Page 1

Installation Guide
Web Smart Managed
10/100 Fast Ethernet Switches
with VLAN Support
KS-1 15FM-V
KS-1 17FM-V
-1-
DOC.030430-KS115FM-V-KS117FM-V-K
Page 2

(C) 2002 KTI Networks Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make
any directive work (such as translation or transformation) without permission from KTI Networks Inc.
KTI Networks Inc. reserves the right to revise this documentation and to
make changes in content from time to time without obligation on the part
of KTI Networks Inc. to provide notification of such revision or change.
For more information, contact:
United States KTI Networks Inc.
P .O. BOX 631008
Houston, T exas 77263-1008
Phone: 713-2663891
Fax: 713-2663893
E-mail: kti@ktinet.com
WWW: http://www.ktinet.com/
International Fax: 886-2-26983873
E-mail: kti@ktinet.com.tw
WWW: http://www.ktinet.com.tw/
-2-
Page 3

The information contained in this document is subject to change without prior notice.
Copyright (C) All Rights Reserved.
TRADEMARKS
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corp.
This device complies with Class A Part 15 the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received including the interference that may cause.
CISPR A COMPLIANCE:
This device complies with EMC directive of the European Community and meets or exceeds the following technical standard.
EN 55022 - Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information
Technology Equipment. This device complies with CISPR Class A.
WARNING: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
CE NOTICE
Marking by the symbol indicates compliance of this equipment to the EMC directive of the
European Community. Such marking is indicative that this equipment meets or exceeds the following
technical standards:
EN 55022: Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference characteristics of Information
Technology Equipment.
EN 50082/1:Generic Immunity Standard -Part 1: Domestic Commercial and Light Industry.
EN 60555-2: Disturbances in supply systems caused by household appliances and similar electrical equipment - Part 2: Harmonics.
-3-
Page 4

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ..................................................................5
1.1 Features ...........................................................................................6
1.2 Specifications .................................................................................. 7
1.3 FX Port Optical Specifications.........................................................8
1.4 Management Specifications ............................................................9
2. Installing the Switches ...............................................10
2.1 Unpacking .....................................................................................10
2.2 Supply the Power ..........................................................................10
2.3 Port Configuration ......................................................................... 1 1
2.4 VLAN Function .............................................................................12
2.5 DHCP and IP Configuration........................................................... 15
2.6 Push Button IP SW ....................................................................... 15
2.7 Making UTP Connections ............................................................. 1 6
2. 8 Making Fiber Connection..............................................................17
2.9 LED Indications ............................................................................. 18
3. Web Management ......................................................19
3.1 Web Browser................................................................................. 19
3.2 Port Setup ...................................................................................... 2 2
3.3 IP Setup ......................................................................................... 2 3
3.4 VLAN Setup .................................................................................. 24
3.4.1 Port-based VLAN ....................................................................... 25
3.4.2 802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................. 27
.5 Password Setup...............................................................................30
3.6 Restore Default..............................................................................3 1
3.7 ReBoot Device...............................................................................32
3.8 About ............................................................................................ 33
Appendix: Factory Default V alues.................................34
Appendix: Effective Time of Setting Changes ..............34
-4-
Page 5
1. Introduction
This guide describes the specifications and installation instructions for
the following two managed 10/100 switch series:
KS-115FM-V series
• Four 10/100BASE-TX auto-negotiation TP switched ports
• One 100BASE-FX Fiber switch port
• Web-based device management support
• Compact Fast Ethernet switch
KS-117FM-V series
• Six 10/100BASE-TX auto-negotiation TP switched ports
• One 100BASE-FX Fiber switch port
• Web-based device management support
• Compact Fast Ethernet switch
-5-
Page 6

1.1 Features
• The 10/100BASE-TX switched ports support:
- Auto speed sensing for 100Mbps or 10Mbps connection
- Auto configuration for connected auto-negotiation devices
- Full-duplex or half-duplex operation
- Port configuration can be changed via web management interface
• The 100BASE-FX switched port supports:
- 100Mbps full duplex connection
- V ariety of fiber connectors such as ST , SC, MT-RJ, LC and VF-45
- Multimode and single mode fiber cables (model dependent)
• Provide the following switch functions:
- Self learning for active MAC addresses up to 2K entries
- Store and forward switching that only good packets are forwarded
- Forwarding and filtering at full wire speed
- Flow control for traffic congestion
- Broadcast packet storm protection
- Port-based VLAN function
- IEEE 802.1Q VLAN function
• Provide the following management functions:
- Web-base interface for easy management
- DHCP support for IP configuration
- Static IP configuration if DHCP is not available
- Port status and configuration
- VLAN configuration
- Security check for management login
- Restore factory default settings
- Remote boot
• Comprehensive LED indicators
-6-
Page 7
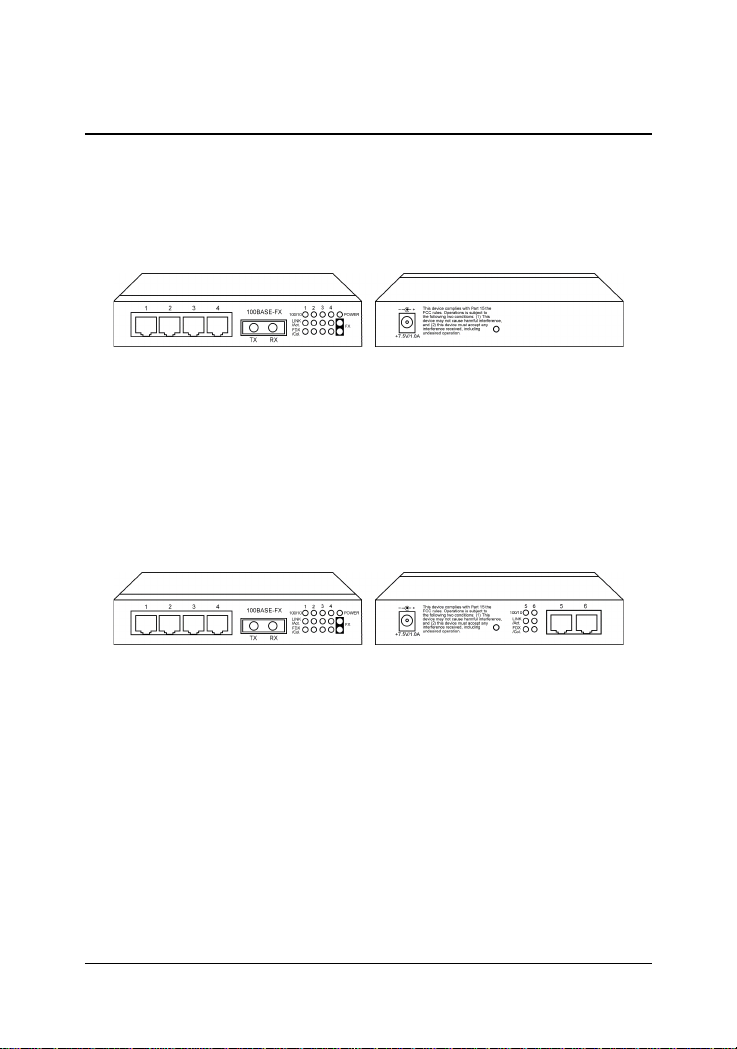
1.2 Specifications
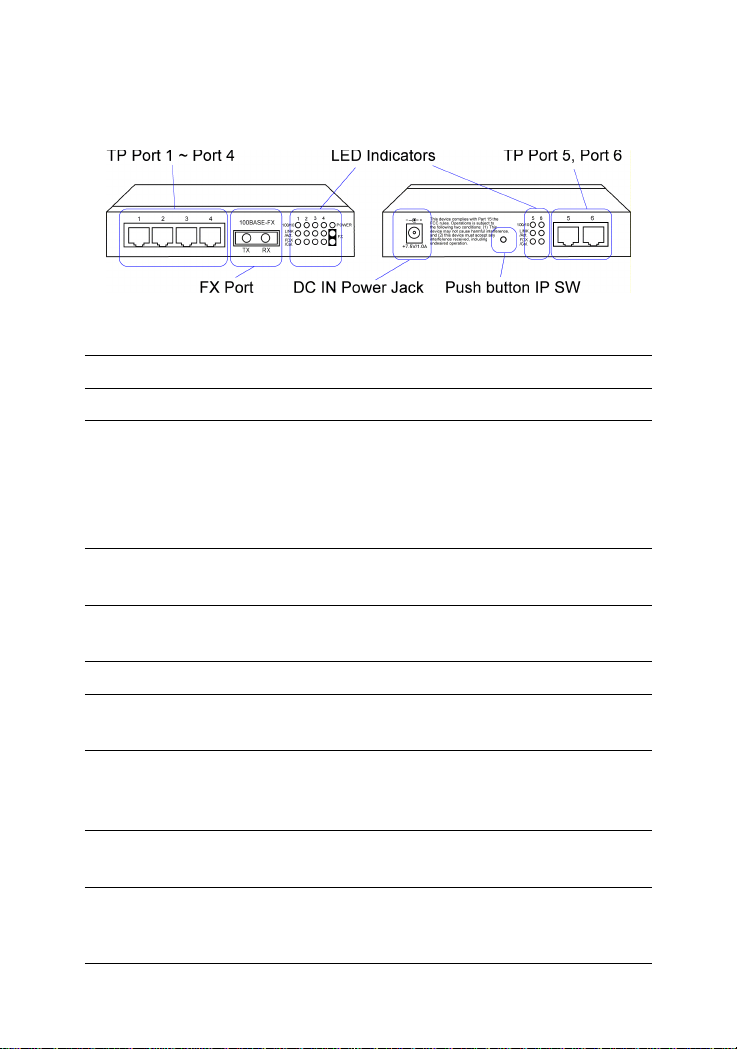
Figure : Major Components on Panels (Ex. KS-1 17FM-V)
KS-115FM P1-P4 Port 1 ~ Port 4 Twisted-pair switched ports (TP ports)
KS-117FM P1-P6 Port 1 ~ Port 6 Twisted-pair switched ports (TP ports)
TP Port IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T , IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX std.
Shielded RJ-45 jacks with Auto MDI-X detection
Auto-negotiation capable
Speed for 10Mbps or 100Mbps
Full-duplex or half-duplex support
FX Port IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-FX compliant
Fixed 100Mbps Full-duplex operation
Flow control IEEE 802.3x pause packet for full duplex operation
Back pressure for half duplex operation
Cables 10BASE-T Cat. 3, 4, 5 or higher (100 meters max.)
100BASE-TX Cat. 5, 5e or higher (100 meters max.)
100BASE-FX multimode or single mode fiber cable
LED indicators Power status
TP ports : Speed, Link/Activity , Duplex/Collision status
FX port : Link/Activity, Duplex/Collision status
Filtering rate 14,880 pps for Ethernet (10BASE-T)
148,800 pps for Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX)
Forwarding rate 14,880 pps for Ethernet (10BASE-T)
148,800 pps for Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX)
-7-
Page 8
Filtering address Multicast/Broadcast/Unicast address
MAC address 2K entries
Aging time 300 seconds
Priority levels 2 outgoing priority queues (Ratio: High/Low = 4/1 )
VLAN mode 1. Port-based VLAN 2. 802.1Q VLAN (T ag-based)
VLAN groups 16 groups (Group 0 ~ 15)
Port PVID Full 12-bit VID, per port setting
Port T ag Mode Tag/Untag mode, per port setting
Environment T emperature 0oC to 40oC
Relative humidity 10% to 90% non-condensing
Dimensions 144 mm x 100 mm x 26 mm (WxDxH)
5.67 x 3.94 x 1.02 inch
DC IN Power Rating +7.5V min. 1A
DC IN Jack D6.3mm D2.0mm
Operating voltage +6.5 ~ +12.5VDC (Device DC Input)
Power Consumption 7W max. (with power adapter)
1.3 FX Port Optical Specifications
Model Ext. Connector Wavelength Tx optical powerRx sensitivity
-VT MM*1 ST 1310nm -20 ~ -14dBm -31dBm
-VC MM S C 1310nm -20 ~ -14dBm -31dBm
-VJM MM MT-RJ 1310nm -20 ~ -14dBm -31dBm
-VVM MM VF-45 1310nm -20 ~ -14dBm -31dBm
-VL MM LC 1310nm -19 ~ -14dBm -34dBm
-VSA2 SM
*2
SC 1310nm -15 ~ - 8dBm -31dBm
*1 : Multimode fiber
*2 : Single Mode fiber
-8-
Page 9

1.4 Management Specifications
Interface In-band web browser for IE4.0 and Netscape4.x
Ping command, ARP command
Protocols IPv4, ARP , ICMP,UDP , TCP,DHCP client, Http server
IP Setting DHCP dynamic IP mode (default mode)
Static IP mode (default : 192.168.0.2)
DHCP DHCP client ID = Device modelname + MAC address
Security Login password checking
Password setting (default : 123)
Port All ports : port status monitoring
Monitoring Link, Speed, Duplex, Flow control status
Port Per TP port configuration settings
Control Auto-negotiation function : enable, disable
Speed : 100M, 10M
Duplex : full, half
VLAN VLAN mode selection: Port-based, 802.1Q (T ag-based)
Port-based 16 VLAN groups
VLAN Member ports setting for each group
PVID (12-bit VLAN ID value) setting for each port
802.1Q 16 VLAN groups
VLAN Member ports setting for each group
PVID (12-bit VLAN ID value) setting for each port
Tag/Untag mode setting for each port
Restore Restore factory default settings
Default Refer to Appendix for factory default settings
Reboot In-band remote boot the switch
-9-
Page 10
2. Installing the Switches
2.1 Unpacking
Check to see that you have everything before you start the installation.
• Installation guide
• The switch unit
• Rubber magnet stand
• One AC power adapter for the unit
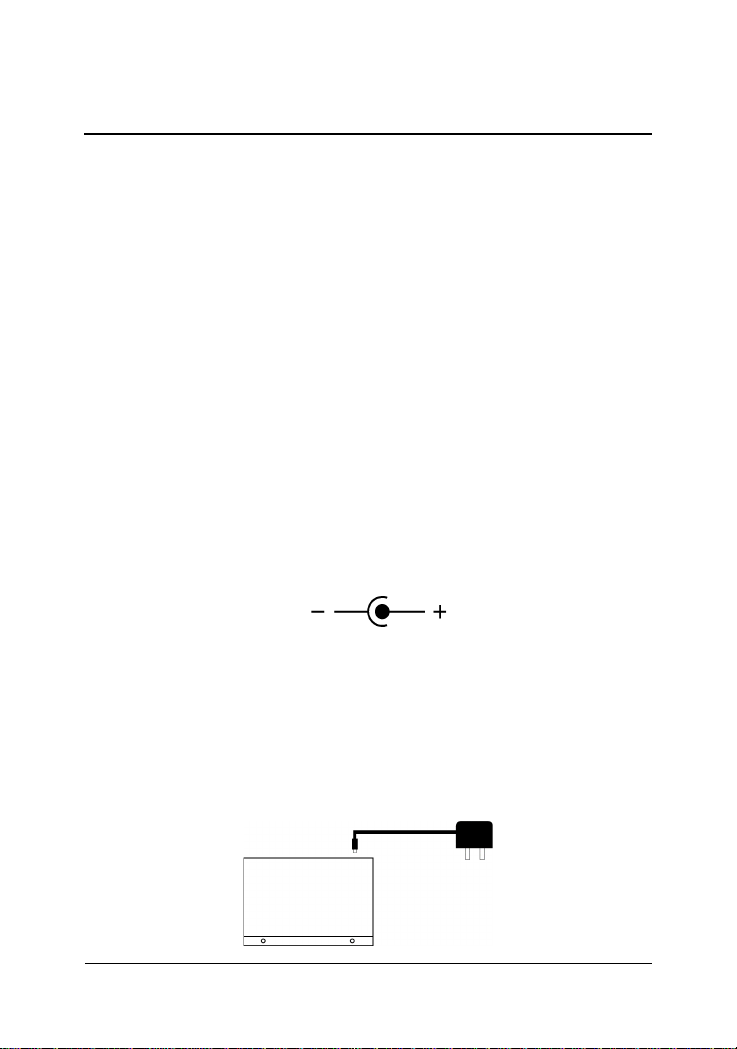
2.2 Supply the Power
Checking AC Power
Before you begin the installation, check the AC voltage of your area. The
AC power adapter which is used to supply the DC power for the unit should
have the AC voltage matching the commercial power voltage in your area.
The specifications of the AC power adapter are:
• AC input power: AC power voltage of your area
• DC output power: Rating +7.5V VDC min. 1.0A
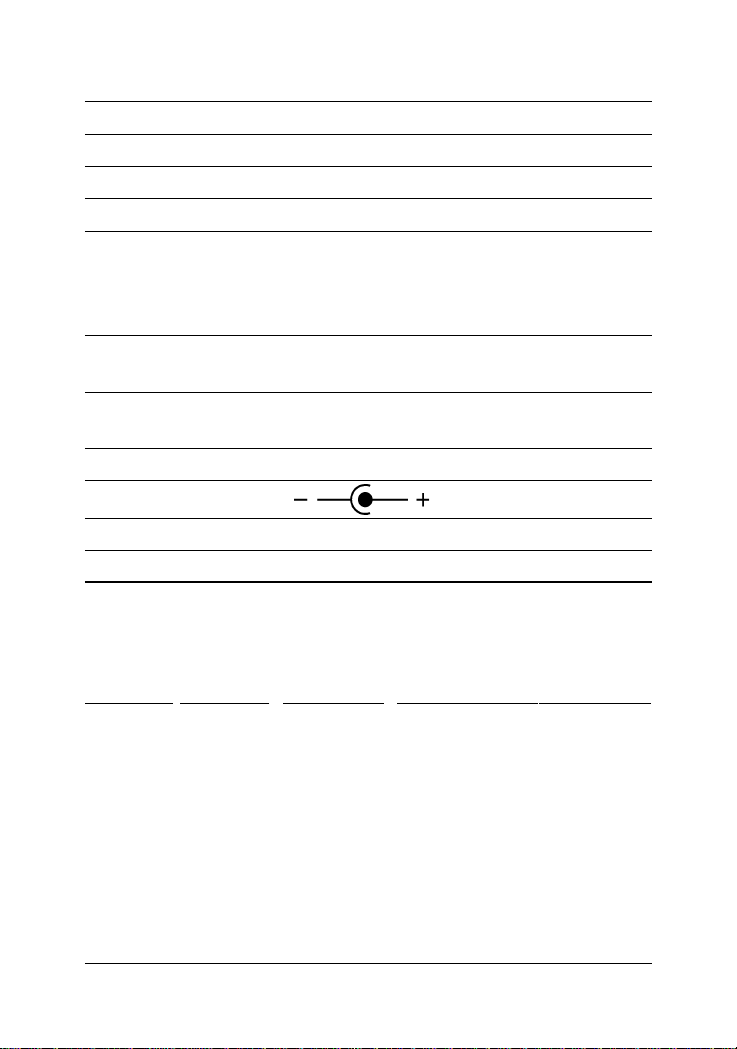
• DC plug type:
DC IN Jack
The DC power jack for the AC power adapter is located on the rear of the
switch. Refer to section 1.2 drawing.
Installing the Switch
1. Install the switch with the AC power adapter provided.
-10-
Page 11
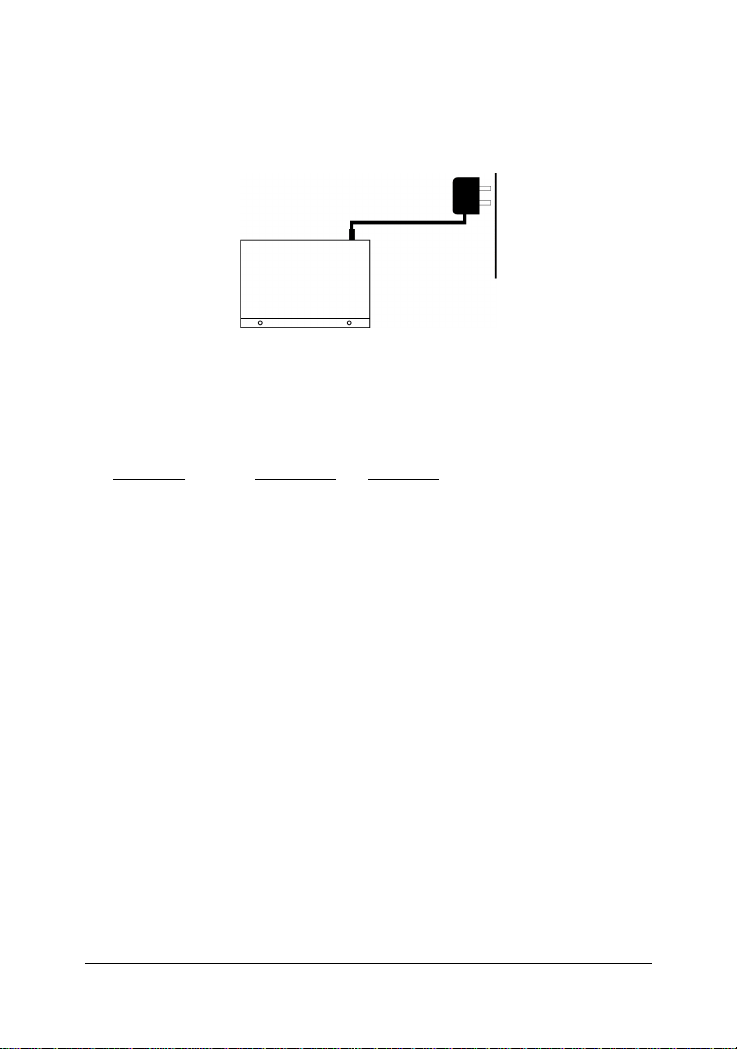
2. Connect the power adapter cable to the switch before connecting
the adapter to the AC outlet.
2.3 Port Configuration
The switches provide port configuration function through the management interface. The setting options are shown as follows:
Port Type TP PORTS FX PORT
Auto-negotiation Enable/Disable Not allowed
Speed options 100M / 10M Not allowed (fixed 100M)
Duplex options Full / Half Not allowed (fixed Full)
When auto-negotiation is enabled, the speed and duplex settings become the port highest ability used for auto-negotiation process. The
final configurations used with the connected device may be different
from the settings after negotiation between two devices. As auto-negotiation is disabled, the speed and duplex settings are the forced operating
configuration for the connection.
The real time port status for each port connection can be monitored
through the management interface. The status are:
Link Physical link status
Speed Connection speed used
Duplex Duplex mode used
Flow Control Flow control status after negotiation
-11-
Page 12

2.4 VLAN Function
The switches support two VLAN modes. One is Port-based VLAN and
the other is 802.1Q VLAN.
The following configuration are supported:
1. VLAN Mode : Port-based mode or 802.1Q mode
2. VLAN mapping table setup : member ports setup for each group
3. Per port PVID setup : PVID setting, T ag mode setting
Port-based VLAN Mode
1. This mode supports 16 VLAN groups, Group 0 ~ Group 15.
2. Packet forwarding is performed only among the member ports in
same group.
3. Every packet, tagged or untagged, is forwarded from input port to
output port transparently without any packet modification.
4. Per port PVID setting is used for index to VLAN Group table. When
a packet is received, the associated PVID setting of the input port is
used to map to one VLAN group in VLAN group table. The mapping
index is retrieved from the least 4 bits (bit 3~0) of the PVID value.
5. Tag mode settings are preset with untagged mode for all ports and
not changeable in Port-based VLAN mode.
6. VLAN tag in every input tagged packet is ignored.
Note:
To provide more flexibility for LAN administrator in performing web management task, the internal MNG port which connects to the built-in Http
server is disclosed for PVID configuration. The MNG port is also configured as the member port for all VLAN groups and untag port permanently.
-12-
Page 13

802.1Q VLAN Mode
1. This mode supports 16 VLAN groups, Group 0 ~ Group 15.
2. When an untagged packet is received, the associated PVID setting
of the input port is used to map to one VLAN group in VLAN group
table. The mapping index is retrieved from the least 4 bits (bit 3~0) of
the PVID value.
3. When a tagged packet is received, the VLAN ID value of the
received packet is used to map to one VLAN group in VLAN group
table. The mapping index is retrieved from the least 4 bits (bit 3~0) of
the VLAN ID value.
4. Packet forwarding is performed only among the member ports in
same group. If the input port of the received packet is not the
member port of the mapped group, the packet will be dropped.
5. For outbound, T ag mode of the output port is applied as follows:
Received untagged packet output to:
Tag port : The packet is inserted with PVID of the input port
as VLAN ID and new CRC.
Untag port : The packet is forwarded with no change.
Received tagged packet output to:
Tag port : The packet is forwarded with no change.
Untag port : The VID of the packet is removed and forwarded
with new CRC.
Note:
When VLAN mode is set from 802.1Q mode to Port-based mode, all ports
are set to Untag ports automatically .
-13-
Page 14

Summary of VLAN Group Lookup (Group Mapping Index)
Input Packet T ype Port-based VLAN Mode 802.1Q VLAN Mode
Untagged packet PVID bit3-0 of input port PVID bit3-0 of input port
Tagged packet PVID bit3-0 of input port VID bit3-0 of the packet
Factory Default Settings
VLAN Mode Port-based mode
VLAN Group 0 MNG port only (No user port)
VLAN Group 1 All user ports and MNG port
VLAN Group 2~15 No user port (MNG port only)
P V ID 1 for all ports and MNG port
T ag Mode Untagged for all ports and MNG port
-14-
Page 15

2.5 DHCP and IP Configuration
Each switch must be designated an IP address before it can be managed
from web browser. Basically, the switches provide two methods for IP
configuration:
1. DHCP mode
The switch requests a dynamic IP address from the first discovered
DHCP server in the network when boot up. In general, the assigned
IP can be monitored in the client list on the DHCP server. The model
name and MAC address of the switch is referred as the DHCP client
ID. If no DHCP server is discovered after a retry period for about 40
seconds, the pre-configured static IP is used automatically.
2. Static IP mode
One pre-configured IP address is used when DHCP mode is disabled
or when DHCP mode is enabled and no DHCP server is available.
The static IP can be configured through management interface. Each
switch comes with one identical factory default IP upon device
reception.
It is important to record the MAC address and location where it is installed for each switch. It would help in tracing the IP and device mapping.
2.6 Push Button IP SW
One push button IP SW located on rear panel is used to disable DHCP mode
and restore static IP back to factory default value. It is useful when you do
not recall your static IP setting and DHCP solution is not available.
T o make the function work, push the SW and keep for at least 5 seconds
when the switch is powered on to be boot up.
-15-
Page 16

2.7 Making UTP Connections
TP Port Configuration
Use management function to set the required TP port configuration. It is
recommended to set the highest ability for the TP ports as follows:
Auto-negotiation = enabled
Speed = 100M
Duplex = Full
This is appropriate to support connection to almost every Ethernet devices including those which are not auto-negotiation capable.
Cables
Depending on the connection speed, use the appropriate UTP cables for
the connections as follows:
Speed Cables used Distance
100M Cat. 5, 5e, or higher grade 100 meters
10 M Cat. 3, 4, 5, 5e, or higher grade 100 meters
Auto-MDI-X Function
An Auto-MDI-X function will automatically detect if a crossover is required and make the swap of Tx pair and Rx pair internally. With this
function, straight-through cable can be used for any connection. MDI to
MDI-X connection rule is not necessary anymore. In the switches, all TP
ports are equipped with this function. You can use just straight-through
type of cables for all your connections.
-16-
Page 17

2.8 Making Fiber Connection
For different fiber connections, several alternative models can be
selected for different fiber connections as follows:
Model Ext. Connector Cable Max. Distance
*
-T ST MM 2 K m
-C SC M M 2 Km
-JM MT-RJ MM 2 Km
-VM VF-45 MM 2 Km
-L LC MM 2 Km
-SA2 S C SM 2 0 Km
*: The maximum distance connecting to a full duplex device
The recommended multimode fiber is 62.5/125mm and 9/125mm for single
mode fiber. The following figure illustrates a connection example between two SC fiber ports:
-17-
Page 18

2.9 LED Indications
Functions
POWER : indicates the status of the power supplied to the switch.
100/10 : indicates the connection speed between the TP port
and the associated connected device.
LINK/Act. : indicates the port link and activity status
FDX/Col. : indicates the duplex mode and collision occurrences
The following table lists the LED states and the indications:
LED State Indication
POWER OFF No power is supplied to the device.
POWER O N Power is supplied to the device.
100/10 OFF 10Mbps is used.
100/10 ON 100Mbps is used.
LINK/Act. OFF No active cable link
LINK/Act. ON An active link is established.
LINK/Act. Blink Tx/Rx activities
FDX/Col O N Full duplex is used.
FDX/Col OFF Half duplex is used.
FDX/Col Blink Half duplex and collision occurrences
-18-
Page 19

3. Web Management
3.1 Web Browser
The system features an http server which can serve the management
requests coming from any web browser software over internet or intranet
network.
Web Browser
Compatible web browser software with JAV A support
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or later
Netscape Communicator 4.x or later
Start connection
Before the switch can be managed from a web browser software, the
switch IP address is required. Consult your LAN administrator if it is not
available. Start your browser software and enter the IP address of the
switch to which you want to connect. The IP address is used as URL for
the browser software to search the device.
URL : http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/
Factory default IP address : 192.168.0.2
When browser software connects to the switch unit successfully, a Login screen is provided for you to login to the device as follows:
-19-
Page 20

Enter your password and click [OK] to login into the switch. The switch
comes with factory default password : 123.
-20-
Page 21

The web page is shown as follows when a successful login is performed:
The left side shows the switch model and menu list. The list includes :
[Port Setup] : shows port status and port configuration setup
[IP Setup] : setup IP mode and related settings
[VLAN Setup] : setup VLAN related settings
[Password Setup] : change password
[Restore Default]: restore factory default settings for the switch
[ReBoot Device] : remote boot the switch
[About] : shows management software information
-21-
Page 22

3.2 Port Setup
The middle part of previous figure shows all port status of the connected
switch. The right side shows port configuration setup page.
Port Status
Port Status page displays the current port status. The status are:
Port Port number (FX : FX port)
Link Port link status, Up = link up, Down = link down
Speed Port speed, 100M = 100Mbps, 10M = 10Mbps
Duplex Duplex mode used, Full = full-duplex, Half = half-duplex
Flow Control Flow control status, enabled, disabled
Note:
The switch is featured with flow control enabled for all ports. However,
the flow control may be disabled after auto negotiation with the connected device, if the connected device does not have flow control ability.
Port Setup
This page is used to set the port configuration for each port. As autonegotiation function is enabled, speed and duplex settings specify the
highest port ability for negotiation process between the switch and the
auto-negotiation capable link partner. When auto-negotiation function
is disabled, speed and duplex settings specify the forced port configuration for the connection. Setup options are:
Auto-negotiation Enabled, disabled
Speed 100M = 100Mbps, 10M = 10Mbps
Duplex Full = full-duplex, Half = half-duplex
It is recommended to set auto-negotiation enabled in most of cases and
set it disabled only when connecting to an auto-negotiation incapable
full-duplex device.
[Apply] Click to make the setup effective immediately
-22-
Page 23

3.3 IP Setup
This page includes the following functions:
IP Status Display information of current IP used
If the current IP address is labeled (DHCP), it means the
IP is assigned by DHCP server.
IP Setup Set static IP address to be used when DHCP is disabled
or when no DHCP server is available.
DHCP Setup Enable to get and use dynamic IP address assigned by
DHCP server. Disable to use Static IP setting.
Any change or click [Apply] do not affect current management connection. They will be effective for next bootup.
-23-
Page 24

3.4 VLAN Setup
VLAN Mode Select
Port-based VLAN : Port-based VLAN
802.1Q base VLAN : IEEE 802.1Q T ag-based VLAN
Click [Apply] to make change effective immediately .
Note:
1. Both modes use same group member port settings and Port PVID
settings. When selecting Port-based VLAN, all ports are set to
Untag ports automatically .
2. Under Port-based VLAN mode, all packets are forwarded transpar-
ently with no packet modification.
-24-
Page 25

3.4.1 Port-based VLAN
Click [VLAN Mapping T able]
This page is used to setup member ports for each VLAN group. T otal of
16 VLAN groups are supported.
The steps to configure the member ports are:
1. Select Group number : 0 ~ 15.
2. Set [Yes] on the selected port to include it into the member port list.
Note:
One port can belong to more than one VLAN groups. VLAN group table
mapping index is based on the least four bits (bit 3 ~ bit 0) of the PVID of
the input port.
-25-
Page 26

Click [Port PVID Setting]
This page is used to setup PVID and Tag mode for each port as follows:
PVID : The setting value is used for VLAN group lookup index. When a
packet is received, the least four bits (bit 3~bit 0) of the PVID setting of
the input port is used as the index mapping to one VLAN group. The
mapped group is used for packet forwarding operation. The valid value
range is 1 ~ 4095.
Refer to section 2.4 for more information about the MNG port.
T ag Mode : T ag mode setting of each port is preset to Untag mode automatically and they are not changeable under Port-based VLAN mode.
-26-
Page 27

3.4.2 802.1Q VLAN
Click [VLAN Mapping T able]
This page is used to setup member ports for each VLAN group. T otal of
16 VLAN groups are supported. Actually, the table are shared by Portbased VLAN mode and 802.1Q VLAN mode.
The steps to configure the member ports are:
1. Select Group number : 0 ~ 15.
2. Set [Yes] on the selected port to include it into the member port list.
802.1Q VLAN group mapping is dependent on the received packet type:
Untagged packet - Use the least four bits of PVID value of the input port
T agged packet - Use the least four bits of the VID value of the packet
-27-
Page 28

Click [Port PVID Setting]
This page is used to setup PVID and Tag mode for each port as follows:
PVID : The valid value range is 1 ~ 4095. The setting value is used for the
following purposes:
1. It is used as VLAN group lookup index when an untagged packet is
received. The least four bits (bit 3~bit 0) of the PVID setting of the
input port is used for mapping to one VLAN group.
2. It is used to be inserted into the packet as VID when an untagged
packet is received and forwarded to a Tag port.
-28-
Page 29

Tag Mode : Setting for each port to be Tag port or Untag port for outbound.
Tag port - All output packets are tagged.
Untag port - All output packets are untagged.
Depending on the received packet type, the rules are applied as follows:
Received untagged packet output to:
Tag port : The packet is inserted with PVID of the input port
as VLAN ID and new CRC.
Untag port : The packet is forwarded with no change.
Received tagged packet output to:
Tag port : The packet is forwarded with no change.
Untag port : The VID of the packet is removed and forwarded
with new CRC.
Note:
1. When VLAN mode is switched from 802.1Q mode to Port-based
mode, the T ag mode settings for all ports are preset to Untag
automatically .
2. When VLAN mode is changed, current group member ports settings
and per port PVID settings are applied to new VLAN mode.
-29-
Page 30

.5 Password Setup
Password is used for checking authority for accessing the switch. To
change password setting, enter your new password and reconfirm the
input again.
Click [Apply] to apply the new password immediately.
-30-
Page 31

3.6 Restore Default
This command is used to restore all settings back to factory default
values. Click [Restore] to apply immediately . Refer to Appendix for factory default values.
-31-
Page 32

3.7 ReBoot Device
The command is used to reboot the switch remotely over the network.
Normally, it is used after IP settings are changed.
-32-
Page 33

3.8 About
About page shows switch model name and software version.
-33-
Page 34

Appendix: Factory Default Values
Settings Factory Default V alues
DHCP mode Enabled
Static IP address 192.168.0.2
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Default gateway IP 192.168.0.1
Login password 123
TP ports Auto-negotiation enabled
TP port speed 100M (the highest ability)
TP port duplex Full duplex (the highest ability)
VLAN mode Port-based VLAN enabled
802.1Q VLAN disabled
VLAN group table Group 0 - MNG port only
Group 1 - all user ports and MNG port
Group 2~15 - MNG port only
Port PVID 1 for all ports
T ag mode Untag for all ports
Appendix: Effective Time of Setting Changes
Settings Effective Time of Changes
DHCP Mode Next boot and permanently
Static IP Setup Next boot and permanently
Password Setup Immediately and permanently
TP Ports Setup Immediately and permanently
VLAN Mode Immediately and permanently
VLAN mapping table Immediately and permanently
Port PVID setup Immediately and permanently
Port T ag mode Setup Immediately and permanently
-34-
 Loading...
Loading...