Page 1

Safe-Drive™ Process
Refractometer PR-23-SD
Generation 1
Best Practices for PR-23-SD
with steam wash system
Page 2

Contents
Section 1 About This Document .......................................................................................................... 3
Section 2 Before Installation ................................................................................................................ 3
2.1 Installation Location Checklist ....................................................................................... 3
2.2 Component Checklist ..................................................................................................... 4
Section 3 Safety Requirements ............................................................................................................ 7
Section 4 Installation Process .............................................................................................................8
4.1 Spool piece assembly .................................................................................................... 8
4.2 Cutting Installation Opening for SDI Valve .................................................................... 9
4.3 Disassembling SDI Valve for Welding ......................................................................... 10
4.4 Welding SDI Valve in Place ..........................................................................................11
4.5 Reassembling SDI Valve ............................................................................................. 12
4.6 Installing Steam Prism Wash System .......................................................................... 14
4.7 Before Installing and Removing PR-23-SD Sensor .................................................... 17
4.8 Installing Sensor .......................................................................................................... 17
4.9 Box Flushing ................................................................................................................ 19
4.10 Removing Sensor ........................................................................................................ 21
4.11 Removing Wash Nozzle ............................................................................................... 23
4.12 Installing Wash Nozzle ................................................................................................ 25
4.13 Installing DTR Transmitter ........................................................................................... 26
Section 5 Commissioning SD Sensor System ................................................................................. 29
5.1 Prism Wash Test .......................................................................................................... 30
5.2 Calibration Check ........................................................................................................ 31
Section 6 Operating and Monitoring SD Sensor System ................................................................ 32
6.1 Preventive Maintenance Plan (PMP) ........................................................................... 32
6.2 Check Valve Maintenance ........................................................................................... 33
6.3 Resetting SD Sensor System ...................................................................................... 33
Section 7 Appendices .........................................................................................................................34
2
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 3

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer
PR-23-SD Generation 1
Best Practices
1 About This Document
This document is intended for individuals
installing, commissioning, operating, and/
or servicing the Safe-Drive™ Process
Refractometer PR-23-SD generation 1
model that has been manufactured in
years 2006–2013. The purpose of this
document is to provide a quick guide for
the abovementioned tasks in the form of
K-Patents recommended best practices.
This document in intended for PR-23-SD applications that have a steam wash system
(typical application for black liquor).
NOTE: These instructions are for quick reference only. For more thorough guidance, please
refer to K-Patents user manual and documentation.
2 Before Installation
2.1 Installation Location Checklist
Before the SD sensor system is installed, it is important to inspect the installation location
carefully for the following conditions:
●
Install the SD sensor system onto either vertical or horizontal pipeline. The
recommended ow rate is 0.4 m/s – 2 m/s (1.5 ft/s – 6 ft/s).
●
Mount the system at waist level. This is the natural and safe height for the system and
enables you to use the tools more ergonomically.
●
Leave a 1 m (approximately 3 ft) space around the installation for operating around the
SD sensor system. For the same reason, the steam connections should be installed
on the sides or back of the sensor system.
●
Recommended maximum ambient temperature of installation location is 45°C (120°F).
●
Avoid locations that are blocked by other piping and/or equipment, or require additional
tools, such as a ladder, to access the sensor. The installation location must be level,
rm, and free of clutter to provide safe and easy access to the system.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
3
Page 4

●
Use suitable type of steam for cleaning the prism. Dry saturated steam and 10-12 bar
(150-180 psi) are recommended.
●
Access to steam. The distance between the steam supply and the SD sensor system
should be considered for the length of steam piping.
●
Access to drain for steam trap condensate outlet.
●
Emergency shower and eye wash should be easily accessible. Water can also be used
for cleaning SDI valve lip seals and sensor after sensor removal.
●
Shut-off valve needs pressurized instrumentation air (5-10 bars / 70-150 psi).
●
Ensure connection to the power supply (110-230V AC).
If these conditions do not apply, please reconsider the intended location for your installation
or contact K-Patents.
2.2 Component Checklist
Before starting installation, make sure you have all the tools and components listed below.
NOTE: Components 4–6 are connected by union nipple or piping not included in
the delivery.
4
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 5
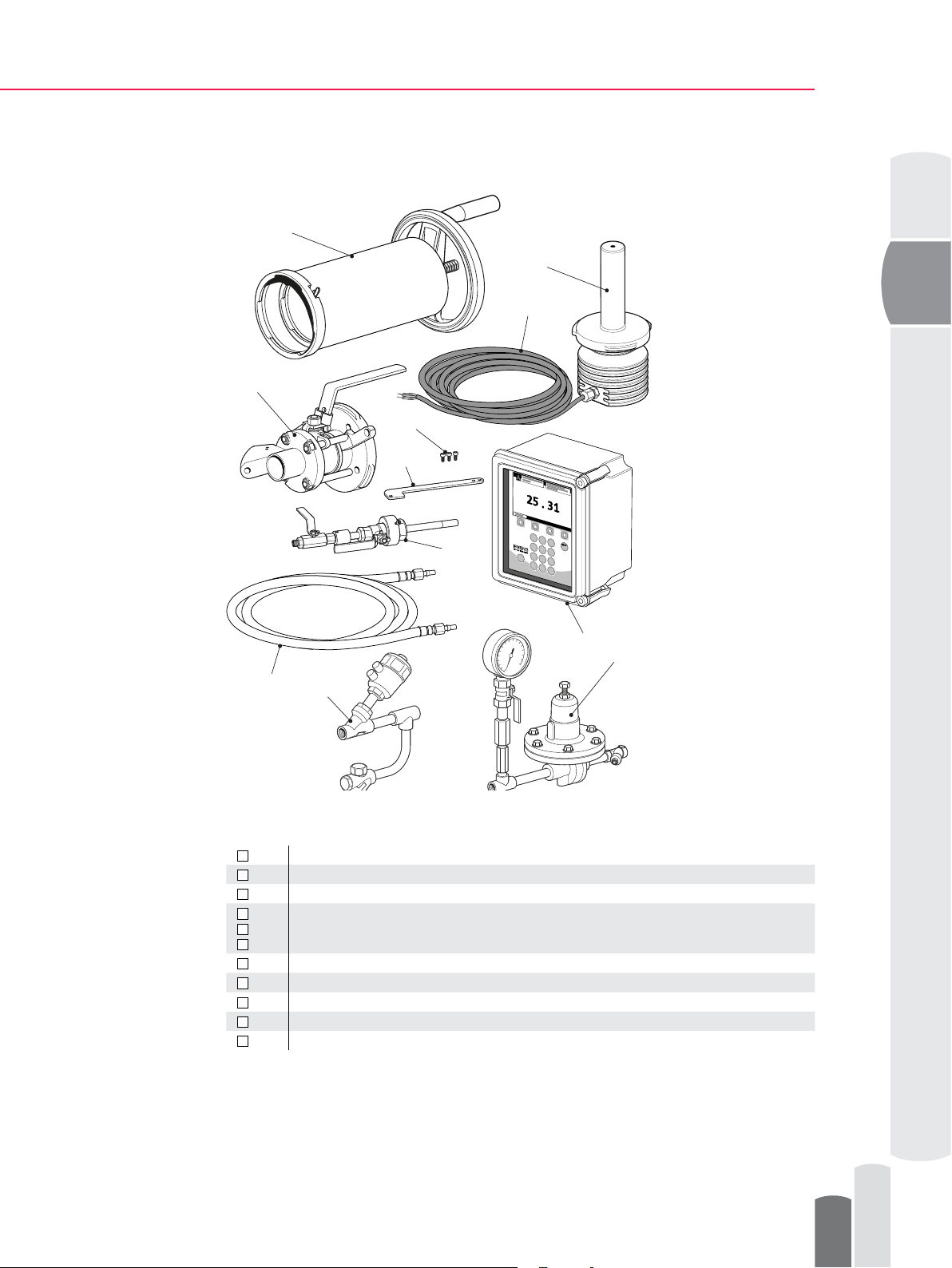
Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
- 0 .
BACK
ENTER
System components included in K-Patents delivery
3
1
7
2
3c
3b
3a
8
5
Figure 1 System components included in K-Patents delivery
1
2
3
3a
3b
3c
4
5
6
7
8
4
PR-23-SD sensor
SDI valve
Retractor tool
Prism wash nozzle assembly
Wash nozzle installation bolts
M5x8 DIN912 A4-70
Compressed air operated solenoid shut-off valve with steam trap
Steam connection hose
Pressure regulator with lter and gauge
Sensor connection cable
DTR transmitter
6
NOTE: If any of tools or components are missing, contact your supplier before
starting installation
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
5
Page 6
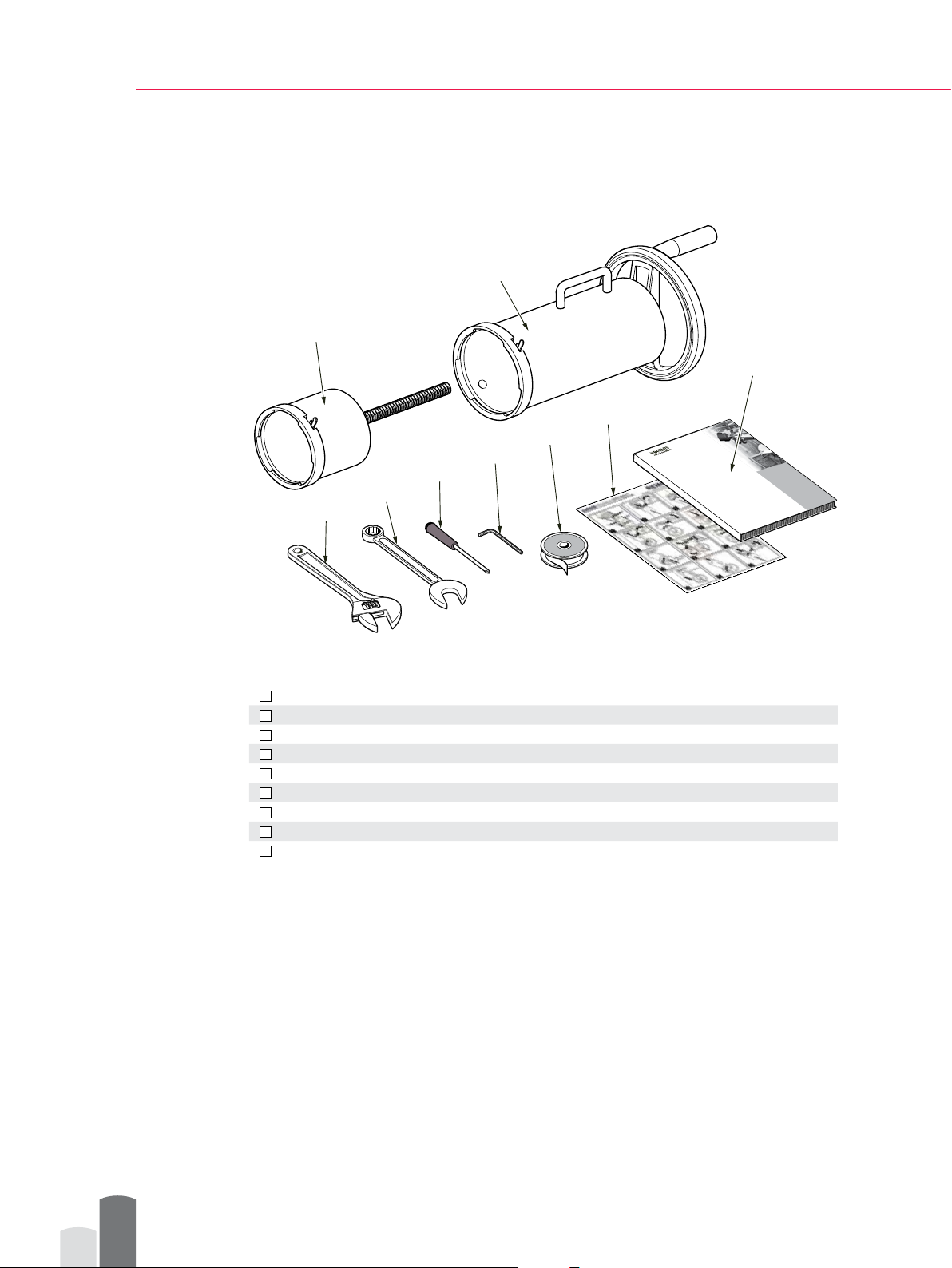
Installation Equipment
1
4
3
2
9
8
7
6
5
PROCESS
REFRACTOMETER
PR-23
Figure 2 Installation equipment
Retractor inner casing Supplied by K- Patents
1
Retractor outer casing Supplied by K- Patents
2
Adjustable wrench
3
Combination wrench, 19 mm / 3/4 in
4
Flat head screwdriver
5
Allen key 8 mm / 5/16 in
6
Thread seak tape
7
Sensor insertion / removal instruction card Supplied by K- Patents
8
Product user manual Supplied by K- Patents
9
NOTE: The material of the SDI valve body that is welded onto a process pipe is Duplex
steel SAF2205 (EN 1.4462, ASTM S32205/S31803). Choose the welding method and
ller accordingly.
K-Patents recommends complying with the applicable EN / ASTM standards.
3 Safety Requirements
These safety requirements must be followed at all times when installing, operating, or
servicing PR-23-SD sensor. These are the minimum safety requirements – your company
may require additional PPE (personal protective equipment).
For more information on safety issues, please see K-Patents Safety Instructions.
6
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 7

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
Figure 3 Safety symbols
WARNING: Watch out for hot steam and process pipes. Wear protective clothing as
instructed below to work safely.
●
Only authorized personnel can perform the tasks instructed in this document.
●
Long-sleeved safety clothing.
●
Safety glasses and/or goggles.
●
Hard hat or helmet.
●
Protective gloves.
●
Locate the nearest emergency shower and eye wash before starting the work.
●
Never operate the Safe-Drive™ Retractor alone.
●
Hard-cap safety boots.
4 Installation Process
For more thorough instructions, please refer to K-Patents user documentation or visit the
K-Patents website to see the instructional video (www.kpatents.com, PR-23-SD SafeDrive™ Operation Guide Video).
Installation of the SD sensor system consists of
●
Cutting pipe opening for SDI isolation valve.
●
Welding and assembling the SDI valve onto the processing piping.
●
Installing the steam prism wash system.
●
Installing the PR-23-SD sensor.
●
Installing the DTR transmitter.
4.1 Spool piece assembly
If the SDI valve was supplied pre-welded and assembled onto a pipe spool piece for
integration in existing piping on site, please skip ahead to installing prism wash.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
7
Page 8
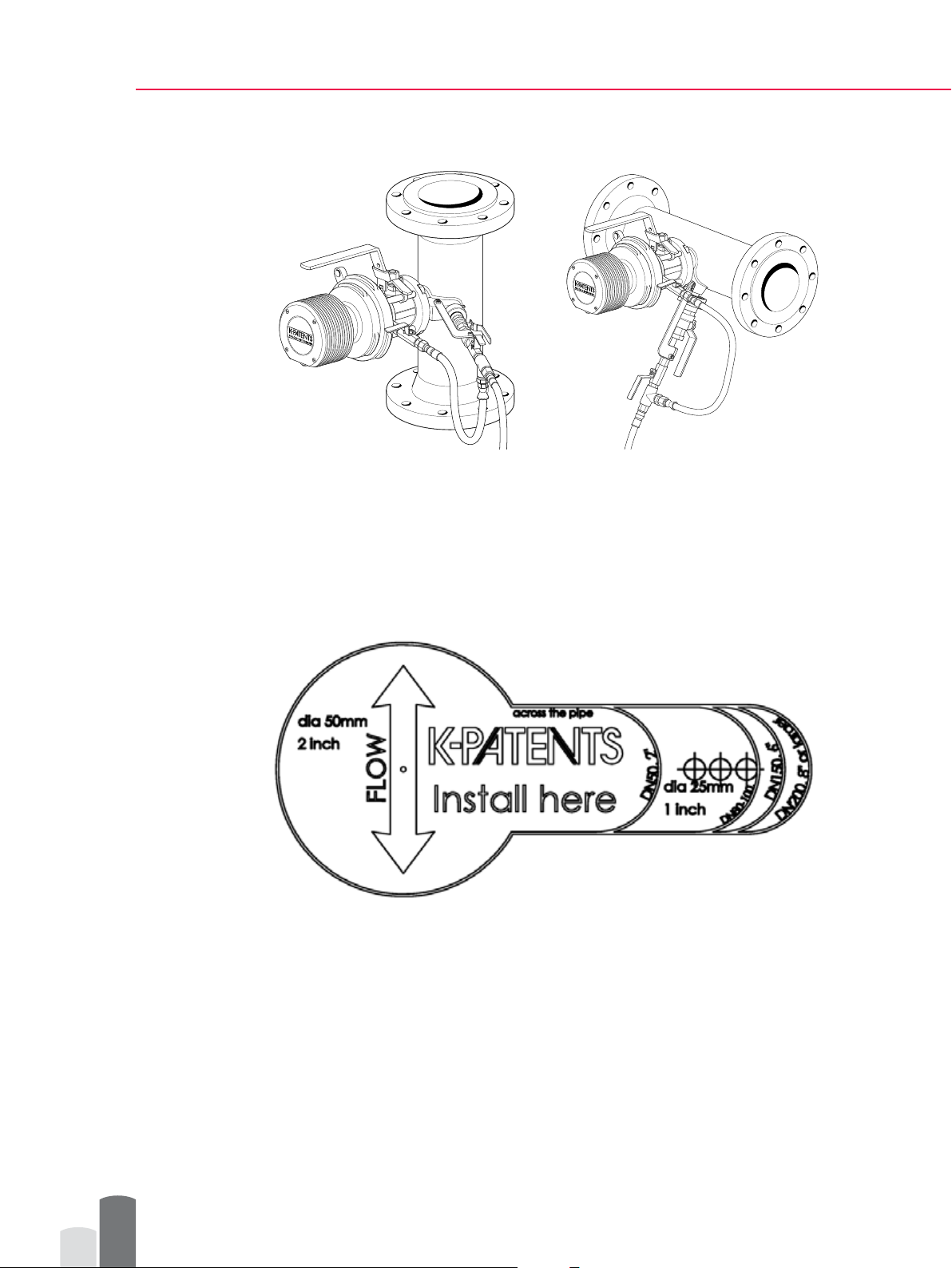
Figure 4 Vertical and horizontal spool piece assemblies
4.2 Cutting Installation Opening for SDI Valve
Use the installation guide sticker provided by K-Patents to determine the installation opening
shape and size suitable for your process pipe. If you do not have the guide sticker at hand,
please follow the instructions in the images below:
Figure 5 Installation guide sticker
NOTE: For larger pipes, use the same dimensions as for 24” (610 mm) pipes.
To cut the installation opening
1. Cut the installation guide sticker to match the pipe size.
2. Clean the surface of the pipe around the installation area and attach the sticker onto
the pipe.
8
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 9
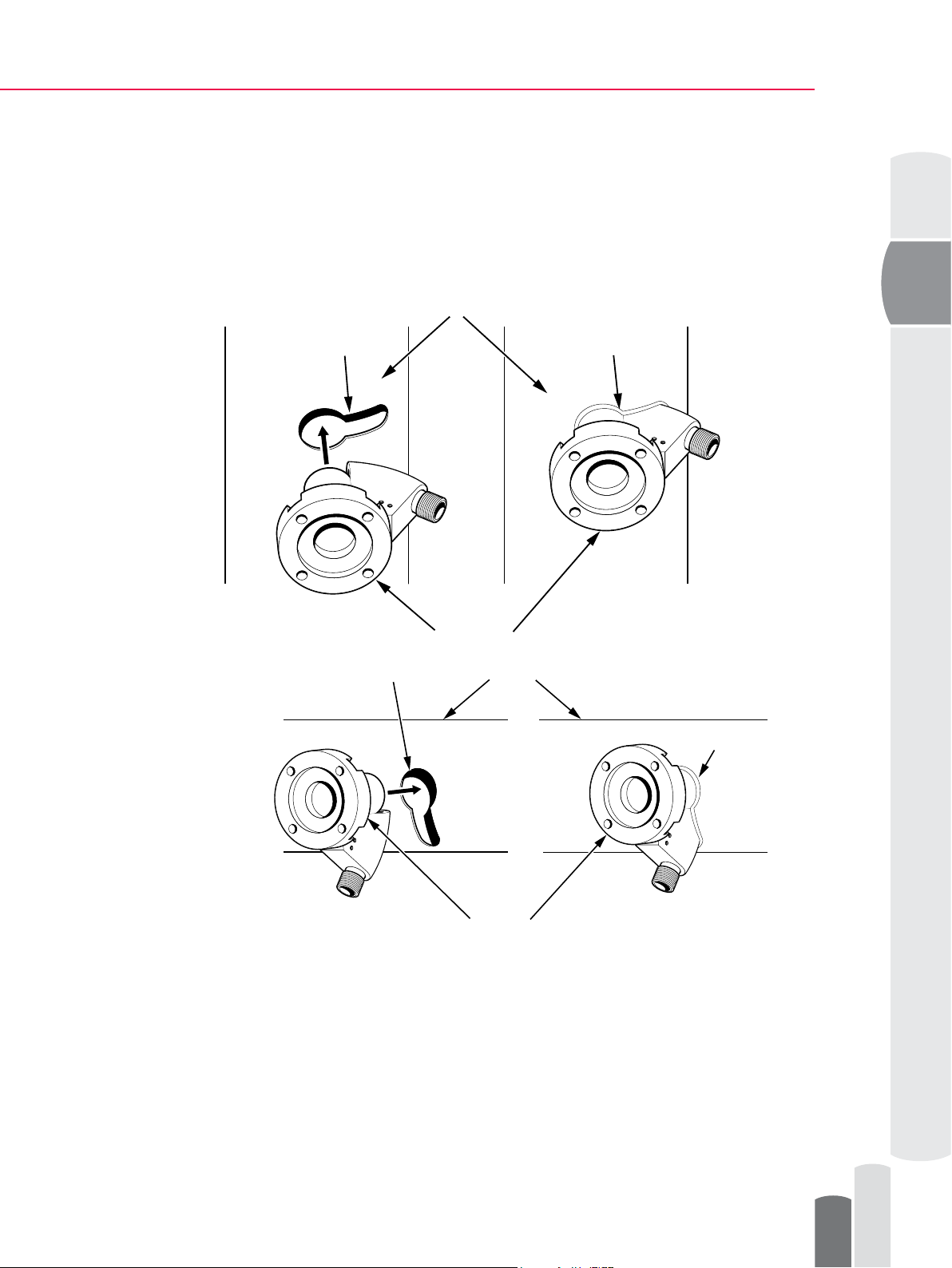
Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
NOTE: Make sure that the FLOW marker is parallel to the pipe and points to the correct
ow direction. On a horizontal pipe the nozzle points downwards and on a vertical pipe
it points to right. The SD sensor system must always be installed in horizontal position
and on the side of the pipe.
3. Drill two holes – 50 mm (2”) and 25 mm (1”) – as guided by the sticker.
4. Remove the bridge between the holes so that the opening is exactly the shape of
the sticker.
Process pipe
Cutout
Cutout
Safe Drive
mounting flange
Process pipe
Weld
Weld
Safe Drive
mounting flange
Figure 6 Installation on vertical and horizontal pipes
4.3 Disassembling SDI Valve for Welding
To avoid thermal damage to the isolation valve sealing, you must separate the valve body
from the valve assembly before it is welded onto the pipe.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
9
Page 10
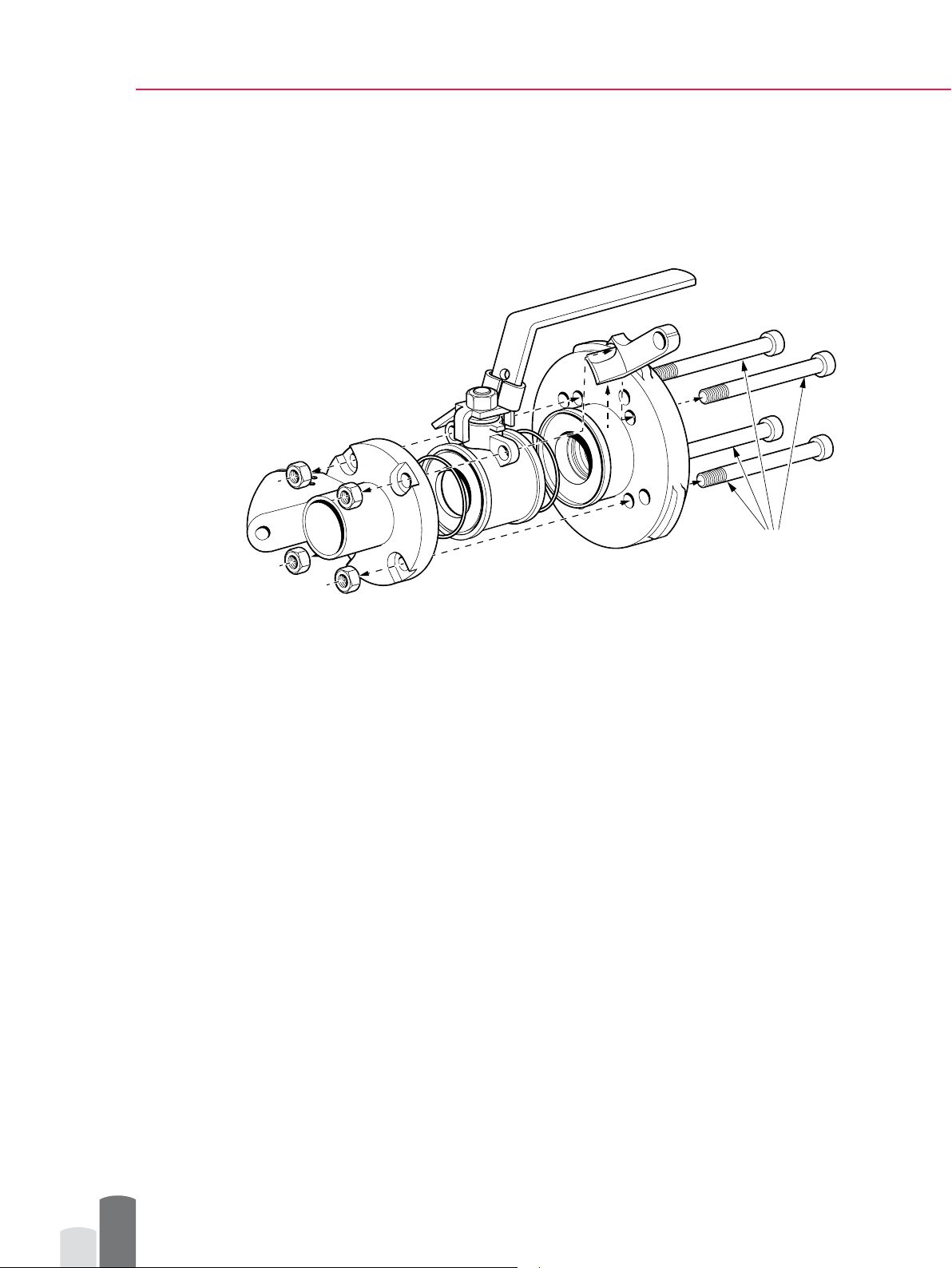
NOTE: Be very careful not to drop or lose any parts that come loose when separating the
body from the assembly.
To disassemble the SDI valve, open the four (4) M10 allen key bolts with an 8 mm (5/16”)
allen key (1).
1
Figure 7 Disassembling valve
4.4 Welding SDI Valve in Place
After you have disassembled the SDI valve, the valve body is welded onto the process pipe.
●
The material of the SDI valve body is Duplex steel SAF2205 (EN 1.4462, ASTM
S32205/S31803). Choose the welding method and ller accordingly.
●
See the attached drawings 2149 (MTG) and MTG472 for more detailed
welding instructions.
●
Follow all local requirements for welding.
●
K-Patents recommends complying with the applicable EN / ASTM standards.
●
Consider the materials and shapes of the welded objects when performing welding
pre-processing (tools, cleaning, preheating).
●
Consider the materials and shapes of the welded objects when performing welding
post-processing (postheating, fluxing).
10
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 11
Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
90°
NOTE!
Weld
The material
of the welded
parts is
Duplex steel
SAF2205
Process
pipe
Figure 8 Welding on vertical and horizontal pipes
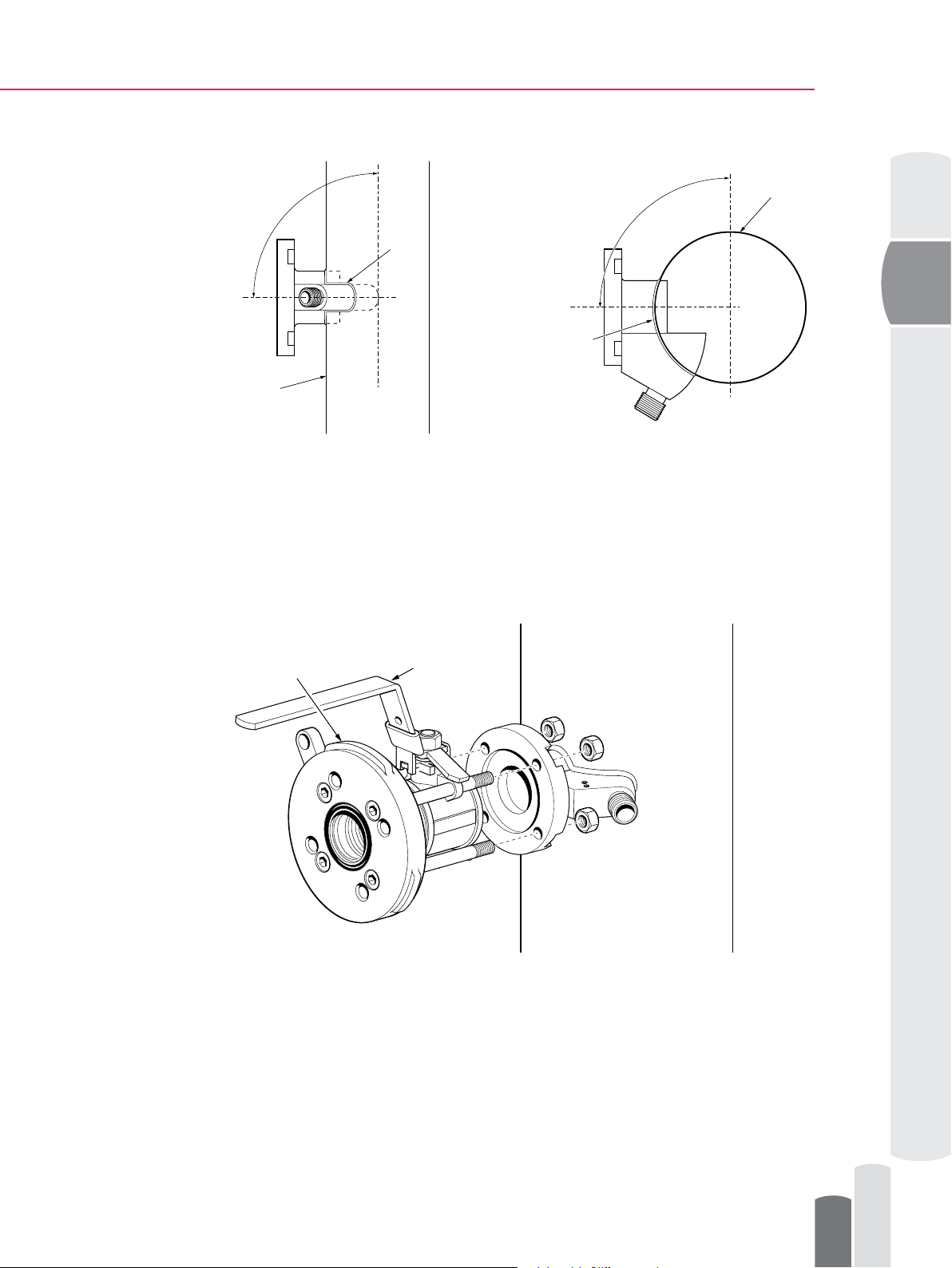
4.5 Reassembling SDI Valve
After the SDI valve body has been welded in place, reassemble the valve in reverse order.
Weld
90°
Process
pipe
NOTE: Make sure that the seals of the ball valve are propely aligned.
Widest bayonet lug
always positioned at top
Valve handle always
positioned at top
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
11
Page 12
Widest bayonet lug
always positioned at top
Figure 9 Reassembling valve on vertical and horizontal pipes
●
Make sure that the SDI valve handle and the largest bayonet connection are on top.
Valve handle always
positioned at top
Otherwise, you will not be able to insert the sensor in its place.
●
Tighten the bolts to a torque of 36 N-m (26 lb-ft) with an 8 mm (5/16”) allen key.
WARNING: Always shut the main steam valve before performing any work on the
wash nozzle.
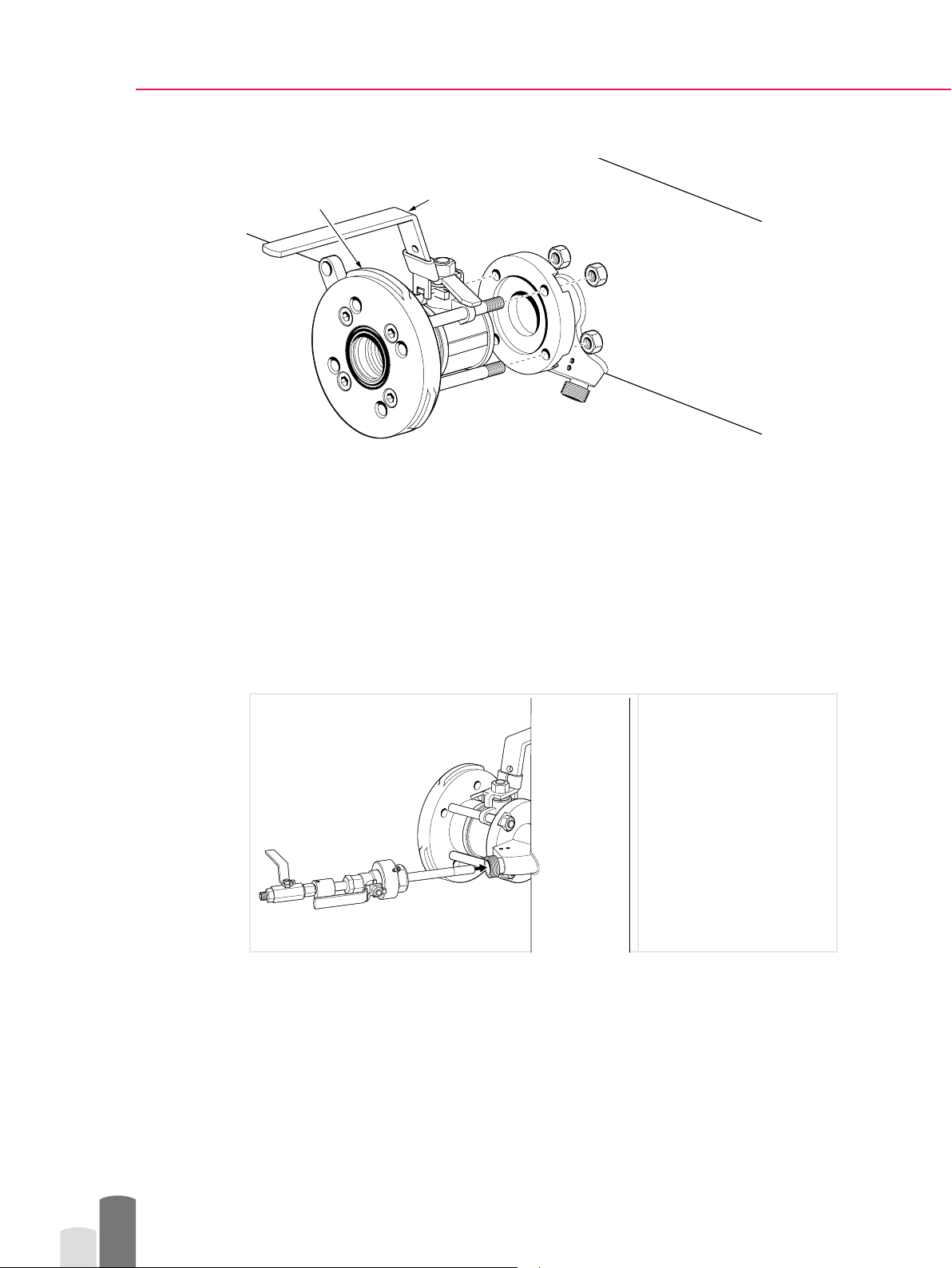
To reinstall the wash nozzle
assembly
1. Insert the wash nozzle
assembly to its place (1)..
1
12
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 13

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
2. Tighten the large nozzle
nut (1).
NOTE: Make sure the valve
orientation is correct.
5
6
4
<
3. Attach the safety cover
over the nozzle nut (2).
4. Tighten the safety cover
M5 Allen screw (3).
5. Attach the nozzle guide
plate (4).
2
6. Tighten the guide plate
with two (2) M5x10
3
1
screws to the welding
body (5).
7. Tighten the M5x8 screw
to nozzle (6)..
2
OPEN
1
4.6 Installing Steam Prism Wash System
In black liquor service material deposit, scaling or coating may occur on the prism surface.
To avoid this, you need to install an integral prism wash with steam that uses the retractable
nozzle included in the SDI valve.
Important Steam Prism Wash Considerations
●
The distance from the steam nozzle on the SDI valve to the steam shut-off valve
should be kept as short as possible to avoid condensate. The recommended length of
the distance is 0.6 m (2 ft) or less.
●
Separate or isolate the power to the solenoid from the power to the transmitter by
installing a safety switch. This enables the steam wash to be serviced without having
to power down the whole SD sensor system.
●
Pipe the steam trap properly to drain so that the trap is not blowing hot steam.
●
Steam piping upstream of shut-off valve is ½” or larger.
8. Attach the steam line (1).
9. Open the steam
connection (2).
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
13
Page 14

●
In addition to the SDI valve steam ttings, the following components must be included
in the steam wash installation:
●
steam shut-off valve
●
air-operated solenoid valve
●
steam trap
●
switch or terminal for power isolation
For K-Patents recommendations, please see K-Patents Steam Instructions.
●
OPTIONAL, in case of contaminants: To remove any contaminants within the
steam source, installing a steam strainer is recommended. See K-Patents list of
recommended accessories.
●
OPTIONAL, in case of excessive pressure: If the steam pressure exceeds to
maximum pressure differential, a pressure reducing valve (PRV) needs to be
installed to reduce the steam pressure to optimal design. See K-Patents list of
recommended accessories.
14
Figure 10 Mounting steam wash system
For more detailed information on steam-realted issues, please see K-Patents
Steam Instructions.
To install the wash system
1. Dene the wash setting values for the wash system:
●
steam source minimum and maximum pressures
●
wash time – the time one wash will last (seconds)
●
recovery time – the time after the wash has nished, before the measurement is
live data again (seconds)
●
interval – the time between washes (minutes)
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 15

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
Recommended steam prism wash settings
Minimum above
process pressure
Steam (SN) 5 bar (75 psi) 8 bar (115 psi) 3-5 s 20-30 s 20-30 min
Maximum above
process pressure
Wash time Recovery Interval
NOTE: Damage caused to prism by excessive pressure or washing is not covered by the
product warranty.
Choose the correct steam source pressure by comparing it to the process pressure.
The steam source pressure must be higher than process pressure to provide adequate
washing, but excessive pressure may also cause premature damage or etching of the
prism. Also, if the washing phase is programmed to last too long, the prism may wear
out prematurely.
2. Install the steam pipes in the SDI valve, as instructed below.
NOTE: All the necessary wash ttings are included in the valve.
3. Connect the steam wash system power supply.
For more information, please see K-Patents Steam Instructions.
Figure 11 Wiring steam wash system
For more information on controlling the prism wash cycle, please refer to chapter
Conguring relays in K-Patents user documentation.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
15
Page 16

4.7 Before Installing and Removing PR-23-SD Sensor
WARNING: Always use the Safe-Drive™ Retractor tool for inserting and removing the
sensor. Removing the sensor without the Retractor tool may cause a life-threatening
situation, if there is any pressure in the process pipe. Inserting or removing sensor without
Retractor tool may also cause damage to the lip seal. Always store the Retractor tool indoors
in a clean and dry location.
Successful sensor insertion and removal can only be guaranteed when the Retractor tool is
used and the instructions for insertion or removal are carefully followed.
NOTE: Check the Retractor tool visually before starting installation / removal process. Make
sure the handwheel rotates freely.
WARNING: If you detect leaking at any point of sensor installation or removal process,
revert immediately to the previous step in the process. Do not continue installation / removal
until the reason for leakage has been cleared and fixed.
Install and remove the sensor as instructed in the following chapters. For more thorough
instructions, please refer to K-Patents user documentation or visit the K-Patents website to
see the instructional video on inserting and removing the sensor (www.kpatents.com, PR-23SD Safe-Drive™ Operation Guide Video).
4.8 Installing Sensor
1
3
2
1
1
2
2
Before you start
●
check that the gaskets and gasket surfaces are clean
and undamaged
●
remove the sensor cable gland and unlock Inner casing
1. Insert the sensor to Inner casing so that the inner casing
latch is slightly to the left of top and sensor cable passage
is straight down.
2. When sensor ange is ush with the bottom of Inner
casing, turn Inner casing 1/6 turn clockwise to lock it to
the flange.
3. Push down the locking latch.
Put the Safe-Drive™ Retractor with sensor onto a table or
similar surface so that the hand wheel has space to turn.
1. Fit Outer casing over Inner casing so that the groove on
Inner casing matches the dot on Outer casing.
2. Turn the hand-wheel clockwise until it stops to draw the
sensor into the Retractor.
16
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 17

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
LIFT POINTS
Lift the Retractor (with sensor) handle up over the isolation
valve ange.
3
2
1
4
2
3
1
5
6
4 x M12
50Nm (37ft/lbs)
140 mm
(5.5")
1. Turn the Retractor a 1/6 turn to the right to lock
the bayonet.
2. Push down the latch on Outer casing.
1. Close the blow-out ball valve underneath the
isolation valve,
2. Lift up the isolation valve handle locking plate.
3. Open the isolation valve by turning the valve handle a
quarter turn to the right.
Turn the hand-wheel counterclockwise until it stops.
WARNING: If you detect leaking, revert immediately to the
previous step. Do not continue installation until the reason for
leakage has been cleared and xed.
Fit the four M12 nuts to the bolts holding the sensor to the
isolation valve and screw them on with a 19 mm or 3/4”
wrench.
7
B
2
3
1
90°
8
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
NOTE: Set the torque at 50 Nm.
A
1. Turn the wheel a quarter turn to the right.
2. Unlock the latch of the outer casing.
3. Turn the casing to the left until the handle is up on top.
17
Page 18

2
1. Turn the hand-wheel to the left to drop the thread.
2. Lift off Outer casing.
9
10
11
12
1
1. Lift up the latch of the inner casing to unlock.
1
2
2. Turn the casing a 1/6 turn to the left to release it from
the flange.
Lift Inner casing away from the sensor head.
1. Take off sensor nameplate and the gasket underneath.
2. Put interconnecting cable through the cable gland.
3
3. Connect the interconnecting cable to the sensor.
4. Screw the cable gland to the sensor.
4
2
1 & 5
5. Fit the gasket and nameplate onto the sensor and screw
the nameplate back on.
Turn on transmitter power to power up the SD sensor system.
4.9 Box Flushing
Carry out box ushing before sensor removal when the sensor has been in process for
several months. Box ushing removes dried process medium from isolation valve and
makes sensor removal easier.
WARNING: Do not activate box steam ush, if the sensor and the Retractor tool are not
installed to the isolation valve!
18
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 19

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
1. Close the 1/4” valve to
2
OPEN
1
CLOSE
the nozzle (1).
2. Open the 1/4” valve to
the box (2).
3. In the DTR transmitter,
go to MENU › SENSOR
STATUS and activate
wash by pressing
WASH button.
4
CLOSE
5
OPEN
Repeat the wash 3–5 times.
4. Close the 1/4” valve to
the box (4).
5. Open the 1/4” valve to
the nozzle (5).
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
19
Page 20

4.10 Removing Sensor
3
2
4
1
2
2
1 & 5
1
Switch off the DTR to cut off power from the sensor.
1. Remove the sensor nameplate and the gasket underneath.
2. Screw off the cable gland.
3. Disconnect the interconnecting cable
4. Remove the cable from sensor
5. Place gasket and nameplate on the sensor head and screw
the sensor nameplate back on.
NOTE: If another inline sensor is connected to the same DTR,
disconnect the loose cable from the DTR and turn power on
again.
1. Unlock the latch on Inner casing.
2. Lift Inner casing over the sensor head. Connect the casing
to the sensor ange bayonet.
1
2
the flange.
2. Lock the inner casing latch.
1. Turn the casing a 1/6 turn to the right to lock it onto
3
1
1. Grab Outer casing with one hand on the handle and the
other hand on the wheel. Fit Outer casing over Inner casing
and all the way to the isolation valve bayonet keeping the
handle upwards.
2. Rotate the hand wheel clockwise to get thread of the inner
4
2
2
casing running through the wheel.
1. Turn Outer casing a 1/6 turn to the right to lock it onto the
1
isolation valve.
2. Push down the outer casing latch.
5
20
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 21

6
Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
4 x M12
Open and remove the four M12 nuts on the bolts holding the
sensor to the isolation valve using a 19 mm or 3/4” wrench.
Turn the hand wheel clockwise until it stops to remove the
sensor from process.
1
140 mm
(5.5")
7
WARNING: If you detect leaking, revert immediately to the
previous step. Do not continue removal until the reason for
leakage has been cleared and xed.
1. Lift up the isolation valve handle locking plate.
2. Close the isolation valve on by turning the handle a quarter
turn to the left.
IM P O RTA NT: The isolation valve is properly closed
1
2
when the handle points away from the sensor and the
locking plate drops down over the handle.
3
3. Open the blow-out valve under the isolation valve.
Some process liquid should leak from the valve. If there is
none, the valve may be defective.
8
WARNING: Watch out for splashing!
4. Carry out box ushing to get rid of any process liquid
inside the isolation valve. See chapter 4.9 Box Flushing
for instructions.
1
2
9
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
1. Lift the outer casing locking latch.
2. Turn Outer casing a 1/6 turn to the left so that the handle
comes up on top.
21
Page 22

10
LIFT POINTS
Take a good grip on the hand wheel and the handle and pull
out the Safe-Drive™ Retractor with the sensor inside.
A rm hold of the tool is essential as the combination of the
tool and the sensor is noticeably heavier than Retractor alone.
NOTE: To ensure the isolation valve after the Safe-Drive tool
with the sensor have been removed, you can bolt a standard
ANSI 1.5” 105 lbs blind ange to it with 1/2” (M12) bolts and
nuts.
WARNING: The sensor tip is hot and may be covered with
liquor. It is recommended to rinse the sensor tip and the
isolation valve with hot water.
2
Put the Safe-Drive™ Retractor with sensor onto a table or
similar surface so that the hand wheel has space to turn.
1. Turn the wheel counterclockwise until the trapezoidal
thread is all the way inside the outer casing and loose from
the wheel.
2. Pull the outer casing off.
11
1
3
1. Open the latch on the inner casing.
1
2
2. Keep sensor steady with one hand and turn Inner casing
counterclockwise with the other hand to unlock Inner
casing from sensor.
3. Pull off the sensor.
12
4.11 Removing Wash Nozzle
Remove the wash nozzle as instructed in the following illustrations: For more thorough
instructions, please refer to K-Patents user documentation or visit the K-Patents website to
see the instructional video on inserting and removing the sensor (www.kpatents.com, PR-23SD Safe-Drive™ Operation Guide Video).
22
WARNING: Always shut the main steam valve before performing any work on the
wash nozzle.
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 23

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
1. Close the steam supply.
2. Close the 1/4” ball valve
(1).
3. Remove the incoming
steam pipe from the 1/4”
1
ball valve (2).
NOTE: Do not remove the
check valve!
2
3
4. Remove the nozzle guide
(3).
5. Loosen the nozzle nut
1/4 turn at time with a 22
mm / 7/8 in wrench until
you can pull the nozzle
about 150 mm / 6 in
outwards (1).
IM P O RTA NT: Do not open
the nozzle not for more than
2 turns.
6. Close the 3/8” ball valve
(2).
7. Loosen the nozzle nut
1
3
entirely (3).
NOTE: Only little process
liquid should ow from the
4
CLOSE
2
LOCK
nozzle. If process liquid
keeps on owing, the nozzle
isolation valve is damaged
and it is not safe to remove
the nozzle. Do not proceed
with nozzle removal.
8. Pull the nozzle out of the
isolation valve (4).
WARNING: The nozzle tip is
hot and may be covered with
liquor. It is recommended
to rinse the nozzle tip and
the isolation valve with hot
water.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
23
Page 24

4.12 Installing Wash Nozzle
Install the wash nozzle as instructed in the following illustrations: For more thorough
instructions, please refer to K-Patents user documentation or visit the K-Patents website to
see the instructional video on inserting and removing the sensor (www.kpatents.com, PR-23SD Safe-Drive™ Operation Guide Video).
WARNING: Always shut the main steam valve before performing any work on the
wash nozzle.
5
1
4
3
OPEN
Check the nozzle and valve
before installing the wash
nozzle. Use teon tape for
all thread connections.
1. Fasten the nozzle to the
3/8” isolation valve (1).
2. Tighten the nozzle nut
(2).
3. Carefully open the 3/8”
2
nozzle isolation valve (3).
NOTE: If process liquid is
LOCK
leaking severely, close the
isolation valve immediately
and do not proceed with
nozzle installation.
4. Push nozzle into the
process pipe (4).
5. Fasten the nozzle guide
(5).
6. Tighten up nozzle nut (2).
7. Attach steam pipe to 1/4”
2
<
ball valve (1).
8. Open the 1/4” ball valve
(2).
1
9. Open the steam supply.
24
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 25

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
4.13 Installing DTR Transmitter
The indicating transmitter DTR is a specialized computer designed to process data received
from one or two sensors. The transmitter consists of a protecting enclosure, a front panel, an
LCD display and a keyboard. Knockout padlock provisions are included for locks to prevent
unauthorized access.
Figure 12 DTR transmitter
●
DTR transmitter location:
●
easily accessible
●
well lit, but no direct sunlight
●
dry
●
ambient temperature range of the transmitter is 0 – 45 °C (32–113 °F)
●
free of vibration or other such disturbances
●
Consider the interconnecting cable length when choosing the installation location.
The standard delivery is 10 meter (33 feet) of cable and the maximum allowed
length is 200 meters (660 feet). You can use your own cable as long as it meets IEC
61158-2 type A standard requirements. For more information, please refer to chapter
Interconnecting cable specications in K-Patents user documentation.
●
Consider installing a drip shield to protect the transmitter from rain, sun and dust,
especially if the transmitter is installed outside.
WARNING: The transmitter does not have a built-in power switch so it is always powered
when connected to a power source. K-Patents recommends mounting an external power
switch to control the power supply.
To install the transmitter
1. Install the transmitter vertically on an upright surface (wall) using the four mounting feet,
preferably on the eye level of the user.
WARNING: Do not drill mounting holes in the enclosure. That would affect the
protection class of the enclosure and damage the electronics.
2. Connect the PR-23-SD sensor:
●
Remove the four (4) screws holding the sensor nameplate.
●
Connect the signal wires to terminals 1 and 2.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
25
Page 26

●
Connect the cable shield to terminal 3.
●
Tighten up the cable gland.
●
Screw the nameplate back on.
NOTE: To avoid damage from stray voltages and short-circuiting, always disconnect
the sensor cables from the transmitter before removing the sensor.
Figure 13 Sensor electrical connections
3. Open the front panel by loosening the front panel screw.
WARNING: Always check that the power is off before opening the front panel. If the
green power indicator light is on, there is still power in the system. To completely
turn off the power, unplug the power supply cord or use the external power switch
(if installed).
26
Figure 14 Opening transmitter front panel
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 27

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
4. Connect the primary AC power to a separate terminal strip in the lower right-hand
corner of the motherboard. The three terminals are marked 31/L, 32/N, and 33/
PE (protective earth), which is directly connected to the exposed metal parts if
the transmitter.
5. Connect the wiring wash relay to solenoid valve from the RELAYS terminals.
6. Connect the 4-20mA output.
Figure 15 Transmitter H1 and motherboard connections
H1
A 1 2 3 Connection for Sensor A, signal wires (1, 2), cable shield (3).
B 1 2 3 Connection for Sensor B, signal wires (1, 2), cable shield (3).
Motherboard
11 12
13 14
21 22 Relay 1, one contact output, max. 250 V AC, max. 3 A.
23 24 Relay 2, one contact output, max. 250 V AC, max. 3 A.
31 32 33
41 42
51 52 53
54 55
4–20 mA output 1, positive (11), negative (12), max. load 1000 Ohm, galvanically
isolated.
4–20 mA output 2, positive (13), negative (14), max. load 1000 Ohm, galvanically
isolated.
Power, L (31), N (32), protective earth (33), 100-240 V AC, 50– 60 Hz. An external
power switch is recommended.
24V terminal for DTR internal use only.
NOTE: Connecting terminal to external 24V supply will void warranty. Connecting
external devices to 24V terminal will void warranty.
Switch inputs: switch 1 (51), switch 2 (52), switch 3 (53), switch 4 (54) and common
(55). A voltage of 3 V DC is provided over each switch.
The switch terminals are galvanically isolated.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
27
Page 28

7. OPTIONAL: Setting up an Ethernet connection. Data can be downloaded from the
transmitter to a computer via an Ethernet connection. The Ethernet connector can be
found on the underside of the front panel.
Figure 16 Ethernet connection location
For more information on Ethernet connection, please refer to chapter Ethernet connection
specication in K-Patents user documentation.
5 Commissioning SD Sensor System
After installing the SDI valve, PR-23-SD sensor, and DTR transmitter, go through the
following check list to make sure the SD sensor system is functioning correctly.
For more thorough instructions, please refer to K-Patents user documentation or visit the
K-Patents website to see the instructional video (www.kpatents.com, PR-23-SD SafeDrive™ Operation Guide Video).
Commissioning checklist
Safe-Drive start-up
Tas k OK Failed Menu path Notes
Check that the wiring has
been done according to the
attached wiring diagram.
Connect the power.
Check that the status is
NORMAL OPER ATION
(if there is a sample)
NO SAMPLE
(if the process pipe is empty)
Check process temperatures.
Check the serial number.
Check that the parameters
are set
according to the delivery data
sheet (DDS).
CALIBRATION
› CHEMICAL
& FIELD
PARAMETERS
28
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 29

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
Congure the mA output. CALIBR ATION ›
Congure prism wash relay
(relay 1 or 2).
Prism wash test
Tas k OK Failed Notes
Observe the temperature
and optical image for slight
changes that indicate that
wash is functioning. One or
more of the following changes
should take place:
- nD value decreasing (most
apparent change)
- T value decreasing
- QF value decreasing or
increasing
Calibration check
Tas k OK Failed Notes
Check that calibration
corresponds to the lab results
OUTPUTS › mA
OUTPUTS
CALIBR ATION ›
RE L AYS
CALIBRATION
› CHEMICAL
& FIELD
PARAMETERS
› FIELD
PARAMETERS
For more information,
see chapter
Conguring mA
Outputs in K-Patents
PR-23 Instruction
Manual.
For more information,
see chapter
Conguring relays
in K-Patents PR-23
Instruction Manual.
For more information,
see chapter 5.1 Prism
Wash Test in these
instructions and
chapter Prism wash
in K-Patents PR-23
Instruction Manual.
For more information,
see chapter 5.2
Calibration Check in
these instructions and
chapter Calibrating
the concentration
measurement in
K-Patents PR-23
Instruction Manual.
5.1 Prism Wash Test
Prism wash system is essential for a fully functional refractometer. Regular testing of the
prism wash is highly recommended.
The curve should react to the wash and the temperature change slightly.
NOTE: Your transmitter may not look excatly like the image above during the wash. The
visible changes in the curve and the temperature depend on viscosity, steam pressure and
temperatures of solids and steam and also to your version of the software.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
29
Page 30

Figure 17 Changes in concentrations during succesful prism wash
5.2 Calibration Check
Extract 3-5 samples in a couple of days’ time. Results from these samples can be used as a
reference for calibration.
In case there are deviations from the lab results, check that washes are functioning correctly
(see Prism wash test in the commissioning checklist).
When comparing lab results if there is a consistent offset, perform a BIAS adjustment from
CALIBRATION menu. For more information, see chapter Calibrating the concentration
measurement in K-Patents PR-23 Instruction Manual.
30
Figure 18 BIAS
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 31

Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
If there is a need for frequent calibration, make sure that wash is functional and remove the
sensor to check visually that the prism is clean and has not been damaged. Re-install the
sensor and run complete eld calibration (see chapter Entering eld calibration parameters
in K-Patents PR-23 Instruction Manual). After this, contact your local supplier.
6 Operating and Monitoring SD Sensor System
The SD sensor system runs automatically and does not need to be separately operated. If
there are no alarming changes in the diagnostic values or no alarm messages, you do not
need to adjust the operation. The main task of the operator is to make sure that the washes
and steam connections are functioning as they should.
To rehearse the use of DTR transmitter, please visit demo.kpatents.net.
K-Patents recommends that all new users participate in K-Patents training before using
the product.
6.1 Preventive Maintenance Plan (PMP)
Preventive Maintenance Plan (PMP) should be adopted in order to prevent bigger
maintenance procedures. Here are the recommended tasks:
Tas k Weekly Annual Notes
Check the functionality of
diagnostics: X See the attached PMI checklist.
CONC (measurement value
of output)
CALC (chemical curve of
calibration)
TEMP (temperature)
QF (quality factor) Typically 30-100. If QF drops 20 units
LED (exposure time) Typically <30. If the LED value increases
HD HUM (internal humidity%
of sensor)
Check the functionality of
wash system.
Check the steam pressure.
Remove the sensor and
check the prism visually for
dirt and wear. X
Inspect the check valve: clean
the small holes and see that
the valve sealing is intact.
X
X
X
This value should be closely monitored
daily for a week to set the default reading
for weekly inspections
This is the default reading from the
chemical curve concentration reading set in
calibration, to which you can compare the
CONC values to.
Process temperature.
below the normal level, perform a prism
wash test (see Commissioning checklist).
signicantly, perform a prism wash test
(see Commissioning checklist).
If HUM HD rises above 50%, the system
issues an alarm to replace the desiccant.
For more information, see K-Patents PR-23
Instruction Manual.
See Prism wash test in Commissioning
checklist.
Typically 5- 6 bar (75-9 0 psi) over process
pressure.
If the prism looks worn, run an nD
verication and replace the prism,
if needed. For more information on
nD verication, see K-Patents PR-23
Instruction Manual
Replace the check valve every 2 years. For
more information, see chapter 6.3 Check
Valve Maintenance.
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
31
Page 32

Clean the lter in the steam
connection line.
Verify calibration. Do this as often as your own quality system
Please use the attached Preventive Maintenance Inspection (PMI) Checklist for recording
the weekly preventive maintenance tasks.
X
6.2 Check Valve Maintenance
Check valve is one of the few moving parts in the wash system. Checking the valve sealing
and cleaning the small holes in case of dirt particles annually is essential.
Figure 19 Taking check valve apart for maintenance
6.3 Resetting SD Sensor System
If the SD sensor system needs to be reset, you can either
●
Switch the power off and back on again,
●
Restart the sensor through transmitter from MENU › SENSOR STATUS › SLOPE ›
SENSOR RESTART or
●
Press the reset button, as instructed below.
and local requirements demand.
32
1. Open the DTR transmitter front panel.
2. Press the reset button on the inside of the front panel using a thin stick or a similar tool.
The display will black out for a few seconds. The SD sensor system will be back up in
operation within 30 seconds.
Figure 20 Reset button
Document/Revision No. BP-EN-SDGEN1 1.0 Effective: April 1, 2013
Page 33

7 Appendices
Preventive Maintenance Inspection Weeklr Checklist
Data Sheets for Accessories
Welding diagrams
Installation diagrams (MTG DIM)
Wiring Diagrams (WRG)
Safe-Drive™ Process Refractometer PR-23-SD Best Practices, Generation 1
© Copyright K-Patents 2013. All rights reserved.
33
Page 34

Preventive Maintenance Inspection
Weekly Checklist
Date CONC CALC TEMP QF LED HD
HUM
Steam Wash
Y/N
Checked
by
Page 35

Page 36

Page 37

www.kpatents.com
K-Patents Oy
P.O. Box 77
FI-01511 Vantaa, Finland
Tel: +358 207 291 570
Fax: +358 207 291 577
Email: info@kpatents.com
K-Patents, Inc.
1804 Centre Point Circle, Suite 106
Naperville, IL 60563, USA
Tel: (630) 955 1545
Fax: (630) 955 1585
Email: info@kpatents-usa.com
 Loading...
Loading...