Page 1

System Board
User’s Manual
935-X38T22-000G
03220807E
Page 2

Copyright
This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No part of it
may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any transformation/adaptation without the prior written permission from the copyright holders.
This publication is provided for informational purposes only. The manufacturer
makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of
this manual and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. The user will assume the
entire risk of the use or the results of the use of this document. Further, the
manufacturer reserves the right to revise this publication and make changes to its
contents at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such
revisions or changes.
© 2008. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
Windows® 2000 and Windows® XP are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation. Award is a registered trademark of Award Software, Inc. Other
trademarks and registered trademarks of products appearing in this manual are
the properties of their respective holders.
FCC and DOC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with the emission
limits.
Page 3

Table of Contents
About this Manual................................................................................
Warranty.................................................................................................
Static Electricity Precaution................................................................
Safety Measures.....................................................................................
About the Package...............................................................................
Before Using the System Board.........................................................
System Board Layout............................................................................
English.....................................................................................................
Français...................................................................................................
Deutsch...................................................................................................
Español....................................................................................................
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
9
36
66
96
Page 4

1
Introduction
About this Manual
An electronic file of this manual is included in the CD. To view the
user’s manual in the CD, insert the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The
autorun screen (Main Board Utility CD) will appear. Click the
“TOOLS” icon then click “Manual” on the main menu.
For additional information on the system board, please download
the complete version of the manual from DFI’s website. Visit
www.dfi.com.
Warranty
1. Warranty does not cover damages or failures that arised from
misuse of the product, inability to use the product, unauthorized
replacement or alteration of components and product specifications.
2. The warranty is void if the product has been subjected to physical abuse, improper installation, modification, accidents or unauthorized repair of the product.
3. Unless otherwise instructed in this user’s manual, the user may
not, under any circumstances, attempt to perform service, adjustments or repairs on the product, whether in or out of warranty.
It must be returned to the purchase point, factory or authorized
service agency for all such work.
4. We will not be liable for any indirect, special, incidental or
consequencial damages to the product that has been modified
or altered.
4
Page 5
Static Electricity Precautions
It is quite easy to inadvertently damage your PC, system board,
components or devices even before installing them in your system
unit. Static electrical discharge can damage computer components
without causing any signs of physical damage. You must take extra
care in handling them to ensure against electrostatic build-up.
1. To prevent electrostatic build-up, leave the system board in its
anti-static bag until you are ready to install it.
2. Wear an antistatic wrist strap.
3. Do all preparation work on a static-free surface.
4. Hold the device only by its edges. Be careful not to touch any of
the components, contacts or connections.
5. Avoid touching the pins or contacts on all modules and connectors. Hold modules or connectors by their ends.
Introduction
1
Important:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your processor, disk
drive and other components. Perform the upgrade instruction
procedures described at an ESD workstation only. If such a
station is not available, you can provide some ESD protection
by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal
part of the system chassis. If a wrist strap is unavailable, establish and maintain contact with the system chassis throughout
any procedures requiring ESD protection.
Safety Measures
To avoid damage to the system:
• Use the correct AC input voltage range
To reduce the risk of electric shock:
• Unplug the power cord before removing the system chassis
cover for installation or servicing. After installation or servicing,
cover the system chassis before plugging the power cord.
..
.
..
Battery:
• Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced.
• Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommend
the manufacturer.
• Dispose of used batteries according to local ordinance.
by
5
Page 6

1
Introduction
About the Package
The system board package contains the following items. If any of
these items are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer or
sales representative for assistance.
; One system board
; One Bernstein audio module with cable
; One Transpiper kit (LP UT series only)
- One Transpiper
- One 90o metal pipe
- One thermal paste
; One copper plate with mounting screws (LP UT series only)
; One Northbridge heat sink cooling kit (LP LT series only)
; One IDE round cable
; One floppy round cable
; Four Serial ATA data cables
; Four Serial ATA power cables
; One I/O shield
; One RAID driver diskette
; One “Mainboard Utility” CD
; One user’s manual
The system board and accessories in the package may not come
similar to the information listed above. This may differ in accordance
to the sales region or models in which it was sold. For more information about the standard package in your region, please contact
your dealer or sales representative.
Before Using the System Board
Before using the system board, prepare basic system components.
If you are installing the system board in a new system, you will need
at least the following internal components.
• A CPU
• Memory module
• Storage devices such as hard disk drive, CD-ROM, etc.
You will also need external system peripherals you intend to use
which will normally include at least a keyboard, a mouse and a video
display monitor.
6
Page 7
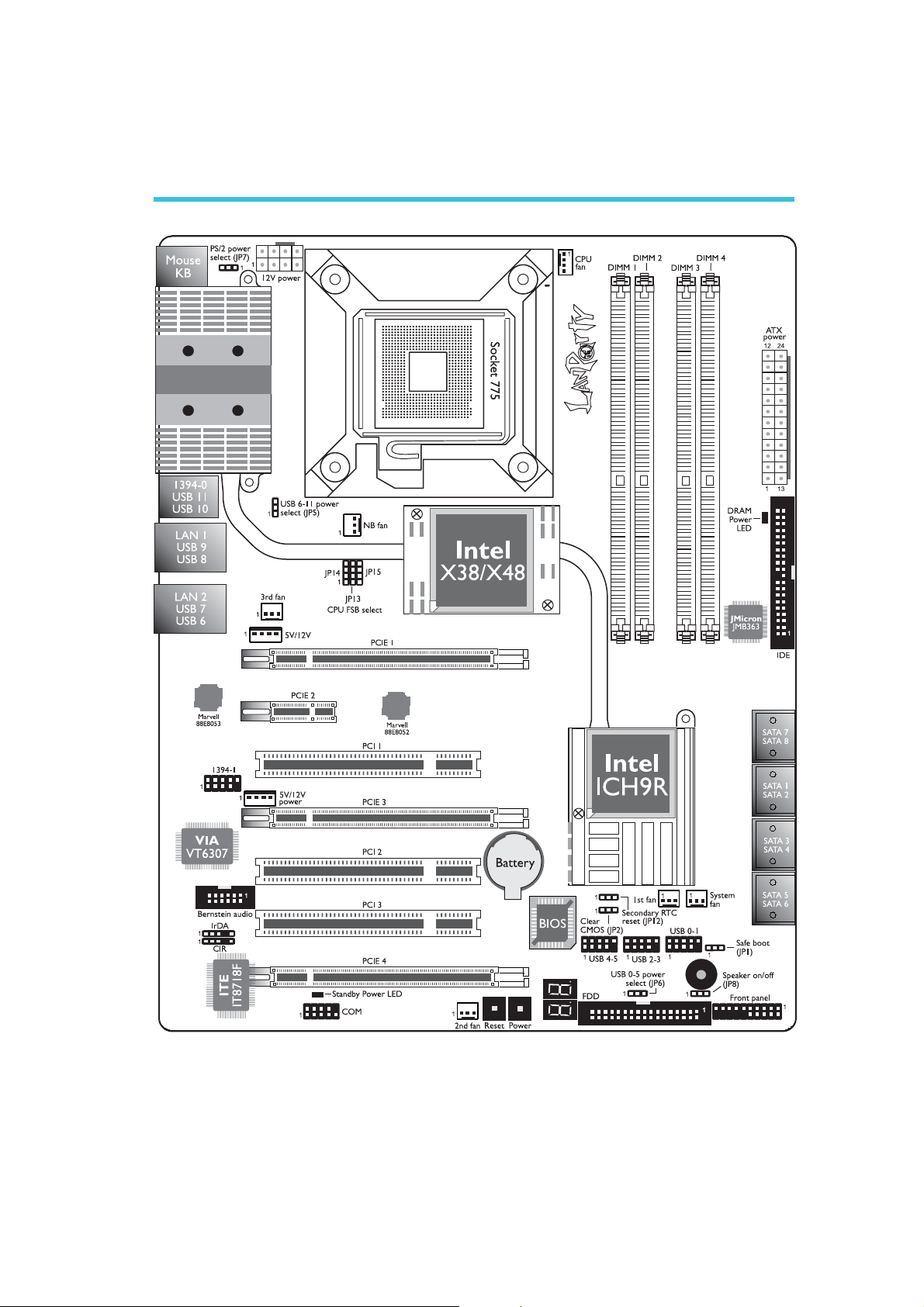
System Board Layout
Introduction
1
LP UT Series
7
Page 8
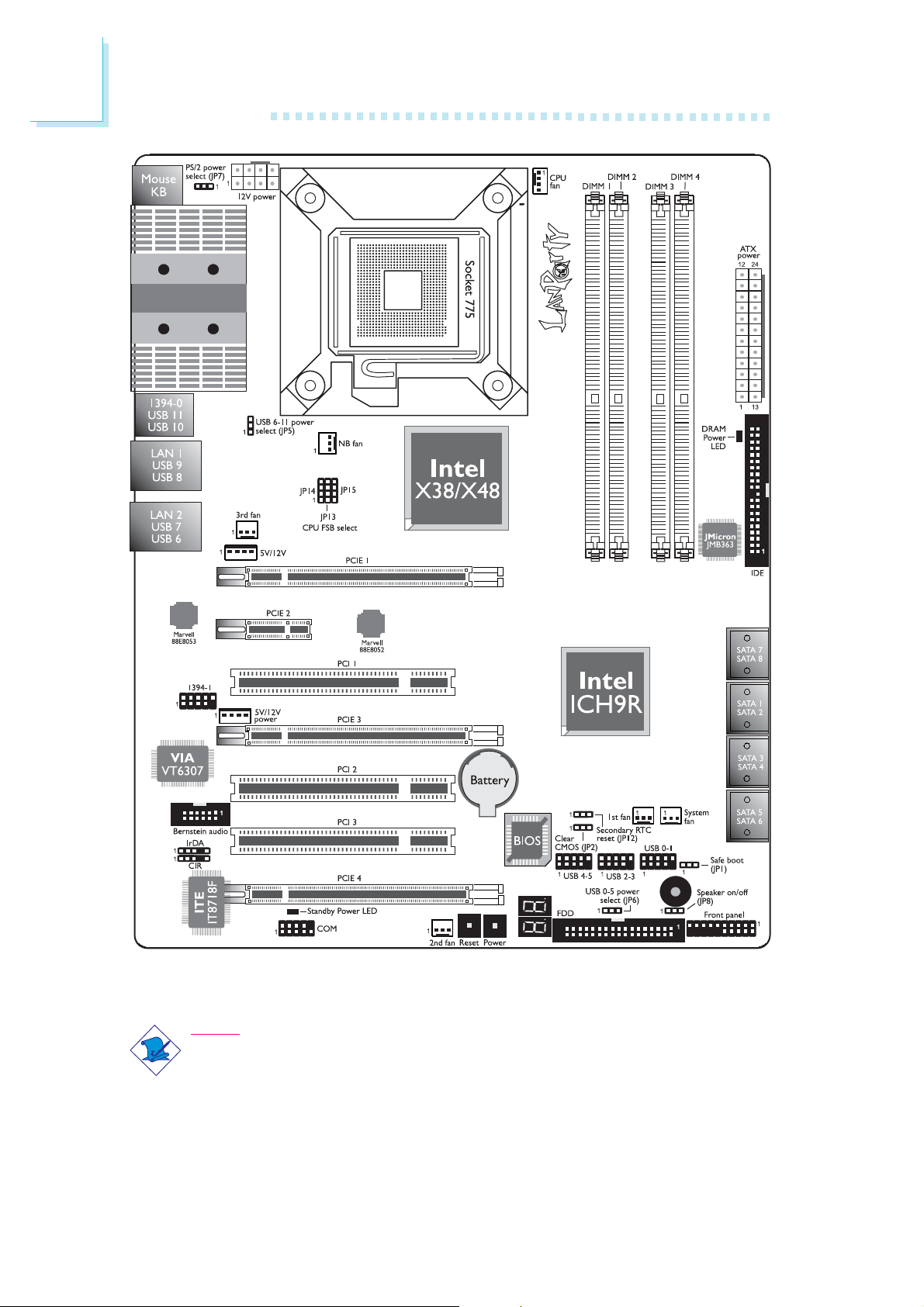
1
Introduction
LP LT Series
Note:
The illustrations on the following pages are based on the LP UT
series system board.
8
Page 9

Chapter 1 - Specifications
English
E
Processor
Chipset
System Memory
• LGA 775 socket for:
- Intel® CoreTM2 Quad and Intel® CoreTM2 Duo
• Supports Intel Enhanced Memory 64 Technology (EMT64T)
• Supports Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST)
• Supports Intel Hyper-Threading Technology
• Supports 1600/1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X48 series)
Supports 1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X38 series)
®
• Intel
• LP UT/LT X38/X48-T2R
• LP UT/LT X38-T3R
• Supports dual channel (128-bit wide) memory interface
• Supports up to 8GB system memory
• Supports unbuffered x8 and x16 DIMMs
chipset
- Northbridge:
Intel® X48 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X48 series)
Intel® X38 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X38 series)
Intel® Fast Memory Access technology
- Southbridge: Intel® ICH9R
- Four 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets
- Supports DDR2 667/800 MHz
- Delivers up to 12.8Gb/s bandwidth
- Four 240-pin DDR3 DIMM sockets
- Supports DDR3 800/1066/1333 MHz
- Delivers up to 21Gb/s bandwidth at 1333MHz
English
Expansion Slots
BIOS
Audio
• 2 PCI Express (Gen 2) x16 slots (PCIE 1 and PCIE 3)
- 2-way CrossFire at x16/x16 bandwidth
- 2-way CrossFire + Physics at x16/x16/x4 bandwidth
• 1 PCI Express x1 slot (PCIE 2)
• 1 PCI Express x4 slot (PCIE 4)
• 3 PCI slots
• Award BIOS
• 8Mbit flash memory
• CMOS Reloaded
• Bernstein audio module
- Realtek ALC885 8-channel High Definition Audio CODEC
- Center/subwoofer, rear R/L and side R/L jacks
- Line-in, line-out (front R/L) and mic-in jacks
- 2 coaxial RCA S/PDIF-in/out jacks
- 1 optical S/PDIF connector
- 1 CD-in connector
- 1 front audio connector
• DAC SNR/ADC SNR of 106dB/101dB
• Full-rate lossless content protection technology
9
Page 10

E
English
English
LAN
Storage
IEEE 1394
Rear Panel I/O
Internal I/O
• Marvell 88E8052 and Marvell 88E8053 PCIE Gigabit LAN
controllers
• Fully compliant to IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T), 802.3u (100BASETX) and 802.3ab (1000BASE-T) standards
• Intel ICH9R chip
- Intel Matrix Storage technology
- Supports up to 6 SATA devices
- SATA speed up to 3Gb/s
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 and RAID 5
• JMicron JMB363 PCI Express to SATA and PATA host controller
- Supports up to 2 UltraDMA 100Mbps IDE devices
- Supports 2 SATA devices
- SATA speed up to 3Gb/s
- RAID 0 and RAID 1
• VIA VT6307
• Supports two 100/200/400 Mb/sec ports
• Mini-DIN-6 PS/2 mouse port and PS/2 keyboard port
• 1 IEEE 1394 port
• 6 USB 2.0/1.1 ports
• 2 RJ45 LAN ports
• 3 connectors for 6 additional external USB 2.0 ports
• 1 connector for an external COM port
• 1 connector for an IEEE 1394 port
• 1 connector for the Bernstein audio module
• 1 front audio connector (on the Bernstein audio module)
• 1 CD-in connector (on the Bernstein audio module)
• 1 S/PDIF connector (on the Bernstein audio module)
• 1 IrDA connector and 1 CIR connector
• 8 Serial ATA connectors
• 1 40-pin IDE connector and 1 floppy connector
• 1 24-pin ATX power connector
• 1 8-pin 12V power connector
• 2 4-pin 5V/12V power connectors (FDD type)
• 1 front panel connector
• 6 fan connectors
• 1 diagnostic LED
• EZ touch switches (power switch and reset switch)
10
Power Management
Hardware Monitor
PCB
• ACPI and OS Directed Power Management
• ACPI STR (Suspend to RAM) function
• Wake-On-PS/2 / Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
• Wake-On-LAN and Wake-On-Ring
• RTC timer to power-on the system
• AC power failure recovery
• Monitors CPU/system/Northbridge temperature and overheat alarm
• Monitors Vcore/Vdimm/Vnb/VCC5/12V/V5sb/Vbat voltages
• Monitors the speed of the cooling fans
• CPU Overheat Protection function monitors CPU temperature
and fan during system boot-up - automatic shutdown upon system overheat
• 6 layers, ATX form factor; 24.5cm (9.64") x 30.5cm (12")
Page 11
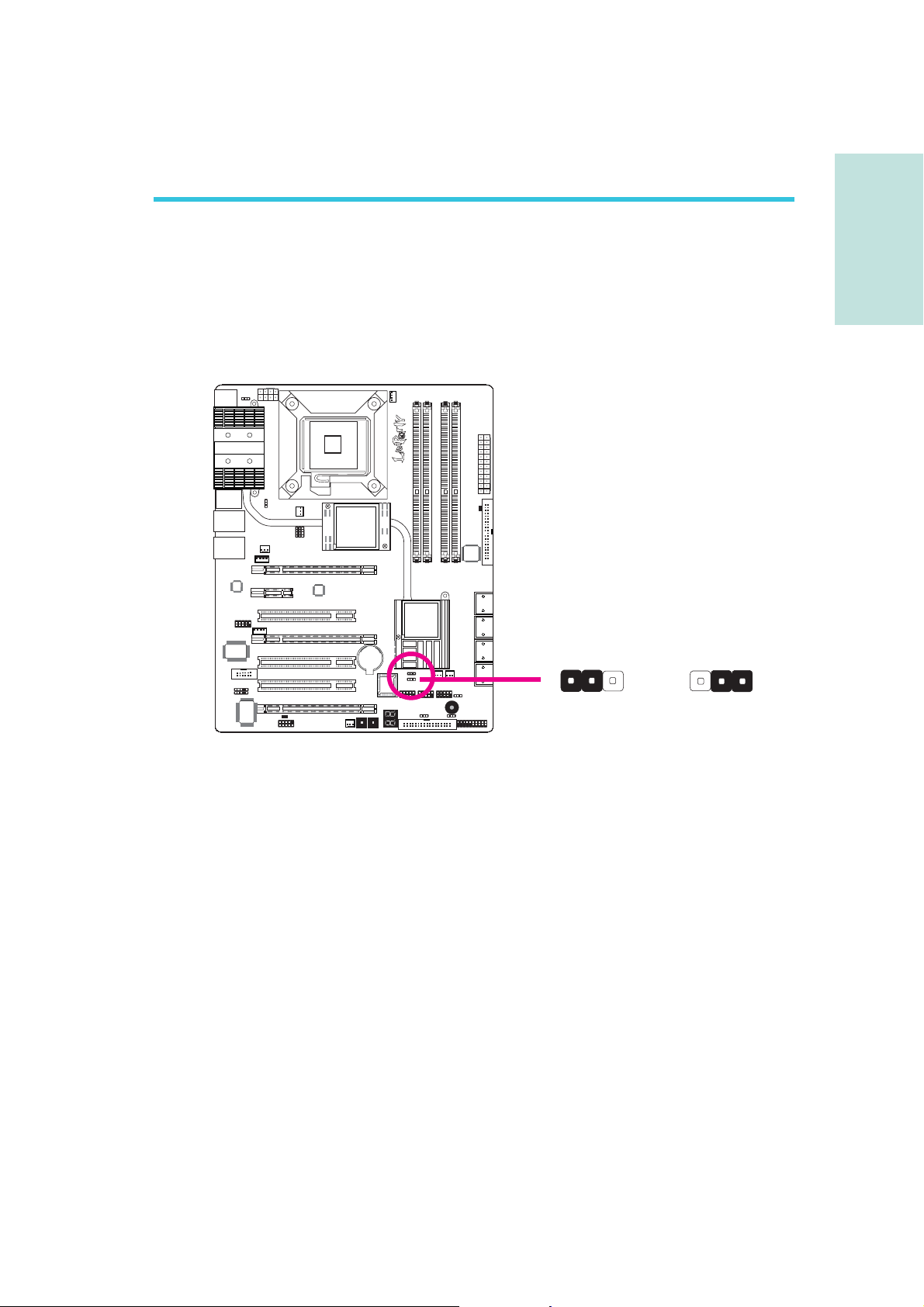
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Jumper Settings
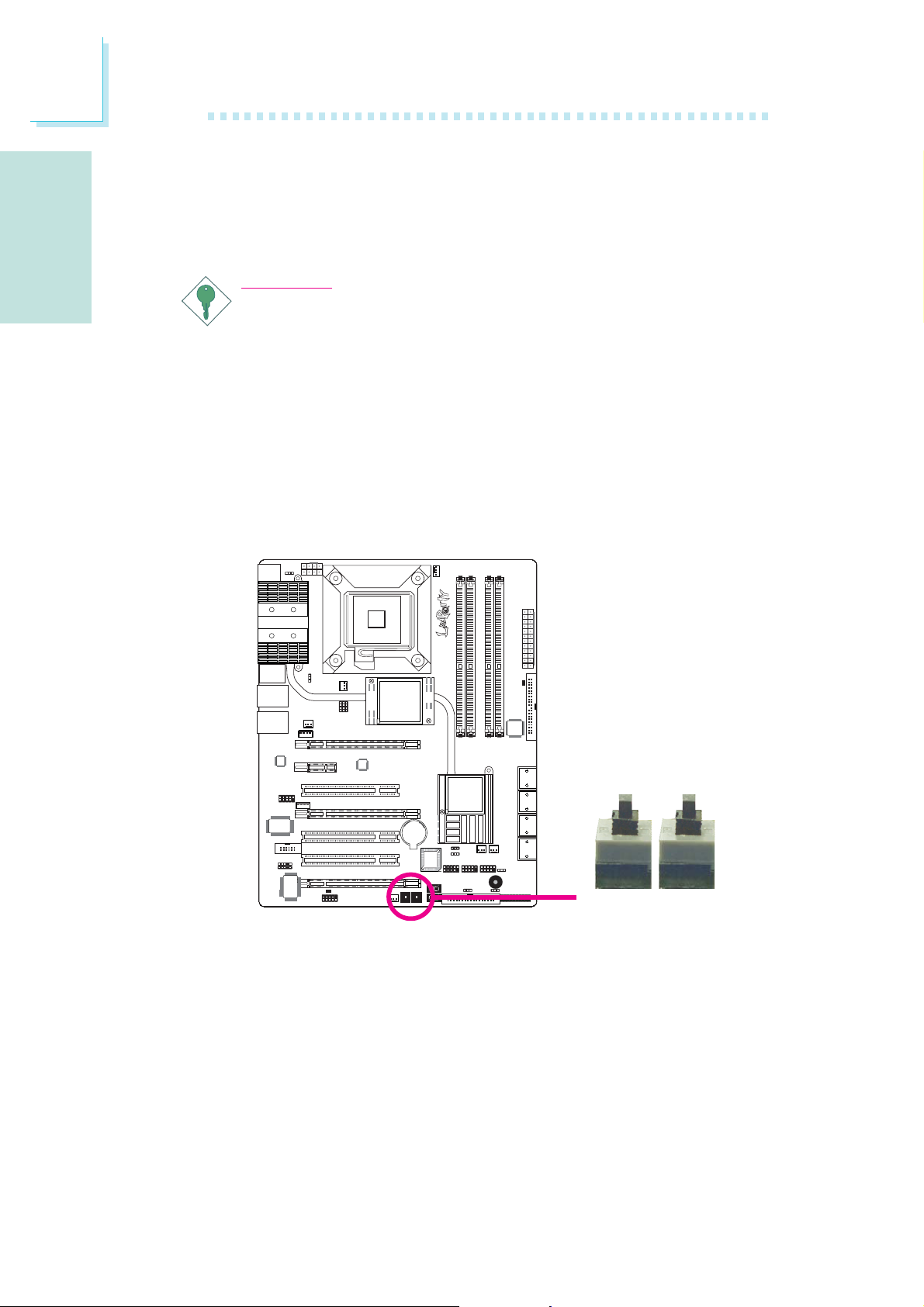
Clear CMOS Data
Clearing CMOS Data using JP2
English
E
English
JP2
312 312
X
1-2 On: Normal
(default)
If you encounter the following,
a) CMOS data becomes corrupted.
b) You forgot the supervisor or user password.
c) The overclocked settings in the BIOS resulted to the system’s in-
stability or caused system boot up problems.
you can reconfigure the system with the default values stored in the
ROM BIOS.
To load the default values stored in the ROM BIOS, please follow
the steps below.
1. Power-off the system then unplug the power cord.
2. Set JP2 pins 2 and 3 to On. Wait for a few seconds and set JP2
back to its default setting, pins 1 and 2 On.
3. Now plug the power cord then power-on the system.
2-3 On:
Clear CMOS Data
11
Page 12
E
English
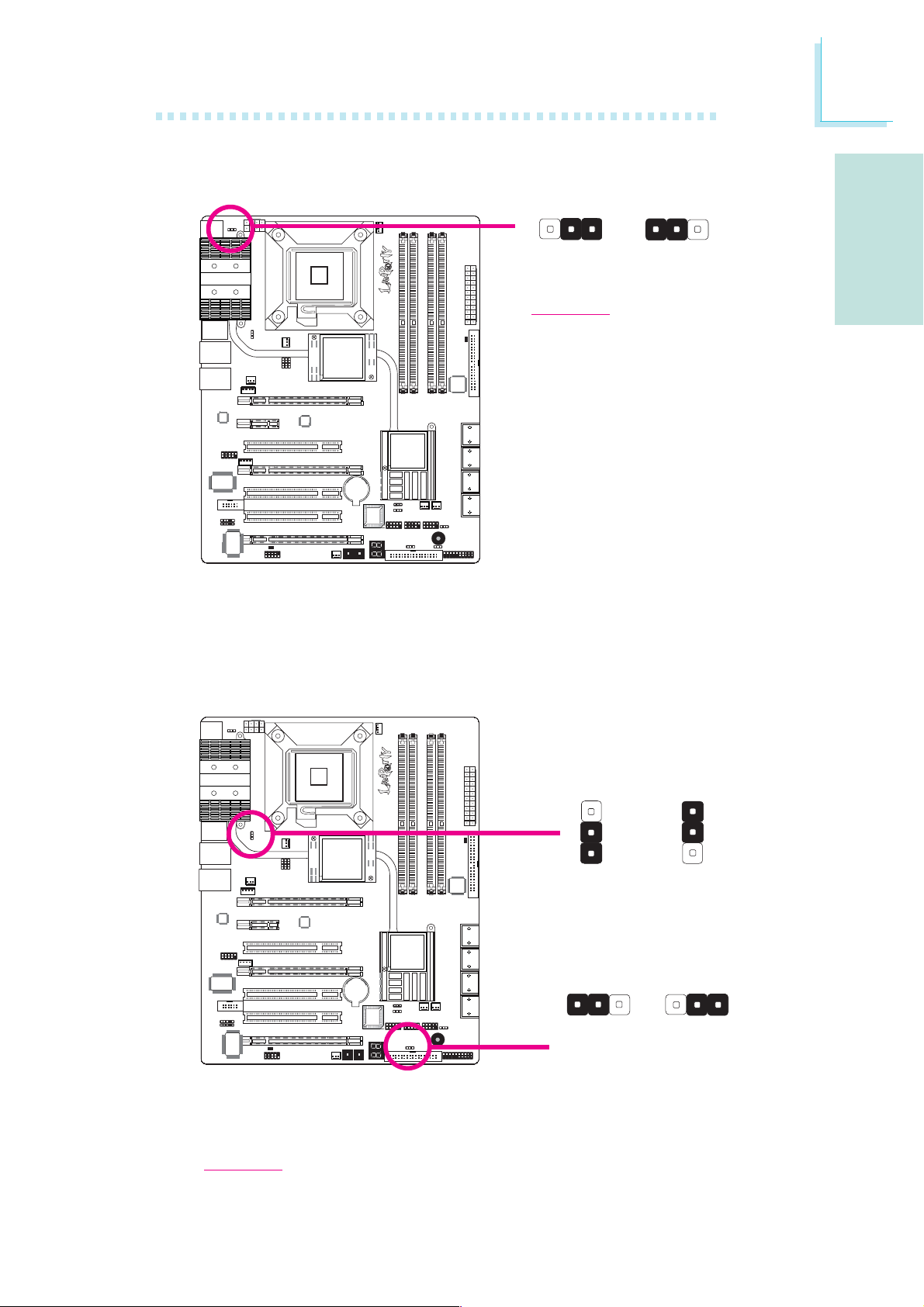
Clearing CMOS Data using the EZ Clear® Function
EZ Clear® bypasses the manual process of using a jumper to clear
the CMOS by simply using the reset and power buttons.
English
Important:
EZ Clear® is supported only if standby power is present in the
system.
To use EZ Clear®:
1. Make sure the standby power is present.
2. Using the EZ touch switches on the system board, first press the
Reset button then the Power button simultaneously for approximately 4 seconds.
12
X
Reset
If the system board is already enclosed in a chassis, apply the
same method using the Reset button and Power button located
at the front panel of the chassis.
3. After 4 seconds, release the power button first then the Reset
button.
4. The CMOS will restore the clock settings back to their default
values.
Power
Page 13
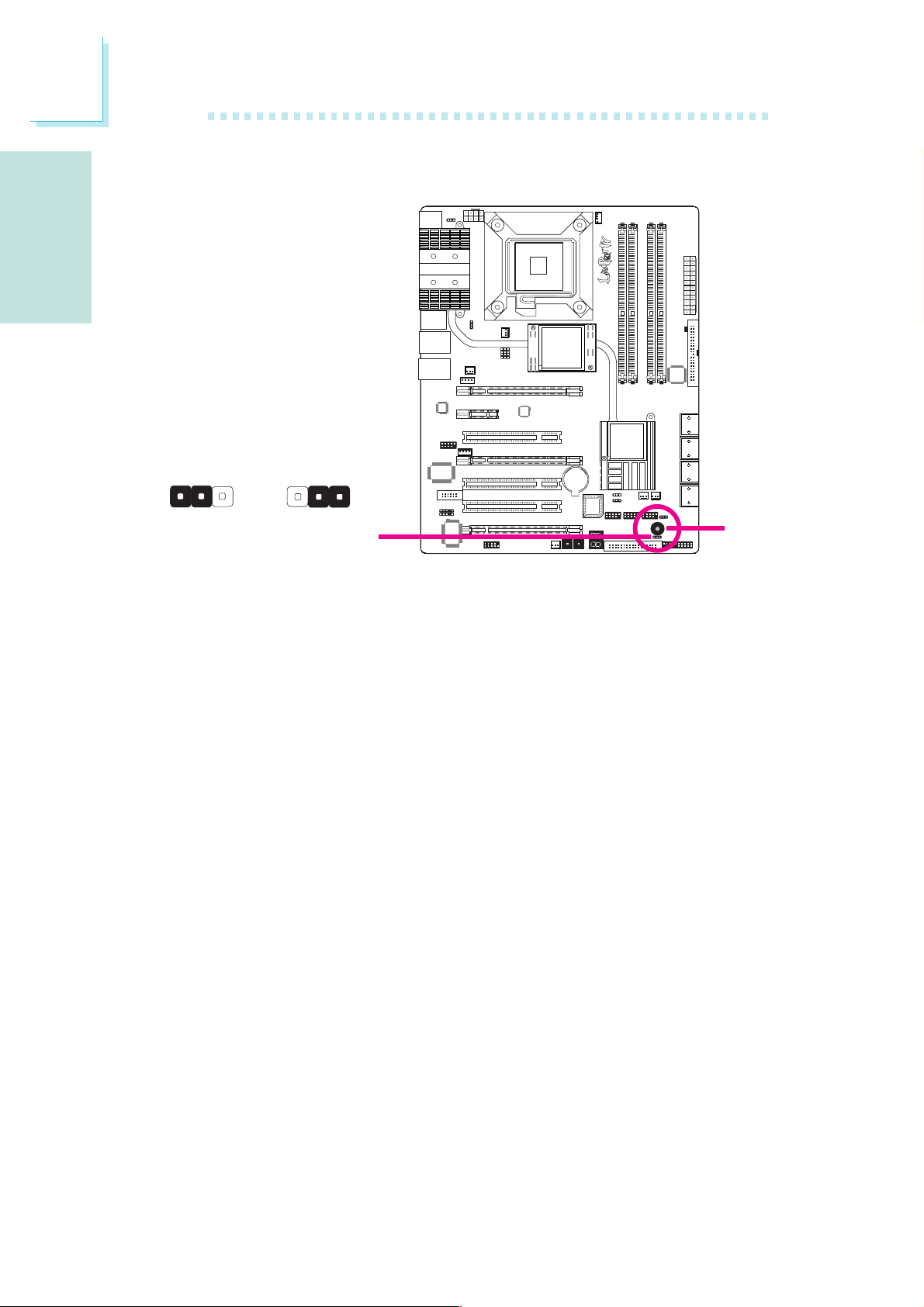
PS/2 Power Select
English
E
JP7
312
31
2
X
1-2 On: 5V
(default)
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your
power supply must support
≥720mA.
Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the PS/2 keyboard or PS/2
mouse to wake up the system.
2-3 On:
5VSB
English
USB Power Select
Selecting 5VSB will allow you to use the USB keyboard or USB
mouse to wake up the system..
Important:
If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse function for 2 USB ports,
the 5VSB power source of your power supply must support ≥1.5A. For 3 or
more USB ports, the 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥2A.
USB 6-11
(JP5)
USB 0-5
(JP6)
X
1-2 On: 5V
(default)
1-2 On: 5V
(default)
X
3
2
1
312
3
2
1
2-3 On:
5VSB
312
2-3 On:
5VSB
13
Page 14
E
English
English
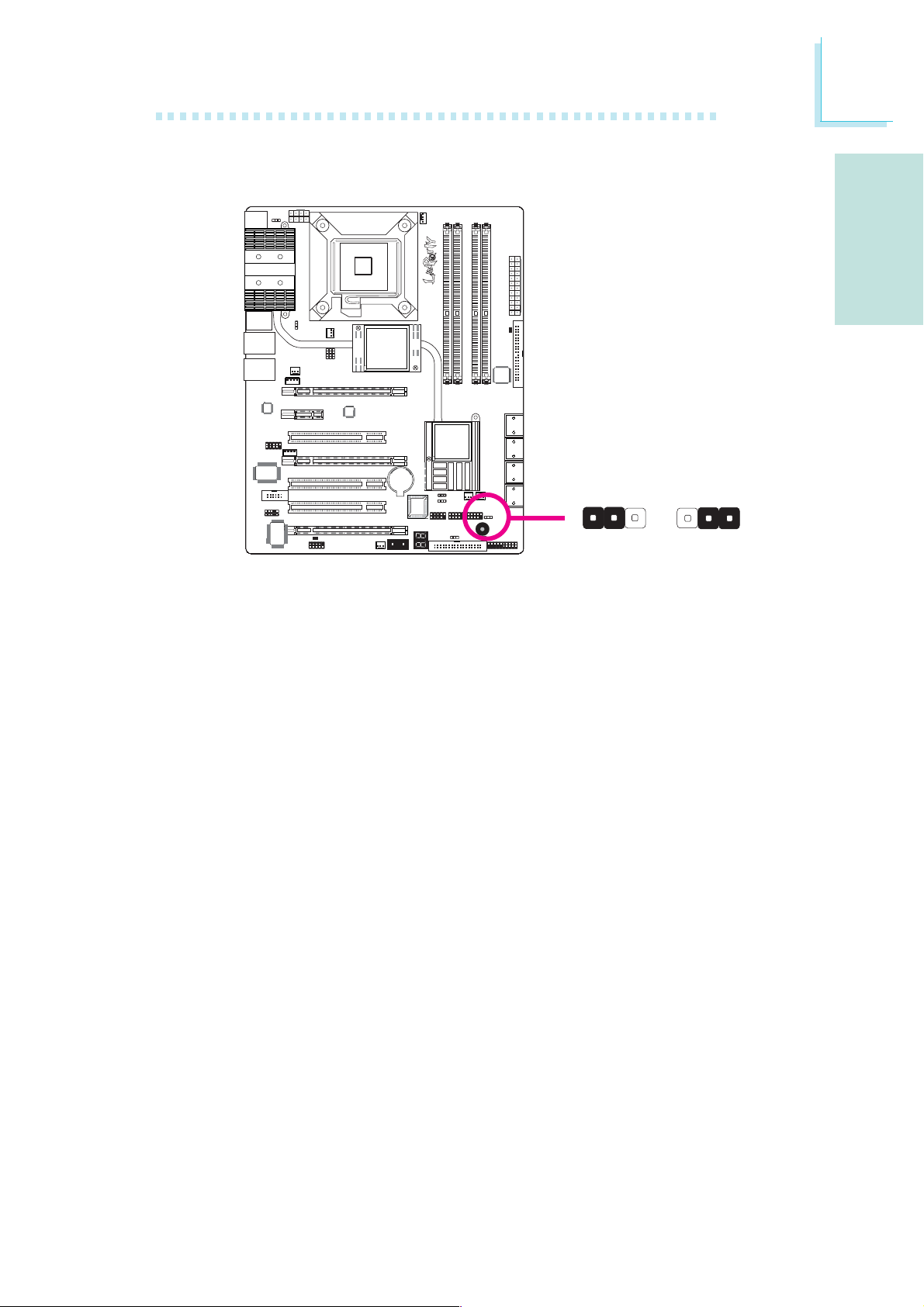
Speaker On/Off Select
312 312
1-2 On:
Speaker Off
The system board is equipped with a buzzer which serves as the
PC’s speaker. By default the buzzer is “on” allowing you to hear the
system’s beep messages and warnings. If you intend to use an external speaker, turn this function off by setting JP8 pins 1 and 2 to On.
2-3 On:
Speaker On
(default)
X
JP8
Buzzer
14
Page 15
Safe Boot
English
E
English
JP1
312 312
X
1-2 On:
Default
This jumper is used to safely reboot the system whenever the system hangs and you are unable to restart the system.
1. Power-off the system then unplug the power cord.
2. Set pins 2 and 3 to On. Wait for a few seconds then set the
jumper back to its default setting, pins 1 and 2 On.
3. Plug the power cord then power-on the system. The system will
reboot normally without losing all data stored in the CMOS.
2-3 On:
Safe boot
15
Page 16
E
English
English
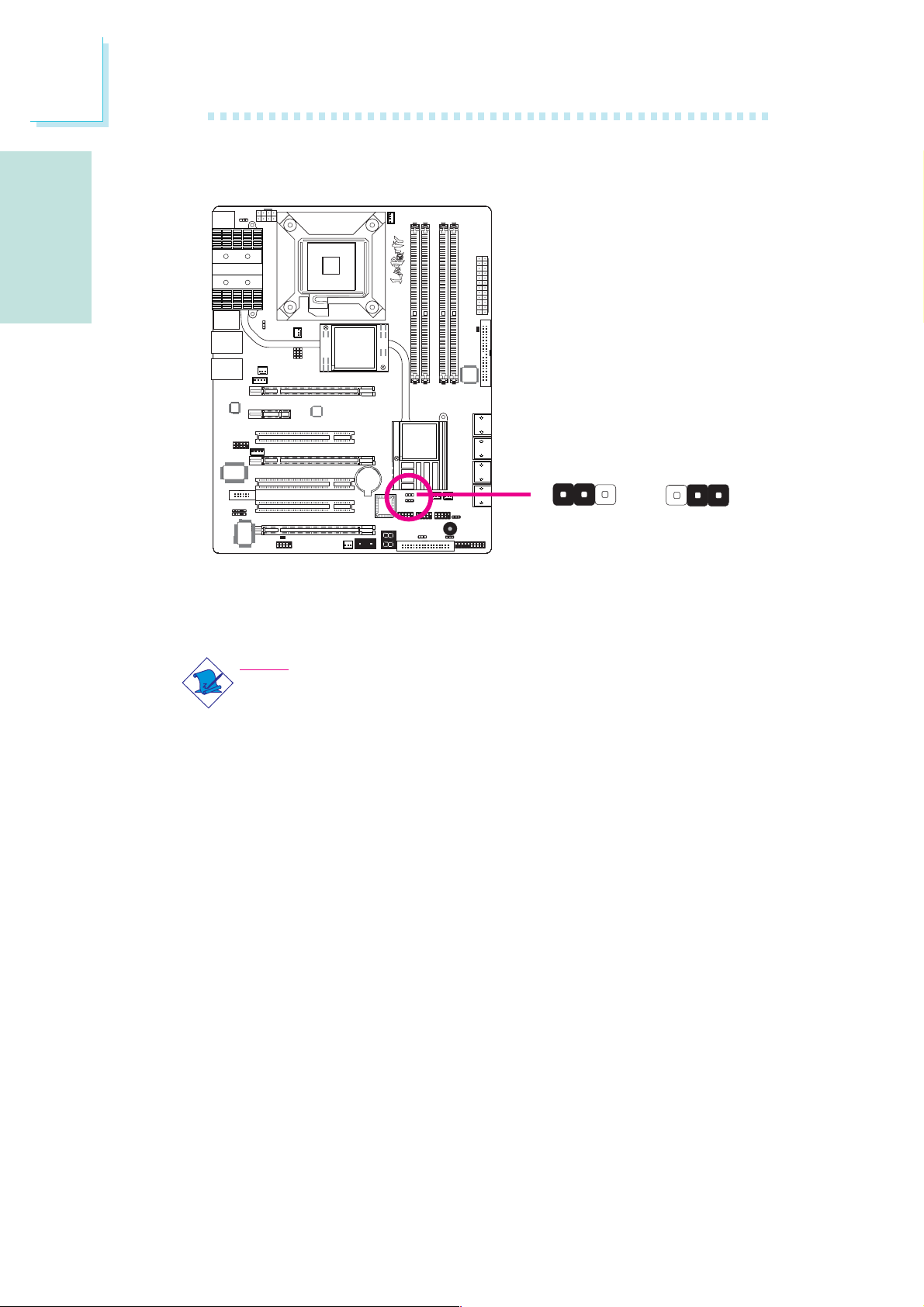
Secondary RTC Reset
JP12
312
312
X
1-2 On: Normal
(default)
When the RTC battery is removed, this jumper resets the
manageability register bits in the RTC.
Note:
1. The SRTCRST# input must always be high when all other
RTC power planes are on.
2. In the case where the RTC battery is dead or missing on
the platform, the SRTCRST# pin must rise before the
RSMRST# pin.
2-3 On:
RTC reset
16
Page 17
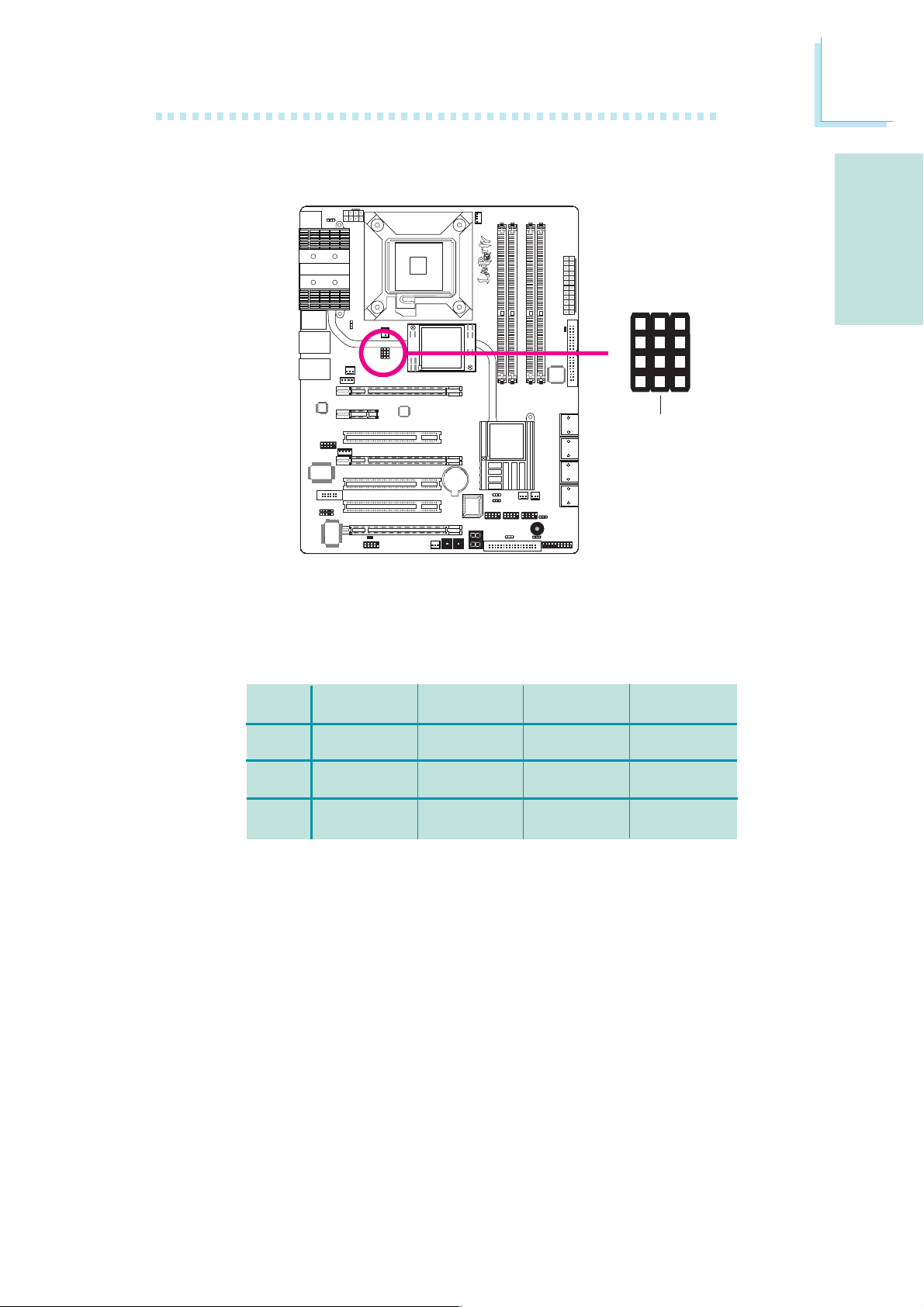
CPU FSB Select
X
JP14
English
E
English
4
3
2
1
JP15
JP13
By default, JP13 to JP15 are set to pins 1 and 2 On. This setting will
allow the system to automatically run according to the CPU’s FSB. If
you want to change the setting, please refer to the table below.
JP14
JP13
JP15
By CPU
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
FSB 800
3-4 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1066
2-3 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1333
2-3 On
2-3 On
3-4 On
17
Page 18
E
English
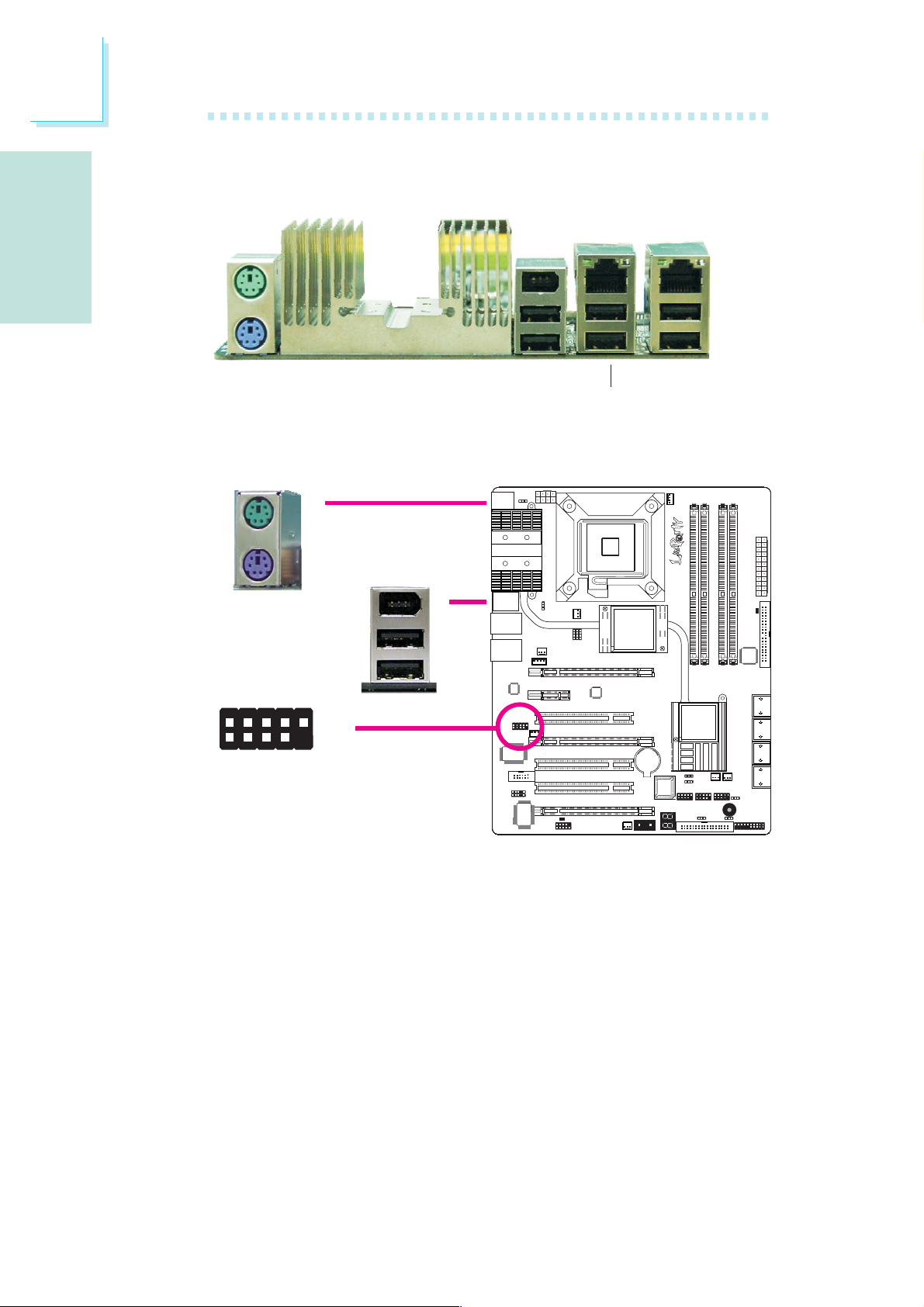
Rear Panel I/O Ports
English
PS/2
Mouse
PS/2
K/B
PS/2 Ports and IEEE 1394 Ports
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 KB
W
1394-0
W
1394-0
USB 10-11
LAN 2LAN 1
USB 6-7
USB 8-9
Ground
TPB-
+12V (fused)
Ground
TPA-
1394-1
2
1
TPA+
Ground
10
9
Key
TPB+
+12V (fused)
W
PS/2 Mouse and PS/2 Keyboard Ports
These ports are used to connect a PS/2 mouse and a PS/2 keyboard.
IEEE 1394 Ports
The IEEE 1394-0 port is used to connect audio/video devices or
storage peripherals. The 10-pin connector allows you to connect an
additional 1394 port. Your 1394 port may come mounted on a
card-edge bracket. Install the card-edge bracket to an available slot
at the rear of the system chassis then connect the 1394 port cable
to this connector.
18
Page 19
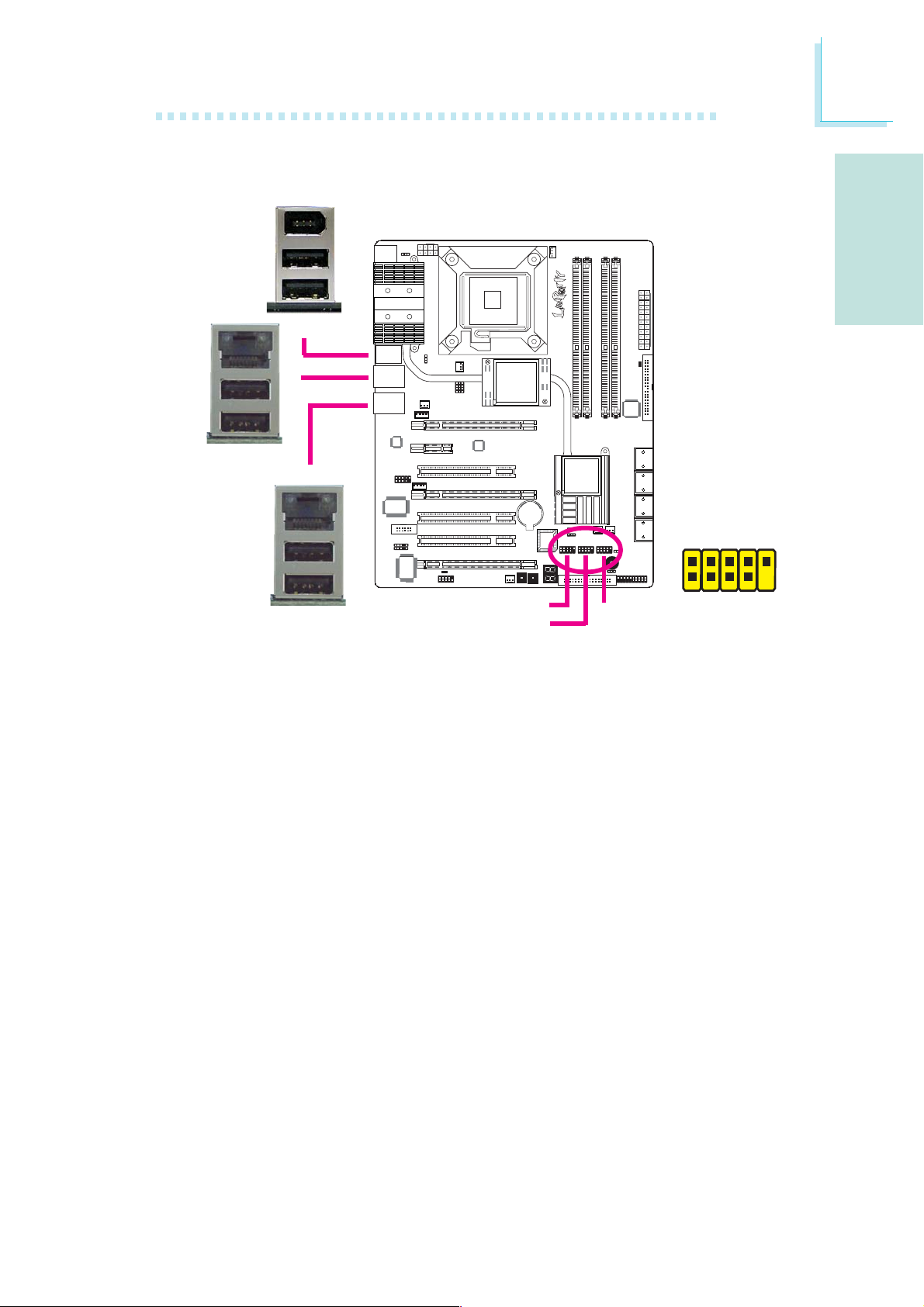
USB Ports and LAN Ports
USB 11
USB 10
W
LAN 1
English
E
English
USB 9
USB 8
W
W
LAN 2
-Data
+Data
-Data
+Data
GND
N. C.
10
Key
GND
VCC
USB 7
USB 6
USB 4-5
USB 2-3
USB 0-1
2
1
VCC
USB Ports
The USB ports are used to connect USB 2.0/1.1 devices. The 10-pin
connectors allow you to connect 6 additional USB 2.0/1.1 ports.
Your USB ports may come mounted on a card-edge bracket. Install
the card-edge bracket to an available slot at the rear of the system
chassis then connect the USB port cables to these connectors.
9
LAN Ports
The LAN ports allow the system board to connect to a local area
network by means of a network hub.
19
Page 20
E
English
English
Bernstein Audio Module
Line-in
Line-out
1
Left audio channel
Ground
Ground
Right audio channel
Mic-in
Center/
Subwoofer
Rear R/L
Side R/L
S/PDIF-out
S/PDIF-in
Line-in Jack (Light Blue)
This jack is used to connect any audio devices such as Hi-fi set, CD
player, tape player, AM/FM radio tuner, synthesizer, etc.
Side view
Bernstein audio
module connector
Mic Jet Detect
SPDIF in
GND
SPDIF out
Key
+5V
4
CD-in
10 9
N. C.
Vcc
GND
Front audio
5
Optical S/PDIF
1
Line out_LeftLine out Jet Detect
Sense
Line out_Right
Mic_Right
Mic_Left
12
20
Line-out Jack (Lime)
This jack is used to connect to the front right and front left speakers
of the audio system.
Mic-in Jack (Pink)
This jack is used to connect an external microphone.
Center/Subwoofer Jack (Orange)
This jack is used to connect to the center and subwoofer speakers
of the audio system.
Rear Right/Left Jack (Black)
This jack is used to connect to the rear right and rear left speakers
of the audio system.
Side Right/Left Jack (Gray)
This jack is used to connect to the side left and side right speakers
of the audio system.
Page 21
English
Coaxial RCA S/PDIF-in and SPDIF-out Jacks
These jacks are used to connect external audio output devices using
coaxial S/PDIF cables.
CD-in Connector
The CD-in connector is used to receive audio from a CD-ROM
drive, TV tuner or MPEG card.
Front Audio Connector
The front audio connector is used to connect to the line-out and
mic-in jacks that are at the front panel of your system.
Optical S/PDIF Connector
The optical S/PDIF connector is used to connect an external audio
output device using an optical S/PDIF cable.
E
English
Important:
DO NOT use optical S/PDIF and coaxial RCA S/PDIF at the
same time.
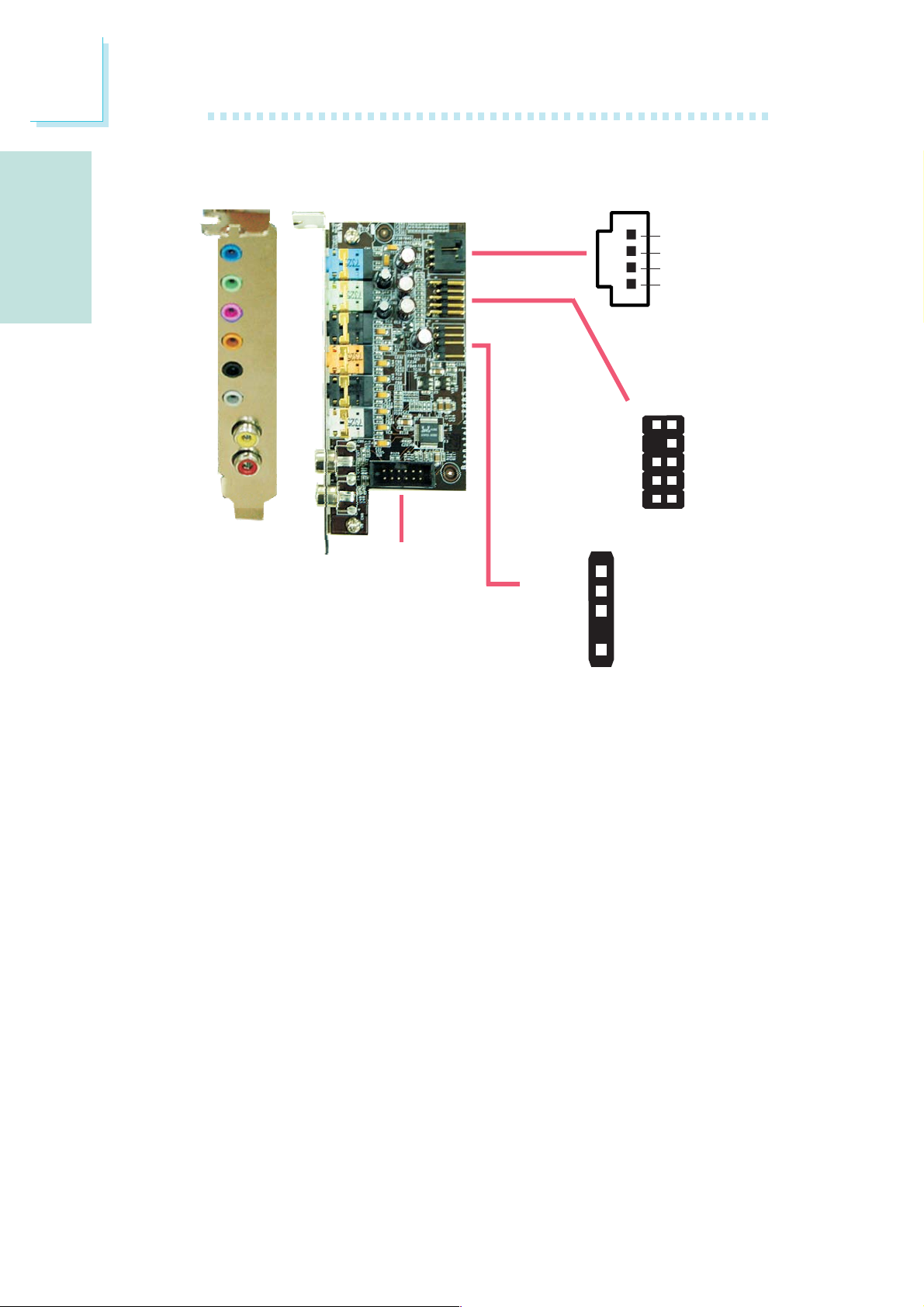
Installing the Bernstein Audio Module
1. The Bernstein audio
module connects to the
system board by means
of the provided audio
cable.
2. Insert one end of the
cable to the Bernstein
audio connector on the
system board and the
other end to the corresponding connector on
the audio module.
X
11
12
1
Bernstein audio
module connector
2
21
Page 22

E
English
English
3. The length of the audio cable
provides the option and flexibility of installing the module on
any available expansion bracket
slot at the rear of the system
chassis. Remove the screw of
the bracket where you want the
audio module installed then remove the bracket. Place the
Bernstein audio module on the
expansion bracket slot then secure the module by replacing the
bracket screw you removed earlier.
I/O Connectors
Audio cable
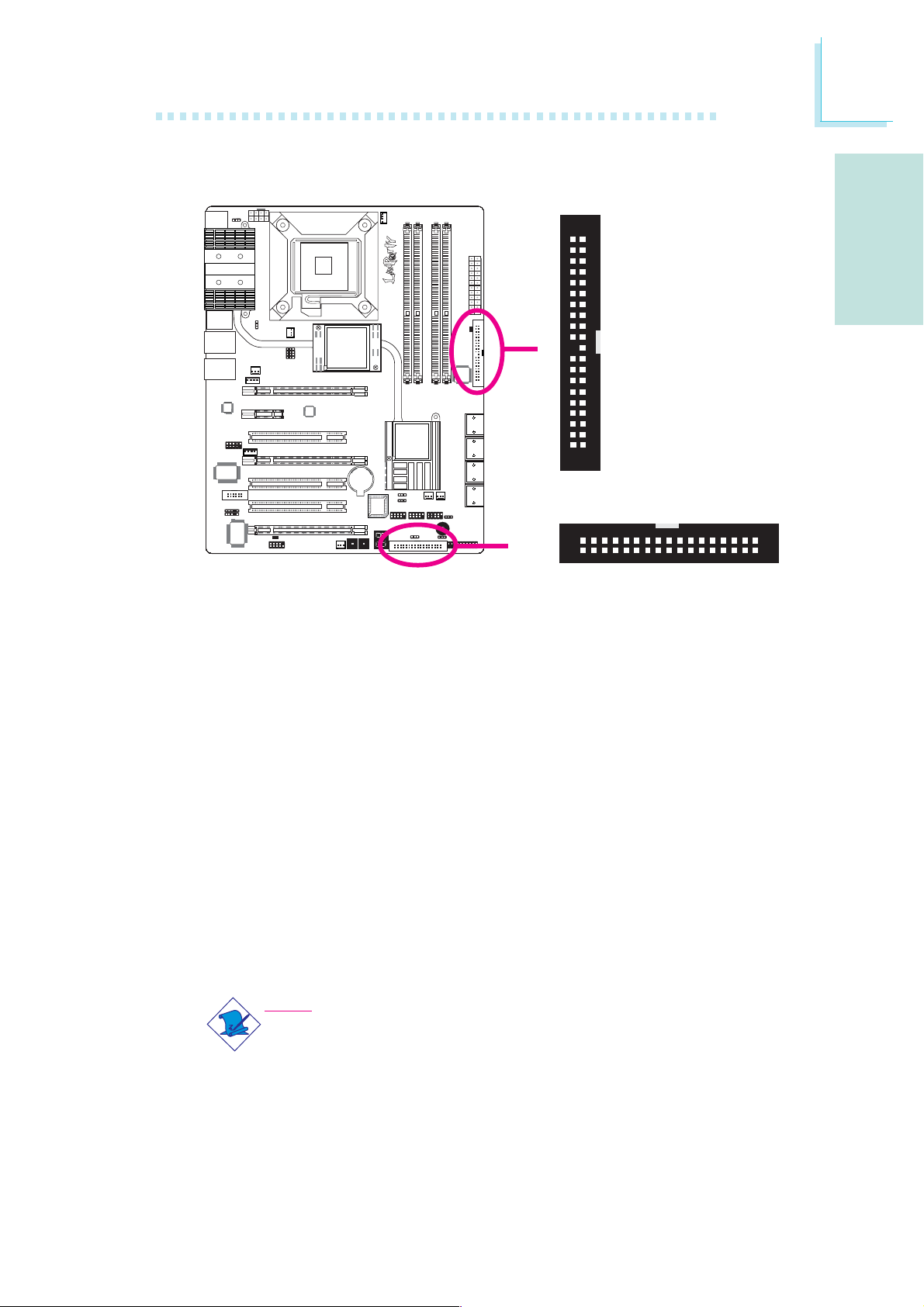
Serial ATA Connectors
The Serial ATA (SATA) connectors are used to connect Serial ATA
drives. Connect one end of the Serial ATA cable to a Serial ATA
connector and the other end to your Serial ATA device.
SATA 7-8
SATA 1-2
SATA 3-4
SATA 5-6
22
ICH9R supports SATA 1 to SATA 6.
JMB363 supports SATA 7 and SATA 8.
Configuring RAID
Refer to the RAID chapter in this manual for more information
about creating RAID on Serial ATA drives.
Page 23
Floppy Disk Drive Connector and IDE Connector
English
E
40
39
X
21
IDE
33
X
34
FDD
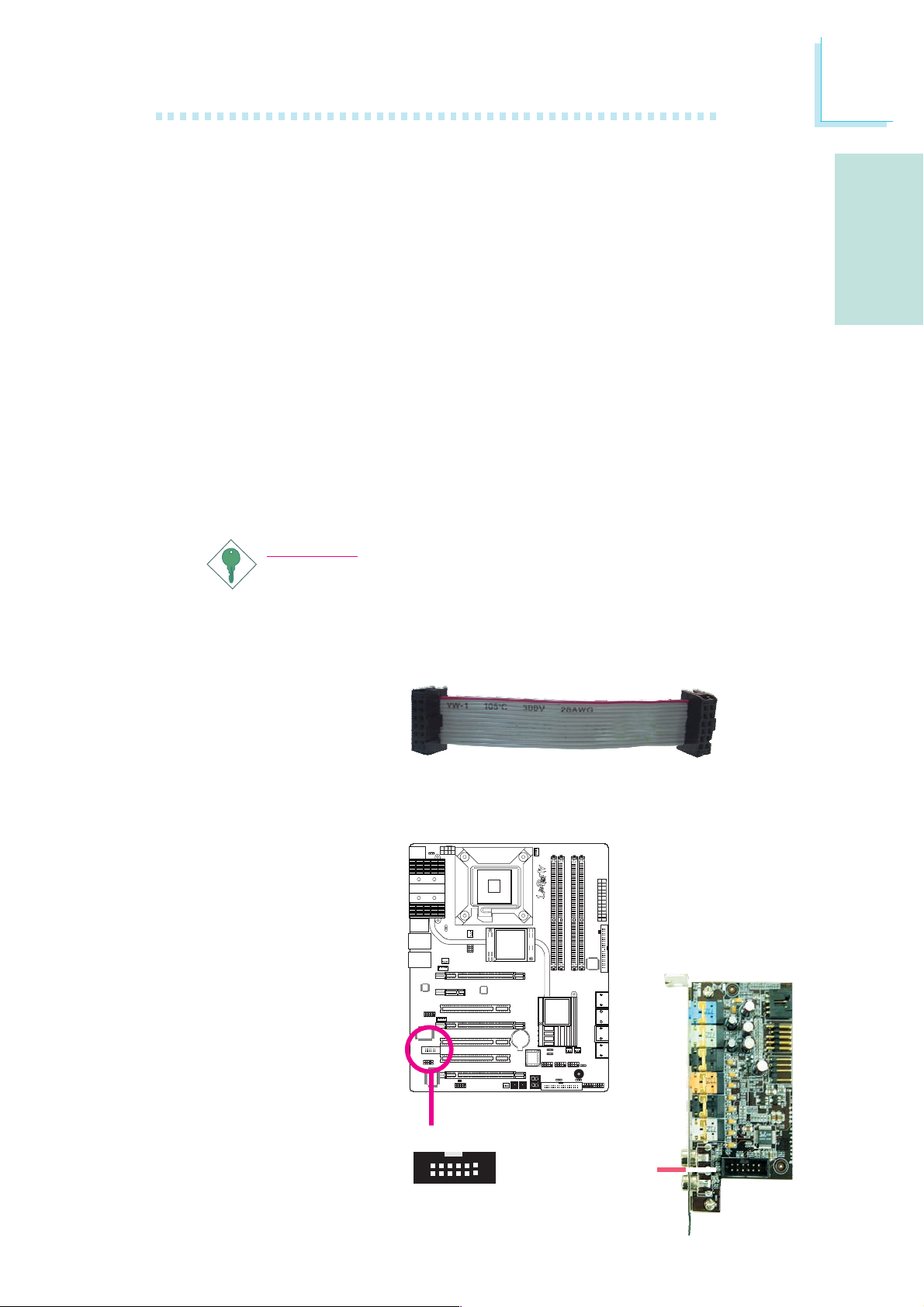
Floppy Disk Drive Connector
The floppy disk drive connector is used to connect a floppy drive.
Insert one end of the floppy cable into this connector and the other
end-most connector to the floppy drive. The colored edge of the
cable should align with pin 1 of this connector.
English
1
2
IDE Disk Drive Connector
The IDE disk drive connector is used to connect 2 IDE disk drives.
An IDE cable have 3 connectors on them, one that plugs into this
connector and the other 2 connects to IDE devices. The connector
at the end of the cable is for the Master drive and the connector in
the middle of the cable is for the Slave drive. The colored edge of
the cable should align with pin 1 of this connector.
Note:
When using two IDE drives, one must be set as the master
and the other as the slave. Follow the instructions provided by
the drive manufacturer for setting the jumpers and/or switches
on the drives.
23
Page 24
E
English
English
IrDA, CIR and Serial (COM) Connectors
IRRX
Ground
IRTX
IrDA
51
N. C.
VCC
COM
CIR
5
CIRTX
CIRRX
W
9
RI
N. C.
X
Ground
DSR
DTR
TD
GND
CTS
RTS
RD
2
1
CD
1
5VSB
IrDA and CIR Connectors
These connectors are used to connect an IrDA module and/or CIR
module.
Note:
The sequence of the pin functions on some IrDA/CIR cable
may be reversed from the pin function defined on the system
board. Make sure to connect the cable connector to the IrDA/
CIR connector according to their pin functions.
24
You may need to install the proper drivers in your operating system
to use the IrDA/CIR function. Refer to your operating system’s
manual or documentation for more information.
Serial (COM) Connector
The serial (COM) connector is used to connect modems, serial printers, remote display terminals, or other serial devices. Your COM port
may come mounted on a card-edge bracket. Install the card-edge
bracket to an available slot at the rear of the system chassis then
connect the serial port cable to this connector. The colored edge of
the cable should align with pin 1 of this connector.
Page 25
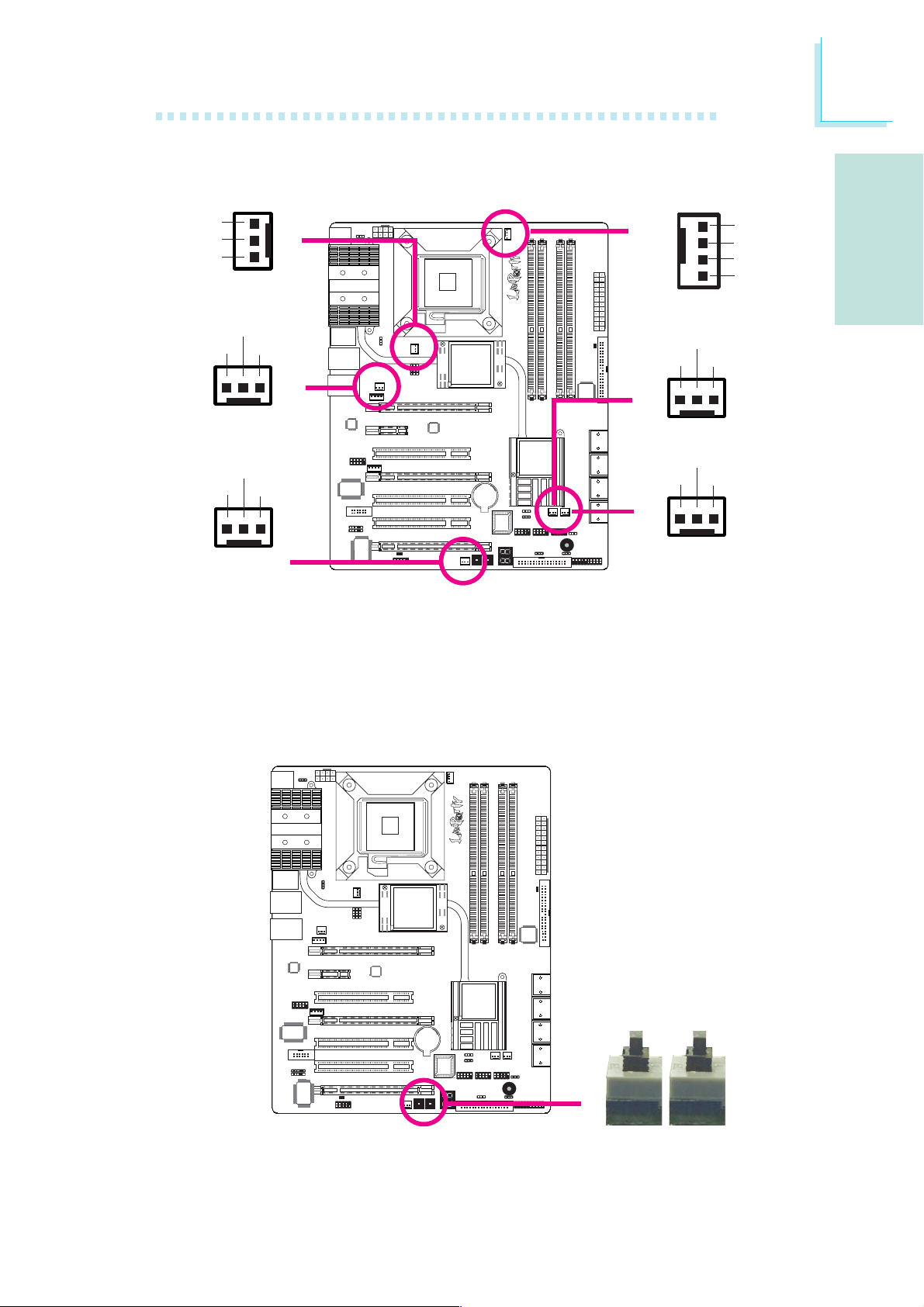
Cooling Fan Connectors
English
E
N. C.
Power
Ground
Ground
NB fan
Power
N. C.
3
X
1
X
Ground
1
4
CPU fan
Power
X
13
3rd fan
Power
Ground
13
N. C.
X
2nd fan
These fan connectors are used to connect cooling fans. Cooling fans
will provide adequate airflow throughout the chassis to prevent overheating the CPU and system board components.
13
X
1st fan
Power
Ground
X
13
System fan
N. C.
N. C.
Ground
Power
Sense
Speed
Control
English
EZ Touch Switches
The presence of the power switch and reset switch on the system
board are user-friendly especially to DIY users. They provide convenience in powering on and/or resetting the system while fine tuning
the system board before it is installed into the system chassis.
Reset Power
X
25
Page 26
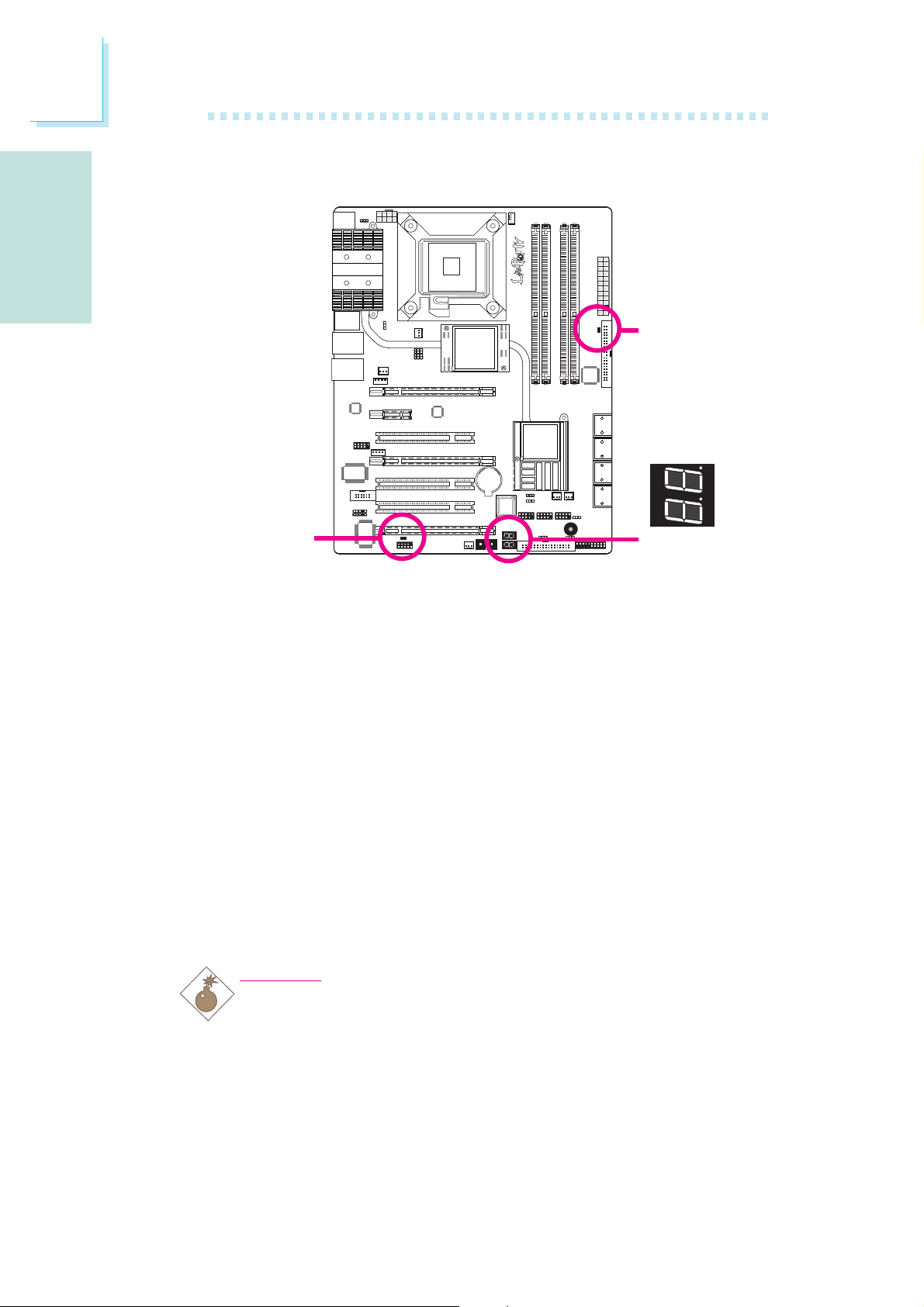
E
English
English
LEDs
DRAM
Power LED
Standby
Power LED
Diagnostic
LED
DRAM Power LED
This LED will light when the system’s power is on.
Standby Power LED
This LED will light when the system is in the standby mode.
Diagnostic LED
The Diagnostic LED displays POST codes. POST (Power-On Self
Tests) which is controlled by the BIOS is performed whenever you
power-on the system. POST will detect the status of the system and
its components. Each code displayed on the LED corresponds to a
certain system status.
.
.
.
.
Warning:
.
.
.
.
When the DRAM Power LED and/or Standby Power LED lit red,
it indicates that power is present on the DIMM sockets and/or
PCI slots. Power-off the PC then unplug the power cord prior to
installing any memory modules or add-in cards. Failure to do so
will cause severe damage to the motherboard and components.
26
Page 27

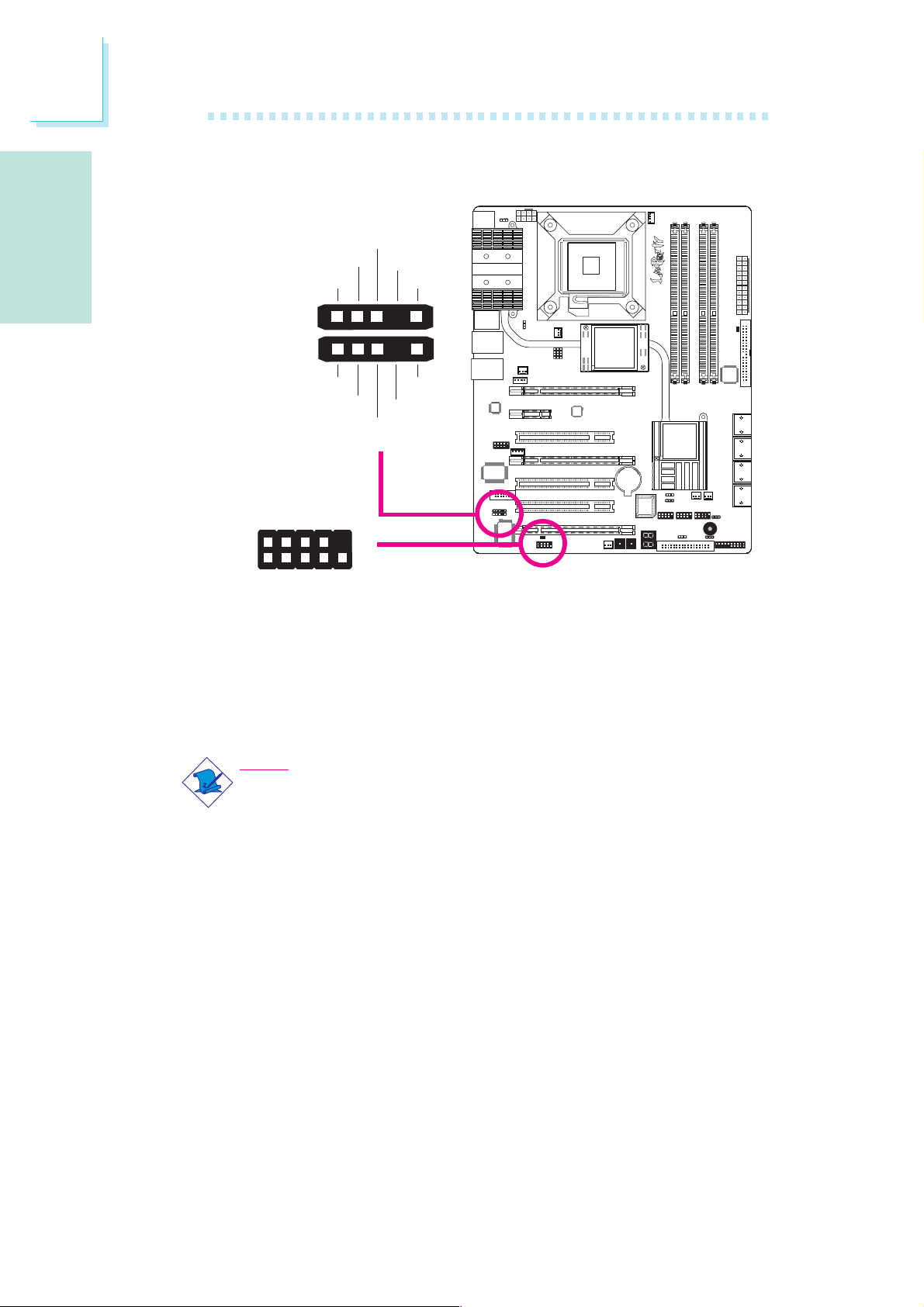
Power Connectors
Use a power supply that complies with the ATX12V Power Supply
Design Guide Version 1.1. An ATX12V power supply unit has a
standard 24-pin ATX main power connector that must be inserted
into this connector.
+3.3VDC
+12VDC
+12VDC
X
PWR_OK
+5VDC
+5VDC
+3.3VDC
+3.3VDC
+5VSB
COM
COM
COM
English
E
English
12 24
COM
+5VDC
+5VDC
+5VDC
NC
COM
COM
COM
PS_ON#
COM
-12VDC
+3.3VDC
131
Your power supply unit may come with an 8-pin or 4-pin +12V
power connector. The +12V power enables the delivery of more
+12VDC current to the processor’s Voltage Regulator Module
(VRM). If available, it is preferable to use the 8-pin power; otherwise
connect a 4-pin power to this connector.
+12V
X
58
14
Ground
27
Page 28
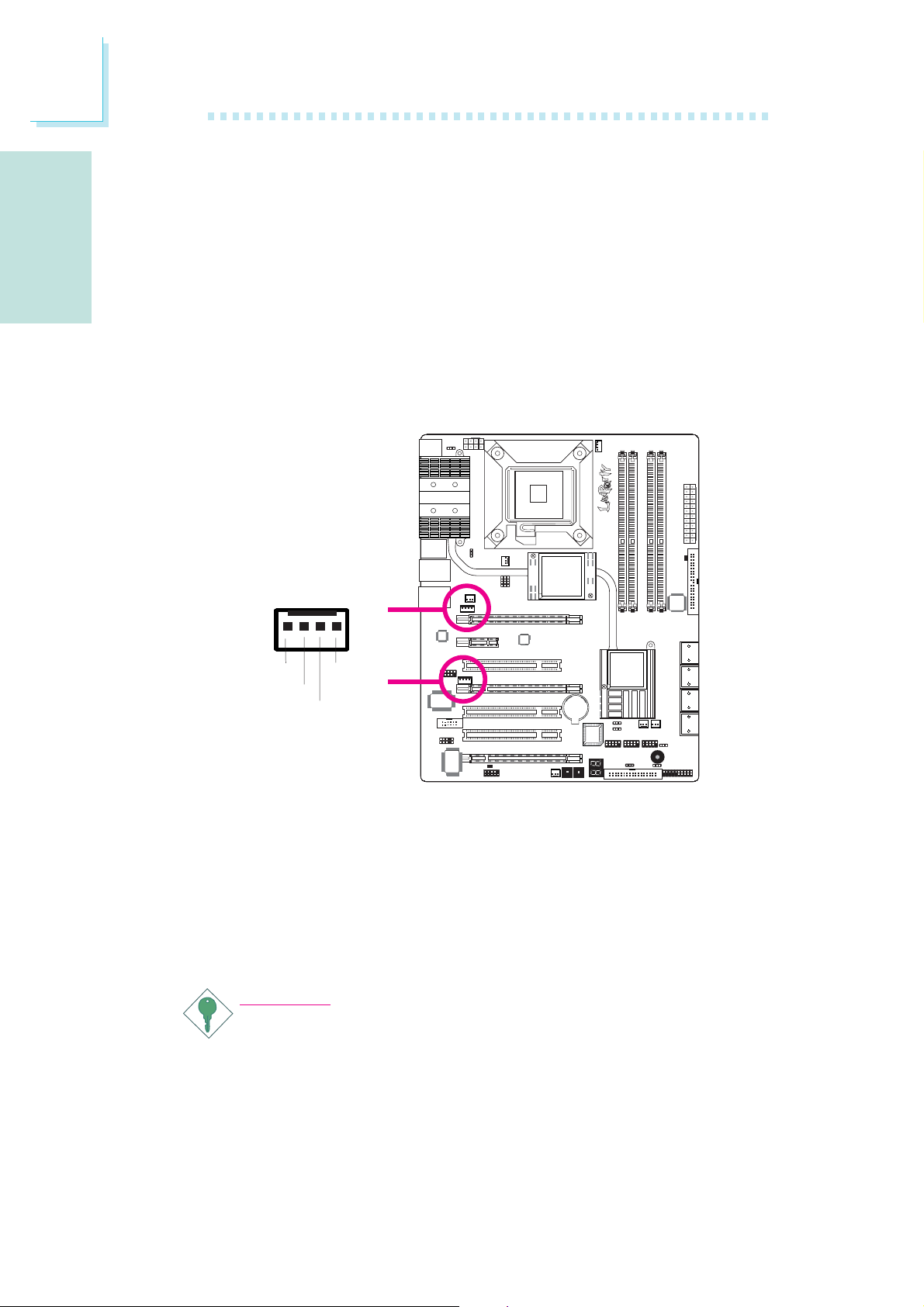
E
English
The power connectors from the power supply unit are designed to
fit the 24-pin and 8-pin connectors in only one orientation. Make
sure to find the proper orientation before plugging the connectors.
English
The FDD-type power connectors are additional power connector.s If
you are using more than one graphics cards, we recommend that
you plug power cables from your power supply unit to the 5V/12V
power connectors. This will provide more stability to the entire system. The system board will still work even if the additional power
connector is not connected.
1
+5V
Ground
Ground
4
+12V
28
The system board requires a minimum of 300 Watt power supply
to operate. Your system configuration (CPU power, amount of
memory, add-in cards, peripherals, etc.) may exceed the minimum
power requirement. To ensure that adequate power is provided, we
strongly recommend that you use a minimum of 400 Watt (or
greater) power supply.
Important:
Insufficient power supplied to the system may result in instability or the add-in boards and peripherals not functioning properly. Calculating the system’s approximate power usage is important to ensure that the power supply meets the system’s
consumption requirements.
Page 29

English
Restarting the PC
Normally, you can power-off the PC by:
1. Pressing the power button at the front panel of the chassis.
or
2. Pressing the power switch that is on the system board (note: not
all system boards come with this switch).
If for some reasons you need to totally cut off the power supplied
to the PC, switch off the power supply or unplug the power cord.
Take note though that if you intend to restart it at once, please
strictly follow the steps below.
1. The time where power is totally discharged varies among power
supplies. It's discharge time is highly dependent on the system's
configuration such as the wattage of the power supply, the sequence of the supplied power as well as the number of peripheral devices connected to the system. Due to this reason, we
strongly recommend that you wait for the Standby Power LED
(refer to the “LEDs” section in this chapter for the location of the
Standby Power LED) to lit off.
E
English
2. After the Standby Power LED has lit off, wait for 6 seconds
before powering on the PC.
If the system board is already enclosed in a chassis which apparently will not make the Standby Power LED visible, wait for 15
seconds before you restore power connections. 15 seconds is
approximately the time that will take the LED to lit off and the
time needed before restoring power.
The above will ensure protection and prevent damage to the
motherboard and components.
29
Page 30

E
English
English
Front Panel Connectors
SPEAKER
RESET
HD-LED
19
X
20
PWR-LED
ATX-SW
HD-LED: Primary/Secondary IDE LED
This LED will light when the hard drive is being accessed.
RESET: Reset Switch
This switch allows you to reboot without having to power off the
system thus prolonging the life of the power supply or system.
SPEAKER: Speaker Connector
This connects to the speaker installed in the system chassis.
ATX-SW: ATX Power Switch
Depending on the setting in the BIOS setup, this switch is a “dual
function power button” that will allow your system to enter the SoftOff or Suspend mode.
1
2
30
Page 31

English
PWR-LED: Power/Standby LED
When the system’s power is on, this LED will light. When the system
is in the S1 (POS - Power On Suspend) or S3 (STR - Suspend To
RAM) state, it will blink every second.
E
Note:
If a system did not boot-up and the Power/Standby LED did
not light after it was powered-on, it may indicate that the CPU
or memory module was not installed properly. Please make
sure they are properly inserted into their corresponding socket.
Pin
Pin Assignment
HD-LED
(Primary/Secondary IDE LED)
Reserved
ATX-SW
(ATX power switch)
Reserved
RESET
(Reset switch)
SPEAKER
(Speaker connector)
PWR-LED
(Power/Standby LED)
3
HDD LED Power
5
HDD
14
N. C.
16
N. C.
8
PWRBT+
10
PWRBT-
18
N. C.
20
N. C.
7
Ground
9
H/W Reset
13
Speaker Data
15
N. C.
17
Ground
19
Speaker Power
2
LED Power (+)
4
LED Power (+)
6
LED Power (-) or Standby Signal
English
31
Page 32

E
English
English
PCI Express Slots
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 1)
PCI Express x1
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 3)
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 4)
PCI Express x16
Install PCI Express x16 graphics card, that comply to the PCI Express specifications, into the PCI Express x16 slot. To install a graphics card into the x16 slot, align the graphics card above the slot then
press it down firmly until it is completely seated in the slot. The
retaining clip of the slot will automatically hold the graphics card in
place.
PCI Express Slots Configuration
Bandwidth
Graphics Mode
2-way CrossFire
2-way CrossFire + Physics
PCIE 1
x16
x16
PCIE 3
x16
x16
PCIE 4
N.C.
x4
PCI Express x1
Install PCI Express cards such as network cards or other cards that
comply to the PCI Express specifications into the PCI Express x1
slot.
32
Page 33

Chapter 3 - RAID
The Intel ICH9R chip alows configuring RAID on Serial ATA drives
connected to SATA 1 to SATA 6. It supports RAID 0, RAID 1,
RAID 0+1 and RAID 5.
The JMicron JMB363 chip allows configuring RAID on another 2 Serial ATA drives connected to SATA 7 and SATA 8. It supports
RAID 0 and RAID 1.
RAID Levels
RAID 0 (Striped Disk Array without Fault Tolerance)
RAID 0 uses two new identical hard disk drives to read and write
data in parallel, interleaved stacks. Data is divided into stripes and
each stripe is written alternately between two disk drives. This improves the I/O performance of the drives at different channel; however it is not fault tolerant. A failed disk will result in data loss in the
disk array.
English
E
English
RAID 1 (Mirroring Disk Array with Fault Tolerance)
RAID 1 copies and maintains an identical image of the data from
one drive to the other drive. If a drive fails to function, the disk array
management software directs all applications to the other drive since
it contains a complete copy of the drive’s data. This enhances data
protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system. Use
two new drives or an existing drive and a new drive but the size of
the new drive must be the same or larger than the existing drive.
RAID 0+1 (Striping and Mirroring)
RAID 0+1 is a combination of data striping and data mirroring
providing the benefits of both RAID 0 and RAID 1. Use four new
drives or an existing drive and three new drives for this
configuration.
RAID 5
RAID 5 stripes data and parity information across hard drives. It is
fault tolerant and provides better hard drive performance and more
storage capacity.
33
Page 34

E
English
Settings
To enable the RAID function, the following settings are required.
English
1. Connect the Serial ATA drives.
2. Configure Serial ATA in the Award BIOS.
3. Configure RAID in the RAID BIOS.
4. Install the RAID driver during OS installation.
5. Install the Intel Matrix Storage Manager
6. Install the JMB36X Driver
Step 1: Connect the Serial ATA Drives
Refer to chapter 2 for details on connecting the Serial ATA drives.
Important:
1. Make sure you have installed the Serial ATA drives and connected the data
cables otherwise you won’t be able to enter the RAID BIOS utility.
2. Treat the cables with extreme caution especially while creating RAID. A damaged cable will ruin the entire installation process and operating system. The
system will not boot and you will lost all data in the hard drives. Please give
special attention to this warning because there is no way of recovering back
the data.
Step 2: Configure Serial ATA in the Award BIOS
1. Power-on the system then press <Del> to enter the main menu
of the Award BIOS.
2. Select the Integrated Peripherals submenu - OnChip IDE Device
section of the BIOS.
3. Configure Serial ATA in the appropriate fields.
4. Press <Esc> to return to the main menu of the BIOS setup
utility. Select “Save & Exit Setup” then press <Enter>.
5. Type <Y> and press <Enter>.
6. Reboot the system.
tep 3: Configure RAID in the RAID BIOS
Configure RAID in the Intel RAID BIOS
When the system powers-up and all drives have been detected, the
Intel RAID BIOS status message screen will appear. Press the
<Ctrl> and <I> keys simultaneously to enter the utility. The utility
allows you to build a RAID system on Serial ATA drives.
34
Page 35

Configure RAID in the JMicron RAID BIOS
When the system powers-up and all hard disk drives have been
detected, the JMicron RAID BIOS status message screen will appear.
Press the <Ctrl> and <J> keys simultaneously to enter the utility.
The utility allows you to build a RAID system on Serial ATA drives.
Step 4: Install the RAID Driver During OS Installation
The RAID driver must be installed during the Windows® XP or
Windows® 2000 installation using the F6 installation method. This is
required in order to install the operating system onto a hard drive
or RAID volume when in RAID mode or onto a hard drive when in
AHCI mode.
1. Start Windows Setup by booting from the installation CD.
English
E
English
2. Press <F6> when prompted in the status line with the ‘Press
F6 if you need to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver’
message.
3. Press <S> to “Specify Additional Device”.
4. At this point you will be prompted to insert a floppy disk
containing the RAID driver. Insert the provided RAID driver
diskette.
5. Locate for the drive where you inserted the diskette then select
RAID or AHCI controller that corresponds to your BIOS setup.
Press <Enter> to confirm.
You have successfully installed the driver. However you must continue
installing the OS. Leave the floppy disk in the floppy drive until the
system reboots itself because Windows setup will need to copy the
files again from the floppy disk to the Windows installation folders.
After Windows setup has copied these files again, remove the floppy
diskette so that Windows setup can reboot as needed.
Step 5: Install the Intel Matrix Storage Manager
Step 6: Install the JMB36X Driver
Refer to the complete version of the manual for steps on installing
the utlity and driver. Please download the manual from DFI’s website.
Visit www.dfi.com.
35
Page 36

F
Français
Chapitre 1 - Spécifications
Français
Processeur
Chipset
Mémoire Système
• LGA 775 socket pour:
- Intel® CoreTM2 Quad et Intel® CoreTM2 Duo
• Intel Ont augmenté La Technologie De la Mémoire 64 (EMT64T)
• Ont augmenté La Technologie D’Intel SpeedStep (EIST)
• Intel Hyper-Filetant La Technologie (Intel Hyper-Threading)
• Soutient 1600/1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X48 série)
Soutient 1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X38 série)
®
• Intel
• LP UT/LT X38/X48-T2R
• LP UT/LT X38-T3R
• L’interface de mémoire deux canaux (128-bit)
• Jusqu’à 8GB de mémoire système
• Non-tamponns DIMM x8 et x16
chipset
- Pont nord:
Intel® X48 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X48 série)
Intel® X38 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X38 série)
La technologie rapide d’accès mémoire d’Intel
- Pont sud: Intel® ICH9R
- 4 sockets DIMM DDR2 240-pin
- Les modules DIMM DDR2 667/800 MHz
- Jusqu’à 12.8GB/s bande passante
- 4 sockets DIMM DDR3 240-pin
- Les modules DDR3 800/1066/1333 MHz
- Offre une bande passante jusqu’à 21Gb/s à 1333MHz
36
Logements
d’Extension
BIOS
Audio
LAN
• 2 PCI Express (Gen 2) x16 fentes (PCIE 1 et PCIE 3)
- CrossFire bi directionnel à bande passante x16/x16
- CrossFire bi directionnel +
x4
• 1 PCI Express x1 slot (PCIE 2)
• 1 PCI Express x4 slot (PCIE 4)
• 3 PCI slots
• Compatible avec Award BIOS
• Mémoire Flash 8Mbit
• CMOS Reloaded
• Bernstein carte audio
- Realtek ALC885 8 canaux HD Audio Codec
- Center/subwoofer, rear R/L et side R/L prises audio
- Line-in, line-out et mic-in prises audio
- 2 ports coaxial RCA S/PDIF
connecteur optique S/PDIF
-1
- 1 connecteur CD-in
- 1 connecteur audio de l’avant
• DAC SNR/ADC SNR de 106dB/101dB
• Technologie protection de contente lossless à toute vitesse
• Marvell 88E8052 et Marvell 88E8053 PCIE Gigabit LAN
• Entièrement conforme IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T), 802.3u
(100BASE-TX) et 802.3ab (1000BASE-T) standard
Physics
à bande passante x16/x16/
Page 37

Français
F
Serial ATA avec
RAID
IEEE 1394
Panneau Arrière
Interne I/O
• Intel ICH9R Chipset
- Technologie de Intel Matrix Storage
- 6 dispositifs de SATA
- SATA allant jusqu’à 3Gb/s
- RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 0+1 et RAID 5
• JMIcron JMB363 PCI Express et SATA et PATA
- Supporte des disques durs jusqu’à UltraDMA 100Mbps
- 2 dispositifs de SATA
- SATA allant jusqu’à 3Gb/s
- RAID 0 et RAID 1
• VIA VT6307
• Supporte 2 100/200/400 Mb/sec ports
I/O
• 1 port souris PS/2 et 1 port clavier PS/2
• 1 port IEEE 1394
• 6 ports USB 2.0/1.1
• 2 ports RJ45 LAN
3 connecteurs pour 6 ports USB 2.0/1.1 supplémentaires
•
• 1 connecteur pour 1 IEEE 1394
• 1 connecteur pour 1 série
• 1 connecteur pour module audio Bernstein
• 1 connecteur audio frontal (sur le module audio Bernstein)
•1 connecteur CD-in (sur le module audio Bernstein)
• 1 port optique S/PDIF (sur le module audio Bernstein)
• 1 connecteur IR et 1 connecteur CIR
•8 connecteurs Serial ATA
• 1 connecteur IDE
• 1 connecteur de FDD
• 1 connecteur d’alimentation 24-pin ATX
• 1 connecteur d’alimentation 8-pin 12V ATX
• 2 prises d’alimentation 4-broches 5V/12V (type-FDD)
• 1 connecteur devant panneau
• 6 connecteurs de ventilateurs
• 1 indicateur diagnostiques
• EZ interrupteurs (bouton de power et reset)
Français
Gestion de
Puissance
Fonctions de
Moniteur de
Matériel
PCB
• ACPI et OS Directed Power Management
• ACPI STR (Suspend to RAM) fonction
• Réveil-Sur-PS/2 Clavier/Souris
• Réveil-Sur-USB Clavier/Souris
• Eveil Sonnerie et Réveil Par Le Réseau
• Minuterie RTC pour allumer le système
• Récupération après Défaillance d’Alimentation CA
• Gère l’alarme de température et de surchauffe de CPU /
système / pont nord
• Gère l’alarme de voltage et d’échec de Vcore/Vdimm/Vnb/
VCC5/12V/V5sb/Vbat
• Gère la vitesse de ventilateur du ventilateur
• Protection du CPU - supporte la mise hors circuit automatique
en cas de surchauffage du système
• Facteur de forme de ATX
• 24.5cm (9.64") x 30.5cm (12")
37
Page 38

F
Français
Chapitre 2 - Installation de Matériel
Cavalier
Français
Effacer les Données CMOS
Effacement des Données CMOS en Utilisant JP2
JP2
312 312
X
1-2 On: Normal
(défaut)
Si vous rencontrez les éléments suivants,
a) Données CMOS devenant corrompues
b) Vous avez oublié le superviseur ou le mot de passe utilisateur
c) Les réglages surcadencés dans le BIOS ont entraîné une instabilité
du système ou causés des problèmes de démarrage du système.
Vous devez reconfigurer le système aux valeurs par défaut stockées
dans la ROM BIOS.
Pour charger les valeurs par défaut dans la ROM BIOS, veuillez
suivre les étapes ci-dessous.
1. Débrancher le système et retirer le cordon d’alimentation.
2. Mettre les broches du JP2 2 et 3 sur ON Attendre quelques
secondes et remettre JP2 par défaut, broches 1 et 2 On.
3. Rebrancher maintenant le cordon d’alimentation et allumer le
système.
2-3 On:
Effacer les données
CMOS
38
Page 39

Français
F
Effacement des Données CMOS en Utilisant la Fonctionnalité EZ Clear
EZ Clear® contourne le processus manuel d’utilisation d’un cavalier
pour effacer CMOS en utilisant simplement les boutons de
réinitialisation et d’alimentation.
Important:
EZ Clear® n’est supportée que si l’alimentation de veille est
présente sur le système.
Pour utiliser EZ Clear®:
1. S’assurer que l’alimentation de veille soit présente. :
2. En utilisant les commutateurs à touche EZ de la carte système,
appuyer d’abord sur le bouton réinitialisation et ensuite
simultanément sur le bouton d’alimentation pendant environ 4
secondes.
®
Français
Réinitialisation
Alimentation
X
Si la carte système est déjà mise dans le châssis, appliquer la
même méthode en utilisant le bouton de réinitialisation et le bouton d’alimentation situés sur le panneau frontal du châssis.
3. Après 4 secondes, relâcher d’abord le bouton d’alimentation et
ensuite le bouton de réinitialisation.
4. Le CMOS restaurera les réglages de l’horloge à leurs valeurs par
défaut.
39
Page 40

F
Français
Sélectionner l’alimentation PS/2
Français
JP7
312
31
2
X
1-2 On: 5V
(
défaut)
Important:
La source d’alimentation 5VSB de
votre alimentation doit supportée
≥720mA.
En sélectionnant 5VSB, vous pourrez utiliser le clavier PS/2 ou la
souris PS/2 pour “réveiller” le système.
2-3 On:
5VSB
Sélectionner l’alimentation USB
En sélectionnant 5VSB, vous pourrez utiliser le clavier USB ou la
souris USB pour “réveiller” le système.
USB 6-11
(JP5)
USB 0-5
(JP6)
X
1-2 On: 5V
(
défaut)
1-2 On: 5V
(
défaut)
X
3
2
1
2-3 On:
5VSB
312 312
2-3 On:
5VSB
3
2
1
40
Important:
Si vous utilisez la fonction Wake-on de la souris/clavier USB pour les 2 ports
USB, la source d’alimentation 5VSB de votre alimentation doit supporter ≥1,5 A.
Pour 3 ou davantage de ports USB, la source d’alimentation 5VSB de votre
alimentation doit supporter ≥2 A.
Page 41

Sélection des Haut-parleurs ON/OFF
312
1-2 On:
Haut-parleurs
OFF
312
Français
F
Français
JP8
2-3 On:
Haut-parleurs ON
(défaut)
La carte système est équipée d’un avertisseur sonore qui sert en
tant que haut-parleur du PC. Par défaut l’avertisseur sonore est
« ON » permettant d’entendre les « bips » des messages et les
avertissements. Si vous voulez utiliser un haut-parleur externe,
éteindre cette fonction en réglant les broches 1 et 2 du JP8 sur On.
X
Avertisseur
sonore
41
Page 42

F
Français
Amorce sécurisée
Français
JP1
312 312
X
1-2 On:
(défaut)
Ce cavalier est utilisé pour rebooter le système en toute sécurité
quand il se bloque ou que vous ne réussissez pas à le redémarrer.
1. Débrancher le système et retirer le cordon d’alimentation.
2. Mettre les broches du JP1 2 et 3 sur ON Attendre quelques
secondes et remettre JP1 par défaut, broches 1 et 2 On.
3. Rebrancher maintenant le cordon d’alimentation et allumer le
système.Le système redémarrera normalement sans perte des
données stockées dans le CMOS.
2-3 On:
Amorce sécurisée
42
Page 43

Réinitialisation de l’horloge temps réel secondaire
2
1
JP12
X
1-2 On: Normal
3
(défaut)
132
2-3 On:
RTC reset
Français
F
Français
Lorsque la pile de l’horloge est enlevée, ce cavalier réinitialise la
capacité de gestion des octets du registre de l’horloge.
Note:
1. L’entrée SRTCRST# doit toujours être élevée lorsque toutes
les autres couches Power plane de l’horloge sont ON.
2. Dans le cas où la pile de l’horloge soit inopérante ou
manquante sur la plateporme la broche SRTCRST# doit
être montée avant la broche RSMRST#.
43
Page 44

F
Français
Sélectionner le FSB du processeur.
Français
X
JP14
4
3
2
1
JP15
JP13
Par défaut, les trois cavaliers sont tous réglés avec les broches 1 et
2 On.Ce réglage permettra au système de fonctionner
automatiquement en fonction du FSB du processeur. Si vous désirez
modifier le réglage, veuillez vous référer au tableau ci-dessous.
JP14
JP13
JP15
Par processeur
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
FSB 800
3-4 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1066
2-3 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1333
2-3 On
2-3 On
3-4 On
44
Page 45

Ports I/O de l’arrière du Panneau
Français
F
PS/2
Mouse
PS/2
K/B
Ports PS/2 et IEEE 1394
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 KB
W
1394-0
W
1394-0
USB 10-11
LAN 2LAN 1
Français
USB 6-7
USB 8-9
Ground
TPB-
+12V (fused)
Ground
TPA-
1394-1
2
1
TPA+
Ground
10
9
Key
TPB+
+12V (fused)
W
Ports Souris PS/2 et Clavier PS/2
Ces ports sont utilisés pour raccorder une souris PS/2 et un clavier
PS/2.
Ports IEEE 1394
Le port IEEE 1394-0 est utilisé pour raccorder les appareils audio/
video ou les périphériques de stockage. Le raccord 10 broches
permet de vous connecter à un appareil 1394 supplémentaire. Votre
port 1394 peut être livré monté sur un support encartable. Installer
le support encartable dans une fente disponible à l’arrière du châssis
du système et raccorder la câble du port 1394 à ce connecteur.
45
Page 46

F
Français
Ports USB et LAN
Français
LAN 1
USB 11
USB 10
W
USB 9
USB 8
W
W
LAN 2
USB 7
USB 6
USB 4-5
USB 2-3
USB 0-1
Ports USB
Les ports USB sont utilisés pour raccorder des appareils USB 2.0/
1.1. Les connecteurs 10 broches vous permettent de raccorder 6
autres ports USB 2.0/1.1. Vos ports USB peuvent être livrés montés
sur un support encartable. Installer le support encartable dans une
fente disponible à l’arrière du châssis du système et raccorder les
câbles des ports USB à ces connecteurs.
2
1
VCC
-Data
VCC
-Data
GND
+Data
GND
+Data
N. C.
10
9
Key
46
Ports LAN
Les ports LAN permettent à la carte système de se connecter à un
réseau local au moyen d’un concentrateur réseau.
Page 47

Module Audio Bernstein
Line-in
Line-out
Français
1
Left audio channel
Ground
Ground
Right audio channel
F
Français
Mic-in
Center/
Subwoofer
Rear R/L
Side R/L
S/PDIF-out
S/PDIF-in
4
CD-in
10 9
Line out_LeftLine out Jet Detect
Sense
Line out_Right
Mic_Right
Mic_Left
12
Side view
Bernstein audio
module connector
Mic Jet Detect
SPDIF in
GND
SPDIF out
Key
+5V
N. C.
Vcc
GND
Front audio
5
Optical S/PDIF
1
Prise entrée (bleue claire)
La prise est utilisée pour raccorder tous les appareils audio tels que
Hi-fi, lecteur CD, lecteur de bande magnétique, radio AM/FM,
synthéthiseur, etc..
Prise de sortie (Citron)
Cette prise est utilisée pour se connecter aux haut-parleurs avant
droits et gauches du système audio.
Prise entrée micro (rose)
Cette prise est utilisée pour connecter un microphone externe.
Prise de caisson de basse/central (orange)
Cette prise est utilisée pour se connecter aux haut-parleurs de
basse et centraux du système audio.
Prise arrière gauche/droite (noire)
Cette prise est utilisée pour se connecter aux haut-parleurs arrière
droits et gauches du système audio.
47
Page 48

F
Français
Français
Prise de côté gauche/droite (grise)
Cette prise est utilisée pour se connecter aux haut-parleurs de côté
droits et gauches du système audio.
Prises coaxiales d’entrée RCA S/PDIF et de sortie SPDIF
Ces prises sont utilisées pour connecter les appareils de sortie audio
externes en utilisant les câbles coaxiaux S/PDIF.
Connecteur d’entrée CD
Le connecteur d’entrée CD est utilisé pour recevoir les signaux audio
d’un lecteur CD-ROM, d’une carte TV ou MPEG.
Connecteur audio frontal
Le connecteur audio frontal est utilisé pour raccorder les prises micro
d’entrée et les sorties de ligne (line-out) sur le panneau frontal de
votre système.
Connecteur optique S/PDIF
Le connecteur optique S/PDIF est utilisé pour raccorder un appareil
de sortie audio externe en utilisant un câble optique S/PDIF.
Important:
NE PAS utiliser un câble S/PDIF et RCA S/PDIF coaxial en
même temps.
Installer le Module Audio Bernstein
1. Le module audio Bernstein
se connecte à la carte
système au moyen du
câble audio fourni.
48
Page 49

2 Insérer une extrémité du
câble sur le connecteur
Audio Bernstein sur la
carte système et l’autre
sur le connecteur
correspondant sur le module audio.
Français
F
Français
X
11
12
3. La longueur du câble audio
donne la possibilité d’installer
le module sur toute fente
d’extension disponible à
l’arrière du châssis système.
Retirer la vis du support à
l’endroit où vous voulez installer le module audio et
retirer le support. Mettre le
module audio Bernstein dans
la fente du support
d’extension et fixer le module en remettant la vis de support que
vous avez retirée à l’étape 3.
1
2
Connecteur de
module Audio
Bernstein
49
Page 50

F
Français
Connecteurs I/O
Les Connecteurs en Série ATA
Français
SATA 7-8
SATA 1-2
SATA 3-4
SATA 5-6
Les connecteurs en série ATA (SATA) sont utilisés pour raccorder les
disques durs ATA en série. Relier une extrémité du câble en série
ATA au connecteur en série ATA et l’autre extrémité sur votre
appareil en série ATA.
ICH9R supporte SATA 1 à SATA 6.
JMB363 supporte SATA 7 et SATA 8.
Configuration du Système RAID
Se référer au chapitre RAID de ce manuel pour obtenir davantage
d‘informations sur la création d’un système RAID sur les disques
durs en série ATA.
50
Page 51

Français
Connecteur de Lecteur de Disquettes et Connecteur IDE
F
40
39
X
21
IDE
33
X
34
FDD
Connecteur de Lecteur de Disquettes
Le connecteur de lecteur de disquettes est utilisé pour raccorder le
lecteur de disquettes. Il possède un mécanisme d’insertion
empêche sa mauvaise installation. Insérer une extrémité du câble du
lecteur de disquette dans ce connecteur et l’autre dans le lecteur de
disquette. Le bord coloré du câble devrait être aligné avec l’ergot 1
de ce connecteur.
1
2
qui
Français
Connecteur de Disque dur IDE
Le connecteur de disque dur IDE est utilisé pour raccorder 2
disques IDE. Il possède un mécanisme d’insertion
mauvaise installation du cable IDE. Un câble IDE comporte 3
connecteurs, un qui se branche sur ce connecteur et les deux autres
qui se connectent sur les appareils IDE. Le connecteur à l’extrémité
du câble est pour le disque maître et celui au milieu du câble est
pour l’esclave. Le bord coloré du câble devrait être aligné avec
l’ergot 1 de ce connecteur.
Note:
Lors de l’utilisation des disques dur IDE, l’un doit être assigné
Maître et l’autre esclave. Suivre les instructions fournies par le
fabricant de disques durs pour mettre les cavaliers et/ou les
commutateurs sur les disques durs.
qui empêche la
51
Page 52

F
Français
Connecteurs IrDA, CIR et en Série (COM)
Français
IRRX
Ground
IRTX
IrDA
51
CIR
51
N. C.
VCC
COM
CIRTX
Ground
DSR
DTR
TD
CTS
RTS
GND
RI
RD
2
1
CD
N. C.
CIRRX
W
X
9
5VSB
Connecteurs IrDA et CIR
.Ces connecteurs sont utilisés pour raccorder le module IrDA ou/et
le module CIR.
Note:
La séquence de la fonction des broches (signal) sur certains
câbles IrDA/CIR peut être inversée à partir de la fonctionnalité
définie sur la carte système. S’assurer de relier le connecteur du
câble sur le connecteur IrDA/CIR selon les fonctions de leurs
broches.
52
Il se peut que vous deviez installer les disques dans votre système
d’exploitation convenants à l’utilisation de la fonctionnalité IrDA/CIR.
Se référer au manuel de votre système d’exploitation ou à la documentation pour obtenir davantage d’informations.
Connecteur en Série (COM)
Le connecteur en série (COM) est utilisé pour raccorder les modems, les imprimantes en série, les terminaux d’affichage à distance
ou autres appareils en série. Votre port COM peut être livré monté
sur un support encartable. Installer le support encartable dans une
Page 53

Français
fente disponible à l’arrière du châssis du système et raccorder le
câble du port en série à ce connecteur. Le bord coloré du câble
devrait être aligné avec l’ergot 1 de ce connecteur.
F
Connecteurs de Ventilateur de Refroidissement
N. C.
Power
Ground
NB fan
Power
Ground
13
3rd fan
Power
Ground
13
2nd fan
N. C.
N. C.
3
X
1
X
Ground
X
13
X
Ground
X
13
X
1
4
CPU fan
Power
N. C.
1st fan
Power
N. C.
System fan
Français
Ground
Power
Sense
Speed
Control
Ces connecteurs de ventilateur sont utilisés pour raccorder les
ventilateurs de refroidissement. Les ventilateurs de refroidissement
fournissent une ventilation adéquate à l’intérieur du châssis afin
d’empêcher toute surchauffe du processeur et des composants de la
carte système.
53
Page 54

F
Français
Commutateurs à Touche EZ
Français
Réinitialisation
Alimentation
X
La présence des commutateurs d’alimentation et de réinitialisation
sur la carte système est conviviale et particulièrement pour les
utilisateurs étant bricoleurs. Ils sont très pratiques pour allumer ou
réinitialiser le système tout en ajustant la carte système avant
l’installation sur le châssis.
54
Page 55

Voyants DEL
Voyant DEL
d’alimentation à
l’état de veille
Français
F
Français
Voyant DEL
d’alimentation
DRAM
Voyant DEL
de diagnostic
Voyant DEL d’alimentation DRAM
Ce voyant DEL s’allumera lorsque le système est allumé.
Voyant DEL d’alimentation à l’état de Veille
Ce voyant DEL s’allumera lorsque le système est en mode veille.
Voyant DEL de Diagnostic
Le voyant DEL de diagnostic affiche les codes POST. POST (tests
automatiques d’alimentation) qui est contrôlé par le BIOS est
effectué à chaque fois que le système est allumé. ¨POST détectera le
statut du système et de ses composants. Chaque code affiché sur le
voyant DEL correspond à un certains statut du système.
.
.
.
.
Avertissement:
.
.
.
.
Lorsque le voyant DEL d’alimentation DRAM et/ou
d’alimentation à l’état de veille sont rouge, cela indique que le
courant passe dans les supports DIMM et/ou dans les fentes
PCI. Eteindre le PC et débrancher le cordon d’alimentation avant
d’installer les modules mémoire ou les cartes d’extension. Un
échec à effectuer ceci peut entraîner des dégâts graves à la
carte mère et ses composants.
55
Page 56

F
Français
Connecteurs d’alimentation
Français
Utiliser une alimentation électrique conforme à la version 1.1 du
guide d’alimentation électrique ATX12V. Une unité d’alimentation
électrique ATX12V possède un connecteur d’alimentation principale
ATX à 24 broches qui doit être inséré dans ce connecteur.
12 24
+3.3VDC
+12VDC
+12VDC
X
PWR_OK
+5VDC
+5VDC
+3.3VDC
+3.3VDC
+5VSB
COM
COM
COM
COM
+5VDC
+5VDC
+5VDC
NC
COM
COM
COM
PS_ON#
COM
-12VDC
+3.3VDC
131
Votre unité d’alimentation électrique peut être livrée avec un
connecteur d’alimentation 12V à 4 ou 8 broches. L’alimentation 12V
permet la fourniture de courant 12VDC en direction du module de
régulation de tension du processeur (VRM - Voltage Regulator Module). Si disponible, il est préférable d’utiliser une alimentation 8
broches, sinon, raccorder une alimentation 4 broches à ce connecteur.
+12V
X
58
14
Ground
56
Page 57

Français
Les connecteurs d’alimentation de l’unité d’alimentation électrique
sont conçus pour s’adapter aux connecteurs à 24 et 8 broches
seulement dans une direction. S’assurer d’observer la bonne orientation avant de brancher les connecteurs.
F
Les connecteurs d’alimentation de type FDD sont des connecteurs
supplémentaires d’alimentation. Si vous utilisez plus d’une carte
graphique, nous vous conseillons de brancher les câbles
d’alimentation depuis votre unité d’alimentation électrique sur des
connecteurs d’alimentation de 5V/12V. Ceci donnera plus de stabilité
à tout le système. La carte système fonctionnera toujours même si le
connecteur d’alimentation supplémentaire n’est pas raccordé.
1
+5V
Ground
Ground
4
+12V
Français
La carte système nécessite une alimentation minimale de 300 Watts
pour pouvoir fonctionner. La configuration de votre système
(alimentation du processeur, cartes d’extension, périphériques etc.)
peut dépasser la puissance minimale requise. Pour s’assurer que la
puissance minimale soit fournie, nous vous conseillons fortement
d’utiliser une alimentation minimale de 400 Watts (ou davantage).
Important:
Une puissance insuffisante fournie au système peut entraîner
une instabilité ou un mauvais fonctionnement des cartes
d’extension et des périphériques. Le calcul de la puissance
approximative requise par le système est important pour
garantir que l’alimentation soit suffisante pour la consommation
du système.
57
Page 58

F
Français
Français
Redémarrage du PC
Normalement vous pouvez éteindre le PC en :
1. Appuyant sur le bouton d’alimentation sur le panneau frontal du
chassis.
ou
2. En appuyant sur le commutateur d’alimentation se trouvant sur la
carte système (note : toutes les cartes systèmes ne possèdent
pas ce commutateur)
Si, pour quelque raison que ce soit, vous devez éteindre l’alimentation
du PC, éteindre l’alimentation ou débrancher le cordon d’alimentation.
Veuillez noter que si vous désirez le redémarrer de suite, suivez les
étapes suivantes :
1. Le temps de déchargement de l’électricité dépend des
alimentations électriques. Le temps de déchargement dépend
entièrement de la configuration du système telle que le nombre
de Watt de l’alimentation, de la séquence de l’alimentation ainsi
que du nombre d’appareils périphériques reliés au système. Pour
ces raisons nous conseillons fortement d’attendre que le voyant
DEL de veille (se référer à la section « voyants DEL » de ce
chapitre pour la localisation de ce voyant) s’éteigne.
2. Une fois le voyant DEL de veille éteint, attendre 6 secondes avant
d’allumer le PC.
Si la carte système est déjà montée dans un châssis qui
apparemment ne laissera pas entrevoir le voyant DEL de veille,
attendre 15 secondes avant de restaurer les connexions
électriques. 15 secondes est environ le temps que prendra le
voyant DEL pour s’éteindre et le temps nécessaire avant la
restauration de l’alimentation.
58
Ceci garantit une protection et empêche les dégâts graves éventuels
à la carte mère et à ses composants.
Page 59

Connecteurs Frontaux du Panneau
SPEAKER
Français
F
Français
RESET
HD-LED
19
X
20
PWR-LED
ATX-SW
HD-LED: Voyant DEL IDE Principal/Secondaire
Ce voyant DEL s’allumera lorsqu’on accède au disque dur.
RESET: Commutateur de Réinitialisation
Ce commutateur vous permet de redémarrer sans avoir à éteindre
le système et par conséquent en permettant une durée de vie de
l’alimentation ou du système prolongée.
SPEAKER: Connecteur du Haut-parleur
Il se connecte au haut parleur installé dans le châssis du système.
1
2
ATX-SW: Commutateur d’alimentation ATX
Dépendant des réglages à l’intérieur du BIOS, ce commutateur est
un « bouton d’alimentation à deux fonctions » qui permettra à votre
système d’entrer en mode Soft-Off ou Suspend.
59
Page 60

F
Français
Français
PWR-LED: Voyant DEL d’alimentation / état de veille
Ce voyant DEL s’allumera lorsque le système est allumé. Lorsque le
système est sur le statut S1 (POS – alimentation suspendue) ou S3
(STR – suspendue dans la RAM), il clignotera toutes les secondes.
Note:
Si le système n’a pas démarré et que le voyant DEL
d’alimentation/veille ne s’est pas allumé après le démarrage,
cela peut indiquer que le processeur ou le module n’ont pas
été installés correctement. Veuillez vous assurer qu’ils soient
correctement insérés dans leur support.
Pin
Pin Assignment
HD-LED
(Primary/Secondary IDE LED)
Reserved
ATX-SW
(ATX power switch)
Reserved
RESET
(Reset switch)
SPEAKER
(Speaker connector)
PWR-LED
(Power/Standby LED)
3
HDD LED Power
5
HDD
14
N. C.
16
N. C.
8
PWRBT+
10
PWRBT-
18
N. C.
20
N. C.
7
Ground
9
H/W Reset
13
Speaker Data
15
N. C.
17
Ground
19
Speaker Power
2
LED Power (+)
4
LED Power (+)
6
LED Power (-) or Standby Signal
60
Page 61

Fentes PCI Express
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 1)
PCI Express x1
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 3)
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 4)
Français
F
Français
PCI Express x16
Installer la carte graphique PCI Express X 16 se conformant aux
spécifications PCI Express dans la fente X 16 du PCI Express. Pour
installer une carte graphique dans la fente x16, aligner la carte
graphique au-dessus de la fente et appuyer vers le bas fermement
jusqu’à ce qu’elle rentre complètement dans la fente. Le clip de
maintien de la fente maintiendra automatiquement la carte graphique
en place.
Configuration des Fentes PCI Express
Bande passante
Mode Graphique
CrossFire bi directionnel
CrossFire bi directionnel + Physics
PCIE 1
x16
x16
PCIE 3
x16
x16
PCIE 4
N.C.
x4
PCI Express x1
Installer les cartes PCI Express telles que les cartes de réseau ou
autres cartes se conformant avec les spécifications PCI Express dans
la fente PCI Express X1.
61
Page 62

F
Français
Chapitre 3 - RAID
Français
Niveaux du Système RAID
La puce Intel ICH9R permet la configuration RAID sur les lecteurs
Série ATA connectés du SATA 1 au SATA 6. Elle supporte les
systèmes RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 et RAID 5.
La puce JMicron JMB363 permet la configuration RAID sur deux
autres lecteurs Série Serial ATA connectés à SATA 7 et SATA 8. Elle
supporte les systèmes RAID 0 et RAID 1.
RAID 0 (matrice de disque à “0” erreur de tolérance)
RAID 0 utilise deux nouveaux disques durs identiques pour lire et
graver en blocs parallèles. Les données sont divisées en bandes et
chaque bande est gravée alternativement d’un disque à l’autre. Ceci
améliore la performance I/O des disques sur les différents canaux,
cependant aucune tolérance d’erreur n’est admise. Un disque
défaillant résultera en une perte des données dans la matrice.
RAID 1 (matrice de disque à écriture mirroir à tolérance
d’erreur)
RAID 1 copie et conserve une image identique des données d’un
disque à l’autre. Si un disque fonctionne incorrectement, le logiciel de
gestion de la matrice envoie toutes les applications en direction de
l’autre disque puisqu’il contient une copie complète des données du
disque. Ceci améliore la protection des données et accroît la
tolérance des erreurs dans tout le système. Utiliser deux nouveaux
disques durs ou un disque existant et un nouveau disque dur mais
la taille du nouveau disque dur doit être identique ou supérieure à
celle de celui existant.
RAID 0+1 (bande et mirroir)
RAID 0+1 est une combinaison de données mirroir et de bandes
de données apportant les avantages des systèmes RAID 0 et RAID
1. Utiliser quatre nouveaux disques durs ou un disque existant et
trois nouveaux disques pour cette configuration.
62
Page 63

RAID 5
RAID 5 répartit en écriture les données et les informations
concernant la parité sur les disques durs. Il est insensible aux
défaillances et permet d’obtenir de bien meilleures performances des
disques durs ainsi qu’une capacité de stockage accrue.
Réglages
Pour activer la fonctionnalité RAID, les réglages suivants sont
nécessaires:
1. Raccorder les disques durs en série ATA.
2. Configurer le disque ATA en série dans le BIOS.
3. Configurer les systèmes RAID dans le BIOS RAID.
4. Installer le driver RAID lors de l’installation du SE (système
d’expl
5. Installer le Intel Matrix Storage Manager
6. Installer le driver de JMB36X.
ion.
Français
F
Français
).
Etape 1 : Raccorder les disques durs en série ATA.
Se référer au chapitre 2 pour obtenir davantage de détails sur la
connexion des disques durs en série ATA.
Important:
1. S’assurer d’avoir installé les disques en série ATA et d’avoir raccordé les
câbles de données sinon vous ne pourrez entrer dans l’utilitaire BIOS RAID.
2. Faire très attention aux câbles et particulièrement en créant le système RAID.
Un câble endommagé détériorera tout le processus d’installation et le SE. Le
système ne démarrera pas et vous perdrez toutes les données des disques
durs. Veuillez prêter attention à cet avertissement car il n’existe aucun moyen
de récupérer les informations.
Etape 2 : Configurer le disque ATA en série dans le BIOS
1. Allumer le système et appuyer sur <Del> pour rentrer dans le
menu principal du BIOS.
2. Sélectionner le sous menu des périphériques intégrés - sur la
partie de puce correspondant au disque IDE du BIOS
3. Configurer le disque ATA en série dans les champs appropriés.
4. Appuyer sur <Esc> pour retourner au menu principal de l’utilitaire
d’installation du BIOS. Sélectionner “Save & Exit Setup” et
appuyer ensuite sur <Enter>.
5. Taper <Y> et appuyer sur <Enter>.
6. Redémarrer le système.
63
Page 64

F
Français
Etape 3 : Configurer le système RAID dans le BIOS RAID
Français
Configurer le système RAID dans le BIOS RAID Intel.
Lorsque le système démarre et que tous les disques durs ont été
détectés, le message de statut du BIOS Intel apparaîtra. Appuyer sur
la touche <Ctrl>+<I> pour entrer dans l’utilitaire. L’utilitaire vous
permet de créer un système RAID sur des disques durs en série
ATA .
Configurer le système RAID dans le BIOS RAID JMicron
Lorsque le système démarre et que tous les disques durs ont été
détectés, le message de statut BIOS JMicron apparaîtra. Appuyer sur
la touche <Ctrl>+<J> pour entrer dans l’utilitaire. L’utilitaire vous
permet de créer un système RAID sur des disques durs en série
ATA .
Etape 4 : Installer le driver RAID lors de l’installation du SE (système
d’explion.).
Le driver RAID doit être installé lors de l’installation de Windows
XP ou de Windows® 2000 en utilisant la méthode d’installation F6.
Ceci est nécessaire afin d’installer le SE sur un disque dur ou sur un
volume RAID lors du mode RAID ou sur un disque dur lors du
mode AHCI.
1. Lancer l’installation de Windows en démarrant depuis le CD
d’installation.
2. Appuyer sur <F6> lors de la demande dans la ligne de statut en
utilisant la touche F6
partie SCSI ou lors d’un message du driver RAID.
3. Appuyer sur <S> pour « spécifier un appareil supplémentaire ».
4. A ce moment on vous demandera d’insérer une disquette
contenant le driver RAID. Insérer la disquette contenant le driver
RAID.
5. Localiser le lecteur dans lequel vous avez inséré la disquette et
sélectionner le système RAID ou le contrôleur AHCI
correspondant à votre installation du BIOS. Appuyer sur <Enter>
pour confirmer.
si vous avez besoin d’installer une troisième
®
64
Page 65

Vous avez réussi à installer le driver. Cependant vous devez
continuer à installer le SE. Laisser la disquette dans le lecteur de
disquette jusqu’à ce que le système rédémarre tout seul car lors de
l’installation de Windows les fichiers seront copiés depuis la disquette
sur les dossiers d’installation de Windows. Une fois les fichiers
copiés lors de l’installation de Windows, retirer la disquette afin de
laisser l’ordinateur redémarrer après l’installation de Windows.
Etape 5: Installer le Intel Matrix Storage Manager
Etape 6: Installer le driver de JMB36X
Se référer à la version complète du manuel pour les étapes
d’installation du progiciel et du pilote. Veuillez télécharger le manuel
depuis le site Web de DFI: www.DFI.com.
Français
F
Français
65
Page 66

G
Deutsch
Kapitel 1 - Spezifikation
Deutsch
Prozessor
Chipset
Systemspeicher
• LGA 775 CPU Einfaßung für:
- Intel® CoreTM2 Quad und Intel® CoreTM2 Duo
• Intel Erhöhten Technologie Des Gedächtnis-64 (EMT64T)
• Erhöhten Intel SpeedStep Technologie (EIST)
• Intel, das Technologie Hyper-Verlegt (Intel Hyper-Threading)
• Stützt 1600/1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X48 reihe)
Stützt 1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X38 reihe)
®
• Intel
• LP UT/LT X38/X48-T2R
- 4 240-pin-Steckplätze DDR2 DIMM
- Moduln DDR2 667/800 MHz
- Bis zum 12.8GB/s-Bandbreite.
• LP UT/LT X38-T3R
- 4 240-pin-Steckplätze DDR3 DIMM
- Moduln DDR3 800/1066/1333 MHz
- Es liefert bis zu 21Gb/s Bandbreit bei 1333MHz
• 128-bit – Speiher mit den zwei Kanälen
• Bis zum 8GB-Systemspeicher
• DIMMs ohne Dämpfer x8 und x16 DIMMs
chipset
- Nordbrücke:
Intel® X48 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X48 reihe)
Intel® X38 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X38 reihe)
Intel® schneller Speicherzugrifftechnologie
- Südbrücke: Intel® ICH9R
Expansion Schlitz
BIOS
Audio
LAN
• 2 PCI Express (Gen 2) x16-Einbauplätzen (PCIE 1 und PCIE 3)
- 2-way CrossFire mit x16/x16 Bandbreite
- 2-way CrossFire + Physics mit x16/x16/x4 Bandbreite
• 1 PCI Express x1-Einbauplätzen (PCIE 2)
• 1 PCI Express x4-Einbauplätzen (PCIE 4)
• 3 PCI-Einbauplätzen
• Kompatibilität mit Award BIOS, Flash-Speicher (8Mbit)
• CMOS Reloaded
• Bernstein-platine
- Realtek ALC885 8-Kanal HD Audio Codec
- Center/subwoofer, rear R/L und side R/LAudio-
Anschlußbuchsen
- Line-in, line-out und mic-in Audio-Anschlußbuchsen
- 2 S/PDIF coaxial RCA-Anschlüsse
- 1 S/PDIF optischen-Anschlüsse
- 1 interne Audioanschlüsse (CD-in)
- 1 Frontaudioanschluß
• DAC SNR/ADC SNR von 106dB/101dB
• Lossless zufriedene Schutzvollwegtechnologie
• Marvell 88E8052 und Marvell 88E8053 PCIE Gigabit LAN
• Völlig gefällig zu IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T), 802.3u (100BASETX) und 802.3ab (1000BASE-T) standards
66
Page 67

Deutsch
G
Serial ATA mit RAID
IEEE 1394
Porte an der
Rückwand
Internes I/O
• Intel ICH9R chip
- Intel Matrix Storage technologie
- 6 SATA-Vorrichtungen
- SATA bis zu 3Gb/s schnell
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 und RAID 5
• JMicron JMB363 PCI Express und SATA und PATA
- Unterstützung der Festplatten bis zum UltraDMA 100Mbps
- 2 SATA-Vorrichtungen
- SATA bis zu 3Gb/s schnell
- RAID 0 und RAID 1
• VIA VT6307
• Unterstützt 2 100/200/400 Mb/sec porte
• 1 Mini-DIN-6-Anschluß für eine PS/2-Maus
• 1 Mini-DIN-6-Anschluß für eine PS/2-Tastatur
• 1 IEEE 1394-Anschlüsse
• 6 USB 2.0/1.1-Anschlüsse und 2 RJ45 LAN-Anschlüsse
Anschlußfassung für 6 zusätzliche externe USB 2.0/1.1-Anschlüsse
•3
• 1 Anschluß für eine externe IEEE 1394 Schnittstelle
• 1 Anschluß für eine externe serieller DB-9-Anschluß
• 1 Anschluß für eine Bernstein Audiomodul
• 1 Front-Audioanschluss (im Bernstein Audiomodul)
• 1 CD-in interne Audioanschlüsse (im Bernstein Audiomodul)
• 1 S/PDIF optischen-Anschlüsse (im Bernstein Audiomodul)
• 1 Anschluß für die IR-Schnittstelle und 1 CIR-Schnittstelle
• 8 Serial ATA-Anschlüsse
• 1 40-polige IDE-Anschlüsse und 1 Floppy-Anschlüsse
• 1 24-polige Anschlußstecker für das ATX-Netzgerät
• 1 8-polige 12V Anschlußstecker für das ATX-Netzgerät
• 2 4-polige 5V/12V Netzstecker (für FDD)
• 1 Vorderseite Füllung Anschlüsse und 6-ventilator-Anschlüsse
• 1 diagnostischen Außenindikatoren
• EZ Umschaltern (der Knopf der Speisung und des Auslasses)
Deutsch
Energie
Management
Kleinteilmonitor
PCB
• ACPI und OS Directed Power Management
• ACPI STR (Suspend to RAM) funktion
• Wecken bei Betätigung der PS/2 Tastatur/Maus
• Wecken bei USB-Tastatur/Maus
• Wecken bei Klingeln und Wecken des Systems durch das Netzwerk
• RTC-Taktgeber zum Einschalten des Systems
• Wiederherstellung der Wechselstromversorgung nach einem
Ausfall
• Überwachung der Temperatur des CPU / Systems /
Nordbrücke sowie Warnsignal bei Überhitzung
• Überwachung der Spannungen des Vcore/Vdimm/Vnb/VCC5/
12V/V5sb/Vbat
• Überwachung der Geschwindigkeit des Ventilators
• Prozessor-Shutz - Die Ausschaltung bei der Überhitzung – die
automatische Ausschaltung des Computers bei der Überhitzung
• ATX Formfaktor
• 24.5cm (9.64") x 30.5cm (12")
67
Page 68

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
Kapitel 2 - Installieren des Hardware
Jumper
Löschen der CMOS Daten
Löschen der CMOS Daten unter Verwendung von JP2
JP2
312 312
X
1-2 On: Normal
(Standardwert)
Sollten Sie eins der folgenden Probleme haben,
a) die CMOS Daten sind beschädigt.
b) Sie haben das Supervisor oder User Passwort vergessen.
c) die Übertaktungseinstellungen im BIOS haben zur Instabilität des
Systems geführt oder Ihr System bereitet Probleme beim Booten.
so können Sie das System mit den im ROM BIOS gespeicherten
Standardwerten rekonfigurieren.
Um die im ROM BIOS gespeicherten Standardwerte zu laden führen
Sie bitte die folgenden Schritte aus.
1. Schalten Sie das System aus und ziehen Sie den Netzstecker.
2. Setzen Sie die JP2 Pins 2 und 3 auf On. Warten Sie nun einige
Sekunden und setzen Sie dann die JP2 Pins zurück in die
Ausgangsposition, Pins 1 und 2 On.
2-3 On: Lösche
CMOS Daten
68
Page 69

Deutsch
3. Verbinden Sie nun wieder den Netzstecker und schalten Sie das
System ein.
G
Löschen der CMOS Daten unter Verwendung der EZ Clear
Funktion
EZ Clear® umgeht den manuellen Prozess des Setzens der Jumper
zum Löschen des CMOS durch einfache Betätigung der Reset- und
Power-Schalter.
Wichtig:
EZ Clear® wird nur unterstützt wenn das System auf Standby
steht.
Verwendung von EZ Clear®:
1. Stellen Sie sicher, dass das System auf Standby steht.
2. Betätigen Sie die EZ touch Schalter auf dem Systemboard, zuerst
den Reset-Schalter und anschliessend gleichzeitig den PowerSchalter für ca. 4 Sekunden.
®
Deutsch
X
Reset
Sollte das Systemboard bereits in ein Gehäuse eingebaut sein, so
wenden Sie die gleiche Methode mit den Reset- und PowerSchaltern an der Frontseite des Gehäuses an.
3. Nach den 4 Sekunden lassen Sie zuerst den Power- und
anschliessend den Reset-Schalter los.
4. Das CMOS wird auf die Werkseinstellungen zurückgesetzt.
Power
69
Page 70

G
Deutsch
PS/2 Power Select
Deutsch
JP7
312
31
2
X
1-2 On: 5V
(Standard)
Wichtig:
Die 5VSB Stromquelle Ihres
Netzteils muss ≥720mA unterstützen.
Die Auswahl von 5VSB erlaubt es Ihnen, Ihr System per PS/2 Keyboard oder PS/2 Maus aufzuwecken.
2-3 On:
5VSB
USB Power Select
Die Auswahl von 5VSB erlaubt es Ihnen, Ihr System per USB Keyboard oder USB Maus aufzuwecken.
USB 6-11
(JP5)
USB 0-5
(JP6)
X
1-2 On: 5V
(Standard)
1-2 On: 5V
(Standard)
X
3
2
1
2-3 On:
5VSB
312 312
2-3 On:
5VSB
3
2
1
70
Wichtig:
Sollten Sie die Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Maus Funktion für 2 USB Ports
verwenden, so muss die 5VSB Stromquelle Ihres Netzteils ≥1.5A unterstützen. Für
3 oder mehr USB Ports , muss die 5VSB Stromquelle Ihres Netzteils ≥2A
unterstützen.
Page 71

Speaker On/Off Auswahl
312 312
JP8
1-2 On:
Speaker Off
2-3 On:
Speaker On
(Standard)
X
Deutsch
Summer
G
Deutsch
Das Systemboard ist mit einem Summer ausgestattet, der als
Lautsprecher des PC’s dient. Ab Werk ist die Standardeinstellung des
Summers “on” wodurch Sie die Warnungen und Piep-Nachrichten des
Systems hören. Falls Sie externe Lautsprecher verwenden wollen, so
schalten Sie diese Funktion durch das Setzen der JP8 Pins 1 und 2
auf On aus.
71
Page 72

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
Zulässiger Start
JP1
312 312
X
1-2 On:
(Standard)
Brücke ist benutzt, um das System zulässig neu zustarten, wenn
das System hängt und Sie das System nicht neu starten können.
1. Schalten Sie das System aus und ziehen Sie den Netzstecker.
2. Setzen Sie die JP1 Pins 2 und 3 auf On. Warten Sie nun einige
Sekunden und setzen Sie dann die Pins zurück in die
Ausgangsposition, JP1 Pins 1 und 2 On.
3. Verbinden Sie nun wieder den Netzstecker und schalten Sie das
System ein. Das System wird neu starten normalerweise ohne
Verlust aller in CMOS gespeicherten Daten.
2-3 On:
Zulässiger Start
72
Page 73

Secondary RTC Reset
Deutsch
G
Deutsch
JP12
312
312
X
1-2 On: Normal
(Standardwert)
Wird die RTC-Batterie entfernt, setzt diese Steckbrücke die
Handhabbarkeit der Registerbits der RTC zurück.
Hinweis:
1. Der SRTCRST# Input muss immer hoch sein, wenn alle
anderen RTC Versorgungslagen laufen.
2. In dem Fall dass die RTC-Batterie leer ist oder ganz fehlt,
muss der SRTCRST# Pin vor dem RSMRST# Pin stehen.
2-3 On:
RTC reset
73
Page 74

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
CPU FSB Select
X
JP14
4
3
2
1
JP15
JP13
Standardmäßig sind alle drei Steckbrücken auf die Pins 1 und 2
gesetzt. Auf diese Weise läuft das System entsprechend dem
Frontside Bus der CPU. Falls Sie die Einstellungen ändern wollen,
finden Sie Informationen in der folgenden Tabelle.
JP14
JP13
JP15
By CPU
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
FSB 800
3-4 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1066
2-3 On
2-3 On
2-3 On
FSB 1333
2-3 On
2-3 On
3-4 On
74
Page 75

Rückseite I/O Ports
Deutsch
G
PS/2
Mouse
PS/2
K/B
PS/2 Ports und IEEE 1394 Ports
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 KB
W
1394-0
W
1394-0
USB 10-11
LAN 2LAN 1
Deutsch
USB 6-7
USB 8-9
Ground
TPB-
+12V (fused)
Ground
TPA-
1394-1
2
1
TPA+
Ground
10
9
Key
TPB+
+12V (fused)
W
PS/2 Maus und PS/2 Keyboard Ports
Diese Ports werden zum Anschluss von PS/2 Maus und PS/2 Keyboard verwendet.
IEEE 1394 Ports
Der IEEE 1394-0 Port dient dem Anschluss von Audio-/VideoGeräten oder externen Massenspeichern. Der 10-Pin Anschluss
erlaubt Ihnen die Verbindung mit einem zusätzlichen 1394-Gerät. Ihr
1394 Port könnte auf einem Halterungsblech befestigt sein.
Installieren Sie das Blech in eine verfügbare Halterung an der
Rückseite des Gehäuses und verbinden Sie das Kabel des 1394
Ports mit dem entsprechenden Anschluss.
75
Page 76

G
Deutsch
USB Ports und LAN Ports
Deutsch
LAN 1
USB 9
USB 8
USB 11
USB 10
LAN 2
USB 7
USB 6
USB Ports
W
W
W
USB 4-5
USB 2-3
USB 0-1
-Data
+Data
-Data
+Data
GND
N. C.
10
Key
GND
9
VCC
2
1
VCC
Über die USB Ports verbinden Sie USB 2.0/1.1 Geräte. Die 10-Pin
Anschlüsse erlauben Ihnen den Anschluss von 6 zusätzlichen USB
2.0/1.1 Ports. Ihre USB Ports könnten auf einem Halterungsblech
befestigt sein. Installieren Sie das Blech in eine verfügbare Halterung
an der Rückseite des Gehäuses und verbinden Sie das Kabel des
USB Ports mit dem entsprechenden Anschluss.
LAN Ports
Über die LAN Ports können Sie das Systemboard über einen
Netzwerk-Hub mit einem lokalen Netzwerk verbinden.
76
Page 77

Bernstein Audio-Modul
Line-in
Line-out
Deutsch
1
Left audio channel
Ground
Ground
Right audio channel
G
Deutsch
Mic-in
Center/
Subwoofer
Rear R/L
Side R/L
S/PDIF-out
S/PDIF-in
4
CD-in
10 9
Line out_LeftLine out Jet Detect
Sense
Line out_Right
Mic_Right
Mic_Left
12
Side view
Bernstein audio
module connector
Mic Jet Detect
SPDIF in
GND
SPDIF out
Key
+5V
N. C.
Vcc
GND
Front audio
5
Optical S/PDIF
1
Center/Subwoofer Stecker (Orange)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie die Center und Subwoofer
Lautsprecher Ihres Audiosystems mit dem System.
Rear Right/Left Jack (Schwarz)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie die hinten links und hinten rechts
Lautsprecher Ihres Audiosystems mit dem System.
Side Right/Left Jack (Grau)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie die seitlich links und seitlich rechts
Lautsprecher des Audiosystems mit dem System.
Line-in Stecker (Hellblau)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie beliebige Audiogeräte wie z.B.
Stereoanlagen, CD-Player, Kassettenrecorder, AM/FM Radios, Synthesizer, etc.mit dem System.
Line-out Stecker (Hellgrün)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie die vorne links und vorne rechts
Lautsprecher Ihres Audiosystems mit dem System.
77
Page 78

G
Deutsch
Mic-in Stecker (Pink)
Mit diesem Stecker verbinden Sie ein externes Mikrophon mit dem
System.
Deutsch
Coaxial RCA S/PDIF-in und SPDIF-out Stecker
Mit diesen Steckern verbinden Sie externe Audioausgabegeräte die
koaxiale S/PDIF Kabel verwenden.
CD-in Anschluss
Der CD-in Anschluss wird verwendet, um Audio von einem CDROM Laufwerk, einer TV Tuner oder MPEG-Karte zu empfangen.
Front Audio Anschluss
Mit dem Front Audio Anschluss werden die line-out und mic-in
Stecker die sich an der Frontseite des Gehäuses befinden verbunden.
Optischer S/PDIF Anschluss
Mit dem optischen S/PDIF Anschluss werden externe
Audioausgabegeräte die optische S/PDIF Kabel verwenden
verbunden.
Wichtig:
Verwenden Sie NICHT optische S/PDIF und koaxiale RCA S/
PDIF gleichzeitig.
Installation des Bernstein Audio Moduls
1. Das Bernstein Audio Modul
wird mit dem Systemboard
anhand des mitgelieferten
Audiokabels verbunden.
78
Page 79

2. Verbinden Sie das eine
Ende des Audiokabels mit
dem Bernstein
Audioanschluss auf dem
Systemboard und das
andere Ende mit dem
entsprechenden Anschluss
auf dem Audiomodul.
X
Deutsch
G
Deutsch
11
12
3. Die Länge des Audiokabels
bietet Ihnen die Option und
Flexibilität, das Modul in jede
beliebige Halterung auf der
Rückseite des Gehäuses
einzusetzen. Lösen Sie die
Schraube der Halterung, die
Sie für das Audiomodul
vorgesehen haben und
entfernen Sie das Blech.
Setzen Sie das Bernstein Audio Module in die Halterung ein und sichern Sie es mit der vorher
gelösten Schraube.
1
2
Bernstein audio
module connector
79
Page 80

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
I/O Anschlüsse
Serial ATA Anschlüsse
SATA 7-8
SATA 1-2
SATA 3-4
SATA 5-6
Über die Serial ATA (SATA) Anschlüsse werden Serial ATA
Laufwerke angeschlossen. Verbinden Sie das eine Ende des Serial ATA
Kabels mit dem Serial ATA Anschluss und das andere Ende mit
Ihrem Serial ATA Gerät.
ICH9R unterstützt SATA 1 zu SATA 6.
JMB363 unterstützt SATA 7 zu SATA 8.
RAID-Konfiguration
Bitte lessen Sie im Kapitel RAID dieses Handbuchs, um weitere
Informationen zur Erzeugung von RAID auf Serial ATA Laufwerken zu
erhalten.
80
Page 81

Floppy Disk Drive Anschluss und IDE Anschluss
Deutsch
G
40
39
X
21
IDE
33
X
34
FDD
Floppy Disk Drive Anschluss
Über den Floppy Disk Drive Anschluss werden Floppy-Laufwerke
angeschlossen. Er verfügt über einen Verbindungsmechanismus der
eine Fehlinstallation vermeidet. Verbinden Sie ein Ende des FloppyKabels mit dem Anschluss auf dem Board und das andere Ende mit
dem Floppy-Laufwerk. Das farblich markierte Ende des Kabels muss
mit Pin 1 des Anschlusses in Übereinstimmung gebracht werden.
1
2
Deutsch
IDE Disk Drive Anschluss
Über den IDE Disk Drive Anschluss werden 2 IDE Laufwerke
angeschlossen. Er verfügt über einen Verbindungsmechanismus der
eine Fehlinstallation vermeidet. Das IDE-Kabel hat 3
Steckverbindungen, eine für den IDE Disk Drive Anschluss und die
anderen beiden für die IDE-Laufwerke. Der Stecker am Ende des
Kabels ist für das Master-Laufwerk und der in der Mitte des Kabels
ist für das Slave-Laufwerk vorgsehen. Das farblich merkierte Ende
des Kabels muss mit Pin 1des Anschlusses in Übereinstimmung
gebracht werden.
Bitte beachten:
Wenn Sie 2 IDE-Laufwerke verwenden muss eins als Master
und eins als Slave eingestellt sein. Folgen Sie den Anweisungen
des Herstellers der Laufwerke bezüglich der Einstellungen der
Jumper und/oder Schalter.
81
Page 82

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
IrDA, CIR und Serial (COM) Anschlüsse
IRRX
Ground
IRTX
IrDA
51
CIR
51
N. C.
VCC
COM
CIRTX
Ground
DSR
DTR
TD
CTS
RTS
GND
RI
RD
2
1
CD
N. C.
CIRRX
W
X
9
5VSB
IrDA und CIR Anschlüsse
Über diese Anschlüsse werden IrDA Module und/oder CIR Module
angeschlossen.
Bitte beachten:
Die Anordnung der PIN-Funktionen kann bei einigen IrDA/CIR
Kabeln abweichend von der Anordnung auf dem Systemboard
sein. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Pinbelegungen des Kabels
und des IrDA/CIR Anschlusses auf dem Systemboard
miteinander übereinstimmen.
82
Um die IrDA/CIR Funktion nutzen zu können könnte es notwendig
sein, die entsprechenden Treiber in Ihrem Betriebssystem zu
installieren. Informationen hierzu erhalten Sie aus dem
Benutzerhandbuch des Betriebssystems.
Serial (COM) Anschluss
Mit dem Serial (COM) Anschluss verbinden Sie Modems, serielle
Drucker, Display Terminals oder andere serielle Geräte mit dem System. Ihr COM Anschluss könnte auf einem Halterungsblech befestigt
sein. Installieren Sie das Blech in eine verfügbare Halterung an der
Rückseite des Gehäuses und verbinden Sie das Kabel des seriellen
Page 83

Deutsch
Ports mit dem entsprechenden Anschluss. Das farblich markierte
Ende des Kabels muss mit Pin 1 des Anschlusses in
Übereinstimmung gebracht werden.
G
Lüfteranschlüsse
N. C.
N. C.
3
X
1
X
X
N. C.
Power
Ground
NB fan
Power
Ground
13
3rd fan
Power
Ground
13
2nd fan
1
X
4
CPU fan
Power
Ground
13
X
1st fan
Power
Ground
X
13
System fan
Ground
Power
Speed
Control
N. C.
N. C.
Deutsch
Sense
Über diese Lüfteranschlüsse werden Lüfter mit dem System
verbunden. Diese Lüfter sorgen für ausreichende Luftzirkulation im
Gehäuse und verhindern somit ein Überhitzen der CPU und der
Komponenten auf dem Systemboard.
83
Page 84

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
EZ Touch Schalter
Reset Power
X
Das Vorhandensein von Power- und Reset-Schaltern auf dem
Systemboard ist speziell für DIY-User sehr anwenderfreundlich. Sie
bieten die Möglichkeit bequem das System ein-/auszuschalten und
einen Reset durchzuführen und somit die Einstellungen des
Systemboards zu verfeinern bevor es in ein Gehäuse eingebaut wird.
84
Page 85

LEDs
Deutsch
DRAM
Power LED
G
Deutsch
Standby
Power LED
Diagnostic
LED
DRAM Power LED
Diese LED leuchtet wenn das System eingeschaltet ist.
Standby Power LED
Diese LED leuchtet wenn das System im Standby Modus ist.
Diagnostic LED
Die Diagnostic LED zeigt POST Codes an. POST (Power-On Self
Tests), die durch das BIOS gesteuert werden, werden bei jedem
Start des Systems durchgeführt. Der POST erkennt den Status des
Systems und seiner Komponenten. Jeder durch die LED angezeigte
Code entspricht einem bestimmten Systemstatus.
.
.
.
.
Warnung:
.
.
.
.
Eine aufleuchtende DRAM Power LED und/oder Standby Power
LED zeigt an, dass die DIMM-Sockel und/oder PCI-Steckplätze
unter Spannung stehen. Schalten Sie den PC aus und ziehen Sie
den Netzstecker bevor Sie Speichermodule oder Zusatzkarten
installieren. Bei Nichtbeachtung drohen erhebliche Schäden am
Motherboard und den Komponenten.
85
Page 86

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
Stromanschlüsse
Verwenden Sie ein Netzteil, dass den ATX12V Netzteil
Designrichtlinien Version 1.1 entspricht. Ein ATX12V Netzteil verfügt
über einen standard 24-Pin ATX Hauptstromanschluss. Verbinden Sie
diese Stromanschlüsse.
+3.3VDC
+12VDC
+12VDC
X
PWR_OK
+5VDC
+5VDC
+3.3VDC
+3.3VDC
+5VSB
COM
COM
COM
12 24
COM
+5VDC
+5VDC
+5VDC
NC
COM
COM
COM
PS_ON#
COM
-12VDC
+3.3VDC
131
Ihr Netzteil könnte über einen 8-Pin oder 4-Pin +12V Anschluss
verfügen. Der +12V Anschluss erlaubt die Bereitstellung von mehr
+12VDC Spannung für das Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) des
Prozessors. Falls verfügbar sollten Sie bevorzugt den 8-Pin Anschluss
verwenden, falls nicht vorhanden den 4-Pin Anschluss.
+12V
X
58
14
Ground
86
Page 87

Deutsch
Die Stromanschlüsse des Netzteils sind so entworfen, dass die die
24-Pin und 8-Pin Anschlüsse nur in einer Ausrichtung verbunden
werden können. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Ausrichtung korrekt ist
bevor Sie die Anschlüsse verbinden.
G
Die FDD-Typ Stromanschlüsse sind zusätzliche Stromanschlüsse.
Sollten Sie mehr als eine Grafikkarte verwenden, so empfehlen wir,
dass Sie die Stromkabel des Netzteils mit den 5V/12V
Stromanschlüssen verbinden. Dies wird das komplette System mit
mehr Stabilität versorgen. Das Systemboard wird nach wie vor
arbeiten, auch wenn die zusätzlichen Stromanschlüsse nicht
angeschlossen sind.
1
+5V
Ground
Ground
4
+12V
Deutsch
Das Systemboard benötigt zum Betrieb ein Netzteil mit mindestens
300 Watt. Ihre Systemkonfiguration (CPU Power, Grösse des
Speichers, Zusatzkarten, Perpheriegeräte, etc.) können den
Strombedarf des Systems zusätzlich erhöhen. Um sicher zu stellen,
dass ausreichende Stromversorgung zur Verfügung steht empfehlen
wir, ein Netzteil mit mindestens 400 Watt oder mehr zu verwenden.
Wichtig:
Ungenügende Stromversorgung kann zu Instabilität führen oder
fehlerhafte Funktion von Zusatzkarten und Peripheriegeräten
zur Folge haben. Die Berechnung des Stromverbrauchs des Systems ist wichtig, um sicherzustellen, dass das eingesetzte
Netzteil den Anforderungen des Systems entspricht.
87
Page 88

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
Neustart des PC’s
In der Regel lässt sich der PC wie folgt ausschalten:
1. Betätigung des Power-Schalters auf der Frontseite des Gehäuses.
oder
2. Betätigung des Power-Schalters der sich auf dem Systemboard
befindet (Anmerkung: nicht alle Systemboards verfügen über
diesen Schalter).
Sollten Sie jedoch die Stromzufuhr zu Ihrem PC komplett
unterbrechen wollen, so schalten Sie das Netzteil aus oder ziehen Sie
den Netzstecker. Wenn Sie den PC sofort neustarten wollen sollten
Sie unbedingt die folgenden Schritte befolgen.
1. Die Dauer in der sich der Strom komplett entlädt ist von Netzteil
zu Netzteil unterschiedlich. Diese Länge der Zeitspanne hängt
dabei stark von der Systemkonfiguration wie z.B. der Wattzahl des
Netzteils, der Anordnung des Netzteils oder der Anzahl der an
das System angeschlossenen Peripheriegeräte ab. Aus diesem
Grund empfehlen wir, auf das Auflleuchten der Standby Power
LED (siehe dazu auch den Abschnitt “LED’s” in diesem Kapitel) zu
warten.
2. Warten Sie mit dem Einschalten des PC’s bis die Power LED
etwa 6 Sekunden erloschen ist.
Sollte das Systemboard bereits in ein Gehäuse eingebaut sein und
die Standby Power LED dadurch nicht sichtbar sein, so warten
Sie bitte 15 Sekunden bevor Sie die Stromzufuhr wieder
herstellen. Es dauert etwa 15 Sekunden bis die LED erlischt und
dies ist auch die Zeitspanne, die vor einem Neustart notwendig
ist.
88
Die o.g. Regeln stellen einen Schutz vor Beschädigung des
Motherboards und der Komponenten dar.
Page 89

Frontanschlüsse
SPEAKER
RESET
HD-LED
Deutsch
G
Deutsch
19
X
20
PWR-LED
ATX-SW
HD-LED: Primäre/Sekundäre IDE LED
Diese LED leuchtet auf, wenn auf die Festplatte zugegriffen wird.
RESET: Reset-Schalter
Dieser Schalter erlaubt es Ihnen einen Neustart durchzuführen ohne
die Stromzufuhr zu unterbrechen. Dadurch wird die Lebensdauer des
Netzteils und des Systems verlängert.
SPEAKER: Lautsprecheranschluss
Dieser stellt die Verbindung zu dem im System installierten
Lautsprecher her.
1
2
ATX-SW: ATX Power-Schalter
Abhängig von den Einstellungen im BIOS Setup ist dieser Schalter ein
“dual function power button” der es erlaubt Ihr System in den SoftOff oder Suspend Modus zu versetzen.
89
Page 90

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
PWR-LED: Power/Standby LED
Diese LED leuchtet, wenn die Stromzufuhr des Systems eingeschaltet
ist. Sollte das System sich im S1 (POS - Power On Suspend) oder
S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) Status befinden, so blinkt die LED
einmal pro Sekunde.
Bitte beachten:
Sollte das System nicht hochfahren und die Power/Standby LED
nicht aufleuchten nachdem Sie den Power-Schalter betätigt
haben, so könnte dies darauf hinweisen, dass die CPU oder die
Speichermodule nicht korrekt installiert wurden. Bitte stellen Sie
sicher, dass diese ordnungsgemäss in ihren entsprechenden
Steckplätzen eingesetzt sind.
Pin
Pin Assignment
HD-LED
(Primary/Secondary IDE LED)
Reserved
ATX-SW
(ATX power switch)
Reserved
RESET
(Reset switch)
SPEAKER
(Speaker connector)
PWR-LED
(Power/Standby LED)
3
HDD LED Power
5
HDD
14
N. C.
16
N. C.
8
PWRBT+
10
PWRBT-
18
N. C.
20
N. C.
7
Ground
9
H/W Reset
13
Speaker Data
15
N. C.
17
Ground
19
Speaker Power
2
LED Power (+)
4
LED Power (+)
6
LED Power (-) or Standby Signal
90
Page 91

PCI Express Steckplätze
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 1)
PCI Express x1
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 3)
PCI Express x16 (PCIE 4)
Deutsch
G
Deutsch
PCI Express x16
Installieren Sie eine PCI Express x16 Grafikkarte, die den PCI Express
Spezifikationen entspricht in den PCI Express x16 Steckplatz. Zur Installation der Grafikkarte in den x16 Steckplatz richten Sie die Grafikkarte
über dem Steckplatz aus und drücken sie dann in den Steckplatz bis
sie fest sitzt. Der Halteclip des Steckplatzes wird automatisch
zuschnappen und die Grafikkarte im Steckplatz verankern.
PCI Express Steckplatz Konfiguration
Bandbreite
Grafik-Modus
2-way CrossFire
2-way CrossFire + Physics
PCIE 1
x16
x16
PCIE 3
x16
x16
PCIE 4
N.C.
x4
PCI Express x1
Installieren Sie PCI Express Karten wie z.B. Netzwerkkarten oder
andere Karten, die den PCI Express Spezifikationen entsprechen in
den PCI Express x1 Steckplatz.
91
Page 92

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
Kapitel 3 - RAID
Intel ICH9R chip erlaubt Konfiguration RAID auf Serial ATA
Laufwerke, welche an SATA 1 zu SATA 6 angeschlossen sind. Er
unterstützt RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 und RAID 5.
JMicron JMB363 chip erlaubt Konfiguration RAID auf andere 2 Serial
ATA Laufwerke, welche an SATA 7 und SATA 8 angeschlossen sind.
Er unterstützt RAID 0 und RAID 1.
RAID Level
RAID 0 (Festplattenanordnung in Datenstreifen ohne
Fehlertoleranz)
RAID 0 verwendet zwei neue identische Festplatten zum parallelen,
in überlappenden Blöcken liegenden Lesen und Schreiben von Daten.
Die Daten werden in Streifen aufgeteilt und jeder Streifen wird
alternativ auf die Festplatten geschrieben. Dies erhöht die I/O Performance der Festplatten, bietet jedoch keine Fehlertoleranz. Eine
fehlerhafte Festplatte kann in diesem RAID zu Datenverlust führen.
RAID 1 (Gespiegelte Festplattenanordnung mit Fehlertoleranz)
RAID 1 kopiert und behält eine identische Spiegelung der Daten
von einem Laufwerk zum anderen bei. Sollte eines der Laufwerke
ausfallen, so leitet die Management Software der
Festplattenanordnung alle Applikationen auf das andere Laufwerk um,
da dort die gleichen Daten gespiegelt vorhanden sind. Dies erhöht
den Schutz Ihrer Daten und erhöht die Fehlertoleranz des
kompletten Systems. Verwenden Sie hierfür zwei neue Laufwerke
oder ein bereits vorhandes und ein neues aber beachten Sie, dass
das neue Laufwerk die gleiche oder eine grössere Kapazität als das
bereits vorhandene aufweisen muss.
92
RAID 0+1 (Datenstreifen und Spiegelung)
RAID 0+1 ist eine Kombination der Speicherung der Daten in
Streifen und als Spiegelung und bietet somit die Vorteile sowohl von
RAID 0 als auch von RAID 1. Verwenden Sie für diese Konfiguration
vier neue Laufwerke oder ein bereits vorhandenes und drei neue
Laufwerke.
Page 93

RAID 5
RAID 5 führt Striping von sowohl Daten- als auch
Paritätsinformationen über Festplatten aus. Zu seinen Vorteilen zählen
Fehlertoleranz, eine bessere Festplattenleistung und höhere
Speicherkapazität.
Einstellungen
Um die RAID-Funktion zu aktivieren sind folgende Einstellungen
notwendig.
1. Schliessen Sie die Serial ATA Laufwerke an.
2. Konfigurieren Sie Serial ATA im Award BIOS.
3. Konfigurieren Sie RAID im RAID BIOS.
4. Installieren Sie den RAID-Treiber während der Installation des
Betriebssystems.
5. Installation des Intel Matrix Storage Manager
6. Installation des JMB36X Driver
Deutsch
G
Deutsch
Schritt 1: Schliessen Sie die Serial ATA Laufwerke an
Informationen zum Anschluss der Serial ATA Laufwerke finden Sie in
Abschnitt 2.
Wichtig:
1. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Serial ATA Laufwerke installiert und dass die
Datenkabel korrekt angeschlossen sind. Ansonsten ist es nicht möglich, das
RAID BIOS Utility Programm zu verwenden.
2. Behandeln Sie die Kabel sehr vorsichtig, besonders beim Einrichten von RAID.
Beschädigte Kabel können den kompletten Installationsprozess zunichte
machen und das Betriebssystem beschädigen. Das System wird nicht
hochfahren und Sie werden alle Daten auf den Festplatten verlieren. Bitte
beachten Sie unbedingt diese Warnung, verlorengegangene Daten können
nicht wieder hergestellt werden!
Schritt 2: Konfiguration von Serial ATA im Award BIOS
1. Schalten Sie das System ein und drücken Sie dann die <Del>
Taste, um in das Hauptmenü des Award BIOS zu gelangen.
2. Wählen Sie das Integrated Peripherals Untermenü – Abschnitt
OnChip IDE Device des BIOS aus.
3. Konfigurieren Sie Serial ATA in den entsprechenden Feldern.
93
Page 94

G
Deutsch
Deutsch
4. Drücken Sie die <Esc> Taste um ins Hauptmenü des BIOS Setup
zu gelangen. Wählen Sie “Save & Exit Setup” aus und drücken Sie
dann die <Enter> Taste.
5. Schreiben Sie <Y> und drücken dann die <Enter> Taste.
6. Führen Sie einen Neustart des Systems durch.
Step 3: Konfiguration von RAID im RAID BIOS
Konfigurieren Sie RAID im Intel RAID BIOS
Wenn das System hochfährt und alle Laufwerke erkannt wurden
erscheint die AMD BIOS Status Nachricht auf dem Bildschirm.
Drücken Sie die <Ctrl>+<I> Taste um das Programm aufzurufen.
Das Programm ermöglicht es Ihnen ein RAID system auf den Serial
ATA Laufwerken einzurichten.
Konfiguration von RAID im JMicron RAID BIOS
Wenn das System hochfährt und alle Laufwerke erkannt wurden
erscheint die Silicon Image BIOS Status Nachricht auf dem Bildschirm.
Drücken Sie die <Ctrl>+<J> Taste um das Programm aufzurufen.
Das Programm ermöglicht es Ihnen ein RAID System auf den Serial
ATA Laufwerken einzurichten.
Schritt 4: Installation des RAID Treibers während der Installation des
Betriebssystems.
Der RAID Treiber muss während der Installation von Windows® XP
oder Windows® 2000 per F6 Installationsmethode eingerichtet
werden. Dies ist notwendig um das Betriebssystem auf eine
Festplatte oder RAID System zu installieren die im RAID-Modus sind
oder auf eine Festplatte wenn sie im AHCI-Modus ist.
1. Starten Sie das Windows Setup indem Sie von der InstallationsCD booten.
2. Drücken Sie die <F6> Taste, wenn die Nachricht ‘Press F6 if you
need to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver’ auf dem
Bildschirm erscheint.
3. Wählen Sie <S> für “Specify Additional Device” aus.
4. Nun werden Sie aufgefordert eine Diskette die den RAID Treiber
enthält einzulegen. Legen Sie die mitgelieferte RAID Treiberdiskette
ein.
94
Page 95

Deutsch
5. Wählen Sie das Laufwerk aus in das Sie die Diskette eingelegt
hatten und wählen Sie anschliessend den RAID oder AHCI Controller der mit Ihrem BIOS Setup übereinstimmt. Drücken Sie die
<Enter> Taste zur Bestätigung.
G
Sie haben nun den Treiber erfolgreich installiert. Sie müssen aber
dennoch mit der Installation des Betriebssystems fortfahren. Belassen
Sie die Diskette im Floppy-Laufwerk bis das System automatisch
neustartet. Das Windows Setup muss noch erneut die Dateien von
der Diskette in die Windows Installationsordner kopieren. Nachdem
das Windows Setup die Dateien kopiert hat können Sie die Diskette
entfernen, so dass das Windows Setup wie erforderlich neustarten
kann.
Schritt 5: Installation des Intel Matrix Storage Manager
Schritt 6: Installation des JMB36X Driver
Es bezieht sich auf ausführliche Version der Montageanweisung für
Dienstprogramm und Treiber. Bitte download die Montageanweisung
von der DFI’s Website: www.DFI.com.
Deutsch
95
Page 96

S
Español
Chapter 1 - Especificaciones
Español
Procesador
Chipset
Memoria de Sistema
• LGA 775 Zócalo de la CPU para:
- Intel® CoreTM2 Quad y Intel® CoreTM2 Duo
• Intel Realzaron Tecnología De la Memoria 64 (EMT64T)
• Realzaron La Tecnología De Intel SpeedStep (EIST)
• Intel Hiperactivo-Que rosca Tecnología (Intel Hyper-Threading)
• 1600/1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X48 serie)
1333/1066/800MHz FSB (LP UT/LT X38 serie)
®
• Intel
• LP UT/LT X38/X48-T2R
• LP UT/LT X38-T3R
• Memoria de dos canales (128-bit)
• Hasta 8GB de memoria sistémica
• Sólo unbuffered x8 y x16 DIMM
chipset
- Puente norte:
®
Intel
X48 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X48 serie)
Intel® X38 Express chipset (LP UT/LT X38 serie)
Tecnología rápida del acceso de memoria de Intel
- Puente sur: Intel® ICH9R
- 4 240-pin mortajas DDR2 DIMM
- Soporta DDR2 667/800 MHz
- Hasta 12.8GB/s de ancho de banda
- 4 240-pin mortajas DDR3 DIMM
- Soporta DDR3 800/1066/1333 MHz
- Entrega la banda ancha de hasta 21Gb/s a 1333MHz
®
96
Ranuras de
Expansión
BIOS
Audio
LAN
• 2 ranuras PCI Express (Gen 2) x 16 (PCIE 1 y PCIE 3)
- CrossFire de dos vías a ancho de banda de x16/x16
- CrossFire de dos vías + Física a ancho de banda de x16/
x16/x4
• 1 slot PCI Express x1 (PCIE 2)
• 1 slot PCI Express x4 (PCIE 4)
• 3 slots PCI
• Award BIOS, Memoria Instante (8Mbitios)
• CMOS Reloaded
• Tablero de Bernstein
- Codec de audio Realtek ALC885 de alta definición de 8 canales
- Center/subwoofer, rear R/L y side R/L enchufes de audio
- Line-in, line-out (front R/L) y mic-in enchufes de audio
- 2 puertos de S/PDIF coaxial RCA
- 1 puerto de S/PDIF óptica
- 1 conector de CD-in audio interno
- 1 conectador audio delantero
• DAC SNR/ADC SNR de 106dB/101dB
• Tecnología protección de la contenta lossless de exploración
completa
• Marvell 88E8052 y Marvell 88E8053 PCIE Gigabit LAN
• Completamente a IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T), 802.3u (100BASETX) y 802.3ab (1000BASE-T) estándar
Page 97

Español
S
Dispositivo de
Almacenaje
IEEE 1394
Panel Trasero I/O
Conectador Interno
• Intel ICH9R chip
- Tecnología Intel Matrix Storage
- 6 dispositivo de Serial ATA
- Velocidad SATA de hasta 3Gb/s
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 y RAID 5
• JMicron JMB363 PCI Express y SATA y PATA
- Soporta las unidades duras hasta de UltraDMA 100Mbps
- 2 dispositivo de Serial ATA
- Velocidad SATA de hasta 3Gb/s
- RAID 0 y RAID 1
• VIA VT6307
• Sopor ta 2 ports 100/200/400 Mb/sec
• 1 puerto de ratón y 1 puerto de teclado mini-DIN-6 PS/2
• 1 puerto de IEEE 1394
• 6 puertos de USB 2.0/1.1
• 2 puertos de RJ45 LAN
• 3 conectores para 6 puertos de USB 2.0/1.1 externo adicional
• 1 conector para un puerto de IEEE 1394
• 1 conector para un puerto de DB-9 serie externa
• 1 conector para un módulo de sonido de Bernstein
• 1 connector de sonido delantera (en el módulo de sonido de
Bernstein)
• 1 conector de CD-in (en el módulo de sonido de Bernstein)
• 1 puerto de S/PDIF óptico (en el módulo de sonido de
Bernstein)
• 1 conector de IR y 1 conector de CIR
• 8 conectores de SATA
• 1 conector de IDE y 1 conector de FDD
• 1 conector 24-pin de fuente de alimentación de ATX
• 1 conector 8-pin 12V de fuente de alimentación de ATX
• 2 4-fichas conectadores de energía de 5V/12V (FDD-tipo)
• 1 conector de panel delante y 6 conectores de abanicos
• 1 indicadore diagnósticos
• EZ conmutadores (conmutadores de alimentación y reset)
Español
Gerencia de la
Energía
Monitor del
Hardware
PCB
• ACPI y OS Directed Power Management
• ACPI STR (Suspend to RAM) función
• PS/2 Teclado/Ratón y USB Teclado/Ratón de Wake-On
• Wake-On-Ring y Wake-On-LAN
• Temporizador de RTC para encender el sistema
• Recuperación de Fracaso de Energía AC
• Monitores de los CPU / sistema / Puente norte temperaturas y
alarma acalorada.
• Monitores de voltajes de Vcore/Vdimm/Vnb/VCC5/12V/V5sb/
Vbat
• Vigila la velocidad del abanico del abanido
• Protección del procesador - Desconección en caso de
recalentamiento –el ordenador se desconecta automáticamente
en caso de recalentamiento
• ATX forme el factor
• 24.5cm (9.64") x 30.5cm (12")
97
Page 98

S
Español
Español
Chapter 2 - Instalación del Hardware
Puente
Borrar Datos CMOS
Borrar Datos CMOS Usando JP2
JP2
312 312
X
1-2 On
(encendido):
Normal
(predeterminado)
En alguno de los siguientes casos,
a) los datos CMOS se corrompen.
b) ha olvidado la contraseña del supervisor o del usuario.
c) La configuración de overlock en el BIOS causó inestabilidad en el
sistema o problemas en el inicio del mismo.
Se puede configurar nuevamente el sistema con los valores
predeterminados almacenados en la ROM BIOS.
Para cargar los valores predeterminados almacenados en la ROM
BIOS, siga los siguientes pasos.
1. Apague el sistema y desenchufe el cable de alimentación.
2. Coloque en posición de encendido los pines JP2 2 y 3. Aguarde
unos segundos y vuelva el JP2 nuevamente a su configuración
predeterminada, pines 1 y 2 encendidos.
3. Luego, enchufe el cable de alimentación y encienda el sistema.
2-3 On
(encendido):
Borrar datos
CMOS
98
Page 99

Español
S
Borrar Datos de CMOS Mediante la Función EZ Clear
EZ Clear® pasa por alto el proceso manual que utiliza un puente de
conexión para borrar el CMOS al utilizar sólo los botones reset
(reinicio) y power (encendido).
Importante:
EZ Clear® es compatible, solamente, si el sistema cuenta con
alimentación de reserva.
Aplicación del EZ Clear®:
1. Asegúrese que el sistema cuenta con alimentación de reserva.
2. Mediante los interruptores sensibles al tacto EZ de la placa del
sistema, pulse, en primer lugar, el botón Reset y luego el botón
Power en forma simultánea durante, aproximadamente, 4
segundos.
®
Español
X
Reset
Si la placa del sistema se encuentra dentro de un armazón,
aplique el mismo método usando los botones Reset y Power del
panel frontal del mismo.
3. Después de 4 segundos, suelte el botón power y luego, el botón
reset.
4. El CMOS restablecerá la configuración del reloj a sus valores
predeterminados.
Power
99
Page 100

S
Español
Selector de Alimentación PS/2
Español
JP7
312
31
2
X
1-2 On: 5V
(predeterminado)
Importante:
La fuente de alimentación 5VSB de
suministro eléctrico debe admitir
≥720mA.
Seleccionar 5VSB le permitirá utilizar el teclado PS/2 o el ratón PS/2
para despertar el sistema.
2-3 On:
5VSB
Selector de Alimentación USB
Seleccionar 5VSB le permitirá utilizar el teclado USB o el ratón USB
para despertar el sistema.
USB 6-11
(JP5)
USB 0-5
(JP6)
3
X
1-2 On: 5V
(predeterminado)
1-2 On: 5V
X
(predeterminado)
2
1
312
3
2
1
2-3 On:
5VSB
312
2-3 On:
5VSB
100
Importante:
Si utiliza la función Wake-On-teclado/ratón USB para 2 puertos USB, la fuente de
alimentación 5VSB del suministro de electricidad debe admitir≥1.5A. Para 3 o
más puertos USB, la fuente de alimentación 5VSB del suministro de electricidad
debe admitir≥2A.
 Loading...
Loading...