KIRLOSKAR UP 50/30B, UP 150/45, UP 65/24, UP 125/30B, UP 125/30A Instruction On Installation, Operation And Maintenance
...
INSTRUCTION ON
INSTALLTION,
OPERATION &
MAINTENANCE
FOR KIRLOSKAR PUMP
TYPE UP METRIC
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS LIMITED
“Yamuna”S.No.98/3 to 7, Baner, Pune 411045


1.
GENERAL
2. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
3. INSTALLATION
4. OPERATION
CONTENTS
5. TECHNICAL DATA
6. MAINTENANCE
7. OVERHAULING
8. GENERAL OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
9. SPARE PART LIST AND CROSS-SECTIONAL DRAWINGS
10. EXPLODED VIEW.
Please ensure these instructions are read fully before installation and operation of the
pump.
Please furnish complete name plate details, part description, part nos, material construction
and quantity while ordering spare parts.

1. GENERAL
1.1 The booklet covers instructions for following types of UP (M) pumps.
UP 50/30A UP 125/24 UP 150/38BC
UP 50/30B UP 125/30A UP 150/45
UP 65/24 UP 125/30B UP 150/45 BC
UP 65/24A UP 100/35 UP 200/30
UP 80/24 UP 100/38 UP 200/38
UP 65/38 UP 125/35 UP 250/30
UP 65/38M UP 150/26N UP 250/38
UP 80/30 UP 150/30 UP 150/53A
UP 80/38 UP 150/30A(N) UP 150/53F
UP 100/24 UP 150/38A UP 200/42
UP 100/29 UP 150/38B
1.2 These are horizontal split casing type pumps with suction and discharge nozzles and
their supporting feet integrally cast in the lower half casing. This construction
enables to remove the rotating unit for inspection and repairs by just removing upper
half casing, and without disturbing alignment, pipe connection or prime mover.
1.3 Pumps when properly installed and given due care in operation and maintenance
should operate satisfactorily for a long period.
1.4 When the pump is received, sometime before the actual use of pump, it should be
inspected and located in dry place. The coupling should be rotated periodically (once
in a month) to prevent pitting of bearing surfaces.
1.5 Generally all the UP pumps mentioned above are similar in construction with minor
changes of some parts.
1.6 Pump Identification: All pumps are designated by serial number, model number, size
and type. This information is stamped on an identification plate which is fixed on the
pump.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 4 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

1.7 Nomenclature of the pump
Nomenclature for pump is as given below.
UP 100/35
UP- Basic pump type
100- Nominal Delivery size in mm
/ - Always slash
35- Nominal Impeller diameter in cm.
PUMP DESCRIPTION
Casing
Impeller
Shaft
- The casing is of axially-split volute design with suction and discharge flanges and
mounting feet cast integral with the lower half casing. Tapped and plugged holes are
provided for priming, vent, drain and gauge connections. Upper half casing is
removable without disturbing suction or discharge piping.
Suction and Discharge is on a common centerline in both the horizontal and vertical
planes.
- The impeller is of the enclosed double-suction (except UP 150/56 pump),
statically and hydraulically balanced. The impeller is keyed to the shaft and
positioned axially by the shaft sleeves. Hub shall have sufficient metal thickness to
allow machining for installation of casing wear rings.
- The shaft shall be of ample size to operate under load with of minimum deflection.
Shaft Sleeves
with the pumped liquid. An O-ring shall be furnished under sleeve to prevent
- The shaft sleeves should protect the shaft from wear and from contact
leakage.
Insert (Stuffing Box)
type gland to permit removal and access to packing. Ample space is provided for
repacking the insert.
Bearings
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 5 of 66
- The bearings are grease lubricated or oil lubricated. The inboard or coupling
end bearing is a single row ball bearing. The outboard bearing is a double row
cylindrical roller bearing which is retained by bearing locknut and lock washer.
- The insert is consisting of at least six packing rings and a split
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Bearing Housings
and assure positive alignment of the rotating element. The housings provides a fit for
the inboard bearing that allows freedom for thermal expansion while the outboard
bearing is clamped in place to take all thrust loads and keep the rotating element in
its proper axial location.
- The bearing housings are bolted to the end of the lower half casing
Base plate
be provided with a drip pan beneath the pump. The drip pan contains a tapped drain
connection.
Coupling
- The base plate is sufficiently rigid to support the pump and driver and shall
- Coupling can be supplied – Snap-wrap / Pin-Bush / Spacer type
Coupling Guard
Rotation
- Pump can have clockwise or counterclockwise rotation when viewed from its
driving end
- The coupling guard can be in MS / AL / Bronze.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 6 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

2. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS:
2.1: General Information
Before performing any actions detailed within this instruction, the Site Health and
Safety instructions must read and fully understood. The instructions in this
document also must be read and fully understood.
Whenever the equipment is operated, maintained or used in any way, the procedures
detailed within the Health and Safety Dossier (DHS) and any procedures detailed
within these instructions shall be followed. The pump supplied by Kirloskar Brothers
Limited (KBL) has been designed with safety in mind, where hazards cannot be
eliminated; the risk has been minimized by the use of guards and other design
features. Some hazards cannot be guarded against and the instructions below MUST
BE COMPLIED WITH for safe operation. These instructions cannot cover all
circumstances. It is the responsibility of the user of the equipment for maintaining
safe working practices at all times.
2.1.1 KBL products are designed for installation in designated areas, which are to be kept
clean and free of obstructions that may restrict safe access to the controls and
maintenance access points.
2.1.2 Pump nameplate is fitted to each unit and must not be removed. Loss of this plate
could make identification impossible. This in turn could affect safety and cause
difficulty in obtaining spare parts. Should accidental loss or damage occur, contact
KBL immediately.
2.1.3 Access to the equipment should be restricted to the personnel responsible for
installation, operation and maintenance and they must be trained, adequately
qualified and supplied with the appropriate tools for their respective tasks.
2.1.4 KBL firmly insists that all personnel responsible for installation, operation and
maintenance of the equipment must read safety instructions mentioned in the
manual before any work is done.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 7 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

2.1.5 Ear defenders should be worn where the specified equipment noise level exceeds
locally defined safe levels. Safety glasses or goggles should be worn where working
with pressurized systems and hazardous substances. Other personal protection
equipment must be worn where local rules apply.
2.2 DO NOT wear loose or frayed clothing or jewellery, which could catch on the
controls or becomes trapped in the equipment.
2.3 Operation of the equipment for the application other than for which it is supplied can
increase the risk from hazards. Please consult KBL before making such change in
the application of the equipment.
2.4 Improper installation, operation and maintenance of the product supplied by KBL
could result in injury or death.
2.5 Within the manual, safety instructions are marked with safety symbols.
Hazard
This symbol refers to general mechanical aspects of safety.
Hazard
This symbol refers to electrical safety.
2.6: Transport handling and storage instructions:
2.6.1: Transport
Pumps are dispatched in duly assembled condition. Pumps are protected against
corrosion and packed for transport by normal road, rail and sea carriers.
2.6.2: Handling
Crushing hazard
When lifting the pump or pump set, use lifting equipment having a safe working load
rating suitable for the weight specified. Use suitable slings for lifting any pump not
provided with lifting points.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 8 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012
The use of suitable forklift truck and four chain crane sling equipment is
recommended but locally approved equipment rating may be used.
Pump should be slung as shown.
PU M P L IFT IN G A R R A N G EM ENT
Pump set must be lifted from the lifting holes provided on the pump by using
suitable four chain lifting equipment.
90°
Max.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 9 of 66
PUMP SET LIFTING ARRANGEMENT
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

2.6.3: Storage.
2.6.3.1: Temporary storage for up to six weeks.
If the pump unit is not be used immediately it should be stored carefully in a
horizontal position, in a sheltered, dry location. Additional rust preventive should be
applied to all unpainted carbon steel or cast iron parts, and should not be removed
until final installation.
2.6.3.2: Long Term Storage.
If the pump is not to be installed and operated soon after arrival, store it in a
clean, dry place, having slow, moderate changes in ambient temperature. Step
should be taken to protect the pump from moisture, dust, dirt, and foreign bodies. It
is recommended that the following procedure is taken:-
a) Ensure that the bearings are packed with the recommended grease, to prevent
moisture from entering around the shaft.
b) Remove the glands, packings and lantern rings from the stuffing box if the pump
is equipped in this manner. If the pump is equipped with mechanical seal, dismantle
and coat the seal with light oil.
c) Ensure that suction and discharge branches of the pump and all other openings
are covered with cardboard, wood or masking tape to prevent foreign objects
entering the pump.
d) If the pump is to be stored where there is no protective covering, it is advisable to
cover the unit with a tarpaulin or other suitable covering.
e) The shaft should be manually rotated periodically to prevent pitting of the bearing
surfaces by moisture.
Shearing Hazard.
Do NOT place fingers or hands etc. into the suction or discharge pipe outlets and do
NOT touch the impeller, if rotated this may cause severe injury. To prevent ingress
of any objects, retain the protection covers or packaging in place until removal is
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 10 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

necessary for installation. If the packaging or suction and discharge covers are
removed for inspection purposes, replace afterwards to protect the pump and
maintain the safety.
Fill the bearing housing with recommended grease to ensure that the shaft and
bearings remain rust free.
2.6.3.3: Exposed or Extreme Conditions Storage.
For exposed storage or extreme variants in atmospheric or environmental conditions,
please refer to KBL for special storage instructions to suit the conditions acceptable.
3 INSTALLATIONS
3.1 Receiving pump
Upon receipt of the pump, a visual check should be made to determine if any
damage occurred during transit or handling. The main items to look for are:-
a) Broken or cracked equipment, including base, motor or pump feet and flanges.
b) Bent shaft
c) Broken motor end bells, bent eyebolts or damaged boxes of motor
d) Missing parts.
e) Pump shaft rotates freely.
Parts or accessories are some times wrapped individually or fastened to the
equipment. If any damage or losses have been incurred; promptly notify your KBL
representative, KBL Dealer and the transport company who delivered the pump.
When unloading pump units, lift equally at four or more points from the base. DO
NOTLIFT ONLY THE DRIVER OR PUMP.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 11 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

3.2 Preparation
Before installing the pump, clean the suction and discharge flanges thoroughly.
Remove the protective coating from the pump shaft.
If the pump has been in storage and prepared for storage in the manner outlined
previously, remove all the grease from the bearings. The bearings should then be
flushed with carbon tetrachloride or kerosene and relubricated.
3.3 Location
The pump should be installed as near the suction supply as possible, with the
shortest and most direct suction pipe practical. The total dynamic suction lift (static lift
plus friction losses in suction line) should not exceed the limits for which the pump was
sold.
The pump must be primed before starting. Whenever possible, the pump should be
located below the fluid level to facilitate priming and assure a steady flow of liquid. This
condition provides a positive suction head on the pump. It is also possible to prime the
pump by pressurizing the suction vessel.
Pumps must be fully primed at all times during operation.
When installing the pump, consider its location in relation to the system to assure that
sufficient Net Positive Suction Head (NPSHA) is available at the pump inlet connection.
Available NPSH must always equal or exceed the required NPSH (NPSHR) of the pump.
The pump should be installed with sufficient accessibility for inspection and
maintenance. A clear space with ample head room should be allowed for the use of an
overhead crane or hoist sufficiently strong to lift the unit.
NOTE: Allow sufficient space to be able to dismantle pump without disturbing the
pump inlet and discharge piping.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 12 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Select a dry place above the floor level wherever possible. Take care to prevent
pump from freezing during cold weather when not in operation. If the possibility of
freezing exists during a shut-down period, the pump should be completely drained, and
all passages and pockets where liquid might collect should be blown out with
compressed air.
Make sure there is a suitable power source available for the pump driver. If motor
driven, the electrical characteristics of the power source should be identical to those
shown on motor data plate.
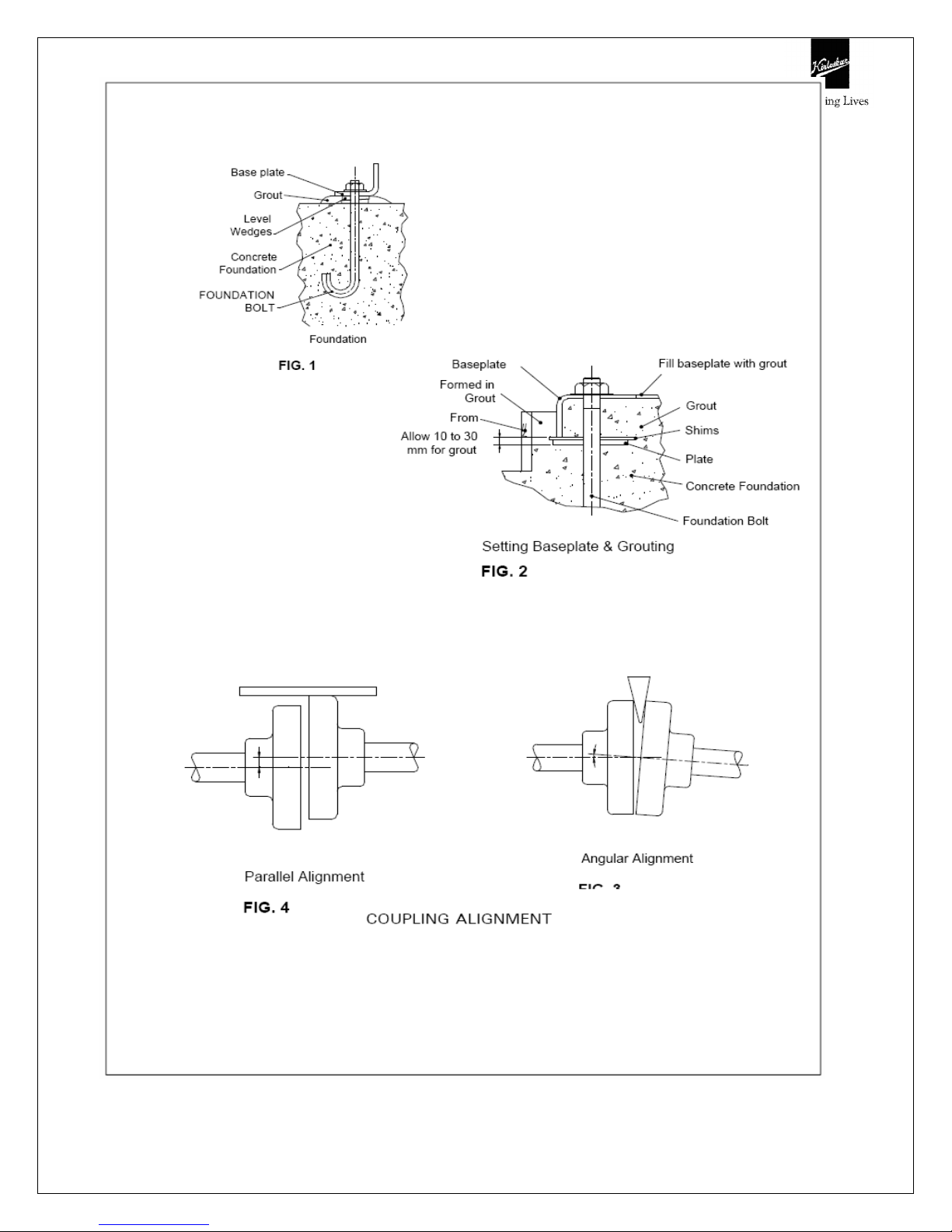
3.4 Foundation
The foundation should be strong enough to reduce vibrations and rigid enough to avoid
any twisting or misalignment.
The foundation should be poured without interruptions to within 20 to 40 mm of the
finished height. The top surface of the foundation should be well scored and glued
before the concrete sets. This provides a bonding surface for the grout. Foundation
bolts should be set in concrete as shown in Fig. 1. Allow enough bolt length for
grout,shims, lower base plate flange, nuts and washers. The foundation should be
allowed to cure for several days before the base plate is shimmed and grouted.
3.5 Baseplate setting
Use blocks and shims under base for support at foundation bolts and midway
between bolts, to position base approximately 25 mm above the concrete
foundation with studs extending through hole in the baseplate.
By adding or removing shims under the base, level the pump shaft and flanges. The
baseplate does not have to be leveled. Draw foundation bolt nuts tight against
baseplate and observe pump and motor shafts or coupling hubs for alignment.
Check to make sure the piping can be aligned to pump flanges without placing pipe
strain on either flange.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 13 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Grout baseplate in completely and allow grout to dry thoroughly before attaching
piping to pump (24 hours is sufficient time with approved grouting procedure).
3.6 Grouting procedure
Grout compensates for uneven foundation, distributes weight of unit and prevents
shifting. Use an approved, non-shrinking grout as follows, after setting and leveling
unit See Fig. 2.
a) Build strong form around foundation to content grout.
b) Soak top of concrete foundation thoroughly, then remove surface water.
c) Baseplate should be completely filled with grout and, if necessary, drill vent holes
to remove trapped air.
d) After grout has thoroughly hardened, check the foundation bolts and tighten if
necessary.
e) Check the alignment after the foundation bolts are tightened.
f) Approximately 14 days after the grout has been poured or when the Grout has
thoroughly dried, apply an oil base paint to the exposed edges of the grout to
prevent air and moisture from coming in contact with the grout.
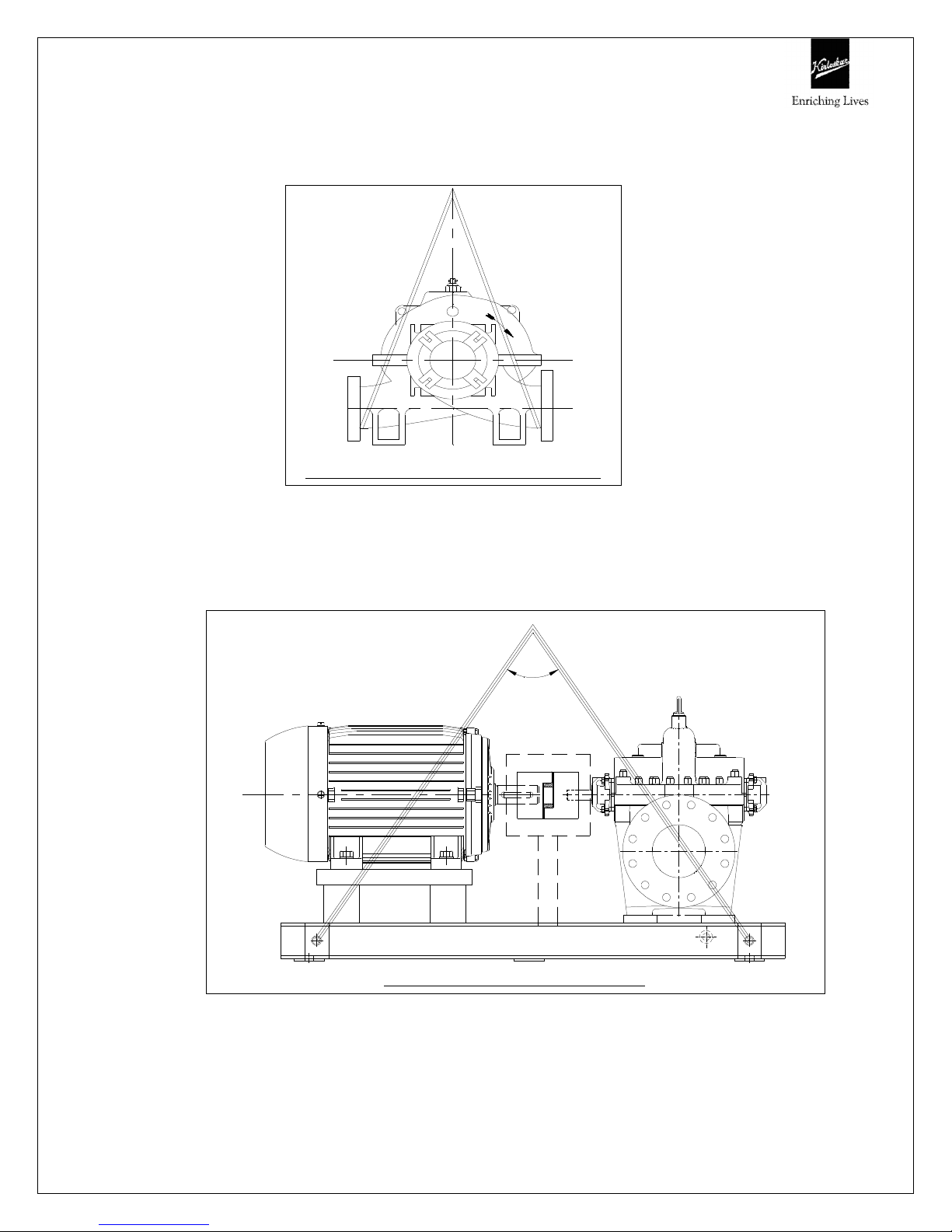
3.7 Alignment procedure
The pump driver, if supplied, is correctly aligned on its base plate at the factory. A
certain amount of deformation of the base plate is possible during transit and it is
therefore essential to check alignment, prior to final grouting.
A flexible coupling will only compensate for small amount of misalignment and
should not be used to compensate for excessive misalignment of the pump and
driver shafts.
Inaccurate alignment results in vibration and excessive wear on the bearings, sleeve
or shaft and wear rings.
Coupling alignment can be checked with dial gauge Indicator also. Alignment should
be performed after the base plate has been properly set and grout has dried
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 14 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

thoroughly according to instructions. Final alignment should be made by shimming
driver only.
Alignment should be made at operating temperatures.
After final alignment, it is necessary to dowel pump and driver feet to the baseplate.
FACTORS THAT MAY DISTURB ALIGNMENT
The unit should be periodically checked for alignment. If the unit does not stay in
line after being properly installed, the following are possible reasons:
a) Setting, Seasoning of the foundation.
b) Pipe strains, distorting or shifting of the machines.
c) Wear of the bearings.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 15 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 16 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

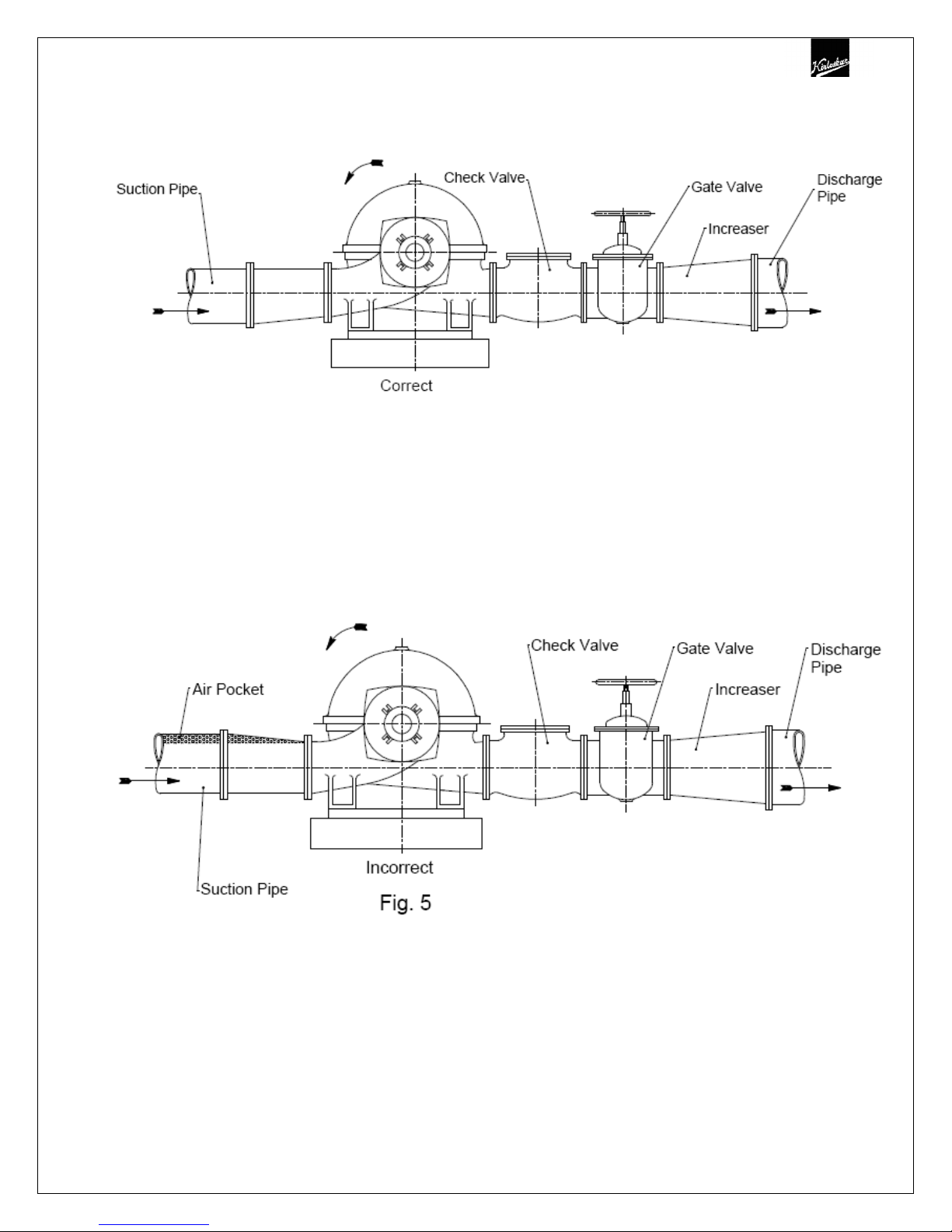
3.8 Suction and Discharge Piping
When installing the pump piping, make sure to observe the following precautions:-
Piping should always run to the pump. Do not move pump to pipe. This could make
final alignment impossible.
Both suction and discharge piping should be supported independently and close to
pump so that no strain is transmitted to the pump when the flange bolts are
tightened.
Use pipe hangers or other supports at necessary intervals to provide support. When
expansion joints are used in the piping system, they must be installed beyond the
piping supports close to the pump.
It is advisable to increase the size of both suction and discharge pipes at the pump
connection to decrease the loss of head from friction.
Install piping as straight as possible, avoiding unnecessary bends. Where necessary,
use 45 degree or long sweep 90 degree fitting to decrease friction losses.
Make sure that all piping joints are air tight. Provide pipe expansions bellows when
hot fluids are to be pumped. Where reducers are used, eccentric reducers are to be
fitted in suction lines and straight taper reducers in discharge and vertical lines (See
Fig.5).
Misuse of reducers may cause the formation of air pockets in the pipe and thus
preventing the correct operation of the pump.
The suction pipe should be as short & direct as possible. Where suction lift is not
very high, it is advisable to use a foot valve. Horizontal suction line must have a
gradual rise to the pump.
The discharge pipe is usually preceded by a non-return valve or check valve and a
discharge gate valve (See Fig. 5). The check valve is to protect the pump from
excessive back pressure and reverse rotation of the unit and to prevent back flow
into the pump in case of stoppage or failure of the driver. The discharge valve is
used in priming, starting and when shutting down the pump.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 17 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

4 OPERATION
4.1 Before Starting
Before initial starting of the pump, make the following inspection:
4.1.1 The unit baseplate is grouted and bolted to the foundation.
4.1.2 Alignment between pump and motor.
4.1.3 Motor is correctly wired to starting device, check voltage, phase and frequency on
motor nameplate with line circuit. Ensure correct direction of rotation prior to
coupling to pump. Check by starting motor and switching off immediately. Observe
rotation is the same as the arrow direction on the pump casing.
4.1.4 Bearing lubrication is provided (see lubrication section), also check driver lubrication.
4.1.5 Mechanical seal has been fitted or stuffing box has been packed.
4.1.6 All rotating parts are found to be free when turned by hand.
4.1.7Pump is primed. Never run the unit dry. The liquid in the pump serves as a lubricant
for close running fits within the pump and the pump may be damaged if operated
dry. The pump may be primed by using an ejector, exhauster or vacuum pump. If a
foot valve is used in the suction line, the pump may be primed by venting and filling
the casing with liquid.
4.2 Starting
4.2.1 Close valve in discharge line.
4.2.2 Open fully all valves in the suction line.
4.2.3 Turn on seal water to the stuffing box where external pipe supplied.
4.2.4 Prime the pump.
4.2.5 Start the pump driver.
4.2.6 When the pump is operating at full speed, open the discharge valve slowly.
Do not operate pump for prolonged periods with closed discharge valve, so as to avoid
overheating.
The pump should be shut down at once and the trouble corrected if the pump is running at
its rated speed and found to have any of the following defects:
a) No liquid delivered.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 18 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

b) Not enough liquid delivered.
c) Not enough pressure.
d) Loss of liquid after starting.
e) Excess vibration.
f) Motor runs hot.
g) Pump bearing overheating.
4.3 Running
While the pump is running, a periodic inspection should be made of:
a) Stuffing box (soft packed pumps only). Ensure there is sufficient leakage to
lubricate the packing.
b) Bearings. Check the bearings for temperature, which should not exceed pumped
liquid temperature or 80 Deg. C whichever is the lower.
c) With mechanical seal fitted pumps, check that there is no leakage from the
stuffing box.
d) Suction and discharge gauge readings.
4.4 Stopping
a) Slowly close delivery valve and shut down driving unit in accordance with
manufacturer’s instructions.
b) Shut off external sealing liquid supply, if supplied, to relieve stuffing box pressure.
c) Successful operation of the pump depends on accurate alignment. It is
recommended to re-check the alignment after preliminary run.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 19 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 20 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5 TECHNICAL DATA
5.1 Direction of Rotation
The standard direction of rotation is anticlockwise when viewed from driving side.
The pumps with reverse direction of rotation (Clockwise) can be supplied on request.
The direction of rotation can be reversed easily without changing any part.
5.2 Bearing Details
The pumps are fitted with antifriction heavy duty ball bearings at driving and non
driving ends. The details of the bearings are as under:
Bearing model
SR.NO PUMP TYPE
1 UP 50/30A
2 UP 50/30B
3 UP 65/24
4 UP 65/24A
5 UP 80/24
6 UP 65/38
7 UP 65/38M
8 UP 80/30
9 UP 80/38
10 UP 100/24
11 UP 100/29
12 UP 125/24
13 UP 125/30A
14 UP 125/30B
15 UP 100/35 MODULE IE 6309 FOR DE & NDE
16 UP 100/38
17 UP 125/35
18 UP 150/26N *
19 UP 150/30
20 UP 150/30A(N) *
21 UP 150/38A
22 UP 150/38B
23 UP 150/38BC *
24 UP 150/45
25 UP 150/45BC
26 UP 200/30
27 UP 200/38
28 UP 250/30
29 UP 250/38
30 UP 150/53A
31 UP 150/53F
32 UP 200/42
no.
MODULE 0 6305 FOR DE &NDE
MODULE I 6306 FOR DE & NDE
MODULE II 6309 FOR DE & NDE
MODULE III 6312 FOR DE & NDE
The designations of bearings are as per SKF catalogue. However, bearings of other
Ball bearing reference no. SKF or
equivalent
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 21 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Make / equivalent are also used.
5.3 Special care for Bearings
These instructions do not supersede any information issued by the bearing
manufacturers, to whom application should be made for more comprehensive
literature by personnel responsible for bearing care, who with it to make a detailed
study.
Care and maintenance of bearings is a matter of ensuring that they are:
a) Correctly lubricated at intervals as laid down in routine maintenance chart.
b) Removed, cleaned and refitted with care.
c) Tools used and work areas should be cleaned.
To remove a bearing, use correctly suited withdrawal equipment.
CAUTION: Damage can be caused by exerting force against the outer ring of a ball
bearing. Ball bearings should not be dismantled. Clean bearings thoroughly with an
approved fluid. Dry the bearings by spinning with dry compressed air or by hand. Do
not spin a clean dry bearing. Inspect the bearing for wear, fractures, cracks,
corrosion or other damage which may necessitate bearing replacement. Pack both
sides of bearing with grease. Check that the bearing, shaft and housing are cleaned
and undamaged. Recharge with grease to a maximum of two thirds full. Refit the
bearing onto the shaft and press for tap into position.
5.4 Lubrication Details
Initially bearings are lubricated during assembly. In the regreasing period these
bearings should be repacked with a high quality, lithium soap base, ball and roller
bearing grease free from resin and acid, not liable to harden or crumble and
possessing rust preventive properties. Re-greasing interval depends upon the
operating speed of the unit.
Operating speed Regressing Interval
1450 RPM 4000 hours
2000 RPM 3000 hours
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 22 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Manufacturer
Trade name
IOCL
SERVOGEM
-
3 OR EQ
IOCL
SERVOGEM
-
2 OR EQ
SHELL
ALVANIA EP 2
EXXON
POLYREX
CHEVRON
SRI GREASE NLGI 2
CHEVRON
BLACK PEARL NLGI 2
TEXACO
MULTIFAK EP2
PHILIPS
POLYTAC
HPCL
NATRA 3 OR LITHON 3
To recharge the bearings with fresh grease, use a grease gun and feed through the
two grease nipples provided.
DO NOT APPLY LUBRICANT WHEN PUMP IS RUNNING.
After 10,000 hours or two years whichever is earlier remove bearings from pumps,
degrease, thoroughly clean, recharge with fresh grease and refit in accordance with
reassembly instructions.
Recommended Grease specifications
5.5 Wearing Details
Pumps are supplied with casing wear rings. The Diametrical clearances between
Impeller and casing rings should be minimum: 0.25 mm and maximum 0.70 mm.
5.6 Impeller Details
Following pump types are fitted with single entry impeller UP 50/30A, UP 50/30B,
UP 80/38, UP 65/38 and UP 65/38M.
For other types, Double entry impellers are fitted.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 23 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.7 Stuffing Box Details
• Packing (Non Asbestos)
On packed pumps the packing is installed prior to shipment. All packing used are the
highest grade material. Before pump is put into operation check the condition of the
packing. If pump is installed within sixty (60) days after shipment the packing will be
in good condition with a sufficient supply of lubrication. If pump is stored for a
longer period it may be necessary to repack the stuffing box. In all cases, however,
we recommend an inspection of the packing before pump is started. The standard
pump packing is made from graphite solid plate cotton packing (non asbestos).
A soft, well-lubricated packing reduces stuffing box resistance and prevents
excessive wear on the shaft or shaft sleeve. Many brands of packing on the market
have the desired qualities.
NOTE: Eccentricity of the shaft or sleeve through the packing could result in excess
leakage that cannot be compensated for. Correction of this defect is very important.
Packing should be checked frequently and replaced as service indicates. Six months
might be a reasonable expected life, depending on operating conditions. It is
impossible to give any exact predictions. A packing tool should be used to remove
all old packing from the stuffing box. Never reuse old and lifeless packing or merely
add some new rings. Make sure the stuffing box is thoroughly cleaned before new
packing is installed. Also check the condition of the shaft or sleeve for possible
scoring or eccentricity, make replacements where necessary.
New packing (non-asbestos) should be placed carefully into the stuffing box. If
molded rings are used, the rings should be opened sideways and the joints pushed
into the stuffing box first. The rings are installed one at a time, each ring seated
firmly and the joints staggered at about a 90° rotation from each preceding joint.
Champion Style – 3116 – Graphited cotton greasy packing is used in the standard
supply. However packing suitable for liquid handled is also supplied against specific
requirement.
Size of gland packing and position of lantern ring
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 24 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Gland packing are fitted with 2+L+2 arrangement L=Lantern Ring.
Module 0 - 8 mm
Module I& I E - 10 mm
Module II - 12 mm
Module III - 12 mm
2
2
2
2
• Mechanical Seal:
General instructions for operation of the various mechanical sealing arrangements
are included below. It is not feasible to include detailed instructions for all mechanical
seals in this booklet because of the almost unlimited number of possible combinations
and arrangements. Instead, seal manufacturer’s instructions will be included as a
separate supplement to this book, where required.
a. Mechanical seals are precision products and should be treated with care. Use special
care when handling seals. Clean oil and clean parts are essential to prevent scratching
the finely lapped sealing faces. Even light scratches on these faces could result in
leaky seals.
b. Normally, mechanical seals require no adjustment or maintenance except routine
replacement of worn or broken parts.
c. A mechanical seal which has been used should not be put back into service until the
sealing faces have been replaced or relapped. (Relapping is generally economical only
in seals two inches in size and above.)
Four important rules which should always be followed for optimum seal life are:
1. Keep the seal faces as clean as possible.
2. Keep the seal as cool as possible.
3. Assure that the seal always has proper lubrication.
4. If seal is lubricated with filtered fluid, clean filter frequently.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 25 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IMPELLER
'A' 'B'
IN MM
IN MM
MECHANICAL SEAL FITTMENT CHART
MECHANICAL SEAL DETAILS
M EC H .S E A L
'A '
'M '
S E A L L O C A TIN G
D I S T A NC E N D E
C O F I M PE LL E R
L
'B '
'N '
S E A L L O C A TIN G
D I S T A NC E D E
S H O U L D E R R I N G
R E S T IN G F A CE
FITMENT OF MECH. SEAL (AS PER DIN 24960 STANDARD)
MOUNTED ON SHAFT
MODULE
PUMP TYPE
UP50/30A
UP50/30B 71 75 175 179
UP65/24 71 75 175 179
UP65/24A 71 75 175 179
UP80/24 71 75 175 179
UP65/38
UP65/38M 77 81 191 195
UP80/30 77 81 191 195
UP80/38 77 81 191 195
UP100/24 77 81 191 195
UP100/29 77 81 191 195
UP125/24 77 81 236.5 240.5
UP125/30A 77 81 236.5 240.5
UP125/30B 77 81 236.5 240.5
UP100/35 IE 40 148 152 231 235
UP100/38
UP125/35 97 101 245 249
UP150/26N
UP150/30 97 101 245 249
UP150/30AN 97 101 245 249
UP150/38A 97 101 245 249
UP150/38B 97 101 245 249
UP150/38BC 97 101 245 249
UP150/45 97 101 245 249
UP150/45BC 97 101 245 249
UP200/30 88.5 92.5 292 296
UP200/38 88.5 92.5 292 296
UP250/30 88.5 92.5 292 296
UP250/38 88.5 92.5 292 296
UP150/53A
UP 150/53F 181 185 444 448
UP200/42 181 185 444 448
NO SEAL SIZE NDE MM DE MM
71 75 175 179
0 30
77 81 191 195
I 35
97 101 245 249
II 50
181 185 444 448
III 65
LOCKING
DISTANCE
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 26 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.8 Coupling Details
Pumps will be supplied with snap wrap coupling as a standard scope of supply
however other types like pin bush, tyre type, spacer coupling can also be provide on
request.
5.9 Minimum safe flow
The pump should not run against closed discharge valve as this will cause an
increase in temperature/formation of steam in the pump. This may cause shaft
damage, impeller erosion, short life of bearings and damage to stuffing boxes or
mechanical shaft seals due to stress or vibration. The minimum flow rate must be at
least 30 % of the best efficiency point flow rate.
5.10 NPSHA (Net Positive Suction Head Available) and NPSHR (Net Positive Suction Head
Required)
NPSHA should be at least greater than 0.5m than NPSHR for satisfactory operation
of the pump. If NPSHA<NPSHR then pump cavitation may occurs which in turns
damage the impeller.
5.11 Pipe line velocities
For satisfactory operation of pumps and to minimize frictional losses, it is
recommended to maintain velocity in suction pipe line as 1.5 to 2 m/s and in
delivery pipe line it should be 2.5 to 3 m/s by providing higher pipe diameters than
pump suction / delivery size.
5.12 Tapping details:
Sr.No Tapping Description Size (in inch)
1
2
3
4
5
Air vent
Priming connection
(plugged)
Sealing connection
Suction & delivery
pressure gauge
connection (plugged)
Casing drain
Rp 3/8
Rp 1/2
Rp 1/4
Rp 3/8
Rp 1/2
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 27 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

NOZZLE
For
ces kg
Moment kg m
Fx Fy Fz Fx Fy Fz
150
133
334
267
204
102
102
5.13 Allowable forces and moments on pump flanges:
SIZE(mm)
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
600
178
210
226
241
256
270
286
317
445
525
566
603
641
680
717
792
356
420
453
483
513
540
573
634
272
320
345
368
391
420
437
483
136
160
172
184
195
215
218
241
136
160
172
184
195
215
218
241
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 28 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.14 Suction & Delivery Size:
SR.NO PUMP TYPE NOMINAL SUCTION
BORE mm
NOMINAL DELIVERY
BORE mm
1 UP 50/30A 65 50
2 UP 50/30B 65 50
3 UP 65/24 80 65
4 UP65/24A 80 65
5 UP 65/38 80 65
6 UP 65/38M 80 65
7 UP 80/24 100 80
8 UP 80/30 125 80
9 UP 80/38 100 80
10 UP 100/24 150 100
11 UP 100/29 150 100
12 UP 100/35 150 100
13 UP 100/38 150 100
14 UP 125/24 150 125
15 UP 125/30A 150 125
16 UP 125/30B 150 125
17 UP 125/35 150 125
18 UP 150/26 (N) 200 150
19 UP 150/30A 200 150
20 UP 150/30A(N) 200 150
21 UP 150/38A 200 150
22 UP 150/38B 200 150
23 UP 150/38BC 200 150
24 UP 150/45 200 150
25 UP 150/45BC 200 150
26 UP 200/30 250 200
27 UP 200/38 200 200
28 UP 250/30 250 250
29 UP 250/38 250 250
30 UP 150/53A 200 150
31 UP 150/53F 200 150
32 UP 200/42 250 200
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 29 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.15 Maximum allowable Speed and water fill capacity
SR.
NO.
1 UP 50/30A 5 1450 2000
2 UP 50/30B 5 1450 2000
PUMP TYPE WATER
FILL
CAPACITY
in LITRES
NOMINAL
SPEED IN RPM
3 UP 65/24 10 1450 1800
4 UP 65/24A 10 1450 1800
5 UP 65/38 11 1450 1500
6 UP 65/38M 11 1450 1800
7 UP 80/24 14 1450 1800
8 UP 80/30 14 1450 2000
9 UP 80/38 12 1450 1930
10 UP 100/24 14 1450 2000
11 UP 100/29 14.5 1450 2000
12 UP 100/35 20.5 1450 1500
13 UP 100/38 25.2 1450 2200
14 UP 125/24 25.2 1450 2000
15 UP 125/30A 24.5 1450 1760
16 UP 125/30B 24.5 1450 1760
17 UP125/35 30.0 1450 1500
18 UP 150/26N 28 2900 3000
19 UP 150/30 30 1450 1800
20 UP 150/30A(N) 30 2900 3000
21 UP 150/38A 28.5 1450 1800
22 UP 150/38B 28.5 1450 1800
23 UP 150/38BC 28.5 1450 2100
24 UP 150/45 48 1450 1800
25 UP 150/45BC 48 1450 1800
26 UP 200/30 50 1450 2000
27 UP 200/38 63 1450 1500
28 UP 250/30 58.5 1450 1500
29 UP 250/38 92 1450 1500
30 UP 150/53A 60 1450 1500
31 UP 150/53F 60 1450 1500
32 UP 200/42 98 1450 2100
MAX.ALLOWABLE
SPEED IN RPM
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 30 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.16 Starting Torque:
CASE 1 starting up with open isolating or regulating valve on delivery side.
CASE 2 starting up with closed isolating or regulating valve with opening the valve when
nominal speed is attained.
CASE 3 starting up with open isolating or regulating valve but against static delivery head
acting on non-return valve.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 31 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.17 Weights and GD^2 values:
Sr no Pump type Approx.net
weight (Kg)
GD^2 value In Kg-
cm^2
1 UP 50/30A 80 2080
2 UP 50/30B 80 2080
3 UP 65/24 84 1080
4 UP 65/24A 84 1080
5 UP 80/24 95 1003
6 UP 65/38 164 7500
7 UP 65/38 M 164 7500
8 UP 80/30 130) 3332
9 UP 80/38 158 9292
10 UP 100/24 158) 2092
11 UP 100/29 137 3572
12 UP 125/24 180 2816
13 UP 125/30A 182 4656
14 UP 125/30B 182 4656
15 UP 100/35 177 4948
16 UP 100/38 240 6976
17 UP 125/35
282
7450
18 UP 150/26N 262 6520
19 UP 150/30 253 6520
20 UP 150/30A (N)
270 5236
21 UP 150/38A 286 10040
22 UP 150/38B 286 10040
23 UP 150/38BC 286 10040
24 UP 150/45 308 18740
25 UP 150/45BC 308 18740
26 UP 200/30 372 8812
27 UP 200/38 350 12212
28 UP 250/30 348 7772
29 UP 250/38 420 21092
30 UP 150/53A 588 50650
31 UP 150/53F 588 50650
32 UP 200/42 560 50650
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 32 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

5.18 Interchangeability of Components
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 33 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

6. MAINTENANCE.
6.1 Maintenance EHS (Environmental Hazard Safety) Instructions
Following hazards may arise during maintenance work.
Fluid Pressure Jet Hazards
Check and ensure that the pump operates at below the maximum Working
Pressure specified.
Hazardous materials:
Wear a suitable mask or respirator when working with chemical material handling.
Hazardous Gases, Mists, Sprays and Leaks.
Be aware of the hazards relating to the pumped fluid, especially the danger from
inhalation from noxious and toxic gases, skin and eye contact or penetration. Obtain
and understand the hazardous substance data sheets relating to the pumped fluid
and note the recommended emergency and first aid procedures.
Before attempting any maintenance on a pump, particularly if it has been handling
any form of hazardous liquid; ensure that the unit is safe to work on. The pump
must be flushed thoroughly with suitable cleanser to purge away any of the product
left in the pump components. The plant operator should carry this out and a
certificate of cleanliness obtained before starting work. To avoid any risk to health it
is also advisable to wear protective clothing as recommended by the site safety
officer, especially when removing old packing that may be contaminated.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 34 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Electric shock and accidental starting hazard:
Isolate the equipment before any maintenance work is done. Switch off the mains
supply, remove fuses, apply lockouts where applicable and affix suitable isolation
warning signs to prevent inadvertent re-connection.
In order to avoid the possibility of maintenance personnel inhaling dangerous fumes
or vapours, it is recommended that maintenance work be carried out away from the
pump location by removal of the rotating unit assembly to a suitable maintenance
area.
6.1 Routine Maintenance Chart
Preventive maintenance schedule is a periodical checks and precautions by which
possibilities of failure and breakdown will be rare.
EVERY WEEK
EVERY MONTH
EVERY 3
MONTHS
EVERY 6
MONTHS
EVERY YEAR
Visually check for leaks
Check for vibration.
Adjust gland as necessary to maintain slight leakage.
Hand test bearing housing for any sign of temperature.
Voltage and current.
Check bearing temperature with thermometer.
Check grease lubricated bearings for saponification.
Check the packing and replace if necessary.
Check shaft or shaft sleeve for scoring.
Check alignment of pump and motor.
Check holding down bolts for tightness.
Check coupling bush/rubber star.
Check rotating element for wear.
Check wear ring clearances.
Clean and regrease bearings.
Measure total suction and discharge Head as a test of pipe
connection
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 35 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

7.0 OVERHAULING
With normal daily operating spell, the pump will be due for overhaul after about
5000 working hours. This work should be done by skilled personnel. Please refer to
the cross sectional drawing while dismantling and reassembling the pump. Please
also refer to chart given at end of this booklet.
7.1 Dismantling Procedure
Note – Store all loose components carefully in a wooden box. Remove sealing
connection given to lantern ring / mechanical seal, temperature indicator, etc.
7.1.1 For SOFT PACKED UP METRIC PUMPS:
7.1.1.1 Disengage pump coupling from motor coupling.
Drain the pump by removing drain plug (60100) and opening air vent valve (45000).
7.1.1.2 Remove the nuts (58001) and locating pin (61100) joining the upper half casing
and lower half casing.
7.1.1.3 Remove all insert joint nuts at both ends (58002).
7.1.1.4 Insert a screw driver or peg bar into the slot between the two halves and separate
two halves, lifting off the upper half casing (12200). Remove the upper half casing,
taking enough care not to damage the impeller and casing (wear) ring.
7.1.1.5 Tap the inserts (97900) with a soft hammer to break the seat between the insert
and lower half casing (12300) and lift the rotating unit out of the lower half casing
so that none of the parts will be damaged. Take out the rotating unit & keep it on
rubber or wooden sheet in clean & dry place for further dismantling purpose.
7.1.1.6 Remove the pump coupling and coupling key.
7.1.1.7 Remove four hex screws (57100) from each bearing housing (24001 and 24002)
and remove the bearing housing from bearings & take it off the shaft.
7.1.1.8 Remove bearing lock nut (33600) and lock washer (41500) from NDE side.
Remove NDE bearing (26000) from the shaft by the use of bearing puller. Remove
driving end bearing in the same manner.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 36 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

7.1.1.9 Remove oil seals (50000) from the insert from DE & NDE side. Remove shoulder
rings (19900) from the shaft by using puller.
7.1.1.10 Remove liquid deflector (23600) from the shaft.
7.1.1.11Remove gland nuts (58200) from each gland. Remove gland (22300) gland
packing (43000) & lantern rings (22700) from each insert.
7.1.1.12Slide inserts (97901, 97902) off the shaft.
7.1.1.13 Take out casing rings (19000) on DE & NDE side.
7.1.1.14 For counter clockwise (CCW) direction of rotation of pump viewed from driving
end, follow steps (i & ii) and then go to point no. 7.1.1.16:
i) Unscrew DE side shaft sleeve and slide it off the shaft from DE side.
Remove impeller from shaft. Remove impeller key.
ii) Unscrew the NDE side shaft sleeve and slide it off the shaft from NDE side.
7.1.1.15 For clockwise (CW) direction of rotation of pump viewed from driving end, follow
steps (i & ii) then go to point no. 7.1.1.16:
i) Unscrew NDE side shaft sleeve and slide it off the shaft from NDE side. Remove
impeller from shaft. Remove impeller key.
ii) Unscrew the DE side shaft sleeve and slide it off the shaft from DE side.
7.1.1.16 Store all parts of rotating assembly in clean and dry place and arrange to store
the parts in well oiled condition.
7.1.1.17 mechanical seal arrangement –
All UPM pumps are fitted with bare mechanical seal only.
a) Dismantling procedure for mechanical seal fitted pump is same as above except step
no. 7.1.1.11. After step no. 7.1.1.10, slide inserts (97901, 97902) off the shaft.
b) Remove grub screws holding mechanical seal & slide off mechanical seal on both
sides from the shaft.
c) Then follow steps 7.1.1.13 to 7.1.1.16.
This completes the dismantling of the pump.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 37 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

7.2 Reassembly Procedure -
7.2.1 For UPM pumps:
7.2.1.1 Check ‘O’ ring (52202) for cut or flaws, discard if faulty, lubricate and roll ‘O’
ring in groove of each shaft sleeve.
7.2.1.2 Wipe over shaft (18001) with clean light oil.
7.2.1.3 Keep shaft so that coupling end extension is in correct position looking from
position of suction and delivery branches.
7.2.1.4 For counter clockwise (CCW) direction of rotation of pump viewed from driving
end, follow steps (i, ii & iii) and then go to point no.7.2.1.6:
i) Locate the locking shaft sleeve (31000) at NDE side with the help of impeller
key (32000) and tighten it on the shaft. Please check that the “o” ring is fitted
in groove of sleeve.
ii) Check impeller vanes for correct direction of rotation. Slide the impeller on the
shaft. Check that keyway provided on shaft extends equally outside the hub of
impeller on both sides.
iii) Slide DE side adjusting sleeve in the shaft and tight it against impeller hub with
the help of set screw.
7.2.1.5 For clockwise (CW) direction of rotation of pump viewed from driving end, follow
steps (i, ii & iii) and then go to point no.7.2.1.6.
i) Locate the locking shaft sleeve (31000) at DE side with the help of impeller key
and tighten it on the shaft. Please check that the “o” ring is fitted in groove of
sleeve.
ii) Check impeller vanes for correct direction of rotation. Slide the impeller on the
shaft. Check that keyway provided on shaft extends equally outside the hub of
impeller on both sides.
iii) Slide the NDE side adjusting sleeve in the shaft and tight it against impeller hub
with the help of set screw.
7.2.1.6 Apply a hand of light oil on casing rings (19000) and place casing rings on the
impeller.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 38 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

7.2.1.7 Check ‘O’ rings (52201) for cracks or flaws, discard if faulty. Lubricate and roll
‘O’ ring (52201) into the groove in each insert (97901, 97902).
7.2.1.8 Slide inserts (97901, 97902) over shaft with guide vane at top position.
7.2.1.9 Slide glands (22300) over the shaft / slide bare mechanical seal over the shaft
and locate the same on the shaft with the help of grub screws.
7.2.1.10 Slide the liquid deflector on the shaft from DE & NDE side.
7.2.1.11 Fit shoulder ring (19900) onto shaft, then fit oil seal (50000) into insert.
Ensure that no foreign particle should enter in bearing assembly. See sectional
drawing.
7.2.1.12 Heat the ball bearing (26000) to approximately 100°C (212°F) using heating
oil bath.
NOTE: DO NOT EXCEED 120°C (250°F).
7.2.1.13 Use hand gloves while handling heated bearings.
Slide the heated bearing on to the shaft to about shoulder ring (19900) at non
driving end. Place locking washer (44500) onto shaft & screw bearing lock
nut (31500) using hook spanner. Tight the lock nut against bearing. Bend the
washer in the slot of bearing lock nut.
7.2.1.14 Cool the bearing to room temperature and coat both sides with grease.
7.2.1.15 Coat the inside of the bearing housing (24002) with grease and slide into
place over bearing. Secure bearing housing to insert with four hex head
screws (57100).
7.2.1.16 At coupling end heat the bearing (26000) to approximately 100°C (212°F)
using heating oil bath.
NOTE: DO NOT EXCEED 120°C (250°F).
7.2.1.17 Slide the heated bearing onto the shaft to about shoulder ring (19900) at
coupling end.
Use hand gloves while handling heated bearings.
7.2.1.18 Cool the bearing to room temperature and coat both sides with grease.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 39 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

7.2.1.19 Coat the inside of the bearing house (24002) with grease and slide into place
over bearing. Secure bearing housing to insert with four hex screws (57100).
7.2.1.20 Fit cylindrical pins (61000) in their respective holes.
7.2.1.21 Lift the rotating unit by means of crane. Set the rotating unit in the lower
casing half. Locate both insert tongues at top position. Correct any excessive
‘O’ ring buckling. Check whether Impeller is centrally placed in volute and
there is no rubbing between impeller and casing.
7.2.1.22 Ensure that casing rings are located in cylindrical pins fitted in lower half
casing. Install gasket (51900) between upper & lower half casing with a light
coat of grease on both gasket surfaces.
Carefully align the inner edge of gasket with the insert ‘O’ rings.
7.2.1.23 Lift upper half casing (12200) and place it on lower half casing and engage
casing joint nuts loosely.
NOTE: When installing casing half upper make sure that the ‘O’ rings (52201)
are not cut or punched.
7.2.1.24 Insert locating pins (61100) for upper & lower half casing and drive them
home. Tighten upper half casing to lower half casing by studs and nuts.
7.2.1.25 Fit insert at DE & NDE side & tight it to upper & lower half casing with the
help of hex screws.
7.2.1.26 Fill the gland packing along with lantern ring in the correct sequence as given
in technical data. Then fit gland to the insert with studs & hex nut. (This step
is not applicable for mechanical seal fitted pump.)
7.2.1.27 Mount all the accessories such as grease nipple, sealing / flushing connection
etc.
7.2.1.28 Rotate the shaft by hand to assure smooth rotation and that it is free from
rubbing or binding.
7.2.1.29 Mount the pump coupling key and fit the pump coupling on the shaft from DE
side.
7.2.1.30 Align motor coupling with pump coupling within 0.05 mm to each other.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 40 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Note - UP150/56, UP200/56, UP200/64M, UP250/33, UP250/66, UP300/34
& UP300/39 pumps are fitted with bare mechanical seal only.
This completes the reassembly of the pump.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 41 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 42 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

JOINT FLANGE
TIGHTENING TORQUES AND SEQUENCE
Stud and Nut use in this main joint flange of UP pumps should be tightened to the
torques stated in table 1 and in the sequence stated in Fig.
STUD SIZE TIGHTENING TORQUES
M12
M16
M20
M24
250Kg-CM
650Kg-CM
1270Kg-CM
2200Kg-CM
2. Tightening sequence.
2.1 Tighten the four corner stud marked ‘X’ 1, 2, 3, and 4
2.2 Work outward along shaft axis towards the stuffing boxes in opposite quarters
tightening nut in regions 5, 6, 7 and 8.
2.3 Work outwards along the branch and in opposite quarters tightening nuts in regions
9, 10, 11, and 12.
2.4 Repeat the whole sequence.
Sleeve Location
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 43 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

INSTALLING STUFFING BOX PACKING
1. Refer to stuffing box data to ascertain size and number of rings required.
2. If the packing is to be cut from a coil or long length:-
a) Wrap the packing around a dummy shaft, equal to the shaft sleeve diameter.
b) To assist in cutting rings, two guide lines parallel to the shaft axis and separated
by a distance equal to the packing section may be drawn on the spiral.
c) Cut the rings from the spiral at an angle of 45° diagonally across the guide lines
no gap is left between the ends.
3. Insert the first ring and tap it to the bottom of the stuffing box. Each following ring
should be installed in the same manner and positioned in the stuffing box so that the
split is advanced 90 Deg.
Install the lantern ring in its proper position to align with the sealing connection
allowing for movement of the ring deeper in to the box as the packing is
compressed.
4. When the correct number of rings have been inserted, the last packing ring should
not protrude past the stuffing box face, so that the gland may be properly seated in
the stuffing box bore.
5. Bring the gland follower up securely against the last packing ring and tighten the
nuts evenly to give pressure.
6. Turn the shaft to ensure it does not bind on the bore or the gland follower.
7. Pressurize the stuffing box, ensuring air is not trapped. A packed gland must leak
and leakage should take place commencing soon after the stuffing box is
pressurized.
8. Until steady leakage takes place, the pump may overheat. If this happens, the pump
must be stopped and allow to cool and, when restarted, leakage should take place.
If it does not, this operation should be repeated. Gland nuts should not be
slackened.
9. After the pump has been running for 10 minutes with steady leakage, tighten the
gland nuts by one sixth of a full turn. Continue to adjust at ten minute intervals,
each time
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 44 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

evenly by one sixth of a full turn, until leakage is reduced to an acceptable level.
There should be leakage of 60 to 80 drops per minute.
CAUTION:
Excessive gland pressure will cause damage by cutting off lubrication to the packing
and packing will burn and damage the sleeve.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 45 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

8.0 GENERAL OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
`
`
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 46 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

9.0 SPARE PART LIST AND CROSS SECTIONAL DRAWINGS
* marked part code nos. are recommended spares.
Part code no. Part description
12200
12300
15900*
19000*
19900
24001
24002
26000*
27000
27101
27102
32000*
32100
33600
41500
44101
45000
47101
47102
50000
51900
52200*
52202*
57100
57101
57102
58001
58002
59001
59002
60500
60600
61000
61100
64000
67000
69100
84901
84902
84903
60000
60100
CASING HALF UPPER
CASING HALF LOWER
IMPELLER
WEARING RING
SHOULDER RING
BEARING HOUSING DE
BEARING HOUSING NDE
BALL BEARING
BEARING COVER DE
BEARING COVER NDE
BEARING COVER DE & NDE
KEY (IMPELLER)
KEY (COUPLING)
LOCK NUT (BEARING)
LOCK WASHER (BEARING)
GREASE NIPPLE
VENT VALVE
PROTECTION COVER (SUC)
PROTECTION COVER (DEL)
OIL SEAL
GASKET (CASING)
O RING (INSERT)
ORING (SLEEVE)
SCREW (BRG.HOUSING)
SCREW (BRG. HSG & CASING)
SCREW (BRG. HSG & INSERT)
NUT (CASING)
NUT (INSERT)
STUD (CASING)
STUD (INSERT)
PIPE PLUG (BEARING HOUSING NDE)
PIPE PLUG (PRIMING)
LOCKING PIN (CASING RING)
LOCATING PIN (CASING)
RIVET (NAME PLATE)
DUTY NAME PLATE
NUT (LOCATING PIN)
WASHER (LOCATING PIN)
WASHER (INSERT)
WASHER (BEARING HOUSING)
GAUGE PLUG
DRAIN PLUG
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 47 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

Soft packed pump components
18001*
22300
22700
23600
31000*
43000*
58200
59200
59404
97901
97902
PUMP SHAFT (SOFT PACKED)
GLAND
LANTERN RING
DEFLECTOR
SHAFT SLEEVE (SOFT PACKED)
GLAND PACKING
NUT (GLAND)
STUD (GLAND)
WAHSER (GLAND)
INSERT DE(SOFT PACKED)
INSERT NDE(SOFT PACKED)
Common for Mechanical Seal & Gland Pack
a) Internal Flushing Components
55902
56002
STUD COUPLING
TUBE FLUSHING
b) External Flushing Components
60200 SEALING PLUG (CASING)
Soft Packed Components
Grease Sealing (If Ordered)
60200
44102
SEALING PLUG (CASING)
GREASE NIPPLE
Gauge and drain connection (If Ordered)
60000
60600
GAUGE PLUG
DRAIN PLUG
Mechanical Seal Components
18000*
23000*
31500*
97900
PUMP SHAFT (MECH.SEAL)
MECH.SEAL
SHAFT-SLEEVE(MECH.SEAL)AGAINST ORDER
INSERT (MECH.SEAL)
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 48 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

CROSS SECTIONALDRAWING FOR UP 50/30A, UP 50/30B, UP 65/38, UP 65/38M AND
UP 80/38 (SOFT PACKED)
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 49 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

CROSS SECTIONAL DRAWINGOF UP50/30A, UP 50/30B, UP 65/38, UP65/38M AND
UP80/38 (MECHANICAL SEAL)
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 50 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

CROSS SECTIONAL DRAWING FOR SOFT PACKED PUMP
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 51 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

CROSS SECTIONAL DRAWING FOR MECHANICAL SEAL PUMP
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 52 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

10.0 EXPLODED VIEW
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 53 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 54 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 55 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 56 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 57 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 58 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 59 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

GENERAL INFORMATION & SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. The products supplied by KBL have been designed with safety in mind. Where hazards cannot be
eliminated, the risk has been minimized by the use of guards and other design features. Some hazards
cannot be guarded against and the instructions below MUST BE COMPLIED WITH for safe operation.
These instructions cannot cover all circumstances. Installation, operation and maintenance personnel
must use safe working practices at all the times.
1.1 KBL products are designed for installation in designated areas, which are to be kept clean and free
of obstructions that may restrict safe access to the controls and maintenance access points.
A pump duty nameplate is fitted to each unit and must not be removed. Loss of this plate could
make identification impossible. This in turn could affect safety and cause difficulty in obtaining
spare parts. If accidental loss or damage occur, contact KBL immediately.
1.2 Access to the equipment should be restricted to the person net responsible for installation,
operation and maintenance and they must be trained, adequately qualified and supplied with
appropriate tools for their respective tasks.
1.3 Most accidents involving product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure to
observe safety rules or precautions. An accident can often be avoided by recognizing potentially
situations before an accident occurs. A person must be aware of potential hazard associated in
activities of installation, operation and maintenance of equipments.
1.4 KBL requires that, all personnel that are responsible for installation, operation or maintenance of the
equipment, have access to and study the product instruction manual BEFORE any work is done and
that they will comply with all local and industry based safety instructions and regulations.
1.5 Ear defenders should be worn where the specified equipment noise level exceeds locally defined
safe levels. Safety glasses or goggles or face shield should be worn where working with pressurized
systems and hazardous substances. Other personal protection equipment must be worn where local
rules apply. Wear safety shoes, helmets and cotton overall [Apron] when you enter pump house.
Noise level should not exceed 90 dbA and 110 dbA for motor driven and engine driven pumps,
respectively.
1.6 Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry, which could catch on the controls or become trapped in the
equipment.
1.7 Read the instruction manual before installation, operation or maintenance of the equipment. Check
and confirm that you are referring relevant copy of the manual by comparing pump type on the
nameplate and with that on the manual.
1.8 Note the “Limits of product application permissible use” specified in the manual. Operation of the
equipment beyond these limits will increase the rist from hazards noted below and may lead to
premature and hazardous pump failure.
1.9 Clear and easy access to all controls, gauges and dials etc must be maintained at all times.
Hazardous or flammable materials must not be stored in pump rooms unless safe areas or racking
and suitable container have been provided.
1.10 Use suitable earthing and tripping devices for electrical equipments.
2. IMPROPER INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE,
LUBRICATION, REPAIR OF THIS KBL PRODUCT COULD
RESULT IN INJURY OR DEATH.
If any tool, procedure, work method and operation technique is not recommended by KIRLOSKAR
BROTHERS LIMITED is used or followed, it should be ensured that it is a safe for personnel around and
others. It should also be ensured that the product will not be damaged or made unsafe by the
operation, lubrication and maintenance or repair procedures you choose.
3. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHILE HANDLING AND STORAGE
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 60 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

When lifting the pump, use the lifting points specified on general arrangement drawing, if provided. Use
lifting equipment having a safe working load rating suitable for the weight specified. Use suitable slings
for lifting pump, which is not provided, with lifting points. The use of forklift truck and chain crane sling
equipment is recommended but locally approved equipment of suitable rating may be used. While
lifting, the equipment adjusts the center of gravity, so that it is balanced properly.
Do not place fingers or hands etc into the suction or discharge pipe outlets and do not touch the
impeller, if rotated this may cause severe injury. To prevent ingress of any objects, retain the protection
covers or packaging in place until removal is necessary for installation. If the packaging or suction and
discharge covers are removed for inspection purposes, replace afterwards to protect the pump and
maintain safety.
4. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHILE ASSEMBLY & INSTALLATION
Shaft alignment must be checked again after the final positioning of the pump unit and connection to
pipework as this may have disturbed the pump or motor mounting positions. If hot liquids [above 80°C]
are being pumped, alignment should be checked and reset with the pump and motor at their normal
operating temperature. If this is not possible, KBL can supply estimated initial offset figures to suit
extreme operating temperatures. Failure to support suction and delivery pipework may result in
distortion of the pump casing, with the possibility of early pump failure.
5. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHILE COMMISSIONING & OPERATION
Never attempt adjustments while the pump is running, unless otherwise specified in the operation,
maintenance manual.
Do not touch any moving or rotating parts. Guards are provided to prevent access to these parts,
where they have been removed for maintenance they must be replaced before operating the equipment.
Check that pump is primed. Pump should never be run dry as the pumped liquid acts as lubricant for the
close running fits surrounding impeller and damage will be incurred.
Failure to supply the stuffing box or mechanical seal with cooling of flush water may result in damage
and premature failure of the pump.
Do not touch surfaces, which during normal running will be sufficiently hot to cause injury. Note that
these surfaces remain hot after the pump has stopped, allow sufficient time for cooling before
maintenance. Be cautious and note that other parts of the pump may become hot if a fault is
developing.
Do not operate water pumps in temperatures below freezing point, without first checking that the
pumped fluid is not frozen and the pump is free to turn. Pumps in these environments should be drained
down during inactivity and re-primed before starting.
In addition to local or site regulations for noise protection, KBL recommend the use of personal ear
protection equipment in all enclosed pump rooms and particularly those containing diesel engines. Care
must be taken to ensure that any audible alarm or warning signal can be heard with car defenders
worn.
Be aware of the hazards relating to the pump fluid, especially the danger from inhalation of noxious and
toxic gases, skin and eye contact or penetration. Obtain and understand the hazardous substance data
sheets relating to the pumped fluid and note the recommended emergency and first aid procedures.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 61 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

6. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHILE MAINTENANCE & SERVICING
Do not attempt repairs of the pump or its accessories which you do not know. Use proper tools.
Before attempting any maintenance on a pump particularly if it has been handling any form of
hazardous liquid, it should be ensured that the unit is safe to work on. The pump must be flushed
thoroughly with suitable cleaner to purge away any of the product left in the pump components.
This should be carried out by the plant operator and a certificate of cleanliness obtained before starting
work. To avoid any risk to health it is also advisable to wear protective clothing as recommended by
the site safety officer especially when removing old packing, which may be contaminated.
Isolate the equipment before any maintenance work is done. Switch off the main supply, remove fuses,
apply lockouts where applicable and affix suitable isolation warning signs to prevent inadvertent
reconnection. In order to avoid the possibility of maintenance personnel inhaling dangerous fumes or
vapours locations by removal of bearing housing and shaft assembly to a suitable maintenance area.
Check and ensure that the pump operates at below the maximum working pressure specified in the
manual or on the pump namepate and before maintenance, ensure that the pump is drained down.
Wear a suitable mask or respirator when working with packing and gasket contain fibrous material, as
these can be hazardous when the fibrous dust is inhaled. Be cautious, if other supplier’s components
have been substituted for genuine KBL parts, these may then contain hazardous materials.
Store all oily rags or other flammable material in a protective container in a safe place. Do not weld or
flame cut on pipes/tubes that contents flammable fluids. Clean them thoroughly with nonflammable
solvent before welding or flame cutting on them. Use solvent/chemical resistant gloves for hand
protection.
Dispose of all wastes like gaskets, gland packing, oil, batteries, packing material etc in accordance with
local regulation.
Adequacy of suitable crane should be checked before lifting the pump/pump components. Also
condition of pulleys, chain and lifting shackles should be checked before use.
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 62 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

ADRESSES OF REGIONAL OFFICE
AHMEDABAD
11, Mill Officers Colony,
Behind La Gajjar Chambers,
Ashram Road, Ahmedabad 380 009
Tel: +91-79-26583739, 26580376,
26583615, 26583258, 26574500, 26574802
Fax: +91-79-26583786
EMAIL ID: ahmedabad@kbl.co.in
BANGALORE
No.5, Lakshmi Complex, II floor, 10th Cross,
RMV Extension, CV Raman Road Bangalore 560
080
Tel: +91-80-23619914, 23619915, 23610027,
23610028
Fax: +91-80-23610095
EMAIL ID: bangalore@.kbl.co.in
BHOPAL
E-1, Shankarnagar, 6 1/2 Bus Stop,
Opposite Parul Hospital,Bhopal 462 016
Tel: +91-0755-4218341
EMAIL ID: bhopal@kbl.co.in
BHUBANESHWAR
Plot No. 969, Part A, Uttam Tower, Block B,1st
Floor, Ashok Nagar, Unit 2,
Bhubaneshwar 751 009
Tel: +91-0674-2536188, 2536421, 2535371
Fax: +91-0674-2534965
EMAIL ID: bhubaneshwar@kbl.co.in
CHENNAI
RAJ PARIS,Trimeni Towers,2nd Floor,
147 GN Chetty Road,T Nagar,
Chennai 600 017
Tel: +91-044-28157769, 28156546 / 7 /8
Fax: 044-28156549
EMAIL ID: chennai@kbl.co.in
JAIPUR
B-8, Durga Das Colony,
Behind Neelkanth Tower,
Bias Godam Circle,
Bhawani Singh Road,
Jaipur - 302001 - Rajasthan
Tel: +91-0141 - 2223830
EMAIL ID: jaipur@kbl.co.in
KOCHI
Veejay Towers, 38/239 A, Salim Rajan Road,
Gandhinagar, Ernakulam,
Kochi - 682 017
Tel: +91-0484-2206651, 2206652
Fax: +91-0484-2206653
EMAIL ID: kochi@kbl.co.in
JAMSHEDPUR
No. 4, 4th Floor, Meghdeep Building,
Q road, Bistupur, Beside Hotel South Park,
Jamshedpur - 834001
KOLKATA
KCI Plaza, 1st Floor,
23 C, Ashutosh Chowdhary Avenue
Kolkata 700 019
Tel: +91-033-2461 4040, 4050, 4060, 5065,
5934, 5325, 4615
Fax: +91-033-2461 4519
EMAIL ID: kolkata@kbl.co.in
LUCKNOW
B-1/7, Sector A, Aliganj
Lucknow 226 024
Tel: +91-0522-2326367, 2326374,
2326387
Fax: +91-0522-2326365
EMAIL ID: lucknow@kbl.co.in
MUMBAI
10, Corporate Park,
Swastik Mills Compound,
Sion-Trombay Road, Chembur
Mumbai 400 071
Tel: +91-022-25289320 to 28
Fax: +91-022-25289329
EMAIL ID: mumbai@kbl.co.in
NEW DELHI
Jeevan Tara Building,
5, Parliament Street,
New Delhi 110 001
Tel: +91-011-41501055 to 62
Fax: +91-011-23342002
EMAIL ID: delhi@kbl.co.in
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 63 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

NAGPUR
Flat No. 7, Sagar Palace, Laxmi Nagar,
Behind 'Bal Jagat', East High Court Road,
Nagpur - 440 022
Tel: +91-0712-2234275, 2234276
Fax: +91-0712-2234276
EMAIL ID: nagpur@kbl.co.in
PUNE
Udyog Bhavan, Tilak Road,
Pune 411 002 (India)
Fax: +33 (0) 1 34 66 07 33
EMAIL ID: pune@kbl.co.in
Tel: +91-020-2444 0770
SECUNDERABAD
P.O. Box. No. 1580, 403, Jade Arcade,
126 MG Road, Paradise Circle,
Secunderabad - 500 003
Tel: +91-040-66874700, 66874712 to 37, 27816075
Fax: +91-040-27894598
EMAIL ID:
secunderabad@kbl.co.in
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 64 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

GLOBAL PRESENCE OF KBL
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS LIMITED
Thuduea Rd, Near Simoung Shell Gas
Station, Ban Thatkhao, Sisattank Dist
Vientiane-Lao PDR
Tel: +856-21-219761
Fax: +856-21-213058
: kbllaos@laotel.com
: Tamil Selevan
: C.A.J. Vinodh
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS LLC
15251 SW 108 Terrace
Miami,– FL – 33196
United States of America
Tel : +1 305-484-9509
: santoshk.kulkarni@kbl.co.in
: Santosh Kulkarni
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS (THAILAND)
LIMITED
Kirloskar Brothers (Thailand) Limited 18/8,
8th Floor,
Fico Place Building, Sukhumvit 21 (Soi
Asoke), Klong
toey Nua, Wattana, Bangkok 10110,
Thailand
Tel : +66 2 665 2781/2
: pumps@kirloskarthailand.com
: Shreekanth Ramaswami
BRAYBAR PUMPS (PTY) LIMITED
5 Indiana Street, Apex Industrial Area,
Benoni, Gauteng, Republic of South Africa
Tel: +27 (0)11 421 5903/ +27 (0)11
421 5904
Fax: +27 (0)11 421 6793
:ajeet@braybar.co.za/
braybar@global.co.za
Website: www.braybar.edx.co.za
: Ajeet Kulkarni
SPP PUMPS, INC.
6716 Best Friend Road,
Norcross, GA 30071,
United States of America
Tel: +1(770) 409-3280
Fax: +1(770) 409-3290
: john_kahren@spppumps.com
: John Kahren
(Business Manager)
SPP PUMPS LIMITED
P O Box 61491,
Jebel Ali,Dubai
United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 (0) 4 8838 733
Fax: +971 (0) 4 8838 735
: general@spppumps.com
: Steven Keen
(General Manager)
SPP PUMPS FRANCE
2, rue du Chateau d'eau, 95450 US
France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 30 27 96 96
Fax: +33 (0) 1 34 66 07 33
: tima@spppumps.com
SPP PUMPS (MENA) LLC
Block 234, Road 36,
6th October City
Egypt
Tel: +202 38334150
Fax: +202 38334151
: Eric Reidy
(General Sales Manager)
: eric_reidy@spppumps.com
Mobile: +2 01114277776
: Ahmed Ali Soliman
(Senior Technical Engineer)
: ahmed_soliman@spppumps.com
Mobile: +2 01114266667
Website: www.spppumps.com
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 65 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012

KIRLOSKAR KENYA LIMITED
P. O. BOX 60061-0200
Nairobi, Kenya.
Tel: + 2542053 3421,6632, 6633, 6634
Fax: +254-20-533390
Mobile: +254-722815398,
+254-734148241
: rspatil@kirloskar.co.ke
: Rajkumar Patil
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS LIMITED
Office No 18,Hotel Cambodiana,
Sisowath Quay,Phnom Penh
Kingdom of Cambodia
Tel: +855-99-614821
: tamil.s@kirloskarthailand.com
: Tamil Selven
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS EUROPE BV
Rooswijkweg 7-9,
1951 MD Velsen-Noord,
The Nederlands
Tel: +31 (0) 251 270000
Fax: +31 (0)251 272415
:info@kirloskar.eu
: Frank Korf , Varinder Dhoot
Website: www.kirloskarpumps.eu
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS (THAILAND)
LIMITED- RO Hanoi
6th Floor, Regus press club building 59A,
Ly thai To,
Hoan Kiem Dist, Hanoi
Tel: +84-902206662
: tamil.s@kirloskarthailand.com
: Tamil Selevan
SPP PUMPS LIMITED (UK
HEADQUARTERS)
Theale Cross, Pincents Lane,
Calcot, Reading, Berkshire
England, RG31 7SP
Tel : +44(0)118 9323123
Fax: +44(0)118 9323302
: solutions@spppumps.com
SPP PUMPS LIMITED
10 Anson Road, #34-06
International Plaza.
Singapore 079903.
Tel: +65 6226 1937
Fax: +65 6226 2985
: solutions@spppumps.com
: Andy Gan
(Regional Sales Manager
SPP PUMPS
Sterling Fluid Systems (SA) (Pty) Ltd
6 B and C Roller Street, Spartan ext 17,
Kempton Park, RSA, 1619
Tel: +27 (0) 860777786
Fax: +27 (0) 860777781
: lvw@spppumps.co.za
: Louis van Wyk
(Managing director)
: Patrick Hindry
(General Sales Manager)
KIRLOSKAR BROTHERS LIMITED (EGYPT
BRANCH OFFICE)
1351, Corniche El Nile, Sahel, Shubra
Cairo, Egypt
Tel: +202 24305296
Fax: +202 24328927
: Narayan A. Mirji
: narayan.mirji@kbl.co.in
Website:www.kbl.co.in
IOM/UP_METRIC Issue Date: 31/12/2007
Page 66 of 66
Last Revision: 12/06/2012
 Loading...
Loading...