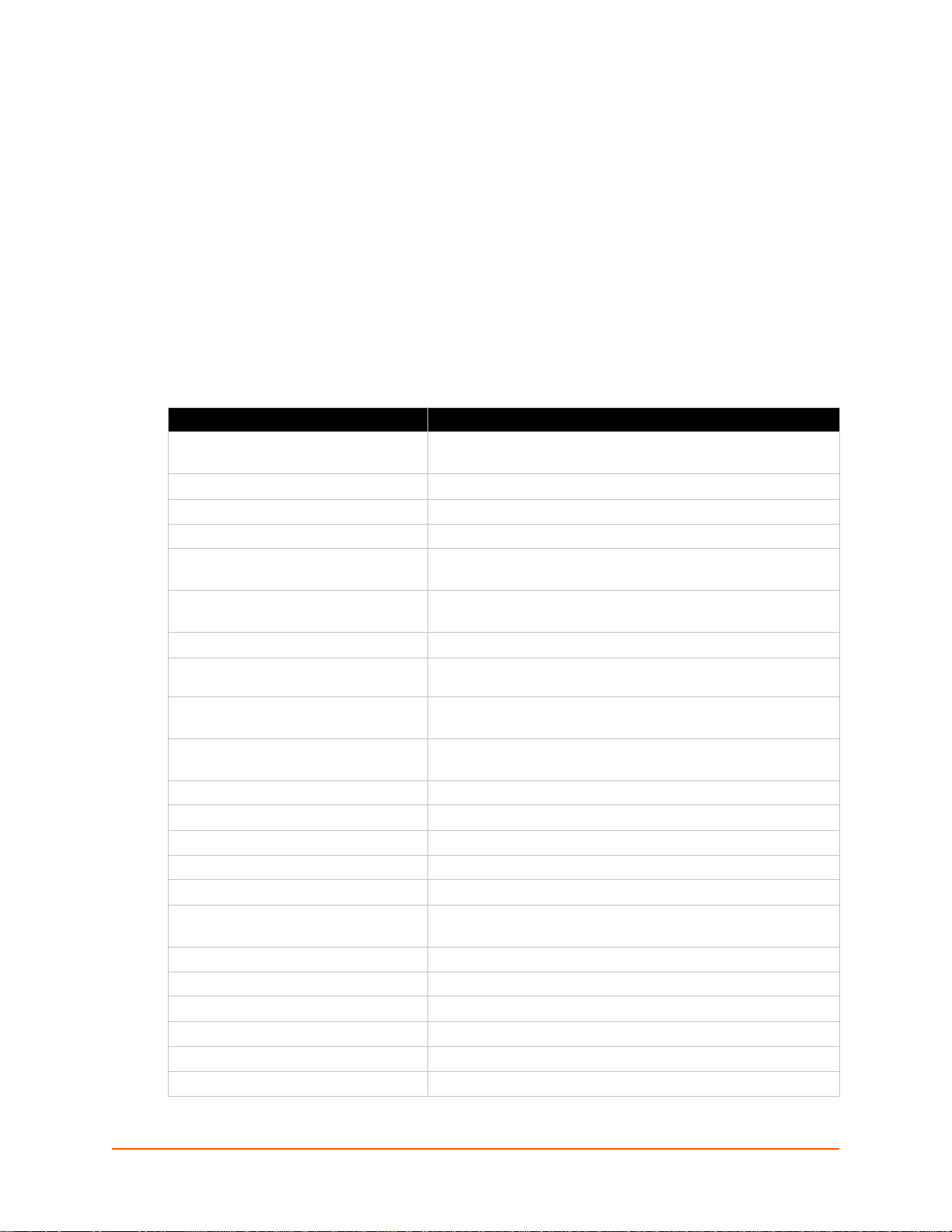
Figure 2-1 Sample xSenso Configuration
2: Introduction
Figure 2-1 is an example of how the xSenso can send sensor data (e.g., temperature a nd humidity
readings), over shared networks or the internet to a PC, laptop, or a smart phone. Third party data
acquisition applications (e.g., DASYLab, LabVIEW or MATLAB) can also be interfaced with the
xSenso to read and log the sensor’s data.
Applications
The xSenso device server connects analog sensors such as those listed below to Ethernet
networks using the IP protocol family.
Temperature Gauge
Environmental Data Sensors
Gas Monitoring Devices
Sensors measuring humidity, pressure, flow, level, force, weight and gas or air quality
Sample Applications
Figure 2-2 below demonstrates three sample xSenso applications:
1. A simple process control example consists of an analog pressure sensor on the input and an
analog valve on the output.
2. Using xSenso 21A2 between the sensor and input of the controller would allow users to
extract data right over the xSenso ethernet port. In this case, the xSenso can be configured to
output the analog signals exactly as receives it on the analog input.
3. The xSenso 21A2 can actually replace the L egacy controller and control the process the exact
way it used to be done.
xSenso User Guide 16
Page 17
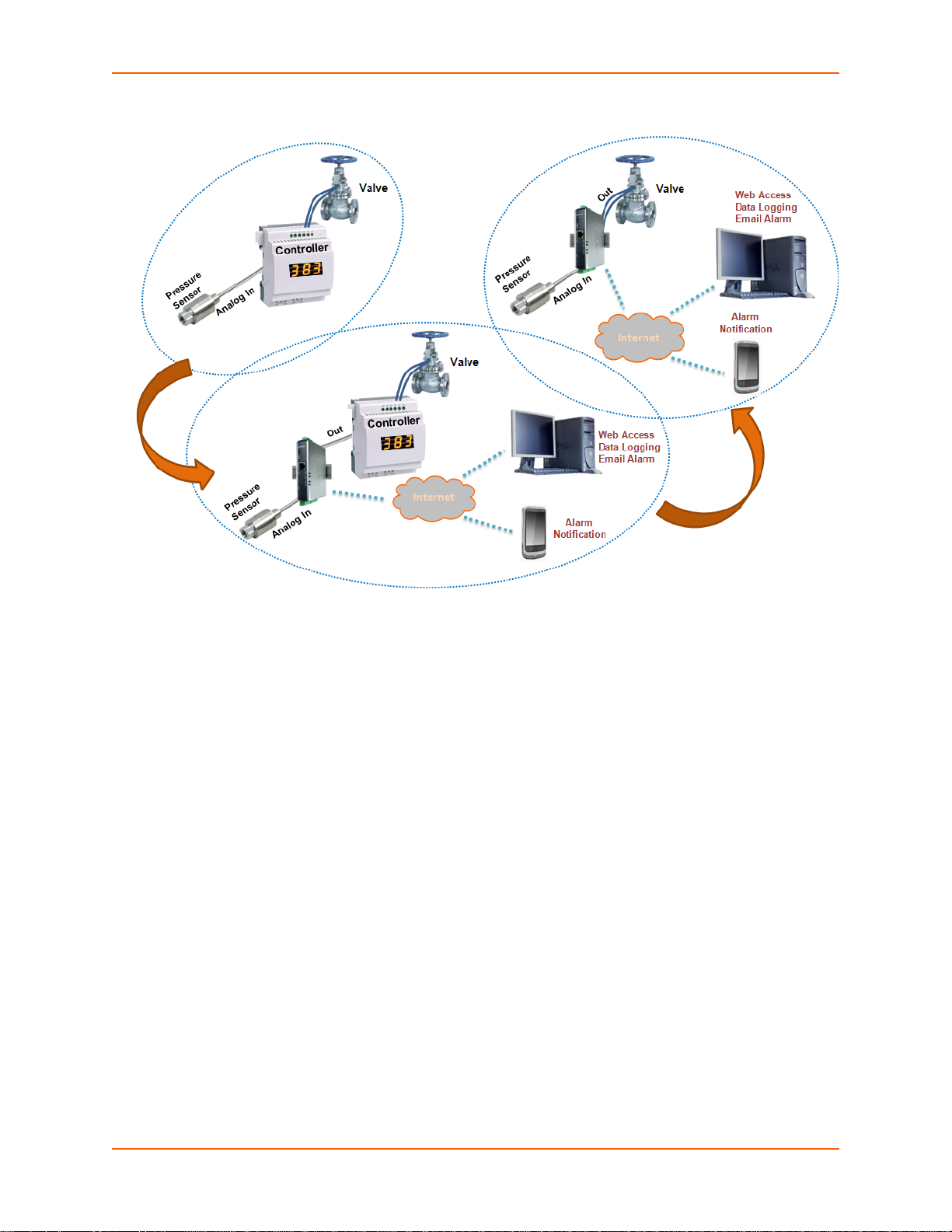
Figure 2-2 Sample Applications
2
1
3
2: Introduction
Note: See Sample Applications on page 16 for an explanation of Figure 2-2.
Protocol Support
The xSenso device server contains a full-featured IP stack. Supported protocols include:
ARP, HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP AUTH, SNMP v1/v2c/v3, Modbus TCP, UDP/IP, TCP/IP, SSH,
SSL, TLS, RSS, UPnP, ICMP, BOOTP, DHCP, Auto IP, Telnet, SNTP, FTP, FTPS, DNS,
TFTP, XML and Syslog for network communications and management.
TFTP for uploading/downloading files.
FTP and HTTP/HTTPS web server for firmware upgrades and uploading/downloading files.
TCP/IP, UDP/IP, Telnet, SSH, SSL, TCP AES and UDP AES for command/response based
data acquisition application or alarm triggered connection
HTTP/HTTPS web based monitoring of input readings, chart and data logging
SMTP AUTH, HTTP/HTTPS Post, FTP/FTPS Put and SNMP Traps for alarm triggered
notification
SNTP for device clock synchronization
xSenso User Guide 17
Page 18

Troubleshooting Capabilities
The xSenso offers a comprehensive diagnostic toolset that lets you troubleshoot problems quickly
and easily. Available from the CLI or Web Manager, the diagnostic tools let you:
View memory and IP socket information.
Perform ping and traceroute operations.
Conduct forward or reverse DNS lookup operations.
View all processes currently running on the xSenso, including CPU utilization.
View system log messages.
Configuration Methods
After installation, the xSenso requires configuration. For the unit to operate correctly on a network,
it must have a unique IP address on the network. There are four basic methods for logging into the
xSenso and assigning IP addresses and other configurable settings:
Web Manager: View and configure all settings easily through a web browser using the
Lantronix Web Manager. (See “Configuration Using Web Manager” on page 42.)
2: Introduction
DeviceInstaller: Configure the IP address and related settings and view current settings on
the xSenso using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) on a PC attached to a network. You will
need the latest version of DeviceInstaller. (See “Using DeviceInstaller” on page 40.)
Command Mode: There are two methods for accessing Command Mode (CLI): making a
Telnet or SSH connection, or connecting a PC or other host running a terminal emulation
program to the unit’s USB port. (See Configuration Using the MGMT (USB) Port below and the
xSenso Command Reference Guide for instructions and available commands.)
XML: The xSenso supports XML-based configuration and setup records that make device
configuration transparent to users and administrators. XML is easily editable with a standard
text or XML editor. (See the xSenso Command Reference Guide for instructions and
commands.)
Configuration Using the MGMT (USB) Port
In order to configure and manage the device, connect the computer via USB cable to the xSenso
MGMT port and run a terminal emulation program (e.g., Tera Term).
Note: Device connection will be lost upon reboot. Close the connection (also close
emulation program terminal if needed), unplug and plug in the USB port, and reopen the
connection.
1. Install the USB device driver, as necessary.
Connection to the MGMT port is via USB-CDC-ACM. This driver is available in Windows. In
order to enable Windows to recognize the USB- CDC-ACM connection to the L antronix device,
the driver installation file referenced below needs to be provided when prompted by the
Windows Device Driver Installation Wizard. For Windows 7 installation, it is recommended to
manually install the driver before plugging in the USB cable to the xSenso device port. This
can be done by installing a legacy driver for a COM port, with the Have Disk... option.
The device installation file (linux-cdc-acm.inf) may be accessed in one of two ways:
xSenso User Guide 18
Page 19
2: Introduction
a. DeviceInstaller installation directory (typically at c:\Program File\Lantronix\Device
Installer\4.3).
b. Follow the instructions inAppendix E: USB-CDC-ACM Device Driver File for Windows
Hosts to create the .inf file and follow the windows driver installation steps as outlined
above.
2. Connect the USB cable to the MGMT (USB) port of the xSenso device.
3. Connect the USB cable from the xSenso to the USB port on your computer.
4. Apply power. If drivers are installed, a virtual com port will be created on the computer.
5. Launch an emulation program terminal (e.g., Tera Term) and select the virtual com port.
6. Open up the virtual com port. The serial setting should be 9600, 8, none, and 1.
7. Click OK.
8. Press Enter in the terminal window. You will be prompted to login.
9. Login to the xSenso to configure it. The default login and password:
- User Name: admin
- Password: PASS
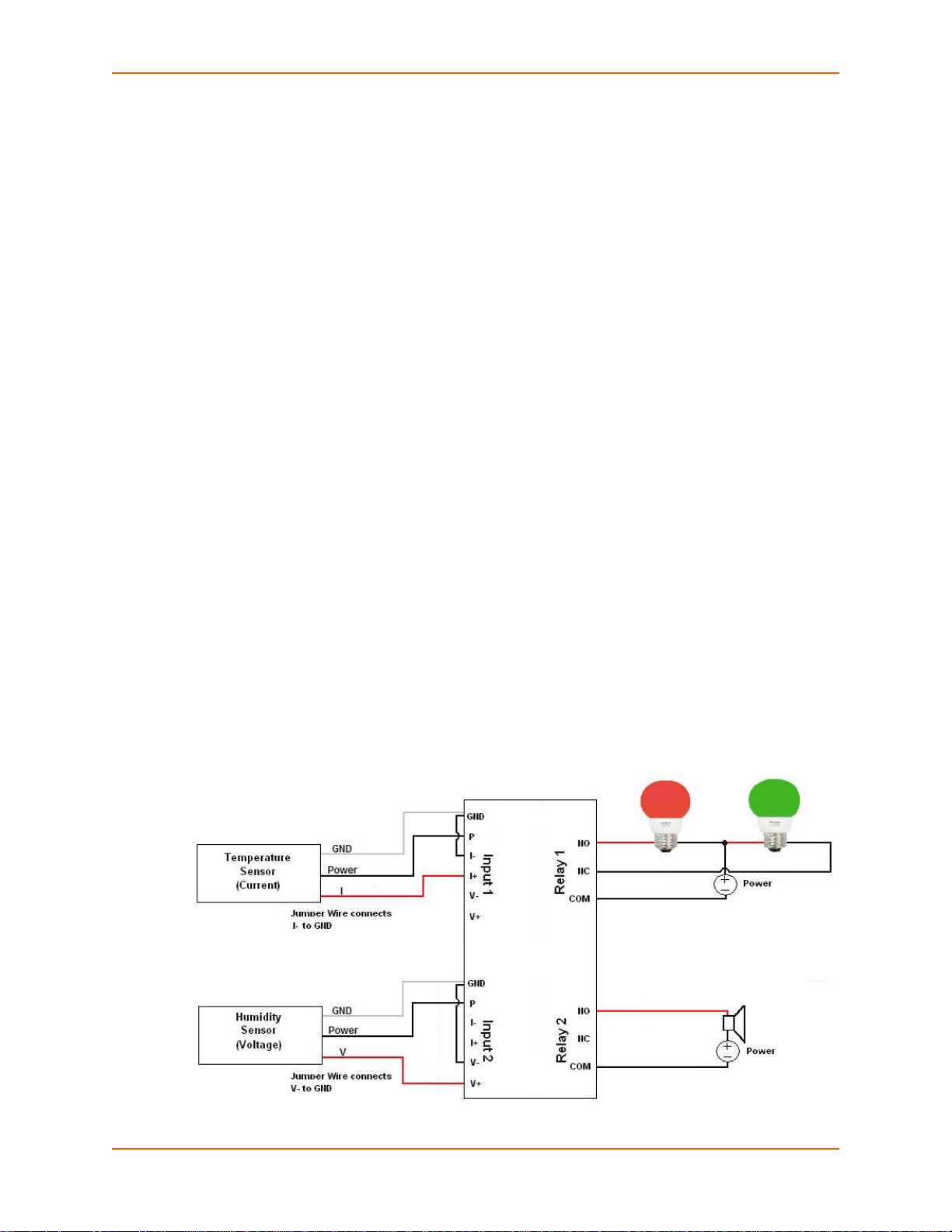
xSenso Wiring Example
In Figure 2-3 below, there are two sensors connected to the inputs of the xSenso. One is the
temperature sensor and the other is the humidity sensor. In this example, Relay 1 is associated
with the temperature sensor and Relay 2 with the hu midi ty sensor. In Relay 1, the Norma lly Open
(NO) pin allows the green light to stay on under normal operations. Once the Normally Closed
(NC) pin is activated, the green light will be turned off and the red light will be turned on indicating
an alarm condition. The threshhold ranges can be defined within the xSenso web interface. In
Relay 2, a buzzer is connected to Normally Open (NO) pin and once the alarm condition is met,
the relay will be closed and the buzzer will sound.
Figure 2-3 xSenso Wiring Diagram
xSenso User Guide 19
Page 20

Addresses and Port Numbers
Note: The hardware address on the
label is also the product serial number.
The hardware address on the label is the
address for the Ethernet (eth0) interface.
Hardware Address
The hardware address is also referred to as the Ethernet address, physical address, or MAC
address. Sample hardware address:
00---14-1B-18
00:::14:1B:18
IP Address
Every device connected to an IP network must have a unique IP add ress. This address references
the specific unit.
Port Numbers
Every TCP connection and every UDP datagram is defined by a destination and source IP
address, and a destination and source port nu mber. For example, a Telnet serv er commonly u ses
TCP port number 23.
The following is a list of the default server port numbers running on the xSenso:
2: Introduction
TCP Port 22: SSH Server (Command Mode configuration)
TCP Port 23: Telnet Server (Command Mode configuration)
TCP Port 80: HTTP (Web Manager configuration)
TCP Port 21: FTP
UDP Port 30718: LDP (Lantronix Discovery Protocol) port
TCP/UDP Port 10001: Tunnel 1 (see note below)
UDP Port 1900 and TCP Port 30179: UPnP
Note: Additional TCP/UDP ports and tunnels will be available, depending on the product
type. The default numbering of each additional TCP/UDP port and corresponding tunnel
will increase sequentially (i.e., TCP/UDP Port 1000X: Tunnel X).
Product Information Label
The product information label on the unit contains the
following information about the specific unit:
Bar code
Product Revision
Part Number
Serial Number (MAC Address)
Manufacturing Date Code
xSenso User Guide 20
Page 21

Figure 2-4 xSenso Product Label
Bar Code
Serial Number
Part Number
Country of Origin
& Manufacture
Revision
Manufacturing
Date Code
2: Introduction
xSenso User Guide 21
Page 22

3: Installation of xSenso
This chapter describes how to install the xSenso analog device server. It contains the following
sections:
Package Contents
User-Supplied Items
Hardware Components
Installing the xSenso
Package Contents
The xSenso package includes the following items:
One xSenso 2100 device
One 3-contact terminal block plug (screw type for power input port)
Two 6-contact terminal block plug (screw type for analog input ports)
Wall Mount Bracket
Four Rubber Feet
Quick Start Guide
User-Supplied Items
To complete your installation, you need the following items:
Analog devices and sensors that require network connectivity.
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working AC power outlet if the unit will be powered from an AC power adapter.
A 9-30VDC power supply either terminal screw or barrel input (both may be used
simultaneously for power redundancy)
xSenso User Guide 22
Page 23
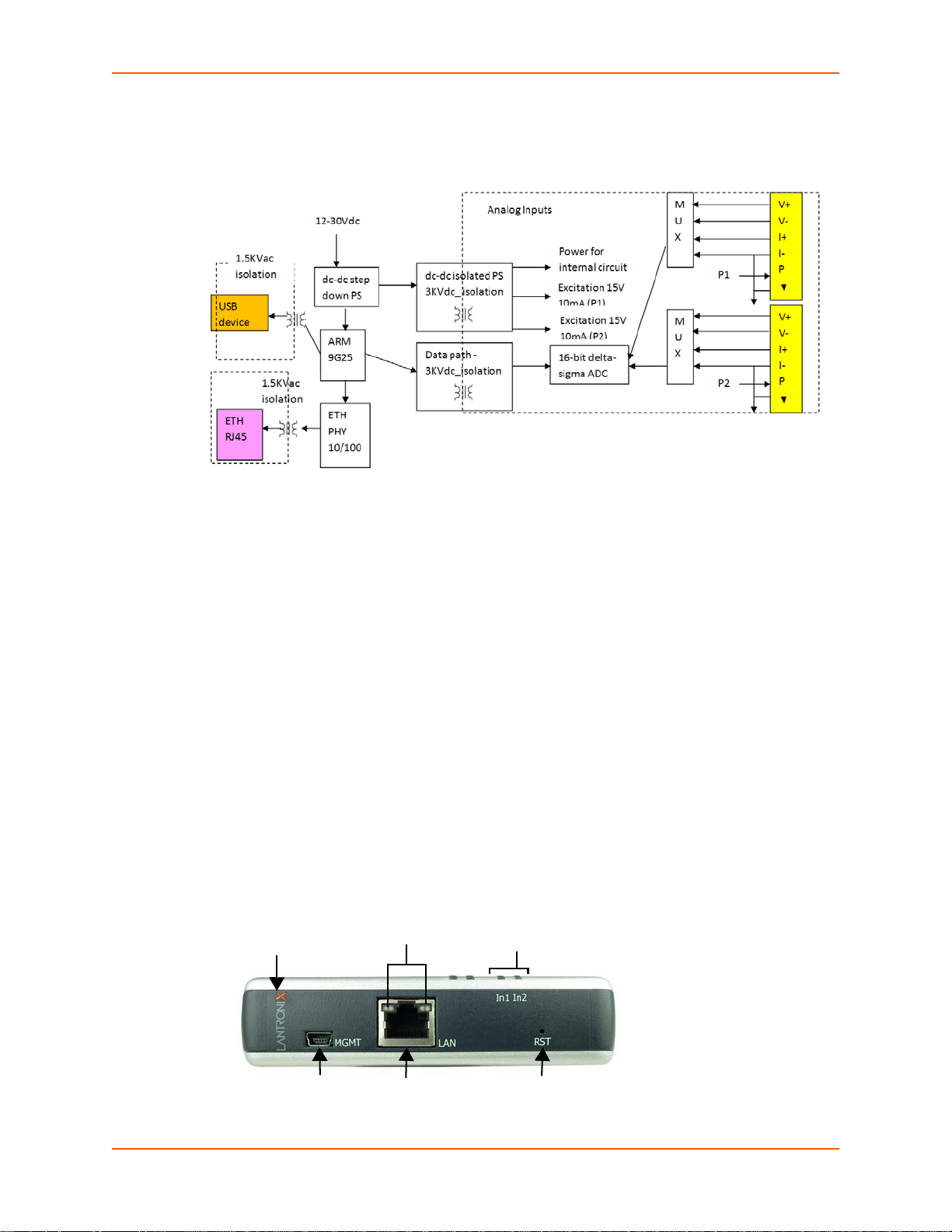
xSenso 2100 Isolation Block Diagram
Analog
Input LEDs
USB Ethernet Reset Button
Port Port (pin hole)
Ethernet LEDs
L R
Note: Though there appear
to be four analog input
LEDs located on the front
panel, only the two right
Input LEDs are supported in
xSenso .
Diagnostic
“X” LED
Figure 3-1 xSenso 2100 Isolation Block Diagram
3: Installation of xSenso
Hardware Components
Front/Top Panel
The following components are located on the front panel (Figure 3-2) of the xSenso :
USB Port - for managing and configuring xSenso device.
RJ-45 Ethernet Port (with Ethernet LEDs) - can connect to an Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast
Ethernet (100 Mbps) network.
RST Button (the Reset Button inside the pin hole) - power cycles and restores factory default
settings.
LED Indicators (2 Analog Input LEDs, 2 Ethernet LEDs, and 1 Diagnostic “X” LED)
- see Table 3-4 and Table 3-5.
LED Indicators
The Analog Input LEDs, the Ethernet LEDs, and the Diagnostic “X” LED are all located on the front
panel of the xSenso device (Figure 3-2).
Figure 3-2 xSenso , Front View
xSenso User Guide 23
Page 24

3: Installation of xSenso
Figure 3-3 xSenso Top/Front View
Table 3-4 and Table 3-5 below explain the LED information displayed in Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3
above.
Table 3-4 Analog Input LEDs
LED Color ON OFF
“X” on top of
xSenso device
(Diagnostic)
Analog Input 1 Green
Analog Input 2 Green
Orange ORANGE ON - power present
ORANGE Blink - during boot process after power cycle or
reset. Also blink patterns represent error conditions:
Loss of Redundant Power: one slow blink followed by
two fast blinks (repeat)
No Ethernet Link: two slow blinks followe d by two fast
blinks (repeat)
No IP Address: three slow blinks followed by three fast
blinks (repeat)
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
No power
Input not utilized
Input not utilized
xSenso User Guide 24
Page 25

3: Installation of xSenso
Table 3-5 Ethernet LEDs
Ethernet LEDs Description
Left (L) GREEN ON - 100 Mbps link established
GREEN Blink - 100Mbps activity
AMBER ON - 10 Mbps link established
AMBER Blink - 10 Mbps activity
Right (R) GREEN ON - Full duplex
OFF - Half duplex
Reset Button
You can reset the xSenso to factory default settings, including clearing the network settings. The
IP address, gateway, and netmask are set to 00s.
To reset the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 3-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for a minimum of 25 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will continue the boot process restoring
it back to the original factory default settings.
To reboot the unit without resetting the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 3-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for 3 to 5 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will reboot.
Right Side Panel
The following are located on the right side panel (Figure 3-6):
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
9-30 VDC 3 Pin Terminal Block Power Input
9-30 VDC Barrel Locking Power Input
Note: There are no inputs or outputs on the left side panel.
xSenso User Guide 25
Page 26
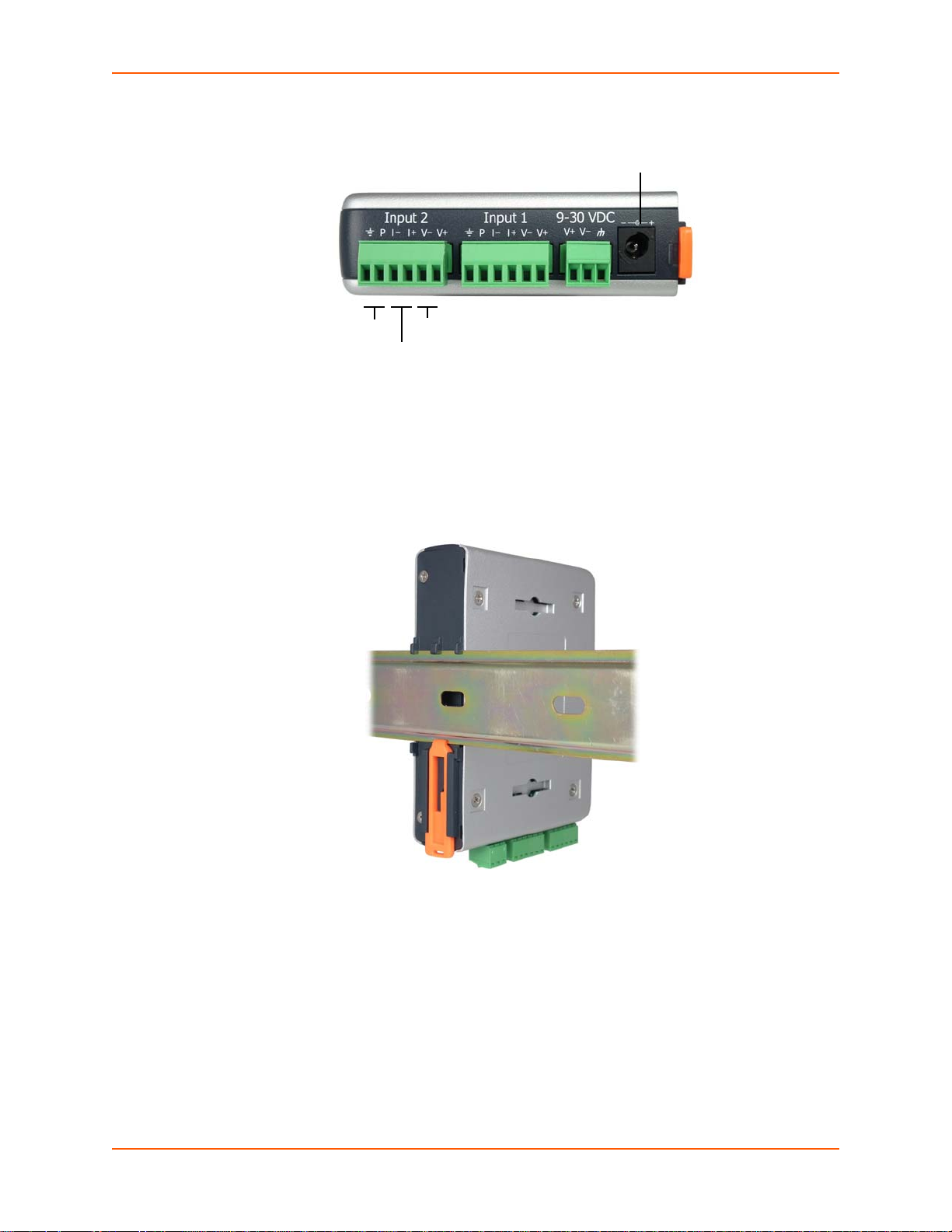
3: Installation of xSenso
9-30 VDC Barrel
Locking Power Input
Excitation Voltage Input
Current Input
Figure 3-6 xSenso, Side View
Back Panel
On the xSenso back panel, there is a mounting bracket with a sliding orange clip which allows you
to mount and dismount the device from a DIN rail, as shown in Figure 3-3. There are also four
rubber feet that can be attached to the bottom-side of the device, if the xSenso is to be placed on
a flat surface.
Installing the xSenso
Figure 3-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View
Be sure to place or mount the device securely on a flat horizontal or vertical surface. The device
comes with mounting brackets for mounting the device vertically, for example on a wall. If using
AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
Observe the following guidelines when connecting the analog input devices:
It is recommended to use twisted-pair wires to connect analog sensors and xSenso. If EMC is
a concern, shielded wires and/or ferrite bead may be used to improve signal integrity in noisy
environment.
xSenso User Guide 26
Page 27

3: Installation of xSenso
Connect your RJ-45 Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 port of the unit.
The xSenso supports a power range of 9 to 30 VDC. You can power up the device with barrel-
power connector and/or the 3 pin terminal connector for backup power supply.
Note: As soon as you plug the device into power, the device/sensors powers up
automatically, the self-test begins, and LEDs would indicate the device's status
Perform the following steps to install your device:
1. Connect analog xSenso to the analog input ports.
2. Hook up power excitations from xSenso to analog sensors/devices if needed and if xSenso
meets the power requirement.
3. Connect a RJ-45 Ethernet cable between the unit and your Ethernet network.
4. Connect the 9-30 VDC to the terminal block, barrel jack or both, and power on the xSenso.
5. Power up analog input devices/sensors if they are not powered by xSenso excitation.
xSenso User Guide 27
Page 28

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
This chapter describes how to install the xSenso 21A2 device serve r. It contain s th e follo wing
sections:
Package Contents
User-Supplied Items
Hardware Components
Hardware Components
Installing the xSenso
Package Contents
The xSenso package includes the following items:
One xSenso 21A2 device
Three 3-contact Terminal Block Plug - screw type for Power Input Port and Analog Output
Ports.
Two 6-contact Terminal Block Plug - screw type for Analog Input Ports
Wall Mount Bracket
Four Rubber Feet
Quick Start Guide
User-Supplied Items
To complete your installation, you need the following items:
Analog devices and sensors that require network connectivity.
Devices to be controlled by analog output.
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working AC power outlet if the unit will be powered from an AC power adapter.
A 9-30VDC power supply either terminal screw or barrel input (both may be used
simultaneously for power redundancy)
xSenso User Guide 28
Page 29
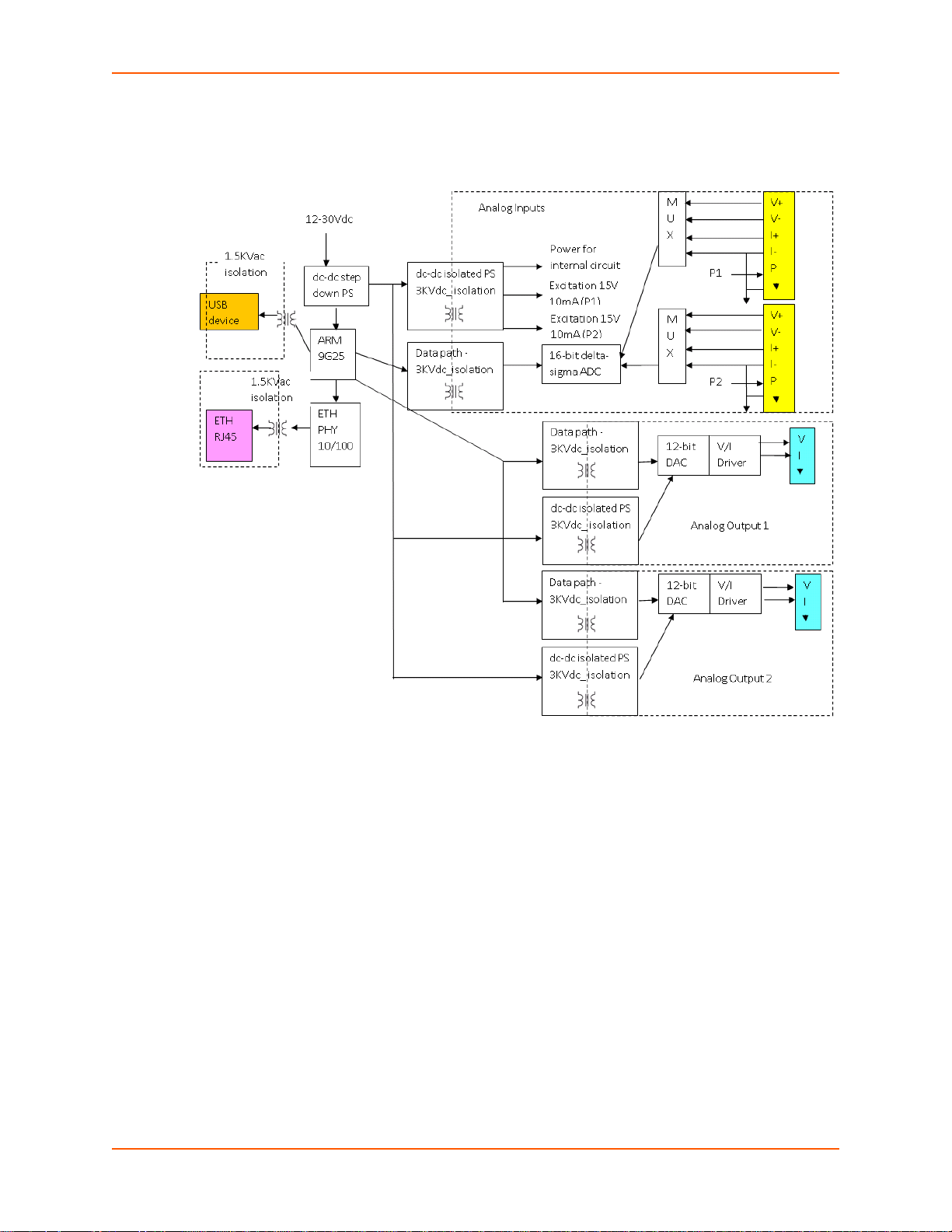
xSenso 21A2 Isolation Block Diagram
Figure 4-1 xSenso 21A2 Isolation Block Diagram
4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
Hardware Components
Front/Top Panel
The following components are located on the front panel (Figure 4-2) of the xSenso 21A2:
USB Port - for managing and configuring xSenso device.
RJ-45 Ethernet Port (with Ethernet LEDs) - can connect to an Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast
Ethernet (100 Mbps) network.
RST Button (the Reset Button inside the pin hole) - power cycles and restores factory default
settings.
LED Indicators (4 Analog Input/Output LEDs, 2 Ethernet LEDs, and 1 Diagnostic “X” LED)
- see Table 4-4 and Table 4-5.
xSenso User Guide 29
Page 30

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
Analog Analog
Output Input
LEDs LEDs
USB Ethernet Reset
Port Port
Ethernet LEDs
L R
Diagnostic
“X” LED
LED Indicators
The Analog Input LEDs, the Analog Output LEDs, the Eth ernet LEDs, and the Diagno stic “X” LED
are all located on the front panel of the xSenso device (Figure 4-3).
Figure 4-2 xSenso 21A2, Front View
Figure 4-3 xSenso 21A2 Top/Front View
Table 4-4 and Table 4-5 below explain the LED information displayed in Figure 4-2 and Figure 4-3
above.
xSenso User Guide 30
Page 31

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
Table 4-4 Analog Input and Analog Output LEDs
LED Color ON OFF
“X” on top of
xSenso device
(Diagnostic)
Analog Input 1 Green
Analog Input 2 Green
Analog Output 1 Green
Analog Output 2 Green
Orange ORANGE ON - power present
ORANGE Blink - during boot process after power cycle or
reset. Also blink patterns represent error conditions:
Loss of Redundant Power: one slow blink followed by
two fast blinks (repeat)
No Ethernet Link: two slow blinks followe d by two fast
blinks (repeat)
No IP Address: three slow blinks followed by three fast
blinks (repeat)
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
Output Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 0-10V output range is selected
ORANGE represents 20mA output range is selected
Output Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 0-10V output range is selected
ORANGE represents 20mA output range is selected
No power
Input not utilized
Input not utilized
Output not utlized.
Output not utlized.
Table 4-5 Ethernet LEDs
Ethernet LEDs Description
Left (L) GREEN ON - 100 Mbps link established
GREEN Blink - 100Mbps activity
AMBER ON - 10 Mbps link established
AMBER Blink - 10 Mbps activity
Right (R) GREEN ON - Full duplex
OFF - Half duplex
Reset Button
You can reset the xSenso to factory default settings, including clearing the network settings. The
IP address, gateway, and netmask are set to 00s.
To reset the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 4-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for a minimum of 25 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will continue the boot process restoring
it back to the original factory default settings.
xSenso User Guide 31
Page 32

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
9-30 VDC Barrel
Locking Power Input
Excitation Voltage Input
Current Input
Analog Analog
Output 1 Output 2
To reboot the unit without resetting the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 4-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for 3 to 5 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will reboot.
Side Panels
The following are located on the side panels (Figure 4-6):
Right Side
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
9-30 VDC 3 Pin Terminal Block Power Input
9-30 VDC Barrel Locking Power Input
Left Side
Analog Output 1
Analog Output 2
Figure 4-6 xSenso, Side Views
Back Panel
On the xSenso back panel, there is a mounting bracket with a sliding orange clip which allows you
to mount and dismount the device from a DIN rail, as shown in Figure 4-7. There are also four
rubber feet that can be attached to the bottom-side of the device, if the xSenso is to be placed on
a flat surface.
xSenso User Guide 32
Page 33

4: Installation of xSenso 21A2
Figure 4-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View
Installing the xSenso
Be sure to place or mount the device securely on a flat horizontal or vertical surface. The device
comes with mounting brackets for mounting the device vertically, for example on a wall. If using
AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
Observe the following guidelines when connecting the analog input and output devices:
It is recommended to use twisted-pair wires to connect analog sensors and xSenso. If EMC is
a concern, shielded wires and/or ferrite bead may be used to improve signal integrity in noisy
environment.
Connect your RJ-45 Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 port of the unit.
The xSenso supports a power range of 9 to 30 VDC. You can power up the device with barrel-
power connector and/or the 3 pin terminal connector for backup power supply.
Note: As soon as you plug the device into power, the device/sensors powers up
automatically, the self-test begins, and LEDs would indicate the device's status
Perform the following steps to install your device:
1. Connect analog devices to the analog input and output ports.
2. Hook up power excitations from xSenso to analog sensors/devices if needed and if xSenso
meets the power requirement.
3. Connect a RJ-45 Ethernet cable between the unit and your Ethernet network.
4. Plug the xSenso into the power outlet by using the included power supply.
5. Power up analog input devices/sensors if they are not powered by xSenso excitation.
6. Power up devices to be controlled by analog output.
xSenso User Guide 33
Page 34

5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
This chapter describes how to install the xSenso 21R2 device server. It contains the following
sections:
Package Contents
User-Supplied Items
Hardware Components
Installing the xSenso
Package Contents
The xSenso package includes the following items:
One xSenso 21R2 device
Three 3-contact Terminal Block Plug - screw type for Power Input Po rt and Relay Output Ports
Two 6-contact Terminal Block Plug - screw type for Analog Input Ports
Wall Mount Bracket
Four Rubber Feet
Quick Start Guide
User-Supplied Items
To complete your installation, you need the following items:
Devices to be controlled by relay
Analog devices and sensors that require network connectivity.
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working AC power outlet if the unit will be powered from an AC power adapter.
A 9-30VDC power supply either terminal screw or barrel input (both may be used
simultaneously for power redundancy)
xSenso User Guide 34
Page 35

xSenso 21R2 Block Diagram
Figure 5-1 xSenso 21R2 Isolation Block Diagram
5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
Hardware Components
Front/Top Panel
The following components are located on the front panel (Figure 5-2) of the xSenso 21R2:
USB Port - for managing and configuring xSenso device.
RJ-45 Ethernet Port (with Ethernet LEDs) - can connect to an Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast
Ethernet (100 Mbps) network.
RST Button (the Reset Button inside the pin hole) - power cycles and restores factory default
settings.
LED Indicators (4 Analog Input/Output LEDs, 2 Ethernet LEDs, and 1 Diagnostic “X” LED)
- see Table 5-4 and Table 5-5 to learn how to read the LED indicators.
LED Indicators
The Analog Input LEDs, the Relay Output LEDs, the Ethernet LEDs, and the Diagnostic “X” LED
are all located on the front panel of the xSenso device (Figure 5-2).
xSenso User Guide 35
Page 36

Figure 5-2 xSenso 21R2, Front View
Relay Analog
Output Input
LEDs LEDs
USB Ethernet Reset
Port Port
Ethernet LEDs
L R
Diagnostic
“X” LED
Figure 5-3 xSenso 21R2 Top/Front View
5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
Table 5-4 and Table 5-5 below explain the LED information displayed in Figure 5-2 and Figure 5-3
above.
xSenso User Guide 36
Page 37

5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
Table 5-4 Analog Input and Relay Output LEDs
LED Color ON OFF
“X” on top of
xSenso device
(Diagnostic)
Analog Input 1 Green
Analog Input 2 Green
Relay Output 1 Green GREEN represents relay is turned on/energized.
Relay Output 2 Green GREEN represents relay is turned on/energized.
Orange ORANGE ON - power present
ORANGE Blink - during boot process after power cycle or
reset. Also blink patterns represent error conditions:
Loss of Redundant Power: one slow blink followed by
two fast blinks (repeat)
No Ethernet Link: two slow blinks followe d by two fast
blinks (repeat)
No IP Address: three slow blinks followed by three fast
blinks (repeat)
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
Input Type (voltage or current)
or
Orange
GREEN represents 100mV, 1V or 10V input range is
selected
ORANGE represents 20mA input range is selected
(i.e. COM = NO)
(i.e. COM = NO)
No power
Input not utilized
Input not utilized
OFF represents
relay is turned off
(i.e. COM = NC)
OFF represents
relay is turned off
(i.e. COM = NC)
Table 5-5 Ethernet LEDs
Ethernet LEDs Description
Left (L) GREEN ON - 100 Mbps link established
GREEN Blink - 100Mbps activity
AMBER ON - 10 Mbps link established
AMBER Blink - 10 Mbps activity
Right (R) GREEN ON - Full duplex
OFF - Half duplex
Reset Button
You can reset the xSenso to factory default settings, including clearing the network settings. The
IP address, gateway, and netmask are set to 00s.
To reset the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 5-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for a minimum of 25 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will continue the boot process restoring
it back to the original factory default settings.
xSenso User Guide 37
Page 38

5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
9-30 VDC Barrel
Locking Power Input
Excitation Voltage Input
Current Input
Relay 1 Relay 2
To reboot the unit without resetting the unit to factory defaults:
1. Place the end of a paper clip or similar object into the RST (reset) opening (see Figure 5-2)
and press and hold down micro switch during a power cycle for 3 to 5 seconds.
2. Remove the paper clip to release the button. The unit will reboot.
Side Panels
The following are located on the side panels (Figure 5-6):
Left Side
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
9-30 VDC 3 Pin Terminal Block Power Input
9-30 VDC Barrel Locking Power Input
Right Side
Relay Output 1
Relay Output 2
Figure 5-6 xSenso, Side Views
Back Panel
On the xSenso back panel, there is a mounting bracket with a sliding orange clip which allows you
to mount and dismount the device from a DIN rail, as shown in Figure 5-7. There are also four
rubber feet that can be attached to the bottom-side of the device, if the xSenso is to be placed on
a flat surface.
xSenso User Guide 38
Page 39

5: Installation of xSenso 21R2
Figure 5-7 xSenso Bottom/Back Panel View
Installing the xSenso
Be sure to place or mount the device securely on a flat horizontal or vertical surface. The device
comes with mounting brackets for mounting the device vertically, for example on a wall. If using
AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
Observe the following guidelines when connecting the analog input and output devices:
It is recommended to use twisted-pair wires to connect analog sensors and xSenso. If EMC is
a concern, shielded wires and/or ferrite bead may be used to improve signal integrity in noisy
environment.
Connect your RJ-45 Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 port of the unit.
The xSenso supports a power range of 9 to 30 VDC. You can power up the device with barrel-
power connector and/or the 3 pin terminal connector for backup power supply.
Note: As soon as you plug the device into power, the device/sensors powers up
automatically, the self-test begins, and LEDs would indicate the device's status
Perform the following steps to install your device:
1. Connect analog devices to the analog input and relay output ports.
2. Hook up power excitations from xSenso to analog sensors/devices if needed and if xSenso
meets the power requirement.
3. Connect a RJ-45 Ethernet cable between the unit and your Ethernet network.
4. Plug the xSenso into the power outlet by using the included power supply.
5. Power up analog input devices/sensors if they are not powered by xSenso excitation.
6. Power up device to be controlled by relay or supply po we r to be con tro lle d by re lay .
xSenso User Guide 39
Page 40

6: Using DeviceInstaller
This chapter covers the steps for locating a xSenso unit and viewing its properties and device
details. DeviceInstaller is a free utility program provided by Lantronix that discovers, configures,
upgrades and manages Lantronix Device Servers.
Notes:
For instructions on using DeviceInstaller to configure the IP address and related
settings or for more advanced features, see the DeviceInstaller Online Help.
Auto IP generates a random IP address in the range of 169.254.0.1 to
169.254.255.254, with a netmask of 255.255.0.0, if no BOOTP or DHCP server is
found. These addresses are not routable.
Accessing xSenso Using DeviceInstaller
Note: Make note of the MAC address. It is needed to locate the xSenso using
DeviceInstaller.
To use the DeviceInstaller utility, first install the latest version from the downloads page on the
Lantronix web site www.lantronix.com/downloads
1. Run the executable to start the installation process and respond to the installation wizard
prompts. (If prompted to select an installation type, select Typical.)
.
2. Click Start -> All Programs -> Lantronix -> DeviceInstaller 4.3 -> DeviceInstaller .
3. When DeviceInstaller starts, it will perform a network device search. To perform another
search, click Search.
4. Expand the xSenso folder by clicking the + symbol next to the folder icon. T he list of availabl e
Lantronix xSenso devices appears.
5. Select the xSenso unit by expanding its entr y and clicking on its IP address to view its
configuration.
6. On the right page, click the Device Details tab. The current xSenso configuration appears.
This is only a subset of the full configuration; the full configuration may be accessed via Web
Manager, CLI or XML.
Device Detail Summary
Note: The settings are Display Only in this table unless otherwise noted
Current Settings Description
Name Shows “xSenso 2100”, “xSenso 21A2” or “xSenso 21R2”.
DHCP Device Name
The name associated with the xSenso’s current IP address, if the IP
address was obtained dynamically.
xSenso User Guide 40
Page 41

6: Using DeviceInstaller
Current Settings Description
Configurable field. Enter a group to categorize the xSenso. Double-click the
Group
Comments
Device Family Shows the xSensodevice family type as “xSenso”.
Short Name Shows “xSenso 2100”, “xSenso 21A2” or “xSenso 21R2” by default.
Long Name Shows Lantronix xSenso 2100”, “Lantronix xSenso 21A2” or “Lantronix
Type Shows the device type as “xSenso 2100 Series”””.
ID Shows the xSenso ID embedded within the unit.
Hardware Address Shows the xSenso hardware (MAC) address.
Firmware Version Shows the firmware currently installed on the xSenso.
Extended Firmware Version Provides additional information on the firmware version.
Online Status Shows the xSenso status as Online, Offline, Unreachable (the xSenso is on
IP Address Shows the xSenso current IP address. To change the IP address, click the
IP Address was Obtained Appears “Dynamically” if the xSenso automatically received an IP address
Subnet Mask Shows the subnet mask specifying the network segment on which the
Gateway Shows the IP address of the router of this network.
Number of Analog Inputs Shows the number of analog inputs on the xSenso device.
Number of Analog Outputs Shows the number of analog outputs on the xSenso device.
Number of Relay Outputs Shows the number of relay outputs on the xSenso device.
Supports Configurable Pins Shows False, indicating configurable pins are not available on the xSenso.
Supports Email Triggers Shows True, indicating email triggers are available on the xSenso .
Telnet Supported Indicates whether Telnet is enabled on this xSenso.
Telnet Port Shows the xSenso port for Telnet sessions.
Web Port Shows the xSenso port for web sessions.
Firmware Upgradable
field, type in the value, and press Enter to complete. This group name is
local to this PC and is not visible on other PCs or laptops using
DeviceInstaller.
Configurable field. Enter comments for the xSenso. Double-click the field,
type in the value, and press Enter to complete. This description or comment
is local to this PC and is not visible on other PCs or laptops using
DeviceInstaller.
xSenso 21R2” by default.
a different subnet), or Busy (the xSenso is currently performing a task).
Assign IP button on the DeviceInstaller menu bar.
(e.g., from DHCP). Appears “Statically” if the IP address was configured
manually.
If the IP address was assigned dynamically, the following fields appear:
Obtain via DHCP with values of True or False.
Obtain via BOOTP with values of True or False.
xSenso resides.
There is no default.
Note: This field only displays for xSenso 21A2 models.
Note: This field only displays for xSenso 21R2 models.
Shows True, indicating the xSenso firmware is upgradable as newer
versions become available.
xSenso User Guide 41
Page 42

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
This chapter describes how to configure xSenso using Web Manager, the Lantronix browserbased configuration tool. The unit’s configuration is stored in nonvolatile memory and is retained
without power. All changes take effect immediately, unless otherwise noted. It contains the
following sections:
Accessing Web Manager
Web Manager Components
Navigating Web Manager
Accessing Web Manager
Note: You can also access the Web Manager by selecting the Web Configuration tab on
the DeviceInstaller window.
To access Web Manager, perform the following steps:
1. Open a standard web browser. Lantronix supports the latest version of Internet Explorer,
Mozilla Suite, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Chrome or Opera.
Note: Lantronix recommends using the latest version of Chrome when viewing and
configuring the Chart tab/page.
2. Enter the IP address or hostname of the xSenso in the address bar. Th e IP a ddress may have
been assigned manually using DeviceInstaller (see the xSenso Quick Start Guide) or
automatically by DHCP.
3. Enter your username and password.The factory-default username is “admin” and the
password is “PASS”. The xSenso Home page displays with a brief summary of current status
information about your xSenso device including product information, network settings and
analog status information.
xSenso User Guide 42
Page 43

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
There are three xSenso models.
The Home page for each model is
identical except for these
differences:
1) The xSenso model can be
identified to the right of the
Product Type in the Home page.
2) xSenso 21A2 has two additional
output status fields.
3) xSenso 21R2 has two additional
relay status fields.
Figure 7-1 xSenso Home Pages
4. Click the Admin tab to get to the Admin > Device Status page. The Device Status web page
displays the same and more information than on the xSenso Home page: configuration,
network settings, analog status, tunneling settings, and product information.
xSenso User Guide 43
Page 44

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
There are three
xSenso models. The
Device Status page for
each model is identical
except for these
differences:
1) The xSenso model
can be identified to the
right of the Product
Type in the Home
page.
2) xSenso 21A2 has
two additional output
status fields.
3) xSenso 21R2 has
two additional relay
status fields.
Figure 7-2 Device Status Pages
Note: The Logout button is available on any web page under the Setup and Admin Tab-
Pages when authentication is enabled (by default). Logging out of the web page would
force re-authentication to take place the next time the web page is accessed.
xSenso User Guide 44
Page 45

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
xSenso Home and Device Status Pages
The xSenso Home page is the first page that appears after you log into Web Manager. The Device
Status page appears when you click Status in the Admin tab/page in Web Manager.
The xSenso Home page and the Device Status pages show overlapping information. For most
users, the xSenso Home page contains the basic product and status information necessary. For
advanced users, the Device Status page contains additional configuration informa tion:
Table 7-3 Comparing xSenso Home Page and Device Status Page Information
Information Provided xSenso Home Page Device Status Page
Product Type x x
Firmware Version x x
Build Date x
Serial Number/MAC
Address
Uptime x x
Permanent Config x
Interface x
Link x
MAC Address x
Hostname x x
IP Address x x
Default Gateway x x
Domain x
Primary DNS x
Secondary DNS x
MTU x
Input 1 x x
Input 2 x x
Output 1
(only for xSenso 21A2)
Output 2
(only for xSenso 21A2)
Relay 1
(only for xSenso 21R2)
Relay 2
(only for xSenso 21R2)
Tunnel 1 x
xx
xx
xx
xx
xx
Tunnel 2 x
xSenso User Guide 45
Page 46

Live Reading Pages and Configuration Pages
Configuration Pages
HOME PAGE
Live Reading Pages
There are five tabs that span the top of the Web Manager page. Beyond the xSenso Home page
accessed through the Home tab at the top left, you may access the other Web Manager pages
through the four other tabs. The Reading, Chart and Logging tab/pages provide live data on the
analog input signals and the Setup and Admin tab/pages provide configuration menus:
Reading: view live readings of analog input, output and relay data.
Chart: view live, customizable charts of analog input, output and relay data.
Logging: view and customize data logs of analog input, output and relay data.
Setup: access the configuration menu to the Action, Analog Input, Analog Output, Relay,
DAQ Format, Email, System and Tunnel configuration pages.
Admin: access the configuration menu to the Status, CLI, Clock, Diagnostics, Discovery,
DNS, Filesystem, FTP, HTTP, Modbus, Network, Protocol Stack, RSS, SMTP, SNMP, SSH,
SSL, Syslog and XML configuration pages.
Figure 7-4 Live Reading vs. Configuration Pages
7: Configuration Using Web Manager
xSenso User Guide 46
Page 47

Web Manager Components
Menu Bar
(only in the
Setup and
Admin tab/
pages)
Links to
subpages
Items to
configure
Information
and Help Area
Header
Footer
Logout
button
Tabs/Pages
The layout of a typical Web Manager page is below.
Figure 7-5 Components of the Web Manager Page
7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Web Manager pages have these sections:
The Home, Reading, Chart, Logging, Setup and Admin tabs at the top of the page provide
direct access to each Web Manager page of the same name. All the functionality in Web
Manager is divided between these tab/pages. For instance, clicking the Admin tab brings you
to the Admin page or the Reading tab to get to the Reading page.
The Reading, Chart and Logging tab/pages provide live sensor data. These pages together
with the xSenso Home page, are designed for users who are simply mon ito ring an alog input,
output and relay data.
The Setup and Admin tab/pages contain several subpages allowing viewing and
configuration of various settings. These pages would be useful for an advanced user wishing
to view and modify xSenso configurations.
The menu bar appears at the left side of the Setup and Admin pages. The menu bar lists the
names of the subpages available in the Setup and Admin pages in Web Manager. To bring up a
page, click it in the menu bar.
Links near the top of many of the pages under Setup and Admin, such as the one in the
example above, enable you to link to additional pages. On some pages, you must also select
the item you are configuring, such as a tunnel.
In the middle of many pages, you can select or enter new configuration settings. Some pages
show status or statistics in this area rather than allow you to enter settings.
xSenso User Guide 47
Page 48

At the bottom of most pages, the current configuration is displayed. In some cases, you can
reset or clear a setting.
The information or help area shows information or instructions associated with the page.
A Logout link is available at the upper right corner of every Setup and Admin page. In
Chrome or Safari, it is necessary to close out of the browser to completely logout. If
necessary, reopen the browser to log back in.
The footer appears at the very bottom of the page. It contains copyright information and a link
to the Lantronix home page.
Navigating Web Manager
The Web Manager provides an intuitive point-and-click interface. A menu bar on the left side of
each page provides links you can click to navigate from one page to another while the Reading,
Chart and Logging pages are accessed by tabs across the top of the page. Some pages are readonly, while others let you change configuration settings.
Note: There may be times when you must reboot the xSenso for the new configuration
settings to take effect. The chapters that follow indicate when a change requires a reboo t.
Anytime you reboot the unit, this operation will take some time to complete. Please wait a
minimum of 10-20 seconds after rebooting the unit before attempting to make any
subsequent connections.
7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Web Manager Page Description See
Page
Status Shows product information, network, analog status, and tunneling settings. 45
Action Allows you to view and configure the actions for a specific alarm or report. 66
Analog Input Allows you to view and configure analog input, shows current input status and
allows you to scale and modify display of both analog inputs.
Analog Output Allows you to view and configure analog output, shows current output
statuses and allows you to modify display of analog outputs.
Charting Shows data on a live chart and chart configuration options. 59
CLI Shows Command Line Interface (CLI) statistics and lets you change the
current CLI configuration settings.
Clock Allows you to view and configure the current date, time and time zone as it
displays in web manager.
DAQ Format Allows you to change data response format in Tunnel and Action connect
applications.
Diagnostics Lets you perform various diagnostic procedures. 96
Discovery Allows you to view and modify the configuration and statistics for device
discovery.
DNS Shows the current configuration of the DNS subsystem and the DNS cache. 77
Email Shows email statistics and lets you clear the email log, configure email
settings, and send an email.
Filesystem Shows file system statistics and lets you browse the file system to view a file,
create a file or directory, upload files using HTTP, copy a file, move a file, or
perform TFTP actions.
55
56
104
100
53
102
103
92
xSenso User Guide 48
Page 49

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Web Manager Page
(continued)
FTP Shows statistics and lets you change the current configuration for the File
HTTP Shows HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) statistics and lets you change the
Logging Shows analog input, output and relay information through a live log and
Modbus Shows the current connection status of the Modubs servers listening on the
Network Shows status and lets you configure the network interface. 50
Protocol Stack Lets you perform lower level network stack-specific activities. 94
Query Port Lets you change configuration settings for the query port. 96
Reading Shows live analog input, output and relay reading information. 64
Relay Allows you to view and configure relay output, shows current relay output
RSS Lets you change current Really Simple Syndication (RSS) settings . 81
SMTP Sho ws and modify the current configuration of SMTP. 83
SNMP Shows and modify the current configuration of SNMP. 82
SSH Lets you change the configuration settings for SSH server host keys, SSH
SSL Lets you upload an existing certificate or create a new self-signed certificate. 88
Description See
Page
78
Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
79
current configuration and authentication settings.
61
provides log file configuration options.
75
TCP ports and configure Modbus TCP server.
57
statuses and allows you to modify display of both relays.
85
server authorized users, SSH client known hosts, and SSH client users.
Syslog Lets you specify the severity of events to log and the serve r and ports to
which the syslog should be sent.
System Lets you reboot device, restore factory defaults, upload new firmware, and
change the device long and short names.
Tunnel Lets you change the current configuration settings for an incoming tunnel
connection.
XML Lets you export XML configuration and status records, and import XML
configuration records.
78
101
73
106
xSenso User Guide 49
Page 50

8: Network Settings
The Network Settings show the status of the Ethernet interface/link and let you configure the
settings on the device. Interface settings are related to the configuration of the IP and related
protocols. Link settings are related to the ph ysical link connection, which carries the IP traffic.
The xSenso contains one network interface. The Ethernet interface is also called interface 1 or
eth0.
Notes:
Some settings require a reboot to take effect. These settings are noted below.
Wait a minimum of 10-20 seconds after rebooting the unit before attempting to make
any subsequent connections.
The blue text in the XML command strings of this chapter are to be replaced with a
user-specified name.
Network Interface Settings
Table 8-1 shows the network interface settings that can be configured.
Table 8-1 Network Interface Settings
Network Interface
Settings
BOOTP Client Select to turn On or Off. At boot up, after the physical link is up, the xSenso will
DHCP Client Select to turn On or Off. At boot up, after the physical link is up, the xSenso will
IP Address Enter the static IP address to use for the interface. You may enter it alone or in
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the router for this network.
Description
attempt to obtain IP settings from a BOOTP server.
Note: Overrides the configured IP address/mask, gateway, hostname, and
domain. When DHCP is Enabled, the system automatically uses DHCP,
regardless of whether BOOTP is Enabled. Changing this value requires you to
reboot the device.
attempt to obtain IP settings from a DHCP server and will periodically renew
these settings with the server.
Note: Overrides BOOTP, the configured IP address/mask, gateway,
hostname, and domain. Changing this value requires you to reboot the device.
Note: Within WebManager, click Renew to renew the DHCP lease.
CIDR format.
Note: This setting will be used if Static IP is active (both DHCP and BOOTP
are Disabled). Changing this value requires you to reboot the device. When
DHCP or BOOTP is enabled, the xSenso tries to obtain an IP address from a
DHCP or BOOTP server. If it cannot, the xSenso generates and uses an Auto
IP address in the range of 169.254.xxx.xxx, with a network mask of
255.255.0.0.
Note: This setting will be used if Static IP is active (both DHCP and BOOTP
are Disabled).
xSenso User Guide 50
Page 51

8: Network Settings
Network Interface
Settings (continued)
Hostname Enter the hostname for the interface. It must begin with a letter or number,
Domain Enter the domain name suffix for the interface.
DHCP Client ID Enter the ID if the DHCP server requires a DHCP Client ID option. The DHCP
Primary DNS Enter the IP address of the primary Domain Name Server.
Secondary DNS Enter the IP address of the secondary Domain Name Server.
MTU When DHCP is enabled, the MTU size is (usually) provided with the IP address.
Description
continue with a sequence of letters, numbers, or hyphens, and end with a letter
or number.
Note: This setting will take effect immediately, but will not register the
hostname with a DNS server until the next reboot.
Note: This setting will be used when either Static IP or Auto IP is active, or if
DHCP/BOOTP is active and no Domain Suffix was acquired from the server.
server’s lease table shows IP addresses and MAC addresses for devices. The
lease table shows the Client ID, in hexadecimal notation, instead of the xSenso
MAC address.
Note: This setting will be used when either Static IP or Auto IP is active, or if
DHCP/BOOTP is active and no DNS server was acquired from the server.
Note: This setting will be used when either Static IP or Auto IP is active, or if
DHCP/BOOTP is active and no DNS server was acquired from the server.
When not provided by the DHCP server, or using a static configuration, this
value is used. The MTU size can be from 576 to 1500 bytes, the default being
1500 bytes.
To Configure Network Interface Settings
Using Web Manager
To modify Ethernet (eth0) settings, go to the Admin tab/page, g o to the Admin tab/page, click
Network on the menu and select Network 1 -> Interface -> Configuration.
Using the CLI
To enter the eth0 command level: enable -> config -> if 1
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name="interface" instance="eth0">
To View Network Interface Status
Using Web Manager
In Network Interface Status, you can view both the current operational settings as well as the
settings that would take affect upon a device reboot.
To view Ethernet (eth0) Status, go to the Admin tab/page and click Network on the menu
and select Network 1 -> Interface -> Status.
xSenso User Guide 51
Page 52

Network Link Settings
Physical link parameters can be configured for an Ethernet (eth0) Network Interface (see
Table 8-2).
8: Network Settings
Table 8-2 Network 1 (eth0) Link Settings
Network 1 Ethernet (eth0)
Description
Link Settings
Speed Select the Ethernet link speed. (Default is Auto)
Auto = Auto-negotiation of Link Speed
10 Mbps = Force 10 Mbps
100 Mbps = Force 100 Mbps
Duplex Select the Ethernet link duplex mode. (Default is Auto)
Auto = Auto-negotiation of Link Duplex
Half = Force Half Duplex
Full = Force Full Duplex
Notes:
When speed is Auto, duplex must be Auto or Half.
When speed is not Auto, duplex must be Half or Full.
Fixed speed Full duplex will produce errors connected to Auto, due to duplex
mismatch.
To Configure Network Link Settings
Using Web Manager
To modify Ethernet (eth0) Link information, go to the Admin tab/page, and click Network on
the menu and select Network 1 -> Link.
Using the CLI
To enter the eth0 Link command level: enable -> config -> if 1 -> link
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name="ethernet" instance="eth0">
xSenso User Guide 52
Page 53

9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Excitation Voltage Input
Current Input
The xSenso supports two analog inputs (Figure 9-1) each of which may be configured to sense
one of four analog signal ranges (±100mV, ±1V, ±10V and ±20mA) with options for selecting
simple offset or scale and offset. xSenso 2100, xSenso 21A2 and xSenso 21R2 have the same
analog inputs but xSenso 21A2 additionally has two analog outputs and xSenso 21R2 has two
relay outputs.
Figure 9-1 Analog Inputs 1 and 2 for xSenso
DAQ Format
DAQ (Data Acquisition) Format configuration applies to Tunnel Accept and Alarm Connect data
response.
Table 9-2 xSenso DAQ Command
Command Description Example xSenso Model
AIN1 Reads Input 1 value. AIN1\r
+10.0000
AIN2 Reads Input 2 value. AIN2\r
-0.00031
AIN* Reads all input values. AINA\r
+10.0000-0.00031
AOUT1 Reads Output 1 current value. AOUT1\r
+5.00000
AOUT2 Reads Output 2 current value AOUT1\r
+10.0000
AOUT* Reads all current output values. AOUT*\r
+5.00000+10.0000
AOUT1 <value> Writes Output 1 value.
Value must have float format:
[+/-]<digits>.<digits>
AOUT1 +5.0\r
SUBMITTED
xSenso 2100
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 2100
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 2100
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21A2
xSenso User Guide 53
Page 54

9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Command (continued) Description Example xSenso Model
AOUT2 <value> Writes Output 2 value.
Value must have float format:
[+/-]<digits>.<digits>
ROUT1 Reads Relay 1 current setting. ROUT1\r
ROUT2 Reads Relay 2 current setting. ROUT2\r
ROUT* Reads all current relay settings. ROUT*\r
ROUT1 <0, 1, or 2> Write Relay 1 setting:
0 to turn off relay
1 to turn on relay
2 to reset latched relay
ROUT2 <0, 1, or 2> Write Relay 2 setting:
0 to turn off relay
1 to turn on relay
2 to reset latched relay
AOUT2 +10.0\r
SUBMITTED
+1
+0
+1 +0
ROUT1 1\r
SUBMITTED
ROUT2 0\r
SUBMITTED
xSenso 21A2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 21R2
xSenso 21R2
Table 9-3 DAQ Settings
DAQ Settings Description
Time Type Select Uptime or Clock time type. If Timestamp is enabled, this selection applies.
Uptime represents the time since the device has powered up. To use Clock time,
first go to Clock settings to set it up.
Timestamp Select whether to enable a time stamp to be placed before each sample value.
Identifier Select whether to enable an alphanumeric identifier to be placed before each
sample value and optional timestamp.
Units Select whether ot enable the applicable unit to be placed after each sample value.
End Character Enter an end character to place this character at the tail end of sample strings. You
may also delete field contents to remove the end character.
To Configure DAQ Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure DAQ Settings, go to the Setup tab/page and click DAQ Format in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the DAQ Settings command level:
enable -> config -> analog -> daqformat
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”daq format”>
xSenso User Guide 54
Page 55

Analog Input
Input Settings Description
Display Select to enable or disable a scaled input value to be displayed with designated title
Title Enter the analog input title as it will appear in web manager, XML and CLI. Leave this
Range Select input range from drop-down menu. Select the measurement range closest to
Adjustment Select the offset adjustment:
Input Low Enter the Input Low value which will be presented as the Reading Low value. For
Reading Low Enter the Reading Low value which will be converted from the Input Low value.
Input High Enter the Input High value which will be presented as the Reading High value.
Reading HIgh Enter the Reading HIgh value which will be presented as the Input HIgh value.
Offset Enter the offset value through which each sampled analog input value may be
Decimal Point Specify the maximum number of digits to be displayed to the right of the decimal point,
Units Enter the unit as it will appear after the presented analog input value. For example, you
Alarm Type Select alarm type to enable monitoring for high and/or low analog input readings:
Alarm High Specify the Alarm High value; an analog input reading above this value that persists
Alarm Low Specify the Alarm Low value; an analog input reading below this value that persists for
Delay Specify the Delay value in seconds; an analog input high or low reading that persists
9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Table 9-4 Analog Input Settings
and units in the web manager, XML and CLI analog chanel as well as Tunnel and
Action Connect application. You can hide an input by disabling it if you are not using it.
field blank to utilize the default “Input N”, where N is the analog input number. For
example, you can name the reading, “Temperature”, if a temperature sensor is
connected to the xSenso device.
your sensor output to get the most accurate measurement.
Select 20mA when input is connected to the I+ and I- terminals.
Select 100nV, 1V or 10V when input is connected to the V+ and V- terminals.
Select Simple offset so that the offset value is simply added to each analog input
with the result presented as an analog reading.
Select Scale and offset to linearly map each analog input sample to its reading value
via specification of two points (one near each end of the linear mapping range).
example, if a sensor measures -40
input low 0
°, input high 10°, reading low -40°, reading high 100° and unit "C".
adjusted. Offset may be positive or negative.
according to the accuracy of signal source. Reading is always limited to have at 5
significant figures at most. For example, if the connected analog output sensor has an
accuracy of 0.1
°C, you can select decimal point to be 1.
can input C or F if a temperature sensor is connected.
Select either High or High and Low to enable monitoring for a reading at or above
the specified Alarm High value.
Select Low or High and Low to enable monitoring for a reading at or belo w the
specified Alarm Low value.
Select None to disable monitoring reading for alarm low and/or high values.
for Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
for Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
° to 100°C with an output of 0 to10V, you can input
xSenso User Guide 55
Page 56

To Configure Analog Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure analog input, go to the Setup tab/page and click Analog Input > Input 1 >
Configuration in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the analog input command level: enable -> config -> analog -> input
<number>
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”analog input” instance=”1”>
Analog Output
9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Note: Analog output is only available on the xSenso 21A2. When output is tracking
input, input is the single source of control. When tracking is disabled, there will be no other
source of control and the state of output is undefined. Instead of leaving it undefined, we
just put it back to startup value which also serves as a safe value to be used when output
is not defined (like during startup output is undefined before any control kicks in).
Table 9-5 Analog Output Settings
Input Settings Description
Display Select to enable or disable an output value to be displayed with designated title and
units in the web manager, XML and CLI analog chanel as well as Tunnel and Action
Connect application. You can hide an output by disabling it if you are not using it.
Title Enter the analog output title as it will appear in web manager, XML and CLI. Leave this
field blank to utilize the default “Output N”, where N is the analog output number. For
example, you can name the reading, “Water Valve”, if a water flow controlling valve is
connected to the xSenso device.
Type Select type of Voltage or Current:
Select Voltage for an output range from 0 to 10 Volts.
Select Current for an output range from 0 to 20 mA.
Startup Value Enter the Startup Value for the initial output value that will be asserted after the device
boots up. This will also take effect when Analog Input or Type is changed to avoid an
undefined output. This value may subsequently be replaced by a value mapped from
an input channel or by a value specified in an output command.
Analog Input Select the appropriate Analog Input from the drop-down menu to specify the channel
number of the analog input the output will track.
Reading Low Enter the Reading Low value which will be presented as the Output Low value.
Output Low Enter the Output Low value which will be converted from the Reading Low value.
Reading HIgh Enter the Reading HIgh value which will be presented as the Output HIgh value.
Output HIgh Enter the Output High value which will be converted from the Reading High value.
xSenso User Guide 56
Page 57

9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Input Settings Description
Alarm Type Select alarm type to enable monitoring for high and/or low analog output readings:
Select either High or High and Low to enable monitoring for a reading at or above
the specified Alarm High value.
Select Low or High and Low to enable monitoring for a reading at or belo w the
specified Alarm Low value.
Alarm High Specify the Alarm High value; an analog output reading above this value that persists
for Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
Alarm Low Specify the Alarm Low value; an analog output reading below this value that persists
for Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
Delay Specify the Delay value in seconds; an analog output high or low reading that persists
for Delay seconds will turn on the alarm.
To Configure Analog Output Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure analog output, go to the Setup tab/page and click Analog Output > Output 1 >
Configuration in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the analog output command level: enable -> config -> analog -> output
<number>
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”analog output” instance=”1”>
Relay Output
Note: Relay output is only available on the xSenso 21R2. When relay is energized/
turned on, Normally Open Port is closed to Common where Normally Closed Port is open/
disconnected from Common. When relay is de-energized/turned off, Normally Open Port
is open/disconnected from Common where Normally Closed Port is closed to Common.
Input Settings Description
Display Select to enable or disable a relay status to be displayed with designated title in the
Title Enter the relay title as it will appear in web manager, XML and CLI. Leave this field
Table 9-6 Relay Output Settings
web manager, XML and CLI analog channel as well as Tunnel and Action Connect
application. You can hide an relay status by disabling it if you are not using it.
blank to utilize the default “Relay N”, where N is the relay number. For example, you
can name the reading, “Buzzer”, if a buzzer is connected to the xSenso device.
xSenso User Guide 57
Page 58

9: Analog Input, Output and Relay Settings
Input Settings
Description
(continued)
Latch Enable or disable Latch controls which determine how a relay will be turned off.
Selecting Enabled will require a user to explicitly reset latched relay and then turn it
off.
Selecting Disabled, the relay will automaticaly turn off after any and all of the alarm
triggers are no longer active.
To Configure Relay Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure relay output, go to the Setup tab/page and click Relay > Relay 1 >
Configuration in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the relay command level:
enable -> config -> analog -> relay <number>
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”relay” instance=”1”>
xSenso User Guide 58
Page 59

10: Chart
xSenso 2100 xSenso 21A2 xSenso 21R2
Note: Lantronix recommends using the latest version of Chrome when viewing and
configuring the Chart tab.
The xSenso Chart tab provides access to live charted analog input, output and relay information
on the Chart page. The chart is configurable and includes an optional alarm indication function.
Chart will poll data sample from xSenso every second. Titles and units are configurable under
Analog Input, Analog Output and Relay Output settings (according to the xSenso device model;
see Figure 10-1). You can point your mouse over data point to see the actual reading presented
on the right side. You can also drag (press and hold mouse left button, drag across chart to see a
box and then release left mouse button) to zoom in to chart. Note that zoomed da ta may get shifted
when the data expired in the current last time span setting. To reset zoom, double click on chart
area. Data polled will be stored in web browser's cache upon leaving the page or closing the
browser. Since browser stores cache per website, it is recommended to have a static IP, reserved
IP address in DHCP server or access unit by hostname. It is highly recommen ded to use the latest
web browser versions to run the chart. Running chart with IE8 or below will be very slow. Also, you
may need to update your graphic card drivers to optimize chart stability.
Figure 10-1 Charting Options in the Chart Tab by xSenso Model
xSenso User Guide 59
Page 60

Data Chart Configuration
Data Chart Settings Description
Last Select the span of time to be charted:
Minute (charts one full minute at 1 second intervals)
Hour (charts one full hour at 5 second intervals)
Day (charts one full day at 1 minute intervals)
Week (charts one full week at 10 minute intervals)
Month (charts one full month at 1 hour intervals)
Input 1/Input 2
Output 1/Output2
Relay 1/Relay 2
Normal/Bold/Hide Select from the drop-down menu to specify the visual appearance of the charted line
Min The minimum span associated with the y-axis of the chart.
Max The maximum span associated with the y-axis of the chart.
Alarm Check to enable display of current alarm point as a line across the time span.
Generate Snapshot Click button to generate a snapshot of the chart at any moment. The snapshot of the
Remove Snapshot Click to remove a snapshot at any moment. The snapshot of the chart will disappear
Select from the drop-down menu to indicate the input, relay and/or output to be
charted along the left/right y axis. Relay is charted as 1 if it is energized/turned on or
0 if it is de-energized/turned off.
Note: Output 1 and Output 2 selections are only supported in xSenso 21A2.
Relay 1 and Relay 2 selections are only supported in xSenso 21R2. See Figure 10-1.
to display on the chart.
chart will appear beneath the live chart. Save a snapshot by following these
directions:
1) Right-click on the snapshot.
2) Select Save As in the popup menu.
3) Save image to desired location.
Note: This button appears only if a snapshot is not currently showing beneath the
live chart.
from beneath the live chart.
Note: This button appears only if a snapshot is currently showing beneath the live
chart.
10: Chart
Table 10-2 Data Chart Settings
To Configure Data Chart Settings
Using Web Manager
To view a chart, click the Chart tab to get to the Chart page.
xSenso User Guide 60
Page 61

11: Logging
The xSenso Logging tab/page provides access to the data logging feature availa ble with browsers
that support HTML5 and filesystem API (e.g., Chrome). Users can run customized data logs
through this page. Upon the first visit, the browser will ask for your permission to allow this device
to store data on your PC. Choose Ok. Browser will poll data from xSenso every period (1 minute
default) as configured by user. Data is stored in the browser sandbox filesystem and its usage and
total size is shown below the start/stop data logging button. In the past, webpages were not
allowed to access the PC's local filesystem because this would raise security issues (this is exactly
what a virus wants to do). A browser supporting filesystem API allows webpage to save dat a i n it s
own dedicated sandbox filesystem, which becomes the only accessible webpage. Data logging
application stores data here and you can click on the filename to download these log files from the
sandbox filesystem to anywhere on your local computer, just like downloading any file from the
web. Please note that the browser stores data in sandbox filesystem per website, so it is
recommended to have static IP, reserved IP address in DHCP server or access unit by ho stname.
It is recommended to use dedicated PC to log data to optimize data logging stability.
Figure 11-1 xSenso 2100 Logging Tab
xSenso User Guide 61
Page 62

Figure 11-2 xSenso 21A2 Logging Tab
11: Logging
Figure 11-3 xSenso 21R2 Logging Tab
xSenso User Guide 62
Page 63

Data Logging Configuration
Table 11-4 Data Logging Settings
11: Logging
Data Logging
Settings
Filename Enter the filename of the log file. This will be saved in the browser's sandbox
Period Specify in seconds, how often the browser will poll data from the xSenso device.
Title
Description
filesystem.
Specify the title as it will appear in the log files.
You can use this besides the
filename to identify each data logging session.
Header‘
Check to enable or disable the header in the log files.
Header gives you
description of each column in the log file, e.g. Date and Time, Input 1 and
Input 2.
Timestamp Select timestamp logged should be generated from local PC running the web
browser or time (uptime/clock) coming from the device.
Input Check the analog inputs to be include d in logging.
Output Check the analog outputs to be included in logging.
Note: This option is only supported in xSenso 21A2.
Relay Check the relay outputs to be included in logging.
Note: This option is only supported in xSenso 21R2.
Start Data Logging Click button to manually begin data logging according to current user settings.
Stop Data Logging Click button to manually stop data logging.
Refresh Files
Click button to refresh log files list.
List may need to be refreshed in order to
view all log files created when multiple data logging session happens on
the same PC.
Remove All Files
Click button to delete any accumulated logs from
filesystem
.
from browser's sandbox
To Configure Data Logging Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure data logging, click the Logging tab to get to the Logging page.
xSenso User Guide 63
Page 64

12: Reading
Note: Max, Min and Average input values
will be lost if you navigate away from this
page. Cumulative values are calculated
since the last time the page was opened.
The xSenso Reading tab provides access to a live readings page of analog inputs, outputs and
relays. This page is read-only, providing the following dynamic information for each input and
analog or relay outputs:
Input Value
Input Alarm High Value (if applicable)
Input Alarm Low Value (if applicable)
Input Maximum Value
Input Average Value
Input Minimum Value
Output Value
Output Alarm High Value (if applicable)
Output Alarm Low Value (if applicable)
Output Maximum Value
Output Average Value
Output Minimum Value
Relay Output Value
Titles and units for this Reading page are configurable under Analog Input, Analog Output and
Relay Output settings, according to xSenso model . You may also hide an input, outputs or relays
by disabling its display. Data is polled from xSenso every second. Maximum, mininum and
average values are calculated based on these data samples. To re set the maximum, mininum and
average values, simply refresh the webpage. An input entering alarm zone will be blinking in red.
Figure 12-1 xSenso 2100 Reading Tab
xSenso User Guide 64
Page 65

Figure 12-2 xSenso 21A2 Reading Tab
12: Reading
Figure 12-3 xSenso 21R2 Reading Tab
Data Reading Configuration
To View Data Reading Settings
Using Web Manager
To view live readings information, click the Reading tab to get to the Reading page.
xSenso User Guide 65
Page 66

13: Action Settings
Actions can be configured for alarms and repo r ts available in the xSenso. Certain alarms and
reports are available in all the xSenso products wherea s the output alarms are only available in the
xSenso 21A2 as seen in Table 13-1 xSenso Alarms and Reports below.
Alarms and Reports
Table 13-1 xSenso Alarms and Reports
xSenso 2100 xSenso 21A2 xSenso 21R2
Terminal Block Power Alarm
Barrel Connector Power Alarm
Input 1 Alarm
Input 2 Alarm
Status Report 1
Status Report 2
Terminal Block Power Alarm
Barrel Connector Power Alarm
Input 1 Alarm
Input 2 Alarm
Status Report 1
Status Report 2
Output 1 Alarm
Output 2 Alarm
Terminal Block Power Alarm
Barrel Connector Power Alarm
Input 1 Alarm
Input 2 Alarm
Status Report 1
Status Report 2
Reference the appropriate action tables below for specific configuration settings for the alarms and
reports listed in Table 13-1 xSenso Alarms and Reports above:
Table 13-3 Make Connection Settings
Table 13-3 Make Connection Settings
Table 13-4 Send Email Settings
Table 13-5 FTP Put Settings
Table 13-6 HTTP Post Settings
Table 13-7 Control Relay SettingsT
Table 13-8 SNMP Trap Settings
Actions Available for Alarms and Reports
Table 13-2 Control Analog Output Settings
Note: Control analog output settings are only available in the xSenso 21A2 and not
available for status reports or analog output alarms.
Contol Analog Output
Settings
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
Description
Select Control Analog Output for the alarm. The Output will appear.
xSenso User Guide 66
Page 67

13: Action Settings
Contol Analog Output
Description
Settings (continued)
Output Select the output number from the drop-down menu. Additional Analog Output
configuration fields become available if a specific output number is selected.
Selecting "None" stops control of analog output and does not reset the output
value.
Alarm Value Provid e the value to be asserted on the selected Analog Output when the alarm
is turned on.
Normal Value Provide the value to be asserted on the selected Analog Output when alarm is
turned off.
Table 13-3 Make Connection Settings
Make Connection
Settings
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
Address To establish a connection when the alarm is on, provide either a DNS or IP
Reporting Check the types of reporting to include:
Reminder Interval Specify how long to wait in seconds before trying to reconnect to the remote
Port Enter the port number.
Mode Select the mode:
Protocol Select the appropriate protocol: TCP, UDP, SSH, Telnet, TCP AES, UDP AES,
Description
Select Make Connection for the alarm or report. The Address field will appear.
You can create up to 10 connections. Repeat entry for the fields below of each
connection. There are a maximum of 10 connections for each alarm type and a
total of 40 hosts under “make connection” across all alarm types.
address of the remote host. Multiple connection and reporting options will
appear.
Serial Number
System Long Name
Terminal Block
Barrel Connector
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Output 1
Analog Output 2
Relay Output 1
Relay Output 2
Note: Analog outputs are only supported for xSenso 21A2 and relay outputs are
only supported for xSenso 21R2. Your reporting selections made here will apply
for all the connections you make.
host. Blank the display field to disable reminders. If more than one Connect host
is specified, connections are attempted without delay; so the single Reminder
Interval applies to the delay between successive attempts to them all. Data will
only be sent once by default.
Sequential
Simultaneous
Note: This configuration field appears when more than one connection is
enabled.
and SSL.
xSenso User Guide 67
Page 68

13: Action Settings
Make Connection
Description
Settings (continued)
SSH Username Specify the SSH Client User for the SSH outgoing connection if the SSH protocol
is selected for this connection. You may select from the drop-down menu of
existing users or you may enter a new user name. This configuration field is only
available if the SSH protocol is selected.
AES Encrypt Key Enter an AES encryption key to encrypt outgoing data and select Hexadecimal
or Text. This configuration field is only available if either TCP AES or UDP AES
protocol is selected.
AES Decrypt Key Enter an AES decryption key to decrypt incoming data and select Hexadecimal
or Text. This configuration field is only available if either TCP AES or UDP AES
protocol is selected.
Validate Certificate Check to enable or disable validation certificate, if SSL protocol is selected. This
configuration field is only available if the SSL protocol is selected.
Enabling Validate Certificate requries the server to verify the remote SSL
server certificate when making a connection.
Disabling Validate Certificate causes the server to skip verification of the
remote SSL certificate.
Credentials Specify the name of the set of RSA and/or DSA certificates and keys to be used
for the SSL connection. This configuration field is only available if the SSL
protocol is selected.
Table 13-4 Send Email Settings
Send Email Settings Description
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
Select Send Email for the alarm or report. Repeat entry for the fields below of
each email.
Alarm Email Select an alarm profile number which will send an email when the alarm is turned
on. Multiple connection and reporting options will appear.
Normal Email Select an alarm profile number which will send an email when the alarm is turned
off. Multiple normal email configuration options will appear.
Reporting Check the types of reporting to include:
Serial Number
System Long Name
Terminal Block
Barrel Connector
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Output 1 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Analog Output 2 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Relay Output 1 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Relay Output 2 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Note: Your reporting selections made here will apply for both the alarm and
normal emails established.
Alarm Message Specify the message that would appear in the alarm email message to be sent.
Alarm Reminder
Interval
Specify how long to wait in minutes after the alarm stays on before another alarm
email is sent. Blank the display field to disable reminders. Email will only be sent
once by default.
Normal Message Specify the message that would appear in the normal email message to be sent.
xSenso User Guide 68
Page 69

13: Action Settings
Send Email Settings Description
Normal Reminder
Interval
Specify how long to wait in minutes after the alarm stays off before another
normal email is sent. If this is a status report, a normal email is sent periodically
according to the stated reminder interval. Blank the display field to disable
reminders. Email will only be sent once by default.
Table 13-5 FTP Put Settings
FTP Put Settings Description
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
Host Enter the FTP server IP address or hostname to be connected to. Multiple FTP
Reporting Check the types of reporting to include:
Reminder Interval Specify how long to wait in minutes before trying to reconnect to the remote host.
Port Enter the port number which FTP server is listening to.
Mode Select the mode:
Filename Enter the file name to be used to upload to remote FTP server. If file already
Protocol Select the appropriate protocol to connect to the FTP server: FTP or FTPS.
Username Specify the Username for logging on to the FTP server. IF FTP server does not
Password Specify the Password for logging on to the FTP server. IF FTP server does not
Select FTP Put for the alarm or report. The Host field will appear. You can
create up to 2 connections. Repeat entry for the fields below of each FTP Put
Host.
Put configuration options will appear.
Serial Number
System Long Name
Terminal Block
Barrel Connector
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Output 1 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Analog Output 2 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Relay Output 1 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Relay Output 2 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Note: Your reporting selections made here will apply for all the connections you
make.
Blank the display field to disable reminders. If more than one Connect host is
specified, connections are attempted without delay; so the single Reminder
Interval applies to the delay between successive attempts to them all. Data will
only be sent once by default.
Sequential
Simultaneous
Note: This configuration field appears when more than one connection is
enabled.
exists, new data will be appended to remote file.
require authentication, use anonymous.
require authentication, a common practice is to use user’s email address.
xSenso User Guide 69
Page 70

13: Action Settings
Table 13-6 HTTP Post Settings
HTTP Post Settings Description
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
Host Enter the HTTP server IP address or hostname to be connected to. Multiple
Reporting Check the types of reporting to include:
Reminder Interval
Port Enter the port number which HTTP server is listening to.
URL Enter the URL to be used to post to remote HTTP se rver.
Protocol Select the appropriate protocol to connect to the HTTP server: HTTP or
Username Specify the Username for logging on to the HTTP server. Both Basic and Digest
Password Specify the Password for logging on to the HTTP server. If HTTP server does
Select HTTP Post for the alarm or report. The Host field will appear. You can
create up to 2 connections. Repeat entry for the fields below of each HTTP Post
Host.
HTTP Post configuration options will appear.
Serial Number
System Long Name
Terminal Block
Barrel Connector
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Output 1 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Analog Output 2 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Relay Output 1 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Relay Output 2 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Note: Your reporting selections made here will apply for all the connections
you make.
Specify how long to wait in minutes befor
e trying to reconnect to the remote
host. Blank the display field to disable reminders. If more than one Connect
host is specified, connections are attempted without delay; so the single
Reminder Interval applies to the delay between successive attempts to them
all. Data will only be sent once by default.
HTTPS.
Authentications are supported. If HTTP server does not require authentication,
leave blank.
not require authentication, leave blank.
Table 13-7 Control Relay Settings
Normally Open Port is closed to Common and Normally Closed Port is open/disconnected from
Common when relay is energized/turned on. Normally Open Port is open/disconnected from
Common and Normally Closed Port is closed to Common when relay is de-energized/turned off.
Note: Control relay settings are only available in the xSenso 21R2 and is not available
for status reports.
Control Relay Settings Description
Add an Action
Select Control Relay for the alarm. The Alarm Energize field will appear.
(drop-down menu)
Alarm Energize Select either Relay 1 or Relay 2 to turn on when this is alarm is turned on.
Selecting None will cause the alarm state to have no effect on either relay.
xSenso User Guide 70
Page 71

13: Action Settings
Table 13-8 SNMP Trap Settings
SNMP Settings Description
Add an Action
(drop-down menu)
State Check to enable or disable:
Reporting Check the types of reporting to include:
Reminder Interval Specify how long to wait in minutes before an SNMP Trap is sent to the remote
Select SNMP Trap for the alarm or report.
Introduce additional SNMP Trap configuration fields when enabled.
Serial Number
System Long Name
Terminal Block
Barrel Connector
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Output 1 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Analog Output 2 (for xSenso 21A2 only)
Relay Output 1 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Relay Output 2 (for xSenso 21R2 only)
Note: Your reporting selections made here will apply for all the connections you
make.
host. Blank the display field to disable reminders. Data will only be sent once by
default.
To Configure Terminal Block Power Alarm Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure terminal block power alarm, go to the Setup tab/page, click Action in the menu,
and select Terminal Block Power Alarm from the drop-down menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the terminal block power alarm command level: enable -> config -> action
-> terminal block power alarm
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name = "action" instance = "Terminal
Block Power Alarm">
To Configure Barrel Connector Power Alarm Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure barrel connector power alarm, go to the Setup tab/page, click Action in the
menu, and select Barrel Connector Power Alarm from the drop-down menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the barrel connector power alarm command level: enable -> config ->
action -> barrel connector block power alarm
xSenso User Guide 71
Page 72

13: Action Settings
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name = "action" instance = "Barrel
Connector Power Alarm">
To Configure Input 1 and 2 Alarm Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure input 1 and input 2 alarms, go to the Setup tab/page, click Action in the menu,
and select Input (1 or 2) Alarm from the drop-down menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the input (1 or 2) alarm command level: enable -> config -> action ->
input 1 alarm
Using XML
Include in your file:
<configgroup name = "action" instance = "Input 1 Alarm">
To Configure Status Reports 1 and 2 Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure status reports 1 or 2, go to the Setup tab/page, click Action in the menu, and
select Status Report (1 or 2) from the drop-down menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the Report (1 or 2) command level: enable -> config -> action -> status
report 1
Using XML
Include in your file:
<configgroup name = "action" instance = "Status Report 1">
To Configure Output 1 and 2 Alarm Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure output 1 or output 2 alarms, go to the Setup tab/page, click Action in the menu,
and select Output (1 or 2) Alarm from the drop-down menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the report (1 or 2) command le vel: enable -> config -> action -> output
1 alarm
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name = "action" instance = "Output 1
Alarm">
xSenso User Guide 72
Page 73

14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings
The xSenso 2100, xSenso 21A2 and xSenso 21R2 have two tunnels thro ugh which you may view
statistics or configure the Accept Mode. The Modbus configuration page allows configuration of
Modbus servers listening on the TCP ports.
Tunnel Settings
Tunneling parameters are configured using the Tunnel menu and submenus. The Tunnel settings
allow you to configure how the Network tunneling operates.
Note: The following section describes the steps to view and configure Tunnel 1 settings;
these steps apply to other tunnel instance s of the de vic e.
Accept Mode
In Accept Mode, the xSenso listens (waits) for incoming connections from the network. A remote
node on the network initiates the connection.
The configurable local port is the port the remote device connects to for this connection.
Table 14-1 Tunnel Accept Mode Settings
Tunnel Accept Mode
Settings
Mode Set the method used to start a tunnel in Accept mode. Choices are:
Local Port Set the port number for use as the network local port. The default local port
Protocol Select the protocol type for use with Accept Mode:
Credentials Specifies the name of the set of RSA and/or DSA certificates and keys to
AES Encrypt Key Specify the text or hexadecimal advanced encryption standard (AES) key
AES Decrypt Key Specify the text or hexadecimal AES key for decrypting incoming data for a
Description
Disable = do not accept an incoming connection.
Always = accept an incoming connection (default).
number:
Tunnel 1 : 10001
Tunnel 2 : 10002
SSH
SSL
TCP (default protocol)
TCP AES
Telnet
be used for an SSL connection.
for encrypting outgoing data for a TCP AES connection.
TCP AES connection.
xSenso User Guide 73
Page 74

14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings
Tunnel Accept Mode
Description
Settings (continued)
TCP Keep Alive Enter the time, in milliseconds, the xSenso waits during a silent TCP
connection before checking if the currently connected network device is
still on the network. If the unit gets no response after 1 attempt, it drops
the connection. Enter 0 to disable.
Block Network Set whethe r Block Network is enabled for debugging purposes. Choices
are:
Enabled = if Enabled, incoming characters from the network will not be
processed. Instead, they will be buffered and will eventually flow off the
network side.
Disabled = this is the default setting; incoming characters from the
network will be processed. Any buffered characters are sent first.
Password Enter a password. This password can be up to 31 characters in length and
must contain only alphanumeric characters and punctuation. When set,
clients must send the correct password string to the unit within 30 seconds
from opening network connection in order to enable data transmission.
The password sent to the unit must be terminated with one of the following:
0A (Line Feed)
00 (Null)
0D 0A (Carriage Return/Line Feed)
0D 00 (Carriage Return/Null)
If, Prompt for Password is set to Enabled and a password is provided,
the user will be prompted for the password upon connection.
Prompt for Password Select Enabled or Disabled (to enable or disable). This option will only
appear if a password is specified above.
Email on Connect Select an email profile number to which an email notification will be sent
upon the establishment of an accept mode tunnel.
Email on Disconnect Select an email profile number to which an email notification will be sent
upon the disconnection of an accept mode tunnel.
To Configure Tunnel Accept Mode Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure the Accept Mode for a specific tunnel, go to the Setup tab/page, click Tunnel in
the menu and select Tunnel 1 -> Accept Mode.
Using the CLI
To enter Tunnel 1 Accept Mode command level: enable -> tunnel 1 -> accept
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name="tunnel accept" instance="1">
xSenso User Guide 74
Page 75

Modbus Settings
The Modbus server, if enabled, is active on TCP port 502. If present, the additional TCP port is
also used. Modbus TCP parameters are configured using the Mod bus menu and submenus under
Admin.
Modbus Settings Description
TCP Server State Click to turn the TCP server state On or Off. The TCP port is 502.
Additional TCP Server Port
Response Timeout Enter the amount of time, in milliseconds, where the Modbus server will
RSS Trace Input Click to turn RSS trace input On or Off. If RSS trace input is enabled, each
To Configure Modbus Settings
14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings
Table 14-2 Modbus Settings
If present,
timeout in lieu of a response.
PDU received on the Modbus serial line creates a non-persistent
descriptive item in the RSS feed.
the Modbus server also listens on this TCP port.
Using Web Manager
To configure the Modbus, go to the Admin tab/page and click Modbus in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the Modbus command level: enable -> config -> modbus
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name="modbus">
Supported Modbus TCP/IP Functions and Registers
Table 14-3 0xxxx Read/Write Coils (Function Codes 1, 5 and 15)
Device Address Modbus Address Description
00001 0x0000 0: Relay 1 Off, 1: Relay 1 On
00002 0x0001 0: Relay 2 Off, 1: Relay 2 On
00003 0x0002 Write 1 to reset latched Relay 1
00004 0x0003 Write 1 to reset latched Relay 2
xSenso User Guide 75
Page 76

14: Tunnel and Modbus Settings
Table 14-4 3xxxx Read Only Registers (Function Codes 4 and 23)
Device Address Modbus Address Description
30001 0x0000 Input 1 high word of float (Float AB CD)
30002 0x0001 In put 1 low word of float (Float AB CD)
30003 0x0002 Input 2 high word of float (Float AB CD)
30004 0x0003 In put 2 low word of float (Float AB CD)
Table 14-5 4xxxx Read/Write Holding Registers (Function Codes 3, 16 and 23)
Device Address Modbus Address Description
40001 0x0000 Output 1 high word of float (Float AB CD)
-1 will be returned if voltage output is shorted.
-2 will be returned if current output is opened.
40002 0x0001 Output 1 low word of float (Float AB CD)
40003 0x0002 Output 2 high word of float (Float AB CD)-1 will be
returned if voltage output is shorted.
-2 will be returned if current output is opened.
40004 0x0003 Output 2 low word of float (Float AB CD)
Note: The device will respond to any unit identifier less than 247 since each unit is
uniquely identified by its IP address already.
xSenso User Guide 76
Page 77

15: Services Settings
DNS Settings
This section describes the active run-time settings for the domain name system (DNS) protocol.
The primary and secondary DNS addresses come from the active interface. The static addresses
from the Network Interface configuration settings may be overridden by DHCP.
Note: The blue text in the XML command strings of this chapter are to be replaced with
a user-specified name.
Setting / Field Description
Lookup Perform one of the following:
Enter an IP address, and perform a reverse Lookup to locate the hostname for
that IP address
Enter a hostname, and perform a forward Lookup to locate the corresponding IP
address
To View or Configure DNS Settings:
Table 15-1 DNS Settings
Using Web Manager
To view DNS current status, go to the Admin tab/page and click DNS in the menu.
To lookup DNS name or IP address, go to the Admin tab/page and click DNS in the menu to
access the Lookup field.
Note: To configure DNS for cases where it is not supplied by a protocol, o to the Admin
tab/page, click Network in the menu and select Interface -> Configuration.
Using the CLI
To enter the DNS command level: enable -> dns
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”interface” instance=”eth0”>
xSenso User Guide 77
Page 78

FTP Settings
The FTP protocol can be used to upload and download user files, and upgrade the xSenso
firmware. A configurable option is provided to enable or disable access via this protocol.
FTP Settings Description
State Select to enable or disable the FTP server:
To Configure FTP Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure FTP, go to the Admin tab/page and click FTP in the menu.
Using the CLI
15: Services Settings
Table 15-2 FTP Settings
Enabled (default)
Disabled
To enter the FTP command level: enable -> config -> ftp
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”ftp server”>
Syslog Settings
The Syslog information shows the current configuration and statistics of the syslog. Here you can
configure the syslog host and the severity of the events to log.
Note: The system log is always saved to local storage, but it is not retained through
reboots unless diagnostics logging to the filesystem is enabled. Saving the system log to a
server that supports remote logging services (see RFC 3164) allows the administrator to
save the complete system log history. The default port is 514.
Syslog Settings Description
State Select to enable or disable the syslog:
Host Enter the IP address of the remote server to which system logs are sent for storage.
Remote Port Enter the number of the port on the remote server that supports logging services.
Table 15-3 Syslog Settings
Enabled
Disabled (default)
The default is 514.
xSenso User Guide 78
Page 79

15: Services Settings
Syslog Settings
(continued)
Severity Log Level Specify the minimum level of system message the should log. This setting applies
To View or Configure Syslog Settings:
Using Web Manager
To configure the Syslog, go to the Admin tab/page and click Syslog in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the Syslog command level: enable -> config -> syslog
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”syslog”>
HTTP Settings
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the transport protocol for communica ting hypertext
documents on the Internet. HTTP defines how messages are formatted and transmitted. It also
defines the actions web servers and browsers should take in response to different commands.
HTTP Authentication enables the requirement of usernames and passwords for access to the
device.
Description
to all syslog facilities. The drop-down list in the Web Manager is in descending order
of severity (e.g., Emergency is more severe than Alert.)
Table 15-4 HTTP Settings
HTTP Settings Description
State Select to enable or disable the HTTP server:
Enabled (default)
Disabled
Port Enter the port for the HTTP server to use. The default is 80.
Secure Port Enter the port for the HTTPS server to use. The default is 443. The HTTP
server only listens on the HTTPS Port when an SSL certificate is configured.
Secure Protocols Select to enable or disable the following protocols:
SSL3 = Secure Sockets Layer version 3
TLS1.0 = Transport Layer Security version 1.0. TLS 1.0 is the successor of
SSL3 as defined by the IETF.
TLS1.1 = Transport Layer Security version 1.1
The protocols are enabled by default.
Note: A server certificate and associated private key need to be installed in
the SSL configuration section to use HTTPS.
Secure Credentials Specify the name of the set of RSA and/or DSA certificates and keys to be
used for the secure connection.
xSenso User Guide 79
Page 80

15: Services Settings
HTTP Settings (continued) Description
Max Timeout Enter the maximum time for the HTTP server to wait when receiving a
request. This prevents Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. The default is 10
seconds.
Max Bytes Enter the maximum number of bytes the HTTP server accepts when receiving
a request. The default is 40 KB (this prevents DoS attacks).
Note: You may need to increase this number in some cases where the
browser is sending data aggressively within TCP windows size limit, when file
(including firmware upgrade) is uploaded from webpage.
Logging State Select to enable or disable HTTP server logging:
Enabled (default)
Disabled
Max Log Entries Set the maximum number of HTTP server log entries. Only the last Max Log
Entries are cached and viewable.
Log Format Set the log format string for the HTTP server. Follow these Log Format rules:
%a - remote IP address (could be a proxy)
%b - bytes sent excluding headers
%B - bytes sent excluding headers (0 = '-')
%h - remote host (same as '%a')
%{h}i - header contents from request (h = header string)
%m - request method
%p - ephemeral local port value used for request
%q - query string (prepend with '?' or empty '-')
%t - timestamp HH:MM:SS (same as Apache '%(%H:%M:%S)t' or
'%(%T)t')
%u - remote user (could be bogus for 401 status)
%U - URL path info
%r - first line of request (same as '%m %U%q <version>')
%s - return status
Authentication Timeout The timeout period applies if the selected authentication type is either Digest
or SSL/Digest. After this period of inactivity, the client must authenticate
again.
To Configure HTTP Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure HTTP settings, o to the Admin tab/page, click HTTP in the menu and select
Configuration.
To view HTTP statistics, click HTTP in the menu and select Statistics.
Using the CLI
To enter the HTTP command level: enable -> config -> http
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”http server”>
xSenso User Guide 80
Page 81

Table 15-5 HTTP Authentication Settings
15: Services Settings
HTTP Authentication
Settings
URI Enter the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
Auth Type Select the authentication type:
Description
Note: The URI must begin with ‘/’ to refer to the filesystem.
None = no authentication is necessary.
Basic = encodes passwords using Base64.
Digest = encodes passwords using MD5.
SSL = can only be accessed over SSL (no password is required).
SSL/Basic = is accessible only over SSL and encodes passwords using Base64.
SSL/Digest = is accessible only over SSL and encodes passwords using MD5.
Note: When changing the parameters of Digest or SSL Digest authentication, it is
often best to close and reopen the browser to ensure it does not attempt to use
cached authentication information.
To Configure HTTP Authentication
Using Web Manager
To configure HTTP Authentication, o to the Admin tab/page, click HTTP in the menu and
select Authentication.
Using the CLI
To enter the HTTP command level: enable -> config -> http
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”http authentication uri”
instance=”uri name”>
RSS Settings
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) (sometimes referred to as Rich Site Summary) is a method of
feeding online content to Web users. Instead of actively searching for configuration changes, RSS
feeds permit viewing only relevant and new information regarding changes made via an RSS
publisher. The RSS feeds may also be stored to the file system cfg_log.txt file.
RSS Settings Description
RSS Feed Select On or Off for RSS feeds to an RSS publisher. The default settin g is off.
Persistent Select On or Off for RSS feed to be written to a file (cfg_log.txt) and to be available
Max Entries Set the maximum number of log entries. Only the last Max Entries are cached and
View Click the button to view RSS feeds.
Table 15-6 RSS Settings
across reboots. The default setting is off.
viewable.
xSenso User Guide 81
Page 82

RSS Settings Description
Clear Click the button to clear RSS feed data.
To Configure RSS Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure RSS, go to the Admin tab/page and click RSS in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the RSS command level: enable -> config -> rss
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”rss”>
SNMP Settings
15: Services Settings
Simple Network management Protocol (SNMP) settings may be viewed and configured in this
section.
Table 15-7 SNMP Settings
RSS Settings Description
State Select to enable or disable the SNMP agent state.
Version Select the SNMP version used by the SNMP agent.
Read Community Specify the read community used by the agent (defaults to public community).
Write Community Specify the write community used by the agent (defaults to private community).
Engine ID Show SNMPv3 Engine ID, if SNMPv3 version is selected.
Username Enter the SNMPv3 Username if SNMPv3 version and authentication are selected.
Security Select whether authentication and/or privacy should be used by the agent, if
SNMPv3 version and authentication are selected.
Authentication
Protocol
Authentication
Password
Privacy Protocol Select the privacy encryption method to be used by the agent, if SNMPv3,
Privacy Password Enter the password to be used for privacy encryption by the agent, if SNMPv3
System Contact Specify the system contact.
System Name Update the system name, as necessary. The default system name is xSenso 2100,
Select which authentication protocol should be used by the agent, if SNMPv3
version and authentication are selected.
Enter the authentication password to be used by the agent, if SNMPv3 version and
authentication are selected. Must be at least eight (8) characters.
authentication and privacy are selected.
version, authentication and privacy are selected. Must be at least eight (8)
characters.
xSenso 21A2 or xSenso 21R2, depending the xSenso model.
xSenso User Guide 82
Page 83

15: Services Settings
RSS Settings Description
System Description Update the system description, as necessary. The default system information
includes the manufacturer name, xSenso model name, version and the serial
number of the device.
System Location Specify a system location for the SNMP setting.
Lantronix MIB File Click the Lantronix MIB file name to save and load it into the MIB browser and trap
receiver.
xSenso MIB File Click the xSenso MIB file name to save and load it into the MIB browser and trap
receiver.
Primary Destination Enter the primary SNMP trap receiver for the enabled SNMP agent. This is either
an IP address or a hostname.
Secondary
Destination
Enter the secondary SNMP trap receiver for the enabled SNMP agent. This is
either an IP address or a hostname.
To Configure SNMP Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure SNMP, go to the Admin tab/page and click SNMP in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the SNMP command level: enable -> config -> snmp
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”snmp”>
SMTP Settings
Protocol Stack SMTP
Settings
From Address Enter the From Address here. This is an email address and is required. If you wish
Server Address Enter the Server Address to direct outbound email messages through a mail
Server Port Enter the SMTP server port number. The default is 25
Username Enter a Username to direct outbound email messages through a mail server.
Password Enter a Password to direct outbound email messages through a mail server.
Overriding Domain Enter the domain name to override the current domain name in EHLO (Extended
Table 15-8 SMTP Network Stack Settings
Description
to direct oubtound email messages through a mail server, put your client email
address here.
server.
Hello).
xSenso User Guide 83
Page 84

15: Services Settings
To Configure SMTP Network Stack Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure SMTP protocol settings, go to the Admin tab/page and click SMTP in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> smtp
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”smtp”>
xSenso User Guide 84
Page 85

16: Security Settings
The xSenso device supports Secure Shell (SSH) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSH is a
network protocol for securely accessing a remote device. SSH provides a secure, encrypted
communication channel between two hosts over a network. It provides authentication and
message integrity services.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol that manages data transmission security over the
Internet. It uses digital certificates for authentication and cryptography against eavesdropping and
tampering. It provides encryption and message integrity services. SSL is widely used for secure
communication to a web server. SSL uses certificates and private keys.
Note: The device supports SSLv3 and its successors, TLS1.0 and TLS1.1. An incoming
SSLv2 connection attempt is answered with an SSLv3 response. If the initiator also
supports SSLv3, SSLv3 handles the rest of the connection.
SSH Settings
SSH is a network protocol for securely accessing a remote device over an encrypted channel. This
protocol manages the security of internet data transmission between two hosts over a network by
providing encryption, authentication, and message integrity services.
Two instances require configuration: when the xSenso is the SSH server and when it is an SSH
client. The SSH server is used by the CLI (Command Mode) and for tunneling in Accept Mode.
The SSH client is for Action Connect Mode.
To configure the xSenso as an SSH server, there are two requirements:
Defined Host Keys: both private and public keys are required. These keys are used for the
Diffie-Hellman key exchange (used for the underlying encryption protocol).
Defined Users: these users are permitted to connect to the xSenso SSH server.
SSH Server Host Keys
The SSH Server Host Keys are used by all applications that play the role of an SSH Server.
Specifically Tunneling in Accept Mode. These keys can be created elsewhere and uploaded to the
device or automatically generated on the device.
If uploading existing keys, take care to ensure the Private Key will not be compromised in transit.
This implies the data is uploaded over some kind of secure private network.
Note: Some SSH Clients require RSA Host Keys to be at least 1024 bits in size.
Table 16-1 SSH Server Host Keys
RSS Settings Description
Private Key Enter the path and name of the existing private key you want to upload. In
WebManager, you can also browse to the private key to be uploaded. Be sure the
private key will not be compromised in transit. This implies the data is uploaded over
some kind of secure private network.
xSenso User Guide 85
Page 86

16: Security Settings
RSS Settings
(continued)
Public Key Enter the path and name of the existing public key you want to upload. In
Key Type Select a key type to use for the new key:
Bit Size Select a bit length for the new key:
Description
WebManager, you can also browse to the public key to be uploaded.
RSA
DSA
512
768
1024
Note: SSH Keys from other programs may be converted to the required format. Use
Open SSH to perform the conversion.
SSH Client Known Hosts
The SSH Client Known Hosts are used by all applications that play the role of an SSH Client.
Specifically in Action Connect Mode. Configuring these public keys are optional but if they exist
another layer of security is offered which helps prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.
Table 16-2 SSH Client Known Hosts
RSS Settings Description
Server Specify either a DNS Hostname or IP Address when adding pu blic host keys for a
Server. This Server name should match the name used as the Remote Address in
Action Connect Mode.
Public RSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public RSA key you want to use with this
user. In WebManager, you can also browse to the public RSA key to be uploaded. If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
Public DSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public DSA key you want to use with this
user. In WebManager, you can also browse to the public DSA key to be uploaded.If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
Note: These settings are not required for communication. They protect against Man-In-
The-Middle (MITM) attacks.
SSH Server Authorized Users
The SSH Server Authorized Users are used by all applications that play the role of an SSH Server
and specifically Tunnel Accept. Every user account must have a Password.
The user's Public Keys are optional and only necessary if public key authentication is wanted.
Using public key authentication will allow a connection to be made without the password being
asked at that time.
Note: When uploading the security keys, ensure the keys are not compromised in
transit.
xSenso User Guide 86
Page 87

16: Security Settings
Table 16-3 SSH Server Authorized Users
RSS Settings Description
Username Enter a new username or edit an existing one.
Password Enter a new password or edit an existing one.
Public RSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public RSA key you want to use with this
user. In WebManager, you can also browse to the public RSA key to be uploaded. If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
Public DSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public DSA key you want to use with this
user. In WebManager, you can also browse to the public DSA key to be uploaded.If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
SSH Client Users
The SSH Client Users are used by all applications that play the role of an SSH Client. Specifically
Action Connect Mode. To configure the xSenso as an SSH client, an SSH client user must be
both configured and also exist on the remote SSH server.
At the very least, a Password or Key Pair must be configured for a user. The keys for public key
authentication can be created elsewhere and uploaded to the device or automatically generated
on the device.
If uploading existing Keys, take care to ensure the Private Key will not be compromised in transit.
This implies the data is uploaded over some kind of secure private network.
The default Remote Command is '<Default login shell>' which tells the SSH Server to execute a
remote shell upon connection. This can be changed to anything the SSH Server on the remote
host can execute.
Note: If you are providing a key by uploading a file, make sure that the key is not
password protected.
Table 16-4 SSH Client Users
RSS Settings Description
Username Enter the name that the device uses to connect to an SSH server.
Password Enter the password associated with the username.
Remote Command Enter the command that can be executed remotely. Default is shell, which tells the
SSH server to execute a remote shell upon connection. This command can be
changed to anything the remote host can perform.
Private Key Enter the path and name of the existing private key you want to upload. In
WebManager, you can also browse to the private key to be uploaded. Be sure the
private key will not be compromised in transit. This implies the data is uploaded over
some kind of secure private network.
Public Key Enter the path and name of the existing public key you want to upload. In
WebManager, you can also browse to the public key to be uploaded.
Key Type Select a bit length for the key:
RSA
DSA
xSenso User Guide 87
Page 88

16: Security Settings
RSS Settings
Description
(continued)
Bit Size Select the bit length of the new key:
512
768
1024
Using a larger Bit Size takes more time to generate the key. Approximate times are:
1 second for a 512 bit RSA key
1 second for a 768 bit RSA key
1 second for a 1024 bit RSA key
2 seconds for a 512 bit DSA key
2 seconds for a 768 bit DSA key
20 seconds for a 1024 bit DSA key
Note: Some SSH clients require RSA host keys to be at least 1024 bits long. This
device generates keys up to 2048 bits long.
To Configure SSH Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure SSH, go to the Admin tab/page and click SSH in the menu.
Using the CLI
To enter the SSH command level: enable -> ssh
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”ssh server”>
and
<configgroup name=”ssh client”>
SSL Settings
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol for managing the security of data transmission over the
Internet. It provides encryption, authentication, and message integrity services. SSL is widely used
for secure communication to a web server.
Certificate/Private key combinations can be obtai ned from an external Certificate Authority (CA)
and uploaded into the unit. Self-signed certificates with associated private key can be generated
by the device server itself.
Note: The blue text in the XML command strings of this chapter are to be replaced with
a user-specified name.
xSenso User Guide 88
Page 89

16: Security Settings
Certificate and Key Generation
The xSenso can generate self signed certificates and their corresponding keys. This can be done
for both the rsa and dsa certificate formats. Certificates can be identified o n the xSenso by a name
provided at generation time.
Table 16-5 Certificate and Key Generation Settings
Certificate Generation
Description
Settings
Country (2 Letter Code) Enter the 2-letter country code to be assigne d to the new self-signed
certificate.
Examples: US for United States and CA for Canada
State/Province Enter the state or province to be assigned to the new self-signed certificate.
Locality (City) Enter the city or locality to be assigned to the new self-signed certificate.
Organization Enter the organization to be associated with the new self-signed certificate.
Organization Unit Enter the organizational unit to be associated with the new self-signed
certificate.
Common Name Enter the common name to be associated with the new self signed
certificate, preferrably matching the host name or the ip address of the
device, whichever will be the intended access approach. This is a required
field.
Expires Enter the expiration date, in mm/dd/yyyy format, for the new self-signed
certificate.
Example: An expiration date of May 9, 2012 is entered as 05/09/2012.
Key length Select the bit size of the new self-signed certificate. Choices are:
512 bits
768 bits
1024 bits
2048 bits
The larger the bit size, the longer it takes to generate the key.
Type Select the type of key:
RSA = Public-Key Cryptography algorithm based on large prime
numbers, invented by Rivest Shamir and Adleman. Used for encryption
and signing.
DSA = Digital Signature Algorithm also based on large prime numbers,
but can only be used for signing. Developed by the US government to
avoid the patents on RSA.
To Create a New Credential
Using Web Manager
To create a new credential, o to the Admin tab/page, click SSL in the menu and select
Credentials.
Using the CLI
To enter the SSL command level: enable -> ssl
To enter the Credentials command level: enable -> ssl -> credentials
xSenso User Guide 89
Page 90

16: Security Settings
Using XML
Not applicable.
Certificate Upload Settings
SSL certificates identify the xSenso to peers. Certificate and key pairs can be uploaded to the
xSenso through either the CLI or XML import mechanisms. Certificates can be identified on the
xSenso by a name provided at upload time.
Table 16-6 Upload Certificate Settings
Upload
Certificate
Settings
New Certificate SSL certificate to be uploaded.
New Private Key The key needs to belong to the certificate entered above.
Description
RSA or DSA certificates are allowed.
The format of the certificate must be PEM. It must start with “
CERTIFICATE-----
Certificate Authorities add comments before and/or after these lines. Those need to be
deleted before upload.
The format of the file must be PEM. It must start with “
PRIVATE KEY-----
Read DSA instead of RSA in case of a DSA key. Some Certificate Authorities add
comments before and/or after these lines. Those need to be deleted before upload.
“ and end with “-----END CERTIFICATE-----“. Some
” and end with “-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----”.
-----BEGIN
-----BEGIN RSA
To Configure an Existing SSL Credential
Using Web Manager
To configure an existing SSL Credential, o to the Admin tab/pag e, click SSL in the menu an d
select Credentials.
Using the CLI
To enter the SSL command level: enable -> ssl
To enter the Credential command level: enable -> ssl -> credentials
Using XML
Include in your file:
<configgroup name=”ssl”>
and <configitem name=”credentials” instance=”name”>
and <value name="RSA certificate"/> or <value name="DSA certificate"/>
xSenso User Guide 90
Page 91

16: Security Settings
Trusted Authorities
One or more authority certificates are needed to verify a peer's identity. These certificates do not
require a private key. SSL certificate for HTTPS and FTPS connections under Action must be
uploaded here.
Table 16-7 Trusted Authority Settings
Trusted Authorities
Settings
Authority SSL authori ty certificate.
Delete Click the Delete button beside a specific certificate authority to delete it.
Description
RSA or DSA certificates are allowed.
The format of the authority certificate can be PEM or PKCS7. PEM files
must start with “-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----” and end with “---
--END CERTIFICATE-----”. Some Certificate Authorities add
comments before and/or after these lines. Those need to be deleted
before upload.
To Upload an Authority Certificate
Using Web Manager
To upload an Authority Certificate, o to the Admin tab/page, click SSL in the menu and select
Trusted Authorities.
Using the CLI
To enter the SSL command level: enable -> ssl
To enter the Trusted Authorities command level: enable -> ssl -> trusted
authorities
Using XML
Include in your file:
<configgroup name=”ssl”>
and <configitem name=”trusted authority” instance =”1”>
and <configitem name=”intermediate authority” instance=”1”>
xSenso User Guide 91
Page 92

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Filesystem Settings
Use the file system to list, view, add, remove, and transfer files. The xSenso uses a flash file
system to store files.
File Display
It is possible to view the list of existing files, and to view their contents in the ASCII or hexadecimal
formats.
Table 17-1 File Display Settings
File Display Commands Description
ls Displays a list of files on the xSenso, and their respective sizes.
cat Displays the specified file in ASCII format.
dump Displays the specified file in a combination of hexadecimal and ASCII
formats.
pwd Print working directory.
cd Change directories.
show tree Display file/directory tree.
To Display Files
Using Web Manager
To view existing files and file contents, go to the Admin tab/page, click FIlesystem in the
menu and select Browse.
Using the CLI
To enter the Filesystem command level: enable -> filesystem
Using XML
Not applicable.
xSenso User Guide 92
Page 93

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
File Modification
The xSenso allows for the creation and removal of files on its filesystem.
Table 17-2 File Modification Settings
File Modification
Commands
rm Removes the specified file from the file system.
touch Creates the specified file as an empty file.
cp Creates a copy of a file.
mkdir Creates a directory on the file system.
rmdir Removes a directory from the file system.
format Format the file system and remove all data.
Description
File Transfer
Files can be transferred to and from the xSenso via the TFTP protocol. This can be useful for
saving and restoring XML configuration files. Files can also be uploaded via HTTP.
Table 17-3 File Transfer Settings
File Transfer Settings Description
Create Browse to location of the file to be created.
Upload File Browse to location of the file to be uploaded.
Copy File Enter the source and destination for file to be copied.
Move Enter the source and destination for file to be moved.
Action Select the action that is to be performed via TFTP:
Get = a “get” command will be executed to store a file locally.
Put = a “put” command will be executed to send a file to a remote
location.
Local File Enter the name of the local file on which the specified “get” or “put” action is
to be performed.
Remote File Enter the name of the file at the remote locati on that is to be stored locally
(“get’) or externally (“put”).
Host Enter the IP address or name of the host involved in this operation.
Port Enter the number of the port involved in TFTP operations.
xSenso User Guide 93
Page 94

To Transfer or Modify Filesystem Files
Using Web Manager
To create a new file or directory, upload an existing file, copy or move a file, o to the Admin
tab/page, click Filesystem in the menu and select Browse.
Using the CLI
To enter the Filesystem command level: enable -> filesystem
Using XML
Not applicable.
Protocol Stack Settings
There are various low level network stack specific items that are available for configuration. This
includes settings related to IP, ICMP, and ARP, which are described in the sections below.
17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
IP Settings
Table 17-4 IP Network Stack Settings
Protocol Stack
IP Settings
IP Time to Live This value typically fills the Time To Live in the IP header.
Multicast Time to Live This value fills the Time To Live in any multicast IP header. Normally this value
Description
Enter the number of hops to be transmitted before the packet is discarded.
will be one so the packet will be blocked at the first router. It is the number of
hops allowed before a Multicast packet is discarded.
Enter the value to be greater than one to intentionally propagate multicast
packets to additional routers.
To Configure IP Network Stack Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure IP protocol settings, go to the Admin tab/page , click Protocol Stack in the menu
and select IP.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> ip
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”ip”>
xSenso User Guide 94
Page 95

ICMP Settings
17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Table 17-5 ICMP Network Stack Settings
Protocol Stack
ICMP Settings
State The State selection is used to turn on/off processing of ICMP messages.
Description
This includes both incoming and outgoing messages. Choose Enabled or
Disabled.
To Configure ICMP Network Stack Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure ICMP protocol settings, go to the Admin tab/page, click Protocol Stack in the
menu and select ICMP.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> icmp
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”icmp”>
ARP Settings
Table 17-6 ARP Network Stack Settings
Protocol Stack
ARP Settings
IP Address Enter the IP address to add to the ARP cache.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address to add to the ARP cache.
Remove Click the Remove link beside a specific address to remove it.
Remove All Click the Remove All link underneath all listed addresses to remove all the
Description
addresses.
To Configure ARP Network Stack Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure ARP protocol settings, go to the Admin tab/page, click Protocol Stack in the
menu and select ARP.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> arp
xSenso User Guide 95
Page 96

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”arp”>
SMTP Settings
Table 17-7 SMTP Settings
SMTP Settings Description
Relay Address Enter the Relay Address to be used to direct all outbound email messages
through a mail server.
Relay Port Enter the Relay Port number to be used for all outbound email messages
through the mail server.
To Configure ARP Network Stack Settings
Using Web Manager
To configure SMTP protocol settings, go to the Admin tab/page, click Protocol Stack in the
menu and select SMTP.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> smtp
Using XML
Include in your file: <configgroup name=”smtp”>
Diagnostics
The xSenso has several tools for diagnostics and statistics. Various options allow for the
configuration or viewing of IP socket information, ping, traceroute, memory, and processes.
Hardware
To View Hardware Information
Using Web Manager
To view hardware information, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and
select Hardware.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> device, show hardware information
xSenso User Guide 96
Page 97

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Using XML
Include in your file: <statusgroup name=”hardware”>
IP Sockets
You can view the list of listening and connected IP sockets.
To View the List of IP Sockets
Using Web Manager
To view IP Sockets, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and select IP
Sockets.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable, show ip sockets
Using XML
Include in your file: <statusgroup name=”ip sockets”>
Ping
The ping command can be used to test connectivity to a remote host.
Table 17-8 Ping Settings
Diagnostics: Ping
Settings (continued)
Host Enter the IP address or host name for the to ping.
Count Enter the number of ping packets should attempt to send to the Host. The default is
Timeout Enter the time, in seconds, for the to wait for a response from the host before timing
Description
5.
out. The default is 5 seconds.
To Ping a Remote Host
Using Web Manager
To ping a Remote Host, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and select
Ping.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable
Using XML
Not applicable.
xSenso User Guide 97
Page 98

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Traceroute
Here you can trace a packet from the xSenso to an Internet host, showing how many hops the
packet requires to reach the host and how long each hop takes. If you visit a web site whose
pages appear slowly, you can use traceroute to determine whe re the longest dela ys are occurrin g.
Table 17-9 Traceroute Settings
Diagnostics:
Traceroute Settings
Host Enter the IP address or DNS hostname. This address is used to show the path
Protocol Specify the traceroute protocol.
Description
between it and the xSenso when issuing the traceroute command.
To Perform a Traceroute
Using Web Manager
To perform a Traceroute, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and select
Traceroute.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable
Using XML
Not applicable.
Log
Table 17-10 Log Settings
Diagnostics: Log Description
Output Select a diagnostic log output type:
Disable - Turn off the login feature.
Filesystem - Directs logging to /log.txt.
Max Length Set the maximum length of the log.txt file.
Note: This setting becomes available when Filesystem is selected.
To Configure the Diagnostic Log Output
Using Web Manager
To configure the Diagnostic Log output, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the
menu and select Log.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> config -> diagnostics -> log
xSenso User Guide 98
Page 99

17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
Using XML
Include in your file:
<configgroup name=”diagnostics”>
and
<configitem name=”log”>
Memory
The memory information shows the total, used, and available memory (in kilobytes).
To View Memory Usage
Using Web Manager
To view memory information, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and
select Memory.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> device, show memory
Using XML
Include in your file: <statusgroup name=”memory”>
Processes
The xSenso Processes information shows all the processes currently running on the system. It
shows the Process ID (PID), Parent Process ID (PPID), user, CPU percentage, percentage of total
CPU cycles, and process command line information.
To View Process Information
Using Web Manager
To view process information, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and
select Processes.
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable, show processes
Using XML
Include in your file: <statusgroup name=”processes”>
xSenso User Guide 99
Page 100

Threads
The xSenso Threads information shows details of th reads in the ltrx_evo task which can be useful
for technical experts in debugging.
To View Thread Information
Using Web Manager
To view thread information, go to the Admin tab/page, click Diagnostics in the menu and
Using the CLI
To enter the command level: enable -> device, show task state
Clock
The current date or time configured in xSenso ca n be view ed and modified . There are two ways to
change the time: manually entering the date and time or synchronizing it with the NTP server.
17: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings
select Threads.
Table 17-11 Clock Settings
Clock Description
Synchronize with
Server: SNTP Client
Set Date and Time Click the Set Date and Time checkbox to make the Date and Time settings fields
Date Select the current Year, Month and Day from the drop-down menus.
Time (24 hour) Select the current Hour, Min (Minute) and Sec (Second) from the drop-down
Time Zone: Directory Select a Time Zone so your device will have a reference in coordinated universal
Enable or disable synchronization of the device clock settings with the NTP Server:
Enabled: enables the SNTP Client to synchronize the device wi th the NTP
Server. Once enabled, the NTP Server field appears with the default
0.pool.ntp.org address as well as the options for manually setting date and
time. Click Submit.
Disabled: allows you to set the date and time manually.
available for configuration.
Note: The Set Date and Time checkbox is available only if you disable
Syncronize with Server above.
Note: The Date configuration field is only available if you disable Syncronize with
Server and then check the Set Date and Time field above.
menus.
Note: The Time configuration field is only available if you disable Syncronize
with Server and then check the Set Date and Time field above.
time (UTC).
xSenso User Guide 100
 Loading...
Loading...