Page 1

CHLOROPHYLL METER
SPAD-502
A lightweight handheld meter for
measuring the chlorophyll content of
leaves without causing damage to plants.
The SPAD-502 is a compact meter
designed to help users improve crop quality and
increase crop yield by providing an indication of the
amount of chlorophyll present in plant leaves. The
chlorophyll content of plant leaves is related to the
Features
Compact and lightweight for portability
The SPAD-502 is small enough to fit in a pocket and is
extremely lightweight (only 225g) so it can be easily taken
anywhere.
Quick, easy measurements
Measurements are taken by simply inserting a leaf and
closing the measuring head. It is not necessary to cut the
leaf, so the same leaf can be measured throughout the
growing process.
Water-resistant
The SPAD-502 is water-resistant, so it can be used
outside even in the rain.
*It is not immersible, and should not be cleaned with water.
Low power consumption
The SPAD-502 uses LED light sources, resulting in
extremely low power consumption. One set of two AA-size
alkaline-manganese batteries can provide approximately
20,000 measurements.
condition of the plant, and thus can be used to
determine when additional fertilizer is necessary. By
optimizing nutrient conditions, healthier plants can be
grown, resulting in a larger crop yield of higher quality.
Small measuring area
The measuring area is only 2 × 3mm, allowing
measurements of even small leaves. A sliding depth stop
is included for accurate positioning of sample leaves.
High accuracy
High measuring accuracy (± 1.0 SPAD unit for rice-plant
leaves) allows close examination of growing conditions.
Data memory
The SPAD-502 has memory space for 30 measurements.
Data in memory can be recalled or deleted at a later time,
and the average value of all data in memory can be
automatically calculated.
Reading checker
A reading checker enables users to check that the SPAD502 is functioning correctly and providing accurate
readings.
Page 2
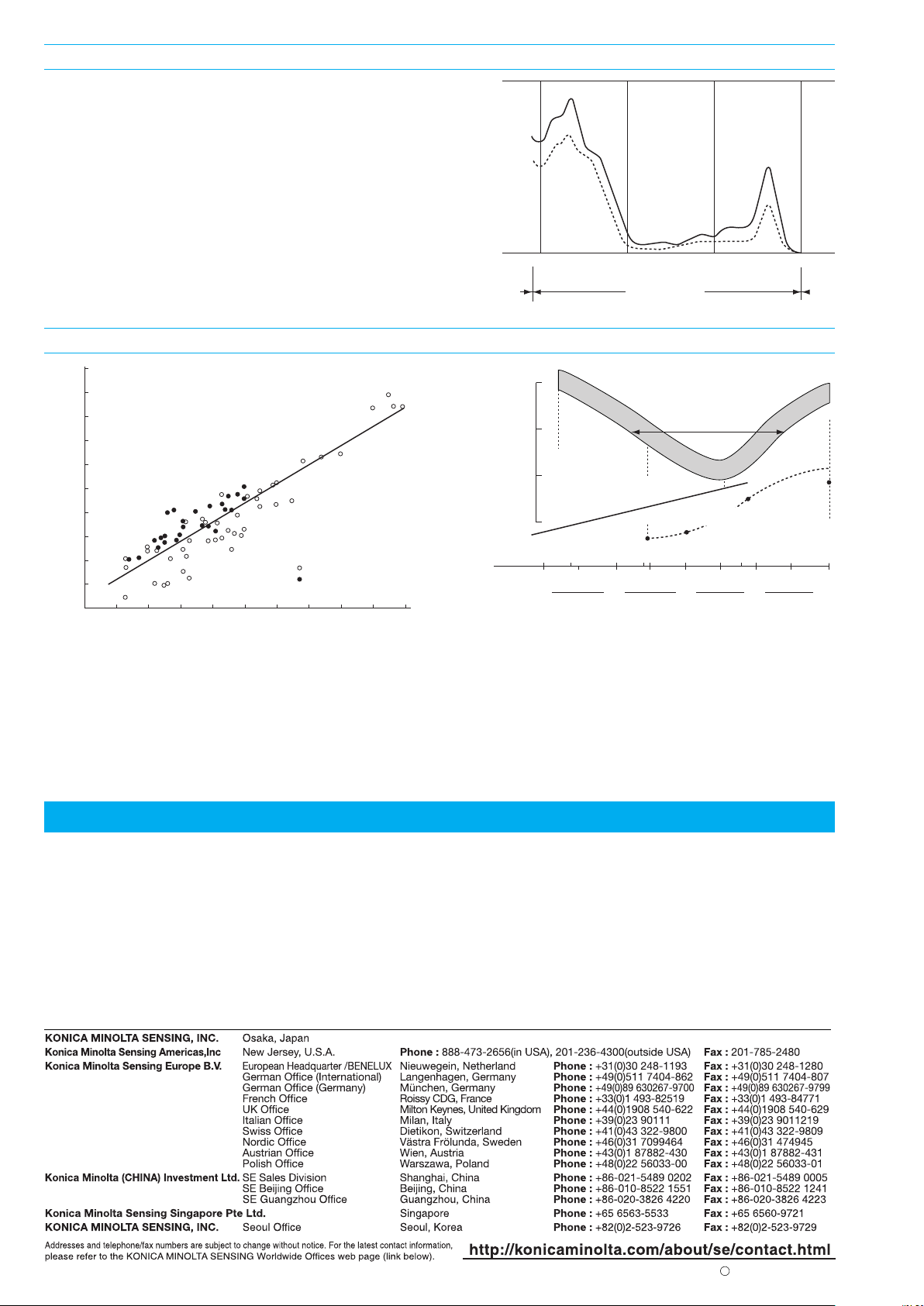
Theory
The SPAD-502 determines the relative amount of chlorophyll
present by measuring the absorbance of the leaf in two
wavelength regions.
The graph at right shows the spectral absorbance of chlorophyll
extracted from two leaf samples using 80% acetone.
From the diagram, it can be seen that chlorophyll has absorbance
peaks in the blue (400-500nm) and red (600-700nm) regions, with
no transmittance in the near-infrared region.
To take advantage of this characteristic of chlorophyll, the
SPAD-502 measures the absorbances of the leaf in the red and
near-infrared regions. Using these two transmittances, the meter
calculates a numerical SPAD value which is proportional to the
amount of chlorophyll present in the leaf.
Applications
3.5
y =0.079 x - 0.154
***
r =0.908
3.3
3.1
2.9
2.7
2.5
2.3
2.1
1.9
Leaf-blade nitrogen concentration
1.7
Checking the nutritional condition of plants
The chlorophyll present in the plant leaves is closely related to
the nutritional condition of the plant. As can be seen from the
graph below, the chlorophyll content (represented by the
measured SPAD value) will increase in proportion to the amount
of nitrogen (an important plant nutrient) present in the leaf. For a
particular plant species, a higher SPAD value indicates a
healthier plant.
n =68
1984
1985
24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42
Measured SPAD value
A
B
Trancemittance
Ultraviolet
Measured SPAD value
Days before fully
formed ears appear
Date(month.day)
400 500
Wavelength Infrared
40
35
Ear differentlation
period
30
25
9.1 9.5 10.3 10.8 12.5 13.0
7.1 7.10 7.20 7.30
Sasanishiki rice plant development
Young ear
formation period
35
Young ear
growth line
(1mm)
30 25 20 15 10 5
600 700(nm)
Ear fertility
(8cm)
Bursting
period
(3mm)
(16 -18cm)
Fully formed
ears appear
Determining when additional fertilizer is necessary
A decrease in the SPAD value indicates a decrease in the
chlorophyll content and nitrogen concentration. This decrease
may be due to a lack of nitrogen available in the soil. This
problem can be solved by adding fertilizer to the soil.
For example, it was determined from past experience that for
Sasanishiki rice plants a SPAD value of 35 or above was
desirable to produce a target yield of 600kg/10a. During the
differentiation and formation of ears, a period of rapid plant
development, the SPAD value fell to between 29 and 32,
indicating that additional fertilizer was necessary.
0
8.14
SPECIFICATIONS
Type: Handheld meter for measuring chlorophyll using optical density
difference at two wavelengths
Measurement sample: Crop leaves
Measurement system: Optical density difference at two wavelengths
Measurement area: 2 × 3mm
Light source: 2 LEDs (light-emitting diodes)
Receptor: 1 SPD (silicon photodiode)
Display: Measurement data: 3-digit LCD with decimal point
Data number: 2-digit LCD
Data memory: Space for 30 data sets
Controls: Power switch, AVERAGE key, ALL DATA DELETE key,
ONE DATA DELETE key, and DATA RECALL key
Power source: 2 AA-size alkaline-manganese (1.5V) batteries
Battery line: More than 20,000 measurements
Minimum interval between measurements: Less than 2 seconds
Accuracy: Within ± 1.0 SPAD unit (at room conditions, SPAD value
between 0 and 50)
Repeatability: Within ± 0.3 SPAD units (SPAD value between 0 and 50)
Reproducibility: Within ± 0.5 SPAD units (SPAD value between
0 and 50)
Temperature drift: Less than ± 0.4 SPAD units/°C
Temperature range: Operation: 0 to 50°C; Storage: - 20 to +55°C
Dimensions: 164 ×78 × 49mm (6-7/16 × 3-1/16 × 1-15/16 in.)
Weight: 225g (7-15/16 oz.) (not including batteries)
Other: Warning buzzer; User calibration function
Specification subject to change without notice
2003 KONICA MINOLTA SENSING, INC.
AHIDPK
13
Printed in Japan9242-4817-41
 Loading...
Loading...