Page 1
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Post-flight Inspection ................................................................ 6-1
Fuel Inspection ...................................................................................6-1
Coolant and Oil Inspections ..............................................................6-2
Rotor Blade Inspection ......................................................................6-2
Air Cleaner Inspection .......................................................................6-3
Servo and Linkage Inspection ...........................................................6-3
Self Monitor Inspection ......................................................................6-4
Tail Rotor Drive Belt Inspection ........................................................6-4
Antenna Inspection ............................................................................6-4
Post-Flight Cleaning and Servicing ......................................... 6-5
Washable Areas ..................................................................................6-6
Non-Washable Areas ..........................................................................6-7
6
Page 2
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Post-flight Inspection
In preparation for the next flight, inspect the helicopter and make sure each area is free of problems. In addition, enter the results in the flight
inspection log.
WARNING
● To prevent injury, make sure the engine is
stopped before performing an inspection.
● The helicopter is very hot immediately
after a flight. To prevent burns, allow the
temperature of the helicopter to lower sufficiently before performing an inspection.
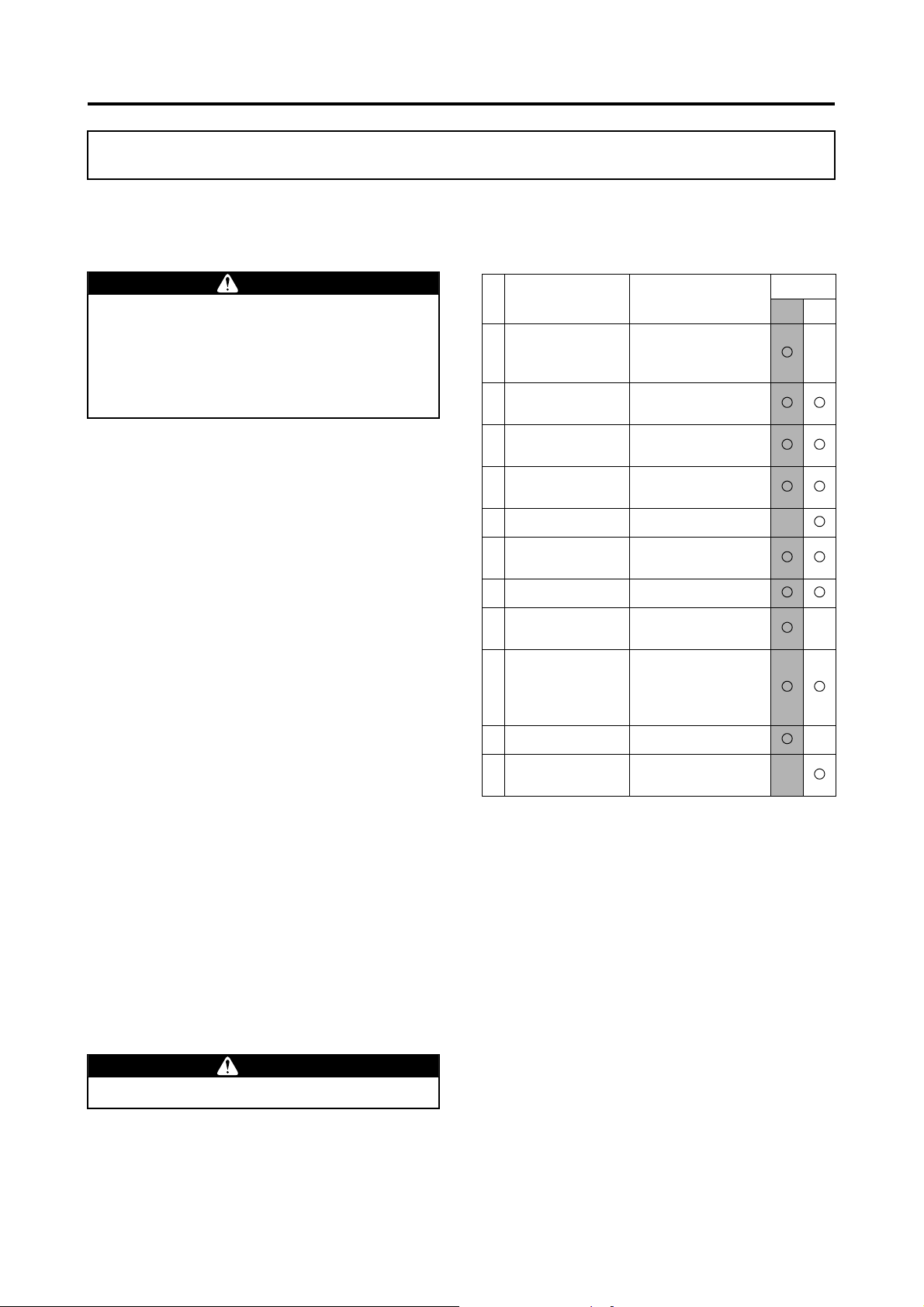
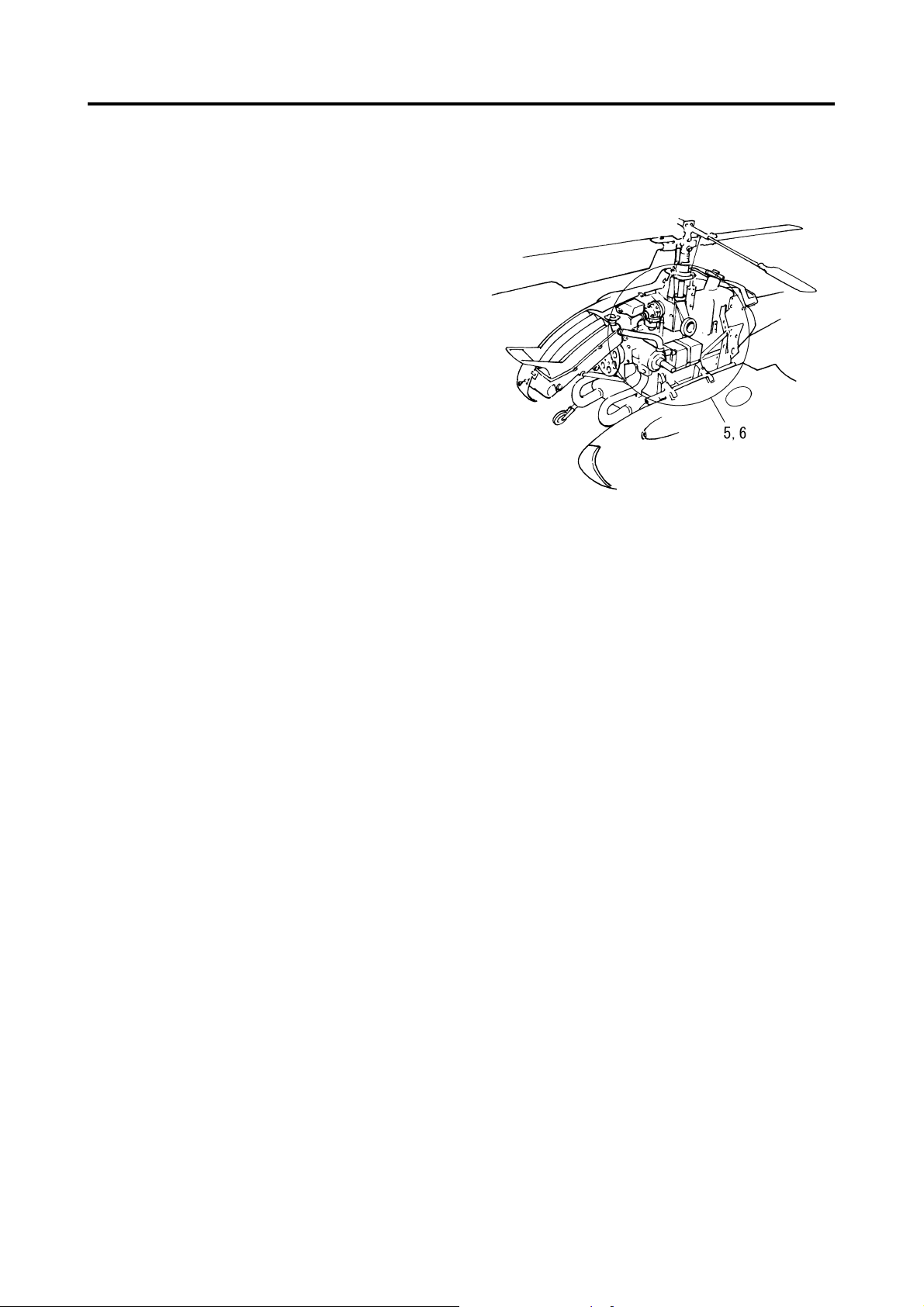
Inspection Point Inspection Items
• Battery Level
Transmitter
1 Fuel
2 Coolant, oil
3 Rotor blades
4 Air cleaner
• Operation
• Antenna installation
• Level
• Leakage
• Level
• Leakage
• Dirtiness, damage
• Movement
• Dirtiness
Flight
Pre Post
Fuel Inspection
Inspect for fuel leakage.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
For details, see page 4-19.
Servo, linkage
5
(rudder, throttle)
6 Self monitor
Radio signal
distance test
7 Tail rotor drive belt
GPS system
8 Antenna
• Operation
• Wobble
• States of lighting
• Radio signal reach
• Tension
• Abnormal noise
• Wear, damage
• Refuel
• States of lighting
• Installation state
• Rust
If you discover any fuel leakage, request a repair by
your dealer before the next flight.
WARNING
Fuel leakage could lead to a fire.
6-1
Page 3
Coolant and Oil Inspections
Inspect the coolant level and check for any coolant
or oil leakage.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
For details, see page 4-20.
A slight stain of coolant or oil does not indicate an
abnormal condition. However, if there are any drops
of coolant or oil leaking, request a repair by your
dealer before the next flight.
NOTICE
● Coolant leakage will adversely affect the
cooling performance of the helicopter and
cause it to overheat.
● Transmission oil leakage will reduce the
internal lubrication of the transmission
and damage the gears and bearings.
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Rotor Blade Inspection
Inspect the rotor blades for damage, dirtiness, and
movement.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
For details, see page 4-22.
If a rotor blade’s surface is dirty, use household
detergent on a soft cloth, wring out the cloth first,
and use it to wipe the rotor blade’s surface.
If a rotor blade is damaged, request a repair by your
dealer before the next flight.
NOTICE
If a main or tail rotor blade does not move
smoothly or is damaged, it could generate
noise or vibration.
6-2
Page 4
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
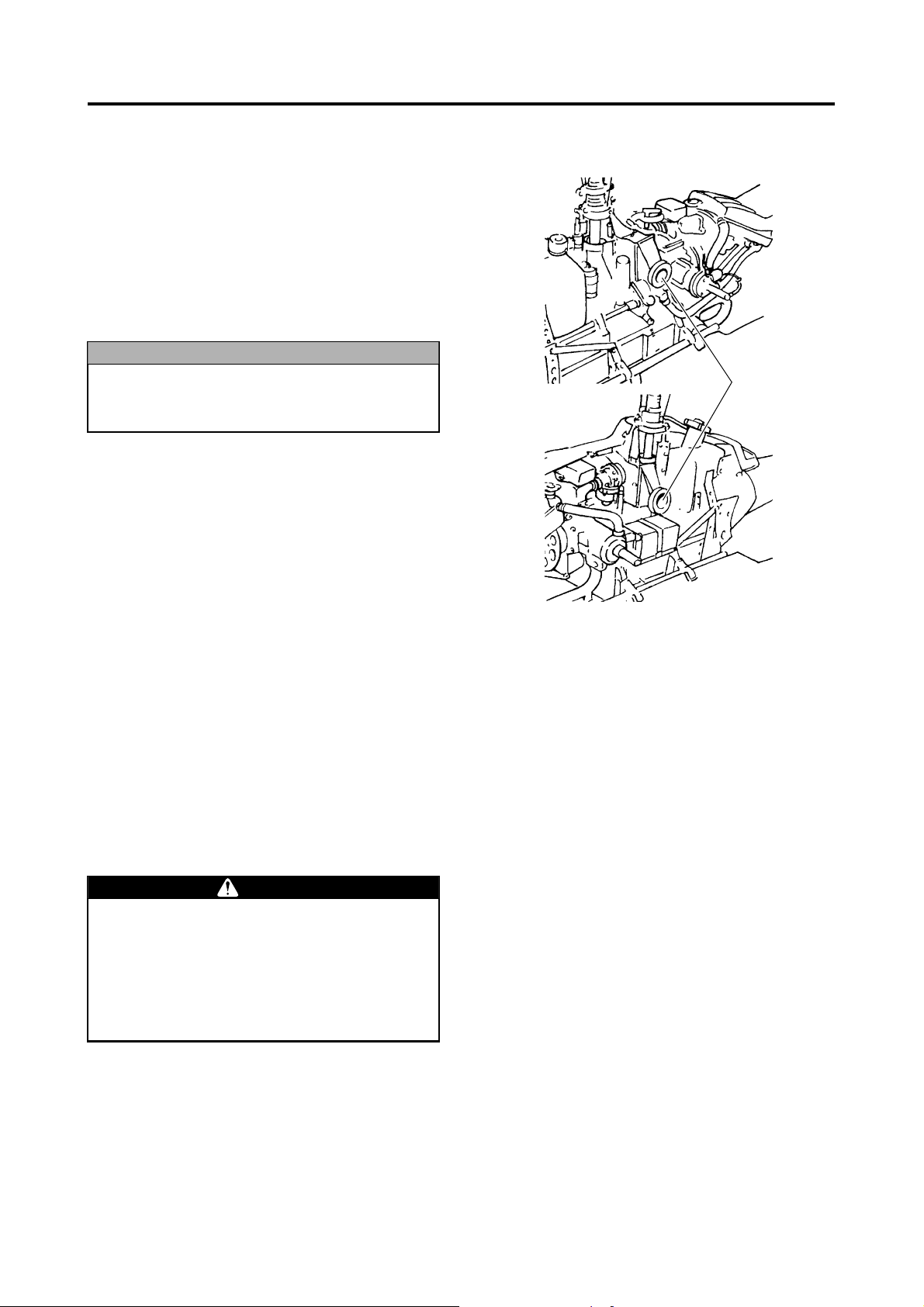
Air Cleaner Inspection
Inspect the air cleaner element for dirtiness.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
Make sure the air cleaner element is free of debris,
dust, pollen, etc.
However, if the air cleaner element is dirty, replace
air cleaner with new ones before the next flight.
NOTICE
A dirty or clogged air cleaner element will
adversely affect the performance of the
engine.
Air cleaner
Servo and Linkage Inspection
Inspect the servos and linkages for proper operation.
Before performing this inspection, turn the power
switch for the transmitter to ON and the main switch
for the helicopter to START.
For details, see page 4-23.
If the servos operate abnormally or the linkages
wobble, request a repair by your dealer before the
next flight.
WARNING
● If the servos operate abnormally or the
linkages wobble, they could adversely
affect the control of the helicopter.
● If the throttle operates abnormally, it could
adversely affect engine control, which
could cause the helicopter to go out of
control.
6-3
Page 5
Self Monitor Inspection
Inspect the illumination of the indicator lights on the
self monitor for proper operation.
Before performing this inspection, turn the power
switch for the transmitter to ON and the main switch
for the helicopter to START.
For details, see the table on page 3-5.
If the lights illuminate abnormally, request a repair
by your dealer before the next flight.
WARNING
Take the appropriate actions in accordance
with the indicator lights. By ignoring the
lights and continuing to fly, you will lose control of the helicopter and cause a serious
accident.
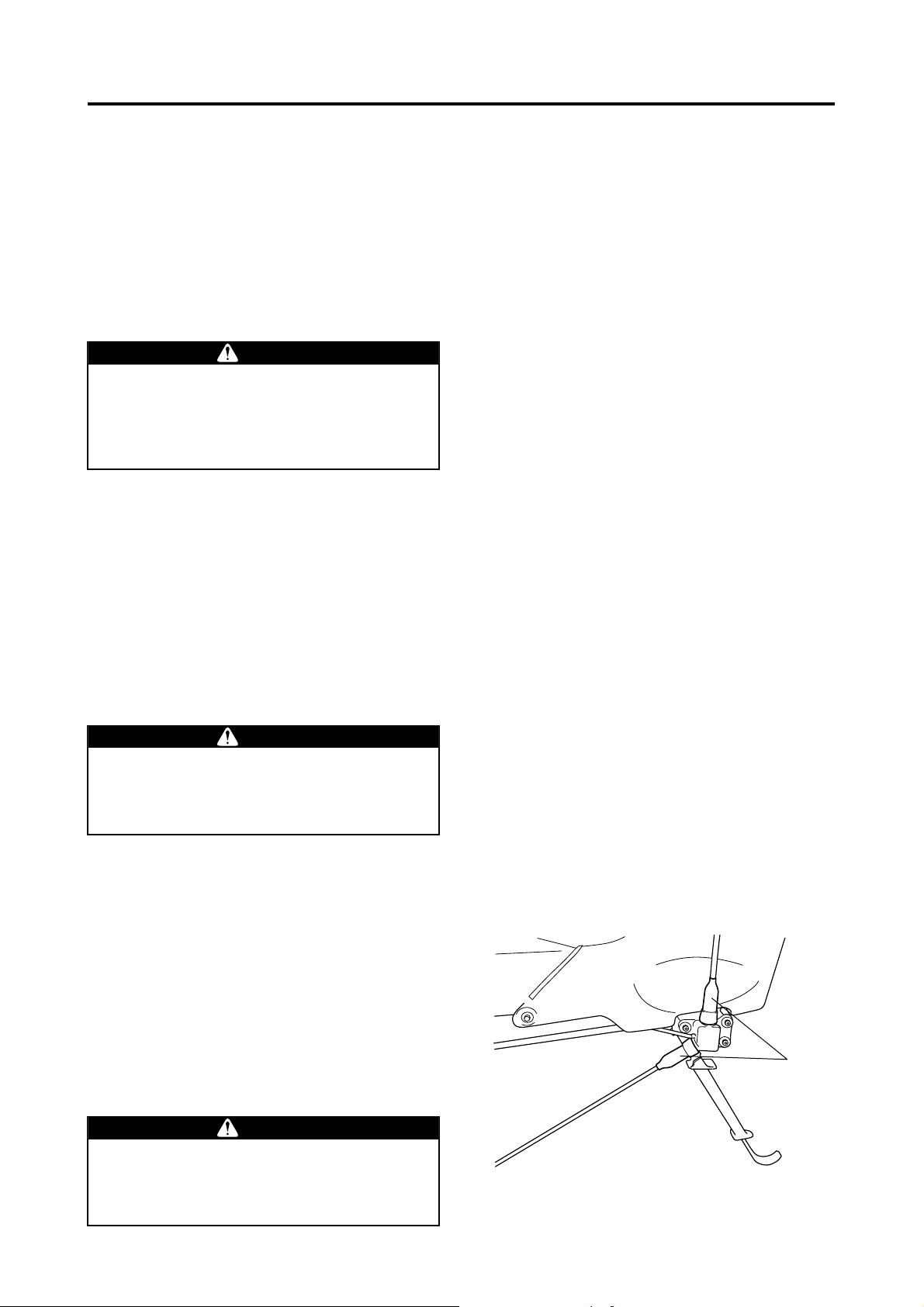
Tail Rotor Drive Belt Inspection
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Inspect the condition of the tail rotor drive belt and
apply lubricant to the belt.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
For details, see page 4-25.
If there is a problem with the belt, request a repair
by your dealer before the next flight.
WARNING
If there is a problem with the tail rotor drive
belt, it could adversely affect the actuation of
the tail rotor, which could cause the helicopter to go out of control.
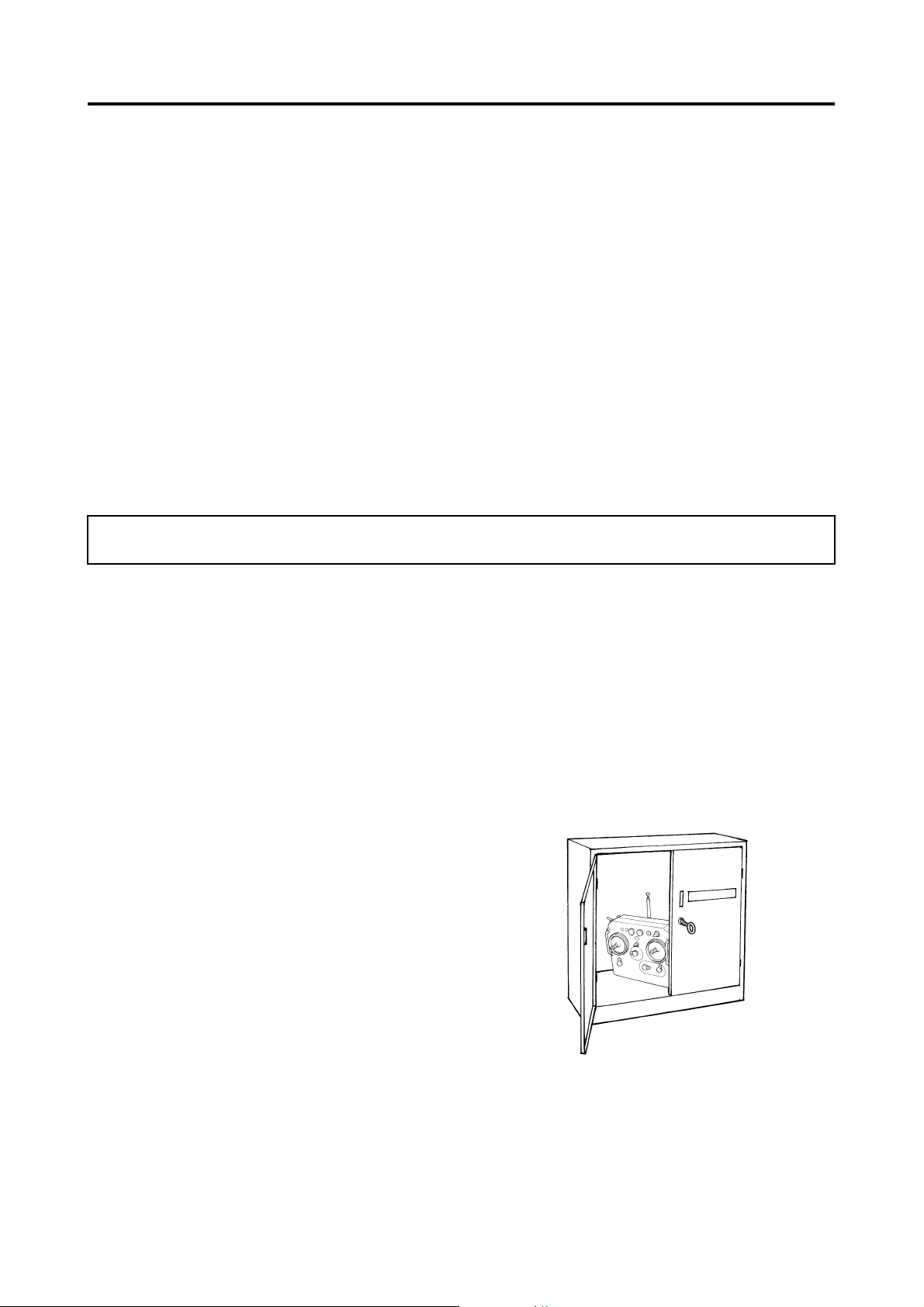
Antenna Inspection
Inspect the antenna to make sure it is not loose or
rusted at the area where it is mounted to the helicopter.
Before performing this inspection, turn OFF both
the main switch for the helicopter and the power
switch for the transmitter.
Peel the dust cover from the base of each antenna
pole and make sure the antenna poles are not
loose or rusted.
If they are loose or rusted, request a repair by your
dealer before the next flight.
WARNING
If the antenna is loose or rusted, it will affect
the reception of control signals, which could
cause the helicopter to go out of control during flight.
Dust Covers
6-4
Page 6
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Post-Flight Cleaning and Servicing
Agricultural chemicals, dust, dead bugs, and pollen
could adhere to the helicopter after an aerial application.
If they remain stuck to the helicopter, they will
cause a chemical reaction, which will lead to rust,
insufficient lubrication, sealant deterioration, and
discoloring.
To prevent these problems, use the methods
described below to clean and service the helicopter
after a flight, in preparation for the next flight. While
cleaning, check all areas of the helicopter for any
damage, abnormal wear, loose fasteners, etc.
WARNING
The helicopter is very hot immediately after a
flight. Therefore, to prevent burns, clean it
only after its temperature has lowered sufficiently.
NOTICE
Washing the helicopter with water will cause
a sudden change in temperature, which
could create problems in electrical parts.
Therefore, clean it only after its temperature
has lowered sufficiently.
6-5
Page 7
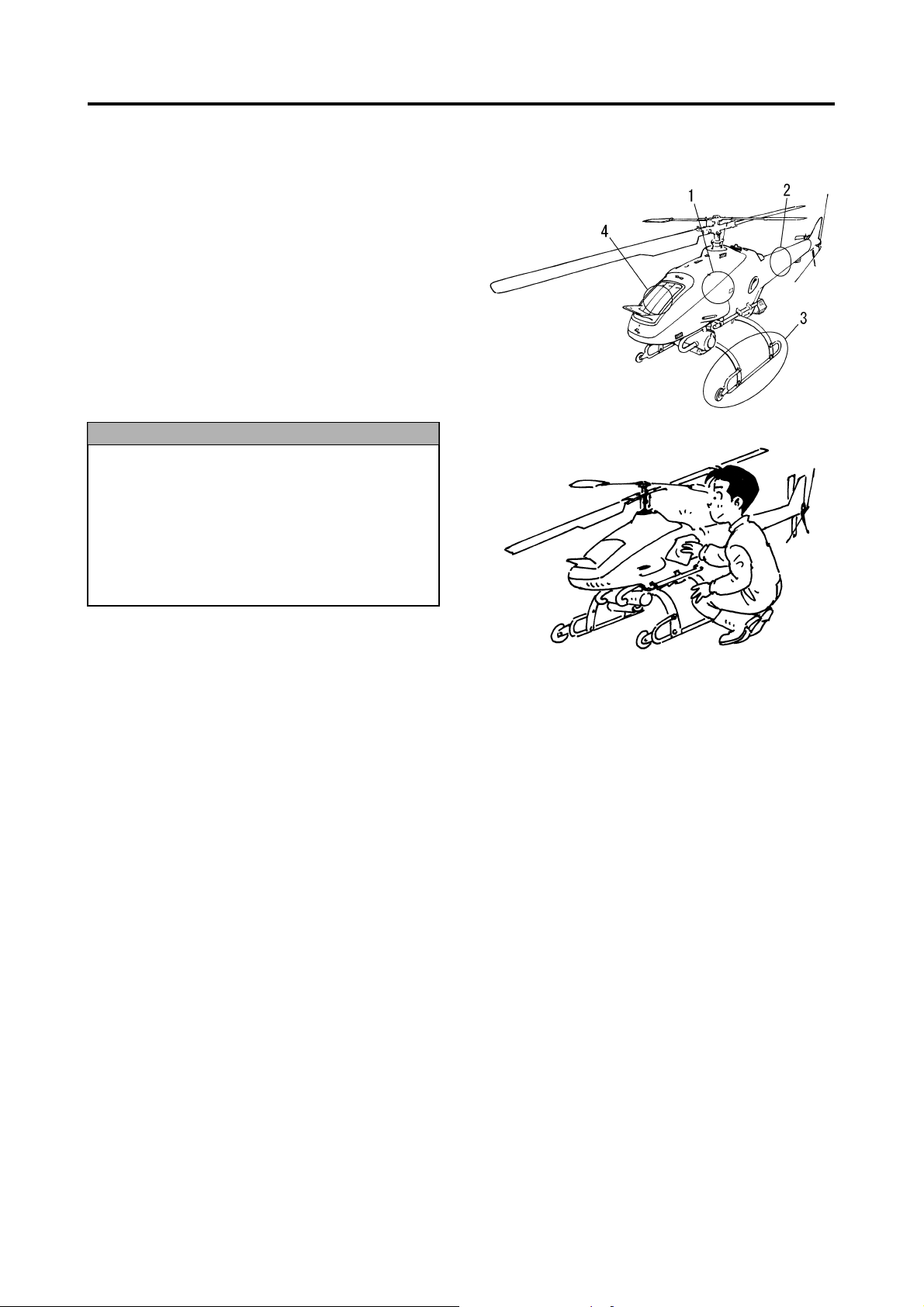
Washable Areas
1 Side covers
They may be washed only after they have been
removed from the helicopter.
Do not wash them in the installed state because
the water could splash on other parts.
2 Tail body
Clean it carefully while making sure to prevent
the GPS system and the gyro sensor from direct
contact with water.
3 Leaves and runners
4Radiator
Clean it by using caution not to damage the fins.
NOTICE
Do not use a high-temperature, high-pressure cleaner to clean areas 1 to 4 above, as it
could damage the film and paint on the surface.
After cleaning the washable areas of the helicopter with water, ensure to wring out your
cloth before you wipe the moisture off the
surface.
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
6-6
Page 8
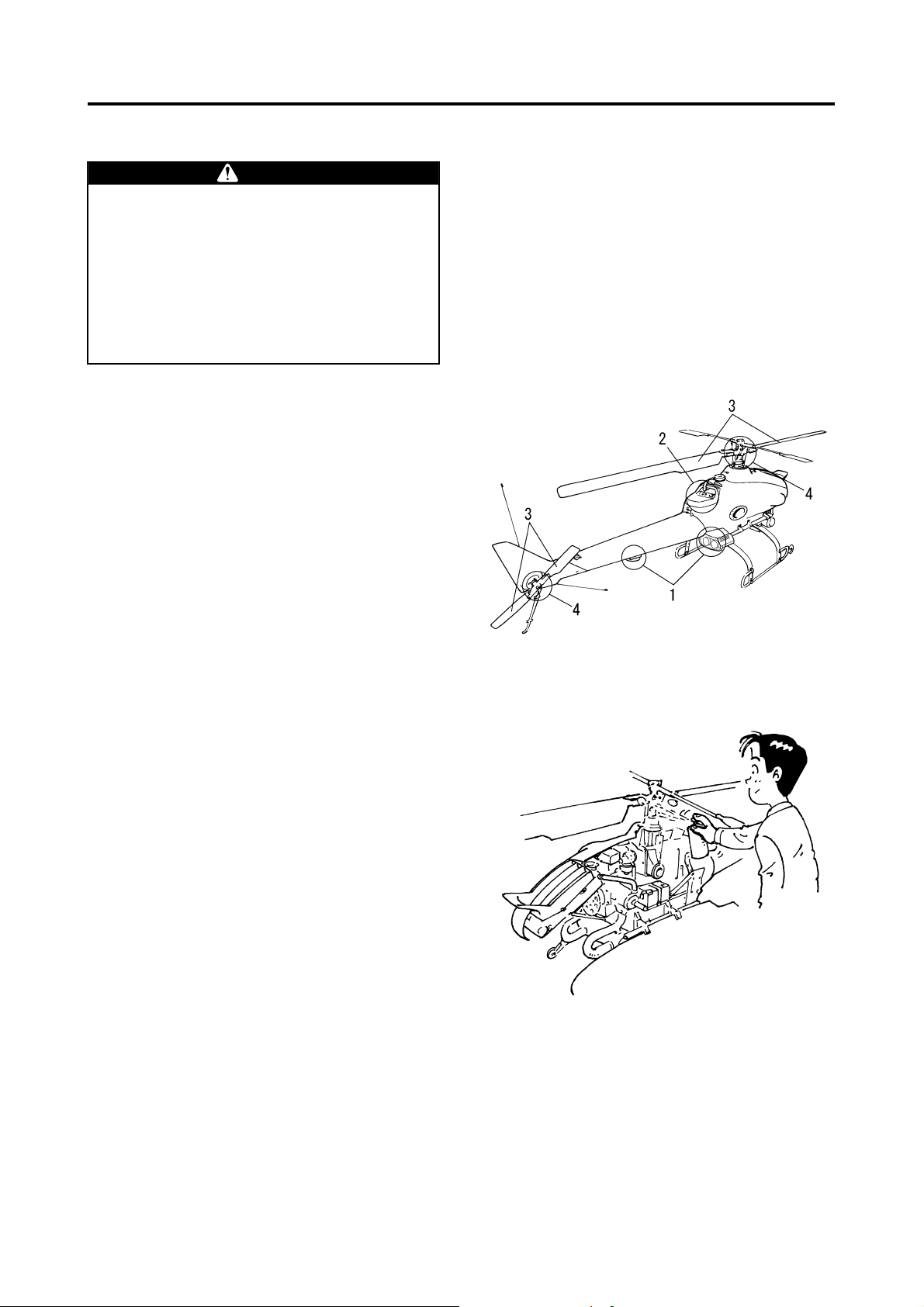
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
Non-Washable Areas
WARNING
The helicopter and the transmitter have a
drip-proof construction and not a water-proof
construction. Therefore, do not use water
directly on areas other than those indicated
in the previous section.
Failure to observe this precaution could
cause the electric parts or the sliding areas
to malfunction, which could lead to a serious
accident.
1 GPS System and Azimuth sensor
Washing these areas with water will cause them
to malfunction as a result of exposure of the
internal components to water.
Therefore, use a soft, moist cloth that has been
wrung out to wipe the dirty areas.
2 Control Panel
Washing these areas with water will cause the
hour meter, GPS antenna, switches, and the
monitor lights to malfunction as a result of exposure of the internal components to water.
Therefore, use a soft, moist cloth that has been
wrung to wipe the dirty areas.
3 Main and Tail Rotor Blades
Washing these areas with water will cause the
rotors to lose their balance and create vibrations
as a result of exposure of the internal components to water.
If the rotor surface is dirty, use household detergent on a soft cloth, wring the cloth, and use it to
wipe the rotor surface.
4 Main and Tail Rotor Head Areas
Washing these areas with water will adversely
affect the lubrication of the bearings and slides,
which could damage or wear those parts.
Therefore, use a soft, moist cloth that has been
wrung out to wipe the dirty areas.
Apply a small amount of the dealer-specified
anti-rust lubricant to the bearings, rod ends, and
sliding portions of parts, and then wipe them with
a dry cloth.
6-7
Page 9
5 Servos and Electrical Parts
Washing these areas with water will cause them
to malfunction as a result of exposure of the
internal components to water.
6 Frame
Washing this area with water will cause the
YACS control to malfunction as a result of exposure of the internal electric components to water.
Therefore, use a soft, moist cloth that has been
wrung out to wipe the dirty areas.
7 Flight Transmitter
Washing this area with water will cause the
transmitter to malfunction as a result of exposure
of the internal switches and electric components
to water. Therefore, use a soft, moist cloth that
has been wrung out to wipe the dirty areas.
Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
6-8
Page 10

Post-Flight Inspection and Cleaning
6-9
Page 11
Simple Maintenance
Battery Recharging Procedure ................................................. 7-1
7
Page 12

Simple Maintenance
Battery Recharging Procedure
This helicopter uses a sealed battery.
It is not necessary to refill or inspect the battery
fluid.
If there is any abnormality in the battery, request a
repair by your dealer.
WARNING
The battery produces flammable gas (hydrogen gas). Mishandling it could lead to an
explosion resulting in injuries. Make sure to
observe the following:
● Fire is strictly prohibited. Do not short a
circuit, cause a spark, or let any fire such
as cigarettes come near. This could cause
an explosion.
● Do not connect to the battery terminals in
the wrong order. Doing so could cause a
fire.
● Recharge in a well ventilated place.
● Keep gasoline, oil, or organic solvent from
getting on the battery, as this could cause
the battery case to crack.
● Do not drop it or apply any other strong
impact.
● The battery fluid is diluted sulfuric acid.
Contact with the skin, eye, or clothing
could lead to a serious injury.
● Keep out of reach of children.
First Aid
● In the unlikely event that the battery fluid
gets on the skin, clothing, etc., immediately rinse with copious amounts of water.
● If it enters the eye, immediately rinse it
with copious amounts of water, and seek
medical attention.
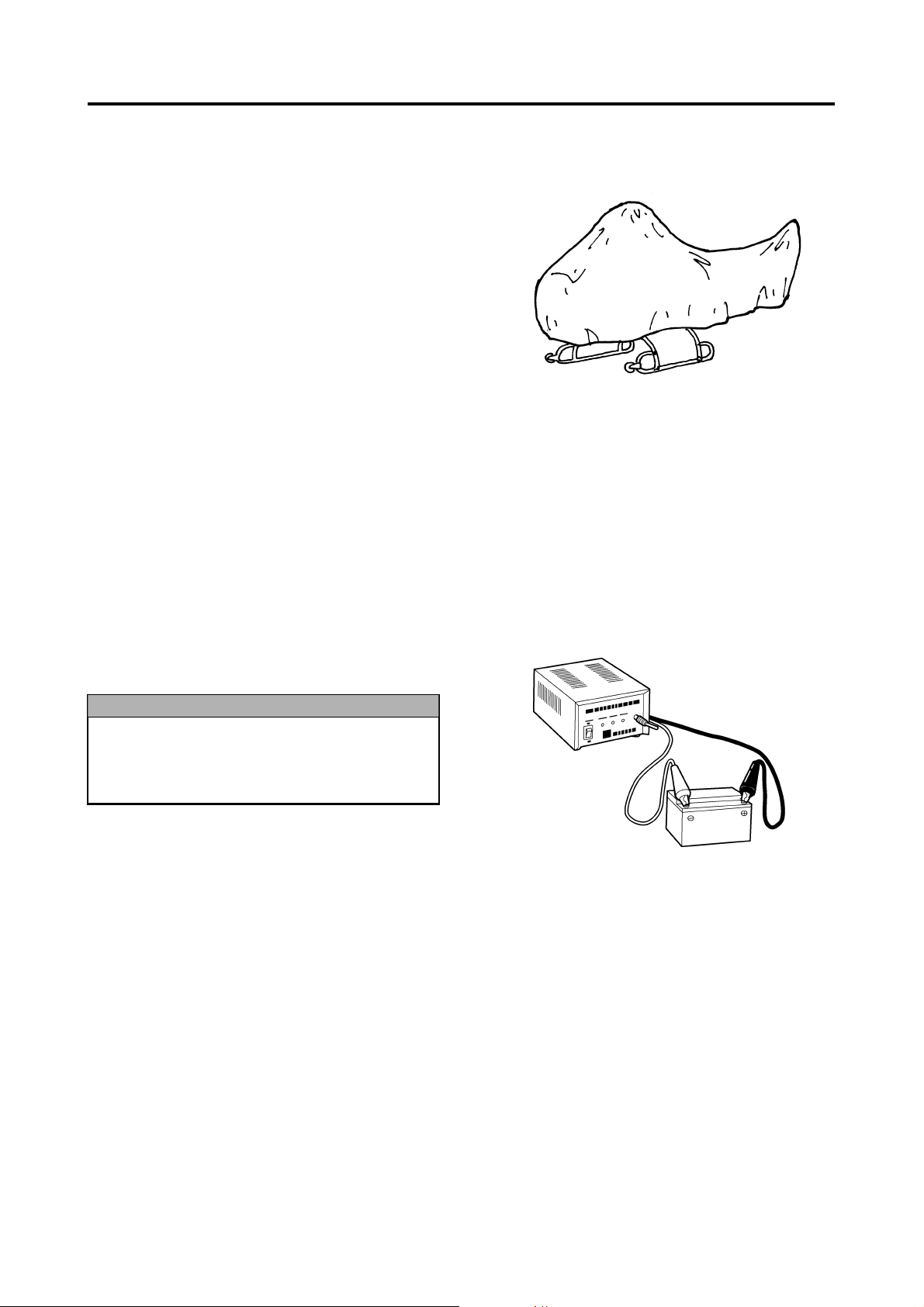
+Terminal (red cap) -Terminal (black cap)
Battery Battery Support Strap
7-1
NOTICE
● This is a sealed 12V battery.
● This battery has been filled with fluid and
charged. No fluid level inspection or refilling is necessary.
● For recharging, use the dedicated sealed
battery recharger. Contact your dealer for
details.
● If the battery is to be left unused for a long
time, remove the battery from the helicopter, and recharge every 3 months.
● When replacing the battery, make sure to
use a genuine battery.
Page 13
Removing the Battery
1 Make sure to turn OFF the main switch on the
control panel.
2 Disconnect the negative - and positive + termi-
nals of the battery, in that order.
3 Remove the battery support strap and take the
battery out of the helicopter.
Reinstalling the Battery
Reinstall the battery in reverse order of removal.
TIP
● Batteries are consumables.
● The battery should be replaced every year.
Simple Maintenance
7-2
Page 14

Simple Maintenance
7-3
Page 15
Proper Management
Storage Precautions .................................................................. 8-1
Daily Storage Procedure ....................................................................8-2
Long-Term Storage Procedure ..........................................................8-2
Operating the Helicopter After Long-Term Storage ........................8-3
Other Types of Management .................................................... 8-5
8
Page 16
Proper Management
This unmanned helicopter for industrial applications
has been manufactured for the purpose of aerial
application of agricultural chemicals, fertilizers, and
seeds.
Secure a storage location for the helicopter and its
auxiliary devices, to prevent theft and illegal use
outside of its intended purpose, such as criminal
acts.
As a measure to prevent illegal use, this product is
equipped with the following features:
• Areas of use are limited
• Specified operation period
• Specified total operation time
Storage Precautions
To select a storage site, consider factors such as
sources of fire or spark, temperature, humidity,
dust, theft, and the presence of any stacked loads
in the area.
We recommend that you provide a dedicated cabinet for storing the auxiliary devices.
In addition to protecting the helicopter from damage
and theft, or the auxiliary devices from loss, these
measures will facilitate the monitoring of their maintenance conditions and ensure efficient preparation
for the next flight.
1 Store the helicopter, rotors, and transmitters in
separate, lockable locations so that they will not
be stolen or subject to other criminal acts.
2 If the helicopter is stolen, immediately report the
theft to your dealer. Then, contact your local
police department.
8-1
Page 17
Daily Storage Procedure
1 Perform “Post-flight Inspection” (P6-1) and
record the results in the flight log.
2 Clean the helicopter. (See page 6-5.)
3 Place the helicopter cover (sold separately) and
store it indoors, in an area that is not damp.
4 Clean the flight transmitter and remove its bat-
tery. (See page 4-2.)
Long-Term Storage Procedure
If the helicopter will not be operated for a few
months, follow the storage procedure given below
in preparation for the subsequent operation.
Proper Management
1 Perform “Post-flight Inspection” (P6-1) and
record the results in the flight log.
2 Clean the helicopter. (See page 6-5.)
3 Remove the onboard battery and recharge it with
a dedicated recharger. (See page 7-1.)
After recharging, store the battery in a cool and
dark location, and recharge it every 3 months.
NOTICE
To disconnect the battery, first disconnect its
negative terminal, followed by the positive
terminal. Reversing this order could cause
the battery to short.
4 Fuel must be drained from the fuel tank and the
carburetor. Request the performance of this
operation by your dealer.
5 Place the helicopter cover and store it indoors, in
an area that is not damp.
6 Clean the flight transmitter and remove its bat-
tery. Store the battery in a cool and dark location.
8-2
Page 18
Proper Management
Operating the Helicopter After Long-Term Storage
TIP
● Have a periodic inspection performed on
the helicopter if you will be operating it
after prolonged storage of 1 year or more.
● Contact your dealer for details.
To operate the helicopter after storing it for a few
months, perform the following preparations:
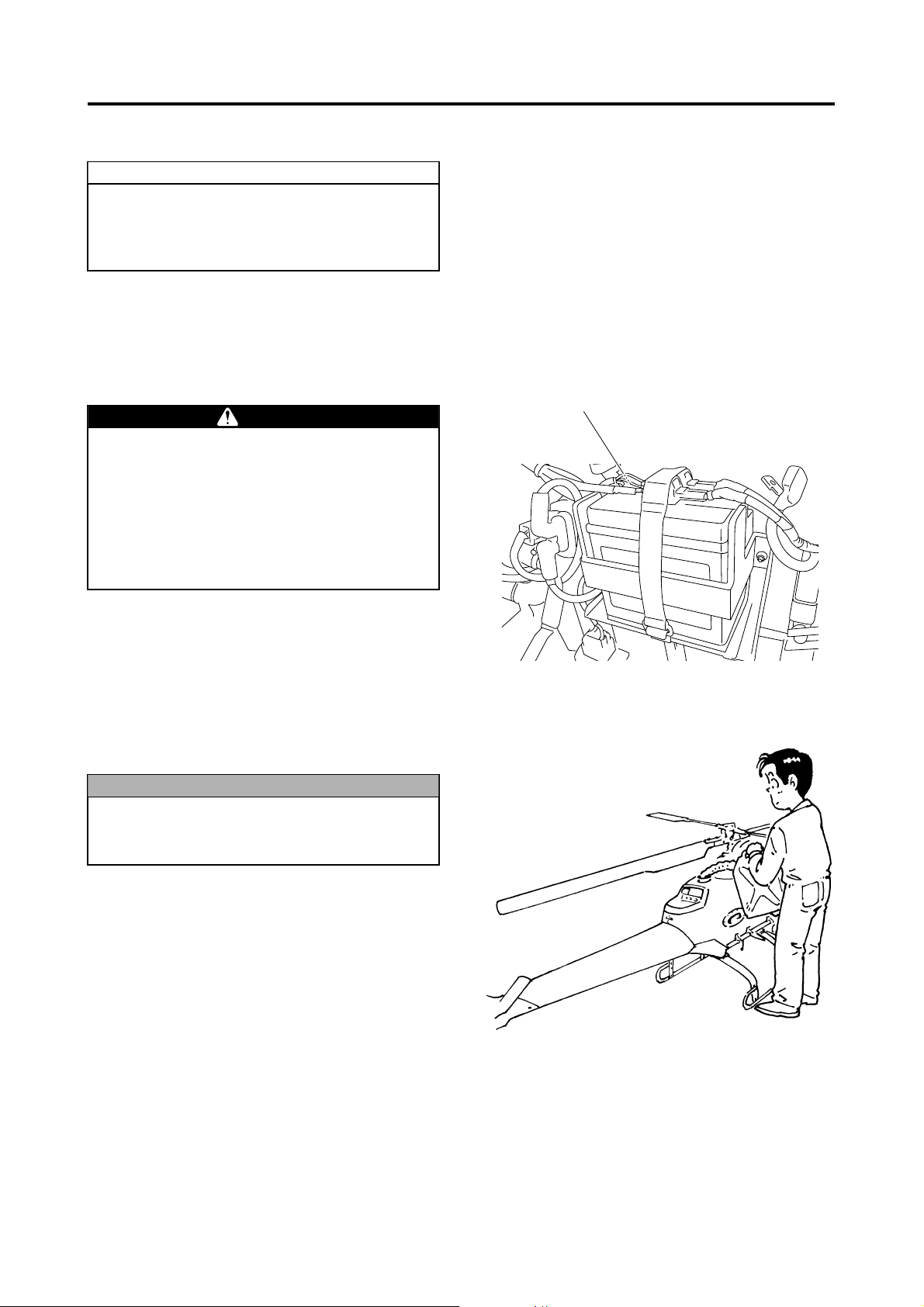
1 Install fully charged batteries in the helicopter
and the flight transmitter, after making sure the
main switch on the helicopter is turned OFF.
WARNING
● Do not interchange the positive and negative poles when connecting the battery terminals, as it could cause a fire or
malfunction.
● To connect the battery, first connect its
positive terminal, followed by the negative
terminal. Reversing this order could cause
the battery to short.
Connect the positive terminal first
2 Prepare fresh fuel and pour it in the fuel tank.
(See page 4-4.)
NOTICE
Never use old leftover fuel.
This could cause the engine to stop or operate poorly
8-3
Page 19
3 Perform pre-flight inspections. (See page 4-17.)
4 Start the engine. After prolonged storage, the
engine will be hard to start because it will take a
while for the fuel to reach the carburetor.
TIP
If the engine does not start within 5 seconds
after you have pressed the starter switch,
wait about 10 seconds to allow the battery
voltage to recover. Then, press the starter
switch again.
Repeat the cycle of operating the starter motor for 5
seconds and waiting 10 seconds, 4 or 5 times. This
will allow the fuel to reach the carburetor and the
engine to start.
Proper Management
8-4
Page 20

Proper Management
Other Types of Management
This helicopter and some parts fall under the listcontrolled items of Japan’s “Foreign Exchange and
Foreign Trade Act”. Use sufficient care to ensure
that the list-controlled items are not stolen or lost.
8-5
Page 21
Troubleshooting
Engine ......................................................................................... 9-1
Helicopter ................................................................................... 9-4
YACS ........................................................................................... 9-6
GPS ............................................................................................. 9-7
Flight Transmitter ...................................................................... 9-8
Sprayer ....................................................................................... 9-9
9
Page 22

Troubleshooting
The problems listed here can be handled primarily
by the user.
Problems or causes that are not listed here are
handled by your dealer. If such problems occur,
cancel the flight and contact your dealer to have the
helicopter inspected and repaired.
● Make sure to follow the instructions given
in the “User Action” column, and do not
take any actions that are not called for.
● If you have any questions, be sure to contact your dealer. If an inspection, adjustment, or part replacement is performed by
a person who does not possess the knowhow and proficiency to service the helicopter, it could lead to a serious accident.
WARNING
Engine
Starter motor does not operate
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Main switch on the helicopter is not turned to
1
START.
2 Power switch of the flight transmitter is not ON. Turn ON the power switch of the flight transmitter. See page 5-3.
Throttle stick on the flight transmitter is not in the
3
SLOWEST position.
4 Decompression is not operating. Operate the decompression lever. See page 5-5.
5 Helicopter battery terminals are loose. Firmly tighten the battery terminals. See page 7-1.
6 Onboard battery is faulty.
Turn the main switch on the helicopter to START. See page 5-3.
Move the throttle stick of the flight transmitter to
the SLOWEST position.
Recharge the battery with a dedicated recharger,
or replace it.
See page 5-5.
See page 7-1.
The starter motor does not operate, and all 3 flight indicator lights,
“”, “”, and “” illuminate simultaneously.
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Request your dealer for repair.
Engine does not start
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 There is no fuel. Pour fresh fuel in the tank. See page 4-4.
2 Poor quality fuel (old fuel) Request your dealer for repair.
3 Carburetor starter does not operate. Operate the starter lever. See page 5-5.
4 Spark plugs are faulty.
5 Spark plug caps are improperly installed. Install the spark plug caps properly.
6 Starter motor spins slowly.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Recharge the onboard battery with a dedicated
recharger.
See page 7-1.
9-1
Page 23
Troubleshooting
Engine speed does not increase
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Main switch on the helicopter is not turned to
1
FLIGHT.
2 Starter lever has not been returned. Return the starter lever. See page 5-6.
3 Decompression lever has not been returned. Return the decompression lever. See page 5-6.
4 Air cleaner element is dirty or clogged.
5 Spark plugs are faulty.
Turn the main switch on the helicopter to FLIGHT. See page 5-7.
Immediately stop the flight and replace air cleaner
with new ones.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Engine has no power
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Engine overheats.
2 Spark plugs are faulty.
3 Air cleaner element is dirty or clogged.
Immediately stop the flight, and check the contents in the next section “Engine overheats”.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Immediately stop the flight and replace air cleaner
with new ones.
Engine overheats
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Replenish coolant.
1 Coolant is leaking or insufficient.
2 Specified coolant is not used.
3 Radiator is dirty or its fins are clogged. Clean the radiator. See page 6-6.
4 Radiator fan motor is not operating.
5 Engine load is excessive. Reduce the payload. See page 4-10.
If coolant is leaking, request a repair by your
dealer.
Use the dealer-specified coolant and tap water
with the proper mixing ratio.
If the motor does not operate when the main
switch on the helicopter is turned to FLIGHT,
request a repair by your dealer.
See page 4-20.
See page 4-20.
Coolant gushed out of recovery tank
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Engine overheats.
Immediately stop the flight, and check the contents in the previous section “Engine overheats”.
9-2
Page 24

Troubleshooting
Helicopter emits a burning smell
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Engine overheats.
2 Oil is leaking.
3 Wires are burned.
Immediately stop the flight, and check the contents in “Engine overheats” on page 9-2.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Engine idle is unstable
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Spark plugs are faulty.
2 Spark plug caps are improperly installed. Install the spark plug caps properly.
3 Starter lever has not been returned. Return the starter lever. See page 5-6.
4 Idle speed is too low.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Slightly raise the throttle trim lever on the flight
transmitter.
Engine idle is too high
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Throttle trim lever is improperly adjusted. Lower the throttle trim lever.
Carburetor throttle valve is not in contact with stop
2
screw.
Check the operation of the carburetor.
If it does not close fully, request a repair by your
dealer.
See page 4-23.
Engine speed does not decrease after landing
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Sensor operates abnormally due to a large shock
1
sustained during landing.
Land the helicopter more gently.
Turn OFF the YACS control switch.
See page 5-11.
Exhaust emits excessive smoke
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Gasoline and oil mixing ratio is improper. Replace the fuel. See page 4-4.
2 Specified oil is not used. Use the Yamaha-specified oil. See page 4-4.
Engine makes noise
9-3
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Engine is damaged internally or lubricated insuffi-
1
ciently.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Page 25

Helicopter
Helicopter vibrates
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Main rotor blades are positioned improperly.
Main rotor or tail rotor retaining bolts are tightened
2
improperly.
3 Main rotor or tail rotor is damaged.
Cushion tape has peeled from the main rotor or
4
tail rotor.
5 Tracking of the main rotor or tail rotor is faulty.
6 Main rotor or tail rotor is imbalanced.
7 Chemical tank is improperly installed. Securely install the chemical tank.
Install the rotor blades by matching their color
marks.
Follow the specified tightening procedure to
tighten the bolts.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Troubleshooting
See page 4-15.
See page 4-15.
See page 4-22.
See page 4-22.
See the operation manual for
the sprayer.
Helicopter cannot take off
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Immediately stop the flight, and check the con-
1 Engine speed does not increase.
2 Engine lacks power.
3 Payload is excessive. Reduce the payload. See page 4-10.
tents in “Engine speed does not increase” on
page 9-2.
Immediately stop the flight, and check the contents in “Engine has no power” on page 9-2.
Helicopter makes noise during takeoff
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Tail belt is loose.
2 Bolts of parts are loose. Check all parts for loose bolts.
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
See page 4-25.
Helicopter descends after takeoff
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Engine lacks power.
2 Payload is excessive. Reduce the payload. See page 4-10.
3 Throttle stick is operated improperly.
Immediately stop the flight, and check the contents in “Engine has no power” on page 9-2.
Operate the throttle stick by making sure the
amount of its movement does not decrease drastically.
9-4
Page 26

Troubleshooting
Helicopter moves considerably in rudder direction after takeoff
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Rudder was operated excessively before takeoff.
Do not operate the rudder excessively when taking off with the YACS control ON.
See page 5-8.
Helicopter drifts in one direction
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Trim is adjusted improperly. Adjust the trims on the flight transmitter. See page 5-9.
Helicopter descends when flare (brake) is applied
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Rotor lift decreased due to an abrupt flare opera-
1
tion.
2 Payload is excessive. Reduce the payload. See page 4-10.
Do not operate the flare abruptly. See page 5-8.
Helicopter moves considerably in rudder direction when flare
(brake) is applied
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Helicopter lost its balance due to an abrupt flare
1
operation.
Do not operate the flare abruptly. See page 5-8.
9-5
Page 27

YAC S
YACS warning light illuminates or flashes
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Identifiable through the illumination or flashing
1
pattern.
Self monitor light other than “” illuminates
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Identifiable through the illumination location.
YACS control configuration takes time
Immediately stop the flight and take appropriate
actions accordance to the information on page 3-7.See page 3-7.
Immediately stop the flight and take appropriate
actions accordance to the information on page 3-5.See page 3-5.
Troubleshooting
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Allow the YACS control to configure itself on a flat
1 Helicopter is not still.
surface. (Configuration will not complete if the
helicopter is tilted or moving.)
“” indicator light remains ON even after refueling
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Keep the refueling tank in a shade because the
1 Fuel temperature is too high.
fuel in it will reach a high temperature if the tank is
left under a scorching sun.
See page 5-4.
9-6
Page 28

Troubleshooting
GPS
GPS control configuration takes time (outer lights flashing)
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Wait until reception is restored or move to another
location and redo the configuration.
1 GPS radio signal reception is poor.
If the symptom does not improve after waiting or
changing the location, request an inspection of
the system by your dealer.
GPS indicator outer lights do not flash (with engine stopped)
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Power switch of the flight transmitter is not ON. Turn ON the power switch of the flight transmitter.
2 GPS system failure
Request your dealer for repair. (The helicopter
can continue to fly under YACS control only.)
See page 3-9.
See page 3-10.
Not all indicators illuminate even when GPS control switch is turned
ON
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Wait until reception is restored or move to another
GPS radio signal reception is poor (outer lights do
1
not illuminate).
2 Transmitter’s GPS control switch is faulty.
location and redo the configuration.
If the symptom does not improve after waiting or
changing the location, request an inspection of
the system by your dealer.
Request your dealer for repair. (The helicopter
can continue to fly under YACS control only.)
See page 3-9.
See page 3-10.
9-7
Page 29

Troubleshooting
Flight Transmitter
Output light does not illuminate
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Transmitter has an internal failure.
Battery monitor light illuminates
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1Battery’s state of charge is low. Replace with a fully charged battery. See page 3-11.
Battery use duration is too short
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Battery failure Replace the battery. See page 3-11.
2Battery’s memory effect
Immediately stop the flight and request a repair
by your dealer.
Use a battery discharger to eliminate the memory
effect. (Contact your dealer on how to eliminate
the memory effect.)
See page 4-18.
Battery monitor light illuminates suddenly
Main Cause User Action Remarks
If the light illuminates when the battery lead wire
1 Battery lead wire is damaged.
is shaken by hand, the battery lead wire is damaged. Immediately stop the flight and request a
repair by your dealer.
Dropped transmitter on ground
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Transmitter may be damaged internally.
Immediately stop the flight and request an inspection of the transmitter by your dealer.
Dropped transmitter into water
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Transmitter may be damaged internally.
Immediately stop the flight and request an inspection of the transmitter by your dealer.
Buzzer sounds a 3-3-7 pattern
See page 4-2.
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Transmitter has an internal failure.
Immediately stop the flight and request an inspection of the transmitter by your dealer.
See page 3-11.
9-8
Page 30

Troubleshooting
Sprayer
Chemical remains in right chemical tank
Main Cause User Action Remarks
This normal condition occurs because the heli-
1 Helicopter is tilting.
Sprayer does not operate
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Sprayer selector switch was operated improperly.
Other problems with liquid sprayer
copter tilts 5 degrees to the right during the flight.
(Ultimately, the sprayer will discharge all the
chemical in the tank.)
Select the switch position in accordance with the
type of sprayer that is being used.
See page 5-3.
See the operation manual for the liquid sprayer.
9-9
Page 31

Specifications
Specifications Data .................................................................. 10-1
Data List ............................................................................................10-1
Dimensions .......................................................................................10-2
10
Page 32

Specifications
Specifications Data
Data List
Product Name RMAX TypeII G UNIT,
Manufacturer Model L25
Performance Chemical Load Capacity* 16 kg
Practical Range (visual range) 150 m
Engine Type 2-cycle, horizontally opposed 2-cylinder
Cylinder Displacement 246 cc
Maximum Output 15.4 kW
System Water-Cooled
Electrical
Helicopter
Dimensions
Cooling
Starting System Electric Starter
Fuel
Control
System
Radiowave Frequencies for
Flying
Battery
Spark Plug
Main Rotor Diameter 3130 mm
Tail Rotor Diameter 535 mm
Overall Length / Overall Length
with Rotor
Overall Width 720 mm
Overall Height 1080 mm
Specified Coolant Mixture of dealer-specified coolant and water
Mixing ratio Dealer-specified ratio
Type Regular gasoline mixed with 2-cycle engine oil
Mixing ratio 50 parts gasoline to 1 part oil
Specified Oil Dealer-specified oil
Tank Capacity 6 liters
Name YACS-G
Warning Device Self Monitor, YACS Warning Light, GPS Indicator Light
Warnin gs
Onboard 12 V, 6.0 Ah, VRLA, leaded battery
Transmitter 9.6 V, 1.0 Ah, Ni-MH battery
Low Fuel Level, Excess Load, Radio Signal Interference, Low Voltage, GPS
Control Condition, Velocity Display, etc.
72.690, 72.730, 72.810, 72.850, 72.910, 72.950 MHz
Unmanned helicopter spark plug (Yamaha P/N 94702-00271)
(NGK P/N BR7HS-10)
2750 mm/3630 mm
* The performance may vary with atmospheric temperature, humidity, and altitude.
10-1
Page 33

Dimensions
Specifications
Unit: mm
10-2
Page 34

Specifications
10-3
Page 35

Inspection
Inspection Types and Descriptions ....................................... 11-1
Pre-Flight Inspection ........................................................................11-1
Post-flight Inspection .......................................................................11-2
30-Hour Inspection ...........................................................................11-2
Periodic Inspection ..........................................................................11-2
General Inspection ...........................................................................11-2
11
Page 36

Inspection
Inspection Types and Descriptions
The prescribed types of inspections are described
below.
• Pre-flight and post-flight inspections are to be
performed by the operator.
• For the 30-hour inspection, periodic inspection,
and general inspection, contact your dealer
(authorized service facility for Yamaha unmanned
helicopters for industrial applications).
WARNING
Have your dealer perform the 30-hour inspection, periodic inspection, general inspection,
and repairs. The performance of these
inspections by a person who is not a certified
unmanned helicopter service technician
could cause the helicopter to malfunction or
result in an accident.
TIP
Do not fly or perform an aerial application
without having a periodic inspection performed every 100 hours of operation.
What are Yamaha-authorized service facilities for
unmanned helicopters for industrial applications?
It is a service facility staffed by certified service
technicians for Yamaha industrial unmanned helicopters and equipped with the prescribed service
equipment.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Ensures that the helicopter and the auxiliary equipment are free of problems before a flight.
See page 4-17 for details on the inspection.
11-1
Page 37

Post-flight Inspection
Ensures that the helicopter and the auxiliary equipment are free of problems after a flight.
See page 6-1 for details on the inspection.
If a problem is detected, cancel the flight and
promptly contact your dealer.
Record the results of the inspection on the flight
log.
30-Hour Inspection
An inspection service performed after the delivery
of a new helicopter, when the hour meter indicates
a total of 30 hours of operation.
Inspection
Periodic Inspection
An inspection service performed at a Yamahaspecified dealer once for every 100 hours of operation indicated by the hour meter. The service
includes testing for durability and performance of
the helicopter and sprayer.
General Inspection
An inspection service to ensure the safety of the
helicopter when the hour meter shows a total of
500 or more hours of operation.
11-2
Page 38

Inspection
11-3
Page 39

Index
A
Air cleaner ......................................................... 2-3
Inspection ................................................... 6-3
Antenna ............................................................. 2-1
Inspection ................................................... 6-4
Azimuth Sensor ................................................. 2-1
B
Basic requirements ........................................... 1-2
Battery ............................................................... 2-3
Recharge .................................................... 7-1
Boom .......................................................... 4-1, 4-6
C
Carburetor ......................................................... 2-3
Check point indicator .................................. 2-2, 3-5
Chemical requirements ................................... 1-11
Chemical tank ............................................ 4-1, 4-6
Control panel ..................................................... 2-2
Coolant
Inspection ................................................. 4-20
Cushion tape ................................................... 4-22
D
Data list ........................................................... 10-1
Decompression lever ................................. 2-1, 5-5
E
Engine
Start ............................................................ 5-3
Stopping ................................................... 5-11
F
Failsafe actions ............................................... 3-12
Filter net ............................................................ 4-5
Flight indicator ............................................ 2-2, 3-5
Flight mode
Selecting ................................................... 4-13
Selector switch .................................. 2-2, 4-13
Flight requirements ........................................... 1-7
Flight transmitter ............................................... 2-4
Antenna .................................................... 4-18
Basic stick operation and helicopter
movement ............................................. 3-1
Recharging and replacing battery ............... 4-1
Basic trim lever operation and helicopter
movement ............................................. 3-2
Fuel
Inspection ................................................. 4-19
Preparing and refueling .............................. 4-4
Fuel filter ......................................................... 4-19
Fuel line ........................................................... 4-19
Fuel tank ........................................................... 2-3
Fuel tank cap .............................................. 2-1, 4-5
G
GPS
Antenna ...................................................... 2-1
Control switch ............................................. 3-3
Indicator light .......................................2-2, 3-9
Inspection ................................................. 4-26
Safety features and actions during
poor signal reception ........................... 3-15
Unit ............................................................. 2-1
Grip handle ........................................................ 4-7
H
Helicopter requirements .................................... 1-5
Hour meter ............................................... 2-2, 4-14
I
Inspection
30-hour inspection .................................... 11-2
General inspection .................................... 11-2
Periodic inspection .................................... 11-2
Post-flight Inspection ......................... 6-1, 11-2
Pre-flight .......................................... 4-17, 11-1
Intermediate transmission ............................... 4-21
L
Landing ........................................................... 5-11
Leaf ................................................................... 2-1
Linkage
Inspection ................................................. 4-23
M
Main rotor blade ................................................ 2-1
Inspection ................................................. 4-22
Main rotor blades
Installing and removing ............................. 4-15
Main switch ................................................ 2-2, 5-3
Malfunction area indicator .......................... 2-2, 3-6
Muffler ............................................................... 2-1
O
Oil
Inspection ................................................. 4-20
Operator requirements ...................................... 1-3
P
Payload inspection .......................................... 4-10
Plug cap ............................................................ 2-3
Post-Flight Cleaning and Servicing ................... 6-5
Product safety label locations ........................... 1-1
Page 40

R
Radiator ............................................................. 2-1
Radiator cap ............................................. 2-3, 4-21
Radio signal
Distance test ............................................. 4-25
Radio signal monitor ................................... 4-9
Radio signal interference inspection ................. 4-9
Recovery tank .......................................... 2-3, 4-20
Rubber hooks ........................................... 2-1, 4-16
Runner ....................................................... 2-1, 4-7
S
Self monitor ....................................... 2-2, 3-5, 4-24
Shutter pump cleaning switch ........................... 2-2
Side cover ......................................................... 2-1
Installing and removing ............................. 4-16
Slide servo ........................................................ 2-3
Inspection ................................................. 4-23
Slide servo thermo sensor ................................ 3-6
Spinner constant rotation switch ....................... 2-2
Spray
Spray switch ............................................... 3-4
Sprayer
Selector switch .................................... 2-2, 4-3
Spraying
Selecting and setting sprayer ..................... 4-3
Stabilizer blade .................................................. 2-1
Starter lever ................................................ 2-1, 5-5
Starter switch ............................................. 2-2, 5-6
Stone guard ............................................... 2-1, 4-6
Storage ............................................................. 8-1
T
Tail body ............................................................ 2-1
Tail cover ........................................................... 2-1
Tail rotor blade .................................................. 2-1
Inspection ................................................. 4-22
Tail rotor drive belt .......................................... 4-25
Takeoff .............................................................. 5-8
Transmission case .......................................... 4-21
Transmitter
Battery monitor light ......................... 3-11, 4-18
Inspection ................................................. 4-18
Transporting procedure ..................................... 4-6
Trim lever
Aileron ................................................. 2-4, 5-9
Elevator ............................................... 2-4, 5-9
Rudder ................................................. 2-4, 5-9
Throttle ................................................ 2-4, 5-5
Y
YACS
Control switch ............................................. 3-3
Warning light ........................................ 2-2, 3-7
Page 41

Please read this manual before using the product.
UNMANNED HELICOPTER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
UNMANNED HELICOPTER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
UNIT,
LIQUID SPRAYER
LIQUID SPRAYER
OPERATION MANUAL
OPERATION MANUAL
Page 42

Foreword
Thank you for using the liquid sprayer for the RMAX TypeII G Unit, unmanned helicopter for
industrial applications.
This operation manual describes the proper operating procedures as well as inspection and
servicing methods for the liquid sprayer for the RMAX TypeII G Unit, helicopter. Before using
this product, please be sure to read this operation manual, along with the separate opera-
tion manual for the RMAX TypeII G Unit, helicopter, and thoroughly understand the informa-
tion contained therein.
In this manual, the warning notes, which are necessary for safe and proper operation of this
product, are categorized and shown as follows. Please make sure to observe these instruc-
tions, as they all contain important information.
DANGER
This indicates that improper operation will
cause imminent danger, which could lead to
serious injury or death.
WARNING
This indicates that improper operation could
lead to minor and serious injuries or death.
NOTICE
Indicates that improper operation could
cause property damage.
TIP
Indicates proper operating procedure and
tips on inspection and maintenance.
Indicates a prohibited action.
The specific prohibited action is illustrated near the symbol.
● After you have read this operation manual, keep it within easy access near the product.
● If you have lost this operation manual, contact your dealer to request another copy.
● Contact your dealer if you have any questions or comments regarding the contents of
this operation manual.
● Some diagrams and contents in this manual may differ from the actual device, due to
specification changes, etc.
Page 43

Table of Contents
Safety Precautions
Product Safety Label Locations ............................................................... 1-1
Requirement ............................................................................................... 1-2
Spraying Precautions ................................................................................1-5
Usage Precautions..................................................................................... 1-9
Part Names
Part Names ................................................................................................. 2-1
Mounting and Removing the Sprayer
Mounting and Removing the Sprayer ...................................................... 3-1
Spraying Method
Relevant Switches ..................................................................................... 4-1
Using the Sprayer ...................................................................................... 4-3
Spray Specifications Settings .................................................................. 4-7
1
2
3
4
Cleaning and Inspections
Cleaning the Sprayer ................................................................................. 5-1
Inspecting and Cleaning Various Parts ................................................... 5-3
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting......................................................................................... 6-1
Specifications
Specifications Data.................................................................................... 7-1
Product Inspection
About Inspections...................................................................................... 8-2
5
6
7
8
Page 44

Safety Precautions
Product Safety Label Locations
Before using the device, please read and understand the affixed product safety labels thoroughly.
NOTICE
1-1
Page 45

Safety Precautions
Requirement
Basic requirements
WARNING
To ensure safe use, please make sure to read
the operation manual thoroughly before use.
WARNING
This liquid sprayer for the unmanned helicopter for industrial applications has been
manufactured for the purpose of aerial application of agricultural chemicals, fertilizers,
and seeds. Do not use it for other applications. It could also cause unexpected accidents.
1
2
3
4
WARNING
Do not modify the helicopter or the auxiliary
devices. Do not use parts other than genuine
parts. Any modification of the helicopter or
use of non-genuine parts may cause unexpected accidents.
5
6
7
8
1-2
Page 46

Safety Precautions
Operator requirements
WARNING
Flying this helicopter requires a high level of
skill.
The helicopter should be operated only by a
person who possesses an appropriate
license.
WARNING
Make sure to wear a helmet during flight. To
perform an aerial application, make sure to
wear clothing that is appropriate for the operation. Performing a flight and an aerial application in clothing that is not appropriate for
the task could cause loss of visibility, maneuvering error, or cause your foot to slip, resulting in unexpected accidents. Furthermore, it
could harm your health through exposure to
agricultural chemicals.
Certificate of
Authorization
Observe the following clothing requirements:
● Wear a helmet.
● Wear goggles and a particle mask.
● Wear long-sleeved clothing with secure buttons
and fasteners.
● Wear slip-proof shoes that are easy to walk with.
● Do not wear objects that could obstruct vision
when there is wind, or adversely affect operation
(especially towels and gloves).
WARNING
A minimum of 3 people is required for an
aerial application: a navigator who has been
briefed on the aerial application procedure,
an assistant who readies, mixes, and supplies agricultural chemicals, and an operator.
Beware that an understaffed operation could
lead to an accident.
1-3
Page 47

WARNING
The operation of an unmanned helicopter
involves considerable mental fatigue. The
operator should not fly the helicopter continuously for more than one hour, but should
take a rest every hour. Prolonged continuous
flight operation could cause the operator to
lose concentration and could lead to an accident.
WARNING
Do not fly the helicopter after drinking alcohol or taking a cold medicine, or if you are in
poor physical condition. Flying the helicopter
in poor physical condition could cause loss
of concentration, and could lead to an accident.
Safety Precautions
1-4
Page 48

Safety Precautions
Spraying Precautions
When operating an unmanned helicopter for the purpose of spraying agricultural chemicals, ensure safe operation, as well as the safety of humans, animals, agricultural products, and the environment during aerial application.
General Flight Pattern for Aerial Application
Example: Disease and pest control of a rice paddy
• Flight altitude: 3 to 4 m
• Flying speed: 10 to 20 km/h
• Flying interval: 5 or 7.5 m
• Wind velocity: 3 m/s maximum
Just passed 10 meters,
and 5 meters
Flying height between
3 and 4 meters
Wind
DANGER
When performing tasks such as refueling,
never approach (or allow others to approach)
within 20 m of the helicopter until the main
rotor has come to a complete stop and the
engine has stopped. Entering within 20 m of
the helicopter could cause a serious accident.
Flying speed between
10 and 20 km/h
Flying interval 5 or 7.5 meters
Affirmative!
1-5
Page 49

Using Registered Agricultural Chemicals
Use nationally registered agricultural chemicals,
and use them properly by reading the usage
instructions and precautions included in the manual
for each respective chemical.
WARNING
Do not use agricultural chemicals other than
those registered. Failure to do so could
expose animals, plants, or people to agricultural chemicals for which the operator will be
held socially responsible.
WARNING
Control and handle agricultural chemicals
strictly in accordance with their manuals.
Negligent control and improper handling of
agricultural chemicals could lead to chemical
pollution or health hazards.
Safety Precautions
1-6
Page 50

Safety Precautions
Spray Chemical
Since the agricultural chemical is diluted at a low
dilution rate, make sure to observe the following:
(1) Agricultural Chemical
● Use nationally registered agricultural chemicals.
● In low-volume liquid spraying, the characteristics
of the agricultural chemical can easily change
when mixed with other agricultural chemicals,
and may produce solids or turn to a gum-like
state. When mixing, use agricultural chemicals
that have been checked in advance for physiochemical change, compatibility with the sprayer,
mixture toxicity, etc.
● Spreading agents (surface active agents) cannot
be added.
Label
(2) Dilution Water
For dilution water, make sure to use tap water. Do
not use agricultural water, as this could lead to
debris clogging or characteristic change in the agricultural chemical.
(3) Dilution Rate
For example, to make 8 of spray solution of an
agricultural chemical diluted to 8x, dilute 1 of
agricultural chemical with 7 of tap water (dilution
water). This will make 8 of spray solution.
Agricultural chemical: 8 × 1/8 = 1
Tap water: 8 - 1 (agricultural
chemical) = 7
Since flowable and water-dispersible chemicals can
easily precipitate, combine and mix them well just
before aerial application flight.
Tap Water
Agricultural
Water
Chemical
Tap Water
Spray Solution
1-7
Page 51

Safety Precautions
Pouring the Spray Solution
● Check the inside of the chemical tank (into which
the solution will be poured), the check valve, the
strainer section, and the filter for any debris or
sediments. If you find any debris or sediments,
make sure to remove them before pouring the
solution.
● Keep the chemical tank load to 8 or less per
side (16 combined for left and right tanks).
TIP
● For higher altitudes and temperatures,
decrease the load.
● For information on load capacity, see the
operation manual for the helicopter.
Check Valve
Filter in the
Chemical Tank
Strainer
Chemical Tank
1-8
Page 52

Safety Precautions
Usage Precautions
Stop the engine when replenishing the chemical.
When replenishing the chemical, make sure to stop
the engine. If this task takes longer than one
minute, turn OFF the main switch on the helicopter.
DANGER
Never approach (or allow others to approach)
within 20 m of the helicopter until the main
rotor has come to a complete stop and the
engine has stopped. Entering within 20 m of
the helicopter could cause a serious accident.
Securely mount the chemical tanks.
Prior to the flight, check that both chemical tanks
are securely mounted.
NOTICE
If the chemical tanks are not securely
mounted, they could come off during flight.
Do not apply excessive force on the boom.
When performing tasks such as replenishing the
chemical, use caution not to trip on the boom.
NOTICE
If an excessive force is applied against the
folding direction of the boom, it could
become damaged.
1-9
Page 53

Part Names
Part N ames
1
Chemical Tank
Right and Left Nozzles
Bracket
Chemical Tank Joint
Boom
Center Nozzle
Boom
Joint
Bracket
Handle
Tank Cap
2
3
Chemical Tank
4
Bracket
Chemical Tank Joint
Boom
Three-way Cock
Nozzle Switching Motor
5
Right and Left Nozzles
6
7
8
Filter Cap
2-1
Page 54

Mounting and Removing the Sprayer
Mounting and Removing the Sprayer
1 Position the sprayer under the frame.
TIP
Extend the sprayer boom, and slide horizontally from between the leaves.
2 Of the three connectors running from the frame,
connect the 2-pole connectors to the sprayer
pump’s power connectors, and the 3-pole connector to the power connector of the nozzle
switching motor.
TIP
If necessary, apply the dealer-specified
grease onto the O-rings of the joints on the
bottom of the chemical tanks.
Sprayer
Leaf
Leaf
3-pole connector
3 Insert the dampers of the sprayer (2 locations)
into the mounting holes (2 locations) on the
frame.
2-pole connector
Mounting Holes
Dampers
3-1
Page 55

Mounting and Removing the Sprayer
4 Lift the rear of the sprayer, and fasten by insert-
ing bolts and washers through the right and left
bracket holes on the frame.
Tightening
Torque
Use a 4 mm hex wrench.
5 Securely mount the left and right chemical tanks
by fitting the sprayer’s brackets into the mounting
stays on the chemical tanks.
If the chemical tanks are not mounted properly, it could cause the helicopter to shake,
the chemical to leak, or the chemical tank to
fall off the helicopter.
3 to 4.5 N·m (0.3 to 0.45 kg·m)
TIP
NOTICE
Bolts/Washers
Bracket Holes
Chemical Tank
1
2
3
4
TIP
If necessary, apply dedicated grease
(Yamaha Grease B) onto the O-rings on the
bottom of the chemical tanks.
(set in securely)
Guide
Mounting Stay
Bracket
Valve Seal
(set in securely)
5
6
7
6 To remove the sprayer, follow the mounting pro-
cedure in reverse order.
O-Rings
Joint
8
3-2
Page 56

Spraying Method
o
Relevant Switches
Helicopter Control Panel
Shutter Pump Cleaning Switch
Spinner Constant Rotation Switch
Used for cleaning the pump.
See “Cleaning the Sprayer” on
page 5-1.
4-1
Sprayer Selector Switch
To use the speed-dependent
function, switch to “”.
When not using the speeddependent function, switch t
“”.
Page 57

Flight Transmitter
Spraying Method
1
Spray Volume Adjuster
(for Liquid)
This adjusts the amount of liquid discharged.
See “Spray Specifications
Settings” on page 4-7.
Power Swi tch
This is the power switch
for the transmitter.
Spray Switch
This is an ON/OFF switch for the
spray pump.
See “Using the Sprayer” on page 4-3.
Spray Volume Switch
This switches between the left/
right nozzles and the center
nozzle.
See “Using the Sprayer” on
page 4-5.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4-2
Page 58

Spraying Method
Using the Sprayer
Spraying with Flight Transmitter
1 Switch the sprayer selector switch on the flight con-
trol panel to “”.
To use the speed-dependent function, switch to
“”.
2 Set the spray volume adjuster and the spray noz-
zle settings according to “Spray Specifications
Settings” on page 4-7.
Sprayer Selector Switch
3 Tur n ON ( “in” position) the spray switch (the ON/
OFF switch) on the flight transmitter to actuate
the spray pump. Press again (“out” position) to
stop.
4 Check the spraying condition. Check if the spray-
ing condition from each nozzle is good.
NOTICE
Do not keep the pump running for more than
10 seconds with nothing spraying out from
the nozzle, or on an empty tank. The pump
could burn out.
Spray Switch
ON (to operate) OFF (to stop)
Push
Illustration of Spraying Conditions
Release
4-3
Good Poor Poor
Page 59

How to Release Air Pockets
When the chemical tanks are plugged/unplugged,
or when the chemical is sprayed until the chemical
tanks are empty, air pockets will get entrained
inside the sprayer piping, causing the spraying condition to deteriorate.
With the chemical tanks set in place, if the air pockets are not completely released by discharging from
the nozzles, turn OFF the sprayer switch, and
release the air pockets as follows:
1 Facing the rear of the helicopter, turn the three-
way cock handle on the rear of the sprayer so
that it points to your left.
2 Turn ON the sprayer switch, and run the spray
pump for 5 to 7 seconds.
3 Point down the three-way cock to the spraying
position, and verify that the discharge condition
from the nozzle is good.
Spraying Method
Three-way Cock Handle
Air Releasing Position (pointing left)
DANGER
When releasing air pockets, do not perform
the task (or allow others to approach the helicopter) until the main rotor has stopped
rotating completely and the engine has
stopped.
TIP
If you are using the speed-dependent function and need to release air after receiving
the GPS signal, set the sprayer selector
switch to “”. After releasing air pockets,
return the sprayer selector switch to “”.
Spraying Position (pointing down)
4-4
Page 60

Spraying Method
Switching Between Nozzles
Set the spray volume switch on the flight transmitter
to “1” (“out” position) to discharge from the right and
left nozzles. Set it to “1/2” (“in” position) to dis-
charge from the center nozzle.
To switch between nozzles, turn OFF the spray
switch, and perform the task after the spray pump
has stopped.
Nozzle
“1”
ON
(to operate)
Release
Sprays from left
and right nozzles
Spray Switch
ON (to operate) OFF (to stop)
Push
Release
Push
“1/2”
Push
Sprays from center nozzle
“1”
OFF
Release
(to stop)
Release
“1/2”
Push
Stops spray pump
TIP
If you switch between nozzles with the spray
volume switch while the spray switch is in
the ON state, the spray pump will stop for
approximately one second, during which the
nozzle switching motor runs.
Spray Volume Switch
“1/2” (Center nozzle) “
Push
1” (Left and right nozzles)
Release
4-5
Page 61

Spraying Method
Using the Speed-Dependent Function
TIP
● The speed-dependent function can be used only when all of the following three conditions are
met:
• Low-volume liquid spraying at 7.5m spray width, 8L/ha
• Left and right nozzles are selected
• The GPS signal reception is good (i.e. the outer GPS indicator lights are ON)
The state of the flight mode selector switch on the helicopter and the GPS control switch on
the flight transmitter are irrelevant.
● When the center nozzle is used, the speed-dependent function does not work, and discharging is
done in proportion to a constant volume set by the spray volume adjuster on the flight transmitter.
1 Switch the sprayer selector switch on the flight
control panel to “ ”.
2 Set the spray volume adjuster and the spray noz-
zle settings according to “Spray Specifications
Settings” on page 4-7.
TIP
If the flight velocity exceeds 20km/h, only the
outer lights of the YACS warning lights illuminate. If this happens, drop the flight velocity
to 20km/h or less.
Sprayer Selector Switch
YACS
Warning Light
GPS
Indicator Light
Only the outer lights
of the YACS warning
lights illuminate
If the GPS signal reception is poor (the outer GPS indicator lights are ON), the speed-dependent function
does not work, and the chemical is discharged at a constant rate set by the spray volume adjuster on the flight
transmitter.
During a GPS-controlled flight, if the GPS signal reception worsens (GPS indicator lights cycles a pattern
“outer lights ON > inner lights ON > OFF”), the speed-dependent function does not work, and the chemical is
discharged at a constant rate set by the spray volume adjuster on the flight transmitter.
In this case, immediately turn OFF the GPS control switch according to the operation manual for the helicopter.
4-6
Page 62

Spraying Method
Spray Specifications Settings
Set the spray volume adjuster and spray nozzles according to the chemical to be used.
Spray Specifications
Low-Volume
Liquid Spraying
Spray
Volu me
(L/ha)
Right and Left
Nozzles
Center Nozzle 8 3.75 Yellow 1 (has groove) Level 24 Standard
8 7.5 Yellow 2 Level 24 Standard
Spray
Width
(m)
Nozzle
Color
Spray Volume Adjuster
Number of
Nozzles
Volu me
Position
Remarks
(b)
0
40
24
32
(a)
TIP
● The adjuster covers a range of volumes, allowing you adjust the spray volume according to the
chemical used.
● When you turn all the way towards the (b) direction, and start turning back towards the (a) direction, the first notch you reach is Level 1.
● Turning in the (a) direction increases the spray volume, and turning in the (b) direction decreases
the spray volume.
● Levels between 32 to 40 use maximum current, therefore, do not use continuously.
● After adjusting the volume, make sure to put the rubber cover back on.
● The spray specifications settings above are only to be used as a guideline. Before the actual
spraying task, make sure to check the spray volume for the chemical you are using.
4-7
Page 63

Cleaning and Inspections
WARNING
Control and handle the agricultural chemicals strictly in accordance with their manuals. Negligent
control and improper handling of agricultural chemicals could lead to chemical pollution or health
hazards.
NOTICE
● Clean the sprayer after every spraying work, as the spraying performance could deteriorate due
chemicals solidifying onto the sprayer.
● Use a drain pipe to collect the leftover chemical and cleaning solutions from cleaning into a container, and dispose it according to the operation manual for the chemical.
● During winter seasons, the pump or the filter cap may become damaged by frozen liquids. Therefore, for long-term storage during winter seasons, drain the leftover chemical and remove the filter cap.
1
2
Cleaning the Sprayer
Cleaning the Spray Pump
1 Turn the sprayer selector switch to “ ”.
2 Mount the chemical tank filled with tap water,
and turn the main switch of the helicopter to
“START”. Press the “ ” switch on the con-
trol panel to clean the inside of the sprayer piping.
3 To switch between the right/left nozzles and the
center nozzle, press the “ ” switch to tem-
porarily stop the pump, then use the “ ”
switch.
4 Drain the chemical inside the spray piping
through the drain pipe, by pointing the three-way
cock handle to the right, thereby actuating the
spray pump.
5 After draining out the chemical, point the three-
way cock handle to the spraying position (down).
Sprayer Selector Switch
3
4
5
6
6 Remove the filter and nozzles, and wash them
with tap water. (See pages 5-3 and 5-4.)
7 If you want to wash the sprayer thoroughly,
remove the sprayer and wash with tap water.
When doing this, use caution to keep the 2-pole
and 3-pole connecters from getting wet. (See
page 3-1.)
7
8
Spinner Constant Rotation Switch
Shutter Pump Cleaning Switch
5-1
Page 64

Cleaning and Inspections
Press once Press again
Switches to right
and left nozzles or
center nozzle
Operates pump Stops pump
Switches to right
and left nozzles or
center nozzle
TIP
● Operating the pump for more than one
minute could drain the battery.
● During cleaning, do not use the flight
transmitter to switch between right/left
nozzles and center nozzle.
Three-way Cock Handle
Drain Pipe
Chemical Draining Position (pointing right)
Spraying Position (pointing down)
5-2
Page 65

Inspecting and Cleaning Various Parts
Filter Inspection and Cleaning
1 Turn OFF the main switch of the helicopter.
2 Remove the left and right chemical tanks.
3 Remove the filter cap, and visually inspect if the
filter inside is clogged.
If clogged, wash it with tap water.
NOTICE
● If a tear exists in the filter, replace it, as it
could cause the spray pump or the nozzles
to become clogged.
● When putting on the filter cap, securely
fasten the O-ring to prevent air entrainment and liquid leakage.
Cleaning and Inspections
Filter
O-Ring
Filter Cap
5-3
Page 66

Cleaning and Inspections
Nozzle Inspection and Cleaning
1 Loosen the nozzle caps and end caps for the
left, right and center nozzles. Remove seat 2,
strainer 2, seat 1, and nozzle, and check them
for damage and wear.
If clogged, wash it with tap water.
2 Reattach the nozzles so that the nozzle spraying
hole and the boom are parallel.
Right and
Left Nozzles
Center Nozzle
Nozzle
Number
XR TEEJET
11002 VS
XR TEEJET
8002 VS
Nozzle
End Cap
Cap Color
Yellow Black
Red Blue
Color
TIP
● When reattaching the nozzles, do not confuse the left/right nozzles and the center
nozzle.
● Only the center nozzle has a groove along
its outer perimeter.
Nozzle
Cap
Right and Left Nozzles
Red Nozzle Cap
Nozzle
Parallel
End Cap
Seat 2
Strainer 2
Seat 1
Nozzle
Black End Cap
Center Nozzle
Parallel
Nozzle
Boom
Red Nozzle Cap
Blue End Cap
Boom
5-4
Only the center nozzle has a groove along its outer perimeter
Page 67

Chemical Tank Inspection and Cleaning
Cleaning and Inspections
1 Inspect the check valve on the chemical tank cap
to check if it is clogged.
2 Remove the strainer and visually check if it is
clogged.
If clogged, wash it with tap water.
Check Valve
Filter in the
Chemical Tank
Strainer
Chemical Tank
3 Remove the filter by turning it counterclockwise,
and visually check if it is clogged.
If clogged, wash it with tap water.
NOTICE
● If a tear exists in the strainer or filter,
replace it, as it could cause the spray
pump or the nozzles to become clogged.
● When using a chemical that precipitates
quickly, frequently remove and clean the
strainer and filter.
● When removing the filter, do not pull it by
the mesh part, as this could damage the
filter.
Chemical Tank Joint Inspection and Cleaning
Visually check if the valve seal part of the chemical
tank joint is clogged.
If clogged, wash it with tap water.
Chemical Tank Joint
5-5
Page 68

Troubleshooting
The problems listed here can be handled primarily
by the user.
Problems or causes that are not listed here are
handled by your dealer. If such problems occur,
cancel the flight and contact your dealer to have the
helicopter inspected and repaired.
The spray pump does not operate
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Poor connection with the power connector of
1
the spray pump.
2 The nozzles are being switched.
3 The onboard battery is faulty.
4 Deterioration in the spray pump performance.
5 A break in the wiring.
6 A blown fuse.
Securely connect the power connector of the
spray pump.
If the nozzles are switched while the spray
pump is running, the nozzle switching motor
runs for approximately one second, during
which the spray pump automatically stops. The
spray pump will resume automatically.
Recharge the battery with a dedicated
recharger, or replace it.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
WARNING
● Make sure to follow the instructions given
in the “User Action” column, and do not
take any actions that are not documented.
● If you have any questions, be sure to contact your dealer. If an inspection, adjustment, or part replacement is performed by
a person who does not possess the knowhow and proficiency to service the helicopter, it could lead to a serious accident.
See page 3-1.
See page 4-5.
See the operation manual for
the helicopter
The spray pump operates, but nothing is discharged
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Air pockets have not been sufficiently released.
2 Clogged chemical tank joint. Clean the chemical tank joint. See page 5-5.
3 Clogged filter. Clean the filter. See page 5-3.
4 Clogged nozzle. Clean the nozzle. See page 5-4.
5 Wrong nozzle attached. Attach the correct parts. See page 5-4.
6 Clogged check valve on the chemical tank cap. Clean the check valve. See page 5-5.
7 Deterioration in the spray pump performance.
Release air pockets by opening the three-way
cock.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
See page 4-4.
6-1
Page 69

Troubleshooting
The discharge volume is low / The spraying angle is narrow / The
chemical is not getting atomized / The chemical drips in large droplets
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Choose a different agricultural chemical.
1 Incompatible agricultural chemical.
2 Poorly adjusted spray volume.
3 Clogged nozzle. Clean the nozzle. See page 5-4.
4 Entrained air pockets in the spray pump.
5 Clogged spray pump
6 Poorly sealed seat 2. Clean seat 2. See page 5-4.
If it is a mixture of two agricultural chemicals,
revise the chemicals that are mixed.
Readjust the spray volume on the flight transmitter.
Release air pockets by opening the three-way
cock.
Clean the spray pump.
If the problem persists, request a repair by your
dealer.
See page 4-7.
See page 4-4.
See page 5-1.
The chemical is leaking.
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1 Poorly sealed seat 2. Clean seat 2. See page 5-4.
2 Loose clamp on a piping joint. Tighten the clamp more tightly.
3 Hardened or deformed hose.
4 Poor sealing in the spray pump.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
1
2
3
4
Nozzles do not switch.
Main Cause User Action Remarks
Bad connection with the power connector of the
1
nozzle switching motor.
2 Malfunction in the nozzle switching motor.
Securely connect the power connector of the
nozzle switching motor.
Quickly cancel the flight, and request a repair
by your dealer.
The speed-dependent function is non-functional.
Main Cause User Action Remarks
1
The sprayer selector switch is not set to “”.Select “”.
2 The GPS radio signal reception is poor.
3 The nozzle switch is set to center nozzle.
Wait until the reception recovers, or spray without the speed-dependent function.
The speed-dependent function cannot be used
with center nozzle. Switch to right and left nozzles.
See page 3-1.
See page 4-6.
See the operation manual of
the helicopter.
See page 4-6.
See page 4-6.
5
6
7
8
6-2
Page 70

Specifications
Specifications Data
Item Data
Device Name Liquid sprayer
Spraying Method Category Low-volume liquid spraying
Spray Volume 8L/ha
Spray
Specifications
Discharge
Performance
Nozzle
Pump
Maximum Chemical Tank
Load Capacity
Device Weight 7.4 kg
Flight Velocity 13 to 20 km/h 15 km/h 10 to 20 km/h
Flight Altitude 3 to 4 m
Flight Width 7.5 m 3.75 m 7.5 m
SpeedDependent
Discharge
Method
Discharge
Method
Discharge
Pressure
Maximum
Discharge
Volu me
Nozzle
Method
Standard
Number of
Nozzles
Pumping
Method
Driving
Method
Power Rating DC12V (supplied by helicopter)
(at 13 to 20 km/h)
Ye s N o N o
Nozzle method
(left/right)
0.17 to 0.44 Mpa
2.0 L/min 0.75 L/min 2.0 L/min
XR11002 XR8002 XR11002
212
Double-acting piston method
Nozzle method
(center)
0.25 Mpa
(at 15 km/h)
Flat type
Motor-driven
16 L (8 L per tank)
Nozzle method
(left/right)
0.44 Mpa
(at 20 km/h)
7-1
Page 71

Product Inspection
About Inspections
The prescribed types of inspections are described below.
• The pre-flight inspection is to be performed by the operator.
• For periodic inspections and replacement of parts, contact your dealer or an authorized service facility for
Yamaha unmanned helicopters for industrial applications.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before a flight, make sure to inspect the following:
Failure to perform pre-flight and regular
inspection could lead to problems. Therefore, make sure to perform these inspections.
Part Names Description
Battery (9.6V for transmitter) Check fully charged
Filter Check for debris and tear
Chemical Tank Check for leaking valve
Joint Check for leaking valve
Cock Release air pockets
Complete Nozzles Check discharge condition
NOTICE
1
2
3
4
Periodic Inspection
Section Description
Joints Disassemble, inspect, adjust, clean, replace
Chemical Tank Inspect and replace
Nozzle Clean
Pump Clean and replace
Hoses Inspect and replace
Filter Clean and replace
Other Inspect, correct, tighten
* The inspection items and descriptions may change for various reasons.
5
6
7
8
8-1
Page 72

Product Inspection
Replacement Parts
The following parts are consumables. If a deterioration in performance is seen due to wear, damage, deterioration of a part, replace these parts.
The replacement parts may change due to various reasons.
Part Names Description of Problems
Seat 1, Seat 2 (Nozzle parts) Leakage, dripping
O-ring (joint) Leakage
Seal valve (joint) Leakage
Valves Leakage
Pump unit assembly Leakage, poor discharge
* The frequency of replacement varies with chemicals used.
8-2
Page 73

Customer Support
To pose any questions regarding the product you are using, to
make a comment regarding service, or to file a complaint, please
contact your dealer.
RMAX
OPERATION MANUAL
©2011 by Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
1st edition, Dec. 2011
All rights reserved.
Any reprinting or unauthorized use
without the written permission of
Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.
is expressly prohibited.
Printed in Japan.
Page 74

PRINTED ON RECYCLED PAPER
11.12 – 0.3
× 1 CR
 Loading...
Loading...