Page 1

In-Vehicle Computing
Hardware Platforms for mobile applications
LVC-5770
V1.2
>>
User's Manual
Publication date:2014-07-01
Page 2
About
About
Overview
Icon Descriptions
The icons are used in the manual to serve as an indication
of interest topics or important messages. Below is a
description of these icons:
NOTE: This check mark indicates that
there is a note of interest and is something
that you should pay special attention to
while using the product.
Online Resources
The listed websites are links to the on-line product
information and technical support.
Resource Website
Lanner http://www.lannerinc.com
Product Resources
RMA http://eRMA.lannerinc.com
WARNING: This exclamation point
indicates that there is a caution or
warning and it is something that could
damage your property or product.
http://www.lannerinc.com/
support/download-center
Acknowledgement
Intel, Pentium and Celeron are registered trademarks of
Intel Corp.
Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks
of Microsoft Corp.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of
their respective owners.
Compliances and Certification
CE Certication
This product has passed the CE test for environmental
specifications. Test conditions for passing included the
equipment being operated within an industrial enclosure.
In order to protect the product from being damaged by
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) and EMI leakage, we strongly
recommend the use of CE-compliant industrial enclosure
products.
FCC Class A Certication
This equipment has been tested and found to comply
with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required
to correct the interference at his own expense.
e Mark Certication
E13 - Luxembourg
Copyright and Trademarks
This document is copyrighted, © 2014. All rights are
reserved. The original manufacturer reserves the right to
make improvements to the products described in this
manual at any time without notice.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied,
translated or transmitted in any form or by any means
without the prior written permission of the original
manufacturer. Information provided in this manual is
intended to be accurate and reliable. However, the original
manufacturer assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for
any infringements upon the rights of third parties that
may result from such use.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
2
Page 3
About
Mechanical compliance
Vibration:
General Vibration (operating): Refer to MIL-STD-810G, •
Method 514.6, Procedure I (Transportation), Category
4 – Common carrier (US highway truck vibration
exposure)
General Vibration (non-operating): Refer to MIL-STD- •
810G, Method 514.6, Procedure I (Transportation),
Category 24 – General minimal integrity
Shock:
Operating (Functional Test for Ground Equipment): •
Refer to MIL-STD-810G, Method 516.6, Procedure I,
40g, 11ms
Non-Operating (Crash Hazard Shock Test for Ground •
Equipment): Refer to MIL-STD-810G, Method 516.6,
Procedure V, 75g, 11ms
Electrical transient conduction along supply lines only
(12V/24V)
About
Revision History
Version Changes
1.2 Change the default BIOS values for DIO
Embedded and Industrial Computing
3
Page 4

TTaTTable of Contentsbeable of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 5
System Specication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 2: System Components 7
System Drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Block Diagram: The MainBoard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Block Diagram: The Ignition Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Front Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Rear Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Power Adaptor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Chapter 3: Board Layout 14
Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Ignition Board Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
External Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Internal Connectors and Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Internal Connectors and Jumpers (backside) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Connectors and Jumpers List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Chapter 4: The Flow Chart 29
Chapter 5: Hardware Setup 30
Preparing the Hardware Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Installing the System Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Wireless Module Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
3G SIM Card Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Installing the Hard Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Connecting Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Appendix A: Using the Ignition System Manager (ISM) 33
Appendix B: Digital Input/Output 34
Appendix C: Accessing the Digital Accelerometer Data from the LVC-5770 40
Appendix D: Accessing the GPS Data from the LVC-5770 42
Appendix E: Programming System Watchdog Timer of the LVC-5770 44
Appendix F: Terms and Conditions 48
Warranty Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
RMA Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
4
Page 5

Chapter 1
Chapter 1:
Introduction
Introduction
Thank you for choosing the LVC-5770. The LVC-5770
is a fanless mobile NVR system which equips with a
suspension kit. It is designed to be installed on a moving
transportation system. In addition, the LVC-5770 is also
a Power sourcing equipment (PSE); the multiple PoE LAN
ports on the system can be used to connect to powered
device (PD) to supply power to the device through the
Ethernet cables.
The system encompasses a wide variety of communication
ports to facilitate every possible in-vehicle applications
including surveillance, event data recorder and the
GPS receiver. It also features an external HDD drive bay
for easy insertion of the HDD/SSD. The following list
highlights the capabilities of the LVC-5770 system.
One PoE power adapter which can accept vehicle •
power for 9~36 input voltage and supply 48VDC
output voltage for PoE power and 9~36 VDC output
for PC power and 9~36VDC for Aux power.
One Digital I/O port for 4 digital input and 3 output •
connections (via a DE-15 connector).
Two additional pins from the above Digital I/O can •
be used for system wake-up to power on the system
automatically.
PC audio ports with • line in, line out and microphone
ports.
Rich I/O ports: 2 RS-232/422/485 via D-Sub 9, 2 LAN •
ports, 6 USB ports (6 type A)
Dual Mini-PCIe connectors for 3G Internet services •
(with 1 SIM card readers for 3G wireless Internet
connections) and an additional PCIe expansion
suitable for Wi-Fi connection.
Dual video display: DVI-D+VGA or HDMI+VGA output •
with Intel HD Graphics 3000
Power ignition control mechanism with programmable •
on/off/delay switch
Wide range of DC power input from 9V to 36V, suitable •
for vehicular 12V or 24V battery with Ignition control.
–Power input current protection by the 10A fuse and
15KP30A TVS
--12V DC output current protection by the 1A Polyfuse
Battery voltage protection: Over Voltage Protection •
and Under Voltage Protection
System Specification
Dimensions (WxHxD)
Processor Intel Sandy Bridge Processors
Chipset Intel HM65
System
Memory
Ethernet Controller Intel 82574Lx2
Graphic Controller Intel integrated HD graphics engine
Audio Controller ALC886
IO
Power Input
PoE Power Adapter LVP-POE936A included
OS Support
Certications CE, FCC Class A, E13, RoHS
Technology DDR3 SO-DIMMx2
Max. Capacity Up to 16GB
SATA
LAN GbE RJ45 x2
Display
Audio
Serial I/O 2xRS-232/422/485 with RI/5V/12V
GPIO
GPS Ublox NEO-6Q GPS receiver module
G-sensor ADXL 345
USB 2.0 Type A x6
Power Input 3-pin terminal block (+, -, ignition)
Expansion
Others
276.4x190x85.3mm
(10.88”x7.48”x3.36”)
Removable 2.5” SSD/HDD drive
bayx2, on-board 8GB SSD
DVI-D, maximum resolution up to
1920x1200@60Hz
VGA, maximum resolution up to
2048x1536@75Hz
HDMI, maximum resolution up to
1920x1200@60Hz
Dual display function supports independent, clone and extended mode
(VGA+DVI or VGA+HDMI).
Mic-in and Line-out with 2 watt by
DB9 female connector
4x DI 12V Level
3x DO 12V Level
2x DI (from MCU) 5V Level
Mini-PCIe x2 (one with SIM card
reader)
External: 3x SMA antenna hole,
reset, Remote Power switch
Internal: 9~36Vdc (max. 10A) On/
Off software controllable
+9~36VDC input range, ATX mode
support ignition delay on/off
control
Linux Kernel 2.6.18 or later
Windows XPE/WES2009, XP Pro
FES, WS7E, Win 7 Pro FES
Standby power consumption are well under 12V/81mA
and 24V/83mA
Extended operating temperature between -20 ~ 55 ºC •
(-4 ~ 131ºF)
Embedded and Industrial Computing
5
Page 6
Chapter 1
Introduction
Compliance
Operating
Temperature
Range
Extended
Standard
Vibration: MIL-STD-810G, Method
514.6 with SSD and suspension kit
Shock: MIL-STD-810G, Method
516.6 with SSD and suspension kit
With Selected Industrial Compo-
nents
-20~55°C/-4~131°F
With Commercial Components
-5~45°C / 23~113°F
Package Contents
Your package contains the following items:
LVC-5770 Fanless Embedded System with a suspension •
kit
Terminal Block Connectors •
(P/N: 2 pin 04AW20021E101, 3 pin 04AW20031E001 ,
4pin 04AW20043E101)
LVP-POE936A POE power adapter •
(P/N:SE9ESSC69R01A)
HDD Screws x 4 (P/N: 070W102400602) •
Mini-PCIe screw x8 (P/N: 070W101000401) •
Embedded and Industrial Computing
6
Page 7
Chapter 2
Chapter 2:
System Components
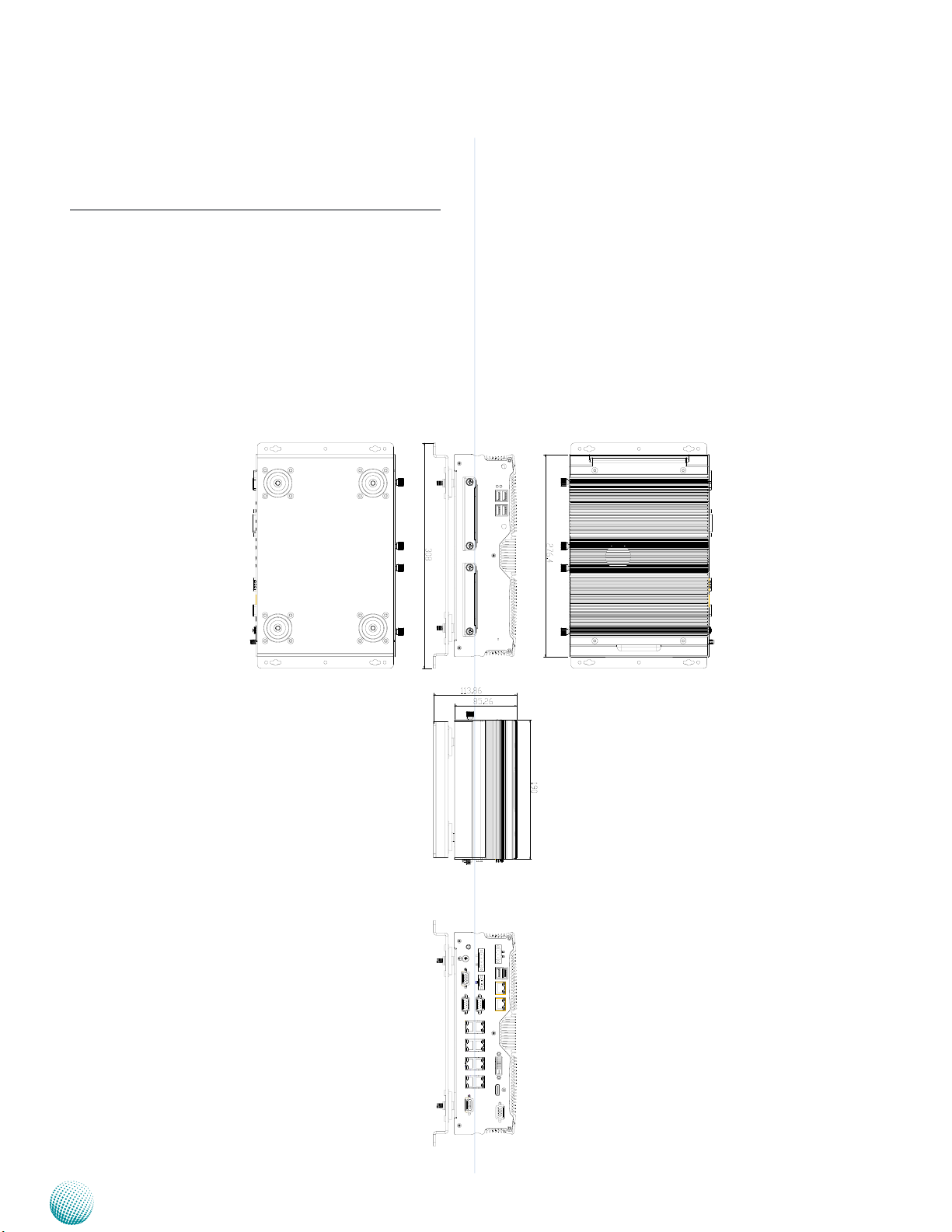
System Drawing
Mechanical dimensions of the LVC-5770 with the
suspension kit
Unit: mm
System Components
Embedded and Industrial Computing
7
Page 8
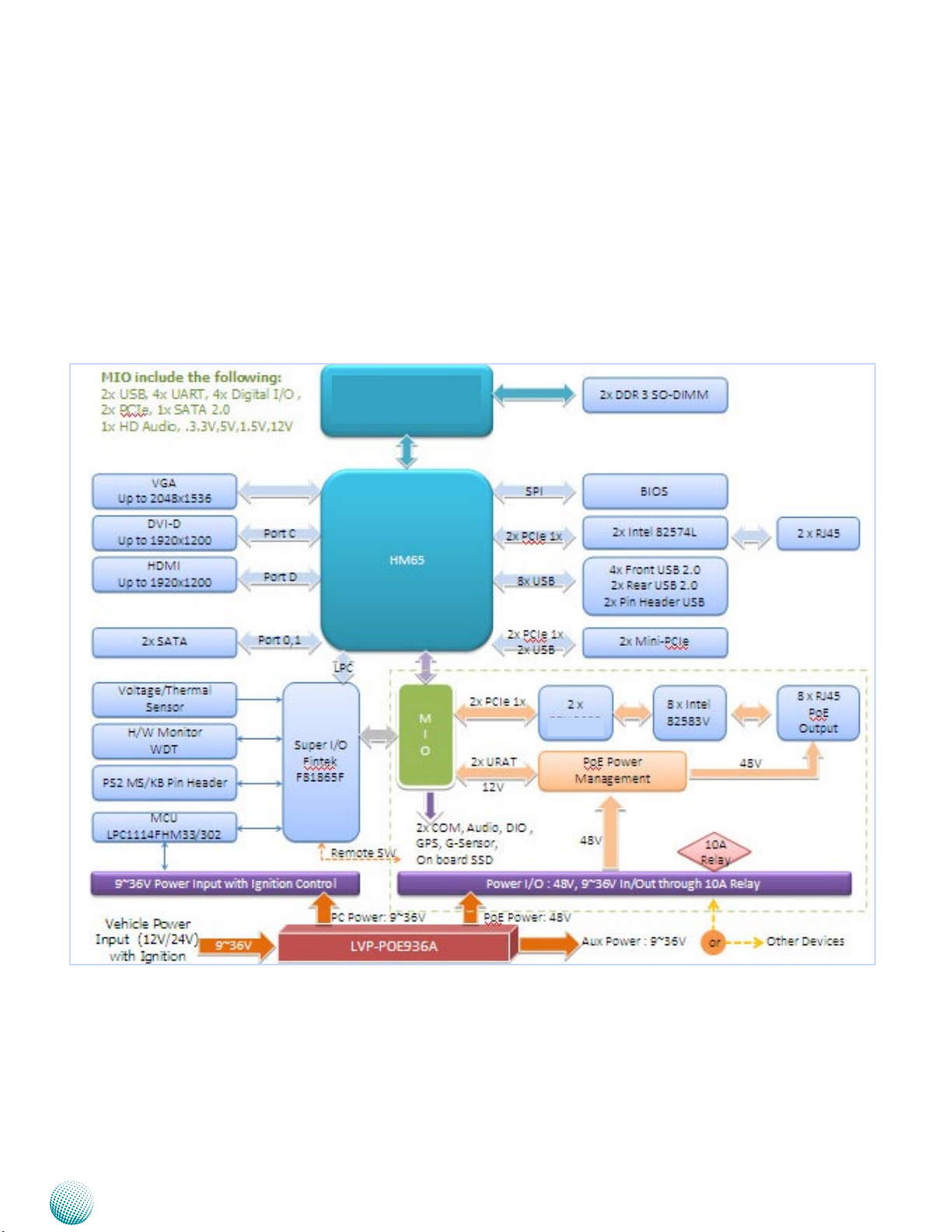
Chapter 2
Block Diagram: The MainBoard
The block diagram depicts the relationships among the
interfaces and modules on the motherboard.
Intel® Sandy Bridge
Processors
System Components
PEx8606
Embedded and Industrial Computing
8
Page 9
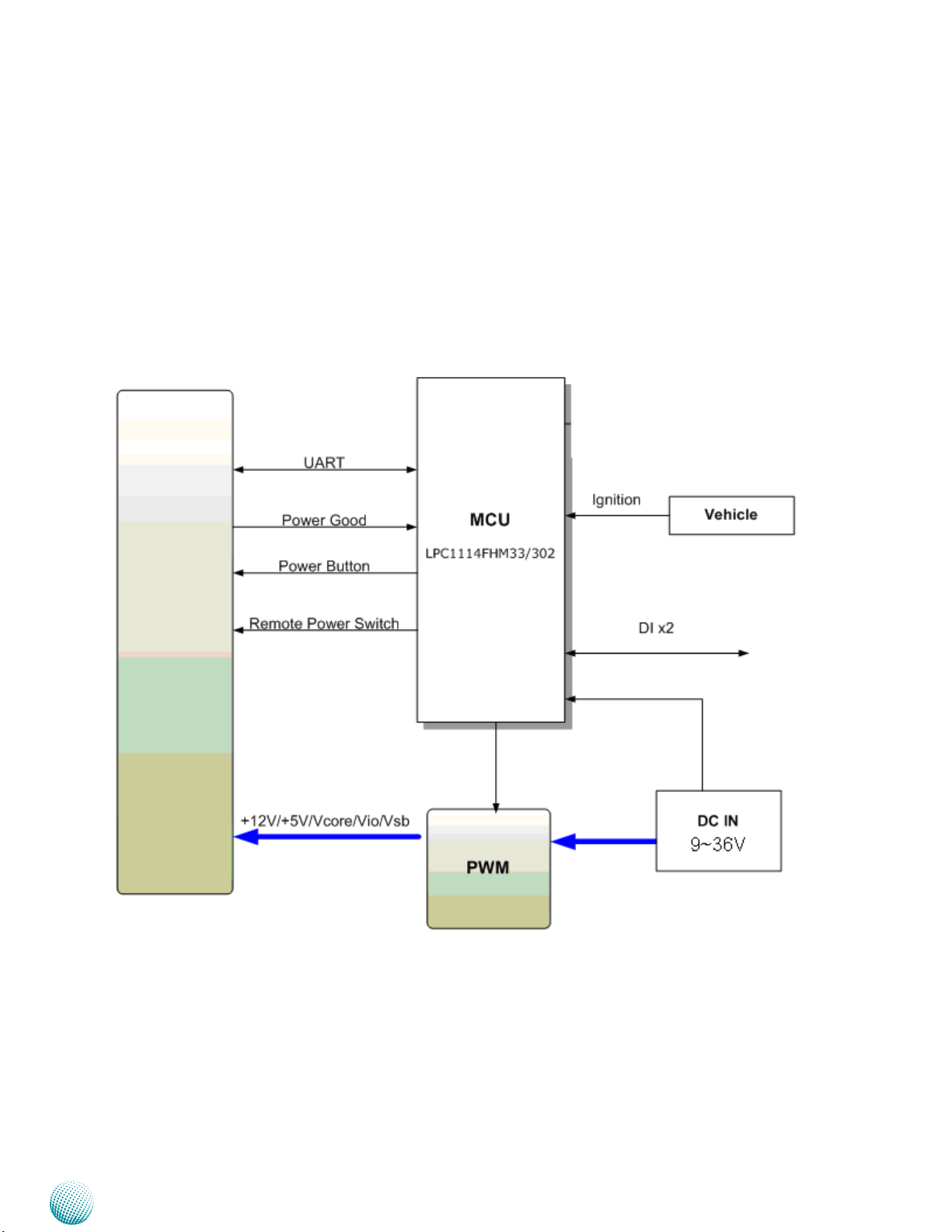
Chapter 2
Block Diagram: The Ignition Board
The block diagram depicts the relationship between the
power ignition board and the mainboard.
System Components
LVB-5770
Embedded and Industrial Computing
9
Page 10
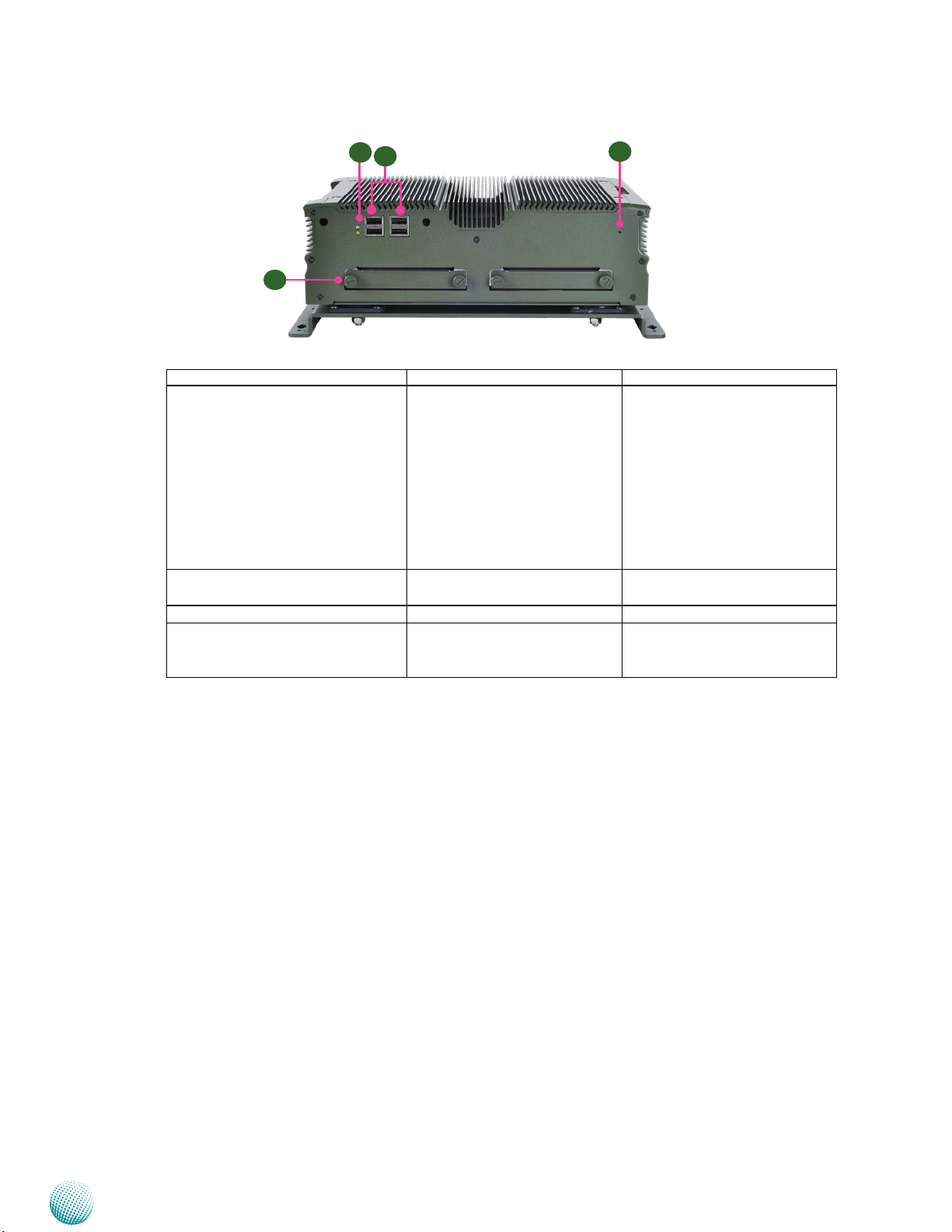
Chapter 2
System Components
Front Components
F1 HDD (Yellow) and
Power LED (Green)
F2 Four USB 2.0 Ports USB type A connectors Dual USB Port #0, #1 and #2, #3
F3 Reset Switch A hardware reset button RST1 on page 24
F4 Hard Disk Slot External SATA 2.5” hard disk
F1
F2
F3
LVC-5770
USB USB
F4
Component Description Pin Definition Reference
RST
HDD
Blinking: data access •
activities
Off: no data access •
activities or no hard disk
present
Power
On: The computer is on.•
Off: The computer is off .•
(USB1,USB2) on page 26
SATA1/SATA2 on page 23
drive for easy access and replacement of the data storage.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
10
Page 11
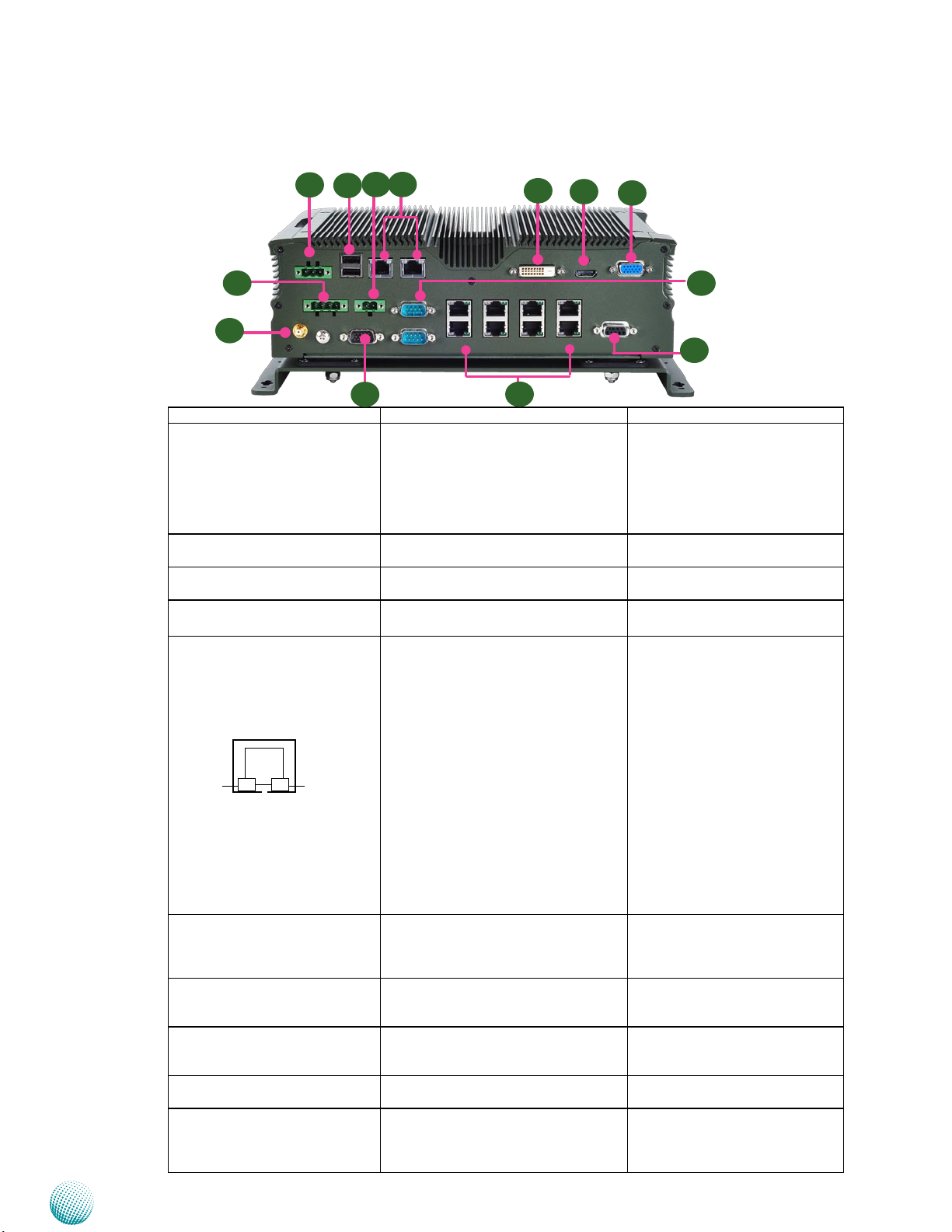
Chapter 2
Rear Components
R9
R2
R1
R4
DC Input 9~36V
USB LAN2 LAN1
OUT + - - + IN
DC Relay Bypass PoE Power 48V
+ -
R3
R5
COM2
COM1
R6
DVI-D HDMI VGA
POE POE POE POE
R7
Audio
System Components
R8
R10
R11
R12
Component Description Pin Definition Reference
R1 Power-In (DC) Power-in with ignition support. The
LVC-5770 support a wide range of
R13
DC_IN Connector (CN4) on page
25
power input (+9V ~ +36) including
the prevalent 12V and 24V vehicular
power system. It has a 2KV ESD
protection on the DC input and
ignition line.
R2 DC Relay Bypass (DC) 9~36V, 10A (GND, Power-Out)
CN4 on page 21
Integrated in 1x 4-pin terminal block
R3 PoE Power 48V 48V power input for supplying power
CN3 on page 21
to the PoE devices
R4 Two USB 2.0 Ports USB type A connectors Dual USB Port Connector #4 and
#5 (USB3) on page 26
R5 Two 10/100/1000Mbps LAN
ports
Two RJ-45 (network) jacks (provided
by Intel 82574L) with LED indicators
LANB1/LANB2 on page 25
as described below
LINK/ACT (Yellow)
On/Flashing: The port is linking •
and active in data transmission.
Off: The port is not linking.•
SPEED
LINK/ACT
SPEED (Green/Amber)
Amber: The connection speed is •
1000Mbps.
Green: The connection speed is •
100Mbps
Off: .The connection speed is •
10Mbps.
R6 DVI-D (*) A DVI-D port (single link) which
DVID1 on page 24
is provided by Intel HD Graphic
Engine. This port can support up to
1920x1200@60Hz resolution.
R7 HDMI Port (*) A DVI-D port (single link) which
HDMI1 on page 24
is provided by Intel GMA 3650
(resolution: 1920x1200@60Hz).
R8 VGA Port (*) It connects an external VGA
VGA1 on page 24
monitor or projector (resolution:
2048x1536@75Hz)
R9 GPS Antenna It connects an antenna for the build-
in GPS module.
R10 Serial Ports COM1 and COM2 provide RS232/
RS422/RS485 communications with
RS-232 COM Port (COM1, COM2)
on page20
a dip switch selecting among these
standards.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
11
Page 12
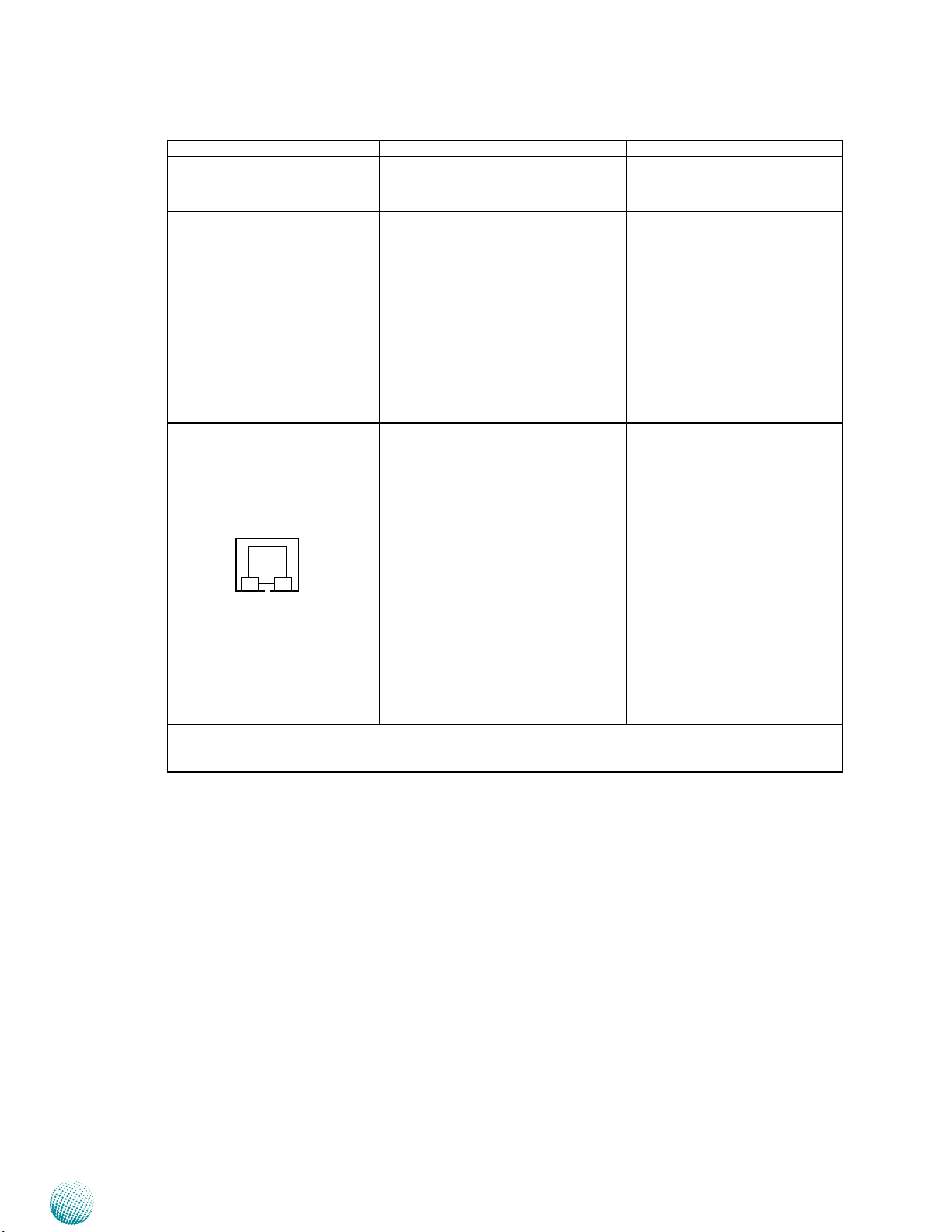
Chapter 2
R11 PC Audio Ports D-sub 9 connector for MIC input and
R12 MIO Connector A DE-15 male connector for 4 Digital-
R13 Power over Ethernet Ports Eight RJ-45 jacks with LED indicators
SPEED
* Only DVI-D +VGA or HDMI + VGA can work at the same time.
System Components
Component Description Pin Definition Reference
Audio1 on page 20
HD Audio output (w/2 Watt) from
LEK-IOA7.
J15 on page 21
In & 3Digital-output, at 12V level.
The digital input helps triggering
between open and closed circuit such
as PIRs, door/window contact, glass
break detector. And the output can
connect to devices such as sirens.
In addition to the above Digital I/O
function, two IGN_in pins can be used
to wake up the system even when the
system is shut down.
LAN1~LAN8 on page 22
LINK/ACT (Yellow)
On/Flashing: The port is linking •
and active in data transmission.
Off: The port is not linking.•
SPEED (Green/Amber)
LINK/ACT
Amber: The connection speed is •
1000Mbps.
Green: The connection speed is •
100Mbps
Off: .The connection speed is •
10Mbps.
They are provided by Intel 82583V
GbE chips with Power over Ethernet
power source capability (48V, 15W).
Embedded and Industrial Computing
12
Page 13
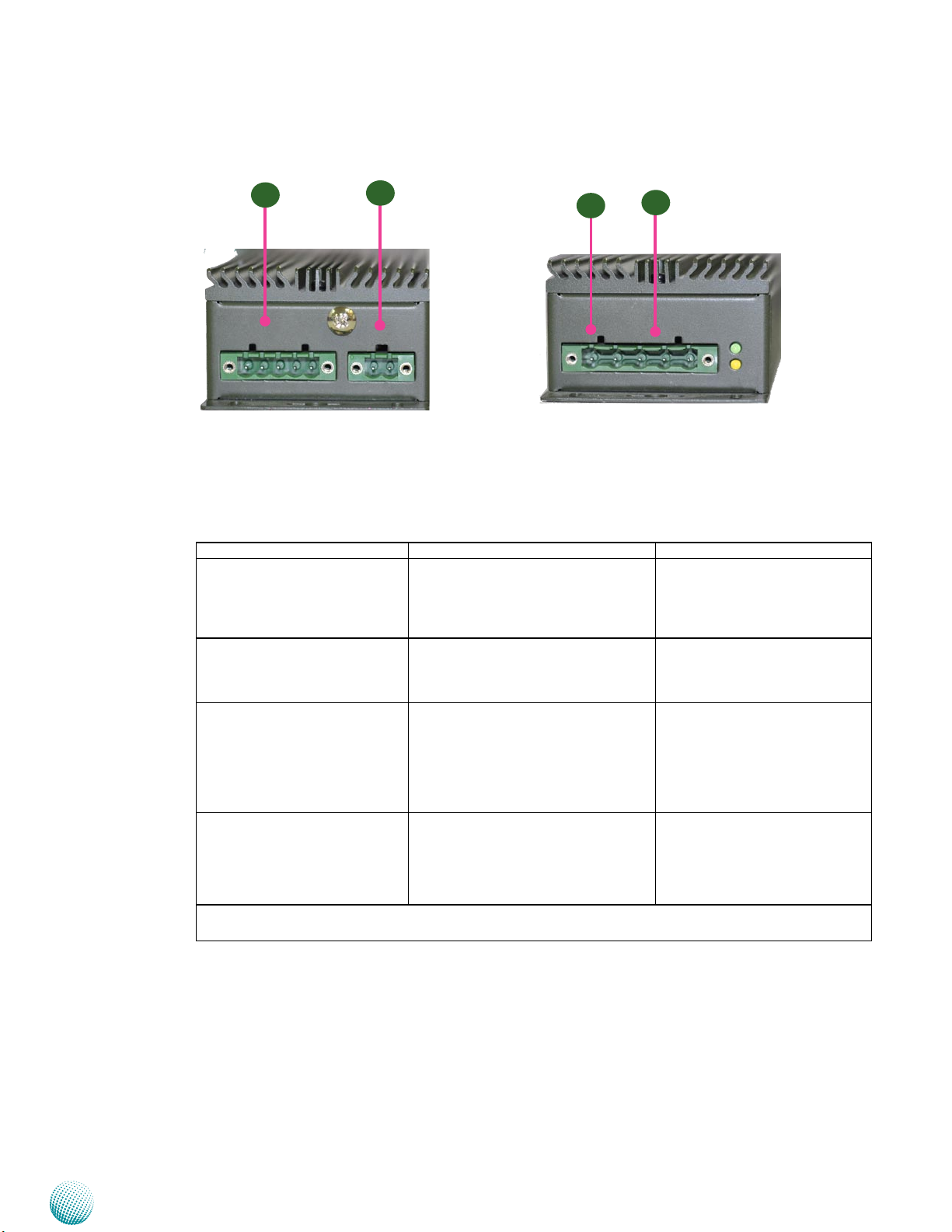
Chapter 2
Power Adaptor
System Components
R1
PoE Power PC Power
48V 9~36 Bypass
Output1 - + IG - + Output2 - + Output3
R2
Aux Power
9~36V Bypass
R3
Vehicle Power (12V/24V) w/ Ignition
IG - + - +
R4
Input Range: 9~36VDC
48V
IG
The system comes with a power adaptor that is capable to transfer power input from 9~36VDC to 48VDC
output.
Component Description Pin Definition Reference
R1 Power output (DC) to the
LVC-5770 System
9~36V, 10A (GND, Power-Out)
Integrated in 1x 5-pin terminal block.
POWER_CON1 on page 28
The output port on the connector
will supply power to the LVC-5770
system.
R2 Power Output (DC) The output port of this connector can
POWER_CON3 on page 28
bypass power from the input port
(see R3) to supply additional 9~36V
power for other uses.
R3 Power Input (DC) with
Ignition control
Power-in with ignition support. The
LVC-5770 support a wide range of
POWER_CON2 on page 28
power input (+9V ~ +36) including
the prevalent 12V and 24V vehicular
power system. It has a 2KV ESD
protection on the DC input and
ignition line.
R4 LED Green: On means that PoE Power 48V
port is connected (refer to R3 on the
rear panel)
Yellow: On means that car ignition is
turned on.
The power board also equips with jumpers that can be switched to enable or disable automatic power
management control.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
13
Page 14
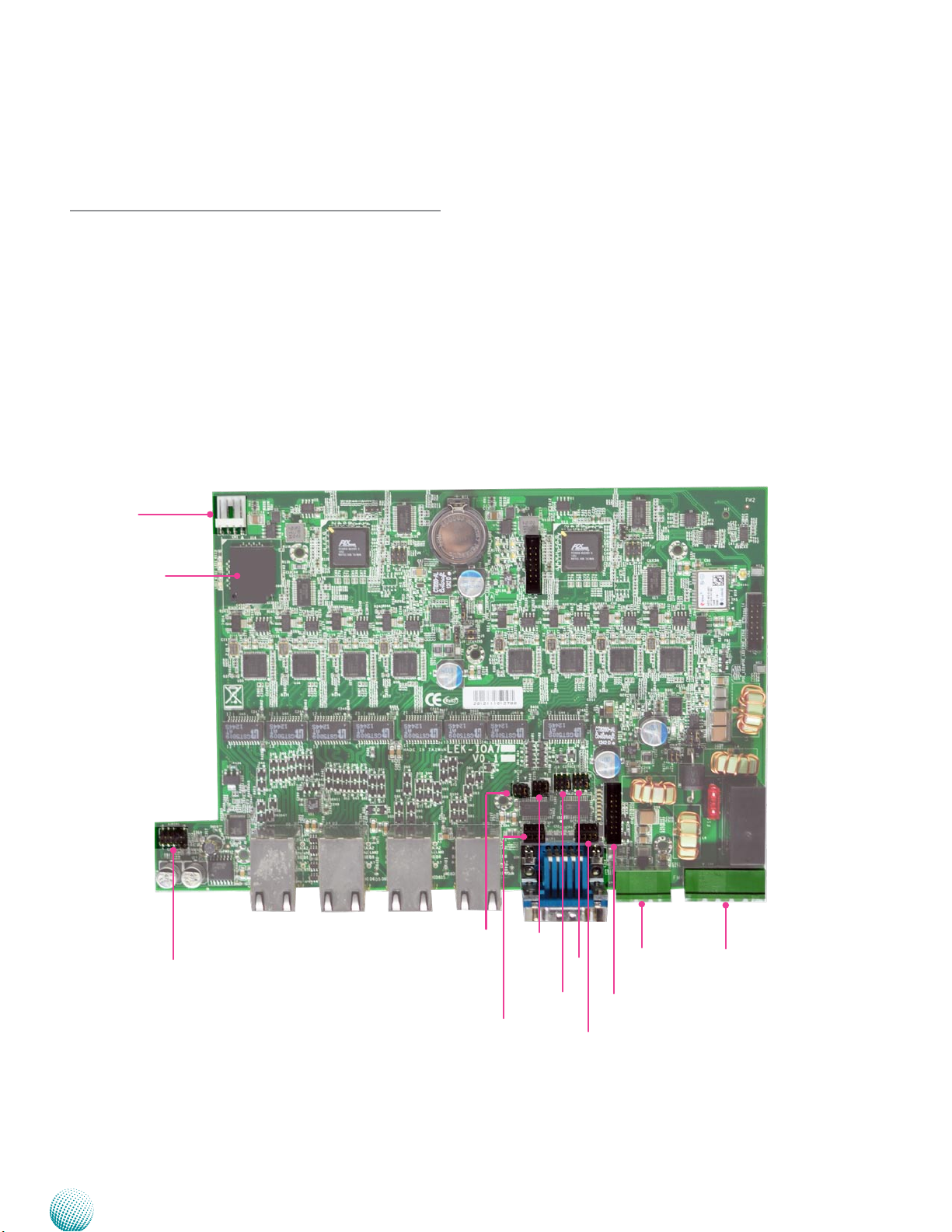
Chapter 3
Chapter 3:
Board Layout
Connectors
The following picture highlights the location of the COM
ports and other connectors on the expansion card. Refer
to the table 3.1 Connector List for more details.
CN1
Board Layout
Onboard 8G SSD
Audio1
SCT2
SCT4
SCT1
J13
J14
SCT3
J15
CN3
CN4
Embedded and Industrial Computing
LEK-IOA7
14
Page 15
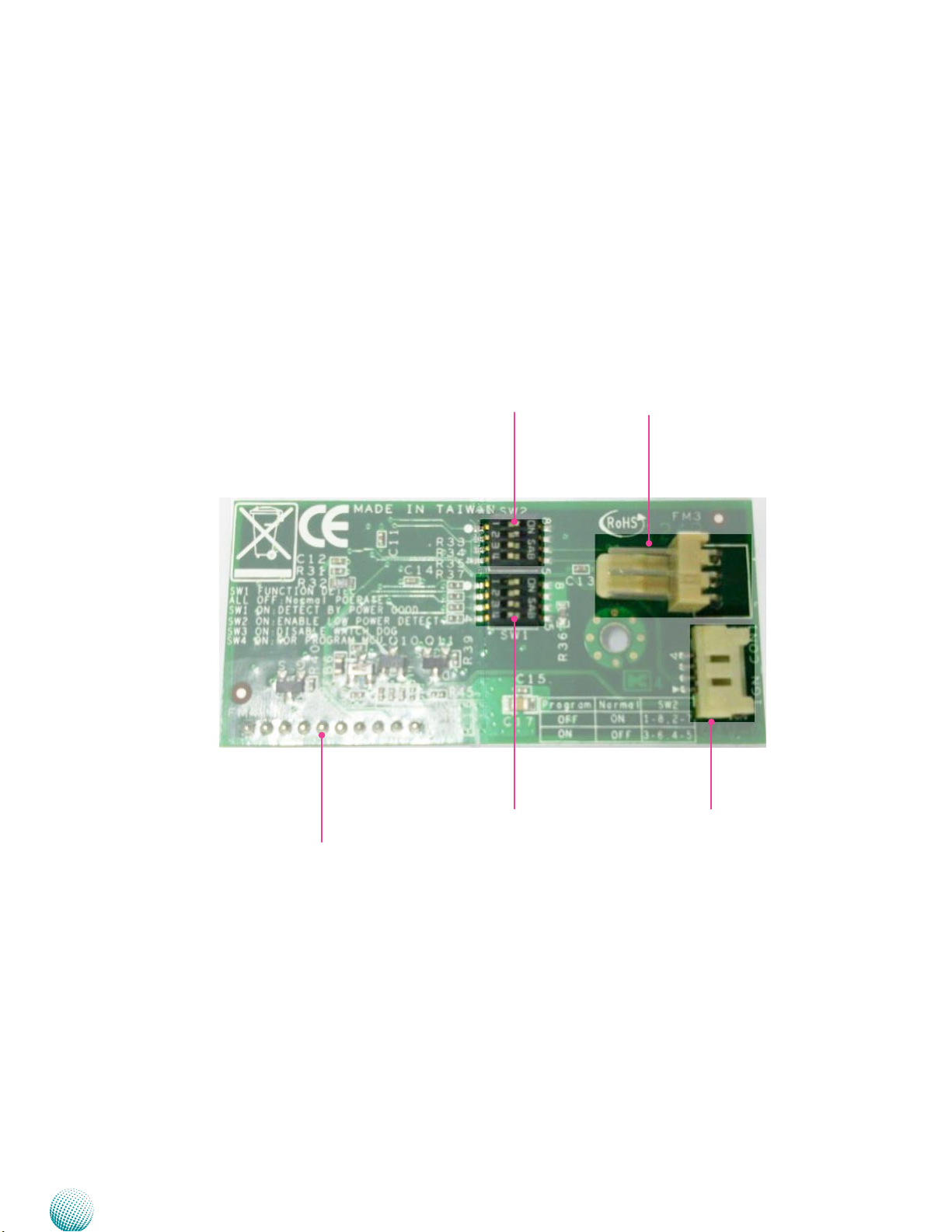
Chapter 3
Ignition Board Connectors
The following picture highlights the location of ignition
board connectors. The ignition board also equips with
jumpers that can be switched to enable or disable
automatic power management control. Refer to the table
3.2 Connector List for more details.
Board Layout
IGNITION1
SW2
SW1
CN1
IGN_CON1
Embedded and Industrial Computing
LEK-IG1
15
Page 16

Chapter 3
External Connectors
The following picture highlights the location of external
input/output connectors. Refer to the table 3.3 Connector
List for more details.
Board Layout
VGA1
HDMI1
DVID1
LAN1/LAN2
USB3
CN4
CN3/
DCJK1
(optional)
USB1
LED1
Embedded and Industrial Computing
USB2
RST1
LEB-5570
16
Page 17

Chapter 3
Internal Connectors and Jumpers
The following picture highlights the location of internal
connectors and jumpers. Refer to the table 3.3 Connector
List for more details.
Board Layout
CMOS2
COMSLT2
COMSLT1
SIM1
SATA_PW2
CMOS1
FAN2
MPCIE2
MPCIE1
LPC1
SPI1
Ignition1
FRONT1
Embedded and Industrial Computing
SO-DIMM
J1
LEB-5570 (The LEB-5570 is used on both
LVC-5570 and LVC-5770)
FAN1
17
Page 18

Chapter 3
Internal Connectors and Jumpers
(backside)
The following picture highlights the location of internal
connectors and jumpers on the backside of the board.
Refer to the table 3.3 Connector List for more details.
Board Layout
MIO1
SATA1
SATA2
SATA_PWR1
PCIEIO1
Embedded and Industrial Computing
KBM1
LEB-5570
18
Page 19

Chapter 3
Board Layout
Connectors and Jumpers List
The tables below list the function of each of the board
jumpers and connectors by labels shown in the above
section. The next section in this chapter gives pin
definitions and instructions on setting jumpers.
Table 3.1 Connector List for LEK-IOA7 Board
Labels Function Pin Denition Reference
Page
AUDIO1 HD Audio Connector (D-Sub) P20
CN3 48V for PoE Power Supply P21
CN4 DC_in and out Connector P21
COM1 RS232/422/485 Serial Port P20
COM2 RS232/422/485 Serial Port P20
J13/J14 Select COM1 and COM2 Pin9 Function P21
JAUD1 Audio Select P22
LAN1~LAN8 POE Ports P22
MIO1(J15) Digital Input and Output P21
MIO Connector to the LEB-5570 board P22
SCT1/SCT3 Select COM2 Protocol Setting P20
SCT2/SCT4 Select COM1 Protocol Setting P20
SSDSLT1 SSD enable/disable P22
Table 3.2Connector List for LEK-IG1 Board
Labels Function Pin Denition Reference
Page
CN1 MCU Programming Connector P27
IGNITION1 Ignition Control Connector P27
IGN_CON1 Power Connector P27
SW1 Power Ignition Behavior Switch P27
The ignition board also equips with jumpers that can be switched to enable or disable automatic power management control.
Table 3.3 Connector List for LEB-5570 Board
Labels Function Pin Denition Reference
Page
CMOS1 Cleaning CMOS Data Including RTC P26
CMOS2 Cleaning CMOS Data Only P29
COMSLT1 Daughter board LEK-IOA7 enable/disable P25
COMSLT2 Daughter board LEK-IG1 enable/disable P26
CN43 Power Connector with Power -ignition Control P25
DCJK1 (optional) Optional DC Jack Type of Power Connector P25
DVID1 DVI-D Connector P24
FAN1/FAN2 System Fan Connector P24
Front1 Front Panel Function Pin Header P23
HDMI1 HDMI Port P24
Ignition1 Connector for power Ignition Control P26
J1 PEG16X Lane Function Selection P24
KBM1 PS/2 Keybaord and Mouse Connector P26
LAN1/LAN2 Ethernet Connector 1/Ethernet Connector 2 P25
LPC1 Low Pin Count Interface Reserved for factory use
MIO1 COM and Audio Expansion Card Connector (to the LEK-IOA7) P23
MPCIE1 Mini-PCIe Connector P25
MPCIE2 Mini-PCIe Connector P25
RST1 Reset Button P24
SATA1/SATA2 Serial-ATA Connector (SATA2 supports SATA-DOM) P23
SATA_PWR1 SATA Power Connector P23
SATA_PW2 Switch for SATA port 2 power state P23
SIM1 SIM Card Reader P25
SPI1 Serial Peripheral Interface Bus Reserved for factory use
USB1/USB2/USB3 USB Type A Connector #0,1; #2,3; #4,5 P26
VGA1 VGA Port P24
Embedded and Industrial Computing
19
Page 20

Chapter 3
Board Layout
Jumper Settings
LEK-IOA7 Board
Line-out Audio Jack (Audio, AUDIO1): a D-sub 9 male
connector for HD Audio
12345
6789
Note: The driver for the VGA and Audio ports
should be installed with the following order:
Chipset INF->Graphic->Audio
COM1 RS-232 Serial Port (COM1): a RS-232/422/485 port
through the D-SUB9 connector.
Pin No. Pin Name
1 DCD TXD- DATA2 RXD TXD+ DATA+
3 TXD RXD+
4 DTR RXD5 GND
6 DSR
7 RTS
8 CTS
9 RI
Pin No. Function Pin No. Function
1 AUDIO_IN_L 6 AUDIO_IN_R
2 N/A 7 N/A
3 FRONT_OUT_L 8 GND
4 FRONT_OUT_R 9 GND
5 N/A 10
12345
6789
RS-232 RS-422 RS-485
SCT2, SCT4: Select COM1 Protocol Setting
SCT2
5
6
1
2
9
5
1
SCT4
12
8
4
RS-232
5
6
1
2
9
5
1
12
8
4
RS-422
5
6
1
2
9
5
1
12
8
4
RS-485
5
6
Switch
1
2
9
5
1
SCT2 SCT4
12
8
4
Protocol
RS-232 (default) 1-2 1-5, 2-6, 3-7, 4-8
(default)
RS-422 3-4 5-9, 6-10, 7-11, 8-12
RS-485 5-6 5-9, 6-10, 7-11, 8-12
SCT1, SCT3: Select COM2 Protocol Setting
RS-232/422/485 Serial Port(COM2): a RS-232/422/485
port through the D-SUB9 connector.
Pin No. Pin Name
RS-232 RS-422 RS-485
1 DCD TXD- DATA2 RXD TXD+ DATA+
3 TXD RXD+
4 DTR RXD5 GND
6 DSR
7 RTS
8 CTS
9 RI
Embedded and Industrial Computing
SCT1
5
6
SCT3
1
2
9
5
1
12
8
4
20
Page 21

Chapter 3
Board Layout
5
6
5
6
5
6
Switch
1
2
1
2
1
2
9
5
1
9
5
1
9
5
1
SCT1 SCT3
12
8
4
12
8
4
12
8
4
Protocol
RS-232 (default) 1-2 1-5, 2-6, 3-7, 4-8
(default)
RS-422 3-4 5-9, 6-10, 7-11, 8-12
RS-485 5-6 5-9, 6-10, 7-11, 8-12
J13, J14: Select COM1 and COM2 Pin9 Function (in
RS-232) respectively. The Ring indicator pinout of the RS232 COM port can be altered according to the following
jumper settings.
Maximum input/output current for each port is
100mA
For all Input/
output pins:
Voltage Logic Register
Di: <0.8V
Low 0
Do: <0.4V
DI: 0.9 ~ 5V
High 1
Do:5V
The default BIOS value is 1 for DI and 1 for DO
Pin 11 is used for remote power switch.1.
Pin 6 is used for relay power switch.2.
Pin12 and pin13 can be used for DI wake-up 3.
function (Refer to the flow chart in Chapter 4 and
the ISM in Appendix A).
DC_in and out (CN4) : 9~36V DC power input and output
Integrated in a 4-pin terminal.
4 3 2 1
Pin No. Function
1 P930V_IN
2 P930V_GND
3 GND_930V
4 P930V_OUT
J13 J14
2
1
6
5
2
1
Pin No. Function
1-2 Supply +5V to
6
3-4 Supply +12V to
5
5-6 Ring-in (default)
the Device
the Device
Digital Input and Output (MIO, J15): A DE-15 Male
Connector for 4 DI & 3 DO, 12V
15 11
5 1
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 RIO_IN0 6 RIO_OUT0 11 EXT_POWER_ON
2 RIO_IN1 7 RIO_OUT1 12 IGN_IN0
3 RIO_IN2 8 RIO_OUT2 13 IGN_IN1
4 RIO_IN3 9 RIO_OUT3 14 GND
5 GND 10 GND 15 12V_OUT (1A)
48V DC_IN for PoE Power Supply (CN3):
2 1
Pin No. Function
1 GND
2 48V_IN
Optional Connector (CN1):
CN1
4 3 2 1
Pin No. Function
1 VCC12
2 GND
3 GND
4 VCC5
Embedded and Industrial Computing
21
Page 22

Chapter 3
Board Layout
LAN1~LAN8 Ports: The LAN ports are provided by Intel
82583V Ethernet controller whose interface complies
with PCI-e 1.1 (2.5 Ghz). Theses ports are PoE capable (48V,
.
15W)
Pin
Description Pin
No.
No.
Description Pin
No.
Description
A1 LAN2_MX0P B1 LAN1_MX0P LED1 LAN2_ACTLED_N
A2 LAN2_MX0N B2 LAN1_MX0N LED2 LAN2_ACTLED_P
A3 LAN2_MX1P B3 LAN1_MX1P LED3 LAN2_L100_N
A4 LAN2_MX1N B4 LAN1_MX1N LED4 LAN2_L1000_N
A5 LAN2_MX2P B5 LAN1_MX2P LED5 LAN1_ACTLED_N
A6 LAN2_MX2N B6 LAN1_MX2N LED6 LAN1_ACTLED_P
A7 LAN2_MX3P B7 LAN1_MX3P LED7 LAN1_L100_N
A8 LAN2_MX3N B8 LAN1_MX3N LED8 LAN1_L1000_N
Enable or disable the onboard SSD memory
(SSDSLT1)
5
6
1
2
Pin No. Function
1-3, 2-4 short
3-5, 4-6 open
3-5, 4-6 Short
1-3, 2-4 open
Enable
Disable
Note: When trying to install an OS on the external
SATA 2.5 hard disk or SSD, disable it first by setting
the jumpers accordingly. Enable it after finishing
the OS installation.
Audio Select (JAUD1): Jumper for mic-in or line-in
switch for connector AUDIO1 (page 20)
Pin No. Function
1-3, 2-4 short Mic-in
3-5, 4-6 Short Line-in
Mini PCI Express Connector (MIO1) on the LEK-IOA7:
Connector for connecting to the mainboard
PIN Pin Name PIN Pin Name
1 GND 51 HDA_BCLK
2 N/A 52 HDA_SYNC
3 N/A 53 HDA_RST
4 GND 54 HDA_SDIN0
5 N/A 55 HDA_SDO
6 N/A 56 SPK
7 GND 57 VCC3_SB
8 VCC3P3_PS 58 VCC3_SB
9 VCC3P3_PS 59 VCC3_SB
10 VCC3P3_PS 60 VCC3_SB
11 GND 61 VCC3_SB
12 N/A 62 N/A
13 N/A 63 N/A
14 N/A 64 N/A
15 N/A 65 N/A
16 N/A 66 N/A
17 N/A 67 N/A
18 IGN_DI2 68 IGN_DI1
19 N/A 69 N/A
20 N/A 70 N/A
21 DCIN_VCC 71 REMOTE_POWER_
ON
22 +12V 72 3G_POWER_ON
23 N/A 73 N/A
24 VCC5_SB 74 N/A
25 VCC5 75 GND
26 VCC5 76 N/A
27 VCC5 77 N/A
28 GND 78 GND
29 N/A 79 N/A
30 N/A 80 N/A
31 N/A 81 N/A
32 N/A 82 N/A
33 GND 83 GND
34 N/A 84 COM1_DCD#
35 N/A 85 COM1_RI#
36 N/A 86 COM1_CTS#
37 N/A 87 COM1_DTR#
38 N/A 88 COM1_RTS#
39 N/A 89 COM1_DSR#
40 N/A 90 COM1_SOUT
41 N/A 91 COM1_SIN
42 GND 92 GND
43 N/A 93 COM2_DCD#
44 N/A 94 COM2_RI#
45 N/A 95 COM2_CTS#
46 N/A 96 COM2_DTR#
47 N/A 97 COM2_RTS#
48 N/A 98 COM2_DSR#
49 N/A 99 COM2_SOUT
50 N/A 100 COM2_SIN
Embedded and Industrial Computing
22
Page 23

Chapter 3
Board Layout
LEB-5570 Board
Serial-ATA Connector (SATA1/SATA2): It is for connecting
a 2.5’’ hard disk to be served as your system’s storage. It
can support SATA II which features Data transfer rates up
to 6.0 Gb/s (600 MB/s). SATA II connector also supports
SATA-DOM (the power line of SATA-DOM can be disabled
with a jumper on, see SATA_PW2).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SATA1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
SATA2
Pin No. Function
1 GND
2 TX0_P
3 TX0_N
4 GND
5 RX0_N
6 RX0_P
7 GND
Pin No. Function
1 GND
2 TX1_P
3 TX1_N
4 GND
5 RX1_N
6 RX1_P
7 VCC5
The controller contains two modes of operation—a
legacy mode using I/O space, and an AHCI mode using
memory space. Software that uses legacy mode will not
have AHCI capabilities.
The AHCI ( Advanced Host Controller Interface) is a
programming interface which defines transactions
between the SATA controller and software and enables
advanced performance and usability with SATA. Platforms
supporting AHCI may take advantage of performance
features such as no master/slave designation for SATA
devices—each device is treated as a master—and
hardware assisted native command queuing. AHCI also
provides usability enhancements such as Hot-Plug.
Use the BIOS menu to configure your hard disk
to be AHCI compatible.
4-pin Serial-ATA Power Connector (SATA_PWR1): It is
for connecting the SATA power cord.
Pin No. Function
1 +12V
4 3 2 1
2 GND
3 GND
4 +5V
SATA_PW2: A switch for supply of SATA Connector II’s
power.
1
2
3
Embedded and Industrial Computing
Pin No. Pin Name
1-2 SATAII Connector without power
2-3 SATA II Connector with 5V power
Front Panel Function Pin Header (FRONT1): It provides
LED signal and button function on the front panel.
10
Pin No. Pin Name Function Pin No. Pin Name Function
1 HD_LED+ HDD LED 2 PWR_LED+ Power LED
3 HD_LED- 4 PWR_LED5 Reset System Reset
7 GND 8 GND
Button
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
6 POWER_BTN Power On/Off
Push Button
Mini PCI Express Connector (MIO1) on the mainboard:
COM and Audio Expansion Card Connector
PIN Pin Name PIN Pin Name
1 GND 51 HDA_BCLK
2 SATATXN2 52 HDA_SYNC
3 SATATXP2 53 HDA_RST
4 GND 54 HDA_SDIN0
5 SATARXN2 55 HDA_SDO
6 SATARXP2 56 SPK
7 GND 57 VCC3_SB
8 VCC3P3_PS 58 VCC3_SB
9 VCC3P3_PS 59 VCC3_SB
10 VCC3P3_PS 60 VCC3_SB
11 GND 61 VCC3_SB
12 PCIE_RXN5 62 PCIE_RXN6
13 PCIE_RXP5 63 PCIE_RXP6
14 PCIE_TXN5 64 PCIE_TXN6
15 PCIE_TXP5 65 PCIE_TXP6
16 PCIE_CKN5 66 PCIE_CKN6
17 PCIE_CKP5 67 PCIE_CKP6
18 IGN_DI2 68 IGN_DI1
19 PLTRST 69 SMBCLK_
20 WAKE_N 70 SMBDATA
21 DCIN_VCC 71 REMOTE_POWER_
22 VCC12_PS 72 3G_POWER_ON
23 VCC5_SB 73 USB_N12
24 VCC5_SB 74 USB_P12
25 VCC5 75 GND
26 VCC5 76 USB_N13
27 VCC5 77 USB_P13
28 GND 78 GND
29 DGOUT_0 79 DGIN_0
30 DGOUT_1 80 DGIN_1
31 DGOUT_2 81 DGIN_2
32 DGOUT_3 82 DGIN_3
33 GND 83 GND
34 COM3_DCD# 84 COM1_DCD#
35 COM3_RI# 85 COM1_RI#
36 COM3_CTS# 86 COM1_CTS#
37 COM3_DTR# 87 COM1_DTR#
38 COM3_RTS# 88 COM1_RTS#
39 COM3_DSR# 89 COM1_DSR#
40 COM3_SOUT 90 COM1_SOUT
41 COM3_SIN 91 COM1_SIN
42 GND 92 GND
43 COM4_DCD# 93 COM2_DCD#
44 COM4_RI# 94 COM2_RI#
45 COM4_CTS# 95 COM2_CTS#
46 COM4_DTR# 96 COM2_DTR#
47 COM4_RTS# 97 COM2_RTS#
48 COM4_DSR# 98 COM2_DSR#
49 COM4_SOUT 99 COM2_SOUT
50 COM4_SIN 100 COM2_SIN
ON
23
Page 24

Chapter 3
Board Layout
DVI-D Connector (DVID1): A single link DVI-D Connector
Pin No. Description Pin No. Description
1 TXD_2- 2 TXD_2+
3 GND 4 N/A
5 N/A 6 DDC_CLK
7 DDC_DATA 8 N/A
9 TXD_1- 10 TXD_1+
11 GND 12 N/A
13 N/A 14 VCC5
15 GND 16 HPD
17 TXD_0- 18 TXD_0+
19 GND 20 N/A
21 N/A 22 GND
23 TXD_CLK_P 24 TXD_CLK_N
HDMI Connector (HDMI1): An HDMI Connector
System FAN Connector (FAN1/FAN2)
FAN1
3 2 1
FAN2
Pin No. Description
3
2
1
1 GND
2 VCC5
3 FAN TAC
Reset Button (RST1)
Pin NO. Description
2
4
1
3
1 RST_BTN
2 GND
3 GND
4 N/A
Pin No. Description Pin No. Description
1 HDMI_DATP2_P 2 GND
3 HDMI_DATP2_N 4 HDMI_DATP1_P
5 GND 6 HDMI_DATP1_N
7 HDMI_DATP0_P 8 GND
9 HDMI_DATP0_N 10 HDMI_CLK_P
11 GND 12 HDMI_CLK_N
13 N/A 14 N/A
15 HDMI_DDC_CLK 16 HDMI_DDC_DAT
17 GND 18 PHDMI
19 HDMI_HPD
VGA (VGA1)
5 4 3 2 1
15 14 13 12 11
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 RED 6 CRT DET 11 N/A
2 GREEN 7 GND 12 DDC DAT
3 BLUE 8 GND 13 HSYNC
4 N/A 9 VCC5 14 VSYNC
5 GND 10 GND 15 DDC CLK
Note: The driver for the VGA and Audio ports
should be installed with the following order:
Chipset INF->Graphic->Audio
Embedded and Industrial Computing
24
Page 25

Chapter 3
Board Layout
MPCIE1: Mini-PCIe Connector with one SIM Card
Reader(SIM1). It supports both Wi-Fi and 3G module.
Both USB and PCIe signal card type can be used on the
connector.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 WAKE# 2 VCC3.3
3 N/A 4 GND
5 N/A 6 VCC1.5
7 CLKREQ# 8 USIM_PWR
9 GND 10 UIM_DATA
11 PCIE_CLK_N3 12 UIM_CLK
13 PCIE_CLK _P3 14 UIM_RESET
15 GND 16 UIM_VPP
17 RSV 18 GND
19 RSV 20 N/A
21 GND 22 PLTRST
23 PCIE_RX_N3 24 VCC3.3
25 PCIE_RX_P3 26 GND
27 GND 28 VCC1.5
29 GND 30 SMBCLK
31 PCIE_TX_N3 32 SMBDATA
33 PCIE_TX_P3 34 GND
35 GND 36 USB_N8
37 GND 38 USB_P8
39 VCC3.3 40 GND
41 VCC3.3 42 N/A
43 GND 44 N/A
45 RSV 46 N/A
47 RSV 48 VCC1.5
49 RSV 50 GND
51 RSV 52 VCC3.3
MPCIE2: Mini-PCIe Connector. It does not come with a
SIM card reader so only Wi-Fi modules are supported.
Both USB and PCIe signal card type can be used on the
connector.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 WAKE# 2 VCC3.3
3 N/A 4 GND
5 N/A 6 VCC1.5
7 CLKREQ# 8 N/A
9 GND 10 N/A
11 PCIE_CLK _N4 12 N/A
13 PCIE_CLK _P4 14 N/A
15 GND 16 N/A
17 RSV 18 GND
19 RSV 20 N/A
21 GND 22 PLTRST
23 PCIE_RX_N4 24 VCC3.3
25 PCIE_RX_P4 26 GND
27 GND 28 VCC1.5
29 GND 30 SMBCLK
31 PCIE_TX_N4 32 SMBDATA
33 PCIE_TX_P4 34 GND
35 GND 36 USB_N9
37 GND 38 USB_P9
39 VCC3.3 40 GND
41 VCC3.3 42 N/A
43 GND 44 N/A
45 RSV 46 N/A
47 RSV 48 VCC1.5
49 RSV 50 GND
51 RSV 52 VCC3.3
SIM Card Socket (SIM1):
C1 C3
C5 C7
Pin No. Description
C1 UIM_PWR
C2 UIM_RST
C3 UIM_CLK
C5 GND
C6 UIM_VPP
C7 UIM_DAT
CN3: A power connector with power -ignition Control
1 2 3
Pin No. Pin Name
1 Ignition
2 GND
3 DC_VIN
DCJK1 (Optional): An optional DC Jack type of Power
Connector
Pin No. Pin Name
1 DC_VIN
2 GND
3 GND
LAN1/LAN2 Ports (LAN1/LAN2): The LAN ports are
provided by Intel 82574L Ethernet controller whose
interface complies with PCI-e 1.1 (2.5 Ghz). It has advanced
management features including IPMI pass-through via
SMBus or NC-SI, WOL, PXE remote boot, ISCSI boot and
VLAN filtering.
Pin No. Description
Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet
1 TX+ BI_DA+
2 TX- BI_DA3 RX+ BI_DB+
4 -- BI_DC+
5 -- BI_DC6 RX- BI_DB7 -- BI_DD+
8 -- BI_DD-
Enable or Disable Daughter Board LEK-IOA7 (COMSLT1):
This jumper is for enabling or disabling COM3/COM4
daughter board LEK-IOA7.
1
2
3
Pin No. Pin Name
1-2 Disable
2-3 Enable
Embedded and Industrial Computing
25
Page 26

Chapter 3
Board Layout
Enable or Disable Daughter Board LEK-IG1 (COMSLT2):
This jumper is for enabling or disabling COM5/COM6 of
daughter board LEK-IG1. If this jumper is set to disable,
the ISM will not work (refer to Appendix A Using the Ignition
System Manager (ISM)).
1
2
3
Pin No. Pin Name
1-2 Disable
2-3 Enable
Dual USB 2.0 Port Connector #0 and #1 (USB1)
Dual USB 2.0 Port Connector #2 and #3 (USB2)
Dual USB 2.0 Port Connector #4 and #5 (USB3)
Pin No. Pin Name
1 VCCUSB
5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4
2 USB0N
3 USB0P
4 GND
5 VCCUSB1
6 USB1N
7 USB1P
8 GND
Clear CMOS jumper (CMOS1/CMOS2): It is for clearing
the CMOS data. CMOS1clears CMOS data with real-time
clock (RTC) whereas CMOS2 clears CMOS data only.
PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector (KBM1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Pin No. Pin Name
1 VCC
3 MDATA
5 KDATA
7 GND
Pin No. Pin Name
2 MCLK
4 NC
6 NC
8 KCLK
Ignition Connector on Board (ignition1): Power
ignition connector.
1 2 3 4 10
Pin No. Pin Name Pin No. Pin Name
1 DCIN_VCC 6 DC2DC_PWROK
2 DC_VIN 7 COM5_SIN
3 GND 8 SOUT
4 SYS_PWROK 9 PWR_BTN_IGN
5 DC2DC_EN 10 IGNITION
1
2
3
Pin No. Pin Name
1-2 Normal (Default)
2-3 Clear CMOS and RTC (CMOS1)
Clear CMOS only (CMOS2)
To erase the CMOS data:
Turn off the computer and unplug the power cord.
Move the jumper cap from pins 1-2 (default) to pins 1.
2-3. Keep the cap on pins 2-3 for about 5-10 seconds,
then move the cap back to pins 1-2.
Plug the power cord and turn on the computer.2.
Enter BIOS setup to re-enter data.3.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
26
Page 27

Chapter 3
Board Layout
LEK-IG1 Board
Select MCU detect function for power ignition behavior
(SW1):
SW1
1
2
3
4
Selector No. SW1 Ignition Function
1 Power Good Detection ON: Enable
2 Low Voltage Detection
3 Watchdog
4 Programming MCU Reserved
The default value is ON for selector 1, ON for selector 2, OFF for selector 3, and OFF for selector 4
8
7
6
5
ON
OFF: Disable
The functions of the above jumpers are further explained
here.
1. : A power-good signal
Power Good Detection
from the main board will be sent to the ignition
controller so that the ignition controller can
decide or alter the power state upon the following
instances. (Refer to the flow chart in Chapter 4):
MCU (Microcontroller) Function Selection (SW1, SW2):
It is for selecting the microcontroller’s function.
SW1
1
2
3
4
ON
Download Data
1
2
3
4
ON
Jumper Pin No. Pin NO.
SW1 1-ON, 2-ON, 3-OFF, 4-ON 1-ON, 2-ON, 3-OFF, 4-OFF
SW2 1-OFF, 2-OFF, 3-ON, 4-ON 1-ON, 2-ON, 3-OFF, 4-OFF
Function Download Data Normal (Default)
1
2
3
4
ON
SW2
1
2
3
4
ON
Normal (Default)
1
2
3
4
ON
1
2
3
4
ON
An external RS-232 connector for MCU programming
(CN1)
1
2
3
Pin No. Pin Name
1 EXT_TXD_R
2 GND
3 EXT_RXD_R
Power-on instance
•
Power-good signal turned-low instance •
Low Voltage Detection2. : Turn on this switch to
enable the automatic detection of low voltage
state of the battery. It will automatically turn
off the system when low voltage state has been
detected (Note: the low-voltage condition needs
to remain 30 seconds continually). The voltage
level can be set in the Ignition System Manager
(ISM) which is provided by Lanner as sample code
for functions on the power ignition module. The
default setting of this function: Shutdown
Voltage in the ISM is disabled. (Refer to the flow
chart in Chapter 4 and the Using the Ignition
System Manager (ISM) in Appendix A.)
Watchdog: 3. Enable this switch to enable shutdown
after watchdog timer count-down to zero. This is a
programmable function. If there is no program to
control and monitor the watchdog timer, set this
jumper to disabled to avoid abnormal shutdown.
The default time-out value is 300 sec( you will need
an AT command to reset watchdog timer; contact
Lanner rep for this program).
IGN_CON1
4
3
2
1
Pin No. Pin Name
1 REMOTE_POWER_ON
2 3G_POWER_ON
3 IGN_DI0
4 IGN_DI1
Ignition Control Connector (IGNITION1)
10 9 8 7 1
Pin No. Pin Name Pin No. Pin Name
1 IGNITION 6 D2D_EN
2 SYS_POWER_
SWITCH
3 COM_SOUT 8 GND
4 COM_SIN 9 DC_VIN
5 D2D_PWROK 10 DCIN_VCC
7 SYS_POWER_OK
Embedded and Industrial Computing
27
Page 28

Chapter 3
LEB-POE936A Board
The following pin definitions refer to the connectors on
the LVP-POE936A board which is the board of the power
adaptor. It corresponds to the connectors of the power
adaptor in Chapter 2 System Components.
Vehicle Power (12V/24V) w/Ignition (Power_CON2):
This connector accepts 9~36V DC power input for
powering the LVC-5770. Additionally, it accepts another
9~36V DC input integrated together in this 5-pin terminal
connector.
Board Layout
1 2 3 4 5
Pin No. Function
1 Ignition
2 GND
3 DC9~36V IN
4 GND
5 DC9~36V IN
POE 48V Output & PC Power 9~36V Out (Power_CON1):
This connector connects to the LVC-5770 and provides
48V DC for POE and 9~36V DC for the entire system.
Pin No. Function
1 2 3 4 5
1 GND
2 48V Out
3 Ignition
4 GND
5 DC 9~36V Out
AUX 9~36V Bypass (Power_CON3): As the Power_CON2
can accept additional power input (9~36V) to be bypassed,
this connector can supply/bypass 9~36V power for other
uses.
1 2
Pin No. Function
1 GND
2 9~36V Out
MCU Programming (CN1)
1 2 3
Embedded and Industrial Computing
Pin No. Function
1 TX
2 GND
3 RX
28
Page 29

Chapter 4
Chapter 4:
The Flow Chart
The flow chart section contains all flow chart used in the
system. The flow chart describes the system’s behavior on
powering on and off the system via power ignition control
or on/off switch when the appropriate timer control
parameters are set.
Flow Chart
Note:
1.
For power-good and low-voltage
mechanism to function in the workflow,
you will need to enable the power-good
and low-voltage detection function
with selector 1 and selector 2 jumper
respectively of SW1 on LEK-IG1 board.
(Refer to Chapter 3 Board Layout).
Embedded and Industrial Computing
For power on and power off delay timer 2.
parameter, refer to Appendix A Using the
Ignition System Manager (ISM).
For DI wake-up function, refer to jumper 3.
MIO (DIO, J15) in Chapter 3 Board Layout.
And refer to Appendix A Using the Ignition
System Manager (ISM) for parameter
setting.
When the system’s shutdown timer starts 4.
counting down 180sec, using ignition
or External PWR_BTN to start the system
again during shutdown process will not
work until the countdown finishes.
29
Page 30

Chapter 5
Hardware Setup
Chapter 5:
Hardware Setup
Preparing the Hardware Installation
To access some components and perform certain service
procedures, you must perform the following procedures
first.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury,
electric shock, or damage to the equipment,
remove the power cord to remove power from
the server. The power switch button does not
completely shut off system power. Portions of the
power supply and some internal circuitry remain
active until power is removed.
Unpower the LVC-5770 and remove the power cord.1.
Unscrew the 4 threaded screws from the top cover.2.
Open the cover.3.
Installing the System Memory
The motherboard supports DDR3 memory to meet the
higher bandwidth requirements of the latest operating
system and Internet applications. It comes with two
Double Data Rate Three (DDR3) Small Outline Dual Inline
Memory Module (SO-DIMM) socket.
Align the memory module’s key with the SO-DIMM 1.
socket’s key.
Install the SO-DIMM.2.
2
1
Note:
If the CPU thermal pad mounting breaks apart,
use your hands to reattach the falling parts and
stick them together.
Note:
The system can support memory of DDR3 SODIMM up to 16 GB in maximum with 2 SO-DIMM
sockets.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
30
Page 31

Chapter 5
Wireless Module Installation
Align the wireless module’s key with the Mini-PCIe slot 1.
notch.
Insert the wireless module into the connector 2.
diagonally.
Push down the wireless module and then tighten it 3.
with the screws.
2
3
Hardware Setup
Lock
Note: To remove the SIM card, slide the card
reader outward to unlock it.
Unlock
3G SIM Card Installation
Unlock the SIM card reader first by sliding it outward.1.
Flip the SIM card reader diagonally. 2.
Place the SIM card in the reader. The angled corner of 3.
the SIM ensures that the card fits only the correct way
in the reader. Make sure the ICs will be in contact with
the SIM card reader.
Insert the 4. SIM card into the reader and close the tray.
You should feel a click when the SIM card is locked
securely in the SIM card reader.
4
2
3
Embedded and Industrial Computing
31
Page 32

Chapter 5
DC_IN
IGNITION
DC_GND
IG - +
LVC-5770
PoE Power 48V
DC Input 9~36V
Ignition Gnd DC9~36V_in Gnd DC9~36V_in
48V_out Gnd Ignition Gnd DC9~36V_out
Gnd DC9~36V_out
+ -
OUT + - - + IN
DC Relay Bypass
Hardware Setup
Installing the Hard Disk
The system can accommodate two Serial-ATA disk. Follow
these steps to install the hard disk into the system:
Place the HDD/SSD on the hard disk tray of the front 1.
panel and align the holes of the hard disk with the
mounting holes on the tray.
Fix the HDD/SSD on the hard disk tray by using 2 2.
mounting screws
Push the HDD/SSD into the hard disk slot and secure it 3.
in place with the thumb screws.
1
Drive Connector
Connecting Power
Connect the LVC-5770 to a +12V or +24V vehicle battery.
The DC power-in connector comes with a 3-pin terminal
block for its Phoenix contact. This power socket can only
accept the power supply with the right pin contact so be
cautious when inserting power to the system.
Note:
Power Connector
The system only supports 2.5” HDD/SSD.1.
Make sure that you insert the HDD in 2.
Silver plate
the right orientation (shown as the
above picture) to prevent damage to the
connectors. Do not force the HDD into the
slot; it indicates wrong orientation if the
insertion is not smooth.
Warning:
Connect the power to the DC-IN connector in the
right orientation or the LVC-5770 will be damaged.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
32
Page 33

Appendix A
Appendix A:
Using the Ignition System
Manager (ISM)
The Ignition System Manager (ISM) is a software that
can monitor the system’s voltage level and configure the
functions that the Power Ignition Module provides.
Using the Ignition System Manager (ISM)
For sample ISM code, see ISM folder under LVC-5770 Utility
on the Driver and Manual CD.
Running the Program
Just double click the ISM.exe to launch the ISM.
The program can configure the following values:
Voltage: It shows the current power system.
Power Input System: Select either 12V or 24V for vehicular
power input.
Startup Voltage (V): If the DC-in voltage is not higher
than this value, the system will not be able to start up.
Shutdown Voltage (V): If the DC-in voltage is lower than
the shutdown voltage, the system will start shutdown
process automatically. (Refer to selector 2 of SW1 dip
switch on the LEK-IG1 board)
Power-on Delay (min/sec): Select power-on delay value
to indicate the time to delay powering on the system.
(Refer to the flow chart in Chapter 4)
Power-off Delay (hr/min/sec): Select power-off delay
value to indicate the time to delay powering off the system
(Refer to the flow chart in Chapter 4)
Serial Port: Select the serial communication port for the
ISM. Choose COM5.
D1/D2 Wakeup: Digital input triggering to enable
automatic wake-up function. Select this option and it will
start the system automatically once an input has been
triggered.
COM5
Note:
You will have to enable (the default is enabled) 1.
the selector 2 (Low Voltage Detection) of SW1
dip switch on the LEK-IG1 to enable automatic
shutdown function. (Refer to Select MCU detect
function for power ignition behavior (SW1) in
Chapter 3 Board Layout).
DI1/DI2 Wakeup function is detected via pin 2.
12/13 of J15 ( the MIO port on the rear panel)
Refer to the 3. flow charts in Chapter 4 for
more information about how the system behave
according to these parameter set here.
.
After you have made changes, click Apply to apply the
changes to the Ignition controller or Cancel to cancel the
changes.
Click Cancel to exit the ISM program.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
33
Page 34

Appendix B
Digital Input/Output Control
Appendix B:
Digital Input/Output
The Digitanl I/O on the rear panel is designed to provide
the input and output operations for the system. For sample
DIO code, see SuperIO folder under LVC-5770 Utility on the
Driver and Manual CD. Make sure that you have installed
the Lanner GPIO driver as instructed below.
Driver Installation
Before you could access or control the operation of the
G-sensor and Digital I/O functions, install the the L_IO
driver which is the library and driver needed for Lanner
General Purpose Input/Output interface or functions.
To install the L_IO driver:
Restart the computer, and then log on with 1.
Administrator privileges.
Insert the Drivers and User’s Manual CD to the USB-2.
optical drive.
Select Next to proceed5.
Answer “Yes” to the question and select Next to 6.
proceed.
Browse the contents of the support CD to locate the 3.
file in the LIO folder.
From the control panel, click the ADD Hardware 4.
program
Select Add a new hardware device.7.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
34
Page 35

Appendix B
Digital Input/Output Control
Choose to select the hardware Manually8.
Choose Show all device and click Next.9.
Click HaveDisk to locate the L_IO.inf file11.
Select the L_IO.inf12.
Click HaveDisk to locate the L_IO.inf file10.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
Select OK to confirm with the installation13.
35
Page 36

Appendix B
Digital Input/Output Control
Select the Lanner IO driver and click Next.14.
Click Next15.
To verify the GPIO driver installation, do the following
steps:
Right-click on the My Computer icon, and then select 1.
Properties form the menu.
Click the Hardware tab, then click the Device Manager 2.
button.
Click the + sign next to the Lanner_Device, then the 3.
Lanner IO Driver should be listed.
Click 16. Complete to close the installation program.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
36
Page 37

Appendix B
A sample DIO program in C:
ioaccess.c: IO access code for Lanner Platfomr Digital IO
program
*********************************************************
**********************/
Digital Input/Output Control
#include <time.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include “../include/config.h”
#ifdef DJGPP
/* standard include file */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/* For DOS DJGPP */
#include <dos.h>
#include <inlines/pc.h>
#else //DJGPP
/* For Linux */
#define delay(x) usleep(x)
#endif
#ifdef MODULE
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#undef delay
#define delay(x) mdelay(x)
#undef fprintf
#define fprintf(S, A) printk(A)
#ifdef DIRECT_IO_ACCESS
/* For Linux direct io access code */
/* standard include file */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#if defined(LINUX_ENV)
#include <sys/io.h>
#endif
#if defined(FreeBSD_ENV)
#include <machine/cpufunc.h>
#endif
Embedded and Industrial Computing
#endif //MODULE
#ifdef KLD_MODULE
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/kernel.h>
#include <sys/bus.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
37
Page 38

Appendix B
Digital Input/Output Control
#include <machine/bus.h>
#include <machine/resource.h>
#endif
#endif
/* local include file */
#include “../include/ioaccess.h”
#if (defined(MODULE) || defined(DIRECT_IO_ACCESS) ||
defined(KLD_MODULE))
/*
*---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---
* LEB-5770 Version V1.0
*output3-0 = GPIO 03-00, input3-0= GPIO 53-50
*---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
outportb(INDEX_PORT, 0xAA);
return;
}
unsigned char read_SIO_reg(int LDN, int reg)
{
outportb(INDEX_PORT, 0x07); //LDN register
delay(5);
outportb(DATA_PORT, LDN);
delay(5);
outportb(INDEX_PORT, reg);
delay(5);
return(inportb(DATA_PORT));
}
void write_SIO_reg(int LDN, int reg, int value)
{
*/
/*
* Device Depend Definition :
*/
#define INDEX_PORT 0x2E
#define DATA_PORT 0x2F
void enter_SIO_config(void)
{
outportb(INDEX_PORT, 0x87); // Must Do It Twice
outportb(INDEX_PORT, 0x87);
return;
}
void exit_SIO_config(void)
{
outportb(INDEX_PORT, 0x07); //LDN register
delay(5);
outportb(DATA_PORT, LDN);
delay(5);
outportb(INDEX_PORT, reg);
delay(5);
outportb(DATA_PORT, value);
return;
}
void dio_gpio_init(void)
{
enter_SIO_config();
write_SIO_reg(0x6, 0x30,0x01); //enable GPIO
Port
write_SIO_reg(0x6, 0xf0,((read_SIO_reg(0x6,
0xf0)& 0xF0)|0x0f)); //RxF0[3-0]=1111b, output
write_SIO_reg(0x6, 0xA0, (read_SIO_reg(0x6,
0xA0)& 0xF0)); //RxA0[3-0]=0000b, input
Embedded and Industrial Computing
38
Page 39

Appendix B
exit_SIO_config();
return;
}
void dio_set_output(unsigned char out_value)
{
enter_SIO_config();
write_SIO_reg(0x6, 0xf1, ((read_SIO_reg(0x6,
0xf1)& 0xF0)|out_value));
exit_SIO_config();
return;
}
unsigned int dio_get_input(void)
{
Digital Input/Output Control
unsigned int tmp=0x00;
enter_SIO_config();
tmp=read_SIO_reg(0x6, 0xA2)& 0x0f;
exit_SIO_config();
return tmp;
}
//======================================
========================================
=================
#endif
Embedded and Industrial Computing
39
Page 40

Appendix C
Accessing the Digital Accelerometer
Appendix C:
Accessing the Digital
Accelerometer Data from
the LVC-5770
The system employs Analog Devices’s ADXL345 Digital
Accelerometer which is a small, thin, ultralow power, 3-axis
accelerometer with high resolution (13-bit) measurement
at up to ±16 g. It interfaces with the LVC-5770 through a
SPI interface.
Driver Installation
To access the G-Sensor data, use the following
instructions:
Make sure you already installed the Lanner GPIO driver on
your LVC-5770 as instructed in Appendix B.
To access the Gsensor data, locate the adxl345_v001 folder
and execute the executable file adxl345 and it will show G
value of 3 axes.
A sample program in C:++
// main.cpp
// The adxl345.exe utility shows the 3 axis G value.
//
// History:
// 07/15/2011: Initial version
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include “ich7.h”
#include “adxl345.h”
void adxl345_init()
{
ich7_SM_WriteByte (0x1D, POWER_CTL, ACT_INACT_
SERIAL | MEASURE) ; // Power CTL:
Measure mode, Activity and Inactivity Serial
ich7_SM_WriteByte (0x1d, BW_RATE, RATE_100);
/ /
Output Data Rate: 100Hz
ich7_SM_WriteByte (0x1d, DATA_FORMAT, FULL_
RESOLUTION | DATA_JUST_LEFT | RANGE_16G);
/ /
Data Format: 16g range, right justified, 256->1g
}
Embedded and Industrial Computing
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
adxl345_init () ;
40
Page 41

Appendix C
while (1)
{
short x = (short) ich7_SM_ReadByte
(0x1d, DATAX1) << 8 | ich7_SM_ReadByte (0x1d,
DATAX0)<<0 ;
short y = (short) ich7_SM_ReadByte
(0x1d, DATAY1) << 8 | ich7_SM_ReadByte (0x1d,
DATAY0)<<0 ;
short z = (short) ich7_SM_ReadByte
(0x1d, DATAZ1) << 8 | ich7_SM_ReadByte (0x1d,
DATAZ0)<<0 ;
printf (“\rX=%.2f Y=%.2f Z=%.2f”, ((float)
x)/2048,((float)y)/2048,((float)z)/2048) ;
}
Accessing the Digital Accelerometer
}
Embedded and Industrial Computing
41
Page 42

Appendix D
Accessing the GPS Data
Appendix D:
Accessing the GPS Data
from the LVC-5770
The LVC-5770 employs an onbard u-blox NEO-6Q GPS
module for vehicle tracking and navigation system. You
could read the GPS data through the RS-232 serial port.
It has the following listed key features and performance
ratings:
Receiver type 50 Channels
GPS L1 frequency, C/A Code
SBAS: WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS
Time-To-First-Fix (All satellites at -130 dBm)
Sensitivity Tracking &Navigation: •
Maximum Navigation
update rate
Horizontal position accurach (CEP, 50%, 24 hours
static, -130dBm, SEP:
<3.5m)
Congurable Timepulse
frequency range
Accuracy for Timepulse
signal
Velocity accuracy 0.1m/s
Heading accuracy 0.5 degrees
Operational Limits Dynamics: less than and
Cold Start: 26 s
Warm Start: 26 s
Hot Start: 1 s
Aided Starts: 1 s
-162dBm
Reacquisition: -160dBm•
Cold Start (without aid-•
ing): -148 dBm
Hot Start: -157 dBm•
5Hz
GPS: 2.5m
SBAS: 2.0m
0.25 Hz to 1 kHz
RMS: 30 ns
99%: <60 ns
Granularity: 21 ns
Compensated: 15 ns
equal to 4g
Altitude: 50,000m
Velocity: 500m/s (Assuming
Airborne <4g platform)
To access the GPS data, follow the following steps:
Select Programs from the Start menu on your windows
and open the Hyper Terminal program.
Choose COM4 from the Connection using drop-down
menu:
Embedded and Industrial Computing
42
Page 43

Appendix D
Specify the following communication parameters:
Bits per Second: 9600
Data Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bit: 1
Flow Control: None
9600
Accessing the GPS Data
The hyper terminal should display GPS data:
Embedded and Industrial Computing
43
Page 44

Appendix E
Programming Watchdog Timer
Appendix E:
Programming System
Watchdog Timer of the
LVC-5770
A watchdog timer is a piece of hardware that can be
used to automatically detect system anomalies and reset
the processor in case there are any problems. Generally
speaking, a watchdog timer is based on a counter that
counts down from an initial value to zero. The software
selects the counter’s initial value and periodically restarts
it. Should the counter reach zero before the software
restarts it, the software is presumed to be malfunctioning
and the processor’s reset signal is asserted. Thus, the
processor will be restarted as if a human operator had
cycled the power.
For sample watchdog code, see watchdog folder under
LVC-5770 Utility on the Driver and Manual CD
#include “F81865.h”
#define PARAMETER_HELP “\n”\
“The F81865 GPIO utility of Lanner\n”\
“-------------------------------------\n”\
“Usage:\n”\
“ F81865_test DIO_IN port_
number\n”\
“ F81865_test DIO_OUT port_number
value\n”\
“ F81865_test PIO port_number
value\n”\
“ F81865_test RunLED port_number
value\n”\
“ F81865_test AlarmLED port_number
value\n”\
“ F81865_test GPS_LED port_number
value\n”\
Executing through the Command Line:
Execute the WD.EXE file under DOS (WD.EXE and CWSDPMI.
EXE should be placed on same directory), then enter the
values from 0~255. The system will reboot automatically
according to the time-out you set.
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
You can write your own program by modifying the source
code F81865_Test.cpp.. The index address is 2EH.
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////
// F81865_Test.cpp : F81865_test.exe utility for F81865.lib
APIs demonstration.
//
// History:
// 7/15/2011 Brand new F81865_test
program.
“ F81865_test WirelessLED port_number
value\n”\
“ F81865_test WatchDog seconds\n”\
“ F81865_test CaseOpen\n”\
“ F81865_test CaseOpen_Clear\n”\
“ F81865_test Sleep
milliseconds\n”\
“\n”\
“Argement:\n”\
“ DIO_IN Read state from DIO
In.\n”\
“ DIO_OUT Set DIO Out state.\n”\
“ PIO Set PIO LED state.\n”\
“ RunLED Set RUN LED state.\n”\
“ AlarmLED Set Alarm LED state.\n”\
#include <winsock2.h>
#include “Windows.h”
#include “stdio.h”
Embedded and Industrial Computing
“ GPS_LED Set GPS LED state.\n”\
“ WirelessLED Set Wireless LED state.\n”\
44
Page 45

Appendix E
Programming Watchdog Timer
“ Watchdog Set
Watchdog timer.\n”\
“ CaseOpen Check case opened state.\n”\
“ CaseOpen_Clear Clear case open state.\n”\
“ port_number The port number.\n”\
“ value 1 for on and 0 for off.\n”\
“ seconds The
watchdog count down seconds. 0 for disable.\n”\
“ milliseconds Milliseconds to
delay\n”
#define RETMSG(a,b) {printf (b) ; return a;}
#define CHECK_ARGC(a) {if (argc
!= a) throw PARAMETER_HELP ;}
// Translate Hex string to a long value
LONG Hex2Long (char *str)
{
LONG nLong ;
if (scanf (str, “%x”, &nLong) != 1)
throw “Error parsing parameter\n” ;
return nLong ;
}
// Make sure the argument is numeric
void CheckNumeric (char *szBuf )
{
int nLen = strlen (szBuf ) ;
for (int i = 0 ; i < nLen ; i++)
if (!strchr (“01234567890ABCDEFabcdef”, szBuf[i]) )
throw “Wrong argument\n” ;
}
// Common GPIO output function definition
#define GPIO_OUT(a,b,c) \
int a (int argc, char *argv[]) \
{
\
CHECK_ARGC (4) ;
\
\
int nPort = atoi (argv[2]) ; \
int nValue = atoi (argv[3]) ; \
\
c (nPort, nValue) ;
\
\
printf (b “ #%d = %d\n”, nPort, nValue) ; \
\
return 0
; \
}
// Function generate by common function definition
GPIO_OUT (mDIO_
OUT , “DIO_OUT” , Write_DIO)
G P I O _ O U T
(mPIO , “DIO_OUT” , PIO)
G P I O _ O U T
(mRunLED , “RunLED” , RunLED)
G P I O _ O U T
(mAlarmLED , “AlarmLED” , AlarmLED)
GPIO_OUT (mGPS_
LED , “GPS_LED” , GPS_LED)
G P I O _ O U T
(mWirelessLED , “WirelessLED” , WirelessLED)
// Check case open
int mCaseOpen (int argc, char* argv[])
{
CHECK_ARGC (2) ;
BOOL bOpen = CaseOpen () ;
printf (“Case is %s\n”, bOpen ? “Open” : “Close”) ;
return bOpen ;
}
CheckNumeric (argv[2]) ; \
CheckNumeric (argv[3]) ; \
Embedded and Industrial Computing
45
Page 46

Appendix E
Programming Watchdog Timer
// Clear case open state
int mCaseOpen_Clear (int argc, char* argv[])
{
CHECK_ARGC (2) ;
CaseOpen_Clear () ;
BOOL bOpen = CaseOpen () ;
printf (“CaseOpen state %s”, bOpen ? “not cleared”
: “cleared”) ;
return bOpen ;
}
// Get DIO_IN state
int mDIO_IN (int argc, char* argv[])
{
CHECK_ARGC (3) ;
CheckNumeric (argv[2]) ;
return 0 ;
}
// Watchdog
int mWatchDog (int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3 && argc != 2)
RETMSG (-1, PARAMETER_HELP) ;
if (argc == 3)
{
CheckNumeric (argv[2]) ;
int nValue = atoi (argv[2]) ;
WatchDog_Enable (nValue) ;
}
int nLeft = WatchDog_GetLeft () ;
int nPort = atoi (argv[2]) ;
BOOL ret = Read_DIO (nPort) ;
printf (“DIO_IN #%d = %d\n”, nPort, ret) ;
return ret ;
}
// Milli-second delay
int mSleep (int argc, char *argv[])
{
CHECK_ARGC (3) ;
CheckNumeric (argv[2]) ;
Sleep (atoi (argv[2]) ) ;
printf (“Watchdog timer left %d seconds\n”, nLeft)
;
return nLeft ;
}
// Argument - function mapping
typedef struct
{
char *szCmd ;
int (*function) (int argc, char *argv[]) ;
} CMD2FUN ;
CMD2FUN c2f[] =
{
Embedded and Industrial Computing
46
Page 47

Appendix E
{“DIO_IN” , mDIO_IN
},
{“DIO_OUT” , mDIO_OUT
},
{“PIO” , mPIO
},
{“RunLED” , mRunLED
},
{“AlarmLED” , mAlarmLED
},
{“GPS_LED” , mGPS_LED
},
{“WirelessLED” , mWirelessLED },
{“CaseOpen” , mCaseOpen },
{“CaseOpen_Clear”,mCaseOpen_Clear},
{“Watchdog” , mWatchDog
},
Programming Watchdog Timer
// No match argument
RETMSG (-1, “Wrong Argument\n”) ;
}
catch (char *str)
{
// Output the error message
printf (“\n%s\n”, str) ;
}
catch (...)
{
// Unknown exception
printf (“\nUnknown Exception\n”) ;
}
{“Sleep” , mSleep }
} ;
// Program start here
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
try
{
// The total argument allowed
int num = sizeof (c2f) / sizeof (c2f[0]) ;
// Too few argument
if (argc < 2)
RETMSG (-1, PARAMETER_HELP)
;
return -1 ;
}
// Find the match argument and execute
the mapping function
for (int i = 0 ; i < num ; i++)
if (stricmp (argv[1], c2f[i].szCmd)
== 0)
return c2f[i].function
(argc, argv) ;
Embedded and Industrial Computing
47
Page 48

Appendix F
Terms and Conditions
Appendix F:
Terms and Conditions
Warranty Policy
All products are under warranty against defects in 1.
materials and workmanship for a period of one year
from the date of purchase.
The buyer will bear the return freight charges for 2.
goods returned for repair within the warranty period;
whereas the manufacturer will bear the after service
freight charges for goods returned to the user.
The buyer will pay for repair (for replaced components 3.
plus service time) and transportation charges (both
ways) for items after the expiration of the warranty
period.
If the RMA Service Request Form does not meet the 4.
stated requirement as listed on “RMA Service,” RMA
goods will be returned at customer’s expense.
The following conditions are excluded from this 5.
warranty:
RMA Service
Requesting a RMA#
To obtain a RMA number, simply fill out and fax the 6.
“RMA Request Form” to your supplier.
The customer is required to fill out the problem code 7.
as listed. If your problem is not among the codes listed,
please write the symptom description in the remarks
box.
Ship the defective unit(s) on freight prepaid terms. 8.
Use the original packing materials when possible.
Mark the RMA# clearly on the box. 9.
Note: Customer is responsible for shipping
damage(s) resulting from inadequate/loose
packing of the defective unit(s). All RMA# are valid
for 30 days only; RMA goods received after the
effective RMA# period will be rejected.
Improper or inadequate maintenance by the customer
Unauthorized modification, misuse, or reversed
engineering of the product Operation outside of the
environmental specifications for the product.
Embedded and Industrial Computing
48
Page 49

Appendix F
RMA Service Request Form
When requesting RMA service, please fill out the following form. Without
this form enclosed, your RMA cannot be processed.
RMA No:
Reasons to Return: Ŀ Repair(Please include failure details)
Ŀ Testing Purpose
Company: Contact Person:
Phone No. Purchased Date:
Fax No.: Applied Date:
Return Shipping Address:
Shipping by: Ŀ Air Freight Ŀ Sea Ŀ Express ___
Ŀ Others:________________
Item Model Name Serial Number Configuration
Item Problem Code Failure Status
*Problem Code:
01:D.O.A.
02: Second Time
R.M.A.
03: CMOS Data Lost
04: FDC Fail
05: HDC Fail
06: Bad Slot
07: BIOS Problem
08: Keyboard Controller Fail
09: Cache RMA Problem
10: Memory Socket Bad
11: Hang Up Software
12: Out Look Damage
13: SCSI
14: LPT Port
15: PS2
16: LAN
17: COM Port
18: Watchdog Timer
19: DIO
20: Buzzer
21: Shut Down
22: Panel Fail
23: CRT Fail
24: Others (Pls specify)
Request Party
Confirmed By Supplier
Authorized Signature / Date Authorized Signature / Date
Terms and Conditions
Embedded and Industrial Computing
49
 Loading...
Loading...