Kortek KT-1982F, KT-1982 Series Service Manual

KT-1982F
COLOR MONITOR
SERVICE
MANUAL
1. PRECAUTIONS -------------------------------------------------- 2
2. PRODUCT SPECIFICATION -------------------------------- 5
3. OPERATING INSTRUCTION -------------------------------- 8
4. ADJUSTMENTS ------------------------------------------------- 10
5. TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE ---------------------------- 18
6. BLOCK DIAGRAM --------------------------------------------- 28
7. CONNECTING DIAGRAM ----------------------------------- 29
CONTENTS

- 2 -
1-1. Safety precautions
Warnings :
Service should not be attempted by anyone unfamiliar with the
necessary on this Monitor.
The followings are the necessary precautions to be observed before servicing.
1) For continued safety, do not attempt to modify the circuit board.
2) Disconnect the AC power before servicing.
3) When the chassis is operating, semiconductor heat sinks are potential
shock hazards.
1-1-1 Servicing the high voltage volume are CRT Warnings
A High Voltage volum e replaced in the wrong direction may cause excessive
X-Ray emissions.
1) Adjust in order to 26KV with signal at Anode.
2) When the troubleshooting a monitor with excessively High Voltage, avoid
being unnecessarily close to the monitor. Do not operate the monitor for
longer than is necessary to locate the cause of excessive voltage.
3) Excessive High Voltage can produce potentially hazardous X-Ray RADIATION. To avoid such hazards, the high voltage m ust be above the
specified lim it. The nominal value of the High voltage of this Monitor is
26KV±0.3KV at zero beam current(m inimum brightness) under a 120V
AC power source. The High Voltage must not (under any circum stances)
exceed 29KV. Each tim e a monitor requires servicing, the High Voltage
should be checked following the High Voltage check procedure on this
manual. It is recommended the reading of the voltage be recorded as a
part of the service record. It is im portant to use an accurate and reliable
High Voltage meter.
4) When the High Voltage regulator is operating properly, there is no possibility of an X-Ray problem.
5) The CRT is especially designed to prohibit X-ray emission. To ensure
continued X-ray protection, replace the CRT only with one that is the
sam e or equivalent type as the original.
6) Handle the CRT only when wearing shatterproof goggles and after completely.
7) Do not lift the CRT by the neck.
1.Precautions
- 3 -
1-1-2. Fire and Shock Hazard
Before returning the monitor to the user,perform the following safety checks:
1) Inspect each lead dress to make certain that the leads are not pinched or
that hardware is not lodged between the chassis and other metal parts
in the monitor.
2) Inspect all protective devices such as nonm etallic control knobs, insulating
materials, cabinet backs, adjustment and com partment cover or shields
isolation resistor-capacitor networks, m echanical insulations, etc.
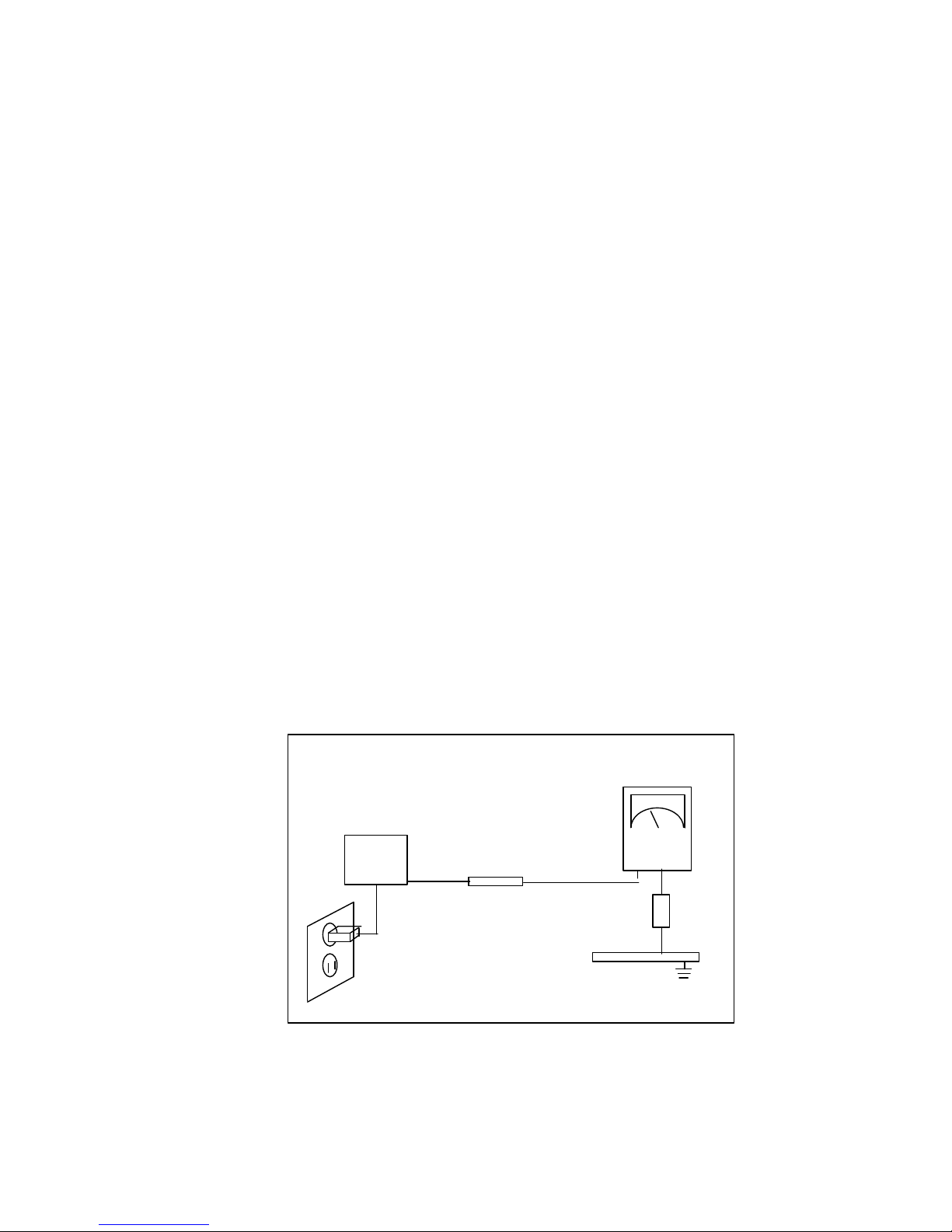
3) To be sure that no shock hazard exists, check for leakage current in the
following manner.
a. Plug the AC line cord directly into a 120 or 230 Volt AC outlet.
(Do not use an isolation transformer for this test)
b. Using two clip leads, connect a 1.5KΩ, 10Watt resistor paralleled by a
0.15Uf capacitor in serial with an exposed metal chassis part and a
known earth ground, such as an electrical conductor and electrical
ground connected to a earth ground.
c. Use a SSVM or VOM with 1000 ohms per-volt or sensitivity to measure
the AC voltage drop across the resistor.
d. Connect the resistor to an exposed metal part having a return path to
the chassis(m etal cabinet, screw heads, knobs, shafts, escutcheon,etc)
and measure the AC voltage drop across the resistor.
e. Any reading of 5.25 volt RMS(this corresponds to 3.5 milliampere AC)
or more is excessive and indicates a potential shock hazard. Correct
the shock hazard before returning the monitor to the user.
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
(READING SHOULD)
NOT BE ABOVE
0.5m A
TEST AL L
EXPOSED METAL
SURFACES
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
2-WIRE
CORD
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
Earth
ground
Figure 1-1. Leakage Current Test Circuit

- 4 -
1-1-3. Product safety notices:
Some electrical and mechanical parts have special safety related characteristics
which are often not evident from visual inspection. The protection they give
may not be obtained by replacing them with components rated for higher voltage,wattage,etc. Parts that have special safety characteristics are identified by
△
on schematics and parts lists.
A substitute replacement that does not have the sam e safety characteristics
as the recommended replacement part might create shock, fire and or other
hazards. Product safety is under review continuously and new instructions
whenever appropriate.
1-2. Servicing Precautions
WARNING 1 : First read the "Safety Precaution" section of this manual. if
unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the servicing
precautions and safety precautions,always follow the safety
precautions.
WARNING 2 : A High Voltage volume replaced in the wrong direction may
cause excessive X-ray emissions.
WARNING 3 : An electrolytic capacitor installed with the wrong polarity might
explode.
1) Servicing precautions are printed on the chassis, and should be followed
closely
2) Always unplug the units AC power cord from the AC power source before
attempting to :(a) remove or reinstall any component or assem bly, (b)
disconnect PCB plugs or connectors,(c) connect all test com ponents in
parallel with an electrolytic capacitor.
3) after servicing, always check that the screws, components and wiring have
been correctly reinstalled. Make sure that the area around the serviced
part has not been dam aged.
4) Check the insulation between the blades of the AC plug and accessible
conductive parts(examples:m etal panels,input terminals and earphone jacks).
5) Never defeat any of the +B voltage interlocks. Do not apply AC power to
the unit(or any of its assemblies) unless all solid-state heat sinks are
correctly installed.
6) Always connect a test instruments ground lead to the instrum ent chassis
ground before connecting the lead; always remove the instruments lead last.
- 5 -
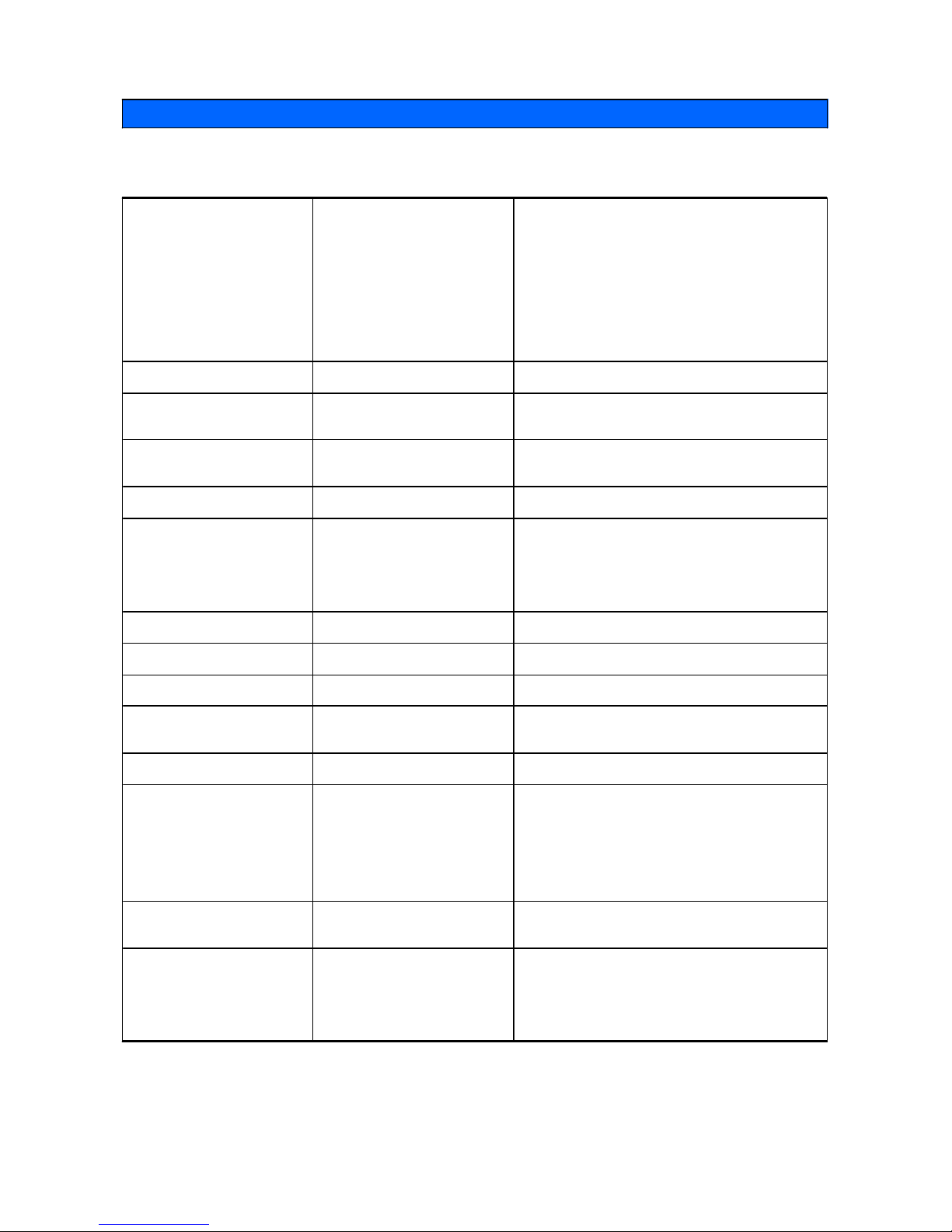
2-1 SPECIFICATION
2. Product Specifications
CDT
Tube
Size
Viewable Image Size
Dot Pitch
Deflection Angle
Focusing Method
FST, Dyna flat (option)
48㎝(19") diagonal
45.7㎝(18")
0.26㎜(H)
90
°
Double Focusing(static & dynam ic)
Bandwidth Maximum 140MHz
Scanning Frequency
(Auto Scanning)
Horizontal
Vertical
30-82KHz
50-120Hz
Display Area Norm al
Maximum
350×262.5
㎜
366×275
㎜
Microprocessor User Saving Mode 7 Modes
User Control Display
Digital
Language
Position,Size,Pincushion,T rapezoid,H/Vcorner,
Pin-B,Trapezoid,Parallel,Tilt,Moire,Zoom
Color T emperature,Recall,Manual Degauss
Eng/Ger/F ra/Esp/Port
Display color Color T emperature 9300°K, 6500°K, User Color
Resolution Maximum M ode 1280 X 1024 @ 75Hz
Signal Input Connect 15 pin D-sub(Fem ale) or Option
Safety & EMC
Safety
EMC
UL,CSA,TUV,CB,DHHS
FCC,CE
Power Voltage AC 90-264V, 60 / 50±3Hz
Power Consumption Nomal Operation
Input Current at 120V
Input Current at 240V
≤
100 Watts
Operating :≤1.5Amps rms.
Turn on :≤30Amps Peak.
Operating :≤0.8Amps rms.
Turn on :≤60Amps Peak.
Linearity Cross Pattern
Horizontal : 5%
Vertical : 5%
Environment
Temperature
Humidity
Operating : 0 to +40
℃
Storage : -40 to +60
℃
Operating : 10 to 85%
Storage : 5 to 95%
- 6 -
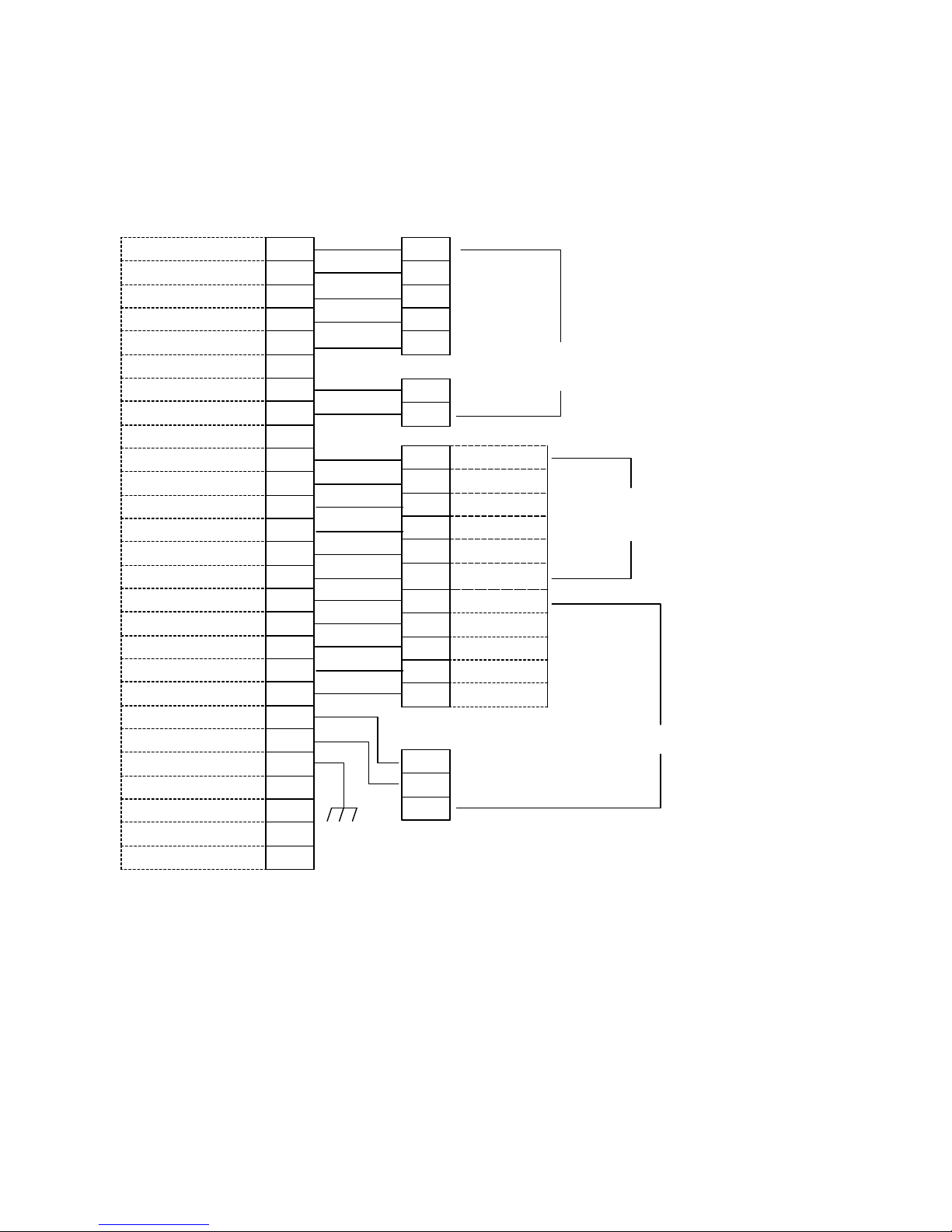
2-2 Monitor Interface Wiring (AMP-25P)
M Reset 14
Touch_ TXD 13
13VCD_Net 20
Touch_ RXD 12
Net Ground 15
13VDC 21
A_Grnd 22
Red 1
Red_GND 2
Green 3
Green_GND 4
Blue 5
Blue_GND 6
Shield GND 7
H Sync 8
V Sync 9
I2C CLK 10
I2C SDA 11
AC Line 24
AC Ntrl 25
Frame GND 23
USB Vcc 16
USBD- 17
USBD+ 18
USB GND 19
1
2
3
4
5
1 Red
2 Red_GND
3 Green
4 Green_GND
5 Blue
6 Blue_GND
1
2
1 Shield GND
2 H Sync
3 V Sync
3 I2C CLK
3 I2C SDA
1
2
3
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
Shield
Shield
Shield
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
22 AWG
18 AWG
18 AWG
Touch Screen
Controller
CRT Neck Board
Video Connector
Main Board Sync Connector
#8 Ring Lug Chassis Ground
- 7 -
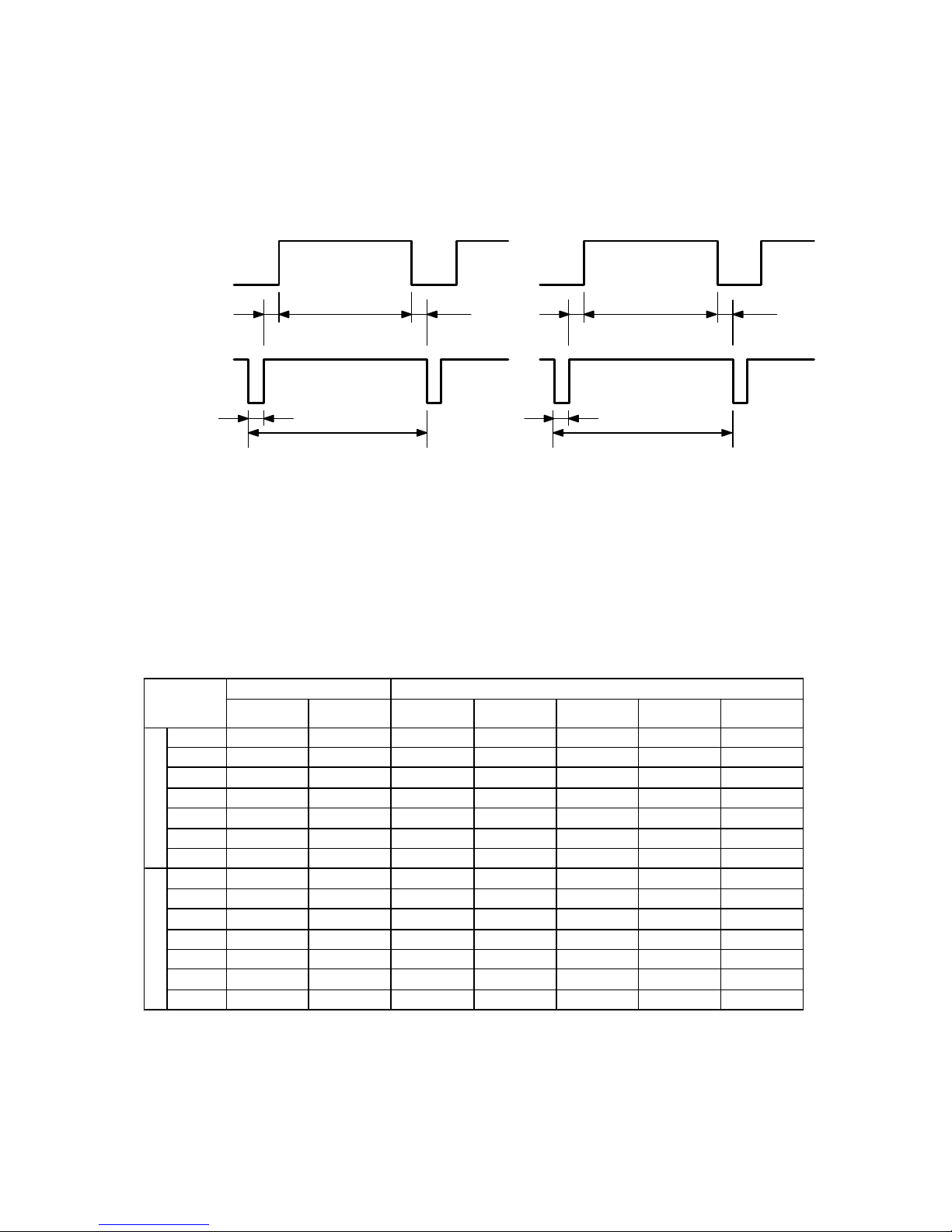
2-3 TIMING CHART
DESCRPTION
IGT VESA
640*480 640*480 640*480 640*480 1024*768 800*600 1024*768
H
f KHz
31.469 31.469 31.469 37.860 48.363 53.674 60.24
A uS
31.8 31.8 31.77 26.413 20.677 18.631 16.60
B uS
2.4 2.4 3.813 1.270 2.092 1.138 1.200
C uS
3.0 3.0 1.906 4.603 2.262 2.702 2.20
D uS
24.0 24.0 25.42 20.317 15.754 14.222 12.80
E uS
2.4 2.4 0.636 0.762 0.369 0.569 0.4
POL.
POS POS NEG POS NEG POS NEG
V
f Hz
50.0 59.940 59.94 72.809 60.00 8 5.0 61 74. 93
O mS
20.000 16.663 16.683 13.735 16.667 11.756 13.346
P mS
0.509 0.254 0.064 0.079 0.124 0.056 0.05
Q mS
0.372 0.890 1.048 0.740 0.60 0.503 0.497
R mS
15.26 15.26 15.253 12.678 15.88 11.179 12.749
S mS
0.509 0.890 0.318 0.238 0.062 0.019 0.050
POL.
POS POS NEG POS NEG POS NEG
VIDEO
SYNC
HORIZONTAL VERTICAL
A
B
C D
E
O
P
Q R
S
A : LINE TIME TOTAL B :HORIZONTAL SYNC WIDTH
C : BACK PORCH D : ACTIVE TIME
E : FRONT PORCH
O : F RAME TIME TOTAL P : VERTICAL SYNC WIDTH
Q : BACK PORCH R : ACTIVE TIME
S : FRONT PORCH

- 8 -
3-1 FRAME-UR (GK+)
3.2 MAIN PCB ASS'Y
3. Operating Instruction
Touch Screen
Main Board
Socket Board
(T he GK+ is without shield
cover)
PFC Board
AMP Connector
- 9 -
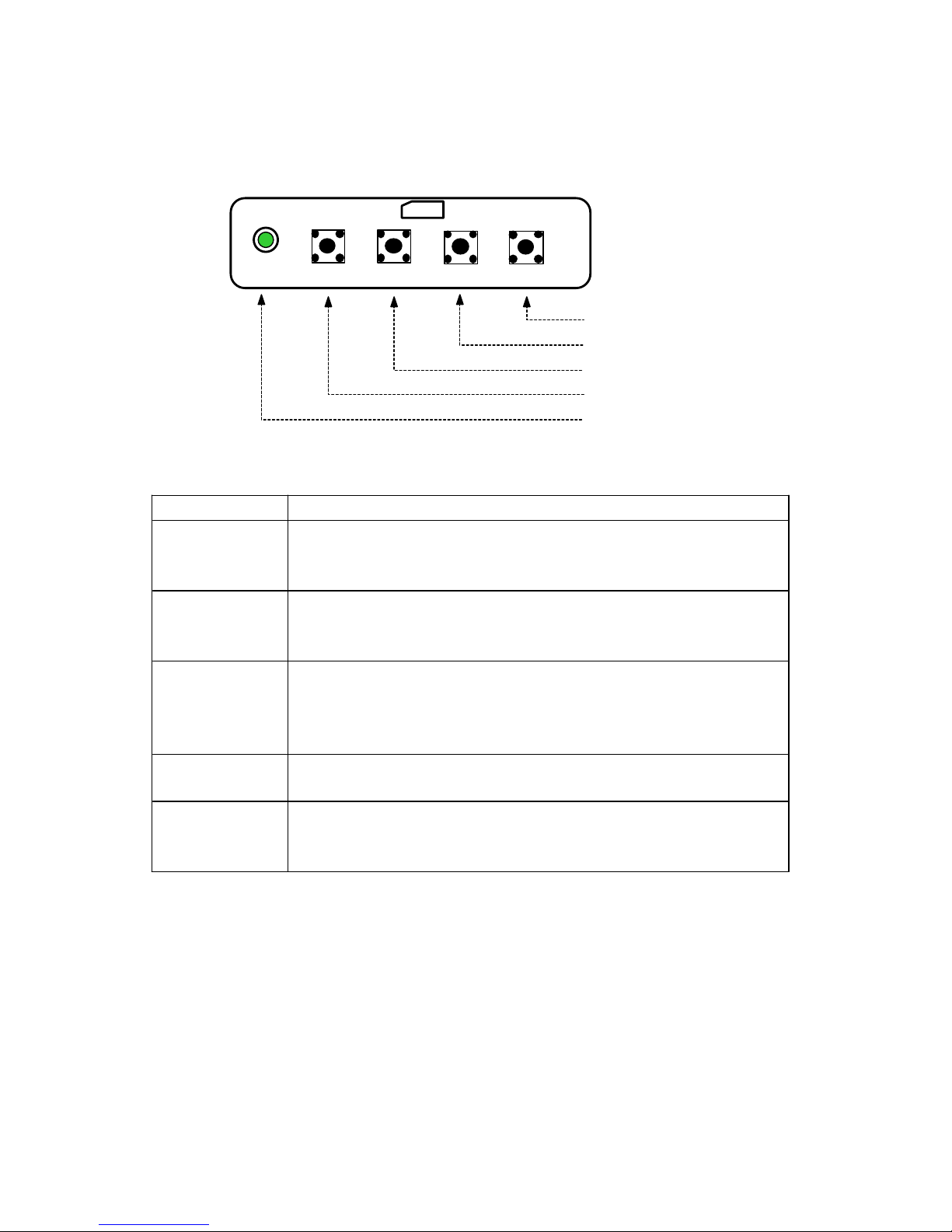
3-3. Function of Control
Control Function
LED
(Power Indicator)
The light of power LED changes according to each state.
◎
on mode : Green LED.
◎
power saving mode : green LED blinking.
SELECT (DEG)
This button is used to select the control item on the MENU.
In M ENU, the control item could be selected and unselected by
this button.
MOD
When you press this button, the MENU appears.The MENU will
disappear in 10 seconds if you don't operate any button.
When you press MOD button again, the MENU disappears.
This button is used to exit the value of any selected control.
UP
This button is used to increase the value of any selected control.
This button is used to locate to the next control item for select.
DOWN
This button is used to decrease the value of any selected control.
This button is used to locate to the previous control item for
select.
UP
DOWN
SELECT(DEG)
MOD
LED
 Loading...
Loading...