Page 1

Page 2
This booklet provides step-by-step instructions for each of the tests
L
M
o
tt
provided in the AG-104 test kit. Please refer to the separate sheets for
proper use of the Direct Reading Titrator and Axial Reader
Comparator where noted.
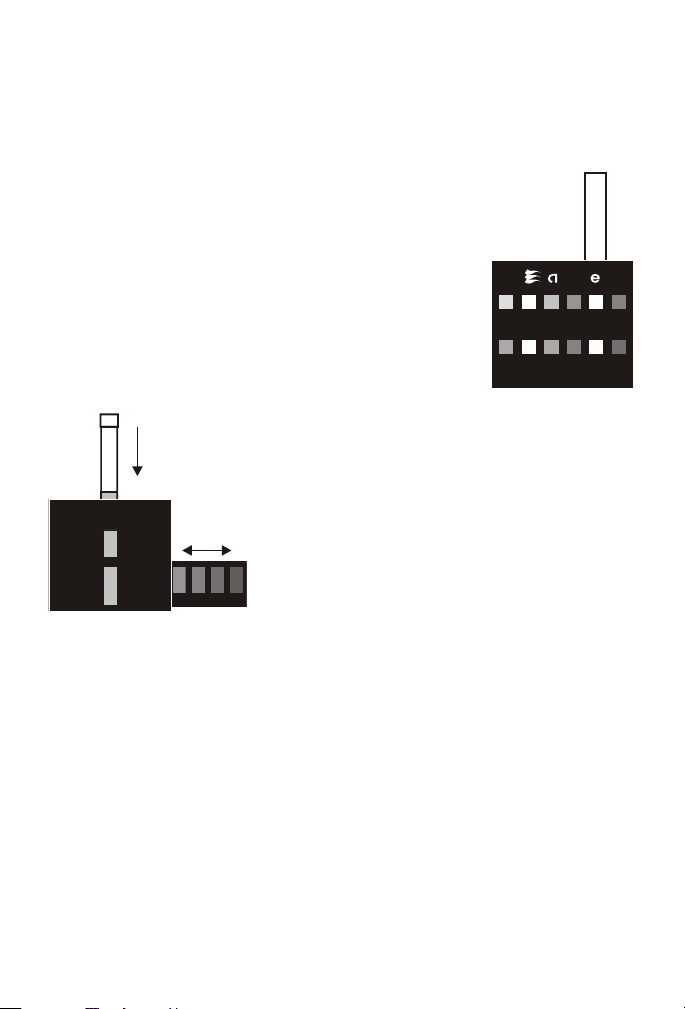
Use of the pH Oc tet Com para tor
The Octet Comparator contains eight permanent
color standards. A test sample is inserted into the
openings in the top of the comparator. The sample
can then be compared to four color standards at
once, and the value read off the comparator. For
optimum color comparison, the comparator should
be positioned between the operator and a light
source, so that the light enters through the special
light-diffusing screen in the back of the comparator.
Avoid viewing the comparator against direct
sunlight or an irregularly lighted background.
Use of the Octa-Slide Viewer
The Octa-Slide Viewer should be held so
non-direct light enters through the back of the
comparator. With sample tube inserted at top,
slide the Octa-Slide bar thorough the viewer
and march with color standard.
TA BLE OF CON TENTS
Alkalinity................................................................................................ 3
Ammonia Nitrogen........................................................................... 4 - 5
Carbon Dioxide ...................................................................................... 6
Dissolved Oxygen............................................................................ 7 - 11
Nitrate Nitrogen................................................................................... 11
Nitrite ................................................................................................... 12
pH ......................................................................................................... 13
Salinity .......................................................................................... 14 - 15
2
Page 3

ALKALINITY
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
100 BCG-MR Indicator Tablets T-2311-J
60 mL *Alkalinity Titration Reagent B *4493DR-H
1 Test Tube, 5-10-15 mL, glass w/cap 0778
1 Direct Reading Titrator, 0-200 Range 0382
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE: Read Direct Reading Titrator Manual before performing test.
Pro ce dure
1. Fill the test tube (0778) to 5 mL line with sample water.
2. Add one BCG-MR Indicator Tablet (T-2311). Cap and shake until
dissolved. A blue-green color will develop.
3. Fill the Direct Reading Titrator (0382) with *Alkalinity Titration
Reagent B (4493DR). Insert Titrator into the center hole of the test
tube cap.
4. While gently swirling the tube, slowly depress plunger to titrate until
the blue-green color changes to pink. Read the test result directly
from the scale where the large ring on the Titrator meets the
Titrator barrel. Record results as Total Alkalinity in ppm (CaCO3).
Each minor division on Titrator scale = 4 ppm Total Alkalinity as
CaCO3.
EXAMPLE: Plunger tip is 3 minor divisions below line 140. The
test result is 140 plus (3 divisions x 4) equals 152 ppm.
5. If the plunger tip reaches the bottom line on the titrator scale (200
ppm) before the endpoint color change occurs, refill the titrator and
continue titration. When recording the test result, be sure to include
the value of the original amount of reagent dispensed (200 ppm).
When testing salt water aquariums, alkalinity may be called carbonate
hardness. Multiply ppm Alkalinity by 0.056 to convert to German
degrees of Hardness.
This test set provides Total Alkalinity readings only. For
comprehensive analysis of Phenolphthalein (P), Total (T), Hydroxide,
Carbonate, and Bicarbonate Alkalinity the Model WAT-MP-DR Test
Set, Code 4533-DR is recommended.
3
Page 4

AMMONIA NITROGEN
Salicylate Method
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
60 mL *Salicylate Ammonia #1 *3978LWT-H
30 mL *Salicylate Ammonia #2 *3979WT-G
30 mL Salicylate Ammonia #3 3982WT-G
2 Test Tubes, plastic, w/cap 0106
1 Octa-Slide Viewer 1100
1 Ammonia-Nitrogen Octa-Slide Bar,
0-2 ppm
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
Pro ce dure
1. Fill a test tube (0106) to the 5 mL line with the water sample.
2. Add 10 drops of Salicylate Ammonia #1 (3978LWT). Cap and mix.
3. Add 7 drops of *Salicylate Ammonia #2 (3979WT). Cap and mix.
Wait one minute.
4. Add 7 drops of Salicylate Ammonia #3 (3982). Cap and mix. Wait
20 minutes.
5. Insert Ammonia Nitrogen Octa-Slide Bar (3441) into the
Octa-Slide Viewer (1100). Insert test tube into Octa-Slide Viewer.
Match sample color to a color standard. Record as ppm Ammonia
Nitrogen (NH
3
_
N).
To express results as Unionized Ammonia (NH3):
ppm Unionized Ammonia (NH3) =
ppm Ammonia Nitrogen (NH3–N) x 1.2
To express results as Ionized Ammonia (NH4):
ppm Ionized Ammonia (NH
+
) =
4
ppm Ammonia Nitrogen (NH3–N) x 1.3
Ammonia in water occurs in two forms: toxic unionized ammonia
(NH3) and the relatively non-toxic ionized form, ammonium ion
+
(NH
). This test method measures both forms as ammonia nitrogen
4
+
(NH
–N) to give the total ammonia nitrogen concentration in water.
4
The actual proportion of each compound depends on temperature,
salinity, and pH. A greater concentration of unionized ammonia is
present when the pH value and salinity increase.
4
3441
Page 5
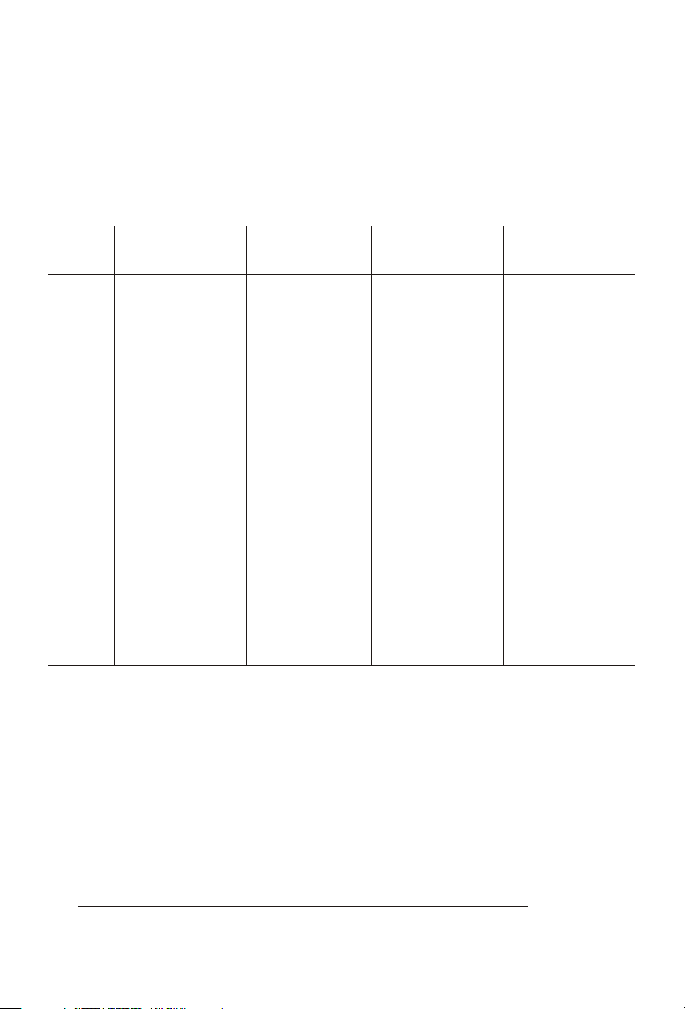
Consult the table to find the percentage that corresponds to the
temperature, pH, and salinity of the sample.
2. To express the test result as ppm Unionized Ammonia Nitrogen
(NH3–N), multiply the total ammonia-nitrogen test result by the
percentage from the table.
3. To express the test result as ppm Ionized Ammonia Nitrogen
+
(NH
–N), subtract the unionized ammonia-nitrogen determined in
4
Step 2 from the total ammonia-nitrogen.
10°C 15°C 20°C 25°C
pH FW1SW
2
FW SW FW SW FW SW
7.0 0.19 0.27 0.40 0.55
7.1 0.23 0.34 0.50 0.70
7.2 0.29 0.43 0.63 0.88
7.3 0.37 0.54 0.79 1.10
7.4 0.47 0.68 0.99 1.38
7.5 0.59 0.459 0.85 0.665 1.24 0.963 1.73 1.39
7.6 0.74 0.577 1.07 0.836 1.56 1.21 2.17 1.75
7.7 0.92 0.726 1.35 1.05 1.96 1.52 2.72 2.19
7.8 1.16 0.912 1.69 1.32 2.45 1.90 3.39 2.74
7.9 1.46 1.15 2.12 1.66 3.06 2.39 4.24 3.43
8.0 1.83 1.44 2.65 2.07 3.83 2.98 5.28 4.28
8.1 2.29 1.80 3.32 2.60 4.77 3.73 6.55 5.32
8.2 2.86 2.26 4.14 3.25 5.94 4.65 8.11 6.61
8.3 3.58 2.83 5.16 4.06 7.36 5.78 10.00 8.18
8.4 4.46 3.54 6.41 5.05 9.09 7.17 12.27 10.10
8.5 5.55 4.41 7.98 6.28 11.18 8.87 14.97 12.40
1
Freshwater data from Trussel (1972).
2
Seawater values from Bower and Bidwell (1978). Salinity for Seawater values = 34% at an
ionic strength of 0.701m.
EXAMPLE:
A fresh water sample sample at 20°C has a pH of 8.5 and the test
result is 1.0 ppm as Total Ammonia Nitrogen.
1. The percentage from the table is 11.18% (or 0.1118).
2. 1.0 ppm Total Ammonia Nitrogen x 0.1118 = 0.1118 ppm
Unionized Ammonia Nitrogen.
3. Total Ammonia-Nitrogen 1.0000 ppm
Unionized Ammonia-Nitrogen - 0.1118 ppm
Ioinized Ammonia-Nitrogen = 0.8882 ppm
5
Page 6

CARBON DIOXIDE
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
15 mL *Phenolphthalein Indicator, 1% *2246-E
60 mL *Carbon Dioxide Reagent B *4253-H
1 Direct Reading Titrator, 0-50 Range 0380
1 Test Tube, 5-10-12.9-15-20-25 mL, w/cap 0608
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE: Read Direct Reading Titrator Manual before performing test.
Pro ce dure
1. Fill test tube (0608) to 20 mL line with sample water. For best
results, test on freshly obtained sample, and avoid splashing or
prolonged contact with air.
2. Add 2 drops of *Phenolphthalein Indicator, 1% (2246). If sample
turns red, no free carbon dioxide is present. If sample is colorless,
continue to Step 3.
3. Fill Direct Reading Titrator (0380) with *Carbon Dioxide Reagent
B (4253). Insert Titrator in center hole of test tube cap.
4. While gently swirling tube, slowly depress plunger to titrate sample
until color changes to a faint pink which persists for 30 seconds.
Read test result where the plunger tip meets the titrator scale.
Record results as ppm Carbon Dioxide.
6
Page 7

DISSOLVED OXYGEN
For determining the dissolved oxygen content of water, this test kit
uses the azide modification of the Winkler Method and employs a
LaMotte Direct Reading Titrator in the final titration.
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
30 mL *Manganous Sulfate Solution *4167-G
30 mL *Alkaline Potassium Iodide Azide Solution *7166-G
30 mL *Sulfuric Acid, 1:1 *6141WT-G
60 mL *Sodium Thiosulfate Solution (0.025N) *4169-H
30 mL Starch Indicator 4170WT-G
1 Direct Reading Titrator, 0-10 Range 0377
1 Test Tube, 5-10-12.9-15-20-25 mL, w/cap 0608
1 Bottle, Water Sampling, 60 mL, glass 0688-DO
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE: Carefully read the instruction manual for the LaMotte Direct
Reading Titrator before performing the test procedure. The Titrator is
calibrated in parts per million (ppm) Dissolved Oxygen.
Col lec tion & Treat ment of the Wa ter Sam ple
Steps 1 through 4 below describe proper sampling technique in shallow
water. For collection of sample at depths beyond arm’s reach, special
water sampling apparatus is required (e.g., the LaMotte Water
Sampling Chamber, Code 1060; Model JT-1 Water Sampler, Code
1077; or Water Sampling Outfit, Code 3103).
1. To avoid contamination, rinse the Water Sampling Bottle
(0688-DO) thoroughly with sample water.
2. Tightly cap the bottle. Submerge to the desired depth, and remove
the cap to allow the bottle to fill.
3. Tap the sides of the submerged bottle to dislodge any air bubbles
clinging to the inside of the bottle. Replace the cap while the bottle
is still submerged.
4. Retrieve the bottle. Examine it carefully to make sure that no air
bubbles are trapped inside of the bottle. Once a satisfactory sample
has been collected, proceed immediately with Steps 5 and 6 to “fix”
the sample.
7
(continued on page 10)
Page 8

ALKALINITY CARBON DIOXIDE
SALINITY
AMMONIA NITROGEN NITRITE NITRATE
pH
0376
0378
2748
0230
0230
2212-G
0382
4493-DR-H
0380
2246-E 7460-E
0608
4253-H
7461-H
0778
0778
T-2311-J
1100
2165-01
6761
w/2071
3978LWT-H
1151
0106
7424-H
7423-H
w/0357
0354
3979WT-G
7454-D
3982WT-G
0843
0843
0843
0727
0106
3441
8
Page 9

DISSOLVED OXYGEN
pH
0377
0230
4167-G
7166-G
4170WT-G
4169-H
6141WT-G
2165-01
3109
V-6278-H
V-6278-H
7454-D
V-6279-C
0843
0843
0843
0608
0688
0688-DO
0820
0820
0699
0727
9
Page 10

“Fix ing” the Wa ter Sam ple
NOTE: Be careful not to introduce air into the sample while adding
the reagents in Steps 5 and 6. Drop the reagents into the test sample,
cap carefully, and mix gently.
5. Add 8 drops of *Manganous Sulfate Solution (4167) and 8 drops of
*Alkaline Potassium Iodide Azide Solution (7166). Cap and mix by
inverting gently several times. A precipitate will form. Allow the
precipitate to settle below the shoulder of the bottle before
proceeding.
6. Add 8 drops of *Sulfuric Acid, 1:1 (6141WT). Cap and gently
invert to mix, until both the reagent and the precipitate have
dissolved. A clear yellow to brown-orange color will develop,
depending on the oxygen content of the sample.
NOTE: Following the completion of Step 6, contact between the
water sample and the atmosphere will not affect the test result.
Once the sample has been “fixed” in this manner, it is not necessary
to perform the actual test procedure immediately.
Test Pro ce dure
1. Fill the test tube (0608) to the 20 mL line with the “fixed” sample.
Cap.
NOTE: If the color of the “fixed” sample is already a very faint
yellow, skip Step 3, perform Step 4, and begin the titration at
Step 5.
2. Fill the DRT (0377) with *Sodium Thiosulfate Solution (4169).
Insert into the center hole of the test tube cap.
3. While gently mixing the tube, slowly press the plunger to titrate
until the yellow-brown color is reduced to a very faint yellow.
4. Remove the Titrator and cap. Be careful not to disturb the Titrator
plunger, as the titration begun in Step 3 will be continued in
Step 5. Add 8 drops of Starch Indicator Solution (4170WT).
Solution will turn blue.
5. Replace the cap and Titrator and continue titrating until the blue
color just disappears. Read result directly from the scale where the
large ring on the Titrator meets the Titrator barrel. Record as ppm
Dissolved Oxygen. Each minor division equals 0.2 ppm.
10
Page 11

NITRATE NITROGEN
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
2 x 60 mL *Mixed Acid Reagent *V-6278-H
5g *Nitrate Reducing Reagent *V-6279-C
1 Spoon, 0.1g, plastic 0699
2 Test Tubes, 2.5 & 5.0 mL, w/cap 0820
1 Bottle, water sample 0688
1 Nitrate-N Comparator, .25-10.0 ppm 3109
1 Dispenser Cap 0692
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE 1: Nitrites can cause serious interference in this test and
should be determined and compensated for if present.
NOTE 2: The best results are obtained when all solutions are kept
close to 23°C.
NOTE 3: Place Dispenser Cap (0692) on *Mixed Acid Reagent
(V-6278). Save this cap for refill reagents.
Pro ce dure
1. Fill sample bottle (0688) with sample water.
2. Fill the test tube (0820) to the first line (2.5 mL) with the sample
from the sample bottle.
3. Add the *Mixed Acid Reagent (V-6278) to the second line (5.0 mL
total). Cap and mix. Wait two minutes.
4. Use the 0.1g spoon (0699) to add one level measure (avoid any
excess) of *Nitrate Reducing Reagent (V-6279). Cap and invert the
tube 50-60 times in one minute. Wait 10 minutes.
5. Mix before inserting tube into the Nitrate-N Comparator (3109).
Match sample color with a color standard. Record result as ppm
Nitrate Nitrogen (N). To obtain ppm Nitrate (NO3), multiply result
by 4.4.
11
Page 12

NITRITE
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
30 mL Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent A 7423-G
60 mL *Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent B *7424-H
10 g Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent C-R 7797-D
1 Pipet, 1.0 mL, plastic 0354
1 Pipet, plain, plastic w/cap 0357
1 Spoon, 0.15 g, plastic 0727
1 Distilled Water Ampoule, 5 mL 2748
1 Axial Reader 2071
1 Nitrite Comparator, 0.02-0.3 ppm 6761
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE: Read Axial Reader Manual before performing test.
Pro ce dure
1. Fill three test tubes (0843) to the 10 mL line with sample water.
Insert two tubes as blanks in the Axial Reader.
2. Use the plain pipet (0357) to add 10 drops of Nitrite Nitrogen
Reagent A (7423) to third test tube.
3. Use the 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 1.0 mL of *Nitrite Nitrogen
Reagent B (7424). Cap and invert to mix. Allow to stand for 30 to
45 seconds.
4. Use the 0.15g spoon (0727) to add one level measure (avoid any
excess) of Nitrite Nitrogen Reagent C-R. Cap and mix. Allow to
stand for 3 minutes. A pink color indicates the presence of nitrite.
5. Remove cap and insert tube in the Axial Reader comparator. Follow
the Axial Reader instructions to compare the sample color with the
standards. Record result as ppm Nitrite (NO2).
12
Page 13

pH
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
30 mL Cresol Red Indicator 2212-G
1 Test Tube, 5 mL, glass 0230
1 Cresol Red Comparator, 7.7 - 8.4 2165-01
Pro ce dure
1. Rinse the test tube with the sample water, then refill the tube to the
5 mL line.
2. Add 8 drops of Cresol Red Indicator (2212) to the sample, one drop
at a time, holding the dropper bottle vertically to dispense uniformly
sized drops.
3. Cap the tube and invert several times to mix the contents.
4. Insert test tube into the Cresol Red Comparator (2165-01). Match
sample color to a color standard. Record as pH.
13
Page 14

SALINITY
QUAN TITY CON TENTS CODE
15 mL *Salinity Indicator Reagent A *7460-E
60 mL *Salinity Titration Reagent B *7461-H
60 mL Demineralizer Bottle 1151
1 Test Tube, 5-10-15 mL, glass, w/cap 0778
1 Direct Reading Titrator, 0-20 Range 0378
1 Direct Reading Titrator, 0-1.0 Range 0376
*WARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered to be potential health hazards.
To view or print a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for these reagents see MSDS
CD or www.lamotte.com. To obtain a printed copy, contact LaMotte by email, phone
or fax.
NOTE: Read Demineralizer Bottle instructions and Direct Reading
Titrator Manual before performing test.
TEST RANGE: 0-20 ppt Salinity
Pro ce dure
1. Fill test tube (0778) to 10 mL line with Demineralized Water
(1151).
2. Fill the 1.0 mL Titrator (0376) to 0 mark with sample water. Wipe
any excess water off the Titrator.
3. Dispense 0.5 mL of sample water into test tube by depressing
plunger until tip is at 0.5 mark. Discard remaining water in Titrator.
4. Add 3 drops of *Salinity Indicator Reagent A (7460). Cap and
gently swirl to mix.
5. Fill 0-20 Direct Reading Titrator (0378) with *Salinity Titration
Reagent B (7461). Insert Titrator in hole of test tube cap.
6. While gently swirling the tube, slowly depress plunger to titrate
sample until yellow color changes to pink-brown. Read test result
directly from the scale where the large ring on the Titrator meets
the Titrator barrel. Each minor Titrator division = 0.4 ppt Salinity.
EXAMPLE: Plunger tip is 3 minor divisions below 10, test result is
10 plus (3 x 0.4) = 11.2 ppt.
14
Page 15

Re la tion ship Be tween Sa lin ity and Spe cific Grav ity
Sa lin ity (0/00) Spe cific Grav ity
of Ar ti fi cial Sea Water
(20°C [68°F])
0.00 1.0000
2.78 1.0020
5.55 1.0041
8.33 1.0061
11.10 1.0082
13.88 1.0102
16.66 1.0123
19.43 1.0144
22.21 1.0164
24.98 1.0185
27.76 1.0206
30.53 1.0227
33.31 1.0248
36.09 1.0269
38.86 1.0290
41.63 1.0311
44.41 1.0332
47.18 1.0353
49.96 1.0374
52.73 1.0396
55.51 1.0417
NOTE: 0/00 = ppt (parts per thousand)
15
Page 16

LaMOTTE COM PANY
Helping Peo ple Solve An a lyt i cal Chal lenges
SM
PO Box 329 • Chestertown • Mary land • 21620 • USA
800-344-3100 • 410-778-3100 (Out side U.S.A.) • Fax 410-778-6394
Visit us on the web at www.lamotte.com
6/09
 Loading...
Loading...