Page 1

» User Guide «
CP6003-SA/RA/RC
IPMI Firmware
Doc. ID: 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
January 12, 2012
If it’s embedded, it’s Kontron.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 2
Preface CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Revision History
Publication Title:
Doc. ID: 1045-5656
Rev. Brief Description of Changes Date of Issue
1.0 Initial issue 11-Aug-2011
2.0 Added description for the CP6003-RA/RC 12-Jan-2012
CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware User Guide
Imprint
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH may be contacted via the following:
MAILING ADDRESS TELEPHONE AND E-MAIL
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH +49 (0) 800-SALESKONTRON
Sudetenstraße 7 sales@kontron.com
D - 87600 Kaufbeuren Germany
For further information about other Kontron products, please visit our Internet website:
P R E L I M I N A R Y
www.kontron.com.
Disclaimer
Copyright © 2012 Kontron AG. All right s reserved. All dat a is for information purposes only and
not guaranteed for legal purposes. Information has been carefully checked and is believed to
be accurate; however, no responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies. Kontron and the Kontron
logo and all other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners and are recognized. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 2 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 3

CP6003-SA/RA/RC Preface
Table of Contents
Revision History ........................................................................................................2
Imprint ....................................................................................................................... 2
Disclaimer .................................................................................................................2
Table of Contents ...................................................................................................... 3
List of Tables ............................................................................................................. 7
1. Introduction ...................................................................................9
1.1 Terminology and Acronym Definitions ..........................................................9
1.2 Related Publications ...................................................................................11
1.3 IPMI Overview .............................................................................................11
2. IPMI Setup ....................................................................................12
2.1 IPMI in a CompactPCI Chassis .................................................................. 12
2.2 IPMI Setup for the CP6003-SA/RA/RC ......................................................12
2.3 IPMI Setup for the Rack .............................................................................13
3. IPMI Controller Hardware ...........................................................13
4. IPMI Firmware ..............................................................................14
4.1 Key Features ..............................................................................................14
5. Supported IPMI and ATCA Commands .....................................15
5.1 Standard IPMI Commands ......................................................................... 15
5.2 AdvancedTCA and AMC Commands ......................................................... 20
P R E L I M I N A R Y
6. OEM Commands and Command Extensions ...........................21
6.1 Get Device ID Command with OEM Extensions ........................................ 21
6.2 Set Firmware Parameters .......................................................................... 22
6.3 Set Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order) ......................................... 23
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 3
Page 4

Preface CP6003-SA/RA/RC
6.4 Get Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order) .........................................24
7. Sensors Implemented on the CP6003-SA/RA/RC .................... 24
7.1 Sensor List ..................................................................................................25
7.2 Sensor Thresholds ......................................................................................28
7.3 OEM Event/Reading Types ........................................................................29
8. IPMI Firmware Code ................................................................... 31
8.1 Structure and Functionality .........................................................................31
8.2 uEFI BIOS/IPMI Controller Interaction ........................................................31
8.3 IPMI Firmware Configuration ......................................................................31
8.4 Firmware Identification ................................................................................32
8.5 Firmware Upgrade ......................................................................................32
8.5.1 Firmware File Formats .......................................................................32
8.5.2 Firmware Upgrade - “ipmitool hpm” ..................................................33
8.5.3 Firmware Upgrade - “ipmitool fwum” .................................................34
8.6 Setting the SEL Time ..................................................................................34
8.7 IPMI Firmware Write Protection ..................................................................34
9. FRU Data .....................................................................................35
9.1 Structure and Functionality .........................................................................35
9.2 FRU Version Identification ..........................................................................35
P R E L I M I N A R Y
9.3 Board-Specific FRU Data ...........................................................................35
9.4 FRU Data Update .......................................................................................36
9.5 FRU Data Write Protection .........................................................................36
10. XMC Card Support ...................................................................... 36
1 1. uEFI BIOS Failover Control - Automatic SPI Boot Flash Selection
37
11.1 Automatic SPI Boot Flash Selection During the Boot Process ...................37
Page 4 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 5

CP6003-SA/RA/RC Preface
11.2 OS Boot Order Selection by OEM IPMI ..................................................... 37
12. Hot Swap and Shutdown ............................................................38
12.1 Hot Swap Handle and Hot Swap (Blue) LED ............................................. 38
12.2 The Hot Swap and Shutdown Processes ................................................... 39
13. LAN Functions .............................................................................40
13.1 Overview ....................................................................................................40
13.2 Setting Up the Ethernet Channel ...............................................................40
13.3 Basic Setup from uEFI Shell ......................................................................41
13.4 Setup by “ipmitool” or IPMI Commands ..................................................... 41
13.5 Setup of User Accounts and Password ...................................................... 41
13.6 IPMI Over LAN (IOL) .................................................................................. 42
13.7 Serial Over LAN (SOL) ............................................................................... 42
14. OS Support / Tools ......................................................................43
14.1 Linux Tools ................................................................................................. 43
14.2 OS Support - Board Support Packages .....................................................43
15. IPMI and Hot Swap LEDs ............................................................44
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 5
Page 6

Preface CP6003-SA/RA/RC
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 6 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 7

CP6003-SA/RA/RC Preface
List of Tables
1 Terminology and Acronym Definitions ............................................................9
2 Related Publications .....................................................................................11
3 Standard IPMI Commands ...........................................................................15
4 AdvancedTCA and AMC Commands ..........................................................20
5 Get Device ID Command with OEM Extensions ..........................................21
6 Set Firmware Parameters ............................................................................ 22
7 Set Control State ..........................................................................................23
8 Get Control State ......................................................................................... 24
9 Sensor List ................................................................................................... 25
10 Gigabit Ethernet Link Sensor Assignment ................................................... 27
11 Thresholds - Standard Temperature Range ................................................. 28
12 Voltage Sensor Thresholds .......................................................................... 28
13 OEM Event/Reading Types .......................................................................... 29
14 IPMI and Hot Swap LEDs Function .............................................................45
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 7
Page 8

Preface CP6003-SA/RA/RC
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 8 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 9

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
1. Introduction
1.1 Terminology and Acronym Definitions
The following table provides descriptions for terms and acronyms used in this guide. The descriptions are derived primarily from the IPMI specifications.
Table 1: Terminology and Acronym Definitions
TERM or ACRONYM DESCRIPTION
BMC Baseboard Management Controller
Each board is equipped with an IPMI controller acting either as a BMC or as an SMC.
However, in a CompactPCI chassis, there can be only one BMC present. The BMC
administrates the SEL and the SDRR for the complete system. The BMC is connected
to the other boards in the shelf via a dedicated bus (IPMB-0). The CP6003-SA/RA/
RC’s IPMI controller can be configured to operate in SMC mode or in BMC mode via
an IPMI OEM command or an uEFI Shell command. The factory setting is SMC.
BSP Board Support Package
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
Every board is a FRU. The FRU data contains information about the board such as
the part number and the serial number. See PICMG Specification 2.9 for complete
details on the FRU data structure. The free Linux tool “ipmitool” can be used to
update or display the FRU data.
FWH Firmware Hub memory location where a complete uEFI BIOS code is stored.
2
I
C
IPMB Intelligent Platform Management Bus
IPMB-0 Intelligent Platform Management Bus which connects all SMCs with the BMC or the
IPMI Intelligent Platform Management Interface
IOL IPMI over LAN. An IPMI controller is accessed via LAN, not IPMB.
KCS Keyboard Controller Style (Interface)
Inter-Integrated Circuit
The dedicated I
shelf manager.
This is the IPMI mandatory interface on the host system (payload) to communicate
with the BMC.
2
C management bus where the BMC and the SMCs communicate.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
MP Management Power
This powers the BMC or SMC controller.
PICMG PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturer Group
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 9
Page 10
IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Table 1: Terminology and Acronym Definitions (Continued)
TERM or ACRONYM DESCRIPTION
PWR Payload Power.
This powers the host side of the board where the application software runs. It is
granted by the BMC or the SMC after all prerequisites are met. Prerequisites can be,
for example, a closed handle switch, power on the backplane etc.
SDR Sensor Data Record
This is the IPMI data structure that defines a sensor.
SDRR Sensor Data Record Repository
The SDRR is located in the BMC and contains all SDRs of the chassis’ boards that
are administrated. A free Linux utility named “ipmitool” makes a full chassis discovery
and fills the SDRR with the SDRs being found.
SEL System Event Log
The SEL is located in the BMC and keeps track of all events in the chassis. If an
event occurs on any board, the sensor event is sent through the IPMB bus to the
BMC, which additionally stores its own events as well.
SMBIOS System Management BIOS
SMC Satellite Management Controller
Each board is equipped with an IPMI controller acting either as a BMC or as an SMC.
In a CompactPCI chassis, there can be several SMCs. The SMC administrates the
sensor and FRU data of the CP6003-SA/RA/RC and makes it available to the BMC.
Each SMC can be connected to the BMC via a dedicated bus (IPMB-0). The CP6003-
SA/RA/RC’s IPMI controller can be configured to operate in SMC mode or in BMC
mode via an IPMI OEM command or an uEFI Shell command. The factory setting is
SMC.
SMS System Management Software (designed to run under the OS)
SOL Serial over LAN
A serial interface is redirected by LAN using the RMCP+ protocol.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 10 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 11

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
1.2 Related Publications
The following publications contain information relating to this product.
Table 2: Related Publications
PRODUCT PUBLICATION
IPMI IPMI Specification V2.0
IPMI IPMI- Platform Management FRU Information Storage Definition v1.0,
Document Revision 1.1
IPMI Addenda, Errata, and Clarifications document revision 4 for IPMI v2.0 rev 1.0
specification
IPMI Intelligent Platform Management Bus Communications Protocol Specification v1.0
Document Revision 1.0, November 1999
IPMI IPMB v1.0 Address Allocation Document Revision 1.0, September 1998
PICMG CompactPCI System Management Specification PICMG 2.9 Rev. 1.0
CompactPCI Hot Swap Specification PICMG 2.1 Rev. 2.0
PICMG® AMC.0 R2.0, Advanced Mezzanine Card Base Specification, Nov. 15, 2006
CP6003-SA/RA/RC CP6003-SA/RA/RC User Guide
CP6003-SA/RA/RC uEFI BIOS User Guide
CP6003-SA/RA/RC Linux Board Support Package
IPMI Tools “ipmitool” documentation: http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net
IPMI Tools OpenIPMI documentation: http://www.openipmi.sourceforge.net
1.3 IPMI Overview
This product fully supports the Intelligent Platform Management Interface a nd PICMG 2.9 R1.0
specifications. All of its IPMI functionality operates under an autonomous management
controller even if the board is held in reset or power-down mode by a management card within
a system designed for high availability.
While the CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI implementation is fully compliant with IPMI v2.0 and has
been designed to operate with any system management software (SMS) that respects this
specification, can be easily integrated with the Service Availability Forum-Hardware Platform
Interface (SAF-HPI) specification.
More information about Service Availability can be found on the following website:
http://www.saforum.org/home
IPMI is an extensible and open standard that defines autonomous system monitoring. It is au-
tonomous because every management controller within a CompactPCI chassis monitors its
own sensors and sends critical events through a dedicated bus to the BMC that logs it into a
non-volatile System Event Log (SEL). The CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI implementation includes
a device SDR repository module that allows the user's system management software to detect
all system components and build a database of all management controller sensors.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
For further information concerning IPMI refer to the following website:
http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 11
Page 12
IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
BMC
IPMB
Address
Fix: 20h
Backplane
SMC
IPMB
Address:
B0h
(1)
SMC
IPMB
Address:
B2h
(1)
SMC
IPMB
Address:
B4h
(1)
SMC
IPMB address for SMC is determined via the location of the slot in the chassis
IPMB
Address:
B6h
SMC
IPMB
Address:
B8h
(1)
(1)
SMC
IPMB
Address:
BAh
(1)
SMC
IPMB
Address:
BCh
(1)
IPMB 0
IPMB 0
(1)
IPMB 1
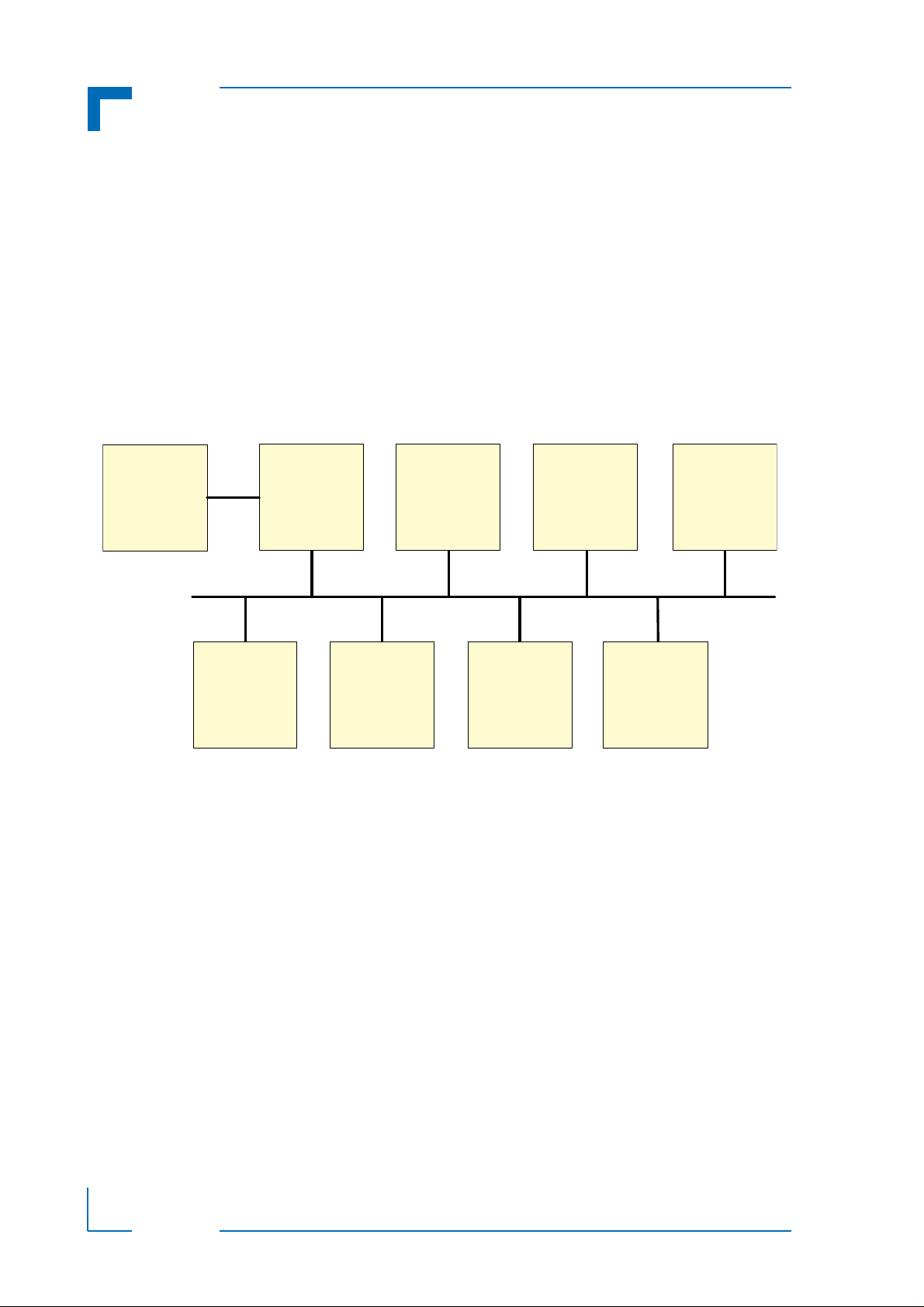
2. IPMI Setup
2.1 IPMI in a CompactPCI Chassis
Kontron's IPMI implementation in the CompactPCI environment is compliant with the PICMG
2.9 R1.0 specification. This specification defines the pinout of the J1 and J2 Comp actPCI connectors as well as the addressing scheme. There should be only one BMC in the chassis, or at
least on the IPMB segment. The BMC may reside either on an CP6003-SA/RA/RC, or on an
external system management card, or in a shelf management controller (ShMC). The specification allows all of these variants. As a BMC in the system slot, the CP6003-SA/RA/RC supports dual-ported IPMB (IPMB-0 to the SMCs and IPMB-1 to the external segments via the
CompactPCI backplane connector in accordance with PICMG 2.9).
To use the IPMI resources in a rack requires an initial setup for IPMI operation. The following
actions must first be performed to achieve operable IPMI functionality.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
2.2 IPMI Setup for the CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Initially the default configuration for the IPMI controller of the CP6003-SA/RA/RC is:
• IRQ = none
• MODE = SMC
• IPMB = single-ported.
If this is the required configuration, no further action is required. If the configuration must be
modified, either the kipmi uEFI Shell command or on e of the open tools “ipmitool” or “ipmicmd”
may be used to modify the configuration as required.
Page 12 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 13

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
Fur further information on the kipmi uEFI Shell command, refer to the CP6003-SA/RA/RC uEFI
BIOS User Guide. When uEFI BIOS stores the configuration, it creates an “IPMI Device Information Record” entry in the SMBIOS table. This record contains information, among others,
about:
• Type of the supported interface (KCS style)
• Selected interrupt (10, 11 or none).
This information is required by the CP6003-SA/RA/RC payload’s IPMI OS kernel drivers for
Linux during their loading time. After the loading, most available IPMI communications tools
which access the IPMI controller via IPMI OS drivers should work (e.g. “ipmicmd”, “ipmitool”,
etc.).
Now it is possible to use such a tool to issue the Set Firmware Parameters OEM IPMI
command to modify the configuration again. Changing the interrupt number always requires a
uEFI BIOS restart for a correct setup of the SMBIOS table.
2.3 IPMI Setup for the Rack
For a working IPMI configuration the SDRR of the BMC must be filled with all sensor data records of all IPMI controllers in the rack. After every system start the BMC uses the SDRR to
initialize all sensors of all boards. The SDRR setup must be done by a management tool e.g.
the open Linux tool “ipmitool”. Then the command is:
ipmitool sdr fill sensors
This will work only if the IPMI controller configured as BMC is addressed. This addressing is
the default if the “ipmitool” is running on the payload side of the board where the BMC is residing.
3. IPMI Controller Hardware
On the CP6003-SA/RA/RC, the IPMI controller is implemented using the NXP ARM7 microcontroller with 512 kB of internal flash and 56 kB of RAM.
An external 64 kB serial EEPROM chip is used for firmware private data and FRU inventory
storage. An additional external 2 MB serial SPI flash is used for redundant firmware image storage.
The IPMI controller implements a local Keyboard Controller Style (KCS) interface (KCS) with
interrupt support for communication with system-side management software and the uEFI BIOS. The IPMB bus is used for interconnection with the BMC or the shelf manager.
IPMI over LAN (IOL) and Serial Over LAN (SOL) are supported on four Ethernet channels
(GbE A – GbE D) of the board. SOL is only available on one Ethernet channel at a time.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
The IPMI controller provides access to various board sensors which permit the monitoring of:
• System power voltages: 5V (PWR), 3.3V, IPMI 5V, 12V, IPMI controller supply 4.7V
• Temperatures: CPU die, chipset, and board temperature
• Power Good, IPMB-0 link, board reset, POST code, boot error, CPU states (processor
hot, THERMTRIP, …), IPMB-L state, Health error, IPMI watchdog etc.
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 13
Page 14

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
4. IPMI Firmware
4.1 Key Features
The following are key features of the CP6003-SA/RA/RC’s IPMI firmware:
• Compliant with IPMI specification 2.0
• Compliant with PICMG 2.9 specification
• Firmware designed and specially made for CompactPCI implementation and easy
integration with SAF-HPI
• KCS SMS interface with interrupt support
• Dual-port IPMB support
• Out-of-band management and monitoring using the IPMB interface permits access to
sensors regardless of the board's CPU state
• Sensor thresholds fully configurable
• Sensor names prefixed with identification of owner (BMC without slot number or SMC
with slot number)
• Complete IPMI watchdog functionality
• Complete SEL, SDR repository and FRU functionality on BMC
• Complete FRU functionality
• Master Write-Read I
EEPROM, FAN)
• Two IPMI firmware banks allow an automatic backup
This allows manual and automatic firmware image roll-back (in case of an upgrade
failure).
• The downloading of a new firmware image does not break currently running firmware or
payload activities.
• Firmware bank management is done by the open tool “ipmitool” function “fwum” which
can update the firmware in the field.
• Firmware fully customizable via OEM IPMI commands to satisfy customer requirements
P R E L I M I N A R Y
• Interoperable with other IPMI solutions
• OEM board supervision and control extensions such as boot flash selection and firmware
boot order configuration
• Automatic switching to an alternative uEFI image after having detected an inoperable
uEFI BIOS
• IPMI over LAN (IOL) support
• Serial over LAN (SOL) support
2
C support for external I2C devices communications (FRU,
• Graceful shutdown support
• Handle switch and blue Hot Swap LED operation
• The I0 and I1 LEDs indicate operational status of the IPMI firmware.
• The board's write protection feature for non-volatile memories is supported. These
memories are:
2
•I
C EEPROM for FRU data and parameters
• SPI flash memory for firmware banks
Page 14 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 15

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
5. Supported IPMI and ATCA Commands
5.1 Sta ndard IPMI Commands
The following table shows an excerpt from the command list specified in the IPMI specification
2.0. The shaded table cells indicate commands supported by the CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI firmware.
M = mandatory, O = optional
Table 3: Standard IPMI Commands
IPMI 2.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
SECTION
IPM DEVICE “GLOBAL” COMMANDS M
Get Device ID 20.1 App 01h
Cold Reset 20.2 App 02h
Warm Reset 20.3 App 03h O / No
Get Self Test Results 20.4 App 04h
Manufacturing Test On 20.5 App 05h O / No
Set ACPI Power State 20.6 App 06h
Get ACPI Power State 20.7 App 07h
Get Device GUID 20.8 App 08h O / No
Broadcast “Get Device ID” 20.9 App 01h
BMC WATCHDOG TIMER COMMANDS
Reset Watchdog Timer 27.5 App 22h
Set Watchdog Timer 27.6 App 24h
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
M / Yes [1]
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
M / Yes
O
O / Yes
O / Yes
Get Watchdog Timer 27.7 App 25h
BMC DEVICE AND MESSAGING COMMANDS O
Set BMC Global Enables 22.1 App 2Eh
Get BMC Global Enables 22.2 App 2Fh
Clear Message Flags 22.3 App 30h
Get Message Flags 22.4 App 31h
Enable Message Channel Receive 22.5 App 32h
Get Message 22.6 App 33h
Send Message 22.7 App 34h
Read Event Message Buffer 22.8 App 35h
Get BT Interface Capabilities 22.9 App 36h O / No
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 15
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 16

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Table 3: Standard IPMI Commands (Continued)
IPMI 2.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
SECTION
Get System GUID 22.14 App 37h O / No
Get Channel Authentication Capabilities 22.13 App 38h
Get Session Challenge 22.15 App 39h
Activate Session 22.17 App 3Ah
Set Session Privilege Level 22.18 App 3Bh
Close Session 22.19 App 3Ch
Get Session Info 22.20 App 3Dh
Get AuthCode 22.21 App 3Fh O / No
Set Channel Access 22.22 App 40h
Get Channel Access 22.23 App 41h
Get Channel Info 22.24 App 42h
Set User Access 22.26 App 43h
Get User Access 22.27 App 44h
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
Set User Name 22.28 App 45h
Get User Name 22.29 App 46h
Set User Password 22.30 App 47h
Activate Payload 24.1 App 48h
Deactivate Payload 24.2 App 49h
Get Payload Activation Status 24.4 App 4Ah
Get Payload Instance Info 24.5 App 4Bh
Set User Payload Access 24.6 App 4Ch
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Get User Payload Access 24.7 App 4Dh
Get Channel Payload Support 24.8 App 4Eh
Get Channel Payload Version 24.9 App 4Fh
Get Channel OEM Payload Info 24.10 App 50h O / No
Master Write-Read 22.11 App 52h
Get Channel Cipher Suits 22.15 App 54h O / No
Suspend/Resume Payload Encryption 24.3 App 55h
Set Channel Security Keys 22.25 App 56h O / No
Get System Interface Capabilities 22.9 App 57h O / No
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
CHASSIS DEVICE COMMANDS O
Get Chassis Capabilities 28.1 Chassis 00h
Page 16 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
O / Yes
Page 17

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
Table 3: Standard IPMI Commands (Continued)
IPMI 2.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
SECTION
Get Chassis Status 28.2 Chassis 01h O / Yes
Chassis Control 28.3 Chassis 02h
Chassis Reset 28.4 Chassis 03h O / No
Chassis Identify 28.5 Chassis 04h O / No
Set Chassis Capabilities 28.7 Chassis 05h O / No
Set Power Restore Policy 28.8 Chassis 06h O / No
Get System Restart Cause 28.11 Chassis 07h O / No
Set System Boot Options 28.12 Chassis 08h O / No
Get System Boot Options 28.13 Chassis 09h O / No
Get POH Counter 28.14 Chassis 0Fh
EVENT COMMANDS M
Set Event Receiver 29.1 S/E 00h
Get Event Receiver 29.2 S/E 01h
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
O / Yes
O / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
Platform Event (a.k.a. “Event Message”) 29.3 S/E 02h
PEF AND ALERTING COMMANDS O
Get PEF Capabilities 30.1 S/E 10h O / No
Arm PEF Postpone Timer 30.2 S/E 11h O / No
Set PEF Configuration Parameters 30.3 S/E 12h O / No
Get PEF Configuration Parameters 30.4 S/E 13h O / No
Set Last Processed Event ID 30.5 S/E 14h O / No
Get Last Processed Event ID 30.6 S/E 15h O / No
Alert Immediate 30.7 S/E 16h O / No
PET Acknowledge 30.8 S/E 17h O / No
SENSOR DEVICE COMMANDS M
Get Device SDR Info 35.2 S/E 20h
Get Device SDR 35.3 S/E 21h
Reserve Device SDR Repository 35.4 S/E 22h
Get Sensor Reading Factors 35.5 S/E 23h O / No
Set Sensor Hysteresis 35.6 S/E 24h
Get Sensor Hysteresis 35.7 S/E 25h
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Set Sensor Threshold 35.8 S/E 26h
Get Sensor Threshold 35.9 S/E 27h
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 17
O / Yes
O / Yes
Page 18

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Table 3: Standard IPMI Commands (Continued)
IPMI 2.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
SECTION
Set Sensor Event Enable 35.10 S/E 28h O / Yes
Get Sensor Event Enable 35.11 S/E 29h
Re-arm Sensor Events 35.12 S /E 2Ah O / No
Get Sensor Event Status 35.13 S/E 2Bh O / No
Get Sensor Reading 35.14 S/E 2Dh
Set Sensor Type 35.15 S/E 2Eh O / No
Get Sensor Type 35.16 S/E 2Fh O / No
FRU DEVICE COMMANDS M
Get FRU Inventory Area Info 34.1 Storage 10h
Read FRU Data 34.2 Storage 11h
Write FRU Data 34.3 Storage 12h
SDR DEVICE COMMANDS O
Get SDR Repository Info 33.9 Storage 20h
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
O / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
O / Yes
Get SDR Repository Allocation Info 33.10 Storage 21h
Reserve SDR Repository 33.11 Storage 22h
Get SDR 33.12 Storage 23h
Add SDR 33.13 Storage 24h
Partial Add SDR 33.14 Storage 25h
Delete SDR 33.15 Storage 26h
Clear SDR Repository 33.16 Storage 27h
Get SDR Repository Time 33.17 S torage 28h O / No
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Set SDR Repository Time 33.18 Storage 29h O / No
Enter SDR Repository Update Mode 33.19 Storage 2Ah O / No
Exit SDR Repository Update Mode 33.20 Storage 2Bh O / No
Run Initialization Agent 33.21 Storage 2Ch
SEL DEVICE COMMANDS O
Get SEL Info 40.2 Storage 40h
Get SEL Allocation Info 40.3 Storage 41h
Reserve SEL 40.4 Storage 42h
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
Get SEL Entry 40.5 Storage 43h
Add SEL Entry 40.6 Storage 44h
Page 18 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
O / Yes
O / Yes
Page 19

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
Table 3: Standard IPMI Commands (Continued)
IPMI 2.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
SECTION
Partial Add SEL Entry 40.7 Storage 45h O / No
Delete SEL Entry 40.8 Storage 46h
Clear SEL 40.9 Storage 47h
Get SEL Time 40.10 Storage 48h
Set SEL Time 40.11 Storage 49h
Get Auxiliary Log Status 40.12 Storage 5Ah O / No
Set Auxiliary Log Status 40.13 Storage 5Bh O / No
LAN DEVICE COMMANDS O
Set LAN Configuration Parameters 23.1 Transport 01h
Get LAN Configuration Parameters 23.2 Transport 02h
Suspend BMC ARPs 23.3 Transport 03h O / No
Get IP/UDP/RMCP Statistics 23.4 Transport 04h
SERIAL/MODEM DEVICE COMMANDS O
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
Set Serial/Modem Configuration 25.1 Transport 10h O / No
Get Serial/Modem Configuration 25.2 Transport 11h O / No
Set Serial/Modem Mux 25.3 Transport 12h O / No
Get TAP Response Codes 25.4 Transport 13h O / No
Set PPP UDP Proxy Transmit Data 25.5 Transport 14h O / No
Get PPP UDP Proxy Transmit Data 25.6 Transport 15h O / No
Send PPP UDP Proxy Packet 25.7 Transport 16h O / No
Get PPP UDP Proxy Receive Data 25.8 Transport 17h O / No
Serial/Modem Connection Active 25.9 Transport 18h O / No
Callback 25.10 Transport 19h O / No
Set User Callback Options 25.11 Transport 1Ah O / No
Get User Callback Options 25.12 Transport 1Bh O / No
SOL Activating 26.1 Transport 20h
Get SOL Configuration Parameters 26.2 Transport 21h
Set SOL Configuration Parameters 26.3 Transport 22h
O / Yes
O / Yes
O / Yes
[1] Has OEM extensions. Please refer to 6.1, Get Device ID Command with OEM Extensions.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Note ...
Some of the above-mentioned commands, such as SDR commands, work
only if the IPMI controller is configured as BMC. For further information, refer
to the IPMI specification 2.0.
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 19
Page 20

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
5.2 AdvancedTCA and AMC Commands
The following table shows an excerpt from the command list specified in the PICMG 3.0 R 2.0
AdvancedTCA Base Specification and the PICMG AMC.0 Advanced Mezzanine Card Specification, R 1.0. The shaded table cells indicate commands supported by the IPMI firmware.
M = mandatory
Table 4: AdvancedTCA and AMC Commands
PICMG 3.0
COMMAND
SPEC.
NETFN CMD
TABLE
AdvancedTCA
Get PICMG Properties 3-9 PICMG 00h
Get Address Info 3-8 PICMG 01h N/A
Get Shelf Address Info 3-13 PICMG 02h N/A
Set Shelf Address Info 3-14 PICMG 03h N/A
FRU Control 3-22 PICMG 04h N/A
Get FRU LED Properties 3-29 PICMG 05h
Get LED Color Capabilities 3-25 PICMG 06h
Set FRU LED State 3-26 PICMG 07h
Get FRU LED State 3-27 PICMG 08h
Set IPMB State 3-51 PICMG 09h N/A
Set FRU Activation Policy 3-17 PICMG 0Ah N/A
KONTRON
SUPPORT
ON IPMI
CONTROLLER
M
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
M / Yes
Get FRU Activation Policy 3-18 PICMG 0Bh N/A
Set FRU Activation 3-16 PICMG 0Ch N/A
Get Device Locator Record ID 3-29 PICMG 0Dh
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Set Port State 3-41 PICMG 0Eh N/A
Get Port State 3-42 PICMG 0Fh N/A
Compute Power Properties 3-60 PICMG 10h N/A
Set Power Level 3-62 PICMG 11h N/A
Get Power Level 3-61 PICMG 12h N/A
Renegotiate Power 3-66 PICMG 13h N/A
Get Fan Speed Properties 3-63 PICMG 14h N/A
Set Fan Level 3-65 PICMG 15h N/A
Get Fan Level 3-64 PICMG 16h N/A
Bused Resource 3-44 PICMG 17h N/A
Get IPMB Link Info 3-49 PICMG 18h N/A
M / Yes
Page 20 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 21

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
6. OEM Commands and Command Extensions
6.1 Get Device ID Command with OEM Extensions
The IPMI specification defines four optional bytes in the response to Get Device ID. The
response bytes [13:16] hold the “Auxiliary Firmware Revision Information”.
Table 5: Get Device ID Command with OEM Extensions
COMMAND LUN NetFn CMD
Get Device ID command with OEM extensions 00h App = 06h 01h
REQUEST DATA
Byte Data Field
--
RESPONSE DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Completion Code
2:12 Regular Get Device ID Command response fields
13 Release number of the IPMI firmware:
10h for R10,
11h for R11,
…
Release number 1… of the IPMI firmware. The open tool “ipmitool” displays this as “SDR” in
the response to the command “ipmitool fwum status”.
14 Board Geographical Address (slot number):
1 … = Board in chassis slot 1…
15 Reserved
16 Reserved
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 21
Page 22

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
6.2 Set Firmware Parameters
This command permits the selection of interrupts to be used during KCS communication.
Please note that parameters which are set while the board is write-protecte d are valid only until
the next IPMI firmware reset.
Table 6: Set Firmware Parameters
COMMAND LUN NetFn CMD
Set Firmware Parameters 03h OEM = 3Eh 05h
REQUEST DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Reserved
B4h
2 Reserved
90h
3 Reserved
91h
4 Reserved
8Bh
5 Cmd Flags
[6:2] Reserved
[1] 0b = get only, 1b = set parameters
[0] 0b = do not reset, 1b = reset IPMI controller after setting parameters
6 Operating Modes
[7:5] Reserved
[4] 0b = IPMB dual-ported, 1b = IPMB single-ported (default)
[3] 1b = IPMB off
[2:1] Reserved
[0] 0b = BMC, 1b = SMC
P R E L I M I N A R Y
7 IRQ number
FFh = do not use interrupts
0Ah = use IRQ10
0Bh = use IRQ11
Any other values = Reserved
RESPONSE DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Completion code
2 Cmd flags
3 Operating modes
4 IRQ number
Page 22 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 23

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
6.3 Set Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order)
Please note that parameters which are set while the board is write-protected are valid only u ntil
the next IPMI firmware reset.
Table 7: Set Control State
COMMAND LUN NetFn CMD
Set Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order) 00h OEM = 3Eh 20h
REQUEST DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Control ID:
00h: SPI boot flash selection
9Dh: uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration
2 Control State for SPI boot flash selection:
(These settings are stored in EEPROM and applied (to logic) each time the IPMI controller
detects power-on)
00h = Standard SPI boot flash is selected (default)
01h = Recovery SPI boot flash is selected
The DIP switch SW1, switch 2, may overwrite this selection. For further information, refer to
Chapter 11.1, Automatic SPI Boot Flash Selection During the Boot Proocess, or to the
CP6003-SA/RA/RC User Guide.
In case of a failing boot process and default setting, the IPMI controller will select the recovery
boot flash and boot the board again. In case of a boot failure from the recovery SPI boot flash,
the board locks up.
Control State for uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration:
(These settings are stored in EEPROM and applied (to logic) each time the IPMI controller
detects power-on)
00h .. 07h = Selected uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration
00h selects the default Boot Order in the uEFI BIOS menu.
uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration:
00h = Boot order is according to uEFI BIOS setup (default)
01h = Next boot device is: Floppy
02h = Next boot device is: HDD
03h = Next boot device is: CD
04h = Next boot device is: Network
05h = Next boot device is: USB Floppy
06h = Next boot device is: USB HDD
07h = Next boot device is: USB CD-ROM
Byte Data Field
1 Completion Code
P R E L I M I N A R Y
RESPONSE DATA
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 23
Page 24

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
6.4 Get Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order)
Table 8: Get Control State
COMMAND LUN NetFn CMD
Get Control State (SPI Boot Flash, Boot Order) 00h OEM = 3Eh 21h
REQUEST DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Control ID:
00h = SPI boot flash selection
9Dh = uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration
RESPONSE DATA
Byte Data Field
1 Completion Code
4 Current Control State (see Chapter 6.3, Set Control State)
00h .. 01h for control ID = SPI boot flash selection
00h .. FFh for control ID = uEFI BIOS Boot Order Configuration
7. Sensors Implemented on the CP6003-SA/RA/RC
The IPMI controller includes several sensors for voltage or temperature monitoring and various
others for pass/fail type signal monitoring.
Every sensor is associated with a Sensor Data Record (SDR). Sensor Data Records contain
information about the sensor’s identification such as sensor type, sensor name, and sensor
unit. SDRs also contain the configuration of a specific sensor such as threshold, hysteresis or
event generation capabilities that specify sensor's behavior . So me fields of the sensor SDR are
configurable using IPMI commands; others are always set to built-in default values.
The IPMI controller supports sensor device commands and uses the static sensor population
feature of IPMI. All Sensor Data Records can be queried using Device SDR commands.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
The sensor name (ID string) has a name prefix which is ‘NNN:’ in the lists below . When reading
the sensor name after board insertion, this prefix becomes automatically adapted to the role
(BMC or SMC) and the physical position (slot number) of the board in a rack. If the IPMI controller is set up as a BMC, the prefix will be ‘BMC:’ independent of the slot where it resides. If
the IPMI controller is set up as an SMC, the prefix will be ‘Sxx:’ where xx is the slot number
(e.g. 09).
The sensor number is the number which identifies the sensor e.g. when using the IPMI command Get Sensor Reading. Please note that “ipmitool” accepts sensor numbers in deci-
mal (e.g. “10”) or hexadecimal (e.g. “0xa”) notation.
The IPMI tool “ipmitool” displays for the command “ipmitool sdr list” the contents of the sensor
data record repository (SDRR) of the whole rack if the SDRR has been generated. The generation of the SDRR must always be redone after adding or removing a board from the rack. Refer to Chapter 2.3, IPMI Setup for the Rack for further information.
Page 24 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 25

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
7.1 Sensor List
The following table indicates all sensors available on the CP6003-SA/RA/RC. Fo r further information on Kontron’s OEM-specific sensor types and sensor event type codes presented in the
following table, please refer to Chapter 7.3, OEM Event/Reading Types.
Table 9: Sensor List
SENSOR NUMBER/
ID STRING
00h /
NNN:Hot Swap
01h /
NNN:Temp CPU
02h /
NNN:Temp Chipset
03h /
NNN:Temp Board
04h /
NNN:Pwr Good
05h /
NNN:Pwr Good Evt
06h /
NNN:Board 3.3V
07h /
NNN:Board 5VIPMI
08h /
NNN:Board 5V
09h /
NNN:Board 12V
0Ah /
NNN:IPMB 5V
0Bh /
NNN:Fan1 Speed
0Ch /
NNN:Fan2 Speed
0Dh /
NNN:Last Reset
0Eh /
NNN:Slot System
0Fh /
NNN:PCI Present
10h /
NNN:CTCA chassis
11h /
NNN:IPMI WD
12h /
NNN:IPMB State
13h /
NNN:ACPI State
SENSOR TYPE (CODE) /
EVENT/READING TYPE
(CODE)
Hot Swap (F0h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Temperature (01h) /
Threshold (01h)
Power supply (08h) /
OEM (73h)
Power supply (08h) /
OEM (73h)
Voltage (02h) /
Threshold (01h)
Voltage (02h) /
Threshold (01h)
Voltage (02h) /
Threshold (01h)
Voltage (02h) /
Threshold (01h)
Voltage (02h) /
Threshold (01h)
Fan (04h) /
Threshold (01h)
Fan (04h) /
Threshold (01h)
OEM (CFh) /
“digital” Discrete (03h)
Entity presence (25h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Entity presence (25h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Entity presence (25h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Watchdog2 (23h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
IPMB status change (F1h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
System ACPI Power State
(022h) / Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Ass. Mask /
Deass. Mask /
Reading Mask
001Fh / 0000h /
001Fh
1A81h / 7A81h /
3939h
0A80h / 7A80h /
3838
7A95h / 7A95h /
3F3F
0000h / 0000h /
009Fh
009Fh / 009Fh /
009Fh
2204h / 2204h /
1212h
2204h / 2204h /
1212h
2204h / 2204h /
1212h
2204h / 2204h /
1212h
2204h / 2204h /
1212h
0000h / 0000h /
1B1Bh
0000h / 0000h /
1B1Bh
0002h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
010Fh / 0000h /
010Fh
000Fh / 0000h /
000Fh
7FFFh / 0000h /
7FFFh
LED I1on
error /
DESCRIPTION
Reading
Mask
Hot swap sensor N
CPU die temperature Y
/ 0F3Ch
Temp Chipset Y
/ 0F3Ch
Temp Board Y
/ 0F3Ch
Status of all power lines N
Power fail events for all
power lines
Board 3.3V supply Y
Management Power (MP)
5V
Board 5V supply Y
Board 12V supply Y
IPMB 5V supply N
Speed [rpm] Fan 1 N
Speed [rpm] Fan 2 N
Board reset event Y
Board is in system slot
(SYSEN)
Board is selected (BDSEL)
and in system slot (SYSEN)
Value is always 1 N
IPMI Watchdog Y
IPMB-0 state (refer to
PICMG 3.0 Rev 2.0, 3.8.4.1)
System ACPI power state N
/ 009Fh
/ 0F3Ch
/ 0F3Ch
/ 0F3Ch
/ 0F3Ch
/ 0002h
/ 010Fh
Y
Y
P R E L I M I N A R Y
N
N
N
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 25
Page 26

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Table 9: Sensor List (Continued)
SENSOR NUMBER/
ID STRING
14h /
NNN:Health Error
15h /
NNN:CPU 0 Status
16h /
NNN:POST Value
17h /
NNN:LanFrontA_Lk
18h /
NNN:LanFrontB_Lk
19h /
NNN:LanRearC_Lk
1Ah /
NNN:LanRearD_Lk
1Bh /
NNN:FWH0 BootErr
1Ch /
NNN:FWH1 BootErr
1Dh /
NNN:XMC present
1Eh /
NNN:FRU Agent
1Fh /
NNN:IPMC Storage
20h /
P R E L I M I N A R Y
NNN:IpmC Reboot
21h /
NNN:Ver change
22h /
NNN:SEL State
23h /
NNN:IPMI Info-1
24h /
NNN:IPMI Info-2
25h /
NNN:IniAgent Err
26h /
NNN:Board Rev
SENSOR TYPE (CODE) /
EVENT/READING TYPE
(CODE)
Platform Alert (24h) /
“digital” Discrete (03h)
Processor (07h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
POST value OEM (C6h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
LAN (27h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
LAN (27h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
LAN (27h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
LAN (27h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Boot error (1Eh) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Boot error (1Eh) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Entity Presence (25h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
OEM FRU Agent (C5h) /
Discrete (0Ah)
Management Subsystem
Health (28h) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Platform Alert (24h) /
“digital” Discrete (03h)
Firmware version changed
(2Bh) /
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Event Logging Disabled (10h)
/ Sensor-specific (6Fh)
OEM Firmware Info 1 (C0h) /
OEM (70h)
OEM Firmware Info 2 (C0h) /
OEM (71h)
Initialization Agent (C2h) /
“digital” Discrete (03h)
OEM Board Revision (CEh)/
Sensor-specific (6Fh)
Ass. Mask /
Deass. Mask /
Reading Mask
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0463h / 0400h /
04E3h
4000h / 0000h /
40FFh
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0008h / 0008h /
0008h
0008h / 0008h /
0008h
0000h / 0000h /
0003h
0140h / 0000h /
0147h
0002h / 0000h /
0003h
0002h / 0000h /
0003h
0002h / 0000h /
0002h
003Ch / 0000h /
003Ch
0003h / 0000h /
7FFFh
0003h / 0000h /
7FFFh
0002h / 0000h /
0003h
0000h / 0000h /
7FFFh
LED I1on
error /
DESCRIPTION
Reading
Mask
Aggregates states (power,
temperatures etc.).
Visualization by the Health
LED (LED I1, red).
CPU status: “Processor
Throttled, THERMTRIP or
CAT error”
POST code value (port 80h) N
LAN link status –
Front Eth. port A (lower)
LAN link status –
Front Eth. port B (upper)
LAN link status –
Rear Eth. port C
LAN link status –
Rear Eth. port D
Boot error on standard SPI
boot flash
Boot error on recovery SPI
boot flash
Presence of XMC board N
FRU initialization agent
state
IPMI controller storage
access error
2 = IPMI controller is (re)booting
Firmware version changed,
update sensor data record
repository
State of event logging N
For internal use only N
For internal use only N
Initialization agent error
status. Used on BMC only.
1 = error free
Board revision information N
/ 0403h
/ 0008h
/ 0008h
/ 0140h
/ 0002h
/ 0002h
N
Y
N
N
N
N
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
Y
Page 26 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 27

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
Table 10: Gigabit Ethernet Link Sensor Assignment
SENSOR NUMBER/
ID STRING
17h /
NNN:LanFrontA_Lk
18h /
NNN:LanFrontB_Lk
19h /
NNN:LanRearC_Lk
1Ah /
NNN:LanRearD_Lk
CP6003-SA
Front GbE A GbE B GbE D
Front GbE B GbE A GbE C
Rear GbE A
(Rear I/O module)
Rear GbE B
(Rear I/O module)
GbE ROUTED TO FRONT
CP6003-RA
GbE A
(Rear I/O module)
GbE B
(Rear I/O module)
CP6003-RA/RC
GbE ROUTED TO REAR
GbE A
GbE B
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 27
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 28

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
7.2 Sensor Thresholds
The following table provides the temperature sensor thresholds.
Table 11: Thresholds - Standard Temperature Range
Sensor Number /
ID string
Upper non-recoverable
Upper critical
Upper non-critical
Normal max.
Nominal
Normal min.
Lower non-critical
Lower critical
Lower non-recoverable
The following table provides the voltage sensor thresholds.
Table 12: Voltage Sensor Thresholds
01h /
NNN:Temp
CPU
110 °C 118 °C 85 °C 95 °C
100 °C 108 °C 80 °C 90 °C
90 °C 98 °C 70 °C 80 °C
85 °C 93 °C 65 °C 75 °C
75 °C 83 °C 55 °C 65 °C
3 °C 3 °C 0 °C 0 °C
1 °C n.a. - 1 °C - 40 °C
n.a. n.a. - 2 °C - 42 °C
n.a. n.a. - 5 °C - 45 °C
02h /
NNN:Temp
Chipset
03h /
NNN:Temp
Board
03h /
NNN:Temp
Board E2
Sensor Number /
ID string
Upper non-recoverable
Upper critical
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Upper non-critical
Normal max.
Nominal
Normal min.
Lower non-critical
Lower critical
Lower non-recoverable
06h /
NNN:Board
3.3V
n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a.
3.488 V 5.289 V 5.289 V 12.773 V 5.289 V
n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a.
3.460 V 5.245 V 5.245 V 12.598 V 5.245 V
3.302 V 5.007 V 5.007 V 12.012 V 5.007 V
3.129 V 4.508 V 4.747 V 11.426 V 4.747 V
n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a.
3.101 V 4.465 V 4.703 V 11.250 V 4.703 V
n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a.
07h /
NNN:Board
5VIPMI
08h /
NNN:Board
5V
09h /
NNN:Board
12V
0Ah /
NNN:Board
IPMB 5V
Page 28 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 29

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
7.3 OEM Event/Reading Types
OEM (Kontron) specific sensor types and codes are presented in the following table.
Table 13: OEM Event/Reading Types
OEM
SENSOR
TYPE (CODE)
Firmware Info 1 (C0h) 70h Internal Diagnostic Data
Firmware Info 2 (C0h) 71h Internal Diagnostic Data
Initialization Agent (C2h) 03h
(“digital” Discrete)
FRU Agent (C5h) 0Ah
(Discrete)
Post Value (C6h) 6Fh
(sensor type specific)
Firmware Upgrade Manager
(C7h)
6Fh
(sensor type specific)
OEM
EVENT/READING
TYPE (CODE)
DESCRIPTION
Offsets / events:
0: Initialization O.K.
1: Initialization Error
FRU initialization agent, using a standard reading type.
Error is detected if the POST code is != 0 and doesn't
change for a defined amount of time.
In case of no error:
Bits [7:0] = POST code (payload Port 80h)
In case of error:
Bits [15:0] = 4000h
Data2 = POST code, low nibble
Data3 = POST code, high nibble
Offsets / events:
0 : First Boot after upgrade
1 : First Boot after rollback (error)
2 : First Boot after errors (watchdog)
3 : First Boot after manual rollback
4..7 : Reserved
8 : Firmware Watchdog Bite, reset occurred
Board Reset (CFh) 03h
(“digital” Discrete)
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 29
Data 2 contains the reset type:
…WARM = 0
…COLD = 1
…FORCED_COLD = 2
…SOFT_RESET = 3
…MAX = 4
Data 3 contains the reset source:
…IPMI_WATCHDOG = 0
…IPMI_COMMAND = 1
…PROC_INT_CHECKSTOP = 2
…PROC_INT_RST = 3
…RESET_BUTTON = 4
…POWER_UP = 5
…LEG_INITIAL_WATCHDOG = 6
…LEG_PROG_WATCHDOG = 7
…SOFTWARE_INITIATED = 8
…SETUP_RESET = 9
…UNKNOWN = 0xFF
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 30

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
Table 13: OEM Event/Reading Types (Continued)
OEM
SENSOR
TYPE (CODE)
e.g. for
Power Good /
Power Good Event
OEM
EVENT/READING
TYPE (CODE)
73h Sensor-specific
Offset
0h HS fault#
1h HS early fault#
2h DEG#
3h FAL#
4h BDSELState
5h n.a.
6h n.a.
7h vccMainGood
8h n.a.
9h n.a.
Ah n.a.
Bh n.a.
DESCRIPTION
Event
Ch n.a.
Dh n.a.
Eh n.a
Board revision (CEh) 6Fh
(sensor type specific)
Bits [7:0] = Board Revision number
This corresponds to Board and PLD Revision register
described in CP6003-SA/RA/RC User Guide.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 30 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 31

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
8. IPMI Firmware Code
8.1 Structure and Functionality
The IPMI firmware code is organized into boot code and operational code, both of which are
stored in a flash device. Upon an IPMI controller reset, the IPMI controller first executes the
boot code which does:
• A self-test to verify the status of the IPMI controller's hardware including its memory
• Performs a checksum of the operational code
After successful verification of the operational code checksum, the firmware will execute the
operational code. Only the operational code is upgradable in the field.
8.2 uEFI BIOS/IPMI Controller Interaction
For communication between the uEFI BIOS and the IPMI controller there is a “private” KCS interface. During the boot process the uEFI BIOS sends the following IPMI commands to the
IPMI controller:
• An OEM command which reports a good or a bad checksum
• A standard IPMI command Set Watchdog Timer to stop a possibly running IPMI
watchdog timer
• A standard IPMI command Set SEL Time to set the event log time to the time which
is kept by the RTC
• The OEM IPMI command Set Firmware Parameters with some parameters which,
for example, sets the IPMI controller to a BMC or an SMC as selected in the uEFI Shell.
•
A standard IPMI command
•Etc.
Set ACPI Power State
to set the state
ACPI legacy on
8.3 IPMI Firmware Configuration
To select the BMC or SMC mode, the kipmi uEFI Shell command (mode, IRQ functions) is
used. Upon every board reset, the uEFI BIOS forwards the user settings (BMC or SMC mode)
to the IPMI controller.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 31
Page 32

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
8.4 Firmware Identification
There are two ways to verify that a IPMI controller resides on a CP6003-SA/RA/RC.
Invoking the IPMI command Get Device ID returns among other information the following
data:
• Manufacturer ID = 3A98h (Kontron IANA ID)
• Product ID = B3C0 for the firmware
• Firmware revision in bytes 4:5 - depends on the core version of the running firmware.
• The SDR revision in byte 13 (OEM part of the response) is a sub-revision of the firmware
revision. It is unique for all versions of the board's firmware.
• The device ID string which can be found by reading the Device Locator Record (SDR
Type 12h) contains the string “BMC:x ... x”. For example, invoking the ipmitool command
ipmitool sdr list mcloc will return the device ID strings of all available boards. If
the CP6003-SA/RA/RC’s IPMI controller is in BMC mode, this string will be displayed
without change. If the CP6003-SA/RA/RC’s IPMI controller is in SMC mode, then the
string will be changed into “Sxx: x ... x” where xx is the slot number where the board is
residing, e.g. “S09: x ... x”.
8.5 Firmware Upgrade
The standard way to upgrade the IPMI's operational code is to use the open tool “ipmitool” (see
Table 2, Related Publications). This tool allows download and activation of new operational
code and also rollback to the “last known good” operational code. Additionally, the status and
the firmware version of the redundant firmware copies can be checked.
For local or remote firmware upgrade, the following IPMI interfaces are available:
• KCS interface (locally, requires active payload, but fast)
• IPMB (remote, independent of the payload state)
• LAN (remote, via IOL, requires also active payload)
During the download process, the currently running operational code operates as usual until
the activation command is issued. During the activation process, the IPMI controller is off-line
P R E L I M I N A R Y
for about 20 seconds while the boot code is re-organizing the firmware storage. Afterwards, it
starts the new operational code. If this doesn't succeed, after a timeout the boot code performs
an automatic rollback to the “last known good” operational code.
8.5.1 Firmware File Formats
Firmware images for upgrade are provided in two formats:
• Firmware in binary format, e.g. FW_IPMI_<BOARD>_<REL>_FWUM.bin,
for usage with “ipmitool fwum ..” commands
• Firmware images in the PICMG defined HPM.1 file format,
e.g. FW_IPMI_<BOARD>_<REL>_FWUM.hpm,
for usage with “ipmitool hpm ..” commands.
where:
<BOARD> identifies to board family of the IPMI firmware (B3C0)
<REL> identifies to release (version) of IPMI firmware.
Page 32 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 33

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
8.5.2 Firmware Upgrade - “ipmitool hpm”
Firmware upgrade using a HPM.1 file requires at least “ipmitool” version 1.8.10.
The firmware upgrade procedure starts with downloading the HPM.1 file using, for example,
the following command:
ipmitool hpm upgrade <HPM.1_FWFile>.hpm all
The next step is the activation of the newly downloaded IPMI firmware. This is done using:
ipmitool hpm activate
Detailed information about the currently active firmware versions or the redundant copies can
be obtained using the commands mentioned below.
To obtain detailed version information of the active IPMI firmware, use the following command:
ipmitool hpm compprop 1 1
To obtain the version of the rollback copy (only valid if a newly downloaded firmware is already
activated), use the following command:
ipmitool hpm compprop 1 3
To obtain the version of the newly downloaded IPMI firmware (only valid after download and
before activation), use the following command:
ipmitool hpm compprop 1 4
To obtain detailed information about the IPMI HPM.1 upgrade capabilities, use the following
command:
ipmitool hpm targetcap
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 33
Page 34

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
8.5.3 Firmware Upgrade - “ipmitool fwum”
“ipmitool” version 1.8.9 doesn’t support HPM.1 correctly. Tool versions prior to this do not
support HPM.1 at all.
The firmware upgrade procedure starts with downloading the binary firmware file using, for
example, the following command:
ipmitool fwum download <Binary_FWFile>.bin
The next step is the activation of the newly downloaded IPMI firmware. This is done using
ipmitool fwum upgrade
Detailed information about the currently active firmware versions and the redundant copies
can be obtained using the following command:
ipmitool fwum status
Some information about the IPMI’s upgrade capabilities can be determined using the command:
ipmitool fwum info
8.6 Setting the SEL Time
The IPMI controller does not have its own hardware real time clock. Therefore, after start-up,
restart or upgrade of the IPMI controller , it s software clock first must be supplied with the curr ent
time. The IPMI controller uses the time when handling event messages which otherwise will
have an out-of-date time stamp.
Every time when the uEFI BIOS starts up, it supplies the IPMI controller with the payload's current real time clock time.
Restarts of the IPMI controller without a following uEFI BIOS reboot will result in invalid date
and time indication. In order to apply correct timestamps to the SEL records, issue the IPMI
P R E L I M I N A R Y
command Set SEL Time. This may be done by application software on the payload side via
the KCS interface or by a remote IPMI controller via the IPMB-0.
8.7 IPMI Firmware Write Protection
If the CP6003-SA/RA/RC is plugged in a write-protected CompactPCI slot, the system write
protection bit SWP in the Device Protection Register (0x284) is set to “1”. In this case, the IPMI
firmware cannot be updated or reprogrammed neither through KCS, nor through IPMB nor
through LAN. The IPMI firmware stores the write protect state in it’s local NV-RAM. The write
protect state changes if the payload is on and the system write prote ction bit SWP is set to “0”.
This bit can be read only when the payload is on.
Note ...
The write protection mode is still active when the payload is off even if the IPMI
firmware reboots. To disable the write protection mode, plug the board in a
non-write-protected CompactPCI slot and switch the payload on.
Page 34 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 35

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
9. FRU Data
9.1 Structure and Functionality
The IPMI controller provides 4 kB non-volatile storage space for FRU information. For further
information regarding the FRU data, refer to IPMI - Platform Management FRU Information
Storage Definition v1.0, Document Revision 1.1.
Full low-level access to read or write the board's FRU Information is provided by regular IPMI
FRU Device commands. Care must be taken when writing FRU informatio n directly using standard IPMI commands because there is no write protection. Invalid FRU information may disturb
a shelf management software which uses the FRU data.
9.2 FRU Version Identification
The FRU data fields, as defined in the IPMI specification , are used to record the ve rsion of the
FRU installed. The revision number is incremented for each new release of FRU data.
Example of board FRU ID: “STD_R10”
Example of product FRU ID: “STD_R10”
9.3 Board-Specific FRU Data
The following FRU data areas and data fields are supported:
FRU Board Info Area
• Manufacturing date / time
• Board manufacturer (C7): “Kontron”
• Board Product Name (C6): “CP6003-SA/RA/RC”
• Board Serial Number (CF): “123456789012345”
• Board Part Number (C9): “123456789”
• FRU File ID (C7): “STD_R10”
FRU Product Info Area
• Product manufacturer (C7): “Kontron”
• Product Name (C6): “CP6003-SA/RA/RC”
• Product Part Number (C2): “00”
• Product Version (D9): “0000000000000000000000000”
• Product Serial Number (D9): “0000000000000000000000000”
• Asset Tag (D9): “_________________________”
1)
1)
1)
P R E L I M I N A R Y
2)
2)
2)
• FRU File ID (C7): “STD_R10”
• CustomData (D5): “MAC=CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC”
1)
Field will be modified during the manufacturing process
2)
Field is free for user. Please note that changes need special care (checksums).
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 35
1)
Page 36

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
9.4 FRU Data Update
Typically, an update of the FRU da ta is not n ecessary because the board’ s correct FRU dat a is
installed at the factory . If an upda te of the FRU data is required, it can be done via regular IPMI
FRU device commands. The correct FRU data must be prepared at the f actory. Please contact
Kontron for further assistance.
9.5 FRU Data Write Protection
If the write protection mode of the IPMI firmware is active, the FRU data cannot be updated,
reprogrammed or modified. For further information on the IPMI firmware write protection,
please refer to Chapter 8.7.
10. XMC Card Support
The presence or absence of an XMC card is reported by the “XMC present” sensor (refer to
sensor description).
If an XMC card is present, the card's FRU data EEPROM is readable/writable. The size of the
EEPROM must be smaller or equal to 256 bytes because of 8-bit EEPROM addressing. Note
that XMC FRU size is always reported as 256 bytes and writing to locations that are higher than
the real capacity should be avoided.
The FRU data of the XMC can be read under Linux using ipmitool fru print 1.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 36 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 37

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
11. uEFI BIOS Failover Control - Automatic SPI
Boot Flash Selection
When the CP6003-SA/RA/RC's payload starts, the first code to be executed is the uEFI BIOS.
There are two SPI boot flash devices (standard an d recovery), which may contain dif ferent uEFI
BIOS codes. Which one of them will be utilized from the next boot process on is defined by one
of two ways:
• The IPMI controller determines whether to boot from the standard or the recovery SPI
boot flash. The IPMI firmware’s parameter used for this function is configured via the
OEM IPMI command Set Control State. The IPMI controller stores this p arameter
in the EEPROM (refer to Chapter 6.3, Set Control State).
• Setting the DIP Switch SW1, switch 2, to ON results in booting from the recovery SPI boot
flash regardless of the IPMI firmware setting.
11.1 Automatic SPI Boot Flash Selection During the Boot Process
After each payload reset the IPMI controller selects the SPI boot flash by applying the related
EEPROM parameter.
Physically the IPMI controller sets or resets a signal line. Afterwards, it waits for a special
message from the uEFI BIOS. This message contains the checksum report, i.e. it indicates the
validity of the SPI boot flash's checksum.
If the Set Control St ate OEM command byte 2 is set to 00h and the DIP switch SW1, switch 2,
is OFF, the uEFI BIOS boots from the st andard SPI b oot flash. If the checksum is wrong or the
message is not received within 60 seconds, then the standard SPI boot flash is assumed to
contain an invalid or a corrupted image. In this case, the IPMI controller selects the recovery
SPI boot flash and reset the board again.
If the Set Control State OEM command byte 2 is set to 01h or the DIP switch SW1, switch 2, is
ON, the uEFI BIOS boots from the recovery SPI boot flash. With this setting, the IPMI controller
does not switch over to the standard SPI boot flash if the checksum is wrong or the message
is not received. In this case, the board freezes. For this reason, it is recommended to use the
standard SPI boot flash as a default boot flash.
In case of a boot failure, the IPMI controller issues a “Boot Error (Invalid boot sector) event” by
setting the appropriate sensor value (sensor “FWHx Boot Err”. x = 0..1). “x” is the number of
the used SPI boot flash (0 = standard SPI boot flash; 1 = recovery SPI boot flash). Afterwards,
it causes a payload-off/on cycle and continues as described at the beginning of this chapter.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
11.2 OS Boot Order Selection by OEM IPMI
Normally the uEFI BIOS will apply the OS boot order which was selected in the uEFI BIOS
menu “uEFI Boot/Boot Option Priorities”. But there is another alternative boot order which is
stored in the IPMI controller's non-volatile memory . This boot order can be set and read by IPMI
OEM commands. At payload start the IPMI controller writes this boot order into a register where
the uEFI BIOS can read it. If this IPMI controller's boot order has a non-zero value, the uEFI
BIOS will use it instead of its own boot order.
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 37
Page 38

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
12. Hot Swap and Shutdown
12.1 Hot Swap Handle and Hot Swap (Blue) LED
To perform the actions required for hot swapping of the CP6003-SA/RA/RC, a hot swap state
machine with the following M-states generated by the IPMI controller is used:
• M0: Board Not Installed
• M1: Board Inactive
• M2: Board Activation Request
• M3: Board Activation in Progress
• M4: Board Active
• M5: Board Deactivation Request
• M6: Board Deactivation in Progress
The blue Hot Swap LED (HS LED) of an inserted board in a powered rack is normally used to
indicate the board's operational status so as to facilitate hot-swapping of the board:
• Hot Swap LED On
The payload is inactive:
• The board may be activated by closing the Hot Swap handle, or
• The board may be extracted. The M-state is 1.
When payload power is off e.g. after a shutdown via an IPMI chassis command and
the handle is still closed, the M-state is 1.
• Hot Swap LED Blinking
Changing from active state to inactive state or vice versa.
Don't extract the board now. The M-state is 2, 5 or 6.
• Hot Swap LED Off
The payload is active.
Don't extract the board now. Normally the extraction is impossible because the handle is
P R E L I M I N A R Y
closed and locked. The M-state is 3 or 4.
Normally the logical states “active” and “inactive” of a payload are identical to the physical
states “handle open” and “handle closed” or “payload power off” and “payload power on”.
If, however, the power is switched on or off using IPMI chassis commands or the payload is
shut down by the OS, then the position of the Hot Swap handle and the power state may become asynchronous. In this case the blue LED is switched on indicating that the payload power
is switched off although the handle is closed. Such actions are not part of the Hot Swap process
and are governed by their own functionality which is not within the scope of this document.
Page 38 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 39

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
12.2 The Hot Swap and Shutdown Processes
Hot Swap, as defined here, is the purposely initiated process to remove and replace an active
board in a powered system. To accomplish this requires that the hot swap process provide for
an orderly transition of the payload from the active to inactive st ate and vice versa. This is necessary to preclude improper system operation and possible loss of data. The CP6003-SA/RA/
RC has all the necessary features including hardware and IPMI software to support hot swapping. On the software side, however , not all available OS’s su pport hot swapping, not even partially . Three possible cases for hot swapping based on OS capabilities are described as follows.
Case 1: Involves an OS which does not support ACPI
After payload power on, the starting uEFI BIOS will inform the IPMI controller by sending the
IPMI command Set ACPI Power State / Set Legacy on. This means that a Hot Swap
(opening of the closed handle) shall immediately lead to payload power-off by the IPMI
controller.
In this event, the application/operator is responsible for the termination of all payload processes
prior to initiating removal/replacement of the board to avoid improper operation or loss of data.
Case 2: Involves an OS which emulates ACPI support
An OS which does not really support ACPI, such as VxWorks, is able to obt ain “Graceful Shutdown” support from the IPMI controller by performing in the following way.
After start-up, such an OS must manipulate the chipset in a way that prevents an immediate
power-off when the “power button” is logically activated.
Then it must send the IPMI command Set ACPI Power State / S0/G0 working to the
IPMI controller to enable this to process later on an S3/G2 soft off command.
During application operation the system must cyclically read the “Hot Swap Sensor” (sensor
#0) using the IPMI command Get Sensor Reading. This allows the tracking of the board's
state. After the board has once reached M-state 4 (sensor reading is 10h) the leaving of this
announces that the handle was opened. Now the time has come to terminate all processes.
After all critical processes have been terminated, the OS must send the IPMI command Set
ACPI Power State / S3/G2 soft off to the IPMI controller which will set the power off
immediately.
Case 3: Involves an OS which supports ACPI
When an OS is started which supports ACPI, the IPMI command Set ACPI Power State
/ S0/G0 working is sent to the IPMI controller. This indicates that the OS has repro-
grammed the chipset in such a manner tha t a “power button” signa l does not le ad to an immediate power-off but only causes an event that can be detected by the OS.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
When the handle is opened, the IPMI controller asserts the “power button” signal to notify the
OS. The OS then shuts down all processes and afterwards causes the transmission of the IPMI
command Set ACPI Power State / S3/G2 soft off to the IPMI controller which then
switches the power off.
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 39
Page 40

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
13. LAN Functions
13.1 Overview
All Ethernet channels except for the GbE E channel support IPMI over LAN (IOL) and Serial
over LAN (SOL). Common for both types of communication is the use of the RMCP/RMCP+
protocol for the packing of the data to be transferred. The RMCP/RMCP+ protocol uses the
TCP port 623 by default.
While IOL serves to transport IPMI commands and their responses, SOL serves to transport
any serial data. In each case, the IPMI controller serves as a protocol encoder and decoder.
IOL is able to use both RMCP and RMCP+ protocols. SOL works only with the RMCP+
protocol.
Please note that IOL and SOL need the Ethernet device to be powered. Therefore, the module
(payload) must be fully powered.
13.2 Setting Up the Ethernet Channel
There are two methods to configure the LAN settings (IOL/SOL) for the four Ethernet channels:
• By use of the kipmi net uEFI Shell command in the uEFI BIOS
• By use of the open tool “ipmitool” or IPMI commands
The setup methods are compatible, i.e. both methods show the parameters which are set by
the other one.
The setup is separate for all four channels. When the MAC addresses are set, the ones which
are programmed into the hardware must be re-used. This is a restriction. The IP addresses of
a channel being used by “normal” payload traffic and IOL/SOL traffic may differ but need not
differ as long as port 623 is not used in parallel by payload and IOL/SOL.
The four Ethernet ports provided by the CP6003-SA are assigned to the following channels:
Channel 2: Rear port GbE D
Channel 3: Rear port GbE C
Channel 4: Front port GbE B
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Channel 5: Front port GbE A
The four Ethernet ports provided by the CP6003-RA are assigned to the following channels:
Channel 2: Rear port GbE D
Channel 3: Rear port GbE C
Channel 4: Front/Rear port GbE A
Channel 5: Front/Rear port GbE B
The four Ethernet ports provided by the CP6003-RC are assigned to the following channels:
Channel 2: Rear port GbE D
Channel 3: Rear port GbE C
Channel 4: Rear port GbE B
Channel 5: Rear port GbE A
Page 40 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 41

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
13.3 Basic Setup from uEFI Shell
With the kipmi net command from uEFI Shell some basic settings such as IP address, sub-net
mask and gateway address can be set up for all of the four Ethernet channels.
13.4 Setup by “ipmitool” or IPMI Commands
The open tool “ipmitool” offers commands for the setup of the four Ethernet channels. All possible options are shown by issuing:
ipmitool lan set
If “ipmitool” is not usable, the LAN parameters can be set by using standard IPMI commands
as defined in the IPMI specification.
To show the current LAN parameters for a channel, “ipmitool” offers the command:
ipmitool lan print <channel = 2, 3, 4, 5>
13.5 Setup of User Accounts and Password
The open tool “ipmitool” offers commands for the listing and manipulation of user accounts for
channels 1 through 4. An overview can be obtained by issuing:
ipmitool user
The predefined user accounts for a channel can be listed using the following command:
ipmitool user list <channel = 2, 3, 4, 5>
For every channel, the CP6003-SA/RA/RC has these predefinitions in non-volatile memory:
ID Name Callin Link Auth IPMI Msg Channel Priv Limit
1 false true true USER
2 admin false true true ADMINISTRATOR
Please note that the ADMINISTRATOR password is preset with admin.
Changed accounts and passwords stay valid after payload power-off.
The accounts must be activated using the following command:
ipmitool user enable <user number>
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 41
Page 42

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
13.6 IPMI Over LAN (IOL)
IPMI over LAN is used to allow the IPMI controller to communicate with the IPMI controller via
LAN using the RMCP or the RMCP+ protocol. The data transferred are IPMI commands and
the responses to them.
To enable LAN support after parameter setup the following command must be issued:
ipmitool lan set <channel = 2, 3, 4, 5> access on
Please note that the following commands must use the IP address which belongs to the enabled channel.
The open tool “ipmitool” can serve as a control program and user interface for this. “ipmitool”
allows the issuing of generic IPMI commands such as:
ipmitool -I lan -H 192.168.3.189 -U adm in -P adm in -A PA SSWOR D raw 6 1
or to call complex functions like “mc.info”:
ipmitool -I lan -H 192.168.3.189 -U admin -P admin -A PASSWORD mc info
This uses many generic IPMI commands to get the information needed.
13.7 Serial Over LAN (SOL)
Serial over LAN connects the COM1 or /dev/ttyS0 respectively of the CP6003-SA/RA/RC's
payload side to an Ethernet channel. The IPMI controller resides between this serial interface
and one of the Ethernet channels. It serves as an encoder and a decoder for the used RMCP+
protocol and controls the data stream. Outside the CP6 003-SA/RA/RC, for examp le, the op en
tool “ipmitool” can be used to drive the SOL session, i.e. it of fers a console function to communicate via Ethernet with the CP6003-SA/RA/RC's serial interface.
The IPMI firmware supports only “straight password authentication” SOL sessions with default
privilege level USER.
Opening an SOL session requires special parameters as shown below:
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ipmitool -I lanplus -H 192.168.3. 18 9 -U adm in -P adm in -L USE R -C 0 sol
activate
The serial interface can be used as a connection, for example:
• To a user program on the CP6003-SA/RA/RC payload
• To the uEFI BIOS. Refer to the Main Setup menu, Serial Port Console Redirection
function in the CP6003-SA/RA/RC uEFI BIOS User Guide. The serial parameters can be
set via this function.
• To a Linux login console. This can be activated after payload start, for example, by the
command:
getty -h 115200 /dev/ttyS0
SOL supports and requires serial hardware handshake. This should be activated for the serial
port. Otherwise transmitted data might get lost. In any case the same serial p arameters for the
payload side serial interface and the IPMI controller's serial interface must be used.
Page 42 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 43

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
The parameters for the IPMI controller's serial interface can be set by using the following command:
ipmitool sol set
This command shows all options that can be set.
Further options are listed after issuing the following command:
ipmitool sol help
14. OS Support / Tools
14.1 Linux Tools
OpenIPMI - KCS driver
Normally all drivers and kernel modules needed for communication between the payload sided
software and the IPMI firmware via the KCS interface come with the distribution. Newest sources can be downloaded from: “http://openipmi.sourceforge.net”. There may be downloaded the
OpenIPMI project as well. The OpenIPMI library package includes some applications and the
needed libraries.
ipmitool
Another very useful all-in-one tool is “ipmitool” (http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net ). It provides a
user-friendly interface to many IPMI features and extensions, for example, to get sensor readings, change sensor thresholds or to access other IPMI controlle rs via IPMB. Befor e “ipmitool”
can be used the OpenIPMI driver, mentioned above, must be loaded too.
14.2 OS Support - Board Support Packages
For information on the operating systems supported with the CP6003-SA/RA/RC, please refer
to the CP6003-SA/RA/RC’s data sheet. Please visit “http://www.kontron.com” to download the
data sheet. Please also have a look at the download section for the latest versions of Board
Support Packages or Firmware Updates.
For further information concerning IPMI, refer to the BSP documentation for the respective OS.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 43
Page 44

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
HS LED
IPMI LEDs
I0 and I1
HS LED
CP6003-SA CP6003-RA
IPMI LEDs
I0 and I1
15. IPMI and Hot Swap LEDs
On the CP6003-SA/RA, there are three LEDs controlled by the IPMI controller, two IPMI S t atus
LEDs and a Hot Swap LED. All three LEDs are located on the front panel of the CP6003-SA/RA.
On the CP6003-RC, there are two IPMI LEDs controlled by the IPMI controller. Both LEDs are
located on the rear side of the CP6003-RC.
The following figure illustrates the location of the two IPMI LEDs and the HS LED on the
CP6003-SA/RA.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 44 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
Page 45

CP6003-SA/RA/RC IPMI Firmware
Temperature Sensor
JP1
DLED 0
DLED 1
DLED 2
DLED 3
R778 R756
R771 R759
IPMI LED I1
IPMI LED I0
IPMI LEDs
I0 and I1
The following figure illustrates the location of the two IPMI LEDs on the CP6003-RC.
The following table describes the functions of the IPMI LEDs and the Hot Swap LED.
Table 14: IPMI and Hot Swap LEDs Function
LED COLOR NORMAL MODE OVERRIDE MODE
I0 (right) red Off = board powered / running Selectable by user
On = board out of service (frmware not running)
green Pulsing = traffic on the IPMB bus
I1 (left) red On = health error detected Selectable by user
green Off = no health error detected
Pulsing = KCS interface active
Blinking = IPMI controller running showing its heart beat
red/amber Slow blinking = health error detected, IPMI controller running
showing its heart beat
Pulsing = health error detected, KCS interface active
HS LED blue On = a) board ready for hot swap extraction, or
b) board has just been inserted in a powered system
Off = board in normal operation (do not extract the board)
Blinking = board hot swap in progress; board not ready for
extraction
• Only lamp test
• Only lamp test
Selectable by user
• Only lamp test
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0 Page 45
Page 46

IPMI Firmware CP6003-SA/RA/RC
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 46 ID 1045-5656, Rev. 2.0
 Loading...
Loading...