Page 1

•
COD
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
PLUS
Colorimeter
OPERATOR’S
MANUAL
CODE 1922/1922-EX2
Page 2

Page 3

T ABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION
Packaging & Delivery ······································································ 5
General Precautions ········································································ 5
Safety Precautions ··········································································· 5
Limits of Liability ············································································ 5
Specifications ·················································································· 6
Contents and Accessories ································································ 7
EPA Compliance ············································································· 7
CE Compliance ················································································ 8
CHEMICAL TESTING
Water Sampling for Chemical Analysis ··········································· 9
Filtration ························································································· 10
An Introduction to Colorimetric Analysis ······································ 11
Reagent Blank ················································································· 12
Colorimeter Tubes ··········································································· 12
Selecting an Appropriate Wavelength ············································ 12
Calibration Curves ·········································································· 13
Standard Additions ········································································· 15
Sample Dilution Techniques & Volumetric Measurements ············ 16
Interferences ··················································································· 17
Stray Light Interference ·································································· 17
OPERATION OF THE COD PLUS COLORIMETER
Overview ························································································· 18
Power Source ··················································································· 18
Components ···················································································· 19
Quick Start ····················································································· 20
GENERAL OPERATING PROCEDURES
The Keypad ····················································································· 22
Sample Holders ················································································ 22
The Display & the Menus ······························································· 23
Looping Menus ················································································ 25
TESTING
Testing Menu ·················································································· 26
Sequences of Tests ··········································································· 27
General Testing Procedures ····························································· 28
Testing With the LaMotte Pre-Programmed Tests ·························· 28
Calibrating With the LaMotte Pre-Programmed Tests····················· 30
Measuring in the %T/ABS Mode ···················································· 32
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 4/03 3
Page 4

T ABLE OF CONTENTS (cont.)
EDITING MENU
Edit a Sequence ·············································································· 34
Adding or Deleting Tests ································································· 35
Edit User Tests ················································································ 38
Naming the Test ·············································································· 39
Selecting the Vial and Wavelength ················································· 41
Entering a New Calibration ···························································· 42
Selecting the Numerical Format of the Result ································ 44
Selecting Units of Concentration····················································· 45
Setting the Clock ············································································· 46
Turning the Data Logger On and Off ·············································· 47
Factory Setup ··················································································· 48
Setting the Power Saver Function···················································· 48
PC LINK
Output ···························································································· 49
Computer Connection ····································································· 49
BATTERY OPERATION
Replacing the Battery······································································· 49
MAINTENANCE
Cleaning ·························································································· 50
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Error Messages ················································································· 50
Helpful Hints ··················································································· 50
SMART REAGENT SYSTEMS
······································································································· 51
COD PLUS COLORIMETER TEST INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX
4 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 4/03
Page 5

GENERAL INFORMATION
PACKAGING & DELIVERY
n
Experienced packaging personnel at LaMotte Company assure adequate
protection against normal hazards encountered in transportation of shipments.
After the product leaves the manufacturer, all responsibility for its safe delivery
is assured by the transportation company. Damage claims must be filed
immediately with the transportation company to receive compensation for
damaged goods.
Should it be necessary to return the instrument for repair or servicing, pack
instrument carefully in suitable container with adequate packing material. A
return authorization number must be obtained from LaMotte Company by
calling 1-800-344-3100. Attach a letter with the authorization number to the
shipping carton which describes the kind of trouble experienced. This valuable
information will enable the service department to make the required repairs
more efficiently.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
n
Before attempting to set up or operate this instrument it is important to read
the instruction manual. Failure to do so could result in personal injury or
damage to the equipment.
The COD PLUS Colorimeter should not be stored or used in a wet or corrosive
environment. Care should be taken to prevent water or reagent chemicals from
wet colorimeter tubes from entering the colorimeter chamber.
NEVER PUT WET TUBES IN COLORIMETER.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
n
Read the labels on all LaMotte reagent containers prior to use. Some
containers include precautionary notices and first aid information. Certain
reagents are considered hazardous substances and are designated witha*inthe
instruction manual. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these
reagents. Read the accompanying MSDS before using these reagents.
Additional information for all LaMotte reagents is available in the United
States from the Poison Control Center listed in the front of the phone book or
by calling 1-800-222-1222. Call 1-813-248-0585 to contact the International
Poison control Center. LaMotte reagents are registered with a computerized
poison control information system available to all local poison control centers.
Be prepared to supply the name and four-digit LaMotte code number found on
the container label , listed in the test procedures, or at the top of the MSDS.
Keep equipment and reagent chemicals out of the reach of young children.
Protect Yourself and Equipment: Use Proper Analytical Techniques
LIMITS OF LIABILITY
n
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 5
Page 6

Under no circumstances shall LaMotte Company be liable for loss of life,
property, profits, or other damages incurred through the use or misuse of its
products.
SPECIFICATIONS
n
n
INSTRUMENT TYPE: Colorimeter
Readout Graphical 4 line, 16 character per line LCD
Wavelengths 430nm, 620 nm
Wavelength Accuracy ±2nm
Readable Resolution Determined by reagent system
Wavelength
10 nm typical
Bandwidth
Photometric Range -2to+2A
Photometric Precision ± 0.001A
Sample Chamber Accepts 25 mm diameter flat-bottomed test tubes, 10
mm square cuvettes, 16 mm COD test tubes
Light Sources 2 LEDs
Detectors 2 silicon photodiodes with integrated interference
filters
Modes Absorbance, pre-programmed tests
Pre-Programmed Tests YES, with automatic wavelength selection
User Defined Tests Up to 10 user tests can be input
RS232 Port 8 pin mini-DIN, 9600b, 8, 1, n
Power Requirements Battery Operation: 9 volt alkaline
Line Operation: 110/220V AC;
50/60 Hz with adapter, 6V 500 mA DC
Dimensions (LxWxH) 8.5 x 16.2 x 16.7 cm, 3.4 x 6.4 x 2.6 inches
Weight 312 g, 11 oz (meter only)
Data Logger 350 test results stored for download to a PC
6 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 7

CONTENTS AND ACCESSORIES
n
n
CONTENTS
COD PLUS Colorimeter
Test Tubes, with Caps (4)
COD Adapter
Power Supply, 110V or 220V
COD PLUS Colorimeter Manual
n
ACCESSORIES
COD Reactor, 8 Vial Capacity, 110V Code 5-0069
COD Reactor, 8 Vial Capacity, 220V Code 5-0070
COD Reactor, 25 Vial Capacity, 110/220V Code 5-0094
COD Safety Shield for 8 Vial Reactor Code 5-0071
Small Field Carrying Case Code 1919-GCS150
Large Field Carrying Case Code 1919-BCS440
SMARTLink 2 Program & Interface Cable (3.5 disk) Code 1912-3
SMARTLink 2 Program & Interface Cable (CD) Code 1912-CD
EPA COMPLIANCE
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter is an EPA-Accepted instrument. EP A-Accepted
means that the instrument meets the requirements for instrumentation as
found in test procedures that are approved for the National Primary Drinking
Water Regulations (NPDWR) or National Pollutant Discharge Elimination
System (NPDES) compliance monitoring programs. EPA-Accepted
instruments may be used with approved test procedures without additional
approval.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 7
Page 8

CE COMPLIANCE
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter has earned the European CE Mark of
Compliance for electromagnetic compatibility and safety.
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Standards to which
Conformity Declared:
Manufacturer's Name:
Manufacturer's Address:
Type of Equipment:
Model Name:
Year of Manufacture:
Testing Performed By:
Chestertown, Maryland
Place
EN61326:1998, IEC61326:1997,
IEC61000-4-2:1995, IEC61000-4-3:1995
IEC61000-4-4:1995, IEC61000-4-5:1995
IEC61000-4-6:1996, IEC61000-4-11:1994,
EN61000-3-2:1995, EN61000-3-3:1994-12,
EN55011/CISPR11, FCCCFR47 Part 15,
EN61558
LaMotte Company
802 Washington Avenue
PO Box 329
Chestertown, MD 21620
Colorimeter
COD Plus
2001
Windermere
2000 Windermere Court
Annapolis, MD 21401
I, the undersigned, hereby declare that the equipment specified above
conforms to the above Directive and Standards.
Signature
1/15/02
Date
8 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Scott H. Steffen
Name
VP New Products & Quality
Position
Page 9

CHEMICAL TESTING
WATER SAMPLING FOR CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
n
n
Taking Representative Samples
The underlying factor to be considered for any type of water sampling is
whether or not the sample is truly representative of the source. To properly
collect a representative sample:
l
Sample as frequently as possible.
l
Collect a large sample or at least enough to conduct whatever tests are
necessary.
l
Make a composite sample for the same sampling area.
l
Handle the sample in such a way as to prevent deterioration or
contamination before the analysis is performed.
l
Perform analysis for dissolved gases such as dissolved oxygen, carbon
dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide immediately at the site of sampling. These
factors, as well as samples for pH, cannot be stored for later examination.
l
Make a list of conditions or observations which may affect the sample.
Other considerations for taking representative samples are dependent
upon the source of the sample. Taking samples from surface waters
involves different considerations than taking samples from impounded and
sub-surface waters.
n
Sampling of Open Water Systems
Surface waters, such as those found in streams and rivers, are usually well
mixed. The sample should be taken downstream from any tributary, industrial
or sewage pollution source. For comparison purposes samples may be taken
upstream and at the source of the pollution before mixing.
In ponds, lakes, and reservoirs with restricted flow, it is necessary to collect a
number of samples in a cross section of the body of water, and where possible
composite samples should be made to ensure representative samples.
To collect samples from surface waters, select a suitable plastic container with a
tight fitting screw cap. Rinse the container several times with the sample to be
tested, then immerse the container below the surface until it is filled to
overflowing and replace the cap. If the sample is not to be tested immediately,
pour a small part of the sample out and reseal. This will allow for any
expansion. Any condition which might affect the sample should be listed.
Sub-surface sampling is required to obtain a vertical profile of streams, lakes,
ponds, and reservoirs at specific depths. This type of sampling requires more
sophisticated sampling equipment.
For dissolved oxygen studies, or for tests requiring small sample sizes, a Water
Sampler (LaMotte Code 1060) will serve as a subsurface or in-depth sampler.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 9
Page 10

This weighted device is lowered to the sampling depth and allowed to rest at
this depth for a few minutes. The water percolates into the sample chamber
displacing the air which bubbles to the surface. When the bubbles cease to rise,
the device has flushed itself approximately five times and it may be raised to
the surface for examination. The inner chamber of the sampling device is lifted
out and portions of the water sample are carefully dispensed for subsequent
chemical analysis.
A Snap-Plunger Water Sampler (LaMotte Code 1077) is another “in-depth”
sampling device which is designed to collect large samples which can be used
for a multitude of tests. Basically, this collection apparatus is a hollow cylinder
with a spring loaded plunger attached to each end. The device is cocked above
the surface of the water and lowered to the desired depth. A weighted
messenger is sent down the calibrated line to trip the closing mechanism and
the plungers seal the sample from mixing with intermediate layers as it is
brought to the surface. A special drain outlet is provided to draw off samples for
chemical analysis.
n
Sampling of Closed System
To obtain representative samples from confined water systems, such as pipe
lines, tanks, vats, filters, water softeners, evaporators and condensers, different
considerations are required because of chemical changes which occur between
the inlet and outlet water. One must have a basic understanding of the type of
chemical changes which occur for the type of equipment used. Also,
consideration should be given to the rate of passage and retaining time for the
process water.
Temperature changes play an important part in deciding exactly what test
should be performed. Process water should be allowed to come to room
temperature, 20–25°C, before conducting any tests.
When drawing off samples from an outlet pipe such as a tap, allow sample to
run for several minutes, rinsing the container several times before taking the
final sample. Avoid splashing and introduction of any contaminating material.
FILTRATION
n
When testing natural waters that contain significant turbidity due to suspended
solids and algae, filtration is an option. Reagent systems, whether EPA,
Standard Methods, LaMotte or any others, will generally only determine
dissolved constituents. Both EPA and Standard Methods suggest filtration
through a 0.45 micron filter membrane, to remove turbidity, for the
determination of dissolved constituents.** T o test for total constituents,
organically bound and suspended or colloidal materials, a rigorous high
temperature acid digestion is necessary.
**LaMotte offers a filtering apparatus: syringe assembly (Code 1050) and membrane
filters, 0.45 micron, (Code 1103).
10 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 11

AN INTRODUCTION TO COLORIMETRIC ANALYSIS
n
Most test substances in water are colorless and undetectable to the human eye.
To test for their presence we must find a way to “see” them. The COD PLUS
Colorimeter can be used to measure a test substance that is itself yellow or
green to blue, or can be reacted to produce these colors. In fact a simple
definition of colorimetry is “the measurement of color” and a colorimetric
method is “any technique used to evaluate an unknown color in reference to
known colors”. In a colorimetric chemical test the intensity of the color from
the reaction must be proportional to the concentration of the substance being
tested. Some reactions have limitations or variances inherent to them that may
give misleading results. Many such interferences are discussed with each
particular test instruction. In the most basic colorimetric method the reacted
test sample is visually compared to a known color standard. However, accurate
and reproducible results are limited by the eyesight of the analyst,
inconsistencies in the light sources, and the fading of color standards.
To avoid these sources of error, a colorimeter can be used to photoelectrically
measure the amount of colored light absorbed by a colored sample in reference
to a colorless sample (blank).
White light is made up of many different colors or wavelengths of light. A
colored sample typically absorbs only one color or one band of wavelengths
from the white light. Only a small difference would be measured between white
light before it passes through a colored sample versus after it passes through a
colored sample. The reason for this is that the one color absorbed by the
sample is only a small portion of the total amount of light passing through the
sample. However, if we could select only that one color or band of wavelengths
of light to which the test sample is most sensitive, we would see a large
difference between the light before it passes through the sample and after it
passes through the sample.
The COD PLUS Colorimeter passes one of two colored light beams through
one of two optical filters which transmits only one particular color or band of
wavelengths of light to the photodectector where it is measured. The difference
in the amount of colored light transmitted by a colored sample is a
measurement of the amount of colored light absorbed by the sample. In most
colorimetric tests the amount of colored light absorbed is directly proportional
to the concentration of the test factor producing the color and the path length
through the sample. However, for some tests the amount of colored light
absorbed is inversely proportional to the concentration.
The choice of the correct wavelength for testing is important. It is interesting
to note that the wavelength that gives the most sensitivity (lower detection
limit) for a test factor is the complementary color of the test sample. For
example the Nitrate-Nitrogen test produces a pink color proportional to the
nitrate concentration in the sample (the greater the nitrate concentration, the
darker the pink color). A wavelength in the green region should be selected to
analyze this sample since a pinkish-red solution absorbs mostly green light.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 11
Page 12

REAGENT BLANK
n
Some tests will provide greater accuracy if a reagent blank is determined to
compensate for any color or turbidity resulting from the reagents themselves. A
reagent blank is performed by running the test procedure on 10 mL of
demineralized water. Use sample water to SCAN BLANK. Insert the reagent
blank in the colorimeter chamber and select SCAN SAMPLE. Note result of
reagent blank. Perform the tests on the sample water as described. Subtract
results of reagent blank from all subsequent test results. NOTE: Some tests
require a reagent blank to be used to SCAN BLANK.
COLORIMETER TUBES
n
Colorimeter tubes which have been scratched through excessive use should be
discarded and replaced with new ones. Dirty tubes should be cleaned on both
the inside and outside. Fingerprints on the exterior of the tubes can cause
excessive light scattering and result in errors. Handle the tubes carefully,
making sure the bottom half of the tube is not handled.
LaMotte Company makes every effort to provide high quality colorimeter
tubes. However, wall thicknesses and diameter of tubes may still vary slightly.
This may lead to slight variations in results (e.g. if a tube is turned while in the
sample chamber, the reading will likely change slightly). To eliminate this error
put the tubes into the sample chamber with the same orientation every time.
The tubes that are included with the colorimeter have an index mark to
facilitate this. If possible, use the same tube to SCAN BLANK and SCAN
SAMPLE.
SELECTING AN APPROPRIATE WAVELENGTH
n
The most appropriate wavelength to use when creating a calibration curve is
usually the one which gives the greatest change from the lowest reacted
standard concentration to the highest reacted standard concentration.
However, the absorbance of the highest reacted standard concentration should
never be greater than 2.0 absorbance units. Scan the lowest and highest reacted
standards at different wavelengths using the absorbance mode to find the
wavelength which gives the greatest change in absorbance without exceeding
2.0 absorbance units. Use this wavelength to create a calibration curve.
12 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 13
Below is a list of suggested wavelengths for the color of the reacted samples.
Use these as a starting point.
Sample
Color
Yellow 430
Pink 520
Red 570
Green and Blue 620
Wavelength
Range
NOTE: Available wavelengths in the COD PLUS are 430 nm and 620 nm
only.
CALIBRATION CURVES
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter contains precalibrated tests for the LaMotte
reagent systems (p. 49). The first step in using a non-LaMotte reagent system
with your COD PLUS Colorimeter is to create a calibration curve for the
reagent system. To create a calibration curve, prepare standard solutions of the
test factor and use the reagent system to test the standard solutions with the
COD PLUS Colorimeter. Select a wavelength for the test as described above.
Plot the results (in ABS or %Transmittance) versus concentration to create a
calibration curve. The calibration curve may then be used to identify the
concentration of an unknown sample by testing the unknown, reading
Absorbance or %T, and finding the corresponding concentration from the
curve. The linear range of the reagent system can be determined and this
information can be used to input a User Test into the COD PLUS Colorimeter
(see EDIT USER TESTS, p. 36).
n
PROCEDURE
1. Prepare 5 or 6 standard solutions of the factor being tested. The
concentration of these standards should be evenly distributed throughout
the range of the reagent system, and should include a 0 ppm standard
(distilled water). For instance, the solutions could measure 0, 10%, 30%,
50%, 70%, and 90% of the system’s maximum range.
2. Turn on the COD PLUS Colorimeter . Select the appropriate wavelength
from the absorbance mode. Be sure to select the appropriate wavelength for
the color produced by the reagent system.
3. Use the unreacted 0 ppm standard to standardize the colorimeter by using it
to scan blank.
4. Following the individual reagent system instructions, react each standard
solution beginning with 0 ppm. Continue with standards in increasing
concentration. Record the reading and the standard solution concentration
on a chart. Readings can be recorded as percent transmittance (%T) or
absorbance (A).
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 13
Page 14
5. Plot results on graph paper or computer using any available plotting
program. If results are as %T versus concentration, semilog graph paper
must be used. Plot the standard solution concentrations on the horizontal,
linear axis, and the %T on the vertical, logarithmic axis. If results are as
absorbance versus standard solution concentration, simple linear graph
paper can be used. Plot the standard solution concentration on the
horizontal axis, and the absorbance on the vertical axis.
6. After plotting the results, draw a line, or curve, of best fit through the
plotted points. The best fit may not connect the points. There should be
approximately an equal number of points above the curve as below the
curve. Some reagent systems will produce a straight line, while others
produce a curve. Many computer spreadsheet programs can produce the
curve of best fit by regression analysis of the standard solution data.
NOTE: Only reagent systems which produce a straight line can be used for a
User Test.
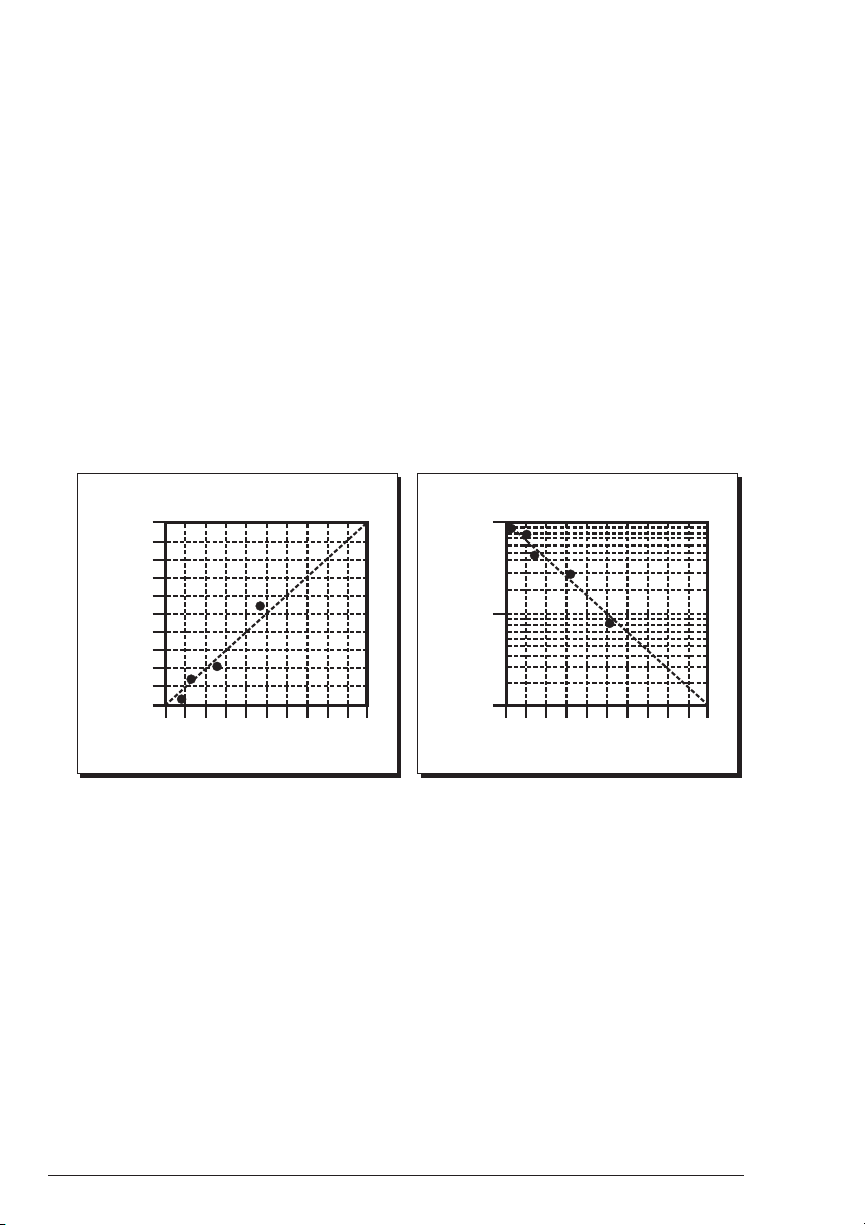
A sample of each type of graph appears below:
CALIBRATION CURVE
Absorbance vs. Concentration
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
Absorbance
0.4
0.2
0.0
123456
Concentration in ppm
CALIBRATION CURVE
%T vs. Concentration
100
10
%T Transmission
1
0
89107
123456
Concentration in ppm
891070
14 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 15
n
PREPARING DILUTE STANDARD SOLUTIONS
Standard solutions should be prepared to create a calibration curve. Standard
solutions can be prepared by diluting a known concentrated standard by
specified amounts. A chart or computer spreadsheet can be created to
determine the proper dilutions. Use volumetric flasks and volumetric pipets for
all dilutions.
1. In Column A – Record the maximum concentration of test as determined
by the range and path length.
2. In Column B – Record the percent of the maximum concentration the
standard solution will be.
3. In Column C – Calculate the final concentration of the diluted standard
solutions by multiplying the maximum concentration (In Column A) by the
% of maximum concentration divided by 100. (C=Ax
B
).
100
4. In Column D – Record the final volume of the diluted sample (i.e. volume
of volumetric flask).
5. In Column E – Record the concentration of the original standard.
6. In Column F – Calculate the milliliters of original standard required
D
(C x
= F).
E
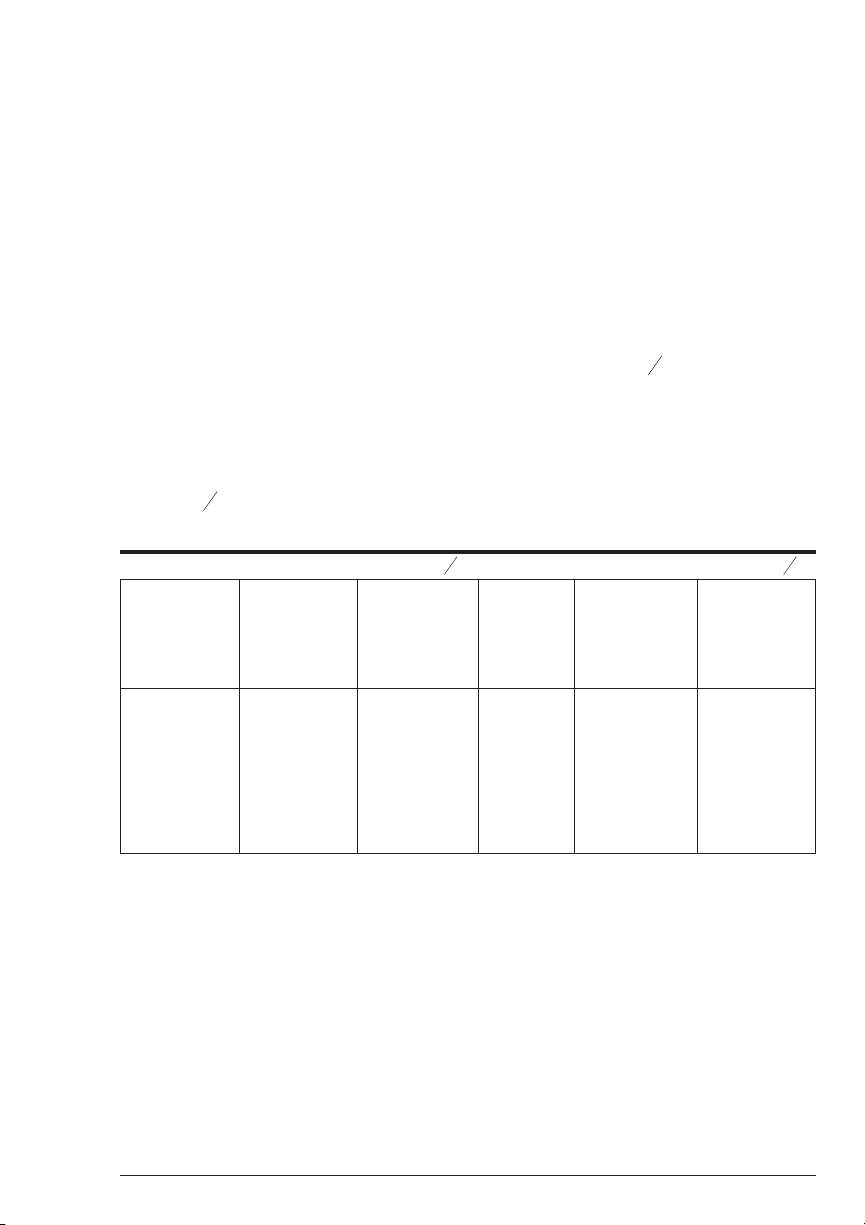
A sample chart appears below:
A B C=Ax
B
I00
D E F=Cx
Final
Maximum
concentration
of test
%of
Maximum
concentration
concentration
of Diluted
Standard
Volume of
Standard
Concentration
of Original
Standard
Standard
Required
10.0 ppm 90 9.0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0.90 mL
10.0 ppm 70 7.0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0.70 mL
10.0 ppm 50 5.0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0.50 mL
10.0 ppm 30 3.0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0.30 mL
10.0 ppm 10 1.0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0.10 mL
10.0 ppm 0 0 ppm 100 mL 1000 ppm 0 mL
mL of
Original
D
E
STANDARD ADDITIONS
n
A common method to check the accuracy and precision of a test is by standard
additions. In this method a sample is tested to determine the concentration of
the test substance. A second sample is then “spiked” by the addition of a
known quantity of the test substance. The second sample is then tested. The
determined concentration of the spiked sample should equal the concentration
of the first plus the amount added with the spike. The procedure can be
repeated with larger and larger “spikes.” If the determined concentrations do
not equal the concentration of the sample plus that added with the “spike”,
then an interference may exist.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 15
Page 16

For example, a 10.0 mL water sample was determined to contain 0.3 ppm iron.
To a second 10.0 mL sample, 0.1 mL of 50 ppm iron standard was added. The
concentration of iron due to the “spike” was (0.10 mL x 50 ppm)/10.0 mL =
0.50 ppm. The concentration of iron determined in the spiked sample should
be 0.3 + 0.5 = 0.8 ppm iron. (Note: any error due to the increased volume from
the “spike” is negligible).
LaMotte offers a line of calibration standards which can be used to generate
calibration curves and perform standard additions.
SAMPLE DILUTION TECHNIQUES
n
& VOLUMETRIC MEASUREMENTS
If a test result using the COD PLUS Colorimeter gives an OVERRANGE message
then the sample concentration could be over range or under range. If it is over
range, the sample must be diluted. Then the test should be repeated on the
diluted sample to obtain a reading which is in the concentration range for the
test. (Note: This is not true for colorimetric determination of pH.)
Example:
Measure 5 mL of the water sample into a graduated cylinder. Add
demineralized water until the cylinder is filled to the 10 mL line. The sample
has been diluted by one-half, and the dilution factor is therefore 2. Perform the
test procedure, then multiply the resulting concentration by 2 to obtain the
test result.
The following table gives quick reference guidelines on dilutions of various
proportions. All dilutions are based on a 10 mL volume, so several dilutions
will require small volumes of the water sample. Graduated pipets should be
used for all dilutions.
Size of Sample
10 mL 0 mL 1
5mL 5mL 2
2.5 mL 7.5 mL 4
1 mL 9 mL 10
0.5 mL 9.5 mL 20
Deionized W ater to Bring
Volume to 10 mL Multiplication Factor
If the above glassware is not available, dilutions can be made with the
colorimeter tube. Fill the tube to the 10 mL line with the sample then transfer
it to another container. Add 10 mL volumes of demineralized water to the
container and mix. T ransfer back 10 mL of the diluted sample to the tube and
follow the test procedure. Continue diluting and testing until a reading, which
is in the concentration range for the test, is obtained. Be sure to multiply the
concentration found by the dilution factor (the number of total 10 mL volumes
used).
Example:
10 mL of sample is diluted with three 10 mL volumes of demineralized water;
the dilution factor is four.
16 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 17

INTERFERENCES
n
LaMotte reagent systems are designed to minimize most common interferences.
Each individual test instruction discusses interferences unique to that test. Be
aware of possible interferences in the water being tested.
The reagent systems also contain buffers to adjust the water sample to the ideal
pH for the reaction. It is possible that the buffer capacity of the water sample
may exceed the buffer capacity of the reagent system and the ideal pH will not
be obtained. If this is suspected, measure the pH of a reacted distilled water
reagent blank using a pH meter. This is the ideal pH for the test. Measure the
pH of a reacted water sample using the pH meter. If the pH is significantly
different from the ideal value, the pH of the sample should be adjusted before
testing.
Interferences due to high concentration of the substance being tested, can be
overcome by sample dilution (p. 16).
STRAY LIGHT INTERFERENCE
n
When scanning samples in 16 mm tubes, such as COD, the sample chamber lid
can not be closed. The COD adapter minimizes stray light. To further reduce
stray light interference, do not scan sample in direct sunlight.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 17
Page 18

OPERA TION OF THE
COD PLUS COLORIMETER
OVERVIEW
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter is a portable, microprocessor controlled, direct
reading colorimeter. It has a graphical 4 line, 16 character liquid crystal display
for graphical, alphabetical and numerical messages. The operation is controlled
with the keypad through menu driven software in response to selections shown
on the display.
The test library consists of 29 LaMotte tests and 10 “User Tests”. The LaMotte
tests are precalibrated for LaMotte reagent systems. The colorimeter displays
the results of these tests directly in units of concentration. The 10 “User Tests”
may be used to enter additional calibrations. All of these tests may be arranged
in any of 3 sequences. These sequences can be modified a limitless number of
times to meet changing testing needs.
The optics feature 2 different colored LEDs. Each LED has a corresponding
silicon photodiode with an integrated interference filter. The interference
filters select a narrow band of light from the corresponding LED for the
colorimetric measurements. The microprocessor automatically selects the
correct LED/photodiode combination for a test.
A RS-232 serial port on the back of the colorimeter, and optional software,
allows the COD PLUS to be interfaced with an IBM compatible personal
computer for real time data acquisition and data storage. This port also allows
an interface with a RS-232 serial printer.
Due to its portability, alternate power sources, and rugged construction, the
COD PLUS Colorimeter is ideal for lab and field use.
POWER SOURCE
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter uses a 6V 500 mA AC adapter. Please refer to
the Parts List for the code number for the correct adapter.
USE OF ANY AC ADAPTER OTHER THAN THE ONE SPECIFIED
FOR USE WITH THE COD PLUS COLORIMETER MAY DAMAGE
THE METER AND WILL VOID THE WARRANTY.
To use the adapter, slide the connector pin from the AC adapter into the small
hole on the left side of the meter. Plug the AC adapter into an appropriate wall
socket or power source.
18 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 19
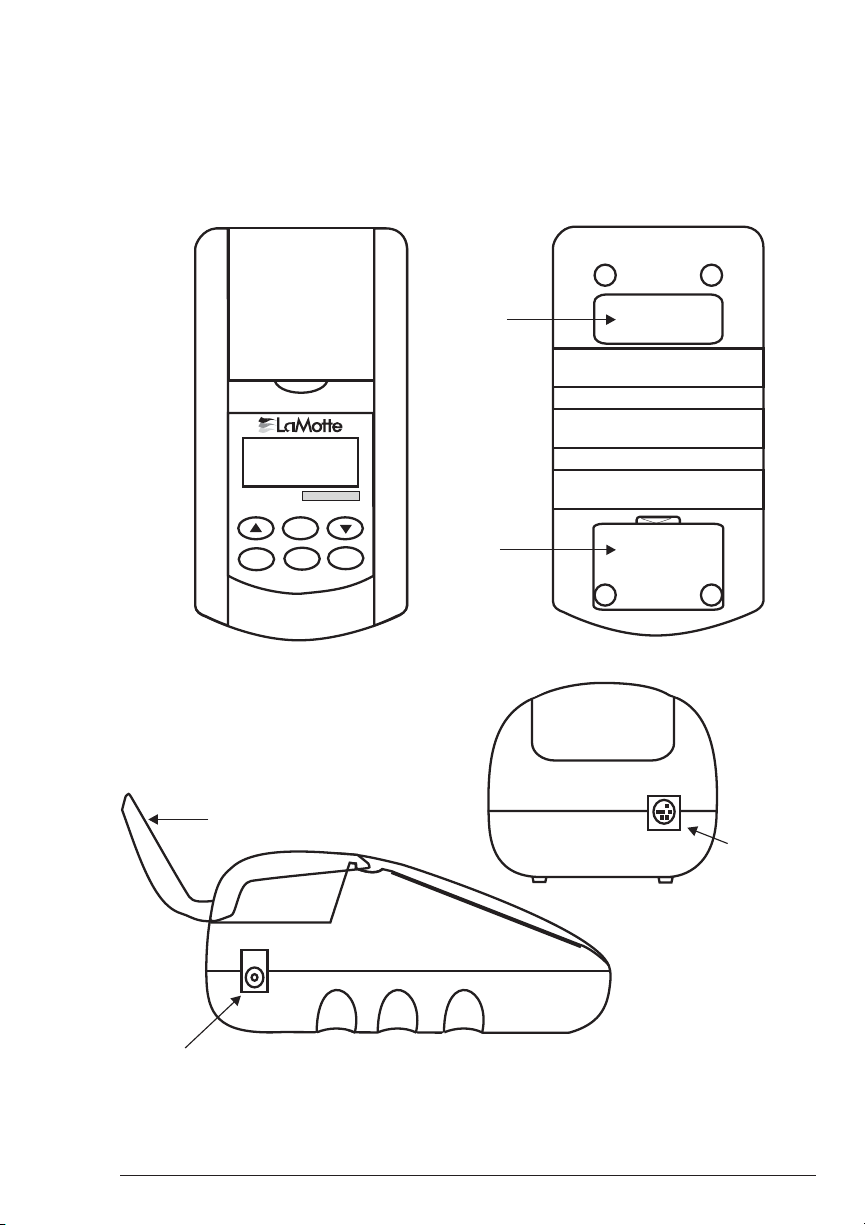
COMPONENTS
n
Figure 1 shows a diagram of the COD PLUS Colorimeter and its components.
Top View
COD PLUS
••••••••••••••••••
ENTER
OFF EXIT
Lid
*
ON
Side Views
Bottom View
Serial
Number
Battery
Compartment
Rs232
Serial Port
AC
Adapter Socket
Figure 1
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 19
Page 20
QUICK START
n
Some quick instructions to get into testing.
1. Press ON to turn on the COD PLUS. The
LaMotte logo screen will appear for about 2
seconds and then the Start screen appears. Press
Q/ENTER to start testing.
2. The Main Menu will appear. Press
Q/ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
3. Press Q/ENTER to select All Tests.
4. Press t or s to move the * to the desired
test.
5. Press Q/ENTER to select test.
VER 1.0
COD PLUS
* Start
MAIN MENU
* Testing Menu
Editing Menu
PC Link
TESTING MENU
* All Tests
Sequence 1
Sequence 2
ALL TESTS
* 001 COD LR
002 COD SR
003 COD HR
ALL TESTS
* 002 COD SR
003 COD HR
004 Ammonia-N LF
6. Insert blank, press Q/ENTER to scan blank.
7. The screen will display Blank Done for about
1 second.
20 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
002 COD SR
* Scan Blank
002 COD SR
Blank Done
* Scan Blank
Page 21

8. Insert the reacted sample. Press Q/ENTER to
scan sample. The COD PLUS will scan the
sample and display the concentration.
002 COD SR
* Scan Sample
9. After recording test result, scroll with t or s
and make another selection with Q/ENTER.
Press EXIT to escape to previous menus.
002 COD SR
722 mgL
* Scan Sample
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 21
Page 22

GENERAL OPERATING PROCEDURES
The operation of the COD PLUS Colorimeter is controlled by a
microprocessor. The microprocessor is programmed with menu driven software.
A menu is a list of choices. This allows a selection of various tasks for the
colorimeter to perform, such as, scan blank, scan sample, and edit test
sequences. The keypad is used to make menu selections which are viewed in
the display. There are three selections accessible from the MAIN MENU:
Testing Menu, Editing Menu and PC Link.
THE KEYPAD
n
The keypad has 6 buttons which are used to perform specific tasks.
ON
t This button will cause the display to scroll down through a list of
s This button will cause the display to scroll up in a list of menu
ENTER
Q
EXIT
OFF
SAMPLE HOLDERS
n
The sample chamber is designed for 25 mm round tubes, and a sample holder
for 16 mm COD tubes is included. A 1 cm square UDV cuvette sample holder
is available for the COD PLUS Colorimeter.
Position the COD adapter in the SMART 2 chamber so that the grooves in the
adapter are aligned with the ridges located at the rear of the chamber. The
adapter should be inserted with the small hole, containing the ball plunger, at
the top. The ball plunger can be adjusted with a small screwdriver to control
the tightness of the fit of the tube in the adapter.
This button is used to turn the colorimeter on.
menu choices. It will move through a list viewed in the display . It
will auto scroll when held down.
choices. It will move through a list viewed in the display. It will
auto scroll when held down.
This button is used to select the menu choice adjacent to the “*”in
a menu viewed in the display.
This button is an exit or escape button. When pressed, the display
will exit from the current menu and go to the previous menu.
This button turns the colorimeter off.
22 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 8/02
Page 23
THE DISPLAY & THE MENUS
n
The display allows menu selections to be viewed and chosen. These choices
instruct the colorimeter to perform specific tasks. The menus are viewed in the
display using two general formats which are followed from one menu to the
next. Each menu is a list of choices or selections.
There are four lines in the display. The top line in each menu is a title or
pertinent instruction. The top line does not change unless a new menu is
selected. The second and third lines are used in two ways. One way is to display
menu choices. The second way takes advantage of the graphical capabilities of
the display. Both lines are used to display important messages, such as test
results, in a large, easy to read format. The fourth line is used for menu choices.
DISPLAY
TESTING MENU
* FIRST CHOICE
SECOND CHOICE
ANOTHER
AND ANOTHER
AND SO ON
TITLE or INSTRUCTION
MENU CHOICE WINDOW
Think of the menu choices as a vertical list in the display which moves up or
down each time an arrow button is pressed. This list or menu is viewed through
a window, the menu choice window, in the display. The menu choice window
is the lower 2 or 3 lines of the display. Pushing the arrow buttons brings
another portion of the menu into menu choice window. This is referred to as
scrolling through the menu.
TESTING MENU
* FIRST CHOICE SECOND CHOICE ANOTHER
SECOND CHOICE * ANOTHER AND ANOTHER
ANOTHER AND ANOTHER * AND SO ON
AND ANOTHER AND SO ON LAST CHOICE
AND SO ON LAST CHOICE
LAST CHOICE
t
TESTING MENU
t
TESTING MENU
An asterisk, “*”, will start in the far left position of the top line in the menu
choice window. As the menu is scrolled through, different choices appear next
to the “*”. The “*” in the display corresponds with the Q/ENTER button.
Pushing the Q/ENTER button selects the menu choice which is adjacent to
the “*” in the menu choice window.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 23
Page 24

The second general format of the display takes advantage of the graphics
capabilities of the display. The top line of the display is still a title line. The
middle two lines of the display are used to display important messages, results or
graphics in a large, easy to read format. The menus work in the same way as
described previously but only one line of the menu is visible at the bottom of
the display.
TESTING MENU
TESTING MENU
t
TESTING MENU
t
Result or Message Result or Message Result or Message
* ANOTHER * AND ANOTHER * AND SO ON
AND ANOTHER AND SO ON LAST CHOICE
AND SO ON LAST CHOICE
LAST CHOICE
As described previously, the EXIT button allows an exit or escape from the
current menu and a return to the previous menu. This allows a rapid exit from
an inner menu to the main menu by repeatedly pushing the
Pushing
OFF at any time will turn the colorimeter off.
EXIT button.
24 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 25
LOOPING MENUS
n
Long menus, such as All Tests, incorporate a looping feature which allow
the user to quickly reach the last choice in the menu from the first choice. In a
looping menu the last choices in the menu are above the first choice and
scrolling upward moves through the menu in reverse order. Scrolling downward
moves through the menu from first choice to last but the menu starts over
following the last choice. So all menu choices can be reached by scrolling in
either direction. The diagrams below demonstrate a looping menu.
AND SO ON AND ANOTHER ANOTHER
: : : AND SO ON AND ANOTHER
: : : : : : AND SON ON
THIRD TO LAST : : : : : :
SECOND TO LAST THIRD TO LAST : : :
LAST CHOICE SECOND TO LAST THIRD TO LAST
TESTING MENU
* FIRST CHOICE * LAST CHOICE * SECOND TO LAST
SECOND CHOICE FIRST CHOICE LAST CHOICE
ANOTHER SECOND CHOICE FIRST CHOICE
AND ANOTHER ANOTHER SECOND CHOICE
AND SO ON AND ANOTHER ANOTHER
: : : AND SO ON AND ANOTHER
: : : : : : AND SO ON
LAST CHOICE : : : : : :
TESTING MENU
s
TESTING MENU
s
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 25
Page 26
TESTING
TESTING MENU
n
The Testing Menu is used to run all LaMotte pre-programmed tests, USER
TESTS and Absorbance test at two wavelengths. Testing from any of three
sequences can also be done.
1. Press the ON button to turn on the
COD PLUS Colorimeter. The LaMotte logo will
appear for about 2 seconds and the the Start screen
appears. Press the Q/ENTER button to begin testing.
2. The MAIN MENU will appear. Press the
Q/ENTER button to select Testing Menu.
3. Scroll with the t or s buttons and make
a selection with the Q/ENTER button. All
Tests has all the available tests. The three
sequences have selected tests and
Absorbance has %T/ABS tests.
VER 1.0
COD PLUS
* Start
MAIN MENU
* Testing Menu
Editing Menu
PC Link
TESTING MENU
* All Tests
Sequence 1
Sequence 2
Sequence 3
Absorbance
26 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 27
SEQUENCES OF TESTS
n
SEQUENCE 1, SEQUENCE 2, and SEQUENCE 3 are alterable sequences. They
may be edited using the Editing Menu. Any of the LaMotte
pre-programmed tests or User T ests may be placed in these sequences in
whatever testing order that is preferred. Some examples of typical sequences are
given below.
SEQUENCE 1 SEQUENCE 2 SEQUENCE 3
* 004 Ammonia-N LF * 008 Cobalt * 001 COD LR
005 Ammonia-N LS 010 Cu Cuprizone 002 COD SR
006 Ammonia-N H 011 Cu - DDC 003 COD HR
007 Boron 015 Hydrazine
001 COD LR 016 Moly HR
002 COD SR 017 Nickel
003 COD HR 018 Ozone-LR
009 Color 021 Phosphate-H
013 DO 022 Potassium
014 Fluoride 023 Silica-Lo
018 Ozone-LR 024 Silica-Hi
020 Phosphate-L 027 Tannin
025 Sulfate-HR 029 Zinc-LR
026 Sulfide-LR
028 Turbidity
These alterable sequences allow a series of tests to be setup that are run
frequently. The order of the individual tests in the sequence is determined by
the user. After running a test, use the t button to scroll to the next test and
press the Q/ENTER button to select the next test in the sequence. Continue
this pattern until the entire sequence has been completed.
All Tests is a fixed sequence containing the LaMotte pre-programmed tests,
User Tests, and Absorbance tests.
Modification of the alterable sequences is accomplished through the Editing
Menu. This menu is explained in greater detail in EDITING MENU (p. 32).
Pressing the EXIT button while in a sequence menu will escape back to the
Testing Menu.
Pressing the OFF button at any time will turn the colorimeter off.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 27
Page 28
GENERAL TESTING PROCEDURES
n
The following are some step by step examples of how to run tests from the
Testing Menu. These test procedures are designed to be used with LaMotte
SMART Reagent Systems.
TESTING WITH THE LaMOTTE
n
PRE-PROGRAMMED TESTS
Press ON to turn on the COD PLUS Colorimeter.
The LaMotte logo will appear for about 2 seconds
and then the Start screen appears. Press the
Q/ENTER button to start testing.
The MAIN MENU will appear. Press the Q/ENTER
button to select Testing Menu.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select All Tests.
Press the t button to move to the 001 COD LR to
*.
VER 1.0
COD PLUS
* Start
MAIN MENU
* Testing Menu
Editing Menu
PC Link
TESTING MENU
* All Tests
Sequence 1
Sequence 2
ALL TESTS
* 001 COD LR
002 COD SR
003 COD HR
Press the Q/ENTER button to select 001 COD LR.
28 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
ALL TESTS
* 001 COD LR
002 COD SR
003 COD HR
Page 29

The COD PLUS Colorimeter is ready to scan at the
correct wavelength. Place the blank in the sample
chamber, close the lid and press the Q/ENTER
button to scan blank.
NOTE: Do not keep the button depressed.
001 COD LR
* Scan Blank
The screen will display Blank Done for about 1
second. Scan Sample will be positioned next to *.
Place the reacted sample in the chamber, close the
lid and press the Q/ENTER button to scan sample.
The colorimeter will scan the sample and the results
screen will appear.
Record test result. To repeat the test, press the
Q/ENTER button to scan the sample again. The
last blank scanned is used to zero the colorimeter for
repeated scans. A different blank can be used by
pressing the s button to scroll back to Scan
Blank and then scanning another blank. Scroll with
the t or s buttons and make another selection
with the Q/ENTER button. The %T or Absorbance
of the last test can be viewed by choosing %T/Abs.
Press the EXIT button to escape to previous menus.
NOTE: The menus loop in this screen so either the
s or t buttons will lead to the menu selection
needed.
001 COD LR
Blank Done
* Scan Blank
001 COD LR
* Scan Sample
001 COD LR
100 mgL
* Scan Blank
Next Test
Previous Test
%/Abs
Scan Blank
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 29
Page 30
CALIBRATING LaMOTTE PRE-PROGRAMMED TESTS
n
The LaMotte Pre-Programmed T ests have been pre-calibrated. Recalibration of
the pre-programmed tests by the user is not possible. However, a procedure to
standardize the calibration can be performed to obtain the most accurate
readings or to meet regulatory requirements.
The LaMotte Pre-Programmed tests are standardized with one standard
solution. To standardize over the full range of the test, the concentration of the
standard should be chosen from the high end of the range. Alternatively , if
samples do not cover the full range of the test, a standard should be chosen that
is close to the concentration of the samples.
The standardization procedure should be followed as often as required by
regulations and laws for compliance monitoring.
In the example below the Aluminum calibration will be standardized.
Prepare a standard solution to be tested. Use 0.10 ppm aluminum.
Use the s or t button to scroll to 002 Aluminum.
Follow instructions in the COD PLUS Manual for
testing the aluminum standard. Scan the blank.
The screen will display Blank Done for about 1
second. Scan Sample will be positioned next to *.
Place the reacted sample in the chamber, close the
lid and press Q/ENTER to scan sample. The result
will be displayed.
The displayed result can now be standardized. Use
the s or t buttons to scroll to Calibrate. Press
Q/ENTER to select.
002 Aluminum
* Scan Blank
002 Aluminum
Blank Done
* Scan Sample
002 Aluminum
* Scan Sample
002 Aluminum
0.09 ppm
* Scan Sample
Next Test
Previous Test
%T/Abs
Calibrate
Scan Blank
30 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 4/03
Page 31

A reverse font (dark background with light
characters) will appear to indicate that the reading
can be adjusted. Use s or t to scroll to the
concentration of the sample, 0.10 ppm in this
example.
002 Alumninum
0.09
* Calibrate
Set the calibration by pressing Q/ENTER to select
Calibrate.
Two menu choices will be offered, Set
Calibration and Factory Setting. Set the
calibration by pressing Q/ENTER to select Set
Calibration;oruses or t to scroll to and select
Factory Setting to revert to the factory
calibration.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to 002 Aluminum test.
The calibration for 002 Aluminum has now been
standardized and can be used for testing. The
standardization can be removed by repeating the
calibration and selecting Factory Setting.
002 Aluminum
0.10
* Calibrate
002 Aluminum
0.10
* Set Calibration
Facctory Setting
Storing
002 Aluminum
* Scan Sample
Next Test
Previous Test
%/Abs
Calibrate
Scan Blank
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 4/03 31
Page 32

MEASURING IN THE ABSORBANCE MODE
n
Press ON to turn on the COD PLUS Colorimeter.
The LaMotte logo will appear for about 2 seconds
and then the Start screen appears. Press the
Q/ENTER button to start testing.
The MAIN MENU will appear. Press the Q/ENTER
button to select Testing Menu.
Press the t button to scroll to Absorbance.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select Absorbance.
VER 1.0
COD PLUS
* Start
MAIN MENU
* Testing Menu
Editing Menu
PC Link
TESTING MENU
All Tests
Sequence 1
Sequence 2
Sequence 3
* Absorbance
TESTING MENU
* Absorbance
Press the tor s buttons to move to the desired test.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select test.
32 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Absorbance
* 101
102 End of List
103 Abs 430
104 Abs 620
Absorbance
* 103 Abs 430
104 Abs 620
Page 33

Insert blank, press the Q/ENTER button to scan
blank.
103 Abs 430
* Scan Blank
The screen will display Blank Done for about 1
second.
Insert the reacted sample. Press the Q/ENTER
button to scan the sample.
Record test result. To repeat the test, press the
Q/ENTER button to scan the sample again. The
last blank scanned is used to zero the colorimeter for
repeated scans. A different blank can be used by
pressing the s button to scroll back to Scan
Blank and then scanning another blank. Scroll with
t or s and make another selection with
Q/ENTER. The %T or Absorbance of the last test
can be viewed by choosing %T/Abs. Press EXIT to
escape to previous menus.
NOTE: The menus loop in this screen so either t or
swill lead to the menu selection needed.
103 Abs 430
Blank Done
* Scan Blank
103 Abs 430
* Scan Sample
103 Abs 430
0.95
* Scan Sample
Next Test
Previous Test
%T/Abs
Scan Blank
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 33
Page 34

EDITING MENU
The EDITING MENU allows the user to edit sequences, edit user tests, set the
clock, edit the logging function, and set the power saving function.
EDIT A SEQUENCE
n
The EDIT SEQUENCE menu allows three alterable test sequences (SEQUENCE
1, SEQUENCE 2, and SEQUENCE 3) to be edited.
Press ON to turn on the COD PLUS Colorimeter.
The LaMotte logo will appear for about 2 seconds and
then the Start screen appears. Press the Q/ENTER
button to start testing.
The Main Menu will appear. Press the t button to
scroll to Editing Menu.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select Editing
Menu.
The Editing Menu appears. Press the Q/ENTER
button to select Editing Sequence.
VER 1.0
COD PLUS
*START
MAIN MENU
* Testing Menu
Editing Menu
PC Link
MAIN MENU
*Editing Menu
PC Link
EDITING MENU
* Edit Sequence
Edit User Test
Set Clock
The Edit Sequence menu appears. Press the
Q/ENTER button to scroll to select Edit
Sequence 1.
34 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
EDIT SEQUENCE
*Edit Sequence 1
Edit Sequence 2
Edit Sequence 3
Page 35

Sequence 1 appears.
ADDING OR DELETING TESTS
n
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
*004 Ammonia-NLF
005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
There are three ways to alter a sequence: Insert Before, Insert After,
and Delete. Insert Before adds a new test to the sequence before the
selected test. Insert After adds a new test to the sequence after the selected
test. Delete is used to remove an existing test from a sequence.
Below is a step by step example of how to add a test to SEQUENCE 1 starting
from the EDIT SEQUENCE 1 menu.
Press the t button to scroll to 005 Ammonia-NLS.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select 005
Ammonia-NLS.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select Insert
Before.
The ALL TESTS menu appears. Press the t button
to move the 001 COD LR to *.
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
004 Ammonia-NLF
005 Ammonia-NLS
* 006 Ammonia-NH
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* 005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
007 Boron
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* Insert Before
Insert After
Delete
ALL TESTS
* 001 COD LR
002 COD SR
003 COD HR
Continued...
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 35
Page 36

Press the Q/ENTER button to select 001 COD LR.
ALL TESTS
* 001 COD LR
002 COD SR
003 COD HR
Sequence 1 appears in EDIT SEQUENCE 1 menu
and 001 COD LR is now before 005
Ammonia-NLS in the sequence. All changes to
Sequence 1 are automatically saved. Press the EXIT
button to exit the EDIT SEQUENCE 1 menu and
return to the EDIT SEQUENCE menu or continue
editing.
The EDIT SEQUENCE menu appears. Select another
sequence to edit or press the EXIT button to return
to the EDITING MENU. Press the EXIT button
again to return the the MAIN MENU.
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* 004 Ammonia-NLF
001 COD LR
005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
007 Boron
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* Edit Sequence 1
Edit Sequence 2
Edit Sequence 3
Below is a step by step example of how to delete a test from SEQUENCE 1
starting from the EDIT SEQUENCE 1 menu. The test 001 COD LR, added in
the previous example, will be deleted.
Press the t button to scroll to 001 COD LR.
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
004 Ammonia-NLF
* 001 COD LR
005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
007 Boron
Press the Q/ENTER button to select 001 COD LR.
36 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* 001 COD LR
005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
Page 37

Press the t button to scroll to Delete.
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* Insert Before
Insert After
Delete
Press the Q/ENTER button to select Delete.
Sequence 1 appears in the EDIT SEQUENCE 1
menu and 002 Aluminum has been deleted. All
changes to SEQUENCE 1 are automatically saved.
Press the
EXIT button to exit the EDIT SEQUENCE
1 menu and return to the EDIT SEQUENCE menu
or continue editing.
The EDIT SEQUENCE menu appears. Select another
sequence to edit or press the EXIT button to return
to the EDITING MENU. Press the EXIT button again
to return the the MAIN MENU.
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* Delete
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* 004 Ammonia-NLF
005 Ammonia-NLS
006 Ammonia-NH
007 Boron
EDIT SEQUENCE 1
* Edit Sequence 1
Edit Sequence 2
Edit Sequence 3
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 37
Page 38

EDIT USER TESTS
n
If a test other than the LaMotte programmed tests is performed regularly , a
calibration for it may be entered in one of the 10 User Tests. These tests are
originally named “User Test1-10". It will be possible to rename the test,
select a wavelength, enter a new calibration, select the number of decimal
places used to display the results, and select the units. A User Test may be
added for a reagent system for which no precalibrated test exists. A calibration
of a LaMotte reagent system may also be entered. The calibration of a User
Test can be changed at any time.
The User Tests have the ability to handle 2 data points. The colorimeter will
determine the absorbance of the standards and calculate a response that will be
stored to determine the concentration of future samples of unknown
concentration. These standards should cover all the concentrations for the
range of the test being performed and be scanned beginning with the low
concentration and finishing with the high concentration (for more
information, see CALIBRATION CURVES, p. 13). Prepare these solutions
prior to entering a new calibration.
NOTE: A calibration procedure must be performed before using any of the
User Tests.
The User Tests can be placed in any of the alterable sequences using EDIT
SEQUENCES.
To edit a User Test, start at the EDITING MENU.
Scroll down to Edit User Test.
Press the Q/ENTER button to select the Edit
User Test.
From the EDIT USER TEST menu, select the User
Test to be entered or changed. In this example,
choose 105 User Test 01. Use the t and s
buttons to scroll to other User Tests if desired. Select
the User Test by pressing the Q/ENTER button.
EDITING MENU
* Edit Sequences
Edit User Test
Set Clock
EDITING MENU
* Edit User Test
Set Clock
Edit Logging
EDIT USER TEST
* 105 User Test01
106 User Test02
107 User Test03
108 User Test04
:::
114 User Test10
38 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 39

NAMING THE TEST
n
A User Test can be up to 11 characters long. The menu choices for each
character are 26 upper case letters A to Z, 26 lower case letters a to z, ten
numerals 0 to 9, a space (SP), a dash (-) and a decimal point (.). The existing
name is displayed on the bottom line of the display. A cursor will be over the
character which is to be edited and that character is also displayed in the
center of the display. The character can be changed by using the t and s
buttons to scroll to other characters. Use the Q/ENTER button to select a
character. The edited name is saved at any time by pressing EXIT or by
pressing the Q/ENTER button after selecting the eleventh character.
From the Edit User Test01 menu press the
Q/ENTER button to select Name The Test and
change the name of User Test 01.
The cursor is over the letter “U”in105 User
Test01 and the letter “U” is displayed in the large
font in the center of the display .
Change the name to H2O. Use the t and s buttons
to scroll to the letter “H” into the center of the
display. Press the Q/ENTER button to select the
letter “H”.
The letter “H” has been entered in the first position
of the name and the cursor has moved to the second
letter “s”.
EDIT USER TEST01
* Name The Test
Select Vial/WL
New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
NAME THE TEST
U
105 User Test01
NAME THE TEST
H
105 User Test01
NAME THE TEST
s
105 User Test01
Use the t and s buttons to scroll to the number
“2” into the center of the display. Press the
Q/ENTER button to select the number “2”.
NAME THE TEST
2
105 Hser Test01
Continued...
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 39
Page 40

The number “2” has been entered in the second
position of the name and the cursor has moved to
the third letter “e”.
NAME THE TEST
e
105 H2er Test01
Use the t and s buttons to scroll to the letter “O”
into the center of the display. Press the Q/ENTER
button to select the letter “O”.
The letter “O” has been entered in the third position
of the name and the cursor has moved to the fourth
letter “r”. Press the EXIT button to save the name
entered up to this point.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDIT USER TEST01 menu.
NAME THE TEST
O
105 H2Or Test01
NAME THE TEST
r
* 105 H2Or Test01
Storing
EDIT USER TEST01
* Name The Test
Select The Vial/WL
New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
40 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 41

SELECTING THE VIAL AND WAVELENGTH
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter uses three different vials (the 25 mm 0290 tube,
UDVs and COD tubes) and 2 different wavelengths (430 and 620 nm). The
colorimeter uses different settings for each of the combinations of vial and
wavelength. These twelve settings are called channels. Choose the channel
with the correct wavelength and vial for the test.
NOTE: 520 nm and 570 nm are not available in the COD PLUS.
Use the t button to scroll to Select Vial/WL
and press Q/ENTER button to select.
Use the t and s buttons to scroll to the
appropriate channel and press Q/ENTER button to
select.
NOTE: This is a looping menu.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDIT USER TEST01 menu.
EDIT USER TEST01
* Name The Test
Select Vial/WL
New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
:::
Ch11 620nm COD
Ch12 570nm COD
SELECT CHANNEL
* Ch1 520nm 25mm
Ch2 430nm 25mm
Ch3 620nm 25mm
Ch4 570nm 25mm
Ch5 520nm UDV
Ch6 430nm UDV
:::
Storing
EDIT USER TEST01
* Select The Vial/WL
New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 41
Page 42

ENTERING A NEW CALIBRATION
n
To enter a new calibration two reacted standards solutions of known
concentration are required: a “low standard” and a “high standard”. These
should be ready to use.
Use the t button to scroll to New Calibration
and press Q/ENTER button to select.
Input the concentration of the LOW STANDARD by
using the t and s buttons to scroll the first digit of
the concentration into the first position on the
display. Press Q/ENTER button to select that digit
(1 for this example).
The number “0” is always the starting point for the
next digit. Continue selecting digits or a decimal
point to enter the concentration (up to seven
characters).
“1.5” has been entered in this example. Press
Q/ENTER button four times to input “0” as the last
four digits. Pressing Q/ENTER after selecting the
last digit saves the concentration.
EDIT USER TEST01
* Select Vial/WL
New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
LOW STANDARD
0______
* Continue
LOW STANDARD
10_____
* Continue
LOW STANDARD
1.50___
* Continue
Input the concentration of the HIGH STANDARD by
using the same method as for the low standard.
42 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
HIGH STANDARD
0______
* Continue
Page 43

Place a clear blank in the sample chamber. Press the
Q/ENTER button to scan the blank.
The screen will display Blank Done for about 1
second.
Insert Blank
* Continue
Blank Done
* Scan Blank
Place the reacted low standard in the sample
chamber. Press Q/ENTER to scan the low standard.
Place the reacted high standard in the sample
chamber. Press Q/ENTER to scan the high
standard.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDIT USER TEST01 menu.
Insert Lo Standard
* Continue
Insert Hi Standard
* Continue
Storing
EDIT USER TEST01
* New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 43
Page 44

SELECTING THE NUMERICAL FORMAT OF THE RESULT
n
To input tests with very different ranges, the number of decimal places
displayed for a result can be selected. A test which ranges from 20 to 1000 ppm
should not be displayed with three decimal places. A test with a range from
0.010 to 0.500 needs three decimal places (the microprocessor will always
calculate the concentration to many more significant figures than will be
displayed). Menu choices of 0, 1, 2, or 3 decimal places will be given for the
display.
Use the t button to scroll to Decimal Places
and press Q/ENTER button to select.
Use the t button to scroll to the number of decimal
places to be shown and press Q/ENTER to select.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDIT USER TEST01 menu.
EDIT USER TEST01
* New Calibration
Decimal Places
Select Units
DECIMAL PLACES?
* None 0
One 0.0
Two 0.00
Three 0.000
Storing
EDIT USER TEST01
* Decimal Places
Select Units
44 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 45

SELECTING THE UNITS OF CONCENTRATION
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter has seven options for units of concentration.
They are No Units, ppm, pH, FTU, ppb, ppt and mgL.
Use the t button to scroll to Select Units and
press Q/ENTER to select.
Use the t button to scroll to the appropriate unit
and press Q/ENTER to select.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDIT USER TEST01 menu.
EDIT USER TEST01
* Decimal Places
Select Units
SELECT UNITS
* No Units
ppm
pH
FTU
ppb
ppt
mgL
Storing
EDIT USER TEST01
* Select Units
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 45
Page 46

SETTING THE CLOCK
n
Setting the clock allows the correct time and date stamp to be stored with each
reading in the data logger and with each reading sent out the serial port.
From the EDITING MENU use the t button to scroll
to Set Clock. Press Q/ENTER to select.
The current date and time are displayed as month day - year on the first line and as hours : minutes :
seconds on the second line. A two-digit number is
displayed for each setting. Use the t and s buttons
to scroll to the appropriate number and press
Q/ENTER to select. The cursor will move to the
next digit. Set all subsequent numbers in the same
manner. Selecting the final digit in the seconds field
stores the date and time and returns to the EDITING
MENU.
NOTE: These are looping menus.
EDITING MENU
* Edit Sequences
Edit User Test
Set Clock
Editing Logging
Factory Setup
Set PWR Save
SET TIME
MM-DD-YY
HH:MM:SS
EDITING MENU
* Set Clock
Editing Logging
Factory Setup
Set PWR Save
46 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 47

TURNING THE DATA LOGGER ON AND OFF
n
The default setting for the datalogger is “Enabled” or turned off. If there is no
need for data logging, this setting is suggested. If data logging is needed, the
data logger can be “Enabled” or turned on.
From the EDITING MENU use the t button to
scroll to Edit Logging. Press
Q/ENTER to
select.
The current setting is always displayed next to the *.
To change the setting, use the t or s buttons to
scroll to the other setting. Press Q/ENTER to select.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDITING MENU.
EDITING MENU
* Edit Sequences
Edit User Test
Set Clock
Editing Logging
Factory Setup
Set PWR Save
EDIT LOGGING
* Enabled
Disabled
Storing
EDITING MENU
* Editing Logging
Factory Setup
Set PWR Save
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 47
Page 48

FACTORY SETUP
n
The Factory Setup menu is used in the manufacturing of the COD PLUS
Colorimeter. This menu is not for use by the operator in the field.
SETTING THE POWER SAVING FUNCTION
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter has a power saving function that turns the meter
off after an interval of inactivity. If no buttons have been pressed during that
interval the meter will turn itself off. This interval can be disabled or set for 5,
15, 30 or 60 minutes. The default setting is 5 minutes.
From the EDITING MENU use the t button to
scroll to Set PWR Save. Press Q/ENTER to select.
The current setting is always displayed next to the *.
To change the setting, use the t or s buttons to
scroll to the appropriate setting. Press Q/ENTER to
select.
The meter will display the message “Storing” and
return to the EDITING MENU.
EDITING MENU
* Edit Sequences
Edit User Test
Set Clock
Editing Logging
Factory Setup
Set PWR Save
Disabled
AUTO SHUTOFF
* 5 Minutes
15 Minutes
30 Minutes
60 Minutes
Storing
EDITING MENU
* Set PWR Save
48 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 49

PC LINK
The COD PLUS Colorimeter may be interfaced with any Windows-based
computer by using the LaMotte SMARTLink2 Program and Interface Cable
(Order Code 1912-3 [3.5 disk] or 1912-CD [compact disk]). The program
stores customer information and test data in a database. It can be used to
download data stored in the COD PLUS datalogger for each test site.
The colorimeter may also be interfaced with an RS-232 serial printer, using an
interface cable (Order Code 1772) and setting the printer configuration to the
Output as described below.
Choose PC Link from the Main Menu. The user can download the entire
datalogging buffer. Downloading does not delete or empty the datalogger.
OUTPUT
n
RS-232 compatible, asynchronous serial, 9600 baud, no parity, 8 data bits, 1
stop bit.
COMPUTER CONNECTION
n
RS-232 interface connection, 8 pin mini-DIN/9 pin F D-submin. (Order Code
1772).
BA TTERY OPERA TION
The colorimeter may be run on battery power or AC using the AC adapter. If
using the meter as a benchtop unit, keep it plugged in if possible. If used on
only battery power, always have a spare battery on hand.
If the battery power is low , the COD PLUS will
display “LOW BATT” and turn off.
REPLACING THE BATTERY
n
The COD PLUS Colorimeter uses a standard 9-volt alkaline battery that is
available worldwide. The battery compartment is located on the bottom of the
the case.
To replace the battery:
1. Open the battery compartment lid.
2. Remove the battery and disconnect the battery from the polarized plug.
3. Carefully connect the new battery to the polarized plug and insert it into the
compartment.
4. Close the battery compartment lid.
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02 49
LOW BATT
Page 50

MAINTENANCE
CLEANING
n
Clean with a damp, lint-free cloth.
DO NOT ALLOW WATER TO ENTER THE COLORIMETER
CHAMBER OR ANY OTHER PARTS OF THE METER.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
ERROR MESSAGES
n
n
OVER RANGE
If the message OVERRANGE is displayed when scanning a sample, the sample
may be over range or under range. If the sample is over range the sample should
be diluted and tested again (see Sample Dilution Techniques and Volumetric
Measurements, p. 16).
If OVERRANGE is displayed, press the Q/ENTER
button to continue testing on diluted samples.
HELPFUL HINTS
n
n
STRAY LIGHT
The COD PLUS Colorimeter should have no problems with stray light. Make
sure that the sample compartment lid is always fully closed, except when
testing COD with the adapter.
015 Chlorine
OVERRANGE
* Continue
50 COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/02
Page 51

COD PLUS COLORIMETER
REAGENT SYSTEMS
COD PLUS REAGENT SYSTEMS LIST
n
Test # Test Factor Range(ppm) Test Method (# of Reagents)
1 COD-Low Range 5-150 Digestion (1) 25
2 COD-Standard Range 0-1500 Digestion (1) 25
3 COD-High Range 0-15000 Digestion (1) 25
4 Ammonia Nitrogen-
Low Range, Fresh Water
5 Ammonia Nitrogen-
Low Range, Salt Water
6 Ammonia Nitrogen-
High Range
7 Boron 0.00-0.80 Azomethine-H (2) 50
8 Cobalt 0.00-2.00 PAN (3) 50
9 Color 0-1000 Platinum Cobalt (0) ¥
10 Copper-Cuprizone 0.00-2.00 Cuprizone (2) 50
11 Copper-DDC 0.00-6.00 Diethyldithiocarbamate (1) 100
12 Cyanuric Acid 5-200 Melamine (1) 50
13 Dissolved Oxygen 0.0-11.0 Winkler colorimetric (3) 300
14 Fluoride 0.00-2.00 SPADNS (2) 50
15 Hydrazine 0.00-1.00 P-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (2) 50
16 Molybdenum-High Range 0.0-50.0 Thioglycolate (3) 50
17 Nickel 0.00-8.00 Dimethylglyoxime (6) 50
18 Ozone-Low Range 0.00-0.40 Indigo (3) 100
19 Ozone-High Range 0.00-2.50 Indigo (3) 50
20 Phosphate-Low Range 0.00-3.00 Ascorbic Acid Reduction (2) 50
21 Phosphate-High Range 0.0-70.0 V anodomolybdphosphoric Acid (1) 50
22 Potassium 0.0-10.0 Tetraphenylboron (2) 100
23 Silica-Low Range 0.0-4.0 Heteropoly Blue (4) 50
24 Silica-High Range 0-75 Silicomolybdate (3) 50
25 Sulfate-High Range 0-100 Barium Chloride (1) 50
26 Sulfide-Low Range 0.00-1.50 Methylene Blue (3) 50
27 Tannin 0.0-10.0 Tungsto-molybdophosphoric Acid (2) 50
28 Turbidity 0-400 Absorption (0) ¥
29 Zinc-Low Range 0.00-3.00 Zincon (6) 50
0.00-1.00 Salicylate (3) 50
0.00-1.00 Salicylate (3) 25
0.00-4.00 Nesslerization (2)
#of
Tests
COD PLUS COLORIMETER 6/03 51
Page 52

COD
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
PLUS
Colorimeter
TEST
INSTRUCTIONS
Page 53

Page 54

COD PLUS COLORIMETER
TEST PROCEDURES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
n
COD - Low Range
COD - Standard Range
COD - High Range
Ammonia Nitrogen - Low Range, Fresh Water
Ammonia Nitrogen - Low Range, Salt Water
Ammonia Nitrogen - High Range
Boron
Cobalt
Color
Copper - Cuprizone
Copper - DDC
Cyanuric Acid
Dissolved Oxygen
Fluoride
Hydrazine
Molybdenum - High Range
Nickel
Ozone - Low Range
Ozone - High Range
Phosphate - Low Range
Phosphate - High Range
Potassium
Silica - Low Range
Silica - High Range
Sulfate - High Range
Sulfide - Low Range
Tannin
Turbidity
Zinc - Low Range
Appendix
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1/1
Page 55

COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 56

COD - LOW RANGE
MERCURY FREE DIGESTION • CODE 5-0072
MERCURY DIGESTION • CODE 5-0075
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
25 *COD Low Range Mercury Free Tubes
or 25 * COD Low Range Mercury Tubes
*W ARNING: Reagent marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
COD Low Range Mercury Free Tubes are not USEP A approved.
COD Low Range Mercury T ubes are USEPA approved.
Equipment needed but not supplied:
1 COD Adapter
1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 110V
or 1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 220V
or 1 COD Reactor, 25 vial, 110/220V
1 Volumetric Pipet, 2.0 mL
1 Pipet Bulb
*5-0072
*5-0075
5-0087
5-0069
5-0070
5-0094
2-2168
2-2164
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a measure of the amount of organic
matter in water which is susceptible to oxidation by chemical oxidants. COD
can be empirically related to the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and
organic carbon content of a specific source of water. This correlation must be
determined experimentally for each source of water.
APPLICATION: Domestic and industrial wastes.
RANGE: 5 - 150 mg/L COD
METHOD: Dichromate in the presence of silver salts, at high
temperature in a closed system, oxidizes most organic
compounds to 95-100% of the theoretical amount. This
process is called digestion. As dichromate oxidizes the
organic compounds, the amount of yellow color is reduced.
The remaining yellow color is measured colorimetrically at
the 420 nm and is directly proportional to the COD of the
sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Collect samples in glass and test as soon as possible. If
samples must be stored, preservation is accomplished by the
addition of concentrated H
to adjust the pH below 2.
2SO4
Samples with suspended solids should be homogenized in a
blender (100 mL for 30 seconds) and then stirred gently with
a magnetic stirrer.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/03 COD - LOW RANGE 1/4
Page 57

INTERFERENCES: Volatile organic compounds are not oxidized to the extent
that they are in the vapor above the digestion solution.
Therefore, they do not contribute to the COD reading.
Chloride concentrations above 10% of COD interfere with
the mercury free tubes. Chloride above 2000 ppm will
interfere with the mercury tubes. Nitrite gives a positive
interference of 1.1 ppm O
per ppm NO2–N which is
2
insignificant unless nitrite concentrations are very high.
Other reduced inorganic compounds are stoichiometrically
oxidized, causing a positive interference. Corrections can be
made for these compounds based upon their stoichiometry
and concentrations.
When scanning samples in 16 mm tubes, such as COD, the
sample chamber lid can not be closed. The COD adapter
minimizes stray light. To further reduce stray light
interference, do not scan sample in direct sunlight.
COD - LOW RANGE 2/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 58

PROCEDURE
Use COD adapter (see p. 22).
1. Homogenize sample if necessary.
2. Preheat COD heater block to 150±2°C.
3. Remove cap from COD tube vial. Hold vial at a 45° angle. Use a
volumetric pipet, to carefully add 2.0 mL sample water allowing the
sample to run down the side of the vial.
4. Cap and mix thoroughly.
5. Rinse the outside of the vial with distilled water. Wipe dry with a paper
towel.
6. Repeat steps 3 through 5 using 2.0 mL distilled water. This is the reagent
blank.
7. Place vials in preheated COD block heater and maintain temperature at
150±2°C for two hours.
8. At the end of the heating period turn the heater off. Wait 20 minutes for
the vials to cool to 120°C or less.
9. Remove vials from block heater. Invert several times to mix.
10. Allow to cool to room temperature.
11. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
12. Press ENTER to start.
13. Press ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
14. Select ALL TESTS (or a sequence containing 1 COD LR) from
PROGRAMMED TESTS menu.
15. Scroll to and select 1 COD LR from menu.
16. Wipe the blank vial with a damp towel to remove fingerprints and
smudges. Wipe with a dry towel.
17. Insert reagent blank tube into chamber. Align the center of the LaMotte
logo on the tube with the arrow shaped mark molded into the housing at
the front edge of the light chamber. Select SCAN BLANK.
18. Remove tube from colorimeter.
19. Insert digested water sample tube into chamber. Position the tube as
instructed above. Select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result. For the most
accurate results, take three readings on each sample and average the
results.
20. Press
OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to
a previous menu or make another menu selection.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 COD - LOW RANGE 3/4
Page 59

NOTES:
l
Reagents are light sensitive. Unused reagents should be stored in the
shipping container, and in the refrigerator if possible, until needed.
l
A reagent blank should be run with each set of samples and with each lot
of reagents.
l
The reacted blank will be stable if stored in the dark.
l
To eliminate error caused by contamination, wash all glassware with 20%
sulfuric acid.
l
For greater accuracy, a minimum of three repetitions should be performed
and the results averaged.
l
Some samples may be digested completely in less than two hours. The
concentration may be measured at 15 minute intervals while the vials are
still hot until the reading remains unchanged. The vials should be cooled
to room temperature before the final measurement is taken.
COD - LOW RANGE 4/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 60

COD - ST ANDARD RANGE
MERCURY FREE DIGESTION • CODE 5-0073
MERCURY DIGESTION • CODE 5-0076
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
25 *COD Standard Range Mercury Free Tubes
or 25 * COD Standard Range Mercury Tubes
*W ARNING: Reagent marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
COD Standard Range Mercury Free Tubes are not USEP A approved.
COD Standard Range Mercury T ubes are USEPA approved.
Equipment needed but not supplied:
1 COD Adapter
1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 110V
or 1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 220V
or 1 COD Reactor, 25 vial, 110/220V
1 Volumetric Pipet, 2.0 mL
1 Pipet Bulb
*5-0073
*5-0076
5-0087
5-0069
5-0070
5-0094
2-2168
2-2164
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a measure of the amount of organic
matter in water which is susceptible to oxidation by chemical oxidants. COD
can be empirically related to the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and
organic carbon content of a specific source of water. This correlation must be
determined experimentally for each source of water.
APPLICATION: Domestic and industrial wastes.
RANGE: 0-1500 mg/L COD
METHOD: Dichromate in the presence of silver salts, at high
temperature in a closed system, oxidizes most organic
compounds to 95-100% of the theoretical amount. This
process is called digestion. As dichromate oxidizes the
organic compounds, a green complex is formed. The
concentration of the green complex is measured at 605 nm
and is directly proportional to the COD of the sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Collect samples in glass and test as soon as possible. If
samples must be stored, preservation is accomplished by the
addition of concentrated H
to adjust the pH below 2.
2SO4
Samples with suspended solids should be homogenized in a
blender (100 mL for 30 seconds) and then stirred gently with
a magnetic stirrer.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/03 COD - STANDARD RANGE 1/4
Page 61

INTERFERENCES: Volatile organic compounds are not oxidized to the extent
that they are in the vapor above the digestion solution.
Therefore, they do not contribute to the COD reading.
Chloride concentrations above 10% of COD interfere with
the mercury free tubes. Chloride above 2000 ppm will
interfere with the mercury tubes. Nitrite gives a positive
interference of 1.1 ppm O
per ppm NO2–N which is
2
insignificant unless nitrite concentrations are very high.
Other reduced inorganic compounds are stoichiometrically
oxidized, causing a positive interference. Corrections can be
made for these compounds based upon their stoichiometry
and concentrations.
When scanning samples in 16 mm tubes, such as COD, the
sample chamber lid can not be closed. The COD adapter
minimizes stray light. To further reduce stray light
interference, do not scan sample in direct sunlight.
COD - STANDARD RANGE 2/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 62

PROCEDURE
Use COD adapter (see p. 22).
1. Homogenize sample if necessary.
2. Preheat COD heater block to 150±2°C.
3. Remove cap from COD tube vial. Hold vial at a 45° angle. Use a
volumetric pipet, to carefully add 2.0 mL sample water allowing the
sample to run down the side of the vial.
4. Cap and mix thoroughly.
5. Rinse the outside of the vial with distilled water. Wipe dry with a paper
towel.
6. Repeat steps 2 through 5 using 2.0 mL distilled water. This is the reagent
blank.
7. Place vials in preheated COD block heater and maintain temperature at
150±2°C for two hours.
8. At the end of the heating period turn the heater off. Wait 20 minutes for
the vials to cool to 120°C or less.
9. Remove vials from block heater. Invert several times to mix.
10. Allow to cool to room temperature.
11. Press and hold
12. Press
13. Press
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
14. Select ALL TESTS (or a sequence containing 2 COD SR) from
PROGRAMMED TESTS menu.
15. Wipe the blank vial with a damp towel to remove fingerprints and
smudges. Wipe with a dry towel.
16. Scroll to and select 2 COD SR from menu.
17. Insert reagent blank tube into chamber. Align the center of the LaMotte
logo on the tube with the arrow shaped mark molded into the housing at
the front edge of the light chamber. Select SCAN BLANK.
18. Remove tube from colorimeter.
19. Insert digested water sample tube into chamber. Position the tube as
instructed above. Select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result. For the most
accurate results, take three readings on each sample and average the
results.
20. Press
OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to
a previous menu or make another menu selection.
ON button until colorimeter turns on.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 COD - STANDARD RANGE 3/4
Page 63

NOTES:
l
Reagents are light sensitive. Unused reagents should be stored in the
shipping container, and in the refrigerator if possible, until needed.
l
A reagent blank should be run with each set of samples and with each lot
of reagents.
l
The reacted blank will be stable if stored in the dark.
l
To eliminate error caused by contamination, wash all glassware with 20%
sulfuric acid.
l
For greater accuracy, a minimum of three repetitions should be performed
and the results averaged.
l
Some samples may be digested completely in less than two hours. The
concentration may be measured at 15 minute intervals while the vials are
still hot until the reading remains unchanged. The vials should be cooled
to room temperature before the final measurement is taken.
COD - STANDARD RANGE 4/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 64

COD - HIGH RANGE
MERCURY FREE DIGESTION • CODE 5-0074
MERCURY DIGESTION • CODE 5-0077
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
25 *COD High Range Mercury Free Tubes
or 25 *COD High Range Mercury Tubes
*W ARNING: Reagent marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
COD High Range Mercury Free Tubes and COD High Range Mercury Tubes
are not USEPA approved.
Equipment needed but not supplied:
1 COD Adapter
1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 110V
or 1 COD Reactor, 8 vial, 220V
or 1 COD Reactor, 25 vial, 110/220V
1 Volumetric Pipet, 2.0 mL
1 Pipet Bulb
*5-0074
*5-0077
5-0087
5-0069
5-0070
5-0094
2-2168
2-2164
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a measure of the amount of organic
matter in water which is susceptible to oxidation by chemical oxidants. COD
can be empirically related to the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and
organic carbon content of a specific source of water. This correlation must be
determined experimentally for each source of water.
APPLICATION: Domestic and industrial wastes.
RANGE: 0-15000 mg/L COD
METHOD: Dichromate in the presence of silver salts, at high
temperature in a closed system, oxidizes most organic
compounds to 95-100% of the theoretical amount. This
process is called digestion. As dichromate oxidizes the
organic compounds, a green complex is formed. The
concentration of the green complex is measured at 605 nm
and is directly proportional to the COD of the sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Collect samples in glass and test as soon as possible. If
samples must be stored, preservation is accomplished by the
addition of concentrated H
to adjust the pH below 2.
2SO4
Samples with suspended solids should be homogenized in a
blender (100 mL for 30 seconds) and then stirred gently with
a magnetic stirrer.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/03 COD - HIGH RANGE 1/4
Page 65

INTERFERENCES: Volatile organic compounds are not oxidized to the extent
that they are in the vapor above the digestion solution.
Therefore, they do not contribute to the COD reading.
Contains mercury sulfate to prevent interference from
chloride. Nitrite gives a positive interference of 1.1 ppm O
per ppm NO2–N, which is insignificant unless nitrite
concentrations are very high. Other reduced inorganic
compounds are stoichiometrically oxidized, causing a
positive interference. Corrections can be made for these
compounds based upon their stoichiometry and
concentrations.
When scanning samples in 16 mm tubes, such as COD, the
sample chamber lid can not be closed. The COD adapter
minimizes stray light. To further reduce stray light
interference, do not scan sample in direct sunlight.
2
COD - HIGH RANGE 2/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 66

PROCEDURE
Use COD adapter (see p. 22).
1. Homogenize sample if necessary.
2. Preheat COD heater block to 150±2°C.
3. Remove cap from COD tube vial. Hold vial at a 45° angle. Use a
graduated pipet, to carefully add 0.2 mL sample water allowing the sample
to run down the side of the vial.
4. Cap and mix thoroughly.
5. Rinse the outside of the vial with distilled water. Wipe dry with a paper
towel.
6. Repeat steps 3 through 5 using 0.2 mL distilled water. This is the reagent
blank.
7. Place vials in preheated COD block heater and maintain temperature at
150±2°C for two hours.
8. At the end of the heating period turn the heater off. Wait 20 minutes for
the vials to cool to 120°C or less.
9. Remove vials from block heater. Invert several times to mix.
10. Allow to cool to room temperature.
11. Press and hold
12. Press
13. Press
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
14. Select ALL TESTS (or a sequence containing 3 COD HR 0-15000) from
PROGRAMMED TESTS menu.
15. Wipe the blank vial with a damp towel to remove fingerprints and
smudges. Wipe with a dry towel.
16. Scroll to and select 3 COD HR 0-15000 from menu.
17. Insert reagent blank tube into chamber. Align the center of the LaMotte
logo on the tube with the arrow shaped mark molded into the housing at
the front edge of the light chamber. Select SCAN BLANK.
18. Remove tube from colorimeter.
19. Insert digested water sample tube into chamber. Position the tube as
instructed above. Select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result. For the most
accurate results, take three readings on each sample and average the
results.
20. Press
OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to
a previous menu or make another menu selection.
ON button until colorimeter turns on.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 COD - HIGH RANGE 3/4
Page 67

NOTES:
l
Reagents are light sensitive. Unused reagents should be stored in the
shipping container, and in the refrigerator if possible, until needed.
l
A reagent blank should be run with each set of samples and with each lot
of reagents.
l
The reacted blank will be stable if stored in the dark.
l
To eliminate error caused by contamination, wash all glassware with 20%
sulfuric acid.
l
For greater accuracy, a minimum of three repetirions should be performed
and the results averaged..
COD - HIGH RANGE 4/4 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 68

AMMONIA-NITROGEN - LOW RANGE
SALICYLATE METHOD • CODE 3659-01-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
60 mL *Salicylate Ammonia #1
10 g * Salicylate #2
5 g *Salicylate #3
1 Spoon, 0.1 g, plastic
1 Spoon, 0.15 g, plastic
1 Pipet, 1.0 mL, plastic
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Data Safety Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Ammonia nitrogen is present in various concentrations in many surface and
ground water supplies. Any sudden change in the concentration of ammonia
nitrogen in a water supply is cause for suspicion. A product of microbiological
activity, ammonia nitrogen is sometimes accepted as chemical evidence of
pollution when encountered in natural waters.
Ammonia is rapidly oxidized in natural water systems by special bacterial
groups that produce nitrite and nitrate. This oxidation requires that dissolved
oxygen be available in the water. Ammonia is an additional source of nitrogen
as a nutrient which may contribute to the expanded growth of undesirable
algae and other forms of plant growth that overload the natural system and
cause pollution.
APPLICATION: Low concentrations of ammonia in fresh, brackish and salt
water; fresh and salt water aquariums.
RANGE: 0.00 – 1.00 ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen
METHOD: Salicylate and ammonia react at high pH in the presence of a
chlorine donor and an iron catalyst to form a blue
indophenol dye, the concentration of which is proportional
to the ammonia concentration in the sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLE &
PRESERVATION:
Ammonia solutions tend to be unstable and should be
analyzed immediately. Samples may be stored for 24 hours at
4°C or 28 days at –20°C.
INTERFERENCES: There are few interferences in most natural waters. High
concentrations of reducing agents, such as hydrazine, react
with the chlorine donor and can result in negative
interferences. Color and turbidity can also interfere.
*3978-H
*7457-D
*7458-C
0699
0727
0354
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 AMMONIA-NITROGEN - HIGH RANGE 1/2
Page 69

PROCEDURE - FRESH WATER
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing
5. Scroll to and select 4 Ammonia-NLF from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK. (See Note.)
8. Remove tube from colorimeter. Use the 1.0 mL plastic pipet (0354) to add
9. Use the 0.15 g spoon (0727) to add two measures of *Salicylate #2
10. At end of 1 minute waiting period use 0.1 g spoon (0699) to add two
11. At the end of the 12 minute waiting period, immediately mix and insert
12. Press
CALCULATIONS:
To express results as Unionized Ammonia (NH
To express results as Ionized Ammonia (NH4):
To determine the percentages of Unionized and Ionized Ammonia-Nitrogen,
consult the Appendix.
NOTE: For the best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents are obtained.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
4 Ammonia-NLF) from TESTING MENU.
sample.
2.0 mL of *Salicylate Ammonia #1 (3978). Cap and mix.
Reagent (7457). Cap and mix until dissolved. Wait 1 minute.
measures of *Salicylate #3 Reagent Powder (7458). Cap and shake
vigorously for at least 30 seconds and all solid has dissolved. Wait 12
minutes for maximum color development.
tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
previous menu or make another menu selection.
):
3
ppm Unionized Ammonia (NH3)=
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
ppm Ionized Ammonia (NH
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
–N) x 1.2
3
+
)=
4
–N) x 1.3
3
AMMONIA-NITROGEN - HIGH RANGE 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 70

PROCEDURE - SALT WA TER
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing
5. Scroll to and select 5 Ammonia-NLS from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK. (See Note.)
8. Remove tube from colorimeter. Use the 1.0 mL plastic pipet (0354) to add
9. Use the 0.15 g spoon (0727) to add two measures of *Salicylate #2
10. At end of 1 minute waiting period use 0.1 g spoon (0699) to add two
11. At the end of the 20 minute waiting period, immediately mix and insert
12. Press
CALCULATIONS:
To express results as Unionized Ammonia (NH
To express results as Ionized Ammonia (NH4):
To determine the percentages of Unionized and Ionized Ammonia-Nitrogen,
consult the Appendix.
NOTE: For the best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents are obtained.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
5 Ammonia-NLS) from TESTING MENU.
sample.
2.0 mL of *Salicylate Ammonia #1 (3978). Cap and mix.
Reagent (7457). Cap and mix until dissolved. Wait 1 minute.
measures of *Salicylate #3 Reagent Powder (7458). Cap and shake
vigorously for at least 30 seconds and all solid has dissolved. Wait 20
minutes for maximum color development.
tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
previous menu or make another menu selection.
):
3
ppm Unionized Ammonia (NH3)=
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
ppm Ionized Ammonia (NH
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
–N) x 1.2
3
+
)=
4
–N) x 1.3
3
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 AMMONIA-NITROGEN - LOW RANGE 1/3
Page 71

AMMONIA-NITROGEN - LOW RANGE 2/3 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 72

AMMONIA-NITROGEN HIGH RANGE
NESSLERIZATION METHOD • CODE 3642-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
30 mL Ammonia Nitrogen Reagent #1
2 x 30 mL *Ammonia Nitrogen Reagent #2
1 Pipet, 1 mL, plastic
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Ammonia nitrogen is present in various concentrations in many surface and
ground water supplies. Any sudden change in the concentration of ammonia
nitrogen in a water supply is cause for suspicion. A product of microbiological
activity, ammonia nitrogen is sometimes accepted as chemical evidence of
pollution when encountered in natural waters.
Ammonia is rapidly oxidized in natural water systems by special bacterial
groups that produce nitrite and nitrate. This oxidation requires that dissolved
oxygen be available in the water. Ammonia is an additional source of nitrogen
as a nutrient which may contribute to the expanded growth of undesirable
algae and other forms of plant growth that overload the natural system and
cause pollution.
APPLICATION: Drinking, surface, and saline waters; domestic and industrial
wastes.
RANGE: 0.00 – 4.00 ppm Ammonia Nitrogen
METHOD: Ammonia forms a colored complex with Nessler’s Reagent in
proportion to the amount of ammonia present in the sample.
Rochelle salt is added to prevent precipitation of calcium or
magnesium in undistilled samples.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
INTERFERENCES: Sample turbidity and color may interfere. Turbidity may be
Ammonia solutions tend to be unstable and should be
analyzed immediately. Sample may be stored for 24 hours at
4°C or 28 days at –20°C.
removed by a filtration procedure. Color interference may be
eliminated by blanking the instrument with a sample blank.
V-4797-G
*V-4798-G
0354
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 AMMONIA-NITROGEN - LOW RANGE 3/3
Page 73

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Scroll to and select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing
5. Scroll to and select 6 Ammonia-NH from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK. (See Note)
8. Remove tube from colorimeter. Add 8 drops of Ammonia Nitrogen
9. Use the 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 1.0 mL of *Ammonia Nitrogen
10. At end of the 5 minute waiting period, immediately mix, insert tube into
11. Press
CALCULATIONS:
To express results as Unionized Ammonia (NH
To express results as Ionized Ammonia (NH4):
To determine the percentages of Unionized and Ionized Ammonia-Nitrogen,
consult the Appendix.
NOTE: For the best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents are obtained.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
6 Ammonia-NH) from TESTING MENU.
sample.
Reagent #1 (V-4797). Cap and mix. Wait 1 minute.
Reagent #2 (V-4798). Cap and mix. Allow 5 minutes for maximum color
development.
chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
OFF button to turn the colorimeter off or press the EXIT button exit
to a previous menu or make another menu selection.
):
3
ppm Unionized Ammonia (NH3)=
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
ppm Ionized Ammonia (NH
ppm Ammonia-Nitrogen (NH
–N) x 1.2
3
+
)=
4
–N) x 1.3
3
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 74

BORON
AZOMETHINE-H METHOD · CODE 4868
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
120 mL *Boron Buffer *4869 - J
10 g *Boron Indicator Powder *4870 - D
1 Pipet, plastic, 1.0 mL 0354
1 Spoon, 0.15 g 0727
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Small amounts of boron are necessary for plant growth but large amounts can
be toxic. In humans, boron aids in the uptake of calcium and the production of
strong bones. An excess of boron can affect the central nervous system
resulting in a syndrome known as borism. Some natural waters may contain
small amounts of boron. Large concentrations may be due to industrial effluent
entering waterways. .Boron compounds are used in cleaning compounds, paper
and paints, fertilizers, glass and ceramics, fire retardants and the production of
alloys. In the atomic energy field, boron is a component of neutron shields and
nuclear reactors. Some swimming pools use boron buffering systems.
APPLICATION: Surface and saline waters, hydroponic solutions, industrial
waste, swimming pools.
RANGE: 0.00 - 0.80 ppm Boron
METHOD: Azomethine-H and borate form a yellow complex at pH 6 in
proportion to the concentration of boron present.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
INTERFERENCES: Interferences in drinking water are unlikely. Manganese,
Store samples in polyethylene bottles. Do not use borate
detergents or glassware.
zirconium, chromium, titanium, copper, vanadium,
aluminum, beryllium and iron may cause high results.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 BORON 1/2
Page 75

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press ENTER to start.
3. Press ENTER to select Testing Menu.
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 7 Boron) from
TESTING MENU.
5. Scroll to and select 7 Boron from menu.
6. Rinse a tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to 10 mL line with sample.
7. Insert the tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove the tube from colorimeter.
9. Use the 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 2 mL of *Boron Buffer (4869). Cap
and mix.
10. Use the 0.15 g spoon (0727) to add one level measure of *Boron Indicator
Powder (4870). Press full spoon against side of jar to compress powder.
Scrape off excess powder on inside neck of bottle. Tap excess off spoon
handle.
11. Cap and shake vigorously for 30 seconds.
12. Insert the tube into chamber. Close lid.
13. Wait 30 minutes. Do not open the lid during the waiting time. The
reaction is photosensitive.
14. Remove tube from chamber. Invert several times to mix.
15. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
result in ppm boron.
16. Press OFF button to turn the colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit
to a previous menu or make another menu selection.
NOTE: For best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents is obtained.
BORON 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 76

COBALT
PAN METHOD · CODE 4851
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
60 mL *Cobalt Buffer *4852-H
60 mL *Cobalt Indicator Reagent *4853-H
30 mL *Stabilizer Solution *4854-G
2 Pipet, 1.0 mL, plastic 0354
1 Pipet, 0.5 mL, plastic 0353
*W ARNING: Reagent marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Cobalt rarely occurs in natural water. It is used in the manufacture of alloys to
increase corrosion resistance and strength. It is found in wastewaters as a
corrosion by-product.
APPLICATION: Industrial wastewater.
RANGE: 0.0 – 2.0 ppm cobalt
METHOD: PAN (1-(2-Pyridylazo)-2-Naphthol) forms a greenish
complex with Cobalt (Co
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Store samples in acid-washed plastic bottles. Adjust pH to
less than 2 with nitric acid. Adjust sample pH to 5 before
testing.
INTERFERENCES: Iron (+2) and high concentrations of heavy metals.
+2
)atapHof5.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 COBALT 1/2
Page 77

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press ENTER to start.
3. Press ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
4. Select All Tests (or another sequence containing 8 Cobalt) from
TESTNG MENU.
5. Scroll to and select 8 Cobalt from menu.
6. Rinse a tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to 10 mL with sample.
7. Insert the tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove the tube from colorimeter.
9. Use the 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 1 mL of *Cobalt Buffer (4852). Cap
and mix.
10. Use the other 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 1 mL of *Cobalt Indicator
Reagent (4853). Cap and mix.
11. Wait 3 minutes.
12. Use the 0.5 mL pipet (0353) to add 0.5 mL *Stabilizer Solution (4854).
Cap and invert 15 times to thoroughly mix.
13. Wait 5 minutes. DO NOT MIX.
14. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
result in ppm cobalt.
15. Press OFF button to turn the colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit
to a previous menu or make another menu selection.
NOTE: For best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents is obtained.
COBALT 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04
Page 78

COLOR
PLATINUM COBALT METHOD · NO REAGENTS REQUIRED
Color in water may be attributed to humus, peat, plankton, vegetation, and
natural metallic ions, such as iron and manganese, or industrial waste. Color is
removed to make water suitable for domestic and industrial use. Color may
have to be removed from industrial waste before it is discharged to a waterway.
APPLICATION: Potable water and water with color due to natural materials.
RANGE: 0 - 1,000 color units
METHOD: Color is determined by a meter that has been calibrated with
colored standards of known platinum cobalt concentration.
True color, the color of water in which the turbidity has been
removed, is measured.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
INTERFERENCES: Turbidity will interfere. Filter before testing.
PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON burton until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press ENTER to start.
3. Press ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 9 Color) from
TESTING MENU.
5. Scroll to and select 9 Color from menu.
6. Rinse a tube (0290) with color-free water (distilled or deionized water).
Fill to 10 mL line with color-free water.
7. Insert the tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove tube from colorimeter. Empty tube.
9. Rinse tube with sample water. Fill to 10 mL line with water sample.
10. Insert tube with sample water, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
result in color units.
11. Press OFF button to turn the colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit
to a previous menu or make another menu selection.
Collect all samples in clean glassware. Determine color as
soon as possible to avoid biological or chemical changes that
could occur in the sample during storage.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 2/04 COLOR 1/1
Page 79

COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 80

COPPER
CUPRIZONE METHOD • CODE 4023
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
15 mL Copper A
15 mL * Copper B
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
The copper content of drinking water generally falls below 0.03 parts per
million, but copper levels as high as 1.0 part per million will give water a bitter
taste. Waters testing as high as 1.0 part per million copper have probably been
treated with a copper compound, like those used in the control of algae, or
have become contaminated from untreated industrial wastes. The addition of
copper sulfate to lakes causes an increase in the copper content of the
sediments. Acid waters and those high in free carbon dioxide may cause the
corrosion or “eating away” of copper, brass and bronze pipes and fittings. This
corrosion results in the addition of copper to the water supply.
APPLICATION: Drinking, surface, and domestic waters. Pools and spas.
RANGE: 0 to 2.0 ppm Copper
METHOD: Copper ions form a blue complex with cuprizone, ina1to2
ratio, at a pH of about 8, in proportion to the concentration
of copper in the sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Copper has a tendency to be adsorbed to the surface of the
sample container. Samples should be analyzed as soon as
possible after collection. If storage is necessary , 0.5 mL of
20% hydrochloric acid per 100 mL of sample will prevent
“plating out”. However, a correction must be made to bring
the reaction into the optimum pH range.
INTERFERENCES: Hg
+1
at 1 ppm. Cr+3,Co+2, and silicate at 10 ppm. As+3,
+3
,Ca+2,Ce+3,Ce+4,Hg+2,Fe+2,Mn+2,Ni+2and
Bi
ascorbate at 100 ppm.
Many other metal cations and inorganic anions at 1000 ppm.
EDTA at all concentrations.
P-6367-E
P-6368-E
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 COPPER - DDC 1/2
Page 81

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 10 Cu-Cuprizone)
5. Scroll to and select 10 Cu-Cuprizone from menu.
6. Rinse a tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with sample.
7. Insert the tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove tube from colorimeter and add 5 drops of Copper A (6367). Cap
9. Add 5 drops of *Copper B (6368). Cap and mix.
10. Wait 5 minutes. Mix.
11. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
12. Press OFF button to turn the colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit
NOTES:
l
The reaction may stain the tubes. Scrub tubes thoroughly after each use.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
from TESTING MENU.
and mix.
result.
to a previous menu or make another menu selection.
For best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to account
for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To determine
the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled or
deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the
test on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent
blank. Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of
unknown samples. It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only
when a new lot number of reagents are obtained.
COPPER - DDC 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 82

COPPER
DIETHYLDITHIOCARBAMATE METHOD • CODE 3646-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
15 mL *Copper 1
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Data Safety Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
The copper content of drinking water generally falls below 0.03 parts per
million, but copper levels as high as 1.0 part per million will give water a bitter
taste. Waters testing as high as 1.0 part per million copper have probably been
treated with a copper compound, like those used in the control of algae, or
have become contaminated from untreated industrial wastes. The addition of
copper sulfate to lakes causes an increase in the copper content of the
sediments. Acid waters and those high in free carbon dioxide may cause the
corrosion or “eating away” of copper, brass and bronze pipes and fittings. This
corrosion results in the addition of copper into the water supply.
APPLICATION: Drinking, surface, and saline waters; domestic and industrial
wastes.
RANGE: 0.00 – 6.00 ppm Copper
METHOD: Cupric ions form a yellow colored chelate with
diethyldithiocarbamate around pH 9-10 in proportion to the
concentration of copper in the sample.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Copper has a tendency to be adsorbed to the surface of the
sample container. Samples should be analyzed as soon as
possible after collection. If storage is necessary , 0.5 mL of
20% hydrochloric acid per 100 mL of sample will prevent
“plating out.” However, a correction must be made to bring
the reaction into the optimum pH range.
INTERFERENCES: Bismuth, cobalt, mercurous, nickel and silver ions and
chlorine (6 ppm or greater) interfere and must be absent.
*6446-E
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 COPPER - CUPRIZONE 1/2
Page 83

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 11 Copper DDC)
5. Scroll to and select 11 Copper DDC from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove tube from colorimeter and add 5 drops of *Copper 1 (6446). Cap
9. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
10. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
NOTE: The reaction may stain the tubes. Scrub the tubes thoroughly after each
use.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
from TESTING MENU.
sample.
and mix. Solution will turn yellow if copper is present.
result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
COPPER - CUPRIZONE 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 84

CYANURIC ACID
MELAMINE METHOD - TURBIDITY • CODE 366I-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
2 x 250 mL *Cyanuric Acid Test Solution
1 Syringe, 5 mL
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Data Safety Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Cyanuric acid is added to swimming pool water as a stabilizing agent for free
chlorine residuals. It minimizes the loss of chlorine from the action of
ultraviolet rays in sunlight. Cyanuric acid levels in pools should be maintained
between 25 and 75 ppm and various public health associations recommend that
the concentration should never exceed 100-150 ppm.
APPLICATION: Swimming pool waters.
RANGE: 5 – 200 ppm Cyanuric Acid
METHOD: A buffered solution of melamine forms a precipitate with
cyanuric acid in proportion to the amount of cyanuric acid
present. The amount of particles in suspension is measured
turbidimetrically.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Cyanuric acid samples should be analyzed as soon as possible
after collection. Deterioration of the sample can be
minimized by keeping samples in the dark or refrigerated
until analysis can be performed.
INTERFERENCES: No known interference from compounds normally found in
pool water. Temperature of the sample should be maintained
between 70°F and 80°F for best results. Check for stray light
interference (see page 17).
*4856-K
0807
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 CYANURIC ACID 1/2
Page 85

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 12 Cyanuric)
5. Scroll to and select 12 Cyanuric from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove tube from colorimeter and pour out water. Use a graduated
9. Use the 5 mL syringe (0807) to add 5 mL of *Cyanuric Acid Test Solution
10. At end of 1 minute waiting period, mix thoroughly, insert tube into
11. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
NOTE: For the most accurate results, the sample and reagents should be at
25±4°C.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
from TESTING MENU.
sample.
cylinder or similar to measure 5 mL of sample water and pour into
colorimeter tube.
(4856). Cap and mix thoroughly. A precipitate will form if cyanuric acid is
present. Wait 1 minute.
NOTE: This reagent bottle has a special fitting which enables the syringe
to be inserted into the top of the bottle. With syringe in place, invert
bottle and withdraw syringe plunger until 5 mL of reagent is contained in
the syringe barrel. Remove syringe from reagent bottle and depress plunger
to dispense into the tube.
chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
CYANURIC ACID 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 86

DISSOLVED OXYGEN
WINKLER COLORIMETRIC METHOD • CODE 3688-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
30 mL *Manganese Sulfate Solution
30 mL *Alkaline Potassium Iodide Azide
30 mL *Sulfuric Acid 1:1
1 Sample Tube, screw cap
1 Cap
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Dissolved oxygen is vital to the survival of aquatic organisms. Naturally
present, dissolved oxygen enters the water when plants photosynthesize. Wind
and wave action also cause oxygen from the air to dissolve into water.
Dissolved oxygen is consumed by aquatic animals and by the oxidation, or
chemical breakdown, of dead and decaying plants and animals. The
concentration of dissolved oxygen in natural waters can range from 0 to 14
ppm and is effected by temperature and salinity.
APPLICATION: This method is applicable for the determination of dissolved
oxygen in drinking water, all surface waters and wastewater.
RANGE: 0.0 – 11.0 ppm Dissolved Oxygen
METHOD: This method uses the azide modification of the Winkler
Method with a colorimetric determination of the yellow
iodine produced from the reaction with the dissolved
oxygen.
INTERFERENCES: The presence of other oxidizing agents may cause positive
interferences. Reducing may cause negative interferences.
Nitrite interferences are eliminated with the azide
modification.
*4167-G
*7166-G
*6141WT-G
29180
28570
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 DISSOLVED OXYGEN 1/3
Page 87

COLLECTION & TREATMENT OF THE WATER SAMPLE
Steps 1 through 4 below describe proper sampling technique in shallow water.
For sample collection at depths beyond arm’s reach, special water sampling
apparatus is required (e.g. the LaMotte W ater Sampling Chamber, Code 1060;
Model JT-1 Water Samplers, Code 1077; Water Sampling Outfit, Code 3103; or
Water Sampling Bottle, Code 3-0026).
1. To avoid contamination, thoroughly rinse the screw cap Sample Tube
(29180) with sample water.
2. Tightly cap Sample Tube and submerge to the desired depth. Remove cap
and allow the Sample T ube to fill.
3. Tap the sides of the submerged tube to dislodge any air bubbles clinging to
the inside. Replace the cap while the Sample Tube is still submerged.
4. Retrieve Sample T ube and examine it carefully to make sure that no air
bubbles are trapped inside. Once a satisfactory sample has been collected,
proceed immediately with Steps 5 and 6 to “fix” the sample.
NOTE: Be careful not to introduce air into the sample while adding the
reagents in steps 5 and 6. Simply drop the reagents into the sample. Cap
carefully, and mix gently.
5. Add 2 drops of *Manganese Sulfate Solution (4167) and 2 drops of
*Alkaline Potassium Iodide Azide (7166). Cap and mix by inverting
several times. A precipitate will form. Allow the precipitate to settle below
the shoulder of the tube before proceeding.
6. Add 8 drops of *Sulfuric Acid, 1:1 (6141WT). Cap and gently mix until
the reagent and the precipitate have dissolved. A clear-yellow to
brown-orange color will develop, depending on the oxygen content of the
sample.
NOTE: It is very important that all “brown flakes” are dissolved
completely. If the water has a high DO level this could take several
minutes. If flakes are not completely dissolved after 5 minutes, add 2 drops
of *Sulfuric Acid 1:1 (6141WT) and continue mixing.
Following the completion of step 6, contact between the water sample and the
atmosphere will not affect the test result. Once the sample has been “fixed” in
this manner, it is not necessary to perform the actual test procedure
immediately. Thus, several samples can be collected and “fixed” in the field, and
then carried back to a testing station or laboratory where the test procedure is to
be performed.
DISSOLVED OXYGEN 2/3 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 88

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 13 DO) from
5. Scroll to and select 13 DO from menu.
6. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with untreated sample water. Fill to the 10 mL
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Fill a second tube (0290) to the 10 line with the treated “Fixed” sample.
9. Remove BLANK from colorimeter, insert SAMPLE tube into chamber,
10. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
TESTING MENU.
line with sample. This tube is the BLANK.
This tube is the SAMPLE.
close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 DISSOLVED OXYGEN 3/3
Page 89

COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 90

FLUORIDE
SPADNS METHOD • CODE 3647-SC-01
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
4 x 30 mL *Acid-Zirconyl-SPADNS Reagent
60 mL * Sodium Arsenite Solution
1 Pipet, 0.5 mL, plastic
1 Pipet, 1.0 mL, plastic
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Fluoride may occur naturally in some ground waters or it may be added to
public drinking water supplies to maintain a 1.0 mg/L concentration to prevent
dental cavities. At higher concentrations, fluoride may produce an
objectionable discoloration of tooth enamel called fluorosis, though levels up
to 8 mg/L have not been found to be physiologically harmful.
NOTE: This procedure uses the EPA approved Reagent System for fluoride
found in method 4500-F-D, 18th Edition of Standard Methods, page 1-27.
APPLICATION Drinking and surface waters; domestic and industrial waters.
RANGE: 0.00 – 2.00 ppm Fluoride
METHOD: Colorimetric test based upon the reaction between fluoride
and zirconium dye lake. The fluoride reacts with the dye
lake, dissociating a portion of it into a colorless complex ion
and dye. As the fluoride concentration increases, the color
produced becomes progressively lighter.
SAMPLE
Samples may be stored and refrigerated in plastic containers.
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
*3875-G
*4128-H
0353
0354
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 FLUORIDE 1/3
Page 91

INTERFERENCES: The following substances produce a positive interference at
the concentration given:
Chloride (Cl–) 7000 mg/L
Phosphate (PO
Hexametaphophate (NaPO
–3
) 16 mg/L
4
3)6
1 mg/L
The following substances produce a negative interference at
the concentration given:
Alkalinity (CaCO
Aluminum (Al
Iron (Fe
Sulfate (SO
3+
) 10 mg/L
4
) 5000 mg/L
3
3+
) 0.1 mg/L
–2
) 200 mg/L
Color and turbidity must be removed or compensated for in
the procedure. Temperature should be maintained within
5°C of room temperature.
FLUORIDE 2/3 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 92

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 14 Fluoride)
5. Scroll to and select 14 Fluoride from menu.
6. This test requires a reagent blank. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with clear,
7. Use the 0.5 mL pipet (0353) to add 0.5 mL of *Sodium Arsenite Solution
8. Use the 1.0 mL pipet (0354) to add 2 measures of *Acid-Zirconyl
9. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
10. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
11. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
12. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
from TESTING MENU.
colorless, fluoride free water. Fill to the 10 mL line with clear, colorless,
fluoride free water.
(4128). Cap and mix.
SPADNS Reagent (3875). Cap and mix thoroughly. (This is the reagent
blank.)
sample water. Repeat steps 7 and 8.
result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 FLUORIDE 3/3
Page 93

COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 94

HYDRAZINE
p-DIMETHYLAMINOBENZALDEHYDE METHOD
CODE 3656-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
2x60 mL * Hydrazine Reagent A
10 g * Hydrazine Reagent B Powder
1 Pipet, 1.0 mL, plastic
1 Spoon, 0.15 g, plastic
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Hydrazine, N2H4, is added to the water in high pressure boilers to reduce
corrosion by acting as an oxygen scavenger.
APPLICATION: Water and boiler water, industrial waste water.
RANGE: 0.000 – 1.00 ppm Hydrazine
METHOD: p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde reacts with hydrazine under
acidic conditions to form a yellow color in proportion to the
amount of hydrazine present.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Samples should be analyzed as soon as possible after
collection due to the ease with which hydrazine becomes
oxidized. Acidification of the sample may increase the time
between collection and analysis.
INTERFERENCES: The substances normally present in water do not interfere
with the test, with the exception of strong oxidizing agents.
*4841-H
*4842-D
0354
0727
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 HYDRAZINE 1/2
Page 95

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 15 Hydrazine)
4. Scroll to and select 15 Hydrazine from menu.
5. Rinse a clean tube (0290) with sample water. Fill to the 10 mL line with
6. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
7. Remove tube from colorimeter. Use the 1 mL pipet (0354) to add 4 mL of
8. Use the 0.15 g spoon (0727) to add one measure of *Hydrazine Reagent B
9. At the end of the 2 minute waiting period, mix, insert tube into chamber,
10. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
NOTE: For best possible results, a reagent blank should be determined to
account for any contribution to the test result by the reagent system. To
determine the reagent blank, follow the above test procedure to scan a distilled
or deionized water blank. Then follow the above procedure to perform the test
on a distilled or deionized water sample. This test result is the reagent blank.
Subtract the reagent blank from all subsequent test results of unknown samples.
It is necessary to determine the reagent blank only when a new lot number of
reagents are obtained.
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
from TESTING MENU.
sample.
*Hydrazine Reagent A (4841). Cap and mix.
Powder (4842). Cap and shake vigorously for 10 seconds. Wait 2 minutes
for maximum color development. An undissolved portion of Hydrazine
Reagent B may remain in bottom of tube without adversely affecting
results.
close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
HYDRAZINE 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 96

MOLYBDENUM - HIGH RANGE
THIOGLYCOLATE METHOD • CODE 3699-02-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
2 x 30 mL *Mo Buffer
2 x 30 mL *Molybdenum Oxidizing Reagent
2.5g *Molybdenum Indicator Powder
1 Spoon, 0.05g, plastic
2 Pipets, 1.0 mL, plastic w/cap
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Molybdenum occurs naturally in the earth’s crust as molybdenite and wolfenite,
and is an important element in many biochemical reactions, including nitrogen
fixation. In industrial processes, such as the operation of boilers and cooling
towers, molybdenum, in the form of sodium molybdate, is used as a corrosion
inhibitor.
APPLICATIONS: Boiler and cooling water.
RANGE: 0.0 – 50.0 ppm Molybdenum
METHOD: Calcium thioglycolate reacts with molybdenum to give a
yellow color with an intensity proportional to the amount of
molybdenum present.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
Molybdenum samples may be stored in either plastic or glass
containers.
PRESERVATION:
INTERFERENCES: Nickel levels less than 50 ppm do not interfere; aluminum
levels less than 10 ppm do not interfere; chromate at higher
concentrations interferes due to the intense yellow color.
Ferrous iron levels below 50 ppm do not interfere, but low
levels of ferric iron will cause a large blank. Highly buffered
samples may exceed the capacity of the system possibly
producing inaccurate results.
*3997-G
*6485-G
*6486-S
0696
0372
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 MOLYBDENUM - HIGH RANGE 1/2
Page 97

PROCEDURE
1. Press and hold ON button until colorimeter turns on.
2. Press
3. Press
4. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 16 Moly-HR) from
5. Scroll to and select 16 Moly-HR from menu.
6. Fill clean tube (0290) to 10 mL line with sample water.
7. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
8. Remove tube from colorimeter. Use a 1.0 mL pipet (0372) to add 1.0 mL
9. Use a second 1.0 mL pipet (0372) to add 1.0 mL of *Molybdenum
10. Use 0.05 g spoon (0696) to add one measure of Molybdenum Indicator
11. Insert tube into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE. Record
12. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
TESTING MENU.
of *Mo Buffer (3997). Cap and mix.
Oxidizing Reagent (6485). Cap and mix.
Powder (6486). Cap and mix until powder dissolves. Solution will turn
yellow if molybdenum is present.
result.
previous menu or make another menu selection.
MOLYBDENUM - HIGH RANGE 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 98

NICKEL
DIMETHYLGLYOXIME METHOD • CODE 3663-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
60 mL *Hydrochloric Acid, 2.5N
30 g *Ammonium Persulfate Reagent
30 mL *Silver Nitrate Solution, 0.0141N
250 mL Sodium Citrate, 10%
60 mL *Dimethylglyoxime, 1%
60 mL *Ammonium Hydroxide, Conc.
3 Pipets, 1.0 mL, plastic
1 Spoon, 0.1 g, plastic
1 Test tube, 5-10-12.9-15-20-25,
glass, w/cap
1 Graduated Cylinder, 10 mL, glass
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with a * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Nickel is not usually found in natural waters except as a result of
contamination from industrial wastewaters as a corrosion product of stainless
steel and nickel alloys. Nickel may also enter surface waters from plating bath
process water.
APPLICATION: Drinking and surface waters; domestic and industrial
wastewater.
RANGE: 0.00 – 8.00 ppm Nickel
METHOD: Nickel under basic conditions forms a colored complex with
dimethylglyoxime in proportion to the concentration of
nickel.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Samples may be collected in either plastic or glass containers
and preserved by adding 5 mL of concentrated nitric acid per
liter.
INTERFERENCES: Organic matter interferes. Cobalt, iron, copper, manganese
and chromium do not interfere if each of the concentrations
is below 15 ppm.
*6251PS-H
*6566-G
*6346WT-G
6253-K
*6254-H
*6537-H
0354
0699
0608
0416
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 NICKEL 1/2
Page 99

PROCEDURE
1. Use the 10 mL graduated cylinder (0416) to measure 10 mL of sample
water. Pour into glass test tube (0608).
2. Use the 1 mL pipet (0354) to add 1 mL of *Hydrochloric Acid, 2.5N
(6251).
3. Use the 0.1 g spoon (0699) to add 2 measures of *Ammonium Persulfate
Reagent (6566). Add two drops of *Silver Nitrate Solution, 0.0141N
(6346WT). Mix until the powder has dissolved. The solution will be
slightly cloudy at this point.
4. Use 10 mL graduated cylinder (0416) to add 5 mL of Sodium Citrate, 10%
(6253).
5. Use a second 1 mL pipet (0354) to add 1 mL of *Ammonium Hydroxide,
Conc. (6537). Mix, then dilute to 25 mL with deionized water.
6. Use a third 1 mL pipet (0354) to add 1 mL of *Dimethylglyoxime, 1%
(6254). Mix. Wait 20 minutes for color development.
7. At end of 20 minute waiting period fill a clean tube (0290) to the 10 mL
line with the developed test sample.
8. Fill a second clean tube (0290) to 10 mL line with deionized water or
untreated sample water. This is the blank.
9. Press and hold
10. Press
11. Press
ENTER to start.
ENTER to select TESTING MENU.
12. Select ALL TESTS (or another sequence containing 17 Nickel) from
TESTING MENU.
13. Scroll to and select 17 Nickel from menu.
14. Insert the blank into chamber, close lid and select SCAN BLANK.
15. Insert test sample into chamber, close lid and select SCAN SAMPLE.
Record result.
16. Press OFF button to turn colorimeter off or press EXIT button to exit to a
previous menu or make another menu selection.
ON button until colorimeter turns on.
NICKEL 2/2 COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02
Page 100

OZONE
INDIGO METHOD • CODE 365I-SC
QUANTITY CONTENTS CODE
15 mL Chlorine Inhibitor
250 mL *Ozone Buffer
30 mL Indigo Blue Stock Solution
1 Sampling Apparatus
1 Pipet, transfer, 1.0 mL
1 Pipet, transfer, 5 mL
1 Pump, 10 mL
1 Bottle, HR Reagent, amber glass
1 Graduated Cylinder, 50 mL, glass
*W ARNING: Reagents marked with * are considered hazardous substances. Material
Data Safety Sheets (MSDS) are supplied for these reagents. For your safety, read label
and accompanying MSDS before using.
Ozone is sometimes used in place of, or in conjunction with, chlorine or other
halogens for disinfection of pool, spa, or drinking waters. Recently, large
aquatic facilities have begun using ozone as a disinfectant in many artificial
habitats.
APPLICATION: Drinking, pool and aquatic waters.
RANGE: 0.00 – 0.40 ppm Ozone, Low Range
0.00 - 2.50 ppm Ozone, High Range
METHOD: Ozone rapidly and stoichiometrically decolorizes Indigo
Trisulfonate under acidic conditions.
SAMPLE
HANDLING &
PRESERVATION:
Ozone is extremely unstable in aqueous solutions. Test must
be performed immediately and the sample must not be
agitated.
INTERFERENCES: Manganese at any level interferes.
3990-E
*3991-K
3989-G
0681
2-2170
0329
30527
0680-J
0418
COD PLUS TEST PROCEDURES 6/02 OZONE 1/3
 Loading...
Loading...