Page 1

XPort Pro
Command Reference
Part Number 900-558
Revision C March 2012
Page 2

Copyright and Trademark
© 2012 Lantronix. All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be transmitted or
reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of Lantronix. Printed in the
United States of America.
Ethernet is a trademark of XEROX Corporation. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open
Group. Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Contacts
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
167 Technology Drive
Irvine, CA 92618, USA
Toll Free: 800-526-8766
Phone: 949-453-3990
Fax: 949-450-7249
Technical Support
Online: www.lantronix.com/support
Sales Offices
For a current list of our domestic and international sales offices, go to the Lantronix web site at
www.lantronix.com/about/contact
.
Disclaimer
The information in this guide may change without notice. The manufacturer assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this guide. For the latest revision of this product
document, please check our online documentation at www.lantronix.com/support/documentation
Revision History
Date Rev. Comments
September 2009 A Initial Document
December 2010 B Updated for firmware v5.2.0.0R20. Includes the new Modbus feature.
March 2012 C Updated for firmware v5.2.0.1R5. Includes new VIP commands.
.
XPort Pro Command Reference 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
List of Figures _____________________________________________________________4
List of Tables ______________________________________________________________5
1: About This Guide 6
Chapter Summaries ________________________________________________________6
Conventions ______________________________________________________________6
Additional Documentation ____________________________________________________7
2: Overview 8
XML Architecture and Device Control ___________________________________________8
Command Line Interface _____________________________________________________8
3: Command Line Interface 9
Configuration Using Telnet ___________________________________________________9
Configuration Using Serial Ports _______________________________________________9
Serial Command Mode ___________________________________________________9
Serial Recovery ________________________________________________________9
Navigating the CLI Hierarchy ________________________________________________10
Using Keyboard Shortcuts and CLI ____________________________________________11
Understanding the CLI Level Hierarchy ________________________________________11
4: Configuration Using XML 14
XML Configuration Record Document Type Definition _____________________________14
Quick Tour of XML Syntax __________________________________________________15
Declaration ___________________________________________________________15
Element Start and End Tags _____________________________________________15
Element Attributes _____________________________________________________15
Record, Group, Item, and Value Tags _________________________________________16
Importing and Exporting an XML Configuration File _______________________________17
Best Practices ____________________________________________________________18
Importing _____________________________________________________________18
Exporting ____________________________________________________________19
Passwords in the XML File _______________________________________________19
XML Configuration Groups __________________________________________________20
XML Status Record Groups and Items _________________________________________33
5: Commands and Levels 47
XPort Pro Command Reference 3
Page 4

List of Figures
Figure 3-1 CLI Level Hierarchy ______________________________________________________12
Figure 3-2 Login Level Commands___________________________________________________13
Figure 3-3 Enable Level Commands__________________________________________________13
Figure 4-1 DTD for XCRs __________________________________________________________14
Figure 4-2 XML Example __________________________________________________________15
Figure 4-3 XML Group Example _____________________________________________________16
Figure 4-4 XML Example of Multiple Named Values _____________________________________16
Figure 4-5 XML Example of Multiple Items _____________________________________________17
Figure 4-6 XML Example with Multiple Groups _________________________________________17
Figure 4-7 XML Example of Supplying Passwords_______________________________________20
XPort Pro Command Reference 4
Page 5

List of Tables
Table 4-8 XCR Groups ____________________________________________________________20
Table 4-9 XSR Groups and Items____________________________________________________34
Table 5-1 Commands and Levels____________________________________________________49
XPort Pro Command Reference 5
Page 6
1: About This Guide
This guide describes how to configure the XPort Pro using the Command Line Interface (CLI) and/
or Extensible Markup Language (XML). It is written for software developers and system
integrators.
Chapter Summaries
This table lists and summarizes each chapter and appendix.
Chapter Summary
Chapter 2: Overview
Chapter 3: Command Line Interface
Chapter 4: Configuration Using XML
Chapter 5: Commands and Levels
Conventions
The table below lists and describes the conventions used in this book.
Convention Description
Bold text Default parameters.
Italic text Required values for parameters
Brackets [ ] Optional parameters.
Angle Brackets < > Possible values for parameters.
Pipe | Choice of parameters.
Gives an overview of CLI and XML.
Lists commands and describes how to use CLI to
configure the XPort Pro.
Lists XCR groups and items and describes how to use
XCRs to configure the XPort Pro.
Provides an index of the CLI Command Hierarchy with
hyperlinks to the corresponding command details.
Warning Warning: Means that you are in a situation that could cause
equipment damage or bodily injury. Before you work on any
equipment, you must be aware of the hazards involved with electrical
circuitry and familiar with standard practices for preventing
accidents.
Note Note: Means take notice. Notes contain helpful suggestions, information,
or references to material not covered in the publication.
Caution Caution: Means you might do something that could result in faulty
equipment operation, or loss of data.
Screen Font
(Courier New)
CLI terminal sessions and examples of CLI input.
XPort Pro Command Reference 6
Page 7

Additional Documentation
Visit the Lantronix web site at www.lantronix.com/support/documentation for the latest
documentation and the following additional documentation.
Document Description
XPort Pro Integration Guide Information about the XPort Pro hardware, testing the XPort Pro
XPort Pro User Guide Instructions for how to install, configure and use the XPort Pro.
1: About This Guide
using the demonstration board, and integrating the XPort Pro into
your product.
XPort Pro Universal Demo Board
Quick Start
XPort Pro Universal Demo Board
User Guide
DeviceInstaller Online Help Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to locate
Secure Com Port Redirector
User Guide
Com Port Redirector
Quick Start and Online Help
Instructions for getting the XPort Pro demonstration board up and
running.
Information for using the XPort Pro on the demo board.
the XPort Pro and to view its current settings.
Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to create
secure virtual com ports.
Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to
create virtual com ports.
XPort Pro Command Reference 7
Page 8

2: Overview
Evolution OS™ is the Lantronix cutting-edge operating system that supports three convenient
configuration methods: Web Manager, Command Line Interface (CLI), and Extensible Markup
Language (XML). For more information about the Web Manager, see the XPort Pro User Guide at
the Lantronix website.
XML Architecture and Device Control
XML is a fundamental building block for the future growth of Machine-to-Machine (M2M) networks.
Evolution supports XML configuration records that make configuring the device server easy for
users and administrators. XML configuration records are easy to edit with a a standard text editor
or an XML editor.
For a brief overview of XML, see Chapter 4: Configuration Using XML . It provides rules on basic
XML syntax, a guide to the specific XML tags used, and a guide to using XML configuration
records.
Command Line Interface
Making the edge-to-enterprise vision a reality, Evolution OS™ uses industry-standard tools for
configuration, communication, and control. For example, the Evolution OS™ uses a command line
interface (CLI) whose syntax is very similar to that used by data center equipment such as routers
and hubs.
For details of the CLI, see Chapter 5: Commands and Levels. It provides an index of the CLI
Command Hierarchy with links to the corresponding command details. The CLI provides
commands for configuring, monitoring, and controlling the device server.
XPort Pro Command Reference 8
Page 9

3: Command Line Interface
This chapter describes accessing the XPort Pro by using Telnet, SSH, or serial ports to configure
the XPort Pro, navigating the Command Line Interface (CLI), typing keyboard shortcuts, and
moving between the levels.
It contains the following sections:
Configuration Using Telnet
Configuration Using Serial Ports
Navigating the CLI Hierarchy
Using Keyboard Shortcuts and CLI
Understanding the CLI Level Hierarchy
Refer to Chapter 5: Commands and Levels for a complete list of levels, commands, and
descriptions.
Configuration Using Telnet
To access and configure the device server by using a Telnet session over the network, you must
first establish a Telnet connection. You can also establish a Telnet connection by clicking the
Telnet Configuration tab in DeviceInstaller. See the DeviceInstaller Online Help for more
information, available on our website www.lantronix.com/support/downloads
.
To access the XPort Pro by using Telnet, perform the following steps.
1. Click Start > Run. The Run dialog box displays.
2. Type cmd in the dialog box and press OK.
3. Type telnet x.x.x.x (x.x.x.x is the IP address). The XPort Pro is online when the
command prompt (>) displays. You are at the root level of the CLI.
Note: Depending on the level of security, a password may be requ i re d.
Configuration Using Serial Ports
Serial Command Mode
The serial port can be configured to operate in command mode permanently or to be triggered
under specified conditions. See the line <line> Level command description for more
information.
Serial Recovery
In this mode, the normal boot process is interrupted, allowing recovery from unknown or incorrect
configuration settings. While the back door is active, the CLI prompt is changed to “>>” (instead of
“>”) and the Web Manager is inaccessible. These serve as an important indication that the device
boot processes has been temporarily halted. To complete the boot process, terminate the serial
CLI session (with the exit command).
XPort Pro Command Reference 9
Page 10

To configure the Lantronix device server locally using a serial port, connect a terminal or a PC
running a terminal emulation program to one of the device server's serial ports. Configure the
terminal for 9600 baud, 8-bit, no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control.
1. Power off the device.
2. Press and hold down the exclamation point (!) key.
3. Power on the device. After about ten seconds, the exclamation point will display on the
terminal or PC screen.
4. Type xyz within 5 seconds to display the CLI prompt.
Navigating the CLI Hierarchy
The CLI is organized into a hierarchy of levels. Each level has a group of commands for a specific
purpose. For example, to configure a setting for the FTP server, one would navigate to the FTP
level, which is under the configuration level.
To move to a different level—Enter the name of the level from within its parent level. For
example, to enter the tunnel level, type tunnel <number> at the enable prompt. This
displays: <enable> tunnel <number>#.
3: Command Line Interface
To exit and return to one level higher—Type exit and press the Enter key. Typing exit at the
login level or the enable level will close the CLI session. If Line — Command Mode is
specified as Always, a new session starts immediately.
To view the current configuration at any level—Type show.
To view the list of commands available at the current level—Type the question mark "?". Items
within < > (e.g. <string>) are required parameters.
To view the available commands and explanations—Type the asterisk ( *).
To view the list of commands available for a partial command—Type the partial command
followed by the question mark "?". For example: <tunnel-1>#echo? displays a list of all
echo commands at the tunnel level.
To view available commands and their explanations for a partial command—Type the partial
command followed by the asterisk ( *). For example: <tunnel-1>#echo* displays a list of all
echo commands and descriptions at the tunnel level.
To view the last 20 commands entered at the CLI—Type show history.
XPort Pro Command Reference 10
Page 11

Using Keyboard Shortcuts and CLI
One useful shortcut built into Evolution OS™ is that the complete text of a command does not
have to be entered to issue a command. Typing just enough characters to uniquely identify a
command, then hitting enter, can be used as a short cut for a command. For example, at the
enable level, "sh" can be used for the "show" command.
Tab Completion is also available. Typing the first few characters of a command, then hitting the
<tab> key displays the first command that begins with those characters. Hitting the <tab> key
again displays the next command that begins with the original characters typed. You can press
<Enter> to execute the command or you can backspace to edit any parameters.
The following key combinations are allowed when configuring the device server using the CLI:
Ctrl + a: place cursor at the beginning of a line
Ctrl + b: backspace one character
Ctrl + d: delete one character
Ctrl + e: place cursor at the end of the line
Ctrl + f: move cursor forward one character
Ctrl + k: delete from the current position to the end of the line
3: Command Line Interface
Ctrl + l: redraw the command line
Ctrl + n: display the next line in the history
Ctrl + p: display the previous line in the history
Ctrl + u: delete entire line and place cursor at start of prompt
Ctrl + w: delete one word back
Ctrl + z: a shortcut for the exit command
Esc + b: move cursor back one word
Esc + f: move cursor forward one word
Understanding the CLI Level Hierarchy
The CLI hierarchy is a series of levels. Arranging commands in a hierarchy of levels provides a
way to organize and group similar commands, provide different levels of security, and reduce the
complexity and number commands and options presented to a user at one time.
When you start a command line session, you begin at the login level. This level can be password
protected and provides access to high level status, a few diagnostic commands, and the enable
level. Further device information and configuration are accessed via the enable level.
The enable level can also be password protected and is the gateway to full configuration and
management of the device server. There are commands for gathering and effecting all elements of
device status and configuration, as well as commands that take you to additional levels. For
instance, tunnel specific status and configuration is found under the "tunnel" level, and network
specific status and configuration commands are found under the "configuration" level.
An overview of the levels in the XPort Pro is presented in Figure 3-1.
XPort Pro Command Reference 11
Page 12
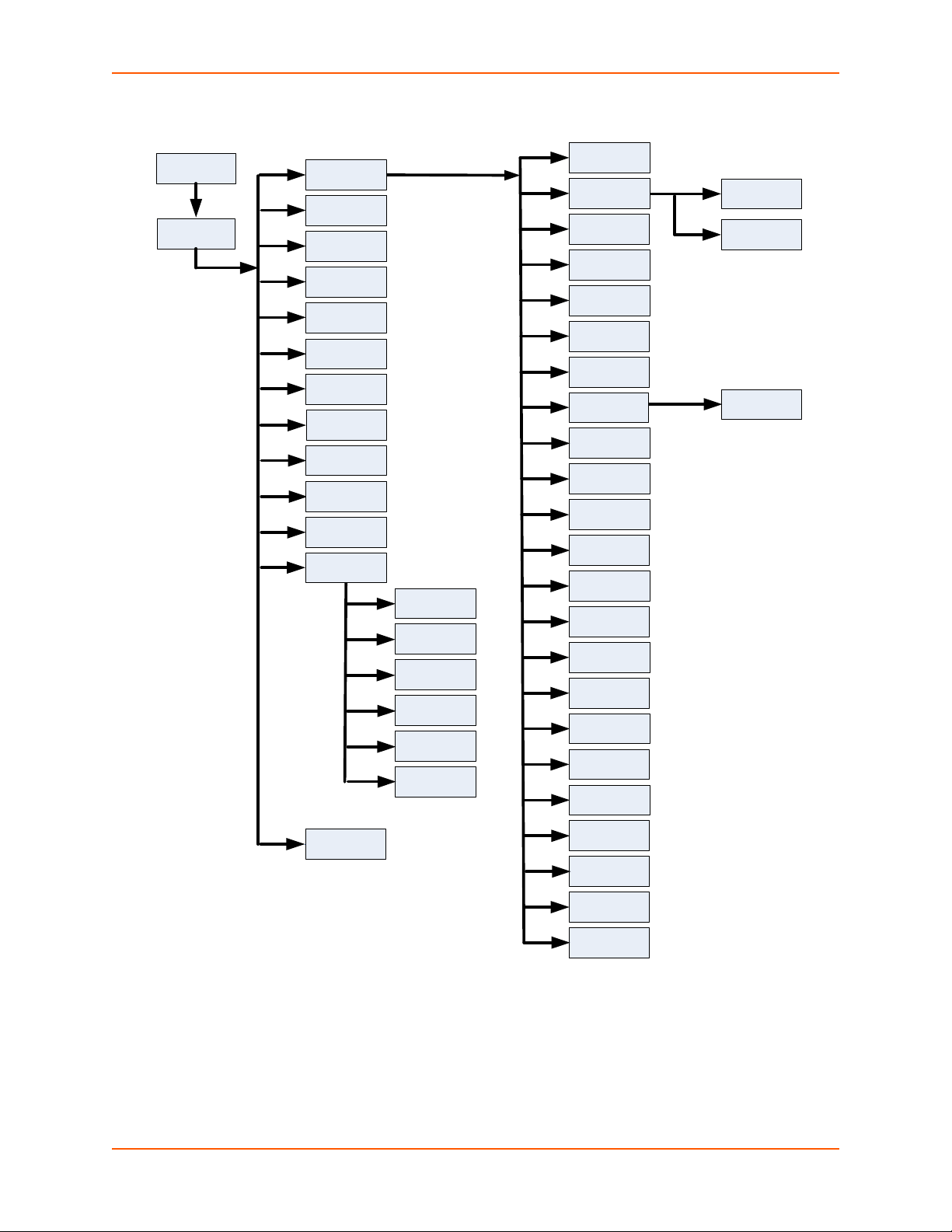
Figure 3-1 CLI Level Hierarchy
(login)
enable
ssl
cli
http
arp
Ethernet
link
If 1
ip
ip filter
query port
rss
snmp
syslog
tcp
tftp
udp
terminal
network
ftp
serial
packing
modem
disconnect
connect
accept
tunnel
<line>
ssh
cpm
line <line>
Filesystem
configure
icmp
device
terminal
<line>
ppp
<number>
lpd
ssh
telnet
modbus
vip
dns
email
host
diagnostics
lpd
<number>
smtp
xml
3: Command Line Interface
Commands at the login level, shown in Figure 3-2, do not affect current configuration settings and
are not displayed initially. If you type <?>, you will see the login sub-commands. These commands
provide diagnostic and status information only.
XPort Pro Command Reference 12
Page 13

3: Command Line Interface
Figure 3-2 Login Level Commands
>?
clrscrn enable
exit ping <host>
ping <host> <count> ping <host> <count> <timeout>
show show xport_pro
show history trace route <host>
>
To configure the XPort Pro, you must be in the enable level and any of its sub-levels. Figure 3-3
shows the enable level commands.
Figure 3-3 Enable Level Commands
>enable
(enable)#?
auto show interfaces auto show processes
clear interfaces counters clrscrn
configure connect
connect line <line> cpm
device disable
dns email <number>
exit filesystem
kill ssh <session> kill telnet <session>
line <line> lpd
no clear interfaces counters ping <host>
ping <host> <count> ping <host> <count> <timeout>
ppp <line> reload
reload factory defaults show
show history show interfaces
show ip sockets show processes
show sessions show xport_pro
ssh ssh <optClientUsername> <host>
ssh <optClientUsername> <host> <port> ssl
telnet <host> telnet <host> <port>
trace route <host> tunnel <line>
write xml
See the Chapter 5: Comma nds and Levels at the end of this document for a complete list of levels,
commands, and descriptions.
XPort Pro Command Reference 13
Page 14
4: Configuration Using XML
<!DOCTYPE configrecord [
<!ELEMENT configrecord (configgroup+)>
<!ELEMENT configgroup (configitem+)>
<!ELEMENT configitem (value+)>
<!ELEMENT value (#PCDATA)>
<!ATTLIST configrecord version CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configgroup name CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configgroup instance CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configitem name CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST value name CDATA #IMPLIED>
]>
The device server provides an Extensible Markup Language (XML) interface that you can use to
configure device server devices. Every configuration setting that can be issued from the device
server Web Manager and CLI can be specified using XML.
The device server can import and export configuration settings as an XML document known as an
XML Configuration Record (XCR). An XCR can be imported or exported via the CLI, a Web
browser, FTP, or the device server filesystem. An XCR can contain many configuration settings or
just a few. For example, it might change all of the configurable parameters for a device server, or it
may only change the baud rate for a single serial line. Using XCRs is a straightforward and flexible
way to manage the configuration of multiple device server devices.
XML Configuration Record Document Type Definition
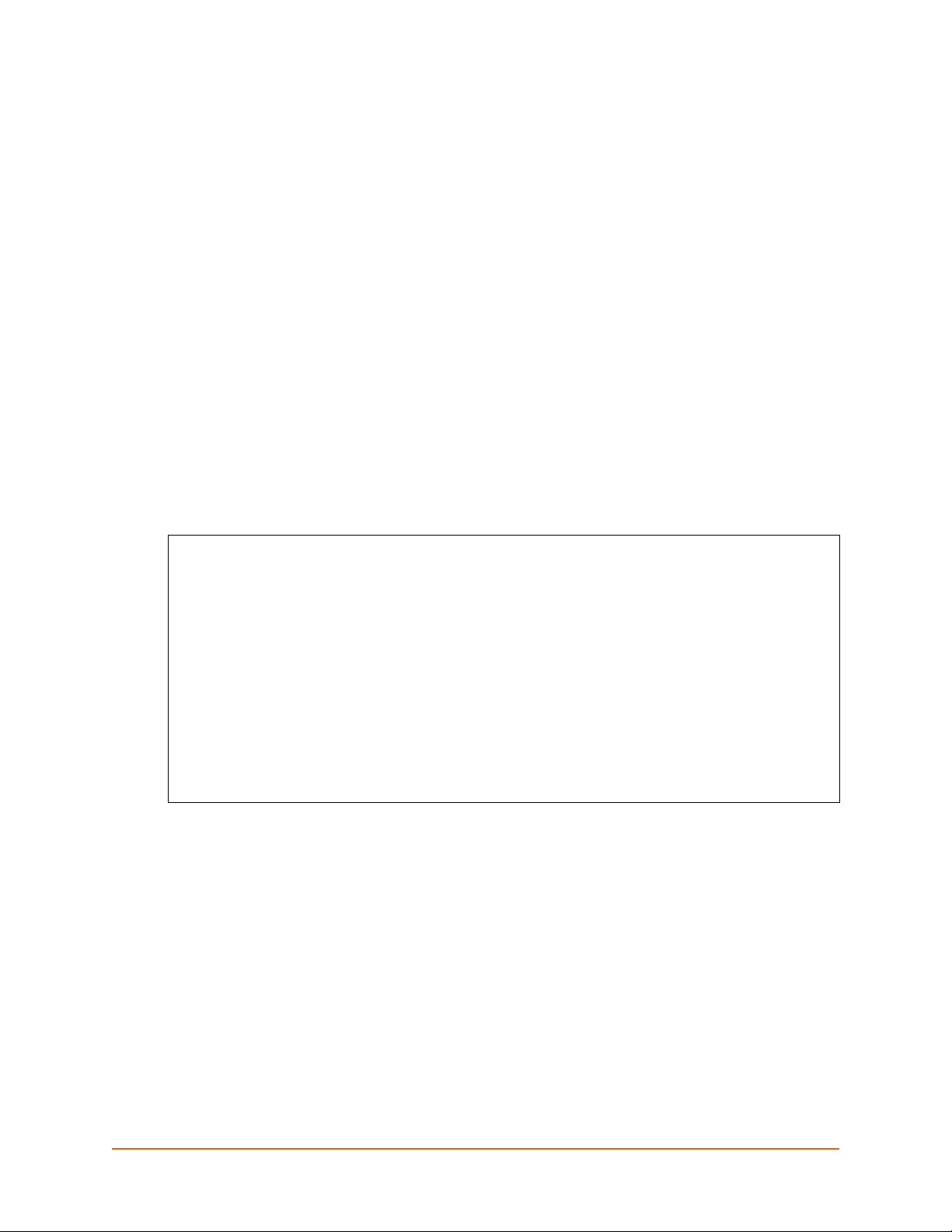
An XML document type definition (DTD) is a description of the structure and content of an XML
document. It verifies that a document is valid. XCRs are exported using the DTD shown in
Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 DTD for XCRs
The device server DTD rules state the following:
The XML document element is a <configrecord> element. This is the root element.
A <configrecord> must have one or more <configgroup> elements and can have a
version attribute.
A <configgroup> must have one or more <configitem> elements and can have name and
instance attributes.
A <configitem> element must have one or more <value> elements and can have a name
attribute.
A <value> element can have only data and can have a name attribute.
The name attribute identifies a group, item, or value. It is always a quoted string.
The instance attribute identifies the specific option, like the serial port number. The “instance”
attribute is always a quoted string.
XPort Pro Command Reference 14
Page 15

Notes:
<?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>
<configrecord>
<configgroup name = “serial command mode” instance = “1”>
<configitem name = “mode serial string”>
<value>disable</value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
</configrecord>
The name for each <configgroup> (specified with the name attribute) is the group
name listed in the Web Manager XCR groups or with the “xcr list” CLI command.
See the XPort Pro User Guide for more information a bout the Web Man ager XCR
groups.
An empty or missing <value> element in each present <configgroup> clears the
setting to its default.
Quick Tour of XML Syntax
Declaration
The first line, <?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>, is called the XML declaration. It
is required and indicates the XML version in use (normally version 1.0). The remainder of the file
consists of nested XML elements, some of which have attributes and content.
Element Start and End Tags
An element typically consists of two tags: start tag and an end tag that surrounds text and other
elements (element content). The start tag consists of a name surrounded by angle brackets, for
example <configrecord>. The end tag consists of the same name surrounded by angle
brackets, but with a forward slash preceding the name, for example </configrecord>.
4: Configuration Using XML
The element content can also contain other “child” elements.
Element Attributes
The XML element attributes that are name-value pairs included in the start tag after the element
name. The values must always be quoted, using single or double quotes. Each attribute name
should appear only once in an element.
Figure 4-2 shows an XML example which consists of a declaration (first line), nested elements with
attributes and content.
Figure 4-2 XML Example
XPort Pro Command Reference 15
The Evolution OS™ uses the attributes in the following subsections to label the group
configuration settings.
Page 16

Record, Group, Item, and Value Tags
<?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>
<configrecord>
<configgroup name = “serial command mode” instance = “1”>
<configitem name = “mode”>
<value>disable</value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
</configrecord>
<?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>
<configgroup name = “ssh server”
<configitem name = “host rsa keys”>
<value name = “public key”></value>
<value name = “private key”></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
A <configgroup> is a logical grouping of configuration parameters and must contain one or
more <configitem> elements. It must have a name attribute and may have an instance
attribute.
A <configitem> is a specific grouping of configuration parameters relevant to its parent group.
An item takes the name attribute and must contain one or more value elements. For example, the
line group might have parameters such as baud rate, data bits, and parity.
A value may specify the value of a configuration parameter. It may contain the name attribute. In
this example, a value of 9600 might be specified for baud rate; 7 may be specified for data bits,
and even may be specified for parity.
A name attribute identifies the group, item, or value. It is always quoted (as are all XML attributes).
For example, a group that contains serial port parameters has the name “line”.
An instance attribute identifies which of several instances is being addressed. It is always quoted.
For example, the serial port name (in the line configgroup) has the instance “1” to indicate serial
port 1 or “2” to specify serial port 2.
The following figures show examples of XML configuration records and the use of the
<configrecord>, <configgroup>, <configitem>, and <value> XML elements.
4: Configuration Using XML
Figure 4-3 XML Group Example
Figure 4-4 XML Example of Multiple Named Values
XPort Pro Command Reference 16
Page 17

Figure 4-5 XML Example of Multiple Items
<?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>
<configgroup name = “email” instance = “1”>
<configitem name = “to”>
<value>john.doe@somewhere.com></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = “from”>
<value>evolution@xportpro.com></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
<?xml version=”1.0” standalone=”yes”?>
<configgroup name = "ftp server">
<configitem name = "state">
<value>enable</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "admin username">
<value>admin</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "admin password">
<value><!-- configured and ignored --></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
<configgroup name = "tftp server">
<configitem name = "state">
<value>enable</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "allow file creation">
<value>disable</value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
Figure 4-6 XML Example with Multiple Groups
4: Configuration Using XML
Importing and Exporting an XML Configuration File
XPort Pro Command Reference 17
An XCR can be imported or exported using the following methods:
Filesystem—XCRs can be saved to the device server file system and imported or accessed as
needed. See Best Practices or the Filesystem Browser section in the XPort Pro User Guide.
CLI—XCRs can be imported (captured) or exported (dumped) directly to a Telnet, SSH, or
serial line CLI session. Capturing an XCR can be started by pasting a valid XCR directly into
the CLI prompt. Evolution OS immediately processes the configuration record, changing any
settings specified. This can be done on any level, including the root. Special tags in the XML
Page 18

allow for providing root and enable level passwords so that this can also be done at the
password prompt.
Web browser—Web Manager can be used to import and export an XCR to the device server
file system. It can also be used to import an XCR from an external source such as your local
hard drive.
FTP—The device server FTP server can export and import XCRs when an FTP get or put
command on the filename xport_pro.xcr is requested. On export (FTP get of xport_pro.xcr),
the FTP server obtains the current XCR from Evolution OS™ and sends it as a file. On import
(FTP put of xport_pro.xcr), the FTP server processes the file by sending it directly to the XML
engine. In both cases the device server filesystem is not accessed. The file xport_pro.xcr is
not read from or written to the file system. See FTP in the XPort Pro User Guide.
TFTP—TFTP supports XCR importing. Due to limited security capabilities of TFTP, the option
is disabled by default.
Best Practices
You can import or export an entire XCR, or just a portion of it, by specifying the group name and/or
group instances. In the examples below, import and export operations are performed from the CLI
on the local filesystem and require a XCR on the local filesystem. The Web Manager provides the
same functionality.
4: Configuration Using XML
Caution: Using Microsoft Word to edit and save an XCR will change the format of
the file and make it incompatible with Evolution OS. This is true even if
the file is saved as Plain Text (.txt) or an XML Document (.xml). Not epad,
a third party text editor, or a specialized XML editor should be used
instead.
Importing
The following syntax can be used to import configurations from a file:
xcr import <file>
xcr import <file> <groups and/or group:instances>
The first line imports all groups specified in the XML config record named in <file>. Any filename
is valid, and the file name and extension are not important.
Caution: The filename xport_pro.xcr is not accept able, because performing a FT P
get on that name produces the current configuration and does not
perform an FTP from the filesystem. Also, the filename xport_pro.xsr is
not acceptable, because performing an FTP get on that name produces
the current status and does not get anything from the filesystem.
In the second line:
Instance follows group with a colon (see the third example on the next page).
Multiple groups are separated with a comma.
Any white space requires the list of groups to be quoted.
Only the named groups get imported, even if the XCR contains additional XCR groups.
The following syntax can be used to export configurations to a file on the device server’s file
system:
XPort Pro Command Reference 18
Page 19

4: Configuration Using XML
xcr export <file>
xcr export <file> <groups and/or group:instances>
The same guidelines above regarding importing configurations also apply to exporting
configurations. If no groups are specified, then the export command will export all configuration
settings to the file. If instances are specified after the groups, only those group instances are
written. If no instance is specified, all instances of that group are written.
Exporting
The following example exports only the accept mode tunneling settings for line 1 to the file
“tunnel_1.xcr” on the device server filesystem:
xcr export tunnel_1.xcr “tunnel accept:1”
The following example exports only the connect mode tunneling settings for all ports to the file
“tunnel_all.xcr” on the device server filesystem:
xcr export tunnel_all.xcr “tunnel connect”
The following example imports only the settings for line 2 from a XCR named “factory_config.xcr”
on the device server filesystem. If “factory_config.xcr” has other configuration settings, they are
ignored:
xcr import factory_config.xcr “line:2”
The following example imports only line settings for all ports from a configuration record on the
device server filesystem named “foobar.xcr”:
xcr import foobar.xcr “line”
To import only disconnect mode tunneling settings for port 1 and serial line settings for port 2 from
an XML configuration record named “production.xcr” that contains these settings (and possibly
more), issue the following command:
xcr import production.xcr "tunnel disconnect:1, line:2"
The following example imports all tunneling settings and line settings for all serial ports from a file
named xcr_file:
xcr import xcr_file "tunnel accept, tunnel connect, tunnel
disconnect, tunnel modem, tunnel packing, tunnel serial, tunnel
start, tunnel stop, line"
The following example exports only accept mode tunneling settings on serial port 1, and line
settings on serial port 2 to a file named tunnel_config_t1_l2.xcr on the device server filesystem.
xcr export tunnel_config_t1_l2.xcr "tunnel accept:1, line:2"
The following example exports connect mode tunneling and line settings for all ports to the file
tunnel_config.xcr on the device server filesystem:
xcr export tunnel_config.xcr "tunnel, line"
Passwords in the XML File
If you log in to a device server to which you will be pasting an XCR, you do not need to include
passwords in the file, because you are already logged into the device. However, if you send an
XCR to one or more devices that are password protected, you can include the appropriate
passwords in the XCR and skip the login steps.
XPort Pro Command Reference 19
Page 20
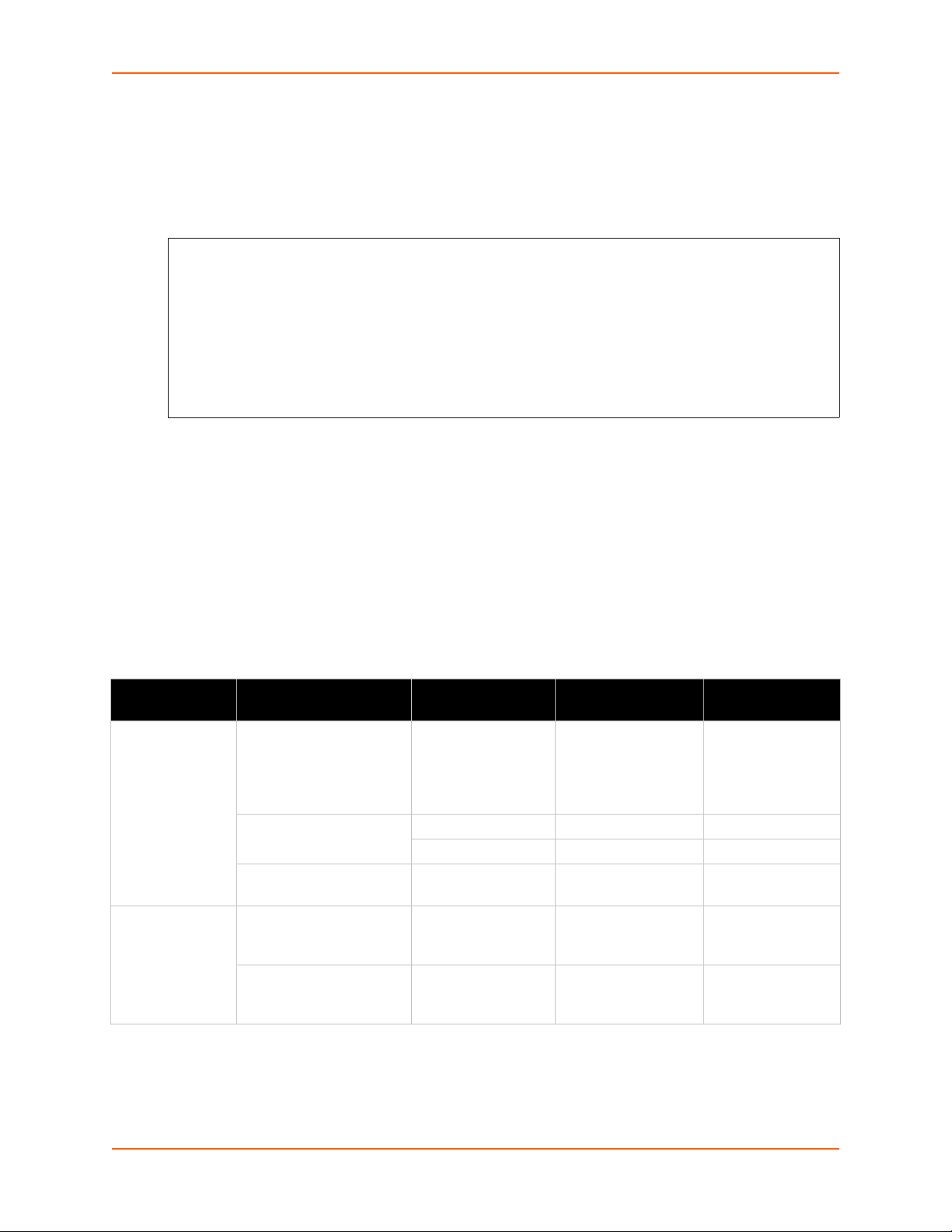
The “xml paste passwords” <configgroup> name is used with the “passwords” <configitem>
<!—To supply passwords when importing via cli capture -->
<configgroup name = "xml paste passwords">
<configitem name = "passwords">
<value name = "cli login"></value>
<value name = "cli enable level"></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
name and “cli login” and “cli enable level” values to specify the passwords to use when the device
has been configured with password protection. The password value is clear text. To protect the
password, establish an SSH connection to the device server. Figure 4-7 shows an example.
Figure 4-7 XML Example of Supplying Passwords
XML Configuration Groups
4: Configuration Using XML
Table 4-8 lists the XPort Pro XCR groups in alphabetical order. This table indicates the various
group items, as well as some possible value names and options.
Note: Any instance of < in the table may be read as < (the html encoded form for
less than) and any instance of > may be read as > ( the html encoded form for gr eater
than).
Table 4-8 XCR Groups
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
arp arp delete ip address Remove an entry
from the ARP
table. Specify the
entry by its IP
address.
arp entry ip address
mac address
timeout Default: 60
seconds
cli login password Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view.
enable level password Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view.
XPort Pro Command Reference 20
Page 21

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
cli (continued) quit connect line Accepts text
containing control
characters, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>L
inactivity timeout
cp group
(Attribute of
“instance” is
required for the
group name.)
device cpu speed
diagnostics log output disable, filesystem,
email
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
state enable Changes state of
cp
(Attribute of “instance is a
number.)
short name
long name
serial number Read only.
firmware version Read only.
to Multiple addresses
cc Multiple addresses
from
reply to
subject
message file
overriding domain
server port Default: 25
local port
priority urgent, high, normal,
bit Bit number
type input
assert low enable
max length Default: 50 Kbytes
severity level debug, information,
<None>,
...
disable
output
disable
line <number>
notice, warning, error
<Random>, ...
low, very low
Default: 15
minutes
the CP group.
Default: disable
Default: debug
may be separated
with semicolons.
may be separated
with semicolons.
Default:
<Random>
Default: normal
XPort Pro Command Reference 21
Page 22
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
ethernet
(Attribute of
“instance” is
“eth0”.)
ftp server state enable, disable Default: enable
host
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
http
authentication uri
(Attribute of
“instance” is the
URI.)
http server state enable, disable Default: enable
speed auto, 10, 100 Default: auto
duplex auto, half, full Default: auto
admin username Default: admin
admin password Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view.
name
protocol telnet, ssh Default: telnet
ssh username
remote address
remote port Default: 0
user delete name Deletes an HTTP
Authentication URI
user. The value
element is used to
specify the user for
deletion.
realm
type
user
(Attribute of “instance” is
the user name.)
port <None>, ... Default: 80
secure port <None>, ... Default: 443
secure protocols ssl3, tls1.0, tls1.1 May contain zero,
max timeout Default: 10
max bytes Default: 40960
logging state enable, disable Default: enable
max log entries Default: 50
log format Default: %h %t
authentication timeout Default: 30
password
one, or more of the
values, separated
by commas.
Default: ssl3,
tls1.0, tls1.1
seconds
"%r" %s %B
"%{Referer}i"
"%{User-Agent}i"
minutes
XPort Pro Command Reference 22
Page 23
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
icmp state enable, disable Default: enable
interface
(Attribute of
“instance” is
eth0”)
ip
bootp enable, disable Default: disable
dhcp enable, disable Default: enable
ip address <None>, ... Accepts an IP
address and mask
as either: (1) IP
address only
(192.168.1.1) gets
a default mask, (2)
CIDR
(192.168.1.1/24),
or (3) Explicit mask
(192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0).
default gateway <None>, ... Accepts in IP
address in dotted
notation, like
192.168.1.1.
hostname
domain
dhcp client id Set the identity of
the client device.
mtu Default: 1500
bytes
primary dns <None>, ... Accepts in IP
address in dotted
notation, like
192.168.1.1.
secondary dns <None>, ... Accepts in IP
address in dotted
notation, like
192.168.1.1.
multicast time to live Default: 1 hops
ip time to live
XPort Pro Command Reference 23
Page 24
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
ip filter delete entries enable, disable If enabled, deletes
any existing
entries before
adding “filter
entry”.
filter delete ip address Deletes a specific
IP filter entry.
net mask Deletes a specific
IP filter entry.
filter entry ip address If configured, is a
specific IP
address.
net mask If configured, is a
specific net mask.
line
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
name
interface rs232, rs485 half-
duplex, rs485 fullduplex
termination enable, disable Default: disable
state enable, disable Default: depends
protocol none, modbus rtu,
modbus ascii, tunnel,
ppp, lpd, lpd or
tunnel
baud rate Default: 9600 bits
parity even, none, odd Default: none
data bits 7, 8 Default: 8
stop bits 1, 2 Default: 1
flow control none, hardware,
software
xon char Accepts a control
Default:
on instance
Default:
per second
Default: none
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>Q
XPort Pro Command Reference 24
Page 25

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
line
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
(continued)
lpd
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
xoff char Accepts a control
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>S
gap timer
threshold Default: 56 bytes
banner enable, disable Default: enable
binary enable, disable Default: disable
soj enable, disable Default: disable
eoj enable, disable Default: disable
formfeed enable, disable Default: disable
convert newline enable, disable Default: disable
soj text
eoj text
queue name
<None>,
...
Default: none
XPort Pro Command Reference 25
Page 26
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
managelinx plaintext dsm credentials dna.xml.replication.
protocol.version
dna.capabilities.tcp.
connect.fail
encrypted dsm
credentials
managelinx common device.dna.system.
managelinx network
interface
dna.dsc.auth.
tunnel.username
dna.dsc.auth.ssh.
pub
dna.dsc.auth.ssh.
priv
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.portlist.list
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.ip.addr
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.ip.list
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.ssh.public
device.dnaid
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.portlist.
httpconnect
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.proxy.host
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.proxy.port
device.dna.dsc.
tunnel.proxy.enable
change.number
device.config.name
device.dna.system.
change.timestamp
device.dna.dsc.
replication.period
device.dna.system.
network.iface.name
device.dna.system.
network.iface.
ipaddress
device.dna.system.
network.iface.vip.
pool
device.viproute.
target.name
enable, disable Default: disable
Default: 1800
seconds
Default: 0
XPort Pro Command Reference 26
Page 27
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
modbus tcp server state enable, disable Default: disable
additional port <None>, ... Default: <None>
response timeout Default: 3000
milliseconds
rss trace input enable, disable Default: disable
ppp
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
query port state
rss feed enable, disable Default: disable
serial command
mode
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
smtp relay address
local ip <None>), ... Accepts an IP
address and mask
as either: (1) IP
address only
(192.168.1.1) gets
a default mask, (2)
CIDR
(192.168.1.1/24),
or (3) Explicit mask
(192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0).
peer ip <None>), ... Accepts in IP
address in dotted
notation, like
192.168.1.1.
authentication mode none, pap, chap, ms-
chap, ms-chapv2
username
password Value is SECRET,
persist enable, disable Default: disable
max entries Default: 100
mode
echo serial string
serial string
signon message
wait time
relay port Default: 25
Default: none
hidden from user
view.
XPort Pro Command Reference 27
Page 28
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
snmp state enable, disable Default: enable
read community Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view. Default:
public
write community Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view. Default:
private
system contact
system name Default: <Default>
system description Default: <Default>
system location
traps state enable, disable Default: enable
primary destination
secondary
destination
ssh state enable, disable Default: enable
port Default: 22
max sessions Default: 3
ssh client delete known hosts enable, disable If enabled, deletes
any existing hosts
before adding
“known host”.
known host delete name Specify the known
host to delete.
known host
(Attribute of “instance” is
required for the known
host name)
delete client users enable, disable If enabled, deletes
client user delete name
client user
(Attribute of “instance” is
required for the user
name)
public rsa key
public dsa key
any existing client
users before
adding “client
user”.
password
remote command
public rsa key
private rsa key
public dsa key
private dsa key
XPort Pro Command Reference 28
Page 29
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
ssh server host rsa keys public key
private key
host dsa keys public key
private key
delete authorized users
authorized user delete name
authorized user
(Attribute of “instance” is
required for the
authorized user name)
ssl RSA certificate certificate Enter the text of
DSA certificate certificate Enter the text of
delete all cas enable, disable If enabled, deletes
syslog state enable, disable Default: disable
host
local port Default: 514
remote port Default: 514
severity log level none, emergency,
tcp resets enable, disable Default: enable
ack limit Number of packets
send data standard, expedited Default: standard
password
public rsa key
public dsa key
the certificate.
private key Enter the text of
the private key.
If configured and
not exporting
secrets, exports
only a placeholder.
the certificate.
private key Enter the text of
the private key.
If configured and
not exporting
secrets, exports
only a placeholder.
any existing
trusted cas before
adding “trusted
ca”.
Default: none
alert, critical, error,
warning, notice,
information, debug
received before an
ACK is forced.
Default: 3 packets
XPort Pro Command Reference 29
Page 30
4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
telnet state enable, disable Default: enable
port Default: 23
max sessions Default: 3
terminal
(Attribute of
“instance” is
either “network”
or a number.)
tftp server state enable, disable Default: enable
tunnel accept
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
terminal type Default:
UNKNOWN
login connect menu enable, disable Default: disable
exit connect menu enable, disable Default: disable
send break Accepts a control
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A
break duration Default: 500
milliseconds
echo enable, disable Default: enable
allow file creation enable, disable Default: disable
allow firmware update enable, disable Default: disable
allow xcr import enable, disable Default: disable
accept mode disable, always, any
character, start
character, modem
control asserted,
modem emulation
start character
flush start character enable, disable Default: enable
local port <None>, ... Default: <None>
protocol tcp, ssh, telnet, tcp
aes, ssl
tcp keep alive <None>, ... Default: 45000
aes encrypt key Value is SECRET,
aes decrypt key Value is SECRET,
flush serial enable, disable Default: disable
Default: always
Accepts a control
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>B
Default: tcp
milliseconds
hidden from user
view.
hidden from user
view.
XPort Pro Command Reference 30
Page 31

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
tunnel accept
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
(continued)
tunnel connect
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
block serial enable, disable Default: disable
block network enable, disable Default: disable
password password Value is SECRET,
hidden from user
view.
prompt enable, disable Default: disable
email connect <None>, ... Default: <None>
email disconnect <None>, ... Default: <None>
connect mode disable, always, any
character, start
character, modem
control asserted,
modem emulation
start character
flush start character enable, disable Default: enable
local port
host (Attribute of
“instance” is a number.)
host mode
reconnect time Default: 15000
flush serial enable, disable Default: disable
block serial enable, disable Default: disable
block network enable, disable Default: disable
email connect <None>, ... Default: <None>
email disconnect <None>, ... Default: <None>
cp output
vip enable, disable Default: disable
address
port
protocol
ssh username
validate certificate
tcp keep alive
aes encrypt key
aes decrypt key
goup connection value,
<Random>, ...
<Random>, ...
sequential, simultaneous
disconnection value
Default: disable
Accepts a control
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>B
Default:
<Random>
Default: sequential
milliseconds
XPort Pro Command Reference 31
Page 32

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
tunnel
disconnect
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
tunnel modem
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
tunnel packing
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
tunnel serial
(Attribute of
“instance” is a
number.)
stop character Accepts a control
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A
flush step character enable, disable Default: disable
modem control enable, disable Default: disable
timeout Default: 0
milliseconds
flush serial enable, disable Default: disable
echo pluses enable, disable Default: disable
echo commands enable, disable Default: enable
verbose response enable, disable Default: enable
response type text, numeric Default: text
error unknown
commands
incoming connection disabled, automatic,
connect string
display remote ip enable, disable Default: disable
packing mode disable, timeout,
timeout Default: 1000
threshold Default: 512 bytes
send character Accepts a control
trailing character Accepts a control
dtr asserted while
enable, disable Default: disable
Default: disabled
manual
Default: disable
send character
milliseconds
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A Default:
<control>M
character, for
example,
<control>
A represents
control-A
Default: asserted
connected,
continuously
asserted,
unasserted, truport
while connected
XPort Pro Command Reference 32
Page 33

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Group Item Value Name Value Options Additional
Information
tunnel start
(Attribute of
“instance is a
number.”
tunnel stop
(Attribute of
“instance is a
number.”
vip state enable, disable default: disable
xml import
control
start character import/export
echo enable import/export
disable
stop character import/export
echo enable import/export
disable
monitor timeout <None>, ...
restore factory
configuration
delete cpm groups enable, disable
cpm group delete name
delete http authentication
uris
http authentication uri
delete
reboot enable, disable Reboots after
name Deletes the
enable, disable Deletes existing
http authentication
uris before
importing new
ones.
specified http
authentication uri.
importing.
XML Status Record Groups and Items
Table 4-9 lists the supported XML Status Record (XSR) groups and items. These groups and
items show the status of the device in XML form and can only be exported. The XSR schema
differs slightly from the XCR groups and items in that the XSR allows groups within groups.
Currently, the only XSR groups that contain any sub groups are buffer pools and tunnel. The buffer
pools group has the following sub groups:
Protocol stack
Ethernet driver
Line
The tunnel group has the following sub groups:
Tunnel Modem
XPort Pro Command Reference 33
Page 34

4: Configuration Using XML
Table 4-9 XSR Groups and Items
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
arp
(Attribute of “instance” is
“eth0”.)
buffer pool this group contains other
cp group
(Attribute of “instance” is
required for the group name.
cps cp
device product info product type
email
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
arp entry ip address
mac address
age
type dynamic
static
groups: ethernet driver,
protocol stack
state disabled
disabled and locked
enabled
enabled and locked
value
cp
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
(Attribute of “instance”is a
number.)
success sent
failed
queued
value
level low
high
logic inverted
not inverted
position
pin
configured as input
output
value
level low
high
logic inverted
not inverted
active group
group
serial number
firmware version
uptime
permanent config saved
unsaved
sent with retries
XPort Pro Command Reference 34
Page 35

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
email log
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
ethernet driver
(Within group “buffer pool”.)
filesystem filesystem size
entry time
log
buffer headers total
free
used
max used
cluster pool cluster size
total
free
used
max used
banks current A
B
firmware begin
firmware end
firmware erase cycles
bank a begin
bank a end
bank a erase cycles
bank b begin
bank b end
bank b erase cycles
available space
clean space
dirty space
file and dir space used
data space used
number of files
number of directories
number of system files
opened files
locked files
opened for sharing
busy yes
no
XPort Pro Command Reference 35
Page 36

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
ftp status running
inactive
connections rejected
accepted
last client ip address
port
hardware cpu type
speed
memory flash size
ram size
http state enabled
disabled
logging entries
bytes
http log entry
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
totals entries
bytes
XPort Pro Command Reference 36
Page 37

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
icmp in messages
messages discarded
errors
destination unreachable
time exceeded messages
parameter problems
source quench requests
redirects
ping requests
ping replies
timestamp requests
timestamp replies
address mask requests
address mask replies
out messages
messages discarded
errors
destination unreachables
time exceeded messages
parameter problems
source quench requests
redirects
ping requests
ping replies
timestamp requests
timestamp replies
address mask requests
address mask replies
XPort Pro Command Reference 37
Page 38

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
interface
(Attribute of “instance” is
“eth0”.)
generic status no link
link up
disabled
unknown
errors (error text)
none
ethernet (Present only for
eth0.)
arp encapsulation ARPA
default gateway
network mask
domain
mac address
hostname
ip address
last change
mtu
primary dns
secondary dns
speed 10
100
duplex full
half
type ARPA
timeout
XPort Pro Command Reference 38
Page 39

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
interface
(Attribute of “instance” is
“eth0”.) (Continued.)
transmit octets
unicast
non unicast
discards
errors
broadcast packets
multicast packets
filtered packets
deferred
multiple retries
one retry
underflows
late collisions
retry errors
carrier lost errors
receive octets
unicast
non unicast
discards
errors
broadcast packets
multicast packets
filtered packets
unknown protocol
framing errors
overflows
crc errors
missed frame errors
XPort Pro Command Reference 39
Page 40

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
ip state enabled
disabled
default ttl
forwarded
route discards
in receives
header errors
address errors
unknown protocols
discarded
delivered
out requests
discards
discards no route
reassembly timeout
needed
success
failures
fragments needed
failures
success
ip sockets ip socket protocol UDP
TCP
rx queue
tx queue
local address
local port
remote address
remote port
state
XPort Pro Command Reference 40
Page 41

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
line
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
line (With no instance.)
(Within group “line” with
instance.)
receiver bytes
breaks
parity errors
framing errors
overrun errors
no receive buffer errors
queued bytes
flow control n/a
stop
go
transmitter bytes
breaks
queued bytes
flow control n/a
stop
go
line levels cts asserted
not asserted
rts asserted
not asserted
dsr asserted
not asserted
dtr asserted
not asserted
state enable
disable
protocol tunnel
baud rate Any value from 300 to
230400.
parity even
none
odd
data bits 7
8
stop bits 1
2
XPort Pro Command Reference 41
Page 42

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
line (With no instance.)
(Within group “line” with
instance.) (continued)
lpd
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
memory main heap condition clean
modbus local slave totals pdus in
modbus tcp server
(Attribute of “instance” is
“permanent” or “additional”.)
flow control hardware
none
software
xon char
xoff char
jobs printed
bytes printed
current client ip address
current client port
last client ip address
last client port
corrupt
total memory
available memory
fragments
allocated blocks
pdus out
exceptions
state down
up
binding
no port
local port
totals uptime
pdus in
pdus out
connections
last connection local ip address
local port
remote ip address
remote port
current connection local ip address
local port
remote ip address
XPort Pro Command Reference 42
Page 43

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
modbus tcp server
(Attribute of “instance” is
“permanent” or “additional”.)
(continued)
processes process
protocol stack (within group
“buffer pool”)
query port status enabled
rss url
sessions
ssh state active
syslog status
current connection ( remote port
uptime
pdus in
pdus out
cpu %
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
buffer headers total
cluster pool cluster size
last connection ip address
in discoveries
out discovery replies
data entries
totals uptime
messages failed
messages send
stack used
stack size
thread name
free
used
max used
total
free
used
max used
port
unknown queries
erroneous packets
errors
bytes
bytes in
bytes out
disabled
waiting
disabled
XPort Pro Command Reference 43
Page 44

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
tcp retransmission algorithm vanj
timeout minimum
timeout maximum
connections maximum
open active
open passive
failed
resets
established
errors in
resets in
out
segments in
out
retransmitted
telnet state active
waiting
disabled
totals uptime
bytes in
bytes out
tftp downloaded
uploaded
status running
inactive
not found
errors read
write
unknown
last client ip address
port
XPort Pro Command Reference 44
Page 45

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
tunnel
(Attribute of “instance” is a
number.)
tunnel modem (within group
“tunnel”)
udp in unknown ports
aggregate completed connects
completed accepts
disconnects
dropped connects
dropped accepts
octets from serial
octets from network
connect connection time
accept connection time
connect dns address
changes
connect dns address
invalids
echo commands enable
disable
verbose response enable
disable
response type text
numeric
error unknown commands disable
enable
incoming connection disabled
automatic
manual
in datagrams
in errors
out datagrams
XPort Pro Command Reference 45
Page 46

4: Configuration Using XML
Group Name Item Name Value Name Valid Values
vip conduit status up
down
disabled
idle
negotiating
closing
conduit uptime
config name
current tunnel port
dsm ip address list
local dna id
time of last replication
tunnel user
tunnel http port list
data bytes receive
transmit
udp packet queue receive
transmit
udp packets receive
transmit
current dsm ip address
tunnel proxy host
tunnel proxy port
vip pools
network interface
(instance is a number.)
xsr out bytes
errors
name
lines
elements
XPort Pro Command Reference 46
Page 47

5: Commands and Levels
Click the level in the tree structure and it will take you to the command list for that level.
root
• enable (enable)
• configure (config)
• arp (config-arp)
• cli (config-cli)
• ssh (config-cli-ssh)
• telnet (config-cli-telnet)
• diagnostics (config-diagnostics)
• log (config-diagnostics-log)
• ftp (config-ftp)
• host 1 (config-host:1)
• host 2 (config-host:2)
• host 3 (config-host:3)
• host 4 (config-host:4)
• host 5 (config-host:5)
• host 6 (config-host:6)
• host 7 (config-host:7)
• host 8 (config-host:8)
• host 9 (config-host:9)
• host 10 (config-host:10)
• host 11 (config-host:11)
• host 12 (config-host:12)
• host 13 (config-host:13)
• host 14 (config-host:14)
• host 15 (config-host:15)
• host 16 (config-host:16)
• http (config-http)
• icmp (config-icmp)
• if 1 (config-if:eth0)
• link (config-ethernet:eth0)
• ip (config-ip)
• ip filter (config-filter)
• lpd 1 (config-lpd:1)
• modbus (modbus)
• rss (modbus-rss)
• query port (config-query_port)
• rss (config-rss)
• smtp (config-smtp)
• snmp (config-snmp)
• traps (config-snmp-traps)
• syslog (config-syslog)
• tcp (config-tcp)
• terminal 1 (config-terminal:1)
• terminal network (config-terminal:network)
• tftp (config-tftp)
• udp (config-udp)
• vip (config-vip)
• cpm (cpm)
XPort Pro Command Reference 47
Page 48

5: Commands and Levels
• device (device)
• dns (dns)
• email 1 (email:1)
• cp (email-cp:1)
• email 2 (email:2)
• cp (email-cp:2)
• email 3 (email:3)
• cp (email-cp:3)
• email 4 (email:4)
• cp (email-cp:4)
• filesystem (filesystem)
• line 1 (line:1)
• lpd (lpd)
• ppp 1 (ppp:1)
• ssh (ssh)
• client (ssh-client)
• server (ssh-server)
• ssl (ssl)
• tunnel 1 (tunnel:1)
• accept (tunnel-accept:1)
• cp output (tunnel-accept-cp_output:1)
• password (tunnel-accept-password:1)
• connect (tunnel-connect:1)
• cp output (tunnel-connect-cp_output:1)
• host 1 (tunnel-connect-host:1:1)
• host 2 (tunnel-connect-host:1:2)
• host 3 (tunnel-connect-host:1:3)
• host 4 (tunnel-connect-host:1:4)
• host 5 (tunnel-connect-host:1:5)
• host 6 (tunnel-connect-host:1:6)
• host 7 (tunnel-connect-host:1:7)
• host 8 (tunnel-connect-host:1:8)
• host 9 (tunnel-connect-host:1:9)
• host 10 (tunnel-connect-host:1:10)
• host 11 (tunnel-connect-host:1:11)
• host 12 (tunnel-connect-host:1:12)
• host 13 (tunnel-connect-host:1:13)
• host 14 (tunnel-connect-host:1:14)
• host 15 (tunnel-connect-host:1:15)
• host 16 (tunnel-connect-host:1:16)
• disconnect (tunnel-disconnect:1)
• modem (tunnel-modem:1)
• packing (tunnel-packing:1)
• serial (tunnel-serial:1)
• xml (xml)
XPort Pro Command Reference 48
Page 49

Table 5-1 Commands and Levels
accept (tunnel-accept:1) level commands
accept mode always
Enables the tunneling server to always accept tunneling
connections.
accept mode any character
Enables the tunneling server to accept tunneling connec-
(serial
port).
accept mode disable
Disables accept mode tunneling.
accept mode modem control asserted
Enables the tunneling server to accept tunneling connec-
control pin is asserted.
accept mode modem emulation
Enables modem emulation for accept mode tunneling.
accept mode start character
Enables accept mode tunneling when the configured start
is received on the line.
aes decrypt key
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the accept tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the accept tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
block network disable
Forwards (tunnels) network data in accept mode tunneling.
block network enable
Discards all data coming in from the accept mode tunnel
it to the serial interface (generally used for debugging).
block serial disable
Forwards (tunnels) serial data in accept mode tunneling.
Discards all data coming in from the serial interface before
ging).
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
cp output
Enters the next lower level.
default accept mode
Restores the default accept mode as "always".
tions only when a
character is received through the corresponding line
tions when the modem
character
5: Commands and Levels
<hexadecimal>
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the accept tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the accept tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
block serial enable
XPort Pro Command Reference 49
before forwarding
forwarding
it to the accept mode tunnel (generally used for debug-
Page 50

5: Commands and Levels
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default start character
Defaults the accept mode start character.
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second accept mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
email connect <number>
Sets an email profile to use to send an email alert upon
<number> = the number of the email profile to use.
email disconnect <number>
Sets an email profile to use to send an email alert upon
<number> = the number of the email profile to use.
exit
Returns to the tunnel level.
flush serial disable
Characters already in the serial data buffer are retained
an accept mode tunneling connection.
flush serial enable
Flushes the serial data buffer upon establishing an accept
connection.
network.
flush start character enable
Disables forwarding of the accept start character into the
network.
kill connection
Disconnects the active accept mode tunneling connection.
local port <number>
Sets the port to use for accept mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the accept tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the accept tunnel AES encrypt key.
no email connect
Discontinues sending email alerts upon establishing an
accept mode tunnel.
mode tunnel.
no local port
Uses the default port number as the local port for accept
for this tunnel.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the accept mode TCP keep alive timeout.
password
Enters the next lower level.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for accept mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for accept mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for accept mode tunneling.
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for accept mode tunneling.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show status
Displays tunnel accept status.
start character <control>
Sets the accept mode start character.
A control character has the form <control>C.
establishing
an accept mode tunnel.
closing
an accept mode tunnel.
upon establishing
mode tunneling
flush start character disable Enables forwarding of the accept start character into the
no email disconnect Discontinues sending email alerts upon closing an accept
mode tunneling.
The default port is 10000 + #, where # is the line number
protocol tcp aes Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for accept mode
The character may be input as text, control, decimal, or
hex.
XPort Pro Command Reference 50
Page 51

5: Commands and Levels
A decimal value character has the form \99.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for accept mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
arp (config-arp) level commands
add <ip address> <MAC address>
Adds an entry to the ARP table, mapping an IP address to
<mac address> = MAC address in colon-separated form.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default timeout
Restores the default ARP cache timeout.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
remove all
Removes all entries from the ARP cache.
<ip address> = address of the entry being removed.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show cache
Displays the ARP cache table.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
timeout <seconds>
Sets the ARP cache timeout.
<seconds> = ARP cache timeout in seconds.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cli (config-cli) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default inactivity timeout
The default inactivity timeout will apply to CLI sessions.
default quit connect line
Restores the default string used to quit the "connect line
<line>" command.
enable level password <text>
Sets the enable-level password.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
inactivity timeout
Sets the inactivity timeout for all CLI sessions.
login password <text>
Sets the CLI login password.
no enable level password
Removes the enable-level password.
no inactivity timeout
No inactivity timeout will apply to CLI sessions.
no login password
Removes the CLI login password.
quit connect line <control>
Sets the string used to quit the "connect line <line>" com-
A control character has the form <control>C.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh
Change to menu level for SSH configuration and status.
telnet
Change to menu level for Telnet configuration and status.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
client (ssh-client) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default user <username> command
Restore the user command to the default login shell
A hex value character has the form 0xFF.
sets the timer.
a MAC address.
<ip address> = IP address to be mapped.
remove ip <ip address>
<minutes>
Removes an entry from the ARP cache.
mand.
The characters may be input as text or control.
XPort Pro Command Reference 51
Page 52

5: Commands and Levels
delete all known hosts
Remove all hnown hosts
delete all users
Remove all users
delete known host <server>
Remove known host
delete user <username>
Delete the named user
exit
Exits to the ssh level.
known host <server>
Set known host RSA or DSA key
no known host <server> dsa
Remove known host DSA key
no known host <server> rsa
Remove known host RSA key
no user <username> dsa
Remove user DSA key
no user <username> rsa
Remove user RSA key
show
Show SSH Client settings
CLI session.
show known host <server>
Show known host RSA and DSA keys
show user <username>
Show information for a user
user <username>
Set username and RSA or DSA keys
user <username> command <command>
Customizes the user command
user <username> generate dsa 1024
Generate DSA public and private keys
user <username> generate dsa 512
Generate DSA public and private keys
user
generate dsa 768
Generate DSA public and private keys
user <username> generate rsa 1024
Generate RSA public and private keys
user <username> generate rsa 512
Generate RSA public and private keys
user <username> generate rsa 768
Generate RSA public and private keys
user <username> password <password>
Set username with password and optional RSA or DSA
keys
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
configure (config) level commands
status.
cli
Change to menu level for CLI configuration and status
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
diagnostics
Enters the diagnostics level.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
ftp
Enters the ftp level.
host
Change to config host level
http
Enters the http level.
Changes to the command level for ICMP configuration and
status.
if <instance>
Changes to the interface configuration level.
status.
ip filter
Enters the config-filter level.
kill ssh <session>
Kills SSH session with index from "show sessions"
kill telnet <session>
Kills Telnet session with index from "show sessions"
lpd <line>
Enters the configure lpd level.
gured.
modbus
Changes to the modbus configuration level.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
<username>
arp Changes to the command level for ARP configuration and
<number>
icmp
ip Changes to the command level for IP configuration and
XPort Pro Command Reference 52
<line> = number of the line (lpd serial port) to be confi-
Page 53

5: Commands and Levels
query port
Enters the query port level.
rss
Change to menu level for RSS configuration and status
show
Displays system information.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
smtp
Changes to the command level for SMTP configuration
and status.
snmp
Enters the snmp level.
syslog
Enters the syslog level.
tcp
Changes to the command level for TCP configuration and
status.
terminal network
Enters the configure-terminal level for the network.
tftp
Enters the tftp level.
udp
Changes to the command level for UDP configuration and
status.
vip
Change to menu level for VIP configuration and status
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
connect (tunnel-connect:1) level commands
block network disable
Forwards (tunnels) network data in connect mode tunneling.
it to the serial interface (generally used for debugging).
block serial disable
Forwards (tunnels) serial data in connect mode tunneling.
block serial enable
Discards all data coming in from the serial interface before
ging).
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
connect mode always
Enables the tunneling server to always establish tunneling
connections.
port).
connect mode disable
Disables connect mode tunneling.
control pin is asserted.
connect mode modem emulation
Enables modem emulation for connect mode tunneling.
connect mode start character
Enables connect mode tunneling when the configured start
is received on the line.
cp output
Enters the next lower level.
default connect mode
Restores the default connect mode as "disable".
nection.
default local port
Uses a random port number as the local port for establishing tunneling
terminal <line>
block network enable Discards all data coming in from the connect mode tunnel
connect mode any character Enables the tunneling server to establish a tunneling con-
Enters the configure-terminal level.
<line> = number of the terminal line (serial port) to be configured.
before forwarding
forwarding
it to the connect mode tunnel (generally used for debug-
nection when a
character is received on the corresponding line (serial
connect mode modem control asserted Enables the tunneling server to make tunneling connec-
default host mode Connects to the first host in the list that accepts the con-
XPort Pro Command Reference 53
tions when the modem
character
Page 54

5: Commands and Levels
connections to other devices.
default reconnect time
Restores the default reconnect time value for connect
mode tunneling.
default start character
Defaults the connect mode start character.
email connect <number>
Sets an email profile to use to send an email alert upon
<number> = the number of the email profile to use.
email disconnect <number>
Sets an email profile to use to send an email alert upon
<number> = the number of the email profile to use.
exit
Returns to the tunnel level.
flush serial disable
Characters already in the serial data buffer are retained
a connect mode tunneling connection.
flush serial enable
Flushes the serial data buffer upon establishing a connect
connection.
network.
flush start character enable
Disables forwarding of the connect start character into the
network.
host <instance>
Enters the next lower level.
Specify the instance for the next lower level.
host mode sequential
Connects to the first host in the list that accepts the connection.
list.
kill connection
Disconnects the active connect mode tunneling connection
or connections.
local port <number>
Sets a specific port for use as the local port.
<number> = the number of the port to use.
connect mode tunnel.
no email disconnect
Discontinues sending email alerts upon closing a connect
mode tunnel.
promote host <number>
Promotes the identified host, exchanging it place with the
to adjust the order of the defined hosts.
reconnect time <milliseconds>
Sets the reconnect time value for tunneling connections
<milliseconds> = timeout in milliseconds.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show status
Displays tunnel connect status.
start character <control>
Sets the connect mode start character.
A hex value character has the form 0xFF.
establishing
a connect mode tunnel.
closing
a connect mode tunnel.
upon establishing
mode tunneling
flush start character disable Enables forwarding of the connect start character into the
host mode simultaneous Selects simultaneous connections to all hosts on the host
no email connect Discontinues sending email alerts upon establishing a
host above it,
established by the
device in milliseconds.
The character may be input as text, control, decimal, or
hex.
A control character has the form <control>C.
A decimal value character has the form \99.
XPort Pro Command Reference 54
Page 55

5: Commands and Levels
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp (email-cp:4) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
Specify a CP group that shall trigger an email.
<text> = configurable pin group.
no group
Disables the trigger to send an email.
no trigger value
Clears the value that shall trigger an email.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
trigger value <number>
Specify a value of the CP group that shall trigger an
hex if prepended with “0x”.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp (email-cp:3) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
<text> = configurable pin group.
no group
Disables the trigger to send an email.
no trigger value
Clears the value that shall trigger an email.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
trigger value <number>
Specify a value of the CP group that shall trigger an
hex if prepended with “0x”.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp (email-cp:2) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
Specify a CP group that shall trigger an email.
<text> = configurable pin group.
no group
Disables the trigger to send an email.
no trigger value
Clears the value that shall trigger an email.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
trigger value
hex if prepended with “0x”.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp (email-cp:1) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
email.
<number> = numeric value to watch for from the CP
group. Can be specified as
Specify a CP group that shall trigger an email.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
email.
<number> = numeric value to watch for from the CP
group. Can be specified as
<number>
XPort Pro Command Reference 55
Specify a value of the CP group that shall trigger an
email.
<number> = numeric value to watch for from the CP
group. Can be specified as
Page 56

5: Commands and Levels
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
Specify a CP group that shall trigger an email.
<text> = configurable pin group.
no group
Disables the trigger to send an email.
no trigger value
Clears the value that shall trigger an email.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
trigger value <number>
hex if prepended with “0x”.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp output (tunnel-connect-cp_output:1) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
<number> = binary to output (typically 1 or 0).
default connection value
Restores the default value for connect mode connection.
default disconnection value
Restores the default value for connect mode disconnection.
<number> = binary to output (typically 1 or 0).
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
Configures the CP Group to set upon making or breaking
<text> = CP Group.
no group
Removes the CP Set Group for connect mode.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cp output (tunnel-accept-cp_output:1) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
connection value <number>
Sets the value to output to the CP Group upon accept
<number> = binary to output (typically 1 or 0).
default connection value
Restores the default value for accept mode connection.
default disconnection value
Restores the default value for accept mode disconnection.
<number> = binary to output (typically 1 or 0).
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
group <text>
Configures the CP Group to set upon making or breaking
<text> = CP Group.
no group
Removes the CP Set Group for accept mode.
show
Shows the current configuration.
Specify a value of the CP group that shall trigger an
email.
<number> = numeric value to watch for from the CP
group. Can be specified as
connection value <number>
disconnection value <number>
Sets the value to output to the CP Group upon connect
mode connection.
Sets the value to output to the CP Group upon connect
mode disconnection.
a connect
mode connection.
mode connection.
disconnection value <number>
XPort Pro Command Reference 56
Sets the value to output to the CP Group upon accept
mode disconnection.
an accept
mode connection.
Page 57

show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
cpm (cpm) level commands
add <cp> to <group>
Adds the specified CP to the specified group.
of the group to which you want to add
the CP.
add <cp> to <group> <bit>
Adds a specified CP to a specified group at a specified bit
<group> = the name of the group to which you want to add
<bit> = bit position.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
create <group>
Creates a configurable pin (CP) group.
<group> = the name for the new group.
delete <cp> from <group>
Removes a CP from a specified group and sets the CP to
<group> = the name of the group.
<group> = the name of the group.
disable
<group> = the name of the group.
enable <group>
Enables a disabled group.
<group> = the name of the group.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
get <group>
Displays the value of the specified group.
<group> = the name of the group.
set <cp> as input
Configures a CP as an asserted high input.
<cp> = configurable pin.
<cp> = configurable pin.
set <cp> as output
Configures a CP as an asserted high output.
<cp> = configurable pin.
set <cp> as output assert low
Configures a CP as an asserted low output.
<cp> = configurable pin.
if prepended with “0x”.
show <group>
Displays group information for specified group.
<group> = the name of the group.
show cp
Displays configuration and group information for all CPs.
show groups
Displays all groups defined and their state.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
device (device) level commands
<cp> = configurable pin.
<group> = the name
position.
<cp> = configurable pin.
the CP.
its default
configuration of input.
<cp> = configurable pin.
5: Commands and Levels
delete <group>
<group>
set <cp> as input assert low
set <group> <value>
Removes a group and resets all CPs in that group to the
default
configuration of input.
Disables the specified group.
Configures a CP as an asserted low input.
Assigns a value to the specified group.
<group> = the name of the group.
<value> = numeric value to assign to the CP group. Can
be specified as hex
XPort Pro Command Reference 57
Page 58

5: Commands and Levels
auto show tlog
Continuously displays the internal trouble log.
auto show upload
Continuously displays the status of firmware upload.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default long name
Restores the default product long name.
default short name
Restores the default product short name.
dhrystone
Runs the Dhrystone benchmark program.
exit
Exit to the enable level.
and the Web interface.
short name <name>
Sets the product short name, displayed in command mode
<name> = maximum of eight characters.
show
Show system information
show buffer pool
Displays information about the various buffer pools.
show codefile memory
Displays memory utilization by code files.
show debug
Displays debug information.
line reference.
show hardware information
Displays information about the hardware.
CLI session.
show linereference memory <code filename>
Displays memory utilization by line reference for one code
file.
show memory
Displays current memory usage information.
show task memory
Displays task memory utilization.
show task state
Displays current task states.
show tlog
Displays the internal trouble log.
show upload
Displays the status of firmware upload.
show xport_pro
Show system information
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
diagnostics (config-diagnostics) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Returns to the config level.
log
Enters the next lower level.
show
Displays the current configuration.
CLI session.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
disconnect (tunnel-disconnect:1) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Returns to the tunnel level.
flush serial disable
Does not flush serial data upon closing a tunneling connection.
flush serial enable
Flushes serial data buffer when a tunneling connection is
closed.
flush stop character disable
Forwards the stop character from the Line to the network.
flush stop character enable
Prevents the stop character from the Line from being forwarded to the network.
long name <name>
show delta memory Displays differences in memory utilization by code files or
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
Sets the product long name, displayed in command mode
and the Web interface.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
XPort Pro Command Reference 58
Page 59

5: Commands and Levels
modem control disable
Does not watch the modem control pin to disconnect.
modem control enable
Watches the modem control pin and disconnects if it is not
asserted.
no stop character
Removes the stop character.
no timeout
Disables disconnect after timeout feature for tunneling
sessions.
show
Displays the current configuration.
CLI session.
stop character <control>
Sets the stop character.
A hex value character has the form 0xFF.
timeout
<milliseconds> = timeout in milliseconds.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
dns (dns) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
lookup <host_or_ip>
Return a lookup on the DNS name or IP address.
remove all
Removes all entries from the DNS Cache.
remove host <host>
Removes an entry from the DNS Cache.
show
Show DNS status and cache entries.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
email 1 (email:1) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously displays email statistics.
cc <text>
Sets Cc addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
clear log
Clears all entries from the mail log.
clear mail counters
Sets the email counters to zero.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
cp
Enters the next lower level.
default local port
Sets the local port (used to send email alerts) to random.
default priority
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
side.
email <number>
Enters the configure email level.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
from <text>
Sets the From address for email alerts.
email alert.
local port <number>
<number> local port to use for email alerts.
message file <text>
Specifies a text file, the contents of which will be the mes-
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
The character may be input as text, control, decimal, or
hex.
A control character has the form <control>C.
A decimal value character has the form \99.
<milliseconds>
Disconnects when no data has been received on the line
(serial port) for the
specified length of time.
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
default server port Restores the factory default port for SMTP on the server
XPort Pro Command Reference 59
<text> = email address to place in the From field of the
Sets the local port used to send email alerts.
Page 60

5: Commands and Levels
sage body
<text> = the name of a local file.
no cc
Removes the Cc addresses for email alerts.
no clear mail counters
Restores the email counters to the aggregate values.
no from
Removes the From address for email alerts.
ty.
no overriding domain
Removes the overriding domain name option.
no reply to
Removes the Reply To address for email alerts.
no subject
Removes subject used for email alerts.
no to
Removes the To addresses for email alerts.
send an email alert instead of the device’s domain name in
priority high
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 2 (high).
priority low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 4 (low).
priority normal
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
priority urgent
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 1 (urgent).
priority very low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 5 (very low).
reply to <text>
Sets the Reply To address for email alerts.
<text> = email address to place in the Reply To field of the
email alert.
send
Sends an email using the current settings.
<number> = port used for SMTP on the server side.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show log
Displays the email log.
show statistics
Displays email statistics.
subject <text>
Sets the Subject for email alerts.
<text> = text to placed as the subject.
to <text>
dresses.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
email 2 (email:2) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously displays email statistics.
cc <text>
Sets Cc addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
clear log
Clears all entries from the mail log.
clear mail counters
Sets the email counters to zero.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
cp
Enters the next lower level.
default local port
Sets the local port (used to send email alerts) to random.
of an email alert.
no message file Removes the file name, so the message body will be emp-
overriding domain <text>
server port <number>
Sets a domain name that will be used when connecting to
an SMTP server to
EHLO.
<text> = domain name to override the current domain
name in EHLO.
Sets the port used by the SMTP server.
XPort Pro Command Reference 60
Sets To addresses for email alerts.
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
Page 61

5: Commands and Levels
default priority
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
default server port
Restores the factory default port for SMTP on the server
side.
email <number>
Enters the configure email level.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
from <text>
Sets the From address for email alerts.
email alert.
local port <number>
Sets the local port used to send email alerts.
<number> local port to use for email alerts.
message file <text>
Specifies a text file, the contents of which will be the mes-
<text> = the name of a local file.
no cc
Removes the Cc addresses for email alerts.
no clear mail counters
Restores the email counters to the aggregate values.
no from
Removes the From address for email alerts.
no message file
Removes the file name, so the message body will be empty.
no overriding domain
Removes the overriding domain name option.
no reply to
Removes the Reply To address for email alerts.
no subject
Removes subject used for email alerts.
no to
Removes the To addresses for email alerts.
overriding domain <text>
Sets a domain name that will be used when connecting to
instead of the device’s domain name in
name in EHLO.
priority high
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 2 (high).
priority low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 4 (low).
priority normal
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
priority urgent
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 1 (urgent).
priority very low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 5 (very low).
reply to
address to place in the Reply To field of the
email alert.
send
Sends an email using the current settings.
server port <number>
Sets the port used by the SMTP server.
<number> = port used for SMTP on the server side.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show log
Displays the email log.
show statistics
Displays email statistics.
<text> = text to placed as the subject.
to <text>
Sets To addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
<text> = email address to place in the From field of the
sage body
of an email alert.
<text>
subject <text>
an SMTP server to
send an email alert
EHLO.
<text> = domain name to override the current domain
Sets the Reply To address for email alerts.
<text> = email
Sets the Subject for email alerts.
XPort Pro Command Reference 61
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
Page 62

5: Commands and Levels
email 3 (email:3) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously displays email statistics.
cc <text>
Sets Cc addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
clear log
Clears all entries from the mail log.
clear mail counters
Sets the email counters to zero.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
cp
Enters the next lower level.
default local port
Sets the local port (used to send email alerts) to random.
default priority
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
default server port
Restores the factory default port for SMTP on the server
side.
email <number>
Enters the configure email level.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
from
email alert.
local port <number>
Sets the local port used to send email alerts.
<number> local port to use for email alerts.
message file <text>
<text> = the name of a local file.
no cc
Removes the Cc addresses for email alerts.
no clear mail counters
Restores the email counters to the aggregate values.
no from
Removes the From address for email alerts.
no message file
Removes the file name, so the message body will be empty.
no overriding domain
Removes the overriding domain name option.
no reply to
Removes the Reply To address for email alerts.
no subject
Removes subject used for email alerts.
no to
Removes the To addresses for email alerts.
overriding domain <text>
Sets a domain name that will be used when connecting to
send an email alert instead of the device’s domain name in
name in EHLO.
priority high
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 2 (high).
priority low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 4 (low).
priority normal
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
priority urgent
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 1 (urgent).
priority very low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 5 (very low).
reply to <text>
Sets the Reply To address for email alerts.
<text> = email address to place in the Reply To field of the
email alert.
send
Sends an email using the current settings.
server port <number>
<number> = port used for SMTP on the server side.
show
Displays the current configuration.
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
<text>
Sets the From address for email alerts.
<text> = email address to place in the From field of the
Specifies a text file, the contents of which will be the message body
of an email alert.
an SMTP server to
EHLO.
<text> = domain name to override the current domain
XPort Pro Command Reference 62
Sets the port used by the SMTP server.
Page 63

show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show log
Displays the email log.
show statistics
Displays email statistics.
subject <text>
Sets the Subject for email alerts.
<text> = text to placed as the subject.
dresses.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
email 4 (email:4) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously displays email statistics.
cc <text>
Sets Cc addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
clear log
Clears all entries from the mail log.
clear mail counters
Sets the email counters to zero.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
cp
Enters the next lower level.
default local port
Sets the local port (used to send email alerts) to random.
default priority
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
default server port
Restores the factory default port for SMTP on the server
side.
email <number>
Enters the configure email level.
exit
Exits to the enable level.
email alert.
local port <number>
Sets the local port used to send email alerts.
<number> local port to use for email alerts.
message file
<text> = the name of a local file.
no cc
Removes the Cc addresses for email alerts.
no clear mail counters
Restores the email counters to the aggregate values.
no from
Removes the From address for email alerts.
no message file
Removes the file name, so the message body will be empty.
no overriding domain
Removes the overriding domain name option.
no reply to
Removes the Reply To address for email alerts.
no subject
Removes subject used for email alerts.
no to
Removes the To addresses for email alerts.
overriding domain
send an email alert instead of the device’s domain name in
name in EHLO.
priority high
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 2 (high).
priority low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 4 (low).
5: Commands and Levels
to <text>
from <text>
Sets To addresses for email alerts.
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
Sets the From address for email alerts.
<text> = email address to place in the From field of the
<text>
<text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 63
Specifies a text file, the contents of which will be the message body
of an email alert.
Sets a domain name that will be used when connecting to
an SMTP server to
EHLO.
<text> = domain name to override the current domain
Page 64

5: Commands and Levels
priority normal
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 3 (normal).
priority urgent
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 1 (urgent).
priority very low
Sets X-Priority for email alerts to 5 (very low).
reply to <text>
Sets the Reply To address for email alerts.
<text> = email address to place in the Reply To field of the
email alert.
send
Sends an email using the current settings.
server port
<number> = port used for SMTP on the server side.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show log
Displays the email log.
show statistics
Displays email statistics.
subject <text>
Sets the Subject for email alerts.
<text> = text to placed as the subject.
to <text>
Sets To addresses for email alerts.
dresses.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
enable (enable) level commands
auto show interfaces
Show interface statistics
auto show processes
Continuously show thread runtime information
clear interfaces counters
Zeros interface session counters
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
configure
Enters the configuration level.
connect
Show name and number for lines.
connect line
Begin session on serial port.
cpm
Enters the CP Manager level.
device
Enters the device level.
disable
Exits the enable level.
dns
Enters the DNS level.
email <number>
Enters the configure email level.
exit
Exit from the system
filesystem
Enters the filesystem level.
kill ssh <session>
Kills SSH session with index from "show sessions"
kill telnet <session>
Kills Telnet session with index from "show sessions"
line <line>
Enters the line level.
<line> = number of the line (serial port) to be configured.
lpd
Enters the lpd level.
no clear interfaces counters
Unzeros interface session counters
ping <host>
Ping destination continuously with 5 second timeout
ping <host> <count>
Ping destination n times with 5 second timeout
ping <host> <count> <timeout>
Ping destination n times with x timeout (in seconds)
ppp <line>
Enters the serial line PPP level.
reload
Reboot system
reload factory defaults
Reload factory defaults to permanent storage
show
Show system information
<number>
<line>
Sets the port used by the SMTP server.
<text> = a quoted, semicolon separated list of email ad-
XPort Pro Command Reference 64
Page 65

show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show interfaces
Show interface statistics
show ip sockets
Show UDP/TCP state information
show processes
Show thread runtime information
show sessions
Show active Telnet and SSH Sessions
show xport_pro
Show system information
ssh
Enters the SSH configuration level.
ssh <optClientUsername> <host>
Begin SSH session on network <host>.
The optClientUserName must match an SSH Client: Users
Use "" in optClientUserName to prompt for host username
and password.
ssh <optClientUsername> <host> <port>
Begin SSH session on network <host>:<port>.
The optClientUserName must match an SSH Client: Users
Use "" in optClientUserName to prompt for host username
and password.
ssl
Enters the SSL configuration level.
telnet <host>
Begin telnet session on network <host>.
telnet <host> <port>
Begin telnet session on network <host>:<port>.
trace route <host>
Trace route to destination
gured.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
xml
Enters the XML level.
filesystem (filesystem) level commands
cat <file>
Show the contents of a file
cd <directory>
Change the current directory to the specified directory
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
compact
Compact the file system, freeing all dirty space
cp <source file> <destination file>
Copy an existing file
dump <file>
Show contents of a file as a hex dump
exit
Exits to the enable level.
format
Format the file system and lose all data
ls
Show all files and directories in the current directory
ls <directory>
Show all files and directories in the specified directory
mkdir
Create a directory
mv
Move a file on the file system
pwd
Print working directory
rm <file>
Remove a file
rmdir <directory>
Remove a directory
show
Show file system statistics
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show tree
Show all files and directories from current directory
tftp get ascii
Get an ascii file using TFTP
tftp get ascii <source file> <destination file> <host> <port>
Get an ascii file using TFTP
configuration entry.
configuration entry.
5: Commands and Levels
tunnel <line>
<directory>
<source file> <destination file>
Enters the tunnel level.
<line> = number of the tunnel line (serial port) to be confi-
<source file> <destination file> <host>
XPort Pro Command Reference 65
Page 66

tftp get binary <source file> <destination file> <host>
Get a binary file using TFTP
tftp get binary <source file> <destination
file> <host> <port>
Get a binary file using TFTP
tftp put ascii <source file> <destination file> <host>
Put an ascii file using TFTP
tftp put ascii <source file> <destination file> <host> <port>
Put an ascii file using TFTP
tftp put binary <source file> <destination file> <host>
Put a binary file using TFTP
tftp put binary <source file> <destination
file> <host> <port>
Put a binary file using TFTP
touch <file>
Create a file
ftp (config-ftp) level commands
admin password <text>
Sets the administrative password for the FTP server.
<text> = administrative password.
It also removes the administrative password.
clear counters
Zeros FTP counters.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default admin username
Resets the FTP username to the default (admin).
exit
Returns to the config level.
no admin password
Removes the FTP administrative password.
no clear counters
Unzeros FTP counters.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
Displays the FTP statistics.
state disable
Disables the FTP server.
state enable
Enables the FTP server.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 1 (tunnel-connect-host:1:1) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
5: Commands and Levels
admin username <text>
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the administrative username for the FTP server.
<text> = administrative username.
with.
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
XPort Pro Command Reference 66
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 67

5: Commands and Levels
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 1 (config-host:1) level commands
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
no address Removes the remote host address used to establish
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
protocol udp aes
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
XPort Pro Command Reference 67
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
Page 68

clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 10 (tunnel-connect-host:1:10) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
Each byte is represented by a single character.
5: Commands and Levels
<text>
remote address <text>
remote port <number>
Sets the name of the host.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
with.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
XPort Pro Command Reference 68
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Page 69

5: Commands and Levels
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 10 (config-host:10) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
spaces.
no address Removes the remote host address used to establish
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
protocol udp aes
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
XPort Pro Command Reference 69
Page 70

default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 11 (tunnel-connect-host:1:11) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
5: Commands and Levels
name <text>
remote address <text>
remote port <number>
Sets the name of the host.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
XPort Pro Command Reference 70
Page 71

5: Commands and Levels
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
<text> = SSH user name.
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 11 (config-host:11) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
<number>
protocol tcp aes Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
ssh username <text>
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunneling connections
with other devices.
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
sets the timer.
<text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 71
Page 72

5: Commands and Levels
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 12 (tunnel-connect-host:1:12) level commands
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
<text>
address <text>
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
<text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 72
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 73

5: Commands and Levels
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneprotocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 12 (config-host:12) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
port <number>
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
ling.
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
XPort Pro Command Reference 73
default value,
Page 74

5: Commands and Levels
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 13 (tunnel-connect-host:1:13) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
<number> = port to be used.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
with.
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
aes encrypt key text <text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 74
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 75

5: Commands and Levels
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 13 (config-host:13) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
protocol tcp aes Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
<text>
<milliseconds>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunneling connections
with other devices.
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
sets the timer.
default value,
XPort Pro Command Reference 75
Page 76

5: Commands and Levels
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 14 (tunnel-connect-host:1:14) level commands
address
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
<text>
<text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
default tcp keep alive Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
XPort Pro Command Reference 76
Page 77

5: Commands and Levels
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
<text> = SSH user name.
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 14 (config-host:14) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
tunneling connections.
protocol tcp aes Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
ssh username <text>
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
name <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunneling connections
with other devices.
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
sets the timer.
default value,
Sets the name of the host.
XPort Pro Command Reference 77
Page 78

5: Commands and Levels
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 15 (tunnel-connect-host:1:15) level commands
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
address <text>
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
default tcp keep alive Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
XPort Pro Command Reference 78
Page 79

5: Commands and Levels
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
ling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 15 (config-host:15) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol telnet Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunne-
CLI session.
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
default value,
XPort Pro Command Reference 79
Page 80

5: Commands and Levels
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 16 (tunnel-connect-host:1:16) level commands
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
<text>
address <text>
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
<text>
default tcp keep alive Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
XPort Pro Command Reference 80
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 81

5: Commands and Levels
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connecno ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
ling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 16 (config-host:16) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host
Change to config host level
name
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
tions.
protocol telnet Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunne-
<number>
<text>
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
default value,
Sets the name of the host.
XPort Pro Command Reference 81
Page 82

5: Commands and Levels
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 2 (tunnel-connect-host:1:2) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
<number> = port to be used.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
with.
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
aes encrypt key text <text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 82
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 83

no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 2 (config-host:2) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
this host is
5: Commands and Levels
tunneling.
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
default remote port Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
XPort Pro Command Reference 83
Page 84

5: Commands and Levels
selected on the login connect menu.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 3 (tunnel-connect-host:1:3) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
<text> = IP address.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
<hexadecimal>
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
XPort Pro Command Reference 84
Page 85

5: Commands and Levels
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
ling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 3 (config-host:3) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
protocol telnet Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunne-
protocol udp aes
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
default remote port Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
XPort Pro Command Reference 85
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
Page 86

remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 4 (tunnel-connect-host:1:4) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
5: Commands and Levels
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
with.
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
aes encrypt key text <text>
XPort Pro Command Reference 86
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Page 87

5: Commands and Levels
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 4 (config-host:4) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
default remote port Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
XPort Pro Command Reference 87
Page 88

5: Commands and Levels
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 5 (tunnel-connect-host:1:5) level commands
address
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
<text>
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
default tcp keep alive Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
no address Removes the remote host address used to establish
XPort Pro Command Reference 88
Page 89

protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 5 (config-host:5) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
5: Commands and Levels
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
default remote port Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
XPort Pro Command Reference 89
Page 90

5: Commands and Levels
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 6 (tunnel-connect-host:1:6) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
<text> = username.
with.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
no address Removes the remote host address used to establish
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
XPort Pro Command Reference 90
Page 91

5: Commands and Levels
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
necting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 6 (config-host:6) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
tunneling.
protocol udp aes
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
validate certificate enable Requires verification of the server certificate when con-
default remote port Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
default value,
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
XPort Pro Command Reference 91
Page 92

write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 7 (tunnel-connect-host:1:7) level commands
address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
tunneling.
5: Commands and Levels
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
spaces.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
<number>
protocol tcp aes Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
XPort Pro Command Reference 92
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
Page 93

5: Commands and Levels
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneprotocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 7 (config-host:7) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 8 (tunnel-connect-host:1:8) level commands
ling.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
ling connections
with other devices.
sets the timer.
<text>
default value,
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
XPort Pro Command Reference 93
Page 94

address <text>
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
no address
Removes the remote host address used to establish
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
tions.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
protocol telnet
Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunneling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
5: Commands and Levels
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
no port Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connec-
port <number>
XPort Pro Command Reference 94
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
Page 95

protocol udp aes
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
<text> = SSH user name.
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 8 (config-host:8) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 9 (tunnel-connect-host:1:9) level commands
address <text>
<text> = IP address or host name of the remote host.
5: Commands and Levels
ssh username <text>
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
name <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunneling connections
with other devices.
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
sets the timer.
default value,
Sets the name of the host.
remote address <text>
remote port <number>
XPort Pro Command Reference 95
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
Sets the remote host to establish tunneling connections
with.
Page 96

5: Commands and Levels
aes decrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes decrypt key text <text>
spaces.
aes encrypt key <hexadecimal>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
aes encrypt key text <text>
Sets the connect tunnel AES encrypt key with up to 16
spaces.
auto show statistics
show connection statistics
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default protocol as "TCP".
default tcp keep alive
Restores the default 45 second connect mode TCP keep
alive timeout.
exit
Exits to the next higher level.
tunneling connections.
no aes decrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES decrypt key.
no aes encrypt key
Removes the connect tunnel AES encrypt key.
no port
Removes the remote port used to establish tunnel connections.
no ssh username
Removes the SSH user name.
no tcp keep alive
Disables the connect mode TCP keep alive timeout.
no vip name
Removes the VIP name.
port <number>
Sets the remote port to use for connect mode tunneling.
<number> = number of the port to use.
protocol ssh
Uses SSH protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol ssl
Uses SSL protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp
Uses TCP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
protocol tcp aes
Uses TCP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
ling.
protocol udp
Uses UDP protocol for connect mode tunneling.
Uses UDP protocol with AES encryption for connect mode
tunneling.
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
Sets the connect tunnel AES decrypt key with up to 16
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by two adjacent hex digits.
Bytes may run together or be separated by optional punctuation:
123ABC "12 3A BC" 12,3A,BC 12.3a.bc 12:3a:bc
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
bytes.
Each byte is represented by a single character.
Note that quotes must enclose the value if it contains
no address Removes the remote host address used to establish
protocol telnet Uses Telnet protocol (with IAC) for connect mode tunne-
protocol udp aes
XPort Pro Command Reference 96
Page 97

show
Shows the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
show connection statistics
ssh username <text>
Sets the SSH user name for use when establishing tunne-
ling connections
<text> = SSH user name.
tcp keep alive <milliseconds>
Enables TCP keep alive for connect mode tunneling and
<milliseconds> = timer value, in milliseconds.
validate certificate disable
Skips verification of the server certificate when connecting.
validate certificate enable
Requires verification of the server certificate when connecting.
vip disable
Makes connections using the specified Address.
vip enable
Makes connections using the VIP name.
vip name <text>
Sets the VIP name.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
host 9 (config-host:9) level commands
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default protocol
Restores the default value of the protocol (Telnet).
default remote port
Sets the remote port (used to connect to the host) to the
which depends on the selected protocol.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
host <number>
Change to config host level
name <text>
Sets the name of the host.
<text> = name of the host.
no name
Clears the name of the host.
no remote address
Clears the remote address of the host.
no ssh username
Clears the SSH username associated with the host.
protocol ssh
Sets the protocol to SSH.
protocol telnet
Sets the protocol to Telnet.
remote address <text>
Sets the IP address of the remote host to connect to when
<text> = IP address.
remote port <number>
Sets the remote port used to connect to the host.
<number> = port to be used.
show
Displays the current configuration.
CLI session.
ssh username <text>
Sets the username for logging into the host via SSH.
<text> = username.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
http (config-http) level commands
auth <uri> <realm>
Creates a new HTTP server authentication directive.
<realm> = domain of the server.
auth type <uri> basic
Sets an HTTP server authentication directive to the Basic
Access
with other devices.
sets the timer.
5: Commands and Levels
default value,
this host is
selected on the login connect menu.
show history Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
XPort Pro Command Reference 97
<uri> = URI of the server.
Page 98

Authentication scheme.
<uri> = URI of the server.
auth type <uri> digest
Sets an HTTP server authentication directive to the Digest
auth type <uri> none
Sets the authentication type for an HTTP server authenti-
auth type <uri> ssl
Sets the authentication type for an HTTP server authenti-
<uri> = URI of the server.
auth type <uri> ssl-basic
Sets the authentication type for an HTTP server authenti-
<uri> = URI of the server.
auth type <uri> ssl-digest
Sets the authentication type for an HTTP server authenti-
<uri> = URI of the server.
auth user <uri> <user> <password>
Creates or modifies a user for an HTTP server authentica-
<password> = password associated with the username.
authentication timeout <minutes>
For any Digest AuthType, sets the timeout for authentica-
<minutes> = authentication timeout value.
clear counters
Sets the HTTP counters to zero.
clear log
Clears the HTTP server log.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default authentication timeout
Resets the authentication timeout to its default value.
default log format
Restores the HTTP Server log format string to its default
value.
default max bytes
Resets the maximum bytes to its default value.
default max log entries
Restores the default maximum number of HTTP Server
log entries.
default max timeout
Resets the timeout to its default value.
default port
Resets the HTTP Server port to its default value.
default secure port
Resets the HTTP Server SSL port to its default value.
default secure protocols
Restores the default secure protocol selections.
delete auth <uri>
Deletes an existing HTTP Server authentication directive.
<uri> = URI of the server.
delete auth user <uri> <user>
<user> = username.
exit
Returns to the config level.
log format <text>
Sets the log format string for the HTTP server, using the
%b bytes sent excluding headers
Access
Authentication scheme.
<uri> = URI of the server.
cation directive to
none.
<uri> = URI of the server.
cation directive to SSL.
cation directive
to SSL-Basic.
cation directive
to SSL-Digest.
tion directive.
<uri> = URI of the server.
<user> = username.
5: Commands and Levels
tion.
Deletes an existing user for an HTTP Server authentication directive.
<uri> = URI of the server.
XPort Pro Command Reference 98
following
directives:
%a remote ip address (could be a proxy)
Page 99

5: Commands and Levels
%B bytes sent excluding headers (0 = '-')
%s return status
logging state disable
Disables HTTP server logging.
logging state enable
Enables HTTP server logging.
max bytes <number>
Sets the maximum number of bytes the HTTP server ac-
a request.
max log entries <number>
Sets the maximum number of HTTP server log entries.
<number> = maximum number of HTTP server log entries.
no clear counters
Restores the HTTP counters to the aggregate values.
no port
Disables the HTTP Server port.
no secure port
Disables the HTTP Server SSL port.
port <number>
Sets the port number the HTTP server will use.
<number> = port number.
secure port
<number> = port number.
secure protocols ssl3 disable
Disables the protocol.
secure protocols ssl3 enable
Enables the protocol.
secure protocols tls1.0 disable
Disables the protocol.
secure protocols tls1.0 enable
Enables the protocol.
secure protocols tls1.1 disable
Disables the protocol.
secure protocols tls1.1 enable
Enables the protocol.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show auth
Displays the HTTP server authentication settings.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show log
Displays the HTTP server log.
show statistics
Displays the HTTP statistics.
state disable
Disables the HTTP server.
state enable
Enables the HTTP server.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
icmp (config-icmp) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously shows ICMP statistics
clear counters
Zeros counters
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
exit
Exits to the configuration level.
no clear counters
Unzeros IP counters
show
Displays the current configuration.
%h remote host (same as %a)
%{h}i header contents from request (h = header string)
%m request method
%p ephemeral local port value used for request
%q query string (prepend with '?' or empty '-')
%t timestamp HH:MM:SS (same as Apache
'%(%H:%M:%S)t')
%u remote user (could be bogus for 401 status)
%U URL path info
%r first line of request (same as '%m %U%q <version>')
cepts when receiving
max timeout <seconds>
<number>
Sets the maximum time the HTTP server waits when receiving a request.
<seconds> = maximum timeout value.
Sets the port number the HTTP server will use over SSL.
XPort Pro Command Reference 99
Page 100

show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show statistics
Shows ICMP statistics
state disable
Prevents ICMP packets from being sent or received.
state enable
Allows ICMP packets to be sent and received.
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
if 1 (config-if:eth0) level commands
bootp disable
Disables BOOTP.
bootp enable
Enables BOOTP.
clrscrn
Clears the screen.
default gateway <ip address>
Sets the configurable gateway IP address to the default
value.
default mtu
Restores the default Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
size.
Within [] use binary decimal up to 255 or hex up to 0xFF.
dhcp client id set <text>
Sets the client id in text format.
dhcp disable
Disables DHCP.
dhcp enable
Enables DHCP.
dhcp renew
Force DHCP to renew
<text> = name of the domain.
exit
Exits to the config level.
hostname <text>
Sets the host name.
<text> = name of the host.
ip address <ip address/cidr>
Sets the IP address and network mask.
"192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0" (explicit mask)
link
Enter link configuration level
mtu
Sets the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size.
no default gateway
Clears the default gateway.
no dhcp client id
Clears the DHCP client ID.
no domain
Clears the domain name.
no hostname
Clears the host name.
no ip address
Clears the IP address.
no primary dns
Clears the name of the primary DNS server.
no secondary dns
Clears the name of the secondary DNS server.
primary dns <ip address>
Sets the IP address of the primary DNS server.
secondary dns <ip address>
Sets the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
show
Displays the current configuration.
show history
Displays the last 20 commands entered during the current
CLI session.
show status
Show interface status
write
Stores the current configuration in permanent memory.
ip (config-ip) level commands
auto show statistics
Continuously shows IP statistics
clear counters
Zeros counters
5: Commands and Levels
dhcp client id binary <binary>
domain <text>
<bytes>
Sets the client id allowing binary characters.
Sets the domain name.
Formats accepted:
192.168.1.1 (default mask)
192.168.1.1/24 (CIDR)
XPort Pro Command Reference 100
 Loading...
Loading...