Page 1

KSD-800M
Series
Industrial Managed 8-Port Fast Ethernet Switches
with Fiber Connectivity
Installation Guide
-1-
DOC.050710
Page 2

(C) 2002 KTI Networks Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in
any form or by any means or used to make any directive work (such as translation or transformation)
without permission from KTI Networks Inc.
KTI Networks Inc. reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content
from time to time without obligation on the part of KTI Networks Inc. to provide notification of such
revision or change.
For more information, contact:
United States KTI Networks Inc.
P.O. BOX 631008
Houston, T exas 77263-1008
Phone: 713-2663891
Fax: 713-2663893
E-mail: kti@ktinet.com
URL: http://www.ktinet.com/
International Fax: 886-2-26983873
E-mail: kti@ktinet.com.tw
URL: http://www .ktinet.com.tw/
-2-
Page 3

The information contained in this document is subject to change without prior notice. Copyright (C). All
Rights Reserved.
TRADEMARKS
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corp.
WARNING:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual may cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
NOTICE:
(1 ) The changes or modifications not expressively approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
(2) Shielded interface cables and AC power cord, if any, must be used in order to comply with the
emission limits.
CISPR A COMPLIANCE:
This device complies with EMC directive of the European Community and meets or exceeds the following
technical standard.
EN 55022 - Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information
T echnology Equipment. This device complies with CISPR Class A.
WARNING: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
CE NOTICE
Marking by the symbol indicates compliance of this equipment to the EMC directive of the Euro-
pean Community . Such marking is indicative that this equipment meets or exceeds the following technical standards:
EN 55022: Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference characteristics of Information
T echnology Equipment.
EN 50082/1:Generic Immunity Standard -Part 1: Domestic Commercial and Light Industry .
EN 60555-2: Disturbances in supply systems caused by household appliances and similar electrical
equipment - Part 2: Harmonics.
-3-
Page 4

Table of Contents
1. Introduction.................................................................................................. 6
1.1 Features ...................................................................................................................7
1.2 Product Panels......................................................................................................... 8
1.3 Front Panel...............................................................................................................9
1.4 Network Ports...........................................................................................................9
1.5 LED Indicators........................................................................................................10
1.6 Top Panel................................................................................................................ 11
1.7 Specifications.........................................................................................................11
1.8 Model Definitions ....................................................................................................14
2. Installation .................................................................................................. 16
2.1 Unpacking...............................................................................................................16
2.2 Safety Cautions ......................................................................................................16
2.3 DIN-Rail Mounting...................................................................................................17
2.4 Panel Mounting.......................................................................................................18
2.5 Applying Power.......................................................................................................20
2.6 Power Failure Relay Output ...................................................................................21
2.7 Reset Button ..........................................................................................................22
2.8 Making UTP Connections .......................................................................................22
2.9 Making Fiber Connections ......................................................................................23
2.10 LED Indication ......................................................................................................24
2.1 1 Configuring IP Address for the Switch...................................................................25
2.12 Configuring User Name and Password.................................................................25
2.13 Configuring SNMP Settings ...................................................................................25
2.14 Configuring Port 7 and Port 8 ................................................................................25
3. Advanced Functions .................................................................................. 26
3.1 QoS Function ..........................................................................................................26
3.1.1 Priority Level.........................................................................................................26
3.1.2 Egress Service Policy ..........................................................................................26
3.1.3 Packet Priority Classification................................................................................26
3.1.3.1 Port-based Priority Setting (per port setting) .....................................................27
3.1.3.2 802.1p Classification (per port setting)..............................................................27
3.1.3.3 DSCP Classification (per port setting) ..............................................................27
3.1.3.4 IP Network Address Classification.....................................................................28
3.1.4 Other QoS Settings..............................................................................................28
3.2 VLAN Function.........................................................................................................29
3.2.1 VLAN Operation....................................................................................................29
3.2.2 Ingress Rules .......................................................................................................30
3.2.2.1 802.1Q T ag A ware VLAN Mode (global setting) .................................................30
3.2.2.2 Ingress Member Filtering (global setting)...........................................................30
-4-
Page 5

3.2.2.3 Unmatched VID Filtering (per port setting) ........................................................30
3.2.3 VLAN Group Mapping ...........................................................................................31
3.2.4 Packet Forwarding under VLAN ...........................................................................31
3.2.5 Egress Tagging Rules ..........................................................................................31
3.2.5.1 Egress Tag Rule (per port setting).....................................................................31
3.2.5.2 Null VID Replacement (per port setting) ............................................................32
3.2.6 Summary of VLAN Function .................................................................................32
4. Software Management ............................................................................... 33
4.1 T elnet Management Interface...................................................................................33
4.2 IP Menu ...................................................................................................................34
4.3 SNMP Menu.............................................................................................................35
4.4 Port Config ..............................................................................................................36
4.5 Administrator ...........................................................................................................37
4.5.1 Administrator -> VLAN Settings............................................................................37
4.5.2 Administrator -> QoS Settings .............................................................................41
4.6 Restore Default V alues............................................................................................44
4.7 Security Manager ....................................................................................................44
4.8 Update Firmware.....................................................................................................45
4.9 Reboot System .......................................................................................................45
4.10 Exit ........................................................................................................................45
5. Web Management ....................................................................................... 46
5.1 Start Browser Software and Making Connection.....................................................46
5.2 Login to the Switch Unit...........................................................................................46
5.3 Port Status Menu.....................................................................................................48
5.4 Administrator ...........................................................................................................49
5.4.1 Basic Menu...........................................................................................................49
5.4.2 Port Controls ........................................................................................................52
5.4.3 VLAN Controls......................................................................................................53
5.4.4 QoS Controls .......................................................................................................58
5.4.5 Security Manager..................................................................................................61
5.4.6 Image Refresh Time.............................................................................................61
5.4.7 Update Firmware..................................................................................................62
5.4.8 Restore Default ....................................................................................................62
5.4.9 Reboot System ....................................................................................................62
6. SNMP Management .................................................................................... 63
6.1 MIB Objects.............................................................................................................63
6.2 SNMP Traps ............................................................................................................63
Appendix. Factory Default Settings .............................................................. 64
-5-
Page 6
1. Introduction
The KSD-800M series are managed 8-port full wire speed Fast Ethernet switches for industrial applications. Depending on the fiber connectivity, the series is provided in three types of configuration as
follows:
Model series 10/100TX TP Ports 100FX fiber ports
800M 8 ports 800M-1xxx 8 ports 1 port
800M-2xxx 8 ports 2 ports
The switches provide the following advantages:
Plug and Play
The switches provide eight 10/100TX copper ports for connections to Ethernet devices or 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet devices. With the featured auto-negotiation function, the switches can detect and configure the connection speed and duplex automatically . The switches also provide auto MDI/MDI-X function, which can detect the connected cable and switch the transmission wire pair and receiving pair
automatically . This auto-crossover function can simplify the type of network cables used.
Auto Copper/Fiber Connections
The 100FX fiber ports can support 100Mbps fiber connection using optic fiber cable and extend a
network connection up to several kilometers via fiber cables. The 100TX ports are designed to share
the same switched ports with the associated 10/100TX copper ports. It means the switched port supports dual network media types, either copper cable or fiber cable and detect link and select the media
type automatically .
Management
The switches are embedded with microprocessor which provides management functions for advanced
network functions including Port Control, Quality of Service, and V irtual LAN functions. The management can be performed via SNMP protocol, Telnet interface and Web based interface over TCP/IP
network.
-6-
Page 7

Designed for Industrial Applications
For industrial environment, the switches are designed with the following enhanced features:
n High and wide operating temperature
n Wide operating voltage range for DC power input
n Power input interface: Screw terminal block and DC jack for adapter
n Relay output for device power failure alarm
n DIN rail mounting support for industrial enclosure
n Panel mounting support for industrial enclosure
1.1 Features
Basic functions
• Fast Ethernet switch with 8 10/100TX copper ports
• Auto MDI/MDI-X detection on all 10/100TX ports
• Auto-negotiation capable on all 10/100TX ports
• 100FX ports support wide range of fiber options
- ST, SC connectors
- Multi-mode fiber, Single mode duplex fiber
• Far End Fault function on 100FX ports
• Auto configuration for 10/100TX or 100FX for port 7 and port 8
• Back pressure flow control for half duplex operation
• IEEE 802.3x flow control for full duplex operation
• Broadcast storm protection function
• Provides comprehensive LED indication
• Support DIN-rail and panel mounting
Management functions
• Port configuration control and status monitoring
• Provides Quality of Service (QoS) control for packet traffic
• Supports tagged Virtual LAN (VLAN) network
• Supports SNMP management interface
• Provides SNMP based event traps
• Supports Telnet management interface
• Supports Web based browsing interface
• In-band embedded firmware upgrade function
-7-
Page 8
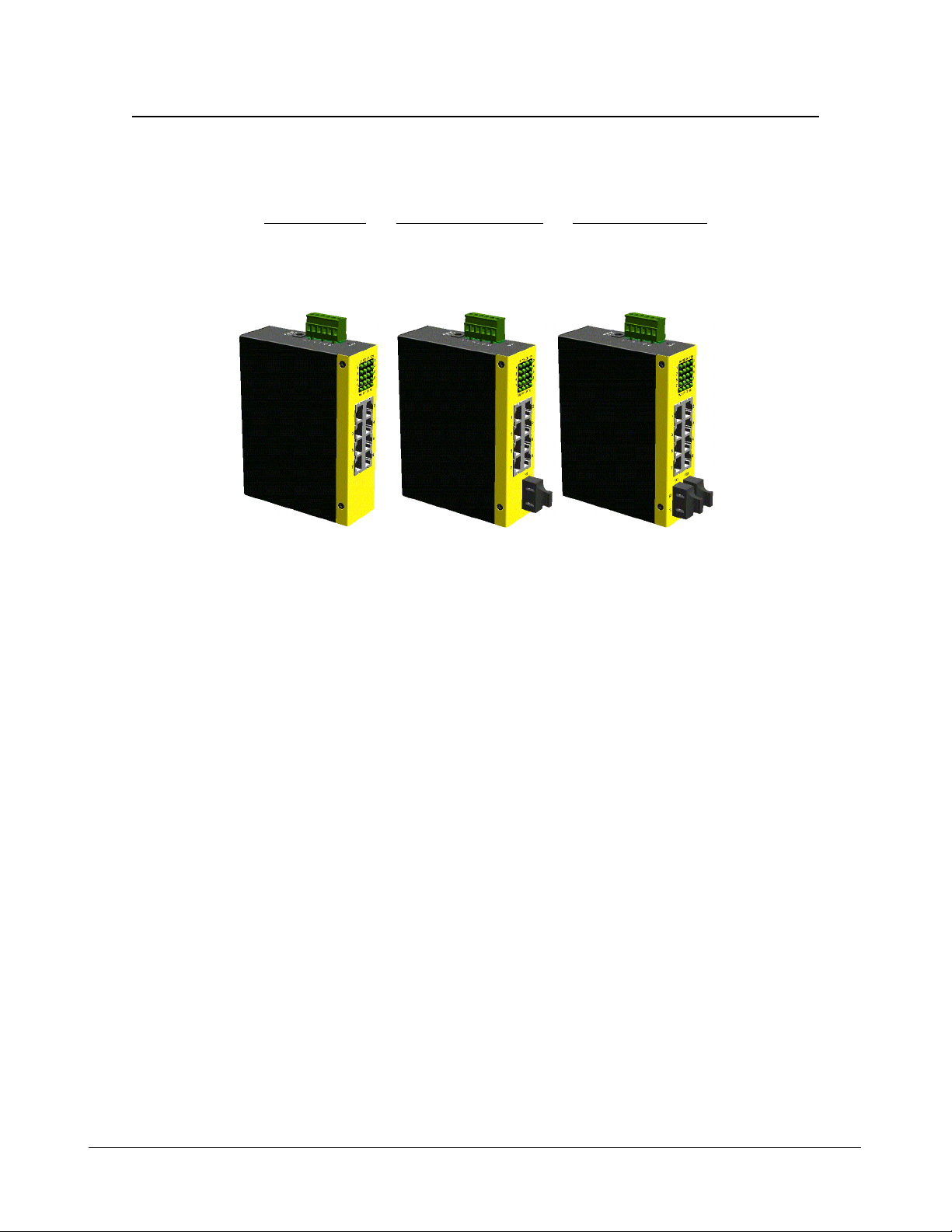
1.2 Product Panels
The following figure illustrates three major panels of model 800-2 series as example:
-8-
Page 9
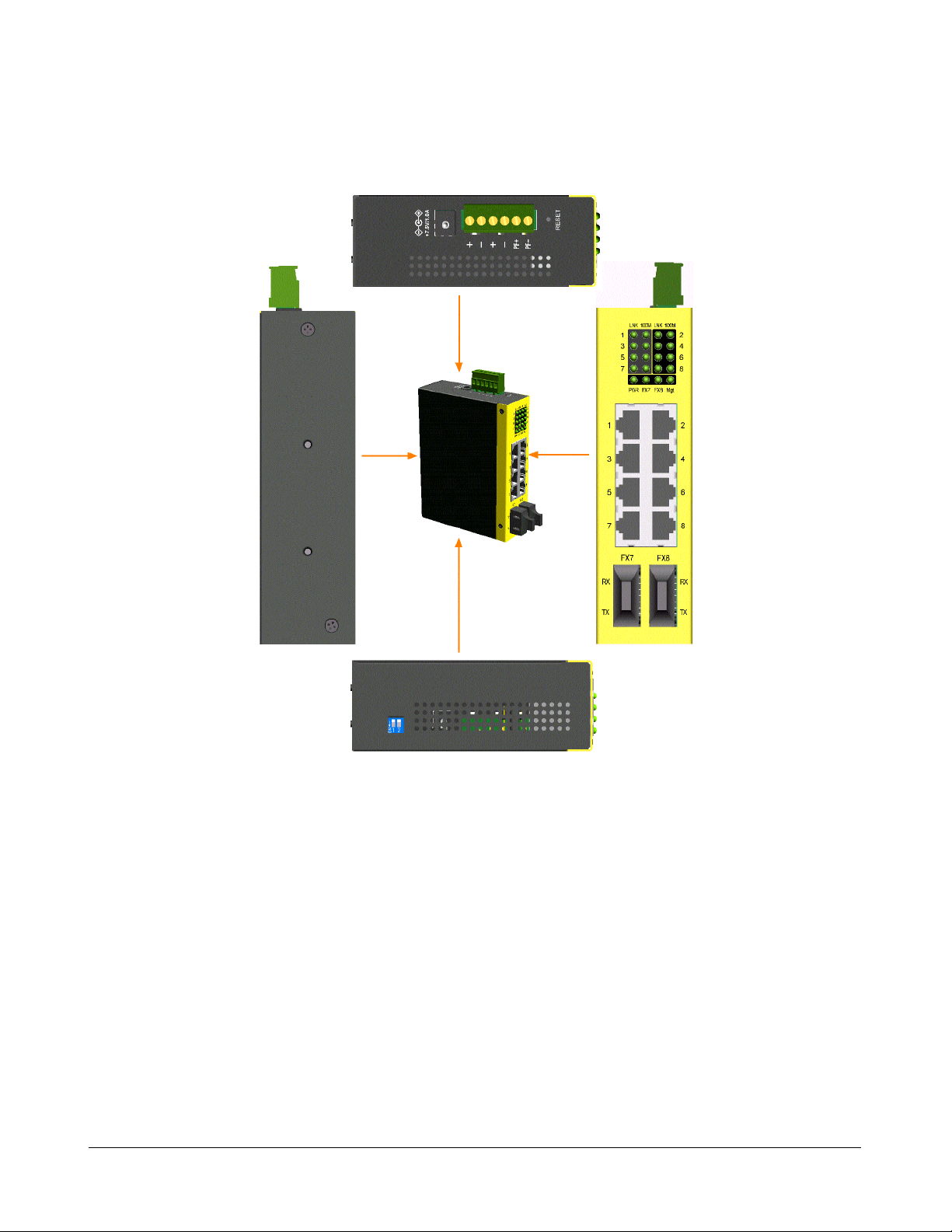
1.3 Front Panel
The figure below shows the individual front panel of three model series. The main difference is the
number of the equipped fiber ports.
1.4 Network Ports
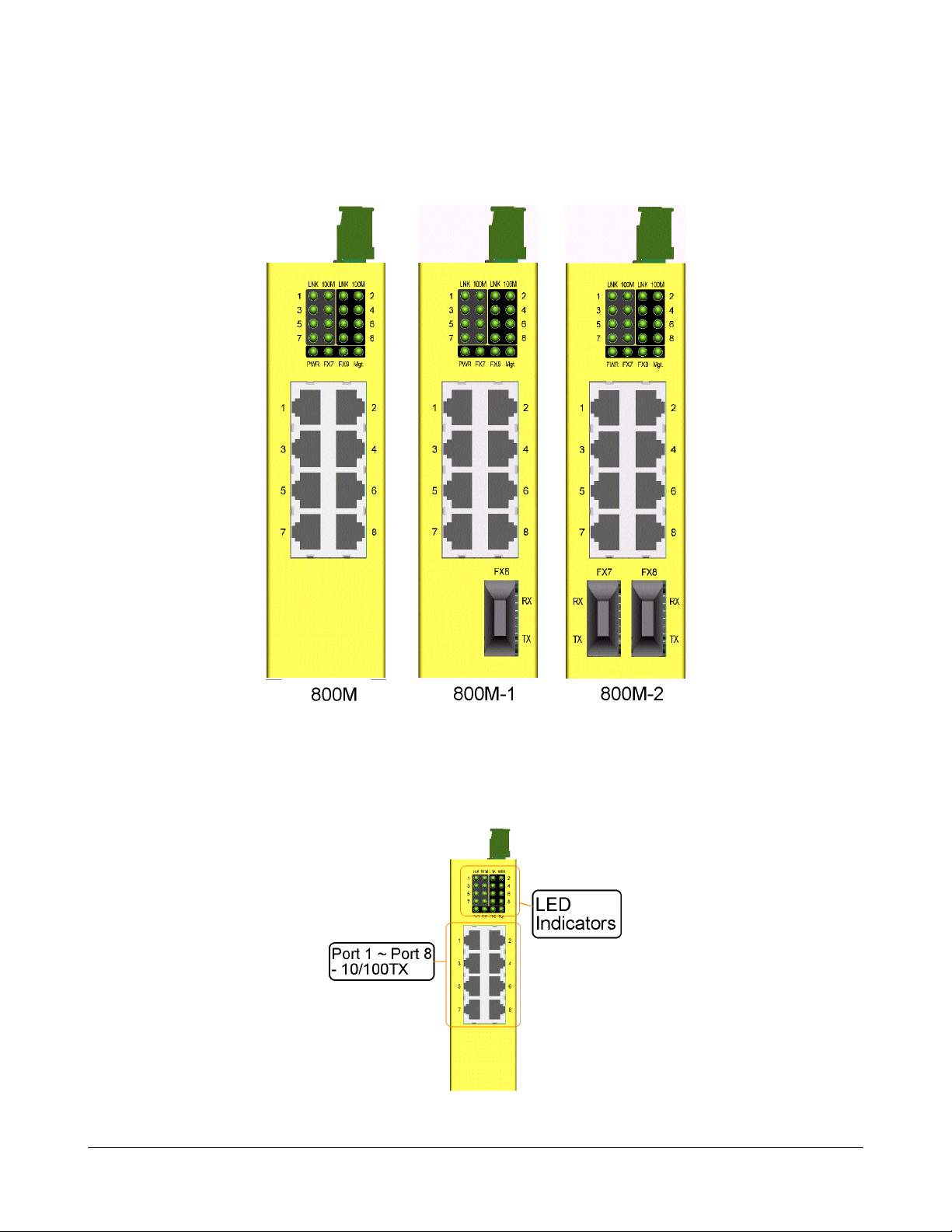
Model 800M provides eight 10/100TX copper ports only . No fiber connectivity is equipped.
-9-
Page 10
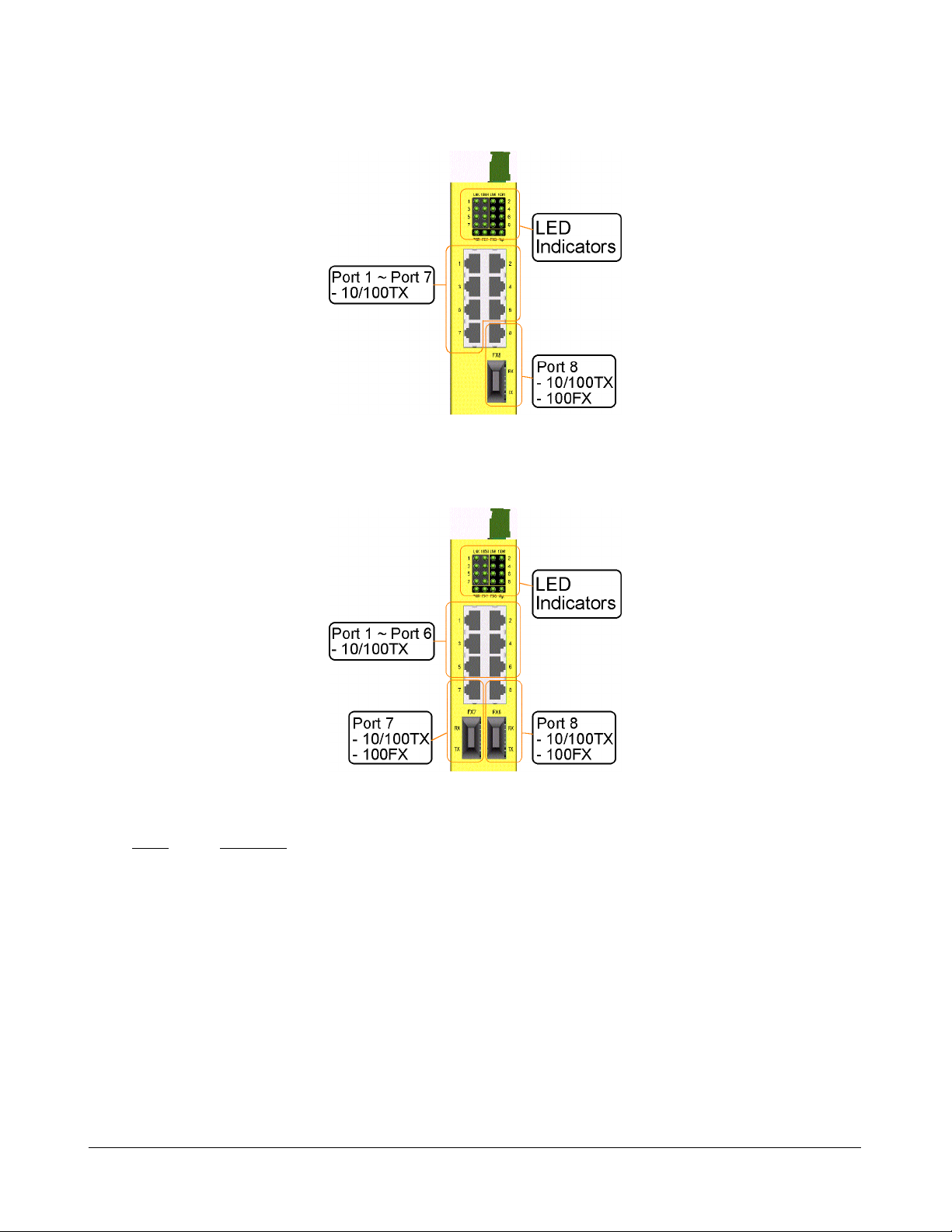
Model 800M-1 series provide eight 10/100TX copper ports and one 100FX fiber connector. Port 8
supports dual network cable types.
Model 800M-2 series provide eight 10/100TX copper ports and two 100FX fiber connectors. Port 7
and Port 8 support dual network cable types.
1.5 LED Indicators
LED Function
PW R Power status
LNK Network port link status (per port)
100M Network port speed status (per port)
FX 7 Fiber port link status (if FX7 is provided on Port 7)
FX 8 Fiber port link status (if FX8 is provided on Port 8)
Mgt. Embedded microprocessor operation status
-10-
Page 11

1.6 Top Panel
All three model series provide same top panel as figure shown below:
The main functions are:
DC Power Jack This connector is used when a AC-DC power adapter is used as a power
source to the switch.
T erminal Block This connector provides the following interfaces:
DC1 Positive(+) and Negative(-) - VDC power input from power system
DC2 Positive(+) and Negative(-) - VDC power cascaded to next device
PF Positive(+) and Negative(-) - Power failure relay output
Reset Hardware reset push button
1.7 Specifications
Network Ports
Switched Port Number Model 800M 800M-1 series 800M-2 series
Port 1 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 2 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 3 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 4 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 5 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 6 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
Port 7 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
100FX
Port 8 10/100TX 10/100TX 10/100TX
100FX 100FX
Note: 10/100TX - TP RJ-45, 100FX - Fiber
-11-
Page 12

10/100TX Twisted Pair Ports
Compliance IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T , IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX
Connectors Shielded RJ-45 jacks
Pin assignments Auto MDI/MDI-X detection
Configuration Auto-negotiation
Transmission rate 10Mbps, 100Mbps
Duplex support Full/Half duplex
Flow control IEEE 802.3x pause frame base for full duplex operation
Back pressure for half duplex operation
Network cable Cat.5 UTP
100FX Fiber Ports
Compliance IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-FX
Configuration Forced 100Mbps, Full duplex
Transmission rate 100Mbps
Far end fault function Capable to receive FEFI (far end fault indication) signal
Capable to send FEFI signal when Rx link failure detected
Flow control IEEE 802.3x pause frame base for full duplex operation
Back pressure for half duplex operation
Network cables MMF 50/125 60/125, SMF 9/125
Eye safety IEC 825 compliant
Optical Specifications Refer to Section 1.8.
Switch Functions
MAC Addresses Table 1K entries
Forwarding & filtering Non-blocking, full wire speed
10Mbps - 14,880 pps at 64-byte packets
100Mbps - 148,800pps at 64-byte packets
Switching technology Store and forward
Maximum packet length 1536 bytes
Broadcast storm 64 consecutive broadcast packets in 800ms
Protection by dropping broadcast storm packets
VLAN function Port-based VLAN & IEEE 802.1Q Tag-based VLAN
QoS function Port-based, 802.1p-based, IP DSCP-based, IP address-based
Port control Port configuration control via software management
LED Indicators
System Power status, Embedded microprocessor operation status
Per 10/100TX port TP port link/activity status, speed status
Per 100FX port FX port link status
-12-
Page 13

Software Management Functions
Interfaces Web, telnet, SNMP MIB-II & private MIB, Traps
Management objects Port configuration control and status
Username and password settings
IP, SNMP related settings
VLAN function settings
QoS function setting
Port Configuration Control Function
Configuration P1 ~ P 6
Port control function Port TX/RX - enable, disable
Port mode - Auto (auto-negotiation), Forced
Port speed - 100Mbps, 10Mbps
Port duplex - full, half
Port Status Port mode, link, speed, duplex
VLAN Function
VLAN groups 8 groups
Global Settings VLAN Mode - Port-based, 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN
Ingress member port filtering mode
VLAN Group Settings 12-bit VLAN ID
Member ports
Per Port Settings Default VLAN group index
Unmatched VID packet ingress filtering mode
Egress T agging Rules
Null VID replacement mode (Egress)
QoS Function
Priority level 2, High priority and Low priority
Priority classifications Port-based priority mode (per port setting)
802.1p classification (per port setting)
Default IP DSCP classification (per port setting)
2 user defined DSCP match classification (global)
2 user defined IP network address match classification (global)
802.1p priority tag Threshold tag value setting for high priority (0 ~ 7)
Egress service policy W eighted round robin ratio : 16:1, always high first, 8:1, 4:1
-13-
Page 14

DC Power Input
Interfaces Euro type terminal block contacts
(DC1 DC2 : 2 sets for power wire cascading)
DC Jack ( -D 6.3mm / + D 2.0mm)
Operating Input Voltages +7V ~ +30V(+5%)
Power consumption Model 800M 4.7W/7.5VDC input, 5.0W/30VDC input
Model 800M-1 6.0W/7.5VDC input, 6.3W/30VDC input
Model 800M-2 8.0W/7.5VDC input, 8.3W/30VDC input
Mechanical
Dimension (base) 140 x 106 x 40 mm
Housing Enclosed metal with no fan
Mounting Support DIN-rail mounting, Panel mounting
W eight Model 800M: 465g, Model 800M-1: 475g, Model 800M-2: 485g
Environmental
o
Operating Temperature Typical -20
o
Storage Temperature -20
C ~ 85oC
C ~ 70oC
Relative Humidity 5% ~ 90%
Electrical Approvals
FCC Part 15 rule Class A
CE EMC, CISPR22 Class A
1.8 Model Definitions
Model TP Port FX Port Connector Cable Distance max. Operating Temperature
800M P1-P8 no -20oC ~ 70oC
800M-1T P1-P8 FX8 ST M MF 2km -10oC ~ 70oC
800M-1C P1-P8 FX8 SC M MF 2km -10oC ~ 70oC
800M-1CL1 P1-P8 FX8 SC MM F 2km -20oC ~ 70oC
800M-1CL2 P1-P8 FX8 SC MM F 2km -20oC ~ 70oC
800M-1SA2 P1-P8 FX8 SC SM F 15km - 20oC ~ 70oC
800M-1SL2 P1-P8 F X8 SC SMF 20km -20oC ~ 70oC
800M-1SL2B P1-P8 F X8 SC SM F 20-30km -20oC ~ 70oC
800M-2T P1-P8 FX7 ST MMF 2km -10oC ~ 70oC
FX8 ST MMF 2km
800M-2C P1-P8 FX7 SC M MF 2km -10oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC MMF 2km
800M-2CL1 P1-P8 FX7 SC MM F 2km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC MMF 2km
800M-2CL2 P1-P8 FX7 SC MM F 2km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC MMF 2km
800M-2SA2 P1-P8 FX7 SC SM F 15km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC SMF 15km
800M-2SL2B P1-P8 F X7 SC SM F 20-30km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC SMF 20-30km
800M-2SL2 P1-P8 F X7 SC SMF 20km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC SMF 20km
800M-2MCSL2B P1-P8 FX7 SC M MF 2km -20oC ~ 70oC
FX8 SC SMF 20-30km
800M-2MCSL2 P1-P8 FX7 SC MMF 2km -20
FX8 SC SMF 20km
-14-
o
C ~ 70oC
Page 15

Optical Specifications
A variety of fiber options and the optical specifications is provided as follows:
Model FX Port & Cable W avelength Tx Power Rx sensitivity Rx max. power
800M-1T FX8 : ST MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
800M-1C FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
800M-1CL1 FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -12 dBm -31 dBm max. -8 dBm min.
800M-1CL2 FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-1SA2 FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -8 dBm -34 dBm max. -7 dBm min.
800M-1SL2B FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -7 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-1SL2 FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -18 ~ -7 dBm -32 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-2T FX7 : ST MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
FX8 : ST MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
800M-2C FX7 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -14 dBm min.
800M-2CL1 FX7 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -12 dBm -31 dBm max. -8 dBm min.
FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -12 dBm -31 dBm max. -8 dBm min.
800M-2CL2 FX7 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
FX8 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-2SA2 FX7 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -8 dBm -34 dBm max. -7 dBm min.
FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -8 dBm -34 dBm max. -7 dBm min.
800M-2SL2B FX7 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -7 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -7 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-2SL2 FX7 : SC SMF 1310nm -18 ~ -7 dBm -32 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -18 ~ -7 dBm -32 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-2MCSL2B FX7 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -15 ~ -7 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
800M-2MCSL2 FX7 : SC MMF 1310nm -19 ~ -14 dBm -34 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
FX8 : SC SMF 1310nm -18 ~ -7 dBm -32 dBm max. -3 dBm min.
-15-
Page 16

2. Installation
2.1 Unpacking
The product package contains:
• The switch unit
• One DIN-rail mounting kit
• One product CD-ROM
2.2 Safety Cautions
To reduce the risk of bodily injury, electrical shock, fire, and damage to the equipment, observe the
following precautions.
• Do not service any product except as explained in your system documentation.
• Opening or removing covers may expose you to electrical shock.
• Only a trained service technician should service components inside these compartments.
• If any of the following conditions occur , unplug the product from the electrical outlet and replace
the part or contact your trained service provider:
- The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged.
- An object has fallen into the product.
- The product has been exposed to water.
- The product has been dropped or damaged.
- The product does not operate correctly when you follow the operating instructions.
• Do not push any objects into the openings of your system. Doing so can cause fire or electric
shock by shorting out interior components.
• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated on the electrical
ratings label. If you are not sure of the type of power source required, consult your service
provider or local power company .
-16-
Page 17
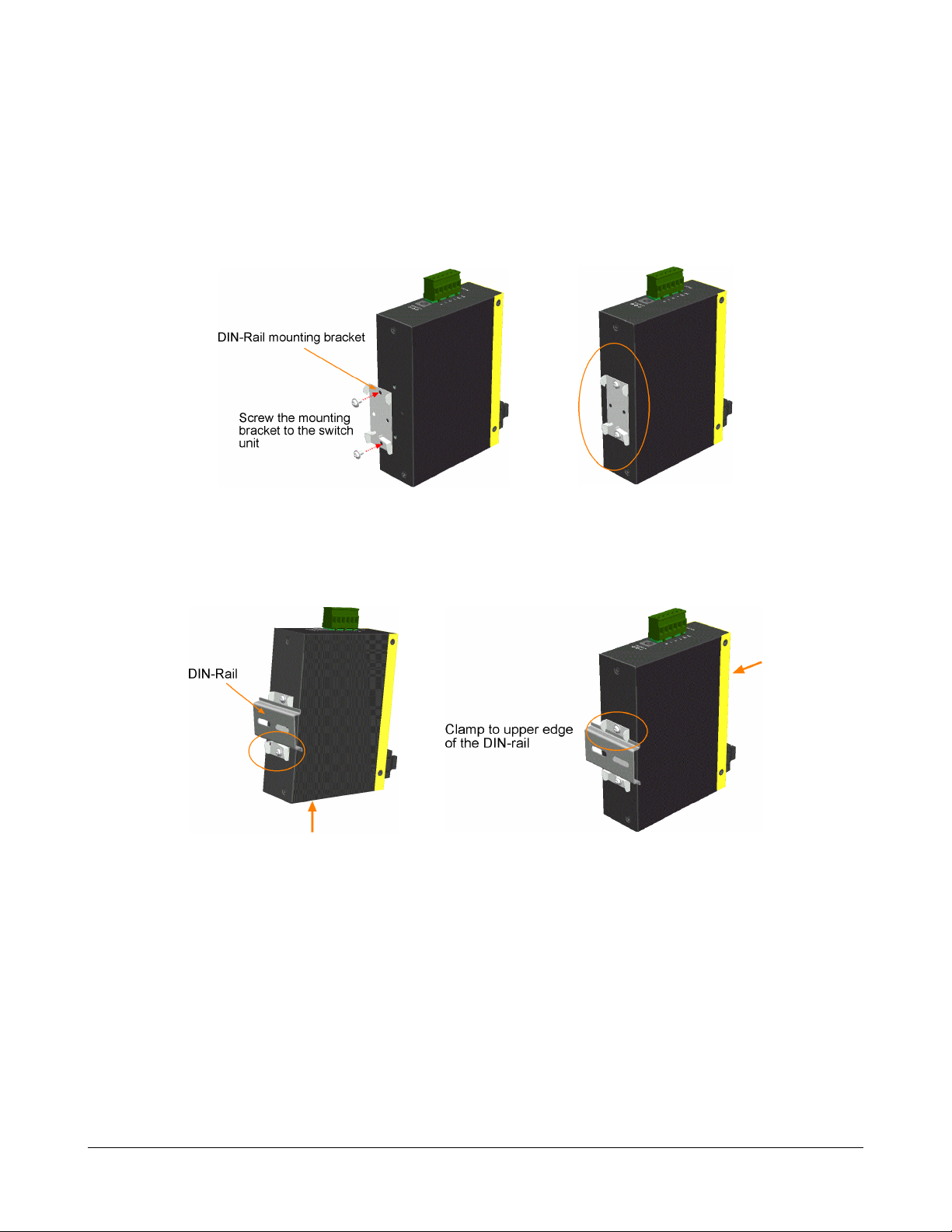
2.3 DIN-Rail Mounting
In the product package, a DIN-rail bracket is provided for mounting the switch in a industrial DIN-rail
enclosure.
The steps to mount the switch onto a DIN rail are:
1. Install the mounting bracket onto the switch unit as shown below:
2. Attach bracket to the lower edge of the DIN rail and push the unit upward a little bit until the
bracket can clamp on the upper edge of the DIN rail.
3. Clamp the unit to the DIN rail and make sure it is mounted securely.
-17-
Page 18
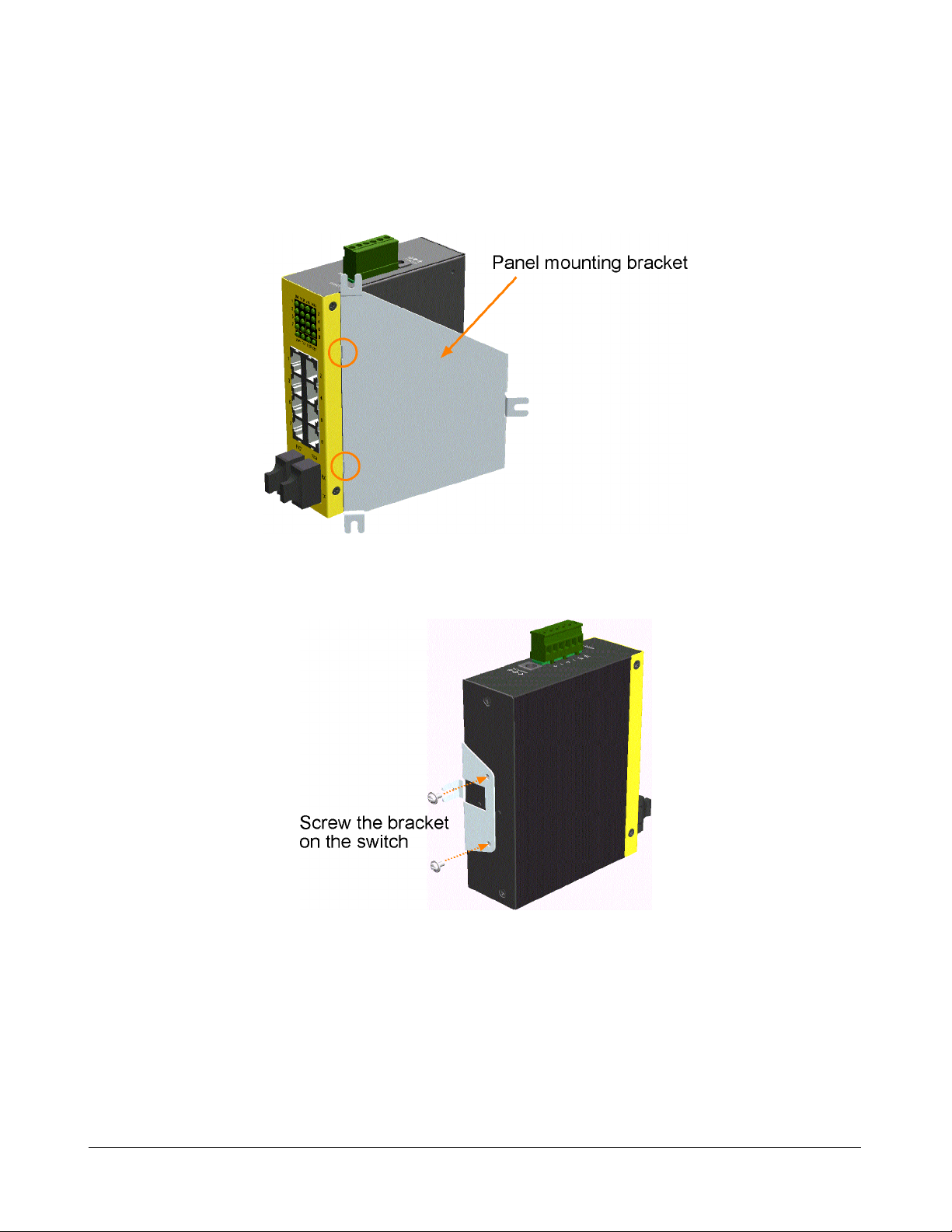
2.4 Panel Mounting
The switches are provided with an optional panel mounting bracket. The bracket support mounting the
switch on a plane surface securely. The mounting steps are:
1. Install the mounting bracket on the switch unit.
2. Screw the bracket on the switch unit.
-18-
Page 19
3. Screw the switch unit on a panel. Three screw locations are shown below:
-19-
Page 20

2.5 Applying Power
The power specifications of the switch are:
Operating Voltage +7 ~ +30VDC
Power Consumption Max. 8.3W @30VDC
The switch provides two types of power interfaces, terminal block and DC power jack for receiving DC
power input from external power supply.
Using Terminal Blocks
Either DC1 interface or DC2 interface can be used to receive DC power from an external power
system. Or, DC2 also can be used to deliver the power received on DC1 to next switch in cascading
way.
DC1 + Vdc Positive (+) terminal
DC1 - Vdc Negative (-) terminal
DC2 + Vdc Positive (+) terminal
DC2 - Vdc Negative (-) terminal
Three 2P terminal plugs are provided together with the switch. Two of the three plugs are used for
DC1 and DC2 interfaces respectively . The plug is shown below:
Power wires : 24 ~ 12AWG (IEC 0.5~2.5mm2)
Install the power source wires with the plug properly. Then, plug in DC1 contacts. If cascading the
power to next switch device is needed, install the power wires and plug for another switch. Then, use
DC2 contacts.
Note: Only up to four device units can be cascaded to receive power from
one main power input source.
-20-
Page 21

Using DC Power Jack
When an external power system is not available, the switch provides a DC jack to receive power from
typical AC-DC power adapter alternatively.
AC Power Adapters: Optional commercial rated adapters are available for purchasing.
Rated AC120V/60Hz DC7.5V 1.5A
Rated AC230V/50Hz DC7.5V 1.5A
Rated AC100V/50-60Hz DC7.5V 1.5A
Rated AC240V/50Hz DC7.5V 1.5A
Note: Before you begin the installation, check the AC voltage of your area. The AC power
adapter which is used to supply the DC power for the unit should have the AC voltage
matching the commercial power voltage in your area.
2.6 Power Failure Relay Output
The switch provides a relay output to report power failure event to a remote alarm monitoring system.
The replay output is provided with two contacts in the terminal block next DC2 interface.
Use the provided 2P terminal plug for signal wiring and plug into the PF+/- contacts. The function is
designed as :
Power is normal PF+ contact is shorted with PF- contact.
Power failure PF+ contact is disconnected with PF- contact.
Note: Be sure the voltage applied on PF+/- contacts is within the specification of
30VDC/1A max. or 120VAC/0.5A max.
-21-
Page 22

2.7 Reset Button
The reset button is used to perform a reset to the switch. It is not used in normal cases and can be used
for diagnostic purpose. If any network hanging problem is suspected, it is useful to push the button to
reset the switch without turning off the power. Check whether the network is recovered.
The button can also be used to restore the software configuration settings to factory default values.
The operations are:
Operation Function
Press the button more than 5 seconds Restore the switch back to factory default settings
Press the button less than 5 seconds Reboot the switch
2.8 Making UTP Connections
The 10/100TX ports supports the following connection types and distances:
Network Cables
10BASE-T: 2-pair UTP Cat. 3,4,5 , EIA/TIA-568B 100-ohm
100BASE-TX: 2-pair UTP Cat. 5, EIA/TIA-568B 100-ohm
Link distance: Up to 100 meters
Auto MDI/MDI-X Function
This function allows the port to auto-detect the twisted-pair signals and adapts itself to form a valid
MDI to MDI-X connection with the remote connected device automatically. No matter a straight
through cable or crossover cable is connected, the ports can sense the receiving pair automatically and
configure itself to match the rule for MDI to MDI-X connection. It simplifies the cable installation.
Auto-negotiation Function
The ports are featured with auto-negotiation function and full capability to support connection to :
• Auto-negotiation devices
• Auto-negotiation incapable 10BASE-T half duplex devices
• Auto-negotiation incapable 100BASE-TX half duplex devices
It performs a negotiation process for the speed and duplex configuration with the connected device
automatically when each time a link is being established. If the connected device is also auto-negotiation capable, both devices will come out the best configuration after negotiation process. If the connected device is incapable in auto-negotiation, the switch will sense the speed and use half duplex for
the connection.
Port Configuration Management
For making proper connection to an auto-negotiation incapable device, it is suggested to use port control function via software management to set forced mode and specify speed and duplex mode which
match the configuration used by the connected device.
-22-
Page 23

2.9 Making Fiber Connections
FX7 port and FX8 port operate on 100Mbps and full duplex.
The following figure illustrates a connection example between two fiber ports:
Make sure the Rx-to-Tx connection rule is followed on the both ends of the fiber cable.
Far End Fault Function
The FX ports are facilitated with this function, which conforms to IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-FX specifications. When the FX port detects a link failure on its receiving circuitry , it will send out an FEFI (Far
End Fault Indication) signal to the remote connected device to indicate a remote fault is detected. It
also is capable to receive FEFI signal sent from the remote link partner. Upon receiving an FEFI signal,
it indicates a link failure occurred on the transmitting path. This function allows the switch to report a
fiber link fault even when a link failure occurred on transmitting fiber cable.
Network Cables
Multimode (MMF) - 50/125, 62.5/125
Single mode (SMF) - 9/125
Note: Since the FX port shares the same switched port with 10/100TX connector, make sure
only one network cable type is used any time. In the case of both cable types are used
at the same time, FX port has higher priority.
-23-
Page 24

2.10 LED Indication
LED Function State Interpretation
PWR Power status ON The power is supplied to the switch.
OFF The power is not supplied to the switch.
LNK Port link status ON An active link is established on the port. (No traffic)
BLINK Port link is up and there is traffic.
OFF Port link is down.
100M Port speed status ON 100Mbps
OFF 10Mbps
FX 7 FX7 link status ON FX7 port is link up.
BLINK Port link is up and there is traffic.
OFF Port link is down.
FX 8 FX8 link status ON FX8 port is link up.
BLINK Port link is up and there is traffic.
OFF Port link is down.
Mgt. Factory Reserved Ignore the indication.
-24-
Page 25

2.11 Configuring IP Address for the Switch
The switch is shipped with the following factory default settings for software management :
Default IP address of the switch : 192.168.0.2 / 255.255.255.0
The IP Address is an identification of the switch in a TCP/IP network. Each switch should be designated a new and unique IP address in the network. Refer to Telnet management interface.
To change the default IP address Use Telnet IP menu.
2.12 Configuring User Name and Password
The switch is shipped with the following factory default settings for software management :
• User name : admin
• Password : 123
The user name and password are used for authentication in accessing to the switch via T elnet interface
and Http web-based interface. For security reason, it is recommended to change the default settings
for the switch before deploying it to your network. Refer to Telnet management interface.
To change user name and password Use Telnet Security Manager menu
2.13 Configuring SNMP Settings
The switch is shipped with the following factory default settings for SNMP software management :
Community strings : public with access right - read only
The community strings are used for authentication in accessing to the switch via SNMP protocol. For
security reason, it is recommended to change the default settings for the switch before deploying it to
your network. Refer to Telnet management interface.
T o change Community strings Use Telnet SNMP menu
2.14 Configuring Port 7 and Port 8
If a 100FX is provided on Port 7 or Port 8 and 100FX fiber connection is selected, configure the port to
auto-negotiation disabled, 100M, and full duplex. Refer to T elnet management interface.
T o change port configuration Use Telnet Port Config menu
-25-
Page 26

3. Advanced Functions
T o help a better understanding about the software management interfaces, this chapter describes some
advanced functions provided by the switch.
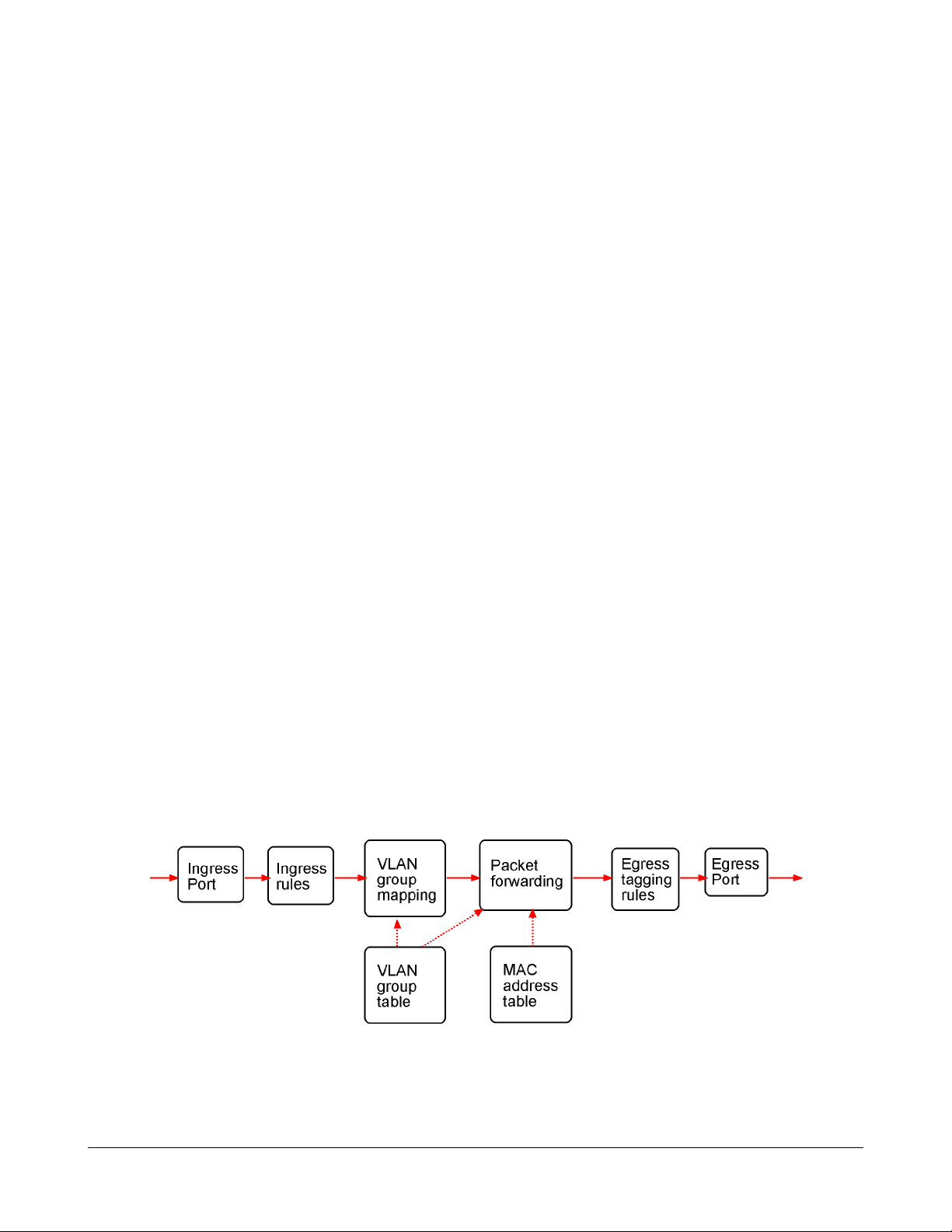
3.1 QoS Function
The switch provides a powerful Quality of Service (QoS) function to guide the packet forwarding in
two priority levels. The versatile classification methods can meet most of the application needs. The
following figure illustrates the QoS operation flow when a packet received on the input port until it is
transmitted out from the output port:
3.1.1 Priority Level
Each output (egress) port in the switch is equipped with two transmission priority queues to store the
packets for transmission. The high priority queue stores the high priority packets and low priority queue
stores the low priority packets.
3.1.2 Egress Service Policy
The packets in high priority queue and low priority queue are transmitted out from a port based on a
user configured round robin ratio, called egress service policy between high priority queue and low
priority queue. The switch provides four ratio options for the service policy:
• [ 4:1 ] : 4 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
• [ 8:1 ] : 8 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
• [ 16 :1 ] : 16 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
• [Always high priority first] : Packets in high priority queue are sent first until the queue is empty
3.1.3 Packet Priority Classification
Each received packet is determined and classified into one of two priority levels, high priority and low
priority upon reception. The switch provides many classification methods including:
• Port based
• 802.1p based
• IP DSCP based
• IP network address based
They all can be configured to be activated or not. Some are per port configuration and some are global
configuration for the switch. More than one classification method can be enabled at the same time. If
a packet is classified as high priority in any one of the enabled (applied) classifications, the packet is
forwarded to the high priority queue of the output port. Otherwise, it is classified as low priority .
-26-
Page 27

3.1.3.1 Port-based Priority Setting (per port setting)
As one port is configured to be enabled for port-based priority , all received packets on the port will be
classified as high priority . The options are:
Enable - All packets received on the port are classified as high priority
Disable - Port-based classification is not applied.
3.1.3.2 802.1p Classification (per port setting)
For a received 802.1Q VLAN tagged packet, the switch will check the 3-bit User Priority value in TCI
(T ag Control Information) field of packet tag data. If the priority value is equal or larger than a configured 802.1p High Priority Tag Setting, the packet is classified as high priority.
Enable - Tagged packets received on the port are classified by comparing the packet ’s User
Priority value and 802.1p High Priority T ag Threshold Setting.
Disable - 802.1p classification is not applied.
3.1.3.3 DSCP Classification (per port setting)
As a port is enabled for IP DSCP classification, the switch will check the DiffServ Code Point (DSCP)
value of the IP packets received on the port.
Enable - IP packets received on the port are classified by checking the packet ’s DSCP value.
Disable - DSCP classification is not applied.
The following checks are performed to classify the packet priority:
1. Default DSCP : If the packet’s DSCP value is one the default code point listed below, the
packet is classified as high priority . EF - <1011 10>, AF - <001010> <010010> <01 1010>
<100010> and Network Control - <11 1000> <110000>.
2. User Defined DSCP : If the packet ’s DSCP value matches the user defined DSCP(A) and
DSCP(B) settings, the packet is classified as high priority . DSCP(A) and DSCP(B) settings will
be described later.
User defined DSCP(A) and DSCP(B) can be enabled respectively.
User Defined DSCP(A) Classification (Global)
User can configure a specific DSCP value in DSCP(A) setting as high priority beside default DSCPs.
Enable - Enable DSCP(A) checking
Disable - DSCP(A) classification is not applied.
User Defined DSCP(B) Classification (Global)
User can configure a specific DSCP value in DSCP(B) setting as high priority beside default DSCPs.
Enable - Enable DSCP(B) checking
Disable - DSCP(B) classification is not applied.
-27-
Page 28

3.1.3.4 IP Network Address Classification
User can configured two IP network address settings, IP(A) and IP(B). If a received IP packet’s
source address or destination address belongs to the user defined IP network addresses. The packet is
classified as high priority .
User Defined IP(A) Classification (Global)
Enable - Enable IP(A) checking
Disable - IP(A) classification is not applied.
User Defined IP(B) Classification (Global)
Enable - Enable IP(B) checking
Disable - IP(B) classification is not applied.
3.1.4 Other QoS Settings
• 802.1p High Priority T ag Setting for 802.1p classification
• User Defined DSCP(A) Setting for DSCP classification
• User Defined DSCP(B) Setting for DSCP classification
• User Defined IP(A) Settings for IP network address classification
- IP(A) IP address setting
- IP(A) IP subnet mask setting
• User Defined IP(B) Settings for IP network address classification
- IP(B) IP address setting
- IP(B) IP subnet mask setting
-28-
Page 29
3.2 VLAN Function
The switch supports port-based VLAN, 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN and eight VLAN groups. Some
VLAN related terminologies are described as follows:
VLAN Group
VLAN group specifies a VLAN information that can be referred by the switch in performing VLAN
mapping and packet forwarding for ingress port and the received packets. The information includes:
•Group Number : index number of the VLAN group ( 1 ~ 8 )
•VID (VLAN ID) : 12-bit value to indicate a VLAN to which the group is associated (1 ~ 4095)
•Member Ports : the ports belong to this VLAN group for egress
Ingress Port
Ingress port is the input port on which a packet is received.
Default VLAN Group Index (Port VLAN index)
Each port has this index, which points to a default VLAN group. It is used for mapping a VLAN group
for the ingress port under Port-based VLAN mode. It is also used for mapping to a VLAN group for
an untagged received packet under 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN mode.
PVID (Port VID)
PVID is the default VID of an ingress port. It is obtained from the VID of the indexed default VLAN
group by the ingress port. It is often used in ingress packet filtering and egress tagging operation.
Egress Port
Egress port is the output port from which a packet is sent out after VLAN operation.
Null VID Packet
A tagged packet is called Null VID packet if the packet’ s VID is equal to 0. Sometimes, it is also called
priority tag packet.
3.2.1 VLAN Operation
The following figure illustrates the basic VLAN operation flow beginning from a packet received on an
ingress port until it is transmitted from an egress port.
-29-
Page 30

The following sections describe the VLAN processes and related settings provided by the switch. A
global setting means the setting is applied to all ports of the switch. A per port setting means each port
can be configured for the setting respectively .
3.2.2 Ingress Rules
When a packet is received on an ingress port, the ingress rules are applied for packet filtering and
mapping a VLAN group. The first rule is :
3.2.2.1 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN Mode (global setting)
Enable - 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN mode is used
Disable - Port-based VLAN mode is used
802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN Mode
Under this mode, the switch will check the content of every received packets. For 802.1Q tagged
packets, the tagged VID on the packet is used to look up the VLAN group table and find the group
whose VID matches the packet tagged VID.
Received packet type VLAN group mapping Final VLAN group used
802.1Q Tagged packets Tagged VID Matched - use the matched VLAN group
No matched - drop the packet
Untagged packets Port VLAN index Default VLAN group of the ingress port
Port-based VLAN Mode
Under this mode, the switch does not check the contents of the received packets. The default VLAN
group indexed by the ingress port is used directly for further VLAN operation.
3.2.2.2 Ingress Member Filtering (global setting)
As this rule is enabled, the received packet is dropped if the ingress port is not the member port of the
mapped VLAN group.
Enable - Drop packet if the ingress port is not the member port of the VLAN group
Disable - No ingress member filtering is applied
3.2.2.3 Unmatched VID Filtering (per port setting)
A tagged received packet will be dropped if the tagged VID does not match the PVID of the ingress
port. PVID is the VID of ingress port’s default VLAN group.
Enable - Drop the tagged packet if the packet’s VID does not match the ingress port’s PVID
Disable - No Unmatched VID filtering is applied to the port
-30-
Page 31

3.2.3 VLAN Group Mapping
The VLAN group mapping is the switch’s decision process to find a right VLAN group for the re-
ceived packet when it is not filtered by ingress rules. The group mapping depends on the VLAN mode
and the packet type. The following table lists the decision rules:
VLAN Mode Packet Type Mapping Method
802.1Q T ag A ware Tagged & non-Null Use packet’ s VID to loop up VLAN group table
Matched - use the group matched
Unmatched - drop the packet
802.1Q Tag Aware Null VID Use ingress port’s default VLAN group directly
802.1Q Tag Aware Untagged Use ingress port’s default VLAN group directly
Port-based VLAN Tagged Use ingress port’s default VLAN group directly
Port-based VLAN Untagged Use ingress port’s default VLAN group directly
3.2.4 Packet Forwarding under VLAN
The forwarding is a switch’s process to forward the received packet to one or more egress ports. The
process uses the following information as forwarding decision:
• The mapped VLAN group’s member ports : the port range for forwarding
• The packet’s destination MAC address : for MAC address table loop up
• The switch’s MAC address table : to find the associated input port for a learned MAC address
If the MAC address table lookup is matched and the associated port is the VLAN member port, the
packet is forwarded to the port (egress port). If the lookup is not matched, the switch will broadcast the
packet to all member ports.
3.2.5 Egress Tagging Rules
Egress T agging rules are used to make change to the packet before it is transmitted out from an egress
port. Two egress tagging settings are provided for each port and are described as follows:
3.2.5.1 Egress Tag Rule (per port setting)
Four basic options are provided for egress tagging :
1 . Tagging with PVID for all packets
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress port’s PVID as tag VID
Tagged packet : the packet’s tag VID is replaced with ingress port ’s PVID as new tag VID
2 . Untagging for all packets
Untagged packet : the packet is not modified
Tagged packet : the packet’s tag VID is removed and becomes an untagged packet
Null VID packet : depending on Null VID Replacement setting in next section
3 . PVID insertion for untagged packets only
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress port’s PVID as tag VID
T agged packet : the packet is not modified
4 . No tag insertion and tag removal
The packet is not modified at all. No tag insertion or tag removal are performed for all packets.
-31-
Page 32

3.2.5.2 Null VID Replacement (per port setting)
The null VID of a Null VID packet will be replaced with the associated ingress port’s PVID. This
setting still works even Egress Tag rule : [PVID insertion for untagged packets only] is selected.
3.2.6 Summary of VLAN Function
Number of VLAN groups : 8 groups at the same time
VLAN ID supported : 1 ~ 4095 (12-bit VID)
VLAN mode options : 802.1Q Tag Aware VLAN, Port-based
Ingress rules :Ingress Member Filtering (global setting)
Unmatched VID Filtering (per port setting)
Egress Tagging rules : Egress Tag Rule (per port setting)
- Tagging with PVID for all packets
- Untagging for all packets
- PVID insertion for untagged packets only
- No tag insertion and tag removal
Null VID Replacement (per port setting)
-32-
Page 33

4. Software Management
The switch provides the following in-band management interfaces for configuring the switch to meet
requirements for different applications:
• Telnet over TCP/IP
• Http web-based over TCP/IP
• SNMP over TCP/IP
4.1 Telnet Management Interface
Use T elnet software to perform the management operation. The most convenient solution is using the
built-in T elnet function in your W indows PC. Execute Telnet command as follows:
>telnet xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
The specified xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of the switch. Factory default IP address is 192.168.0.2.
A welcome message and login prompt are displayed if the connection is established properly .
Welcome to Telnet Server
login:xxxxx
password: xxx
Welcome xxxxx
Factory default login name : admin
Factory default password : 123
It is suggested to change the user name and password first before performing other configuration. To
change the user name and password, select [6] Security Manager for configuration.
Main Menu
INET>
Setup Menu
TCP/IP stack v1.0
[0] Print this menu
[1] IP Menu
[2] SNMP Menu
[3] Port Config
[4] Administrator
[5] Restore Default Values
[6] Security Manager
[7] Update firmware
[8] Reboot System
[Q] Exit
Please Select(0-9)....
Note: If [Unchange] option is provided during configuration, it means keeping current
setting.
-33-
Page 34

4.2 IP Menu
Select [1] IP Menu to configure IP protocol related settings for the switch.
IP Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] Set IP Address
[2] View IP status
[Q] Back Menu
Please Select(0-3)....
INET>1
Enter Esc to abort..
Please Input IP Address(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx):192.168.0.232
replacing net[0] IP address192.168.0.232 with 192.168.0.232
Please Input Subnet Mask(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx):255.255.255.0
replacing subnet mask[0]255.255.255.0 with 255.255.255.0
Please Input Gateway IP(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx):192.168.0.1
replacing gatewqy IP addr[0] 192.168.0.1 with 192.168.0.1
Do you want to Change IP setting?(Y/N):
IP Settings Description
IP Address : IP address assigned to the switch
Subnet Mask : IP subnet mask of the switch
Gateway IP : IP address of the default gateway of the switch
To view current IP settings of the switch, select [2] View IP status.
IP Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] Set IP Address
[2] View IP status
[Q] Back Menu
Please Select(0-3)....
INET> 2
IP Addr: 192.168.0.232 Submask: 255.255.255.0 Gateway: 192.168.0.1
INET>
-34-
Page 35

4.3 SNMP Menu
This menu is used for configuring SNMP protocol related settings.
Snmp Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] View Snmp Setting
[2] Set Snmp Name
[3] Set Snmp Location
[4] Set Snmp Contact
[5] Set Snmp Community
[6] Set Snmp Trap Manager
[7] Set Port Link Trap Function
[8] Set Login Failure Trap Function
[Q] Back Menu
Please Select(0-9)....
INET>
SNMP Settings Description
System Name Name of the switch for SNMP management
System Location Location of the switch for SNMP management
System Contact Contact person for the switch
Community Name Community Name allowed for SNMP access to the switch
Up to 4 communities can be configured.
Community Access Right Access Right associated to the community name, options
R(read-only) - only read operation is allowed
W(read-write) - both read and write operations are allowed.
Trap Manager IP Address of the SNMP station which can receives trap
Up to 3 trap stations can be configured.
Trap Community Name Community string sent with a trap message
Port Link Trap Function Enable or disable SNMP trap for port link change events
Login Failure Trap Function Enable or disable SNMP trap for login failure events
-35-
Page 36

4.4 Port Config
Select [3] Port Config to configure port configuration.
Port Config Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] Port Status
[2] Port Config
[Q] Back Menu
Please Select(0-3)
Select [1] Port Status to view current port status for all ports as example below:
INET> Port Status:
Port Port Link Auto Speed Duplex Port Auto_No Speed Duplex
+-----+----+------+--------+------+------+--------+--------+-------+-------+
1 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
2 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
3 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
4 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
5 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
6 TP Up Enable 100 M Full Enable Enable 100 M Full
7 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
8 TP Down -- -- -- Enable Enable 100 M Full
+-----+----+------+--------+------+------+--------+--------+-------+-------+
INET>
Status Description
Port The port number
Port Type TP - 10/100TX port (for Port 7 and Port 8 10/100TX is selected)
FX - 100FX is selected (for Port 7 and Port 8 only)
Link Status Port link status
Down - port link down (no status is displayed.)
Up - port link up
Auto Negotia. Auto-negotiation configuration
Enable - auto-negotiation is enabled
Disable - auto-negotiation is disabled (forced mode is used)
Speed Status Port speed status
100M - 100Mbps is used
10M - 10Mbps is used
Duplex Status Port duplex status
Full - full duplex is used
Half - half duplex is used
Port Control Port function configuration
Enable - Port function (Tx/Rx) is enabled
Disable - Port function (Tx/Rx) is disabled
Auto-No Control Port auto-negotiation function
Enable - enable port auto-negotiation
Disable - disable port auto-negotiation (use forced mode)
-36-
Page 37

Speed Control Speed configuration when auto-negotiation is disabled
100M - 100Mbps
10M - 10Mbps
Duplex Control Duplex configuration when auto-negotiation is disabled
Full - full duplex
Half - half duplex
Select [2] Port Config to view current port status for all ports as example below:
Port Setting Description
Ports Select port range to be configured.
More than one group can be configured at the same time.
Examples:
123 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
1 2 3 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
1,2,3 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
Port Control Enable / disable port function (Tx/Rx)
Auto Negotiation Enable / disable port auto-negotiation function
Speed Configure speed when port auto-negotiation function is disabled
Duplex Configure duplex when port auto-negotiation function is disabled
4.5 Administrator
Select [4] Administrator to configure advanced settings including VLAN and QoS settings:
Administrator:
[0] Print this menu
[1] VLAN Settings
[2] QoS Settings
[Q] Back Menu
Please Select(0-4)
4.5.1 Administrator -> VLAN Settings
Select [1] VLAN Settings to configure VLAN function related settings:
VLAN Settings Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] VLAN Group Information
[2] VLAN Select
[3] VLAN Global Settings
[4] VLAN Group Member Settings
[5] VLAN Group VID Settings
[6] VLAN Per Port Settings
[Q] Back Administrator
Please Select(0-7)
-37-
Page 38

Select [1] VLAN Group Information to view all groups.
VLAN Select: Disable VLAN
Member Ports (O : member, - : not member):
G\P 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
1 O O O O O O O O
2 - O - - - - - 3 - - O - - - - 4 - - - O - - - 5 - - - - O - - 6 - - - - - O - 7 - - - - - - O 8 - - - - - - - O
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
VLAN ID:
Group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
+-------+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+
VLAN ID 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
+-------+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+
INET>
VLAN Information Description
VLAN Select VLAN function of the switch is enabled or disabled.
Member ports Table list for member ports :
X axis - port number
Y axis - group number
VLAN ID VLAN ID configuration of each group
Select [2] VLAN Select to enable or disable VLAN function of the switch.
Select [3] VLAN Global Settings to configure 802.1Q Tag Aware Mode and Ingress Member Filtering Mode:
VLAN Other Settings:
[0] Print this menu
[1] View VLAN Global Settings
[2] 802.1Q Tag Aware Mode
[3] Ingress Member Filtering Mode
[Q] Back VLAN
Please Select(0-4)
-38-
Page 39
VLAN Global Settings Description
802.1Q Tag Aware Mode Enable - Under this mode, the switch will check the content of
every received packets. For 802.1Q tagged packets, the tagged
VID on the packet is used to look up the VLAN group table and
find the group whose VID matches the packet tagged VID.
Disable - Under this mode, the switch does not check the contents
of the received packets. The default VLAN group indexed by the
ingress port is used directly for further VLAN operation.
Ingress Member Filtering Mode Enable - Drop packet if the ingress port is not the member port of
the VLAN group
Disable - No ingress member filtering is applied
Select [4] VLAN Group Member Settings to configure member ports for VLAN groups.
Input Description
Groups Specify group list to be configured. More than one group can be configured at the same
time. Examples:
123 - Group 1, Group 2, Group 3
1 2 3 - Group 1, Group 2, Group 3
1,2,3 - Group 1, Group 2, Group 3
Ports Enter port list for the selected groups
Examples:
123 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
1 2 3 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
1,2,3 - Port 1, Port 2, Port 3
Select [5] VLAN Group VID Settings to configure VLAN ID for VLAN groups.
VID Setting Description
Groups Select group list to be configured.
VLAN ID Enter VLAN ID for the selected groups
V alid values : 1 - 4095
-39-
Page 40

Select [6] VLAN Per Port Settings to configure VLAN ID for VLAN groups.
VLAN Per Port Settings:
Port Default Unmatched Egress Null
No. Group VID tag rule VID
+-----+--------+-----------+---------+---------+
1 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
2 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
3 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
4 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
5 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
6 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
7 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
8 1 Disabled 4 Disabled
+-----+--------+-----------+---------+---------+
Enter Esc to abort..
Please Input Ports (1~8):
Per Port Settings Description
Ports Input port list for configuration.
Default Group Index to the default group of the selected ports
Unmatched VID Enable - Drop the tagged packet if the packet’s VID does not match the
ingress port’s PVID
Disable - No Unmatched VID filtering is applied to the port
Egress tag rule Egress Tagging rules are used to make change to the packet before it is
transmitted out from an egress port. Options are:
(1) Tagging with ingress PVID for all packets -
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress
port’s PVID as tag VID
Tagged packet : the packet’s tag VID is replaced with ingress port’s
PVID as new tag VID
(2) Untagging for all packets -
Untagged packet : the packet is not modified
Tagged packet : the packet’s tag VID is removed and becomes an
untagged packet
Null VID packet : depending on next Null VID Replacement setting
(3) Ingress PVID insertion for untagged packets only -
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress
port’s PVID as tag VID
Tagged packet : the packet is not modified
(4) No tag insertion and tag removal -
The packet is not modified at all. No tag insertion or tag removal are
performed for all packets.
-40-
Page 41

Null VID The null VID of a Null VID packet will be replaced with the associated
ingress port’s PVID. This setting still works even Egress Tag rule :
[PVID insertion for untagged packets only] is selected.
Enable - Null VID is replaced with Port’s PVID for Null VID packets
Disable - Null VID replacement rule is not applied.
4.5.2 Administrator -> QoS Settings
Select [4] Administrator -> [2] QoS Settings to configure QoS function related settings for the
switch.
QoS Settings Menu:
[0] Print this menu
[1] QoS Per Port Settings
[2] QoS Other Settings
[Q] Back Administrator
Please Select(0-3)
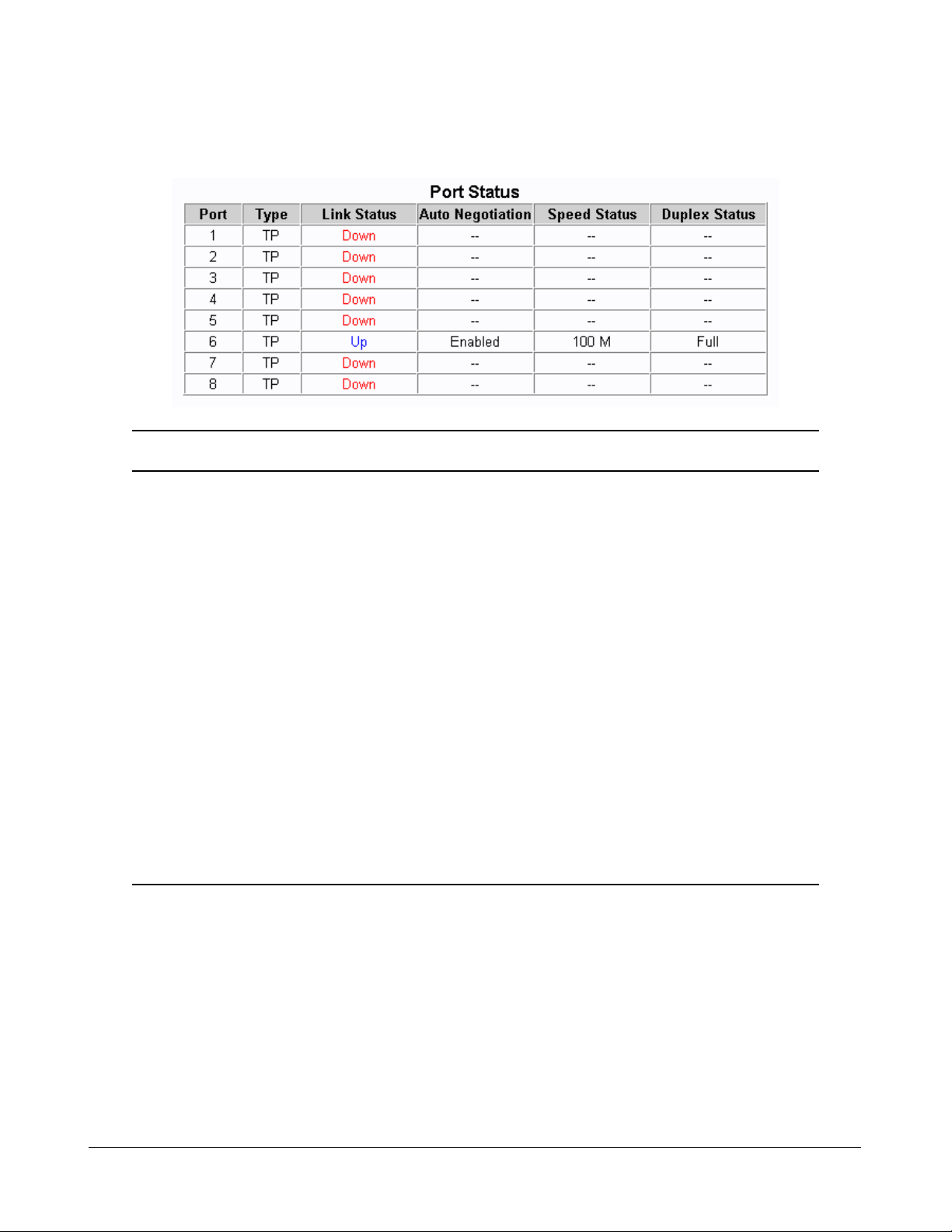
Select [1] QoS Per Port Settings to configure port related QoS settings:
QoS Per Port Settings:
Port Port based 802.1p Default TOS/DS
No. priority classification classification
+-----+----------+--------------+--------------+
1 Disabled Disabled Disabled
2 Disabled Disabled Disabled
3 Disabled Disabled Disabled
4 Disabled Disabled Disabled
5 Disabled Disabled Disabled
6 Disabled Disabled Disabled
7 Disabled Disabled Disabled
8 Disabled Disabled Disabled
+-----+----------+--------------+--------------+
Enter Esc to abort..
Please Input Ports (1~8):
Per Port Settings Description
Ports Input port list for configuration.
Port based priority Enable - All packets received on the port are classified as high
priority
Disable - Port-based classification is not applied.
802.1p classification Enable - Tagged packets received on the port are classified by
comparing the packet’s User Priority value and 802.1p High
Priority T ag Setting.
Disable - 802.1p classification is not applied.
-41-
Page 42

Default TOS/DS classification Enable - If the packets DSCP value is one the default code point
listed below, the packet is classified as high priority. EF - <1011 10>,
AF - <001010> <010010> <011010> <100010> and Network
Control - <11 1000> <110000>
Disable - Default DSCP classification is not applied.
Select [2] QoS Other Settings to configure QoS global settings:
QoS Other Settings:
[0] Print this menu
[1] Show QoS Other Status
[2] 802.1p priority tag
[3] Egress service policy
[4] Specific DS Settings
[5] Specific IP Settings
[Q] Back QoS
Please Select(0-6)
Select [1] Show QoS Other Status to view other settings (global):
802.1p priority tag : 4
Egress service policy : 16 : 1
Specific DS(A) Setting : Disabled
Specific DS(A) Value : 111111
Specific DS(B) Setting : Disabled
Specific DS(B) Value : 111111
Specific IP(A) Setting : Disabled
Specific IP(A) Value : 255.255.255.255
Specific IP(A) Mask Value : 255.255.255.255
Specific IP(B) Setting : Disabled
Specific IP(B) Value : 255.255.255.255
Specific IP(B) Mask Value : 255.255.255.255
INET>
-42-
Page 43

Select [2] - [5] to configure other settings as follows:
QoS Other Settings Description
802.1p priority tag 802.1p High Priority Tag Threshold Setting for 802.1p classification
Valid values : 0 - 7
Egress service policy W eighted Round Robin ratio:
(1) 4:1 - 4 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
(2) 8:1 - 8 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
(3) 16 :1 - 16 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
(4) Always high first - Packets in high priority queue are sent first
until the queue is empty
Specific DS(A) Setting Enable - Enable user defined DSCP(A) checking
Disable - User defined DSCP(A) classification is not applied.
Specific DS(A) Value Enter user defined DSCP(A) value for classification.
Specific DS(B) Setting Enable - Enable user defined DSCP(B) checking
Disable - User defined DSCP(B) classification is not applied.
Specific DS(B) Value Enter user defined DSCP(B) value for classification.
Specific IP(A) Setting If a received IP packet’s source address or destination address
belongs to the user defined IP network addresses. The packet is
classified as high priority .
Enable - Enable user defined IP(A) network address checking
Disable - IP(A) classification is not applied.
Specific IP(A) Value Set user defined IP(A) address for classification.
Specific IP(A) Mask Value Set user defined IP(A) subnet mask for classification.
IP(A) address and IP(A) subnet mask specify IP(A) user defined
IP network address for IP packet classification.
Specific IP(B) Setting If a received IP packet’s source address or destination address
belongs to the user defined IP network addresses. The packet is
classified as high priority .
Enable - Enable user defined IP(B) network address checking
Disable - IP(B) classification is not applied.
Specific IP(B) Value Set user defined IP(B) address for classification.
Specific IP(B) Mask Value Set user defined IP(B) subnet mask for classification.
IP(B) address and IP(B) subnet mask specify IP(B) user defined
IP network address for IP packet classification.
-43-
Page 44

4.6 Restore Default Values
Select [6] Restore Default Values to restore all settings of the switch back to factory default values.
Do you want to restore system default settings?(Y/N):
Refer to Appendix for factory default values.
4.7 Security Manager
Select [7] Security Manager to change user name and password. The user name and password are
used for access authentication to the switch in telnet management and web management.
Current username: admin
Current password: ********
Press ESC to abort ...
Change username[admin]:admin
Enter password(1-8):***
Confirm password:***
Password updating ........
Password updated.
User is requested to enter new password again for confirmation. A new password is accepted only
two passwords are identical.
It is suggested to change the factory default user name and password before installing the switch into
your network.
-44-
Page 45

4.8 Update Firmware
Select [7] Update Firmware to update the firmware of the switch. A new firmware may be released
by the factory due to function enhancement. The update method is via TFTP protocol.
The steps are:
1. A TFTP server must be available in the network before updating the firmware.
2. Place the new firmware on the TFTP server with filename [image.bin].
3. Use [7] Update firmware to specify the IP address of the TFTP server and start downloading
of the new firmware as follows:
Enter Esc to abort..
Please Input TFTP Server IP Address(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx):yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
TFTP Server :yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
Do you want to start download new image? (Y/N)
Setting Description
TFTP IP Address IP address of the TFTP server from where a new firmware is down-
loaded.
4.9 Reboot System
Select [7] Reboot System to reboot the switch.
Do you want to reboot system ?(Y/N):y
Start rebooting.....
Press [Y] to confirm to reboot the switch with current configuration settings. Note that the current
telnet connection will be disconnected after confirmation.
You must restart your telnet and login into the switch again.
4.10 Exit
Select [Q] Exit to stop telnet connection with the switch.
-45-
Page 46

5. Web Management
The switch features an http server which can serve the management requests coming from any web
browser software over internet or intranet network.
Web Browser
Compatible web browser software with JAVA support
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or later
Netscape Communicator 4.x or later
Set IP Address for the System Unit
Before the switch can be managed from a web browser software, make sure a unique IP address is
configured for the switch.
5.1 Start Browser Software and Making Connection
Start your browser software and enter the IP address of the switch unit to which you want to connect.
The IP address is used as URL for the browser software to search the device.
URL : http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/
Factory default IP address : 192.168.0.2
5.2 Login to the Switch Unit
When browser software connects to the switch unit successfully , a Login screen is provided for you to
login to the device as follows:
Login
Factory default Username : Admin
Factory default Password : 123
-46-
Page 47

The following screen shows welcome screen when a successful login is performed.
In addition to the device image, the screen supports the following menus on the right side:
1. Home : home page and device image
2. Port Status : view all switched port status
3. Administrator : other management functions
-47-
Page 48
5.3 Port Status Menu
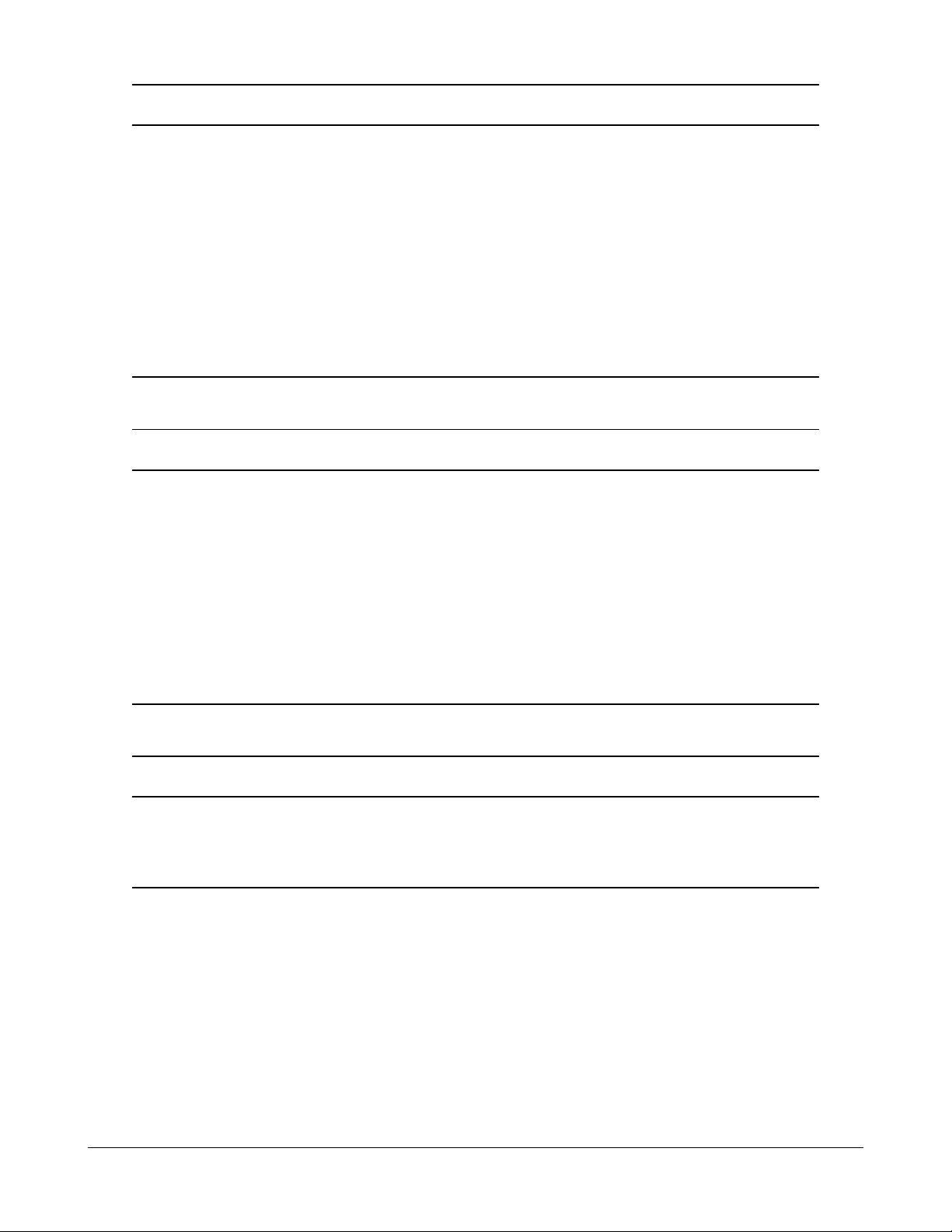
Click >Port Status Menu to display the port status for all switched ports. The pop-up port status list is
as follows:
Port Status Description
Port Number 1 - 6 : 10/100TX ports - P1 ~ P2
7 - 8 : 100FX ports - F1 F2
Type Port media type
TP - 10/100TX
FX - 100FX (for Port 7 and Port 8 only)
Link Status Port link status
Up - port link up (an active link is established with a link partner)
Down - port link down
Auto Negotiation Auto negotiation mode status
Enabled - auto negotiation mode is enabled
Disabled - auto negotiation mode is disabled (forced mode)
Speed Status Port speed status
100M - 100Mbps
10M - 10Mbps
Duplex Status Port duplex status
Full - full duplex
Half - half duplex
Clicking the port icons on the product image in web page also will pop-up the port status.
-48-
Page 49

5.4 Administrator
Click >Administrator to perform more advanced management functions as follows:
Menu Function
Basic Configure IP and SNMP settings for the switch
Port Control Change port configuration including auto-negotiation, speed, duplex
VLAN Controls Configure VLAN related settings
QoS Controls Configure QoS related settings
Security Manager Change user name and password
Image Refresh Time Set the image refresh time for the web device image
Update Firmware Update firmware of the switch
Restore Default Restore the switch back to factory default settings
Reboot System Reboot the switch
5.4.1 Basic Menu
Click Basic menu to configure IP settings and SNMP settings for the switch:
-49-
Page 50

IP Address
IP Address Setting Description
IP Address IP address for the switch
Submask Subnet mask of the IP address
Gateway IP address of the default gateway
SNMP Entries
SNMP settings include system settings, community settings and Snmp trap settings as follows:
System Settings Description
Name Set a system name for the switch
Location Set the location where the switch unit is installed
Contact Set the contact person for the switch unit
-50-
Page 51

Community Settings Description
Community String Community strings which are allowed to access the switch unit via SNMP
protocol
Access Right The access right assigned to the community string, options are:
RO - read only
RW - read / write
<<Add>> Add one new community string specified in String box.
Up to 4 community strings are allowed.
Remove Remove the specified community string from list.
-51-
Page 52

Trap Manager Settings Description
IP Address Specify the IP address of the trap manager to which the switch will
send Snmp traps when predefined events occur.
Community Community string used together with the trap messages sent to the
trap manager
<<Add>> Button to add a new trap manager (specified by an IP and Commu-
nity) into manager list
Remove Button to remove the trap manager
Enable Link Change Trap Button to enable the switch to send a trap when any port link
changes
Enable Login Failure Trap Button to enable the switch to send a trap when any login failure is
detected
5.4.2 Port Controls
Port Settings Description
Port Specify the ports for the new settings.
More than one port can be configured at the same time. Use <Shift> key
and <Ctrl> key to specify multiple ports.
Port Function Enable port transmission function, options:
N - unchanged
Enable - enable the port function
Disable - disable the port function
Auto Negotiation Enable auto negotiation function, options:
Null - unchanged
Enable - enable the port auto-negotiation function
Disable - disable the port auto-negotiation function and use forced mode
-52-
Page 53

Speed Control Select port speed when auto-negotiation is disabled, options:
Null - unchanged
100M - 100Mbps
10M - 10Mbps
Duplex Control Select port duplex when auto-negotiation is disabled, options:
Null - unchanged
Full - full duplex
Half - half duplex
Apply Button to confirm the settings
The current port settings for all ports are also listed below the control dialog window .
5.4.3 VLAN Controls
VLAN settings are divided into three categories:
1. Global - Settings which are applied for the switch and not for specific ports
2. Group - Settings for VLAN groups
3. Per Port - Settings applied to each port
-53-
Page 54

Global Settings Description
VLAN
VLAN Select Enable VLAN - Enable switch VLAN function
Disable VLAN - disable switch VLAN function
Ingress Rules
802.1Q tag aware VLAN Enable - Under this mode, the switch will check the content of
every received packets. For 802.1Q tagged packets, the tagged
VID on the packet is used to look up the VLAN group table and
find the group whose VID matches the packet’s tagged VID.
Disable - Under this mode, the switch does not check the contents
of the received packets. The default VLAN group indexed by the
ingress port is used directly for further VLAN operation.
Ingress member filtering Mode Enable - Drop packet if the ingress port is not the member port of
the found VLAN group
Disable - ingress member filtering rule is not applied
VLAN Group Configuration
-54-
Page 55

Group Settings Description
Groups Specify the VLAN group for member port configuration
Port Specify the port to be added into or deleted from the specified group.
N - unchanged
Add - add the port into member port list of the group
Del - delete the port from member list of the group
Apply Button to confirm the settings
Group Settings Description
VLAN ID Current VLAN ID of each VLAN group
Settings Set new VLAN ID of VLAN group, valid values : 1 ~ 4095
? Button to view information about VLAN ID
Apply Button to confirm the settings
-55-
Page 56

Per Port Settings
-56-
Page 57

Per Port Settings Description
Port Select port list for configuration.
Ingress Rules
Default Group Index to the default VLAN group of the selected ports, group 1 ~ 8
Unmatched VID N - unchanged
Enable - Drop the tagged packet if the packet VID does not match the
ingress port PVID
Disable - No Unmatched VID filtering is applied to the port
Egress Rules
Egress tag rule This tagging rule is used to make change to the packet before it is trans-
mitted out from an egress port. Options are:
N - unchanged
1 Tagging with ingress PVID for all packets -
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress port
PVID as tag VID
Tagged packet : the packet tag VID is replaced with ingress port PVID
as new tag VID
2 Untagging for all packets -
Untagged packet : the packet is not modified
Tagged packet : the packet tag VID is removed and becomes an un-
tagged packet
Null VID packet : depending on next Null VID Replacement setting
3 Ingress PVID insertion for untagged packets only -
Untagged packet : the packet is inserted with the associated ingress port
PVID as tag VID
Tagged packet : the packet is not modified
4 No tag insertion and tag removal -
The packet is not modified at all. No tag insertion or tag removal are
performed for all packets.
Null VID The null VID of a Null VID packet will be replaced with the associated
ingress port’s PVID. This setting still works even Egress Tag rule : [PVID
insertion for untagged packets only] is selected.
N - unchanged
Enable - Null VID is replaced with Port’s PVID for Null VID packets
Disable - Null VID replacement rule is not applied.
? Button to view more information about the associated setting
Apply Button to confirm the settings
-57-
Page 58
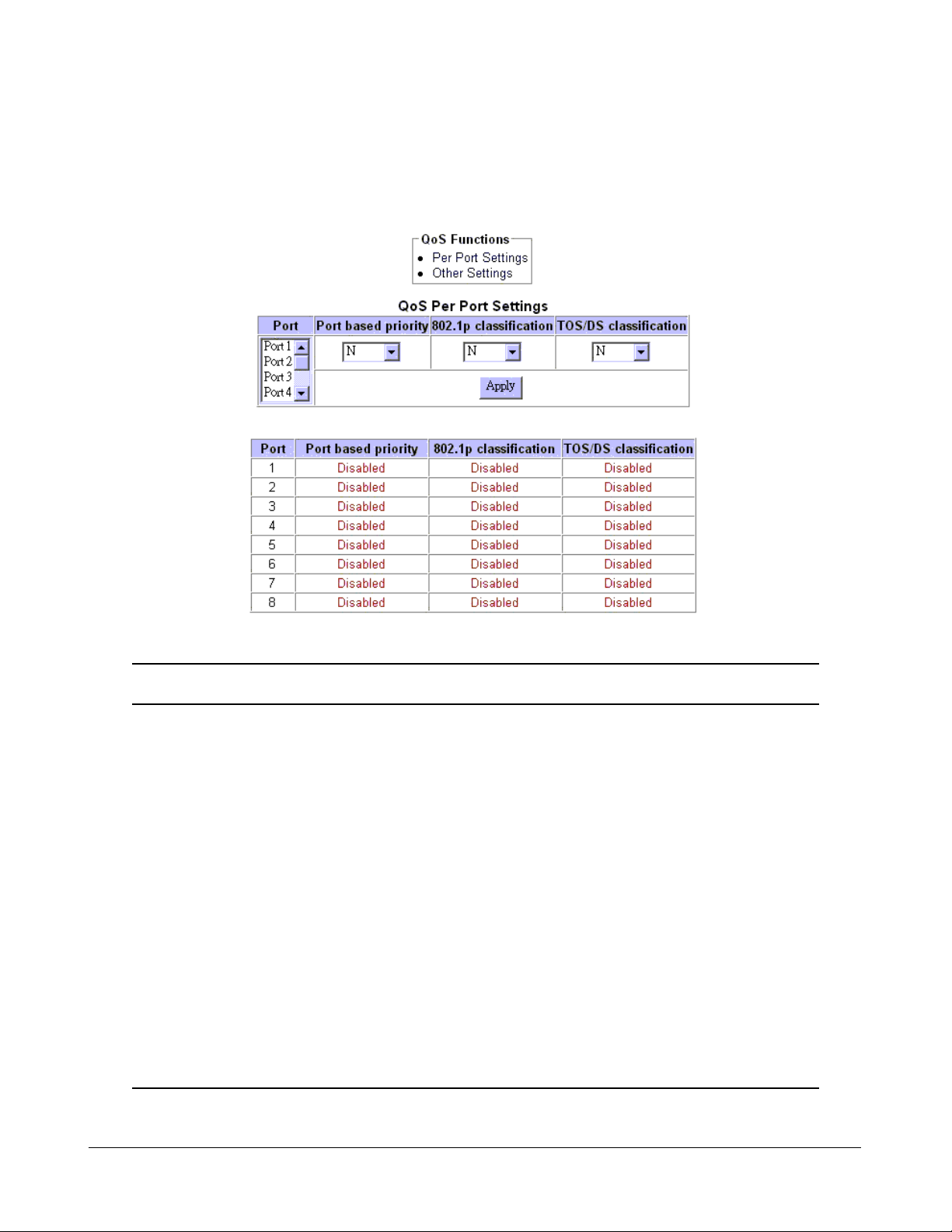
5.4.4 QoS Controls
QoS settings are divided into two categories:
1. Per Port Settings - QoS settings for each port
2. Other Settings - Some global QoS settings
QoS Per Port Settings Description
Port Select port list for the per port QoS configuration.
Port based priority Port based priority classification
Enable - All packets received on the port are classified as high priority
Disable - Port-based classification is not applied.
N - unchanged
802.1p classification Enable - Tagged packets received on the port are classified by comparing
the packet’s User Priority value and 802.1p High Priority Tag Setting.
Disable - 802.1p classification is not applied.
N - unchanged
TOS/DS classification Enable - If the packets DSCP value is one the default code point listed
below , the packet is classified as high priority . EF - <101 1 10>, AF <001010> <010010> <011010> <100010> and Network Control <11 1000> <110000>
Disable - Default DSCP classification is not applied.
N - unchanged
Apply Button to confirm settings.
-58-
Page 59

QoS Global Settings Description
802.1p high priority threshold 802.1p High Priority Tag Setting for 802.1p classification
Valid values : 0 - 7
Egress service policy W eighted Round Robin ratio:
4:1 - 4 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
8:1 - 8 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
16 :1 - 16 high priority packets then 1 low priority packet
Always high first - Packets in high priority queue are sent first
until the queue is empty
Specific DSCP(A) Enable - Enable user defined DSCP(A) checking
Disable - DSCP(A) classification is not applied.
Specific DSCP(A) Value Enter user defined DSCP(A) value for classification.
Specific DSCP(B) Enable - Enable user defined DSCP(B) checking
Disable - DSCP(B) classification is not applied.
Specific DSCP(B) Value Enter user defined DSCP(B) value for classification.
Specific IP & Mask (A) If a received IP packet’s source address or destination address
belongs to the user defined IP network addresses. The packet is
classified as high priority .
Enable - Enable user defined IP(A) network address checking
Disable - IP(A) classification is not applied.
Specific IP Address (A) Enter user defined IP(A) address for classification.
Specific Mask (A) Enter user defined IP(A) subnet mask for classification.
-59-
Page 60

IP(A) address and IP(A) subnet mask specify IP(A) user defined
IP network address for IP packet classification.
Specific IP & Mask (B) If a received IP packet’s source address or destination address
belongs to the user defined IP network addresses. The packet is
classified as high priority .
Enable - Enable user defined IP(B) network address checking
Disable - IP(B) classification is not applied.
Specific IP Address (B) Enter user defined IP(B) address for classification.
Specific Mask (B) Enter user defined IP(B) subnet mask for classification.
IP(B) address and IP(B) subnet mask specify IP(B) user defined
IP network address for IP packet classification.
Apply Button to confirm the settings
A received packet on an ingress port is classified as high priority if it meets one the following classifications:
1. The ingress port is enabled for port based high priority .
2. The ingress port is enabled for 802.1p classification and the packet is 802.1Q tagged with a tag
value equal to or higher than 802.1p high priority tag threshold setting.
3. The ingress port is enabled for Default TOS/DS classification and the packet is an IP packet
with DSCP value <1011 10>, <001010>, <010010>, <011010>, <100010>, <1 11000> or <1 10000>.
4. Specific DSCP(A) classification is enabled and the packet is an IP packet with DSCP value
matched Specific DSCP(A) setting.
5. Specific DSCP(B) classification is enabled and the packet is an IP packet with DSCP value
matched Specific DSCP(B) setting.
6. Specific IP & Mask (A) classification is enabled and the packet is an IP packet whose source or
destination address belong to the network address specified by Specific IP & Mask (A) settings.
7. Specific IP & Mask (B) classification is enabled and the packet is an IP packet whose source or
destination address belong to the network address specified by Specific IP & Mask (B) settings.
If none of above classifications is matched, the received packet is classified as low priority. It is
suggested to enable those classifications which are required for your application only and disable the
rest.
-60-
Page 61

5.4.5 Security Manager
This menu is used to change the user name and password. User name and password are used for
access login in telnet and web management interfaces of the switch.
Settings Description
User Name New user name
Assign/Change password New password
Reconfirm password Retype the new password
5.4.6 Image Refresh Time
The switch image shown in web pages is updated periodically to present the latest status. The default
time interval of refreshing the image is 20 seconds. It can be changed by clicking any of the time
buttons displayed. This is a run time setting and not a permanent setting.
-61-
Page 62
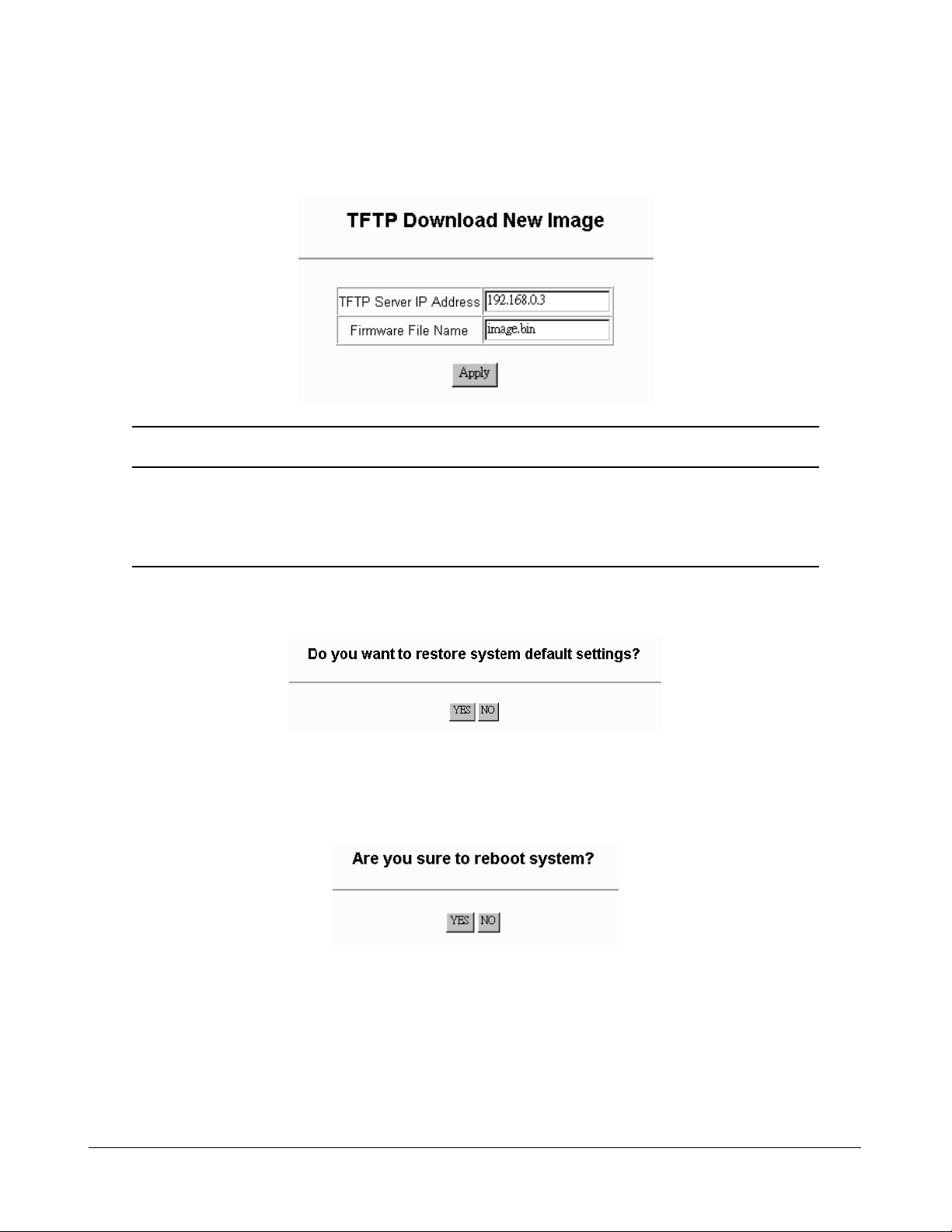
5.4.7 Update Firmware
This menu is used to perform firmware (switch software) upgrade via TFTP protocol. Before doing
TFTP operation, one TFTP server must be available in the network to where this switch is connected
and the new firmware file image.bin is placed in the server.
Settings Description
TFTP Server IP Address Specify the IP address of the TFTP server
Firmware File Name Specify the file name of the new firmware
Apply Button to confirm the settings
5.4.8 Restore Default
This menu is used to restore all settings of the switch with factory default values. Note that this menu
might change the current IP address of the switch and make your current http connection lost.
5.4.9 Reboot System
This menu is used to reboot the switch unit with current configuration remotely . Starting this menu will
make your current http connection lost. You must rebuild the connection to perform any management
operation to the unit.
-62-
Page 63
6. SNMP Management
The switch supports SNMP v1 protocol for SNMP management. One device MIB file is provided in
the product CD. The MIB file is used for SNMP management software to set or get the management
information objects provided in the switch.
6.1 MIB Objects
The device private management objects provided by the SNMP agent in the switch are:
Objects OID Description
Enterprise 867 Manufacturer ID
Device 37 Device ID (Snmp agent)
Software 867.37.1.1 Device firmware version
867.37.1.2 MIB version supported
Port Status 867.37.4.1 Port status information including:
Link, Auto-negotiation, speed, duplex
Port Control 867.37.4.2 Port control information including:
Port function, auto-negotiation, speed, duplex
VLAN 867.37.5 VLAN function related status and control objects
QoS 867.37.6 QoS function related status and control objects
6.2 SNMP Traps
In addition to the MIB, the switch also provides SNMP trap function for sending associated trap
messages to trap managers when the predefined events are detected. The following trap events are
supported:
Trap Event Description
Cold Start The switch is powered on and complete initialization
Login failure T elnet and web authentication failure
Port link change Any port link change among the switched ports
- Port link down to link up
- Port link up to link down
The Login failure trap and port link change trap can be disabled individually. The trap manager
settings must also be properly configured to make the trap function works. Refer to Trap Manager
menu in telnet management interface and Administrator->Basic menu in web management interface.
-63-
Page 64

Appendix. Factory Default Settings
IP Settings
IP Address 192.168.0.2
IP Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP 192.168.0.1
Security Manager Settings
User name admin
Password 123
SNMP Settings
System name Null
System location Null
System contact Null
Community string 1 Public, Access right - read only
Community string 2-4 Null
Trap manager 1-3 IP Null
Trap manager 1-3 Community Null
Login failure trap Enabled
Port link change trap Enabled
Port Control Settings
Port 1 - 8 Port function Enabled
Port 1 - 6 Auto-negotiation Enabled
Port 1 - 8 Port speed 100Mbps
Port 1 - 8 Port duplex Full
VLAN Settings
VLAN function Disabled
802.1Q tag aware VLAN Disabled
Ingress member filtering Disabled
VLAN group 1 member : P1 - P8, VID : 1
VLAN group 2 member : P2, VID : 2
VLAN group 3 member : P3, VID : 3
VLAN group 4 member : P4, VID : 4
-64-
Page 65

VLAN group 5 member : P5, VID : 5
VLAN group 6 member : P6, VID : 6
VLAN group 7 member : P7, VID : 7
VLAN group 8 member : P8, VID : 8
Default VLAN group index 1 (group 1) for Port 1 - Port 8
Unmatched VID Disabled for Port 1 - Port 8
Egress tag rule 4 for Port 1 - Port 8
Null VID replacement Disabled for Port 1 - Port 8
QoS Settings
Port based priority Disabled for Port 1 - Port 8
802.1p classification Disabled for Port 1 - Port 8
Default TOS/DS classification Disabled for Port 1 - Port 8
802.1p high priority threshold 4
Egress service policy 16:1
Specific DSCP (A) Disabled
Specific DSCP (A) setting 111111
Specific DSCP (B) Disabled
Specific DSCP (B) setting 111111
Specific IP & Mask (A) Disabled
Specific IP address (A) 255.255.255.255
Specific IP mask (A) 255.255.255.255
Specific IP & Mask (B) Disabled
Specific IP address (B) 255.255.255.255
Specific IP mask (B) 255.255.255.255
-65-
 Loading...
Loading...