Page 1

Korenix JetNet 7850G-2XG 6852G Series
48G+2 x 10G SFP+/48G+4G SFP Ports
Industrial Gigabit Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
User Manual
Version 1.0, Oct. 2014
www.korenix.com
Page 2

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Revision
Date
Remark
V1.0
Otc. 14, 2014
The 1st release version
Document History
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 2/1246
Page 3

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
CONTENTS
1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 10
1.1 Switch Description ................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Features ................................................................................................................... 10
1.3 Dimension ................................................................................................................ 12
1.4 Front-Panel Components ......................................................................................... 13
1.5 Rear Panel Description ............................................................................................. 14
1.6 Management Options .............................................................................................. 15
1.7 Web-based Management Interface ......................................................................... 15
1.8 Command Line Console Interface Through the Serial Port or Telnet ...................... 15
1.9 SNMP-Based Management ...................................................................................... 16
2 Installation and Quick Startup ................................................................................................. 18
2.1 Package Contents ..................................................................................................... 18
2.2 Switch Installation .................................................................................................... 18
2.3 Installing the Switch in a Rack.................................................................................. 19
2.4 Quick Starting the Switch......................................................................................... 20
2.5 System Information Setup ....................................................................................... 21
2.5.1 Quick Start up Software Version Information .................................................. 21
2.5.2 Quick Start up Physical Port Data .................................................................... 21
2.5.3 Quick Start up User Account Management ..................................................... 22
2.5.4 Quick Start up IP Address ................................................................................ 23
2.5.5 Quick Start up Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC .............................. 24
2.5.6 Quick Start up Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch ......................... 24
2.5.7 Quick Start up Downloading from TFTP Server ............................................... 24
2.5.8 Quick Start up Factory Defaults ....................................................................... 25
3 Console and Telnet Administration Interface .......................................................................... 26
3.1 Local Console Management..................................................................................... 26
3.2 Set Up your Switch Using Console Access ................................................................ 26
3.3 Set Up your Switch Using Telnet Access ................................................................... 27
4 Web-Based Management ........................................................................................................ 28
4.1 Overview .................................................................................................................. 28
4.2 How to log in ............................................................................................................ 29
4.3 Web-Based Management Menu .............................................................................. 30
5 Command Line Interface Structure and Mode-based CLI ....................................................... 34
5.1 CLI Command Format .............................................................................................. 34
5.2 CLI Mode-based Topology ........................................................................................ 35
6 Switching Commands .............................................................................................................. 37
6.1 System Information and Statistics commands ......................................................... 37
6.1.1 show arp .......................................................................................................... 37
6.1.2 show calendar .................................................................................................. 38
6.1.3 show process cpu ............................................................................................. 39
6.1.4 show eventlog .................................................................................................. 41
6.1.5 show running-config ........................................................................................ 42
6.1.6 show sysinfo ..................................................................................................... 43
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 3/1246
Page 4

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.7 show system .................................................................................................... 44
6.1.8 show tech-support ........................................................................................... 45
6.1.9 show hardware ................................................................................................ 46
6.1.10 show version .................................................................................................... 48
6.1.11 show loginsession ............................................................................................ 49
6.1.12 show command filter ....................................................................................... 50
6.2 Device Configuration Commands ............................................................................ 51
6.2.1 Interface ........................................................................................................... 51
6.2.2 L2 MAC Address and Multicast Forwarding Database Tables .......................... 67
6.2.3 VLAN Management .......................................................................................... 76
6.2.4 Double VLAN commands ................................................................................. 99
6.2.5 GVRP and Bridge Extension ........................................................................... 101
6.2.6 IGMP Snooping .............................................................................................. 112
6.2.7 IGMP Snooping Querier ................................................................................. 122
6.2.8 MLD Snooping ................................................................................................ 129
6.2.9 MLD Snooping Querier .................................................................................. 140
6.2.10 Port Channel .................................................................................................. 147
6.2.11 Storm Control ................................................................................................ 161
6.2.12 L2 Priority ....................................................................................................... 169
6.2.13 Port Mirror ..................................................................................................... 171
6.2.14 Link State ....................................................................................................... 174
6.2.15 Port Backup .................................................................................................... 177
6.2.16 Rapid Super Ring Member Mode Commands ............................................... 179
6.3 Management Commands ...................................................................................... 181
6.3.1 Network Commands ...................................................................................... 181
6.3.2 Serial Interface Commands ............................................................................ 186
6.3.3 Telnet Session Commands ............................................................................. 190
6.3.4 SSH Client Session Commands ....................................................................... 198
6.3.5 SNMP Server Commands ............................................................................... 202
6.3.6 SNMP Trap Commands .................................................................................. 214
6.3.7 SNMP Inform Commands .............................................................................. 223
6.3.8 HTTP commands ............................................................................................ 227
6.3.9 Secure Shell (SSH) Commands ....................................................................... 231
6.3.10 Management Security Commands ................................................................ 234
6.3.11 DHCP Client Commands................................................................................. 235
6.3.12 DHCPv6 Client Commands ............................................................................. 236
6.3.13 DHCP Relay Commands ................................................................................. 238
6.3.14 sFlow Commands ........................................................................................... 240
6.3.15 Service Port Commands ................................................................................. 248
6.3.16 Time Range Commands ................................................................................. 253
6.4 Spanning Tree Commands ..................................................................................... 257
6.4.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 257
6.4.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 266
6.5 System Log Management Commands ................................................................... 280
6.5.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 280
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 4/1246
Page 5

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.5.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 283
6.6 Script Management Commands ............................................................................ 289
6.6.1 script apply .................................................................................................... 289
6.6.2 script delete ................................................................................................... 289
6.6.3 script show ..................................................................................................... 290
6.6.4 script validate ................................................................................................. 291
6.7 User Account Management Commands ................................................................ 292
6.7.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 292
6.7.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 295
6.8 Security Commands ............................................................................................... 302
6.8.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 302
6.8.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 334
6.8.3 Dot1x Configuration Commands ................................................................... 337
6.8.4 Captive Portal Commands ............................................................................. 347
6.8.5 TACACS+ Configuration Commands ............................................................... 390
6.8.6 LDAP Configuration Commands..................................................................... 394
6.8.7 Port Security Configuration Commands ........................................................ 397
6.8.8 Denial Of Service Commands......................................................................... 400
6.9 CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) Commands ........................................................... 411
6.9.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 411
6.9.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 415
6.10 SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) Commands ............................................... 418
6.10.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 418
6.10.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 421
6.11 MAC-Based Voice VLAN Commands ...................................................................... 427
6.11.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 427
6.11.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 429
6.12 LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) Commands .................................................. 432
6.12.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 432
6.12.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 447
6.13 VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) Commands ............................................................ 457
6.13.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 457
6.13.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 460
6.14 Protected Ports Commands ................................................................................... 465
6.14.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 465
6.14.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 467
6.15 Static MAC Filtering Commands ............................................................................ 468
6.15.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 468
6.15.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 469
6.16 System Utilities ...................................................................................................... 472
6.16.1 clear ............................................................................................................... 472
6.16.2 copy ............................................................................................................... 486
6.16.3 delete ............................................................................................................. 489
6.16.4 dir ................................................................................................................... 490
6.16.5 whichboot ...................................................................................................... 491
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 5/1246
Page 6

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.16.6 boot-system ................................................................................................... 491
6.16.7 ping ................................................................................................................ 492
6.16.8 traceroute ...................................................................................................... 495
6.16.9 logging cli-command...................................................................................... 497
6.16.10 calendar set ........................................................................................... 498
6.16.11 reload ..................................................................................................... 498
6.16.12 configure ................................................................................................ 499
6.16.13 disconnect .............................................................................................. 499
6.16.14 hostname ............................................................................................... 500
6.16.15 quit ......................................................................................................... 500
6.16.16 cablestatus ............................................................................................. 501
6.17 DHCP Snooping Commands ................................................................................... 502
6.17.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 503
6.17.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 510
6.18 IP Source Guard (IPSG) Commands ....................................................................... 519
6.18.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 520
6.18.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 522
6.19 Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) Command ............................................................. 523
6.19.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 523
6.19.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 526
6.20 Differentiated Service Command ........................................................................... 531
6.20.1 General Commands ....................................................................................... 532
6.20.2 Class Commands ............................................................................................ 533
6.20.3 Policy Commands........................................................................................... 551
6.20.4 Service Commands ........................................................................................ 560
6.20.5 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 563
6.21 ACL Command........................................................................................................ 571
6.21.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 571
6.21.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 576
6.22 IPv6 ACL Command ................................................................................................ 584
6.22.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 584
6.22.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 586
6.23 CoS (Class of Service) Command ........................................................................... 590
6.23.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 590
6.23.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 594
6.24 Auto-Voice over IP Commands .............................................................................. 599
6.24.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 599
6.24.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 600
6.25 iSCSI Optimization Commands ............................................................................... 601
6.25.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 601
6.25.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 603
6.26 Domain Name Server Relay Commands ................................................................ 607
6.26.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 607
6.26.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 610
6.27 UDLD Commands ................................................................................................... 617
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 6/1246
Page 7

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.27.1 Show command ............................................................................................. 617
6.27.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 618
7 Routing Commands ............................................................................................................... 621
7.1 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Commands ..................................................... 621
7.1.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 621
7.1.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 624
7.2 IP Routing Commands ............................................................................................ 629
7.2.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 629
7.2.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 642
7.3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Commands ......................................................... 648
7.3.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 648
7.3.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 666
7.4 BOOTP/DHCP Relay Commands ............................................................................. 694
7.4.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 694
7.4.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 695
7.5 IP Helper Commands ............................................................................................. 698
7.5.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 698
7.5.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 700
7.6 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Commands .................................................... 703
7.6.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 703
7.6.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 706
7.7 Router Discovery Protocol Commands .................................................................. 715
7.7.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 715
7.7.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 716
7.8 VLAN Routing Commands ...................................................................................... 719
7.8.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 719
7.8.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 720
7.9 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) Commands ...................................... 721
7.9.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 721
7.9.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 726
8 IP Multicast Commands ......................................................................................................... 734
8.1 Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) Commands ....................... 734
8.1.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 734
8.1.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 740
8.2 Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Commands .................................. 742
8.2.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 742
8.2.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 747
8.3 Multicast Commands ............................................................................................. 752
8.3.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 752
8.3.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 758
8.4 IPv4 Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Commands ....................................... 761
8.4.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 761
8.4.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 767
8.5 IGMP Proxy Commands ......................................................................................... 775
8.5.1 Show Commands ........................................................................................... 775
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 7/1246
Page 8

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
8.5.2 Configuration Commands .............................................................................. 780
9 Web-Based Management Interface ....................................................................................... 782
9.1 Overview ................................................................................................................ 782
9.2 Management Menu ............................................................................................... 784
9.2.1 Viewing Information ...................................................................................... 784
9.2.2 Configuring Management Session and Network Parameters ........................ 789
9.2.3 Managing System Utilities ............................................................................. 805
9.2.4 File Management ........................................................................................... 811
9.2.5 User Management ......................................................................................... 816
9.2.6 Viewing Logs .................................................................................................. 830
9.2.7 Viewing Statistics ........................................................................................... 838
9.2.8 Managing SNMP and Trap ............................................................................. 847
9.2.9 Managing SNTP .............................................................................................. 859
9.2.10 Managing CDP Function ................................................................................ 866
9.2.11 Managing UDLD ............................................................................................. 869
9.2.12 Managing LLDP .............................................................................................. 871
9.2.13 Managing LLDP-MED ..................................................................................... 881
9.2.14 Managing sFlow ............................................................................................. 888
9.2.15 Managing DHCP Client ................................................................................... 894
9.2.16 Managing Time Ranges ................................................................................. 896
9.2.17 Managing DNS Relay Function ....................................................................... 900
9.2.18 Managing DDNS Function .............................................................................. 905
9.3 Switching Menu ..................................................................................................... 906
9.3.1 Defining Forwarding Database ...................................................................... 906
9.3.2 Managing Switch Interface ............................................................................ 908
9.3.3 Managing DHCP Snooping ............................................................................. 915
9.3.4 DHCP Snooping Information Option 82 ......................................................... 921
9.3.5 Managing IP Source Guard (IPSG) ................................................................. 925
9.3.6 Managing Port-Based VLAN ........................................................................... 928
9.3.7 Managing DVLAN ........................................................................................... 934
9.3.8 Managing Protected Ports ............................................................................. 936
9.3.9 Managing Protocol-based VLAN .................................................................... 938
9.3.10 Managing IP Subnet-based VLAN .................................................................. 941
9.3.11 Managing MAC-based VLAN .......................................................................... 943
9.3.12 Managing MAC-based Voice VLAN ................................................................ 945
9.3.13 Managing Voice VLAN.................................................................................... 947
9.3.14 Managing MAC Filters ................................................................................... 948
9.3.15 Managing GARP ............................................................................................. 950
9.3.16 Managing VTP ................................................................................................ 954
9.3.17 Managing Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) ...................................................... 956
9.3.18 Managing IGMP Snooping ............................................................................. 962
9.3.19 Managing IGMP Snooping Querier ................................................................ 971
9.3.20 Managing MLD Snooping............................................................................... 975
9.3.21 Managing MLD Snooping Querier ................................................................. 983
9.3.22 Viewing Multicast Forwarding Database ....................................................... 987
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 8/1246
Page 9

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
9.3.23 Managing Port-Channel ................................................................................. 992
9.3.24 Managing Spanning Tree ............................................................................... 995
9.3.25 Managing Link State .................................................................................... 1007
9.3.26 Managing Port-Backup ................................................................................ 1009
9.3.27 Rapid Super Ring Menu ............................................................................... 1011
9.4 Security Menu ...................................................................................................... 1013
9.4.1 Managing Access Control (802.1x)............................................................... 1013
9.4.2 Managing Port Security ............................................................................... 1031
9.4.3 Managing Captive Portal.............................................................................. 1036
9.4.4 Managing RADIUS ........................................................................................ 1058
9.4.5 Managing TACACS+ Configuration ............................................................... 1068
9.4.6 Managing LDAP Configuration ..................................................................... 1070
9.4.7 Managing Access Control Lists ..................................................................... 1071
9.4.8 Managing IP Filter Configuration ................................................................. 1093
9.4.9 Managing Secure HTTP Configuration ......................................................... 1095
9.4.10 Managing Secure Shell Configuration .......................................................... 1097
9.4.11 Managing Denial of Service Page................................................................. 1099
9.5 QOS Menu............................................................................................................ 1101
9.5.1 Managing Differentiated Services ................................................................ 1101
9.5.2 Configuring Diffserv Wizard Page ................................................................ 1113
9.5.3 Managing Auto VoIP .................................................................................... 1115
9.5.4 Managing iSCSI ............................................................................................ 1118
9.5.5 Managing Class of Service ........................................................................... 1122
9.6 Routing Menu ...................................................................................................... 1129
9.6.1 Managing ARP Table .................................................................................... 1129
9.6.2 Managing IP Interfaces ................................................................................ 1132
9.6.3 Managing OSPF ........................................................................................... 1139
9.6.5 Managing IP Helper ..................................................................................... 1169
9.6.6 Managing Routing Information Protocol (RIP) ............................................ 1175
9.6.7 Managing Router Discovery......................................................................... 1183
9.6.8 Managing Route Table ................................................................................. 1185
9.6.9 Managing VLAN Routing .............................................................................. 1189
9.6.10 Managing VRRP ........................................................................................... 1191
9.6.11 Managing Loopbacks ................................................................................... 1205
9.7 IPv4 Multicast Menu ............................................................................................ 1208
9.7.1 Configuring IPv4 Multicast Global ............................................................... 1208
9.7.2 Configuring IPv4 Multicast Interface ........................................................... 1209
9.7.3 Configuring Multicast Admin Boundary ...................................................... 1210
9.7.4 Viewing IPv4 Multicast Admin Boundary Summary .................................... 1211
9.7.5 Managing DVMRP ........................................................................................ 1212
9.7.6 Managing IGMP ........................................................................................... 1219
9.7.7 Managing PIM Protocol ............................................................................... 1231
9.7.8 Viewing IPv4 Multicast Mroute Table.......................................................... 1242
9.7.9 Configuring IPv4 Multicast Static MRoute Table Configuration .................. 1244
9.7.10 Viewing IPv4 Multicast Static MRoute Table Summary ............................... 1245
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 9/1246
Page 10

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1 Introduction
1.1 Switch Description
JetNet 7850G-2XG is a 48-port 10/100/1000BASE-T with 2 10GbE SFP+ uplinks Layer-3 Ethernet
switch and JetNet 6852G is 48-port 10/100/1000BASE-T with 4 SFP 1GbE uplinks Layer-3 Ethernet
switch.
JetNet 7850G-2XG/6852G provide a management platform and uplinks to backbone. Alternatively, the
switch can utilize up to 48 Gigabit Ethernet ports to function as a central distribution hub for other
switches, and switch groups. The one built-in 1000/100/10Mbps Ethernet port for out of band
management. The SFP+ port of JetNet 7850G-2XG also provides 1G speed by manually setting.
1.2 Features
Supports 48 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet ports
Supports 2 SFP+ 10Gigabit Ethernet ports (JetNet 7850G-2XG)
Supports 4 SFP 1Gigabit Ethernet ports (JetNet 6852G)
1 built-in 1000/100/10Mbps Ethernet port for out of band switch mangement.
IEEE 802.3x compliant Flow Control for all ports
Supports 802.1D STP, 802.1S MSTP, and 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree for redundant back up
bridge paths
Supports 802.1Q VLAN, Protocol-based VLAN, Subnet-based VLAN, MAC-based VLAN, Protected
Port, Double VLAN, Voice VLAN, GVRP,
Support 802.1p Priority Queues
Support port mirroring
Support Link Agregation (802.1ad LACP)
Supports VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)
Supports CDP
Supports LLDP with potential communication problems detection
Supports Port Security
Multiple Super Ring member mode
Multi-layer Access Control (based on MAC address, IP address, VLAN, Protocol, 802.1p, DSCP)
Quality of Service (QoS) customized control
802.1x (port-based) access control and RADIUS Client support
TACACS+ support
LDAP support
Administrator-definable port security
Supports DHCP Snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection and IP Source Guard (IPSG)
ARP support
GMRP,
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 10/1246
Page 11

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
IP Routing support
VLAN routing support
OSPF v1/v2 support
RIP v1/v2 support
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) support
IP Helper
IP Multicast support
IGMP v1, v2, and v3 support
DVMRP support
Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
DHCP Client and Relay support
DNS Client and Relay support
DDNS client support
Per-port bandwidth control
SNMP v.1, v.2, v.3 network management, RMON support
Supports Web-based management
CLI management support
Fully configurable either in-band or out-of-band control via RS-232 console serial connection
Telnet remote control console
TraceRoute support
Traffic Segmentation
TFTP/FTP upgrade
SysLog support
Simple Network Time Protocol support
Web GUI Traffic Monitoring
SSH Secure Shell version 1 and 2 support
SSL Secure HTTP TLS Version 1 and SSL version 3 support
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 11/1246
Page 12

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1.3 Dimension
The JetNet 7850G-2XG and JetNet 6852G Industrial Gigabit Layer 3 Managed Switch dimension ( H
x W x D) is 44mm x 440mm x 292.1mm.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 12/1246
Page 13

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1.4 Front-Panel Components
The front panel of the Switch consists of 48 10/100/1000BASE-T interfaces, 2 SFP+ 10-Gigabit
interfaces, or 4 SFP 1Gigabit interfaces, 1 built-in 1000/100/10 RJ-45 Ethernet service ports, an RS-232
communication port.
JetNet 7850G -2XG 48 10/100/1000BASE-T with 2 SFP+ 10G interfaces
JetNet 6852G 48 10/100/1000BASE-T with 4 SFP 1G interfaces
An RS-232 DCE console port is for setting up and managing the Switch via a connection to a console
terminal or PC using a terminal emulation program.
Each 100/100/1000BASE-T port including management port has two LED indicators: The Left side
represents speed and Right side represents Link/Activity. The speed light will has three different colors
for connecting speed 10M (LED off), 100M (Color Green), and 1G (Color Orange). The Link/Activity light
will have a green blinking once the port has a receive/transmit data.
Each 10Gbps SFP+ port and 1Gbps SFP port has two LED indicators: The Left side represents Link and
Right side represents Activity. The Link light will have green color if the port is link up. The Activity light
will have a green blinking once the port has a receive/transmit data.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 13/1246
Page 14

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1.5 Rear Panel Description
The rear panel of the Switch contains AC/DC power connector and three fans.
Rear panel with DC power connector
Rear panel with AC power connector
The DC power range support -48V(-36 ~ -72V) DC input.
The AC power connector is a standard three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug the
female connector of the provided power cord into this socket, and the male side of the cord into a power
outlet. The Switch automatically adjusts its power setting to any supply voltage in the range from 100 ~
240 VAC at 50 ~ 60 Hz.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 14/1246
Page 15
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
!
1.6 Management Options
The system may be managed by using one Service Ports through a Web Browser,Telent, SNMP
function and using the console port on the front panel through CLI command.
1.7 Web-based Management Interface
After you have successfully installed the Switch, you can configure the Switch, monitor the LED panel,
and display statistics graphically using a Web browser, such as Mozilla FireFox (version 3.6 or higher) or
Microsoft® Internet Explorer (version 5.0 or above).
To access the Switch through a Web browser, the computer running the Web browser must
have IP-based network access to the Switch.
1.8 Command Line Console Interface Through the Serial Port or
Telnet
You can also connect a computer or terminal to the serial console port or use Telnet to access the
Switch. The command-line-driven interface provides complete access to all switch management
features.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 15/1246
Page 16

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1.9 SNMP-Based Management
You can manage the Switch with an SNMP-compatible console program. The Switch supports SNMP
version 1.0, version 2.0, and version 3.0. The SNMP agent decodes the incoming SNMP messages and
responds to requests with MIB objects stored in the database. The SNMP agent updates the MIB objects
to generate statistics The Switch supports a comprehensive set of MIB extensions:
RFC1493 Bridge
RFC 2819 RMON-MIB
RFC 2233 Interface MIB
RFC 2618 (Radius-Auth-Client-MIB)
RFC 2620 (Radius-Acc-Client-MIB)
RFC 1724 (RIPv2-MIB)
RFC 1850 (OSPF-MIB)
RFC 1850 (OSPF-TRAP-MIB)
RFC 2787 (VRRP-MIB)
RFC 3289 - DIFFSERV-DSCP-TC
RFC 3289 - DIFFSERV-MIB
QOS-DIFFSERV-EXTENSIONS-MIB
QOS-DIFFSERV-PRIVATE-MIB
RFC 2674 802.1p
RFC 2932 (IPMROUTE-MIB)
ROUTING-MIB
MGMD-MIB
RFC 2934 PIM-MIB
DVMRP-STD-MIB
IANA-RTPROTO-MIB
IEEE8021-PAE-MIB
INVENTORY-MIB
MGMT-SECURITY-MIB
QOS-MIB
QOS-ACL-MIB
QOS-COS-MIB
QOS-AUTOVOIP-MIB
QOS-DIFFSERV-PRIVATE-MIB
QOS-ISCSI-MIB
RFC 1907 - SNMPv2-MIB
RFC 2465 - IPV6-MIB
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 16/1246
Page 17

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
RFC 2466 - IPV6-ICMP-MIB
TACACS-MIB
IGMP/MLD Snooping
IGMP/MLD Layer2 Multicast
QoS – IPv6 ACL
Voice VLAN
Guest VLAN
LLDP-MIB
LLDP MED
RFC 2925 (DISMAN-TRACEROUTE-MIB)
RFC 2571 - SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB
RFC 2572 - SNMP-MPD-MIB
RFC 2573 - SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB
RFC 2573 - SNMP-TARGET-MIB
RFC 2574 - SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB
RFC 2576 - SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB
RFC 2263 - USM-TARGET-TAG-MIB
RFC 3176 - SFLOW-MIB
IEEE8023-LAG-MIB (IEEE Std 802.3ad)
RFC 2674 - P-BRIDGE-MIB
RFC 2674 - Q-BRIDGE-MIB
RFC 2737 - ENTITY-MIB
RFC 2863 - IF-MIB
RFC 3635 - Etherlike-MIB
PORTSECURITY-PRIVATE-MIB
RADIUS-CLIENT-PRIVATE-MIB
CAPTIVE-PORTAL-MIB
RFC 3419 - TRANSPORT-ADDRESS-MIB
IANA-MAU-MIB
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 17/1246
Page 18
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
2 Installation and Quick Startup
2.1 Package Contents
Before you begin installing the Switch, confirm that your package contains the following items:
The Rack Mount Managed Ethernet Switch
Console Cable
Rackmount kit
Power Cord (Depend on Country, JetNet 7850G-2XG-DC48 and JetNet 6852G-DC48 no Power Cord)
QIG
2.2 Switch Installation
Installing the Switch Without the Rack
1. Install the Switch on a level surface that can safely support the weight of the Switch and its attached
cables. The Switch must have adequate space for ventilation and for accessing cable connectors.
2. Set the Switch on a flat surface and check for proper ventilation. Allow at least 5 cm (2 inches) on
each side of the Switch and 15 cm (6 inches) at the back for the power cable.
3. Attach the rubber feet on the marked locations on the bottom of the chassis.
The rubber feet are recommended to keep the unit from slipping.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 18/1246
Page 19
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
2.3 Installing the Switch in a Rack
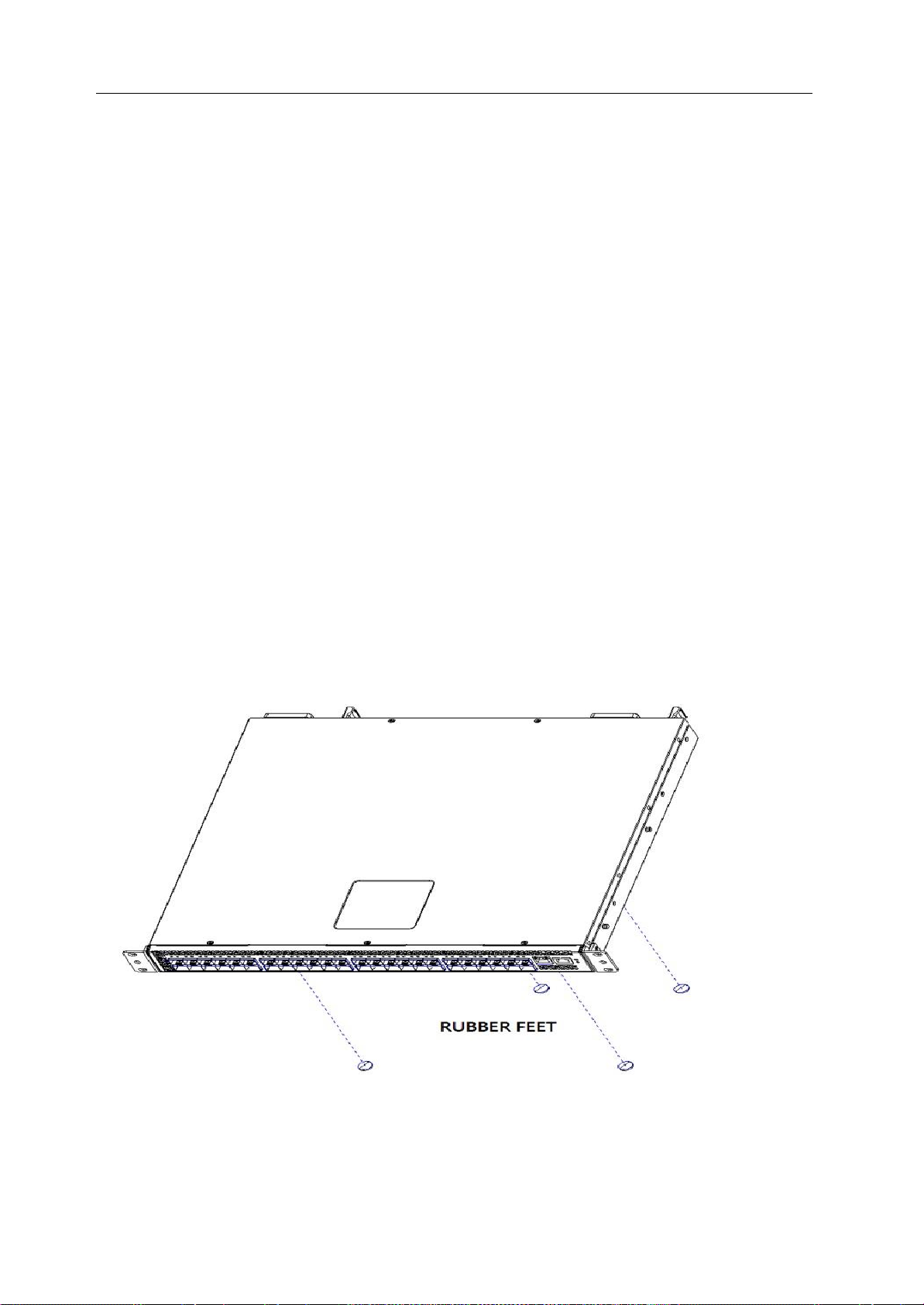
You can install the Switch in most standard 19-inch (48.3-cm) racks. Refer to the illustrations below.
1. Use the supplied screws to attach a mounting bracket to each side of the Switch.
2. Align the holes in the mounting bracket with the holes in the rack.
3. Insert and tighten two screws through each of the mounting brackets.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 19/1246
Page 20

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
2.4 Quick Starting the Switch
1. Read the device Installation Guide for the connectivity procedure. In-band connectivity allows access
to the JetNet 7850G-2XG/6852G Switch locally. From a remote workstation, the device must be
configured with IP information (IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway).
2. Turn the Power ON.
3. Allow the device to load the software until the login prompt appears. The device initial state is called
the default mode.
4. When the prompt asks for operator login, do the following:
Type the word admin in the login area. Since a number of the Quick Setup commands require
administrator account rights, suggesting logging into an administrator account.
Enter a default password admin
Press the <Enter> key.
The CLI Privileged EXEC mode prompt will be displayed.
Use “configure” to switch to the Global Config mode from Privileged EXEC.
Use “exit” to return to the previous mode.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 20/1246
Page 21
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command
Details
show hardware
Allows the user to see the HW & SW version the device
contains
System Description - switch's model name
show version
Allows the user to see Serial Number, Part Number, and Model
name
See SW loader, bootrom and operation version
See HW version
Command
Details
show Interface status [<slot/port>]
Displays the Ports slot/port
Type - Indicates if the port is a special type of port
Admin Mode - Selects the Port Control Administration State
Physical Mode - Selects the desired port speed and duplex
mode
Physical Status - Indicates the port speed and duplex mode
Link Status - Indicates whether the link is up or down
Link Trap - Determines whether or not to send a trap when link
status changes
LACP Mode - Displays whether LACP is enabled or disabled on
this port
Flow Mode - Indicates the status of flow control on this port
Cap. Status - Indicates the port capabilities during
auto-negotiation
2.5 System Information Setup
2.5.1 Quick Start up Software Version Information
Table 2-1. Quick Start up Software Version Information
2.5.2 Quick Start up Physical Port Data
Table 2-2. Quick Start up Physical Port
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 21/1246
Page 22
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command
Details
show users
Displays all users that are allowed to access the switch
User Access Mode - Shows whether the user is able to change
parameters on the switch (Read/Write) or is only able to view
(Read Only).
As a factory default, admin has Read/Write access and guest
has Read Only access. There can only be one Read/Write user
and up to 5 Read Only users.
show loginsession
Displays all login session information
username <username> {passwd |
nopasswd}
Allows the user to set passwords or change passwords needed
to login
A prompt will appear after the command is entered requesting
the old password. In the absence of an old password leave the
area blank. The operator must press enter to execute the
command.
The system then prompts the user for a new password then a
prompt to confirm the new password. If the new password and
the confirmed password match a message will be displayed.
The user password should not be more than eight characters in
length.
copy running-config startup-config
[filename]
This will save passwords and all other changes to the device.
If you do not save config, all configurations will be lost when a
power cycle is performed on the switch or when the switch is
reset.
2.5.3 Quick Start up User Account Management
Table 2-3. Quick Start up User Account Management
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 22/1246
Page 23
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command
Details
show ip interface
Displays the Network Configurations
Interface Status – Indicates whether the interface is up or
down.
IP Address - IP Address of the interface
Default IP is 192.168.2.1
Subnet Mask - IP Subnet Mask for the interface. Default is
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway - The default Gateway for this interface
Default value is 0.0.0.0
Burned in MAC Address - The Burned in MAC Address used for
inband connectivity
Network Configurations Protocol Current - Indicates which
network protocol is being used. Default is none
Management VLAN Id - Specifies VLAN id
Web Mode - Indicates whether HTTP/Web is enabled.
Java Mode - Indicates whether java mode is enabled.
ip address
(Config)#interface vlan 1
(if-vlan 1)#ip address <ipaddr> <netmask>
(if-vlan 1)#exit
(Config)#ip default-gateway <gateway>
IP Address range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Subnet Mask range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Gateway Address range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Displays all of the login session information
2.5.4 Quick Start up IP Address
To view the network parameters the operator can access the device by the following three methods.
Simple Network Management Protocol - SNMP
Telnet
Web Browser
Table 2-4. Quick Start up IP Address
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 23/1246
Page 24
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command
Details
copy startup-config xmodem
<filename>
This starts the upload and displays the mode of uploading and
the type of upload it is and confirms the upload is taking place.
For example:
If the user is using HyperTerminal, the user must specify where
the file is going to be received by the pc.
Command
Details
copy xmodem startup-config
<filename>
Sets the download datatype to be an image or config file.
The URL must be specified as: xmodem: filepath/ filename
For example:
If the user is using HyperTerminal, the user must specify which
file is to be sent to the switch. The Switch will restart
automatically once the code has been downloaded.
Command
Details
copy <url> startup-config <filename>
Sets the download datatype to be an image or config file.
The URL must be specified as: tftp://ipAddr/filepath/fileName.
The startup-config option downloads the config file using tftp
and image option downloads the code file.
2.5.5 Quick Start up Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC
Table 2-5. Quick Start up Uploading from Switch to Out-of-Band PC (XMODEM)
2.5.6 Quick Start up Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch
Table 2-6 Quick Start up Downloading from Out-of-Band PC to Switch
2.5.7 Quick Start up Downloading from TFTP Server
Before starting a TFTP server download, the operator must complete the Quick Start up for the
IPAddress.
Table 2-7 Quick Start up Downloading from TFTP Server
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 24/1246
Page 25
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command
Details
clear config
Enter yes when the prompt pops up to clear all the
configurations made to the switch.
copy running-config startup-config
[filename]
Enter yes when the prompt pops up that asks if you want to
save the configurations made to the switch.
reload
Enter yes when the prompt pops up that asks if you want to
reset the system.
You can reset the switch or cold boot the switch; both work
effectively.
2.5.8 Quick Start up Factory Defaults
Table 2-8 Quick Start up Factory Defaults
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 25/1246
Page 26

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
3 Console and Telnet Administration Interface
This chapter discusses many of the features used to manage the Switch, and explains many concepts
and important points regarding these features. Configuring the Switch to implement these concepts is
discussed in detail in chapter 6.
3.1 Local Console Management
Local console management involves the administration of the Switch via a direct connection to the
RS-232 DCE console port. This is an Out-of-band connection, meaning that it is on a different circuit
than normal network communications, and thus works even when the network is down.
The local console management connection involves a terminal or PC running terminal
software
network administrator can manage, control, and monitor many functions of the Switch. Hardware
components in the Switch allow it to be an active part of a manageable network. These components
include a CPU, memory for data storage, other related hardware, and SNMP agent firmware. Activities
on the Switch can be monitored with these components, while the Switch can be manipulated to
out
to operate the Switch’s built-in console program (see Chapter 6). Using the console program, a
specific tasks.
3.2 Set Up your Switch Using Console Access
Out-of-band management requires connecting a terminal, such as a VT-100 or a PC running a
terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal, which is automatically installed with Microsoft
Windows) to the RS-232 DCE console port of the Switch. Switch management using the RS-232 DCE
console port is called Local Console Management to differentiate it from management done via
management platforms, such as DView or HP OpenView.
Make sure the terminal or PC you are using to make this connection is configured to match these
settings. If you are having problems making this connection on a PC, make sure the emulation is set to
VT-100 or ANSI. If you still don’t see anything, try pressing <Ctrl> + r to refresh the screen.
First-time configuration must be carried out through a console, that is, either (a) a VT100-type serial data
terminal, or (b) a computer running communications software set to emulate a VT100. The console must
be connected to the Diagnostics port. This is an RS-232 port with a 9-socket D-shell connector and
DCE-type wiring. Make the connection as follows:
1. Obtain suitable cabling for the connection.You can use a null-modem RS-232 cable or an
ordinary RS-232 cable and a null-modem adapter. One end of the cable (or cable/adapter
combination) must have a 9-pin D-shell connector suitable for the Diagnostics port; the other end
must have a connector suitable for the console’s serial communications port.
emulat ion
carry
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 26/1246
Page 27

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
2. Power down the devices, attach the cable (or cable/adapter combination) to the correct ports,
and restore power.
3. Set the console to use the following communication parameters for your terminal:
The console port is set for the following configuration:
Baud rate: 115,200
Data width: 8 bits
Parity: none
Stop bits: 1
Flow Control: none
A typical console connection is illustrated below:
Figure 3-1: Console Setting Environment
3.3 Set Up your Switch Using Telnet Access
Once you have set an IP address for your Switch, you can use a Telnet program (in a VT-100 compatible
terminal mode) to access and control the Switch. Most of the screens are identical, whether accessed
from the console port or from a Telnet interface.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 27/1246
Page 28
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
4 Web-Based Management
4.1 Overview
The Korenix JetNet 7850G-2XG/6852G provides a built-in browser interface that lets you configure and
manage it remotely using a standard Web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later or
Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later. This interface also allows for system monitoring and management of the
switch. The ‘help’ page covers many of the basic functions and features of the switch and its Web
interface. When you configure the switch for the first time from the console, you can assign an IP
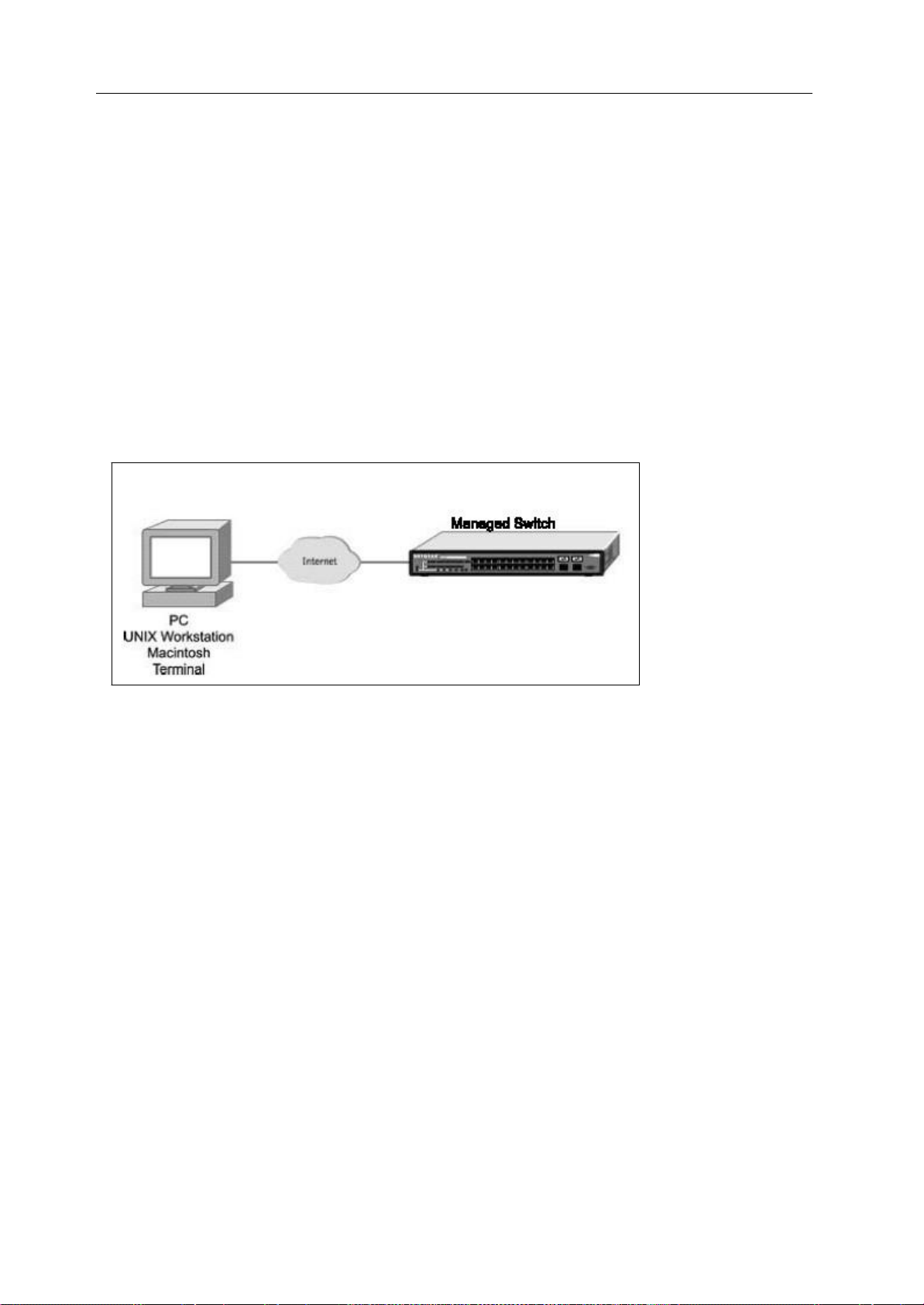
address and subnet mask to the switch. Thereafter, you can access the switch’s Web interface directly
using your Web browser by entering the switch’s IP address into the address bar. In this
use your Web browser to manage the switch from a central location, just as if you were directly
connected to the switch’s console port. Below figure shows this management method.
way, you
can
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 28/1246
Page 29
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
4.2 How to log in
The Korenix JetNet 7850G-2XG/6852G can be configured remotely from Microsoft Internet
Explorer (version 5.0 or above), or Mozilla FireFox (version 3.6 or above).
1. Determine the IP address of your managed switch.
2. Open your Web browser.
3. Log in to the managed switch using whatever IP address the unit is currently configured with.
4. Type the default user name of admin and default of admin, or whatever password you have set up.
Once you have entered your access point name, your Web browser automatically finds the JetNet 7850G2XG/6852G Layer 3 Managed Switch and display the home page, as shown below.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 29/1246
Page 30
Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
4.3 Web-Based Management Menu
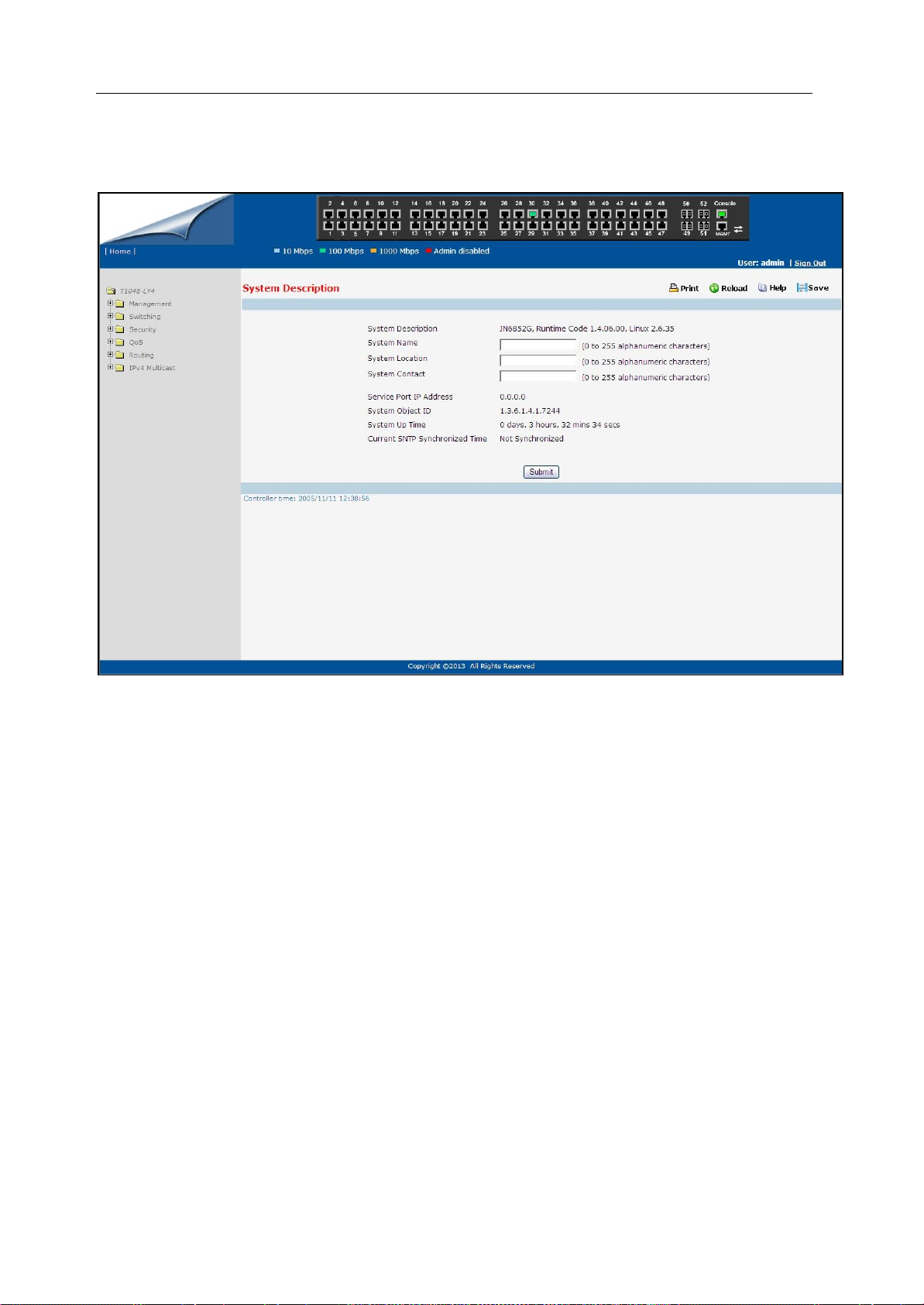
This above page displays system information, such as:
System Description
System Name
System Location
System Contact
IP Address
Service Port IP Address
System Object ID (OID)
System Up Time
Menus
The Web-based interface enables navigation through several menus. The main navigation menu is on
the left of every page and contains the screens that let you access all the commands and statistics the
switch provides.
Main Menus
Management
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 30/1246
Page 31

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Switching
Security
QoS
Routing
IPv4 Multicast
Secondary Menus
The Secondary Menus under the Main Menu contain a host of options that you can use to configure your
switch. The online help contains a detailed description of the features on each screen. You can click the
‘help’ or the question mark at the top right of each screen to view the help menu topics.
The Secondary Menus are detailed below, with cross-references to the sections in this manual that
contain the corresponding command descriptions.
Management
Information— see “show arp” and “show hardware”
Configuration — see “Management Commands and Device Configuration Commands”
System Utilities — see “System Utilities”
File Management — see “Copy and Delete Commands”
User Management — see “User Account and AAA Commands”
Statistics — see “show interface counters”
Logs — see “System Information and Statistics Commands”
SNMP — see “SNMP Server Commands and SNMP Trap Commands”
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 31/1246
Page 32

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
SNTP — see “SNTP Commands”
CDP — see “CDP Commands”
LLDP — see “LLDP Commands”
UDLD — see “UDLD Commands”
sFlow — see “sFlow Commands”
DHCP Client — see “DHCP Client Commands”
DNS Relay — see “Domain Name Server Relay Commands”
DDNS – see “DDNS Commands”
Switching
Forwarding Database — see “Device Configuration Commands’ L2MAC Address”
Port — see “Device Configuration Commands’ Interface”
DHCP Snooping — see “DHCP snooping Commands”
VLAN — see “VLAN Management Commands”
DVLAN—see “DVLAN Management Commands”
Portected Port — see “Portected Port Commands”
Protocol-based VLAN — see “Protocol-based VLAN Commands”
IP Subnet-based VLAN — see “IP Subnet-based VLAN Commands”
MAC-based VLAN — see “MAC-based Commands”
MAC-based Vocie VLAN — see “MAC-based Vocie VLAN Commands”
Voice VLAN — see “Voice VLAN Commands”
VTP — see “VTP Commands”
GARP — see “GVRP and Bridge Extension Commands”
MAC Filters — see “MAC Filters Commands”
Dynamic Arp Inspection — see “DAI Commands”
IGMP Snooping — see “IGMP Snooping Commands”
IGMP Snooping Querier — see “IGMP Snooping Querier Commands”
MLD Snooping — see “MLD Snooping Commands”
MLD Snooping Querier — see “MLD Snooping Querier Commands”
Port Channel — see “Port Channel Commands”
Multicast Forwarding DataBase — see “L2 MAC Address and Multicast Forwarding Database Tables
Commands”
Spanning Tree — see “Spanning Tree Commands”
Link State — see “Link state Commands”
Port Backup — see “Port backup Commands”
Rapid Super Ring —see “Rapid Super Ring Commands”
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 32/1246
Page 33

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Security
Port Access Control — see “Dot1x Configuration Commands”
Port Security — see “Port Security Configuration Commands”
Captive Portal — see “Captive Portal Commands”
RADIUS — see “Radius Configuration Commands”
TACACS+ — see “TACACS+ Configuration Commands”
LDAP – see “LDAP Configuration Commands”
Access Control List — see “ACL Commands”IP Filter — see “Network Commands”
Secure HTTP — see “HTTP Commands”
Secure Shell — see “Secure Shell (SSH) Commands”
Denial of Service — see “Denial of Service Commands”
QoS
Diffserv — see “Differentiated Services Commands”
Class of Service — see "Class of Service Commands" and “L2 Priority Commands”
Auto VoIP — “Auto-Voice over IP Commands”
iSCSI — “iSCSI Optimization Commands”
Routing
ARP — see “Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Commands”
IP — see “IP Routing Commands”
OSPF — see “Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Commands”
BOOTP/DHCP Relay Agent — see “BOOTP/DHCP Re lay Commands”
DHCP Client — see “DHCP Client Commands”
IP Helper — see “IP Helper Commands”
RIP — see “Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Commands”
Router Discovery — see “Router Discovery Protocol Commands”
Router — see “IP Routing Commands”
VLAN Routing — see “VLAN Routing Commands”
VRRP — see “Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) Commands”
Loopbacks — see “Loopbacks Commands”
IPv4 Multicast
DVMRP — see “DVMRP Commands”
IGMP — see “IGMP Commands”
PIM — see “PIM Commands”
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 33/1246
Page 34

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
5 Command Line Interface Structure and
Mode-based CLI
The Command Line Interface (CLI) syntax, conventions, and terminology are described in this section.
Each CLI command is illustrated using the structure outlined below.
5.1 CLI Command Format
Commands are followed by values, parameters, or both.
Example 1
ip address <ipaddr> <netmask> [<gateway>]
ip address is the command name.
<ipaddr> <netmask> are the required values for the command.
[<gateway>] is the optional value for the command.
Example 2
snmp-server location <loc>
snmp-server location is the command name.
<loc> is the required parameter for the command.
Example 3
clear vlan
clear vlan is the command name.
Command
The text in bold, non-italic font must be typed exactly as shown.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 34/1246
Page 35

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
5.2 CLI Mode-based Topology
Parameters
Parameters are order dependent.
The text in bold italics should be replaced with a name or number. To use spaces as part of a name
parameter, enclose it in double quotes like this: "System Name with Spaces".
Parameters may be mandatory values, optional values, choices, or a combination.
<parameter>. The <> angle brackets indicate that a mandatory parameter must be entered in
Values
place of the brackets and text inside them.
[parameter]. The [] square brackets indicate that an optional parameter may be entered in place
of the brackets and text inside them.
choice1 | choice2. The | indicates that only one of the parameters should be
The {} curly braces indicate that a parameter must be chosen from the list of
choices.
entered.
ipaddr This parameter is a valid IP address, made up of four decimal bytes ranging from 0 to 255.
The default for all IP parameters consists of zeros (that is, 0.0.0.0). The interface IP address of 0.0.0.0 is
invalid.
macaddr The MAC address format is six hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, for example
00:06:29:32:81:40.
areaid Area IDs may be entered in dotted-decimal notation (for example, 0.0.0.1). An area ID of
0.0.0.0 is reserved for the backbone. Area IDs have the same form as IP addresses, but are distinct from
IP addresses. The IP network number of the sub-netted network may be used for the area ID.
routerid The value of <router id> must be entered in 4-digit dotted-decimal notation (for example,
0.0.0.1). A router ID of 0.0.0.0 is invalid.
slot/port This parameter denotes a valid slot number, and a valid port number. For example, 0/1
represents unit number 1, slot number 0 and port number 1. The <slot/port> field is composed of a valid
slot number and a valid port number separated by a forward slash (/).
logical slot/port This parameter denotes a logical slot number, and logical port number assigned. This
is applicable in the case of a port-channel (LAG). The operator can use the logical slot number, and the
logical port number to configure the port-channel.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 35/1246
Page 36

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Address Type
Format
Range
IPAddr
A.B.C.D
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
MacAddr
YY:YY:YY:YY:YY:YY
hexidecimal digit pairs
Conventions
Network addresses are used to define a link to a remote host, workstation, or network. Network
addresses are shown using the following syntax:
Table 5-1. Network Address Syntax
Double quotation marks such as "System Name with Spaces" set off user defined strings. If the operator
wishes to use spaces as part of a name parameter then it must be enclosed in double quotation marks.
Empty strings (““) are not valid user defined strings. Command completion finishes spelling the
command when enough letters of a command are typed to uniquely identify the command word. The
command may be executed by typing <enter> (command abbreviation) or the command word may be
completed by typing the <tab> (command completion).
The value 'Err' designates that the requested value was not internally accessible. This should never
happen and indicates that there is a case in the software that is not handled correctly.
The value of '-----' designates that the value is unknown.
Annotations
The CLI allows the user to type single-line annotations at the command prompt for use when writing test
or configuration scripts and for better readability. The exclamation point (‘!’) character flags the beginning
of a comment. The comment flag character can begin a word anywhere on the command line and all
input following this character is ignored. Any command line that begins with the character ‘!’
recognized
as a comment line and ignored by the parser.
Some examples are provided below:
! Script file for displaying the ip interface
! Display information about interfaces
show ip interface 0/1 !Displays the information about the first interface
! Display information about the next interface
show ip interface 0/2
! End of the script file
is
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 36/1246
Page 37

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6 Switching Commands
6.1 System Information and Statistics commands
6.1.1 show arp
This command displays connectivity between the switch and other devices. The Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) cache identifies the MAC addresses of the IP stations communicating with the switch.
Syntax
show arp
Default Setting
Command Mode
Display Message
None
Privileged Exec
MAC Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons. For
example: 00:23:45:67:89:AB
IP Address: The IP address assigned to each interface.
Interface: Valid slot number and a valid port number.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 37/1246
Page 38

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.2 show calendar
This command displays the system time.
Syntax
show calendar
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Current Time: displays system time
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 38/1246
Page 39

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1035
bcmCNTR.0
1.59%
1.42%
1.19%
1038
bcmLINK.0
2.99%
2.84%
2.44%
1040
bcmL2X.1
1.99%
2.09%
1.81%
1041
bcmCNTR.1
1.39%
1.40%
1.19%
1042
bcmLINK.1
2.99%
2.87%
2.45%
6.1.3 show process cpu
This command provides the percentage utilization of the CPU by different tasks.
Syntax
show process cpu
It is not necessarily the traffic to the CPU, but different tasks that keep the CPU busy
i
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
The following shows example CLI display output for the command.
Memory Utilization Report
status bytes
------ ---------free 250978304
alloc 275599360
CPU Utilization:
PID Name 5 Secs 60 Secs 300
-----------------------------------------------------------------
1030 osapiTimer 0.00% 0.02% 0.02%
1032 _interrupt_thread 0.00% 0.02% 0.02%
1034 bcmL2X.0 1.99% 2.10% 1.81%
Secs
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 39/1246
Page 40

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
1043 bcmRX 0.19% 0.19% 0.16%
1044 cpuUtilMonitorTask 0.19% 0.14% 0.11%
1046 tL7Timer0 0.00% 0.02% 0.01%
1054 simPts_task 0.00% 0.02% 0.01%
1058 Detecting SFP+ Modu 0.00% 0.02% 0.01%
1080 emWeb 0.00% 0.08% 0.06%
1085 StormCtrl Log Table 0.00% 0.03% 0.03%
1091 SNMPTask 1.79% 12.48% 37.44%
1101 dot1s_timer_task 0.19% 0.07% 0.04%
1118 sFlowTask 0.00% 0.09% 0.11%
1135 RMONTask 0.00% 0.12% 0.15%
1137 udldTask 0.00% 0.01% 0.01%
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Total CPU Utilization 15.37% 26.14% 49.21%
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 40/1246
Page 41

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.4 show eventlog
This command displays the event log, which contains error messages from the system, in the Primary
Management System or in the specified unit. The event log is not cleared on a system reset.
Syntax
show eventlog [unit]
unit - The unit number of the remote system. The range is 1 to 8.
unit parameter is only support for stacking platform.
!
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
File: The file in which the event originated.
Line: The line number of the event.
Task Id: The task ID of the event.
Code: The event code.
Time: The time this event occurred.
Event log information is retained across a switch reset.
!
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 41/1246
Page 42

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.5 show running-config
This command is used to display/capture the current setting of different protocol packages supported on
switch. This command displays/captures only commands with settings/configurations with values that
differ from the default value. The output is displayed in script format, which can be used to configure
another switch with the same configuration.
When a script name is provided, the output is redirected to a configuration script. The option [all] will also
enable the display/capture of all commands with settings/configurations that include values that
are same
as the default values. If the optional <scriptname> is provided with a file name extension of “.scr”, the
output will be redirected to a script file.
Syntax
show running-config [all | <scriptname>]
all - enable the display/capture of all commands with settings/configurations that include values that
are same as the default values.
<scriptname> - redirect the output to the file <scriptname>.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 42/1246
Page 43

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.6 show sysinfo
This command displays switch brief information and MIBs supported.
Syntax
show sysinfo
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
System Description: The text used to identify this switch.
System Name: The name used to identify the switch.
System Location: The text used to identify the location of the switch. May be up to 255
alpha-numeric characters. The factory default is blank.
System Contact: The text used to identify a contact person for this switch. May be up to 255
alphanumeric characters. The factory default is blank.
System Object ID: The manufacturing ID.
System Up Time: The time in days, hours and minutes since the last switch reboot.
Current SNTP Syncronized Time: The time which is synchronized from SNTP server.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 43/1246
Page 44

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.7 show system
This command displays switch system information.
Syntax
show system
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
System Description: Text used to identify this switch.
System Object ID: The manufacturing ID
System Information
System Up Time: The time in days, hours and minutes since the last switch reboot.
System Name: Name used to identify the switch.
System Location: Text used to identify the location of the switch. May be up to 255
alpha-numeric characters. The factory default is blank.
System Contact: Text used to identify a contact person for this switch. May be up to 255
alphanumeric characters. The factory default is blank.
MAC Address: The burned in MAC address used for in-band connectivity.
Web Server: Displays to enable/disable web server function
Web Server Port: Displays the web server http port
Web Server Java Mode: Specifies if the switch should allow access to the Java applet in the
header frame. Enabled means the applet can be viewed. The factory default is disabled.
Protocol Current: Indicates which network protocol is being used. The options are bootp | dhcp |
none.
DHCP Client Identifier TEXT: DCHP client identifier for this switch.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 44/1246
Page 45

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.8 show tech-support
This command displays system and configuration information when you contact technical support. The
output of the show tech-support command combines the output of the following commands: show
version, show sysinfo, show interface status, show logging, show event log, show logging buffered,
show trap log, show running config, … etc.
Syntax
show tech-support
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
!
This command is only support on console port.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 45/1246
Page 46

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.9 show hardware
This command displays inventory information for the switch.
Syntax
show hardware
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
System Description: Text used to identify the product name of this
Machine Type: Specifies the machine model as defined by the Vital Product Data.
Machine Model: Specifies the machine model as defined by the Vital Product Data.
Serial Number: The unique box serial number for this switch.
switch.
Label Revision Number: The label revision serial number of this switch is used for manufacturing
purposes.
Part Number: Manufacturing part number.
Hardware Version: The hardware version of this switch. It is divided into four parts. The first byte is
the major version and the second byte represents the minor version.
ADT7470: Now Temperature: The temperature of sensor of ADT7470.
ADT7470_1: Fan 1 Status: Status of Fan1. It could be active or inactive.
ADT7470_1: Fan 2 Status: Status of Fan2. It could be active or inactive.
ADT7470_1: Fan 3 Status: Status of Fan3. It could be active or inactive.
Below 10-Giga/1G-Giga interface information depend on plugging SFP+/SFP Transceiver
!
Interface y: (The yth 10-Giga information of switch 1).
10 Gigabit Ethernet Compliance Codes: Transceiver’s compliance codes.
Vendor Name: The SFP transceiver vendor name shall be the full name of the corporation, a
commonly accepted abbreviation of the name of the corporation, the SCSI company code for the
corporation, or the stock exchange code for the corporation.
Vendor Part Number: Part number provided by SFP transceiver vendor.
Vendor Serial Number: Serial number provided by vendor.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 46/1246
Page 47

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Vendor Revision Number: Revision level for part number provided by vendor.
Vendor Manufacturing Date: The vendor’s manufacturing date.
Additional Packages: This displays the additional packages that are incorporated into this system.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 47/1246
Page 48

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.10 show version
This command displays inventory information for the switch.
Syntax
show version
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
System Description: Text used to identify the product name of this
Machine Type: Specifies the machine model as defined by the Vital Product Data.
Machine Model: Specifies the machine model as defined by the Vital Product Data.
Serial Number: The unique box serial number for this switch.
FRU Number: The field replaceable unit number.
Part Number: Manufacturing part number.
Maintenance Level: The identification of the hardware change level.
Manufacturer: The two-octet code that identifies the manufacturer.
Burned In MAC Address: The burned-in universally administered MAC address of this switch.
Software Version: The platform.function.release. maintenance number of the code currently
running on the switch.
Operating System: The operating system currently running on the switch.
Network Processing Device: Identifies the network processor hardware.
Additional Packages: A list of the optional software packages installed on the switch, if any. For
example, QOS, IPv6 Management or Multicast.
switch.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 48/1246
Page 49

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.11 show loginsession
This command displays current telnet and serial port connections to the switch.
Syntax
show loginsession
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
ID: Login Session ID
User Name: The name the user will use to login using the serial port or Telnet. A new user may be
added to the switch by entering a name in a blank entry. The user name may be up to 8 characters,
and is not case sensitive. Two users are included as the factory default, admin, and guest.
Connection From: IP address of the telnet client machine or EIA-232 for the serial port connection.
Idle Time: Time this session has been idle.
Session Time: Total time this session has been connected.
Session Type: Shows the type of session: telnet, serial port, SSH or HTTP/HTTPS.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 49/1246
Page 50

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.1.12 show command filter
This command displays the information that begin/include/exclude the regular expression.
Syntax
show command [| begin/include/exclude <LINE>]
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
command: Any show command of the CLI
begin: Begin with the line that matches
include: Include lines that match
exclude: Exclude lines that match
<LINE>: Regular Expression
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 50/1246
Page 51

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2 Device Configuration Commands
6.2.1 Interface
6.2.1.1 show interface status
This command displays the Port monitoring information for the system.
Syntax
show interface status [<slot/port>]
<slot/port> - is the desired interface number.
no parameter - Displays information for all interfaces.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Intf: The physical slot and physical port.
Type: If not blank, this field indicates that this port is a special type of port. The possible values are:
Source: This port is a monitoring port.
PC Mbr: This port is a member of a port-channel (LAG).
Dest: This port is a probe port.
Admin Mode: Selects the Port control administration state. The port must be enabled in order for it
to be allowed into the network. It may be enabled or disabled. The factory default is enabled.
Physical Mode: Selects the desired port speed and duplex mode. If auto-negotiation support is
selected, then the duplex mode and speed will be set from the auto-negotiation process. Note that
the port's maximum capability (full duplex 100M) will be advertised. Otherwise, this object will
determine the port's duplex mode and transmission rate. The factory default is Auto.
Physical Status: Indicates the port speed and duplex mode.
Link Status: Indicates whether the Link is up or down.
Link Trap: This object determines whether to send a trap when link status changes. The factory
default is enabled.
LACP Mode: Displays whether LACP is enabled or disabled on this port.
Flow Control Mode: Displays flow control mode. The possible values are:
Disable: This port is disabled flow control.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 51/1246
Page 52

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Enable: This port is enabled flow control.
Capabilities Status: Displays interface capabilities.
6.2.1.2 show interface counters
This command displays a summary of statistics for a specific interface or all interfaces.
Syntax
show interface counters [<slot/port>]
<slot/port> - is the desired interface number.
no paramter - Displays statistics information for all interfaces.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
The display parameters when the argument is '<slot/port>' are as follows:
Packets Received Without Error: The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and
multicast packets) received by the processor.
Packets Received With Error: The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Broadcast Packets Received: The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Packets Transmitted Without Error: The total number of packets transmitted out of the interface.
Transmit Packets Errors: The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because
of errors.
Collisions Frames: The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this Ethernet segment.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared: The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since
the statistics for this port were last cleared.
The display parameters if no argument is used are as follows:
Interface: The physical slot and physical port or the logical slot and logical port.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 52/1246
Page 53

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Packets Received Without Error: The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and
multicast packets) received.
Packets Received With Error: The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Broadcast Packets Received: The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Packets Transmitted Without Error: The total number of packets transmitted.
Transmit Packets Errors: The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because
of errors.
Collisions Frames: The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this Ethernet segment.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared: The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since
the statistics for this port were last cleared.
This command displays detailed statistics for a specific port or for all CPU traffic based upon the
argument.
Syntax
show interface counters detailed {<slot/port> | switchport}
<slot/port> - is the desired interface number.
switchport - This parameter specifies whole switch or all interfaces.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
The display parameters when the argument is ' <slot/port>' are as follows:
Total Packets Received (Octets): The total number of octets of data (including those in bad
packets) received on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets). This object can
be used as a reasonable estimate of Ethernet utilization. If greater precision is desired, the
etherStatsPkts and etherStatsOctets objects should be sampled before and after a common interval.
The result of this equation is the value Utilization which is the percent utilization of the Ethernet
segment on a scale of 0 to 100 percent.
Packets Received 64 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received 65-127 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 53/1246
Page 54

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Packets Received 128-255 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 256-511 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 512-1023 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 1024-1518 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
octets).
including FCS
Packets Received > 1522 Octets: The total number of packets received that were longer than 1522
octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well formed.
Packets RX and TX 64 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 65-127 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets RX and TX 128-255 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets RX and TX 256-511 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets RX and TX 512-1023 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets RX and TX 1024-1518 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 1519-1522 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 1519 and 1522 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 1523-2047 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 1523 and 2047 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 2048-4095 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 2048 and 4095 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 4096-9216 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 4096 and 9216 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Total Packets Received Without Errors
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 54/1246
Page 55

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Unicast Packets Received: The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer
protocol.
Multicast Packets Received: The total number of good packets received that were directed to a
multicast address. Note that this number does not include packets directed to the broadcast address.
Broadcast Packets Received: The total number of good packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Total Packets Received with MAC Errors
Jabbers Received: The total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and had either a bad FCS with an integral number
of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral number of octets (Alignment Error). Note that
this definition of jabber is different than the definition in IEEE-802.3 section 8.2.1.5 (10BASE5) and
section 10.3.1.4 (10BASE2). These documents define jabber as the condition where any packet
exceeds 20 ms. The allowed range to detect jabber is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Undersize Received: The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets in length
with GOOD CRC(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Fragments Received: The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets in length
with ERROR CRC(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Alignment Errors: The total number of packets received that had a length (excluding framing bits,
but including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad FCS with a
non-integral number of octets.
FCS Errors: The total number of packets received that had a length (excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad FCS with an integral
number of octets
Overruns: The total number of frames discarded as this port was overloaded with incoming packets,
and could not keep up with the inflow.
Total Packets Transmitted (Octets)
Packets Transmitted 64 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 65-127 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Transmitted 128-255 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 256-511 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 512-1023 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted 1024-1518 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 55/1246
Page 56

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Packets Transmitted 1519-1522 Octets: The total number of packets (including bad packets)
received that were between 1519 and 1522 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
Max Info: The maximum size of the Info (non-MAC) field that this port will receive or transmit.
Total Packets Transmitted Successfully
Unicast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Multicast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested
be transmitted to a Multicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested
be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Total Transmit Errors
FCS Errors: The total number of packets transmitted that had a length (excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had a bad FCS with an integral
number of octets
Tx Oversized: The total number of frames that exceeded the max permitted frame size. This
counter has a max increment rate of 815 counts per sec. at 10 Mb/s.
Underrun Errors: The total number of frames discarded because the transmit FIFO buffer became
empty during frame transmission.
Total Transmited Packets Discards
Single Collision Frames: A count of the number of successfully transmitted frames on a particular
interface for which transmission is inhibited by exactly one collision.
Multiple Collision Frames: A count of the number of successfully transmitted frames on a particular
interface for which transmission is inhibited by more than one collision.
Excessive Collisions: A count of frames for which transmission on a particular interface fails due to
excessive collisions.
GVRP PDUs Received: The count of GVRP PDUs received in the GARP layer.
GVRP PDUs Transmitted: The count of GVRP PDUs transmitted from the GARP layer.
GVRP Failed and Registrations: The number of times attempted GVRP registrations could not be
completed.
GMRP PDUs received: The count of GMRP PDUs received in the GARP layer.
GMRP PDUs Transmitted: The count of GMRP PDUs transmitted from the GARP layer.
GMRP Failed Registrations: The number of times attempted GMRP registrations could not be
completed.
STP BPDUs Transmitted: Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
STP BPDUs Received: Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
RSTP BPDUs Transmitted: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
RSTP BPDUs Received: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 56/1246
Page 57

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
MSTP BPDUs Transmitted: Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
MSTP BPDUs Received: Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
EAPOL Frames Received: The number of valid EAPOL frames of any type that have been received
by this authenticator.
EAPOL Frames Transmitted: The number of EAPOL frames of any type that have been
transmitted by this authenticator.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared: The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since
the statistics for this port were last cleared.
The display parameters when the argument is ‘switchport’ are as follows:
Total Packets Received (Octets): The total number of octets of data received by the processor
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received Without Error: The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and
multicast packets) received by the processor.
Unicast Packets Received: The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer
protocol.
Multicast Packets Received: The total number of packets received that were directed to a multicast
address. Note that this number does not include packets directed to the broadcast address.
Broadcast Packets Received: The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Receive Packets Discarded: The number of inbound packets which were chosen to be discarded
even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free up buffer space.
Octets Transmitted: The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing
characters.
Packets Transmitted without Errors: The total number of packets transmitted out of the interface.
Unicast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Multicast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested
be transmitted to a Multicast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested
be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Packets Discarded: The number of outbound packets which were chosen to be
discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a
higher-layer protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free up buffer space.
Most Address Entries Ever Used: The highest number of Forwarding Database Address Table
entries that have been learned by this switch since the most recent reboot.
Address Entries Currently in Use: The number of Learned and static entries in the Forwarding
Database Address Table for this switch.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 57/1246
Page 58

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Maximum VLAN Entries: The maximum number of Virtual LANs (VLANs) allowed on this switch.
Most VLAN Entries Ever Used: The largest number of VLANs that have been active on this switch
since the last reboot.
Static VLAN Entries: The number of presently active VLAN entries on this switch that have been
created statically.
Dynamic VLAN Entries: The number of presently active VLAN entries on this switch that have been
created by GVRP registration.
VLAN Deletes: The number of VLANs on this switch that have been created and then deleted since
the last reboot.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared: The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds, since
the statistics for this switch were last cleared.
6.2.1.3 show interface switch
This command displays a summary of statistics for all CPU traffic.
Syntax
show interface switch
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Broadcast Packets Received: The total number of packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
Packets Received With Error: The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
Packets Transmitted Without Error: The total number of packets transmitted out of the interface.
Broadcast Packets Transmitted: The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested
to be transmitted to the Broadcast address, including those that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Packet Errors: The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of
errors.
Address Entries Currently In Use: The total number of Forwarding Database Address Table
entries now active on the switch, including learned and static entries.
VLAN Entries Currently In Use: The number of VLAN entries presently occupying the VLAN table.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared: The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since
the statistics for this switch were last cleared.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 58/1246
Page 59

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
i
6.2.1.4 interface
This command is used to enter Interface configuration mode.
Syntax
interface <slot/port>
<slot/port> - is the desired interface number.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
6.2.1.5 speed-duplex
This command is used to set the speed and duplex mode for the interface.
The 10G interfaces could be configured to operate at 10G or 1G speed. Use ‘speed-duplex
1000’ to change the speed of 10G port to 1G speed.
The auto negotiate function has to be disabled before setting the speed for
10/100/1000BASE-T ports.
Syntax
speed-duplex <10|100|1000>
no speed-duplex 1000
1000 – 1000Mbps, only valid for 10G ports.
10|100 – 10/100Mbps only valid for 10/100/1000BASE-T ports
no - This command will be back to 10G speed from 1G speed for 10G port.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 59/1246
Page 60

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
i
This command is used to set the speed and duplex mode for all interfaces.
Syntax
speed-duplex all <10|100|1000>
no speed-duplex all 1000
1000 – 1000 Mbps, only valid for 10G ports.
10|100 – 10/100Mbps only valid for 10/100/1000BASE-T ports.
all - This command represents all interfaces.
no - This command will be back to 10G speed from 1G speed for all 10G ports.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
6.2.1.6 negotiate
This command enables automatic negotiation on a port. The default value is enabled.
The 10G SFP+ and 1G SFP interfaces do not provide the following command. Automatic
negotiation of 10G SFP+ and 1G SFP interfaces is default disabled and can’t be enabled.
Syntax
negotiate
no negotiate
no - This command disables automatic negotiation on a port.
Default Setting
Enable
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 60/1246
Page 61

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
This command enables automatic negotiation on all interfaces. The default value is enabled.
Syntax
negotiate all
no negotiate all
all - This command represents all interfaces.
no - This command disables automatic negotiation on all interfaces.
Default Setting
Enable
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 61/1246
Page 62

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Syntax
capabilities {{10 | 100 } {full-duplex | half-duplex}} | {1000 full-duplex }
no capabilities {{10 | 100 } {full-duplex | half-duplex}} | {1000 full-duplex }
Syntax
capabilities all {{10 | 100} {full-duplex | half-duplex}} | {1000 full-duplex }
no capabilities all {{10 | 100} {full-duplex | half-duplex}} | {1000 full-duplex }
6.2.1.7 capabilities
This command is used to set the capabilities on specific interface.
i
The 10G SFP+ and 1G SFP interfaces do not provide the following command.
10 - 10BASE-T
100 - 100BASE-T
1000 - 1000BASE-T
full-duplex - Full duplex
half-duplex - Half duplex
no - This command removes the advertised capability with using parameter.
Default Setting
10G full-duplex for 10G SFP+ ports
1G full-duplex for 1G SFP ports
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command is used to set the capabilities on all interfaces.
10 - 10BASE-T
100 - 100BASE-T
1000 - 1000BASE-T
full-duplex - Full duplex
half-duplex - Half duplex
all - This command represents all interfaces.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 62/1246
Page 63

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
no - This command removes the advertised capability with using parameter
Default Setting
10G full-duplex for 10G SFP+ ports
1G full-duplex for 1G SFP ports
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 63/1246
Page 64

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
i
i
6.2.1.8 storm-control flowcontrol
This command enables 802.3x flow control for the switch.
802.3x flow control only applies to full-duplex mode ports. If PFC feature is enabled on the
same interface, 802.3x flow control will be disabled internally.
Syntax
storm-control flowcontrol
no storm-control flowcontrol
no - This command disables 802.3x flow control for the switch.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Global Config
This command enables 802.3x flow control for the specific interface.
802.3x flow control only applies to full-duplex mode ports. If PFC feature is enabled on the
same interface, 802.3x flow control will be disabled internally.
Syntax
storm-control flowcontrol
no storm-control flowcontrol
no - This command disables 802.3x flow control for the specific interface.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 64/1246
Page 65

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.1.9 shutdown
This command is used to disable a port.
Syntax
shutdown
no shutdown
no - This command enables a port.
Default Setting
Enabled
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command is used to disable all ports.
Syntax
shutdown all
no shutdown all
all - This command represents all ports.
no - This command enables all ports.
Default Setting
Enabled
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 65/1246
Page 66

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.1.10 description
This command is used to create an alpha-numeric description of the port.
Syntax
description <description>
no description
no - This command removes the description of the port.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Interface Config
6.2.1.11 mdi
This command is used to configure the physical port MDI/MDIX state.
This command is not provided for the 10G SFP+ interface and 1G SFP interface.
i
Syntax
mdi {auto|across|normal}
no mdi
auto - This type is auto selecting cable type.
across - This type is only allowed the Across-over cable.
normal - This type is only allowed the Normal cable.
no - This command restore the port mode to Auto.
Default Setting
Auto
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 66/1246
Page 67

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2 L2 MAC Address and Multicast Forwarding Database Tables
6.2.2.1 show mac-addr-table
This command displays the forwarding database entries. If the command is entered with no parameter,
the entire table is displayed. The administrator can enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for
the requested MAC address and all entries following the requested MAC address.
Syntax
show mac-addr-table [{<macaddr> <vlanid>}]
<macaddr> - enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for the requested MAC address.
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093)
no parameter – Displays the entire table.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Mac Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
Interface: The port on which this L2 MAC address was learned.
if Index: This object indicates the if Index of the interface table entry associated with this port.
Status: The status of this entry.
The meanings of the values are:
Static: The value of the corresponding instance was added by the system or a user when a static
MAC filter was defined. It cannot be relearned.
Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned by observing the source MAC
addresses of incoming traffic, and is currently in use.
Management: The value of the corresponding instance (system MAC address) is also the value of
an existing instance of dot1dStaticAddress. It is identified with interface 3/1 and is currently used
when enabling VLANs for routing.
Self: The value of the corresponding instance is the address of one of the switch’s physical
interfaces (the system’s own MAC address).
GMRP Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned via GMRP and applies to
Multicast.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 67/1246
Page 68

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Other: The value of the corresponding instance does not fall into one of the other categories.
6.2.2.2 show mac-addr-table count
This command displays the total forwarding database entries, the number of static and learnning mac
address, and the max address available on the switch.
Syntax
show mac-addr-table count
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Dynamic Address count: The total learning mac addresses on the L2 MAC address Table.
Static Address (User-defined) count: The total user-defined addresses on the L2 MAC address
Table.
Total MAC Addresses in use: This number of addresses are used on the L2 MAC address table.
Total MAC Addresses available: The switch supports max value on the L2 MAC address table.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 68/1246
Page 69

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.3 show mac-addr-table interface
This command displays the forwarding database entries. The user can search FDB table by using
interface number <slot/port>.
Syntax
show mac-addr-table interface <slot/port>
<slot/port> - Interface number.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Mac Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
VLAN ID: The VLAN id of that mac address.
Status: The status of this entry.
The meanings of the values are:
Static: The value of the corresponding instance was added by the system or a user when a
static MAC filter was defined. It cannot be relearned.
Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned by observing the source MAC
addresses of incoming traffic, and is currently in use.
Management: The value of the corresponding instance (system MAC address) is also the value
of an existing instance of dot1dStaticAddress. It is identified with interface 3/1 and is currently
used when enabling VLANs for routing.
Self: The value of the corresponding instance is the address of one of the switch’s physical
interfaces (the system’s own MAC address).
GMRP Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned via GMRP and applies to
Multicast.
Other: The value of the corresponding instance does not fall into one of the other categories.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 69/1246
Page 70

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.4 show mac-addr-table vlan
This command displays the forwarding database entries. The user can search FDB table by using VLAN
id.
Syntax
show mac-addr-table vlan <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093)
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Mac Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
Interface: The port on which this L2 MAC address was learned.
Status: The status of this entry.
The meanings of the values are:
Static: The value of the corresponding instance was added by the system or a user when a
static MAC filter was defined. It cannot be relearned.
Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned by observing the source MAC
addresses of incoming traffic, and is currently in use.
Management: The value of the corresponding instance (system MAC address) is also the value
of an existing instance of dot1dStaticAddress. It is identified with interface 3/1 and is currently
used when enabling VLANs for routing.
Self: The value of the corresponding instance is the address of one of the switch’s physical
interfaces (the system’s own MAC address).
GMRP Learned: The value of the corresponding instance was learned via GMRP and applies to
Multicast.
Other: The value of the corresponding instance does not fall into one of the other categories.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 70/1246
Page 71

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.5 show mac-address-table gmrp
This command displays the GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) entries in the Multicast
Forwarding Database (MFDB) table.
Syntax
show mac-address-table gmrp
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
MAC Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address is displayed as 8 bytes.
Type: This displays the type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end user.
Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Description: The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces: The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 71/1246
Page 72

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.6 show mac-address-table igmpsnooping
This command displays the IGMP Snooping entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) table.
Syntax
show mac-address-table igmpsnooping
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Mac Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
Type: This displays the type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end user.
Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Description: The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces: The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 72/1246
Page 73

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.7 show mac-address-table multicast
This command displays the MFDB information. If the command is entered with no parameter, the entire
table is displayed. This is the same as entering the all parameter. The user can display the table entry for
one MAC Address by specifying the MAC address as an optional parameter.
Syntax
show mac-address-table multicast [{<macaddr> <vlanid>]]
<macaddr> - enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for the requested MAC address
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093)
no parameter – Displays the entire table.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Mac Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
Type: This displays the type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end user.
Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Source: The component that is responsible for this entry in the Multicast Forwarding Database.
Possible values are IGMP Snooping, GMRP, and Static Filtering.
Description: The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces: The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
Forwarding Interfaces: The resultant forwarding list is derived from combining all the component’s
forwarding interfaces and removing the interfaces that are listed as the static filtering interfaces.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 73/1246
Page 74

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.8 show mac-address-table stats
This command displays the MFDB statistics.
Syntax
show mac-address-table stats
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Max MFDB Table Entries: This displays the total number of entries that can possibly be in the
MFDB.
Most MFDB Entries Since Last Reset: This displays the largest number of entries that have been
present in the Multicast Forwarding Database table. This value is also known as the MFDB
high-water mark.
Current Entries: This displays the current number of entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database
table.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 74/1246
Page 75

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.2.9 show mac-addr-table agetime
This command displays the forwarding database address aging timeout.
Syntax
show mac-addr-table agetime
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Address Aging Timout: This displays the total number of seconds for Forwarding Database table.
6.2.2.10 mac-addr-table aging-time
This command configures the forwarding database address aging timeout in seconds.
Syntax
mac-addr-table aging-time <10-1000000>
no mac-addr-table aging-time
<10-1000000> - aging-time (Range: 10-1000000) in seconds
no - This command sets the forwarding database address aging timeout to 300 seconds.
Default Setting
300
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 75/1246
Page 76

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3 VLAN Management
6.2.3.1 show vlan
This command displays brief information on a list of all configured VLANs.
Syntax
show vlan
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
VLAN ID: There is a VLAN Identifier (vlanid) associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID
is 1 to 4093.
VLAN Name: A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be up to 16 alphanumeric
characters, including blanks. The default is blank. VLAN ID 1 is always named `Default`. This field is
optional.
VLAN Type: Type of VLAN, which can be Default, (VLAN ID = 1), can be static (one that is
configured and permanently defined), or Dynamic (one that is created by GVRP registration).
Interface(s): Indicates by slot id and port number which port belongs to this VLAN.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 76/1246
Page 77

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.2 show vlan id
This command displays detailed information, including interface information, for a specific VLAN.
Syntax
show vlan {id <vlanid> | name <vlanname>}
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093)
<vlanname> - vlan name (up to 32 alphanumeric characters)
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
VLAN ID: There is a VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1 to 4093.
VLAN Name: A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters, including blanks. The default is blank. VLAN ID 1 is always named `Default`. This field is
optional.
VLAN Type: Type of VLAN, which can be Default, (VLAN ID = 1), can be static (one that is
configured and permanently defined), or Dynamic (one that is created by GVRP registration).
Interface: Indicates by slot id and port number which port is controlled by the fields on this line.
It is possible to set the parameters for all ports by using the selectors on the top line.
Current: Determines the degree of participation of this port in this VLAN. The permissible values
are:
Include: This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed in the
IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Exclude: This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration forbidden in
the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Autodetect: Specifies to allow the port to be dynamically registered in this VLAN via GVRP. The
port will not participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this port. This is
equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Configured: Determines the configured degree of participation of this port in this VLAN. The
permissible values are:
Include: This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed in the
IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Exclude: This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration forbidden in
the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 77/1246
Page 78

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Autodetect: Specifies to allow the port to be dynamically registered in this VLAN via GVRP. The
port will not participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this port. This is
equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Tagging: Select the tagging behavior for this port in this VLAN.
Tagged: Specifies to transmit traffic for this VLAN as tagged frames.
Untagged: Specifies to transmit traffic for this VLAN as untagged frames.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 78/1246
Page 79

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.3 show vlan association mac
This command displays the VLAN associated with a specific configured MAC address. If no MAC
address is specified, the VLAN associations of all the configured MAC addresses are displayed.
Syntax
show vlan association mac [<macaddr>]
<macaddr> - Enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for the requested MAC address.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
MAC Address: A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes. In an
SVL system, the MAC address will be displayed as 6 bytes. Note: This software version only
supports IVL systems.
VLAN ID: There is a VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1 to 4093.
Priority: There is a priority for each MAC-based.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 79/1246
Page 80

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.4 show vlan association subnet
This command displays the VLAN associated with a specific configured IP-Address and net mask. If no
IP Address and net mask are specified, the VLAN associations of all the configured IP-subnets are
displayed.
Syntax
show vlan association subnet [<ipaddr> <netmask>]
<ipaddr> - The IP address.
<netmask> - The subnet mask.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
IP Subnet: The IP address assigned to each interface.
IP Mask: The subnet mask.
VLAN ID: There is a VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1 to 4093.
Priority: There is a priority for each IPsubnet-based.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 80/1246
Page 81

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.5 show vlan internal usage
This command displays the VLAN assigned to port-based routing interfaces.
Syntax
show vlan internal usage
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Base VLAN ID: This is the Base VLAN ID for Internal allocation of VLANs to the routing interface.
Allocation Policy: Allocation Policy for VLAN ID in ascending or descending order.
VLAN: This is the Used Internal VLAN ID for the Interface.
Usage: This is the switch interface.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 81/1246
Page 82

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.6 show protocol group
This command displays the Protocol-based VLAN information for either the entire system, or for the
indicated group.
Syntax
show protocol group [<group-name>]
<group-name> - The group name of an entry in the Protocol-based VLAN table.
no parameter – Displays the entire table.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Group Name: This field displays the group name of an entry in the Protocol-based VLAN table.
Group ID: This field displays the group identifier of the protocol group.
Protocol(s): This field indicates the type of protocol(s) for this group.
VLAN: This field indicates the VLAN associated with this protocol group.
Interface(s): This field lists the slot/port interface(s) that are associated with this protocol group.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 82/1246
Page 83

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.7 show interface switchport
This command displays VLAN port information.
Syntax
show interface switchport [<slot/port>]
<slot/port> - Interface number.
no parameter – Display the entire table.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Interface: Indicates by slot id and port number which port is controlled by the fields on this line. It is
possible to set the parameters for all ports by using the selectors on the top line.
Port VLAN ID: The VLAN ID that this port will assign to untagged frames or priority tagged frames
received on this port. The value must be for an existing VLAN. The factory default is 1.
Acceptable Frame Types: Specifies the types of frames that may be received on this port. The
options are 'VLAN only' and 'Admit All'. When set to 'VLAN only', untagged frames or priority tagged
frames received on this port are discarded. When set to 'Admit All', untagged frames or priority
tagged frames received on this port are accepted and assigned the value of the Port VLAN ID for this
port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance to the 802.1Q VLAN
specification.
Ingress Filtering: May be enabled or disabled. When enabled, the frame is discarded if this port is
not a member of the VLAN with which this frame is associated. In a tagged frame, the VLAN is
identified by the VLAN ID in the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the Port VLAN ID specified
for the port that received this frame. When disabled, all frames are forwarded in accordance with the
802.1Q VLAN bridge specification. The factory default is disabled.
GVRP: May be enabled or disabled.
Default Priority: The 802.1p priority assigned to untagged packets arriving on the port.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 83/1246
Page 84

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.8 vlan database
This command is used to enter VLAN Interface configuration mode.
Syntax
vlan database
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
6.2.3.9 vlan
This command creates a new VLAN and assigns it an ID. The ID is a valid VLAN identification
number (ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN). VLAN range is 2-4093.
Syntax
vlan <vlan-list>
no vlan <vlan-list>
<vlan-list> - VLAN ID (Range: 2 –4093) – separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and
no zeros in between the range; Use '-' for range.
no - This command deletes an existing VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number (ID 1 is
reserved for the default VLAN). VLAN range is 2-4093.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
VLAN database
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 84/1246
Page 85

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.10 vlan name
This command changes the name of a VLAN. The name is an alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters, and the ID is a valid VLAN identification number. ID range is 1- 4093.
Syntax
vlan name <vlanid> <newname>
no vlan name <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
<newname> - Configure a new VLAN Name (up to 32 alphanumeric characters).
no - This command sets the name of a VLAN to a blank string. The VLAN ID is a valid VLAN
identification number. ID range is 1-4093.
Default Setting
The name for VLAN ID 1 is always Default. The name for other VLANs is defaulted to a blank string.
Command Mode
VLAN database
6.2.3.11 vlan association mac
This command associates a MAC address to a VLAN.
Syntax
vlan association mac <macaddr> <vlanid> [<priority>]
no vlan association mac <macaddr>
<macaddr> - Enter a MAC Address to display the table entry for the requested MAC address.
<vlandid> - VLAN identification number. ID range is 1-4093.
< priority> - The priority value for untagged frames received. Valid priority value is 0 to 7.
no - This command removes the association of a MAC address to a VLAN.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
VLAN database
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 85/1246
Page 86

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.12 vlan association subnet
This command removes the association of a MAC address to a VLAN.
Syntax
vlan association subnet <ipaddr> <netmask> <vlanid> [<priority>]
no vlan association subnet <ipaddr> <netmask>
<ipaddr> - The IP address.
<netmask> - The subnet mask.
<vlandid> - VLAN identification number. ID range is 1-4093.
<priority> - The priority value for untagged frames received. Valid priority value is 0 to 7.
no - This command removes association of a specific IP-subnet to a VLAN.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
VLAN database
6.2.3.13 vlan makestatic
This command changes a dynamically created VLAN (one that is created by GVRP registration) to a
static VLAN (one that is permanently configured and defined). The ID is a valid VLAN identification
number. VLAN range is 2-4093.
Syntax
vlan makestatic <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 2 –4093).
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
VLAN database
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 86/1246
Page 87

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.14 protocol group
This command attaches a <vlanid> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <group-name>. A group
may only be associated with one VLAN at a time, however the VLAN association can be changed.
Syntax
protocol group <group-name> <vlanid>
no protocol group <group-name> <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
<group-name> - a VLAN Group Name (a character string of 1 to 16 characters).
no - This command removes the <vlanid> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by
this <group-name>.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
VLAN database
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 87/1246
Page 88

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.15 switchport acceptable-frame-type
This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface. For VLAN Only mode, untagged
frames or
priority frames received on this interface are discarded. For Admit All mode, untagged frames or priority
frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this
port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
specification.
Syntax
switchport acceptable-frame-type {tagged | all}
no switchport acceptable-frame-type {tagged | all}
tagged - VLAN only mode.
all - Admit all mode.
no - This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface to Admit All. For Admit All mode,
untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned the value of
the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in
accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Default Setting
Admit all
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces. For VLAN Only mode, untagged
frames or priority frames received on this interface are discarded. For Admit All mode, untagged frames
or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned the value of the interface VLAN
ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE
802.1Q VLAN specification.
Syntax
switchport acceptable-frame-type all {tagged | all}
no switchport acceptable-frame-type all {tagged | all}
tagged - VLAN only mode.
all – One is for Admit all mode. The other one is for all interfaces.
no - This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces to Admit All. For Admit All
mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned the
value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in
accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 88/1246
Page 89

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Default Setting
Admit all
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 89/1246
Page 90

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.16 switchport ingress-filtering
This command enables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received with VLAN IDs
that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted and forwarded to ports
that are members of that VLAN.
Syntax
switchport ingress-filtering
no switchport ingress-filtering
no - This command disables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received with
VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted and
forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command enables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received with
VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted and
forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Syntax
switchport ingress-filtering all
no switchport ingress-filtering all
all - All interfaces.
no - This command disables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames
received with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are
admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 90/1246
Page 91

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.17 switchport native vlan
This command changes the VLAN ID which will be assigned to untagged or priority tagged frames per
interface.
Syntax
switchport native vlan <vlanid>
no switchport native vlan <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
no - This command sets the VLAN ID per interface to 1.
Default Setting
1
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command changes the VLAN ID which will be assigned to untagged or priority tagged frames for all
interfaces.
Syntax
switchport native vlan all <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
all - All interfaces.
no - This command sets the VLAN ID for all interfaces to 1.
Default Setting
1
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 91/1246
Page 92

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.18 switchport allowed vlan
This command configures the degree of participation for a specific interface in a VLAN. The ID is a valid
VLAN identification number, and the interface is a valid interface number.
Syntax
switchport allowed vlan {add [tagged | untagged] | remove} <vlan-list>
<vlan-list> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093) – separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and
no zeros in between the range; Use '-' for range.
add - The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed.
tagged - All frames transmitted for this VLAN will be tagged.
untagged - All frames transmitted for this VLAN will be untagged.
remove - The interface is removed from the member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
forbidden.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command configures the degree of participation for all interfaces in a VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN
identification number.
Syntax
switchport allowed vlan {add {tagged | untagged} | remove} all <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
all - All interfaces.
add - The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed.
tagged - all frames transmitted for this VLAN will be tagged.
untagged - all frames transmitted for this VLAN will be untagged.
remove - The interface is removed from the member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
forbidden.
Default Setting
None
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 92/1246
Page 93

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Command Mode
Global
Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 93/1246
Page 94

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.19 switchport tagging
This command configures the tagging behavior for a specific interface in a VLAN to enable. If tagging is
enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as untagged
frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number.
Syntax
switchport tagging <vlan-list>
no switchport tagging <vlan-list>
<vlan-list> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093) – separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and
no zeros in between the range; Use '-' for range.
no - This command configures the tagging behavior for a specific interface in a VLAN to disabled. If
tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification
number.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Interface Config
This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to be enabled. If tagging is
enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as untagged
frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number.
Syntax
switchport tagging all <vlanid>
<vlanid> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093).
all - All interfaces
no - This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to disabled. If
tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification
number.
Default Setting
Disabled
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 94/1246
Page 95

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.3.20 switchport forbidden vlan
This command used to configure forbidden VLANs.
Syntax
switchport forbidden vlan {add | remove} <vlan-list>
no switchport forbidden
<vlan-list> - VLAN ID (Range: 1 – 4093) – separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and
no zeros in between the range; Use '-' for range.
add - VLAND ID to add.
remove - VLAND ID to remove.
no - Remove the list of forbidden VLANs.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Interface Config
6.2.3.21 switchport priority
This command configures the default 802.1p port priority assigned for untagged packets for a specific
interface.
Syntax
switchport priority <0-7>
no switchport priority
<0-7> - The range for the priority is 0 - 7.
no – This command restore the priority configuration to default value.
Default Setting
0
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 95/1246
Page 96

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
This command configures the port priority assigned for untagged packets for all ports presently plugged
into the device. Any subsequent per port configuration will override this configuration setting.
Syntax
switchport priority all <0-7>
no switchport priority all
<0-7> - The range for the priority is 0-7.
all – All interfaces
no – This command restores the priority value to default value for all interfaces.
Default Setting
0
Command Mode
Global Config
6.2.3.22 switchport protocol group
This command adds the physical <slot/port> interface to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<group-name>. A group may have more than one interface associated with it. Each interface and
protocol combination can only be associated with one group. If adding an interface to a group causes
any conflicts with protocols currently associated with the group, this command will fail, and the
interface(s) will not be added to the group.
Syntax
switchport protocol group <group-name>
no switchport protocol group <group-name>
<group-name> - a VLAN Group Name (a character string of 1 to 16 characters).
no - This command removes the interface from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by
this <group-name>.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 96/1246
Page 97

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
This command adds a protocol-based VLAN group to the system. The <group-name> is a character
string of 1 to 16 characters. When it is created, the protocol group will be assigned a unique number that
will be used to identify the group in subsequent commands.
Syntax
switchport protocol group <group-name>
no switchport protocol group <group-name>
<group-name> - a VLAN Group Name (a character string of 1 to 16 characters).
no - This command removes the protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by this <group-name>.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
This command adds all physical interfaces to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <group-name>. A
group may have more than one interface associated with it. Each interface and protocol combination can
only be associated with one group. If adding an interface to a group causes any conflicts with protocols
currently associated with the group, this command will fail, and the interface(s) will not be added to the
group.
Syntax
switchport protocol group all <group-name>
no switchport protocol group all <group-name>
<group-name> - a VLAN Group Name (a character string of 1 to 16 characters).
all - All interfaces.
no - This command removes all interfaces from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by
this <group-name>.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
This command adds the <protocol> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <group-name>. A group
may have more than one protocol associated with it. Each interface and protocol combination can only
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 97/1246
Page 98

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Syntax
switchport protocol group add protocol <group-name> {ip | arp | ipx}
no switchport protocol group add protocol <group-name> {ip | arp | ipx}
be associated with one group. If adding a protocol to a group causes any conflicts with interfaces
currently associated with the group, this command will fail, and the protocol will not be added to the
group. The possible values for protocol are ip, arp, and ipx.
<group-name> - a VLAN Group Name (a character string of 1 to 16 characters).
ip - IP protocol.
arp - ARP protocol.
ipx - IPX protocol.
no - This command removes the <protocol> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified
by this <group-name>. The possible values for protocol are ip, arp, and ipx.
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Global Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 98/1246
Page 99

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
6.2.4 Double VLAN commands
6.2.4.1 show dvlan-tunnel/ dot1q-tunnel
This command is used without the optional parameters to display all interfaces enabled for Double VLAN
Tunneling. Use the optional parameters to display detailed information about Double VLAN Tunneling for
the specified interface or all interfaces.
Syntax
show
{dot1q-tunnel|dvlan-tunnel}
[interface {<slot/port>}]
Default Setting
None
Command Mode
Privileged Exec
Display Message
Interfaces Enabled for DVLAN Tunneling: Valid interface(s) support(s) DVLAN Tunneling.
When using ‘sho w {d o t 1q -tunnel|dvlan-t u n n el} int
erf ace’:
Interface: Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
Mode: This field specifies the administrative mode through which Double VLAN Tunneling can be
enabled or disabled. The default value for this field is disabled.
EtherType This field represents a 2-byte hex EtherType to be used as the first 16 bits of the DVLAN
tunnel. There are three different EtherType tags. The first is 802.1Q, which represents the commonly
used value of 0x8100. The second is vMAN, which represents the commonly used value of 0x88A8.
If EtherType is not one of these two values, then it is a custom tunnel value, representingany value in
the range of 0 to 65535.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 99/1246
Page 100

Korenix Technology Co., Ltd.
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet Switch
Syntax
switchport {dvlan-tunnel | dot1q-tunnel } [ethertype {802.1Q|custom <0-65535>|vman}]
no switchport {dvlan-tunnel | dot1q-tunnel} [ethertype]
6.2.4.2 switchport dvlan-tunnel/ dot1q-tunnel
This command is used to enable Double VLAN Tunneling on the specified interface.
Syntax
switchport {dvlan-tunnel|dot1q-tunnel}
no switchport {dvlan-tunnel|dot1q-tunnel}
Default Setting
Disable
Command Mode
Interface Config
6.2.4.3 switchport dvlan-tunnel/ dot1q-tunnel ethertype
This command configures the ether-type for specific interface. The ether-type may have the values of
802.1Q, vMAN, or custom. If the ether-type has a value of custom, the optional value of the custom ether
type must be set to a value from 0 to 65535.
Default
Command Mode
Setting
802.1Q
Interface Config
_____________________________________________________________________________
Industrial Layer 3 Managed Ethernet SwitchUser Manual Page: 100/1246
 Loading...
Loading...