Kollmorgen AKM13C, AKM13D, AKM21C, AKM21E, AKM22E Technical Description, Installation, Setup
...Page 1

www.DanaherMotion.com
Synchronous servomotors
AKM
Technical description, Installation, Setup
Edition 05/2006
File akm_e.xxx
Page 2

Choose your Motor:
Typ
AKM1
AKM2
AKM3
AKM4
AKM5
AKM6
AKM7
Flange
Standstill torque
40 0,18..0,41
58 0,48..1,42
70 1,15..2,88
84 1,95..6
108 4,7..14,4
138 11,9..25
188 29,4..53
0105020 70130540
0,5
Already published editions
Edition Comments
03 / 2004 First edition
12 / 2004 Performance curves corrected, polenumbers, gearhead mounts, several corrections
09 / 2005 centering AKM7, chapter 1, several corrections, BISS interface, protection class
05 / 2006 Performance curves deleted, order numbers cables, new label
Page
Þ 24
Þ 26
Þ 28
Þ 30
Þ 32
Þ 34
Þ 36
Nm
Technical changes to improve the performance of the equipment may be made without prior notice!
Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany
All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced in any form (by printing, photocopying, microfilm or any
other method) or stored, processed, copied or distributed by electronic means without the written permission of
Danaher Motion.
Page 3

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Contents
Page
NewTableof Contents
1 General
1.1 About this manual ....................................................................... 5
1.2 Use as directed ......................................................................... 5
1.3 Symbols used in this manual:............................................................... 5
1.4 Safety Notes ........................................................................... 6
1.5 Important Notes ......................................................................... 7
1.6 Design of the motors ..................................................................... 8
1.7 General technical data .................................................................... 8
1.8 Standard features........................................................................ 9
1.8.1 Style............................................................................. 9
1.8.2 Shaft end, A-side ................................................................... 9
1.8.3 Flange ........................................................................... 9
1.8.4 Protection class .................................................................... 9
1.8.5 Protective device ................................................................... 9
1.8.6 Insulation material class.............................................................. 9
1.8.7 Vibration class .................................................................... 10
1.8.8 Connection method ................................................................ 10
1.8.9 Feedback unit .................................................................... 10
1.8.10 Holding brake..................................................................... 10
1.8.11 Pole numbers..................................................................... 10
1.9 Options............................................................................... 11
1.10 Selection criteria........................................................................ 11
1.10.1 Model number description ........................................................... 12
1.10.2 Nameplate ....................................................................... 12
2 Installation / Setup
2.1 Important notes ........................................................................ 13
2.2 Assembly / Wiring ...................................................................... 14
2.2.1 Connection of the motors with preassembled cables....................................... 16
2.2.1.1 Wiring diagram for motors with resolver .............................................17
2.2.1.2 Wiring diagram for motors with encoder ............................................. 18
2.2.1.3 Wiring diagram for motors with SFD ................................................ 19
2.2.1.4 Wiring diagram for motors with ComCoder ........................................... 20
2.2.1.5 Wiring diagram for motors with BISS................................................ 21
2.3 Setup ................................................................................ 22
3 Technical Data
3.1 Definitions ............................................................................ 23
3.2 AKM1 ................................................................................ 24
3.3 AKM2 ................................................................................ 26
3.4 AKM3 ................................................................................ 28
3.5 AKM4 ................................................................................ 30
3.6 AKM5 ................................................................................ 32
3.7 AKM6 ................................................................................ 34
3.8 AKM7 ................................................................................ 36
4 Appendix
4.1 Assignment of RediMount gearhead mounts .................................................. 38
4.2 Delivery package, transport, storage, maintenance, disposal ..................................... 39
4.3 Removing faults ........................................................................ 40
4.4 Index ................................................................................ 41
Servomotors AKM 3
Page 4

Manufacturer declaration
According to the EG-Machine-guideline 98/37/EC, appendix II B
We, the company
Danaher Motion GmbH
Wacholderstrasse 40-42
40489 Düsseldorf
declare, that the product
Motor series AKM
(Types AKM1, AKM2, AKM3, AKM4, AKM5, AKM6, AKM7)
05/2006 Kollmorgen
is intended exclusively, in its standard version, for installation in another machine and that its setup is forbid
den until it has been established that the machine into which this product is to be installed conforms to the pro
visions of the EC Directive in its version 98/37/ECW.
We confirm that the above-mentioned product conforms to the following standards:
73/23/EEC Low voltage directive
VDE 0530 / DIN 57530 Provisions for rotating machinery
DIN EN 60034-7 Design
DIN 748 Cylindrical shaft ends
DIN 6885 Keyway and Key
DIN 42955 True running, coaxiality and concentricity
DIN EN 60034-14 Vibration class
Issued by: Management
Michel van Roozendaal
-
-
This Declaration does not contain any assurance of properties. The notes on safety and protection in the ope
rating instructions must always be observed.
4 Servomotors AKM
-
Page 5
Kollmorgen 05/2006 General
1 General
1.1 About this manual
This manual describes the AKM series of synchronous servomotors (standard
version). Among other things, you find information about:
General description, standard version of the motors Chapter 1
l
Installation, Setup, Wiring Chapter 2
l
Technical data, dimensions Chapter 3
l
Notes on Transport, Storage, Maintenance, Disposal Chapter 4
l
This Manual is intended for the use of qualified staff with professional knowledge of electri
cal and mechanical engineering.
The motors are operated in drive systems together with servo amplifiers SERVOSTAR. Please
observe the entire system documentation, consisting of:
— Installation and setup instructions for the servo amplifier
— Installation and setup instructions for any expansion card which is connected
— Operating manual for the Operator Software of the servo amplifier
— Technical description of the AKM series of motors
1.2 Use as directed
The AKM series of synchronous servomotors is designed especially for drives for industrial robots,
machine tools, textile and packing machinery and similar with high requirements for dynamics.
The user is only permitted to operate the motors under the ambient conditions which are defined in
this documentation.
The AKM series of motors is exclusively intended to be driven by servo amplifiers from the
SERVOSTAR series under speed and / or torque control.
The motors are installed as components in electrical apparatus or machines and can only be commissioned and put into operation as integral components of such apparatus or machines.
The motors must never be connected directly to the mains supply.
The thermal contact which is integrated in the motor windings must be observed and evaluated.
-
The conformity of the servo-system to the standards mentioned in the manufacturers
declaration on page 4 is only guaranteed when the components (servo amplifier, motor, cables etc.)
that are used have been supplied by us.
1.3 Symbols used in this manual:
Danger to personnel from electricity
and its effects
see page/chapter (cross reference) l special emphasis
Þ
General warning
general instruction
mechanical hazard
Servomotors AKM 5
Page 6

General 05/2006 Kollmorgen
1.4 Safety Notes
Only properly qualified personnel are permitted to perform such tasks as transport,
l
assembly, setup and maintenance. Properly qualified personnel are persons who are
familiar with the transport, assembly, installation, setup and operation of motors, and
who have the appropriate qualifications for their jobs. The qualified personnel must
know and observe the following standards and regulations:
IEC 364 resp. CENELEC HD 384 or DIN VDE 0100
IEC-report 664 or DIN VDE 0110
national regulations for safety / accident prevention or BGV A3
Read the available documentation before assembly and setup. Incorrect handling of
l
the motors can result in injury and damage to persons and machinery. Keep strictly
to the technical data and the information on the connection requirements (nameplate
and documentation).
The manufacturer of the machine must generate a hazard analysis for the machine,
l
and take appropriate measures to ensure that unforeseen movements cannot cause
injury or damage to any person or property.
It is vital that you ensure that the motor housing is safely earthed to the PE(protective
l
earth) busbar in the switch cabinet. Electrical safety is impossible without a low-re
sistance earth connection.
Do not unplug any connectors during operation. This creates the danger of death, se
l
vere injury, or extensive material damage.
-
-
Power connections may be live even when the motor is not rotating. Never discon-
l
nect the power connections of the motor while the equipment is energised. This can
cause flashovers with resulting injuries to persons and damage to the contacts.
After disconnecting the servo amplifier from the supply voltage, wait at least five mi-
l
nutes before touching any components which are normally live (e.g. contacts, screw
connections) or opening any connections.
The capacitors in the servo amplifier can still carry a dangerous voltage up to five minutes after switching off the supply voltages. To be quite safe, measure the DC-link
voltage and wait until the voltage has fallen below 40V.
l
The surfaces of the motors can be very hot in operation, according to their protection
category. The surface temperature can exceed 100°C. Measure the temperature, and
wait until the motor has cooled down below 40°C before touching it.
l
Remove any fitted key (if present) from the shaft before letting the motor run indepen
dently, to avoid the dangerous results of the key being thrown out by centrifugal for
ces.
-
-
6 Servomotors AKM
Page 7
Kollmorgen 05/2006 General
1.5 Important Notes
Servomotors are precision equipment. The flange and shaft are especially vulnerable
l
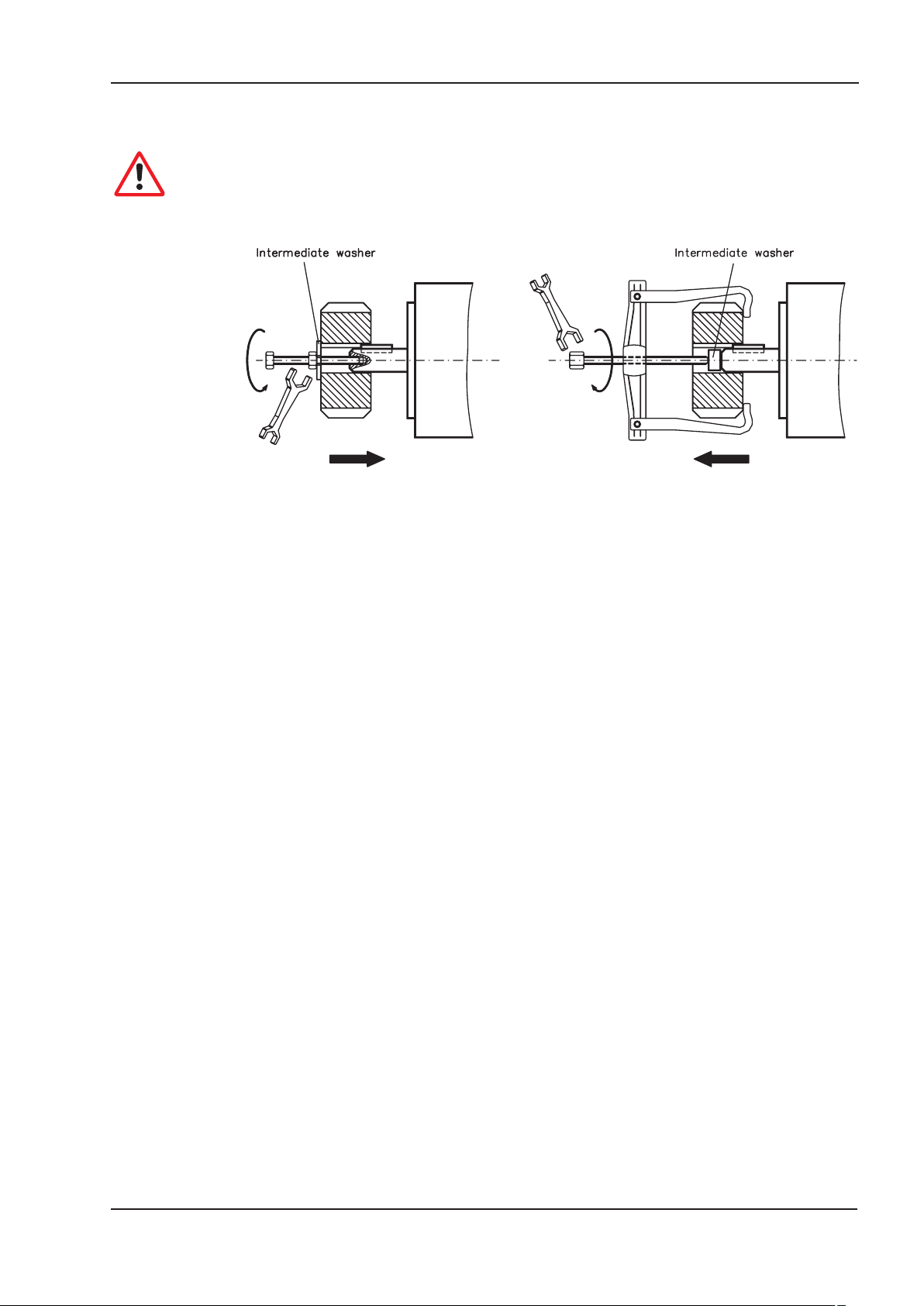
during storage and assembly — so avoid brute force. Precision requires delicacy. It is
important to use the locking thread which is provided to tighten up couplings, gear
wheels or pulley wheels and warm up the drive components, where possible. Blows
or the use of force will lead to damage to the bearings and the shaft.
Wherever possible, use only backlash-free, frictionally-locking collets or couplings.
l
Ensure correct alignment of the couplings. A displacement will cause unacceptable
vibration and the destruction of the bearings and the coupling.
For toothed belts, it is vital to observe the permissible radial forces. An excessive ra
l
dial load on the shaft will significantly shorten the life of the motor.
Avoid axial loads on the motor shaft, as far as possible. Axial loading significantly
l
shortens the life of the motor.
In all cases, do not create a mechanically constrained motor shaft mounting by using
l
a rigid coupling with additional external bearings (e.g. in a gearbox).
l
For mounting style V3 (shaft end upwards), make sure that no liquid can enter the upper bearing.
l
Take note of the no. of motor poles and the no. of resolver poles, and ensure that the
correct setting is made in the servo amplifier which is used. An incorrect setting can
lead to the destruction of the motor, especially with small motors.
-
Servomotors AKM 7
Page 8

General 05/2006 Kollmorgen
1.6 Design of the motors
Synchronous servomotors in the AKM series are brushless DC motors for demanding servo appli
cations. When combined with our digital servo amplifiers they are especially suited for positioning
tasks in industrial robots, machine tools, transfer lines etc. With high requirements for dynamics and
stability.
The servomotors have permanent magnets in the rotor. The rare earth neodymium -iron-boron
magnetic material is an important factor in making it possible to drive these motors in a highly dyna
mic fashion. A three-phase winding which is driven by the servo amplifier is integrated into the sta
tor. The motor does not have any brushes since commutation is performed electronically by the
servo amplifier
The temperature of the winding is monitored by temperature sensors in the stator windings and is
signalled via an electrically isolated thermistor (PTC, £550W / ³1330W).
A resolver is built into the motors as standard feedback element. The servo amplifiers in the
SERVOSTAR series evaluate the resolver position and supply sinusoidal currents to the motors.
The alternatively offered feedback systems partly cause a change of the motor length and cannot
be retrofitted.
The motors can be delivered with or without a built-in holding brake. Retrofitting of the brake is not
possible.
The motors are enamelled in matt black (RAL 9005). This finish is not resistant against solvents
(e.g. trichlorethylene, nitro-thinners, or similar).
1.7 General technical data
Climate category 3K3 to EN 50178
-
-
-
Ambient temperature 5...+40°C for site altitude up to 1000m amsl (at rated values) It is vital to consult our applications department for
ambient temperatures above 40°C and encapsulated
mounting of the motors.
Permissible humidity 95% rel. humidity, no condensation
(at rated values)
Power derating 1%/Kinrange 40°C...50°C up to 1000m amsl (currents and torques) for site altitude above 1000m amsl and 40°C
6% up to 2000m amsl
17% up to 3000m amsl
30% up to 4000m amsl
55% up to 5000m amsl
No derating for site altitudes above 1000m amsl
with temperature reduction of 10K / 1000m
Ball-bearing life ³ 20.000 operating hours
Technical data Þ p.23
Storage data Þ p.39
8 Servomotors AKM
Page 9

Kollmorgen 05/2006 General
1.8 Standard features
1.8.1 Style
The basic style for the AKM synchronous motors is style IM B5 according to DIN EN 60034-7. The
permitted mounting positions may be read from the technical data of the motor series.
1.8.2 Shaft end, A-side
Power transmission is made through the cylindrical shaft end A, fit k6 (AKM1: h7) to DIN 748, with a
locking thread but without a fitted-keyway.
If the motors drive via pinions or toothed belts, then high radial forces will occur. The permissible
values at the end of the shaft may be read from the diagrams in chapter 3. The maximum values at
rated speed you will find at the technical data. Power take-off from the middle of the free end of the
shaft allows a 10% increase in F
The curves are based on a bearing life of 20.000 operating hours.
The axial force F
Double-coned collets have proved to be ideal zero-backlash coupling devices, combined, if required, with metal bellows couplings.
.
R
must not exceed FR/3.
A
1.8.3 Flange
Flange dimensions to IEC standard, fit j6 (AKM1: h7), accuracy according to DIN 42955.
Tolerance class: N
1.8.4 Protection class
Standard version IP65
Standard shaft bushing IP54
Shaft bushing with shaft-sealing ring IP67
1.8.5 Protective device
The standard version of each motor is fitted with an electrically isolated PTC. The switching point is
at 155°C ± 5%. The thermostat does not provide any protection against short, heavy overloading.
Provided that our preassembled resolver cable is used, the thermostat contact is integrated into the
monitoring system of the digital servo amplifier SERVOSTAR.
1.8.6 Insulation material class
The motors come up to insulation material class F according to DIN 57530. - E.4.929.4/09
Servomotors AKM 9
Page 10
General 05/2006 Kollmorgen
1.8.7 Vibration class
The motors are made to vibration class N according to DIN EN 60034-14.
1.8.8 Connection method
The motors are equipped with angular connectors (AKM1: straight connectors at cable ends) for
power supply and feedback signals .
The mating connectors are not part of the delivery package. We can supply preassembled resolver
and power cables. On page 16 you will find notes on the cable materials.
1.8.9 Feedback unit
Standard
Option
Option
Option
Option
Option
Resolver Two-pole hollow-shaft EnDat Encoder, Single-Turn AKM2-AKM4: ECN 1113, AKM5-AKM7: ECN1313 EnDat Encoder, Multi-Turn AKM2-AKM4: EQN 1125, AKM5-AKM7: EQN1325
ComCoder
SFD fully digital resolver interface
BiSS Encoder, Single-/Multi-Turn AKM2-AKM4: AD36, AKM5-AKM7: AD58
The motor length depends on the mounted feedback unit. Retrofitting is not possible.
1.8.10 Holding brake
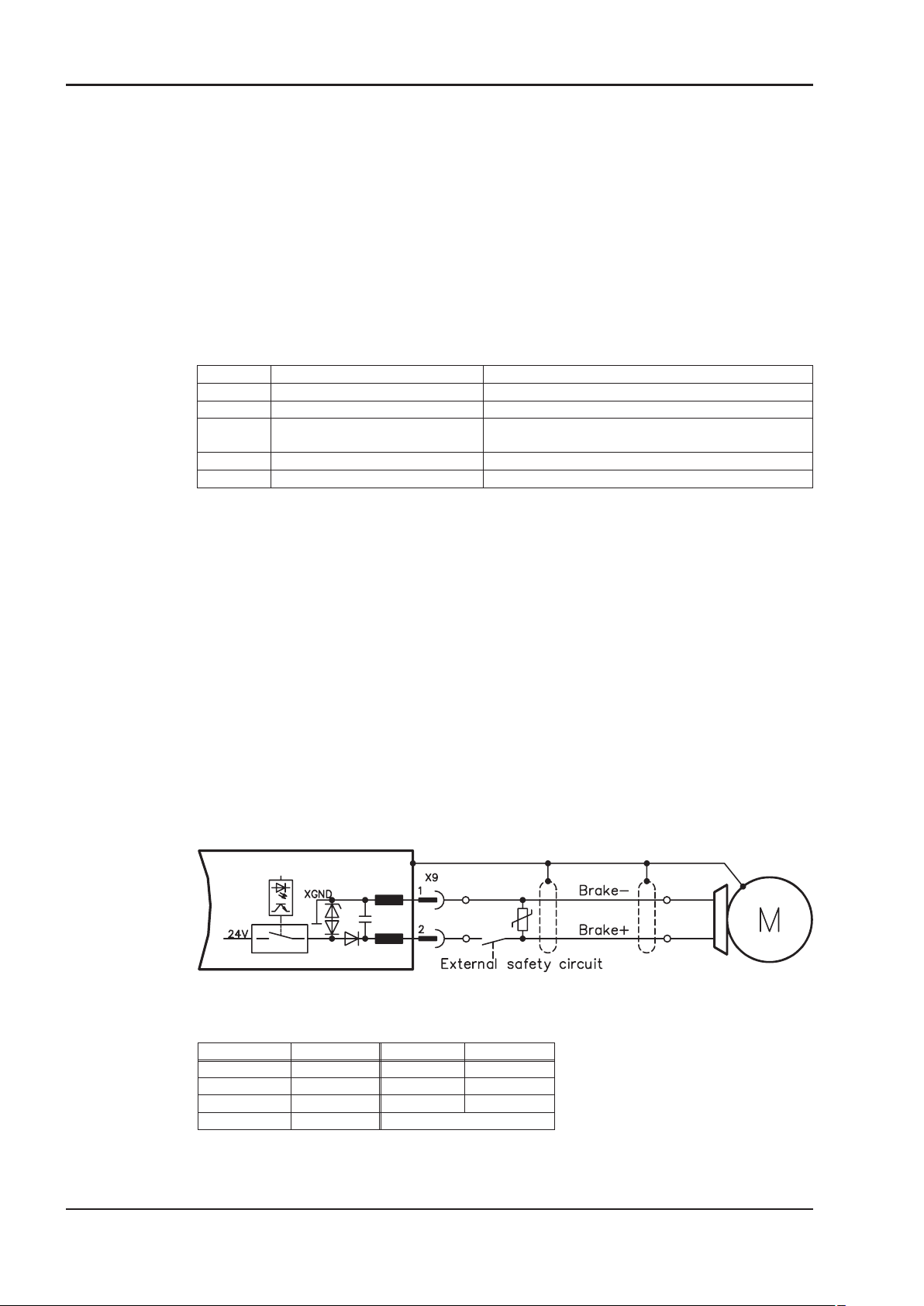
The AKM2-AKM7 motors are optionally available with a holding brake.
A spring applied brake (24V DC) is integrated into the motors. When this brake is de-energized it
blocks the rotor. The holding brakes are designed as standstill brakes and are not suited for
repeated operational braking. If the brake is released then the rotor can be moved without a remanent torque. The motor length increases when a holding brake is mounted.
The holding brake can be controlled directly by SERVOSTAR-servo amplifier (no personal safety !),
the winding is suppressed in the servo amplifier — additional circuitry is not required.
If the holding brake is not controlled directly by the servo amplifier, an additional wiring (e.g. varistor) is required. Consult our applications department beforehand.
A personal safe operation of the holding brake requires an additional contact (normally opened) in
the braking circuit and an anti-surge-device (e.g. Varistor) for the brake.
Wiring example for SERVOSTAR 600
Incremental encoder with commutation,
resolution 500-10000 lines
SERVOSTAR 600
1.8.11 Pole numbers
Motor Poles Motor Poles
AKM1 6 AKM5 10
AKM2 6 AKM6 10
AKM3 8 AKM7 10
AKM4 10
- A.4.031.1/35
10 Servomotors AKM
Page 11

Kollmorgen 05/2006 General
1.9 Options
— Holding brake
Built-in holding brake.
Motor length increases by the holding brake.
— Radial shaft-sealing rings
A radial shaft-sealing ring can be supplied at extra charge to seal against oil mist
and oil spray. This increases the protection rating of the shaft bushing to IP67.
— Keyway
The motors are available with keyway and key inserted according to DIN6885
The shaft is balanced with a short (half) key.
— EnDat, BISS, ComCoder, SFD
Another feedback system is mounted instead of the resolver. The motor length
can increase by the alternative feedback.
With exception of the radial shaft seal the options cannot be retrofitted. Options such as radial shaft
seal, holding brake, EnDat or Comcoder can lead to a reduction of rated data.
1.10 Selection criteria
The three-phase servomotors are designed to operate with SERVOSTAR servo amplifiers. Toget
her, both units form a closed speed or torque control loop.
The most important selection criteria are:
— Standstill torque M
— Rated speed n
— Moment of inertia of motor and load J [kgcm²]
— Effective torque (calculated) M
When calculating the motors and servo amplifiers which are required, take account of the static load
and the dynamic load (acceleration/braking). Collected formulae and examples of the calculations
are available from our applications department.
0
n
rms
[Nm]
[min-1]
[Nm]
-
Servomotors AKM 11
Page 12
General 05/2006 Kollmorgen
1.10.1 Model number description
AKM62P- ANCNDA-00
Flange size
1 40mm
2 58mm
3 70mm
4 84mm
5 108mm
6 138mm
7 188mm
Rotor length
1
2
3
4
5
Winding type
A..Z
S special
Flange
A IEC
B NEMA
C alternative IEC standard
D other standard
G alternative IEC standard
H alternative IEC standard
S special
Shaft
C keyway
K open keyway
N smooth shaft
S special
Customization
00 standard
01 with shaft seal
xx special
Feedback
1 Comcoder with 1024 PPR
2 Comcoder with 2048 PPR
AA Acuro(Biss) Single Turn
AB Acuro(Biss) Multi Turn
C Smart Feedback Device
DA ECN1x13
DB EQN1x25
R Resolver
S special
Brake
2 24V holding brake
N w/o brake
S special
Connectors
B angular connectors
rotatable (AKM2)
C 0.5m shielded cable with
IP65 connector (AKM1/2),
angular connectors
rotatable (AKM3..7)
D single aangular connector,
rotatable (AKM3/4
with SFD, w/o brake)
M 0.5m shielded cable with
IP20 connectors (In < 6A)
P 0.5m shielded cable with
single IP20 connector
(In < 6A and SFD)
S special
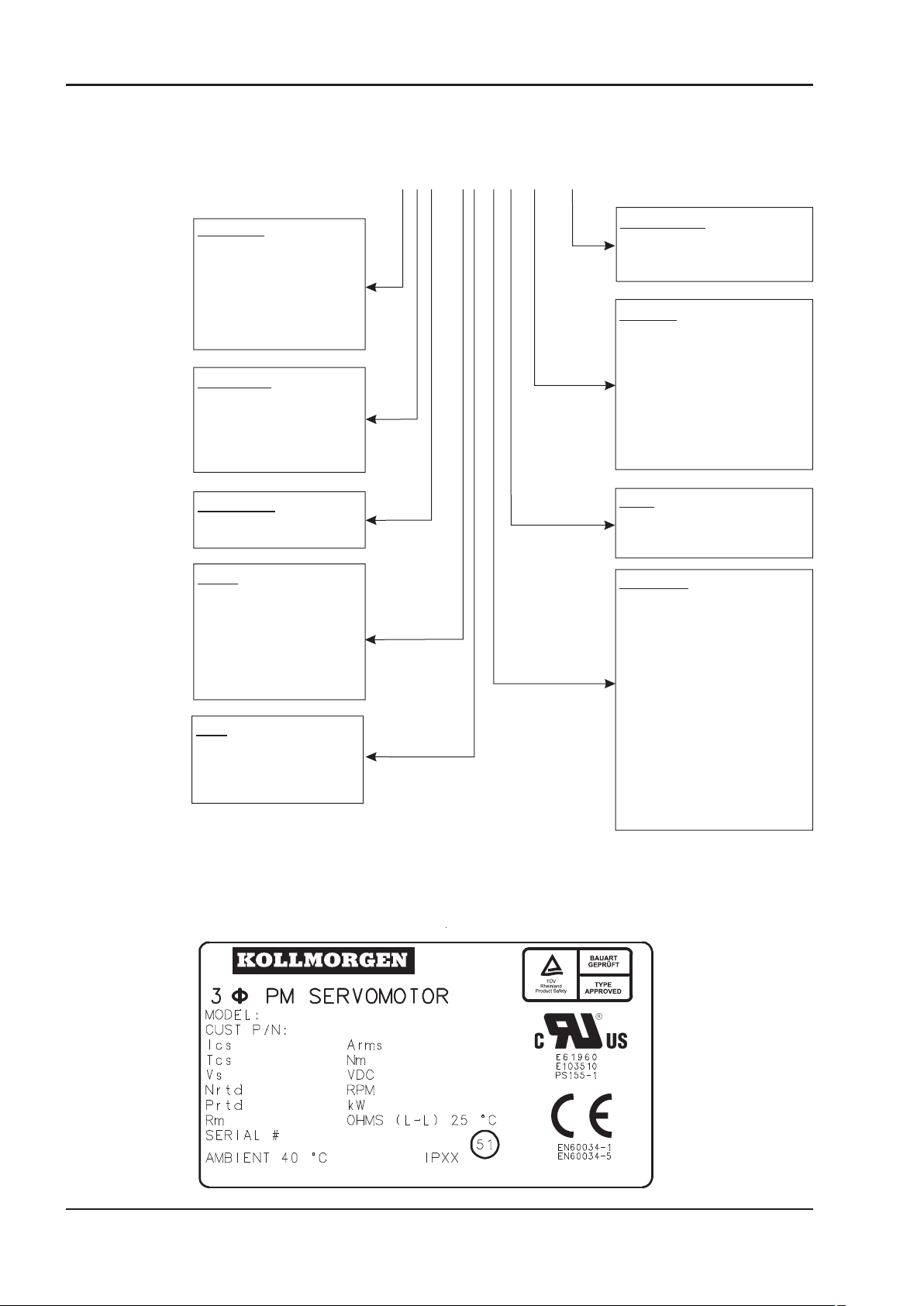
1.10.2 Nameplate
- A.4.028.6/44
12 Servomotors AKM
Page 13

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Installation / Setup
2 Installation / Setup
2.1 Important notes
Check that the servo amplifier and motor match each other. Compare the rated voltage and
l
rated current of the unit. Carry out the wiring according to the wiring diagram in the Installati
on and Setup Instructions for the servo amplifier. The connections to the motor are shown
on pages 17f. Notes on the connection methods can be found on page 16.
Ensure that there is proper earthing of the servo amplifier and the motor.
l
Route the power and control cables as separately as possible from one another (separation
l
> 20 cm). This will improve the immunity of the system to electromagnetic interference.
If a motor power cable is used which includes integral brake control leads, then these brake
control leads must be shielded. The shielding must be connected at both ends (see under
Installation Instructions for the servo amplifier).
Install all cables carrying a heavy current with an adequate cross-section, as per EN 60204.
l
The recommended cross-section can be found in the Technical data.
Caution!
If a servo amplifier of the series SERVOSTAR is used and the motor cable exceeds
25m, a motor choke (type 3YLNxx, see manual of the servo amplifier) and motor leads
with the following diameters must be used:
-
Rated output current of the servo amplifier
1...6 A 4 x 1mm²
10...20 A 4 x 2,5mm²
l Connect up all shielding via a wide surface-area contact (low impedance) and metallized
Maximum lead diameter of the motor cable
(cable length > 25m and motor choke)
connector housings or EMC-cable glands.
l
Check the compliance to the permitted radial and axial forces FRand FA.
When you use a toothed belt drive, the minimal permitted diameter of the pinion e.g. follows
M
from the equation:
d
min
³´02
.
F
R
Caution!
Never undo the electrical connections to the motor while it is energised. A dangerous
voltage, resulting from residual charge, can be still present on the capacitors up to 5
minutes after switch-off of the mains supply.
Measure the DC-link voltage and wait until it has fallen below 40V.
Even when the motor is not rotating, control and power leads may be live.
Servomotors AKM 13
Page 14

Installation / Setup 05/2006 Kollmorgen
2.2 Assembly / Wiring
Only qualified staff with knowledge of mechanical engineering are permitted to assemble
the motor.
Only staff qualified and trained in electrical engineering are allowed to wire up the motor.
The procedure is described as an example. A different method may be appropriate or necessary,
depending on the application of the equipment.
Warning!
Protect the motor from unacceptable stresses.
Take care, especially during transport and handling, that components are not bent and that
insulation clearances are not altered.
Always make sure that the motors are de-energized during assembly and wiring, i.e. No vol
tage may be switched on for any piece of equipment which is to be connected.
Ensure that the switch cabinet remains turned off (barrier, warning signs etc.).
The individual voltages will only be turned on again during setup.
-
Note!
The ground symbol
must provide an electrical connection, with as large a surface area as possible, between the
unit indicated and the mounting plate in the switch cabinet. This connection is to suppress
HF interference and must not be confused with the PE (protective earth) symbol (protective
measure to EN 60204).
To wire up the motor, use the wiring diagrams in the Installation and Setup Instructions of
the servo amplifier which is used.
X, which you will find in the wiring diagrams, indicates that you
14 Servomotors AKM
Page 15

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Installation / Setup
The following notes should help you to carry out the assembly and wiring in an appropriate
sequence, without overlooking anything.
The site must be free of conductive and aggressive material. For
Site
V3-mounting (shaft end upwards), make sure that no liquids can enter
the bearings. If an encapsulated assembly is required, please consult
our applications department beforehand
.
Ventilation
Assembly
Cable selection
Earthing / Shielding
Wiring
Check
Ensure an unhindered ventilation of the motors and observe the permis
sible ambient and flange temperatures. For ambient temperatures abo
ve 40°C please consult our applications department beforehand
During assembly, take care that the motor is not overstressed when it is
fixed in place
Select cables according to EN 60204.
See the table on page 13 when cable length exceeds 25m.
Use correct earthing and EMC-shielding according to the Installation in
structions for the servo amplifier which is used. Earth the mounting pla
te and motor casing. For connection methods see chapter 2.2.1
— Route power cables as separately as possible from control cables
— Connect up the resolver or encoder.
— Connect the motor cables, install motor chokes close to the
servo amplifier, connect shields to shielding terminals or EMC
connectors at both ends
— Connect the holding brake, if used, Connect shielding at both ends
Final check of the installed wiring, according to the wiring diagram
which was used
.
.
.
-
-
-
-
.
Servomotors AKM 15
Page 16

Installation / Setup 05/2006 Kollmorgen
2.2.1 Connection of the motors with preassembled cables
Carry out the wiring in accordance with the valid standards and regulations.
l
Only use our preassembled shielded cables for the resolver and power connections.
l
Connect up the shielding according to the wiring diagrams in the installation instructions for
l
the servo amplifier.
Incorrectly installed shielding inevitably cables to EMC interference.
l
In the table below you find all cables supplied by us. Further information referring to
chemical, mechanical and electrical qualities can be received from our applications department.
Insulating material
Sheathing PUR (Polyurethane, identification 11Y)
core insulation PETP (Polyesteraphtalate, identification 12Y)
Capacity
Motor cable less than 150 pF/m Resolver cable less than 120 pF/m
Technical Data
— All cables are UL-listed. The UL-Style-number is printed on the sheathing.
— All cables are suitable for trailing. Technical data refer to mobile usage of cables.
Life time: 1 Million bending cycles
— The temperature range refers to the operation temperature.
— N=number, F=color acc. to DIN 47100, ()= shielding
Cores
[mm²]
(4x1,0) N -30 / +80 10 100
(4x2,5) N -30 / +80 12,6 125
(4x1,0+(2x0,75)) F -30 / +80 10,5 100
(4x1,5+(2x0,75)) N -30 / +80 11,5 120
(4x2,5+(2x1)) F -30 / +80 14,2 145
(4x2x0,25) F -30 / +80 7,7 70 Resolver cable
(7x2x0,25) F -30 / +80 9,9 80 Encoder cable
(8x2x0,25) F -30 / +80 10,5 100 Comcoder cable
Identifi-
cation
Temperature
range
[°C]
Cable
diameter
[mm]
Bending
radius
[mm]
Remarks
Motor cable(4x1,5) N -30 / +80 10,5 105
Motor cable with integral
brake control leads
Feedback cables with connectors
Article EU order code
Resolver cable 5m (4x(2x0.25))
Resolver cable 10m (4x(2x0.25))
Resolver cable 15m (4x(2x0.25))
Resolver cable 20m (4x(2x0.25))
Resolver cable 25m (4x(2x0.25))
Encoder cable 5m (7x(2x0.25))
Encoder cable 10m (7x(2x0.25))
Encoder cable 15m (7x(2x0.25))
Encoder cable 20m (7x(2x0.25))
Encoder cable 25m (7x(2x0.25))
Comcoder cable 5m (8x(2x0.25))
Comcoder cable 10m (8x(2x0.25))
Comcoder cable 15m (8x(2x0.25))
Comcoder cable 20m (8x(2x0.25))
Comcoder cable 25m (8x(2x0.25))
DE-84972
DE-84973
DE-84974
DE-84975
DE-87655
DE-90287
DE-91019
DE-91811
DE-91807
DE-92205
DE-107915
DE-107916
DE-107917
DE-107918
DE-107919
other lengths on request,
16 Servomotors AKM
Page 17

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Installation / Setup
2.2.1.1 Wiring diagram for motors with resolver
- A.4.050.4/09
SERVOSTAR
Servomotors AKM 17
Page 18

Installation / Setup 05/2006 Kollmorgen
2.2.1.2 Wiring diagram for motors with encoder
- A.4.050.4/10
SERVOSTAR
18 Servomotors AKM
Page 19

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Installation / Setup
2.2.1.3 Wiring diagram for motors with SFD
- A.4.050.4/26
SERVOSTAR
Servomotors AKM 19
Page 20

Installation / Setup 05/2006 Kollmorgen
2.2.1.4 Wiring diagram for motors with ComCoder
-A.4.050.4/27
SERVOSTAR
20 Servomotors AKM
Page 21

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Installation / Setup
2.2.1.5 Wiring diagram for motors with BISS
SERVOSTAR
Servomotors AKM 21
Page 22

Installation / Setup 05/2006 Kollmorgen
2.3 Setup
The procedure for setup is described as an example. A different method may be appropriate or
necessary, depending on the application of the equipment.
Only specialist personnel with extensive knowledge in the areas of electrical engineering / drive
technology are allowed to commission the drive unit of servo amplifier and motor.
Check that all live connection points (terminal boxes) are safe against accidental contact.
Deadly voltages can occur, up to 900V.
Never undo the electrical connections to the motor when it is live. The residual charge in the
capacitors of the servo amplifier can produce dangerous voltages up to 5 minutes after the
mains supply has been switched off.
The surface temperature of the motor can exceed 100°C in operation.
Check (measure) the temperature of the motor. Wait until the motor has cooled down below
40°C before touching it.
Make sure that, even if the drive starts to move unintentionally, no danger can result for per
sonnel or machinery.
Check the assembly and orientation of the motor.
l
Check the drive components (clutch, gear unit, belt pulley) for the correct seating and
l
setting (observe the permissible radial and axial forces).
Check the wiring and connections to the motor and the servo amplifier. Check that
l
the earthing is correct.
Test the function of the holding brake, if used. (apply 24V, the brake must be relea-
l
sed).
l
Check whether the rotor of the motor revolves freely (release the brake, if necessary).
Listen out for grinding noises.
l
Check that all the required measures against accidental contact with live and moving
parts have been carried out.
l
Carry out any further tests which are specifically required for your system.
l
Now commission the drive according to the setup instructions for the servo amplifier.
l
In multi-axis systems, individually commission each drive unit (servo amplifier and
motor).
-
22 Servomotors AKM
Page 23

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
3 Technical Data
All data valid for 40°C environmental temperature and 100K overtemperature of the winding. The
data can have a tolerance of +/- 10%.
3.1 Definitions
Standstill torque M0[Nm]
The standstill torque can be maintained indefinitely at a speed n<100 min
-1
and rated ambient con
ditions.
Rated torque M
n
[Nm]
The rated torque is produced when the motor is drawing the rated current at the rated speed. The
rated torque can be produced indefinitely at the rated speed in continuous operation (S1).
Standstill current I
The standstill current is the effective sinusoidal current which the motor draws at n<100 min
0rms
[A]
-1
to
produce the standstill torque.
Peak current (pulse current) I
The peak current (effective sinusoidal value) is approximately equivalent to 4-times the rated cur
0max
[A]
-
rent. The actual value is determined by the peak current of the servo amplifier which is used.
Torque constant K
The torque constant defines how much torque in Nm is produced by the motor with 1A r.m.s. cur
rent. The relationship is M=I x K
Voltage constant K
Trms
Erms
[Nm/A]
(uptoI=2xI0)
T
[mV/min-1]
-
The voltage constant defines the induced motor EMF, as an effective sinusoidal value between two
terminals, per 1000 rpm
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²]
The constant J is a measure of the acceleration capability of the motor. For instance, at I
leration time t
from 0 to 3000 rpm is given as:
b
ts
[]=
b
´
3000 2
Msmcm
´
60 10
0
p
´
42
´
2
with M
J
´
in Nm and J in kgcm²
0
the acce-
0
-
Thermal time constant t
The constant t
defines the time for the cold motor, under a load of I0, to heat up to an overtempe
th
th
[min]
rature of 0.63 x 105 Kelvin. This temperature rise happens in a much shorter time when the motor is
loaded with the rated current.
Release delay time t
[ms] / Application delay time t
BRH
These constants define the response times of the holding brake when operated with the rated vol
[ms] of the brake
BRL
-
tage from the servo amplifier.
Servomotors AKM 23
Page 24

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.2 AKM1
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
11B 11C 11E 12C 12E 13C 13D
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
[Nm] 0,18 0,18 0,18 0,31 0,31 0,41 0,40
0
[A] 1,16 1,45 2,91 1,51 2,72 1,48 2,40
0rms
[VAC] 230VAC
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] — — 6000 — 3000 — 2000
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] — — 0,18 — 0,31 — 0,40
n
[kW]
P
n
— — 0,11 — 0,10 — 0,08
Rated speed nn[min-1] 4000 6000 — 4000 8000 3000 7000
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 0,18 0,18 — 0,30 0,28 0,41 0,36
n
[kW]
P
n
0,08 0,11 — 0,13 0,23 0,13 0,27
Rated speed nn[min-1] 8000 — — 8000 — 8000 —
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 0,17 — — 0,28 — 0,36 —
n
[kW]
P
n
0,14 — — 0,23 — 0,30 —
Rated speed nn[min-1] ———————
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] ———————
n
P
n
[kW]
———————
Rated speed nn[min-1] ———————
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant K
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] ———————
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 4,65 5,79 11,6 6,06 10,9 5,93 9,6
0max
[Nm] 0,61 0,61 0,61 1,08 1,08 1,46 1,44
0max
[Nm/A] 0,16 0,13 0,06 0,21 0,11 0,28 0,17
Trms
[mVmin] 10,2 8,3 4,1 13,3 7,2 17,9 10,9
Erms
R
[W]
25
———————
20,2 13,1 3,3 12,4 3,9 13,5 5,2
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 12,5 8,3 2,0 9,1 2,7 10,3 3,8
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 0,017 0,031 0,045
Pole number 6 6 6
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,0011 0,0021 0,0031
R
[min] 4 6 7
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 0,35 0,49 0,63
Radial load permitted at shaft
end @ 8000 min
Axial load permitted at shaft
end @ 8000 min
-1
-1
FR[N]
FA[N]
* reference flange Aluminium 254mm * 254mm * 6,35mm
AKM
30
12
Connections and cables
Data AKM1
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, on Cable 0,5m
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 1
Motor cable with control leads,
shielded
4x1+2x0,75
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, on Cable 0,5m
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Comcoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, on Cable 0,5m
24 Servomotors AKM
Page 25

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
Servomotors AKM 25
Page 26

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.3 AKM2
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
21C 21E 21G 22C 22E 22G 23C 23D 23F 24C 24D 24F
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
[Nm] 0,48 0,50 0,50 0,84 0,87 0,88 1,13 1,16 1,18 1,38 1,41 1,42
0
[A] 1,58 3,11 4,87 1,39 2,73 4,82 1,41 2,19 4,31 1,42 2,21 3,89
0rms
[VAC] 480
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] — 2000 4000 — 1000 2500 — — 1500 — — 1000
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] — 0,48 0,46 — 0,85 0,83 — — 1,15 — — 1,39
n
[kW]
P
n
— 0,10 0,19 — 0,09 0,22 — — 0,18 — — 0,15
Rated speed nn[min-1] 2500 7000 — 1000 3500 7000 1000 1500 4500 — 1500 3000
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 0,46 0,41 — 0,83 0,81 0,74 1,11 1,12 1,07 — 1,36 1,33
n
[kW]
P
n
0,12 0,30 — 0,09 0,30 0,54 0,12 0,18 0,50 — 0,21 0,42
Rated speed nn[min-1] 8000 — — 3500 8000 — 2500 5000 8000 2000 4000 8000
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 0,39 — — 0,78 0,70 — 1,08 1,03 0,94 1,32 1,29 1,12
n
[kW]
P
n
0,32 — — 0,29 0,59 — 0,28 0,54 0,79 0,28 0,54 0,94
Rated speed nn[min-1] — — — 8000 — — 5500 8000 — 4500 8000 —
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] — — — 0,68 — — 0,99 0,92 — 1,25 1,11 —
n
P
n
[kW]
— — — 0,57 — — 0,57 0,77 — 0,59 0,93 —
Rated speed nn[min-1] — — — 8000 — — 7000 8000 — 5500 8000 —
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant K
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] — — — 0,68 — — 0,95 0,92 — 1,22 1,11 —
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 6,3 12,4 19,5 5,6 10,9 19,3 5,6 8,8 17,2 5,7 8,8 15,6
0max
[Nm] 1,47 1,49 1,51 2,73 2,76 2,79 3,77 3,84 3,88 4,73 4,76 4,82
0max
[Nm/A] 0,30 0,16 0,10 0,61 0,32 0,18 0,80 0,52 0,27 0,97 0,63 0,36
Trms
[mVmin] 19,5 10,2 6,6 39 20,4 11,7 51,8 33,8 17,6 62,4 40,8 23,4
Erms
R
[W]
25
— — — 0,57 — — 0,70 0,77 — 0,70 0,93 —
13,0 3,42 1,44 19,4 5,09 1,69 20,3 8,36 2,23 20,4 8,4 2,77
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 19 5,2 2,18 35,5 9,7 3,19 40,7 17,3 4,68 43,8 18,7 6,16
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 0,11 0,16 0,22 0,27
Pole number 6666
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,002 0,005 0,007 0,01
R
[min] 8 9 10 11
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 0,82 1,1 1,38 1,66
Radial load permitted at shaft
end @ 5000 min
Axial load permitted at shaft
end @ 5000 min
-1
-1
FR[N]
FA[N]
* reference flange Aluminium 254mm * 254mm * 6,35mm
AKM
145
60
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 1,42
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 8,4
BR
[kgcm²] 0,011
BR
[ms] 20
BRH
[ms] 18
BRL
[kg] 0,27
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,46
26 Servomotors AKM
Page 27

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM2
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 1
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4x1+2x0,75
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, angular
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/01, 13
Servomotors AKM 27
Page 28

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.4 AKM3
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
31C 31E 31H 32C 32D 32H 33C 33E 33H
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
[Nm] 1,15 1,20 1,23 2,00 2,04 2,10 2,71 2,79 2,88
0
[A] 1,37 2,99 5,85 1,44 2,23 5,50 1,47 2,58 5,62
0rms
[VAC] 480
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] — 750 2000 — — 1200 — — 800
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] — 1,19 1,20 — — 2,06 — — 2,82
n
[kW]
P
n
— 0,09 0,25 — — 0,26 — — 0,24
Rated speed nn[min-1] — 2500 6000 — 1000 3000 — — 2500
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] — 1,17 0,97 — 2,00 1,96 — — 2,66
n
[kW]
P
n
— 0,31 0,61 — 0,21 0,62 — — 0,70
Rated speed nn[min-1] 2500 6000 — 1500 2500 7000 1000 2000 5500
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 1,12 0,95 — 1,95 1,93 1,45 2,64 2,62 2,27
n
[kW]
P
n
0,29 0,60 — 0,31 0,51 1,06 0,28 0,55 1,31
Rated speed nn[min-1] 5000 — — 3000 5500 — 2000 4500 —
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 1,00 — — 1,86 1,65 — 2,54 2,34 —
n
P
n
[kW]
0,52 — — 0,58 0,95 — 0,53 1,10 —
Rated speed nn[min-1] 6000 — — 3500 6000 — 2500 5000 —
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant K
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] 0,91 — — 1,83 1,58 — 2,50 2,27 —
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 5,5 12,0 23,4 5,7 8,9 22,0 5,9 10,3 22,5
0max
[Nm] 3,88 4,00 4,06 6,92 7,05 7,26 9,76 9,96 10,2
0max
[Nm/A] 0,85 0,41 0,21 1,40 0,92 0,39 1,86 1,10 0,52
Trms
[mVmin] 54,5 26,1 13,7 89,8 59,0 24,8 120 70,6 33,4
Erms
R
[W]
25
0,57 — — 0,67 0,99 — 0,65 1,19 —
21,4 4,58 1,25 23,0 9,57 1,64 25,4 8,36 1,82
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 37,5 8,6 2,4 46,5 20,1 3,55 53,6 18,5 4,1
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 0,33 0,59 0,85
Pole number 8 8 8
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,014 0,02 0,026
R
[min] 14 17 20
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 1,55 2,23 2,9
Radial load permitted at shaft
end @ 3000 min
Axial load permitted at shaft
end @ 3000 min
-1
-1
FR[N]
FA[N]
* reference flange Aluminium 254mm * 254mm * 6,35mm
AKM
195
65
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 2,5
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 10,1
BR
[kgcm²] 0,011
BR
[ms] 25
BRH
[ms] 10
BRL
[kg] 0,35
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,46
28 Servomotors AKM
Page 29

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM3
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 1
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4x1+2x0,75
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, angular
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/02, 13 - A.4.043.3/02, 044.3/05, 09, 10
Servomotors AKM 29
Page 30

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.5 AKM4
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
41C 41E 41H 42C 42E 42G 42J 43E 43G 43K 44E 44G 44J
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
[Nm] 1,95 2,02 2,06 3,35 3,42 3,53 3,56 4,70 4,80 4,90 5,76 5,88 6,00
0
[A] 1,46 2,85 5,60 1,40 2,74 4,80 8,40 2,76 4,87 9,60 2,90 5,00 8,80
0rms
[VAC] 480
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] — — 1000 ——————————
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] — — 1,99 ——————————
n
[kW]
P
n
— — 0,21 ——————————
Rated speed nn[min-1] — 1200 3000 — — — 3000 — — 2500 — — —
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] — 1,94 1,86 — — — 3,03 — — 4,08 — — —
n
[kW]
P
n
— 0,24 0,58 — — — 0,95 — — 1,07 — — —
Rated speed nn[min-1] 1200 3000 6000 — 1800 3500 6000 1500 2500 6000 1200 2000 4000
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 1,88 1,82 1,62 — 3,12 2,90 2,38 4,24 4,00 2,62 5,22 4,90 3,84
n
[kW]
P
n
0,24 0,57 1,02 — 0,59 1,06 1,50 0,67 1,05 1,65 0,66 1,03 1,61
Rated speed nn[min-1] 3000 6000 — 1500 3500 6000 — 2500 5000 — 2000 4000 6000
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 1,77 1,58 — 3,10 2,81 2,35 — 3,92 3,01 — 4,80 3,76 2,75
n
P
n
[kW]
0,56 0,99 — 0,49 1,03 1,48 — 1,03 1,58 — 1,01 1,57 1,73
Rated speed nn[min-1] 3500 6000 — 2000 4000 6000 — 3000 6000 — 2500 5000 6000
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant K
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] 1,74 1,58 — 3,02 2,72 2,35 — 3,76 2,57 — 4,56 3,19 2,75
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 5,8 11,4 22,4 5,61 11,0 19,2 33,7 11,0 19,5 38,3 11,4 20,0 35,2
0max
[Nm] 6,12 6,28 6,36 11,1 11,3 11,5 11,6 15,9 16,1 16,3 19,9 20,2 20,4
0max
[Nm/A] 1,34 0,71 0,37 2,40 1,26 0,74 0,43 1,72 0,99 0,52 2,04 1,19 0,69
Trms
[mVmin] 86,3 45,6 23,7 154 80,9 47,5 27,5 111 63,9 33,2 132 76,6 44,2
Erms
R
[W]
25
0,64 0,99 — 0,63 1,14 1,48 — 1,18 1,61 — 1,19 1,67 1,73
21,7 5,7 1,51 27,5 7,22 2,38 0,80 8,04 2,61 0,70 8,08 2,65 0,88
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 66,1 18,4 5,0 97,4 26,8 9,2 3,1 32,6 10,8 2,9 33,9 11,5 3,8
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 0,81 1,5 2,1 2,7
Pole number 10 10 10 10
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,014 0,026 0,038 0,05
R
[min] 13 17 20 24
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 2,44 3,39 4,35 5,3
Radial load permitted at shaft
end @ 3000 min
Axial load permitted at shaft
end @ 3000 min
-1
-1
FR[N]
FA[N]
* reference flange Aluminium 254mm * 254mm * 6,35mm
AKM
450
180
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 6
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 12,8
BR
[kgcm²] 0,068
BR
[ms] 35
BRH
[ms] 15
BRL
[kg] 0,63
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,37
30 Servomotors AKM
Page 31

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM4
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 1,5
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4x1+2x0,75
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, angular
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/03, 13 - A.4.043.3/03, 044.3/12, 15, 16
Servomotors AKM 31
Page 32

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.6 AKM5
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
51E 51G 51K 52E 52G 52K 52M 53G 53K 53M 53P 54G 54K 54L 54N
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
Rated speed nn[min-1]
Rated torque* Mn[Nm]
Rated power
U = 75VDC
Rated speed nn[min-1]
Rated torque* Mn[Nm]
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
Rated speed nn[min-1]
Rated torque* Mn[Nm]
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 4,70 4,75 4,90 8,34 8,43 8,60 8,60 11,4 11,6 11,4 11,4 14,3 14,4 14,1 14,1
0
[A] 2,75 4,84 9,4 2,99 4,72 9,3 13,1 4,77 9,4 13,4 19,1 5,0 9,7 12,5 17,8
0rms
[VAC] 480
N
P
[kW]
n
P
[kW]
n
P
[kW]
n
———————————————
———————————————
———————————————
— — 2500 ————————————
— — 4,15 ————————————
— — 1,09 ————————————
1200 2500 5500 — 1500 3000 4500 1000 2000 3000 5000 — 1800 2500 3500
4,41 4,02 2,35 — 7,69 6,80 5,20 10,7 10,1 8,72 5,88 — 12,7 11,5 9,85
0,55 1,05 1,35 — 1,21 2,14 2,45 1,12 2,12 2,74 3,08 — 2,39 3,00 3,61
Rated speed nn[min-1] 2500 5000 — 1500 2500 5500 — 2000 4000 — — 1500 3500 4500 —
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
Rated speed nn[min-1]
[Nm] 3,98 2,62 — 7,61 7,06 3,90 — 9,85 7,65 — — 12,9 10,0 8,13 —
n
P
[kW]
n
1,04 1,37 — 1,20 1,85 2,25 — 2,06 3,20 — — 2,03 3,68 3,83 —
3000 6000 — 2000 3000 6000 — 2400 4500 — — 2000 4000 — —
Rated torque* Mn[Nm] 3,80 1,94 — 7,28 6,66 3,25 — 9,50 6,85 — — 12,3 9,25 — —
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque
Torque constant
Voltage constant
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[kW]
P
n
0max
M
0max
[Nm]
K
Trms
[Nm/A]
K
Erms
[mVmin]
R
25
1,19 1,22 — 1,52 2,09 2,04 — 2,39 3,23 — — 2,57 3,87 — —
[A] 8,24 14,5 28,3 9,00 14,2 27,8 39,4 14,3 28,1 40,3 57,4 14,9 29,2 37,5 53,4
11,6 11,7 12,0 21,3 21,5 21,9 21,9 29,7 30,1 29,8 29,8 37,8 38,4 37,5 37,6
1,72 0,99 0,52 2,79 1,79 0,93 0,66 2,39 1,24 0,85 0,60 2,88 1,50 1,13 0,80
110 63,6 33,5 179 115 60,1 42,4 154 79,8 54,7 38,4 185 96,6 72,9 51,3
8,47 2,75 0,75 8,59 3,47 0,93 0,48 3,75 1,00 0,51 0,27 3,80 1,02 0,63 0,33
[W]
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 36,6 12,1 3,40 44,7 18,5 5,00 2,50 21,3 5,70 2,70 1,30 22,9 6,20 3,50 1,80
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 3,4 6,2 9,1 12
Pole number 10 10 10 10
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,022 0,04 0,058 0,077
R
[min] 20 24 28 31
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 4,2 5,8 7,4 9
Radial load permitted at
shaft end @ 3000 min
Axial load permitted at
shaft end @ 3000 min
FR[N]
-1
FA[N]
-1
* reference flange Aluminium 305mm * 305mm * 12,7mm
AKM
450
180
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 14,5
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 19,5
BR
[kgcm²] 0,173
BR
[ms] 80
BRH
[ms] 15
BRL
[kg] 1,1
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,31
32 Servomotors AKM
Page 33

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM5
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 1,5 4 x 2,5
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4 x 1,5+2x0,75 4 x 2,5+2x1
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, angular
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/04, 13
Servomotors AKM 33
Page 34

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.7 AKM6
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
62G 62K 62M 62P 63G 63K 63M 63N 64K 64L 64P 65K 65M 65N
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
Mains voltage U
[Nm] 11,9 12,2 12,2 12,3 16,5 16,8 17,0 17,0 20,8 21,0 20,4 24,8 25,0 24,3
0
[A] 4,9 9,6 13,4 18,8 4,5 9,9 13,8 17,4 9,2 12,8 18,6 9,8 13,6 17,8
0rms
[VAC] 230-480
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] ——————————————
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] ——————————————
n
[kW]
P
n
——————————————
Rated speed nn[min-1] ——————————————
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] ——————————————
n
[kW]
P
n
——————————————
Rated speed nn[min-1] — 2000 3000 4500 — 1500 2000 3000 1200 1500 2500 1000 1500 2000
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] — 10,4 9,50 8,10 — 14,9 14,3 13,0 18,8 18,4 16,0 22,8 21,9 19,8
n
[kW]
P
n
— 2,18 2,98 3,82 — 2,34 2,99 4,08 2,36 2,89 4,19 2,39 3,44 4,15
Rated speed nn[min-1] 1800 3500 6000 — 1200 3000 4000 5000 2000 3000 4500 2000 2500 3500
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 10,4 9,00 5,70 — 14,9 12,9 11,3 9,60 17,2 15,6 11,9 20,2 19,2 16,0
n
P
n
[kW]
1,96 3,30 3,58 — 1,87 4,05 4,73 5,03 3,60 4,90 5,61 4,23 5,03 5,86
Rated speed nn[min-1] 2000 4500 6000 — 1500 3500 4500 6000 2500 3500 5500 2200 3000 4000
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] 10,2 8,00 5,70 — 14,6 12,0 10,5 7,00 16,3 14,4 9,00 19,7 18,1 14,7
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 14,6 28,7 40,3 56,5 13,4 29,7 41,4 52,2 27,5 38,4 55,9 29,4 40,9 53,3
0max
[Nm] 29,8 30,1 30,2 30,4 41,8 42,6 43,0 43,0 53,5 54,1 52,9 64,5 65,2 63,7
0max
[Nm/A] 2,47 1,28 0,91 0,66 3,70 1,71 1,24 0,98 2,28 1,66 1,10 2,54 1,85 1,38
Trms
K
Erms
[mVmin]
R
[W]
25
2,14 3,77 3,58 — 2,29 4,40 4,95 4,40 4,27 5,28 5,18 4,54 5,69 6,16
159 82,1 58,8 42,2 238 110 79,9 63,3 147 107 71,0 164 119 88,8
3,94 1,05 0,55 0,30 5,16 1,09 0,58 0,38 1,34 0,71 0,36 1,27 0,68 0,42
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 31,7 8,5 4,4 2,2 43,5 9,3 4,9 3,1 11,8 6,2 2,8 11,4 6,1 3,4
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 17 24 32 40
Pole number 10 10 10 10
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,05 0,1 0,15 0,2
R
[min] 20 25 30 35
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 8,9 11,1 13,3 15,4
Radial load permitted at
shaft end @ 3000 min
Axial load permitted at
shaft end @ 3000 min
FR[N]
-1
FA[N]
-1
* reference flange Aluminium 457mm * 457mm * 12,7mm
AKM
770
280
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 25
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 25,7
BR
[kgcm²] 0,61
BR
[ms] 105
BRH
[ms] 20
BRL
[kg] 2
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,24
34 Servomotors AKM
Page 35

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM6
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 2,5
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4 x 2,5+2x1
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17 poles, round, angular
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/05, 13
Servomotors AKM 35
Page 36

Technical Data 05/2006 Kollmorgen
3.8 AKM7
Technical data
Data
Symbol
[Unit]
72K 72M 72P 73M 73P 74L 74P
Electrical data
Standstill torque* M
Standstill current I
max. Mains voltage U
[Nm] 29,7 30,0 29,4 42,0 41,6 53,0 52,5
0
[A] 9,3 13,0 18,7 13,6 19,5 12,9 18,5
0rms
[VAC] 480
N
Rated speed nn[min-1] ———————
Rated torque* M
Rated power
U = 75VDC
[Nm] ———————
n
[kW]
P
n
———————
Rated speed nn[min-1] ———————
Rated torque* M
= 115V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] ———————
n
[kW]
P
n
———————
Rated speed nn[min-1] — — 1800 — 1300 — —
Rated torque* M
= 230V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] — — 23,8 — 34,7 — —
n
[kW]
P
n
— — 4,49 — 4,72 — —
Rated speed nn[min-1] 1500 2000 3000 1500 2400 1200 1800
Rated torque* M
= 400V
N
Rated power
U
[Nm] 25,1 23,6 20,1 33,8 28,5 43,5 39,6
n
P
n
[kW]
3,94 4,94 6,31 5,31 7,16 5,47 7,46
Rated speed nn[min-1] 1800 2500 3500 1800 2800 1400 2000
Rated torque* M
= 480V
N
Rated power
U
Peak current I
Peak torque M
Torque constant K
Voltage constant K
Winding resistance Ph-Ph
[Nm] 24,0 22,1 18,2 32,1 26,3 41,5 35,9
n
[kW]
P
n
[A] 27,8 38,9 56,1 40,8 58,6 38,7 55,5
0max
[Nm] 79,2 79,7 78,5 113 111 143 142
0max
[Nm/A] 3,23 2,33 1,58 3,10 2,13 4,14 2,84
Trms
[mVmin] 208 150 102 200 137 266 183
Erms
R
[W]
25
4,52 5,79 6,67 6,05 7,71 6,08 7,52
1,22 0,64 0,33 0,68 0,35 0,85 0,43
Winding inductance Ph-Ph L [mH] 20,7 10,8 5,0 12,4 5,9 16,4 7,7
Mechanical data
Rotor moment of inertia J [kgcm²] 65 92 120
Pole number 10 10 10
Static friction torque M
Thermal time constant t
[Nm] 0,16 0,24 0,33
R
[min] 46 53 60
TH
Weight standard G [kg] 19,7 26,7 33,6
Radial load permitted at shaft
end @ 1000 min
Axial load permitted at shaft
end @ 1000 min
-1
-1
FR[N]
FA[N]
* reference flange Aluminium 457mm * 457mm * 12,7mm
AKM
1300
500
Brake data
Data Symbol [Unit] Value
Holding torque @ 120°C M
Operating voltage
electrical power P
Moment of inertia J
Release delay time t
Application delay time t
Weight of the brake G
[Nm] 53
BR
U
[VDC]
BR
[W] 35,6
BR
[kgcm²] 1,64
BR
[ms] 110
BRH
[ms] 35
BRL
[kg] 2,1
BR
24 ± 10 %
Typical backlash [ °mech.] 0,2
36 Servomotors AKM
Page 37

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Technical Data
Connections and cables
Data AKM7
Power connection 4 + 4 poles, round, angular
Motorcable, shielded 4 x 2,5
Motor cable with control leads, shielded 4 x 2,5+2x1
Steueradern, geschirmt 4 x 1
Resolver connection 12 poles, round, angular
Resolver cable, shielded 4x2x0,25mm²
Encoder connection (option) 17-polig, rund
Encoder cable, shielded 7x2x0,25mm²
Dimensions (drawing in principle)
Radial-/axial forces at the shaft end
- A.4.043.4/10, 14
Servomotors AKM 37
Page 38

Appendix 05/2006 Kollmorgen
4 Appendix
4.1 Assignment of RediMount gearhead mounts
Motor RediMount Flange length [mm] Motor RediMount Flange length [mm]
AKM1xx-A RM060-130 35,1
AKM1xx-C RM060-XXX in preparation RM090-124 44,1
RM060-6 31,0 RM100-124 43,7
AKM2xx-A
AKM2xx-C
AKM3xx-A
AKM3xx-C
AKM4xx-A
RM075-6 in preparation RM115-124 48,9
RM090-6 62,7
RM100-6 in preparation RM100-71 43,7
RM060-17 31,0 RM115-71 48,9
RM075-17 42,9 RM142-71 69,6
RM090-17 44,1 RM180-71 91,4
RM100-17 62,7
RM115-17 48,9 RM100-53 in preparation
RM060-19 31,0 RM115-53 59,9
RM075-19 42,9 RM142-53 in preparation
RM090-19 44,1 RM180-53 in preparation
RM100-19 58,9
RM060-XXX in preparation RM142-92 81,5
RM075-XXX in preparation RM180-92 91,4
RM090-XXX in preparation RM220-92 69,5
RM100-XXX in preparation
RM075-40 42,9 RM180-114 91,4
RM090-40 44,1 RM220-114 69,6
RM100-40 43,7
RM115-40 48,9
AKM4xx-C
AKM5xx-A
AKM5xx-C
AKM6xx-A
AKM7xx-A
RM075-124 42,9
RM090-71 62,7
RM090-53 in preparation
RM115-92 in preparation
RM142-114S 85,3
These gearheads can be fitted to RediMount:
RM060: DT60, DTR60, DTRS60, DTRH60, NT23, NTP23, NT60, NTR23, UT006,
UTR006, EQ23, EQ60
RM075: UT075, UTR075, UT090, UTR090
RM090: DT90, DTR90, DTRS90, DTRD90, DTRH90, NT34, NTP34, NT90, NTR34
RM100: UT010, UTR010, ET010, UT115, UTR115
RM115: DT115, DTR115, DTRS115, DTRD115, DTRH115, NT42, NTP42, NT115,
NTR42
RM142: DT142, DTR142, DTRS142, DTRD142, DTRH142, NT142, UT014, UTR014,
ET014
RM180: UT018, UTR018, ET018
RM220: UT220
You can find further information on Redimount and gearheads on our website.
38 Servomotors AKM
Page 39

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Appendix
4.2 Delivery package, transport, storage, maintenance, disposal
Delivery package: — Motor from the AKM series
— Technical description (documentation), 1 copy per delivery
— Motor package leaflet (short info)
Transport: — Climate category 2K3 to EN 50178
— Transport temperature -25...+70°C, max. 20K/hr change
— Transport humidity rel. humidity 5% - 95% , no condensation
— only by qualified personnel
— only in the manufacturer’s original recyclable packaging
— avoid shocks
— if the packaging is damaged, check the motor for visible damage.
— Inform the carrier and, if appropriate, the manufacturer.
®
Packaging: — Cardboard packing with Instapak
— You can return the plastic portion to the supplier or a certified
— disposal company. Ask us for addresses.
Motor type Carton Max.stacking height
AKM1 X 10
AKM2 X 10
AKM3 X 6
AKM4 X 6
AKM5 X 5
AKM6 X 1
AKM7 X 1
foam cushion.
Storage: — Climate category 1K4 to EN 50178
— Storage temperature -25...+55°C, max. variation 20K/hr. — Humidity rel. humidity 5% - 95%, no condensation
— only in the manufacturer’s original recyclable packaging
— max. stacking height see table under Packaging
— Storage time unlimited
Maintenance: — Only by qualified personnel
— The ball bearings have a grease packing which is adequate for
— 20,000 hours of operation under normal conditions. The bearings
— should be replaced after 20,000 hours of operation under rated
— conditions.
— Check the motor for bearing noise every 2500 operating hours,
— respectively each year. If any noises are heard, then the operation
— of the motor must stop, the bearings must be replaced.
— Opening the motor invalidates the warranty.
Cleaning: — If the housing is dirty: clean with Isopropanol or similar.
do not immerse or spray
Disposal : In accordance to the WEEE-2002/96/EG-Guidelines we take old devices and
accessories back for professional disposal, if the transport costs are taken
over by the sender. Send the devices to:
Danaher Motion GmbH
Robert-Bosch-Straße 10
D-64331 Weiterstadt
Germany
Servomotors AKM 39
Page 40

Appendix 05/2006 Kollmorgen
4.3 Removing faults
The following table is to be seen as a “First Aid” box. There can be a large number of different rea
sons for a fault, depending on the particular conditions in your system. The fault causes described
below are mostly those which directly influence the motor. Peculiarities which show up in the control
loop behaviour can usually be traced back to an error in the parameterization of the servo amplifier.
The documentation for the servo amplifier and the setup software provides information on these
matters.
For multi-axis systems there may be further hidden reasons for faults.
Our applications department can give you further help with your problems.
Fault Possible cause
— Servo-amplifier not enabled
Motor doesn’t
rotate
Motor runs away
Motor oscillates
Error message:
brake
Error message:
output stage fault
Error message:
resolver
Error message:
motor temperature
Brake does not
grip
— Break in setpoint lead
— Motor phases in wrong sequence
— Brake not released
— Drive is mechanically blocked
— Motor phases in wrong sequence — Correct the phase sequence
— Break in the shielding of the resolver cable
— amplifier gain to high
— Short-circuit in the supply voltage lead to
the motor holding brake
— Faulty motor holding brake
— Motor cable has short-circuit or earth short
— Motor has short-circuit or earth short
— Resolver connector is not properly plugged
in
— Break in resolver cable, cable crushed or
similar
— Motor thermostat has switched
— Loose resolver connector or break in
resolver cable
— Required holding torque too high
— Brake faulty
— Motor shaft axially overloaded
Measures to remove the cause of the
fault
— Supply ENABLE signal
— Check setpoint lead
— Correct the phase sequence
— Check brake controls
— Check mechanism
— Replace resolver cable
— use motor default values
— Remove the short-circuit
— Replace motor
— Replace cable
— Replace motor
— Check connector
— Check cables
— Wait until the motor has cooled
down. Then investigate why the
motor becomes so hot.
— Check connector, replace resolver
cable if necessary
— Check the dimensioning
— Replace motor
— Check the axial load, reduce it.
Replace motor, since the bearings
have been damaged
40 Servomotors AKM
Page 41

Kollmorgen 05/2006 Appendix
4.4 Index
IndexA AKM1 ..................24
AKM2 .................. 26
AKM3 .................. 28
AKM4 .................. 30
AKM5 .................. 32
AKM6 .................. 34
AKM7 .................. 36
Ambient temperature ........... 8
Axial force .................9
B BISS ...................21
Break response times ..........23
C ComCoder ................ 20
Connection method ........... 10
Coupling .................. 9
D Delivery package .............39
Disposal ................. 39
E Earthing ................. 15
Encoder .................10
F Feedback unit .............. 10
G Gearhead mount .............38
Ground symbol ..............14
H Holding brake ..............10
I Insulation material class ..........9
M Maintenance ............... 39
Manufacturer declaration .........4
Model number ..............12
Motor cable................16
N Nameplate ................ 12
O Options..................11
P Peak current ...............23
Pole numbers .............. 10
Power derating .............. 8
Protection class .............. 9
Protective device .............9
R Radial force ................9
Rated torque ...............23
Resolver ................. 10
Resolver cable ..............16
Rotor moment of inertia .........23
S Safety notes ................6
Servo amplifier ..............8
Setup...................22
SFD ...................19
Shielding .................15
Standstill current .............23
Standstill torque .............23
Storage.................. 39
Storage humidity .............39
Storage temperature ...........39
Storage time ............... 39
Style ....................9
T Thermal time constant ..........23
Torque constant .............23
Transport.................39
V Ventilation ................ 15
Vibration class .............. 10
Voltage constant .............23
W Wiring .................. 15
Servomotors AKM 41
Page 42

www.DanaherMotion.com
Sales and Service
We are committed to quality customer service. In order to serve in the most effective way,
please contact your local sales representative for assistance.
If you are unaware of your local sales representative, please contact us.
Europe
Visit the European Danaher Motion web site at www.DanaherMotion.net for Setup Software upgrades,
application notes, technical publications and the most recent version of our product manuals.
Danaher Motion Customer Support - Europe
Internet www.DanaherMotion.net
E-Mail support@danahermotion.net
Phone: +49(0)203 - 99 79 - 0
Fax: +49(0)203 - 99 79 - 155
North America
Visit the North American Danaher Motion web site at www.DanaherMotion.com for Setup Software
upgrades, application notes, technical publications and the most recent version of our product manuals.
Danaher Motion Customer Support North America
Internet www.DanaherMotion.com
E-Mail DMAC@danahermotion.com
Phone: +1 - 540 - 633 - 3400
Fax: +1 - 540 - 639 - 4162
 Loading...
Loading...