Page 1

i
JetBox 8100 User Manual
Modbus Gatewa y
Copyright@2007
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Customer Service: KoreCARE@korenix.com
V1.0
Page 2

ii
Copyright Notice
Copyright© 2007 Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable.
However, the original manufacturer assumes no r esponsibility for i t s use, or for
any infringements upon the rights of third parties that may result from its use.
The material in this document is for product information only and is subject to
change without notice. Whil e re asonable effort s have been made in the
preparation of this document to assure its accuracy, Korenix assumes no
liabilities result ing fro m er ror s or omissi ons i n thi s docu ment, or fro m the us e o f
the information contained herein.
Korenix reserves the right to make changes in the product design without
notice to its users.
Acknowledgments
Korenix is a registered trademark of Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks or registered marks in the manual belong to their
respective manufacturers.
Page 3

iii
Table of Contents
JetBox 8100 User Manual ............................................................................... i
Modbus Gateway ............................................................................................ i
Copyright Notice ........................................................................... ii
Acknowledgments ........................................................................ ii
Chapter 1 Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII Gateway Application ...................... 1
1.1 Overview ....................................................................................... 1
1.2 Argument s .................................................................................... 2
1.3 Scenarios ...................................................................................... 2
1.4 Limitations .................................................................................... 3
Chapter 2 Appendix ....................................................................................... 5
2.1 Chart Index ................................................................................... 5
2.2 Customer Service ........................................................................ 5
Page 4

Page 5
JetBox 8100 User Manual_Modbus_1.0-r1.doc
Chapter 1 Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII Gateway Application
1
Chapter 1 Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII
Gateway Application
1.1 Overview
Modbus is one of the most popular industrial protocols in the world. It is
supported by the traditional RS-232/422/485 devices and recently by the
Ethernet devices. Lots of industrial devices, such as PLCs, DCSs, HMIs,
instruments, and meters, use Modbus as their communication standard.
A Modbus TCP to RTU /ASC II g at eway application is desi gned as a bridge
for the Modbus TCP (Ethernet) masters and Modbus RTU/ASCII (serial)
slaves. It allows the Ethernet-based HMIs or PLCs to control devices over
RS-232/422/485 without additional programming or effort.
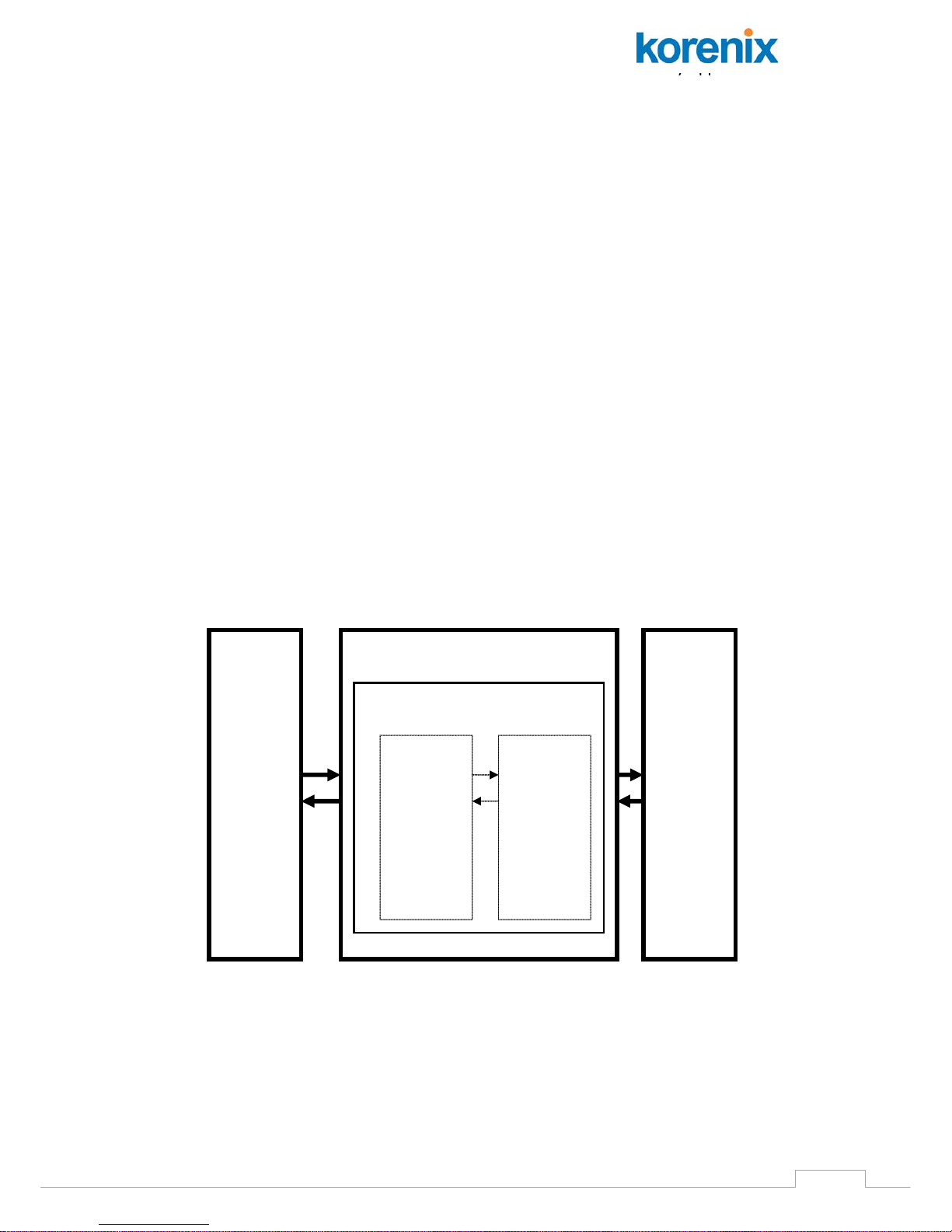
Figure 1-1 shows the block diagrams of Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII
gateway application.
Figure 1-1 Block Diagrams of Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII Gateway Application
Modbus
TCP
Master
(HMI or
PLC)
JetBox 8100/8210/8220
ModbusT2R.exe
Modbus
TCP
Slave
Modbus
RTU/
ASCII
Master
Modbus
RTU/
ASCII
Slave
(PLC,
DCS)
Page 6

JetBox 8100 User Manual_Modbus_1.0-r1.doc
2
1.2 Arguments
Table 1-2 is the description of the arguments of the “ModbusT2R.exe”
application. The following command example, “-p 5501 –s COM1: -b
9600 –m RTU –id0 1 –id1 10”, means the g atew ay applicat ion cr eat es on e
Modbus TCP slave service on TCP port 5501 and create one Modbus
RTU master service on “COM1:” with 9600 baud rate and the valid
Modbus RTU slave station ID is from 1 to 10.
Application Name: ModbusT2R.exe
Arguments Description
-help
Lists all the syntax of arguments.
-f [file name]
Specifies an argument file.
-p [TCP port number]
Specifies the TCP port number of Modbus TCP
slave. Default port is 5501.
-s [serial port name]
Specifies the serial port name of Modbus
RTU/ASCII master. Default port is “COM1:”.
-b [baud rate]
Specifies the baud rate of Modbus RTU/ASCII
master. Default baud rate is 9600.
-m [“rtu”|“ascii”]
Specifies the protocol of Modbus RTU/ASCII
master. Default protocol is RTU.
-id0 [begin ID]
Specifies the begin ID of a range of Modbus slave
ID. Default begin ID is 0.
-id1 [end ID]
Specifies the end ID of a range of Modbus slave
ID. Default end ID is 247.
Table 1-2 Description of the Arguments of the “ModbusT2R.exe” Application
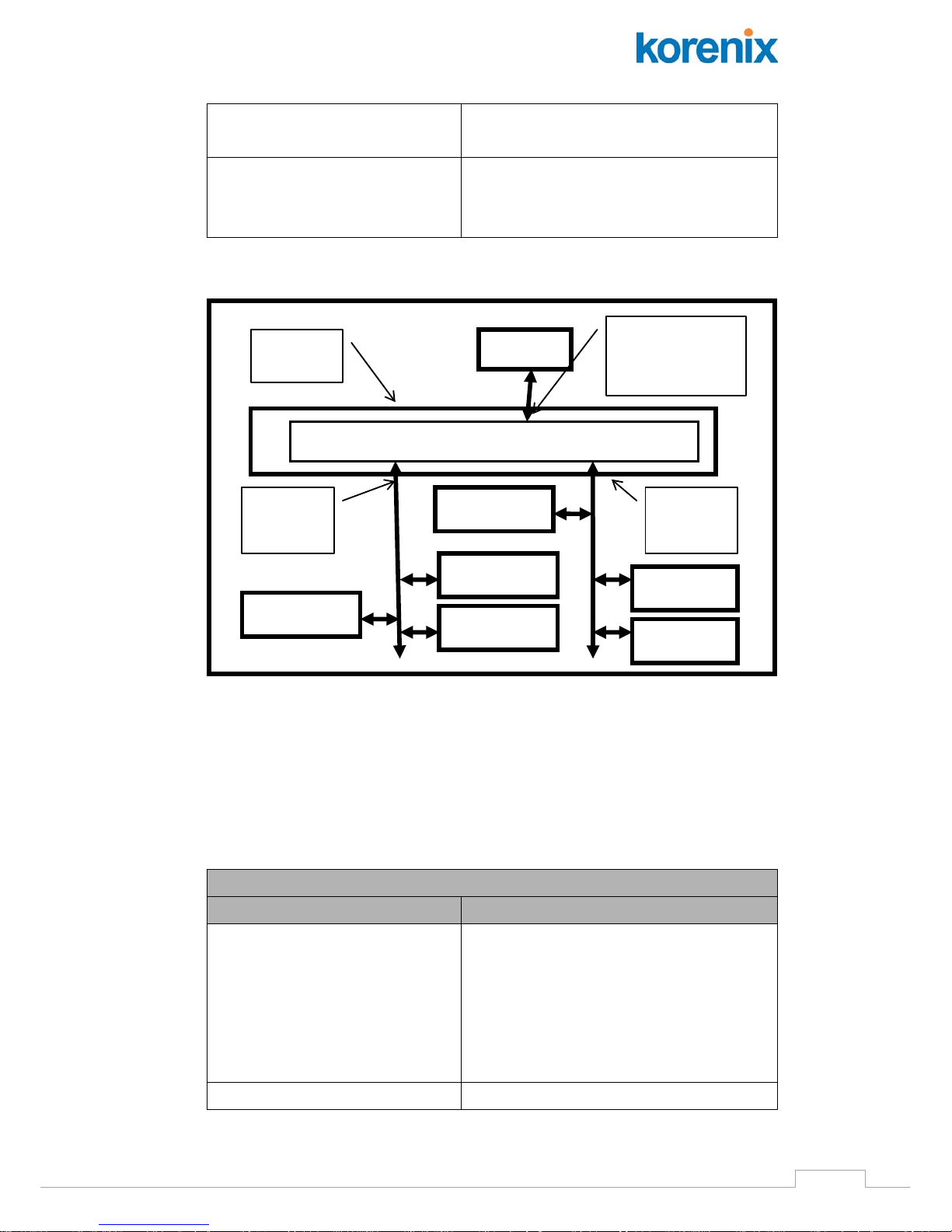
1.3 Scenarios
The following script file, “demo.ini”, specifies one Modbus TCP slave
service and one Modbus RTU master service and one Modbus ASCII
master service. Table 1-3 shows the contents of the script file “demo.ini”.
Execute the “ModbusT2R.exe” with arguments “-f demo.ini” to start the
gateway application with script file. Figure 1-4 shows this demo scenario.
Script File Name: demo.ini
Contents Description
-p 5501 –s COM1: -b 9600 –m
One Modbus TCP master on TCP port 5501
Page 7
JetBox 8100 User Manual_Modbus_1.0-r1.doc
-p 5501 –s COM1: -b 9600 –m RTU –id0 1 –id1 10
3
RTU –id0 1 –id1 10
and One Modbus RTU master on serial
“COM1:”. Valid station ID range from 1 to 10.
-p 5501 –s COM2: -b 9600 –m
ASCII –id0 11 –id1 20
One Modbus TCP master on TCP port 5501
and One Modbus ASCII master on serial
“COM2:”. Valid station ID range from 11 to 20.
Table 1-3 Contents of the Script File “demo.ini”
Table 1-4 Scenario of Running “ModbusT2R.exe” with “demo.ini” Script File
1.4 Limitations
Some limitations while running “ModbusT2R.exe” are detailed in the Table
1-5.
Application Name: ModbusT2R.exe
Limitations Description
No same station ID
Modbus station ID is used as an index
for the gateway application in the
current design, so Modbus RTU/ASCII
slave device with the same station ID
is not allowed to join the gateway
network.
No TCP request buffering
Modbus TCP master is not allowed to
SCADA
Ethernet
TCP port 5501
PLC ID=2
COM1:
RS 485
DCS ID=3
Meter ID=1
PLC ID=12
COM2:
RS 485
DCS ID=13
Meter
JetBox
Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII Gateway Application
Page 8
JetBox 8100 User Manual_Modbus_1.0-r1.doc
4
send multiple requests to slaves
located in the Modbus RTU/ASCII
network. Because no request buffering
is supported, the request will be
redirected to the specific serial port
immediately. If it is a RS-485 serial
port, a collision could happen.
No timeout
Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII gateway
application is desig ned w i thout t im eou t
mechanism. Modbus TCP master
should take care of the response
timeout for individual M odbus
RTU/ASCII slaves.
No broadcast
Request for station ID 0 will not be
broadcast to the Modbus serial
network.
Hardcode serial parameters
The serial port parameters are
hardcode to even parity, 8 data bits, 1
stop bit and none flow control for RTU
protocol and even parity, 7 data bits, 1
stop bit and none flow control for
ASCII protocol
One TCP port per instance
Only one Modbus TCP slave service
will be created on the first specified
TCP port number for one instance.
Multiple instances of gateway
application are allowed.
Executable without UI
A standalone executable and no UI
available.
Not a service
It’s not a service, no start and stop
behaviors are supported.
Table 1-5 Limitations While Running “ModbusT2R.exe” Application
Page 9

JetBox 8100 User Manual_Modbus_1.0-r1.doc
Chapter 2 Appendix
5
Chapter 2 Appendix
2.1 Chart Index
Figure 1-1 Block Diagrams of Modbus TCP to RTU/ASCII Gateway Application…………1
Table 1-2 Description of the Arguments of the “ModbusT2R.exe” Application……………2
Table 1-3 Contents of the Script File “demo.ini”……………………………………………....2
Table 1-4 Scenario of Running “ModbusT2R.exe” with “demo.ini” Script File……………..3
Table 1-5 Limitations While Running “ModbusT2R.exe” Application……………………….3
2.2 Customer Service
Korenix Technologies Co., Ltd.
Business service : sales@korenix.com
Customer service: koreCARE@korenix.com
Web Site: http://www.korenix.com
 Loading...
Loading...