Page 1

Network
Application Platforms
Hardware platforms for next generation networking infrastructure
MR-320
>>
User's Manual
Publication date:2010-07-23
Page 2
About
About
Overview
Icon Descriptions
The icons are used in the manual to serve as an indication
of interest topics or important messages. Below is a
description of these icons:
NOTE: This check mark indicates that
there is a note of interest and is something
that you should pay special attention to
while using the product.
Online Resources
The listed websites are links to the on-line product
information and technical support.
Resource Website
Lanner http://www.lannerinc.com
Product Resources http://assist.lannerinc.com
WARNING: This exclamation point
indicates that there is a caution or
warning and it is something that could
damage your property or product.
Acknowledgement
Intel, Pentium and Celeron are registered trademarks of
Intel Corp.
Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks
of Microsoft Corp.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of
their respective owners.
Compliances
CE
This product has passed the CE test for environmental
specifications. Test conditions for passing included the
equipment being operated within an industrial enclosure.
In order to protect the product from being damaged by
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) and EMI leakage, we strongly
recommend the use of CE-compliant industrial enclosure
products.
FCC Class A
This equipment has been tested and found to comply
with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required
to correct the interference at his own expense.
RMA http://eRMA.lannerinc.com
Copyright and Trademarks
This document is copyrighted, © 2010. All rights are
reserved. The original manufacturer reserves the right to
make improvements to the products described in this
manual at any time without notice.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied,
translated or transmitted in any form or by any means
without the prior written permission of the original
manufacturer. Information provided in this manual is
intended to be accurate and reliable. However, the original
manufacturer assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for
any infringements upon the rights of third parties that
may result from such use.
Network Application Platforms
i
Page 3

TTaTTable of Contentsbeable of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
System Specication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Front Panel Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Rear Panel Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Chapter 2: Hardware Setup 5
Preparing the Hardware Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Installing a CompactFlash Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Chapter 3: Motherboard Information 6
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Board Dimension. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Motherboard Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 4: Building the Bootloader Image 12
Building the U-boot image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Updating the U-boot Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Recovering from a failsafe bootload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Booting from the CompactFlash Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Chapter 5: Bootloader Functionalities 14
Conguring/Save the environment variables:. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Query the Hard Disk information (IDE conguration information):. . . . . . . . . . . .14
Query the CompactFlash Card information (IDE conguration information): . . . . .14
Reading the MII Register: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Reading/Writing the multichip mode switch through the SMI interface . . . . . . . .14
Scanning and displaying PCI device information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
I2C device conguration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Read/Write CPU Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
UART Conguration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Running the Operating System and Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Appendix A: Terms and Conditions 16
Warranty Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
RMA Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
ii
Page 4

Chapter 1
Introduction
Chapter 1: Introduction
Based on a new generation high-performance OCTEON
network processors ( Models have CN50xx series single
and dual core or CN30xx series single and dual core MIPS
processor), the MR-320 offers up to 2 cnMIPS64 cores on a
single chip. The chipset supports a variety of I/O interfaces
including Gigabit Ethernet, USB and Mini-PCI interfaces.
The built-in encryption TCP acceleration, and QoS engine
provides reliable security functions at top speed. These
advanced acceleration technologies are integrated in the
4 port Gigabit Ethernet switch and the dual Gigabit WAN
port, making it a perfect platform for high quality voice,
video and data services.
The Quick Start Guide will takes you through the basic
steps necessary to install your MR-320 System.
Please refer to the chart below for a summary of the
system’s specifications.
System Specification
Features Descriptions
Form Factor
Processor
Max Speed
Processor Cores
Platform
System Memory
Networking
I/O Interface
Expansion
Cooling
Environmental
Parameters
Physical
Dimensions
Power
Approvals &
Compliance
Ordering
Instructions per
Second (Max)
Encryption Engine
Networking Engine
QoS Engine
TCP Acceleration
Technology
Capacity
Storage Interface
NOR Boot Flash
No. of ports (Max)
Controller
Console
USB 2.0
Processor
Temperature,
Ambient Operating
Temperature,
Ambient Storage
Humidity (RH),
Ambient Operating
and Non-Operating
Internal RTC
Dimensions (WxHxD)
Weight
Type / Watts
Input
Output
System
Desktop
OCTEON CN3010/CN5020
500MHz
1
1G
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
DDR2 533MHz
512MB (1GB Max.)
CompactFlash (type II) x 1
8/16 MB
2 GbE (RJ45 x 2)
4 GbE (RJ45 x 4)
Marvell 88E1111 (RGMII
interface), Marvell 88E6161
(RGMII interface)
DB9 x 1
1
Mini-PCI x 1
Passive CPU heatsink
0~40°C
-20~70°C
5% ~ 95%, non condensing
Yes
240 x 300 x155.5mm
(9.4x1.2x6.1 in)
1.3Kg
Adapter
AC 100-240V@50Hz~60Hz
DC 12V 2A
CE Emission, FCC Class A,
RoHS
MR-320A:
CN5020-500,512MB
MB-320C:
CN5020-500,1GB
Network Application Platforms
1
Page 5

Chapter 1
Package Contents
Your package contains the following items:
MR-320 Network Security Platform•
Power cable•
1 crossover Ethernet cable (1.8 meters)•
1 straight-through Ethernet cable (1.8 meters)•
1 RJ-45 to DB-9 female console cable•
Serial-ATA hard drive cable •
1 threaded screw set•
1 ear bracket set (Optional)•
Drivers and user’s manual CD.•
Introduction
Network Application Platforms
2
Page 6
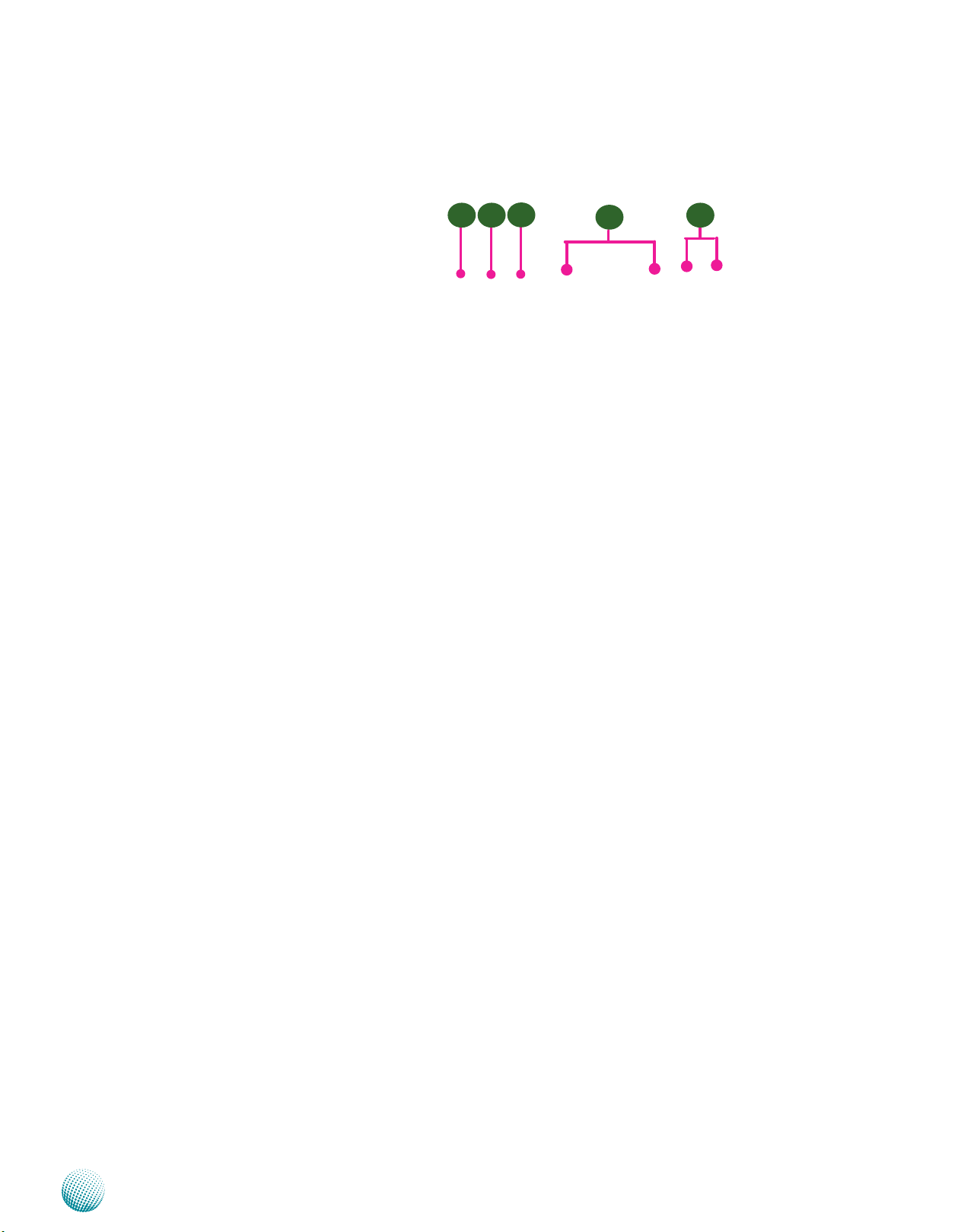
Chapter 1
Front Panel Features
F1 Power Led:
Green indicates that the system is powered on.
F2 Storage LED
Introduction
F3
F2F1
F4
F5
It is an LED indicator (amber) for the CompactFlash card. If the LED is on, it indicates that the system’s storage is functional.
If it is off, it indicates that the system’s storage is not functional. If it is flashing, it indicates data access activities.
F3 Status
If the LED is green, it indicates that the system’s operational state is normal. If it is amber, it indicates that the system is
malfunctioning.
F4 Switch
These LEDs are indicators for the four ports of the switch module on the back panel.
Speed LED: If the LED is amber, it indicates that the connection speed is 1000Mbps. If the LED is green, it indicates that
the connection speed is 100Mbps. And if it is off, it indicates that the speed is 10Mbps.
Link/ACT LED: If the LED is on, it indicates that the port is active. If it blinks, it indicates that there is traffic.
F5 GbE-1/GbE-2
These LEDs are indicators for the two Gigabit Ethernet ports which can serve as WAN connections on the back panel. For
the LED behavior, refer to the above Speed and Link/ACT LED description of F4.
Network Application Platforms
3
Page 7

Chapter 1
Rear Panel Features
Introduction
R1
R2
R1 Power Adapter socket
It requires a DC 12V/2A power input. Only use the power adapter supplied with the MR-320 System.
R2 Reset Switch
It is a hardware reset switch. Use a pointed object to press it 5 seconds then release it to reset the system without
turning off the power.
R3 RS-232 COM Port:
It requires a DB-9 Male Connector. Using suitable RS-232 cable, you can connect an appropriate device, for example, a
terminal console for diagnostics.
Terminal Configuration Parameters: 115200 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit , no flow control.
R3
R4
R5
R6
R4 USB 2.0 Ports
It connects to any USB devices, for example, a flash drive. Besides this external USB port, there is another one offered
with the onboard pin header connectors (refer to Jumper Setting on Chapter 3 Motherboard Information)
R5 4 Ethernet LAN Port switch module (From left to right: LAN1 to LAN4)
Using suitable RJ-45 cable, you can connect MR-320 System to a computer, or to any other piece of equipment that has
an Ethernet connection such as a hub or a switch.
R6 Gigabit WAN Port1(Left) and Port2(Right)
These two ports can be utilized for broadband connection to connect the device to an Internet service. Since the GbE-1
and GbE-2 ports are separate from the above mentioned switch module, implementation of routing is required for the
LAN ports on the switch (R5) to connect the Internet.
Network Application Platforms
4
Page 8

Chapter 2
Hardware Setup
Chapter 2: Hardware Setup
Preparing the Hardware Installation
To access some components and perform certain service
procedures, you must perform the following procedures
first.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury,
electric shock, or damage to the equipment,
remove the power cord to remove power from
the server. The front panel Power On/Standby
button (if there is one) does not completely shut
off system power. Portions of the power supply
and some internal circuitry remain active until AC
power is removed.
Unpower the MR-320 and remove the power cord.1.
Unscrew the 8 threaded screws from the two sides and 2.
two screws at the rear of the top cover of the MR-320
System.
Installing a CompactFlash Card
MR-320 provides one CompactFlash slot slot. Follow the
procedures bellow to install a CompactFlash card.
Align CompactFlash card and the card slot with the 1.
arrow pointing toward the connector.
Push the card to insert into the connector.2.
Accessing the CompactFlash card3.
1
2
Slide the cover backwards and open the cover 3.
upwards.
3
In the linux environment, you could access the CF card
with the following commands:
MR320# mount /dev/cfa1 /mnt/cf
MR320# ls /mnt/cf
To put files on the CF Card, use the following procedures:
2
Connect the CF card. It will usually be assigned as the following 1.
device:
/dev/cfa1
Mount the CF le system. 2.
MR320#mount /dev/cfa1 /mnt/cf
Copy program le(s) to CF. 3.
MR320#cp hello.txt /mnt/cf
Unmount CF le system. 4.
MR320#umount /mnt/cf
Network Application Platforms
5
Page 9

Chapter 3
Chapter 3: Motherboard Information
Block Diagram
The block diagram depicts the relationships among the
interfaces or modules on the motherboard. Please refer
to the following figure for your motherboard’s layout
design.
Motherboard Information
Network Application Platforms
6
Page 10

Chapter 3
Board Dimension
The following diagram shows the physical dimension of
the PCB board. (unit-inches)
Motherboard Information
Network Application Platforms
7
Page 11

Chapter 3
Motherboard Layout
The motherboard layout shows the connectors and
jumpers on the board. Refer to the following picture
as a reference of the pin assignments and the internal
connectors.
M1
JTag(JP4)
Mini-PCI Connector (PX1)
M3
M2
USB Interface
Connector (JP2)
JP1: Flash Mode
M4
Selector (JP1)
Motherboard Information
NetROM Downloader (P3)
M5
CompactFlash Connector
M6
(P1)
Reset Switch (Sw1)
M13
B o o t l o a de r M od e
Jumper
M7
M9
Internal Serial Port (JP6)
M8
External Serial Port (P3)
M10
USB2.0 Ports (P4)
218mm
M11
Ethernet Ports (P5)
146mm
M12
WAN Ports (P6, P7)
Network Application Platforms
8
Page 12

Chapter 3
Motherboard Information
Jumper Settings
M1
Jtag (JP4): The Jtag is a debug port provided as a
means for testing the main board and looking for
possibility of field faults.
Function JTAG_
PIN NO. 5 4 3 2 1
PIN NO. 6 7 8 9 10
Function EJTAG_
M2
Mini-PCI Connector (PX1): The 124-pin Mini-PCI
RST#
slot enables a Mini-PCI expansion module to be
connected to the board. For example, a Wi-Fi module
or a SATA controller. The Mini-PCI bus has 32 bit data
width with 66Mhz.
PIN NO. FUNCTION PIN NO. FUNCTION
1 TIP 2 RING
3 8PMJ-3 4 8PMJ-1
5 8PMJ-6 6 8PMJ-2
7 8PMJ-7 8 8PMJ-4
9 8PMJ-8 10 8PMJ-5
11 LED1_GRNP 12 LED2_YELP
13 LED1_GRNN 14 LED2_YELP
15 CHSGND 16 RESERVED
17 INT-B 18 +5V
19 +3.3V 20 INT-A
21 RESERVED 22 RESERVED
23 GROUND 24 3.3VAUX
25 CLK 26 RST
27 GROUND 28 +3.3V
29 REO 30 GNT
31 +3.3V 32 GROUND
33 AD31 34 PME
35 AD29 36 RESERVED
37 GROUND 38 AD30
39 AD27 40 +3.3V
41 AD25 42 AD28
43 RESERVED 44 AD26
45 C_BE-3 46 AD24
47 AD23 48 IDSEL
49 GROUND 50 GROUND
51 AD21 52 AD22
53 AD19 54 AD20
55 GROUND 56 PAR
57 AD17 58 AD18
59 C_BE-2 60 AD16
61 IRDY 62 GROUND
Network Application Platforms
EJTAG_
TDI
TRST_L
5 4 3 2 1
6 7 8 9 10
NC NC NC EJTAG_TDO
JTAG_TMS 3.3V TAG_
1
2
.
.
.
.
.
124
TCK
63 +3.3V 64 FRAME
65 CLKRUN 66 TRDY
67 SERR 68 STOP
69 GROUND 70 +3.3V
71 PERR 72 DEVSEL
73 C_BE-1 74 GROUND
75 AD14 76 AD15
77 GROUND 78 AD13
79 AD12 80 AD11
81 AD10 82 GROUND
83 GROUND 84 AD9
85 AD8 86 C_BE-0
87 AD7 88 +3.3V
89 +3.3V 90 AD6
91 AD5 92 AD4
93 RESERVED 94 AD2
95 AD3 96 AD0
97 +5V 98 RESERVED-WIP
99 AD1 100 RESERVED-WIP
101 GROUND 102 GROUND
103 AC_SYNC 104 M66EN
105 AC_SDATA_IN 106 AC_SDATA_OUT
107 AC_BIT_CLK 108 AC_CODEC_ID0
109 AC_CODEC_ID1 110 AC_RESET
111 MOD_AUDIO_
113 AUDIO_GND 114 GROUND
115 SYS_AUDIO_OUT 116 SYS_AUDIO_IN
117 SYS_AUDIO_OUT
119 AUDIO_GND 120 AUDIO_GND
121 RESERVED 122 MPCIACT
123 VCC5VA 124 3.3AUX
M3
USB Interface Connector(JP2): It is for connecting
MON
GND118
112 RESERVED
118 SYS_AUDIO_IN GND
the USB module cable. It complies with USB2.0 and
support up to 480 Mbps connection speed. It is
enabled by the OCTEON's integrated PHY through
the I/O bridge.
Function USBGND USBDP1 USBDM1 NC USB_
PIN NO. 5 4 3 2 1
5 4 3 2 1
6 7 8 9 10
PIN NO. 6 7 8 9 10
Function USB_
Port2_
VBUS
M4
Flash Mode Selector(JP1): It is a jumper for selecting
NC USBDM2 USBDP2 USBGND
Port1_
VBUS
the flash mode from either normal or Net mode.
The Net mode is for debugging purpose. Adjust this
jumper to the Net mode when connecting NetROM
connector (JP3).
9
Page 13

Chapter 3
1 2 3
Pin No. Function
Short 1-2 Normal
Short 2-3 Debug
M5
NetRom Connector(JP3): The Net ROM device is the
tool for simulating the boot image during project
developing stage. The NetROM eliminates the need
to burn EPROMs or flash to debug code by utilizing
the Ethernet to download the code images
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Pin No. Function Pin No. Function
1 NET_A19 2 NET_A16
3 NET_A15 4 NET_A12
5 NET_A7 6 NET_A6
7 NET_A5 8 NET_A4
9 NET_A3 10 NET_A2
11 NET_A1 12 NET_A0
13 NET_D0 14 NET_D1
15 NET_D2 16 GND
17 NET_D3 18 NET_D4
19 NET_D5 20 NET_D6
21 NET_D7 22 NET_CE#
23 NET_A10 24 BOOT_OE#
25 NET_A11 26 NET_A9
27 NET_A8 28 NET_A13
29 NET_A14 30 NET_A17
31 NET_A18 32 5V
Motherboard Information
Pin No. Function Pin No. Function
1 Ground 2 Data 3
3 Data 4 4 Data 5
5 Data 6 6 Data 7
7 CS1# 8 N.C.
9 Ground 10 N.C.
11 N.C. 12 N.C.
13 +5V 14 N.C.
15 N.C. 16 N.C.
17 N.C. 18 Addr 2
19 Addr 1 20 Addr 0
21 Data 0 22 Data 1
23 Data 2 24 N.C.
25 N.C. 26 N.C.
27 Data 11 28 Data 12
29 Data 13 30 Data 14
31 Data 15 32 CS3#
33 N.C. 34 IOR#
35 IOW# 36 +5V
37 IRQ 15 38 +5V
39 N.C. 40 N.C.
41 Reset# 42 IOCHRDY
43 DMA REQ# 44 DMA ACK#
45 CF Active 46 PDIAG#
47 Data 8 48 Data 9
49 Data 10 50 Ground
M7
Bootloader Mode Jumper (JP5): There are two
bootloader modes on the MR-320 board; namely,
failsafe and normal bootloader mode. Use this
jumper to switch between them.
1
2
3
Pin No. Function
Short 1-2 Failsafe
Short 2-3 Normal
M6
CompactFlash Connector (P1): It is for connecting
a Compact Flash card to be served as your system’s
storage. The connector is a CF Type II slot which could
fit both CF Type I or CF Type II cards.
50
25
24
.
.
.
.
.
26
Network Application Platforms
.
.
.
.
.
1
M8
External Serial Port(P3): It is the RS-232 serial port.
Pin No. Pin name
1 N.C.
2 CMA3
3 N.C.
4 N.C.
5 N.C.
1 2 3 4 5
9 8 7 6
Pin No. Pin name
6 N.C.
7 MA5
8 N.C.
9 N.C.
10
Page 14

Chapter 3
Motherboard Information
M9
Serial Interface Connectors(JP6): It is for connecting
the RS-232 serial port module cable.
Function GND N.C. TXD 1 RXD 1 VCC3
PIN NO. 5 4 3 2 1
678910
1 2 3 4 5
PIN NO. 10 9 8 7 6
Function N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C.
M10
USB 2.0 Connector (P4): The system provides 2 USB
type A connectors; one is external and the other one
is internal (JP2).
Function USB_Por2_
VBUS
PIN NO. 1 2 3 4
DM2 DP2 USBGND
Tx/ 1000Base-T
Auto-adjusting between 10M/100M/1000M •
connection speed
Auto-negotiation between MDI and MDIX •
crossover at all speeds of operation
Auto-detection of fiber or copper operation•
M13
Reset Switch (SW1): The reset switch can be used to
restart the system without turning off the power.
Pin No. Function
1 2
1 GND
2 Factory_Reset
PIN NO. 6 5
Function GND GND
M11
Ethernet Switch (P5): The Ethernet switch of 4 Gigabit
ports is provided by the Marvell Linkstreet 88E6161
PHY through RGMII. It has the following capabilities:
Auto-adjusting among 10M/100M/1000M •
connection speed
Auto-detecting between Half/Full-duplex mode•
Compliant with theIEEE 802.3 10Base-T/100Base-•
Tx/ 1000Base-T
Compliant with IEEE802.3x flow control and Back •
Pressure
Auto-negotiation between MDI and MDIX•
Store and Forward architecture•
10K jumbo frame support•
M12
Gigabit WAN Port(P6,P7): These two Gbe (RJ-45) ports
are provided by the Marvell 88E1111 GbE PHY It has
the following capabilities:
Compliant with theIEEE 802.3 10Base-T/100Base-•
Network Application Platforms
11
Page 15

Chapter 4
Building the Bootloader Image
Chapter 4: Building the Bootloader Image
Building the U-boot image
To rebuild u-boot for the EM-8230 board, run the following
commands to compile the bootloader configuration file in
the u-boot directory whose path is bootloader/u-boot/:
MR320# cd /bootloader/u-boot
MR320# make MR320_config
MR320# make
It will create a boot image file: u-boot-MR320.bin.
Updating the U-boot Image
There are two u-boot images in flash– the failsafe
bootloader and the normal bootloader. The failsafe
bootloader is programmed by Lanner before the board is
shipped and cannot be updated. The failsafe bootloader
provides a means to recover from a failed loading of the
bootloader. The board also contains a normal bootloader
as well, and that is upgradable. To upgrade the bootloader,
, put the new bootloader image onto a compact flash card,
insert the card to the Main board, and power it up.
And then reset the board.
Note: Remember to configure the Ethernet port
first by setting the following variables:
MR320#setenv ipaddr 192.168.0.2
MR320#setenv serverip 192.168.0.1
MR320#saveenv
Below is the physical address of the flash memory and the
SDRAM for your reference:
0xbfc0 0000
64K
7808K
env
Runtime
0xbfbe 0000
0xbf45 0000
Bootloader
320K
0xbf40 0000
You could also accomplish the update through the serial
port:
MR320# loadb 100000
## Total Size = 0x00795670 = 7951984 Bytes
Load the image into memory with the command:
MR320# fatload ide 0 100000 <bootloader image
filename>
Burn the new bootloader image with the command:
MR320# run bootloader_flash_update
Nuke environment variables on the flash.
MR320# run nuke_env
Reset the board. It will boot up with the new bootloader.
Another method is through the tftp over the network:
The physical address of the flash is: 0xbf400000
MR320#tftp 100000 <bootloader image filename>
MR320#run bootloader_flash_update
## Start Addr = 0x00b000000
Recovering from a failsafe bootload
If booting from the normal bootloader fails, the failsafe
bootloader can be used to recover the normal bootloader
image. You can boot up with the failsafe bootloader
image to recover the normal bootloader when it cannot
bootup successfully.
Adjust jumper JP5 to Failsafe bootloader (refer to jumper
settings, Chapter 3) on the main board. This will select
failsafe bootloader to bootup, and then power on the
board. The failsafe bootloader image should now boot
and press “Crtl - C” to interrupt factory test. The bootloader
prompt should identify itself as the failsafe bootloader.
Following the instructions below to update normal-mode
bootloader:
Power on the system, press “ctrl - C” while the following
messages are displayed during the booting process:
Network Application Platforms
12
Page 16

Chapter 4
Building the Bootloader Image
MR320#bootoctlinux <addr> [coremask=<hexmask>]
Clearing DRAM........ done
BIST check passed.
Bus 0 (CF Card): OK
ide 0: Model: InnoDisk Corp. - iCF2000 512MB
Firm: YUAN1026 Ser#:
Type: Hard Disk
Capacity: 495.6 MB = 0.4 GB (1015056 x 512)
Then, Execute the following procedures:
Load the image to the DRAM with the command:
MR320# fatload ide 0 100000 image-filename
Burn the new image with the command:
MR320# run bootloader_flash_update
Burn the new image with the command:
MR320#run bootloader_flash_update
Nuke environment variables on flash.
MR320# Failsafe bootloader#run nuke_env
Booting from the CompactFlash Card
Type the following command to load the program into
the RAM:
MR320# fatload ide 0 <addr> <file name>
<addr> is the address where the program was loaded
by using the fatload command listed above
<hexmask> optionally specifies which cores will execute
the program on.
Note: To boot up the linux O.S. from the
CompactFlash, use the following method as a
guideline to make the Linux kernel and copy it on
to the CF Card.
Build Linux for the MR-320.
$ cd $(OCTEON_ROOT_Directory)/linux
$ make -s clean
$ make -s kernel
Copy the Linux kernel to a compact flash.
$ mkdir -p /mnt/cfa1
$ mips64-octeon-linux-gnu-strip kernel_2.6/linux/
vmlinux.64
$ fdisk -l /dev/cfa1
$ mount /dev/cfa1 /mnt/cf
$ cp kernel_2.6/linux/vmlinux.64 /mnt/cf
$ sync
$ umount /mnt/cf
<addr> is the address in which the file will be loaded
in memory.
For example: 21000000
<file name> is the name of the bootloader image on
the CF
For Example :traffic-gen
Follow these procedures to boot programs from CF card:
boot diagnostic bin first by typing the command:
MR320# bootoct <addr> [coremask=<hexmask>]
then, boot linux kernel bin by typing the command
Network Application Platforms
13
Page 17

Chapter 5
Bootloader Functionalities
Chapter 5: Bootloader Functionalities
The bootloader has several functionalities including
initializing the SDRAM and FLASH, downloading and
upgrading Bootloader, as well as loading and executing
the Operating System.
Here are some useful commands that can be used in the
Bootloader environment:
Configuring/Save the environment variables:
We are setting the MR-320’s IP address as an example:
MR320# setenv serverip 192.168.0.72
MR320# setenv ipaddr 192.168.0.2
MR320# saveenv
Saving Environment to Flash...
Un-Protected 1 sectors
Erasing Flash...
. done
Erased 1 sectors
Query the CompactFlash Card information (IDE configuration information):
MR320# fatls ide 0
15779752 vmlinux.64
485741 hw-speed-usb
10308320 vmlinux-adk15p.64
13031504 vmlinux_cn3005_ipsec.64
9956160 vmlinux-ipfwd.64
26 smm.conf
26 smm.default
67 firebase.default
67 firebase.conf
29910520 vmlinux_3010se.64
36108 cavmodexp.ko
11 file(s), 0 dir(s)
MR320# fatload ide 0 b000000 vmlinux.64
reading vmlinux.64
20368280 bytes read
Writing to Flash... done
Protected 1 sectors
Then, ping the Ethernet port of the system to check its
connectivity:
MR320# ping 192.168.0.72
Interface 0 has 3 ports (RGMII)
Using octeth0 device
octeth0: Up 1000 Mbps Full duplex (port 0)
host 192.168.0.72 is alive
Query the Hard Disk information (IDE configura-
Use the following command to obtain the information of
tion information):
the hard disk which is the CompactFlash card in our case:
MR320# ide info
IDE device 0: Model: SanDisk SDCFJ-512 Firm: HDX 4.03
Ser#: 012004E0208S4048
Reading the MII Register:
MR320# smi r 0x10 0x0 0x0
MR320# smi w 0x10 0x0 0x0 0x0
Reading/Writing the multichip mode switch through the SMI interface
smi w smiaddr (: smi address, in this case of our board it is:
0x10) devaddr (in this case our PHY address is 0x0~0x3 and
the designated port address is 0x10~0x15) regaddr
or
smi r smiaddr (:smi address, in this case of our board it is:
0x10) devaddr (in this case our PHY address is 0x0~0x3
and the designated port address is 0x10~0x15regaddr
Type: Removable Hard Disk
Capacity: 488.7 MB = 0.4 GB (1000944 x 512)
Network Application Platforms
14
Page 18

Chapter 5
Bootloader Functionalities
The following shows an example of this command:
MR320# smi r 0x10 0x0 0x0
or
For example, type the following command:
MR320# smi w 0x10 0x0 0x0 0x0
Scanning and displaying PCI device information
MR320# pci
base address 0 = 0x80000000
base address 1 = 0x00000000
base address 2 = 0x00000000
base address 3 = 0x00000000
base address 4 = 0x00000000
base address 5 = 0x00000000
cardBus CIS pointer = 0x00000000
Read/Write CPU Register
MR320# write64 1070000000810 01
writing 0x0000000000000001 to address:
0x8001070000000810
MR320# read64 1070000000810
attempting to read from addr: 0x8001070000000810
0x8001070000000810: 0x0000000000000001
MR320# write64 1070000000888 02
writing 0x0000000000000002 to address:
0x8001070000000888
UART Configuration
MR320# setenv console_uart 1
Running the Operating System and Diagnostics
MR320# bootoctlinux <DRAM address>
For example:
MR320# bootoctlinux b000000
sub system vendor ID = 0x1033
sub system ID = 0x0035
expansion ROM base address = 0x00000000
interrupt line = 0x00
interrupt pin = 0x01
min Grant = 0x01
max Latency = 0x2a
2
I
C device configuration
MR320# iprobe
Valid chip addresses: 51 68
MR320# imd 51 0.2
0000: 12 34 56 78 ab cd ef 00 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff .4Vx............
MR320# imw 51 0.2 33
MR320# imd 51 0.2
0000: 33 34 56 78 ab cd ef 00 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff 34Vx............
Network Application Platforms
15
Page 19

Appendix A
Terms and Conditions
Appendix A: Terms and Conditions
Warranty Policy
All products are under warranty against defects in 1.
materials and workmanship for a period of one year
from the date of purchase.
The buyer will bear the return freight charges for 2.
goods returned for repair within the warranty period;
whereas the manufacturer will bear the after service
freight charges for goods returned to the user.
The buyer will pay for repair (for replaced components
3.
plus service time) and transportation charges (both
ways) for items after the expiration of the warranty
period.
If the RMA Service Request Form does not meet the 4.
stated requirement as listed on “RMA Service,” RMA
goods will be returned at customer’s expense.
The following conditions are excluded from this 5.
warranty:
RMA Service
Requesting a RMA#
To obtain a RMA number, simply fill out and fax the 6.
“RMA Request Form” to your supplier.
The customer is required to fill out the problem code 7.
as listed. If your problem is not among the codes listed,
please write the symptom description in the remarks
box.
Ship the defective unit(s) on freight prepaid terms. 8.
Use the original packing materials when possible.
Mark the RMA# clearly on the box. 9.
Note: Customer is responsible for shipping
damage(s) resulting from inadequate/loose
packing of the defective unit(s). All RMA# are valid
for 30 days only; RMA goods received after the
effective RMA# period will be rejected.
Improper or inadequate maintenance by the customer
Unauthorized modification, misuse, or reversed
engineering of the product Operation outside of the
environmental specifications for the product.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
16
Page 20

Appendix A
RMA Service Request Form
When requesting RMA service, please fill out the following form. Without
this form enclosed, your RMA cannot be processed.
RMA No:
Reasons to Return: Ŀ Repair(Please include failure details)
Ŀ Testing Purpose
Company: Contact Person:
Phone No. Purchased Date:
Fax No.: Applied Date:
Return Shipping Address:
Shipping by: Ŀ Air Freight Ŀ Sea Ŀ Express ___
Ŀ Others:________________
Item Model Name Serial Number Configuration
Item Problem Code Failure Status
*Problem Code:
01:D.O.A.
02: Second Time
R.M.A.
03: CMOS Data Lost
04: FDC Fail
05: HDC Fail
06: Bad Slot
07: BIOS Problem
08: Keyboard Controller Fail
09: Cache RMA Problem
10: Memory Socket Bad
11: Hang Up Software
12: Out Look Damage
13: SCSI
14: LPT Port
15: PS2
16: LAN
17: COM Port
18: Watchdog Timer
19: DIO
20: Buzzer
21: Shut Down
22: Panel Fail
23: CRT Fail
24: Others (Pls specify)
Request Party
Confirmed By Supplier
Authorized Signature / Date Authorized Signature / Date
Terms and Conditions
Embedded and Industrial Computing
17
 Loading...
Loading...